User login
Why Cardiac Biomarkers Don’t Help Predict Heart Disease
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s the counterintuitive stuff in epidemiology that always really interests me. One intuition many of us have is that if a risk factor is significantly associated with an outcome, knowledge of that risk factor would help to predict that outcome. Makes sense. Feels right.
But it’s not right. Not always.
Here’s a fake example to illustrate my point. Let’s say we have 10,000 individuals who we follow for 10 years and 2000 of them die. (It’s been a rough decade.) At baseline, I measured a novel biomarker, the Perry Factor, in everyone. To keep it simple, the Perry Factor has only two values: 0 or 1.
I then do a standard associational analysis and find that individuals who are positive for the Perry Factor have a 40-fold higher odds of death than those who are negative for it. I am beginning to reconsider ascribing my good name to this biomarker. This is a highly statistically significant result — a P value <.001.
Clearly, knowledge of the Perry Factor should help me predict who will die in the cohort. I evaluate predictive power using a metric called the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC, referred to as the C-statistic in time-to-event studies). It tells you, given two people — one who dies and one who doesn’t — how frequently you “pick” the right person, given the knowledge of their Perry Factor.
A C-statistic of 0.5, or 50%, would mean the Perry Factor gives you no better results than a coin flip; it’s chance. A C-statistic of 1 is perfect prediction. So, what will the C-statistic be, given the incredibly strong association of the Perry Factor with outcomes? 0.9? 0.95?
0.5024. Almost useless.
Let’s figure out why strength of association and usefulness for prediction are not always the same thing.
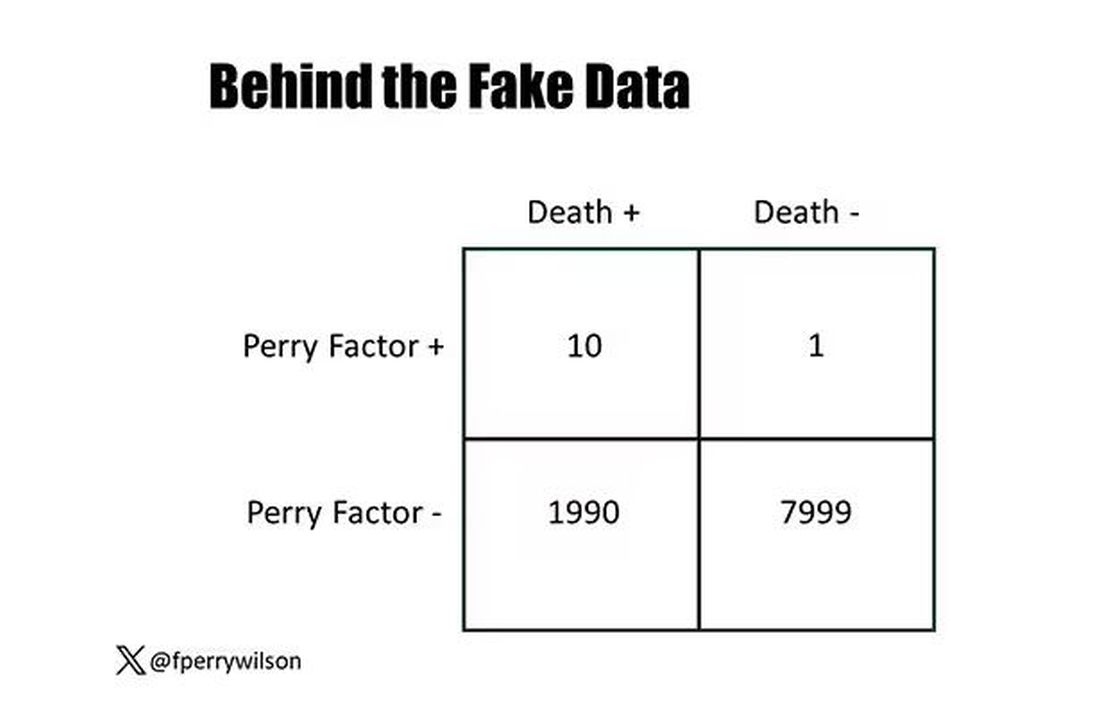
I constructed my fake Perry Factor dataset quite carefully to illustrate this point. Let me show you what happened. What you see here is a breakdown of the patients in my fake study. You can see that just 11 of them were Perry Factor positive, but 10 of those 11 ended up dying.
That’s quite unlikely by chance alone. It really does appear that if you have Perry Factor, your risk for death is much higher. But the reason that Perry Factor is a bad predictor is because it is so rare in the population. Sure, you can use it to correctly predict the outcome of 10 of the 11 people who have it, but the vast majority of people don’t have Perry Factor. It’s useless to distinguish who will die vs who will live in that population.
Why have I spent so much time trying to reverse our intuition that strength of association and strength of predictive power must be related? Because it helps to explain this paper, “Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population,” appearing in JAMA, which is a very nice piece of work trying to help us better predict cardiovascular disease.
I don’t need to tell you that cardiovascular disease is the number-one killer in this country and most of the world. I don’t need to tell you that we have really good preventive therapies and lifestyle interventions that can reduce the risk. But it would be nice to know in whom, specifically, we should use those interventions.
Cardiovascular risk scores, to date, are pretty simple. The most common one in use in the United States, the pooled cohort risk equation, has nine variables, two of which require a cholesterol panel and one a blood pressure test. It’s easy and it’s pretty accurate.
Using the score from the pooled cohort risk calculator, you get a C-statistic as high as 0.82 when applied to Black women, a low of 0.71 when applied to Black men. Non-Black individuals are in the middle. Not bad. But, clearly, not perfect.
And aren’t we in the era of big data, the era of personalized medicine? We have dozens, maybe hundreds, of quantifiable biomarkers that are associated with subsequent heart disease. Surely, by adding these biomarkers into the risk equation, we can improve prediction. Right?
The JAMA study includes 164,054 patients pooled from 28 cohort studies from 12 countries. All the studies measured various key biomarkers at baseline and followed their participants for cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, coronary revascularization, and so on.
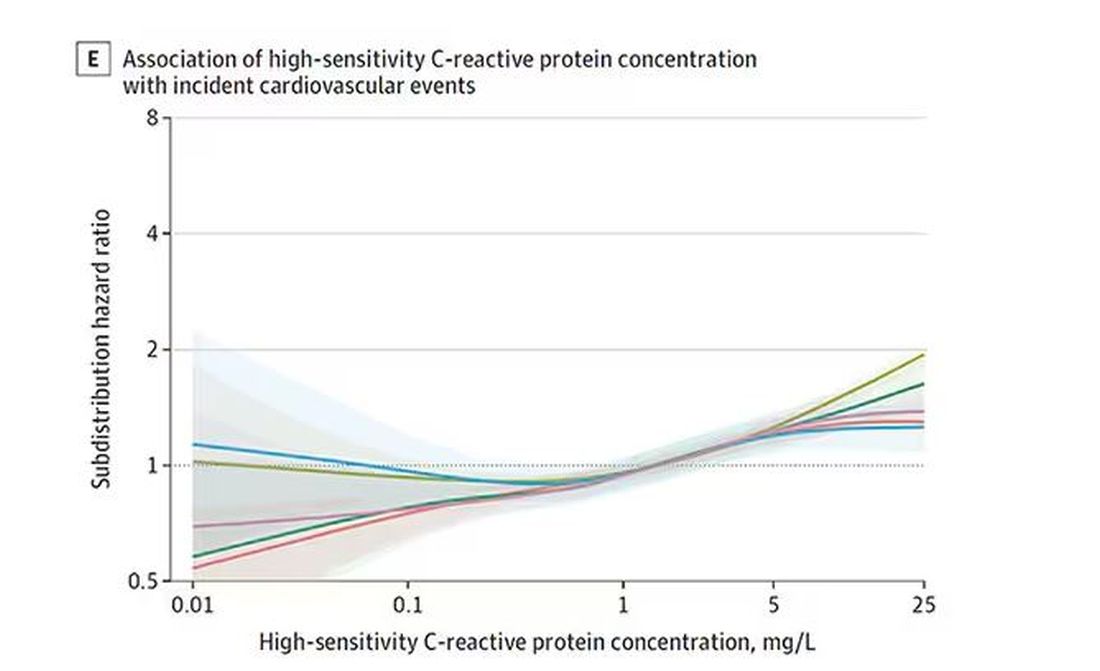
The biomarkers in question are really the big guns in this space: troponin, a marker of stress on the heart muscle; NT-proBNP, a marker of stretch on the heart muscle; and C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation. In every case, higher levels of these markers at baseline were associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease in the future.
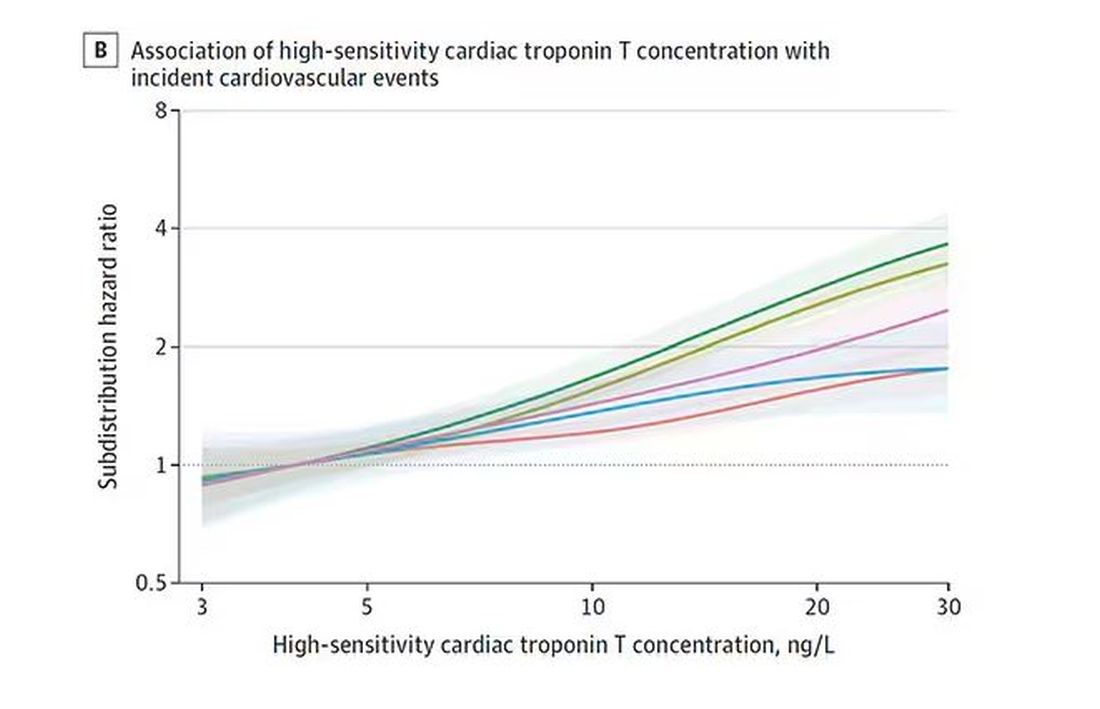
Troponin T, shown here, has a basically linear risk with subsequent cardiovascular disease.
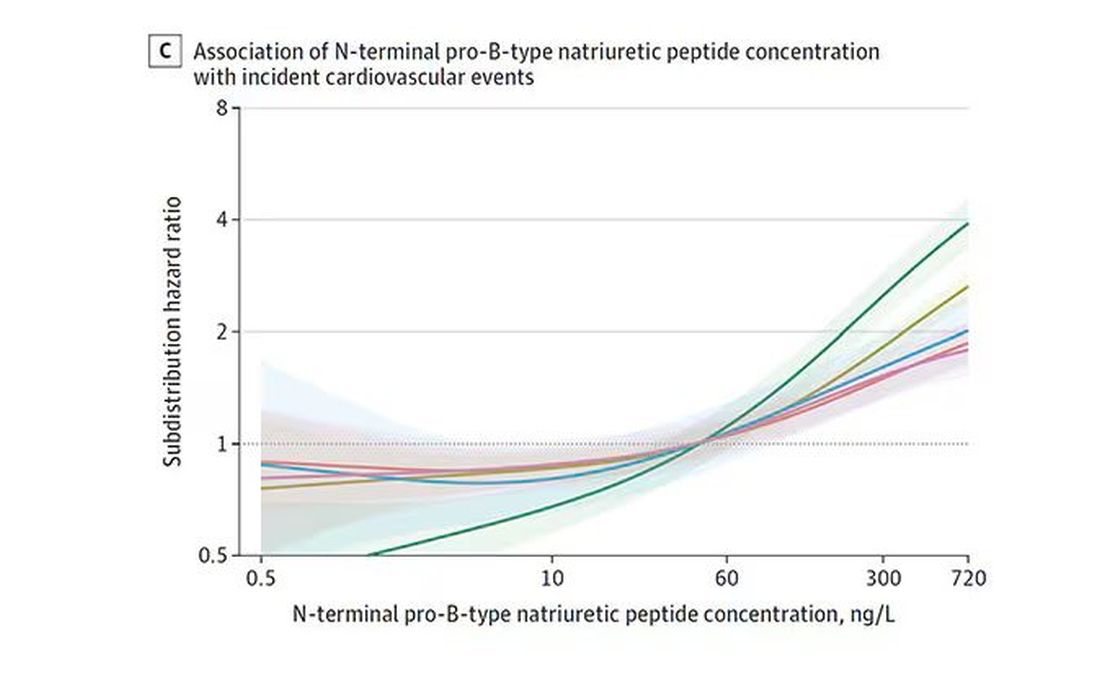
BNP seems to demonstrate more of a threshold effect, where levels above 60 start to associate with problems.
