User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
High-dose prophylactic anticoagulation benefits patients with COVID-19 pneumonia
High-dose prophylactic anticoagulation or therapeutic anticoagulation reduced de novo thrombosis in patients with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, based on data from 334 adults.
Patients with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia are at increased risk of thrombosis and anticoagulation-related bleeding, therefore data to identify the lowest effective anticoagulant dose are needed, wrote Vincent Labbé, MD, of Sorbonne University, Paris, and colleagues.
Previous studies of different anticoagulation strategies for noncritically ill and critically ill patients with COVID-19 pneumonia have shown contrasting results, but some institutions recommend a high-dose regimen in the wake of data showing macrovascular thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 who were treated with standard anticoagulation, the authors wrote.
However, no previously published studies have compared the effectiveness of the three anticoagulation strategies: high-dose prophylactic anticoagulation (HD-PA), standard dose prophylactic anticoagulation (SD-PA), and therapeutic anticoagulation (TA), they said.
In the open-label Anticoagulation COVID-19 (ANTICOVID) trial, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers identified consecutively hospitalized adults aged 18 years and older being treated for hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia in 23 centers in France between April 2021 and December 2021.
The patients were randomly assigned to SD-PA (116 patients), HD-PA (111 patients), and TA (112 patients) using low-molecular-weight heparin for 14 days, or until either hospital discharge or weaning from supplemental oxygen for 48 consecutive hours, whichever outcome occurred first. The HD-PA patients received two times the SD-PA dose. The mean age of the patients was 58.3 years, and approximately two-thirds were men; race and ethnicity data were not collected. Participants had no macrovascular thrombosis at the start of the study.
The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality and time to clinical improvement (defined as the time from randomization to a 2-point improvement on a 7-category respiratory function scale).
The secondary outcome was a combination of safety and efficacy at day 28 that included a composite of thrombosis (ischemic stroke, noncerebrovascular arterial thrombosis, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary artery thrombosis, and central venous catheter–related deep venous thrombosis), major bleeding, or all-cause death.
For the primary outcome, results were similar among the groups; HD-PA had no significant benefit over SD-PA or TA. All-cause death rates for SD-PA, HD-PA, and TA patients were 14%, 12%, and 13%, respectively. The time to clinical improvement for the three groups was approximately 8 days, 9 days, and 8 days, respectively. Results for the primary outcome were consistent across all prespecified subgroups.
However, HD-PA was associated with a significant fourfold reduced risk of de novo thrombosis compared with SD-PA (5.5% vs. 20.2%) with no observed increase in major bleeding. TA was not associated with any significant improvement in primary or secondary outcomes compared with HD-PA or SD-PA.
The current study findings of no improvement in survival or disease resolution in patients with a higher anticoagulant dose reflects data from previous studies, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Our study results together with those of previous RCTs support the premise that the role of microvascular thrombosis in worsening organ dysfunction may be narrower than estimated,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the open-label design and the relatively small sample size, the lack of data on microvascular (vs. macrovascular) thrombosis at baseline, and the predominance of the Delta variant of COVID-19 among the study participants, which may have contributed to a lower mortality rate, the researchers noted.
However, given the significant reduction in de novo thrombosis, the results support the routine use of HD-PA in patients with severe hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, they concluded.
Results inform current clinical practice
Over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, “Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 manifested the highest risk for thromboembolic complications, especially patients in the intensive care setting,” and early reports suggested that standard prophylactic doses of anticoagulant therapy might be insufficient to prevent thrombotic events, Richard C. Becker, MD, of the University of Cincinnati, and Thomas L. Ortel, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Although there have been several studies that have investigated the role of anticoagulant therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, this is the first study that specifically compared a standard, prophylactic dose of low-molecular-weight heparin to a ‘high-dose’ prophylactic regimen and to a full therapeutic dose regimen,” Dr. Ortel said in an interview.
“Given the concerns about an increased thrombotic risk with prophylactic dose anticoagulation, and the potential bleeding risk associated with a full therapeutic dose of anticoagulation, this approach enabled the investigators to explore the efficacy and safety of an intermediate dose between these two extremes,” he said.
In the current study, , a finding that was not observed in other studies investigating anticoagulant therapy in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19,” Dr. Ortel told this news organization. “Much initial concern about progression of disease in patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 focused on the role of microvascular thrombosis, which appears to be less important in this process, or, alternatively, less responsive to anticoagulant therapy.”
The clinical takeaway from the study, Dr. Ortel said, is the decreased risk for venous thromboembolism with a high-dose prophylactic anticoagulation strategy compared with a standard-dose prophylactic regimen for patients hospitalized with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, “leading to an improved net clinical outcome.”
Looking ahead, “Additional research is needed to determine whether a higher dose of prophylactic anticoagulation would be beneficial for patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia who are not in an intensive care unit setting,” Dr. Ortel said. Studies are needed to determine whether therapeutic interventions are equally beneficial in patients with different coronavirus variants, since most patients in the current study were infected with the Delta variant, he added.
The study was supported by LEO Pharma. Dr. Labbé disclosed grants from LEO Pharma during the study and fees from AOP Health unrelated to the current study.
Dr. Becker disclosed personal fees from Novartis Data Safety Monitoring Board, Ionis Data Safety Monitoring Board, and Basking Biosciences Scientific Advisory Board unrelated to the current study. Dr. Ortel disclosed grants from the National Institutes of Health, Instrumentation Laboratory, Stago, and Siemens; contract fees from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; and honoraria from UpToDate unrelated to the current study.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High-dose prophylactic anticoagulation or therapeutic anticoagulation reduced de novo thrombosis in patients with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, based on data from 334 adults.
Patients with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia are at increased risk of thrombosis and anticoagulation-related bleeding, therefore data to identify the lowest effective anticoagulant dose are needed, wrote Vincent Labbé, MD, of Sorbonne University, Paris, and colleagues.
Previous studies of different anticoagulation strategies for noncritically ill and critically ill patients with COVID-19 pneumonia have shown contrasting results, but some institutions recommend a high-dose regimen in the wake of data showing macrovascular thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 who were treated with standard anticoagulation, the authors wrote.
However, no previously published studies have compared the effectiveness of the three anticoagulation strategies: high-dose prophylactic anticoagulation (HD-PA), standard dose prophylactic anticoagulation (SD-PA), and therapeutic anticoagulation (TA), they said.
In the open-label Anticoagulation COVID-19 (ANTICOVID) trial, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers identified consecutively hospitalized adults aged 18 years and older being treated for hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia in 23 centers in France between April 2021 and December 2021.
The patients were randomly assigned to SD-PA (116 patients), HD-PA (111 patients), and TA (112 patients) using low-molecular-weight heparin for 14 days, or until either hospital discharge or weaning from supplemental oxygen for 48 consecutive hours, whichever outcome occurred first. The HD-PA patients received two times the SD-PA dose. The mean age of the patients was 58.3 years, and approximately two-thirds were men; race and ethnicity data were not collected. Participants had no macrovascular thrombosis at the start of the study.
The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality and time to clinical improvement (defined as the time from randomization to a 2-point improvement on a 7-category respiratory function scale).
The secondary outcome was a combination of safety and efficacy at day 28 that included a composite of thrombosis (ischemic stroke, noncerebrovascular arterial thrombosis, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary artery thrombosis, and central venous catheter–related deep venous thrombosis), major bleeding, or all-cause death.
