User login
Dupilumab for Dyshidrotic Eczema With Secondary Improvement in Eosinophilic Interstitial Lung Disease
To the Editor:
Biologic medications are increasingly utilized in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) that is inadequately controlled with topical medication. By targeting the IL-4 receptor alpha subunit, dupilumab inhibits the biologic effects of IL-4 and IL-13, resulting in remarkable improvement in disease and quality of life for many patients with refractory AD.1
In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration approved dupilumab for use in AD, asthma, and chronic rhinosinusitis. However, there is evidence of the drug’s off-label efficacy in conditions such as eosinophilic annular erythema.2 We present a patient with dyshidrotic eczema treated with dupilumab who experienced contemporaneous secondary improvement in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) and interstitial lung disease (ILD).
A 45-year-old man was referred to our dermatology clinic for chronic hand dermatitis refractory to increasing strengths of topical corticosteroids. He had a history of progressive shortness of breath of unknown cause, which began 2 years prior, and he was being followed at our institution’s ILD clinic. Earlier pulmonary function testing revealed a restrictive pattern with interstitial infiltrates seen on chest computed tomography. A lung biopsy demonstrated features of fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis with superimposed eosinophilic pneumonia. His pulmonary symptoms had progressively worsened; over a period of several months, the supplemental oxygen requirement had increased to 6 L at rest and 12 L upon exertion. Prednisone therapy was initiated, which alleviated respiratory symptoms; however, the patient was unable to tolerate a gradual wean of the medication, which rendered him steroid dependent at 30 mg/d.
Along with respiratory symptoms, the patient reported symptoms consistent with an autoimmune process, including dry eyes. Muscle weakness and tenderness also were noted. Ultimately, a diagnosis of anti–PL-7 (anti-threonyl-transfer RNA synthetase) antisynthetase syndrome was rendered by identification of anti–PL-7 antibodies and an elevated level of creatinine kinase.
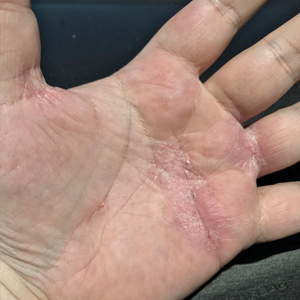
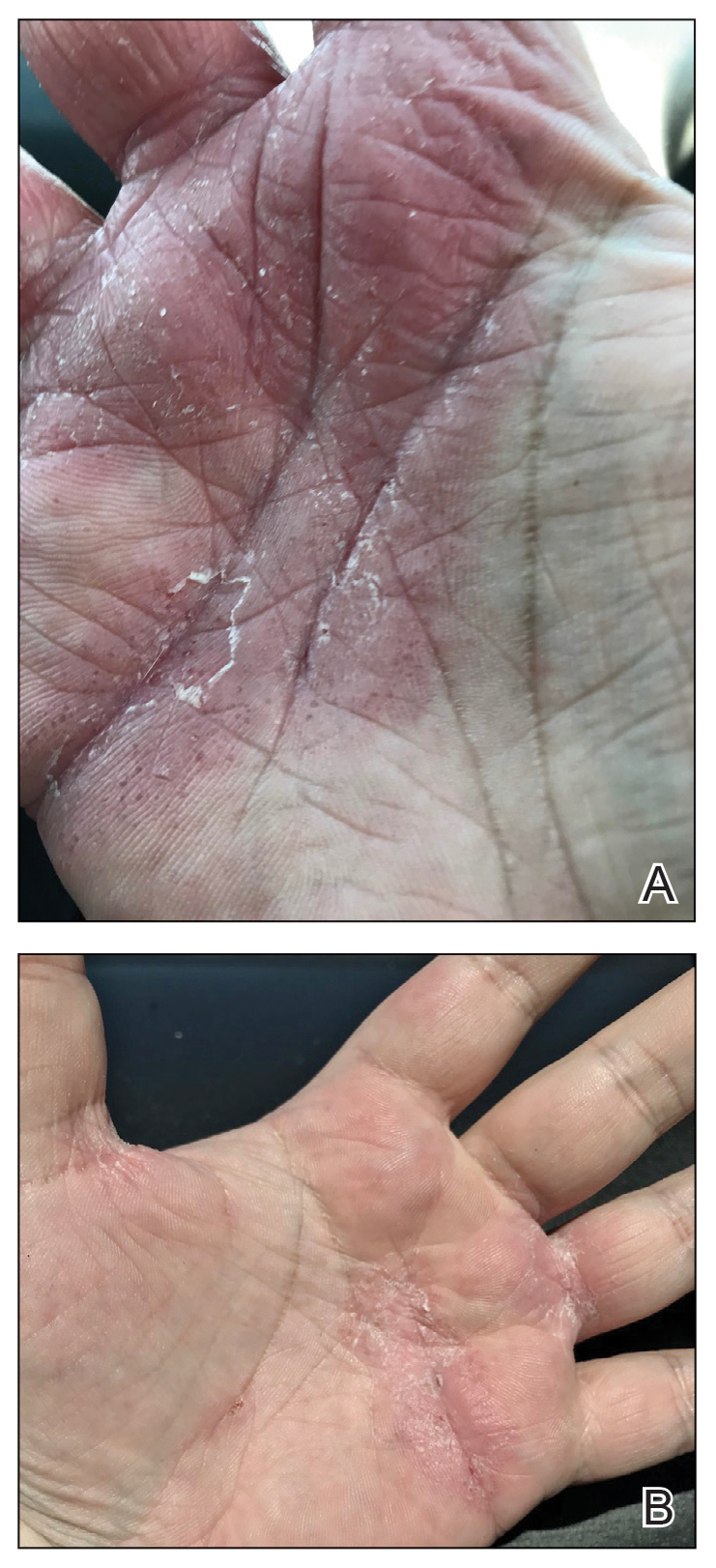
Physical examination at our clinic revealed subtle palmar scaling on the hands and multiple small clear vesicles on the lateral aspects of the digits (Figure, A), consistent with dyshidrotic eczema. He initially was treated with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05%. Despite adherence to this high-potency topical corticosteroid, he experienced only minimal improvement over a period of 3 months. Dupilumab was started at standard dosing—600 mg at initiation, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. The patient reported rapid improvement in dyshidrotic eczema over several months with near-complete resolution (Figure, B).
Concurrent with initiation and continued use of dupilumab, without other changes in his medication regimen, the patient noted gradual improvement in respiratory symptoms. At 6-month follow-up he reported notable improvement in respiratory function and quality of life. He then tolerated a gradual wean of prednisone to 10 mg/d, with a similar reduction in supplemental oxygen.
Off-label use of dupilumab for various eosinophilic conditions has shown promising efficacy. Our patient experienced improvement in CEP shortly after initiation of dupilumab, enabling weaning of prednisone, which has a well established adverse effect profile associated with long term use.3,4 In comparison, dupilumab generally is well tolerated, with rare ophthalmologic complications and injection-site reactions.5
One case report suggested that CEP may represent a potential rare adverse effect of dupilumab initiation.6 However, prior to initiation of dupilumab, that patient had poorly controlled asthma requiring frequent oral corticosteroid therapy. It is possible that CEP was subclinical prior to initiation of dupilumab and became more noticeable once the patient was weaned from corticosteroids, which had served as an indirect treatment.6 Nonetheless, more research is needed to definitively establish the efficacy of dupilumab in CEP prior to more widespread use.
Irrespective of the potential efficacy of dupilumab for the treatment of CEP, our case highlights the growing body of evidence that dupilumab should be considered in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema, particularly in cases refractory to topical treatment.7 When a systemic medication is preferred, dupilumab likely represents an option with a relatively well-tolerated adverse effect profile compared to traditional systemic treatments for dyshidrotic eczema.