And CRP does a similar thing, with levels above 1.
All of these findings were statistically significant. If you have higher levels of one or more of these biomarkers, you are more likely to have cardiovascular disease in the future.
Of course, our old friend the pooled cohort risk equation is still here — in the background — requiring just that one blood test and measurement of blood pressure. Let’s talk about predictive power.
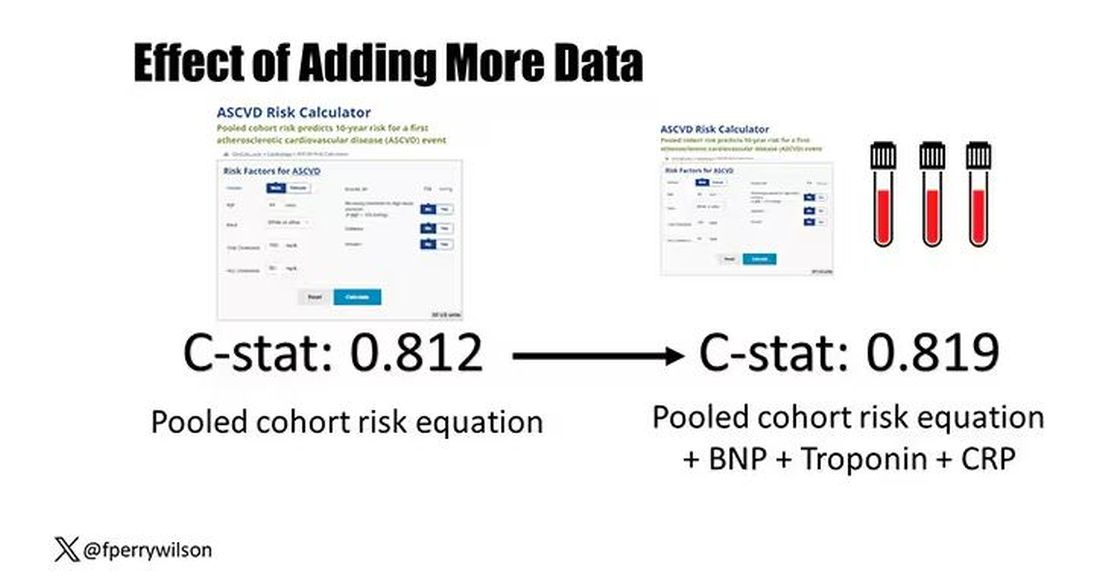
The pooled cohort risk equation score, in this study, had a C-statistic of 0.812.
By adding troponin, BNP, and CRP to the equation, the new C-statistic is 0.819. Barely any change.
Now, the authors looked at different types of prediction here. The greatest improvement in the AUC was seen when they tried to predict heart failure within 1 year of measurement; there the AUC improved by 0.04. But the presence of BNP as a biomarker and the short time window of 1 year makes me wonder whether this is really prediction at all or whether they were essentially just diagnosing people with existing heart failure.
Why does this happen? Why do these promising biomarkers, clearly associated with bad outcomes, fail to improve our ability to predict the future? I already gave one example, which has to do with how the markers are distributed in the population. But even more relevant here is that the new markers will only improve prediction insofar as they are not already represented in the old predictive model.
Of course, BNP, for example, wasn’t in the old model. But smoking was. Diabetes was. Blood pressure was. All of that data might actually tell you something about the patient’s BNP through their mutual correlation. And improvement in prediction requires new information.
This is actually why I consider this a really successful study. We need to do studies like this to help us find what those new sources of information might be.
We will never get to a C-statistic of 1. Perfect prediction is the domain of palm readers and astrophysicists. But better prediction is always possible through data. The big question, of course, is which data?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s the counterintuitive stuff in epidemiology that always really interests me. One intuition many of us have is that if a risk factor is significantly associated with an outcome, knowledge of that risk factor would help to predict that outcome. Makes sense. Feels right.
But it’s not right. Not always.
Here’s a fake example to illustrate my point. Let’s say we have 10,000 individuals who we follow for 10 years and 2000 of them die. (It’s been a rough decade.) At baseline, I measured a novel biomarker, the Perry Factor, in everyone. To keep it simple, the Perry Factor has only two values: 0 or 1.
I then do a standard associational analysis and find that individuals who are positive for the Perry Factor have a 40-fold higher odds of death than those who are negative for it. I am beginning to reconsider ascribing my good name to this biomarker. This is a highly statistically significant result — a P value <.001.
Clearly, knowledge of the Perry Factor should help me predict who will die in the cohort. I evaluate predictive power using a metric called the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC, referred to as the C-statistic in time-to-event studies). It tells you, given two people — one who dies and one who doesn’t — how frequently you “pick” the right person, given the knowledge of their Perry Factor.
A C-statistic of 0.5, or 50%, would mean the Perry Factor gives you no better results than a coin flip; it’s chance. A C-statistic of 1 is perfect prediction. So, what will the C-statistic be, given the incredibly strong association of the Perry Factor with outcomes? 0.9? 0.95?
0.5024. Almost useless.
Let’s figure out why strength of association and usefulness for prediction are not always the same thing.
I constructed my fake Perry Factor dataset quite carefully to illustrate this point. Let me show you what happened. What you see here is a breakdown of the patients in my fake study. You can see that just 11 of them were Perry Factor positive, but 10 of those 11 ended up dying.
That’s quite unlikely by chance alone. It really does appear that if you have Perry Factor, your risk for death is much higher. But the reason that Perry Factor is a bad predictor is because it is so rare in the population. Sure, you can use it to correctly predict the outcome of 10 of the 11 people who have it, but the vast majority of people don’t have Perry Factor. It’s useless to distinguish who will die vs who will live in that population.
Why have I spent so much time trying to reverse our intuition that strength of association and strength of predictive power must be related? Because it helps to explain this paper, “Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population,” appearing in JAMA, which is a very nice piece of work trying to help us better predict cardiovascular disease.
I don’t need to tell you that cardiovascular disease is the number-one killer in this country and most of the world. I don’t need to tell you that we have really good preventive therapies and lifestyle interventions that can reduce the risk. But it would be nice to know in whom, specifically, we should use those interventions.
Cardiovascular risk scores, to date, are pretty simple. The most common one in use in the United States, the pooled cohort risk equation, has nine variables, two of which require a cholesterol panel and one a blood pressure test. It’s easy and it’s pretty accurate.
Using the score from the pooled cohort risk calculator, you get a C-statistic as high as 0.82 when applied to Black women, a low of 0.71 when applied to Black men. Non-Black individuals are in the middle. Not bad. But, clearly, not perfect.
And aren’t we in the era of big data, the era of personalized medicine? We have dozens, maybe hundreds, of quantifiable biomarkers that are associated with subsequent heart disease. Surely, by adding these biomarkers into the risk equation, we can improve prediction. Right?
The JAMA study includes 164,054 patients pooled from 28 cohort studies from 12 countries. All the studies measured various key biomarkers at baseline and followed their participants for cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, coronary revascularization, and so on.
The biomarkers in question are really the big guns in this space: troponin, a marker of stress on the heart muscle; NT-proBNP, a marker of stretch on the heart muscle; and C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation. In every case, higher levels of these markers at baseline were associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease in the future.
Troponin T, shown here, has a basically linear risk with subsequent cardiovascular disease.
BNP seems to demonstrate more of a threshold effect, where levels above 60 start to associate with problems.
And CRP does a similar thing, with levels above 1.
All of these findings were statistically significant. If you have higher levels of one or more of these biomarkers, you are more likely to have cardiovascular disease in the future.
Of course, our old friend the pooled cohort risk equation is still here — in the background — requiring just that one blood test and measurement of blood pressure. Let’s talk about predictive power.
The pooled cohort risk equation score, in this study, had a C-statistic of 0.812.
By adding troponin, BNP, and CRP to the equation, the new C-statistic is 0.819. Barely any change.
Now, the authors looked at different types of prediction here. The greatest improvement in the AUC was seen when they tried to predict heart failure within 1 year of measurement; there the AUC improved by 0.04. But the presence of BNP as a biomarker and the short time window of 1 year makes me wonder whether this is really prediction at all or whether they were essentially just diagnosing people with existing heart failure.
Why does this happen? Why do these promising biomarkers, clearly associated with bad outcomes, fail to improve our ability to predict the future? I already gave one example, which has to do with how the markers are distributed in the population. But even more relevant here is that the new markers will only improve prediction insofar as they are not already represented in the old predictive model.
Of course, BNP, for example, wasn’t in the old model. But smoking was. Diabetes was. Blood pressure was. All of that data might actually tell you something about the patient’s BNP through their mutual correlation. And improvement in prediction requires new information.
This is actually why I consider this a really successful study. We need to do studies like this to help us find what those new sources of information might be.
We will never get to a C-statistic of 1. Perfect prediction is the domain of palm readers and astrophysicists. But better prediction is always possible through data. The big question, of course, is which data?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s the counterintuitive stuff in epidemiology that always really interests me. One intuition many of us have is that if a risk factor is significantly associated with an outcome, knowledge of that risk factor would help to predict that outcome. Makes sense. Feels right.
But it’s not right. Not always.
Here’s a fake example to illustrate my point. Let’s say we have 10,000 individuals who we follow for 10 years and 2000 of them die. (It’s been a rough decade.) At baseline, I measured a novel biomarker, the Perry Factor, in everyone. To keep it simple, the Perry Factor has only two values: 0 or 1.
I then do a standard associational analysis and find that individuals who are positive for the Perry Factor have a 40-fold higher odds of death than those who are negative for it. I am beginning to reconsider ascribing my good name to this biomarker. This is a highly statistically significant result — a P value <.001.
Clearly, knowledge of the Perry Factor should help me predict who will die in the cohort. I evaluate predictive power using a metric called the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC, referred to as the C-statistic in time-to-event studies). It tells you, given two people — one who dies and one who doesn’t — how frequently you “pick” the right person, given the knowledge of their Perry Factor.
A C-statistic of 0.5, or 50%, would mean the Perry Factor gives you no better results than a coin flip; it’s chance. A C-statistic of 1 is perfect prediction. So, what will the C-statistic be, given the incredibly strong association of the Perry Factor with outcomes? 0.9? 0.95?
0.5024. Almost useless.
Let’s figure out why strength of association and usefulness for prediction are not always the same thing.
I constructed my fake Perry Factor dataset quite carefully to illustrate this point. Let me show you what happened. What you see here is a breakdown of the patients in my fake study. You can see that just 11 of them were Perry Factor positive, but 10 of those 11 ended up dying.
That’s quite unlikely by chance alone. It really does appear that if you have Perry Factor, your risk for death is much higher. But the reason that Perry Factor is a bad predictor is because it is so rare in the population. Sure, you can use it to correctly predict the outcome of 10 of the 11 people who have it, but the vast majority of people don’t have Perry Factor. It’s useless to distinguish who will die vs who will live in that population.
Why have I spent so much time trying to reverse our intuition that strength of association and strength of predictive power must be related? Because it helps to explain this paper, “Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population,” appearing in JAMA, which is a very nice piece of work trying to help us better predict cardiovascular disease.
I don’t need to tell you that cardiovascular disease is the number-one killer in this country and most of the world. I don’t need to tell you that we have really good preventive therapies and lifestyle interventions that can reduce the risk. But it would be nice to know in whom, specifically, we should use those interventions.
Cardiovascular risk scores, to date, are pretty simple. The most common one in use in the United States, the pooled cohort risk equation, has nine variables, two of which require a cholesterol panel and one a blood pressure test. It’s easy and it’s pretty accurate.
Using the score from the pooled cohort risk calculator, you get a C-statistic as high as 0.82 when applied to Black women, a low of 0.71 when applied to Black men. Non-Black individuals are in the middle. Not bad. But, clearly, not perfect.
