User login
IDSA guidelines cover N95 use and reuse
The Infectious Disease Society of America has released new guidelines on the use and reuse of personal protective equipment, most of which address the use of face protection, for health care workers caring for COVID-19 patients. In releasing the guidelines, the IDSA expert guideline panel acknowledged gaps in evidence to support the recommendations, which is why they will be updated regularly as new evidence emerges.
“Our real goal here is to update these guidelines as a live document,” panel chair John Lynch III, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in a press briefing. “Looking at whatever research is coming out where it gets to the point where we find that the evidence is strong enough to make a change, I think we’ll need to readdress these recommendations.”
The panel tailored recommendations to the availability of supplies: conventional capacity for usual supplies; contingency capacity, when supplies are conserved, adapted and substituted with occasional reuse of select supplies; and crisis capacity, when critical supplies are lacking.
The guidelines contain the following eight recommendations for encounters with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patients:
1) Either a surgical mask or N95 (or N99 or PAPR [powered & supplied air respiratory protection]) respirator for routine patient care in a conventional setting.
2) Either a surgical mask or reprocessed respirator as opposed to no mask for routine care in a contingency or crisis setting.
3) No recommendation on the use of double gloves vs. single gloves.
4) No recommendation on the use of shoe covers for any setting.
5) An N95 (or N99 or PAPR) respirator for aerosol-generating procedures in a conventional setting.
6) A reprocessed N95 respirator as opposed to a surgical mask for aerosol-generating procedures in a contingency or crisis setting.
7) Adding a face shield or surgical mask as a cover for an N95 respirator to allow for extended use during respirator shortages when performing aerosol-generating procedures in a contingency or crisis setting. This recommendation carries a caveat: It assumes correct doffing sequence and hand hygiene before and after taking off the face shield or surgical mask cover.
8) In the same scenario, adding a face shield or surgical mask over the N95 respirator so it can be reused, again assuming the correct sequence for hand hygiene.
The guideline was developed using the GRADE approach – for Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation – and a modified methodology for developing rapid recommendations. The levels of evidence supporting each recommendation vary from moderate for the first two to knowledge gap for the third and fourth to very low certainty for the last four.
“You can see that the eight recommendations that were made, a large part of them are really focused on masks, but there are a huge number of other disparate questions that need to be answered where there is really no good evidence basis,” Dr. Lynch said. “If we see any new evidence around that, we can at least provide commentary but I would really hope evidence-based recommendations around some of those interventions.”
Panel member Allison McGeer, MD, FRCPC, of the University of Toronto, explained the lack of evidence supporting infection prevention in hospitals. “In medicine we tend to look at individual patterns and individual patient outcomes,” she said. “When you’re looking at infection prevention, you’re looking at health systems and their outcomes, and it’s much harder to randomize hospitals or a state or a country to one particular policy about how to protect patients from infections in hospitals.”
The latest guidelines follow IDSA’s previously released guidelines on treatment and management of COVID-19 patients. The panel also plans to release guidelines on use of diagnostics for COVID-19 care.
Dr. Lynch has no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. McGeer disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Merck, Sanofi Pasteur, Seqirus, GlaxoSmithKline and Cidara.
SOURCE: Lynch JB et al. IDSA. April 27, 2020.
The Infectious Disease Society of America has released new guidelines on the use and reuse of personal protective equipment, most of which address the use of face protection, for health care workers caring for COVID-19 patients. In releasing the guidelines, the IDSA expert guideline panel acknowledged gaps in evidence to support the recommendations, which is why they will be updated regularly as new evidence emerges.
“Our real goal here is to update these guidelines as a live document,” panel chair John Lynch III, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in a press briefing. “Looking at whatever research is coming out where it gets to the point where we find that the evidence is strong enough to make a change, I think we’ll need to readdress these recommendations.”
The panel tailored recommendations to the availability of supplies: conventional capacity for usual supplies; contingency capacity, when supplies are conserved, adapted and substituted with occasional reuse of select supplies; and crisis capacity, when critical supplies are lacking.
The guidelines contain the following eight recommendations for encounters with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patients:
1) Either a surgical mask or N95 (or N99 or PAPR [powered & supplied air respiratory protection]) respirator for routine patient care in a conventional setting.
2) Either a surgical mask or reprocessed respirator as opposed to no mask for routine care in a contingency or crisis setting.
3) No recommendation on the use of double gloves vs. single gloves.
4) No recommendation on the use of shoe covers for any setting.
5) An N95 (or N99 or PAPR) respirator for aerosol-generating procedures in a conventional setting.
6) A reprocessed N95 respirator as opposed to a surgical mask for aerosol-generating procedures in a contingency or crisis setting.
7) Adding a face shield or surgical mask as a cover for an N95 respirator to allow for extended use during respirator shortages when performing aerosol-generating procedures in a contingency or crisis setting. This recommendation carries a caveat: It assumes correct doffing sequence and hand hygiene before and after taking off the face shield or surgical mask cover.
8) In the same scenario, adding a face shield or surgical mask over the N95 respirator so it can be reused, again assuming the correct sequence for hand hygiene.
The guideline was developed using the GRADE approach – for Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation – and a modified methodology for developing rapid recommendations. The levels of evidence supporting each recommendation vary from moderate for the first two to knowledge gap for the third and fourth to very low certainty for the last four.
“You can see that the eight recommendations that were made, a large part of them are really focused on masks, but there are a huge number of other disparate questions that need to be answered where there is really no good evidence basis,” Dr. Lynch said. “If we see any new evidence around that, we can at least provide commentary but I would really hope evidence-based recommendations around some of those interventions.”
Panel member Allison McGeer, MD, FRCPC, of the University of Toronto, explained the lack of evidence supporting infection prevention in hospitals. “In medicine we tend to look at individual patterns and individual patient outcomes,” she said. “When you’re looking at infection prevention, you’re looking at health systems and their outcomes, and it’s much harder to randomize hospitals or a state or a country to one particular policy about how to protect patients from infections in hospitals.”
The latest guidelines follow IDSA’s previously released guidelines on treatment and management of COVID-19 patients. The panel also plans to release guidelines on use of diagnostics for COVID-19 care.
Dr. Lynch has no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. McGeer disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Merck, Sanofi Pasteur, Seqirus, GlaxoSmithKline and Cidara.
SOURCE: Lynch JB et al. IDSA. April 27, 2020.
The Infectious Disease Society of America has released new guidelines on the use and reuse of personal protective equipment, most of which address the use of face protection, for health care workers caring for COVID-19 patients. In releasing the guidelines, the IDSA expert guideline panel acknowledged gaps in evidence to support the recommendations, which is why they will be updated regularly as new evidence emerges.
“Our real goal here is to update these guidelines as a live document,” panel chair John Lynch III, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in a press briefing. “Looking at whatever research is coming out where it gets to the point where we find that the evidence is strong enough to make a change, I think we’ll need to readdress these recommendations.”
The panel tailored recommendations to the availability of supplies: conventional capacity for usual supplies; contingency capacity, when supplies are conserved, adapted and substituted with occasional reuse of select supplies; and crisis capacity, when critical supplies are lacking.
The guidelines contain the following eight recommendations for encounters with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patients:
1) Either a surgical mask or N95 (or N99 or PAPR [powered & supplied air respiratory protection]) respirator for routine patient care in a conventional setting.
2) Either a surgical mask or reprocessed respirator as opposed to no mask for routine care in a contingency or crisis setting.
3) No recommendation on the use of double gloves vs. single gloves.
4) No recommendation on the use of shoe covers for any setting.
5) An N95 (or N99 or PAPR) respirator for aerosol-generating procedures in a conventional setting.
6) A reprocessed N95 respirator as opposed to a surgical mask for aerosol-generating procedures in a contingency or crisis setting.
7) Adding a face shield or surgical mask as a cover for an N95 respirator to allow for extended use during respirator shortages when performing aerosol-generating procedures in a contingency or crisis setting. This recommendation carries a caveat: It assumes correct doffing sequence and hand hygiene before and after taking off the face shield or surgical mask cover.
8) In the same scenario, adding a face shield or surgical mask over the N95 respirator so it can be reused, again assuming the correct sequence for hand hygiene.
The guideline was developed using the GRADE approach – for Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation – and a modified methodology for developing rapid recommendations. The levels of evidence supporting each recommendation vary from moderate for the first two to knowledge gap for the third and fourth to very low certainty for the last four.
“You can see that the eight recommendations that were made, a large part of them are really focused on masks, but there are a huge number of other disparate questions that need to be answered where there is really no good evidence basis,” Dr. Lynch said. “If we see any new evidence around that, we can at least provide commentary but I would really hope evidence-based recommendations around some of those interventions.”
Panel member Allison McGeer, MD, FRCPC, of the University of Toronto, explained the lack of evidence supporting infection prevention in hospitals. “In medicine we tend to look at individual patterns and individual patient outcomes,” she said. “When you’re looking at infection prevention, you’re looking at health systems and their outcomes, and it’s much harder to randomize hospitals or a state or a country to one particular policy about how to protect patients from infections in hospitals.”
The latest guidelines follow IDSA’s previously released guidelines on treatment and management of COVID-19 patients. The panel also plans to release guidelines on use of diagnostics for COVID-19 care.
Dr. Lynch has no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. McGeer disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Merck, Sanofi Pasteur, Seqirus, GlaxoSmithKline and Cidara.
SOURCE: Lynch JB et al. IDSA. April 27, 2020.
FROM INFECTIOUS DISEASE SOCIETY OF AMERICA
AAD offers guidance for reopening practices
Dermatology practices that are resuming in-person services amid the ongoing pandemic face a range of questions and concerns when it comes to restarting patient visits.
To address these questions and considerations, the . Among the subjects covered are how practices can properly prepare clinic space to ensure staff and patients are safe and how to organize and educate employees on social distancing and safety protocols.
“All along, [we have] had guidance to help practices continue taking care of patients for essential services,” George J. Hruza, MD, immediate past president of the AAD, said in an interview. “This is really an extension of those as some states are opening up and relaxing some of the restrictions on elective procedures. We wanted to help our practices that are going to be reopening or going back to more regular services so they have a bit of a road map.”
The first step to reopening and resuming services is understanding your community’s COVID-19 prevalence and keeping updated on transmission information from local and state authorities, according to the AAD guidance. Keep in mind the federal government has specified that there should be a downward trajectory of documented cases over a 14-day period before opening practices to elective visits and procedures.
Preparing the practice through sanitation and reorganizing to minimize patient contact is also essential when reopening or resuming services. This includes cleaning and disinfecting based on World Health Organization standards, adding markings where necessary to maintain appropriate social distance, and supplying additional hand sanitizers and wipes for patients and staff, according to the guidance.