For the primary outcome, results were similar among the groups; HD-PA had no significant benefit over SD-PA or TA. All-cause death rates for SD-PA, HD-PA, and TA patients were 14%, 12%, and 13%, respectively. The time to clinical improvement for the three groups was approximately 8 days, 9 days, and 8 days, respectively. Results for the primary outcome were consistent across all prespecified subgroups.
However, HD-PA was associated with a significant fourfold reduced risk of de novo thrombosis compared with SD-PA (5.5% vs. 20.2%) with no observed increase in major bleeding. TA was not associated with any significant improvement in primary or secondary outcomes compared with HD-PA or SD-PA.
The current study findings of no improvement in survival or disease resolution in patients with a higher anticoagulant dose reflects data from previous studies, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Our study results together with those of previous RCTs support the premise that the role of microvascular thrombosis in worsening organ dysfunction may be narrower than estimated,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the open-label design and the relatively small sample size, the lack of data on microvascular (vs. macrovascular) thrombosis at baseline, and the predominance of the Delta variant of COVID-19 among the study participants, which may have contributed to a lower mortality rate, the researchers noted.
However, given the significant reduction in de novo thrombosis, the results support the routine use of HD-PA in patients with severe hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, they concluded.
Results inform current clinical practice
Over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, “Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 manifested the highest risk for thromboembolic complications, especially patients in the intensive care setting,” and early reports suggested that standard prophylactic doses of anticoagulant therapy might be insufficient to prevent thrombotic events, Richard C. Becker, MD, of the University of Cincinnati, and Thomas L. Ortel, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Although there have been several studies that have investigated the role of anticoagulant therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, this is the first study that specifically compared a standard, prophylactic dose of low-molecular-weight heparin to a ‘high-dose’ prophylactic regimen and to a full therapeutic dose regimen,” Dr. Ortel said in an interview.
“Given the concerns about an increased thrombotic risk with prophylactic dose anticoagulation, and the potential bleeding risk associated with a full therapeutic dose of anticoagulation, this approach enabled the investigators to explore the efficacy and safety of an intermediate dose between these two extremes,” he said.
In the current study, , a finding that was not observed in other studies investigating anticoagulant therapy in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19,” Dr. Ortel told this news organization. “Much initial concern about progression of disease in patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 focused on the role of microvascular thrombosis, which appears to be less important in this process, or, alternatively, less responsive to anticoagulant therapy.”
The clinical takeaway from the study, Dr. Ortel said, is the decreased risk for venous thromboembolism with a high-dose prophylactic anticoagulation strategy compared with a standard-dose prophylactic regimen for patients hospitalized with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, “leading to an improved net clinical outcome.”
Looking ahead, “Additional research is needed to determine whether a higher dose of prophylactic anticoagulation would be beneficial for patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia who are not in an intensive care unit setting,” Dr. Ortel said. Studies are needed to determine whether therapeutic interventions are equally beneficial in patients with different coronavirus variants, since most patients in the current study were infected with the Delta variant, he added.
The study was supported by LEO Pharma. Dr. Labbé disclosed grants from LEO Pharma during the study and fees from AOP Health unrelated to the current study.
Dr. Becker disclosed personal fees from Novartis Data Safety Monitoring Board, Ionis Data Safety Monitoring Board, and Basking Biosciences Scientific Advisory Board unrelated to the current study. Dr. Ortel disclosed grants from the National Institutes of Health, Instrumentation Laboratory, Stago, and Siemens; contract fees from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; and honoraria from UpToDate unrelated to the current study.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High-dose prophylactic anticoagulation or therapeutic anticoagulation reduced de novo thrombosis in patients with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, based on data from 334 adults.
Patients with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia are at increased risk of thrombosis and anticoagulation-related bleeding, therefore data to identify the lowest effective anticoagulant dose are needed, wrote Vincent Labbé, MD, of Sorbonne University, Paris, and colleagues.
Previous studies of different anticoagulation strategies for noncritically ill and critically ill patients with COVID-19 pneumonia have shown contrasting results, but some institutions recommend a high-dose regimen in the wake of data showing macrovascular thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 who were treated with standard anticoagulation, the authors wrote.
However, no previously published studies have compared the effectiveness of the three anticoagulation strategies: high-dose prophylactic anticoagulation (HD-PA), standard dose prophylactic anticoagulation (SD-PA), and therapeutic anticoagulation (TA), they said.
In the open-label Anticoagulation COVID-19 (ANTICOVID) trial, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers identified consecutively hospitalized adults aged 18 years and older being treated for hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia in 23 centers in France between April 2021 and December 2021.
The patients were randomly assigned to SD-PA (116 patients), HD-PA (111 patients), and TA (112 patients) using low-molecular-weight heparin for 14 days, or until either hospital discharge or weaning from supplemental oxygen for 48 consecutive hours, whichever outcome occurred first. The HD-PA patients received two times the SD-PA dose. The mean age of the patients was 58.3 years, and approximately two-thirds were men; race and ethnicity data were not collected. Participants had no macrovascular thrombosis at the start of the study.
The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality and time to clinical improvement (defined as the time from randomization to a 2-point improvement on a 7-category respiratory function scale).
The secondary outcome was a combination of safety and efficacy at day 28 that included a composite of thrombosis (ischemic stroke, noncerebrovascular arterial thrombosis, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary artery thrombosis, and central venous catheter–related deep venous thrombosis), major bleeding, or all-cause death.
For the primary outcome, results were similar among the groups; HD-PA had no significant benefit over SD-PA or TA. All-cause death rates for SD-PA, HD-PA, and TA patients were 14%, 12%, and 13%, respectively. The time to clinical improvement for the three groups was approximately 8 days, 9 days, and 8 days, respectively. Results for the primary outcome were consistent across all prespecified subgroups.
However, HD-PA was associated with a significant fourfold reduced risk of de novo thrombosis compared with SD-PA (5.5% vs. 20.2%) with no observed increase in major bleeding. TA was not associated with any significant improvement in primary or secondary outcomes compared with HD-PA or SD-PA.
The current study findings of no improvement in survival or disease resolution in patients with a higher anticoagulant dose reflects data from previous studies, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Our study results together with those of previous RCTs support the premise that the role of microvascular thrombosis in worsening organ dysfunction may be narrower than estimated,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the open-label design and the relatively small sample size, the lack of data on microvascular (vs. macrovascular) thrombosis at baseline, and the predominance of the Delta variant of COVID-19 among the study participants, which may have contributed to a lower mortality rate, the researchers noted.
However, given the significant reduction in de novo thrombosis, the results support the routine use of HD-PA in patients with severe hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, they concluded.
Results inform current clinical practice
Over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, “Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 manifested the highest risk for thromboembolic complications, especially patients in the intensive care setting,” and early reports suggested that standard prophylactic doses of anticoagulant therapy might be insufficient to prevent thrombotic events, Richard C. Becker, MD, of the University of Cincinnati, and Thomas L. Ortel, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Although there have been several studies that have investigated the role of anticoagulant therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, this is the first study that specifically compared a standard, prophylactic dose of low-molecular-weight heparin to a ‘high-dose’ prophylactic regimen and to a full therapeutic dose regimen,” Dr. Ortel said in an interview.
“Given the concerns about an increased thrombotic risk with prophylactic dose anticoagulation, and the potential bleeding risk associated with a full therapeutic dose of anticoagulation, this approach enabled the investigators to explore the efficacy and safety of an intermediate dose between these two extremes,” he said.