And aren’t we in the era of big data, the era of personalized medicine? We have dozens, maybe hundreds, of quantifiable biomarkers that are associated with subsequent heart disease. Surely, by adding these biomarkers into the risk equation, we can improve prediction. Right?
The JAMA study includes 164,054 patients pooled from 28 cohort studies from 12 countries. All the studies measured various key biomarkers at baseline and followed their participants for cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, coronary revascularization, and so on.
The biomarkers in question are really the big guns in this space: troponin, a marker of stress on the heart muscle; NT-proBNP, a marker of stretch on the heart muscle; and C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation. In every case, higher levels of these markers at baseline were associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease in the future.
Troponin T, shown here, has a basically linear risk with subsequent cardiovascular disease.
BNP seems to demonstrate more of a threshold effect, where levels above 60 start to associate with problems.
And CRP does a similar thing, with levels above 1.
All of these findings were statistically significant. If you have higher levels of one or more of these biomarkers, you are more likely to have cardiovascular disease in the future.
Of course, our old friend the pooled cohort risk equation is still here — in the background — requiring just that one blood test and measurement of blood pressure. Let’s talk about predictive power.
The pooled cohort risk equation score, in this study, had a C-statistic of 0.812.
By adding troponin, BNP, and CRP to the equation, the new C-statistic is 0.819. Barely any change.
Now, the authors looked at different types of prediction here. The greatest improvement in the AUC was seen when they tried to predict heart failure within 1 year of measurement; there the AUC improved by 0.04. But the presence of BNP as a biomarker and the short time window of 1 year makes me wonder whether this is really prediction at all or whether they were essentially just diagnosing people with existing heart failure.
Why does this happen? Why do these promising biomarkers, clearly associated with bad outcomes, fail to improve our ability to predict the future? I already gave one example, which has to do with how the markers are distributed in the population. But even more relevant here is that the new markers will only improve prediction insofar as they are not already represented in the old predictive model.
Of course, BNP, for example, wasn’t in the old model. But smoking was. Diabetes was. Blood pressure was. All of that data might actually tell you something about the patient’s BNP through their mutual correlation. And improvement in prediction requires new information.
This is actually why I consider this a really successful study. We need to do studies like this to help us find what those new sources of information might be.
We will never get to a C-statistic of 1. Perfect prediction is the domain of palm readers and astrophysicists. But better prediction is always possible through data. The big question, of course, is which data?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Incorporating Obstetric History Matters for CVD Risk Management in Autoimmune Diseases
NEW YORK — Systemic autoimmune disease is well-recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but less recognized as a cardiovascular risk factor is a history of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, and cardiologists and rheumatologists need to include an obstetric history when managing patients with autoimmune diseases, a specialist in reproductive health in rheumatology told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
“Autoimmune diseases, lupus in particular, increase the risk for both cardiovascular disease and maternal placental syndromes,” Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, a professor at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and a specialist in reproductive health issues in rheumatology patients, told attendees. “For those patients who have complications during pregnancy, it further increases their already increased risk for later cardiovascular disease.”
CVD Risk Double Whammy
A history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and problematic pregnancy can be a double whammy for CVD risk. Dr. Sammaritano cited a 2022 meta-analysis that showed patients with SLE had a 2.5 times greater risk for stroke and almost three times greater risk for myocardial infarction than people without SLE.
Maternal placental syndromes include pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, preeclampsia, premature membrane rupture, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise, Dr. Sammaritano said. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, formerly called adverse pregnancy outcomes, she noted, include gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Pregnancy complications can have an adverse effect on the mother’s postpartum cardiovascular health, Dr. Sammaritano noted, a fact borne out by the cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes population-based retrospective cohort study and a 2007 meta-analysis that found a history of preeclampsia doubles the risk for venous thromboembolism, stroke, and ischemic heart disease up to 15 years after pregnancy.
“It is always important to obtain a reproductive health history from patients with autoimmune diseases,” Dr. Sammaritano told this news organization in an interview. “This is an integral part of any medical history. In the usual setting, this includes not only pregnancy history but also use of contraception in reproductive-aged women. Unplanned pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes in the setting of active or severe autoimmune disease or when teratogenic medications are used.”
Pregnancy history can be a factor in a woman’s cardiovascular health more than 15 years postpartum, even if a woman is no longer planning a pregnancy or is menopausal. “As such, this history is important in assessing every woman’s risk profile for CVD in addition to usual traditional risk factors,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“It is even more important for women with autoimmune disorders, who have been shown to have an already increased risk for CVD independent of their pregnancy history, likely related to a chronic inflammatory state and other autoimmune-related factors such as presence of antiphospholipid antibodies [aPL] or use of corticosteroids.”
Timing of disease onset is also an issue, she said. “In patients with SLE, for example, onset of CVD is much earlier than in the general population,” Dr. Sammaritano said. “As a result, these patients should likely be assessed for risk — both traditional and other risk factors — earlier than the general population, especially if an adverse obstetric history is present.”
At the younger end of the age continuum, women with autoimmune disease, including SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, who are pregnant should be put on guideline-directed low-dose aspirin preeclampsia prophylaxis, Dr. Sammaritano said. “Whether every patient with SLE needs this is still uncertain, but certainly, those with a history of renal disease, hypertension, or aPL antibody clearly do,” she added.
The evidence supporting hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in these patients is controversial, but Dr. Sammaritano noted two meta-analyses, one in 2022 and the other in 2023, that showed that HCQ lowered the risk for preeclampsia in women.
“The clear benefit of HCQ in preventing maternal disease complications, including flare, means we recommend it regardless for all patients with SLE at baseline and during pregnancy [if tolerated],” Dr. Sammaritano said. “The benefit or optimal use of these medications in other autoimmune diseases is less studied and less certain.”
Dr. Sammaritano added in her presentation, “We really need better therapies and, hopefully, those will be on the way, but I think the takeaway message, particularly for practicing rheumatologists and cardiologists, is to ask the question about obstetric history. Many of us don’t. It doesn’t seem relevant in the moment, but it really is in terms of the patient’s long-term risk for cardiovascular disease.”
The Case for Treatment During Pregnancy
Prophylaxis against pregnancy complications in patients with autoimmune disease may be achievable, Taryn Youngstein, MBBS, consultant rheumatologist and codirector of the Centre of Excellence in Vasculitis Research, Imperial College London, London, England, told this news organization after Dr. Sammaritano’s presentation. At the 2023 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, her group reported the safety and effectiveness of continuing tocilizumab in pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis, a large-vessel vasculitis predominantly affecting women of reproductive age.
“What traditionally happens is you would stop the biologic particularly before the third trimester because of safety and concerns that the monoclonal antibody is actively transported across the placenta, which means the baby gets much more concentration of the drug than the mum,” Dr. Youngstein said.
It’s a situation physicians must monitor closely, she said. “The mum is donating their immune system to the baby, but they’re also donating drug.”
“In high-risk patients, we would share decision-making with the patient,” Dr. Youngstein continued. “We have decided it’s too high of a risk for us to stop the drug, so we have been continuing the interleukin-6 [IL-6] inhibitor throughout the entire pregnancy.”
The data from Dr. Youngstein’s group showed that pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis who continued IL-6 inhibition therapy all carried to term with healthy births.
“We’ve shown that it’s relatively safe to do that, but you have to be very careful in monitoring the baby,” she said. This includes not giving the infant any live vaccines at birth because it will have the high levels of IL-6 inhibition, she said.
Dr. Sammaritano and Dr. Youngstein had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Systemic autoimmune disease is well-recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but less recognized as a cardiovascular risk factor is a history of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, and cardiologists and rheumatologists need to include an obstetric history when managing patients with autoimmune diseases, a specialist in reproductive health in rheumatology told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
“Autoimmune diseases, lupus in particular, increase the risk for both cardiovascular disease and maternal placental syndromes,” Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, a professor at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and a specialist in reproductive health issues in rheumatology patients, told attendees. “For those patients who have complications during pregnancy, it further increases their already increased risk for later cardiovascular disease.”
CVD Risk Double Whammy
A history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and problematic pregnancy can be a double whammy for CVD risk. Dr. Sammaritano cited a 2022 meta-analysis that showed patients with SLE had a 2.5 times greater risk for stroke and almost three times greater risk for myocardial infarction than people without SLE.
Maternal placental syndromes include pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, preeclampsia, premature membrane rupture, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise, Dr. Sammaritano said. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, formerly called adverse pregnancy outcomes, she noted, include gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Pregnancy complications can have an adverse effect on the mother’s postpartum cardiovascular health, Dr. Sammaritano noted, a fact borne out by the cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes population-based retrospective cohort study and a 2007 meta-analysis that found a history of preeclampsia doubles the risk for venous thromboembolism, stroke, and ischemic heart disease up to 15 years after pregnancy.
“It is always important to obtain a reproductive health history from patients with autoimmune diseases,” Dr. Sammaritano told this news organization in an interview. “This is an integral part of any medical history. In the usual setting, this includes not only pregnancy history but also use of contraception in reproductive-aged women. Unplanned pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes in the setting of active or severe autoimmune disease or when teratogenic medications are used.”
Pregnancy history can be a factor in a woman’s cardiovascular health more than 15 years postpartum, even if a woman is no longer planning a pregnancy or is menopausal. “As such, this history is important in assessing every woman’s risk profile for CVD in addition to usual traditional risk factors,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“It is even more important for women with autoimmune disorders, who have been shown to have an already increased risk for CVD independent of their pregnancy history, likely related to a chronic inflammatory state and other autoimmune-related factors such as presence of antiphospholipid antibodies [aPL] or use of corticosteroids.”
Timing of disease onset is also an issue, she said. “In patients with SLE, for example, onset of CVD is much earlier than in the general population,” Dr. Sammaritano said. “As a result, these patients should likely be assessed for risk — both traditional and other risk factors — earlier than the general population, especially if an adverse obstetric history is present.”
At the younger end of the age continuum, women with autoimmune disease, including SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, who are pregnant should be put on guideline-directed low-dose aspirin preeclampsia prophylaxis, Dr. Sammaritano said. “Whether every patient with SLE needs this is still uncertain, but certainly, those with a history of renal disease, hypertension, or aPL antibody clearly do,” she added.
The evidence supporting hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in these patients is controversial, but Dr. Sammaritano noted two meta-analyses, one in 2022 and the other in 2023, that showed that HCQ lowered the risk for preeclampsia in women.
“The clear benefit of HCQ in preventing maternal disease complications, including flare, means we recommend it regardless for all patients with SLE at baseline and during pregnancy [if tolerated],” Dr. Sammaritano said. “The benefit or optimal use of these medications in other autoimmune diseases is less studied and less certain.”
Dr. Sammaritano added in her presentation, “We really need better therapies and, hopefully, those will be on the way, but I think the takeaway message, particularly for practicing rheumatologists and cardiologists, is to ask the question about obstetric history. Many of us don’t. It doesn’t seem relevant in the moment, but it really is in terms of the patient’s long-term risk for cardiovascular disease.”
The Case for Treatment During Pregnancy
Prophylaxis against pregnancy complications in patients with autoimmune disease may be achievable, Taryn Youngstein, MBBS, consultant rheumatologist and codirector of the Centre of Excellence in Vasculitis Research, Imperial College London, London, England, told this news organization after Dr. Sammaritano’s presentation. At the 2023 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, her group reported the safety and effectiveness of continuing tocilizumab in pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis, a large-vessel vasculitis predominantly affecting women of reproductive age.
“What traditionally happens is you would stop the biologic particularly before the third trimester because of safety and concerns that the monoclonal antibody is actively transported across the placenta, which means the baby gets much more concentration of the drug than the mum,” Dr. Youngstein said.
It’s a situation physicians must monitor closely, she said. “The mum is donating their immune system to the baby, but they’re also donating drug.”
“In high-risk patients, we would share decision-making with the patient,” Dr. Youngstein continued. “We have decided it’s too high of a risk for us to stop the drug, so we have been continuing the interleukin-6 [IL-6] inhibitor throughout the entire pregnancy.”
The data from Dr. Youngstein’s group showed that pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis who continued IL-6 inhibition therapy all carried to term with healthy births.
“We’ve shown that it’s relatively safe to do that, but you have to be very careful in monitoring the baby,” she said. This includes not giving the infant any live vaccines at birth because it will have the high levels of IL-6 inhibition, she said.