A top challenge as practices reopen is making patients feel comfortable with coming back to the practice for in-person care, said Dr. Hruza, who practices in St. Louis and is president of the Missouri State Medical Association. The AAD’s road map recommends informing patients about the reopening or reexpansion of elective procedures and communicating the steps the practice is taking to prevent COVID-19 infections and keep patients safe. It may be necessary to start with fewer patients than normal to adjust to the new safety steps until it becomes routine, according to the guidance.
Educating staff on social distancing and personal protective equipment (PPE) also is key. Staff should wear PPE for office staff meetings or sit at least 6 feet apart, according to the AAD guidelines. Practices also must determine what procedures may require additional PPE.
“If you’re doing some laser procedures, there may be a little more of a problem with tissue getting into the air or in the environment, so you may need to increase your protections a bit more,” Dr. Hruza said. “That may be a setting where you want to wear a N95 [mask].”
The AAD advises that practices be prepared to take necessary steps if a resurgence of COVID-19 cases in their community or clinic arises after reopening. Follow recommendations as they develop, be flexible, and be prepared to respond and reschedule patients, if necessary, Dr. Hruza said.
Dermatology practices that are resuming in-person services amid the ongoing pandemic face a range of questions and concerns when it comes to restarting patient visits.
To address these questions and considerations, the . Among the subjects covered are how practices can properly prepare clinic space to ensure staff and patients are safe and how to organize and educate employees on social distancing and safety protocols.
“All along, [we have] had guidance to help practices continue taking care of patients for essential services,” George J. Hruza, MD, immediate past president of the AAD, said in an interview. “This is really an extension of those as some states are opening up and relaxing some of the restrictions on elective procedures. We wanted to help our practices that are going to be reopening or going back to more regular services so they have a bit of a road map.”
The first step to reopening and resuming services is understanding your community’s COVID-19 prevalence and keeping updated on transmission information from local and state authorities, according to the AAD guidance. Keep in mind the federal government has specified that there should be a downward trajectory of documented cases over a 14-day period before opening practices to elective visits and procedures.
Preparing the practice through sanitation and reorganizing to minimize patient contact is also essential when reopening or resuming services. This includes cleaning and disinfecting based on World Health Organization standards, adding markings where necessary to maintain appropriate social distance, and supplying additional hand sanitizers and wipes for patients and staff, according to the guidance.
A top challenge as practices reopen is making patients feel comfortable with coming back to the practice for in-person care, said Dr. Hruza, who practices in St. Louis and is president of the Missouri State Medical Association. The AAD’s road map recommends informing patients about the reopening or reexpansion of elective procedures and communicating the steps the practice is taking to prevent COVID-19 infections and keep patients safe. It may be necessary to start with fewer patients than normal to adjust to the new safety steps until it becomes routine, according to the guidance.
Educating staff on social distancing and personal protective equipment (PPE) also is key. Staff should wear PPE for office staff meetings or sit at least 6 feet apart, according to the AAD guidelines. Practices also must determine what procedures may require additional PPE.
“If you’re doing some laser procedures, there may be a little more of a problem with tissue getting into the air or in the environment, so you may need to increase your protections a bit more,” Dr. Hruza said. “That may be a setting where you want to wear a N95 [mask].”
The AAD advises that practices be prepared to take necessary steps if a resurgence of COVID-19 cases in their community or clinic arises after reopening. Follow recommendations as they develop, be flexible, and be prepared to respond and reschedule patients, if necessary, Dr. Hruza said.
Dermatology practices that are resuming in-person services amid the ongoing pandemic face a range of questions and concerns when it comes to restarting patient visits.
To address these questions and considerations, the . Among the subjects covered are how practices can properly prepare clinic space to ensure staff and patients are safe and how to organize and educate employees on social distancing and safety protocols.
“All along, [we have] had guidance to help practices continue taking care of patients for essential services,” George J. Hruza, MD, immediate past president of the AAD, said in an interview. “This is really an extension of those as some states are opening up and relaxing some of the restrictions on elective procedures. We wanted to help our practices that are going to be reopening or going back to more regular services so they have a bit of a road map.”
The first step to reopening and resuming services is understanding your community’s COVID-19 prevalence and keeping updated on transmission information from local and state authorities, according to the AAD guidance. Keep in mind the federal government has specified that there should be a downward trajectory of documented cases over a 14-day period before opening practices to elective visits and procedures.
Preparing the practice through sanitation and reorganizing to minimize patient contact is also essential when reopening or resuming services. This includes cleaning and disinfecting based on World Health Organization standards, adding markings where necessary to maintain appropriate social distance, and supplying additional hand sanitizers and wipes for patients and staff, according to the guidance.
A top challenge as practices reopen is making patients feel comfortable with coming back to the practice for in-person care, said Dr. Hruza, who practices in St. Louis and is president of the Missouri State Medical Association. The AAD’s road map recommends informing patients about the reopening or reexpansion of elective procedures and communicating the steps the practice is taking to prevent COVID-19 infections and keep patients safe. It may be necessary to start with fewer patients than normal to adjust to the new safety steps until it becomes routine, according to the guidance.
Educating staff on social distancing and personal protective equipment (PPE) also is key. Staff should wear PPE for office staff meetings or sit at least 6 feet apart, according to the AAD guidelines. Practices also must determine what procedures may require additional PPE.
“If you’re doing some laser procedures, there may be a little more of a problem with tissue getting into the air or in the environment, so you may need to increase your protections a bit more,” Dr. Hruza said. “That may be a setting where you want to wear a N95 [mask].”
The AAD advises that practices be prepared to take necessary steps if a resurgence of COVID-19 cases in their community or clinic arises after reopening. Follow recommendations as they develop, be flexible, and be prepared to respond and reschedule patients, if necessary, Dr. Hruza said.
Ob.gyns., peds, other PCPs seeking COVID-19 financial relief from feds
A handful of specialties – including family medicine, obstetrics/gynecology, pediatrics, and other primary care specialties – are calling for targeted and urgent relief payments from the federal government, saying that they have been left out of distributions aimed at alleviating the financial fallout associated with the novel coronavirus.
The federal government has already distributed about $150 billion – through direct payments and advances on reimbursement – to clinicians, but, to date, the money has only been given to providers who bill Medicare, and not even all of those individuals have received payments.
“It is critical that frontline physicians who may not participate in Medicare fee-for-service, in whole or in part, including obstetrician/gynecologists, pediatricians, and family physicians, have the resources they need to continue providing essential health care to patients amid the pandemic and in the months to come,” said the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in a letter to Health & Human Services (Secretary Alex Azar.
In particular, the organizations are concerned that no money has been distributed or earmarked for clinicians who serve Medicaid recipients.
“The organizations that signed that letter are the primary providers of care to the Medicaid population,” Shawn Martin, senior VP for the AAFP, said in an interview. That’s true even for family physicians.
“Typically, in an average family medicine practice, their Medicaid panel size is equal to if not greater than the Medicare panel size,” he said.
On April 23, Mr. Azar said HHS was working on a distribution plan for providers who only take Medicaid, as well as for dentists and skilled nursing facilities. An HHS spokesperson confirmed that the agency still intends to provide money to those groups of providers and that the agency is committed to distributing funds quickly and with transparency.
Mr. Azar had also announced that the government would soon start distributing $20 billion in payments to Medicare providers, on top of the $30 billion that had already been handed out to clinicians on April 10 and 17.
That $50 billion came from the COVID-19–related $100 billion Provider Relief Fund, which was part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, signed into law on March 27.
Additionally, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had distributed some $100 billion to providers who participated in Medicare Part A or B through the Medicare Advance Payment program, which is a deferred loan. The agency brought that program to a halt on April 27.
An additional $75 billion will now be available through the Public Health and Social Services Emergency Fund (PHSSEF) as part of the third congressional COVID relief package, signed into law on April 24.
Mr. Martin said that the AAFP and other physician organizations have been talking with HHS about how to distribute money from that new pool of funds. “There’s been a lot of progress, but there hasn’t been any action,” he said, adding that the purpose of the joint letter to HHS “is to say it’s time for action.”
COVID-19 damage
AAFP, AAP, and ACOG noted in the letter the damage that’s being inflicted by COVID-19. They cited data that show a 50% decline in measles, mumps, and rubella shots, a 42% drop in diphtheria and whooping cough vaccinations, and a 73% decline in human papillomavirus shots. The groups also noted a rise in child abuse injuries that are being seen in EDs and the potential for a worsening of the maternal mortality crisis in the United States.
Primary care physicians are also the go-to doctors for upper respiratory infections, noted the groups in the letter.
“Put simply, our physician members need to be able to keep their doors open and continue treating patients,” said the groups.
A study by Harvard University and Phreesia, a health care technology company, found that ambulatory practice visits had declined by at least half since early February, with a 71% drop in visits by 7- to 17-year-olds and a 59% decline in visits by neonates, infants, and toddlers (up to age 6). Overall, pediatric practices experienced a 62% drop-off in visits.
Research conducted by the Physicians Foundation and Merritt Hawkins shows that 21% of 842 physicians who responded to an early April survey said they’d been furloughed or been given a pay cut. That number rose to 30% among doctors who are not treating COVID-19 patients.
Although the majority in the survey (66%) said they planned to keep practicing in the same manner during the pandemic, 32% said they planned to change practices, opt out of patient care roles, close their practices temporarily, or retire. The survey has a margin of error of ±3.5%.
Internists seek consideration, too
The American College of Physicians also has urged HHS to give special consideration to its members. The group wrote to Mr. Azar on April 28, recommending that payments from the new $75 billion PHSSEF be prioritized for primary care, as well as for smaller practices, those that provide care in underserved areas, and internal medicine subspecialty practices.
“Internal medicine specialists and other primary care physicians have an essential role in delivering primary, preventive, and comprehensive care not only to patients with symptoms or diagnoses of COVID-19, but also to patients with other underlying medical conditions, including conditions like heart disease and diabetes that put them at greater risk of mortality from COVID-19,” wrote ACP President Jacqueline Fincher, MD, MACP.
ACP said the government could pay physicians on the basis of the amount of additional expenses incurred that were related to COVID-19, such as extra staffing or temporary relocation of their place of residence to prevent exposing family members to the virus. Pay should also be based on the percentage of revenue losses from all payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial insurers, Dr. Fincher said in the letter.
AAFP, AAP, and ACOG also had a suggestion for distributing payments to non-Medicare providers. “Given that most women’s health, pediatric, and family practices have received less financial relief to date, we recommend that HHS provide these practices with a larger proportion of funds relative to their reported revenue than is provided on average across specialties,” they wrote.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A handful of specialties – including family medicine, obstetrics/gynecology, pediatrics, and other primary care specialties – are calling for targeted and urgent relief payments from the federal government, saying that they have been left out of distributions aimed at alleviating the financial fallout associated with the novel coronavirus.
The federal government has already distributed about $150 billion – through direct payments and advances on reimbursement – to clinicians, but, to date, the money has only been given to providers who bill Medicare, and not even all of those individuals have received payments.
