User login
Should There Be a Mandatory Retirement Age for Physicians?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Fecal Immunochemical Test Performance for CRC Screening Varies Widely
, new research suggests.
In a comparative performance analysis of five commonly used FITs for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, researchers found statistically significant differences in positivity rates, sensitivity, and specificity, as well as important differences in rates of unusable tests.
“Our findings have practical importance for FIT-based screening programs as these differences affect the need for repeated FIT, the yield of ACN detection, and the number of diagnostic colonoscopies that would be required to follow-up on abnormal findings,” wrote the researchers, led by Barcey T. Levy, MD, PhD, with University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Wide Variation Found
Despite widespread use of FITs for CRC screening, there is limited data to help guide test selection. Understanding the comparative performance of different FITs is “crucial” for a successful FIT-based screening program, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Levy and colleagues directly compared the performance of five commercially available FITs — including four qualitative tests (Hemoccult ICT, Hemosure iFOB, OC-Light S FIT, and QuickVue iFOB) and one quantitative test (OC-Auto FIT) — using colonoscopy as the reference standard.
Participants included a diverse group of 3761 adults (mean age, 62 years; 63% women). Each participant was given all five tests and completed them using the same stool sample. They sent the tests by first class mail to a central location, where FITs were analyzed by a trained professional on the day of receipt.
The primary outcome was test performance (sensitivity and specificity) for ACN, defined as advanced polyps or CRC.
A total of 320 participants (8.5%) were found to have ACN based on colonoscopy results, including nine with CRC (0.2%) — rates that are similar to those found in other studies.
The sensitivity for detecting ACN ranged from 10.1% (Hemoccult ICT) to 36.7% (OC-Light S FIT), and specificity varied from 85.5% (OC-Light S FIT) to 96.6% (Hemoccult ICT).
“Given the variation in FIT cutoffs reported by manufacturers, it is not surprising that tests with lower cutoffs (such as OC-Light S FIT) had higher sensitivity than tests with higher cutoffs (such as Hemoccult ICT),” Dr. Levy and colleagues wrote.
Test positivity rates varied fourfold across FITs, from 3.9% for Hemoccult ICT to 16.4% for OC-Light S FIT.
The rates of tests deemed unevaluable (due to factors such as indeterminant results or user mistakes) ranged from 0.2% for OC-Auto FIT to 2.5% for QuickVue iFOB.
The highest positive predictive value (PPV) was observed with OC-Auto FIT (28.9%) and the lowest with Hemosure iFOB (18.2%). The negative predictive value was similar across tests, ranging from 92.2% to 93.3%, indicating consistent performance in ruling out disease.
The study also identified significant differences in test sensitivity based on factors such as the location of neoplasia (higher sensitivity for distal lesions) and patient characteristics (higher sensitivity in people with higher body mass index and lower income).
Dr. Levy and colleagues said their findings have implications both in terms of clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness of CRC screening using FITs.
“Tests with lower sensitivity will miss more patients with CRC and advanced polyps, and tests with higher sensitivity and lower PPV will require more colonoscopies to detect patients with actionable findings,” they wrote.
‘Jaw-Dropping’ Results
The sensitivity results are “jaw-dropping,” Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice-president for cancer screening at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “A patient should have at least a 50/50 chance of having their colorectal cancer detected with a stool test at the time of testing.”
“What these numbers show is that the level that the manufacturers believe their test is performing is not reproduced,” Dr. Smith added.
This study adds to “concerns that have been raised about the inherent limitations and the performance of these tests that have been cleared for use and that are supposed to be lifesaving,” he said.
Clearance by the US Food and Drug Administration should mean that there’s essentially “no risk to using the test in terms of the test itself being harmful,” Dr. Smith said. But that’s not the case with FITs “because it’s harmful if you have cancer and your test doesn’t find it.”
By way of study limitations, Dr. Levy and colleagues said it’s important to note that they did not evaluate the “programmatic” sensitivity of repeating FIT testing every 1-2 years, as is generally recommended in screening guidelines. Therefore, the sensitivity of a single FIT may be lower than that of a repeated FIT. Also, variability in the FIT collection process by participants might have affected the results.
The study had no commercial funding. Disclosures for authors are available with the original article. Dr. Smith had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a comparative performance analysis of five commonly used FITs for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, researchers found statistically significant differences in positivity rates, sensitivity, and specificity, as well as important differences in rates of unusable tests.
“Our findings have practical importance for FIT-based screening programs as these differences affect the need for repeated FIT, the yield of ACN detection, and the number of diagnostic colonoscopies that would be required to follow-up on abnormal findings,” wrote the researchers, led by Barcey T. Levy, MD, PhD, with University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Wide Variation Found
Despite widespread use of FITs for CRC screening, there is limited data to help guide test selection. Understanding the comparative performance of different FITs is “crucial” for a successful FIT-based screening program, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Levy and colleagues directly compared the performance of five commercially available FITs — including four qualitative tests (Hemoccult ICT, Hemosure iFOB, OC-Light S FIT, and QuickVue iFOB) and one quantitative test (OC-Auto FIT) — using colonoscopy as the reference standard.
Participants included a diverse group of 3761 adults (mean age, 62 years; 63% women). Each participant was given all five tests and completed them using the same stool sample. They sent the tests by first class mail to a central location, where FITs were analyzed by a trained professional on the day of receipt.
The primary outcome was test performance (sensitivity and specificity) for ACN, defined as advanced polyps or CRC.
A total of 320 participants (8.5%) were found to have ACN based on colonoscopy results, including nine with CRC (0.2%) — rates that are similar to those found in other studies.
The sensitivity for detecting ACN ranged from 10.1% (Hemoccult ICT) to 36.7% (OC-Light S FIT), and specificity varied from 85.5% (OC-Light S FIT) to 96.6% (Hemoccult ICT).
“Given the variation in FIT cutoffs reported by manufacturers, it is not surprising that tests with lower cutoffs (such as OC-Light S FIT) had higher sensitivity than tests with higher cutoffs (such as Hemoccult ICT),” Dr. Levy and colleagues wrote.
Test positivity rates varied fourfold across FITs, from 3.9% for Hemoccult ICT to 16.4% for OC-Light S FIT.
The rates of tests deemed unevaluable (due to factors such as indeterminant results or user mistakes) ranged from 0.2% for OC-Auto FIT to 2.5% for QuickVue iFOB.
The highest positive predictive value (PPV) was observed with OC-Auto FIT (28.9%) and the lowest with Hemosure iFOB (18.2%). The negative predictive value was similar across tests, ranging from 92.2% to 93.3%, indicating consistent performance in ruling out disease.
The study also identified significant differences in test sensitivity based on factors such as the location of neoplasia (higher sensitivity for distal lesions) and patient characteristics (higher sensitivity in people with higher body mass index and lower income).
Dr. Levy and colleagues said their findings have implications both in terms of clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness of CRC screening using FITs.
“Tests with lower sensitivity will miss more patients with CRC and advanced polyps, and tests with higher sensitivity and lower PPV will require more colonoscopies to detect patients with actionable findings,” they wrote.
‘Jaw-Dropping’ Results
The sensitivity results are “jaw-dropping,” Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice-president for cancer screening at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “A patient should have at least a 50/50 chance of having their colorectal cancer detected with a stool test at the time of testing.”
“What these numbers show is that the level that the manufacturers believe their test is performing is not reproduced,” Dr. Smith added.
This study adds to “concerns that have been raised about the inherent limitations and the performance of these tests that have been cleared for use and that are supposed to be lifesaving,” he said.
Clearance by the US Food and Drug Administration should mean that there’s essentially “no risk to using the test in terms of the test itself being harmful,” Dr. Smith said. But that’s not the case with FITs “because it’s harmful if you have cancer and your test doesn’t find it.”
By way of study limitations, Dr. Levy and colleagues said it’s important to note that they did not evaluate the “programmatic” sensitivity of repeating FIT testing every 1-2 years, as is generally recommended in screening guidelines. Therefore, the sensitivity of a single FIT may be lower than that of a repeated FIT. Also, variability in the FIT collection process by participants might have affected the results.
The study had no commercial funding. Disclosures for authors are available with the original article. Dr. Smith had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a comparative performance analysis of five commonly used FITs for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, researchers found statistically significant differences in positivity rates, sensitivity, and specificity, as well as important differences in rates of unusable tests.
“Our findings have practical importance for FIT-based screening programs as these differences affect the need for repeated FIT, the yield of ACN detection, and the number of diagnostic colonoscopies that would be required to follow-up on abnormal findings,” wrote the researchers, led by Barcey T. Levy, MD, PhD, with University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Wide Variation Found
Despite widespread use of FITs for CRC screening, there is limited data to help guide test selection. Understanding the comparative performance of different FITs is “crucial” for a successful FIT-based screening program, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Levy and colleagues directly compared the performance of five commercially available FITs — including four qualitative tests (Hemoccult ICT, Hemosure iFOB, OC-Light S FIT, and QuickVue iFOB) and one quantitative test (OC-Auto FIT) — using colonoscopy as the reference standard.
Participants included a diverse group of 3761 adults (mean age, 62 years; 63% women). Each participant was given all five tests and completed them using the same stool sample. They sent the tests by first class mail to a central location, where FITs were analyzed by a trained professional on the day of receipt.
The primary outcome was test performance (sensitivity and specificity) for ACN, defined as advanced polyps or CRC.
A total of 320 participants (8.5%) were found to have ACN based on colonoscopy results, including nine with CRC (0.2%) — rates that are similar to those found in other studies.
The sensitivity for detecting ACN ranged from 10.1% (Hemoccult ICT) to 36.7% (OC-Light S FIT), and specificity varied from 85.5% (OC-Light S FIT) to 96.6% (Hemoccult ICT).
“Given the variation in FIT cutoffs reported by manufacturers, it is not surprising that tests with lower cutoffs (such as OC-Light S FIT) had higher sensitivity than tests with higher cutoffs (such as Hemoccult ICT),” Dr. Levy and colleagues wrote.