In the current study, , a finding that was not observed in other studies investigating anticoagulant therapy in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19,” Dr. Ortel told this news organization. “Much initial concern about progression of disease in patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 focused on the role of microvascular thrombosis, which appears to be less important in this process, or, alternatively, less responsive to anticoagulant therapy.”
The clinical takeaway from the study, Dr. Ortel said, is the decreased risk for venous thromboembolism with a high-dose prophylactic anticoagulation strategy compared with a standard-dose prophylactic regimen for patients hospitalized with hypoxemic COVID-19 pneumonia, “leading to an improved net clinical outcome.”
Looking ahead, “Additional research is needed to determine whether a higher dose of prophylactic anticoagulation would be beneficial for patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia who are not in an intensive care unit setting,” Dr. Ortel said. Studies are needed to determine whether therapeutic interventions are equally beneficial in patients with different coronavirus variants, since most patients in the current study were infected with the Delta variant, he added.
The study was supported by LEO Pharma. Dr. Labbé disclosed grants from LEO Pharma during the study and fees from AOP Health unrelated to the current study.
Dr. Becker disclosed personal fees from Novartis Data Safety Monitoring Board, Ionis Data Safety Monitoring Board, and Basking Biosciences Scientific Advisory Board unrelated to the current study. Dr. Ortel disclosed grants from the National Institutes of Health, Instrumentation Laboratory, Stago, and Siemens; contract fees from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; and honoraria from UpToDate unrelated to the current study.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID led to rise in pregnancy-related deaths: New research
The rise in deaths was most pronounced among Black mothers.
In 2021, 1,205 women died from pregnancy-related causes, making the year one of the worst for maternal mortality in U.S. history, according to newly released data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Maternal mortality is defined as occurring during pregnancy, at delivery, or soon after delivery.
COVID was the driver of the increased death rate, according to a study published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology. The researchers noted that unvaccinated pregnant people are more likely to get severe COVID, and that prenatal and postnatal care were disrupted during the early part of the pandemic. From July 2021 to March 2023, the rate of women being vaccinated before pregnancy has risen from 22% to 70%, CDC data show.
Maternal mortality rates jumped the most among Black women, who in 2021 had a maternal mortality rate of nearly 70 deaths per 100,000 live births, which was 2.6 times the rate for White women.
Existing risks based on a mother’s age also increased from 2020 to 2021. The maternal mortality rates by age in 2021 per 100,000 live births were:
- 20.4 for women under age 25.
- 31.3 for women ages 25 to 39.
- 138.5 for women ages 40 and older.
Iffath Abbasi Hoskins, MD, FACOG, president of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, called the situation “stunning” and “preventable.”
The findings “send a resounding message that maternal health and evidence-based efforts to eliminate racial health inequities need to be, and remain, a top public health priority,” Dr. Hoskins said in a statement.
“The COVID-19 pandemic had a dramatic and tragic effect on maternal death rates, but we cannot let that fact obscure that there was – and still is – already a maternal mortality crisis to compound,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The rise in deaths was most pronounced among Black mothers.
In 2021, 1,205 women died from pregnancy-related causes, making the year one of the worst for maternal mortality in U.S. history, according to newly released data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Maternal mortality is defined as occurring during pregnancy, at delivery, or soon after delivery.
COVID was the driver of the increased death rate, according to a study published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology. The researchers noted that unvaccinated pregnant people are more likely to get severe COVID, and that prenatal and postnatal care were disrupted during the early part of the pandemic. From July 2021 to March 2023, the rate of women being vaccinated before pregnancy has risen from 22% to 70%, CDC data show.
Maternal mortality rates jumped the most among Black women, who in 2021 had a maternal mortality rate of nearly 70 deaths per 100,000 live births, which was 2.6 times the rate for White women.
Existing risks based on a mother’s age also increased from 2020 to 2021. The maternal mortality rates by age in 2021 per 100,000 live births were:
- 20.4 for women under age 25.
- 31.3 for women ages 25 to 39.
- 138.5 for women ages 40 and older.
Iffath Abbasi Hoskins, MD, FACOG, president of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, called the situation “stunning” and “preventable.”
The findings “send a resounding message that maternal health and evidence-based efforts to eliminate racial health inequities need to be, and remain, a top public health priority,” Dr. Hoskins said in a statement.
“The COVID-19 pandemic had a dramatic and tragic effect on maternal death rates, but we cannot let that fact obscure that there was – and still is – already a maternal mortality crisis to compound,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The rise in deaths was most pronounced among Black mothers.
In 2021, 1,205 women died from pregnancy-related causes, making the year one of the worst for maternal mortality in U.S. history, according to newly released data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Maternal mortality is defined as occurring during pregnancy, at delivery, or soon after delivery.
COVID was the driver of the increased death rate, according to a study published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology. The researchers noted that unvaccinated pregnant people are more likely to get severe COVID, and that prenatal and postnatal care were disrupted during the early part of the pandemic. From July 2021 to March 2023, the rate of women being vaccinated before pregnancy has risen from 22% to 70%, CDC data show.
Maternal mortality rates jumped the most among Black women, who in 2021 had a maternal mortality rate of nearly 70 deaths per 100,000 live births, which was 2.6 times the rate for White women.
Existing risks based on a mother’s age also increased from 2020 to 2021. The maternal mortality rates by age in 2021 per 100,000 live births were:
- 20.4 for women under age 25.
- 31.3 for women ages 25 to 39.
- 138.5 for women ages 40 and older.
Iffath Abbasi Hoskins, MD, FACOG, president of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, called the situation “stunning” and “preventable.”
The findings “send a resounding message that maternal health and evidence-based efforts to eliminate racial health inequities need to be, and remain, a top public health priority,” Dr. Hoskins said in a statement.
“The COVID-19 pandemic had a dramatic and tragic effect on maternal death rates, but we cannot let that fact obscure that there was – and still is – already a maternal mortality crisis to compound,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID in pregnancy may affect boys’ neurodevelopment: Study
Boys born to mothers infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 during pregnancy may be more likely to receive a diagnosis of a neurodevelopmental disorder by age 12 months, according to new research.
Andrea G. Edlow, MD, MSc, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues examined data from 18,355 births between March 1, 2020, and May 31, 2021, at eight hospitals across two health systems in Massachusetts.
Of these births, 883 (4.8%) were to individuals who tested positive for SARS‐CoV‐2 during pregnancy. Among the children exposed to SARS‐CoV‐2 in the womb, 26 (3%) received a neurodevelopmental diagnosis, including disorders of motor function, speech and language, and psychological development, by age 1 year. In the group unexposed to the virus, 1.8% received such a diagnosis.
After adjusting for factors such as race, insurance, maternal age, and preterm birth, Dr. Edlow’s group found that a positive test for SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy was associated with an increased risk for neurodevelopmental diagnoses at 12 months among boys (adjusted odds ratio, 1.94; 95% confidence interval, 1.12-3.17; P = .01), but not among girls.
In a subset of children with data available at 18 months, the correlation among boys at that age was less pronounced and not statistically significant (aOR, 1.42; 95% CI, 0.92-2.11; P = .10).
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open
Prior epidemiological research has suggested that maternal infection during pregnancy is associated with heightened risk for a range of neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and schizophrenia, in offspring, the authors wrote.
“The neurodevelopmental risk associated with maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection was disproportionately high in male infants, consistent with the known increased vulnerability of males in the face of prenatal adverse exposures,” Dr. Edlow said in a news release about the findings.
Larger studies and longer follow‐up are needed to confirm and reliably estimate the risk, the researchers said.