“It is critical that frontline physicians who may not participate in Medicare fee-for-service, in whole or in part, including obstetrician/gynecologists, pediatricians, and family physicians, have the resources they need to continue providing essential health care to patients amid the pandemic and in the months to come,” said the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in a letter to Health & Human Services (Secretary Alex Azar.
In particular, the organizations are concerned that no money has been distributed or earmarked for clinicians who serve Medicaid recipients.
“The organizations that signed that letter are the primary providers of care to the Medicaid population,” Shawn Martin, senior VP for the AAFP, said in an interview. That’s true even for family physicians.
“Typically, in an average family medicine practice, their Medicaid panel size is equal to if not greater than the Medicare panel size,” he said.
On April 23, Mr. Azar said HHS was working on a distribution plan for providers who only take Medicaid, as well as for dentists and skilled nursing facilities. An HHS spokesperson confirmed that the agency still intends to provide money to those groups of providers and that the agency is committed to distributing funds quickly and with transparency.
Mr. Azar had also announced that the government would soon start distributing $20 billion in payments to Medicare providers, on top of the $30 billion that had already been handed out to clinicians on April 10 and 17.
That $50 billion came from the COVID-19–related $100 billion Provider Relief Fund, which was part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, signed into law on March 27.
Additionally, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had distributed some $100 billion to providers who participated in Medicare Part A or B through the Medicare Advance Payment program, which is a deferred loan. The agency brought that program to a halt on April 27.
An additional $75 billion will now be available through the Public Health and Social Services Emergency Fund (PHSSEF) as part of the third congressional COVID relief package, signed into law on April 24.
Mr. Martin said that the AAFP and other physician organizations have been talking with HHS about how to distribute money from that new pool of funds. “There’s been a lot of progress, but there hasn’t been any action,” he said, adding that the purpose of the joint letter to HHS “is to say it’s time for action.”
COVID-19 damage
AAFP, AAP, and ACOG noted in the letter the damage that’s being inflicted by COVID-19. They cited data that show a 50% decline in measles, mumps, and rubella shots, a 42% drop in diphtheria and whooping cough vaccinations, and a 73% decline in human papillomavirus shots. The groups also noted a rise in child abuse injuries that are being seen in EDs and the potential for a worsening of the maternal mortality crisis in the United States.
Primary care physicians are also the go-to doctors for upper respiratory infections, noted the groups in the letter.
“Put simply, our physician members need to be able to keep their doors open and continue treating patients,” said the groups.
A study by Harvard University and Phreesia, a health care technology company, found that ambulatory practice visits had declined by at least half since early February, with a 71% drop in visits by 7- to 17-year-olds and a 59% decline in visits by neonates, infants, and toddlers (up to age 6). Overall, pediatric practices experienced a 62% drop-off in visits.
Research conducted by the Physicians Foundation and Merritt Hawkins shows that 21% of 842 physicians who responded to an early April survey said they’d been furloughed or been given a pay cut. That number rose to 30% among doctors who are not treating COVID-19 patients.
Although the majority in the survey (66%) said they planned to keep practicing in the same manner during the pandemic, 32% said they planned to change practices, opt out of patient care roles, close their practices temporarily, or retire. The survey has a margin of error of ±3.5%.
Internists seek consideration, too
The American College of Physicians also has urged HHS to give special consideration to its members. The group wrote to Mr. Azar on April 28, recommending that payments from the new $75 billion PHSSEF be prioritized for primary care, as well as for smaller practices, those that provide care in underserved areas, and internal medicine subspecialty practices.
“Internal medicine specialists and other primary care physicians have an essential role in delivering primary, preventive, and comprehensive care not only to patients with symptoms or diagnoses of COVID-19, but also to patients with other underlying medical conditions, including conditions like heart disease and diabetes that put them at greater risk of mortality from COVID-19,” wrote ACP President Jacqueline Fincher, MD, MACP.
ACP said the government could pay physicians on the basis of the amount of additional expenses incurred that were related to COVID-19, such as extra staffing or temporary relocation of their place of residence to prevent exposing family members to the virus. Pay should also be based on the percentage of revenue losses from all payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial insurers, Dr. Fincher said in the letter.
AAFP, AAP, and ACOG also had a suggestion for distributing payments to non-Medicare providers. “Given that most women’s health, pediatric, and family practices have received less financial relief to date, we recommend that HHS provide these practices with a larger proportion of funds relative to their reported revenue than is provided on average across specialties,” they wrote.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A handful of specialties – including family medicine, obstetrics/gynecology, pediatrics, and other primary care specialties – are calling for targeted and urgent relief payments from the federal government, saying that they have been left out of distributions aimed at alleviating the financial fallout associated with the novel coronavirus.
The federal government has already distributed about $150 billion – through direct payments and advances on reimbursement – to clinicians, but, to date, the money has only been given to providers who bill Medicare, and not even all of those individuals have received payments.
“It is critical that frontline physicians who may not participate in Medicare fee-for-service, in whole or in part, including obstetrician/gynecologists, pediatricians, and family physicians, have the resources they need to continue providing essential health care to patients amid the pandemic and in the months to come,” said the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in a letter to Health & Human Services (Secretary Alex Azar.
In particular, the organizations are concerned that no money has been distributed or earmarked for clinicians who serve Medicaid recipients.
“The organizations that signed that letter are the primary providers of care to the Medicaid population,” Shawn Martin, senior VP for the AAFP, said in an interview. That’s true even for family physicians.
“Typically, in an average family medicine practice, their Medicaid panel size is equal to if not greater than the Medicare panel size,” he said.
On April 23, Mr. Azar said HHS was working on a distribution plan for providers who only take Medicaid, as well as for dentists and skilled nursing facilities. An HHS spokesperson confirmed that the agency still intends to provide money to those groups of providers and that the agency is committed to distributing funds quickly and with transparency.
Mr. Azar had also announced that the government would soon start distributing $20 billion in payments to Medicare providers, on top of the $30 billion that had already been handed out to clinicians on April 10 and 17.
That $50 billion came from the COVID-19–related $100 billion Provider Relief Fund, which was part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, signed into law on March 27.
Additionally, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had distributed some $100 billion to providers who participated in Medicare Part A or B through the Medicare Advance Payment program, which is a deferred loan. The agency brought that program to a halt on April 27.
An additional $75 billion will now be available through the Public Health and Social Services Emergency Fund (PHSSEF) as part of the third congressional COVID relief package, signed into law on April 24.
Mr. Martin said that the AAFP and other physician organizations have been talking with HHS about how to distribute money from that new pool of funds. “There’s been a lot of progress, but there hasn’t been any action,” he said, adding that the purpose of the joint letter to HHS “is to say it’s time for action.”
COVID-19 damage
AAFP, AAP, and ACOG noted in the letter the damage that’s being inflicted by COVID-19. They cited data that show a 50% decline in measles, mumps, and rubella shots, a 42% drop in diphtheria and whooping cough vaccinations, and a 73% decline in human papillomavirus shots. The groups also noted a rise in child abuse injuries that are being seen in EDs and the potential for a worsening of the maternal mortality crisis in the United States.
Primary care physicians are also the go-to doctors for upper respiratory infections, noted the groups in the letter.
“Put simply, our physician members need to be able to keep their doors open and continue treating patients,” said the groups.
A study by Harvard University and Phreesia, a health care technology company, found that ambulatory practice visits had declined by at least half since early February, with a 71% drop in visits by 7- to 17-year-olds and a 59% decline in visits by neonates, infants, and toddlers (up to age 6). Overall, pediatric practices experienced a 62% drop-off in visits.
Research conducted by the Physicians Foundation and Merritt Hawkins shows that 21% of 842 physicians who responded to an early April survey said they’d been furloughed or been given a pay cut. That number rose to 30% among doctors who are not treating COVID-19 patients.
Although the majority in the survey (66%) said they planned to keep practicing in the same manner during the pandemic, 32% said they planned to change practices, opt out of patient care roles, close their practices temporarily, or retire. The survey has a margin of error of ±3.5%.
Internists seek consideration, too
The American College of Physicians also has urged HHS to give special consideration to its members. The group wrote to Mr. Azar on April 28, recommending that payments from the new $75 billion PHSSEF be prioritized for primary care, as well as for smaller practices, those that provide care in underserved areas, and internal medicine subspecialty practices.
“Internal medicine specialists and other primary care physicians have an essential role in delivering primary, preventive, and comprehensive care not only to patients with symptoms or diagnoses of COVID-19, but also to patients with other underlying medical conditions, including conditions like heart disease and diabetes that put them at greater risk of mortality from COVID-19,” wrote ACP President Jacqueline Fincher, MD, MACP.
ACP said the government could pay physicians on the basis of the amount of additional expenses incurred that were related to COVID-19, such as extra staffing or temporary relocation of their place of residence to prevent exposing family members to the virus. Pay should also be based on the percentage of revenue losses from all payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial insurers, Dr. Fincher said in the letter.
AAFP, AAP, and ACOG also had a suggestion for distributing payments to non-Medicare providers. “Given that most women’s health, pediatric, and family practices have received less financial relief to date, we recommend that HHS provide these practices with a larger proportion of funds relative to their reported revenue than is provided on average across specialties,” they wrote.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
TERAVOLT data suggest high death rate in lung cancer patients with COVID-19
Registry data suggest an “unexpectedly high” mortality rate among patients with thoracic cancers who develop COVID-19, according to a presenter at the AACR virtual meeting I.
Data from the TERAVOLT registry showed a 34.6% mortality rate among 200 patients with COVID-19 and thoracic cancer, according to Marina Chiara Garassino, MD, of Fondazione IRCCS Instituto Nazionale dei Tumor in Milan, Italy, who presented the data at the meeting in a session on cancer and COVID-19.
Cancer patients infected with COVID-19 have been reported to be at increased risk of death, but the magnitude of increase is uncertain (Lancet Oncol. 2020 Mar;21[3]:335-7; JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4683).
Patients with thoracic cancer may be particularly vulnerable because of older age, tobacco use, preexisting cardiopulmonary comorbidities, and the immunosuppressive effects of treatment.
The global TERAVOLT registry was begun in late March 2020 to provide outcome data for coronavirus infections in thoracic cancer patients specifically. It is hoped that the data collected will guide patient management and define factors influencing morbidity and mortality.
Dr. Garassino said institutions from 21 countries have joined the TERAVOLT registry thus far. Currently, about 17 new patients with thoracic cancer and laboratory confirmed or clinically suspected COVID-19 are added to the registry each week.
As of April 12, 2020, there were 200 patients included in the registry. Their median age was 68 years, and 70.5% were men. Non–small cell lung cancer was the histology in 75.5% and small-cell lung cancer in 14.5% of patients. Most patients (73.5%) had stage IV disease. Approximately 27% of patients had at least three comorbid conditions.
About 74% of patients were on current cancer treatment, with 19% on tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone, 32.7% on chemotherapy alone, 23.1% on immunotherapy alone, and 13.6% on chemotherapy plus immunotherapy.