1. Barbarot S, Wollenberg A, Silverberg JI, et al. Dupilumab provides rapid and sustained improvement in SCORAD outcomes in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: combined results ofour randomized phase 3 trials. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:266-277. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1750550
2. Gordon SC, Robinson SN, Abudu M, et al. Eosinophilic annular erythema treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E255-E256. doi:10.1111/pde.13533
3. Callaghan DJ 3rd. Use of Google Trends to examine interest in Mohs micrographic surgery: 2004 to 2016. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:186-192. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001270
4. Fowler C, Hoover W. Dupilumab for chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020;55:3229-3230. doi:10.1002/ppul.25096
5. Simpson EL, Akinlade B, Ardeleanu M. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1090-1091. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1700366
6. Menzella F, Montanari G, Patricelli G, et al. A case of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia in a patient treated with dupilumab. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019;15:869-875. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S207402
7. Waldman RA, DeWane ME, Sloan B, et al. Dupilumab for the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema in 15 consecutive patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1251-1252. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.053
To the Editor:
Biologic medications are increasingly utilized in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) that is inadequately controlled with topical medication. By targeting the IL-4 receptor alpha subunit, dupilumab inhibits the biologic effects of IL-4 and IL-13, resulting in remarkable improvement in disease and quality of life for many patients with refractory AD.1
In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration approved dupilumab for use in AD, asthma, and chronic rhinosinusitis. However, there is evidence of the drug’s off-label efficacy in conditions such as eosinophilic annular erythema.2 We present a patient with dyshidrotic eczema treated with dupilumab who experienced contemporaneous secondary improvement in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) and interstitial lung disease (ILD).
A 45-year-old man was referred to our dermatology clinic for chronic hand dermatitis refractory to increasing strengths of topical corticosteroids. He had a history of progressive shortness of breath of unknown cause, which began 2 years prior, and he was being followed at our institution’s ILD clinic. Earlier pulmonary function testing revealed a restrictive pattern with interstitial infiltrates seen on chest computed tomography. A lung biopsy demonstrated features of fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis with superimposed eosinophilic pneumonia. His pulmonary symptoms had progressively worsened; over a period of several months, the supplemental oxygen requirement had increased to 6 L at rest and 12 L upon exertion. Prednisone therapy was initiated, which alleviated respiratory symptoms; however, the patient was unable to tolerate a gradual wean of the medication, which rendered him steroid dependent at 30 mg/d.
Along with respiratory symptoms, the patient reported symptoms consistent with an autoimmune process, including dry eyes. Muscle weakness and tenderness also were noted. Ultimately, a diagnosis of anti–PL-7 (anti-threonyl-transfer RNA synthetase) antisynthetase syndrome was rendered by identification of anti–PL-7 antibodies and an elevated level of creatinine kinase.
Physical examination at our clinic revealed subtle palmar scaling on the hands and multiple small clear vesicles on the lateral aspects of the digits (Figure, A), consistent with dyshidrotic eczema. He initially was treated with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05%. Despite adherence to this high-potency topical corticosteroid, he experienced only minimal improvement over a period of 3 months. Dupilumab was started at standard dosing—600 mg at initiation, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. The patient reported rapid improvement in dyshidrotic eczema over several months with near-complete resolution (Figure, B).

Concurrent with initiation and continued use of dupilumab, without other changes in his medication regimen, the patient noted gradual improvement in respiratory symptoms. At 6-month follow-up he reported notable improvement in respiratory function and quality of life. He then tolerated a gradual wean of prednisone to 10 mg/d, with a similar reduction in supplemental oxygen.
Off-label use of dupilumab for various eosinophilic conditions has shown promising efficacy. Our patient experienced improvement in CEP shortly after initiation of dupilumab, enabling weaning of prednisone, which has a well established adverse effect profile associated with long term use.3,4 In comparison, dupilumab generally is well tolerated, with rare ophthalmologic complications and injection-site reactions.5
One case report suggested that CEP may represent a potential rare adverse effect of dupilumab initiation.6 However, prior to initiation of dupilumab, that patient had poorly controlled asthma requiring frequent oral corticosteroid therapy. It is possible that CEP was subclinical prior to initiation of dupilumab and became more noticeable once the patient was weaned from corticosteroids, which had served as an indirect treatment.6 Nonetheless, more research is needed to definitively establish the efficacy of dupilumab in CEP prior to more widespread use.
Irrespective of the potential efficacy of dupilumab for the treatment of CEP, our case highlights the growing body of evidence that dupilumab should be considered in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema, particularly in cases refractory to topical treatment.7 When a systemic medication is preferred, dupilumab likely represents an option with a relatively well-tolerated adverse effect profile compared to traditional systemic treatments for dyshidrotic eczema.
To the Editor:
Biologic medications are increasingly utilized in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) that is inadequately controlled with topical medication. By targeting the IL-4 receptor alpha subunit, dupilumab inhibits the biologic effects of IL-4 and IL-13, resulting in remarkable improvement in disease and quality of life for many patients with refractory AD.1
In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration approved dupilumab for use in AD, asthma, and chronic rhinosinusitis. However, there is evidence of the drug’s off-label efficacy in conditions such as eosinophilic annular erythema.2 We present a patient with dyshidrotic eczema treated with dupilumab who experienced contemporaneous secondary improvement in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) and interstitial lung disease (ILD).
A 45-year-old man was referred to our dermatology clinic for chronic hand dermatitis refractory to increasing strengths of topical corticosteroids. He had a history of progressive shortness of breath of unknown cause, which began 2 years prior, and he was being followed at our institution’s ILD clinic. Earlier pulmonary function testing revealed a restrictive pattern with interstitial infiltrates seen on chest computed tomography. A lung biopsy demonstrated features of fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis with superimposed eosinophilic pneumonia. His pulmonary symptoms had progressively worsened; over a period of several months, the supplemental oxygen requirement had increased to 6 L at rest and 12 L upon exertion. Prednisone therapy was initiated, which alleviated respiratory symptoms; however, the patient was unable to tolerate a gradual wean of the medication, which rendered him steroid dependent at 30 mg/d.
Along with respiratory symptoms, the patient reported symptoms consistent with an autoimmune process, including dry eyes. Muscle weakness and tenderness also were noted. Ultimately, a diagnosis of anti–PL-7 (anti-threonyl-transfer RNA synthetase) antisynthetase syndrome was rendered by identification of anti–PL-7 antibodies and an elevated level of creatinine kinase.
Physical examination at our clinic revealed subtle palmar scaling on the hands and multiple small clear vesicles on the lateral aspects of the digits (Figure, A), consistent with dyshidrotic eczema. He initially was treated with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05%. Despite adherence to this high-potency topical corticosteroid, he experienced only minimal improvement over a period of 3 months. Dupilumab was started at standard dosing—600 mg at initiation, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. The patient reported rapid improvement in dyshidrotic eczema over several months with near-complete resolution (Figure, B).

Concurrent with initiation and continued use of dupilumab, without other changes in his medication regimen, the patient noted gradual improvement in respiratory symptoms. At 6-month follow-up he reported notable improvement in respiratory function and quality of life. He then tolerated a gradual wean of prednisone to 10 mg/d, with a similar reduction in supplemental oxygen.
Off-label use of dupilumab for various eosinophilic conditions has shown promising efficacy. Our patient experienced improvement in CEP shortly after initiation of dupilumab, enabling weaning of prednisone, which has a well established adverse effect profile associated with long term use.3,4 In comparison, dupilumab generally is well tolerated, with rare ophthalmologic complications and injection-site reactions.5
One case report suggested that CEP may represent a potential rare adverse effect of dupilumab initiation.6 However, prior to initiation of dupilumab, that patient had poorly controlled asthma requiring frequent oral corticosteroid therapy. It is possible that CEP was subclinical prior to initiation of dupilumab and became more noticeable once the patient was weaned from corticosteroids, which had served as an indirect treatment.6 Nonetheless, more research is needed to definitively establish the efficacy of dupilumab in CEP prior to more widespread use.