“It is not clear that the changes we can detect at 12 and 18 months will be indicative of persistent risks for disorders such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, or schizophrenia,” they write.
New data published online by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that in 11 communities in 2020, 1 in 36 (2.8%) 8-year-old children had been identified with autism spectrum disorder, an increase from 2.3% in 2018. The data also show that the early months of the pandemic may have disrupted autism detection efforts among 4-year-olds.
The investigators were supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative. Coauthors disclosed consulting for or receiving personal fees from biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Boys born to mothers infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 during pregnancy may be more likely to receive a diagnosis of a neurodevelopmental disorder by age 12 months, according to new research.
Andrea G. Edlow, MD, MSc, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues examined data from 18,355 births between March 1, 2020, and May 31, 2021, at eight hospitals across two health systems in Massachusetts.
Of these births, 883 (4.8%) were to individuals who tested positive for SARS‐CoV‐2 during pregnancy. Among the children exposed to SARS‐CoV‐2 in the womb, 26 (3%) received a neurodevelopmental diagnosis, including disorders of motor function, speech and language, and psychological development, by age 1 year. In the group unexposed to the virus, 1.8% received such a diagnosis.
After adjusting for factors such as race, insurance, maternal age, and preterm birth, Dr. Edlow’s group found that a positive test for SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy was associated with an increased risk for neurodevelopmental diagnoses at 12 months among boys (adjusted odds ratio, 1.94; 95% confidence interval, 1.12-3.17; P = .01), but not among girls.
In a subset of children with data available at 18 months, the correlation among boys at that age was less pronounced and not statistically significant (aOR, 1.42; 95% CI, 0.92-2.11; P = .10).
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open
Prior epidemiological research has suggested that maternal infection during pregnancy is associated with heightened risk for a range of neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and schizophrenia, in offspring, the authors wrote.
“The neurodevelopmental risk associated with maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection was disproportionately high in male infants, consistent with the known increased vulnerability of males in the face of prenatal adverse exposures,” Dr. Edlow said in a news release about the findings.
Larger studies and longer follow‐up are needed to confirm and reliably estimate the risk, the researchers said.
“It is not clear that the changes we can detect at 12 and 18 months will be indicative of persistent risks for disorders such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, or schizophrenia,” they write.
New data published online by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that in 11 communities in 2020, 1 in 36 (2.8%) 8-year-old children had been identified with autism spectrum disorder, an increase from 2.3% in 2018. The data also show that the early months of the pandemic may have disrupted autism detection efforts among 4-year-olds.
The investigators were supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative. Coauthors disclosed consulting for or receiving personal fees from biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Boys born to mothers infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 during pregnancy may be more likely to receive a diagnosis of a neurodevelopmental disorder by age 12 months, according to new research.
Andrea G. Edlow, MD, MSc, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues examined data from 18,355 births between March 1, 2020, and May 31, 2021, at eight hospitals across two health systems in Massachusetts.
Of these births, 883 (4.8%) were to individuals who tested positive for SARS‐CoV‐2 during pregnancy. Among the children exposed to SARS‐CoV‐2 in the womb, 26 (3%) received a neurodevelopmental diagnosis, including disorders of motor function, speech and language, and psychological development, by age 1 year. In the group unexposed to the virus, 1.8% received such a diagnosis.
After adjusting for factors such as race, insurance, maternal age, and preterm birth, Dr. Edlow’s group found that a positive test for SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy was associated with an increased risk for neurodevelopmental diagnoses at 12 months among boys (adjusted odds ratio, 1.94; 95% confidence interval, 1.12-3.17; P = .01), but not among girls.
In a subset of children with data available at 18 months, the correlation among boys at that age was less pronounced and not statistically significant (aOR, 1.42; 95% CI, 0.92-2.11; P = .10).
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open
Prior epidemiological research has suggested that maternal infection during pregnancy is associated with heightened risk for a range of neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and schizophrenia, in offspring, the authors wrote.
“The neurodevelopmental risk associated with maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection was disproportionately high in male infants, consistent with the known increased vulnerability of males in the face of prenatal adverse exposures,” Dr. Edlow said in a news release about the findings.
Larger studies and longer follow‐up are needed to confirm and reliably estimate the risk, the researchers said.
“It is not clear that the changes we can detect at 12 and 18 months will be indicative of persistent risks for disorders such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, or schizophrenia,” they write.
New data published online by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that in 11 communities in 2020, 1 in 36 (2.8%) 8-year-old children had been identified with autism spectrum disorder, an increase from 2.3% in 2018. The data also show that the early months of the pandemic may have disrupted autism detection efforts among 4-year-olds.
The investigators were supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative. Coauthors disclosed consulting for or receiving personal fees from biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Nurse makes millions selling her licensing exam study sheets
Ms. Beggs, 28, sells one-page study sheets or bundles of sheets, sometimes with colorful drawings, conversation bubbles and underlining, that boil down concepts for particular conditions into easy-to-understand language.
The biggest seller on Ms. Beggs’ online marketplace Etsy site, RNExplained, is a bundle of study guides covering eight core nursing classes. The notes range in price from $2 to $150. More than 70,000 customers have bought the $60 bundle, according to the website.
Ms. Beggs’ business developed in a “very unintentional” way when COVID hit with just months left in her nursing program at Mount Saint Mary’s University, Los Angeles, she told this news organization.
Classes had switched to Zoom, and she had no one to study with as she prepared to take her board exams.
“The best way I know how to study is to teach things out loud. But because I had nobody to teach out loud to, I would literally teach them to the wall,” Ms. Beggs said. “I would record myself so I could play it back and teach myself these topics that were hard for me to understand.”
Just for fun, she says, she posted them on TikTok and the responses started flowing in, with followers asking where she was selling the sheets. She now has more than 660,000 TikTok followers and 9 million likes.
Ms. Beggs said that every sheet highlights a condition, and she has made 308 of them.
Traditional classroom lessons typically teach one medical condition in 5-6 pages, Ms. Beggs said. “I go straight to the point.”
One reviewer on Ms. Beggs’ Etsy site appreciated the handwritten notes, calling them “simplified and concise.” Another commented: “Definitely helped me pass my last exam.”
Ms. Beggs says that her notes may seem simple, but each page represents comprehensive research.
“I have to go through not just one source of information to make sure my information is factual,” Ms. Beggs says. “What you teach in California might be a little different than what you teach in Florida. It’s very meticulous. The lab values will be a little different everywhere you go.”
She acknowledges her competition, noting that there are many other study guides for the NCLEX and nursing courses.
Nursing groups weigh in
Dawn Kappel, spokesperson for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, which oversees NCLEX, said in an interview that “NCSBN has no issue with the current content of Stephanee Beggs’ business venture.”
For many students, the study guides will be helpful, especially for visual learners, said Carole Kenner, PhD, RN, dean and professor in the School of Nursing and Health Sciences at The College of New Jersey.
But for students “who are less confident in their knowledge, I would want to see a lot more in-depth explanation and rationale,” Dr. Kenner said.
“Since the NCLEX is moving to more cased-based scenarios, the next-gen unfolding cases, you really have to understand a lot of the rationale.”
The notes remind Dr. Kenner of traditional flash cards. “I don’t think it will work for all students, but even the fanciest of onsite review courses are useful to everyone,” she said.
‘Not cutting corners’
As an emergency nurse, Ms. Beggs said, “I have the experience as a nurse to show people that what you are learning will be seen in real life.”