In all, 152 patients (76.0%) were hospitalized. However, 91.2% of patients were not admitted to the ICU, either because of a shortage of equipment or institutional policy.
The most common complications were pneumonia/pneumonitis (79.6%), acute respiratory distress syndrome (26.8%), multiorgan failure (7.6%), and sepsis (5.1%).
A total of 66 patients (34.6%) died. Most deaths were attributed to COVID-19 and not the underlying cancer, Dr. Garassino said.
A univariate analysis showed no association between cancer treatment and an increased risk of hospitalization or death. However, Dr. Garassino and colleagues are collecting more data to confirm these results.
In a multivariate analysis, no factors were associated with the risk of death, although data from a larger number of patients may shed more light on that issue.
TERAVOLT will continue to collect and provide data to identify characteristics associated with severe COVID-19–related illness, to guide physicians with information applicable to patients with thoracic malignancies, tailored to individual risk.
Like the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium and the ESMO CoCare registry, TERAVOLT represents a way for the patient care and translational science communities to share lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic.
AACR plans to help share those lessons as well, in another session on COVID-19 and cancer at the AACR virtual meeting II in June and at a conference on COVID-19 and cancer in July, according to session moderator Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Garassino disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, and other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Registry data suggest an “unexpectedly high” mortality rate among patients with thoracic cancers who develop COVID-19, according to a presenter at the AACR virtual meeting I.
Data from the TERAVOLT registry showed a 34.6% mortality rate among 200 patients with COVID-19 and thoracic cancer, according to Marina Chiara Garassino, MD, of Fondazione IRCCS Instituto Nazionale dei Tumor in Milan, Italy, who presented the data at the meeting in a session on cancer and COVID-19.
Cancer patients infected with COVID-19 have been reported to be at increased risk of death, but the magnitude of increase is uncertain (Lancet Oncol. 2020 Mar;21[3]:335-7; JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4683).
Patients with thoracic cancer may be particularly vulnerable because of older age, tobacco use, preexisting cardiopulmonary comorbidities, and the immunosuppressive effects of treatment.
The global TERAVOLT registry was begun in late March 2020 to provide outcome data for coronavirus infections in thoracic cancer patients specifically. It is hoped that the data collected will guide patient management and define factors influencing morbidity and mortality.
Dr. Garassino said institutions from 21 countries have joined the TERAVOLT registry thus far. Currently, about 17 new patients with thoracic cancer and laboratory confirmed or clinically suspected COVID-19 are added to the registry each week.
As of April 12, 2020, there were 200 patients included in the registry. Their median age was 68 years, and 70.5% were men. Non–small cell lung cancer was the histology in 75.5% and small-cell lung cancer in 14.5% of patients. Most patients (73.5%) had stage IV disease. Approximately 27% of patients had at least three comorbid conditions.
About 74% of patients were on current cancer treatment, with 19% on tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone, 32.7% on chemotherapy alone, 23.1% on immunotherapy alone, and 13.6% on chemotherapy plus immunotherapy.
In all, 152 patients (76.0%) were hospitalized. However, 91.2% of patients were not admitted to the ICU, either because of a shortage of equipment or institutional policy.
The most common complications were pneumonia/pneumonitis (79.6%), acute respiratory distress syndrome (26.8%), multiorgan failure (7.6%), and sepsis (5.1%).
A total of 66 patients (34.6%) died. Most deaths were attributed to COVID-19 and not the underlying cancer, Dr. Garassino said.
A univariate analysis showed no association between cancer treatment and an increased risk of hospitalization or death. However, Dr. Garassino and colleagues are collecting more data to confirm these results.
In a multivariate analysis, no factors were associated with the risk of death, although data from a larger number of patients may shed more light on that issue.
TERAVOLT will continue to collect and provide data to identify characteristics associated with severe COVID-19–related illness, to guide physicians with information applicable to patients with thoracic malignancies, tailored to individual risk.
Like the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium and the ESMO CoCare registry, TERAVOLT represents a way for the patient care and translational science communities to share lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic.
AACR plans to help share those lessons as well, in another session on COVID-19 and cancer at the AACR virtual meeting II in June and at a conference on COVID-19 and cancer in July, according to session moderator Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Garassino disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, and other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Registry data suggest an “unexpectedly high” mortality rate among patients with thoracic cancers who develop COVID-19, according to a presenter at the AACR virtual meeting I.
Data from the TERAVOLT registry showed a 34.6% mortality rate among 200 patients with COVID-19 and thoracic cancer, according to Marina Chiara Garassino, MD, of Fondazione IRCCS Instituto Nazionale dei Tumor in Milan, Italy, who presented the data at the meeting in a session on cancer and COVID-19.
Cancer patients infected with COVID-19 have been reported to be at increased risk of death, but the magnitude of increase is uncertain (Lancet Oncol. 2020 Mar;21[3]:335-7; JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4683).
Patients with thoracic cancer may be particularly vulnerable because of older age, tobacco use, preexisting cardiopulmonary comorbidities, and the immunosuppressive effects of treatment.
The global TERAVOLT registry was begun in late March 2020 to provide outcome data for coronavirus infections in thoracic cancer patients specifically. It is hoped that the data collected will guide patient management and define factors influencing morbidity and mortality.
Dr. Garassino said institutions from 21 countries have joined the TERAVOLT registry thus far. Currently, about 17 new patients with thoracic cancer and laboratory confirmed or clinically suspected COVID-19 are added to the registry each week.
As of April 12, 2020, there were 200 patients included in the registry. Their median age was 68 years, and 70.5% were men. Non–small cell lung cancer was the histology in 75.5% and small-cell lung cancer in 14.5% of patients. Most patients (73.5%) had stage IV disease. Approximately 27% of patients had at least three comorbid conditions.
About 74% of patients were on current cancer treatment, with 19% on tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone, 32.7% on chemotherapy alone, 23.1% on immunotherapy alone, and 13.6% on chemotherapy plus immunotherapy.
In all, 152 patients (76.0%) were hospitalized. However, 91.2% of patients were not admitted to the ICU, either because of a shortage of equipment or institutional policy.
The most common complications were pneumonia/pneumonitis (79.6%), acute respiratory distress syndrome (26.8%), multiorgan failure (7.6%), and sepsis (5.1%).
A total of 66 patients (34.6%) died. Most deaths were attributed to COVID-19 and not the underlying cancer, Dr. Garassino said.
A univariate analysis showed no association between cancer treatment and an increased risk of hospitalization or death. However, Dr. Garassino and colleagues are collecting more data to confirm these results.
In a multivariate analysis, no factors were associated with the risk of death, although data from a larger number of patients may shed more light on that issue.
TERAVOLT will continue to collect and provide data to identify characteristics associated with severe COVID-19–related illness, to guide physicians with information applicable to patients with thoracic malignancies, tailored to individual risk.
Like the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium and the ESMO CoCare registry, TERAVOLT represents a way for the patient care and translational science communities to share lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic.
AACR plans to help share those lessons as well, in another session on COVID-19 and cancer at the AACR virtual meeting II in June and at a conference on COVID-19 and cancer in July, according to session moderator Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Garassino disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, and other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
FROM AACR 2020
COVID-19: An opportunity, challenge for addiction treatment, NIDA boss says
The COVID-19 pandemic is posing significant challenges while also providing unique opportunities for patients with substance use disorders (SUD), a leading expert says.
Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said that the pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, making it easier for patients with SUD to access treatment. It has also led to the proliferation of more mental health hotlines, which is critical since the vast majority of these patients have comorbid mental illness.
In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased availability of “alternative” peer support mechanisms via cellphones or computers to aid individuals’ sobriety.
Dr. Volkow spoke at the virtual American Psychiatric Association Spring Highlights Meeting 2020, which is replacing the organization’s canceled annual meeting.
While methadone clinics have had to close during the pandemic, making it challenging for those on medically assisted treatment to receive methadone or buprenorphine, some of the rules and regulations have been relaxed in order to make these medications accessible without the need for in-person attendance at a clinic. In addition, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs.
Social isolation, stigma intensified
A pandemic increases anxiety in the general population, but for patients with SUD who may be also be struggling with homelessness and comorbid mental illness, the situation can further exacerbate social stigma and isolation – leading to relapse, more overdoses, and overdose deaths, Dr. Volkow said. Social interaction is “extraordinarily important” for patients and “one of the most powerful tools we have” to build resilience.
Right now, said Dr. Volkow, “we are in the dark as to how COVID infections have affected the number of overdose deaths.”
However, she noted that
“So even through this devastation, we can actually extract something that may help others in future,” she said.
Dr. Volkow noted that during the pandemic it is critical to reinforce the importance of engaging in – and remaining in – treatment to SUD patients. It’s also crucial to make patients aware of social support systems and behavioral interventions to help them cope with stress and to mitigate relapse risk.
COVID-19 and relapse
Elie G. Aoun, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at New York University and vice chair of the APA’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said in an interview that Dr. Volkow’s presentation provided “exactly the kind of accessible information” clinicians need.
Dr. Aoun said he sees the impact of the COVID-19 crisis in his practice every day. Patients with SUD “are getting the short end of the stick.”
Social distancing measures prompted by the pandemic can be “very triggering” for SUD patients, he said. One of his patients told him the current isolation, loneliness, movement restrictions, and boredom remind her of the way she felt when she used drugs.
Dr. Aoun said four of his patients have relapsed since the pandemic began. Two of them had just started treatment after years of using drugs, so this was a “major setback” for them.
He and his colleagues were “not really prepared” to provide care via video link, which he believes is not as effective as in-person sessions.
In addition to disrupting patient care, said Dr. Aoun, the pandemic is forcing the medical community to face social determinants of health, such as poverty and homelessness, as they relate to addiction disorders and whether or not someone receives care.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is posing significant challenges while also providing unique opportunities for patients with substance use disorders (SUD), a leading expert says.
Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said that the pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, making it easier for patients with SUD to access treatment. It has also led to the proliferation of more mental health hotlines, which is critical since the vast majority of these patients have comorbid mental illness.
In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased availability of “alternative” peer support mechanisms via cellphones or computers to aid individuals’ sobriety.
Dr. Volkow spoke at the virtual American Psychiatric Association Spring Highlights Meeting 2020, which is replacing the organization’s canceled annual meeting.
While methadone clinics have had to close during the pandemic, making it challenging for those on medically assisted treatment to receive methadone or buprenorphine, some of the rules and regulations have been relaxed in order to make these medications accessible without the need for in-person attendance at a clinic. In addition, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs.
Social isolation, stigma intensified
A pandemic increases anxiety in the general population, but for patients with SUD who may be also be struggling with homelessness and comorbid mental illness, the situation can further exacerbate social stigma and isolation – leading to relapse, more overdoses, and overdose deaths, Dr. Volkow said. Social interaction is “extraordinarily important” for patients and “one of the most powerful tools we have” to build resilience.
Right now, said Dr. Volkow, “we are in the dark as to how COVID infections have affected the number of overdose deaths.”