Test positivity rates varied fourfold across FITs, from 3.9% for Hemoccult ICT to 16.4% for OC-Light S FIT.
The rates of tests deemed unevaluable (due to factors such as indeterminant results or user mistakes) ranged from 0.2% for OC-Auto FIT to 2.5% for QuickVue iFOB.
The highest positive predictive value (PPV) was observed with OC-Auto FIT (28.9%) and the lowest with Hemosure iFOB (18.2%). The negative predictive value was similar across tests, ranging from 92.2% to 93.3%, indicating consistent performance in ruling out disease.
The study also identified significant differences in test sensitivity based on factors such as the location of neoplasia (higher sensitivity for distal lesions) and patient characteristics (higher sensitivity in people with higher body mass index and lower income).
Dr. Levy and colleagues said their findings have implications both in terms of clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness of CRC screening using FITs.
“Tests with lower sensitivity will miss more patients with CRC and advanced polyps, and tests with higher sensitivity and lower PPV will require more colonoscopies to detect patients with actionable findings,” they wrote.
‘Jaw-Dropping’ Results
The sensitivity results are “jaw-dropping,” Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice-president for cancer screening at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “A patient should have at least a 50/50 chance of having their colorectal cancer detected with a stool test at the time of testing.”
“What these numbers show is that the level that the manufacturers believe their test is performing is not reproduced,” Dr. Smith added.
This study adds to “concerns that have been raised about the inherent limitations and the performance of these tests that have been cleared for use and that are supposed to be lifesaving,” he said.
Clearance by the US Food and Drug Administration should mean that there’s essentially “no risk to using the test in terms of the test itself being harmful,” Dr. Smith said. But that’s not the case with FITs “because it’s harmful if you have cancer and your test doesn’t find it.”
By way of study limitations, Dr. Levy and colleagues said it’s important to note that they did not evaluate the “programmatic” sensitivity of repeating FIT testing every 1-2 years, as is generally recommended in screening guidelines. Therefore, the sensitivity of a single FIT may be lower than that of a repeated FIT. Also, variability in the FIT collection process by participants might have affected the results.
The study had no commercial funding. Disclosures for authors are available with the original article. Dr. Smith had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When You and Your Malpractice Insurer Disagree on Your Case
You’ve been sued for medical malpractice. If you are a physician in the United States, that is not an unlikely scenario.
An analysis by the American Medical Association shows that almost half of all physicians are sued by the time they reach 54. In some specialties, such as ob.gyn., one is almost guaranteed to be sued at some point.
But that’s what medical malpractice insurance is for, right? Your medical malpractice insurer will assign an attorney to take care of you and help you through this situation. Won’t they?
Maybe so, but the attorney and the claims representative your insurer assigns to your case may have a different idea about how to proceed than you do. Though the defense attorney assigned to you represents you, he or she gets paid by the insurance carrier.
This can create a conflict when your defense counsel and your insurance claims representative aim to take your case in a direction you don’t like.
Disagreements might include:
- Choice of expert witnesses
- Tactical decisions related to trial strategy
- Public relations considerations
- Admissions of liability
- Allocation of resources
To Settle or Not?
One of the most challenging — and common — disagreements is whether to settle the case.
Sometimes a malpractice insurer wants to settle the case against the defendant doctor’s wishes. Or the doctor wants to settle but is pushed into going to trial. In the following case, one doctor had to face the consequences of a decision he didn’t even make.
The Underlying Medical Malpractice Case
Dr. D was sued by a patient who had allegedly called Dr. D’s office six times in 2 days complaining of intermittent chest pain.
Dr. D had been swamped with patients and couldn’t squeeze this patient in for an office visit, but he did call back. The patient later claimed that during the call he told the doctor he was suffering from chest pain. The doctor recalled that the patient had complained of abdominal discomfort that began after he had exercised.
The physician wrote a prescription for an ECG at the local hospital and called to ensure that the patient could just walk in. The ECG was allegedly abnormal but was not read as representing an impending or current heart attack. Later that evening, however, the patient went to the emergency department of another hospital where it was confirmed that he had suffered a heart attack. The patient underwent cardiac catheterization and stent placement to address a blockage in his left anterior descending artery.
The patient subsequently sued Dr. D and the hospital where he had the original ECG. Dr. D contacted his medical malpractice insurance company. The insurance company assigned an attorney to represent Dr. D. Discovery in the case began.
The plaintiff’s own medical expert testified in a deposition that there was no way for the heart attack to have been prevented and that the treatment would have been the same either way. But Dr. D could not find a record of the phone calls with the patient, and he had not noted his conversation the patient in their medical records.
Dr. D held a policy for $1 million, and his state had a fund that would kick in an additional $1 million. But the plaintiffs demanded $4 million to settle.
A month before trial, the plaintiff’s attorney sent a threatening letter to Dr. D’s attorney warning him that Dr. D was underinsured and suggesting that it would be in the physician’s best interests to settle.
“I want to stress to you that it is not my desire to harm your client’s reputation or to destroy his business,” wrote the plaintiff’s attorney. “However, now is the time to avoid consequences such as these by making a good faith effort to get this case resolved.”
The letter went on to note that the defense attorney should give Dr. D a copy of the letter so that everyone would be aware of the potential consequences of an award against Dr. D in excess of his limits of insurance coverage. The plaintiff’s attorney even suggested that Dr. D should retain personal counsel.
Dr. D’s defense attorney downplayed the letter and assured him that there was no reason to worry.
Meanwhile the case inched closer to trial.
The codefendant hospital settled with the plaintiff on the night before jury selection, leaving Dr. D in the uncomfortable position of being the only defendant in the case. At this point, Dr. D decided he would like to settle, and he sent his attorney an email telling him so. But the attorney instead referred him to an insurance company claims.
Just days before the trial was to start, Dr. D repeatedly told the claims representative assigned to his claim that he did not want to go to trial but rather wanted to settle. The representative told Dr. D that he had no choice in whether the action settled.
A committee at the insurance company had decided to proceed with the trial rather than settle.
The trial proved a painful debacle for Dr. D. His attorney’s idea of showing a “gotcha” video of the allegedly permanently injured plaintiff carrying a large, heavy box backfired when the jury was shown by the plaintiff that the box actually contained ice cream cones and weighed very little.
Prior to trial, the plaintiff offered to settle for $1 million. On the first day of trial, they lowered that amount to $750,000, yet the defense attorney did not settle the case, and it proceeded to a jury verdict. The jury awarded the plaintiff over $4 million — well in excess of Dr. D’s policy limits.
The Follow-up
Dr. D was horrified, but the insurance company claims representative said the insurer would promptly offer $2 million in available insurance coverage to settle the case post verdict. This did not happen. Instead, the insurer chose to appeal the verdict against Dr. D’s wishes.
Ultimately, Dr. D was forced to hire his own lawyer. He ultimately sued the insurance company for breach of contract and bad faith.
The insurance company eventually attempted to settle with the plaintiffs’ counsel, but the plaintiff refused to accept the available insurance coverage. The insurance carrier still has not posted the entire appeal bond. The case is still pending.
Protecting Yourself
The lesson from Dr. D’s experience: Understand that the insurance company is not your friend. It’s a business looking out for its own interests.
The plaintiff’s attorney was absolutely correct in suggesting that Dr. D retain his own attorney to represent his own interests. You should hire your own lawyer when:
- You disagree with your insurer on how to proceed in a case.
- You receive a demand that exceeds your available insurance coverage or for damages that may not be covered by your policy, such as punitive damages.
- Your insurance carrier attempts to deny insurance coverage for your claim or sends you a letter stating that it is “reserving its rights” not to cover or to limit coverage for your claim.
Retaining independent counsel protects your interests, not those of your insurance company.
Independent counsel can give you a second opinion on the strengths and weaknesses of your claim, help you prepare for your deposition, and attend court dates with you to ensure that you are completely protected.
Independent counsel can challenge your insurance company’s decision to deny or limit your insurance coverage and ensure that you receive all of the benefits to which you are entitled under your insurance policy. Some policies may include an independent lawyer to be paid for by your insurance carrier in case of a conflicts.
The most important takeaway? Your medical malpractice insurance carrier is not your friend, so act accordingly in times of conflict.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
You’ve been sued for medical malpractice. If you are a physician in the United States, that is not an unlikely scenario.
An analysis by the American Medical Association shows that almost half of all physicians are sued by the time they reach 54. In some specialties, such as ob.gyn., one is almost guaranteed to be sued at some point.
But that’s what medical malpractice insurance is for, right? Your medical malpractice insurer will assign an attorney to take care of you and help you through this situation. Won’t they?
Maybe so, but the attorney and the claims representative your insurer assigns to your case may have a different idea about how to proceed than you do. Though the defense attorney assigned to you represents you, he or she gets paid by the insurance carrier.
This can create a conflict when your defense counsel and your insurance claims representative aim to take your case in a direction you don’t like.
Disagreements might include:
- Choice of expert witnesses
- Tactical decisions related to trial strategy
- Public relations considerations
- Admissions of liability
- Allocation of resources
To Settle or Not?
One of the most challenging — and common — disagreements is whether to settle the case.
Sometimes a malpractice insurer wants to settle the case against the defendant doctor’s wishes. Or the doctor wants to settle but is pushed into going to trial. In the following case, one doctor had to face the consequences of a decision he didn’t even make.
The Underlying Medical Malpractice Case
Dr. D was sued by a patient who had allegedly called Dr. D’s office six times in 2 days complaining of intermittent chest pain.
Dr. D had been swamped with patients and couldn’t squeeze this patient in for an office visit, but he did call back. The patient later claimed that during the call he told the doctor he was suffering from chest pain. The doctor recalled that the patient had complained of abdominal discomfort that began after he had exercised.
The physician wrote a prescription for an ECG at the local hospital and called to ensure that the patient could just walk in. The ECG was allegedly abnormal but was not read as representing an impending or current heart attack. Later that evening, however, the patient went to the emergency department of another hospital where it was confirmed that he had suffered a heart attack. The patient underwent cardiac catheterization and stent placement to address a blockage in his left anterior descending artery.