“The way I teach my brand is not to take shortcuts. I love to teach to understand rather than teaching to memorize for an exam.”
She said she sees her guides as a supplement to learning, not a replacement.
“It’s not cutting corners,” she says. “I condense a medical condition that could take a very long time to understand and break it into layman’s terms.”
Ms. Beggs said when people hear about the $2 million, they often ask her whether she plans to give up her shifts in the emergency department for the more lucrative venture.
The answer is no, at least not yet.
“Aside from teaching, I genuinely love being at the bedside,” Ms. Beggs said. “I don’t foresee myself leaving that for good for as long as I can handle both.” She acknowledged, though, that her business now takes up most of her time.
“I love everything about both aspects, so it’s hard for me to choose.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Beggs, 28, sells one-page study sheets or bundles of sheets, sometimes with colorful drawings, conversation bubbles and underlining, that boil down concepts for particular conditions into easy-to-understand language.
The biggest seller on Ms. Beggs’ online marketplace Etsy site, RNExplained, is a bundle of study guides covering eight core nursing classes. The notes range in price from $2 to $150. More than 70,000 customers have bought the $60 bundle, according to the website.
Ms. Beggs’ business developed in a “very unintentional” way when COVID hit with just months left in her nursing program at Mount Saint Mary’s University, Los Angeles, she told this news organization.
Classes had switched to Zoom, and she had no one to study with as she prepared to take her board exams.
“The best way I know how to study is to teach things out loud. But because I had nobody to teach out loud to, I would literally teach them to the wall,” Ms. Beggs said. “I would record myself so I could play it back and teach myself these topics that were hard for me to understand.”
Just for fun, she says, she posted them on TikTok and the responses started flowing in, with followers asking where she was selling the sheets. She now has more than 660,000 TikTok followers and 9 million likes.
Ms. Beggs said that every sheet highlights a condition, and she has made 308 of them.
Traditional classroom lessons typically teach one medical condition in 5-6 pages, Ms. Beggs said. “I go straight to the point.”
One reviewer on Ms. Beggs’ Etsy site appreciated the handwritten notes, calling them “simplified and concise.” Another commented: “Definitely helped me pass my last exam.”
Ms. Beggs says that her notes may seem simple, but each page represents comprehensive research.
“I have to go through not just one source of information to make sure my information is factual,” Ms. Beggs says. “What you teach in California might be a little different than what you teach in Florida. It’s very meticulous. The lab values will be a little different everywhere you go.”
She acknowledges her competition, noting that there are many other study guides for the NCLEX and nursing courses.
Nursing groups weigh in
Dawn Kappel, spokesperson for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, which oversees NCLEX, said in an interview that “NCSBN has no issue with the current content of Stephanee Beggs’ business venture.”
For many students, the study guides will be helpful, especially for visual learners, said Carole Kenner, PhD, RN, dean and professor in the School of Nursing and Health Sciences at The College of New Jersey.
But for students “who are less confident in their knowledge, I would want to see a lot more in-depth explanation and rationale,” Dr. Kenner said.
“Since the NCLEX is moving to more cased-based scenarios, the next-gen unfolding cases, you really have to understand a lot of the rationale.”
The notes remind Dr. Kenner of traditional flash cards. “I don’t think it will work for all students, but even the fanciest of onsite review courses are useful to everyone,” she said.
‘Not cutting corners’
As an emergency nurse, Ms. Beggs said, “I have the experience as a nurse to show people that what you are learning will be seen in real life.”
“The way I teach my brand is not to take shortcuts. I love to teach to understand rather than teaching to memorize for an exam.”
She said she sees her guides as a supplement to learning, not a replacement.
“It’s not cutting corners,” she says. “I condense a medical condition that could take a very long time to understand and break it into layman’s terms.”
Ms. Beggs said when people hear about the $2 million, they often ask her whether she plans to give up her shifts in the emergency department for the more lucrative venture.
The answer is no, at least not yet.
“Aside from teaching, I genuinely love being at the bedside,” Ms. Beggs said. “I don’t foresee myself leaving that for good for as long as I can handle both.” She acknowledged, though, that her business now takes up most of her time.
“I love everything about both aspects, so it’s hard for me to choose.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Beggs, 28, sells one-page study sheets or bundles of sheets, sometimes with colorful drawings, conversation bubbles and underlining, that boil down concepts for particular conditions into easy-to-understand language.
The biggest seller on Ms. Beggs’ online marketplace Etsy site, RNExplained, is a bundle of study guides covering eight core nursing classes. The notes range in price from $2 to $150. More than 70,000 customers have bought the $60 bundle, according to the website.
Ms. Beggs’ business developed in a “very unintentional” way when COVID hit with just months left in her nursing program at Mount Saint Mary’s University, Los Angeles, she told this news organization.
Classes had switched to Zoom, and she had no one to study with as she prepared to take her board exams.
“The best way I know how to study is to teach things out loud. But because I had nobody to teach out loud to, I would literally teach them to the wall,” Ms. Beggs said. “I would record myself so I could play it back and teach myself these topics that were hard for me to understand.”
Just for fun, she says, she posted them on TikTok and the responses started flowing in, with followers asking where she was selling the sheets. She now has more than 660,000 TikTok followers and 9 million likes.
Ms. Beggs said that every sheet highlights a condition, and she has made 308 of them.
Traditional classroom lessons typically teach one medical condition in 5-6 pages, Ms. Beggs said. “I go straight to the point.”
One reviewer on Ms. Beggs’ Etsy site appreciated the handwritten notes, calling them “simplified and concise.” Another commented: “Definitely helped me pass my last exam.”
Ms. Beggs says that her notes may seem simple, but each page represents comprehensive research.
“I have to go through not just one source of information to make sure my information is factual,” Ms. Beggs says. “What you teach in California might be a little different than what you teach in Florida. It’s very meticulous. The lab values will be a little different everywhere you go.”
She acknowledges her competition, noting that there are many other study guides for the NCLEX and nursing courses.
Nursing groups weigh in
Dawn Kappel, spokesperson for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, which oversees NCLEX, said in an interview that “NCSBN has no issue with the current content of Stephanee Beggs’ business venture.”
For many students, the study guides will be helpful, especially for visual learners, said Carole Kenner, PhD, RN, dean and professor in the School of Nursing and Health Sciences at The College of New Jersey.
But for students “who are less confident in their knowledge, I would want to see a lot more in-depth explanation and rationale,” Dr. Kenner said.
“Since the NCLEX is moving to more cased-based scenarios, the next-gen unfolding cases, you really have to understand a lot of the rationale.”
The notes remind Dr. Kenner of traditional flash cards. “I don’t think it will work for all students, but even the fanciest of onsite review courses are useful to everyone,” she said.
‘Not cutting corners’
As an emergency nurse, Ms. Beggs said, “I have the experience as a nurse to show people that what you are learning will be seen in real life.”
“The way I teach my brand is not to take shortcuts. I love to teach to understand rather than teaching to memorize for an exam.”
She said she sees her guides as a supplement to learning, not a replacement.
“It’s not cutting corners,” she says. “I condense a medical condition that could take a very long time to understand and break it into layman’s terms.”
Ms. Beggs said when people hear about the $2 million, they often ask her whether she plans to give up her shifts in the emergency department for the more lucrative venture.
The answer is no, at least not yet.
“Aside from teaching, I genuinely love being at the bedside,” Ms. Beggs said. “I don’t foresee myself leaving that for good for as long as I can handle both.” She acknowledged, though, that her business now takes up most of her time.