Irrespective of the potential efficacy of dupilumab for the treatment of CEP, our case highlights the growing body of evidence that dupilumab should be considered in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema, particularly in cases refractory to topical treatment.7 When a systemic medication is preferred, dupilumab likely represents an option with a relatively well-tolerated adverse effect profile compared to traditional systemic treatments for dyshidrotic eczema.
1. Barbarot S, Wollenberg A, Silverberg JI, et al. Dupilumab provides rapid and sustained improvement in SCORAD outcomes in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: combined results ofour randomized phase 3 trials. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:266-277. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1750550
2. Gordon SC, Robinson SN, Abudu M, et al. Eosinophilic annular erythema treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E255-E256. doi:10.1111/pde.13533
3. Callaghan DJ 3rd. Use of Google Trends to examine interest in Mohs micrographic surgery: 2004 to 2016. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:186-192. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001270
4. Fowler C, Hoover W. Dupilumab for chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020;55:3229-3230. doi:10.1002/ppul.25096
5. Simpson EL, Akinlade B, Ardeleanu M. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1090-1091. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1700366
6. Menzella F, Montanari G, Patricelli G, et al. A case of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia in a patient treated with dupilumab. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019;15:869-875. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S207402
7. Waldman RA, DeWane ME, Sloan B, et al. Dupilumab for the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema in 15 consecutive patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1251-1252. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.053
1. Barbarot S, Wollenberg A, Silverberg JI, et al. Dupilumab provides rapid and sustained improvement in SCORAD outcomes in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: combined results ofour randomized phase 3 trials. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:266-277. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1750550
2. Gordon SC, Robinson SN, Abudu M, et al. Eosinophilic annular erythema treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E255-E256. doi:10.1111/pde.13533
3. Callaghan DJ 3rd. Use of Google Trends to examine interest in Mohs micrographic surgery: 2004 to 2016. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:186-192. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001270
4. Fowler C, Hoover W. Dupilumab for chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020;55:3229-3230. doi:10.1002/ppul.25096
5. Simpson EL, Akinlade B, Ardeleanu M. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1090-1091. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1700366
6. Menzella F, Montanari G, Patricelli G, et al. A case of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia in a patient treated with dupilumab. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019;15:869-875. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S207402
7. Waldman RA, DeWane ME, Sloan B, et al. Dupilumab for the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema in 15 consecutive patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1251-1252. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.053
Practice Points
- Dupilumab can be considered for treatment of refractory dyshidrotic eczema.
- Dupilumab may provide secondary efficacy in patients with dyshidrotic eczema who also have an eosinophilic condition such as eosinophilic pneumonia.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Care for Patients With Atopic Dermatitis
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a widely prevalent dermatologic condition that can severely impact a patient’s quality of life.1 Individuals with AD have been substantially affected during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the increased use of irritants, decreased access to care, and rise in psychological stress.1,2 These factors have resulted in lower quality of life and worsening dermatologic symptoms for many AD patients over the last few years.1 One major potential contributory component of these findings is decreased accessibility to in-office care during the pandemic, with a shift to telemedicine instead. Accessibility to care during the COVID-19 pandemic for AD patients compared to those without AD remains unknown. Therefore, we explored the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on care for patients with AD in a large US population.
Using anonymous survey data from the 2021 National Health Interview Survey,3 we conducted a population-based, cross-sectional study to evaluate access to care during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with AD compared to those without AD. We assigned the following 3 survey questions as outcome variables to assess access to care: delayed medical care due to COVID-19 pandemic (yes/no), did not get care due to COVID-19 pandemic (yes/no), and virtual medical appointment in the last 12 months (yes/no). In Table 1, numerous categorical survey variables, including sex, health insurance status, race/ethnicity, education, US citizenship, birth in the United States, public assistance/welfare, and region, were analyzed using χ2 testing to evaluate for differences among individuals with and without AD. Multivariable logistic regression models evaluating the relationship between AD and access to care were constructed using Stata/MP 17 (StataCorp LLC). In our analysis we controlled for age, sex, health insurance status, race/ethnicity, education, US citizenship, birth in the United States, public assistance/welfare, and region.
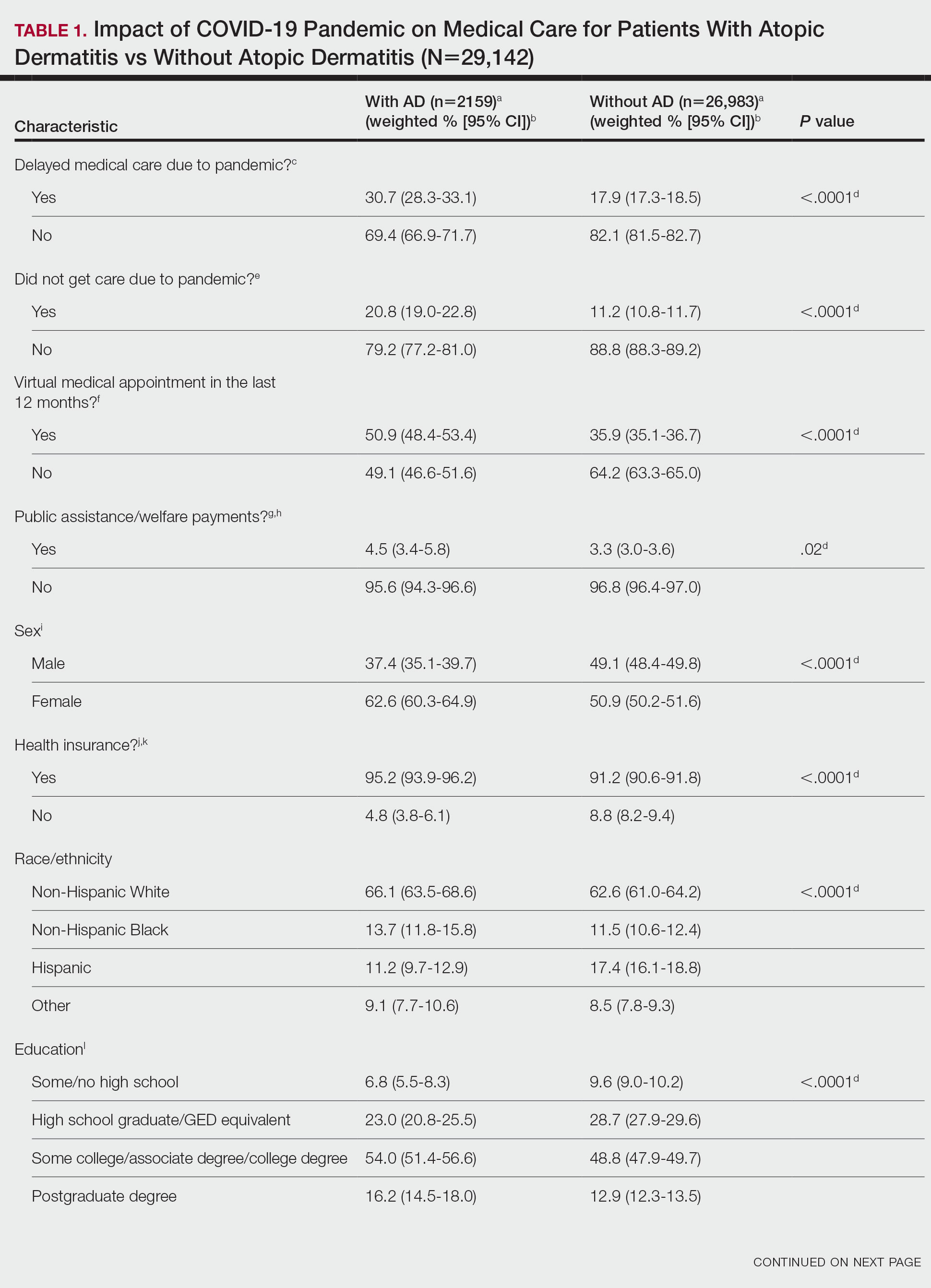
There were 29,142 adult patients (aged ≥18 years) included in our analysis. Approximately 7.4% (weighted) of individuals had AD (Table 1). After adjusting for confounding variables, patients with AD had a higher odds of delaying medical care due to the COVID-19 pandemic (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.69-2.16; P<.001), not receiving care due to the COVID-19 pandemic (AOR, 1.94; 95% CI, 1.71-2.22; P<.001), and having a virtual medical visit in the last 12 months (AOR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.54-1.93; P<.001)(Table 2) compared with patients without AD.