The patient subsequently sued Dr. D and the hospital where he had the original ECG. Dr. D contacted his medical malpractice insurance company. The insurance company assigned an attorney to represent Dr. D. Discovery in the case began.
The plaintiff’s own medical expert testified in a deposition that there was no way for the heart attack to have been prevented and that the treatment would have been the same either way. But Dr. D could not find a record of the phone calls with the patient, and he had not noted his conversation the patient in their medical records.
Dr. D held a policy for $1 million, and his state had a fund that would kick in an additional $1 million. But the plaintiffs demanded $4 million to settle.
A month before trial, the plaintiff’s attorney sent a threatening letter to Dr. D’s attorney warning him that Dr. D was underinsured and suggesting that it would be in the physician’s best interests to settle.
“I want to stress to you that it is not my desire to harm your client’s reputation or to destroy his business,” wrote the plaintiff’s attorney. “However, now is the time to avoid consequences such as these by making a good faith effort to get this case resolved.”
The letter went on to note that the defense attorney should give Dr. D a copy of the letter so that everyone would be aware of the potential consequences of an award against Dr. D in excess of his limits of insurance coverage. The plaintiff’s attorney even suggested that Dr. D should retain personal counsel.
Dr. D’s defense attorney downplayed the letter and assured him that there was no reason to worry.
Meanwhile the case inched closer to trial.
The codefendant hospital settled with the plaintiff on the night before jury selection, leaving Dr. D in the uncomfortable position of being the only defendant in the case. At this point, Dr. D decided he would like to settle, and he sent his attorney an email telling him so. But the attorney instead referred him to an insurance company claims.
Just days before the trial was to start, Dr. D repeatedly told the claims representative assigned to his claim that he did not want to go to trial but rather wanted to settle. The representative told Dr. D that he had no choice in whether the action settled.
A committee at the insurance company had decided to proceed with the trial rather than settle.
The trial proved a painful debacle for Dr. D. His attorney’s idea of showing a “gotcha” video of the allegedly permanently injured plaintiff carrying a large, heavy box backfired when the jury was shown by the plaintiff that the box actually contained ice cream cones and weighed very little.
Prior to trial, the plaintiff offered to settle for $1 million. On the first day of trial, they lowered that amount to $750,000, yet the defense attorney did not settle the case, and it proceeded to a jury verdict. The jury awarded the plaintiff over $4 million — well in excess of Dr. D’s policy limits.
The Follow-up
Dr. D was horrified, but the insurance company claims representative said the insurer would promptly offer $2 million in available insurance coverage to settle the case post verdict. This did not happen. Instead, the insurer chose to appeal the verdict against Dr. D’s wishes.
Ultimately, Dr. D was forced to hire his own lawyer. He ultimately sued the insurance company for breach of contract and bad faith.
The insurance company eventually attempted to settle with the plaintiffs’ counsel, but the plaintiff refused to accept the available insurance coverage. The insurance carrier still has not posted the entire appeal bond. The case is still pending.
Protecting Yourself
The lesson from Dr. D’s experience: Understand that the insurance company is not your friend. It’s a business looking out for its own interests.
The plaintiff’s attorney was absolutely correct in suggesting that Dr. D retain his own attorney to represent his own interests. You should hire your own lawyer when:
- You disagree with your insurer on how to proceed in a case.
- You receive a demand that exceeds your available insurance coverage or for damages that may not be covered by your policy, such as punitive damages.
- Your insurance carrier attempts to deny insurance coverage for your claim or sends you a letter stating that it is “reserving its rights” not to cover or to limit coverage for your claim.
Retaining independent counsel protects your interests, not those of your insurance company.
Independent counsel can give you a second opinion on the strengths and weaknesses of your claim, help you prepare for your deposition, and attend court dates with you to ensure that you are completely protected.
Independent counsel can challenge your insurance company’s decision to deny or limit your insurance coverage and ensure that you receive all of the benefits to which you are entitled under your insurance policy. Some policies may include an independent lawyer to be paid for by your insurance carrier in case of a conflicts.
The most important takeaway? Your medical malpractice insurance carrier is not your friend, so act accordingly in times of conflict.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
You’ve been sued for medical malpractice. If you are a physician in the United States, that is not an unlikely scenario.
An analysis by the American Medical Association shows that almost half of all physicians are sued by the time they reach 54. In some specialties, such as ob.gyn., one is almost guaranteed to be sued at some point.
But that’s what medical malpractice insurance is for, right? Your medical malpractice insurer will assign an attorney to take care of you and help you through this situation. Won’t they?
Maybe so, but the attorney and the claims representative your insurer assigns to your case may have a different idea about how to proceed than you do. Though the defense attorney assigned to you represents you, he or she gets paid by the insurance carrier.
This can create a conflict when your defense counsel and your insurance claims representative aim to take your case in a direction you don’t like.
Disagreements might include:
- Choice of expert witnesses
- Tactical decisions related to trial strategy
- Public relations considerations
- Admissions of liability
- Allocation of resources
To Settle or Not?
One of the most challenging — and common — disagreements is whether to settle the case.
Sometimes a malpractice insurer wants to settle the case against the defendant doctor’s wishes. Or the doctor wants to settle but is pushed into going to trial. In the following case, one doctor had to face the consequences of a decision he didn’t even make.
The Underlying Medical Malpractice Case
Dr. D was sued by a patient who had allegedly called Dr. D’s office six times in 2 days complaining of intermittent chest pain.
Dr. D had been swamped with patients and couldn’t squeeze this patient in for an office visit, but he did call back. The patient later claimed that during the call he told the doctor he was suffering from chest pain. The doctor recalled that the patient had complained of abdominal discomfort that began after he had exercised.
The physician wrote a prescription for an ECG at the local hospital and called to ensure that the patient could just walk in. The ECG was allegedly abnormal but was not read as representing an impending or current heart attack. Later that evening, however, the patient went to the emergency department of another hospital where it was confirmed that he had suffered a heart attack. The patient underwent cardiac catheterization and stent placement to address a blockage in his left anterior descending artery.
The patient subsequently sued Dr. D and the hospital where he had the original ECG. Dr. D contacted his medical malpractice insurance company. The insurance company assigned an attorney to represent Dr. D. Discovery in the case began.
The plaintiff’s own medical expert testified in a deposition that there was no way for the heart attack to have been prevented and that the treatment would have been the same either way. But Dr. D could not find a record of the phone calls with the patient, and he had not noted his conversation the patient in their medical records.
Dr. D held a policy for $1 million, and his state had a fund that would kick in an additional $1 million. But the plaintiffs demanded $4 million to settle.
A month before trial, the plaintiff’s attorney sent a threatening letter to Dr. D’s attorney warning him that Dr. D was underinsured and suggesting that it would be in the physician’s best interests to settle.
“I want to stress to you that it is not my desire to harm your client’s reputation or to destroy his business,” wrote the plaintiff’s attorney. “However, now is the time to avoid consequences such as these by making a good faith effort to get this case resolved.”
The letter went on to note that the defense attorney should give Dr. D a copy of the letter so that everyone would be aware of the potential consequences of an award against Dr. D in excess of his limits of insurance coverage. The plaintiff’s attorney even suggested that Dr. D should retain personal counsel.
Dr. D’s defense attorney downplayed the letter and assured him that there was no reason to worry.
Meanwhile the case inched closer to trial.
The codefendant hospital settled with the plaintiff on the night before jury selection, leaving Dr. D in the uncomfortable position of being the only defendant in the case. At this point, Dr. D decided he would like to settle, and he sent his attorney an email telling him so. But the attorney instead referred him to an insurance company claims.
Just days before the trial was to start, Dr. D repeatedly told the claims representative assigned to his claim that he did not want to go to trial but rather wanted to settle. The representative told Dr. D that he had no choice in whether the action settled.
A committee at the insurance company had decided to proceed with the trial rather than settle.
The trial proved a painful debacle for Dr. D. His attorney’s idea of showing a “gotcha” video of the allegedly permanently injured plaintiff carrying a large, heavy box backfired when the jury was shown by the plaintiff that the box actually contained ice cream cones and weighed very little.
Prior to trial, the plaintiff offered to settle for $1 million. On the first day of trial, they lowered that amount to $750,000, yet the defense attorney did not settle the case, and it proceeded to a jury verdict. The jury awarded the plaintiff over $4 million — well in excess of Dr. D’s policy limits.
The Follow-up
Dr. D was horrified, but the insurance company claims representative said the insurer would promptly offer $2 million in available insurance coverage to settle the case post verdict. This did not happen. Instead, the insurer chose to appeal the verdict against Dr. D’s wishes.
Ultimately, Dr. D was forced to hire his own lawyer. He ultimately sued the insurance company for breach of contract and bad faith.
The insurance company eventually attempted to settle with the plaintiffs’ counsel, but the plaintiff refused to accept the available insurance coverage. The insurance carrier still has not posted the entire appeal bond. The case is still pending.
Protecting Yourself
The lesson from Dr. D’s experience: Understand that the insurance company is not your friend. It’s a business looking out for its own interests.
The plaintiff’s attorney was absolutely correct in suggesting that Dr. D retain his own attorney to represent his own interests. You should hire your own lawyer when:
- You disagree with your insurer on how to proceed in a case.
- You receive a demand that exceeds your available insurance coverage or for damages that may not be covered by your policy, such as punitive damages.
- Your insurance carrier attempts to deny insurance coverage for your claim or sends you a letter stating that it is “reserving its rights” not to cover or to limit coverage for your claim.
Retaining independent counsel protects your interests, not those of your insurance company.
Independent counsel can give you a second opinion on the strengths and weaknesses of your claim, help you prepare for your deposition, and attend court dates with you to ensure that you are completely protected.
Independent counsel can challenge your insurance company’s decision to deny or limit your insurance coverage and ensure that you receive all of the benefits to which you are entitled under your insurance policy. Some policies may include an independent lawyer to be paid for by your insurance carrier in case of a conflicts.