Dr. Sammaritano and Dr. Youngstein had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Systemic autoimmune disease is well-recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but less recognized as a cardiovascular risk factor is a history of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, and cardiologists and rheumatologists need to include an obstetric history when managing patients with autoimmune diseases, a specialist in reproductive health in rheumatology told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
“Autoimmune diseases, lupus in particular, increase the risk for both cardiovascular disease and maternal placental syndromes,” Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, a professor at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and a specialist in reproductive health issues in rheumatology patients, told attendees. “For those patients who have complications during pregnancy, it further increases their already increased risk for later cardiovascular disease.”
CVD Risk Double Whammy
A history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and problematic pregnancy can be a double whammy for CVD risk. Dr. Sammaritano cited a 2022 meta-analysis that showed patients with SLE had a 2.5 times greater risk for stroke and almost three times greater risk for myocardial infarction than people without SLE.
Maternal placental syndromes include pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, preeclampsia, premature membrane rupture, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise, Dr. Sammaritano said. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, formerly called adverse pregnancy outcomes, she noted, include gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Pregnancy complications can have an adverse effect on the mother’s postpartum cardiovascular health, Dr. Sammaritano noted, a fact borne out by the cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes population-based retrospective cohort study and a 2007 meta-analysis that found a history of preeclampsia doubles the risk for venous thromboembolism, stroke, and ischemic heart disease up to 15 years after pregnancy.
“It is always important to obtain a reproductive health history from patients with autoimmune diseases,” Dr. Sammaritano told this news organization in an interview. “This is an integral part of any medical history. In the usual setting, this includes not only pregnancy history but also use of contraception in reproductive-aged women. Unplanned pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes in the setting of active or severe autoimmune disease or when teratogenic medications are used.”
Pregnancy history can be a factor in a woman’s cardiovascular health more than 15 years postpartum, even if a woman is no longer planning a pregnancy or is menopausal. “As such, this history is important in assessing every woman’s risk profile for CVD in addition to usual traditional risk factors,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“It is even more important for women with autoimmune disorders, who have been shown to have an already increased risk for CVD independent of their pregnancy history, likely related to a chronic inflammatory state and other autoimmune-related factors such as presence of antiphospholipid antibodies [aPL] or use of corticosteroids.”
Timing of disease onset is also an issue, she said. “In patients with SLE, for example, onset of CVD is much earlier than in the general population,” Dr. Sammaritano said. “As a result, these patients should likely be assessed for risk — both traditional and other risk factors — earlier than the general population, especially if an adverse obstetric history is present.”
At the younger end of the age continuum, women with autoimmune disease, including SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, who are pregnant should be put on guideline-directed low-dose aspirin preeclampsia prophylaxis, Dr. Sammaritano said. “Whether every patient with SLE needs this is still uncertain, but certainly, those with a history of renal disease, hypertension, or aPL antibody clearly do,” she added.
The evidence supporting hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in these patients is controversial, but Dr. Sammaritano noted two meta-analyses, one in 2022 and the other in 2023, that showed that HCQ lowered the risk for preeclampsia in women.
“The clear benefit of HCQ in preventing maternal disease complications, including flare, means we recommend it regardless for all patients with SLE at baseline and during pregnancy [if tolerated],” Dr. Sammaritano said. “The benefit or optimal use of these medications in other autoimmune diseases is less studied and less certain.”
Dr. Sammaritano added in her presentation, “We really need better therapies and, hopefully, those will be on the way, but I think the takeaway message, particularly for practicing rheumatologists and cardiologists, is to ask the question about obstetric history. Many of us don’t. It doesn’t seem relevant in the moment, but it really is in terms of the patient’s long-term risk for cardiovascular disease.”
The Case for Treatment During Pregnancy
Prophylaxis against pregnancy complications in patients with autoimmune disease may be achievable, Taryn Youngstein, MBBS, consultant rheumatologist and codirector of the Centre of Excellence in Vasculitis Research, Imperial College London, London, England, told this news organization after Dr. Sammaritano’s presentation. At the 2023 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, her group reported the safety and effectiveness of continuing tocilizumab in pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis, a large-vessel vasculitis predominantly affecting women of reproductive age.
“What traditionally happens is you would stop the biologic particularly before the third trimester because of safety and concerns that the monoclonal antibody is actively transported across the placenta, which means the baby gets much more concentration of the drug than the mum,” Dr. Youngstein said.
It’s a situation physicians must monitor closely, she said. “The mum is donating their immune system to the baby, but they’re also donating drug.”
“In high-risk patients, we would share decision-making with the patient,” Dr. Youngstein continued. “We have decided it’s too high of a risk for us to stop the drug, so we have been continuing the interleukin-6 [IL-6] inhibitor throughout the entire pregnancy.”
The data from Dr. Youngstein’s group showed that pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis who continued IL-6 inhibition therapy all carried to term with healthy births.
“We’ve shown that it’s relatively safe to do that, but you have to be very careful in monitoring the baby,” she said. This includes not giving the infant any live vaccines at birth because it will have the high levels of IL-6 inhibition, she said.
Dr. Sammaritano and Dr. Youngstein had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Self-Monitoring Better Than Usual Care Among Patients With Hypertension
TOPLINE:
Blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring and medication management may be better than usual care for controlling hypertension, a new study published in JAMA Network Open suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The secondary analysis of a randomized, unblinded clinical trial included patients aged ≥ 40 years with uncontrolled hypertension in Valencia, Spain, between 2017 and 2020.
- The 111 patients in the intervention group received educational materials and instructions for self-monitoring of BP with a home monitor and medication adjustment as needed without contacting their healthcare clinicians.
- The 108 patients in the control group received usual care, including education on BP control.
- After 24 months, researchers recorded BP levels, the number of people who achieved a target BP (systolic BP < 140 mm Hg and diastolic BP < 90 mm Hg), adverse events, quality of life, behavioral changes, and health service use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients in the intervention group had a lower average systolic BP reading at 24 months than patients who received usual care (adjusted mean difference, -3.4 mm Hg).
- Patients in the intervention group also had a lower average diastolic BP reading than usual care (adjusted mean difference, -2.5 mm Hg).
- The percentage of people who achieved the target BP was similar in both groups (64% in the intervention group compared with 54% in the control group).
- Researchers found no difference between groups in terms of adverse events, use of health services, behavioral changes such as smoking status or body weight, or quality of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Gabriel Sanfélix-Gimeno, PhD, Pharm D, head of the Health Services Research & Pharmacoepidemiology Unit at Fisabio Research Institute in Valencia, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Some study participants were lost to follow-up due to COVID-19 restrictions. The trial was unblinded, which may have led to biases among patients and clinicians. Clinicians treated both the control and intervention groups. The results may not be extrapolated to those with controlled hypertension, very high BP, or people who are pregnant because they were not included in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported receiving grants from RTI Health Solutions or personal fees from GSK and MSD outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III at the Spanish Ministry of Research, Innovation and Universities, the European Regional Development Fund, and Spanish Clinical Research Network.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring and medication management may be better than usual care for controlling hypertension, a new study published in JAMA Network Open suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The secondary analysis of a randomized, unblinded clinical trial included patients aged ≥ 40 years with uncontrolled hypertension in Valencia, Spain, between 2017 and 2020.
- The 111 patients in the intervention group received educational materials and instructions for self-monitoring of BP with a home monitor and medication adjustment as needed without contacting their healthcare clinicians.
- The 108 patients in the control group received usual care, including education on BP control.
- After 24 months, researchers recorded BP levels, the number of people who achieved a target BP (systolic BP < 140 mm Hg and diastolic BP < 90 mm Hg), adverse events, quality of life, behavioral changes, and health service use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients in the intervention group had a lower average systolic BP reading at 24 months than patients who received usual care (adjusted mean difference, -3.4 mm Hg).
- Patients in the intervention group also had a lower average diastolic BP reading than usual care (adjusted mean difference, -2.5 mm Hg).
- The percentage of people who achieved the target BP was similar in both groups (64% in the intervention group compared with 54% in the control group).
- Researchers found no difference between groups in terms of adverse events, use of health services, behavioral changes such as smoking status or body weight, or quality of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Gabriel Sanfélix-Gimeno, PhD, Pharm D, head of the Health Services Research & Pharmacoepidemiology Unit at Fisabio Research Institute in Valencia, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Some study participants were lost to follow-up due to COVID-19 restrictions. The trial was unblinded, which may have led to biases among patients and clinicians. Clinicians treated both the control and intervention groups. The results may not be extrapolated to those with controlled hypertension, very high BP, or people who are pregnant because they were not included in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported receiving grants from RTI Health Solutions or personal fees from GSK and MSD outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III at the Spanish Ministry of Research, Innovation and Universities, the European Regional Development Fund, and Spanish Clinical Research Network.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring and medication management may be better than usual care for controlling hypertension, a new study published in JAMA Network Open suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The secondary analysis of a randomized, unblinded clinical trial included patients aged ≥ 40 years with uncontrolled hypertension in Valencia, Spain, between 2017 and 2020.
- The 111 patients in the intervention group received educational materials and instructions for self-monitoring of BP with a home monitor and medication adjustment as needed without contacting their healthcare clinicians.
- The 108 patients in the control group received usual care, including education on BP control.
- After 24 months, researchers recorded BP levels, the number of people who achieved a target BP (systolic BP < 140 mm Hg and diastolic BP < 90 mm Hg), adverse events, quality of life, behavioral changes, and health service use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients in the intervention group had a lower average systolic BP reading at 24 months than patients who received usual care (adjusted mean difference, -3.4 mm Hg).
- Patients in the intervention group also had a lower average diastolic BP reading than usual care (adjusted mean difference, -2.5 mm Hg).
- The percentage of people who achieved the target BP was similar in both groups (64% in the intervention group compared with 54% in the control group).
- Researchers found no difference between groups in terms of adverse events, use of health services, behavioral changes such as smoking status or body weight, or quality of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Gabriel Sanfélix-Gimeno, PhD, Pharm D, head of the Health Services Research & Pharmacoepidemiology Unit at Fisabio Research Institute in Valencia, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Some study participants were lost to follow-up due to COVID-19 restrictions. The trial was unblinded, which may have led to biases among patients and clinicians. Clinicians treated both the control and intervention groups. The results may not be extrapolated to those with controlled hypertension, very high BP, or people who are pregnant because they were not included in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported receiving grants from RTI Health Solutions or personal fees from GSK and MSD outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III at the Spanish Ministry of Research, Innovation and Universities, the European Regional Development Fund, and Spanish Clinical Research Network.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Traffic Noise Negatively Impacts Health
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Red Meat Healthy? Multiverse Analysis Has Lessons Beyond Meat
Observational studies on red meat consumption and lifespan are prime examples of attempts to find signal in a sea of noise.
Randomized controlled trials are the best way to sort cause from mere correlation. But these are not possible in most matters of food consumption. So, we look back and observe groups with different exposures.
My most frequent complaint about these nonrandom comparison studies has been the chance that the two groups differ in important ways, and it’s these differences — not the food in question — that account for the disparate outcomes.
But selection biases are only one issue. There is also the matter of analytic flexibility. Observational studies are born from large databases. Researchers have many choices in how to analyze all these data.
A few years ago, Brian Nosek, PhD, and colleagues elegantly showed that analytic choices can affect results. His Many Analysts, One Data Set study had little uptake in the medical community, perhaps because he studied a social science question.
Multiple Ways to Slice the Data
Recently, a group from McMaster University, led by Dena Zeraatkar, PhD, has confirmed the analytic choices problem, using the question of red meat consumption and mortality.
Their idea was simple: Because there are many plausible and defensible ways to analyze a dataset, we should not choose one method; rather, we should choose thousands, combine the results, and see where the truth lies.
You might wonder how there could be thousands of ways to analyze a dataset. I surely did.
The answer stems from the choices that researchers face. For instance, there is the selection of eligible participants, the choice of analytic model (logistic, Poisson, etc.), and covariates for which to adjust. Think exponents when combining possible choices.
Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues are research methodologists, so, sadly, they are comfortable with the clunky name of this approach: specification curve analysis. Don’t be deterred. It means that they analyze the data in thousands of ways using computers. Each way is a specification. In the end, the specifications give rise to a curve of hazard ratios for red meat and mortality. Another name for this approach is multiverse analysis.
For their paper in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, aptly named “Grilling the Data,” they didn’t just conjure up the many analytic ways to study the red meat–mortality question. Instead, they used a published systematic review of 15 studies on unprocessed red meat and early mortality. The studies included in this review reported 70 unique ways to analyze the association.
Is Red Meat Good or Bad?
Their first finding was that this analysis yielded widely disparate effect estimates, from 0.63 (reduced risk for early death) to 2.31 (a higher risk). The median hazard ratio was 1.14 with an interquartile range (IQR) of 1.02-1.23. One might conclude from this that eating red meat is associated with a slightly higher risk for early mortality.
Their second step was to calculate how many ways (specifications) there were to analyze the data by totaling all possible combinations of choices in the 70 ways found in the systematic review.
