User login
Psilocybin-Assisted Group Therapy Promising for Depression in Cancer Patients
TOPLINE:
, a small study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Depression remains common in patients with cancer, and common treatment approaches — antidepressants and psychotherapy — have demonstrated limited success.
- Researchers explored the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted group therapy in 30 patients with major depressive disorder and cancer — about half with earlier-stage disease and half with metastatic disease.
- In this single-center, open-label, phase 2 study, participants received one-on-one and group therapy sessions before, during, and after receiving a single 25-mg psilocybin dose.
- Alongside individual therapy sessions, each cohort of three to four participants received group sessions guided by a therapist who provided educational material and worked to foster trust among participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants experienced a significant reduction in depression severity, demonstrating a 19.1-point reduction in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores from baseline to follow-up at week 8.
- Overall, 80% of patients showed a lasting response to psilocybin treatment and 50% showed full remission of depressive symptoms by week 1, which persisted for at least 8 weeks.
- The approach was effective for patients with curable and noncurable cancer — with almost 80% in the curable group and 62% in the noncurable group showing clinically meaningful declines in depressive symptoms. The researchers also noted improvements in patients’ anxiety, pain, demoralization, disability, and spiritual well-being.
- No suicidality or other serious treatment-related adverse events occurred; treatment-related nausea and headache were generally mild and expected.
IN PRACTICE:
“Beyond tolerability, psilocybin therapy led to clinically meaningful reductions in depressive symptoms,” the authors concluded. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the feasibility of a group-therapy approach for psilocybin‐assisted treatment in patients with cancer. This innovative framework offers increased scalability and dissemination of psilocybin treatment in real‐world settings.”
Among the 28 participants available for exit interviews, the authors reported that, overall, “participants described that the group/simultaneous model fostered a sense of connectedness, meaning, and transcendence through the shared psilocybin experience and group integration.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Manish Agrawal, MD, Sunstone Therapies, Rockville, Maryland, was published online on December 21, 2023, in Cancer, along with an editorial and related article on patient acceptability of psilocybin-assisted group therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, and the sample size was small and lacked diversity. The study was also not powered to statistically adjust efficacy measures on a possible group effect.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded in part by Compass Pathways. Some authors reported various relationships with Compass Pathways and Sunstone Therapies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, a small study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Depression remains common in patients with cancer, and common treatment approaches — antidepressants and psychotherapy — have demonstrated limited success.
- Researchers explored the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted group therapy in 30 patients with major depressive disorder and cancer — about half with earlier-stage disease and half with metastatic disease.
- In this single-center, open-label, phase 2 study, participants received one-on-one and group therapy sessions before, during, and after receiving a single 25-mg psilocybin dose.
- Alongside individual therapy sessions, each cohort of three to four participants received group sessions guided by a therapist who provided educational material and worked to foster trust among participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants experienced a significant reduction in depression severity, demonstrating a 19.1-point reduction in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores from baseline to follow-up at week 8.
- Overall, 80% of patients showed a lasting response to psilocybin treatment and 50% showed full remission of depressive symptoms by week 1, which persisted for at least 8 weeks.
- The approach was effective for patients with curable and noncurable cancer — with almost 80% in the curable group and 62% in the noncurable group showing clinically meaningful declines in depressive symptoms. The researchers also noted improvements in patients’ anxiety, pain, demoralization, disability, and spiritual well-being.
- No suicidality or other serious treatment-related adverse events occurred; treatment-related nausea and headache were generally mild and expected.
IN PRACTICE:
“Beyond tolerability, psilocybin therapy led to clinically meaningful reductions in depressive symptoms,” the authors concluded. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the feasibility of a group-therapy approach for psilocybin‐assisted treatment in patients with cancer. This innovative framework offers increased scalability and dissemination of psilocybin treatment in real‐world settings.”
Among the 28 participants available for exit interviews, the authors reported that, overall, “participants described that the group/simultaneous model fostered a sense of connectedness, meaning, and transcendence through the shared psilocybin experience and group integration.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Manish Agrawal, MD, Sunstone Therapies, Rockville, Maryland, was published online on December 21, 2023, in Cancer, along with an editorial and related article on patient acceptability of psilocybin-assisted group therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, and the sample size was small and lacked diversity. The study was also not powered to statistically adjust efficacy measures on a possible group effect.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded in part by Compass Pathways. Some authors reported various relationships with Compass Pathways and Sunstone Therapies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, a small study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Depression remains common in patients with cancer, and common treatment approaches — antidepressants and psychotherapy — have demonstrated limited success.
- Researchers explored the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted group therapy in 30 patients with major depressive disorder and cancer — about half with earlier-stage disease and half with metastatic disease.
- In this single-center, open-label, phase 2 study, participants received one-on-one and group therapy sessions before, during, and after receiving a single 25-mg psilocybin dose.
- Alongside individual therapy sessions, each cohort of three to four participants received group sessions guided by a therapist who provided educational material and worked to foster trust among participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants experienced a significant reduction in depression severity, demonstrating a 19.1-point reduction in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores from baseline to follow-up at week 8.
- Overall, 80% of patients showed a lasting response to psilocybin treatment and 50% showed full remission of depressive symptoms by week 1, which persisted for at least 8 weeks.
- The approach was effective for patients with curable and noncurable cancer — with almost 80% in the curable group and 62% in the noncurable group showing clinically meaningful declines in depressive symptoms. The researchers also noted improvements in patients’ anxiety, pain, demoralization, disability, and spiritual well-being.
- No suicidality or other serious treatment-related adverse events occurred; treatment-related nausea and headache were generally mild and expected.
IN PRACTICE:
“Beyond tolerability, psilocybin therapy led to clinically meaningful reductions in depressive symptoms,” the authors concluded. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the feasibility of a group-therapy approach for psilocybin‐assisted treatment in patients with cancer. This innovative framework offers increased scalability and dissemination of psilocybin treatment in real‐world settings.”
Among the 28 participants available for exit interviews, the authors reported that, overall, “participants described that the group/simultaneous model fostered a sense of connectedness, meaning, and transcendence through the shared psilocybin experience and group integration.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Manish Agrawal, MD, Sunstone Therapies, Rockville, Maryland, was published online on December 21, 2023, in Cancer, along with an editorial and related article on patient acceptability of psilocybin-assisted group therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, and the sample size was small and lacked diversity. The study was also not powered to statistically adjust efficacy measures on a possible group effect.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded in part by Compass Pathways. Some authors reported various relationships with Compass Pathways and Sunstone Therapies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Federal Rule for Prior Authorizations a ‘Major Win’ for Patients, Doctors
Physicians groups on January 17 hailed a new federal rule requiring health insurers to streamline and disclose more information about their prior authorization processes, saying it will improve patient care and reduce doctors’ administrative burden.
Health insurers participating in federal programs, including Medicare Advantage and Medicaid, must now respond to expedited prior authorization requests within 72 hours and other requests within 7 days under the long-awaited final rule, released on January 17 by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
Insurers also must include their reasons for denying a prior authorization request and will be required to publicly release data on denial and approval rates for medical treatment. They’ll also need to give patients more information about their decisions to deny care. Insurers must comply with some of the rule’s provisions by January 2026 and others by January 2027.
The final rule “is an important step forward” toward the Medical Group Management Association’s goal of reducing the overall volume of prior authorization requests, said Anders Gilberg, the group’s senior vice president for government affairs, in a statement.
“Only then will medical groups find meaningful reprieve from these onerous, ill-intentioned administrative requirements that dangerously impede patient care,” Mr. Gilberg said.
Health insurers have long lobbied against increased regulation of prior authorization, arguing that it’s needed to rein in healthcare costs and prevent unnecessary treatment.
“We appreciate CMS’s announcement of enforcement discretion that will permit plans to use one standard, rather than mixing and matching, to reduce costs and speed implementation,” said America’s Health Insurance Plans, an insurers’ lobbying group, in an unsigned statement. “However, we must remember that the CMS rule is only half the picture; the Office of the Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) should swiftly require vendors to build electronic prior authorization capabilities into the electronic health record so that providers can do their part, or plans will build a bridge to nowhere.”
The rule comes as health insurers have increasingly been criticized for onerous and time-consuming prior authorization procedures that physicians say unfairly delay or deny the medical treatment that their patients need. With federal legislation to rein in prior authorization overuse at a standstill, 30 states have introduced their own bills to address the problem. Regulators and lawsuits also have called attention to insurers’ increasing use of artificial intelligence and algorithms to deny claims without human review.
“Family physicians know firsthand how prior authorizations divert valuable time and resources away from direct patient care. We also know that these types of administrative requirements are driving physicians away from the workforce and worsening physician shortages,” said Steven P. Furr, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, in a statement praising the new rule.
Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, called the final rule “ a major win” for patients and physicians, adding that its requirements for health insurers to integrate their prior authorization procedures into physicians’ electronic health records systems will also help make “the current time-consuming, manual workflow” more efficient.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians groups on January 17 hailed a new federal rule requiring health insurers to streamline and disclose more information about their prior authorization processes, saying it will improve patient care and reduce doctors’ administrative burden.
Health insurers participating in federal programs, including Medicare Advantage and Medicaid, must now respond to expedited prior authorization requests within 72 hours and other requests within 7 days under the long-awaited final rule, released on January 17 by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
Insurers also must include their reasons for denying a prior authorization request and will be required to publicly release data on denial and approval rates for medical treatment. They’ll also need to give patients more information about their decisions to deny care. Insurers must comply with some of the rule’s provisions by January 2026 and others by January 2027.
The final rule “is an important step forward” toward the Medical Group Management Association’s goal of reducing the overall volume of prior authorization requests, said Anders Gilberg, the group’s senior vice president for government affairs, in a statement.
“Only then will medical groups find meaningful reprieve from these onerous, ill-intentioned administrative requirements that dangerously impede patient care,” Mr. Gilberg said.
Health insurers have long lobbied against increased regulation of prior authorization, arguing that it’s needed to rein in healthcare costs and prevent unnecessary treatment.
“We appreciate CMS’s announcement of enforcement discretion that will permit plans to use one standard, rather than mixing and matching, to reduce costs and speed implementation,” said America’s Health Insurance Plans, an insurers’ lobbying group, in an unsigned statement. “However, we must remember that the CMS rule is only half the picture; the Office of the Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) should swiftly require vendors to build electronic prior authorization capabilities into the electronic health record so that providers can do their part, or plans will build a bridge to nowhere.”
The rule comes as health insurers have increasingly been criticized for onerous and time-consuming prior authorization procedures that physicians say unfairly delay or deny the medical treatment that their patients need. With federal legislation to rein in prior authorization overuse at a standstill, 30 states have introduced their own bills to address the problem. Regulators and lawsuits also have called attention to insurers’ increasing use of artificial intelligence and algorithms to deny claims without human review.
“Family physicians know firsthand how prior authorizations divert valuable time and resources away from direct patient care. We also know that these types of administrative requirements are driving physicians away from the workforce and worsening physician shortages,” said Steven P. Furr, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, in a statement praising the new rule.
Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, called the final rule “ a major win” for patients and physicians, adding that its requirements for health insurers to integrate their prior authorization procedures into physicians’ electronic health records systems will also help make “the current time-consuming, manual workflow” more efficient.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians groups on January 17 hailed a new federal rule requiring health insurers to streamline and disclose more information about their prior authorization processes, saying it will improve patient care and reduce doctors’ administrative burden.
Health insurers participating in federal programs, including Medicare Advantage and Medicaid, must now respond to expedited prior authorization requests within 72 hours and other requests within 7 days under the long-awaited final rule, released on January 17 by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
Insurers also must include their reasons for denying a prior authorization request and will be required to publicly release data on denial and approval rates for medical treatment. They’ll also need to give patients more information about their decisions to deny care. Insurers must comply with some of the rule’s provisions by January 2026 and others by January 2027.
The final rule “is an important step forward” toward the Medical Group Management Association’s goal of reducing the overall volume of prior authorization requests, said Anders Gilberg, the group’s senior vice president for government affairs, in a statement.
“Only then will medical groups find meaningful reprieve from these onerous, ill-intentioned administrative requirements that dangerously impede patient care,” Mr. Gilberg said.
Health insurers have long lobbied against increased regulation of prior authorization, arguing that it’s needed to rein in healthcare costs and prevent unnecessary treatment.
“We appreciate CMS’s announcement of enforcement discretion that will permit plans to use one standard, rather than mixing and matching, to reduce costs and speed implementation,” said America’s Health Insurance Plans, an insurers’ lobbying group, in an unsigned statement. “However, we must remember that the CMS rule is only half the picture; the Office of the Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) should swiftly require vendors to build electronic prior authorization capabilities into the electronic health record so that providers can do their part, or plans will build a bridge to nowhere.”
The rule comes as health insurers have increasingly been criticized for onerous and time-consuming prior authorization procedures that physicians say unfairly delay or deny the medical treatment that their patients need. With federal legislation to rein in prior authorization overuse at a standstill, 30 states have introduced their own bills to address the problem. Regulators and lawsuits also have called attention to insurers’ increasing use of artificial intelligence and algorithms to deny claims without human review.
“Family physicians know firsthand how prior authorizations divert valuable time and resources away from direct patient care. We also know that these types of administrative requirements are driving physicians away from the workforce and worsening physician shortages,” said Steven P. Furr, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, in a statement praising the new rule.
Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, called the final rule “ a major win” for patients and physicians, adding that its requirements for health insurers to integrate their prior authorization procedures into physicians’ electronic health records systems will also help make “the current time-consuming, manual workflow” more efficient.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Continued Caution Needed Combining Nitrates With ED Drugs
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.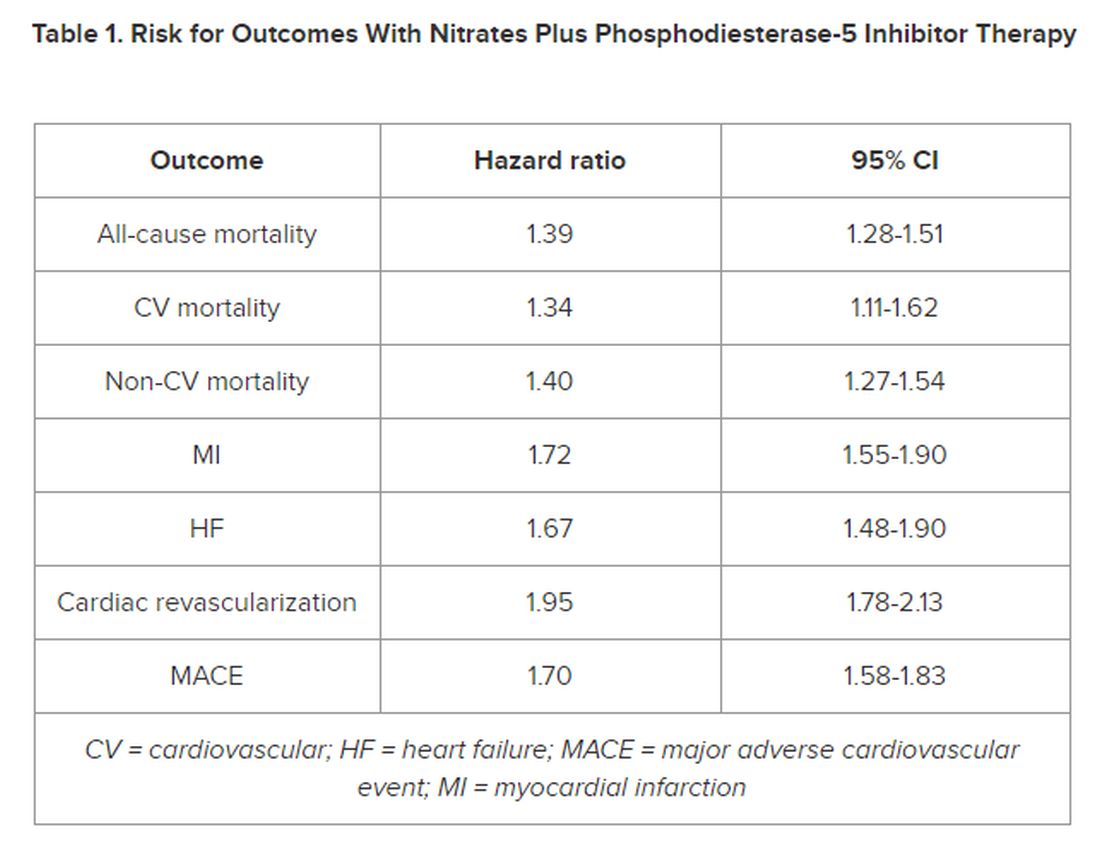
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Are You Unwittingly Aiding the Rise of Superfungi?
Unnecessary or incorrect use of topical antifungal medications is driving the spread of fungal infections like ringworm, which are becoming more difficult to treat, according to a January 11 study published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
If a patient’s condition is not caused by a fungus but is treated as such, treatment will be ineffective.
such as clotrimazole or combinations of antifungals and corticosteroids. And because many topical treatments are also available over-the-counter, doctors should advise patients about how to use them correctly.
“In the last few years, there have been many antifungal resistant cases of tinea corporisand onychomycosisreported,” or ringworm and finger or toenail infections, respectively, said Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, and an author of the study.
Many of these cases originated in South Asia and have also been reported in Europe and Canada. In 2023, the first cases of a new strain of antifungal-resistant ringworm were reported in the United States. This species, Trichophyton indotineae, does not respond to topical medications, requiring oral treatment instead.
“It’s really a serious problem and a huge public health concern,” Dr. Lipner said.
For the new study, Dr. Lipner and colleagues examined prescription patterns from 2021 Medicare Part D claims of topical antifungals. They report that 6.5 million topical antifungal prescriptions were filled that year, some of which included steroids in the formulation. Primary care clinicians wrote 40% of these prescriptions, the most for any clinician group. The estimate is almost certainly an undercount of topical antifungal use because the database did not include over-the-counter purchases or data from other insurance payers.
The number of prescriptions equate to 1 in every 8 Medicare Part D beneficiary receiving an antifungal, the researchers reported.
“If I think about the patients that come into my office, I’m certainly not giving an antifungal to 1 in 8 of them, and I see a lot of fungal infections,” Dr. Lipner said. The findings suggest to Dr. Lipner that some clinicians are diagnosing ringworm by eyesight alone rather than confirming the diagnosis with techniques such as microscopy, fungal culture testing, or polymerase chain reaction testing.
Sometimes what looks like ringworm may actually be eczema, in which case, the topical antifungal would not be appropriate, according to Avrom Caplan, MD, a dermatologist at NYU Langone Health in New York.
“If you’re prescribing something to somebody that they don’t need, you’re basically exposing them to the side effects without the benefit,” Dr. Caplan, who was not part of the study, said.
Dr. Caplan, who reported the first cases of ringworm that only responded to oral medications in the United States, stressed that topical treatments work fine for many ringworm cases today. But if indiscriminate prescribing spurs the development of more resilient fungi, more situations may arise in which only oral medications work in the future, Dr. Caplan said. In addition, oral medications are inherently more demanding on a patient than something they can rub on their skin, Dr. Caplan added.
“We hope that physicians will really think hard about this study and change their practices if they’re not confirming the diagnosis,” Dr. Lipner said.
Dr. Lipner and Dr. Caplan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Unnecessary or incorrect use of topical antifungal medications is driving the spread of fungal infections like ringworm, which are becoming more difficult to treat, according to a January 11 study published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
If a patient’s condition is not caused by a fungus but is treated as such, treatment will be ineffective.
such as clotrimazole or combinations of antifungals and corticosteroids. And because many topical treatments are also available over-the-counter, doctors should advise patients about how to use them correctly.
“In the last few years, there have been many antifungal resistant cases of tinea corporisand onychomycosisreported,” or ringworm and finger or toenail infections, respectively, said Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, and an author of the study.
Many of these cases originated in South Asia and have also been reported in Europe and Canada. In 2023, the first cases of a new strain of antifungal-resistant ringworm were reported in the United States. This species, Trichophyton indotineae, does not respond to topical medications, requiring oral treatment instead.
“It’s really a serious problem and a huge public health concern,” Dr. Lipner said.
For the new study, Dr. Lipner and colleagues examined prescription patterns from 2021 Medicare Part D claims of topical antifungals. They report that 6.5 million topical antifungal prescriptions were filled that year, some of which included steroids in the formulation. Primary care clinicians wrote 40% of these prescriptions, the most for any clinician group. The estimate is almost certainly an undercount of topical antifungal use because the database did not include over-the-counter purchases or data from other insurance payers.
The number of prescriptions equate to 1 in every 8 Medicare Part D beneficiary receiving an antifungal, the researchers reported.
“If I think about the patients that come into my office, I’m certainly not giving an antifungal to 1 in 8 of them, and I see a lot of fungal infections,” Dr. Lipner said. The findings suggest to Dr. Lipner that some clinicians are diagnosing ringworm by eyesight alone rather than confirming the diagnosis with techniques such as microscopy, fungal culture testing, or polymerase chain reaction testing.
Sometimes what looks like ringworm may actually be eczema, in which case, the topical antifungal would not be appropriate, according to Avrom Caplan, MD, a dermatologist at NYU Langone Health in New York.
“If you’re prescribing something to somebody that they don’t need, you’re basically exposing them to the side effects without the benefit,” Dr. Caplan, who was not part of the study, said.
Dr. Caplan, who reported the first cases of ringworm that only responded to oral medications in the United States, stressed that topical treatments work fine for many ringworm cases today. But if indiscriminate prescribing spurs the development of more resilient fungi, more situations may arise in which only oral medications work in the future, Dr. Caplan said. In addition, oral medications are inherently more demanding on a patient than something they can rub on their skin, Dr. Caplan added.
“We hope that physicians will really think hard about this study and change their practices if they’re not confirming the diagnosis,” Dr. Lipner said.
Dr. Lipner and Dr. Caplan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Unnecessary or incorrect use of topical antifungal medications is driving the spread of fungal infections like ringworm, which are becoming more difficult to treat, according to a January 11 study published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
If a patient’s condition is not caused by a fungus but is treated as such, treatment will be ineffective.
such as clotrimazole or combinations of antifungals and corticosteroids. And because many topical treatments are also available over-the-counter, doctors should advise patients about how to use them correctly.
“In the last few years, there have been many antifungal resistant cases of tinea corporisand onychomycosisreported,” or ringworm and finger or toenail infections, respectively, said Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, and an author of the study.
Many of these cases originated in South Asia and have also been reported in Europe and Canada. In 2023, the first cases of a new strain of antifungal-resistant ringworm were reported in the United States. This species, Trichophyton indotineae, does not respond to topical medications, requiring oral treatment instead.
“It’s really a serious problem and a huge public health concern,” Dr. Lipner said.
For the new study, Dr. Lipner and colleagues examined prescription patterns from 2021 Medicare Part D claims of topical antifungals. They report that 6.5 million topical antifungal prescriptions were filled that year, some of which included steroids in the formulation. Primary care clinicians wrote 40% of these prescriptions, the most for any clinician group. The estimate is almost certainly an undercount of topical antifungal use because the database did not include over-the-counter purchases or data from other insurance payers.
The number of prescriptions equate to 1 in every 8 Medicare Part D beneficiary receiving an antifungal, the researchers reported.
“If I think about the patients that come into my office, I’m certainly not giving an antifungal to 1 in 8 of them, and I see a lot of fungal infections,” Dr. Lipner said. The findings suggest to Dr. Lipner that some clinicians are diagnosing ringworm by eyesight alone rather than confirming the diagnosis with techniques such as microscopy, fungal culture testing, or polymerase chain reaction testing.
Sometimes what looks like ringworm may actually be eczema, in which case, the topical antifungal would not be appropriate, according to Avrom Caplan, MD, a dermatologist at NYU Langone Health in New York.
“If you’re prescribing something to somebody that they don’t need, you’re basically exposing them to the side effects without the benefit,” Dr. Caplan, who was not part of the study, said.
Dr. Caplan, who reported the first cases of ringworm that only responded to oral medications in the United States, stressed that topical treatments work fine for many ringworm cases today. But if indiscriminate prescribing spurs the development of more resilient fungi, more situations may arise in which only oral medications work in the future, Dr. Caplan said. In addition, oral medications are inherently more demanding on a patient than something they can rub on their skin, Dr. Caplan added.
“We hope that physicians will really think hard about this study and change their practices if they’re not confirming the diagnosis,” Dr. Lipner said.
Dr. Lipner and Dr. Caplan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Left-Handed Med Students Still ‘Left Out’ in Surgery
of 31 individuals from 15 US institutions.
“Surgical education is designed for the right-handed,” wrote Timothy J. Gilbert, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. Left-handed medical students “contend with instruments designed for right-handed use, perform worse on surgical skills assessments that are biased toward the right-handed, and are assumed to be right-handed by educators,” they said.
Challenges for left-handed medical students are not new. A study published in 2010 in the Journal of Surgical Education identified eight major issues for left-handed surgeons:
- Anxiety about laterality
- Lack of mentoring on lateral preference
- Difficulty handling traditional instruments
- Difficulty with minimally invasive instruments
- Inconvenience while assisting a right-handed person
- Pressure to change lateral preference
- Possible disadvantages with certain procedures
- Possible advantage situs inversus
Previous studies have shown reports of stigmatization and a lack of training and educational resources as barriers to improving the experience and fostering the skills of left-handed students, but the current data on the subjective experiences of left-handed students are limited, the authors said.
“Some of the members of the research team are left-handed, and I think their personal experience/understanding of the topic informed their desire to do projects within this space, since handedness is so thoroughly taken for granted by the right-handed majority,” Dr. Gilbert, who is right-handed, said in an interview. “It was important for our study to have parity between handedness to reduce bias in data interpretation,” he said. “In an era where much has been done to ensure equity between different groups, there’s not as much discussion about handedness within surgery as I believe there should be.”
In a new study published in Academic Medicine, the researchers recruited 31 self-identified left-handed surgical residents and fellows in six surgical specialties (general surgery, urology, plastic surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, otolaryngology, and neurosurgery) and conducted semi-structured interviews between January 31, 2021, and June 20, 2021. The study population included 21 seniors (postgraduate year of 3 or higher), five juniors (postgraduate years 1 or 2), and five surgical fellows.
Overall, three themes surfaced from the participants’ educational experiences:
- Disorienting advice from faculty or residents
- Discouraging right-handed pressures and left-handed stigmatization
- Expression of the educational wishes of left-handed medical students
Conflicting Advice
The interviewees described feeling confused by conflicting advice about how to manage surgical procedures given their left-handedness, the researchers said. Some respondents reported being told to learn to do everything with the right hand; others were told to use their dominant hand (right or left) for fine motor skill elements but use the right hand for sewing.
Persistent Stigma and Switching
Survey respondents reported perceptions that others in the surgical setting were judgmental and inconsiderate; workshops involved demonstrations with a right-handed focus; and surgical technicians prepared needles that were loaded right-handed. “To minimize this negativity, participants often changed to their right hand,” the authors wrote. Some students who changed handedness reported an improved learning experience, in part because their handedness aligned with the instruments they used.
Educational Wish List
Study participants expressed the need for destigmatization of left-handedness in surgical through strategies including tangible mentorship, more granular and meaningful instruction, and normalization of left-handedness.
The study was limited by several factors including the focus only on surgical residents and fellows, with no left-handed medical students who pursued other specialties, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the retrospective design and potential bias from left-handed members of the research team, they said.
Notably, left-handed medical students reported negative experiences during training whether they operated with the right or left hand, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “From a strictly technical perspective, a left-handed medical student who is operatively left-handed will struggle to use hand-discordant tools in their dominant hand, whereas one who is operatively right-handed will struggle to use hand-concordant tools in their nondominant hand,” they said.
The researchers emphasized the need to consider the data in context; a nervous left-handed student who has been shown only right-handed tools and techniques and has not disclosed their left-handedness struggles when asked to close an incision may see themselves as the problem rather than the surgical education.
Takeaways to Improve Training
The current study showed the diversity of needs of left-handed surgical trainees and how more positive encouragement and support could improve their experiences, Dr. Gilbert told this news organization.
The strategies to improve training for left-handed medical students vary according to educational level, said Dr. Gilbert. “If you’re a surgical fellow or chief resident, you probably want more formal training, different tools, access to attendings who have experience performing an operation left-handed. If you’re a medical student, that is likely less important than feeling like you won’t be penalized of looked down upon for your handedness,” he said.
In the survey responses, “I at least was struck by how far a few accepting words could do when said in the right way at the right time,” he said.
“I think the most important takeaway is that educators should consider more what they say and do in the operating room to these junior students/trainees, as our data suggest even a single sentence at such a vulnerable point in time can push them into a choosing their handedness,” Dr. Gilbert said. “That’s not a small decision to make, and educators should be more thoughtful when engaging in the topic.”
Also, educators should offer left-handed resources during clerkship orientations on techniques such as knot-tying, he said. “This normalized handedness and may make students more comfortable with themselves in the operating room.”
Finally, “educators should be able to teach medical students the level-appropriate skills in either hand. If a medical student asks how to tie a knot or throw a stitch in their left hand, the educator should be able to demonstrate this to them effectively,” Dr. Gilbert added.
More research is needed to understand the needs and wants of left-handed medical students, including those who do not pursue surgery and of the skills of the residents and attendings who are tasked with educating these students, Dr. Gilbert told this news organization.
“Eventually, the goal is to implement concrete changes to improve resources for these students, but I think the most effective way to design these resources is to fully grasp the desires and concerns of all involved parties,” he said.
Residency Director Perspective
“We are increasingly sensitive to individual differences, but for some reason, left-handedness is a blind spot, although 10% of the population is left-handed,” said Stephen M. Kavic, MD, professor of surgery at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, in an interview.
“Interestingly, we do not ask handedness on residency applications, suggesting that it may be viewed as a negative trait in the selection process,” said Dr. Kavic, who also serves as program director of residency in surgery at the University of Maryland.
“While not left-handed myself, as Program Director, I have been tasked with training left-handed residents, and I appreciate the challenges,” Dr. Kavic said. “Our department is about 6% left-handed. Most left-handed surgeons are far more comfortable with their nondominant hand than right-handers are with theirs,” he noted. “We do have left-handed instruments available, but the ratio of sets is easily 100:1 right to left.”
With regard to the current study, Dr. Kavic said it was understandable that left-handed medical students feel stigmatized. A message for educators is to not presume right-handedness; instead, ask students about the hand preference on first meeting, and then training will be more inclusive, he said.
“There is a fundamental difference in mirror image training when a righty tries to teach a lefty. How do we do this better and in a standardized fashion? This article clearly shows that we still have a problem; now we must do the work to fix it,” Dr. Kavic said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kavic had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
of 31 individuals from 15 US institutions.
“Surgical education is designed for the right-handed,” wrote Timothy J. Gilbert, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. Left-handed medical students “contend with instruments designed for right-handed use, perform worse on surgical skills assessments that are biased toward the right-handed, and are assumed to be right-handed by educators,” they said.
Challenges for left-handed medical students are not new. A study published in 2010 in the Journal of Surgical Education identified eight major issues for left-handed surgeons:
- Anxiety about laterality
- Lack of mentoring on lateral preference
- Difficulty handling traditional instruments
- Difficulty with minimally invasive instruments
- Inconvenience while assisting a right-handed person
- Pressure to change lateral preference
- Possible disadvantages with certain procedures
- Possible advantage situs inversus
Previous studies have shown reports of stigmatization and a lack of training and educational resources as barriers to improving the experience and fostering the skills of left-handed students, but the current data on the subjective experiences of left-handed students are limited, the authors said.
“Some of the members of the research team are left-handed, and I think their personal experience/understanding of the topic informed their desire to do projects within this space, since handedness is so thoroughly taken for granted by the right-handed majority,” Dr. Gilbert, who is right-handed, said in an interview. “It was important for our study to have parity between handedness to reduce bias in data interpretation,” he said. “In an era where much has been done to ensure equity between different groups, there’s not as much discussion about handedness within surgery as I believe there should be.”
In a new study published in Academic Medicine, the researchers recruited 31 self-identified left-handed surgical residents and fellows in six surgical specialties (general surgery, urology, plastic surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, otolaryngology, and neurosurgery) and conducted semi-structured interviews between January 31, 2021, and June 20, 2021. The study population included 21 seniors (postgraduate year of 3 or higher), five juniors (postgraduate years 1 or 2), and five surgical fellows.
Overall, three themes surfaced from the participants’ educational experiences:
- Disorienting advice from faculty or residents
- Discouraging right-handed pressures and left-handed stigmatization
- Expression of the educational wishes of left-handed medical students
Conflicting Advice
The interviewees described feeling confused by conflicting advice about how to manage surgical procedures given their left-handedness, the researchers said. Some respondents reported being told to learn to do everything with the right hand; others were told to use their dominant hand (right or left) for fine motor skill elements but use the right hand for sewing.
Persistent Stigma and Switching
Survey respondents reported perceptions that others in the surgical setting were judgmental and inconsiderate; workshops involved demonstrations with a right-handed focus; and surgical technicians prepared needles that were loaded right-handed. “To minimize this negativity, participants often changed to their right hand,” the authors wrote. Some students who changed handedness reported an improved learning experience, in part because their handedness aligned with the instruments they used.
Educational Wish List
Study participants expressed the need for destigmatization of left-handedness in surgical through strategies including tangible mentorship, more granular and meaningful instruction, and normalization of left-handedness.
The study was limited by several factors including the focus only on surgical residents and fellows, with no left-handed medical students who pursued other specialties, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the retrospective design and potential bias from left-handed members of the research team, they said.
Notably, left-handed medical students reported negative experiences during training whether they operated with the right or left hand, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “From a strictly technical perspective, a left-handed medical student who is operatively left-handed will struggle to use hand-discordant tools in their dominant hand, whereas one who is operatively right-handed will struggle to use hand-concordant tools in their nondominant hand,” they said.
The researchers emphasized the need to consider the data in context; a nervous left-handed student who has been shown only right-handed tools and techniques and has not disclosed their left-handedness struggles when asked to close an incision may see themselves as the problem rather than the surgical education.
Takeaways to Improve Training
The current study showed the diversity of needs of left-handed surgical trainees and how more positive encouragement and support could improve their experiences, Dr. Gilbert told this news organization.
The strategies to improve training for left-handed medical students vary according to educational level, said Dr. Gilbert. “If you’re a surgical fellow or chief resident, you probably want more formal training, different tools, access to attendings who have experience performing an operation left-handed. If you’re a medical student, that is likely less important than feeling like you won’t be penalized of looked down upon for your handedness,” he said.
In the survey responses, “I at least was struck by how far a few accepting words could do when said in the right way at the right time,” he said.
“I think the most important takeaway is that educators should consider more what they say and do in the operating room to these junior students/trainees, as our data suggest even a single sentence at such a vulnerable point in time can push them into a choosing their handedness,” Dr. Gilbert said. “That’s not a small decision to make, and educators should be more thoughtful when engaging in the topic.”
Also, educators should offer left-handed resources during clerkship orientations on techniques such as knot-tying, he said. “This normalized handedness and may make students more comfortable with themselves in the operating room.”
Finally, “educators should be able to teach medical students the level-appropriate skills in either hand. If a medical student asks how to tie a knot or throw a stitch in their left hand, the educator should be able to demonstrate this to them effectively,” Dr. Gilbert added.
More research is needed to understand the needs and wants of left-handed medical students, including those who do not pursue surgery and of the skills of the residents and attendings who are tasked with educating these students, Dr. Gilbert told this news organization.
“Eventually, the goal is to implement concrete changes to improve resources for these students, but I think the most effective way to design these resources is to fully grasp the desires and concerns of all involved parties,” he said.
Residency Director Perspective
“We are increasingly sensitive to individual differences, but for some reason, left-handedness is a blind spot, although 10% of the population is left-handed,” said Stephen M. Kavic, MD, professor of surgery at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, in an interview.
“Interestingly, we do not ask handedness on residency applications, suggesting that it may be viewed as a negative trait in the selection process,” said Dr. Kavic, who also serves as program director of residency in surgery at the University of Maryland.
“While not left-handed myself, as Program Director, I have been tasked with training left-handed residents, and I appreciate the challenges,” Dr. Kavic said. “Our department is about 6% left-handed. Most left-handed surgeons are far more comfortable with their nondominant hand than right-handers are with theirs,” he noted. “We do have left-handed instruments available, but the ratio of sets is easily 100:1 right to left.”
With regard to the current study, Dr. Kavic said it was understandable that left-handed medical students feel stigmatized. A message for educators is to not presume right-handedness; instead, ask students about the hand preference on first meeting, and then training will be more inclusive, he said.
“There is a fundamental difference in mirror image training when a righty tries to teach a lefty. How do we do this better and in a standardized fashion? This article clearly shows that we still have a problem; now we must do the work to fix it,” Dr. Kavic said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kavic had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
of 31 individuals from 15 US institutions.
“Surgical education is designed for the right-handed,” wrote Timothy J. Gilbert, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. Left-handed medical students “contend with instruments designed for right-handed use, perform worse on surgical skills assessments that are biased toward the right-handed, and are assumed to be right-handed by educators,” they said.
Challenges for left-handed medical students are not new. A study published in 2010 in the Journal of Surgical Education identified eight major issues for left-handed surgeons:
- Anxiety about laterality
- Lack of mentoring on lateral preference
- Difficulty handling traditional instruments
- Difficulty with minimally invasive instruments
- Inconvenience while assisting a right-handed person
- Pressure to change lateral preference
- Possible disadvantages with certain procedures
- Possible advantage situs inversus
Previous studies have shown reports of stigmatization and a lack of training and educational resources as barriers to improving the experience and fostering the skills of left-handed students, but the current data on the subjective experiences of left-handed students are limited, the authors said.
“Some of the members of the research team are left-handed, and I think their personal experience/understanding of the topic informed their desire to do projects within this space, since handedness is so thoroughly taken for granted by the right-handed majority,” Dr. Gilbert, who is right-handed, said in an interview. “It was important for our study to have parity between handedness to reduce bias in data interpretation,” he said. “In an era where much has been done to ensure equity between different groups, there’s not as much discussion about handedness within surgery as I believe there should be.”
In a new study published in Academic Medicine, the researchers recruited 31 self-identified left-handed surgical residents and fellows in six surgical specialties (general surgery, urology, plastic surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, otolaryngology, and neurosurgery) and conducted semi-structured interviews between January 31, 2021, and June 20, 2021. The study population included 21 seniors (postgraduate year of 3 or higher), five juniors (postgraduate years 1 or 2), and five surgical fellows.
Overall, three themes surfaced from the participants’ educational experiences:
- Disorienting advice from faculty or residents
- Discouraging right-handed pressures and left-handed stigmatization
- Expression of the educational wishes of left-handed medical students
Conflicting Advice
The interviewees described feeling confused by conflicting advice about how to manage surgical procedures given their left-handedness, the researchers said. Some respondents reported being told to learn to do everything with the right hand; others were told to use their dominant hand (right or left) for fine motor skill elements but use the right hand for sewing.
Persistent Stigma and Switching
Survey respondents reported perceptions that others in the surgical setting were judgmental and inconsiderate; workshops involved demonstrations with a right-handed focus; and surgical technicians prepared needles that were loaded right-handed. “To minimize this negativity, participants often changed to their right hand,” the authors wrote. Some students who changed handedness reported an improved learning experience, in part because their handedness aligned with the instruments they used.
Educational Wish List
Study participants expressed the need for destigmatization of left-handedness in surgical through strategies including tangible mentorship, more granular and meaningful instruction, and normalization of left-handedness.
The study was limited by several factors including the focus only on surgical residents and fellows, with no left-handed medical students who pursued other specialties, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the retrospective design and potential bias from left-handed members of the research team, they said.
Notably, left-handed medical students reported negative experiences during training whether they operated with the right or left hand, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “From a strictly technical perspective, a left-handed medical student who is operatively left-handed will struggle to use hand-discordant tools in their dominant hand, whereas one who is operatively right-handed will struggle to use hand-concordant tools in their nondominant hand,” they said.
The researchers emphasized the need to consider the data in context; a nervous left-handed student who has been shown only right-handed tools and techniques and has not disclosed their left-handedness struggles when asked to close an incision may see themselves as the problem rather than the surgical education.
Takeaways to Improve Training
The current study showed the diversity of needs of left-handed surgical trainees and how more positive encouragement and support could improve their experiences, Dr. Gilbert told this news organization.
The strategies to improve training for left-handed medical students vary according to educational level, said Dr. Gilbert. “If you’re a surgical fellow or chief resident, you probably want more formal training, different tools, access to attendings who have experience performing an operation left-handed. If you’re a medical student, that is likely less important than feeling like you won’t be penalized of looked down upon for your handedness,” he said.
In the survey responses, “I at least was struck by how far a few accepting words could do when said in the right way at the right time,” he said.
“I think the most important takeaway is that educators should consider more what they say and do in the operating room to these junior students/trainees, as our data suggest even a single sentence at such a vulnerable point in time can push them into a choosing their handedness,” Dr. Gilbert said. “That’s not a small decision to make, and educators should be more thoughtful when engaging in the topic.”
Also, educators should offer left-handed resources during clerkship orientations on techniques such as knot-tying, he said. “This normalized handedness and may make students more comfortable with themselves in the operating room.”
Finally, “educators should be able to teach medical students the level-appropriate skills in either hand. If a medical student asks how to tie a knot or throw a stitch in their left hand, the educator should be able to demonstrate this to them effectively,” Dr. Gilbert added.
More research is needed to understand the needs and wants of left-handed medical students, including those who do not pursue surgery and of the skills of the residents and attendings who are tasked with educating these students, Dr. Gilbert told this news organization.
“Eventually, the goal is to implement concrete changes to improve resources for these students, but I think the most effective way to design these resources is to fully grasp the desires and concerns of all involved parties,” he said.
Residency Director Perspective
“We are increasingly sensitive to individual differences, but for some reason, left-handedness is a blind spot, although 10% of the population is left-handed,” said Stephen M. Kavic, MD, professor of surgery at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, in an interview.
“Interestingly, we do not ask handedness on residency applications, suggesting that it may be viewed as a negative trait in the selection process,” said Dr. Kavic, who also serves as program director of residency in surgery at the University of Maryland.
“While not left-handed myself, as Program Director, I have been tasked with training left-handed residents, and I appreciate the challenges,” Dr. Kavic said. “Our department is about 6% left-handed. Most left-handed surgeons are far more comfortable with their nondominant hand than right-handers are with theirs,” he noted. “We do have left-handed instruments available, but the ratio of sets is easily 100:1 right to left.”
With regard to the current study, Dr. Kavic said it was understandable that left-handed medical students feel stigmatized. A message for educators is to not presume right-handedness; instead, ask students about the hand preference on first meeting, and then training will be more inclusive, he said.
“There is a fundamental difference in mirror image training when a righty tries to teach a lefty. How do we do this better and in a standardized fashion? This article clearly shows that we still have a problem; now we must do the work to fix it,” Dr. Kavic said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kavic had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACADEMIC MEDICINE
CMS Okays Payment for Novel AI Prostate Test
The Centers for Medicare & Medicare Services (CMS) on January 1 approved the payment rate for ArteraAI as a clinical diagnostic laboratory test. The test is the first that can both predict therapeutic benefit and prognosticate long-term outcomes in localized prostate cancer.
Daniel Spratt, MD, chair of radiation oncology at UH Seidman Cancer Center in Cleveland, who has been involved in researching ArteraAI, told this news organization that the test improves risk stratification or prognostication over standard clinical and pathologic tools, such as prostate-specific antigen, Gleason score, and T-stage, or risk groupings such as those from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
“Medicare approval allows this test to reach more patients without the financial burden of covering the test out of pocket. The test is found among other tests in NCCN guidelines as a tool to improve risk stratification and personalization of treatment,” said Dr. Spratt, who serves on the network’s prostate cancer panel.
ArteraAI combines a patient’s standard clinical and pathologic information into an algorithm, alongside a digitized image analysis of the patients’ prostate biopsy. The result is a score that estimates a patient’s risk of developing metastasis or dying from prostate cancer.
Dr. Spratt was the lead author of article last June in NEJM Evidence that validated ArteraAI. He said ArteraAI is 80% accurate as a prognostic test compared with 65% accuracy using NCCN stratification systems.
The AI test spares about two thirds of men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer who are starting radiation therapy from androgen deprivation and its side effects, such as weight gain, breast enlargement, hot flashes, heart disease, and brain problems, Dr. Spratt added.
Andre Esteva, CEO and co-founder of San Francisco-based ArteraAI, said, “After someone is diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, deciding on a treatment can feel very overwhelming as there are so many factors to consider. During this time, knowledge is power, and having detailed, personalized information can increase confidence when making these challenging decisions. The ArteraAI Prostate Test was developed with this in mind and can predict whether a patient will benefit from hormone therapy and estimate long-term outcomes.”
Bruno Barrey is one of Dr. Spratt’s patients. Barrey, a robotics engineer from suburban Detroit who was transitioning from active surveillance with Gleason 3+4 intermediate-risk prostate cancer to radiation therapy, said, “I was concerned about the side effects from androgen-deprivation therapy. I was relieved that the AI test allowed me to avoid hormone therapy.”
Dr. Spratt reported working with NRG Oncology, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute, and as an academic collaborator with ArteraAI.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicare Services (CMS) on January 1 approved the payment rate for ArteraAI as a clinical diagnostic laboratory test. The test is the first that can both predict therapeutic benefit and prognosticate long-term outcomes in localized prostate cancer.
Daniel Spratt, MD, chair of radiation oncology at UH Seidman Cancer Center in Cleveland, who has been involved in researching ArteraAI, told this news organization that the test improves risk stratification or prognostication over standard clinical and pathologic tools, such as prostate-specific antigen, Gleason score, and T-stage, or risk groupings such as those from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
“Medicare approval allows this test to reach more patients without the financial burden of covering the test out of pocket. The test is found among other tests in NCCN guidelines as a tool to improve risk stratification and personalization of treatment,” said Dr. Spratt, who serves on the network’s prostate cancer panel.
ArteraAI combines a patient’s standard clinical and pathologic information into an algorithm, alongside a digitized image analysis of the patients’ prostate biopsy. The result is a score that estimates a patient’s risk of developing metastasis or dying from prostate cancer.
Dr. Spratt was the lead author of article last June in NEJM Evidence that validated ArteraAI. He said ArteraAI is 80% accurate as a prognostic test compared with 65% accuracy using NCCN stratification systems.
The AI test spares about two thirds of men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer who are starting radiation therapy from androgen deprivation and its side effects, such as weight gain, breast enlargement, hot flashes, heart disease, and brain problems, Dr. Spratt added.
Andre Esteva, CEO and co-founder of San Francisco-based ArteraAI, said, “After someone is diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, deciding on a treatment can feel very overwhelming as there are so many factors to consider. During this time, knowledge is power, and having detailed, personalized information can increase confidence when making these challenging decisions. The ArteraAI Prostate Test was developed with this in mind and can predict whether a patient will benefit from hormone therapy and estimate long-term outcomes.”
Bruno Barrey is one of Dr. Spratt’s patients. Barrey, a robotics engineer from suburban Detroit who was transitioning from active surveillance with Gleason 3+4 intermediate-risk prostate cancer to radiation therapy, said, “I was concerned about the side effects from androgen-deprivation therapy. I was relieved that the AI test allowed me to avoid hormone therapy.”
Dr. Spratt reported working with NRG Oncology, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute, and as an academic collaborator with ArteraAI.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicare Services (CMS) on January 1 approved the payment rate for ArteraAI as a clinical diagnostic laboratory test. The test is the first that can both predict therapeutic benefit and prognosticate long-term outcomes in localized prostate cancer.
Daniel Spratt, MD, chair of radiation oncology at UH Seidman Cancer Center in Cleveland, who has been involved in researching ArteraAI, told this news organization that the test improves risk stratification or prognostication over standard clinical and pathologic tools, such as prostate-specific antigen, Gleason score, and T-stage, or risk groupings such as those from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
“Medicare approval allows this test to reach more patients without the financial burden of covering the test out of pocket. The test is found among other tests in NCCN guidelines as a tool to improve risk stratification and personalization of treatment,” said Dr. Spratt, who serves on the network’s prostate cancer panel.
ArteraAI combines a patient’s standard clinical and pathologic information into an algorithm, alongside a digitized image analysis of the patients’ prostate biopsy. The result is a score that estimates a patient’s risk of developing metastasis or dying from prostate cancer.
Dr. Spratt was the lead author of article last June in NEJM Evidence that validated ArteraAI. He said ArteraAI is 80% accurate as a prognostic test compared with 65% accuracy using NCCN stratification systems.
The AI test spares about two thirds of men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer who are starting radiation therapy from androgen deprivation and its side effects, such as weight gain, breast enlargement, hot flashes, heart disease, and brain problems, Dr. Spratt added.
Andre Esteva, CEO and co-founder of San Francisco-based ArteraAI, said, “After someone is diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, deciding on a treatment can feel very overwhelming as there are so many factors to consider. During this time, knowledge is power, and having detailed, personalized information can increase confidence when making these challenging decisions. The ArteraAI Prostate Test was developed with this in mind and can predict whether a patient will benefit from hormone therapy and estimate long-term outcomes.”
Bruno Barrey is one of Dr. Spratt’s patients. Barrey, a robotics engineer from suburban Detroit who was transitioning from active surveillance with Gleason 3+4 intermediate-risk prostate cancer to radiation therapy, said, “I was concerned about the side effects from androgen-deprivation therapy. I was relieved that the AI test allowed me to avoid hormone therapy.”
Dr. Spratt reported working with NRG Oncology, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute, and as an academic collaborator with ArteraAI.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Prostate Cancer Risk
TOPLINE:
Testosterone replacement therapy in middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism does not increase the risk for high-grade or any prostate cancer, new data confirmed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Epidemiologic studies have shown inconsistent findings, and clinical trials have not examined prostate safety. As a result, guidelines generally advise against testosterone replacement therapy in men with a history of or increased risk for prostate cancer.
- The current placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group randomized study included 5204 men, ages 45-80, who had two fasting testosterone concentrations < 300 ng/dL, one or more hypogonadal symptoms, and a history of cardiovascular disease or increased . Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either testosterone replacement therapy or placebo.
- The primary prostate safety endpoint was incident high-grade prostate cancer (Gleason score 4 + 3 or higher).
- Secondary endpoints included incidence of any prostate cancer, acute urinary retention, invasive procedure for , , and new pharmacologic treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of high-grade prostate cancer did not differ significantly between groups. Over a mean follow-up of 33 months, only 0.19% (5 of 2596 participants) in the testosterone replacement therapy group and 0.12% (3 of 2602) in the placebo group were diagnosed with high-grade disease (hazard ratio [HR], 1.62; P = .51).
- The rate of any prostate cancer also did not differ significantly between the testosterone vs placebo groups (0.46% vs 0.42%; HR, 1.07; P = .87).
- The rates of acute urinary retention (0.77% vs 0.61%; HR, 1.25; P = .50), invasive procedures for benign prostatic hyperplasia (0.89% vs 0.46%; HR, 1.91; P = .07), prostate biopsy (0.62% vs 0.54%; HR, 1.13; P = .74), or new treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms (3.89% vs 3.34%; HR, 1.16; P = .32) did not differ significantly between the testosterone vs placebo groups.
- Compared with placebo, testosterone therapy did increase prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, but the differences were small and did not increase after 12 months.
IN PRACTICE:
In a population of middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism, “the incidences of high-grade or any prostate cancer and other prostate events were low and did not differ significantly between testosterone- and placebo-treated men,” the authors concluded. “The study’s findings will facilitate a more informed appraisal of the potential prostate risks of testosterone replacement therapy.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Shalender Bhasin, MB, BS, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
These study findings do not apply to men with known prostate cancer, higher PSA values, or those without confirmed hypogonadism. The study design did not include prostate imaging or other biomarker tests after PSA testing, which may have affected the decision to perform a biopsy. Also, the rates of treatment discontinuation and loss to follow-up were high.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by a consortium of testosterone manufacturers led by AbbVie Inc., with additional financial support from Endo Pharmaceuticals, Acerus Pharmaceuticals Corporation, and Upsher-Smith Laboratories. Bhasin, Lincoff, and Khera reported receiving grants and consulting and personal fees from various sources. The remaining authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Testosterone replacement therapy in middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism does not increase the risk for high-grade or any prostate cancer, new data confirmed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Epidemiologic studies have shown inconsistent findings, and clinical trials have not examined prostate safety. As a result, guidelines generally advise against testosterone replacement therapy in men with a history of or increased risk for prostate cancer.
- The current placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group randomized study included 5204 men, ages 45-80, who had two fasting testosterone concentrations < 300 ng/dL, one or more hypogonadal symptoms, and a history of cardiovascular disease or increased . Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either testosterone replacement therapy or placebo.
- The primary prostate safety endpoint was incident high-grade prostate cancer (Gleason score 4 + 3 or higher).
- Secondary endpoints included incidence of any prostate cancer, acute urinary retention, invasive procedure for , , and new pharmacologic treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of high-grade prostate cancer did not differ significantly between groups. Over a mean follow-up of 33 months, only 0.19% (5 of 2596 participants) in the testosterone replacement therapy group and 0.12% (3 of 2602) in the placebo group were diagnosed with high-grade disease (hazard ratio [HR], 1.62; P = .51).
- The rate of any prostate cancer also did not differ significantly between the testosterone vs placebo groups (0.46% vs 0.42%; HR, 1.07; P = .87).
- The rates of acute urinary retention (0.77% vs 0.61%; HR, 1.25; P = .50), invasive procedures for benign prostatic hyperplasia (0.89% vs 0.46%; HR, 1.91; P = .07), prostate biopsy (0.62% vs 0.54%; HR, 1.13; P = .74), or new treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms (3.89% vs 3.34%; HR, 1.16; P = .32) did not differ significantly between the testosterone vs placebo groups.
- Compared with placebo, testosterone therapy did increase prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, but the differences were small and did not increase after 12 months.
IN PRACTICE:
In a population of middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism, “the incidences of high-grade or any prostate cancer and other prostate events were low and did not differ significantly between testosterone- and placebo-treated men,” the authors concluded. “The study’s findings will facilitate a more informed appraisal of the potential prostate risks of testosterone replacement therapy.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Shalender Bhasin, MB, BS, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
These study findings do not apply to men with known prostate cancer, higher PSA values, or those without confirmed hypogonadism. The study design did not include prostate imaging or other biomarker tests after PSA testing, which may have affected the decision to perform a biopsy. Also, the rates of treatment discontinuation and loss to follow-up were high.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by a consortium of testosterone manufacturers led by AbbVie Inc., with additional financial support from Endo Pharmaceuticals, Acerus Pharmaceuticals Corporation, and Upsher-Smith Laboratories. Bhasin, Lincoff, and Khera reported receiving grants and consulting and personal fees from various sources. The remaining authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Testosterone replacement therapy in middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism does not increase the risk for high-grade or any prostate cancer, new data confirmed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Epidemiologic studies have shown inconsistent findings, and clinical trials have not examined prostate safety. As a result, guidelines generally advise against testosterone replacement therapy in men with a history of or increased risk for prostate cancer.
- The current placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group randomized study included 5204 men, ages 45-80, who had two fasting testosterone concentrations < 300 ng/dL, one or more hypogonadal symptoms, and a history of cardiovascular disease or increased . Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either testosterone replacement therapy or placebo.
- The primary prostate safety endpoint was incident high-grade prostate cancer (Gleason score 4 + 3 or higher).
- Secondary endpoints included incidence of any prostate cancer, acute urinary retention, invasive procedure for , , and new pharmacologic treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of high-grade prostate cancer did not differ significantly between groups. Over a mean follow-up of 33 months, only 0.19% (5 of 2596 participants) in the testosterone replacement therapy group and 0.12% (3 of 2602) in the placebo group were diagnosed with high-grade disease (hazard ratio [HR], 1.62; P = .51).
- The rate of any prostate cancer also did not differ significantly between the testosterone vs placebo groups (0.46% vs 0.42%; HR, 1.07; P = .87).
- The rates of acute urinary retention (0.77% vs 0.61%; HR, 1.25; P = .50), invasive procedures for benign prostatic hyperplasia (0.89% vs 0.46%; HR, 1.91; P = .07), prostate biopsy (0.62% vs 0.54%; HR, 1.13; P = .74), or new treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms (3.89% vs 3.34%; HR, 1.16; P = .32) did not differ significantly between the testosterone vs placebo groups.
- Compared with placebo, testosterone therapy did increase prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, but the differences were small and did not increase after 12 months.
IN PRACTICE:
In a population of middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism, “the incidences of high-grade or any prostate cancer and other prostate events were low and did not differ significantly between testosterone- and placebo-treated men,” the authors concluded. “The study’s findings will facilitate a more informed appraisal of the potential prostate risks of testosterone replacement therapy.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Shalender Bhasin, MB, BS, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
These study findings do not apply to men with known prostate cancer, higher PSA values, or those without confirmed hypogonadism. The study design did not include prostate imaging or other biomarker tests after PSA testing, which may have affected the decision to perform a biopsy. Also, the rates of treatment discontinuation and loss to follow-up were high.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by a consortium of testosterone manufacturers led by AbbVie Inc., with additional financial support from Endo Pharmaceuticals, Acerus Pharmaceuticals Corporation, and Upsher-Smith Laboratories. Bhasin, Lincoff, and Khera reported receiving grants and consulting and personal fees from various sources. The remaining authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Time Off Isn’t Really Off-Time for Most Physicians, Study Finds
About 20% of US physicians took less than 1 week of vacation in the previous year, a new study found. When doctors did go on vacation, 70% reported working on their days off to handle patient-related tasks.
, according to the cross-sectional study, which was published on January 12, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.“It’s important to provide physicians with adequate time to disconnect from work and recharge,” said study coauthor Tait Shanafelt, MD, chief wellness officer at Stanford Medicine, in an interview.
The study’s conclusion that most US physicians work on their days off “is a marker of inadequate staffing, suboptimal teamwork, and poorly designed coverage systems,” he added. “Simply allocating people a number of vacation days is not enough.”
According to Dr. Shanafelt, there’s been little research into vacation’s impact on physician well-being. However, it is clear that work overload and exhaustion are major problems among American physicians. “Inadequate time off may magnify these challenges.”
Research suggests that physicians suffer more burnout than other US workers even after adjusting for confounders, he said. Extensive evidence shows that burnout in physicians contributes to medical errors and erodes quality of care and patient satisfaction, he added.
For the new study, researchers mailed surveys to 3671 members of the American Medical Association from 2020 to 2021, and 1162 (31.7%) responded. Another 6348 (7.1%) responded to an email survey sent to 90,000 physicians. An analysis suggested the respondents were representative of all US practicing physicians.
Among 3024 respondents who responded to a subsurvey about vacations, about 40% took more than 15 days of vacation over the past year, about 40% took 6-15 days, and about 20% took 5 or fewer days.
Fewer than half of physicians said their electronic health record (EHR) inboxes were fully covered by others while they were away. About 70% said they worked while on vacation, with nearly 15% working an hour or more each day.
Emergency physicians were the least likely and anesthesiologists were the most likely to take at least 15 days of vacation per year, according to the study.
Women were more likely than men to work 30 or more minutes a day on vacation. Physicians aged 65 years and older were more likely to take 15 or more days of vacation per year than those under 35 years.
An adjusted analysis linked complete EHR inbox coverage to lower odds of taking time during vacation to work (odds ratio [OR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.57-0.80).
“For many, difficulty finding clinical coverage, lack of EHR inbox coverage, and returning to an overwhelming backlog of EHR inbox work at were identified as barriers to taking vacation,” Dr. Shanafelt said.
Researchers linked lower rates of burnout to taking more than 3 weeks of vacation per year (OR, 0.59-0.66, depending on time spent; 95% CI, 0.40-0.98) vs none. They also linked less burnout to full EHR inbox coverage while on vacation (OR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.63-0.88) and more burnout to spending 30 minutes or more on work while on a typical vacation day (OR, 1.58-1.97, depending on time spent; 95% CI, 1.22-2.77).
Study limitations include the low participation rate and lack of insight into causation. It’s not clear how burnout and less vacation time are related and whether one causes the other, Shanafelt said. “It is possible there are a number of interacting factors rather than a simple, linear relationship.”
In an interview, Lazar J. Greenfield, Jr., MD, PhD, professor and chairman of neurology at UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, said his department encourages clinicians to plan vacations well ahead of time, and “we make a real strong effort to make sure that people are fully covered and someone has their Epic inbox.”
Dr. Greenfield, who wasn’t involved in the new study, recommended that physicians plan active vacations, so they have less downtime to catch up on work matters. But he acknowledged that stepping away from emails can be difficult, especially when physicians fear pileups of work upon their return or don’t want to annoy patients with tardy responses.
“They have a hard time disengaging from their moral obligations to patients,” he said. “Another issue, particularly in my field of neurology, is that there’s a lot of subspecialties. Finding somebody with the exact subspecialty and expertise to cover a very specific patient population they treat can be really hard.”
The Stanford WellMD Center, Mayo Clinic Department of Medicine Program on Physician Well-being, and American Medical Association funded the study.
Dr. Shanafelt discloses coinventing the Well-Being Index and its derivatives with another study author; Mayo Clinic licensed the Well-Being Index and pays them royalties outside the submitted work. Dr. Shanafelt also reported support for grand rounds, lectures, and advising for healthcare organizations outside the submitted work. Other authors reported personal fees from Marvin Behavioral Health and grants from the National Institute of Nursing Research, National Science Foundation, and Med Ed Solutions.
Dr. Greenfield had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
About 20% of US physicians took less than 1 week of vacation in the previous year, a new study found. When doctors did go on vacation, 70% reported working on their days off to handle patient-related tasks.
, according to the cross-sectional study, which was published on January 12, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.“It’s important to provide physicians with adequate time to disconnect from work and recharge,” said study coauthor Tait Shanafelt, MD, chief wellness officer at Stanford Medicine, in an interview.
The study’s conclusion that most US physicians work on their days off “is a marker of inadequate staffing, suboptimal teamwork, and poorly designed coverage systems,” he added. “Simply allocating people a number of vacation days is not enough.”
According to Dr. Shanafelt, there’s been little research into vacation’s impact on physician well-being. However, it is clear that work overload and exhaustion are major problems among American physicians. “Inadequate time off may magnify these challenges.”
Research suggests that physicians suffer more burnout than other US workers even after adjusting for confounders, he said. Extensive evidence shows that burnout in physicians contributes to medical errors and erodes quality of care and patient satisfaction, he added.
For the new study, researchers mailed surveys to 3671 members of the American Medical Association from 2020 to 2021, and 1162 (31.7%) responded. Another 6348 (7.1%) responded to an email survey sent to 90,000 physicians. An analysis suggested the respondents were representative of all US practicing physicians.
Among 3024 respondents who responded to a subsurvey about vacations, about 40% took more than 15 days of vacation over the past year, about 40% took 6-15 days, and about 20% took 5 or fewer days.
Fewer than half of physicians said their electronic health record (EHR) inboxes were fully covered by others while they were away. About 70% said they worked while on vacation, with nearly 15% working an hour or more each day.
Emergency physicians were the least likely and anesthesiologists were the most likely to take at least 15 days of vacation per year, according to the study.
Women were more likely than men to work 30 or more minutes a day on vacation. Physicians aged 65 years and older were more likely to take 15 or more days of vacation per year than those under 35 years.
An adjusted analysis linked complete EHR inbox coverage to lower odds of taking time during vacation to work (odds ratio [OR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.57-0.80).
“For many, difficulty finding clinical coverage, lack of EHR inbox coverage, and returning to an overwhelming backlog of EHR inbox work at were identified as barriers to taking vacation,” Dr. Shanafelt said.
Researchers linked lower rates of burnout to taking more than 3 weeks of vacation per year (OR, 0.59-0.66, depending on time spent; 95% CI, 0.40-0.98) vs none. They also linked less burnout to full EHR inbox coverage while on vacation (OR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.63-0.88) and more burnout to spending 30 minutes or more on work while on a typical vacation day (OR, 1.58-1.97, depending on time spent; 95% CI, 1.22-2.77).
Study limitations include the low participation rate and lack of insight into causation. It’s not clear how burnout and less vacation time are related and whether one causes the other, Shanafelt said. “It is possible there are a number of interacting factors rather than a simple, linear relationship.”
In an interview, Lazar J. Greenfield, Jr., MD, PhD, professor and chairman of neurology at UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, said his department encourages clinicians to plan vacations well ahead of time, and “we make a real strong effort to make sure that people are fully covered and someone has their Epic inbox.”
Dr. Greenfield, who wasn’t involved in the new study, recommended that physicians plan active vacations, so they have less downtime to catch up on work matters. But he acknowledged that stepping away from emails can be difficult, especially when physicians fear pileups of work upon their return or don’t want to annoy patients with tardy responses.
“They have a hard time disengaging from their moral obligations to patients,” he said. “Another issue, particularly in my field of neurology, is that there’s a lot of subspecialties. Finding somebody with the exact subspecialty and expertise to cover a very specific patient population they treat can be really hard.”
The Stanford WellMD Center, Mayo Clinic Department of Medicine Program on Physician Well-being, and American Medical Association funded the study.
Dr. Shanafelt discloses coinventing the Well-Being Index and its derivatives with another study author; Mayo Clinic licensed the Well-Being Index and pays them royalties outside the submitted work. Dr. Shanafelt also reported support for grand rounds, lectures, and advising for healthcare organizations outside the submitted work. Other authors reported personal fees from Marvin Behavioral Health and grants from the National Institute of Nursing Research, National Science Foundation, and Med Ed Solutions.
Dr. Greenfield had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
About 20% of US physicians took less than 1 week of vacation in the previous year, a new study found. When doctors did go on vacation, 70% reported working on their days off to handle patient-related tasks.
, according to the cross-sectional study, which was published on January 12, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.“It’s important to provide physicians with adequate time to disconnect from work and recharge,” said study coauthor Tait Shanafelt, MD, chief wellness officer at Stanford Medicine, in an interview.
The study’s conclusion that most US physicians work on their days off “is a marker of inadequate staffing, suboptimal teamwork, and poorly designed coverage systems,” he added. “Simply allocating people a number of vacation days is not enough.”
According to Dr. Shanafelt, there’s been little research into vacation’s impact on physician well-being. However, it is clear that work overload and exhaustion are major problems among American physicians. “Inadequate time off may magnify these challenges.”
Research suggests that physicians suffer more burnout than other US workers even after adjusting for confounders, he said. Extensive evidence shows that burnout in physicians contributes to medical errors and erodes quality of care and patient satisfaction, he added.
For the new study, researchers mailed surveys to 3671 members of the American Medical Association from 2020 to 2021, and 1162 (31.7%) responded. Another 6348 (7.1%) responded to an email survey sent to 90,000 physicians. An analysis suggested the respondents were representative of all US practicing physicians.
Among 3024 respondents who responded to a subsurvey about vacations, about 40% took more than 15 days of vacation over the past year, about 40% took 6-15 days, and about 20% took 5 or fewer days.
Fewer than half of physicians said their electronic health record (EHR) inboxes were fully covered by others while they were away. About 70% said they worked while on vacation, with nearly 15% working an hour or more each day.
Emergency physicians were the least likely and anesthesiologists were the most likely to take at least 15 days of vacation per year, according to the study.
Women were more likely than men to work 30 or more minutes a day on vacation. Physicians aged 65 years and older were more likely to take 15 or more days of vacation per year than those under 35 years.
An adjusted analysis linked complete EHR inbox coverage to lower odds of taking time during vacation to work (odds ratio [OR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.57-0.80).
“For many, difficulty finding clinical coverage, lack of EHR inbox coverage, and returning to an overwhelming backlog of EHR inbox work at were identified as barriers to taking vacation,” Dr. Shanafelt said.
Researchers linked lower rates of burnout to taking more than 3 weeks of vacation per year (OR, 0.59-0.66, depending on time spent; 95% CI, 0.40-0.98) vs none. They also linked less burnout to full EHR inbox coverage while on vacation (OR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.63-0.88) and more burnout to spending 30 minutes or more on work while on a typical vacation day (OR, 1.58-1.97, depending on time spent; 95% CI, 1.22-2.77).
Study limitations include the low participation rate and lack of insight into causation. It’s not clear how burnout and less vacation time are related and whether one causes the other, Shanafelt said. “It is possible there are a number of interacting factors rather than a simple, linear relationship.”
In an interview, Lazar J. Greenfield, Jr., MD, PhD, professor and chairman of neurology at UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, said his department encourages clinicians to plan vacations well ahead of time, and “we make a real strong effort to make sure that people are fully covered and someone has their Epic inbox.”
Dr. Greenfield, who wasn’t involved in the new study, recommended that physicians plan active vacations, so they have less downtime to catch up on work matters. But he acknowledged that stepping away from emails can be difficult, especially when physicians fear pileups of work upon their return or don’t want to annoy patients with tardy responses.
“They have a hard time disengaging from their moral obligations to patients,” he said. “Another issue, particularly in my field of neurology, is that there’s a lot of subspecialties. Finding somebody with the exact subspecialty and expertise to cover a very specific patient population they treat can be really hard.”
The Stanford WellMD Center, Mayo Clinic Department of Medicine Program on Physician Well-being, and American Medical Association funded the study.
Dr. Shanafelt discloses coinventing the Well-Being Index and its derivatives with another study author; Mayo Clinic licensed the Well-Being Index and pays them royalties outside the submitted work. Dr. Shanafelt also reported support for grand rounds, lectures, and advising for healthcare organizations outside the submitted work. Other authors reported personal fees from Marvin Behavioral Health and grants from the National Institute of Nursing Research, National Science Foundation, and Med Ed Solutions.
Dr. Greenfield had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
SUDs rates highest in head, neck, and gastric cancer survivors
.
The association between cancer and substance use is well known, but data on the prevalence of different substance use disorders (SUDs) in different types of cancer are limited, Katie F. Jones, PhD, of the VA Boston Healthcare System, and colleagues, wrote in their paper.
“Substance use and use disorders are on the rise in general and among older adults, who represent the majority of people diagnosed with cancer, and SUDs have significant potential to complicate cancer care and negatively impact cancer outcomes,” corresponding author Devon K. Check, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “We thought it was important to understand whether SUDs are more common with certain types of cancer. We can use that information to guide resources toward populations where interventions to integrate SUD treatment and cancer treatment are most needed,” he said. “In addition, because different SUDs (opioid use disorder, alcohol use disorder) might complicate cancer treatment in different ways and necessitate different types of interventions, we thought it was important to understand the distribution of specific disorders,” he explained.
In the cross-sectional study published in JAMA Oncology, the researchers reviewed data from 6,101 adult cancer survivors who participated in the National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) between 2015 and 2020.
The study population included survivors of solid tumor cancers. SUD was defined as meeting at least one of four criteria for substance abuse or at least 3 of 6 criteria for dependence based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (Fourth Edition) criteria.
Overall, 3.83% of the participants met criteria for SUD. Survivors of head and neck cancers and survivors of gastric and esophageal cancers had the highest rates of SUDs (approximately 9%), followed by cervical cancer and melanoma survivors (approximately 6%).
Alcohol use disorder was the most common SUD both overall (2.8%) and among survivors of head and neck cancers, cervical cancers, and melanoma.
Cannabis use disorder was the most prevalent SUD among esophageal and gastric cancer survivors (approximately 9%).
The prevalence of SUDs overall and within the past year (active) was approximately 4%, but the prevalence of active SUDs was significantly higher for those with head and neck cancers and cervical cancer (18.73% and 15.70%, respectively). However, the distribution of specific SUDs was different in the newly diagnosed patients. Sedative use disorder took the top spot as the most common SUD for head and neck cancer survivors (9.81%), while alcohol use disorder was the most common SUD among cervical cancer survivors (10.49%).
Limitations and Implications
The findings were limited by several factors, including the nature of the study population and the data source, said Dr. Check.
“The average prevalence of SUD (or the prevalence across cancer types) was lower than we might have expected,” but the results make sense given the mainly older and female study population, he said. SUDs are less common among older adults compared with younger adults and among women compared with men, and the study’s data source (NSDUH) has been shown in other research to underestimate the prevalence of opioid use disorder, he added.
“Otherwise, the study findings were generally consistent with what we would expect,” Dr. Check said in an interview. “For example, alcohol use disorder is the most common SUD in the general U.S. population, and that was true for our study population of cancer survivors as well. In addition, SUD prevalence was higher in cancers such as cervical cancer and head and neck cancers that are causally linked to alcohol and/or tobacco use,” he said.
Integrated care is needed
“Among people diagnosed with certain types of cancers, including cervical and head and neck cancers, the estimated prevalence of SUD is similar to those [with] medical comorbidities such as diabetes and cardiopulmonary conditions,” said Dr. Check. “Within the field, there is an increasing emphasis on ensuring that people diagnosed with cancer have access to integrated care for their comorbid medical conditions. Similar efforts for people who concurrently manage cancer and SUD are largely absent but critically needed; these efforts should prioritize cancer populations where SUD prevalence is high,” he said.
Looking ahead, “We need to understand more about the specific challenges that arise at the intersection of cancer and SUD so we can design interventions and programs to better support both patients who concurrently manage cancer and SUD and the clinicians who care for them,” Dr. Check added.
Recognize risk factors
“It is very important to study overall substance use disorders in patients with cancer, because understanding the risks of developing these issues after treatment helps us develop approaches to best support these patients following their cancer therapies,” Henry S. Park, MD, a radiation oncologist at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, said in an interview.
The current study findings “are generally consistent with my experience and intuition, but it is still helpful to see the actual data,” said Dr. Park, who was not involved in the study. “This may be partially because of the baseline elevated risk of preexisting SUDs for certain patients from the higher-prevalence disease sites. However, it may also be related to the intense side effects that survivors of some types of cancers, such as head and neck cancer, gastroesophageal cancer, and cervical cancer, may experience soon after treatment, and even chronically long after treatment,” he said.
Individualize risk assessment
“Ultimately, clinicians should be aware that not all patients with cancer are the same, and that the majority do not necessarily develop SUDs,” Dr. Park said in an interview. “We should be careful to treat symptoms appropriately, and not withhold therapies purely because of an elevated risk of developing SUDs. However, there are some patients who are at higher risk of SUDs who will need extra support and care from physicians, advanced practice providers, nutritionists, social workers, psychologists, dietitians, and survivorship clinics, both in the short-term and long-term,” he emphasized.
As for additional research, “more work needs to be done on which particular patients within each disease subset are most likely to develop SUDs,” said Dr. Park. “Most importantly, once we identify our high-risk group as reliably as possible, we will have to study interventions that rely on supporting and partnering with patients to decrease the risk of developing SUDs as much as possible, while adequately treating residual symptoms and quality-of-life effects following cancer treatment,” he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Check disclosed grants from Duke University during the study period and grants from the National Institutes of Health and AstraZeneca unrelated to the current study. Dr. Park had no financial conflicts to disclose.
.
The association between cancer and substance use is well known, but data on the prevalence of different substance use disorders (SUDs) in different types of cancer are limited, Katie F. Jones, PhD, of the VA Boston Healthcare System, and colleagues, wrote in their paper.
“Substance use and use disorders are on the rise in general and among older adults, who represent the majority of people diagnosed with cancer, and SUDs have significant potential to complicate cancer care and negatively impact cancer outcomes,” corresponding author Devon K. Check, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “We thought it was important to understand whether SUDs are more common with certain types of cancer. We can use that information to guide resources toward populations where interventions to integrate SUD treatment and cancer treatment are most needed,” he said. “In addition, because different SUDs (opioid use disorder, alcohol use disorder) might complicate cancer treatment in different ways and necessitate different types of interventions, we thought it was important to understand the distribution of specific disorders,” he explained.
In the cross-sectional study published in JAMA Oncology, the researchers reviewed data from 6,101 adult cancer survivors who participated in the National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) between 2015 and 2020.
The study population included survivors of solid tumor cancers. SUD was defined as meeting at least one of four criteria for substance abuse or at least 3 of 6 criteria for dependence based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (Fourth Edition) criteria.
Overall, 3.83% of the participants met criteria for SUD. Survivors of head and neck cancers and survivors of gastric and esophageal cancers had the highest rates of SUDs (approximately 9%), followed by cervical cancer and melanoma survivors (approximately 6%).
Alcohol use disorder was the most common SUD both overall (2.8%) and among survivors of head and neck cancers, cervical cancers, and melanoma.
Cannabis use disorder was the most prevalent SUD among esophageal and gastric cancer survivors (approximately 9%).
The prevalence of SUDs overall and within the past year (active) was approximately 4%, but the prevalence of active SUDs was significantly higher for those with head and neck cancers and cervical cancer (18.73% and 15.70%, respectively). However, the distribution of specific SUDs was different in the newly diagnosed patients. Sedative use disorder took the top spot as the most common SUD for head and neck cancer survivors (9.81%), while alcohol use disorder was the most common SUD among cervical cancer survivors (10.49%).
Limitations and Implications
The findings were limited by several factors, including the nature of the study population and the data source, said Dr. Check.
“The average prevalence of SUD (or the prevalence across cancer types) was lower than we might have expected,” but the results make sense given the mainly older and female study population, he said. SUDs are less common among older adults compared with younger adults and among women compared with men, and the study’s data source (NSDUH) has been shown in other research to underestimate the prevalence of opioid use disorder, he added.
“Otherwise, the study findings were generally consistent with what we would expect,” Dr. Check said in an interview. “For example, alcohol use disorder is the most common SUD in the general U.S. population, and that was true for our study population of cancer survivors as well. In addition, SUD prevalence was higher in cancers such as cervical cancer and head and neck cancers that are causally linked to alcohol and/or tobacco use,” he said.
Integrated care is needed
“Among people diagnosed with certain types of cancers, including cervical and head and neck cancers, the estimated prevalence of SUD is similar to those [with] medical comorbidities such as diabetes and cardiopulmonary conditions,” said Dr. Check. “Within the field, there is an increasing emphasis on ensuring that people diagnosed with cancer have access to integrated care for their comorbid medical conditions. Similar efforts for people who concurrently manage cancer and SUD are largely absent but critically needed; these efforts should prioritize cancer populations where SUD prevalence is high,” he said.
Looking ahead, “We need to understand more about the specific challenges that arise at the intersection of cancer and SUD so we can design interventions and programs to better support both patients who concurrently manage cancer and SUD and the clinicians who care for them,” Dr. Check added.
Recognize risk factors
“It is very important to study overall substance use disorders in patients with cancer, because understanding the risks of developing these issues after treatment helps us develop approaches to best support these patients following their cancer therapies,” Henry S. Park, MD, a radiation oncologist at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, said in an interview.
The current study findings “are generally consistent with my experience and intuition, but it is still helpful to see the actual data,” said Dr. Park, who was not involved in the study. “This may be partially because of the baseline elevated risk of preexisting SUDs for certain patients from the higher-prevalence disease sites. However, it may also be related to the intense side effects that survivors of some types of cancers, such as head and neck cancer, gastroesophageal cancer, and cervical cancer, may experience soon after treatment, and even chronically long after treatment,” he said.
Individualize risk assessment
“Ultimately, clinicians should be aware that not all patients with cancer are the same, and that the majority do not necessarily develop SUDs,” Dr. Park said in an interview. “We should be careful to treat symptoms appropriately, and not withhold therapies purely because of an elevated risk of developing SUDs. However, there are some patients who are at higher risk of SUDs who will need extra support and care from physicians, advanced practice providers, nutritionists, social workers, psychologists, dietitians, and survivorship clinics, both in the short-term and long-term,” he emphasized.
As for additional research, “more work needs to be done on which particular patients within each disease subset are most likely to develop SUDs,” said Dr. Park. “Most importantly, once we identify our high-risk group as reliably as possible, we will have to study interventions that rely on supporting and partnering with patients to decrease the risk of developing SUDs as much as possible, while adequately treating residual symptoms and quality-of-life effects following cancer treatment,” he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Check disclosed grants from Duke University during the study period and grants from the National Institutes of Health and AstraZeneca unrelated to the current study. Dr. Park had no financial conflicts to disclose.
.
The association between cancer and substance use is well known, but data on the prevalence of different substance use disorders (SUDs) in different types of cancer are limited, Katie F. Jones, PhD, of the VA Boston Healthcare System, and colleagues, wrote in their paper.
“Substance use and use disorders are on the rise in general and among older adults, who represent the majority of people diagnosed with cancer, and SUDs have significant potential to complicate cancer care and negatively impact cancer outcomes,” corresponding author Devon K. Check, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “We thought it was important to understand whether SUDs are more common with certain types of cancer. We can use that information to guide resources toward populations where interventions to integrate SUD treatment and cancer treatment are most needed,” he said. “In addition, because different SUDs (opioid use disorder, alcohol use disorder) might complicate cancer treatment in different ways and necessitate different types of interventions, we thought it was important to understand the distribution of specific disorders,” he explained.
In the cross-sectional study published in JAMA Oncology, the researchers reviewed data from 6,101 adult cancer survivors who participated in the National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) between 2015 and 2020.
The study population included survivors of solid tumor cancers. SUD was defined as meeting at least one of four criteria for substance abuse or at least 3 of 6 criteria for dependence based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (Fourth Edition) criteria.
Overall, 3.83% of the participants met criteria for SUD. Survivors of head and neck cancers and survivors of gastric and esophageal cancers had the highest rates of SUDs (approximately 9%), followed by cervical cancer and melanoma survivors (approximately 6%).
Alcohol use disorder was the most common SUD both overall (2.8%) and among survivors of head and neck cancers, cervical cancers, and melanoma.
Cannabis use disorder was the most prevalent SUD among esophageal and gastric cancer survivors (approximately 9%).
The prevalence of SUDs overall and within the past year (active) was approximately 4%, but the prevalence of active SUDs was significantly higher for those with head and neck cancers and cervical cancer (18.73% and 15.70%, respectively). However, the distribution of specific SUDs was different in the newly diagnosed patients. Sedative use disorder took the top spot as the most common SUD for head and neck cancer survivors (9.81%), while alcohol use disorder was the most common SUD among cervical cancer survivors (10.49%).
Limitations and Implications
The findings were limited by several factors, including the nature of the study population and the data source, said Dr. Check.
“The average prevalence of SUD (or the prevalence across cancer types) was lower than we might have expected,” but the results make sense given the mainly older and female study population, he said. SUDs are less common among older adults compared with younger adults and among women compared with men, and the study’s data source (NSDUH) has been shown in other research to underestimate the prevalence of opioid use disorder, he added.
“Otherwise, the study findings were generally consistent with what we would expect,” Dr. Check said in an interview. “For example, alcohol use disorder is the most common SUD in the general U.S. population, and that was true for our study population of cancer survivors as well. In addition, SUD prevalence was higher in cancers such as cervical cancer and head and neck cancers that are causally linked to alcohol and/or tobacco use,” he said.
Integrated care is needed
“Among people diagnosed with certain types of cancers, including cervical and head and neck cancers, the estimated prevalence of SUD is similar to those [with] medical comorbidities such as diabetes and cardiopulmonary conditions,” said Dr. Check. “Within the field, there is an increasing emphasis on ensuring that people diagnosed with cancer have access to integrated care for their comorbid medical conditions. Similar efforts for people who concurrently manage cancer and SUD are largely absent but critically needed; these efforts should prioritize cancer populations where SUD prevalence is high,” he said.
Looking ahead, “We need to understand more about the specific challenges that arise at the intersection of cancer and SUD so we can design interventions and programs to better support both patients who concurrently manage cancer and SUD and the clinicians who care for them,” Dr. Check added.
Recognize risk factors
“It is very important to study overall substance use disorders in patients with cancer, because understanding the risks of developing these issues after treatment helps us develop approaches to best support these patients following their cancer therapies,” Henry S. Park, MD, a radiation oncologist at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, said in an interview.
The current study findings “are generally consistent with my experience and intuition, but it is still helpful to see the actual data,” said Dr. Park, who was not involved in the study. “This may be partially because of the baseline elevated risk of preexisting SUDs for certain patients from the higher-prevalence disease sites. However, it may also be related to the intense side effects that survivors of some types of cancers, such as head and neck cancer, gastroesophageal cancer, and cervical cancer, may experience soon after treatment, and even chronically long after treatment,” he said.
Individualize risk assessment
“Ultimately, clinicians should be aware that not all patients with cancer are the same, and that the majority do not necessarily develop SUDs,” Dr. Park said in an interview. “We should be careful to treat symptoms appropriately, and not withhold therapies purely because of an elevated risk of developing SUDs. However, there are some patients who are at higher risk of SUDs who will need extra support and care from physicians, advanced practice providers, nutritionists, social workers, psychologists, dietitians, and survivorship clinics, both in the short-term and long-term,” he emphasized.
As for additional research, “more work needs to be done on which particular patients within each disease subset are most likely to develop SUDs,” said Dr. Park. “Most importantly, once we identify our high-risk group as reliably as possible, we will have to study interventions that rely on supporting and partnering with patients to decrease the risk of developing SUDs as much as possible, while adequately treating residual symptoms and quality-of-life effects following cancer treatment,” he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Check disclosed grants from Duke University during the study period and grants from the National Institutes of Health and AstraZeneca unrelated to the current study. Dr. Park had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
FDA Rejects GI Cancer Drug Over Manufacturing Issues
the company announced January 8.
The monoclonal antibody was under priority review as the first agent specifically for locally advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma that is claudin 18.2-positive. Overexpression of claudin 18.2 in gastric cancer cells is associated with tumor growth and progression.
The FDA, however, could not approve zolbetuximab by the planned decision date of January 12, 2024, because of “unresolved deficiencies following its pre-license inspection of a third-party manufacturing facility for zolbetuximab,” according to the company press release.
Astellas “is working closely with the FDA and the third-party manufacturer to establish a timeline to quickly resolve” the issues, the company said.
Astellas also clarified that the FDA isn’t asking for additional efficacy and safety data. In phase 3 testing, zolbetuximab improved median progression-free and overall survival by about 2-3 months over chemotherapy alone.
If zolbetuximab is approved, “pathologists will have to be facile with claudin 18.2 testing as a companion diagnostic before [it] can be used,” Mark Lewis, MD, a gastrointestinal oncologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah, told this news organization.
The agent is also under review in Japan, Europe, and China.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
the company announced January 8.
The monoclonal antibody was under priority review as the first agent specifically for locally advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma that is claudin 18.2-positive. Overexpression of claudin 18.2 in gastric cancer cells is associated with tumor growth and progression.
The FDA, however, could not approve zolbetuximab by the planned decision date of January 12, 2024, because of “unresolved deficiencies following its pre-license inspection of a third-party manufacturing facility for zolbetuximab,” according to the company press release.
Astellas “is working closely with the FDA and the third-party manufacturer to establish a timeline to quickly resolve” the issues, the company said.
Astellas also clarified that the FDA isn’t asking for additional efficacy and safety data. In phase 3 testing, zolbetuximab improved median progression-free and overall survival by about 2-3 months over chemotherapy alone.
If zolbetuximab is approved, “pathologists will have to be facile with claudin 18.2 testing as a companion diagnostic before [it] can be used,” Mark Lewis, MD, a gastrointestinal oncologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah, told this news organization.
The agent is also under review in Japan, Europe, and China.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
the company announced January 8.
The monoclonal antibody was under priority review as the first agent specifically for locally advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma that is claudin 18.2-positive. Overexpression of claudin 18.2 in gastric cancer cells is associated with tumor growth and progression.
The FDA, however, could not approve zolbetuximab by the planned decision date of January 12, 2024, because of “unresolved deficiencies following its pre-license inspection of a third-party manufacturing facility for zolbetuximab,” according to the company press release.
Astellas “is working closely with the FDA and the third-party manufacturer to establish a timeline to quickly resolve” the issues, the company said.
Astellas also clarified that the FDA isn’t asking for additional efficacy and safety data. In phase 3 testing, zolbetuximab improved median progression-free and overall survival by about 2-3 months over chemotherapy alone.
If zolbetuximab is approved, “pathologists will have to be facile with claudin 18.2 testing as a companion diagnostic before [it] can be used,” Mark Lewis, MD, a gastrointestinal oncologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah, told this news organization.
The agent is also under review in Japan, Europe, and China.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.