The most important takeaway? Your medical malpractice insurance carrier is not your friend, so act accordingly in times of conflict.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Minimal Access Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy a Safer Option?
TOPLINE:
Given that both procedures appear safe overall, the choice may be guided by patients’ preference.
METHODOLOGY:
- Compared with a conventional mastectomy, a nipple-sparing mastectomy offers superior esthetic outcomes in patients with breast cancer. However, even the typical nipple-sparing approach often results in visible scarring and a high risk for nipple or areola necrosis. A minimal access approach, using endoscopic or robotic techniques, offers the potential to minimize scarring and better outcomes, but the complication risks are not well understood.
- Researchers performed a retrospective study that included 1583 patients with breast cancer who underwent conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy (n = 1356) or minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy (n = 227) between 2018 and 2020 across 21 institutions in the Republic of Korea.
- Postoperative complications, categorized as short term (< 30 days) and long term (< 90 days), were compared between the two groups.
- The minimal access group had a higher percentage of premenopausal patients (73.57% vs 66.67%) and women with firm breasts (66.08% vs 31.27%).
TAKEAWAY:
- In total, 72 individuals (5.31%) in the conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy group and 7 (3.08%) in the minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy group developed postoperative complications of grade IIIb or higher.
- The rate of complications between the conventional and minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy groups in the short term (34.29% for conventional vs 32.16% for minimal access; P = .53) and long term (38.72% vs 32.16%, respectively; P = .06) was not significantly different.
- The conventional group experienced significantly fewer wound infections — both in the short term (1.62% vs 7.49%) and long term (4.28% vs 7.93%) — but a significantly higher rate of seroma (14.23% vs 9.25%), likely because of the variations in surgical instruments used during the procedures.
- Necrosis of the nipple or areola occurred more often in the minimal access group in the short term (8.81% vs 3.91%) but occurred more frequently in the conventional group in the long term (6.71% vs 2.20%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The similar complication rates suggest that both C-NSM [conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy] and M-NSM [minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy] may be equally safe options,” the authors wrote. “Therefore, the choice of surgical approach should be tailored to patient preferences and individual needs.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Joo Heung Kim, MD, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, South Korea, was published online on August 14, 2024, in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design comes with inherent biases. The nonrandom assignment of the participants to the two groups and the relatively small number of cases of minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy may have affected the findings. The involvement of different surgeons and use of early robotic surgery techniques may have introduced bias as well.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by Yonsei University College of Medicine and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Two authors reported receiving grants and consulting fees outside of this work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Given that both procedures appear safe overall, the choice may be guided by patients’ preference.
METHODOLOGY:
- Compared with a conventional mastectomy, a nipple-sparing mastectomy offers superior esthetic outcomes in patients with breast cancer. However, even the typical nipple-sparing approach often results in visible scarring and a high risk for nipple or areola necrosis. A minimal access approach, using endoscopic or robotic techniques, offers the potential to minimize scarring and better outcomes, but the complication risks are not well understood.
- Researchers performed a retrospective study that included 1583 patients with breast cancer who underwent conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy (n = 1356) or minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy (n = 227) between 2018 and 2020 across 21 institutions in the Republic of Korea.
- Postoperative complications, categorized as short term (< 30 days) and long term (< 90 days), were compared between the two groups.
- The minimal access group had a higher percentage of premenopausal patients (73.57% vs 66.67%) and women with firm breasts (66.08% vs 31.27%).
TAKEAWAY:
- In total, 72 individuals (5.31%) in the conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy group and 7 (3.08%) in the minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy group developed postoperative complications of grade IIIb or higher.
- The rate of complications between the conventional and minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy groups in the short term (34.29% for conventional vs 32.16% for minimal access; P = .53) and long term (38.72% vs 32.16%, respectively; P = .06) was not significantly different.
- The conventional group experienced significantly fewer wound infections — both in the short term (1.62% vs 7.49%) and long term (4.28% vs 7.93%) — but a significantly higher rate of seroma (14.23% vs 9.25%), likely because of the variations in surgical instruments used during the procedures.
- Necrosis of the nipple or areola occurred more often in the minimal access group in the short term (8.81% vs 3.91%) but occurred more frequently in the conventional group in the long term (6.71% vs 2.20%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The similar complication rates suggest that both C-NSM [conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy] and M-NSM [minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy] may be equally safe options,” the authors wrote. “Therefore, the choice of surgical approach should be tailored to patient preferences and individual needs.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Joo Heung Kim, MD, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, South Korea, was published online on August 14, 2024, in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design comes with inherent biases. The nonrandom assignment of the participants to the two groups and the relatively small number of cases of minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy may have affected the findings. The involvement of different surgeons and use of early robotic surgery techniques may have introduced bias as well.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by Yonsei University College of Medicine and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Two authors reported receiving grants and consulting fees outside of this work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Given that both procedures appear safe overall, the choice may be guided by patients’ preference.
METHODOLOGY:
- Compared with a conventional mastectomy, a nipple-sparing mastectomy offers superior esthetic outcomes in patients with breast cancer. However, even the typical nipple-sparing approach often results in visible scarring and a high risk for nipple or areola necrosis. A minimal access approach, using endoscopic or robotic techniques, offers the potential to minimize scarring and better outcomes, but the complication risks are not well understood.
- Researchers performed a retrospective study that included 1583 patients with breast cancer who underwent conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy (n = 1356) or minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy (n = 227) between 2018 and 2020 across 21 institutions in the Republic of Korea.
- Postoperative complications, categorized as short term (< 30 days) and long term (< 90 days), were compared between the two groups.
- The minimal access group had a higher percentage of premenopausal patients (73.57% vs 66.67%) and women with firm breasts (66.08% vs 31.27%).
TAKEAWAY:
- In total, 72 individuals (5.31%) in the conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy group and 7 (3.08%) in the minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy group developed postoperative complications of grade IIIb or higher.
- The rate of complications between the conventional and minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy groups in the short term (34.29% for conventional vs 32.16% for minimal access; P = .53) and long term (38.72% vs 32.16%, respectively; P = .06) was not significantly different.
- The conventional group experienced significantly fewer wound infections — both in the short term (1.62% vs 7.49%) and long term (4.28% vs 7.93%) — but a significantly higher rate of seroma (14.23% vs 9.25%), likely because of the variations in surgical instruments used during the procedures.
- Necrosis of the nipple or areola occurred more often in the minimal access group in the short term (8.81% vs 3.91%) but occurred more frequently in the conventional group in the long term (6.71% vs 2.20%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The similar complication rates suggest that both C-NSM [conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy] and M-NSM [minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy] may be equally safe options,” the authors wrote. “Therefore, the choice of surgical approach should be tailored to patient preferences and individual needs.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Joo Heung Kim, MD, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, South Korea, was published online on August 14, 2024, in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design comes with inherent biases. The nonrandom assignment of the participants to the two groups and the relatively small number of cases of minimal access nipple-sparing mastectomy may have affected the findings. The involvement of different surgeons and use of early robotic surgery techniques may have introduced bias as well.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by Yonsei University College of Medicine and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Two authors reported receiving grants and consulting fees outside of this work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should Genetic Testing Be Routine for Breast Cancer?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Traditional risk-based criteria, including family history and ancestry, are used to guide genetic testing decisions in women with breast cancer. However, these criteria may overlook patients with actionable genetic variants, particularly those outside the typical risk profile.
- To assess the efficacy of universal genetic testing, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study that included 729 women (median age at diagnosis, 53 years; 65.4% White women) newly diagnosed with invasive breast cancer between September 2019 and April 2022 at three Canadian institutions.
- All patients received genetic counseling followed by testing for the presence of germline pathogenic variants in 17 breast cancer susceptibility genes. The primary gene panel included screening for BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2, and the optional secondary panel included 14 additional breast cancer susceptibility genes.
- Of the participants, 659 (90.4%) were tested for both primary and secondary gene panels, whereas 70 (9.6%) underwent testing for only the primary panel. The majority of the cohort (66.8) were diagnosed with estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer, while 15.4% had triple-negative breast cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of germline pathogenic variants was 7.3% (53 patients) — 5.3% for the primary gene panel and 2.1% for the secondary panel.
- Younger age (< 40 years; odds ratio [OR], 6.83), family history of ovarian cancer (OR, 9.75), high-grade disease (OR, 1.68), and triple-negative breast cancer (OR, 3.19) were independently associated with the presence of pathogenic genetic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2.
- Overall, 34.3% of patients with germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2, and 85.7% of carriers of secondary panel variants would not have qualified for traditional genetic testing according to the current risk factors.
- A total of 13 patients with BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2 variants had confirmed pathogenic mutations and were eligible for poly(adenosine diphosphate–ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings have “informed our clinical practice, and we now offer mainstream, oncology-led genetic testing to all women diagnosed with incident invasive breast cancer younger than 50 years of age, those with triple-negative breast cancer and/or bilateral breast cancer, those potentially eligible for PARP inhibitors,” as well as to men with breast cancer, the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Zoulikha Rezoug, MSc, Lady Davis Institute of the Jewish General Hospital, McGill University in Montreal, Québec, Canada. It was published online on September 3, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a 6-month recruitment pause. Adjustments in recruitment criteria, focus on younger patients and those with triple-negative breast cancer could have overestimated prevalence of genetic pathogenic variants among women aged ≥ 70 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Jewish General Hospital Foundation and the Québec Breast Cancer Foundation, as well as an award from the Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé. Two authors reported receiving grants or personal fees from various sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Traditional risk-based criteria, including family history and ancestry, are used to guide genetic testing decisions in women with breast cancer. However, these criteria may overlook patients with actionable genetic variants, particularly those outside the typical risk profile.
- To assess the efficacy of universal genetic testing, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study that included 729 women (median age at diagnosis, 53 years; 65.4% White women) newly diagnosed with invasive breast cancer between September 2019 and April 2022 at three Canadian institutions.
- All patients received genetic counseling followed by testing for the presence of germline pathogenic variants in 17 breast cancer susceptibility genes. The primary gene panel included screening for BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2, and the optional secondary panel included 14 additional breast cancer susceptibility genes.
