User login
Swedish study finds low risk of developing psoriasis in bariatric surgery patients
Obese patients who undergo bariatric surgery have a lower risk of later developing psoriasis, according to results of nonrandomized, longitudinal intervention trial.
Cristina Maglio, MD, of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and her associates found that over a 26-year follow-up period, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of developing psoriasis was 0.65 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.47-0.89; P = .008) for patients who underwent bariatric surgery, compared with those who received conventional, nonsurgical obesity treatments. Psoriasis developed in 3.6% of 1,991 patients in the surgery group during follow-up and in 5.1% of 2,018 control patients during follow-up.
Conversely, the difference in the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA), experienced by up to one-third of patients with psoriasis, was not statistically significant (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.43-1.37; P = .287). PsA developed in 1% of subjects from the surgery group and 1.3% from the control group.
To understand how surgery affected the development of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, the researchers conducted a trial with a control group and surgery group. In the control group, 2,018 patients received standard obesity treatments that included recommendations on eating behavior, food selection, and physical activity. The 1,991 patients in the surgery group underwent gastric banding (375), vertical banded gastroplasty (1,354), or gastric bypass (262). At the start of the study, patients were evaluated for baseline measurements, then again at 6 months. After the 6-month mark, patients were reevaluated at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 years, respectively. All study participants, regardless of trial group, were examined and presented patient health questionnaires at each follow-up. The endpoint for this study was the first diagnosis of either psoriasis or PsA. Body mass index decreased significantly in the surgery group, compared with virtually no change in the control group.
Vertical banded gastroplasty was found to significantly lower the incidence of psoriasis, compared with usual treatment. But using gastric banding as a reference, vertical banded gastroplasty (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.46-1.39; P = .418) and gastric bypass (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.29-1.71; P = 0.439) were found to have similar effects on the prevention of psoriasis.
The researchers also identified several risk factors that significantly increased the risk of developing psoriasis. Smoking (HR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.26-2.42; P = .001), a known risk factor in the development of psoriasis, and the length of time a patient had been obese (HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55; P = .014) were found to be independently associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
As part of their risk analysis, Dr. Maglio and her colleagues analyzed the interactions of baseline risk factors such as BMI and obesity duration with the bariatric surgery. This analysis found no significant interactions between baseline risk factors and bariatric surgery. It did reveal that patients who were older at baseline evaluation had slightly better responses to bariatric surgery with lower incidences of psoriasis, compared with younger patients, but the differences were not statistically significant.
“The preventive role of bariatric surgery on the risk of psoriasis has been recently highlighted by a retrospective Danish study (JAMA Surg. 2017 Apr 1;152[4]:344-9),” noted Dr. Maglio and her colleagues. “However, we lent strength to the previous results by confirming this association in a large prospective intervention trial designed to examine the effect of bariatric surgery on obesity-related comorbidities in comparison with usual obesity care.
This study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Swedish Rheumatism association, the Swedish Research Council, the University of Gothenburg, and the Swedish federal government. Dr. Anna Rudin reported that part of her salary at Sahlgrenska University is supported by a grant from AstraZeneca. Dr. Lena M.S. Carlsson has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Maglio and Dr. Markku Peltonen had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maglio et al. Obesity. 2017. Dec; 25[12]:2068-73.
Obese patients who undergo bariatric surgery have a lower risk of later developing psoriasis, according to results of nonrandomized, longitudinal intervention trial.
Cristina Maglio, MD, of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and her associates found that over a 26-year follow-up period, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of developing psoriasis was 0.65 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.47-0.89; P = .008) for patients who underwent bariatric surgery, compared with those who received conventional, nonsurgical obesity treatments. Psoriasis developed in 3.6% of 1,991 patients in the surgery group during follow-up and in 5.1% of 2,018 control patients during follow-up.
Conversely, the difference in the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA), experienced by up to one-third of patients with psoriasis, was not statistically significant (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.43-1.37; P = .287). PsA developed in 1% of subjects from the surgery group and 1.3% from the control group.
To understand how surgery affected the development of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, the researchers conducted a trial with a control group and surgery group. In the control group, 2,018 patients received standard obesity treatments that included recommendations on eating behavior, food selection, and physical activity. The 1,991 patients in the surgery group underwent gastric banding (375), vertical banded gastroplasty (1,354), or gastric bypass (262). At the start of the study, patients were evaluated for baseline measurements, then again at 6 months. After the 6-month mark, patients were reevaluated at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 years, respectively. All study participants, regardless of trial group, were examined and presented patient health questionnaires at each follow-up. The endpoint for this study was the first diagnosis of either psoriasis or PsA. Body mass index decreased significantly in the surgery group, compared with virtually no change in the control group.
Vertical banded gastroplasty was found to significantly lower the incidence of psoriasis, compared with usual treatment. But using gastric banding as a reference, vertical banded gastroplasty (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.46-1.39; P = .418) and gastric bypass (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.29-1.71; P = 0.439) were found to have similar effects on the prevention of psoriasis.
The researchers also identified several risk factors that significantly increased the risk of developing psoriasis. Smoking (HR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.26-2.42; P = .001), a known risk factor in the development of psoriasis, and the length of time a patient had been obese (HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55; P = .014) were found to be independently associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
As part of their risk analysis, Dr. Maglio and her colleagues analyzed the interactions of baseline risk factors such as BMI and obesity duration with the bariatric surgery. This analysis found no significant interactions between baseline risk factors and bariatric surgery. It did reveal that patients who were older at baseline evaluation had slightly better responses to bariatric surgery with lower incidences of psoriasis, compared with younger patients, but the differences were not statistically significant.
“The preventive role of bariatric surgery on the risk of psoriasis has been recently highlighted by a retrospective Danish study (JAMA Surg. 2017 Apr 1;152[4]:344-9),” noted Dr. Maglio and her colleagues. “However, we lent strength to the previous results by confirming this association in a large prospective intervention trial designed to examine the effect of bariatric surgery on obesity-related comorbidities in comparison with usual obesity care.
This study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Swedish Rheumatism association, the Swedish Research Council, the University of Gothenburg, and the Swedish federal government. Dr. Anna Rudin reported that part of her salary at Sahlgrenska University is supported by a grant from AstraZeneca. Dr. Lena M.S. Carlsson has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Maglio and Dr. Markku Peltonen had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maglio et al. Obesity. 2017. Dec; 25[12]:2068-73.
Obese patients who undergo bariatric surgery have a lower risk of later developing psoriasis, according to results of nonrandomized, longitudinal intervention trial.
Cristina Maglio, MD, of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and her associates found that over a 26-year follow-up period, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of developing psoriasis was 0.65 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.47-0.89; P = .008) for patients who underwent bariatric surgery, compared with those who received conventional, nonsurgical obesity treatments. Psoriasis developed in 3.6% of 1,991 patients in the surgery group during follow-up and in 5.1% of 2,018 control patients during follow-up.
Conversely, the difference in the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA), experienced by up to one-third of patients with psoriasis, was not statistically significant (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.43-1.37; P = .287). PsA developed in 1% of subjects from the surgery group and 1.3% from the control group.
To understand how surgery affected the development of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, the researchers conducted a trial with a control group and surgery group. In the control group, 2,018 patients received standard obesity treatments that included recommendations on eating behavior, food selection, and physical activity. The 1,991 patients in the surgery group underwent gastric banding (375), vertical banded gastroplasty (1,354), or gastric bypass (262). At the start of the study, patients were evaluated for baseline measurements, then again at 6 months. After the 6-month mark, patients were reevaluated at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 years, respectively. All study participants, regardless of trial group, were examined and presented patient health questionnaires at each follow-up. The endpoint for this study was the first diagnosis of either psoriasis or PsA. Body mass index decreased significantly in the surgery group, compared with virtually no change in the control group.
Vertical banded gastroplasty was found to significantly lower the incidence of psoriasis, compared with usual treatment. But using gastric banding as a reference, vertical banded gastroplasty (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.46-1.39; P = .418) and gastric bypass (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.29-1.71; P = 0.439) were found to have similar effects on the prevention of psoriasis.
The researchers also identified several risk factors that significantly increased the risk of developing psoriasis. Smoking (HR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.26-2.42; P = .001), a known risk factor in the development of psoriasis, and the length of time a patient had been obese (HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.55; P = .014) were found to be independently associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
As part of their risk analysis, Dr. Maglio and her colleagues analyzed the interactions of baseline risk factors such as BMI and obesity duration with the bariatric surgery. This analysis found no significant interactions between baseline risk factors and bariatric surgery. It did reveal that patients who were older at baseline evaluation had slightly better responses to bariatric surgery with lower incidences of psoriasis, compared with younger patients, but the differences were not statistically significant.
“The preventive role of bariatric surgery on the risk of psoriasis has been recently highlighted by a retrospective Danish study (JAMA Surg. 2017 Apr 1;152[4]:344-9),” noted Dr. Maglio and her colleagues. “However, we lent strength to the previous results by confirming this association in a large prospective intervention trial designed to examine the effect of bariatric surgery on obesity-related comorbidities in comparison with usual obesity care.
This study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Swedish Rheumatism association, the Swedish Research Council, the University of Gothenburg, and the Swedish federal government. Dr. Anna Rudin reported that part of her salary at Sahlgrenska University is supported by a grant from AstraZeneca. Dr. Lena M.S. Carlsson has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Maglio and Dr. Markku Peltonen had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Maglio et al. Obesity. 2017. Dec; 25[12]:2068-73.
FROM OBESITY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Obese patients who underwent bariatric surgery had a lower incidence of psoriasis over a 26-year period (HR, 0.65; 95% CI: 0.47-0.89; P = .008), compared with usual care.
Study details: Swedish Obese Subjects study, a longitudinal, nonrandomized intervention trial comprising 1,991 surgery group patients and 2,018 control patients.
Disclosures: This study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Swedish Rheumatism association, the Swedish Research Council, the University of Gothenburg, and the Swedish federal government. Dr. Anna Rudin reported that part of her salary at Sahlgrenska University is supported by a grant from AstraZeneca. Dr. Lena M.S. Carlsson has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Maglio and Dr. Markku Peltonen had no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Maglio et al. Obesity. 2017. Dec; 25[12]:2068-2073.