“I love everything about both aspects, so it’s hard for me to choose.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID can mimic prostate cancer symptoms
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccinations lag in youngest children
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
NOVIDs: Do some have the genes to dodge COVID?
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pandemic hit Black children harder, study shows
Black children had almost three times as many COVID-related deaths as White children and about twice as many hospitalizations, according to a new study.
The study said that 1,556 children have died from the start of the pandemic until Nov. 30, 2022, with 593 of those children being 4 and under. Black children died of COVID-related causes 2.7 times more often than White children and were hospitalized 2.2 times more often than White children, the study said.
Lower vaccination rates for Black people may be a factor. The study said 43.6% of White children have received two or more vaccinations, compared with 40.2% of Black children.
“First and foremost, this study repudiates the misunderstanding that COVID-19 has not been of consequence to children who have had more than 15.5 million reported cases, representing 18 percent of all cases in the United States,” Reed Tuckson, MD, a member of the Black Coalition Against COVID board of directors and former District of Columbia public health commissioner, said in a news release.
“And second, our research shows that like their adult counterparts, Black and other children of color have shouldered more of the burden of COVID-19 than the White population.”
The study was commissioned by BCAC and conducted by the Satcher Health Leadership Institute of the Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta. It’s based on studies conducted by other agencies over 2 years.
Black and Hispanic children also had more severe COVID cases, the study said. Among 281 pediatric patients in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut, 23.3% of severe cases were Black and 51% of severe cases were Hispanic.
The study says 1 in 310 Black children lost a parent or caregiver to COVID between April 2020 and June 2012, compared with 1 in 738 White children.
Economic and health-related hardships were experienced by 31% of Black households, 29% of Latino households, and 16% of White households, the study said.
“Children with COVID-19 in communities of color were sicker, [were] hospitalized and died at higher rates than White children,” Sandra Harris-Hooker, the interim executive director at the Satcher Health Leadership Institute of Morehouse School, said in the release. “We can now fully understand the devastating impact the virus had on communities of color across generations.”
The study recommends several changes, such as modifying eligibility requirements for the Children’s Health Insurance Program to help more children who fall into coverage gaps and expanding the Child Tax Credit.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Black children had almost three times as many COVID-related deaths as White children and about twice as many hospitalizations, according to a new study.
The study said that 1,556 children have died from the start of the pandemic until Nov. 30, 2022, with 593 of those children being 4 and under. Black children died of COVID-related causes 2.7 times more often than White children and were hospitalized 2.2 times more often than White children, the study said.
Lower vaccination rates for Black people may be a factor. The study said 43.6% of White children have received two or more vaccinations, compared with 40.2% of Black children.
“First and foremost, this study repudiates the misunderstanding that COVID-19 has not been of consequence to children who have had more than 15.5 million reported cases, representing 18 percent of all cases in the United States,” Reed Tuckson, MD, a member of the Black Coalition Against COVID board of directors and former District of Columbia public health commissioner, said in a news release.
“And second, our research shows that like their adult counterparts, Black and other children of color have shouldered more of the burden of COVID-19 than the White population.”
The study was commissioned by BCAC and conducted by the Satcher Health Leadership Institute of the Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta. It’s based on studies conducted by other agencies over 2 years.
Black and Hispanic children also had more severe COVID cases, the study said. Among 281 pediatric patients in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut, 23.3% of severe cases were Black and 51% of severe cases were Hispanic.
The study says 1 in 310 Black children lost a parent or caregiver to COVID between April 2020 and June 2012, compared with 1 in 738 White children.
Economic and health-related hardships were experienced by 31% of Black households, 29% of Latino households, and 16% of White households, the study said.
“Children with COVID-19 in communities of color were sicker, [were] hospitalized and died at higher rates than White children,” Sandra Harris-Hooker, the interim executive director at the Satcher Health Leadership Institute of Morehouse School, said in the release. “We can now fully understand the devastating impact the virus had on communities of color across generations.”
The study recommends several changes, such as modifying eligibility requirements for the Children’s Health Insurance Program to help more children who fall into coverage gaps and expanding the Child Tax Credit.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Black children had almost three times as many COVID-related deaths as White children and about twice as many hospitalizations, according to a new study.
The study said that 1,556 children have died from the start of the pandemic until Nov. 30, 2022, with 593 of those children being 4 and under. Black children died of COVID-related causes 2.7 times more often than White children and were hospitalized 2.2 times more often than White children, the study said.
Lower vaccination rates for Black people may be a factor. The study said 43.6% of White children have received two or more vaccinations, compared with 40.2% of Black children.
“First and foremost, this study repudiates the misunderstanding that COVID-19 has not been of consequence to children who have had more than 15.5 million reported cases, representing 18 percent of all cases in the United States,” Reed Tuckson, MD, a member of the Black Coalition Against COVID board of directors and former District of Columbia public health commissioner, said in a news release.
“And second, our research shows that like their adult counterparts, Black and other children of color have shouldered more of the burden of COVID-19 than the White population.”
The study was commissioned by BCAC and conducted by the Satcher Health Leadership Institute of the Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta. It’s based on studies conducted by other agencies over 2 years.
Black and Hispanic children also had more severe COVID cases, the study said. Among 281 pediatric patients in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut, 23.3% of severe cases were Black and 51% of severe cases were Hispanic.
The study says 1 in 310 Black children lost a parent or caregiver to COVID between April 2020 and June 2012, compared with 1 in 738 White children.
Economic and health-related hardships were experienced by 31% of Black households, 29% of Latino households, and 16% of White households, the study said.
“Children with COVID-19 in communities of color were sicker, [were] hospitalized and died at higher rates than White children,” Sandra Harris-Hooker, the interim executive director at the Satcher Health Leadership Institute of Morehouse School, said in the release. “We can now fully understand the devastating impact the virus had on communities of color across generations.”
The study recommends several changes, such as modifying eligibility requirements for the Children’s Health Insurance Program to help more children who fall into coverage gaps and expanding the Child Tax Credit.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: A look back as the fourth year begins
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?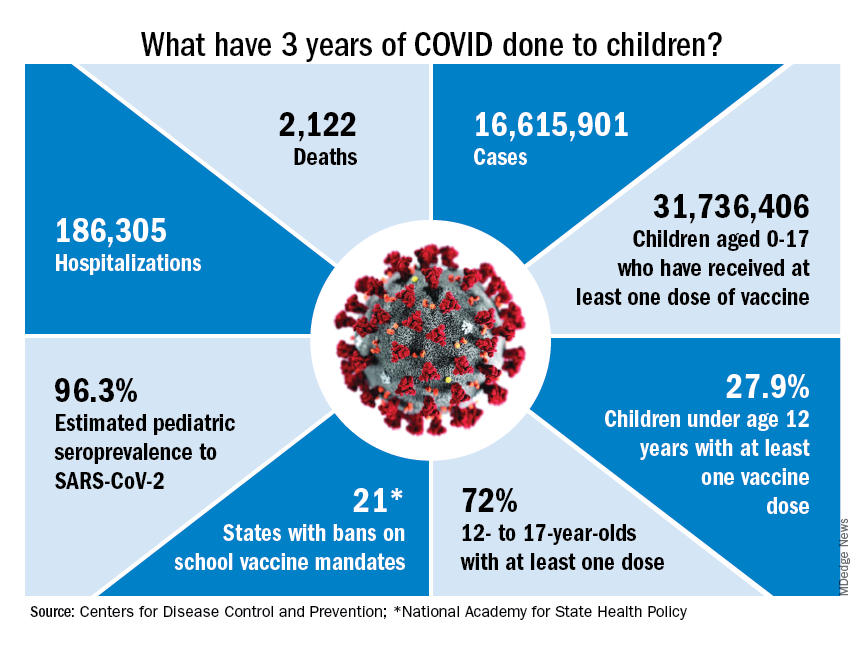
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
COVID raises risk for long-term GI complications
, a large new study indicates.