- Of the participants, 659 (90.4%) were tested for both primary and secondary gene panels, whereas 70 (9.6%) underwent testing for only the primary panel. The majority of the cohort (66.8) were diagnosed with estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer, while 15.4% had triple-negative breast cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of germline pathogenic variants was 7.3% (53 patients) — 5.3% for the primary gene panel and 2.1% for the secondary panel.
- Younger age (< 40 years; odds ratio [OR], 6.83), family history of ovarian cancer (OR, 9.75), high-grade disease (OR, 1.68), and triple-negative breast cancer (OR, 3.19) were independently associated with the presence of pathogenic genetic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2.
- Overall, 34.3% of patients with germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2, and 85.7% of carriers of secondary panel variants would not have qualified for traditional genetic testing according to the current risk factors.
- A total of 13 patients with BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2 variants had confirmed pathogenic mutations and were eligible for poly(adenosine diphosphate–ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings have “informed our clinical practice, and we now offer mainstream, oncology-led genetic testing to all women diagnosed with incident invasive breast cancer younger than 50 years of age, those with triple-negative breast cancer and/or bilateral breast cancer, those potentially eligible for PARP inhibitors,” as well as to men with breast cancer, the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Zoulikha Rezoug, MSc, Lady Davis Institute of the Jewish General Hospital, McGill University in Montreal, Québec, Canada. It was published online on September 3, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a 6-month recruitment pause. Adjustments in recruitment criteria, focus on younger patients and those with triple-negative breast cancer could have overestimated prevalence of genetic pathogenic variants among women aged ≥ 70 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Jewish General Hospital Foundation and the Québec Breast Cancer Foundation, as well as an award from the Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé. Two authors reported receiving grants or personal fees from various sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Traditional risk-based criteria, including family history and ancestry, are used to guide genetic testing decisions in women with breast cancer. However, these criteria may overlook patients with actionable genetic variants, particularly those outside the typical risk profile.
- To assess the efficacy of universal genetic testing, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study that included 729 women (median age at diagnosis, 53 years; 65.4% White women) newly diagnosed with invasive breast cancer between September 2019 and April 2022 at three Canadian institutions.
- All patients received genetic counseling followed by testing for the presence of germline pathogenic variants in 17 breast cancer susceptibility genes. The primary gene panel included screening for BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2, and the optional secondary panel included 14 additional breast cancer susceptibility genes.
- Of the participants, 659 (90.4%) were tested for both primary and secondary gene panels, whereas 70 (9.6%) underwent testing for only the primary panel. The majority of the cohort (66.8) were diagnosed with estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer, while 15.4% had triple-negative breast cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of germline pathogenic variants was 7.3% (53 patients) — 5.3% for the primary gene panel and 2.1% for the secondary panel.
- Younger age (< 40 years; odds ratio [OR], 6.83), family history of ovarian cancer (OR, 9.75), high-grade disease (OR, 1.68), and triple-negative breast cancer (OR, 3.19) were independently associated with the presence of pathogenic genetic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2.
- Overall, 34.3% of patients with germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2, and 85.7% of carriers of secondary panel variants would not have qualified for traditional genetic testing according to the current risk factors.
- A total of 13 patients with BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2 variants had confirmed pathogenic mutations and were eligible for poly(adenosine diphosphate–ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings have “informed our clinical practice, and we now offer mainstream, oncology-led genetic testing to all women diagnosed with incident invasive breast cancer younger than 50 years of age, those with triple-negative breast cancer and/or bilateral breast cancer, those potentially eligible for PARP inhibitors,” as well as to men with breast cancer, the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Zoulikha Rezoug, MSc, Lady Davis Institute of the Jewish General Hospital, McGill University in Montreal, Québec, Canada. It was published online on September 3, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a 6-month recruitment pause. Adjustments in recruitment criteria, focus on younger patients and those with triple-negative breast cancer could have overestimated prevalence of genetic pathogenic variants among women aged ≥ 70 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Jewish General Hospital Foundation and the Québec Breast Cancer Foundation, as well as an award from the Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé. Two authors reported receiving grants or personal fees from various sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Reform School’ for Pharmacy Benefit Managers: How Might Legislation Help Patients?
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).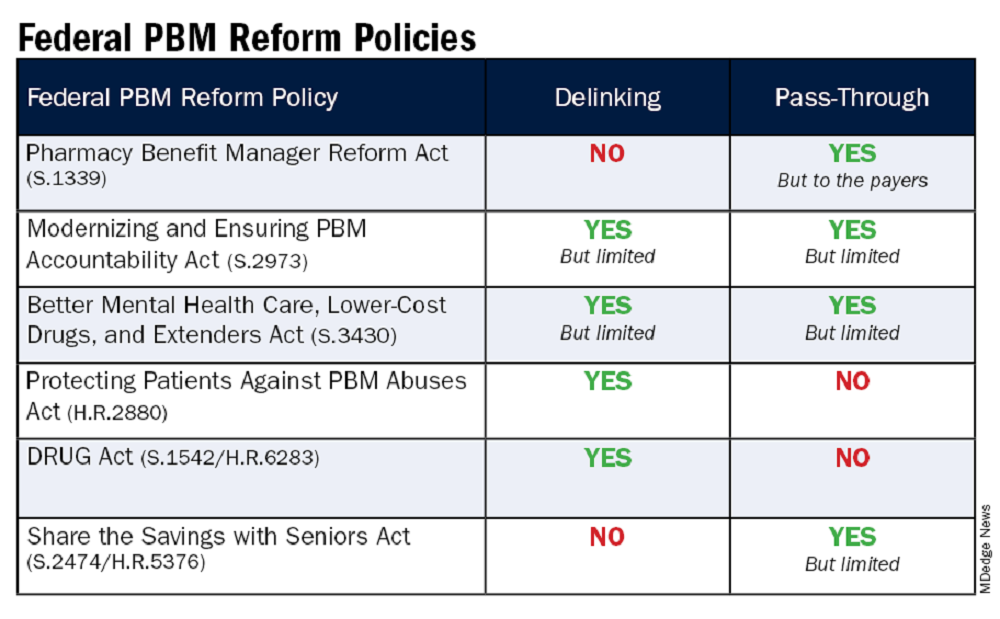
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
AI-Powered Clinical Documentation Tool Reduces EHR Time for Clinicians
TOPLINE:
An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered clinical documentation tool helped reduce time spent on electronic health records (EHR) at home for almost 48% physicians, and nearly 45% reported less weekly time spent on EHR tasks outside of normal work hours.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers recruited 112 clinicians from family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics in North Carolina and Georgia.
- Patients were divided into an intervention group (n = 85) and control group (n = 55), with the intervention group receiving a 1-hour training program on a commercially available AI tool.
- A seven-question survey was administered to participants before and 5 weeks after the intervention to evaluate their experience.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers found 47.1% of clinicians in the intervention group reported spending less time on the EHR at home compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001); 44.7% reported decreased weekly time on the EHR outside normal work hours compared with 20% in the control group (P = .003).
- The study revealed 43.5% of physicians who used the AI instrument reported spending less time on documentation after visits compared with 18.2% in the control group (P = .002).
- Further, 44.7% reported less frustration when using the EHR compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Approximately half of clinicians using the AI-powered clinical documentation tool based on interest reported a positive outcome, potentially reducing burnout. However, a significant subset did not find time-saving benefits or improved EHR experience,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tsai-Ling Liu, PhD, Center for Health System Sciences, Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported potential selection and recall bias in both groups. Additional research is needed to find areas of improvement and assess the effects on clinician groups and health systems, they said.
DISCLOSURES:
Andrew McWilliams, MD, MPH, reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, the National Institutes of Health, and the Duke Endowment unrelated to this work. Ajay Dharod, MD, reported his role as an electronic health record consultant for the Association of American Medical College CORE program. Jeffrey Cleveland, MD, disclosed his participation on the Executive Client Council, a noncompensated advisory group, for Nuance/Microsoft.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered clinical documentation tool helped reduce time spent on electronic health records (EHR) at home for almost 48% physicians, and nearly 45% reported less weekly time spent on EHR tasks outside of normal work hours.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers recruited 112 clinicians from family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics in North Carolina and Georgia.
- Patients were divided into an intervention group (n = 85) and control group (n = 55), with the intervention group receiving a 1-hour training program on a commercially available AI tool.
- A seven-question survey was administered to participants before and 5 weeks after the intervention to evaluate their experience.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers found 47.1% of clinicians in the intervention group reported spending less time on the EHR at home compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001); 44.7% reported decreased weekly time on the EHR outside normal work hours compared with 20% in the control group (P = .003).
- The study revealed 43.5% of physicians who used the AI instrument reported spending less time on documentation after visits compared with 18.2% in the control group (P = .002).
- Further, 44.7% reported less frustration when using the EHR compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Approximately half of clinicians using the AI-powered clinical documentation tool based on interest reported a positive outcome, potentially reducing burnout. However, a significant subset did not find time-saving benefits or improved EHR experience,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tsai-Ling Liu, PhD, Center for Health System Sciences, Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported potential selection and recall bias in both groups. Additional research is needed to find areas of improvement and assess the effects on clinician groups and health systems, they said.
DISCLOSURES:
Andrew McWilliams, MD, MPH, reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, the National Institutes of Health, and the Duke Endowment unrelated to this work. Ajay Dharod, MD, reported his role as an electronic health record consultant for the Association of American Medical College CORE program. Jeffrey Cleveland, MD, disclosed his participation on the Executive Client Council, a noncompensated advisory group, for Nuance/Microsoft.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered clinical documentation tool helped reduce time spent on electronic health records (EHR) at home for almost 48% physicians, and nearly 45% reported less weekly time spent on EHR tasks outside of normal work hours.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers recruited 112 clinicians from family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics in North Carolina and Georgia.
- Patients were divided into an intervention group (n = 85) and control group (n = 55), with the intervention group receiving a 1-hour training program on a commercially available AI tool.