Long-term specialist care reduces post-RYGB anemia risk
Patients who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) without long-term bariatric specialist follow-up experienced a significantly higher rate of anemia at 10 years than did patients who had such specialist follow-up, according to findings from a database review.
Among 74 patients available for analysis – 58 men and 16 women with a mean age of 51 years who underwent RYGB at a single Veterans Affairs medical center between 2002 and 2006 – the mean rate of preoperative anemia was 20% (15 patients). The rate increased to 28% (21 patients) at 1 year, 31% (23 patients) at 5 years, and 47% (35 patients) at 10 years, according to a research letter by Gao Linda Chen, MD, and her colleagues in the surgical service of the VA Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System (JAMA Surg. 2017. Sep 20. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.3158).
Among 58 patients with no bariatric specialist follow-up after 5 years, the anemia rate increased from 22% (13 patients) before surgery to 57% (33 patients) at 10 years, while the corresponding rates for those with specialty follow-up were 19% (3 patients) and 13% (2 patients). After adjustment for preoperative anemia, those without specialist follow-up had significantly higher odds of anemia at 10 years (odds ratio, 6.1).
“Long-term complications of RYGB, such as anemia, may go unrecognized by nonbariatric specialists,” the investigators wrote, noting that the high rates of anemia at 10 years “may reflect a mixed vitamin and mineral deficiency, because patients had normocytic anemia.
“Our study suggests that follow-up with bariatric specialists more than 5 years after surgery, rather than with specialists with no bariatric expertise, can decrease long-term anemia risk,” they continued. “This finding may demonstrate the bariatric specialist’s specific understanding of the long-term risk for nutritional deficiency after RYGB and the importance of vitamin and mineral supplementation.”
The findings suggest a bariatric team approach with planning for long-term follow-up. “We implemented a hub-and-spoke model for bariatric care, including health care specialist education, in which the bariatric team communicates regularly with the patient’s primary care clinician before and after surgery.”
Although the study is limited by small sample size, the findings nevertheless underscore that “long-term follow-up should be an integral part of bariatric programs, and additional studies are needed to identify potential barriers to successful follow-up,” they concluded.
The authors reported having no disclosures.
Patients who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) without long-term bariatric specialist follow-up experienced a significantly higher rate of anemia at 10 years than did patients who had such specialist follow-up, according to findings from a database review.
Among 74 patients available for analysis – 58 men and 16 women with a mean age of 51 years who underwent RYGB at a single Veterans Affairs medical center between 2002 and 2006 – the mean rate of preoperative anemia was 20% (15 patients). The rate increased to 28% (21 patients) at 1 year, 31% (23 patients) at 5 years, and 47% (35 patients) at 10 years, according to a research letter by Gao Linda Chen, MD, and her colleagues in the surgical service of the VA Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System (JAMA Surg. 2017. Sep 20. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.3158).
Among 58 patients with no bariatric specialist follow-up after 5 years, the anemia rate increased from 22% (13 patients) before surgery to 57% (33 patients) at 10 years, while the corresponding rates for those with specialty follow-up were 19% (3 patients) and 13% (2 patients). After adjustment for preoperative anemia, those without specialist follow-up had significantly higher odds of anemia at 10 years (odds ratio, 6.1).
“Long-term complications of RYGB, such as anemia, may go unrecognized by nonbariatric specialists,” the investigators wrote, noting that the high rates of anemia at 10 years “may reflect a mixed vitamin and mineral deficiency, because patients had normocytic anemia.
“Our study suggests that follow-up with bariatric specialists more than 5 years after surgery, rather than with specialists with no bariatric expertise, can decrease long-term anemia risk,” they continued. “This finding may demonstrate the bariatric specialist’s specific understanding of the long-term risk for nutritional deficiency after RYGB and the importance of vitamin and mineral supplementation.”
The findings suggest a bariatric team approach with planning for long-term follow-up. “We implemented a hub-and-spoke model for bariatric care, including health care specialist education, in which the bariatric team communicates regularly with the patient’s primary care clinician before and after surgery.”
Although the study is limited by small sample size, the findings nevertheless underscore that “long-term follow-up should be an integral part of bariatric programs, and additional studies are needed to identify potential barriers to successful follow-up,” they concluded.
The authors reported having no disclosures.
Patients who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) without long-term bariatric specialist follow-up experienced a significantly higher rate of anemia at 10 years than did patients who had such specialist follow-up, according to findings from a database review.
Among 74 patients available for analysis – 58 men and 16 women with a mean age of 51 years who underwent RYGB at a single Veterans Affairs medical center between 2002 and 2006 – the mean rate of preoperative anemia was 20% (15 patients). The rate increased to 28% (21 patients) at 1 year, 31% (23 patients) at 5 years, and 47% (35 patients) at 10 years, according to a research letter by Gao Linda Chen, MD, and her colleagues in the surgical service of the VA Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System (JAMA Surg. 2017. Sep 20. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.3158).
Among 58 patients with no bariatric specialist follow-up after 5 years, the anemia rate increased from 22% (13 patients) before surgery to 57% (33 patients) at 10 years, while the corresponding rates for those with specialty follow-up were 19% (3 patients) and 13% (2 patients). After adjustment for preoperative anemia, those without specialist follow-up had significantly higher odds of anemia at 10 years (odds ratio, 6.1).
“Long-term complications of RYGB, such as anemia, may go unrecognized by nonbariatric specialists,” the investigators wrote, noting that the high rates of anemia at 10 years “may reflect a mixed vitamin and mineral deficiency, because patients had normocytic anemia.
“Our study suggests that follow-up with bariatric specialists more than 5 years after surgery, rather than with specialists with no bariatric expertise, can decrease long-term anemia risk,” they continued. “This finding may demonstrate the bariatric specialist’s specific understanding of the long-term risk for nutritional deficiency after RYGB and the importance of vitamin and mineral supplementation.”
The findings suggest a bariatric team approach with planning for long-term follow-up. “We implemented a hub-and-spoke model for bariatric care, including health care specialist education, in which the bariatric team communicates regularly with the patient’s primary care clinician before and after surgery.”
Although the study is limited by small sample size, the findings nevertheless underscore that “long-term follow-up should be an integral part of bariatric programs, and additional studies are needed to identify potential barriers to successful follow-up,” they concluded.
The authors reported having no disclosures.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: RYGB patients without specialist follow-up had significantly higher odds of anemia at 10 years (adjusted odds ratio, 6.1).
Data source: A retrospective review of 74 patients from a prospective 10-year database.
Disclosures: The authors reported having no disclosures.
Diagnostic laparoscopy pinpoints postop abdominal pain in bariatric patients
The etiology of chronic pain after bariatric surgery can be difficult to pinpoint, but diagnostic laparoscopy can detect causes in about half of patients, findings from a small study have shown.
In an investigation conducted by Mohammed Alsulaimy, MD, a surgeon at the Bariatric and Metabolic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, and his colleagues, 35 patients underwent diagnostic laparoscopy (DL) to identify the causes of their chronic abdominal pain after bariatric surgery. Patients included in the study had a history of abdominal pain lasting longer than 30 days after their bariatric procedure, a negative CT scan of their abdomen and pelvis, a gallstone-negative abdominal ultrasound, and an upper GI endoscopy with no abnormalities. Researchers collected patient data including age, gender, body, weight, and body mass index, type of previous bariatric procedure, and time between surgery and onset of pain.
The results of DL were either positive (presence detected of pathology or injury) or negative (no disease or injury detected).
Twenty patients (57%) had positive findings on DL including the presence of adhesions, chronic cholecystitis, mesenteric defect, internal hernia, and necrotic omentum, and of this group, 43% had treatment that led to improvement of pain symptoms. Only 1 of the 15 patients with negative DL findings had eventual improvement of their pain symptoms. Most patients with negative DL findings had persistent abdominal pain, possibly because of nonorganic causes and were referred to the chronic pain management service, the investigators wrote.
“About 40% of patients who undergo DL and 70% of patients with positive findings on DL experience significant symptom improvement,” the investigators said. “This study highlights the importance of offering DL as both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool in post–bariatric surgery patients with chronic abdominal of unknown etiology.”
The investigators had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
The etiology of chronic pain after bariatric surgery can be difficult to pinpoint, but diagnostic laparoscopy can detect causes in about half of patients, findings from a small study have shown.
In an investigation conducted by Mohammed Alsulaimy, MD, a surgeon at the Bariatric and Metabolic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, and his colleagues, 35 patients underwent diagnostic laparoscopy (DL) to identify the causes of their chronic abdominal pain after bariatric surgery. Patients included in the study had a history of abdominal pain lasting longer than 30 days after their bariatric procedure, a negative CT scan of their abdomen and pelvis, a gallstone-negative abdominal ultrasound, and an upper GI endoscopy with no abnormalities. Researchers collected patient data including age, gender, body, weight, and body mass index, type of previous bariatric procedure, and time between surgery and onset of pain.
The results of DL were either positive (presence detected of pathology or injury) or negative (no disease or injury detected).
Twenty patients (57%) had positive findings on DL including the presence of adhesions, chronic cholecystitis, mesenteric defect, internal hernia, and necrotic omentum, and of this group, 43% had treatment that led to improvement of pain symptoms. Only 1 of the 15 patients with negative DL findings had eventual improvement of their pain symptoms. Most patients with negative DL findings had persistent abdominal pain, possibly because of nonorganic causes and were referred to the chronic pain management service, the investigators wrote.
“About 40% of patients who undergo DL and 70% of patients with positive findings on DL experience significant symptom improvement,” the investigators said. “This study highlights the importance of offering DL as both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool in post–bariatric surgery patients with chronic abdominal of unknown etiology.”
The investigators had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
The etiology of chronic pain after bariatric surgery can be difficult to pinpoint, but diagnostic laparoscopy can detect causes in about half of patients, findings from a small study have shown.
In an investigation conducted by Mohammed Alsulaimy, MD, a surgeon at the Bariatric and Metabolic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, and his colleagues, 35 patients underwent diagnostic laparoscopy (DL) to identify the causes of their chronic abdominal pain after bariatric surgery. Patients included in the study had a history of abdominal pain lasting longer than 30 days after their bariatric procedure, a negative CT scan of their abdomen and pelvis, a gallstone-negative abdominal ultrasound, and an upper GI endoscopy with no abnormalities. Researchers collected patient data including age, gender, body, weight, and body mass index, type of previous bariatric procedure, and time between surgery and onset of pain.