They calculated a total of 10 quadrillion possible unique analyses. A quadrillion is 1 with 15 zeros. Computing power cannot handle that amount of analyses yet. So, they generated 20 random unique combinations of covariates, which narrowed the number of analyses to about 1400. About 200 of these were excluded due to implausibly wide confidence intervals.
Voilà. They now had about 1200 different ways to analyze a dataset; they chose an NHANES longitudinal cohort study from 2007-2014. They deemed each of the more than 1200 approaches plausible because they were derived from peer-reviewed papers written by experts in epidemiology.
Specification Curve Analyses Results
Each analysis (or specification) yielded a hazard ratio for red meat exposure and death.
- The median HR was 0.94 (IQR, 0.83-1.05) for the effect of red meat on all-cause mortality — ie, not significant.
- The range of hazard ratios was large. They went from 0.51 — a 49% reduced risk for early mortality — to 1.75: a 75% increase in early mortality.
- Among all analyses, 36% yielded hazard ratios above 1.0 and 64% less than 1.0.
- As for statistical significance, defined as P ≤.05, only 4% (or 48 specifications) met this threshold. Zeraatkar reminded me that this is what you’d expect if unprocessed red meat has no effect on longevity.
- Of the 48 analyses deemed statistically significant, 40 indicated that red meat consumption reduced early death and eight indicated that eating red meat led to higher mortality.
- Nearly half the analyses yielded unexciting point estimates, with hazard ratios between 0.90 and 1.10.
Paradigm Changing
As a user of evidence, I find this a potentially paradigm-changing study. Observational studies far outnumber randomized trials. For many medical questions, observational data are all we have.
Now think about every observational study published. The authors tell you — post hoc — which method they used to analyze the data. The key point is that it is one method.
Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues have shown that there are thousands of plausible ways to analyze the data, and this can lead to very different findings. In the specific question of red meat and mortality, their many analyses yielded a null result.
Now imagine other cases where the researchers did many analyses of a dataset and chose to publish only the significant ones. Observational studies are rarely preregistered, so a reader cannot know how a result would vary depending on analytic choices. A specification curve analysis of a dataset provides a much broader picture. In the case of red meat, you see some significant results, but the vast majority hover around null.
What about the difficulty in analyzing a dataset 1000 different ways? Dr. Zeraatkar told me that it is harder than just choosing one method, but it’s not impossible.
The main barrier to adopting this multiverse approach to data, she noted, was not the extra work but the entrenched belief among researchers that there is a best way to analyze data.
I hope you read this paper and think about it every time you read an observational study that finds a positive or negative association between two things. Ask: What if the researchers were as careful as Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues and did multiple different analyses? Would the finding hold up to a series of plausible analytic choices?
Nutritional epidemiology would benefit greatly from this approach. But so would any observational study of an exposure and outcome. I suspect that the number of “positive” associations would diminish. And that would not be a bad thing.
Dr. Mandrola, a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Kentucky, disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Observational studies on red meat consumption and lifespan are prime examples of attempts to find signal in a sea of noise.
Randomized controlled trials are the best way to sort cause from mere correlation. But these are not possible in most matters of food consumption. So, we look back and observe groups with different exposures.
My most frequent complaint about these nonrandom comparison studies has been the chance that the two groups differ in important ways, and it’s these differences — not the food in question — that account for the disparate outcomes.
But selection biases are only one issue. There is also the matter of analytic flexibility. Observational studies are born from large databases. Researchers have many choices in how to analyze all these data.
A few years ago, Brian Nosek, PhD, and colleagues elegantly showed that analytic choices can affect results. His Many Analysts, One Data Set study had little uptake in the medical community, perhaps because he studied a social science question.
Multiple Ways to Slice the Data
Recently, a group from McMaster University, led by Dena Zeraatkar, PhD, has confirmed the analytic choices problem, using the question of red meat consumption and mortality.
Their idea was simple: Because there are many plausible and defensible ways to analyze a dataset, we should not choose one method; rather, we should choose thousands, combine the results, and see where the truth lies.
You might wonder how there could be thousands of ways to analyze a dataset. I surely did.
The answer stems from the choices that researchers face. For instance, there is the selection of eligible participants, the choice of analytic model (logistic, Poisson, etc.), and covariates for which to adjust. Think exponents when combining possible choices.
Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues are research methodologists, so, sadly, they are comfortable with the clunky name of this approach: specification curve analysis. Don’t be deterred. It means that they analyze the data in thousands of ways using computers. Each way is a specification. In the end, the specifications give rise to a curve of hazard ratios for red meat and mortality. Another name for this approach is multiverse analysis.
For their paper in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, aptly named “Grilling the Data,” they didn’t just conjure up the many analytic ways to study the red meat–mortality question. Instead, they used a published systematic review of 15 studies on unprocessed red meat and early mortality. The studies included in this review reported 70 unique ways to analyze the association.
Is Red Meat Good or Bad?
Their first finding was that this analysis yielded widely disparate effect estimates, from 0.63 (reduced risk for early death) to 2.31 (a higher risk). The median hazard ratio was 1.14 with an interquartile range (IQR) of 1.02-1.23. One might conclude from this that eating red meat is associated with a slightly higher risk for early mortality.
Their second step was to calculate how many ways (specifications) there were to analyze the data by totaling all possible combinations of choices in the 70 ways found in the systematic review.
They calculated a total of 10 quadrillion possible unique analyses. A quadrillion is 1 with 15 zeros. Computing power cannot handle that amount of analyses yet. So, they generated 20 random unique combinations of covariates, which narrowed the number of analyses to about 1400. About 200 of these were excluded due to implausibly wide confidence intervals.
Voilà. They now had about 1200 different ways to analyze a dataset; they chose an NHANES longitudinal cohort study from 2007-2014. They deemed each of the more than 1200 approaches plausible because they were derived from peer-reviewed papers written by experts in epidemiology.
Specification Curve Analyses Results
Each analysis (or specification) yielded a hazard ratio for red meat exposure and death.
- The median HR was 0.94 (IQR, 0.83-1.05) for the effect of red meat on all-cause mortality — ie, not significant.
- The range of hazard ratios was large. They went from 0.51 — a 49% reduced risk for early mortality — to 1.75: a 75% increase in early mortality.
- Among all analyses, 36% yielded hazard ratios above 1.0 and 64% less than 1.0.
- As for statistical significance, defined as P ≤.05, only 4% (or 48 specifications) met this threshold. Zeraatkar reminded me that this is what you’d expect if unprocessed red meat has no effect on longevity.
- Of the 48 analyses deemed statistically significant, 40 indicated that red meat consumption reduced early death and eight indicated that eating red meat led to higher mortality.
- Nearly half the analyses yielded unexciting point estimates, with hazard ratios between 0.90 and 1.10.
Paradigm Changing
As a user of evidence, I find this a potentially paradigm-changing study. Observational studies far outnumber randomized trials. For many medical questions, observational data are all we have.
Now think about every observational study published. The authors tell you — post hoc — which method they used to analyze the data. The key point is that it is one method.
Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues have shown that there are thousands of plausible ways to analyze the data, and this can lead to very different findings. In the specific question of red meat and mortality, their many analyses yielded a null result.
Now imagine other cases where the researchers did many analyses of a dataset and chose to publish only the significant ones. Observational studies are rarely preregistered, so a reader cannot know how a result would vary depending on analytic choices. A specification curve analysis of a dataset provides a much broader picture. In the case of red meat, you see some significant results, but the vast majority hover around null.
What about the difficulty in analyzing a dataset 1000 different ways? Dr. Zeraatkar told me that it is harder than just choosing one method, but it’s not impossible.
The main barrier to adopting this multiverse approach to data, she noted, was not the extra work but the entrenched belief among researchers that there is a best way to analyze data.
I hope you read this paper and think about it every time you read an observational study that finds a positive or negative association between two things. Ask: What if the researchers were as careful as Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues and did multiple different analyses? Would the finding hold up to a series of plausible analytic choices?
Nutritional epidemiology would benefit greatly from this approach. But so would any observational study of an exposure and outcome. I suspect that the number of “positive” associations would diminish. And that would not be a bad thing.
Dr. Mandrola, a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Kentucky, disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Observational studies on red meat consumption and lifespan are prime examples of attempts to find signal in a sea of noise.
Randomized controlled trials are the best way to sort cause from mere correlation. But these are not possible in most matters of food consumption. So, we look back and observe groups with different exposures.
My most frequent complaint about these nonrandom comparison studies has been the chance that the two groups differ in important ways, and it’s these differences — not the food in question — that account for the disparate outcomes.
But selection biases are only one issue. There is also the matter of analytic flexibility. Observational studies are born from large databases. Researchers have many choices in how to analyze all these data.
A few years ago, Brian Nosek, PhD, and colleagues elegantly showed that analytic choices can affect results. His Many Analysts, One Data Set study had little uptake in the medical community, perhaps because he studied a social science question.
Multiple Ways to Slice the Data
Recently, a group from McMaster University, led by Dena Zeraatkar, PhD, has confirmed the analytic choices problem, using the question of red meat consumption and mortality.
Their idea was simple: Because there are many plausible and defensible ways to analyze a dataset, we should not choose one method; rather, we should choose thousands, combine the results, and see where the truth lies.
You might wonder how there could be thousands of ways to analyze a dataset. I surely did.
The answer stems from the choices that researchers face. For instance, there is the selection of eligible participants, the choice of analytic model (logistic, Poisson, etc.), and covariates for which to adjust. Think exponents when combining possible choices.
Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues are research methodologists, so, sadly, they are comfortable with the clunky name of this approach: specification curve analysis. Don’t be deterred. It means that they analyze the data in thousands of ways using computers. Each way is a specification. In the end, the specifications give rise to a curve of hazard ratios for red meat and mortality. Another name for this approach is multiverse analysis.
For their paper in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, aptly named “Grilling the Data,” they didn’t just conjure up the many analytic ways to study the red meat–mortality question. Instead, they used a published systematic review of 15 studies on unprocessed red meat and early mortality. The studies included in this review reported 70 unique ways to analyze the association.
Is Red Meat Good or Bad?
Their first finding was that this analysis yielded widely disparate effect estimates, from 0.63 (reduced risk for early death) to 2.31 (a higher risk). The median hazard ratio was 1.14 with an interquartile range (IQR) of 1.02-1.23. One might conclude from this that eating red meat is associated with a slightly higher risk for early mortality.
Their second step was to calculate how many ways (specifications) there were to analyze the data by totaling all possible combinations of choices in the 70 ways found in the systematic review.
They calculated a total of 10 quadrillion possible unique analyses. A quadrillion is 1 with 15 zeros. Computing power cannot handle that amount of analyses yet. So, they generated 20 random unique combinations of covariates, which narrowed the number of analyses to about 1400. About 200 of these were excluded due to implausibly wide confidence intervals.
Voilà. They now had about 1200 different ways to analyze a dataset; they chose an NHANES longitudinal cohort study from 2007-2014. They deemed each of the more than 1200 approaches plausible because they were derived from peer-reviewed papers written by experts in epidemiology.
Specification Curve Analyses Results
Each analysis (or specification) yielded a hazard ratio for red meat exposure and death.
- The median HR was 0.94 (IQR, 0.83-1.05) for the effect of red meat on all-cause mortality — ie, not significant.
- The range of hazard ratios was large. They went from 0.51 — a 49% reduced risk for early mortality — to 1.75: a 75% increase in early mortality.
- Among all analyses, 36% yielded hazard ratios above 1.0 and 64% less than 1.0.
- As for statistical significance, defined as P ≤.05, only 4% (or 48 specifications) met this threshold. Zeraatkar reminded me that this is what you’d expect if unprocessed red meat has no effect on longevity.
- Of the 48 analyses deemed statistically significant, 40 indicated that red meat consumption reduced early death and eight indicated that eating red meat led to higher mortality.
- Nearly half the analyses yielded unexciting point estimates, with hazard ratios between 0.90 and 1.10.
Paradigm Changing
As a user of evidence, I find this a potentially paradigm-changing study. Observational studies far outnumber randomized trials. For many medical questions, observational data are all we have.
Now think about every observational study published. The authors tell you — post hoc — which method they used to analyze the data. The key point is that it is one method.
Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues have shown that there are thousands of plausible ways to analyze the data, and this can lead to very different findings. In the specific question of red meat and mortality, their many analyses yielded a null result.
Now imagine other cases where the researchers did many analyses of a dataset and chose to publish only the significant ones. Observational studies are rarely preregistered, so a reader cannot know how a result would vary depending on analytic choices. A specification curve analysis of a dataset provides a much broader picture. In the case of red meat, you see some significant results, but the vast majority hover around null.