- A seven-question survey was administered to participants before and 5 weeks after the intervention to evaluate their experience.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers found 47.1% of clinicians in the intervention group reported spending less time on the EHR at home compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001); 44.7% reported decreased weekly time on the EHR outside normal work hours compared with 20% in the control group (P = .003).
- The study revealed 43.5% of physicians who used the AI instrument reported spending less time on documentation after visits compared with 18.2% in the control group (P = .002).
- Further, 44.7% reported less frustration when using the EHR compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Approximately half of clinicians using the AI-powered clinical documentation tool based on interest reported a positive outcome, potentially reducing burnout. However, a significant subset did not find time-saving benefits or improved EHR experience,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tsai-Ling Liu, PhD, Center for Health System Sciences, Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported potential selection and recall bias in both groups. Additional research is needed to find areas of improvement and assess the effects on clinician groups and health systems, they said.
DISCLOSURES:
Andrew McWilliams, MD, MPH, reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, the National Institutes of Health, and the Duke Endowment unrelated to this work. Ajay Dharod, MD, reported his role as an electronic health record consultant for the Association of American Medical College CORE program. Jeffrey Cleveland, MD, disclosed his participation on the Executive Client Council, a noncompensated advisory group, for Nuance/Microsoft.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs Subcutaneous Atezolizumab Formulation for Multiple Cancer Indications
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Osimertinib/Savolitinib Combo Shows Promise in NSCLC
according to results of the phase 2 FLOWERS study.
Compared with EGFR inhibitor osimertinib alone, the combination demonstrated a clinically meaningful improvement in the objective response rate — the study’s primary endpoint — with a positive trend in progression-free survival and a manageable safety profile.
About 30% patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC fail to respond well to EGFR–tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), explained Jin-Ji Yang, MD, with Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute, Guangzhou, China, who reported the study results at the annual meeting of the World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Data suggested that de novo MET amplification occurs in up to 5% patients with treatment-naive, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC, and MET overexpression occurs in up to 15% these patients.
Coexistence of EGFR mutation and MET amplification/overexpression reduces sensitivity to EGFR-TKI therapy “and is likely the mechanism for mediating primary resistance to first-line EGFR-TKI monotherapy,” Dr. Yang explained in her presentation.
Osimertinib is a third-generation EGFR-TKI recommended as the first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC. Savolitinib is a highly selective MET-TKI which has demonstrated antitumor activity in various cancers with MET alterations.
The FLOWERS study is the first to test whether combining the two agents could improve efficacy and overcome MET-driven primary resistance in these patients.
The phase 2 study enrolled 44 treatment-naive patients with de novo MET-aberrant, EGFR-mutant, stage IIIB-IV NSCLC; 23 were randomly allocated to receive oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) alone and 21 to receive oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) plus savolitinib (300 mg twice daily).
At a median follow-up of 8.2 months, the objective response rate was 60.9% with osimertinib monotherapy vs 90.5% with combination therapy. The disease control rate was also better with the combination therapy than with monotherapy (95.2% vs 87%).
Median duration of response (not yet mature) was 8.4 months with monotherapy vs 18.6 months with combination therapy.
Preliminary progression-free survival data also showed a trend in favor of combination therapy over monotherapy (a median of 19.3 vs 9.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.59).
Most treatment-related adverse events were grade 1 or 2, and there were no fatal adverse events.
Treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or higher were more common with combination therapy (57.1% vs 8.7%). The most common events with monotherapy were diarrhea (56.5%), rash (52.2%), and pruritus (43.5%) and with dual therapy were rash (52.4%), thrombocytopenia (52.4%), and peripheral edema (42.9%).
The results showed that the combination therapy has the potential to become a first-line treatment option for patients who do not respond well to EGFR-TKIs alone, Dr. Yang said in a press release.
Discussant for the study Paul Paik, MD, thoracic oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said this study “adds to data suggesting high MET expression might be a poor prognostic or predictive marker, the outcomes of which are improved with MET inhibition.”
He cautioned, however, that there appears to be “quality of life, side-effect trade-offs with dual MET plus EGFR TKI upfront.”
Dr. Paik said he looks forward to results from FLOWERS on serial circulating tumor DNA and formal androgen receptor testing, which “might aid in further assessing clonality and characterizing MET as a co-driver in this setting.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca China. Dr. Yang had no disclosures. Dr. Paik disclosed relationships with EMD Serono, Bicara, Novartis, and Summit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results of the phase 2 FLOWERS study.
Compared with EGFR inhibitor osimertinib alone, the combination demonstrated a clinically meaningful improvement in the objective response rate — the study’s primary endpoint — with a positive trend in progression-free survival and a manageable safety profile.
About 30% patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC fail to respond well to EGFR–tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), explained Jin-Ji Yang, MD, with Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute, Guangzhou, China, who reported the study results at the annual meeting of the World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Data suggested that de novo MET amplification occurs in up to 5% patients with treatment-naive, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC, and MET overexpression occurs in up to 15% these patients.
Coexistence of EGFR mutation and MET amplification/overexpression reduces sensitivity to EGFR-TKI therapy “and is likely the mechanism for mediating primary resistance to first-line EGFR-TKI monotherapy,” Dr. Yang explained in her presentation.
Osimertinib is a third-generation EGFR-TKI recommended as the first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC. Savolitinib is a highly selective MET-TKI which has demonstrated antitumor activity in various cancers with MET alterations.
The FLOWERS study is the first to test whether combining the two agents could improve efficacy and overcome MET-driven primary resistance in these patients.
The phase 2 study enrolled 44 treatment-naive patients with de novo MET-aberrant, EGFR-mutant, stage IIIB-IV NSCLC; 23 were randomly allocated to receive oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) alone and 21 to receive oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) plus savolitinib (300 mg twice daily).
At a median follow-up of 8.2 months, the objective response rate was 60.9% with osimertinib monotherapy vs 90.5% with combination therapy. The disease control rate was also better with the combination therapy than with monotherapy (95.2% vs 87%).
Median duration of response (not yet mature) was 8.4 months with monotherapy vs 18.6 months with combination therapy.
Preliminary progression-free survival data also showed a trend in favor of combination therapy over monotherapy (a median of 19.3 vs 9.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.59).
Most treatment-related adverse events were grade 1 or 2, and there were no fatal adverse events.
Treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or higher were more common with combination therapy (57.1% vs 8.7%). The most common events with monotherapy were diarrhea (56.5%), rash (52.2%), and pruritus (43.5%) and with dual therapy were rash (52.4%), thrombocytopenia (52.4%), and peripheral edema (42.9%).
The results showed that the combination therapy has the potential to become a first-line treatment option for patients who do not respond well to EGFR-TKIs alone, Dr. Yang said in a press release.
Discussant for the study Paul Paik, MD, thoracic oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said this study “adds to data suggesting high MET expression might be a poor prognostic or predictive marker, the outcomes of which are improved with MET inhibition.”
He cautioned, however, that there appears to be “quality of life, side-effect trade-offs with dual MET plus EGFR TKI upfront.”
Dr. Paik said he looks forward to results from FLOWERS on serial circulating tumor DNA and formal androgen receptor testing, which “might aid in further assessing clonality and characterizing MET as a co-driver in this setting.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca China. Dr. Yang had no disclosures. Dr. Paik disclosed relationships with EMD Serono, Bicara, Novartis, and Summit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results of the phase 2 FLOWERS study.
Compared with EGFR inhibitor osimertinib alone, the combination demonstrated a clinically meaningful improvement in the objective response rate — the study’s primary endpoint — with a positive trend in progression-free survival and a manageable safety profile.
About 30% patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC fail to respond well to EGFR–tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), explained Jin-Ji Yang, MD, with Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute, Guangzhou, China, who reported the study results at the annual meeting of the World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Data suggested that de novo MET amplification occurs in up to 5% patients with treatment-naive, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC, and MET overexpression occurs in up to 15% these patients.
Coexistence of EGFR mutation and MET amplification/overexpression reduces sensitivity to EGFR-TKI therapy “and is likely the mechanism for mediating primary resistance to first-line EGFR-TKI monotherapy,” Dr. Yang explained in her presentation.
Osimertinib is a third-generation EGFR-TKI recommended as the first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC. Savolitinib is a highly selective MET-TKI which has demonstrated antitumor activity in various cancers with MET alterations.
The FLOWERS study is the first to test whether combining the two agents could improve efficacy and overcome MET-driven primary resistance in these patients.
The phase 2 study enrolled 44 treatment-naive patients with de novo MET-aberrant, EGFR-mutant, stage IIIB-IV NSCLC; 23 were randomly allocated to receive oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) alone and 21 to receive oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) plus savolitinib (300 mg twice daily).
At a median follow-up of 8.2 months, the objective response rate was 60.9% with osimertinib monotherapy vs 90.5% with combination therapy. The disease control rate was also better with the combination therapy than with monotherapy (95.2% vs 87%).
Median duration of response (not yet mature) was 8.4 months with monotherapy vs 18.6 months with combination therapy.
Preliminary progression-free survival data also showed a trend in favor of combination therapy over monotherapy (a median of 19.3 vs 9.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.59).
Most treatment-related adverse events were grade 1 or 2, and there were no fatal adverse events.
Treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or higher were more common with combination therapy (57.1% vs 8.7%). The most common events with monotherapy were diarrhea (56.5%), rash (52.2%), and pruritus (43.5%) and with dual therapy were rash (52.4%), thrombocytopenia (52.4%), and peripheral edema (42.9%).
The results showed that the combination therapy has the potential to become a first-line treatment option for patients who do not respond well to EGFR-TKIs alone, Dr. Yang said in a press release.
Discussant for the study Paul Paik, MD, thoracic oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said this study “adds to data suggesting high MET expression might be a poor prognostic or predictive marker, the outcomes of which are improved with MET inhibition.”
He cautioned, however, that there appears to be “quality of life, side-effect trade-offs with dual MET plus EGFR TKI upfront.”