The results of DL were either positive (presence detected of pathology or injury) or negative (no disease or injury detected).
Twenty patients (57%) had positive findings on DL including the presence of adhesions, chronic cholecystitis, mesenteric defect, internal hernia, and necrotic omentum, and of this group, 43% had treatment that led to improvement of pain symptoms. Only 1 of the 15 patients with negative DL findings had eventual improvement of their pain symptoms. Most patients with negative DL findings had persistent abdominal pain, possibly because of nonorganic causes and were referred to the chronic pain management service, the investigators wrote.
“About 40% of patients who undergo DL and 70% of patients with positive findings on DL experience significant symptom improvement,” the investigators said. “This study highlights the importance of offering DL as both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool in post–bariatric surgery patients with chronic abdominal of unknown etiology.”
The investigators had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
FROM OBESITY SURGERY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: In the study group, 57% of patients had a positive diagnostic laparoscopy results identifying the source of their chronic abdominal pain.
Data source: Retrospective review of post–bariatric surgery patients who underwent diagnostic laparoscopy (DL) during 2003-2015.
Disclosures: The investigators had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass produced durable clinical improvements at 12 years
Severely obese individuals in the United States who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) averaged a 27% weight loss 12 years later, with only a 3% incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and a 51% rate of diabetes remission, according to the results of a large multicenter observational prospective study.
In striking contrast, patients who did not undergo bariatric surgery averaged a 1%-2% weight loss at 12 years, a 26% incidence of diabetes, and only a 5%-10% rate of diabetes remission, said Ted D. Adams, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and his associates. RYGB surgery also conferred substantial and statistically significant improvements long-term improvements in systolic hypertension and lipid levels, the researchers reported in the New England Journal of Medicine (2017 Sep 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1700459).
“The follow-up rate exceeded 90% at 12 years,” the researchers wrote. Two years after undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, patients had lost an average of 45 kg (95% confidence interval, 43-47 kg). By postoperative year 6, they had regained an average of 9 kg (average loss from baseline, 36 kg; 95% CI, 34-39 kg). But they typically gained only about 1.3 kg more between years 6 and 12, and they had about a 92% lower odds of developing diabetes mellitus, compared with individuals who did not undergo bariatric surgery (odds ratio, 0.08; P less than .001). “Remission of type 2 diabetes was much more likely if the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass occurred before [patients began] treatment with insulin, presumably owing to the ability of partially viable beta cells to improve their function,” the researchers noted.
Funders included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Research Resources, Weill Cornell Medicine, and Intermountain Healthcare. Dr. Adams reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed royalties from licensing a questionnaire on weight loss and quality of life, and another coinvestigator disclosed fees for services rendered during a trial of an intragastric balloon. The remaining researchers had no relevant disclosures.
Severely obese individuals in the United States who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) averaged a 27% weight loss 12 years later, with only a 3% incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and a 51% rate of diabetes remission, according to the results of a large multicenter observational prospective study.
In striking contrast, patients who did not undergo bariatric surgery averaged a 1%-2% weight loss at 12 years, a 26% incidence of diabetes, and only a 5%-10% rate of diabetes remission, said Ted D. Adams, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and his associates. RYGB surgery also conferred substantial and statistically significant improvements long-term improvements in systolic hypertension and lipid levels, the researchers reported in the New England Journal of Medicine (2017 Sep 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1700459).
“The follow-up rate exceeded 90% at 12 years,” the researchers wrote. Two years after undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, patients had lost an average of 45 kg (95% confidence interval, 43-47 kg). By postoperative year 6, they had regained an average of 9 kg (average loss from baseline, 36 kg; 95% CI, 34-39 kg). But they typically gained only about 1.3 kg more between years 6 and 12, and they had about a 92% lower odds of developing diabetes mellitus, compared with individuals who did not undergo bariatric surgery (odds ratio, 0.08; P less than .001). “Remission of type 2 diabetes was much more likely if the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass occurred before [patients began] treatment with insulin, presumably owing to the ability of partially viable beta cells to improve their function,” the researchers noted.
Funders included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Research Resources, Weill Cornell Medicine, and Intermountain Healthcare. Dr. Adams reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed royalties from licensing a questionnaire on weight loss and quality of life, and another coinvestigator disclosed fees for services rendered during a trial of an intragastric balloon. The remaining researchers had no relevant disclosures.
Severely obese individuals in the United States who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) averaged a 27% weight loss 12 years later, with only a 3% incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and a 51% rate of diabetes remission, according to the results of a large multicenter observational prospective study.
In striking contrast, patients who did not undergo bariatric surgery averaged a 1%-2% weight loss at 12 years, a 26% incidence of diabetes, and only a 5%-10% rate of diabetes remission, said Ted D. Adams, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and his associates. RYGB surgery also conferred substantial and statistically significant improvements long-term improvements in systolic hypertension and lipid levels, the researchers reported in the New England Journal of Medicine (2017 Sep 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1700459).
“The follow-up rate exceeded 90% at 12 years,” the researchers wrote. Two years after undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, patients had lost an average of 45 kg (95% confidence interval, 43-47 kg). By postoperative year 6, they had regained an average of 9 kg (average loss from baseline, 36 kg; 95% CI, 34-39 kg). But they typically gained only about 1.3 kg more between years 6 and 12, and they had about a 92% lower odds of developing diabetes mellitus, compared with individuals who did not undergo bariatric surgery (odds ratio, 0.08; P less than .001). “Remission of type 2 diabetes was much more likely if the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass occurred before [patients began] treatment with insulin, presumably owing to the ability of partially viable beta cells to improve their function,” the researchers noted.
Funders included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Research Resources, Weill Cornell Medicine, and Intermountain Healthcare. Dr. Adams reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed royalties from licensing a questionnaire on weight loss and quality of life, and another coinvestigator disclosed fees for services rendered during a trial of an intragastric balloon. The remaining researchers had no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass produced durable results on numerous clinical outcome measures.
Major finding: Twelve years after surgery, RYGB patients averaged a 27% weight loss from baseline, with a 51% rate of remission and a 3% incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Data source: A prospective study of 1,156 severely obese individuals, of whom 418 underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Disclosures: Funders included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Research Resources, Weill Cornell Medicine, and Intermountain Healthcare. Dr. Adams reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed royalties from licensing a questionnaire on weight loss and the quality of life, and another coinvestigator disclosed fees for services rendered during a trial of an intragastric balloon. The remaining researchers had no relevant disclosures.
Immobility implicated in increased complications after bariatric surgery
NEW YORK –
“The importance of this study is to help us as an institution, but then also nationally, to try to focus on quality initiatives to improve the complication rate and safety profile of these patients, who are incredibly high risk for bariatric surgery,” said Rana Higgins, MD, a general surgeon at Froedtert Hospital and the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
Dr. Higgins and her colleagues compared 2,969 immobile patients with 145,741 who were ambulatory before surgery. The most common bariatric procedure was sleeve gastrectomy at 56%. Another 30% had gastric bypass, 3% had the gastric band, and the remaining 1% underwent other procedures, such as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. The MBSAQIP (Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program) defines immobility as a patient with limited ambulation who requires assistive devices, such as a scooter or wheelchair, to ambulate most or all of the time. In addition, with regard to negotiating stairs, immobile patients need a home lift or an elevator.
Only three complications evaluated by the researchers were not statistically different between groups: intraoperative or postoperative coma, stroke, and myocardial infarction.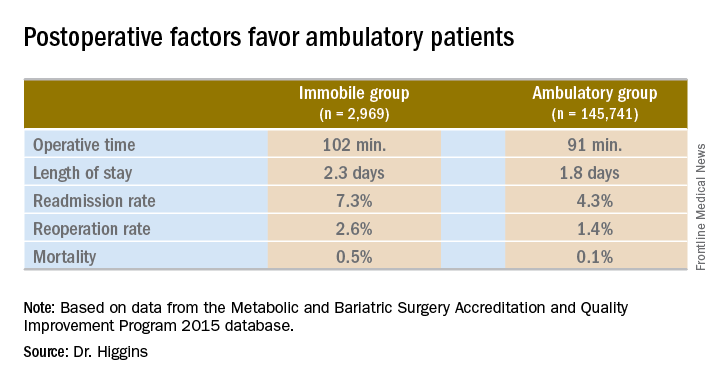
Operative time was longer in the immobile group, about 102 minutes vs. 91 minutes (P less than .001). A meeting attendee asked what accounted for the difference. Dr. Higgins replied, “We’ll have to go back and look at our data. My hypothesis is that the immobile patients had a higher BMI [body mass index]. They may also have had other comorbidities that contributed to increased operative time.”
Hospital length of stay was also significantly longer among immobile patients at 2.3 days vs. 1.8 days in the ambulatory group (P less than .001).
The readmission rate was higher among immobile patients – 7.3% vs. 4.3% for the ambulatory group. The reoperation rate was higher at 2.6% vs. 1.4%. Both these findings were statistically significant as well (P less than .001).
Immobile patients had a statistically higher risk of mortality at 0.5%, compared with 0.1% among ambulatory patients (OR, 4.6).
A meeting attendee asked Dr. Higgins if her institution addresses mobility issues. She replied that there is preoperative education about the importance of ambulation, but the interventions are focused on ambulation in the postoperative period. “We order physical therapy, immediately postoperatively; typically the patients will receive it that day or the next day. We make sure patients are up and moving as much as possible, but there are limitations if they have limited mobility.”
The same attendee suggested preoperative physical therapy could help, even if only 2-4 weeks prior to surgery. Dr. Higgins agreed that would be a good quality initiative to explore in the future.
She had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK –
“The importance of this study is to help us as an institution, but then also nationally, to try to focus on quality initiatives to improve the complication rate and safety profile of these patients, who are incredibly high risk for bariatric surgery,” said Rana Higgins, MD, a general surgeon at Froedtert Hospital and the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
Dr. Higgins and her colleagues compared 2,969 immobile patients with 145,741 who were ambulatory before surgery. The most common bariatric procedure was sleeve gastrectomy at 56%. Another 30% had gastric bypass, 3% had the gastric band, and the remaining 1% underwent other procedures, such as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. The MBSAQIP (Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program) defines immobility as a patient with limited ambulation who requires assistive devices, such as a scooter or wheelchair, to ambulate most or all of the time. In addition, with regard to negotiating stairs, immobile patients need a home lift or an elevator.