What about the difficulty in analyzing a dataset 1000 different ways? Dr. Zeraatkar told me that it is harder than just choosing one method, but it’s not impossible.
The main barrier to adopting this multiverse approach to data, she noted, was not the extra work but the entrenched belief among researchers that there is a best way to analyze data.
I hope you read this paper and think about it every time you read an observational study that finds a positive or negative association between two things. Ask: What if the researchers were as careful as Dr. Zeraatkar and colleagues and did multiple different analyses? Would the finding hold up to a series of plausible analytic choices?
Nutritional epidemiology would benefit greatly from this approach. But so would any observational study of an exposure and outcome. I suspect that the number of “positive” associations would diminish. And that would not be a bad thing.
Dr. Mandrola, a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Kentucky, disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vast Majority of Adults At Risk for Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome
TOPLINE:
Nearly 90% of adults were at risk of developing cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome between 2011 and 2020, according to new research published in JAMA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In 2023, the American Heart Association defined to acknowledge how heart and kidney diseases, diabetes, and obesity interact and are increasingly co-occurring conditions.
- Researchers used data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2011 and 2020.
- More than 10,000 adults over age 20 years were included; all of them received a physical and fasting laboratory measurements and self-reported their cardiovascular disease (CVD) status.
- Researchers created categories for risk, ranging from 0 (no risk factors) to 4, using factors such as kidney disease, obesity, and hypertension.
TAKEAWAY:
- (having metabolic risk factors like hypertension or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease).
- 14.6% met the criteria for advanced stage 3 (very high-risk chronic kidney disease or a high risk for 10-year CVD) and stage 4 CKM syndrome (established CVD) combined.
- Men, adults over age 65 years, and Black individuals were at a greater risk for advanced stages of the CKM syndrome.
- Almost half of people met the criteria for stage 2 (having metabolic risk factors like hypertension or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease).
- 14.6% met the criteria for advanced stage 3 (very high-risk chronic kidney disease or a high risk for 10-year CVD) and stage 4 CKM syndrome (established CVD) combined.
- Men, adults over age 65 years, and Black individuals were at a greater risk for advanced stages of the CKM syndrome.
IN PRACTICE:
“Equitable health care approaches prioritizing CKM health are urgently needed,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, cardiologist and researcher at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
LIMITATIONS:
Established CVD statuses were self-reported. Some data that would indicate advanced CKM stages were not available (eg, cardiac biomarkers, echocardiography, and coronary angiography), which may have led to an underestimation of rates.
DISCLOSURES:
One author received grants from Bristol Myers Squibb–Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Vaduganathan received grants from and was an adviser and committee trial member for various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work. The authors reported no other disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 90% of adults were at risk of developing cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome between 2011 and 2020, according to new research published in JAMA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In 2023, the American Heart Association defined to acknowledge how heart and kidney diseases, diabetes, and obesity interact and are increasingly co-occurring conditions.
- Researchers used data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2011 and 2020.
- More than 10,000 adults over age 20 years were included; all of them received a physical and fasting laboratory measurements and self-reported their cardiovascular disease (CVD) status.
- Researchers created categories for risk, ranging from 0 (no risk factors) to 4, using factors such as kidney disease, obesity, and hypertension.
TAKEAWAY:
- (having metabolic risk factors like hypertension or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease).
- 14.6% met the criteria for advanced stage 3 (very high-risk chronic kidney disease or a high risk for 10-year CVD) and stage 4 CKM syndrome (established CVD) combined.
- Men, adults over age 65 years, and Black individuals were at a greater risk for advanced stages of the CKM syndrome.
- Almost half of people met the criteria for stage 2 (having metabolic risk factors like hypertension or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease).
- 14.6% met the criteria for advanced stage 3 (very high-risk chronic kidney disease or a high risk for 10-year CVD) and stage 4 CKM syndrome (established CVD) combined.
- Men, adults over age 65 years, and Black individuals were at a greater risk for advanced stages of the CKM syndrome.
IN PRACTICE:
“Equitable health care approaches prioritizing CKM health are urgently needed,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, cardiologist and researcher at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
LIMITATIONS:
Established CVD statuses were self-reported. Some data that would indicate advanced CKM stages were not available (eg, cardiac biomarkers, echocardiography, and coronary angiography), which may have led to an underestimation of rates.
DISCLOSURES:
One author received grants from Bristol Myers Squibb–Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Vaduganathan received grants from and was an adviser and committee trial member for various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work. The authors reported no other disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 90% of adults were at risk of developing cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome between 2011 and 2020, according to new research published in JAMA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In 2023, the American Heart Association defined to acknowledge how heart and kidney diseases, diabetes, and obesity interact and are increasingly co-occurring conditions.
- Researchers used data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2011 and 2020.
- More than 10,000 adults over age 20 years were included; all of them received a physical and fasting laboratory measurements and self-reported their cardiovascular disease (CVD) status.
- Researchers created categories for risk, ranging from 0 (no risk factors) to 4, using factors such as kidney disease, obesity, and hypertension.
TAKEAWAY:
- (having metabolic risk factors like hypertension or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease).
- 14.6% met the criteria for advanced stage 3 (very high-risk chronic kidney disease or a high risk for 10-year CVD) and stage 4 CKM syndrome (established CVD) combined.
- Men, adults over age 65 years, and Black individuals were at a greater risk for advanced stages of the CKM syndrome.
- Almost half of people met the criteria for stage 2 (having metabolic risk factors like hypertension or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease).
- 14.6% met the criteria for advanced stage 3 (very high-risk chronic kidney disease or a high risk for 10-year CVD) and stage 4 CKM syndrome (established CVD) combined.
- Men, adults over age 65 years, and Black individuals were at a greater risk for advanced stages of the CKM syndrome.
IN PRACTICE:
“Equitable health care approaches prioritizing CKM health are urgently needed,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, cardiologist and researcher at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
LIMITATIONS:
Established CVD statuses were self-reported. Some data that would indicate advanced CKM stages were not available (eg, cardiac biomarkers, echocardiography, and coronary angiography), which may have led to an underestimation of rates.
DISCLOSURES:
One author received grants from Bristol Myers Squibb–Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Vaduganathan received grants from and was an adviser and committee trial member for various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work. The authors reported no other disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Evaluates CVD, Mortality Risks In Patients With Prurigo Nodularis
TOPLINE:
, particularly among women and White patients.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies have shown increased risks for cardiovascular diseases in patients with PN, but limited sample sizes have hindered further subgroup analysis. Given PN’s pronounced sex and ethnicity skew, it is important to examine underrepresented groups to accurately assess their cardiovascular risk.
- In this propensity-score matched analysis, researchers identified 64,801 patients (59.44% women) with PN using electronic health reports from the Global Collaborative Network of TriNetX and matched to individuals without PN.
- Researchers calculated risks for 15 cardiovascular endpoints and all-cause mortality within 10 years of diagnosis. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) included acute cerebral and myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, ventricular arrhythmia, and sudden cardiac death.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with PN showed a higher risk for death (hazard ratio [HR], 1.1243) and MACE (HR, 1.117) (P < .0001 for both).
- PN was also associated with a higher risk for heart failure (HR, 1.062), thrombotic venous disease (HR, 1.26), angina pectoris (HR, 1.096), and peripheral arterial diseases (HR, 1.082) (P < .0001 for all) and for acute MI (HR, 1.11; P = .0015) and valve disorders (HR, 1.08; P = .0018).
- White patients with PN had a significantly increased risk for MACE, death, heart failure, cardiac arrest, vascular diseases, and acute MI, but this was not observed in people of color.
- Women exhibited a higher risk for MACE, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, acute MI, conduction disease, and valve disorders, while men did not have an increased risk for major or acute cardiovascular events. Both men and women had a higher risk for death, chronic ischemic heart disease, and venous disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although no novel PN-specific treatment rationale can be derived from the presented data, the potential risk of subsequent cardiovascular disease should be considered in the care of patients with PN, which includes screening and optimal management of other additional cardiovascular risk factors,” the authors wrote.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective observational design introduced inherent biases. Misdiagnosis or false coding in electronic health records could affect the data accuracy and ethnicity-specific analyses.
SOURCE:
This work, led by Henning Olbrich, from the Department of Dermatology, University of Lübeck, Germany, was published online in eBioMedicine.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the University of Lübeck, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, and the State of Schleswig-Holstein. One author declared financial ties outside this work, and one author is an employee of TriNetX.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, particularly among women and White patients.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies have shown increased risks for cardiovascular diseases in patients with PN, but limited sample sizes have hindered further subgroup analysis. Given PN’s pronounced sex and ethnicity skew, it is important to examine underrepresented groups to accurately assess their cardiovascular risk.
- In this propensity-score matched analysis, researchers identified 64,801 patients (59.44% women) with PN using electronic health reports from the Global Collaborative Network of TriNetX and matched to individuals without PN.
- Researchers calculated risks for 15 cardiovascular endpoints and all-cause mortality within 10 years of diagnosis. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) included acute cerebral and myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, ventricular arrhythmia, and sudden cardiac death.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with PN showed a higher risk for death (hazard ratio [HR], 1.1243) and MACE (HR, 1.117) (P < .0001 for both).
- PN was also associated with a higher risk for heart failure (HR, 1.062), thrombotic venous disease (HR, 1.26), angina pectoris (HR, 1.096), and peripheral arterial diseases (HR, 1.082) (P < .0001 for all) and for acute MI (HR, 1.11; P = .0015) and valve disorders (HR, 1.08; P = .0018).
- White patients with PN had a significantly increased risk for MACE, death, heart failure, cardiac arrest, vascular diseases, and acute MI, but this was not observed in people of color.
- Women exhibited a higher risk for MACE, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, acute MI, conduction disease, and valve disorders, while men did not have an increased risk for major or acute cardiovascular events. Both men and women had a higher risk for death, chronic ischemic heart disease, and venous disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although no novel PN-specific treatment rationale can be derived from the presented data, the potential risk of subsequent cardiovascular disease should be considered in the care of patients with PN, which includes screening and optimal management of other additional cardiovascular risk factors,” the authors wrote.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective observational design introduced inherent biases. Misdiagnosis or false coding in electronic health records could affect the data accuracy and ethnicity-specific analyses.
SOURCE:
This work, led by Henning Olbrich, from the Department of Dermatology, University of Lübeck, Germany, was published online in eBioMedicine.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the University of Lübeck, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, and the State of Schleswig-Holstein. One author declared financial ties outside this work, and one author is an employee of TriNetX.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, particularly among women and White patients.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies have shown increased risks for cardiovascular diseases in patients with PN, but limited sample sizes have hindered further subgroup analysis. Given PN’s pronounced sex and ethnicity skew, it is important to examine underrepresented groups to accurately assess their cardiovascular risk.
- In this propensity-score matched analysis, researchers identified 64,801 patients (59.44% women) with PN using electronic health reports from the Global Collaborative Network of TriNetX and matched to individuals without PN.
- Researchers calculated risks for 15 cardiovascular endpoints and all-cause mortality within 10 years of diagnosis. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) included acute cerebral and myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, ventricular arrhythmia, and sudden cardiac death.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with PN showed a higher risk for death (hazard ratio [HR], 1.1243) and MACE (HR, 1.117) (P < .0001 for both).
- PN was also associated with a higher risk for heart failure (HR, 1.062), thrombotic venous disease (HR, 1.26), angina pectoris (HR, 1.096), and peripheral arterial diseases (HR, 1.082) (P < .0001 for all) and for acute MI (HR, 1.11; P = .0015) and valve disorders (HR, 1.08; P = .0018).
- White patients with PN had a significantly increased risk for MACE, death, heart failure, cardiac arrest, vascular diseases, and acute MI, but this was not observed in people of color.
- Women exhibited a higher risk for MACE, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, acute MI, conduction disease, and valve disorders, while men did not have an increased risk for major or acute cardiovascular events. Both men and women had a higher risk for death, chronic ischemic heart disease, and venous disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although no novel PN-specific treatment rationale can be derived from the presented data, the potential risk of subsequent cardiovascular disease should be considered in the care of patients with PN, which includes screening and optimal management of other additional cardiovascular risk factors,” the authors wrote.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective observational design introduced inherent biases. Misdiagnosis or false coding in electronic health records could affect the data accuracy and ethnicity-specific analyses.
SOURCE:
This work, led by Henning Olbrich, from the Department of Dermatology, University of Lübeck, Germany, was published online in eBioMedicine.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the University of Lübeck, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, and the State of Schleswig-Holstein. One author declared financial ties outside this work, and one author is an employee of TriNetX.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What Underlies Sex Differences in CKD Cardiovascular Risk?