Dr. Paik said he looks forward to results from FLOWERS on serial circulating tumor DNA and formal androgen receptor testing, which “might aid in further assessing clonality and characterizing MET as a co-driver in this setting.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca China. Dr. Yang had no disclosures. Dr. Paik disclosed relationships with EMD Serono, Bicara, Novartis, and Summit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM WCLC 2024
Montana Hospital to Pay $10.8M to Settle False Claims Oncology Suit
As the deadline nears for a Montana healthcare system to pay what has been called a “jaw-dropping” settlement of nearly $11 million dollars to resolve an alleged violation of the False Claims Act, the legal troubles for the oncologist at the center of the case are ongoing and escalating.
On August 26, the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Montana and other agencies announced the settlement agreement with St. Peter’s Health, a nonprofit healthcare system in Helena, to resolve allegations that it submitted “false claims for payments to federal health care programs for services performed by an oncology doctor.”
“This settlement would not have been possible without the cooperation of St. Peter’s Health, who voluntarily disclosed the misconduct and cooperated with federal investigators to identify the problem and amount of false billing,” said US Attorney Jesse Laslovich in a press release announcing the settlement.
On the same day, the US Attorney’s Office also filed a civil complaint against the oncologist Thomas Weiner, MD, accusing him of “false health care claims and improper prescribing of controlled substances.” Among the numerous allegations, the civil complaint specifies that Dr. Weiner used his position as the chief medical oncologist at St. Peter’s Health “to order medically unnecessary treatment,” including chemotherapy, blood tests, and imaging, as well as “knowingly falsified records” to double bill for office visits.
When It Began
The legal troubles for Dr. Weiner, now 61, started about 4 years ago. Dr. Weiner, who was the sole oncologist at St. Peter’s Health and worked there for 24 years, was suspended in October 2020 and then fired in November 2020 for allegedly providing unnecessary treatments and failing to refer patients to other specialists for care, among other claims.
“The magnitude of Dr. Weiner’s violations is staggering,” St. Peter’s CEO, Wade Johnson, had said in a December 2020 press statement.
At the time, Dr. Weiner had filed a lawsuit against St. Peter’s Health, claiming he was denied due process and seeking damages and a jury trial. Dr. Weiner’s lead lawyer, J. Devlan Geddes, said it was hard to believe that Dr. Weiner had suddenly become a danger to patients after more than 2 decades on the job.
Before 2020, Dr. Weiner had a clean record with Montana’s Board of Medical Examiners and had never been the subject of an internal investigation related to quality of care, according to his lawyers. He also served on St. Peter’s board of directors and as chief of medical staff.
Dr. Weiner’s exit from St. Peter’s in 2020 led to an outpouring of support from former patients and community members who formed the Facebook group, “ We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner.” The group soon grew to almost 4000 people.
Four years later, despite the new legal developments, community support for Dr. Weiner has held strong. Supporters continue to have regular rallies outside St. Peter’s Health as well as post messages and personal stories on two Facebook groups now devoted to the cause.
John Larson, 76, a Helena resident who was treated by Dr. Weiner, echoed a common sentiment from supporters. “I’m completely certain that Tom Weiner is not guilty of what the government is now involved in charging him with,” Dr. Larson said in an interview.
$10.8 Million: ‘It’s a Big Number’
At the press conference announcing the recent settlement, Mr. Laslovich recalled a participant describe the total as jaw-dropping, he said in an interview. While there haven’t been many such recent cases in the district, he agreed it’s a big number. The only other recent case he could remember was a 2018 settlement in Kalispell for $24 million.
The current settlement contends that St. Peter’s Health submitted false claims for payments to federal health care programs related to services performed and referred by Weiner. The infractions allegedly occurred between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2020.
According to the Department of Justice (DOJ), St. Peter Health’s “knew, or should have known,” that the oncologist submitted claims for office visits that were coded at a higher level of service than was performed — ie upcoded claims — or did not meet the requirements of a significant, separately identifiable service when performed on the same day chemotherapy was administered — ie non-payable claims.
The DOJ contended that the healthcare system violated the False Claims Act “by knowingly submitting the upcoded and non-payable” claims to the Federal Health Care Programs. And, as a result, St. Peter’s compensated the oncologist with a salary based on the false claims.
“We had documents showing some of the claims that were being submitted were being done because the doctor wanted more in compensation and of course you can’t do that,” Laslovich said. “For me, the message to providers, and I said this during our press conference, is that coding is critical.”
“The claims resolved by the settlement are allegations only,” the US Attorney’s Office press release clarified, and “there has been no determination of liability.”
The leadership at St. Peter’s Health issued a press release on August 27, stating it relied on Dr. Weiner’s medical record documentation and billing certification, though declined to comment further on the settlement
Bob Wade, a partner at Nelson Mullins, Nashville, Tennessee, and lead outside counsel representing St. Peter’s Health on the settlement, said in an interview that the quality issue was first identified in fall 2020.
“I first conducted a fair market value review for their entire system and noted that he [Weiner] was an extreme outlier with regard to his productivity,” Mr. Wade said.
In a separate statement, Mr. Wade praised the integrity of the health system, saying, “when the medical record documentation and medical necessity issues related to Dr. Weiner were identified, my client, St. Peter’s Health, through the Board and Executive Leadership took decisive action and authorized me to self-report to the Office of Inspector General and Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services and fully cooperated with the Department of Justice to reach an amicable settlement.”
Dr. Weiner still faces legal issues. According to the recent civil complaint filed against Weiner, the oncologist allegedly ordered “medically unnecessary treatments” for patients, “knowingly falsified records to double bill for patient office visits,” and “directed these false claims to increase his personal income, with little regard for the potential patient harm his conduct created.”
The complaint goes on to note that Dr. Weiner saw 50-70 patients a day — about four to five times more than most oncologists see in a given day. He allegedly wanted this schedule, the civil complaint said, “because it maximized his income.”
The civil complaint seeks treble damages, which is triple the actual damages awarded to the plaintiff, as well as civil penalties.
The Montana Board of Medical Examiners shows Dr. Weiner’s license as active, expiring March 31, 2025.
A Community’s Support
Over the past 4 years, Dr. Weiner has encountered strong, continued support from the community.
Rhonda Good, a Helena resident since 2002, is one of the nearly 4000 members of the “We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner” public Facebook group. Her son was treated for cancer by Dr. Weiner and is doing well.
Like other residents, she has strong opinions about the settlement.
“My feeling was, St. Peter’s Health, by settling, basically admitted that if they went to court, they wouldn’t be able to defend their billing procedures and so they settled out of court and that probably saved them money,” she said. “Since I have lived here, St. Peter’s Health billing has been a topic of conversation. And it is not a good conversation.”
Dayna Schwartz, 58, founded a private Facebook support group for Weiner, which she said has about 730 members.
Ms. Schwartz believes the doctor was set up and she plans to continue the weekly rallies. Those who show up, she said, are only a fraction of the supporters.
“A lot of the staunch supporters maintain a low profile,” she said, as the healthcare system employs more than 1700 residents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the deadline nears for a Montana healthcare system to pay what has been called a “jaw-dropping” settlement of nearly $11 million dollars to resolve an alleged violation of the False Claims Act, the legal troubles for the oncologist at the center of the case are ongoing and escalating.
On August 26, the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Montana and other agencies announced the settlement agreement with St. Peter’s Health, a nonprofit healthcare system in Helena, to resolve allegations that it submitted “false claims for payments to federal health care programs for services performed by an oncology doctor.”
“This settlement would not have been possible without the cooperation of St. Peter’s Health, who voluntarily disclosed the misconduct and cooperated with federal investigators to identify the problem and amount of false billing,” said US Attorney Jesse Laslovich in a press release announcing the settlement.
On the same day, the US Attorney’s Office also filed a civil complaint against the oncologist Thomas Weiner, MD, accusing him of “false health care claims and improper prescribing of controlled substances.” Among the numerous allegations, the civil complaint specifies that Dr. Weiner used his position as the chief medical oncologist at St. Peter’s Health “to order medically unnecessary treatment,” including chemotherapy, blood tests, and imaging, as well as “knowingly falsified records” to double bill for office visits.
When It Began
The legal troubles for Dr. Weiner, now 61, started about 4 years ago. Dr. Weiner, who was the sole oncologist at St. Peter’s Health and worked there for 24 years, was suspended in October 2020 and then fired in November 2020 for allegedly providing unnecessary treatments and failing to refer patients to other specialists for care, among other claims.
“The magnitude of Dr. Weiner’s violations is staggering,” St. Peter’s CEO, Wade Johnson, had said in a December 2020 press statement.
At the time, Dr. Weiner had filed a lawsuit against St. Peter’s Health, claiming he was denied due process and seeking damages and a jury trial. Dr. Weiner’s lead lawyer, J. Devlan Geddes, said it was hard to believe that Dr. Weiner had suddenly become a danger to patients after more than 2 decades on the job.
Before 2020, Dr. Weiner had a clean record with Montana’s Board of Medical Examiners and had never been the subject of an internal investigation related to quality of care, according to his lawyers. He also served on St. Peter’s board of directors and as chief of medical staff.
Dr. Weiner’s exit from St. Peter’s in 2020 led to an outpouring of support from former patients and community members who formed the Facebook group, “ We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner.” The group soon grew to almost 4000 people.
Four years later, despite the new legal developments, community support for Dr. Weiner has held strong. Supporters continue to have regular rallies outside St. Peter’s Health as well as post messages and personal stories on two Facebook groups now devoted to the cause.
John Larson, 76, a Helena resident who was treated by Dr. Weiner, echoed a common sentiment from supporters. “I’m completely certain that Tom Weiner is not guilty of what the government is now involved in charging him with,” Dr. Larson said in an interview.
$10.8 Million: ‘It’s a Big Number’
At the press conference announcing the recent settlement, Mr. Laslovich recalled a participant describe the total as jaw-dropping, he said in an interview. While there haven’t been many such recent cases in the district, he agreed it’s a big number. The only other recent case he could remember was a 2018 settlement in Kalispell for $24 million.