Only three complications evaluated by the researchers were not statistically different between groups: intraoperative or postoperative coma, stroke, and myocardial infarction.
Operative time was longer in the immobile group, about 102 minutes vs. 91 minutes (P less than .001). A meeting attendee asked what accounted for the difference. Dr. Higgins replied, “We’ll have to go back and look at our data. My hypothesis is that the immobile patients had a higher BMI [body mass index]. They may also have had other comorbidities that contributed to increased operative time.”
Hospital length of stay was also significantly longer among immobile patients at 2.3 days vs. 1.8 days in the ambulatory group (P less than .001).
The readmission rate was higher among immobile patients – 7.3% vs. 4.3% for the ambulatory group. The reoperation rate was higher at 2.6% vs. 1.4%. Both these findings were statistically significant as well (P less than .001).
Immobile patients had a statistically higher risk of mortality at 0.5%, compared with 0.1% among ambulatory patients (OR, 4.6).
A meeting attendee asked Dr. Higgins if her institution addresses mobility issues. She replied that there is preoperative education about the importance of ambulation, but the interventions are focused on ambulation in the postoperative period. “We order physical therapy, immediately postoperatively; typically the patients will receive it that day or the next day. We make sure patients are up and moving as much as possible, but there are limitations if they have limited mobility.”
The same attendee suggested preoperative physical therapy could help, even if only 2-4 weeks prior to surgery. Dr. Higgins agreed that would be a good quality initiative to explore in the future.
She had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK –
“The importance of this study is to help us as an institution, but then also nationally, to try to focus on quality initiatives to improve the complication rate and safety profile of these patients, who are incredibly high risk for bariatric surgery,” said Rana Higgins, MD, a general surgeon at Froedtert Hospital and the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
Dr. Higgins and her colleagues compared 2,969 immobile patients with 145,741 who were ambulatory before surgery. The most common bariatric procedure was sleeve gastrectomy at 56%. Another 30% had gastric bypass, 3% had the gastric band, and the remaining 1% underwent other procedures, such as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. The MBSAQIP (Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program) defines immobility as a patient with limited ambulation who requires assistive devices, such as a scooter or wheelchair, to ambulate most or all of the time. In addition, with regard to negotiating stairs, immobile patients need a home lift or an elevator.
Only three complications evaluated by the researchers were not statistically different between groups: intraoperative or postoperative coma, stroke, and myocardial infarction.
Operative time was longer in the immobile group, about 102 minutes vs. 91 minutes (P less than .001). A meeting attendee asked what accounted for the difference. Dr. Higgins replied, “We’ll have to go back and look at our data. My hypothesis is that the immobile patients had a higher BMI [body mass index]. They may also have had other comorbidities that contributed to increased operative time.”
Hospital length of stay was also significantly longer among immobile patients at 2.3 days vs. 1.8 days in the ambulatory group (P less than .001).
The readmission rate was higher among immobile patients – 7.3% vs. 4.3% for the ambulatory group. The reoperation rate was higher at 2.6% vs. 1.4%. Both these findings were statistically significant as well (P less than .001).
Immobile patients had a statistically higher risk of mortality at 0.5%, compared with 0.1% among ambulatory patients (OR, 4.6).
A meeting attendee asked Dr. Higgins if her institution addresses mobility issues. She replied that there is preoperative education about the importance of ambulation, but the interventions are focused on ambulation in the postoperative period. “We order physical therapy, immediately postoperatively; typically the patients will receive it that day or the next day. We make sure patients are up and moving as much as possible, but there are limitations if they have limited mobility.”
The same attendee suggested preoperative physical therapy could help, even if only 2-4 weeks prior to surgery. Dr. Higgins agreed that would be a good quality initiative to explore in the future.
She had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT THE ACS QUALITY & SAFETY CONFERENCE
Key clinical point: Patients immobile before bariatric surgery could require closer monitoring for postoperative complications.
Major finding: Thirty-day mortality after bariatric surgery in immobile patients was 0.5%, vs. 0.1% for an ambulatory group (P less than .0001).
Data source: A comparison of 2015 MBSAQIP data for 145,741 ambulatory patients and 2,969 immobile patients before bariatric surgery.
Disclosures: Dr. Higgins had no relevant financial disclosures.
Think beyond BMI to optimize bariatric patients presurgery
NEW YORK – A structured, four-pronged approach to get patients as fit and healthy as possible prior to bariatric surgery holds the potential to improve postoperative outcomes. In general, bariatric surgery patients are in a better position than most surgery candidates because of a longer preoperative period. During this time, surgeons can work with a multidisciplinary team to optimize any medical, nutritional, exercise-related, and mental health concerns.
“People focus on the size of our patients and the weight of our patients, but [body mass index] is only one factor. They can have many other comorbidities that are significant,” Dr. LaMasters said. Patients can present with cardiac and pulmonary issues, hypertension, sleep apnea, diabetes, asthma, reflux and “a very high incidence of anxiety and depression.”
“So we have a lot of challenges,” she added. “We take care of complex, high-risk patients, and our goal is to improve outcomes. Using presurgery optimization can be a key to that.”
Maximizing medical readiness
Multiple providers drive the medical intervention, Dr. LaMasters said, including surgeons and primary care doctors, as well as advanced practice providers, medical weight loss providers, and other specialists. “We do try to get patients to lose weight before surgery, but that’s not an absolute requirement. More important is adjustment of other risk factors like pulmonary risk factors, control of hypertension, treatment of sleep apnea, and control of hyperglycemia. We’d like to have their A1c [test results to be] under 8%. We want to start [proton pump inhibitors] early because there is a very high prevalence of reflux and gastritis in this population.”
Bariatric surgery patients “are uniquely positioned to have a substantial benefit from that ‘prehabilitation,’ but this only works if you have a multidisciplinary team,” Dr. LaMasters said at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference. “Think of this as down-staging disease, like in a cancer model.”
“The message from this is there is an opportunity if we build it into the prehab phase of care. It’s a new way of thinking in surgery. You can change your results,” said session moderator David B. Hoyt, MD, FACS, Executive Director of the American College of Surgeons.
Nutritional know-how
Dietitians determine the second component – how to optimize nutrition before surgery. They focus on education, evaluation, setting goals, “and very importantly, supporting patients to attain those goals,” Dr. LaMasters said. Goals include increasing protein intake prior to surgery to a recommended 1.5 g/kg/day and starting nutritional supplements ahead of time.
Even though they typically consume an excess amount of calories, “many of our patients have baseline malnutrition,” Dr. LaMasters said. Establishing mindful behavior for meal planning, preparation, and eating is a potential solution, as is addressing any socioeconomic factors that can present challenges to healthy eating.
Emphasizing exercise
“The exercise piece is really key for our patients,” Dr. LaMasters said. Many candidates for bariatric surgery have mobility issues. “The first thing many say is ‘I can’t exercise.’ We instruct them that they can exercise. Our job is to find out what they can do – there are many different exercise modalities.”
A good baseline assessment is a 6-minute walk test to assess their distance limits, oxygen level, and any resulting symptoms.
“Our goal is to get them to walking – even those who can barely walk with a walker – for 5-10 minutes, six times a day,” Dr. LaMasters said. “We feel that is a minimum threshold to prevent blood clots after surgery.” Another recommendation is to get surgical candidates to do some activity 30 minutes a day, four times a week, at a minimum. “Eventually, after surgery and when they’ve lost weight and are healthier, the goal is going to be 1 hour, five days a week.”
Start the exercise program at least 4-8 weeks prior to surgery. Most studies show significant benefit if you start at least 4 weeks prior to surgery, Dr. LaMasters suggested. “In our own practice, we’ve seen if you can start a daily walking program even just 2 weeks prior to surgery, we see a significant benefit.”
Addressing anxiety or depression
The mental health piece is very important and should be guided by mental health providers on the multidisciplinary team, Dr. LaMasters said.
“Our patients have a high degree of stress in their lives, especially related to socioeconomic factors. A patient who does not have their anxiety or depression under control will not do as well after surgery.”
Optimization in other specialties
The benefits of a prehabilitation exercise program have been demonstrated across many other specialties, especially in colorectal surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and orthopedic surgery, Dr. LaMasters said. In randomized, controlled studies, this optimization is associated with decreased complications, mortality, and length of hospital stay.
“There is actually way less data from bariatric studies. I suggest to you that our bariatric surgery patients have similar comorbidities when compared with those other specialties – specialties that refer their patients to us for treatment,” Dr. LaMasters said.
In a study of cardiorespiratory fitness before bariatric surgery, other researchers found that the most serious postoperative complications occurred more often among patients who were less fit preoperatively (Chest. 2006 Aug;130[2]:517-25). These investigators measured peak oxygen consumption (VO2) preoperatively in 109 patients. “Each unit increase in peak VO2 rate was associated with 61% decrease in overall complications,” Dr. LaMasters said. “So a small increase in fitness led to a big decrease in complications.”
Other researchers compared optimization of exercise, nutrition, and psychological factors before and after surgery in 185 patients with colorectal cancer (Acta Oncol. 2017 Feb;56[2]:295-300). A control group received the interventions postoperatively. “They found a statistically significant difference in the prehabilitation group in increased functional capacity, with more than a 30-meter improvement in 6-minute walk test before surgery,” Dr. LaMasters said. Although the 6-minute walk test results decreased 4 weeks after surgery, as might be expected, by 8 weeks the prehabilitation patients performed better than controls – and even better than their own baseline, she added. “This model of optimization can be very well applied in bariatric surgery.”
“The goal is safe surgery with outstanding long-term outcomes,” Dr. LaMasters said. “It is really not enough in this era to ‘get a patient through surgery.’ We really need to optimize the risk factors we can and identify any areas where they will have additional needs after surgery,” she added. “This will allow us to have excellent outcomes in this complex patient population.”
Dr. LaMasters and Dr. Hoyt had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – A structured, four-pronged approach to get patients as fit and healthy as possible prior to bariatric surgery holds the potential to improve postoperative outcomes. In general, bariatric surgery patients are in a better position than most surgery candidates because of a longer preoperative period. During this time, surgeons can work with a multidisciplinary team to optimize any medical, nutritional, exercise-related, and mental health concerns.