Older men with chronic kidney disease (CKD) show higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity, but not vascular stiffness, compared with older women, offering clues to the underlying reasons why men with CKD have a higher cardiovascular risk than do women with the disease.
“Although it is well established that sympathetic nerve system activity is chronically elevated in patients with impaired kidney function, we show for the first time that males with CKD have higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity compared with females with CKD,” report the authors on research published in the American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.
“For clinicians, the key takeaway is the importance of recognizing sex-specific differences in sympathetic activity and vascular function when assessing cardiovascular risk in CKD patients,” first author Matias G. Zanuzzi, MD, of the Division of Renal Medicine, Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, told this news organization.
In the general population, cardiovascular risk is lower in younger women vs men, but their risks converge in older age as women develop similar levels of sympathetic overactivity, vascular stiffness, and cardiovascular risk.
However, an exception to that pattern is seen in the CKD population, where men continue to have a higher cardiovascular mortality risk vs women even in older age.
Studies evaluating the reasons for that have been conflicting, with some reporting a tendency of higher muscle sympathetic nerve activity in older women compared with men and others suggest the opposite finding — lower activity vs men.
To further investigate, Dr. Zanuzzi and colleagues enrolled 129 participants, including 96 men and 33 women with stage III or IV CKD.
The mean age of the study participants was 64 years for men and65 years for women. Most had obesity, and importantly, more than 80% of participants in each group was Black. There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of body mass index or comorbidities, including smoking, diabetes, or hypertension.
At two separate study visits, vascular stiffness was assessed with carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity measurement, and resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity was measured using microneurography.
The results showed that men with CKD had significantly higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity compared with women with CKD (68 vs 55 bursts per 100 heartbeats; P = .005), whereas no differences in vascular stiffness were observed between the genders (P = .248).
“The findings suggest that the higher cardiovascular disease risk observed in older males with CKD may be influenced by elevated sympathetic activity,” Dr. Zanuzzi explained.
“However, the lack of significant differences in vascular stiffness between genders implies that additional factors beyond vascular remodeling may contribute to the observed sex-specific differences in cardiovascular risk,” he said.
Of note, resting vascular stiffness was not associated with muscular sympathetic nerve activity in either men or women, which was surprising to the authors, Dr. Zanuzzi noted.
“This underscores the multifactorial nature of vascular pathophysiology in CKD and underscores the need for further research to unravel the underlying mechanisms.”
In other findings, although prior studies have shown a positive correlation between age and resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity in White, healthy women and men without obesity,, no similar relationship was observed in men or women with CKD.
“These findings suggest that the protective effect of younger age on sympathetic function may not be present in the setting of decreased kidney function in both males and females,” the authors note.
In addition, whereas previous research has shown a clear association between sympathetic overactivity and a wide variety of measures of obesity, in the current study, that association was only observed in men with CKD.
Important limitations of the study include the cross-sectional design and that the population was predominantly Black, Dr. Zanuzzi noted.
“Generalizability to other demographic groups may be limited, and future longitudinal studies are needed to validate these findings and explore potential causal relationships,” he said.
The findings underscore “the need for novel therapeutic approaches targeting sympathetic overactivity and vascular stiffness in CKD patients, especially considering the observed sex-specific differences,” Dr. Zanuzzi added.
“Potential interventions may include pharmacological agents that modulate sympathetic tone or vascular remodeling pathways,” he said.
“Lifestyle modifications focusing on stress reduction and cardiovascular health promotion could also play a crucial role in mitigating cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Zanuzzi concluded that “tailoring treatment strategies to address these differences may lead to more personalized and effective management approaches, ultimately improving clinical outcomes in this high-risk population.”
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older men with chronic kidney disease (CKD) show higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity, but not vascular stiffness, compared with older women, offering clues to the underlying reasons why men with CKD have a higher cardiovascular risk than do women with the disease.
“Although it is well established that sympathetic nerve system activity is chronically elevated in patients with impaired kidney function, we show for the first time that males with CKD have higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity compared with females with CKD,” report the authors on research published in the American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.
“For clinicians, the key takeaway is the importance of recognizing sex-specific differences in sympathetic activity and vascular function when assessing cardiovascular risk in CKD patients,” first author Matias G. Zanuzzi, MD, of the Division of Renal Medicine, Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, told this news organization.
In the general population, cardiovascular risk is lower in younger women vs men, but their risks converge in older age as women develop similar levels of sympathetic overactivity, vascular stiffness, and cardiovascular risk.
However, an exception to that pattern is seen in the CKD population, where men continue to have a higher cardiovascular mortality risk vs women even in older age.
Studies evaluating the reasons for that have been conflicting, with some reporting a tendency of higher muscle sympathetic nerve activity in older women compared with men and others suggest the opposite finding — lower activity vs men.
To further investigate, Dr. Zanuzzi and colleagues enrolled 129 participants, including 96 men and 33 women with stage III or IV CKD.
The mean age of the study participants was 64 years for men and65 years for women. Most had obesity, and importantly, more than 80% of participants in each group was Black. There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of body mass index or comorbidities, including smoking, diabetes, or hypertension.
At two separate study visits, vascular stiffness was assessed with carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity measurement, and resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity was measured using microneurography.
The results showed that men with CKD had significantly higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity compared with women with CKD (68 vs 55 bursts per 100 heartbeats; P = .005), whereas no differences in vascular stiffness were observed between the genders (P = .248).
“The findings suggest that the higher cardiovascular disease risk observed in older males with CKD may be influenced by elevated sympathetic activity,” Dr. Zanuzzi explained.
“However, the lack of significant differences in vascular stiffness between genders implies that additional factors beyond vascular remodeling may contribute to the observed sex-specific differences in cardiovascular risk,” he said.
Of note, resting vascular stiffness was not associated with muscular sympathetic nerve activity in either men or women, which was surprising to the authors, Dr. Zanuzzi noted.
“This underscores the multifactorial nature of vascular pathophysiology in CKD and underscores the need for further research to unravel the underlying mechanisms.”
In other findings, although prior studies have shown a positive correlation between age and resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity in White, healthy women and men without obesity,, no similar relationship was observed in men or women with CKD.
“These findings suggest that the protective effect of younger age on sympathetic function may not be present in the setting of decreased kidney function in both males and females,” the authors note.
In addition, whereas previous research has shown a clear association between sympathetic overactivity and a wide variety of measures of obesity, in the current study, that association was only observed in men with CKD.
Important limitations of the study include the cross-sectional design and that the population was predominantly Black, Dr. Zanuzzi noted.
“Generalizability to other demographic groups may be limited, and future longitudinal studies are needed to validate these findings and explore potential causal relationships,” he said.
The findings underscore “the need for novel therapeutic approaches targeting sympathetic overactivity and vascular stiffness in CKD patients, especially considering the observed sex-specific differences,” Dr. Zanuzzi added.
“Potential interventions may include pharmacological agents that modulate sympathetic tone or vascular remodeling pathways,” he said.
“Lifestyle modifications focusing on stress reduction and cardiovascular health promotion could also play a crucial role in mitigating cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Zanuzzi concluded that “tailoring treatment strategies to address these differences may lead to more personalized and effective management approaches, ultimately improving clinical outcomes in this high-risk population.”
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older men with chronic kidney disease (CKD) show higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity, but not vascular stiffness, compared with older women, offering clues to the underlying reasons why men with CKD have a higher cardiovascular risk than do women with the disease.
“Although it is well established that sympathetic nerve system activity is chronically elevated in patients with impaired kidney function, we show for the first time that males with CKD have higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity compared with females with CKD,” report the authors on research published in the American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.
“For clinicians, the key takeaway is the importance of recognizing sex-specific differences in sympathetic activity and vascular function when assessing cardiovascular risk in CKD patients,” first author Matias G. Zanuzzi, MD, of the Division of Renal Medicine, Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, told this news organization.
In the general population, cardiovascular risk is lower in younger women vs men, but their risks converge in older age as women develop similar levels of sympathetic overactivity, vascular stiffness, and cardiovascular risk.
However, an exception to that pattern is seen in the CKD population, where men continue to have a higher cardiovascular mortality risk vs women even in older age.
Studies evaluating the reasons for that have been conflicting, with some reporting a tendency of higher muscle sympathetic nerve activity in older women compared with men and others suggest the opposite finding — lower activity vs men.
To further investigate, Dr. Zanuzzi and colleagues enrolled 129 participants, including 96 men and 33 women with stage III or IV CKD.
The mean age of the study participants was 64 years for men and65 years for women. Most had obesity, and importantly, more than 80% of participants in each group was Black. There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of body mass index or comorbidities, including smoking, diabetes, or hypertension.
At two separate study visits, vascular stiffness was assessed with carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity measurement, and resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity was measured using microneurography.
The results showed that men with CKD had significantly higher resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity compared with women with CKD (68 vs 55 bursts per 100 heartbeats; P = .005), whereas no differences in vascular stiffness were observed between the genders (P = .248).
“The findings suggest that the higher cardiovascular disease risk observed in older males with CKD may be influenced by elevated sympathetic activity,” Dr. Zanuzzi explained.
“However, the lack of significant differences in vascular stiffness between genders implies that additional factors beyond vascular remodeling may contribute to the observed sex-specific differences in cardiovascular risk,” he said.
Of note, resting vascular stiffness was not associated with muscular sympathetic nerve activity in either men or women, which was surprising to the authors, Dr. Zanuzzi noted.
“This underscores the multifactorial nature of vascular pathophysiology in CKD and underscores the need for further research to unravel the underlying mechanisms.”
In other findings, although prior studies have shown a positive correlation between age and resting muscle sympathetic nerve activity in White, healthy women and men without obesity,, no similar relationship was observed in men or women with CKD.
“These findings suggest that the protective effect of younger age on sympathetic function may not be present in the setting of decreased kidney function in both males and females,” the authors note.
In addition, whereas previous research has shown a clear association between sympathetic overactivity and a wide variety of measures of obesity, in the current study, that association was only observed in men with CKD.
Important limitations of the study include the cross-sectional design and that the population was predominantly Black, Dr. Zanuzzi noted.
“Generalizability to other demographic groups may be limited, and future longitudinal studies are needed to validate these findings and explore potential causal relationships,” he said.
The findings underscore “the need for novel therapeutic approaches targeting sympathetic overactivity and vascular stiffness in CKD patients, especially considering the observed sex-specific differences,” Dr. Zanuzzi added.
“Potential interventions may include pharmacological agents that modulate sympathetic tone or vascular remodeling pathways,” he said.
“Lifestyle modifications focusing on stress reduction and cardiovascular health promotion could also play a crucial role in mitigating cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Zanuzzi concluded that “tailoring treatment strategies to address these differences may lead to more personalized and effective management approaches, ultimately improving clinical outcomes in this high-risk population.”
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Plus HIV Ups Risk for CVD but Not Liver Disease
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The History of Aspirin in Heart Disease Prevention
As the pendulum has swung against recommending aspirin for the primary prevention of heart attacks and strokes, clinicians should focus on other ways to help patients avoid cardiovascular events.
A landmark study published in 1988 in The New England Journal of Medicine reported an astonishing 44% drop in the number of heart attacks among US male physicians aged 40-84 years who took aspirin.
Aspirin subsequently became a daily habit for millions of Americans. In 2017, nearly a quarter of Americans over age 40 who did not have cardiovascular disease (CVD) took the drug, and over 20% of those were doing so without a physician’s recommendation.
But in 2018, three studies (ASCEND, ARRIVE, and ASPREE) showed a stunning reversal in the purported benefit, according to John Wong, MD, vice-chair of the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).
The calculus for taking aspirin appeared to have changed dramatically: The drug decreased the risk for myocardial infarction by only 11% among study subjects, while its potential harms were much more pronounced.
According to Dr. Wong, who is also a professor of medicine and a primary care physician at Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston, Massachusetts, patients taking low-dose aspirin had a 58% increase in their risk for gastrointestinal bleeding compared with those not on aspirin, as well as a 31% increased risk for intracranial bleeding.
who haven’t had a heart attack or stroke.”
Fewer Americans smoke cigarettes, more realize the benefits of a healthy diet and physical activity, and the medical community better recognizes and treats hypertension. New classes of medications such as statins for high cholesterol are also moving the needle.
But a newer class of drugs may provide a safer replacement for aspirin, according to Muhammad Maqsood, MD, a cardiology fellow at DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center at Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas. P2Y purinoceptor 12 (P2Y12) inhibitors are effective in lowering the risk for heart attack and stroke in patients with acute coronary syndrome or those undergoing elective percutaneous coronary interventions.
“They have shown a better bleeding profile, especially clopidogrel compared to aspirin,” Dr. Maqsood said.