The current settlement contends that St. Peter’s Health submitted false claims for payments to federal health care programs related to services performed and referred by Weiner. The infractions allegedly occurred between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2020.
According to the Department of Justice (DOJ), St. Peter Health’s “knew, or should have known,” that the oncologist submitted claims for office visits that were coded at a higher level of service than was performed — ie upcoded claims — or did not meet the requirements of a significant, separately identifiable service when performed on the same day chemotherapy was administered — ie non-payable claims.
The DOJ contended that the healthcare system violated the False Claims Act “by knowingly submitting the upcoded and non-payable” claims to the Federal Health Care Programs. And, as a result, St. Peter’s compensated the oncologist with a salary based on the false claims.
“We had documents showing some of the claims that were being submitted were being done because the doctor wanted more in compensation and of course you can’t do that,” Laslovich said. “For me, the message to providers, and I said this during our press conference, is that coding is critical.”
“The claims resolved by the settlement are allegations only,” the US Attorney’s Office press release clarified, and “there has been no determination of liability.”
The leadership at St. Peter’s Health issued a press release on August 27, stating it relied on Dr. Weiner’s medical record documentation and billing certification, though declined to comment further on the settlement
Bob Wade, a partner at Nelson Mullins, Nashville, Tennessee, and lead outside counsel representing St. Peter’s Health on the settlement, said in an interview that the quality issue was first identified in fall 2020.
“I first conducted a fair market value review for their entire system and noted that he [Weiner] was an extreme outlier with regard to his productivity,” Mr. Wade said.
In a separate statement, Mr. Wade praised the integrity of the health system, saying, “when the medical record documentation and medical necessity issues related to Dr. Weiner were identified, my client, St. Peter’s Health, through the Board and Executive Leadership took decisive action and authorized me to self-report to the Office of Inspector General and Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services and fully cooperated with the Department of Justice to reach an amicable settlement.”
Dr. Weiner still faces legal issues. According to the recent civil complaint filed against Weiner, the oncologist allegedly ordered “medically unnecessary treatments” for patients, “knowingly falsified records to double bill for patient office visits,” and “directed these false claims to increase his personal income, with little regard for the potential patient harm his conduct created.”
The complaint goes on to note that Dr. Weiner saw 50-70 patients a day — about four to five times more than most oncologists see in a given day. He allegedly wanted this schedule, the civil complaint said, “because it maximized his income.”
The civil complaint seeks treble damages, which is triple the actual damages awarded to the plaintiff, as well as civil penalties.
The Montana Board of Medical Examiners shows Dr. Weiner’s license as active, expiring March 31, 2025.
A Community’s Support
Over the past 4 years, Dr. Weiner has encountered strong, continued support from the community.
Rhonda Good, a Helena resident since 2002, is one of the nearly 4000 members of the “We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner” public Facebook group. Her son was treated for cancer by Dr. Weiner and is doing well.
Like other residents, she has strong opinions about the settlement.
“My feeling was, St. Peter’s Health, by settling, basically admitted that if they went to court, they wouldn’t be able to defend their billing procedures and so they settled out of court and that probably saved them money,” she said. “Since I have lived here, St. Peter’s Health billing has been a topic of conversation. And it is not a good conversation.”
Dayna Schwartz, 58, founded a private Facebook support group for Weiner, which she said has about 730 members.
Ms. Schwartz believes the doctor was set up and she plans to continue the weekly rallies. Those who show up, she said, are only a fraction of the supporters.
“A lot of the staunch supporters maintain a low profile,” she said, as the healthcare system employs more than 1700 residents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the deadline nears for a Montana healthcare system to pay what has been called a “jaw-dropping” settlement of nearly $11 million dollars to resolve an alleged violation of the False Claims Act, the legal troubles for the oncologist at the center of the case are ongoing and escalating.
On August 26, the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Montana and other agencies announced the settlement agreement with St. Peter’s Health, a nonprofit healthcare system in Helena, to resolve allegations that it submitted “false claims for payments to federal health care programs for services performed by an oncology doctor.”
“This settlement would not have been possible without the cooperation of St. Peter’s Health, who voluntarily disclosed the misconduct and cooperated with federal investigators to identify the problem and amount of false billing,” said US Attorney Jesse Laslovich in a press release announcing the settlement.
On the same day, the US Attorney’s Office also filed a civil complaint against the oncologist Thomas Weiner, MD, accusing him of “false health care claims and improper prescribing of controlled substances.” Among the numerous allegations, the civil complaint specifies that Dr. Weiner used his position as the chief medical oncologist at St. Peter’s Health “to order medically unnecessary treatment,” including chemotherapy, blood tests, and imaging, as well as “knowingly falsified records” to double bill for office visits.
When It Began
The legal troubles for Dr. Weiner, now 61, started about 4 years ago. Dr. Weiner, who was the sole oncologist at St. Peter’s Health and worked there for 24 years, was suspended in October 2020 and then fired in November 2020 for allegedly providing unnecessary treatments and failing to refer patients to other specialists for care, among other claims.
“The magnitude of Dr. Weiner’s violations is staggering,” St. Peter’s CEO, Wade Johnson, had said in a December 2020 press statement.
At the time, Dr. Weiner had filed a lawsuit against St. Peter’s Health, claiming he was denied due process and seeking damages and a jury trial. Dr. Weiner’s lead lawyer, J. Devlan Geddes, said it was hard to believe that Dr. Weiner had suddenly become a danger to patients after more than 2 decades on the job.
Before 2020, Dr. Weiner had a clean record with Montana’s Board of Medical Examiners and had never been the subject of an internal investigation related to quality of care, according to his lawyers. He also served on St. Peter’s board of directors and as chief of medical staff.
Dr. Weiner’s exit from St. Peter’s in 2020 led to an outpouring of support from former patients and community members who formed the Facebook group, “ We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner.” The group soon grew to almost 4000 people.
Four years later, despite the new legal developments, community support for Dr. Weiner has held strong. Supporters continue to have regular rallies outside St. Peter’s Health as well as post messages and personal stories on two Facebook groups now devoted to the cause.
John Larson, 76, a Helena resident who was treated by Dr. Weiner, echoed a common sentiment from supporters. “I’m completely certain that Tom Weiner is not guilty of what the government is now involved in charging him with,” Dr. Larson said in an interview.
$10.8 Million: ‘It’s a Big Number’
At the press conference announcing the recent settlement, Mr. Laslovich recalled a participant describe the total as jaw-dropping, he said in an interview. While there haven’t been many such recent cases in the district, he agreed it’s a big number. The only other recent case he could remember was a 2018 settlement in Kalispell for $24 million.
The current settlement contends that St. Peter’s Health submitted false claims for payments to federal health care programs related to services performed and referred by Weiner. The infractions allegedly occurred between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2020.
According to the Department of Justice (DOJ), St. Peter Health’s “knew, or should have known,” that the oncologist submitted claims for office visits that were coded at a higher level of service than was performed — ie upcoded claims — or did not meet the requirements of a significant, separately identifiable service when performed on the same day chemotherapy was administered — ie non-payable claims.
The DOJ contended that the healthcare system violated the False Claims Act “by knowingly submitting the upcoded and non-payable” claims to the Federal Health Care Programs. And, as a result, St. Peter’s compensated the oncologist with a salary based on the false claims.
“We had documents showing some of the claims that were being submitted were being done because the doctor wanted more in compensation and of course you can’t do that,” Laslovich said. “For me, the message to providers, and I said this during our press conference, is that coding is critical.”
“The claims resolved by the settlement are allegations only,” the US Attorney’s Office press release clarified, and “there has been no determination of liability.”
The leadership at St. Peter’s Health issued a press release on August 27, stating it relied on Dr. Weiner’s medical record documentation and billing certification, though declined to comment further on the settlement
Bob Wade, a partner at Nelson Mullins, Nashville, Tennessee, and lead outside counsel representing St. Peter’s Health on the settlement, said in an interview that the quality issue was first identified in fall 2020.
“I first conducted a fair market value review for their entire system and noted that he [Weiner] was an extreme outlier with regard to his productivity,” Mr. Wade said.
In a separate statement, Mr. Wade praised the integrity of the health system, saying, “when the medical record documentation and medical necessity issues related to Dr. Weiner were identified, my client, St. Peter’s Health, through the Board and Executive Leadership took decisive action and authorized me to self-report to the Office of Inspector General and Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services and fully cooperated with the Department of Justice to reach an amicable settlement.”
Dr. Weiner still faces legal issues. According to the recent civil complaint filed against Weiner, the oncologist allegedly ordered “medically unnecessary treatments” for patients, “knowingly falsified records to double bill for patient office visits,” and “directed these false claims to increase his personal income, with little regard for the potential patient harm his conduct created.”
The complaint goes on to note that Dr. Weiner saw 50-70 patients a day — about four to five times more than most oncologists see in a given day. He allegedly wanted this schedule, the civil complaint said, “because it maximized his income.”
The civil complaint seeks treble damages, which is triple the actual damages awarded to the plaintiff, as well as civil penalties.
The Montana Board of Medical Examiners shows Dr. Weiner’s license as active, expiring March 31, 2025.
A Community’s Support
Over the past 4 years, Dr. Weiner has encountered strong, continued support from the community.
Rhonda Good, a Helena resident since 2002, is one of the nearly 4000 members of the “We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner” public Facebook group. Her son was treated for cancer by Dr. Weiner and is doing well.
Like other residents, she has strong opinions about the settlement.
“My feeling was, St. Peter’s Health, by settling, basically admitted that if they went to court, they wouldn’t be able to defend their billing procedures and so they settled out of court and that probably saved them money,” she said. “Since I have lived here, St. Peter’s Health billing has been a topic of conversation. And it is not a good conversation.”
Dayna Schwartz, 58, founded a private Facebook support group for Weiner, which she said has about 730 members.
Ms. Schwartz believes the doctor was set up and she plans to continue the weekly rallies. Those who show up, she said, are only a fraction of the supporters.
“A lot of the staunch supporters maintain a low profile,” she said, as the healthcare system employs more than 1700 residents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