“People focus on the size of our patients and the weight of our patients, but [body mass index] is only one factor. They can have many other comorbidities that are significant,” Dr. LaMasters said. Patients can present with cardiac and pulmonary issues, hypertension, sleep apnea, diabetes, asthma, reflux and “a very high incidence of anxiety and depression.”
“So we have a lot of challenges,” she added. “We take care of complex, high-risk patients, and our goal is to improve outcomes. Using presurgery optimization can be a key to that.”
Maximizing medical readiness
Multiple providers drive the medical intervention, Dr. LaMasters said, including surgeons and primary care doctors, as well as advanced practice providers, medical weight loss providers, and other specialists. “We do try to get patients to lose weight before surgery, but that’s not an absolute requirement. More important is adjustment of other risk factors like pulmonary risk factors, control of hypertension, treatment of sleep apnea, and control of hyperglycemia. We’d like to have their A1c [test results to be] under 8%. We want to start [proton pump inhibitors] early because there is a very high prevalence of reflux and gastritis in this population.”
Bariatric surgery patients “are uniquely positioned to have a substantial benefit from that ‘prehabilitation,’ but this only works if you have a multidisciplinary team,” Dr. LaMasters said at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference. “Think of this as down-staging disease, like in a cancer model.”
“The message from this is there is an opportunity if we build it into the prehab phase of care. It’s a new way of thinking in surgery. You can change your results,” said session moderator David B. Hoyt, MD, FACS, Executive Director of the American College of Surgeons.
Nutritional know-how
Dietitians determine the second component – how to optimize nutrition before surgery. They focus on education, evaluation, setting goals, “and very importantly, supporting patients to attain those goals,” Dr. LaMasters said. Goals include increasing protein intake prior to surgery to a recommended 1.5 g/kg/day and starting nutritional supplements ahead of time.
Even though they typically consume an excess amount of calories, “many of our patients have baseline malnutrition,” Dr. LaMasters said. Establishing mindful behavior for meal planning, preparation, and eating is a potential solution, as is addressing any socioeconomic factors that can present challenges to healthy eating.
Emphasizing exercise
“The exercise piece is really key for our patients,” Dr. LaMasters said. Many candidates for bariatric surgery have mobility issues. “The first thing many say is ‘I can’t exercise.’ We instruct them that they can exercise. Our job is to find out what they can do – there are many different exercise modalities.”
A good baseline assessment is a 6-minute walk test to assess their distance limits, oxygen level, and any resulting symptoms.
“Our goal is to get them to walking – even those who can barely walk with a walker – for 5-10 minutes, six times a day,” Dr. LaMasters said. “We feel that is a minimum threshold to prevent blood clots after surgery.” Another recommendation is to get surgical candidates to do some activity 30 minutes a day, four times a week, at a minimum. “Eventually, after surgery and when they’ve lost weight and are healthier, the goal is going to be 1 hour, five days a week.”
Start the exercise program at least 4-8 weeks prior to surgery. Most studies show significant benefit if you start at least 4 weeks prior to surgery, Dr. LaMasters suggested. “In our own practice, we’ve seen if you can start a daily walking program even just 2 weeks prior to surgery, we see a significant benefit.”
Addressing anxiety or depression
The mental health piece is very important and should be guided by mental health providers on the multidisciplinary team, Dr. LaMasters said.
“Our patients have a high degree of stress in their lives, especially related to socioeconomic factors. A patient who does not have their anxiety or depression under control will not do as well after surgery.”
Optimization in other specialties
The benefits of a prehabilitation exercise program have been demonstrated across many other specialties, especially in colorectal surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and orthopedic surgery, Dr. LaMasters said. In randomized, controlled studies, this optimization is associated with decreased complications, mortality, and length of hospital stay.
“There is actually way less data from bariatric studies. I suggest to you that our bariatric surgery patients have similar comorbidities when compared with those other specialties – specialties that refer their patients to us for treatment,” Dr. LaMasters said.
In a study of cardiorespiratory fitness before bariatric surgery, other researchers found that the most serious postoperative complications occurred more often among patients who were less fit preoperatively (Chest. 2006 Aug;130[2]:517-25). These investigators measured peak oxygen consumption (VO2) preoperatively in 109 patients. “Each unit increase in peak VO2 rate was associated with 61% decrease in overall complications,” Dr. LaMasters said. “So a small increase in fitness led to a big decrease in complications.”
Other researchers compared optimization of exercise, nutrition, and psychological factors before and after surgery in 185 patients with colorectal cancer (Acta Oncol. 2017 Feb;56[2]:295-300). A control group received the interventions postoperatively. “They found a statistically significant difference in the prehabilitation group in increased functional capacity, with more than a 30-meter improvement in 6-minute walk test before surgery,” Dr. LaMasters said. Although the 6-minute walk test results decreased 4 weeks after surgery, as might be expected, by 8 weeks the prehabilitation patients performed better than controls – and even better than their own baseline, she added. “This model of optimization can be very well applied in bariatric surgery.”
“The goal is safe surgery with outstanding long-term outcomes,” Dr. LaMasters said. “It is really not enough in this era to ‘get a patient through surgery.’ We really need to optimize the risk factors we can and identify any areas where they will have additional needs after surgery,” she added. “This will allow us to have excellent outcomes in this complex patient population.”
Dr. LaMasters and Dr. Hoyt had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – A structured, four-pronged approach to get patients as fit and healthy as possible prior to bariatric surgery holds the potential to improve postoperative outcomes. In general, bariatric surgery patients are in a better position than most surgery candidates because of a longer preoperative period. During this time, surgeons can work with a multidisciplinary team to optimize any medical, nutritional, exercise-related, and mental health concerns.
“People focus on the size of our patients and the weight of our patients, but [body mass index] is only one factor. They can have many other comorbidities that are significant,” Dr. LaMasters said. Patients can present with cardiac and pulmonary issues, hypertension, sleep apnea, diabetes, asthma, reflux and “a very high incidence of anxiety and depression.”
“So we have a lot of challenges,” she added. “We take care of complex, high-risk patients, and our goal is to improve outcomes. Using presurgery optimization can be a key to that.”
Maximizing medical readiness
Multiple providers drive the medical intervention, Dr. LaMasters said, including surgeons and primary care doctors, as well as advanced practice providers, medical weight loss providers, and other specialists. “We do try to get patients to lose weight before surgery, but that’s not an absolute requirement. More important is adjustment of other risk factors like pulmonary risk factors, control of hypertension, treatment of sleep apnea, and control of hyperglycemia. We’d like to have their A1c [test results to be] under 8%. We want to start [proton pump inhibitors] early because there is a very high prevalence of reflux and gastritis in this population.”
Bariatric surgery patients “are uniquely positioned to have a substantial benefit from that ‘prehabilitation,’ but this only works if you have a multidisciplinary team,” Dr. LaMasters said at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference. “Think of this as down-staging disease, like in a cancer model.”
“The message from this is there is an opportunity if we build it into the prehab phase of care. It’s a new way of thinking in surgery. You can change your results,” said session moderator David B. Hoyt, MD, FACS, Executive Director of the American College of Surgeons.
Nutritional know-how
Dietitians determine the second component – how to optimize nutrition before surgery. They focus on education, evaluation, setting goals, “and very importantly, supporting patients to attain those goals,” Dr. LaMasters said. Goals include increasing protein intake prior to surgery to a recommended 1.5 g/kg/day and starting nutritional supplements ahead of time.
Even though they typically consume an excess amount of calories, “many of our patients have baseline malnutrition,” Dr. LaMasters said. Establishing mindful behavior for meal planning, preparation, and eating is a potential solution, as is addressing any socioeconomic factors that can present challenges to healthy eating.
Emphasizing exercise
“The exercise piece is really key for our patients,” Dr. LaMasters said. Many candidates for bariatric surgery have mobility issues. “The first thing many say is ‘I can’t exercise.’ We instruct them that they can exercise. Our job is to find out what they can do – there are many different exercise modalities.”
A good baseline assessment is a 6-minute walk test to assess their distance limits, oxygen level, and any resulting symptoms.
“Our goal is to get them to walking – even those who can barely walk with a walker – for 5-10 minutes, six times a day,” Dr. LaMasters said. “We feel that is a minimum threshold to prevent blood clots after surgery.” Another recommendation is to get surgical candidates to do some activity 30 minutes a day, four times a week, at a minimum. “Eventually, after surgery and when they’ve lost weight and are healthier, the goal is going to be 1 hour, five days a week.”
Start the exercise program at least 4-8 weeks prior to surgery. Most studies show significant benefit if you start at least 4 weeks prior to surgery, Dr. LaMasters suggested. “In our own practice, we’ve seen if you can start a daily walking program even just 2 weeks prior to surgery, we see a significant benefit.”
Addressing anxiety or depression
The mental health piece is very important and should be guided by mental health providers on the multidisciplinary team, Dr. LaMasters said.
“Our patients have a high degree of stress in their lives, especially related to socioeconomic factors. A patient who does not have their anxiety or depression under control will not do as well after surgery.”
Optimization in other specialties
The benefits of a prehabilitation exercise program have been demonstrated across many other specialties, especially in colorectal surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and orthopedic surgery, Dr. LaMasters said. In randomized, controlled studies, this optimization is associated with decreased complications, mortality, and length of hospital stay.
“There is actually way less data from bariatric studies. I suggest to you that our bariatric surgery patients have similar comorbidities when compared with those other specialties – specialties that refer their patients to us for treatment,” Dr. LaMasters said.
In a study of cardiorespiratory fitness before bariatric surgery, other researchers found that the most serious postoperative complications occurred more often among patients who were less fit preoperatively (Chest. 2006 Aug;130[2]:517-25). These investigators measured peak oxygen consumption (VO2) preoperatively in 109 patients. “Each unit increase in peak VO2 rate was associated with 61% decrease in overall complications,” Dr. LaMasters said. “So a small increase in fitness led to a big decrease in complications.”
Other researchers compared optimization of exercise, nutrition, and psychological factors before and after surgery in 185 patients with colorectal cancer (Acta Oncol. 2017 Feb;56[2]:295-300). A control group received the interventions postoperatively. “They found a statistically significant difference in the prehabilitation group in increased functional capacity, with more than a 30-meter improvement in 6-minute walk test before surgery,” Dr. LaMasters said. Although the 6-minute walk test results decreased 4 weeks after surgery, as might be expected, by 8 weeks the prehabilitation patients performed better than controls – and even better than their own baseline, she added. “This model of optimization can be very well applied in bariatric surgery.”