The researchers estimate that, so far, SARS-CoV-2 infections have contributed to more than 6 million new cases of GI disorders in the United States and 42 million new cases worldwide.
The diagnoses more common among patients who’ve had COVID ranged from stomach upset to acute pancreatitis, say the researchers, led by Evan Xu, a data analyst at the Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research and Development Service, VA St. Louis Health Care System.
Signs and symptoms of GI problems, such as constipation and diarrhea, also were more common among patients who had had the virus, the study found.
“Altogether, our results show that people with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders in the post-acute phase of COVID-19,” the researchers write. “Post-COVID care should involve attention to gastrointestinal health and disease.”
The results were published online in Nature Communications.
Disease risks jump
The researchers used data from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs national health care databases to identify 154,068 people with confirmed COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2021. They used statistical modeling to compare those patients with 5.6 million patients with similar characteristics who had not been infected during the same period and an historical control group of 5.9 million patients from March 1, 2018, to Dec. 31, 2019, before the virus began to spread across the globe.
The study included hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID patients. The majority of the study population was male, but the study included almost 1.2 million female patients.
Compared with control persons, post-COVID patients’ increased risk of a GI diagnosis and the excess disease burden at 1 year, respectively, were as follows.
- 102% for cholangitis; 0.22 per 1,000 persons
- 62% for peptic ulcer disease; 1.57 per 1,000 persons
- 54% for irritable bowel syndrome; 0.44 per 1,000 persons
- 47% for acute gastritis; 0.47 per 1,000 persons
- 46% for acute pancreatitis; 0.6 per 1,000 persons
- 36% for functional dyspepsia; 0.63 per 1,000 persons
- 35% for gastroesophageal reflux disease; 15.5 per 1,000 persons
Patients who’d had the virus were also at higher risk for GI symptoms than their COVID-free peers. Their risk was 60% higher for constipation, 58% for diarrhea, 52% for vomiting, 46% for bloating, and 44% for abdominal pain, the investigators found.
The risk of developing GI symptoms increased with COVID-19 severity and was highest for those who received intensive care because of the virus, the researchers note.
Subgroup analyses found that the risks of composite gastrointestinal outcome were evident in all subgroups based on age, race, sex, obesity, smoking, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, the authors write.
Disease burden rises
The increased numbers of GI patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection are altering the burden on the health care system, senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
The shift may be pronounced in primary care, where GI concerns should be seen as a trigger for questions about prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, Dr. Al-Aly said.
Patients may encounter longer wait times at GI clinics or may give up on trying to schedule appointments if waits become too long, he said. They may also present to emergency departments if they can’t get an outpatient appointment, he added.
Simon C. Mathews, MD, assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization that he’s seeing increased wait times since COVID emerged.
“We know that the pandemic impacted patients’ ability and willingness to seek GI care. There continues to be a long backlog for patients who are only now getting reconnected to care. As a result, our clinics are busier than ever, and our wait times for appointments are unfortunately longer than we would like,” said Dr. Mathews, who was not involved in the research.
Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation continue to be among the most common symptoms Dr. Mathews sees in clinic, he said.
Kyle Staller, MD, a Massachusetts General Brigham gastroenterologist, said in an interview that it’s important to distinguish symptoms from eventual diagnoses, which lag behind.
“Are patients attributing their symptoms to COVID, or is COVID itself creating a background of inflammation or changes in the nerves that are making these symptoms more common? My suspicion is a little bit of both,” said Dr. Staller, who is director of the Gastrointestinal Motility Laboratory at Mass General, Boston.
Although his clinic is seeing patients with the GI signs and symptoms listed in the article, “we’re not seeing as much of some of the diagnoses, like peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis,” he said. “I wonder if those may be related to some of the consequences of being critically ill in general, rather than COVID specifically. Those diagnoses I would be more skeptical about.”
Duration of symptoms unclear
It’s hard to tell patients how long their GI symptoms might last after COVID, given the relatively short time researchers have had to study the virus, said Dr. Staller, who was not involved in the research.
The symptoms he’s seeing in patients after COVID mimic those of postinfectious IBS, which literature says could last for months or years, Dr. Staller said. “But they should improve over time,” he added.
Senior author Dr. Al-Aly agreed that the duration of post-COVID GI symptoms is unclear.
“What I can tell you is that even people who got SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 are still coming back for GI problems,” he said.
Unlike other symptoms of long COVID, such as brain fog, gastroenterologists fortunately know how to treat the GI disorders that evolve from SARS-CoV-2 infection, said Dr. Al-Aly, who has studied the long-term effects of the virus on the brain, kidneys, heart, and other organs.
All health care providers “need to be thinking about COVID as a risk factor for all these diseases” and should ask patients about SARS-CoV-2 infection when they take their histories, he said.
The authors, Dr. Staller, and Dr. Mathews report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large new study indicates.
The researchers estimate that, so far, SARS-CoV-2 infections have contributed to more than 6 million new cases of GI disorders in the United States and 42 million new cases worldwide.
The diagnoses more common among patients who’ve had COVID ranged from stomach upset to acute pancreatitis, say the researchers, led by Evan Xu, a data analyst at the Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research and Development Service, VA St. Louis Health Care System.
Signs and symptoms of GI problems, such as constipation and diarrhea, also were more common among patients who had had the virus, the study found.
“Altogether, our results show that people with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders in the post-acute phase of COVID-19,” the researchers write. “Post-COVID care should involve attention to gastrointestinal health and disease.”
The results were published online in Nature Communications.
Disease risks jump
The researchers used data from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs national health care databases to identify 154,068 people with confirmed COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2021. They used statistical modeling to compare those patients with 5.6 million patients with similar characteristics who had not been infected during the same period and an historical control group of 5.9 million patients from March 1, 2018, to Dec. 31, 2019, before the virus began to spread across the globe.
The study included hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID patients. The majority of the study population was male, but the study included almost 1.2 million female patients.
Compared with control persons, post-COVID patients’ increased risk of a GI diagnosis and the excess disease burden at 1 year, respectively, were as follows.
- 102% for cholangitis; 0.22 per 1,000 persons
- 62% for peptic ulcer disease; 1.57 per 1,000 persons
- 54% for irritable bowel syndrome; 0.44 per 1,000 persons
- 47% for acute gastritis; 0.47 per 1,000 persons
- 46% for acute pancreatitis; 0.6 per 1,000 persons
- 36% for functional dyspepsia; 0.63 per 1,000 persons
- 35% for gastroesophageal reflux disease; 15.5 per 1,000 persons
Patients who’d had the virus were also at higher risk for GI symptoms than their COVID-free peers. Their risk was 60% higher for constipation, 58% for diarrhea, 52% for vomiting, 46% for bloating, and 44% for abdominal pain, the investigators found.
The risk of developing GI symptoms increased with COVID-19 severity and was highest for those who received intensive care because of the virus, the researchers note.