However, the findings come from trials of patients who already had CVD, so results cannot yet be extrapolated to primary prevention. Dr. Maqsood said the gap highlights the need for clinical trials that evaluate P2Y12 inhibitors for primary prevention, but no such study is registered on clinicaltrials.gov.
Benefits Persist for Some Patients
The new evidence led the USPSTF to publish new guidelines in 2022, downgrading the recommendation for low-dose aspirin use for primary prevention. Previously, the organization stated that clinicians “should” initiate daily low-dose aspirin in adults aged 50-59 years and “consider” its use in adults aged 60-69 years whose 10-year risk for CVD was higher than 10%.
The updated guidelines stated that the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin in adults aged 40-59 years with a greater than 10% risk for CVD “should be an individual one,” based on professional judgment and individual patient preferences. The USPSTF also recommended against the use of aspirin in anyone over the age of 60.
Meanwhile, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association also dialed down previously strong recommendations on low-dose aspirin to a more nuanced recommendation stating, “low-dose aspirin might be considered for primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40-70 years of age.”
With a varying age limit for recommending aspirin, clinicians may take into consideration several variables.
“Is there a magic age? I don’t think there is,” said Douglas Lloyd-Jones, the former president of the American Heart Association and current chair of the Department of Preventive Medicine and a practicing cardiologist at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, Illinois.
For a patient over age 60 who is at a high risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, is unable to quit smoking, and is not likely to experience problematic bleeding, a clinician might recommend aspirin, Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. He said he sometimes also assesses coronary artery calcium to guide his clinical decisions: If elevated (an Agatston score above 100), he might recommend low-dose aspirin.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones also reiterated that patients should continue taking low-dose aspirin if they have already experienced a heart attack, stroke, episode of atrial fibrillation, or required a vascular stent.
Unless a patient with established CVD has intractable bleeding, “the aspirin is really for life,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. Patients who have a stent or who are at high risk for recurrence of stroke are more likely to experience thrombosis, and aspirin can decrease the risk.
“In our cardiology community, we don’t just strictly use the age of 70; the decision is always individualized,” Dr. Maqsood said.
Dr. Wong said primary care providers should focus on the USPSTF’s other recommendations that address CVD (Table), such as smoking cessation and screening for hypertension.
“I think our challenge is that we have so many of those A and B recommendations,” Dr. Wong said. “And I think part of the challenge for us is working with the patient to find out what’s most important to them.”
Discussing heart attacks and strokes often will strike a chord with patients because someone they know has been affected.
Dr. Maqsood emphasized the importance of behavioral interventions, such as helping patients decrease their body mass index and control their hyperlipidemia.
“The behavioral interventions are those which are the most cost-effective without any side effects,” he said.
His other piece of advice is to inquire with younger patients about a family history of heart attacks. Familial hypercholesteremia is unlikely to be controlled by diet and exercise and will need medical therapy.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones described the discussions he has with patients about preventing heart attacks as “the most important conversations we can have: Remember that cardiovascular disease is still the leading cause of death and disability in the world and in the United States.”
Dr. Wong, Dr. Lloyd-Jones, and Dr. Maqsood reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As the pendulum has swung against recommending aspirin for the primary prevention of heart attacks and strokes, clinicians should focus on other ways to help patients avoid cardiovascular events.
A landmark study published in 1988 in The New England Journal of Medicine reported an astonishing 44% drop in the number of heart attacks among US male physicians aged 40-84 years who took aspirin.
Aspirin subsequently became a daily habit for millions of Americans. In 2017, nearly a quarter of Americans over age 40 who did not have cardiovascular disease (CVD) took the drug, and over 20% of those were doing so without a physician’s recommendation.
But in 2018, three studies (ASCEND, ARRIVE, and ASPREE) showed a stunning reversal in the purported benefit, according to John Wong, MD, vice-chair of the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).
The calculus for taking aspirin appeared to have changed dramatically: The drug decreased the risk for myocardial infarction by only 11% among study subjects, while its potential harms were much more pronounced.
According to Dr. Wong, who is also a professor of medicine and a primary care physician at Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston, Massachusetts, patients taking low-dose aspirin had a 58% increase in their risk for gastrointestinal bleeding compared with those not on aspirin, as well as a 31% increased risk for intracranial bleeding.
who haven’t had a heart attack or stroke.”
Fewer Americans smoke cigarettes, more realize the benefits of a healthy diet and physical activity, and the medical community better recognizes and treats hypertension. New classes of medications such as statins for high cholesterol are also moving the needle.
But a newer class of drugs may provide a safer replacement for aspirin, according to Muhammad Maqsood, MD, a cardiology fellow at DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center at Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas. P2Y purinoceptor 12 (P2Y12) inhibitors are effective in lowering the risk for heart attack and stroke in patients with acute coronary syndrome or those undergoing elective percutaneous coronary interventions.
“They have shown a better bleeding profile, especially clopidogrel compared to aspirin,” Dr. Maqsood said.
However, the findings come from trials of patients who already had CVD, so results cannot yet be extrapolated to primary prevention. Dr. Maqsood said the gap highlights the need for clinical trials that evaluate P2Y12 inhibitors for primary prevention, but no such study is registered on clinicaltrials.gov.
Benefits Persist for Some Patients
The new evidence led the USPSTF to publish new guidelines in 2022, downgrading the recommendation for low-dose aspirin use for primary prevention. Previously, the organization stated that clinicians “should” initiate daily low-dose aspirin in adults aged 50-59 years and “consider” its use in adults aged 60-69 years whose 10-year risk for CVD was higher than 10%.
The updated guidelines stated that the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin in adults aged 40-59 years with a greater than 10% risk for CVD “should be an individual one,” based on professional judgment and individual patient preferences. The USPSTF also recommended against the use of aspirin in anyone over the age of 60.
Meanwhile, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association also dialed down previously strong recommendations on low-dose aspirin to a more nuanced recommendation stating, “low-dose aspirin might be considered for primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40-70 years of age.”
With a varying age limit for recommending aspirin, clinicians may take into consideration several variables.
“Is there a magic age? I don’t think there is,” said Douglas Lloyd-Jones, the former president of the American Heart Association and current chair of the Department of Preventive Medicine and a practicing cardiologist at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, Illinois.
For a patient over age 60 who is at a high risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, is unable to quit smoking, and is not likely to experience problematic bleeding, a clinician might recommend aspirin, Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. He said he sometimes also assesses coronary artery calcium to guide his clinical decisions: If elevated (an Agatston score above 100), he might recommend low-dose aspirin.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones also reiterated that patients should continue taking low-dose aspirin if they have already experienced a heart attack, stroke, episode of atrial fibrillation, or required a vascular stent.
Unless a patient with established CVD has intractable bleeding, “the aspirin is really for life,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. Patients who have a stent or who are at high risk for recurrence of stroke are more likely to experience thrombosis, and aspirin can decrease the risk.
“In our cardiology community, we don’t just strictly use the age of 70; the decision is always individualized,” Dr. Maqsood said.
Dr. Wong said primary care providers should focus on the USPSTF’s other recommendations that address CVD (Table), such as smoking cessation and screening for hypertension.
“I think our challenge is that we have so many of those A and B recommendations,” Dr. Wong said. “And I think part of the challenge for us is working with the patient to find out what’s most important to them.”
Discussing heart attacks and strokes often will strike a chord with patients because someone they know has been affected.
Dr. Maqsood emphasized the importance of behavioral interventions, such as helping patients decrease their body mass index and control their hyperlipidemia.
“The behavioral interventions are those which are the most cost-effective without any side effects,” he said.
His other piece of advice is to inquire with younger patients about a family history of heart attacks. Familial hypercholesteremia is unlikely to be controlled by diet and exercise and will need medical therapy.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones described the discussions he has with patients about preventing heart attacks as “the most important conversations we can have: Remember that cardiovascular disease is still the leading cause of death and disability in the world and in the United States.”
Dr. Wong, Dr. Lloyd-Jones, and Dr. Maqsood reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As the pendulum has swung against recommending aspirin for the primary prevention of heart attacks and strokes, clinicians should focus on other ways to help patients avoid cardiovascular events.
A landmark study published in 1988 in The New England Journal of Medicine reported an astonishing 44% drop in the number of heart attacks among US male physicians aged 40-84 years who took aspirin.
Aspirin subsequently became a daily habit for millions of Americans. In 2017, nearly a quarter of Americans over age 40 who did not have cardiovascular disease (CVD) took the drug, and over 20% of those were doing so without a physician’s recommendation.
But in 2018, three studies (ASCEND, ARRIVE, and ASPREE) showed a stunning reversal in the purported benefit, according to John Wong, MD, vice-chair of the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).
The calculus for taking aspirin appeared to have changed dramatically: The drug decreased the risk for myocardial infarction by only 11% among study subjects, while its potential harms were much more pronounced.
According to Dr. Wong, who is also a professor of medicine and a primary care physician at Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston, Massachusetts, patients taking low-dose aspirin had a 58% increase in their risk for gastrointestinal bleeding compared with those not on aspirin, as well as a 31% increased risk for intracranial bleeding.
who haven’t had a heart attack or stroke.”
Fewer Americans smoke cigarettes, more realize the benefits of a healthy diet and physical activity, and the medical community better recognizes and treats hypertension. New classes of medications such as statins for high cholesterol are also moving the needle.
But a newer class of drugs may provide a safer replacement for aspirin, according to Muhammad Maqsood, MD, a cardiology fellow at DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center at Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas. P2Y purinoceptor 12 (P2Y12) inhibitors are effective in lowering the risk for heart attack and stroke in patients with acute coronary syndrome or those undergoing elective percutaneous coronary interventions.
“They have shown a better bleeding profile, especially clopidogrel compared to aspirin,” Dr. Maqsood said.
However, the findings come from trials of patients who already had CVD, so results cannot yet be extrapolated to primary prevention. Dr. Maqsood said the gap highlights the need for clinical trials that evaluate P2Y12 inhibitors for primary prevention, but no such study is registered on clinicaltrials.gov.
Benefits Persist for Some Patients
The new evidence led the USPSTF to publish new guidelines in 2022, downgrading the recommendation for low-dose aspirin use for primary prevention. Previously, the organization stated that clinicians “should” initiate daily low-dose aspirin in adults aged 50-59 years and “consider” its use in adults aged 60-69 years whose 10-year risk for CVD was higher than 10%.
The updated guidelines stated that the decision to initiate low-dose aspirin in adults aged 40-59 years with a greater than 10% risk for CVD “should be an individual one,” based on professional judgment and individual patient preferences. The USPSTF also recommended against the use of aspirin in anyone over the age of 60.
Meanwhile, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association also dialed down previously strong recommendations on low-dose aspirin to a more nuanced recommendation stating, “low-dose aspirin might be considered for primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40-70 years of age.”
With a varying age limit for recommending aspirin, clinicians may take into consideration several variables.
“Is there a magic age? I don’t think there is,” said Douglas Lloyd-Jones, the former president of the American Heart Association and current chair of the Department of Preventive Medicine and a practicing cardiologist at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, Illinois.
For a patient over age 60 who is at a high risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, is unable to quit smoking, and is not likely to experience problematic bleeding, a clinician might recommend aspirin, Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. He said he sometimes also assesses coronary artery calcium to guide his clinical decisions: If elevated (an Agatston score above 100), he might recommend low-dose aspirin.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones also reiterated that patients should continue taking low-dose aspirin if they have already experienced a heart attack, stroke, episode of atrial fibrillation, or required a vascular stent.
Unless a patient with established CVD has intractable bleeding, “the aspirin is really for life,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. Patients who have a stent or who are at high risk for recurrence of stroke are more likely to experience thrombosis, and aspirin can decrease the risk.
“In our cardiology community, we don’t just strictly use the age of 70; the decision is always individualized,” Dr. Maqsood said.
Dr. Wong said primary care providers should focus on the USPSTF’s other recommendations that address CVD (Table), such as smoking cessation and screening for hypertension.
“I think our challenge is that we have so many of those A and B recommendations,” Dr. Wong said. “And I think part of the challenge for us is working with the patient to find out what’s most important to them.”
Discussing heart attacks and strokes often will strike a chord with patients because someone they know has been affected.
Dr. Maqsood emphasized the importance of behavioral interventions, such as helping patients decrease their body mass index and control their hyperlipidemia.
“The behavioral interventions are those which are the most cost-effective without any side effects,” he said.
His other piece of advice is to inquire with younger patients about a family history of heart attacks. Familial hypercholesteremia is unlikely to be controlled by diet and exercise and will need medical therapy.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones described the discussions he has with patients about preventing heart attacks as “the most important conversations we can have: Remember that cardiovascular disease is still the leading cause of death and disability in the world and in the United States.”
Dr. Wong, Dr. Lloyd-Jones, and Dr. Maqsood reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.