“The goal is safe surgery with outstanding long-term outcomes,” Dr. LaMasters said. “It is really not enough in this era to ‘get a patient through surgery.’ We really need to optimize the risk factors we can and identify any areas where they will have additional needs after surgery,” she added. “This will allow us to have excellent outcomes in this complex patient population.”
Dr. LaMasters and Dr. Hoyt had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT THE ACS QUALITY & SAFETY CONFERENCE
MBSAQIP data helped target problem areas to cut readmissions
NEW YORK – Targeted interventions aimed at reducing patient readmission after bariatric surgery at a high-volume academic medical center led to a 61% overall decrease year over year. The center also saw a substantial reduction in readmissions linked to the top three factors of readmission identified by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program, as well as a precipitous drop in the revisional surgery readmission rate.
“Our center, like so many others, has quarterly meetings in accordance with the MBSAQIP to look at our data. And this led to recognition of some common reasons for readmission,” said Chetan V. Aher, MD, a general surgeon at the department of surgery at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. Oral (PO) intolerance, dehydration, and nonemergent abdominal pain were the top reasons flagged by the MBSAQIP registry data at the medical center. Dr. Aher and his colleagues moved to focus on postoperative diet, administration of medications, management of patients who return to the hospital after surgery, and optimal staffing.
“Notably, the readmission rate for revisional procedures decreased by a whopping 90%,” Dr. Aher said. “I think a lot of these targeted interventions just really helped these patients who were at a higher risk to begin with to be readmitted.”
New dietary dos and don’ts
“We changed our postoperative diet,” Dr. Aher said. Instead of a soft food diet a couple of days after surgery, the full liquid diet was extended to 3 weeks post surgery.
The clinicians also implemented what they called a ‘no MEALS’ policy, which stands for no Meat, Eggs And Leftovers. “We were having problems with meat, although tender fish was okay, and some other things that went down easily,” Dr. Aher said at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference. “We had some complaints about no eggs after surgery. A lot of patients love eggs,” he added. But they recommended avoiding eggs for 1 month after bariatric surgery to avoid nausea.
“Avoiding leftovers was also a big deal for patients,” Dr. Aher said. But patients who microwaved leftovers would “then come into the hospital with problems.”
Medication modifications
Another frequent cause of nausea was a “terrible and off-putting” taste when crushed tablets or medication capsules were added to the patient’s diet. Changing how patients took their medication “was a big help.” At the same time, there was a large institutional effort at Vanderbilt to start providing discharge medications in the hospital to increase postoperative compliance. “Bariatric surgery was one of the pilot programs for this,” Dr. Aher said. Discharge medications were filled by the pharmacy at Vanderbilt and delivered to the patient’s room, and a pharmacist or pharmacy intern explained how to use them. Compliance on medications increased, which may in turn have had an impact on readmissions.
Changes to patient management
Dr. Aher and his colleagues also changed where they treated patients who returned with problems. “Previously, when patients called in, the clinic diverted them to the emergency room. We stopped doing that, and increased our capacity to see these patients in the clinic instead.” This led to an increase in use of IV hydration in the clinic.
A meeting attendee asked if providing this service led to any problems with clinic capacity.
“Sometimes,” Dr. Aher said. “We don’t have a huge number of patients coming in for IV hydration, but when we had two come in on the same day, it did take up a couple of exam rooms.” To address this, the clinicians found other space in the clinic that would offer privacy for patients while not tying up exam rooms.
In addition, the clinic expanded nurse practitioner availability to 5 days a week to make the discharge process more consistent. “Of course, as we rolled all these things out, we made sure our educational material was updated accordingly,” Dr. Aher said.
The study demonstrates that a collaborative team effort and targeted interventions can result in a significant reduction in readmissions, Dr. Aher said. “Regular quality focused meetings are really important to facilitate recognition of various areas for improvement, especially in a high-volume center. Introducing an MBSAQIP registry serves as an excellent tool to effect these changes,” he said.
Dr. Aher had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – Targeted interventions aimed at reducing patient readmission after bariatric surgery at a high-volume academic medical center led to a 61% overall decrease year over year. The center also saw a substantial reduction in readmissions linked to the top three factors of readmission identified by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program, as well as a precipitous drop in the revisional surgery readmission rate.
“Our center, like so many others, has quarterly meetings in accordance with the MBSAQIP to look at our data. And this led to recognition of some common reasons for readmission,” said Chetan V. Aher, MD, a general surgeon at the department of surgery at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. Oral (PO) intolerance, dehydration, and nonemergent abdominal pain were the top reasons flagged by the MBSAQIP registry data at the medical center. Dr. Aher and his colleagues moved to focus on postoperative diet, administration of medications, management of patients who return to the hospital after surgery, and optimal staffing.
“Notably, the readmission rate for revisional procedures decreased by a whopping 90%,” Dr. Aher said. “I think a lot of these targeted interventions just really helped these patients who were at a higher risk to begin with to be readmitted.”
New dietary dos and don’ts
“We changed our postoperative diet,” Dr. Aher said. Instead of a soft food diet a couple of days after surgery, the full liquid diet was extended to 3 weeks post surgery.
The clinicians also implemented what they called a ‘no MEALS’ policy, which stands for no Meat, Eggs And Leftovers. “We were having problems with meat, although tender fish was okay, and some other things that went down easily,” Dr. Aher said at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference. “We had some complaints about no eggs after surgery. A lot of patients love eggs,” he added. But they recommended avoiding eggs for 1 month after bariatric surgery to avoid nausea.
“Avoiding leftovers was also a big deal for patients,” Dr. Aher said. But patients who microwaved leftovers would “then come into the hospital with problems.”
Medication modifications
Another frequent cause of nausea was a “terrible and off-putting” taste when crushed tablets or medication capsules were added to the patient’s diet. Changing how patients took their medication “was a big help.” At the same time, there was a large institutional effort at Vanderbilt to start providing discharge medications in the hospital to increase postoperative compliance. “Bariatric surgery was one of the pilot programs for this,” Dr. Aher said. Discharge medications were filled by the pharmacy at Vanderbilt and delivered to the patient’s room, and a pharmacist or pharmacy intern explained how to use them. Compliance on medications increased, which may in turn have had an impact on readmissions.
Changes to patient management
Dr. Aher and his colleagues also changed where they treated patients who returned with problems. “Previously, when patients called in, the clinic diverted them to the emergency room. We stopped doing that, and increased our capacity to see these patients in the clinic instead.” This led to an increase in use of IV hydration in the clinic.
A meeting attendee asked if providing this service led to any problems with clinic capacity.
“Sometimes,” Dr. Aher said. “We don’t have a huge number of patients coming in for IV hydration, but when we had two come in on the same day, it did take up a couple of exam rooms.” To address this, the clinicians found other space in the clinic that would offer privacy for patients while not tying up exam rooms.
In addition, the clinic expanded nurse practitioner availability to 5 days a week to make the discharge process more consistent. “Of course, as we rolled all these things out, we made sure our educational material was updated accordingly,” Dr. Aher said.
The study demonstrates that a collaborative team effort and targeted interventions can result in a significant reduction in readmissions, Dr. Aher said. “Regular quality focused meetings are really important to facilitate recognition of various areas for improvement, especially in a high-volume center. Introducing an MBSAQIP registry serves as an excellent tool to effect these changes,” he said.
Dr. Aher had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – Targeted interventions aimed at reducing patient readmission after bariatric surgery at a high-volume academic medical center led to a 61% overall decrease year over year. The center also saw a substantial reduction in readmissions linked to the top three factors of readmission identified by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program, as well as a precipitous drop in the revisional surgery readmission rate.
“Our center, like so many others, has quarterly meetings in accordance with the MBSAQIP to look at our data. And this led to recognition of some common reasons for readmission,” said Chetan V. Aher, MD, a general surgeon at the department of surgery at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. Oral (PO) intolerance, dehydration, and nonemergent abdominal pain were the top reasons flagged by the MBSAQIP registry data at the medical center. Dr. Aher and his colleagues moved to focus on postoperative diet, administration of medications, management of patients who return to the hospital after surgery, and optimal staffing.
“Notably, the readmission rate for revisional procedures decreased by a whopping 90%,” Dr. Aher said. “I think a lot of these targeted interventions just really helped these patients who were at a higher risk to begin with to be readmitted.”
New dietary dos and don’ts
“We changed our postoperative diet,” Dr. Aher said. Instead of a soft food diet a couple of days after surgery, the full liquid diet was extended to 3 weeks post surgery.
The clinicians also implemented what they called a ‘no MEALS’ policy, which stands for no Meat, Eggs And Leftovers. “We were having problems with meat, although tender fish was okay, and some other things that went down easily,” Dr. Aher said at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference. “We had some complaints about no eggs after surgery. A lot of patients love eggs,” he added. But they recommended avoiding eggs for 1 month after bariatric surgery to avoid nausea.
“Avoiding leftovers was also a big deal for patients,” Dr. Aher said. But patients who microwaved leftovers would “then come into the hospital with problems.”
Medication modifications
Another frequent cause of nausea was a “terrible and off-putting” taste when crushed tablets or medication capsules were added to the patient’s diet. Changing how patients took their medication “was a big help.” At the same time, there was a large institutional effort at Vanderbilt to start providing discharge medications in the hospital to increase postoperative compliance. “Bariatric surgery was one of the pilot programs for this,” Dr. Aher said. Discharge medications were filled by the pharmacy at Vanderbilt and delivered to the patient’s room, and a pharmacist or pharmacy intern explained how to use them. Compliance on medications increased, which may in turn have had an impact on readmissions.
Changes to patient management
Dr. Aher and his colleagues also changed where they treated patients who returned with problems. “Previously, when patients called in, the clinic diverted them to the emergency room. We stopped doing that, and increased our capacity to see these patients in the clinic instead.” This led to an increase in use of IV hydration in the clinic.
A meeting attendee asked if providing this service led to any problems with clinic capacity.
“Sometimes,” Dr. Aher said. “We don’t have a huge number of patients coming in for IV hydration, but when we had two come in on the same day, it did take up a couple of exam rooms.” To address this, the clinicians found other space in the clinic that would offer privacy for patients while not tying up exam rooms.
In addition, the clinic expanded nurse practitioner availability to 5 days a week to make the discharge process more consistent. “Of course, as we rolled all these things out, we made sure our educational material was updated accordingly,” Dr. Aher said.
The study demonstrates that a collaborative team effort and targeted interventions can result in a significant reduction in readmissions, Dr. Aher said. “Regular quality focused meetings are really important to facilitate recognition of various areas for improvement, especially in a high-volume center. Introducing an MBSAQIP registry serves as an excellent tool to effect these changes,” he said.
Dr. Aher had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT THE ACS QUALITY & SAFETY CONFERENCE
Key clinical point: A collaborative effort and target interventions can successfully reduce bariatric surgery readmissions.
Major finding: The overall bariatric surgery readmission rate dropped 61% in the year after intervention compared to the previous year.
Data source: Comparison of 471 bariatric procedures in 2015 to 539 others in 2016 at Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Disclosures: Dr. Aher had no relevant financial disclosures.
Safety alert for intragastric balloon systems
The Food and Drug Administration announced a safety alert on Aug. 10, 2017, for liquid-filled intragastric balloon systems, as they have caused five reports of unanticipated deaths that occurred from 2016 to present in patients.
The cause or incidence of patient death is still unknown, and the FDA has not been able to definitively attribute the deaths to the devices or the insertion procedures for these devices. All five reports show that patient deaths occurred within a month or less of balloon placement. In three of the reports, death occurred as soon as 1-3 days after balloon placement. The FDA has also received two additional reports of deaths in the same time period related to potential complications associated with balloon treatment.
The FDA continues to recommend that health care providers closely monitor patients treated with these devices for complications. Any adverse events related to intragastric balloon systems should be reported through MedWatch. The FDA will keep the public informed as new information becomes available.
Read the full safety alert on the FDA’s website.
The Food and Drug Administration announced a safety alert on Aug. 10, 2017, for liquid-filled intragastric balloon systems, as they have caused five reports of unanticipated deaths that occurred from 2016 to present in patients.
The cause or incidence of patient death is still unknown, and the FDA has not been able to definitively attribute the deaths to the devices or the insertion procedures for these devices. All five reports show that patient deaths occurred within a month or less of balloon placement. In three of the reports, death occurred as soon as 1-3 days after balloon placement. The FDA has also received two additional reports of deaths in the same time period related to potential complications associated with balloon treatment.
The FDA continues to recommend that health care providers closely monitor patients treated with these devices for complications. Any adverse events related to intragastric balloon systems should be reported through MedWatch. The FDA will keep the public informed as new information becomes available.
Read the full safety alert on the FDA’s website.
The Food and Drug Administration announced a safety alert on Aug. 10, 2017, for liquid-filled intragastric balloon systems, as they have caused five reports of unanticipated deaths that occurred from 2016 to present in patients.
The cause or incidence of patient death is still unknown, and the FDA has not been able to definitively attribute the deaths to the devices or the insertion procedures for these devices. All five reports show that patient deaths occurred within a month or less of balloon placement. In three of the reports, death occurred as soon as 1-3 days after balloon placement. The FDA has also received two additional reports of deaths in the same time period related to potential complications associated with balloon treatment.
The FDA continues to recommend that health care providers closely monitor patients treated with these devices for complications. Any adverse events related to intragastric balloon systems should be reported through MedWatch. The FDA will keep the public informed as new information becomes available.
Read the full safety alert on the FDA’s website.
Fluid protocol takes aim at bariatric surgery readmissions
NEW YORK – With dehydration considered a contributor to hospital readmission after bariatric weight loss surgery, a multidisciplinary team of clinicians searched for a way to get patients to drink up. Specifically,
The project results were presented at a poster session at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference.
“Our QI project was to streamline that process to ultimately eliminate or decrease those readmits,” Ms. Melei said.
They used 8-ounce water bottles. To track water consumption, they also numbered the bottles one through six for each patient. One-ounce cups were used during mealtimes. RNs, certified nursing assistants, and food service staff were educated about the fluid intake initiative. Only fluids provided by nursing were permitted and patients also received a clear message about fluid goals.
Another focus was standardizing communication with patients. They were not getting a consistent message from staff on what to expect before, during, and after surgery. “So we had to make sure [we] were all saying the same thing.”
The nurses and the other staff now ask the patients “Did you finish the bottle?” or “Where are you with the bottles?” Ms. Melei said. “At the end of a shift, the nurses document fluid consumption.”
During a 2-month baseline period, 12 patients drank an average 381.5 mL over 24 hours. Since the close of the project, the average daily fluid intake for patients undergoing bariatric surgery is 1,007 mL. In 12 months post implementation, average fluid intake for 39 patients jumped to 1,109.5 mL over 24 hours. “It was just such a hugely successful program. We had buy-in from every department, it worked really well, and we had great results,” said Cheryl Williams, the current bariatric program coordinator at Greenwich Hospital.
Sometimes dehydrated patients present to an emergency department complaining of vomiting, headache, and dizziness if they are not properly hydrated after surgery, Ms. Williams said. “Preventing dehydration helps to improve the patient’s recovery, as well as decrease emergency room visits and hospital admissions.”
Ashutosh Kaul, MD, FACS, medical director of the bariatric surgery program at Greenwich Hospital, said this study shows the importance of team building to improve patient care. “We built a core team that implemented a simple, low-cost, structured, and well-defined water distribution and documentation process, which resulted in better compliance of water intake. This reduced variability and improved postoperative intake progression, and we are presently studying its effect on reduction of readmissions and facilitating early discharge.”
Greenwich Hospital’s bariatric surgery center is accredited by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP), a collaboration between the American College of Surgeons and the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Ms. Williams and Ms. Melei had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – With dehydration considered a contributor to hospital readmission after bariatric weight loss surgery, a multidisciplinary team of clinicians searched for a way to get patients to drink up. Specifically,
The project results were presented at a poster session at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference.
“Our QI project was to streamline that process to ultimately eliminate or decrease those readmits,” Ms. Melei said.
They used 8-ounce water bottles. To track water consumption, they also numbered the bottles one through six for each patient. One-ounce cups were used during mealtimes. RNs, certified nursing assistants, and food service staff were educated about the fluid intake initiative. Only fluids provided by nursing were permitted and patients also received a clear message about fluid goals.
Another focus was standardizing communication with patients. They were not getting a consistent message from staff on what to expect before, during, and after surgery. “So we had to make sure [we] were all saying the same thing.”
The nurses and the other staff now ask the patients “Did you finish the bottle?” or “Where are you with the bottles?” Ms. Melei said. “At the end of a shift, the nurses document fluid consumption.”
During a 2-month baseline period, 12 patients drank an average 381.5 mL over 24 hours. Since the close of the project, the average daily fluid intake for patients undergoing bariatric surgery is 1,007 mL. In 12 months post implementation, average fluid intake for 39 patients jumped to 1,109.5 mL over 24 hours. “It was just such a hugely successful program. We had buy-in from every department, it worked really well, and we had great results,” said Cheryl Williams, the current bariatric program coordinator at Greenwich Hospital.
Sometimes dehydrated patients present to an emergency department complaining of vomiting, headache, and dizziness if they are not properly hydrated after surgery, Ms. Williams said. “Preventing dehydration helps to improve the patient’s recovery, as well as decrease emergency room visits and hospital admissions.”
Ashutosh Kaul, MD, FACS, medical director of the bariatric surgery program at Greenwich Hospital, said this study shows the importance of team building to improve patient care. “We built a core team that implemented a simple, low-cost, structured, and well-defined water distribution and documentation process, which resulted in better compliance of water intake. This reduced variability and improved postoperative intake progression, and we are presently studying its effect on reduction of readmissions and facilitating early discharge.”
Greenwich Hospital’s bariatric surgery center is accredited by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP), a collaboration between the American College of Surgeons and the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Ms. Williams and Ms. Melei had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – With dehydration considered a contributor to hospital readmission after bariatric weight loss surgery, a multidisciplinary team of clinicians searched for a way to get patients to drink up. Specifically,
The project results were presented at a poster session at the American College of Surgeons Quality and Safety Conference.
“Our QI project was to streamline that process to ultimately eliminate or decrease those readmits,” Ms. Melei said.
They used 8-ounce water bottles. To track water consumption, they also numbered the bottles one through six for each patient. One-ounce cups were used during mealtimes. RNs, certified nursing assistants, and food service staff were educated about the fluid intake initiative. Only fluids provided by nursing were permitted and patients also received a clear message about fluid goals.
Another focus was standardizing communication with patients. They were not getting a consistent message from staff on what to expect before, during, and after surgery. “So we had to make sure [we] were all saying the same thing.”
The nurses and the other staff now ask the patients “Did you finish the bottle?” or “Where are you with the bottles?” Ms. Melei said. “At the end of a shift, the nurses document fluid consumption.”
During a 2-month baseline period, 12 patients drank an average 381.5 mL over 24 hours. Since the close of the project, the average daily fluid intake for patients undergoing bariatric surgery is 1,007 mL. In 12 months post implementation, average fluid intake for 39 patients jumped to 1,109.5 mL over 24 hours. “It was just such a hugely successful program. We had buy-in from every department, it worked really well, and we had great results,” said Cheryl Williams, the current bariatric program coordinator at Greenwich Hospital.
Sometimes dehydrated patients present to an emergency department complaining of vomiting, headache, and dizziness if they are not properly hydrated after surgery, Ms. Williams said. “Preventing dehydration helps to improve the patient’s recovery, as well as decrease emergency room visits and hospital admissions.”
Ashutosh Kaul, MD, FACS, medical director of the bariatric surgery program at Greenwich Hospital, said this study shows the importance of team building to improve patient care. “We built a core team that implemented a simple, low-cost, structured, and well-defined water distribution and documentation process, which resulted in better compliance of water intake. This reduced variability and improved postoperative intake progression, and we are presently studying its effect on reduction of readmissions and facilitating early discharge.”
Greenwich Hospital’s bariatric surgery center is accredited by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP), a collaboration between the American College of Surgeons and the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Ms. Williams and Ms. Melei had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT THE ACS QUALITY & SAFETY CONFERENCE
Key clinical point: QI project to increase water intake after bariatric surgery could decrease hospital readmission rates.
Major finding: Multidisciplinary protocol increases 24-hour fluid intake from 382 mL to 1,110 mL on average.
Data source: Comparison of water consumed by 12 patients before versus 39 patients after implementation.
Disclosures: Ms. Williams and Ms. Melei had no relevant financial disclosures.
Better bariatric surgery outcomes with lower preoperative BMI
Delaying bariatric surgery until body mass index is highly elevated may reduce the likelihood of achieving a BMI of less than 30 within a year, according to a paper published online July 26 in JAMA Surgery.
A retrospective study using prospectively gathered clinical data of 27,320 adults who underwent bariatric surgery in Michigan showed around one in three (36%) achieved a BMI below 30 within a year after surgery (JAMA Surgery 2017, July 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.2348). But obese patients with a body mass index of less than 40 kg/m2 before undergoing bariatric surgery are significantly more likely to achieve a postoperative BMI of under 30.
Individuals who had a preoperative BMI of less than 40 had a 12-fold higher chance of getting their BMI below 30, compared to those whose preoperative BMI was 40 or above (95% confidence interval 1.71-14.16, P less than .001). Only 8.5% of individuals with a BMI at or above 50 achieved a postoperative BMI below 30.
The likelihood of getting below 30 within a year was eightfold higher in patients who had a sleeve gastrectomy, 21 times greater in those who underwent Roux-en-Y bypass, and 82 times higher in those who had a duodenal switch, compared with patients who had adjustable gastric banding (P less than .001).
The researchers also compared other outcomes in individuals whose BMI dropped below 30 and in those who did not achieve this degree of weight loss. The analysis showed that those with a BMI below 30 after 1 year had at least a twofold greater chance of discontinuing cholesterol-lowering medications, insulin, diabetes medications, antihypertensives, and CPAP for sleep apnea, compared with those whose BMI remained at 30 or above. They were also more than three times more likely to report being ‘very satisfied’ with the outcomes of surgery.
The authors noted that the cohort’s mean BMI was 48, which was above the established threshold for bariatric surgery, namely a BMI of 40, or 35 with weight-related comorbidities.
“Our results suggest that patients with morbid obesity should be targeted for surgery when their BMI is still less than 40, as these patients are more likely to achieve a target BMI that results in substantial reduction in weight-related comorbidities,” the authors wrote.
However, they stressed that their findings should not be taken as a reason to exclude patients with a BMI above 40 from surgery, pointing out that even for patients with higher preoperative BMIs, bariatric surgery offered substantial health and quality of life benefits.
They also acknowledged that 1-year weight data was available for around 50% of patients in the registry, which may have led to selection bias.
“Policies and practice patterns that delay or incentivize patients to pursue bariatric surgery only once the BMI is highly elevated can result in inferior outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan/Blue Care Network funded the study. Three authors had received salary support from Blue Cross Blue Shield. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
The authors’ conclusion that bariatric surgery should be more liberally applied to patients with less severe obesity is consistent with multiple reports of improved control of type 2 diabetes, if not remission, among lower-BMI patient populations following MBS [metabolic and bariatric surgery]. However, these reports generally do not refute the importance of weight loss in achieving important clinical benefit among patients with obesity-related comorbid disease.
One strength of the present study is that it is a clinical database. However, 50% attrition of the follow-up weight loss data at 1 year is potentially problematic.
Bruce M. Wolfe, MD, FACS, and Elizaveta Walker, MPH, are in the division of bariatric surgery, department of surgery, at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (JAMA Surgery 2017 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.2349). No conflicts of interest were declared.
The authors’ conclusion that bariatric surgery should be more liberally applied to patients with less severe obesity is consistent with multiple reports of improved control of type 2 diabetes, if not remission, among lower-BMI patient populations following MBS [metabolic and bariatric surgery]. However, these reports generally do not refute the importance of weight loss in achieving important clinical benefit among patients with obesity-related comorbid disease.
One strength of the present study is that it is a clinical database. However, 50% attrition of the follow-up weight loss data at 1 year is potentially problematic.
Bruce M. Wolfe, MD, FACS, and Elizaveta Walker, MPH, are in the division of bariatric surgery, department of surgery, at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (JAMA Surgery 2017 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.2349). No conflicts of interest were declared.
The authors’ conclusion that bariatric surgery should be more liberally applied to patients with less severe obesity is consistent with multiple reports of improved control of type 2 diabetes, if not remission, among lower-BMI patient populations following MBS [metabolic and bariatric surgery]. However, these reports generally do not refute the importance of weight loss in achieving important clinical benefit among patients with obesity-related comorbid disease.
One strength of the present study is that it is a clinical database. However, 50% attrition of the follow-up weight loss data at 1 year is potentially problematic.
Bruce M. Wolfe, MD, FACS, and Elizaveta Walker, MPH, are in the division of bariatric surgery, department of surgery, at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (JAMA Surgery 2017 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.2349). No conflicts of interest were declared.
Delaying bariatric surgery until body mass index is highly elevated may reduce the likelihood of achieving a BMI of less than 30 within a year, according to a paper published online July 26 in JAMA Surgery.
A retrospective study using prospectively gathered clinical data of 27,320 adults who underwent bariatric surgery in Michigan showed around one in three (36%) achieved a BMI below 30 within a year after surgery (JAMA Surgery 2017, July 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.2348). But obese patients with a body mass index of less than 40 kg/m2 before undergoing bariatric surgery are significantly more likely to achieve a postoperative BMI of under 30.
Individuals who had a preoperative BMI of less than 40 had a 12-fold higher chance of getting their BMI below 30, compared to those whose preoperative BMI was 40 or above (95% confidence interval 1.71-14.16, P less than .001). Only 8.5% of individuals with a BMI at or above 50 achieved a postoperative BMI below 30.
The likelihood of getting below 30 within a year was eightfold higher in patients who had a sleeve gastrectomy, 21 times greater in those who underwent Roux-en-Y bypass, and 82 times higher in those who had a duodenal switch, compared with patients who had adjustable gastric banding (P less than .001).
The researchers also compared other outcomes in individuals whose BMI dropped below 30 and in those who did not achieve this degree of weight loss. The analysis showed that those with a BMI below 30 after 1 year had at least a twofold greater chance of discontinuing cholesterol-lowering medications, insulin, diabetes medications, antihypertensives, and CPAP for sleep apnea, compared with those whose BMI remained at 30 or above. They were also more than three times more likely to report being ‘very satisfied’ with the outcomes of surgery.
The authors noted that the cohort’s mean BMI was 48, which was above the established threshold for bariatric surgery, namely a BMI of 40, or 35 with weight-related comorbidities.
“Our results suggest that patients with morbid obesity should be targeted for surgery when their BMI is still less than 40, as these patients are more likely to achieve a target BMI that results in substantial reduction in weight-related comorbidities,” the authors wrote.
However, they stressed that their findings should not be taken as a reason to exclude patients with a BMI above 40 from surgery, pointing out that even for patients with higher preoperative BMIs, bariatric surgery offered substantial health and quality of life benefits.
They also acknowledged that 1-year weight data was available for around 50% of patients in the registry, which may have led to selection bias.
“Policies and practice patterns that delay or incentivize patients to pursue bariatric surgery only once the BMI is highly elevated can result in inferior outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan/Blue Care Network funded the study. Three authors had received salary support from Blue Cross Blue Shield. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
Delaying bariatric surgery until body mass index is highly elevated may reduce the likelihood of achieving a BMI of less than 30 within a year, according to a paper published online July 26 in JAMA Surgery.
A retrospective study using prospectively gathered clinical data of 27,320 adults who underwent bariatric surgery in Michigan showed around one in three (36%) achieved a BMI below 30 within a year after surgery (JAMA Surgery 2017, July 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.2348). But obese patients with a body mass index of less than 40 kg/m2 before undergoing bariatric surgery are significantly more likely to achieve a postoperative BMI of under 30.
Individuals who had a preoperative BMI of less than 40 had a 12-fold higher chance of getting their BMI below 30, compared to those whose preoperative BMI was 40 or above (95% confidence interval 1.71-14.16, P less than .001). Only 8.5% of individuals with a BMI at or above 50 achieved a postoperative BMI below 30.
The likelihood of getting below 30 within a year was eightfold higher in patients who had a sleeve gastrectomy, 21 times greater in those who underwent Roux-en-Y bypass, and 82 times higher in those who had a duodenal switch, compared with patients who had adjustable gastric banding (P less than .001).
The researchers also compared other outcomes in individuals whose BMI dropped below 30 and in those who did not achieve this degree of weight loss. The analysis showed that those with a BMI below 30 after 1 year had at least a twofold greater chance of discontinuing cholesterol-lowering medications, insulin, diabetes medications, antihypertensives, and CPAP for sleep apnea, compared with those whose BMI remained at 30 or above. They were also more than three times more likely to report being ‘very satisfied’ with the outcomes of surgery.
The authors noted that the cohort’s mean BMI was 48, which was above the established threshold for bariatric surgery, namely a BMI of 40, or 35 with weight-related comorbidities.
“Our results suggest that patients with morbid obesity should be targeted for surgery when their BMI is still less than 40, as these patients are more likely to achieve a target BMI that results in substantial reduction in weight-related comorbidities,” the authors wrote.
However, they stressed that their findings should not be taken as a reason to exclude patients with a BMI above 40 from surgery, pointing out that even for patients with higher preoperative BMIs, bariatric surgery offered substantial health and quality of life benefits.
They also acknowledged that 1-year weight data was available for around 50% of patients in the registry, which may have led to selection bias.
“Policies and practice patterns that delay or incentivize patients to pursue bariatric surgery only once the BMI is highly elevated can result in inferior outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan/Blue Care Network funded the study. Three authors had received salary support from Blue Cross Blue Shield. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Key clinical point: A BMI below 40 prior to undergoing bariatric surgery gives patients a significantly better chance of achieving a 1-year postoperative BMI under 30.
Major finding: Obese patients with a BMI less than 40 before undergoing bariatric surgery are more than 12 times more likely to achieve a postoperative BMI of under 30.
Data source: A retrospective study using prospectively gathered clinical data of 27, 320 adults who underwent bariatric surgery.
Disclosures: Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan/Blue Care Network funded the study. Three authors had received salary support from Blue Cross Blue Shield. No other conflicts of interest were declared.