Subgroup analyses found that the risks of composite gastrointestinal outcome were evident in all subgroups based on age, race, sex, obesity, smoking, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, the authors write.
Disease burden rises
The increased numbers of GI patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection are altering the burden on the health care system, senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
The shift may be pronounced in primary care, where GI concerns should be seen as a trigger for questions about prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, Dr. Al-Aly said.
Patients may encounter longer wait times at GI clinics or may give up on trying to schedule appointments if waits become too long, he said. They may also present to emergency departments if they can’t get an outpatient appointment, he added.
Simon C. Mathews, MD, assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization that he’s seeing increased wait times since COVID emerged.
“We know that the pandemic impacted patients’ ability and willingness to seek GI care. There continues to be a long backlog for patients who are only now getting reconnected to care. As a result, our clinics are busier than ever, and our wait times for appointments are unfortunately longer than we would like,” said Dr. Mathews, who was not involved in the research.
Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation continue to be among the most common symptoms Dr. Mathews sees in clinic, he said.
Kyle Staller, MD, a Massachusetts General Brigham gastroenterologist, said in an interview that it’s important to distinguish symptoms from eventual diagnoses, which lag behind.
“Are patients attributing their symptoms to COVID, or is COVID itself creating a background of inflammation or changes in the nerves that are making these symptoms more common? My suspicion is a little bit of both,” said Dr. Staller, who is director of the Gastrointestinal Motility Laboratory at Mass General, Boston.
Although his clinic is seeing patients with the GI signs and symptoms listed in the article, “we’re not seeing as much of some of the diagnoses, like peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis,” he said. “I wonder if those may be related to some of the consequences of being critically ill in general, rather than COVID specifically. Those diagnoses I would be more skeptical about.”
Duration of symptoms unclear
It’s hard to tell patients how long their GI symptoms might last after COVID, given the relatively short time researchers have had to study the virus, said Dr. Staller, who was not involved in the research.
The symptoms he’s seeing in patients after COVID mimic those of postinfectious IBS, which literature says could last for months or years, Dr. Staller said. “But they should improve over time,” he added.
Senior author Dr. Al-Aly agreed that the duration of post-COVID GI symptoms is unclear.
“What I can tell you is that even people who got SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 are still coming back for GI problems,” he said.
Unlike other symptoms of long COVID, such as brain fog, gastroenterologists fortunately know how to treat the GI disorders that evolve from SARS-CoV-2 infection, said Dr. Al-Aly, who has studied the long-term effects of the virus on the brain, kidneys, heart, and other organs.
All health care providers “need to be thinking about COVID as a risk factor for all these diseases” and should ask patients about SARS-CoV-2 infection when they take their histories, he said.
The authors, Dr. Staller, and Dr. Mathews report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large new study indicates.
The researchers estimate that, so far, SARS-CoV-2 infections have contributed to more than 6 million new cases of GI disorders in the United States and 42 million new cases worldwide.
The diagnoses more common among patients who’ve had COVID ranged from stomach upset to acute pancreatitis, say the researchers, led by Evan Xu, a data analyst at the Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research and Development Service, VA St. Louis Health Care System.
Signs and symptoms of GI problems, such as constipation and diarrhea, also were more common among patients who had had the virus, the study found.
“Altogether, our results show that people with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders in the post-acute phase of COVID-19,” the researchers write. “Post-COVID care should involve attention to gastrointestinal health and disease.”
The results were published online in Nature Communications.
Disease risks jump
The researchers used data from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs national health care databases to identify 154,068 people with confirmed COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2021. They used statistical modeling to compare those patients with 5.6 million patients with similar characteristics who had not been infected during the same period and an historical control group of 5.9 million patients from March 1, 2018, to Dec. 31, 2019, before the virus began to spread across the globe.
The study included hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID patients. The majority of the study population was male, but the study included almost 1.2 million female patients.
Compared with control persons, post-COVID patients’ increased risk of a GI diagnosis and the excess disease burden at 1 year, respectively, were as follows.
- 102% for cholangitis; 0.22 per 1,000 persons
- 62% for peptic ulcer disease; 1.57 per 1,000 persons
- 54% for irritable bowel syndrome; 0.44 per 1,000 persons
- 47% for acute gastritis; 0.47 per 1,000 persons
- 46% for acute pancreatitis; 0.6 per 1,000 persons
- 36% for functional dyspepsia; 0.63 per 1,000 persons
- 35% for gastroesophageal reflux disease; 15.5 per 1,000 persons
Patients who’d had the virus were also at higher risk for GI symptoms than their COVID-free peers. Their risk was 60% higher for constipation, 58% for diarrhea, 52% for vomiting, 46% for bloating, and 44% for abdominal pain, the investigators found.
The risk of developing GI symptoms increased with COVID-19 severity and was highest for those who received intensive care because of the virus, the researchers note.
Subgroup analyses found that the risks of composite gastrointestinal outcome were evident in all subgroups based on age, race, sex, obesity, smoking, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, the authors write.
Disease burden rises
The increased numbers of GI patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection are altering the burden on the health care system, senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
The shift may be pronounced in primary care, where GI concerns should be seen as a trigger for questions about prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, Dr. Al-Aly said.
Patients may encounter longer wait times at GI clinics or may give up on trying to schedule appointments if waits become too long, he said. They may also present to emergency departments if they can’t get an outpatient appointment, he added.
Simon C. Mathews, MD, assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization that he’s seeing increased wait times since COVID emerged.
“We know that the pandemic impacted patients’ ability and willingness to seek GI care. There continues to be a long backlog for patients who are only now getting reconnected to care. As a result, our clinics are busier than ever, and our wait times for appointments are unfortunately longer than we would like,” said Dr. Mathews, who was not involved in the research.
Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation continue to be among the most common symptoms Dr. Mathews sees in clinic, he said.
Kyle Staller, MD, a Massachusetts General Brigham gastroenterologist, said in an interview that it’s important to distinguish symptoms from eventual diagnoses, which lag behind.
“Are patients attributing their symptoms to COVID, or is COVID itself creating a background of inflammation or changes in the nerves that are making these symptoms more common? My suspicion is a little bit of both,” said Dr. Staller, who is director of the Gastrointestinal Motility Laboratory at Mass General, Boston.
Although his clinic is seeing patients with the GI signs and symptoms listed in the article, “we’re not seeing as much of some of the diagnoses, like peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis,” he said. “I wonder if those may be related to some of the consequences of being critically ill in general, rather than COVID specifically. Those diagnoses I would be more skeptical about.”
Duration of symptoms unclear
It’s hard to tell patients how long their GI symptoms might last after COVID, given the relatively short time researchers have had to study the virus, said Dr. Staller, who was not involved in the research.
The symptoms he’s seeing in patients after COVID mimic those of postinfectious IBS, which literature says could last for months or years, Dr. Staller said. “But they should improve over time,” he added.
Senior author Dr. Al-Aly agreed that the duration of post-COVID GI symptoms is unclear.
“What I can tell you is that even people who got SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 are still coming back for GI problems,” he said.
Unlike other symptoms of long COVID, such as brain fog, gastroenterologists fortunately know how to treat the GI disorders that evolve from SARS-CoV-2 infection, said Dr. Al-Aly, who has studied the long-term effects of the virus on the brain, kidneys, heart, and other organs.
All health care providers “need to be thinking about COVID as a risk factor for all these diseases” and should ask patients about SARS-CoV-2 infection when they take their histories, he said.
The authors, Dr. Staller, and Dr. Mathews report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS