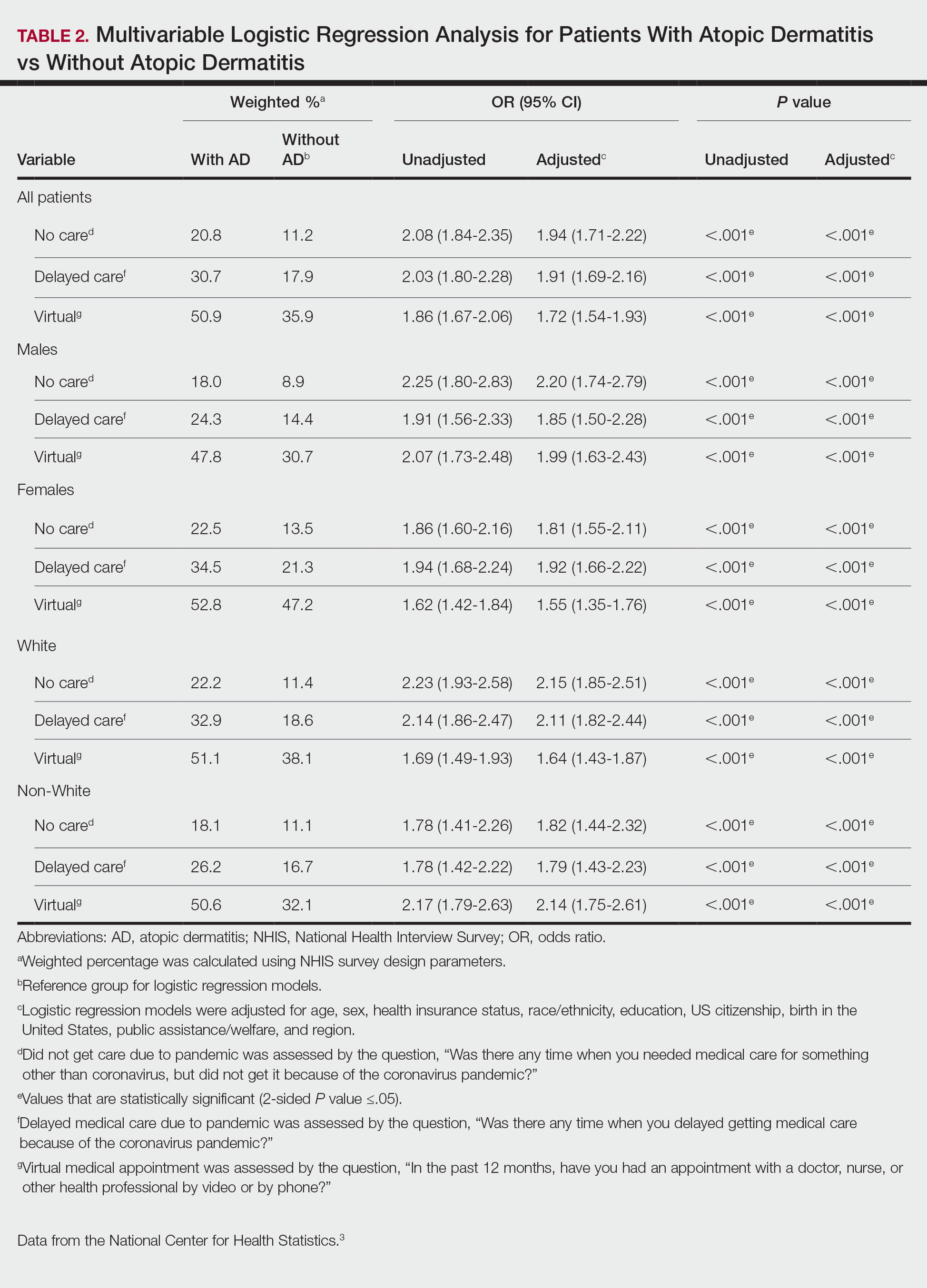
Our findings support the association between AD and decreased access to in-person care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, telemedicine was utilized more among individuals with AD, possibly due to the accessibility of diagnostic tools for dermatologic diagnoses, such as high-quality photographs.4 According to Trinidad et al,4 telemedicine became an invaluable tool for dermatology hospitalists during the COVID-19 pandemic, as many physicians were able to comfortably diagnose patients with cutaneous diseases without an in-person visit. Utilizing telemedicine for patient care can help reduce the risk for COVID-19 transmission while also providing quality care for individuals living in rural areas.5 Chiricozzi et al6 discussed the importance of telemedicine in Italy during the pandemic, as many AD patients were able to maintain control of their disease while on systemic treatments.
Limitations of this study include self-reported measures; inability to compare patients with AD to individuals with other cutaneous diseases; and additional potential confounders, such as chronic comorbidities. Future studies should evaluate the use of telemedicine and access to care among individuals with other common skin diseases and help determine why such discrepancies exist. Understanding the difficulties in access to care and the viable alternatives in place may increase awareness and assist clinicians with adequate management of patients with AD.
1. Sieniawska J, Lesiak A, Cia˛z˙yn´ski K, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on atopic dermatitis patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:1734. doi:10.3390/ijerph19031734
2. Pourani MR, Ganji R, Dashti T, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on patients with atopic dermatitis [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:T286-T293. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2021.08.004
3. National Center for Health Statistics. NHIS Data, Questionnaires and Related Documentation. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/data-questionnaires-documentation.htm
4. Trinidad J, Gabel CK, Han JJ, et al. Telemedicine and dermatology hospital consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-centre observational study on resource utilization and conversion to in-person consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:E323-E325. doi:10.1111/jdv.17898
5. Marasca C, Annunziata MC, Camela E, et al. Teledermatology and inflammatory skin conditions during COVID-19 era: new perspectives and applications. J Clin Med. 2022;11:1511. doi:10.3390/jcm11061511
6. Chiricozzi A, Talamonti M, De Simone C, et al. Management of patients with atopic dermatitis undergoing systemic therapy during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: data from the DA-COVID-19 registry. Allergy. 2021;76:1813-1824. doi:10.1111/all.14767
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a widely prevalent dermatologic condition that can severely impact a patient’s quality of life.1 Individuals with AD have been substantially affected during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the increased use of irritants, decreased access to care, and rise in psychological stress.1,2 These factors have resulted in lower quality of life and worsening dermatologic symptoms for many AD patients over the last few years.1 One major potential contributory component of these findings is decreased accessibility to in-office care during the pandemic, with a shift to telemedicine instead. Accessibility to care during the COVID-19 pandemic for AD patients compared to those without AD remains unknown. Therefore, we explored the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on care for patients with AD in a large US population.
Using anonymous survey data from the 2021 National Health Interview Survey,3 we conducted a population-based, cross-sectional study to evaluate access to care during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with AD compared to those without AD. We assigned the following 3 survey questions as outcome variables to assess access to care: delayed medical care due to COVID-19 pandemic (yes/no), did not get care due to COVID-19 pandemic (yes/no), and virtual medical appointment in the last 12 months (yes/no). In Table 1, numerous categorical survey variables, including sex, health insurance status, race/ethnicity, education, US citizenship, birth in the United States, public assistance/welfare, and region, were analyzed using χ2 testing to evaluate for differences among individuals with and without AD. Multivariable logistic regression models evaluating the relationship between AD and access to care were constructed using Stata/MP 17 (StataCorp LLC). In our analysis we controlled for age, sex, health insurance status, race/ethnicity, education, US citizenship, birth in the United States, public assistance/welfare, and region.


There were 29,142 adult patients (aged ≥18 years) included in our analysis. Approximately 7.4% (weighted) of individuals had AD (Table 1). After adjusting for confounding variables, patients with AD had a higher odds of delaying medical care due to the COVID-19 pandemic (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.69-2.16; P<.001), not receiving care due to the COVID-19 pandemic (AOR, 1.94; 95% CI, 1.71-2.22; P<.001), and having a virtual medical visit in the last 12 months (AOR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.54-1.93; P<.001)(Table 2) compared with patients without AD.

Our findings support the association between AD and decreased access to in-person care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, telemedicine was utilized more among individuals with AD, possibly due to the accessibility of diagnostic tools for dermatologic diagnoses, such as high-quality photographs.4 According to Trinidad et al,4 telemedicine became an invaluable tool for dermatology hospitalists during the COVID-19 pandemic, as many physicians were able to comfortably diagnose patients with cutaneous diseases without an in-person visit. Utilizing telemedicine for patient care can help reduce the risk for COVID-19 transmission while also providing quality care for individuals living in rural areas.5 Chiricozzi et al6 discussed the importance of telemedicine in Italy during the pandemic, as many AD patients were able to maintain control of their disease while on systemic treatments.
Limitations of this study include self-reported measures; inability to compare patients with AD to individuals with other cutaneous diseases; and additional potential confounders, such as chronic comorbidities. Future studies should evaluate the use of telemedicine and access to care among individuals with other common skin diseases and help determine why such discrepancies exist. Understanding the difficulties in access to care and the viable alternatives in place may increase awareness and assist clinicians with adequate management of patients with AD.
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a widely prevalent dermatologic condition that can severely impact a patient’s quality of life.1 Individuals with AD have been substantially affected during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the increased use of irritants, decreased access to care, and rise in psychological stress.1,2 These factors have resulted in lower quality of life and worsening dermatologic symptoms for many AD patients over the last few years.1 One major potential contributory component of these findings is decreased accessibility to in-office care during the pandemic, with a shift to telemedicine instead. Accessibility to care during the COVID-19 pandemic for AD patients compared to those without AD remains unknown. Therefore, we explored the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on care for patients with AD in a large US population.
Using anonymous survey data from the 2021 National Health Interview Survey,3 we conducted a population-based, cross-sectional study to evaluate access to care during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with AD compared to those without AD. We assigned the following 3 survey questions as outcome variables to assess access to care: delayed medical care due to COVID-19 pandemic (yes/no), did not get care due to COVID-19 pandemic (yes/no), and virtual medical appointment in the last 12 months (yes/no). In Table 1, numerous categorical survey variables, including sex, health insurance status, race/ethnicity, education, US citizenship, birth in the United States, public assistance/welfare, and region, were analyzed using χ2 testing to evaluate for differences among individuals with and without AD. Multivariable logistic regression models evaluating the relationship between AD and access to care were constructed using Stata/MP 17 (StataCorp LLC). In our analysis we controlled for age, sex, health insurance status, race/ethnicity, education, US citizenship, birth in the United States, public assistance/welfare, and region.


There were 29,142 adult patients (aged ≥18 years) included in our analysis. Approximately 7.4% (weighted) of individuals had AD (Table 1). After adjusting for confounding variables, patients with AD had a higher odds of delaying medical care due to the COVID-19 pandemic (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.69-2.16; P<.001), not receiving care due to the COVID-19 pandemic (AOR, 1.94; 95% CI, 1.71-2.22; P<.001), and having a virtual medical visit in the last 12 months (AOR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.54-1.93; P<.001)(Table 2) compared with patients without AD.

Our findings support the association between AD and decreased access to in-person care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, telemedicine was utilized more among individuals with AD, possibly due to the accessibility of diagnostic tools for dermatologic diagnoses, such as high-quality photographs.4 According to Trinidad et al,4 telemedicine became an invaluable tool for dermatology hospitalists during the COVID-19 pandemic, as many physicians were able to comfortably diagnose patients with cutaneous diseases without an in-person visit. Utilizing telemedicine for patient care can help reduce the risk for COVID-19 transmission while also providing quality care for individuals living in rural areas.5 Chiricozzi et al6 discussed the importance of telemedicine in Italy during the pandemic, as many AD patients were able to maintain control of their disease while on systemic treatments.
Limitations of this study include self-reported measures; inability to compare patients with AD to individuals with other cutaneous diseases; and additional potential confounders, such as chronic comorbidities. Future studies should evaluate the use of telemedicine and access to care among individuals with other common skin diseases and help determine why such discrepancies exist. Understanding the difficulties in access to care and the viable alternatives in place may increase awareness and assist clinicians with adequate management of patients with AD.
1. Sieniawska J, Lesiak A, Cia˛z˙yn´ski K, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on atopic dermatitis patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:1734. doi:10.3390/ijerph19031734
2. Pourani MR, Ganji R, Dashti T, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on patients with atopic dermatitis [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:T286-T293. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2021.08.004
3. National Center for Health Statistics. NHIS Data, Questionnaires and Related Documentation. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/data-questionnaires-documentation.htm
4. Trinidad J, Gabel CK, Han JJ, et al. Telemedicine and dermatology hospital consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-centre observational study on resource utilization and conversion to in-person consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:E323-E325. doi:10.1111/jdv.17898
5. Marasca C, Annunziata MC, Camela E, et al. Teledermatology and inflammatory skin conditions during COVID-19 era: new perspectives and applications. J Clin Med. 2022;11:1511. doi:10.3390/jcm11061511
6. Chiricozzi A, Talamonti M, De Simone C, et al. Management of patients with atopic dermatitis undergoing systemic therapy during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: data from the DA-COVID-19 registry. Allergy. 2021;76:1813-1824. doi:10.1111/all.14767
1. Sieniawska J, Lesiak A, Cia˛z˙yn´ski K, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on atopic dermatitis patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:1734. doi:10.3390/ijerph19031734
2. Pourani MR, Ganji R, Dashti T, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on patients with atopic dermatitis [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:T286-T293. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2021.08.004
3. National Center for Health Statistics. NHIS Data, Questionnaires and Related Documentation. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/data-questionnaires-documentation.htm
4. Trinidad J, Gabel CK, Han JJ, et al. Telemedicine and dermatology hospital consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-centre observational study on resource utilization and conversion to in-person consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:E323-E325. doi:10.1111/jdv.17898
5. Marasca C, Annunziata MC, Camela E, et al. Teledermatology and inflammatory skin conditions during COVID-19 era: new perspectives and applications. J Clin Med. 2022;11:1511. doi:10.3390/jcm11061511
6. Chiricozzi A, Talamonti M, De Simone C, et al. Management of patients with atopic dermatitis undergoing systemic therapy during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: data from the DA-COVID-19 registry. Allergy. 2021;76:1813-1824. doi:10.1111/all.14767
Practice Points
- The landscape of dermatology has seen major changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic, as many patients now utilize telemedicine to receive care.
- Understanding accessibility to in-person care for patients with atopic dermatitis during the COVID-19 pandemic can assist with the development of methods to enhance management.
Factors influencing clinical response to dupilumab treatment in AD
Key clinical point: Patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) presenting with classic or generalized lichenoid and inflammatory phenotypes vs other non-classic phenotypes and with Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores < 29 vs ≥ 29 showed an early response to dupilumab by achieving a mild disease state.
Major finding: Factors with a significant predictive value for an early response to dupilumab included the classic phenotype (odds ratio [OR] 6.92; 95% CI 2.04-23.48) or generalized lichenoid and inflammatory phenotypes (OR 4.22; 95% CI 1.22-14.66) vs the nummular eczema phenotype and a baseline EASI score of ≤ 24 (OR 3.13; 95% CI 1.81-5.41) or 24-29 (OR 1.79; 95% CI 1.05-3.07) vs ≥ 29.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective single-center observational study including 492 patients (age > 12 years) with moderate-to-severe AD treated with dupilumab.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. S Ferrucci and AV Marzano declared serving as speakers or advisory board members of various organizations. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ferrucci S et al. Predictive factors of early response to dupilumab in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(20):6575 (Oct 17). doi: 10.3390/jcm12206575.
Key clinical point: Patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) presenting with classic or generalized lichenoid and inflammatory phenotypes vs other non-classic phenotypes and with Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores < 29 vs ≥ 29 showed an early response to dupilumab by achieving a mild disease state.
Major finding: Factors with a significant predictive value for an early response to dupilumab included the classic phenotype (odds ratio [OR] 6.92; 95% CI 2.04-23.48) or generalized lichenoid and inflammatory phenotypes (OR 4.22; 95% CI 1.22-14.66) vs the nummular eczema phenotype and a baseline EASI score of ≤ 24 (OR 3.13; 95% CI 1.81-5.41) or 24-29 (OR 1.79; 95% CI 1.05-3.07) vs ≥ 29.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective single-center observational study including 492 patients (age > 12 years) with moderate-to-severe AD treated with dupilumab.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. S Ferrucci and AV Marzano declared serving as speakers or advisory board members of various organizations. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ferrucci S et al. Predictive factors of early response to dupilumab in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(20):6575 (Oct 17). doi: 10.3390/jcm12206575.
Key clinical point: Patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) presenting with classic or generalized lichenoid and inflammatory phenotypes vs other non-classic phenotypes and with Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores < 29 vs ≥ 29 showed an early response to dupilumab by achieving a mild disease state.
Major finding: Factors with a significant predictive value for an early response to dupilumab included the classic phenotype (odds ratio [OR] 6.92; 95% CI 2.04-23.48) or generalized lichenoid and inflammatory phenotypes (OR 4.22; 95% CI 1.22-14.66) vs the nummular eczema phenotype and a baseline EASI score of ≤ 24 (OR 3.13; 95% CI 1.81-5.41) or 24-29 (OR 1.79; 95% CI 1.05-3.07) vs ≥ 29.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective single-center observational study including 492 patients (age > 12 years) with moderate-to-severe AD treated with dupilumab.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. S Ferrucci and AV Marzano declared serving as speakers or advisory board members of various organizations. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ferrucci S et al. Predictive factors of early response to dupilumab in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(20):6575 (Oct 17). doi: 10.3390/jcm12206575.
Adults with moderate-to-severe AD are prone to renal malignancy
Key clinical point: Adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) are at a significantly higher risk for renal malignancy, with the risk for overall malignancy being higher in adults with AD regardless of the disease severity.
Major finding: Compared with adults without AD, those with moderate-to-severe AD had a significantly increased risk for renal malignancy (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.533; 95% CI 1.209-1.944); moreover, the risk for overall malignancy was higher in adults with mild (aHR 1.061; 95% CI 1.006-1.118) and moderate-to-severe (aHR 1.061; 95% CI 1.014-1.110) AD.
Study details: Findings are from a population-based cohort study including 22,430 adults with mild AD, 34,187 adults with moderate-to-severe AD, and 3,810,530 adults without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Oh J et al. Increased risk of renal malignancy in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(20):5007 (Oct 16). doi: 10.3390/cancers15205007
Key clinical point: Adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) are at a significantly higher risk for renal malignancy, with the risk for overall malignancy being higher in adults with AD regardless of the disease severity.
Major finding: Compared with adults without AD, those with moderate-to-severe AD had a significantly increased risk for renal malignancy (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.533; 95% CI 1.209-1.944); moreover, the risk for overall malignancy was higher in adults with mild (aHR 1.061; 95% CI 1.006-1.118) and moderate-to-severe (aHR 1.061; 95% CI 1.014-1.110) AD.
Study details: Findings are from a population-based cohort study including 22,430 adults with mild AD, 34,187 adults with moderate-to-severe AD, and 3,810,530 adults without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Oh J et al. Increased risk of renal malignancy in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(20):5007 (Oct 16). doi: 10.3390/cancers15205007
Key clinical point: Adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) are at a significantly higher risk for renal malignancy, with the risk for overall malignancy being higher in adults with AD regardless of the disease severity.
Major finding: Compared with adults without AD, those with moderate-to-severe AD had a significantly increased risk for renal malignancy (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.533; 95% CI 1.209-1.944); moreover, the risk for overall malignancy was higher in adults with mild (aHR 1.061; 95% CI 1.006-1.118) and moderate-to-severe (aHR 1.061; 95% CI 1.014-1.110) AD.
Study details: Findings are from a population-based cohort study including 22,430 adults with mild AD, 34,187 adults with moderate-to-severe AD, and 3,810,530 adults without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Oh J et al. Increased risk of renal malignancy in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(20):5007 (Oct 16). doi: 10.3390/cancers15205007
Meta-analysis evaluates the comparative efficacy of systemic immunomodulators against AD
Key clinical point: The binary outcomes of atopic dermatitis (AD) were most effectively improved up to week 16 by 30 mg upadacitinib daily and 200 mg abrocitinib daily, followed by 15 mg upadacitinib daily, and 600 mg dupilumab and subsequently 300 mg dupilumab every 2 weeks.
Major finding: The odds of achieving 50% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index scores were higher with daily doses of 200 mg abrocitinib (odds ratio [OR] 1.5, 95% credible interval [CrI] 1.1-2.2), 30 mg upadacitinib (OR 2.5, 95% CrI 1.3-5.0), and 15 mg upadacitinib (OR 1.7; 95% CrI 0.9-3.3) and lower with 100 mg abrocitinib daily (OR 0.7; 95% CrI 0.5-1.0) and 4 mg baricitinib daily (OR 0.5; 95% CrI 0.3-0.7) compared with dupilumab every 2 weeks.
Study details: This network meta-analysis of 83 trials included 22,122 patients with moderate-to-severe AD receiving systemic immunomodulatory treatment for ≥8 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by a UK National Institute for Health Research Career Development Fellowship held by C Flohr and other funds. Seven authors declared ties with various sources.
Source: Drucker AM et al. Comparing binary efficacy outcomes for systemic immunomodulatory treatments for atopic dermatitis in a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 13). doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad393
Key clinical point: The binary outcomes of atopic dermatitis (AD) were most effectively improved up to week 16 by 30 mg upadacitinib daily and 200 mg abrocitinib daily, followed by 15 mg upadacitinib daily, and 600 mg dupilumab and subsequently 300 mg dupilumab every 2 weeks.
Major finding: The odds of achieving 50% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index scores were higher with daily doses of 200 mg abrocitinib (odds ratio [OR] 1.5, 95% credible interval [CrI] 1.1-2.2), 30 mg upadacitinib (OR 2.5, 95% CrI 1.3-5.0), and 15 mg upadacitinib (OR 1.7; 95% CrI 0.9-3.3) and lower with 100 mg abrocitinib daily (OR 0.7; 95% CrI 0.5-1.0) and 4 mg baricitinib daily (OR 0.5; 95% CrI 0.3-0.7) compared with dupilumab every 2 weeks.
Study details: This network meta-analysis of 83 trials included 22,122 patients with moderate-to-severe AD receiving systemic immunomodulatory treatment for ≥8 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by a UK National Institute for Health Research Career Development Fellowship held by C Flohr and other funds. Seven authors declared ties with various sources.
Source: Drucker AM et al. Comparing binary efficacy outcomes for systemic immunomodulatory treatments for atopic dermatitis in a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 13). doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad393
Key clinical point: The binary outcomes of atopic dermatitis (AD) were most effectively improved up to week 16 by 30 mg upadacitinib daily and 200 mg abrocitinib daily, followed by 15 mg upadacitinib daily, and 600 mg dupilumab and subsequently 300 mg dupilumab every 2 weeks.
Major finding: The odds of achieving 50% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index scores were higher with daily doses of 200 mg abrocitinib (odds ratio [OR] 1.5, 95% credible interval [CrI] 1.1-2.2), 30 mg upadacitinib (OR 2.5, 95% CrI 1.3-5.0), and 15 mg upadacitinib (OR 1.7; 95% CrI 0.9-3.3) and lower with 100 mg abrocitinib daily (OR 0.7; 95% CrI 0.5-1.0) and 4 mg baricitinib daily (OR 0.5; 95% CrI 0.3-0.7) compared with dupilumab every 2 weeks.
Study details: This network meta-analysis of 83 trials included 22,122 patients with moderate-to-severe AD receiving systemic immunomodulatory treatment for ≥8 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by a UK National Institute for Health Research Career Development Fellowship held by C Flohr and other funds. Seven authors declared ties with various sources.
Source: Drucker AM et al. Comparing binary efficacy outcomes for systemic immunomodulatory treatments for atopic dermatitis in a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 13). doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad393
Atopic dermatitis is a potential risk factor for cognitive dysfunction in middle-aged and older adults
Key clinical point: Atopic dermatitis (AD) significantly increases the risk for cognitive dysfunction, particularly that of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease-related dementia, in middle-aged adults (age 45-59 years) and older adults (age ≥60 years).
Major finding: Patients with AD vs control individuals had a significantly higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (pooled hazard ratio [HR] 1.16; 95% CI 1.10-1.23) and Alzheimer’s disease-related dementia (pooled HR 1.28; 95% CI 1.01-1.63). However, no significant association was observed between AD and vascular dementia (pooled HR 1.42; 95% CI 0.99-2.04).
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of five studies including 8,595,252 patients with AD and a corresponding number of control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhou Q et al. Atopic dermatitis and cognitive dysfunction in middle-aged and older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2023;18(10):e0292987 (Oct 25). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292987
Key clinical point: Atopic dermatitis (AD) significantly increases the risk for cognitive dysfunction, particularly that of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease-related dementia, in middle-aged adults (age 45-59 years) and older adults (age ≥60 years).
Major finding: Patients with AD vs control individuals had a significantly higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (pooled hazard ratio [HR] 1.16; 95% CI 1.10-1.23) and Alzheimer’s disease-related dementia (pooled HR 1.28; 95% CI 1.01-1.63). However, no significant association was observed between AD and vascular dementia (pooled HR 1.42; 95% CI 0.99-2.04).
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of five studies including 8,595,252 patients with AD and a corresponding number of control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhou Q et al. Atopic dermatitis and cognitive dysfunction in middle-aged and older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2023;18(10):e0292987 (Oct 25). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292987
Key clinical point: Atopic dermatitis (AD) significantly increases the risk for cognitive dysfunction, particularly that of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease-related dementia, in middle-aged adults (age 45-59 years) and older adults (age ≥60 years).
Major finding: Patients with AD vs control individuals had a significantly higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (pooled hazard ratio [HR] 1.16; 95% CI 1.10-1.23) and Alzheimer’s disease-related dementia (pooled HR 1.28; 95% CI 1.01-1.63). However, no significant association was observed between AD and vascular dementia (pooled HR 1.42; 95% CI 0.99-2.04).
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of five studies including 8,595,252 patients with AD and a corresponding number of control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhou Q et al. Atopic dermatitis and cognitive dysfunction in middle-aged and older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2023;18(10):e0292987 (Oct 25). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292987
Children with atopic dermatitis have a higher risk for multiple comorbidities
Key clinical point: Children with atopic dermatitis (AD) have an increased risk for multiple comorbidities, even beyond atopic disorders, with a positive association between AD severity and the risk for comorbidity onset.
Major finding: In children with vs without AD, the risk for hypersensitivity and allergic disorders was the highest (hazard ratio [HR] 3.87; 95% CI 3.77-3.97), followed by that for malignancies (HR 2.53; 95% CI 1.96-3.26) and immunological and inflammatory disorders (HR 2.36; 95% CI 2.22-2.50). Hypersensitivity onset risk increased in children with mild-to-moderate (adjusted HR 2.71; 95% CI 2.41-3.05) and severe (adjusted HR 3.56; 95% CI 3.10-4.09) AD compared with those in remission.
Study details: This observational, retrospective cohort study included 165,145 children with AD (age < 18 years) who were matched with 165,145 children without AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Some authors declared receiving research grants or consultancy fees from or serving as advisors, investigators, etc., for Pfizer and others. Six authors declared being employees of or holding stock or stock options in Pfizer.
Source: von Kobyletzki L et al. Comorbidities in childhood atopic dermatitis: A population-based study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 (Oct 12). doi: 10.1111/jdv.19569
Key clinical point: Children with atopic dermatitis (AD) have an increased risk for multiple comorbidities, even beyond atopic disorders, with a positive association between AD severity and the risk for comorbidity onset.
Major finding: In children with vs without AD, the risk for hypersensitivity and allergic disorders was the highest (hazard ratio [HR] 3.87; 95% CI 3.77-3.97), followed by that for malignancies (HR 2.53; 95% CI 1.96-3.26) and immunological and inflammatory disorders (HR 2.36; 95% CI 2.22-2.50). Hypersensitivity onset risk increased in children with mild-to-moderate (adjusted HR 2.71; 95% CI 2.41-3.05) and severe (adjusted HR 3.56; 95% CI 3.10-4.09) AD compared with those in remission.
Study details: This observational, retrospective cohort study included 165,145 children with AD (age < 18 years) who were matched with 165,145 children without AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Some authors declared receiving research grants or consultancy fees from or serving as advisors, investigators, etc., for Pfizer and others. Six authors declared being employees of or holding stock or stock options in Pfizer.
Source: von Kobyletzki L et al. Comorbidities in childhood atopic dermatitis: A population-based study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 (Oct 12). doi: 10.1111/jdv.19569
Key clinical point: Children with atopic dermatitis (AD) have an increased risk for multiple comorbidities, even beyond atopic disorders, with a positive association between AD severity and the risk for comorbidity onset.
Major finding: In children with vs without AD, the risk for hypersensitivity and allergic disorders was the highest (hazard ratio [HR] 3.87; 95% CI 3.77-3.97), followed by that for malignancies (HR 2.53; 95% CI 1.96-3.26) and immunological and inflammatory disorders (HR 2.36; 95% CI 2.22-2.50). Hypersensitivity onset risk increased in children with mild-to-moderate (adjusted HR 2.71; 95% CI 2.41-3.05) and severe (adjusted HR 3.56; 95% CI 3.10-4.09) AD compared with those in remission.
Study details: This observational, retrospective cohort study included 165,145 children with AD (age < 18 years) who were matched with 165,145 children without AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Some authors declared receiving research grants or consultancy fees from or serving as advisors, investigators, etc., for Pfizer and others. Six authors declared being employees of or holding stock or stock options in Pfizer.
Source: von Kobyletzki L et al. Comorbidities in childhood atopic dermatitis: A population-based study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 (Oct 12). doi: 10.1111/jdv.19569
Lebrikizumab compared with dupilumab leads to equal or superior long-term outcomes in AD
Key clinical point: Compared with dupilumab, lebrikizumab in less frequent doses shows equal or improved long-term maintenance of efficacy and overall adverse event rates in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Between weeks 16 and 52, patients receiving lebrikizumab every 4 weeks (Q4W) vs dupilumab weekly or biweekly (QW/Q2W) were more likely to maintain Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 or 1 (risk ratio [RR] 1.334; P = .035). Lebrikizumab and dupilumab were comparable in terms of adverse event rates (RR 1.052; P = .526) and maintenance of 75% improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index scores (RR 0.937; P = .490).
Study details: This matching-adjusted indirect comparison study analyzed the data of adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received lebrikizumab Q4W (n = 101) in ADvocate1 and ADvocate2 or dupilumab QW/Q2W (n = 169) in SOLO-CONTINUE and achieved a treatment response at week 16.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Almirall S.A., Spain. Two authors declared being employees of Almirall S.A. The other authors declared ties with various sources, including Almirall.
Source: Rand K et al. Matching-adjusted indirect comparison of the long-term efficacy maintenance and adverse event rates of lebrikizumab versus dupilumab in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 (Oct 28). doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01058-z
Key clinical point: Compared with dupilumab, lebrikizumab in less frequent doses shows equal or improved long-term maintenance of efficacy and overall adverse event rates in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Between weeks 16 and 52, patients receiving lebrikizumab every 4 weeks (Q4W) vs dupilumab weekly or biweekly (QW/Q2W) were more likely to maintain Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 or 1 (risk ratio [RR] 1.334; P = .035). Lebrikizumab and dupilumab were comparable in terms of adverse event rates (RR 1.052; P = .526) and maintenance of 75% improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index scores (RR 0.937; P = .490).
Study details: This matching-adjusted indirect comparison study analyzed the data of adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received lebrikizumab Q4W (n = 101) in ADvocate1 and ADvocate2 or dupilumab QW/Q2W (n = 169) in SOLO-CONTINUE and achieved a treatment response at week 16.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Almirall S.A., Spain. Two authors declared being employees of Almirall S.A. The other authors declared ties with various sources, including Almirall.
Source: Rand K et al. Matching-adjusted indirect comparison of the long-term efficacy maintenance and adverse event rates of lebrikizumab versus dupilumab in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 (Oct 28). doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01058-z
Key clinical point: Compared with dupilumab, lebrikizumab in less frequent doses shows equal or improved long-term maintenance of efficacy and overall adverse event rates in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Between weeks 16 and 52, patients receiving lebrikizumab every 4 weeks (Q4W) vs dupilumab weekly or biweekly (QW/Q2W) were more likely to maintain Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 or 1 (risk ratio [RR] 1.334; P = .035). Lebrikizumab and dupilumab were comparable in terms of adverse event rates (RR 1.052; P = .526) and maintenance of 75% improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index scores (RR 0.937; P = .490).
Study details: This matching-adjusted indirect comparison study analyzed the data of adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received lebrikizumab Q4W (n = 101) in ADvocate1 and ADvocate2 or dupilumab QW/Q2W (n = 169) in SOLO-CONTINUE and achieved a treatment response at week 16.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Almirall S.A., Spain. Two authors declared being employees of Almirall S.A. The other authors declared ties with various sources, including Almirall.
Source: Rand K et al. Matching-adjusted indirect comparison of the long-term efficacy maintenance and adverse event rates of lebrikizumab versus dupilumab in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 (Oct 28). doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01058-z
Study shows bidirectional association between alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: Patients with alopecia areata (AA) have an increased risk for atopic dermatitis (AD) and vice versa.
Major finding: Patients with AA vs control individuals had a significantly higher risk of developing AD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 4.42; P < .001). Reciprocally, patients with AD vs control individuals also had a significantly higher risk of developing AA (aOR 5.08; P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a nested case-control study including 984 patients with AA from the All of Us database (USA), who were matched with 3936 control individuals without AA using nearest neighbor propensity-score matching.
Disclosures: This study did not disclose any funding source. E Guttman-Yassky and B Ungar declared receiving institutional grants from, serving as consultants for, or having other ties with various sources. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Diaz MJ et al. Association between alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis: A nested case-control study of the All of Us database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 21). doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.031
Key clinical point: Patients with alopecia areata (AA) have an increased risk for atopic dermatitis (AD) and vice versa.
Major finding: Patients with AA vs control individuals had a significantly higher risk of developing AD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 4.42; P < .001). Reciprocally, patients with AD vs control individuals also had a significantly higher risk of developing AA (aOR 5.08; P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a nested case-control study including 984 patients with AA from the All of Us database (USA), who were matched with 3936 control individuals without AA using nearest neighbor propensity-score matching.
Disclosures: This study did not disclose any funding source. E Guttman-Yassky and B Ungar declared receiving institutional grants from, serving as consultants for, or having other ties with various sources. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Diaz MJ et al. Association between alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis: A nested case-control study of the All of Us database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 21). doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.031
Key clinical point: Patients with alopecia areata (AA) have an increased risk for atopic dermatitis (AD) and vice versa.
Major finding: Patients with AA vs control individuals had a significantly higher risk of developing AD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 4.42; P < .001). Reciprocally, patients with AD vs control individuals also had a significantly higher risk of developing AA (aOR 5.08; P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a nested case-control study including 984 patients with AA from the All of Us database (USA), who were matched with 3936 control individuals without AA using nearest neighbor propensity-score matching.
Disclosures: This study did not disclose any funding source. E Guttman-Yassky and B Ungar declared receiving institutional grants from, serving as consultants for, or having other ties with various sources. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Diaz MJ et al. Association between alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis: A nested case-control study of the All of Us database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 21). doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.031
Real-world efficacy and safety of dupilumab in children with atopic dermatitis age < 12 years
Key clinical point: In real-world settings, dupilumab is safe and effective in children with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) who are age > 2 to < 12 years.
Major finding: Dupilumab led to significant improvements in the Eczema Area and Severity Index scores and Body Surface Area scores in children age > 2 to < 6 years (both P < .001) and ≥ 6 to < 12 years (both P < .001) but not in those age ≤ 2 years (P = .191 and P = .092, respectively). No serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 63 children with moderate-to-severe AD who were classified relative to age: ≤ 2 years (n = 4), > 2 to < 6 years (n = 25), and ≥ 6 to < 12 years (n = 34), with most having received prior systemic immunosuppressive therapies and all being treated with dupilumab.
Disclosures: This study did not disclose any funding source. Several authors declared receiving grants or honoraria from or serving as investigators, advisors, consultants, or speakers for various sources.
Source: Martinez-Cabriales S et al. Multicenter Canadian case series of pediatric patients less than 12 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 31). doi: 10.1111/pde.15418
Key clinical point: In real-world settings, dupilumab is safe and effective in children with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) who are age > 2 to < 12 years.
Major finding: Dupilumab led to significant improvements in the Eczema Area and Severity Index scores and Body Surface Area scores in children age > 2 to < 6 years (both P < .001) and ≥ 6 to < 12 years (both P < .001) but not in those age ≤ 2 years (P = .191 and P = .092, respectively). No serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 63 children with moderate-to-severe AD who were classified relative to age: ≤ 2 years (n = 4), > 2 to < 6 years (n = 25), and ≥ 6 to < 12 years (n = 34), with most having received prior systemic immunosuppressive therapies and all being treated with dupilumab.
Disclosures: This study did not disclose any funding source. Several authors declared receiving grants or honoraria from or serving as investigators, advisors, consultants, or speakers for various sources.
Source: Martinez-Cabriales S et al. Multicenter Canadian case series of pediatric patients less than 12 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 31). doi: 10.1111/pde.15418
Key clinical point: In real-world settings, dupilumab is safe and effective in children with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) who are age > 2 to < 12 years.
Major finding: Dupilumab led to significant improvements in the Eczema Area and Severity Index scores and Body Surface Area scores in children age > 2 to < 6 years (both P < .001) and ≥ 6 to < 12 years (both P < .001) but not in those age ≤ 2 years (P = .191 and P = .092, respectively). No serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 63 children with moderate-to-severe AD who were classified relative to age: ≤ 2 years (n = 4), > 2 to < 6 years (n = 25), and ≥ 6 to < 12 years (n = 34), with most having received prior systemic immunosuppressive therapies and all being treated with dupilumab.
Disclosures: This study did not disclose any funding source. Several authors declared receiving grants or honoraria from or serving as investigators, advisors, consultants, or speakers for various sources.
Source: Martinez-Cabriales S et al. Multicenter Canadian case series of pediatric patients less than 12 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023 (Oct 31). doi: 10.1111/pde.15418