However, she noted that
“So even through this devastation, we can actually extract something that may help others in future,” she said.
Dr. Volkow noted that during the pandemic it is critical to reinforce the importance of engaging in – and remaining in – treatment to SUD patients. It’s also crucial to make patients aware of social support systems and behavioral interventions to help them cope with stress and to mitigate relapse risk.
COVID-19 and relapse
Elie G. Aoun, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at New York University and vice chair of the APA’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said in an interview that Dr. Volkow’s presentation provided “exactly the kind of accessible information” clinicians need.
Dr. Aoun said he sees the impact of the COVID-19 crisis in his practice every day. Patients with SUD “are getting the short end of the stick.”
Social distancing measures prompted by the pandemic can be “very triggering” for SUD patients, he said. One of his patients told him the current isolation, loneliness, movement restrictions, and boredom remind her of the way she felt when she used drugs.
Dr. Aoun said four of his patients have relapsed since the pandemic began. Two of them had just started treatment after years of using drugs, so this was a “major setback” for them.
He and his colleagues were “not really prepared” to provide care via video link, which he believes is not as effective as in-person sessions.
In addition to disrupting patient care, said Dr. Aoun, the pandemic is forcing the medical community to face social determinants of health, such as poverty and homelessness, as they relate to addiction disorders and whether or not someone receives care.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is posing significant challenges while also providing unique opportunities for patients with substance use disorders (SUD), a leading expert says.
Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said that the pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, making it easier for patients with SUD to access treatment. It has also led to the proliferation of more mental health hotlines, which is critical since the vast majority of these patients have comorbid mental illness.
In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased availability of “alternative” peer support mechanisms via cellphones or computers to aid individuals’ sobriety.
Dr. Volkow spoke at the virtual American Psychiatric Association Spring Highlights Meeting 2020, which is replacing the organization’s canceled annual meeting.
While methadone clinics have had to close during the pandemic, making it challenging for those on medically assisted treatment to receive methadone or buprenorphine, some of the rules and regulations have been relaxed in order to make these medications accessible without the need for in-person attendance at a clinic. In addition, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs.
Social isolation, stigma intensified
A pandemic increases anxiety in the general population, but for patients with SUD who may be also be struggling with homelessness and comorbid mental illness, the situation can further exacerbate social stigma and isolation – leading to relapse, more overdoses, and overdose deaths, Dr. Volkow said. Social interaction is “extraordinarily important” for patients and “one of the most powerful tools we have” to build resilience.
Right now, said Dr. Volkow, “we are in the dark as to how COVID infections have affected the number of overdose deaths.”
However, she noted that
“So even through this devastation, we can actually extract something that may help others in future,” she said.
Dr. Volkow noted that during the pandemic it is critical to reinforce the importance of engaging in – and remaining in – treatment to SUD patients. It’s also crucial to make patients aware of social support systems and behavioral interventions to help them cope with stress and to mitigate relapse risk.
COVID-19 and relapse
Elie G. Aoun, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at New York University and vice chair of the APA’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said in an interview that Dr. Volkow’s presentation provided “exactly the kind of accessible information” clinicians need.
Dr. Aoun said he sees the impact of the COVID-19 crisis in his practice every day. Patients with SUD “are getting the short end of the stick.”
Social distancing measures prompted by the pandemic can be “very triggering” for SUD patients, he said. One of his patients told him the current isolation, loneliness, movement restrictions, and boredom remind her of the way she felt when she used drugs.
Dr. Aoun said four of his patients have relapsed since the pandemic began. Two of them had just started treatment after years of using drugs, so this was a “major setback” for them.
He and his colleagues were “not really prepared” to provide care via video link, which he believes is not as effective as in-person sessions.
In addition to disrupting patient care, said Dr. Aoun, the pandemic is forcing the medical community to face social determinants of health, such as poverty and homelessness, as they relate to addiction disorders and whether or not someone receives care.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Trials and tribulations: Neurology research during COVID-19
However, researchers remain determined to forge ahead – with many redesigning their studies, at least in part to optimize the safety of their participants and research staff.
Keeping people engaged while protocols are on hold; expanding normal safety considerations; and re-enlisting statisticians to keep their findings as significant as possible are just some of study survival strategies underway.
Alzheimer’s disease research on hold
The pandemic is having a significant impact on Alzheimer’s disease research, and medical research in general, says Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Many clinical trials worldwide are pausing, changing, or halting the testing of the drug or the intervention,” she told Medscape Medical News. “How the teams have adapted depends on the study,” she added. “As you can imagine, things are changing on a daily basis.”
The US Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) trial, for example, is on hold until at least May 31. The Alzheimer’s Association is helping to implement and fund the study along with Wake Forest University Medical Center.
“We’re not randomizing participants at this point in time and the intervention — which is based on a team meeting, and there is a social aspect to that — has been paused,” Dr. Snyder said.
Another pivotal study underway is the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s study (the A4 Study). Investigators are evaluating if an anti-amyloid antibody, solanezumab (Eli Lilly), can slow memory loss among people with amyloid on imaging but no symptoms of cognitive decline at baseline.
“The A4 Study is definitely continuing. However, in an effort to minimize risk to participants, site staff and study integrity, we have implemented an optional study hiatus for both the double-blind and open-label extension phases,” lead investigator Reisa Anne Sperling, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“We wanted to prioritize the safety of our participants as well as the ability of participants to remain in the study … despite disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Sperling, who is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Alzheimer Research and Treatment at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The ultimate goal is for A4 participants to receive the full number of planned infusions and assessments, even if it takes longer, she added.
Many Alzheimer’s disease researchers outside the United States face similar challenges. “As you probably are well aware, Spain is now in a complete lockdown. This has affected research centers like ours, the Barcelona Brain Research Center, and the way we work,” José Luís Molinuevo Guix, MD, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
All participants in observational studies like the ALFA+ study and initiatives, as well as those in trials including PENSA and AB1601, “are not allowed, by law, to come in, hence from a safety perspective we are on good grounds,” added Dr. Molinuevo Guix, who directs the Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders unit at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
The investigators are creating protocols for communicating with participants during the pandemic and for restarting visits safely after the lockdown has ended.
Stroke studies amended or suspended
A similar situation is occurring in stroke trials. Stroke is “obviously an acute disease, as well as a disease that requires secondary prevention,” Mitchell Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, told Medscape Medical News.
“One could argue that patients with stroke are going to be in the hospital anyway – why not enroll them in a study? They’re not incurring any additional risk,” he said. “But the staff have to come in to see them, and we’re really trying to avoid exposure.”
One ongoing trial, the Atrial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke (ARCADIA), stopped randomly assigning new participants to secondary prevention with apixaban or aspirin because of COVID-19. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues plan to provide medication to the 440 people already in the trial.
“Wherever possible, the study coordinators are shipping the drug to people and doing follow-up visits by phone or video,” said Dr. Elkind, chief of the Division of Neurology Clinical Outcomes Research and Population Sciences at Columbia University in New York City.
Protecting patients, staff, and ultimately society is a “major driving force in stopping the randomizations,” he stressed.
ARCADIA is part of the StrokeNet prevention trials network, run by the NIH’s National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Additional pivotal trials include the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST) and the Multi-arm Optimization of Stroke Thrombolysis (MOST) studies, he said.
Joseph Broderick, MD, director of the national NIH StrokeNet, agreed that safety comes first. “It was the decision of the StrokeNet leadership and the principal investigators of the trials that we needed to hold recruitment of new patients while we worked on adapting processes of enrollment to ensure the safety of both patients and researchers interacting with study patients,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Potential risks vary based on the study intervention and the need for in-person interactions. Trials that include stimulation devices or physical therapy, for example, might be most affected, added Dr. Broderick, professor and director of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio.
Nevertheless, “there are potential ways … to move as much as possible toward telemedicine and digital interactions during this time.”
Multiple challenges in multiple sclerosis
At the national level, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an “unprecedented impact on almost all the clinical trials funded by NINDS,” said Clinton Wright, MD, director of the Division of Clinical Research at NINDS. “Investigators have had to adapt quickly.”
Supplementing existing grants with money to conduct research on COVID-19 and pursuing research opportunities from different institutes are “some of the creative approaches [that] have come from the NIH [National Institutes of Health] itself,” Dr. Wright said. “Other creative approaches have come from investigators trying to keep their studies and trials going during the pandemic.”
In clinical trials, “everything from electronic consent to in-home research drug delivery is being brought to bear.”
“A few ongoing trials have been able to modify their protocols to obtain consent and carry out evaluations remotely by telephone or videoconferencing,” Dr. Wright said. “This is especially critical for trials that involve medical management of specific risk factors or conditions, where suspension of the trial could itself have adverse consequences due to reduced engagement with research participants.”
For participants already in MS studies, “each upcoming visit is assessed for whether it’s critical or could be done virtually or just skipped. If a person needs a treatment that cannot be postponed or skipped, they come in,” Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, told Medscape Medical News.
New study enrollment is largely on hold and study visits for existing participants are limited, said Dr. Cohen, who is also president of the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Some of the major ongoing trials in MS are “looking at very fundamental questions in the field,” Dr. Cohen said. The Determining the Effectiveness of earLy Intensive Versus Escalation Approaches for RRMS (DELIVER-MS) and Traditional Versus Early Aggressive Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis (TREAT-MS) trials, for example, evaluate whether treatment should be initiated with one of the less efficacious agents with escalation as needed, or whether treatment should begin with a high-efficacy agent.
Both trials are currently on hold because of the pandemic, as is the Best Available Therapy Versus Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Sclerosis (BEAT-MS) study.
“There has been a lot of interest in hematopoietic stem cell transplants and where they fit into our overall treatment strategy, and this is intended to provide a more definitive answer,” Dr. Cohen said.
Making the most of down time
“The pandemic has been challenging” in terms of ongoing MS research, said Benjamin M. Segal, MD, chair of the Department of Neurology and director of the Neuroscience Research Institute at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“With regard to the lab, our animal model experiments have been placed on hold. We have stopped collecting samples from clinical subjects for biomarker studies.
“However, my research team has been taking advantage of the time that has been freed up from bench work by analyzing data sets that had been placed aside, delving more deeply into the literature, and writing new grant proposals and articles,” he added.
Two of Dr. Segal’s trainees are writing review articles on the immunopathogenesis of MS and its treatment. Another postdoctoral candidate is writing a grant proposal to investigate how coinfection with a coronavirus modulates CNS pathology and the clinical course of an animal model of MS.
“I am asking my trainees to plan out experiments further in advance than they ever have before, so they are as prepared as possible to resume their research agendas once we are up and running again,” Dr. Segal said.
Confronting current challenges while planning for a future less disrupted by the pandemic is a common theme that emerges.
“The duration of this [pandemic] will dictate how we analyze the data at the end [for the US POINTER study]. There is a large group of statisticians working on this,” Dr. Snyder said.
Dr. Sperling of Harvard Medical School also remains undeterred. “This is definitely a challenging time, as we must not allow the COVID-19 to interfere with our essential mission to find a successful treatment to prevent cognitive decline in AD. We do need, however, to be as flexible as possible to protect our participants and minimize the impact to our overall study integrity,” she said.
NIH guidance
Dr. Molinuevo Guix, of the Barcelona Brain Research Center, is also determined to continue his Alzheimer’s disease research. “I am aware that after the crisis, there will be less [risk] but still a COVID-19 infection risk, so apart from trying to generate part of our visits virtually, we want to make sure we have all necessary safety measures in place. We remain very active to preserve the work we have done to keep up the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia,” he said.
Such forward thinking also applies to major stroke trials, said Dr. Broderick of the University of Cincinnati. “As soon as we shut down enrollment in stroke trials, we immediately began to make plans about how and when we can restart our stroke trials,” he explained. “One of our trials can do every step of the trial process remotely without direct in-person interactions and will be able to restart soon.”
An individualized approach is needed, Dr. Broderick added. “For trials involving necessary in-person and hands-on assessments, we will need to consider how best to use protective equipment and expanded testing that will likely match the ongoing clinical care and requirements at a given institution.
“Even if a trial officially reopens enrollment, the decision to enroll locally will need to follow local institutional environment and guidelines. Thus, restart of trial enrollment will not likely be uniform, similar to how trials often start in the first place,” Dr. Broderick said.
The NIH published uniform standards for researchers across its institutes to help guide them during the pandemic. Future contingency plans also are underway at the NINDS.
“As the pandemic wanes and in-person research activities restart, it will be important to have in place safety measures that prevent a resurgence of the virus, such as proper personal protective equipment for staff and research participants, said Dr. Wright, the clinical research director at NINDS.
For clinical trials, NINDS is prepared to provide supplemental funds to trial investigators to help support additional activities undertaken as a result of the pandemic.
“This has been an instructive experience. The pandemic will end, and we will resume much of our old patterns of behavior,” said Ohio State’s Dr. Segal. “But some of the strategies that we have employed to get through this time will continue to influence the way we communicate information, plan experiments, and prioritize research activities in the future, to good effect.”
Drs. Snyder, Sperling, Molinuevo Guix, Elkind, Broderick, Wright, Cohen, and Segal have disclosed no relevant disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, researchers remain determined to forge ahead – with many redesigning their studies, at least in part to optimize the safety of their participants and research staff.
Keeping people engaged while protocols are on hold; expanding normal safety considerations; and re-enlisting statisticians to keep their findings as significant as possible are just some of study survival strategies underway.
Alzheimer’s disease research on hold
The pandemic is having a significant impact on Alzheimer’s disease research, and medical research in general, says Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Many clinical trials worldwide are pausing, changing, or halting the testing of the drug or the intervention,” she told Medscape Medical News. “How the teams have adapted depends on the study,” she added. “As you can imagine, things are changing on a daily basis.”
The US Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) trial, for example, is on hold until at least May 31. The Alzheimer’s Association is helping to implement and fund the study along with Wake Forest University Medical Center.
“We’re not randomizing participants at this point in time and the intervention — which is based on a team meeting, and there is a social aspect to that — has been paused,” Dr. Snyder said.
Another pivotal study underway is the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s study (the A4 Study). Investigators are evaluating if an anti-amyloid antibody, solanezumab (Eli Lilly), can slow memory loss among people with amyloid on imaging but no symptoms of cognitive decline at baseline.
“The A4 Study is definitely continuing. However, in an effort to minimize risk to participants, site staff and study integrity, we have implemented an optional study hiatus for both the double-blind and open-label extension phases,” lead investigator Reisa Anne Sperling, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“We wanted to prioritize the safety of our participants as well as the ability of participants to remain in the study … despite disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Sperling, who is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Alzheimer Research and Treatment at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The ultimate goal is for A4 participants to receive the full number of planned infusions and assessments, even if it takes longer, she added.
Many Alzheimer’s disease researchers outside the United States face similar challenges. “As you probably are well aware, Spain is now in a complete lockdown. This has affected research centers like ours, the Barcelona Brain Research Center, and the way we work,” José Luís Molinuevo Guix, MD, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
All participants in observational studies like the ALFA+ study and initiatives, as well as those in trials including PENSA and AB1601, “are not allowed, by law, to come in, hence from a safety perspective we are on good grounds,” added Dr. Molinuevo Guix, who directs the Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders unit at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
The investigators are creating protocols for communicating with participants during the pandemic and for restarting visits safely after the lockdown has ended.
Stroke studies amended or suspended
A similar situation is occurring in stroke trials. Stroke is “obviously an acute disease, as well as a disease that requires secondary prevention,” Mitchell Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, told Medscape Medical News.
“One could argue that patients with stroke are going to be in the hospital anyway – why not enroll them in a study? They’re not incurring any additional risk,” he said. “But the staff have to come in to see them, and we’re really trying to avoid exposure.”
One ongoing trial, the Atrial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke (ARCADIA), stopped randomly assigning new participants to secondary prevention with apixaban or aspirin because of COVID-19. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues plan to provide medication to the 440 people already in the trial.
“Wherever possible, the study coordinators are shipping the drug to people and doing follow-up visits by phone or video,” said Dr. Elkind, chief of the Division of Neurology Clinical Outcomes Research and Population Sciences at Columbia University in New York City.
Protecting patients, staff, and ultimately society is a “major driving force in stopping the randomizations,” he stressed.
ARCADIA is part of the StrokeNet prevention trials network, run by the NIH’s National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Additional pivotal trials include the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST) and the Multi-arm Optimization of Stroke Thrombolysis (MOST) studies, he said.
Joseph Broderick, MD, director of the national NIH StrokeNet, agreed that safety comes first. “It was the decision of the StrokeNet leadership and the principal investigators of the trials that we needed to hold recruitment of new patients while we worked on adapting processes of enrollment to ensure the safety of both patients and researchers interacting with study patients,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Potential risks vary based on the study intervention and the need for in-person interactions. Trials that include stimulation devices or physical therapy, for example, might be most affected, added Dr. Broderick, professor and director of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio.
Nevertheless, “there are potential ways … to move as much as possible toward telemedicine and digital interactions during this time.”
Multiple challenges in multiple sclerosis
At the national level, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an “unprecedented impact on almost all the clinical trials funded by NINDS,” said Clinton Wright, MD, director of the Division of Clinical Research at NINDS. “Investigators have had to adapt quickly.”
Supplementing existing grants with money to conduct research on COVID-19 and pursuing research opportunities from different institutes are “some of the creative approaches [that] have come from the NIH [National Institutes of Health] itself,” Dr. Wright said. “Other creative approaches have come from investigators trying to keep their studies and trials going during the pandemic.”
In clinical trials, “everything from electronic consent to in-home research drug delivery is being brought to bear.”
“A few ongoing trials have been able to modify their protocols to obtain consent and carry out evaluations remotely by telephone or videoconferencing,” Dr. Wright said. “This is especially critical for trials that involve medical management of specific risk factors or conditions, where suspension of the trial could itself have adverse consequences due to reduced engagement with research participants.”
For participants already in MS studies, “each upcoming visit is assessed for whether it’s critical or could be done virtually or just skipped. If a person needs a treatment that cannot be postponed or skipped, they come in,” Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, told Medscape Medical News.
New study enrollment is largely on hold and study visits for existing participants are limited, said Dr. Cohen, who is also president of the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Some of the major ongoing trials in MS are “looking at very fundamental questions in the field,” Dr. Cohen said. The Determining the Effectiveness of earLy Intensive Versus Escalation Approaches for RRMS (DELIVER-MS) and Traditional Versus Early Aggressive Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis (TREAT-MS) trials, for example, evaluate whether treatment should be initiated with one of the less efficacious agents with escalation as needed, or whether treatment should begin with a high-efficacy agent.
Both trials are currently on hold because of the pandemic, as is the Best Available Therapy Versus Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Sclerosis (BEAT-MS) study.
“There has been a lot of interest in hematopoietic stem cell transplants and where they fit into our overall treatment strategy, and this is intended to provide a more definitive answer,” Dr. Cohen said.
Making the most of down time
“The pandemic has been challenging” in terms of ongoing MS research, said Benjamin M. Segal, MD, chair of the Department of Neurology and director of the Neuroscience Research Institute at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“With regard to the lab, our animal model experiments have been placed on hold. We have stopped collecting samples from clinical subjects for biomarker studies.
“However, my research team has been taking advantage of the time that has been freed up from bench work by analyzing data sets that had been placed aside, delving more deeply into the literature, and writing new grant proposals and articles,” he added.
Two of Dr. Segal’s trainees are writing review articles on the immunopathogenesis of MS and its treatment. Another postdoctoral candidate is writing a grant proposal to investigate how coinfection with a coronavirus modulates CNS pathology and the clinical course of an animal model of MS.
“I am asking my trainees to plan out experiments further in advance than they ever have before, so they are as prepared as possible to resume their research agendas once we are up and running again,” Dr. Segal said.
Confronting current challenges while planning for a future less disrupted by the pandemic is a common theme that emerges.
“The duration of this [pandemic] will dictate how we analyze the data at the end [for the US POINTER study]. There is a large group of statisticians working on this,” Dr. Snyder said.
Dr. Sperling of Harvard Medical School also remains undeterred. “This is definitely a challenging time, as we must not allow the COVID-19 to interfere with our essential mission to find a successful treatment to prevent cognitive decline in AD. We do need, however, to be as flexible as possible to protect our participants and minimize the impact to our overall study integrity,” she said.
NIH guidance
Dr. Molinuevo Guix, of the Barcelona Brain Research Center, is also determined to continue his Alzheimer’s disease research. “I am aware that after the crisis, there will be less [risk] but still a COVID-19 infection risk, so apart from trying to generate part of our visits virtually, we want to make sure we have all necessary safety measures in place. We remain very active to preserve the work we have done to keep up the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia,” he said.
Such forward thinking also applies to major stroke trials, said Dr. Broderick of the University of Cincinnati. “As soon as we shut down enrollment in stroke trials, we immediately began to make plans about how and when we can restart our stroke trials,” he explained. “One of our trials can do every step of the trial process remotely without direct in-person interactions and will be able to restart soon.”
An individualized approach is needed, Dr. Broderick added. “For trials involving necessary in-person and hands-on assessments, we will need to consider how best to use protective equipment and expanded testing that will likely match the ongoing clinical care and requirements at a given institution.
“Even if a trial officially reopens enrollment, the decision to enroll locally will need to follow local institutional environment and guidelines. Thus, restart of trial enrollment will not likely be uniform, similar to how trials often start in the first place,” Dr. Broderick said.
The NIH published uniform standards for researchers across its institutes to help guide them during the pandemic. Future contingency plans also are underway at the NINDS.
“As the pandemic wanes and in-person research activities restart, it will be important to have in place safety measures that prevent a resurgence of the virus, such as proper personal protective equipment for staff and research participants, said Dr. Wright, the clinical research director at NINDS.
For clinical trials, NINDS is prepared to provide supplemental funds to trial investigators to help support additional activities undertaken as a result of the pandemic.
“This has been an instructive experience. The pandemic will end, and we will resume much of our old patterns of behavior,” said Ohio State’s Dr. Segal. “But some of the strategies that we have employed to get through this time will continue to influence the way we communicate information, plan experiments, and prioritize research activities in the future, to good effect.”
Drs. Snyder, Sperling, Molinuevo Guix, Elkind, Broderick, Wright, Cohen, and Segal have disclosed no relevant disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, researchers remain determined to forge ahead – with many redesigning their studies, at least in part to optimize the safety of their participants and research staff.
Keeping people engaged while protocols are on hold; expanding normal safety considerations; and re-enlisting statisticians to keep their findings as significant as possible are just some of study survival strategies underway.
Alzheimer’s disease research on hold
The pandemic is having a significant impact on Alzheimer’s disease research, and medical research in general, says Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Many clinical trials worldwide are pausing, changing, or halting the testing of the drug or the intervention,” she told Medscape Medical News. “How the teams have adapted depends on the study,” she added. “As you can imagine, things are changing on a daily basis.”
The US Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) trial, for example, is on hold until at least May 31. The Alzheimer’s Association is helping to implement and fund the study along with Wake Forest University Medical Center.
“We’re not randomizing participants at this point in time and the intervention — which is based on a team meeting, and there is a social aspect to that — has been paused,” Dr. Snyder said.
Another pivotal study underway is the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s study (the A4 Study). Investigators are evaluating if an anti-amyloid antibody, solanezumab (Eli Lilly), can slow memory loss among people with amyloid on imaging but no symptoms of cognitive decline at baseline.
“The A4 Study is definitely continuing. However, in an effort to minimize risk to participants, site staff and study integrity, we have implemented an optional study hiatus for both the double-blind and open-label extension phases,” lead investigator Reisa Anne Sperling, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“We wanted to prioritize the safety of our participants as well as the ability of participants to remain in the study … despite disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Sperling, who is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Alzheimer Research and Treatment at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The ultimate goal is for A4 participants to receive the full number of planned infusions and assessments, even if it takes longer, she added.
Many Alzheimer’s disease researchers outside the United States face similar challenges. “As you probably are well aware, Spain is now in a complete lockdown. This has affected research centers like ours, the Barcelona Brain Research Center, and the way we work,” José Luís Molinuevo Guix, MD, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
All participants in observational studies like the ALFA+ study and initiatives, as well as those in trials including PENSA and AB1601, “are not allowed, by law, to come in, hence from a safety perspective we are on good grounds,” added Dr. Molinuevo Guix, who directs the Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders unit at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
The investigators are creating protocols for communicating with participants during the pandemic and for restarting visits safely after the lockdown has ended.
Stroke studies amended or suspended
A similar situation is occurring in stroke trials. Stroke is “obviously an acute disease, as well as a disease that requires secondary prevention,” Mitchell Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, told Medscape Medical News.
“One could argue that patients with stroke are going to be in the hospital anyway – why not enroll them in a study? They’re not incurring any additional risk,” he said. “But the staff have to come in to see them, and we’re really trying to avoid exposure.”
One ongoing trial, the Atrial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke (ARCADIA), stopped randomly assigning new participants to secondary prevention with apixaban or aspirin because of COVID-19. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues plan to provide medication to the 440 people already in the trial.
“Wherever possible, the study coordinators are shipping the drug to people and doing follow-up visits by phone or video,” said Dr. Elkind, chief of the Division of Neurology Clinical Outcomes Research and Population Sciences at Columbia University in New York City.
Protecting patients, staff, and ultimately society is a “major driving force in stopping the randomizations,” he stressed.
ARCADIA is part of the StrokeNet prevention trials network, run by the NIH’s National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Additional pivotal trials include the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST) and the Multi-arm Optimization of Stroke Thrombolysis (MOST) studies, he said.
Joseph Broderick, MD, director of the national NIH StrokeNet, agreed that safety comes first. “It was the decision of the StrokeNet leadership and the principal investigators of the trials that we needed to hold recruitment of new patients while we worked on adapting processes of enrollment to ensure the safety of both patients and researchers interacting with study patients,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Potential risks vary based on the study intervention and the need for in-person interactions. Trials that include stimulation devices or physical therapy, for example, might be most affected, added Dr. Broderick, professor and director of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio.
Nevertheless, “there are potential ways … to move as much as possible toward telemedicine and digital interactions during this time.”
Multiple challenges in multiple sclerosis
At the national level, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an “unprecedented impact on almost all the clinical trials funded by NINDS,” said Clinton Wright, MD, director of the Division of Clinical Research at NINDS. “Investigators have had to adapt quickly.”
Supplementing existing grants with money to conduct research on COVID-19 and pursuing research opportunities from different institutes are “some of the creative approaches [that] have come from the NIH [National Institutes of Health] itself,” Dr. Wright said. “Other creative approaches have come from investigators trying to keep their studies and trials going during the pandemic.”
In clinical trials, “everything from electronic consent to in-home research drug delivery is being brought to bear.”
“A few ongoing trials have been able to modify their protocols to obtain consent and carry out evaluations remotely by telephone or videoconferencing,” Dr. Wright said. “This is especially critical for trials that involve medical management of specific risk factors or conditions, where suspension of the trial could itself have adverse consequences due to reduced engagement with research participants.”
For participants already in MS studies, “each upcoming visit is assessed for whether it’s critical or could be done virtually or just skipped. If a person needs a treatment that cannot be postponed or skipped, they come in,” Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, told Medscape Medical News.
New study enrollment is largely on hold and study visits for existing participants are limited, said Dr. Cohen, who is also president of the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Some of the major ongoing trials in MS are “looking at very fundamental questions in the field,” Dr. Cohen said. The Determining the Effectiveness of earLy Intensive Versus Escalation Approaches for RRMS (DELIVER-MS) and Traditional Versus Early Aggressive Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis (TREAT-MS) trials, for example, evaluate whether treatment should be initiated with one of the less efficacious agents with escalation as needed, or whether treatment should begin with a high-efficacy agent.
Both trials are currently on hold because of the pandemic, as is the Best Available Therapy Versus Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Sclerosis (BEAT-MS) study.
“There has been a lot of interest in hematopoietic stem cell transplants and where they fit into our overall treatment strategy, and this is intended to provide a more definitive answer,” Dr. Cohen said.
Making the most of down time
“The pandemic has been challenging” in terms of ongoing MS research, said Benjamin M. Segal, MD, chair of the Department of Neurology and director of the Neuroscience Research Institute at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“With regard to the lab, our animal model experiments have been placed on hold. We have stopped collecting samples from clinical subjects for biomarker studies.
“However, my research team has been taking advantage of the time that has been freed up from bench work by analyzing data sets that had been placed aside, delving more deeply into the literature, and writing new grant proposals and articles,” he added.
Two of Dr. Segal’s trainees are writing review articles on the immunopathogenesis of MS and its treatment. Another postdoctoral candidate is writing a grant proposal to investigate how coinfection with a coronavirus modulates CNS pathology and the clinical course of an animal model of MS.
“I am asking my trainees to plan out experiments further in advance than they ever have before, so they are as prepared as possible to resume their research agendas once we are up and running again,” Dr. Segal said.
Confronting current challenges while planning for a future less disrupted by the pandemic is a common theme that emerges.
“The duration of this [pandemic] will dictate how we analyze the data at the end [for the US POINTER study]. There is a large group of statisticians working on this,” Dr. Snyder said.
Dr. Sperling of Harvard Medical School also remains undeterred. “This is definitely a challenging time, as we must not allow the COVID-19 to interfere with our essential mission to find a successful treatment to prevent cognitive decline in AD. We do need, however, to be as flexible as possible to protect our participants and minimize the impact to our overall study integrity,” she said.
NIH guidance
Dr. Molinuevo Guix, of the Barcelona Brain Research Center, is also determined to continue his Alzheimer’s disease research. “I am aware that after the crisis, there will be less [risk] but still a COVID-19 infection risk, so apart from trying to generate part of our visits virtually, we want to make sure we have all necessary safety measures in place. We remain very active to preserve the work we have done to keep up the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia,” he said.
Such forward thinking also applies to major stroke trials, said Dr. Broderick of the University of Cincinnati. “As soon as we shut down enrollment in stroke trials, we immediately began to make plans about how and when we can restart our stroke trials,” he explained. “One of our trials can do every step of the trial process remotely without direct in-person interactions and will be able to restart soon.”
An individualized approach is needed, Dr. Broderick added. “For trials involving necessary in-person and hands-on assessments, we will need to consider how best to use protective equipment and expanded testing that will likely match the ongoing clinical care and requirements at a given institution.
“Even if a trial officially reopens enrollment, the decision to enroll locally will need to follow local institutional environment and guidelines. Thus, restart of trial enrollment will not likely be uniform, similar to how trials often start in the first place,” Dr. Broderick said.
The NIH published uniform standards for researchers across its institutes to help guide them during the pandemic. Future contingency plans also are underway at the NINDS.
“As the pandemic wanes and in-person research activities restart, it will be important to have in place safety measures that prevent a resurgence of the virus, such as proper personal protective equipment for staff and research participants, said Dr. Wright, the clinical research director at NINDS.
For clinical trials, NINDS is prepared to provide supplemental funds to trial investigators to help support additional activities undertaken as a result of the pandemic.
“This has been an instructive experience. The pandemic will end, and we will resume much of our old patterns of behavior,” said Ohio State’s Dr. Segal. “But some of the strategies that we have employed to get through this time will continue to influence the way we communicate information, plan experiments, and prioritize research activities in the future, to good effect.”
Drs. Snyder, Sperling, Molinuevo Guix, Elkind, Broderick, Wright, Cohen, and Segal have disclosed no relevant disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remdesivir now ‘standard of care’ for COVID-19, Fauci says
, according to a preliminary data analysis from a U.S.-led randomized, controlled trial.
On the basis of as yet unpublished data, remdesivir “will be the standard of care” for patients with COVID-19, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), said during a press conference at the White House April 29.
The randomized, placebo-controlled international trial was sponsored by NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, and enrolled 1,063 patients. It began on Feb. 21.
The interim results, discussed in the press conference and in a NIAID press release, show that time to recovery (i.e., being well enough for hospital discharge or to return to normal activity level) was 31% faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo (P < .001).
The median time to recovery was 11 days for patients treated with remdesivir, compared with 15 days for those who received placebo. Results also suggested a survival benefit, with a mortality rate of 8.0% for the group receiving remdesivir and 11.6% for the patients who received placebo (P = .059).
The study, known as the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT), is the first clinical trial launched in the United States to evaluate an experimental treatment for COVID-19. It is being conducted at 68 sites – 47 in the United States and 21 in countries in Europe and Asia.
The data are being released after an interim review by the independent data safety monitoring board found significant benefit with the drug, Dr. Fauci said.
“The reason we are making the announcement now is something that people don’t fully appreciate: Whenever you have clear-cut evidence that a drug works, you have an ethical obligation to let the people in the placebo group know so they could have access,” he explained.
“When I was looking at the data with our team the other night, it was reminiscent of 34 years ago in 1986 when we were struggling for drugs for HIV,” said Dr. Fauci, who was a key figure in HIV/AIDS research. “We did the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial with AZT. It turned out to have an effect that was modest but that was not the endgame because, building on that, every year after, we did better and better.”
Similarly, new trials of drugs for COVID-19 will build on remdesivir, with other agents being added to block other pathways or viral enzymes, Dr. Fauci said.
The study will be submitted to a journal for peer review, he noted, but the New York Times is reporting that the Food and Drug Administration will approve remdesivir for emergency use soon.
In contrast to the positive results Dr. Fauci described from the NIAID-sponsored trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of remdesivir among hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in China was inconclusive.
The study, published online in The Lancet, showed some nonsignificant trends toward benefit but did not meet its primary endpoint.
The study was stopped early after 237 of the intended 453 patients were enrolled, owing to a lack of additional patients who met the eligibility criteria. The trial was thus underpowered.
Results showed that treatment with remdesivir did not significantly speed recovery or reduce deaths from COVID-19, but with regard to prespecified secondary outcomes, time to clinical improvement and duration of invasive mechanical ventilation were shorter among a subgroup of patients who began undergoing treatment with remdesivir within 10 days of showing symptoms, in comparison with patients who received standard care.
“To me, the studies reported here in The Lancet appear to be less promising than some statements released today from the NIH, so the situation is a bit puzzling to me,” said Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not involved in the study. “I would need to look more closely at the data which NIH is looking at to understand the differences.”
Trial details
The published trial was conducted at 10 hospitals in Hubei, China. Enrollment criteria included being admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 12 days of symptom onset, having oxygen saturation of 94% or less, and having radiologically confirmed pneumonia.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive intravenous remdesivir (200 mg on day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2–10 in single daily infusions) or placebo infusions for 10 days. Patients were permitted concomitant use of lopinavir-ritonavir, interferons, and corticosteroids.
The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement to day 28, defined as the time (in days) from randomization to the point of a decline of two levels on a six-point ordinal scale of clinical status (on that scale, 1 indicated that the patient was discharged, and 6 indicated death) or to the patient’s being discharged alive from hospital, whichever came first.
The trial was stopped early because stringent public health measures used in Wuhan led to marked reductions in new patient presentations and because lack of available hospital beds resulted in most patients being enrolled later in the course of disease.
Between Feb. 6, 2020, and March 12, 2020, 237 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (n = 158) or placebo (n = 79).
Results showed that use of remdesivir was not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-1.75).
Although not statistically significant, time to clinical improvement was numerically faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo among patients with symptom duration of 10 days or less (median, 18 days vs. 23 days; HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.95-2.43).
The mortality rates were similar for the two groups (14% of patients who received remdesivir died vs. 13% of those who received placebo). There was no signal that viral load decreased differentially over time between the two groups.
Adverse events were reported in 66% of remdesivir recipients, vs. 64% of those who received placebo. Remdesivir was stopped early because of adverse events in 12% of patients; it was stopped early for 5% of those who received placebo.
The authors, led by Yeming Wang, MD, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, noted that compared with a previous study of compassionate use of remdesivir, the population in the current study was less ill and was treated somewhat earlier in the disease course (median, 10 days vs. 12 days).
Because the study was terminated early, the researchers said they could not adequately assess whether earlier treatment with remdesivir might have provided clinical benefit.
“However, among patients who were treated within 10 days of symptom onset, remdesivir was not a significant factor but was associated with a numerical reduction of 5 days in median time to clinical improvement,” they stated.
They added that remdesivir was adequately tolerated and that no new safety concerns were identified.
In an accompanying comment in The Lancet, John David Norrie, MD, Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, United Kingdom, pointed out that this study “has not shown a statistically significant finding that confirms a remdesivir treatment benefit of at least the minimally clinically important difference, nor has it ruled such a benefit out.”
Dr. Norrie was cautious about the fact that the subgroup analysis suggested possible benefit for those treated within 10 days.
Although he said it seems biologically plausible that treating patients earlier could be more effective, he added that “as well as being vigilant against overinterpretation, we need to ensure that hypotheses generated in efficacy-based trials, even in subgroups, are confirmed or refuted in subsequent adequately powered trials or meta-analyses.”
Noting that several other trials of remdesivir are underway, he concluded: “With each individual study at heightened risk of being incomplete, pooling data across possibly several underpowered but high-quality studies looks like our best way to obtain robust insights into what works, safely, and on whom.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a preliminary data analysis from a U.S.-led randomized, controlled trial.
On the basis of as yet unpublished data, remdesivir “will be the standard of care” for patients with COVID-19, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), said during a press conference at the White House April 29.
The randomized, placebo-controlled international trial was sponsored by NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, and enrolled 1,063 patients. It began on Feb. 21.
The interim results, discussed in the press conference and in a NIAID press release, show that time to recovery (i.e., being well enough for hospital discharge or to return to normal activity level) was 31% faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo (P < .001).
The median time to recovery was 11 days for patients treated with remdesivir, compared with 15 days for those who received placebo. Results also suggested a survival benefit, with a mortality rate of 8.0% for the group receiving remdesivir and 11.6% for the patients who received placebo (P = .059).
The study, known as the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT), is the first clinical trial launched in the United States to evaluate an experimental treatment for COVID-19. It is being conducted at 68 sites – 47 in the United States and 21 in countries in Europe and Asia.
The data are being released after an interim review by the independent data safety monitoring board found significant benefit with the drug, Dr. Fauci said.
“The reason we are making the announcement now is something that people don’t fully appreciate: Whenever you have clear-cut evidence that a drug works, you have an ethical obligation to let the people in the placebo group know so they could have access,” he explained.
“When I was looking at the data with our team the other night, it was reminiscent of 34 years ago in 1986 when we were struggling for drugs for HIV,” said Dr. Fauci, who was a key figure in HIV/AIDS research. “We did the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial with AZT. It turned out to have an effect that was modest but that was not the endgame because, building on that, every year after, we did better and better.”
Similarly, new trials of drugs for COVID-19 will build on remdesivir, with other agents being added to block other pathways or viral enzymes, Dr. Fauci said.
The study will be submitted to a journal for peer review, he noted, but the New York Times is reporting that the Food and Drug Administration will approve remdesivir for emergency use soon.
In contrast to the positive results Dr. Fauci described from the NIAID-sponsored trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of remdesivir among hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in China was inconclusive.
The study, published online in The Lancet, showed some nonsignificant trends toward benefit but did not meet its primary endpoint.
The study was stopped early after 237 of the intended 453 patients were enrolled, owing to a lack of additional patients who met the eligibility criteria. The trial was thus underpowered.
Results showed that treatment with remdesivir did not significantly speed recovery or reduce deaths from COVID-19, but with regard to prespecified secondary outcomes, time to clinical improvement and duration of invasive mechanical ventilation were shorter among a subgroup of patients who began undergoing treatment with remdesivir within 10 days of showing symptoms, in comparison with patients who received standard care.
“To me, the studies reported here in The Lancet appear to be less promising than some statements released today from the NIH, so the situation is a bit puzzling to me,” said Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not involved in the study. “I would need to look more closely at the data which NIH is looking at to understand the differences.”
Trial details
The published trial was conducted at 10 hospitals in Hubei, China. Enrollment criteria included being admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 12 days of symptom onset, having oxygen saturation of 94% or less, and having radiologically confirmed pneumonia.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive intravenous remdesivir (200 mg on day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2–10 in single daily infusions) or placebo infusions for 10 days. Patients were permitted concomitant use of lopinavir-ritonavir, interferons, and corticosteroids.
The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement to day 28, defined as the time (in days) from randomization to the point of a decline of two levels on a six-point ordinal scale of clinical status (on that scale, 1 indicated that the patient was discharged, and 6 indicated death) or to the patient’s being discharged alive from hospital, whichever came first.
The trial was stopped early because stringent public health measures used in Wuhan led to marked reductions in new patient presentations and because lack of available hospital beds resulted in most patients being enrolled later in the course of disease.
Between Feb. 6, 2020, and March 12, 2020, 237 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (n = 158) or placebo (n = 79).
Results showed that use of remdesivir was not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-1.75).
Although not statistically significant, time to clinical improvement was numerically faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo among patients with symptom duration of 10 days or less (median, 18 days vs. 23 days; HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.95-2.43).
The mortality rates were similar for the two groups (14% of patients who received remdesivir died vs. 13% of those who received placebo). There was no signal that viral load decreased differentially over time between the two groups.
Adverse events were reported in 66% of remdesivir recipients, vs. 64% of those who received placebo. Remdesivir was stopped early because of adverse events in 12% of patients; it was stopped early for 5% of those who received placebo.
The authors, led by Yeming Wang, MD, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, noted that compared with a previous study of compassionate use of remdesivir, the population in the current study was less ill and was treated somewhat earlier in the disease course (median, 10 days vs. 12 days).
Because the study was terminated early, the researchers said they could not adequately assess whether earlier treatment with remdesivir might have provided clinical benefit.
“However, among patients who were treated within 10 days of symptom onset, remdesivir was not a significant factor but was associated with a numerical reduction of 5 days in median time to clinical improvement,” they stated.
They added that remdesivir was adequately tolerated and that no new safety concerns were identified.
In an accompanying comment in The Lancet, John David Norrie, MD, Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, United Kingdom, pointed out that this study “has not shown a statistically significant finding that confirms a remdesivir treatment benefit of at least the minimally clinically important difference, nor has it ruled such a benefit out.”
Dr. Norrie was cautious about the fact that the subgroup analysis suggested possible benefit for those treated within 10 days.
Although he said it seems biologically plausible that treating patients earlier could be more effective, he added that “as well as being vigilant against overinterpretation, we need to ensure that hypotheses generated in efficacy-based trials, even in subgroups, are confirmed or refuted in subsequent adequately powered trials or meta-analyses.”
Noting that several other trials of remdesivir are underway, he concluded: “With each individual study at heightened risk of being incomplete, pooling data across possibly several underpowered but high-quality studies looks like our best way to obtain robust insights into what works, safely, and on whom.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a preliminary data analysis from a U.S.-led randomized, controlled trial.
On the basis of as yet unpublished data, remdesivir “will be the standard of care” for patients with COVID-19, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), said during a press conference at the White House April 29.
The randomized, placebo-controlled international trial was sponsored by NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, and enrolled 1,063 patients. It began on Feb. 21.
The interim results, discussed in the press conference and in a NIAID press release, show that time to recovery (i.e., being well enough for hospital discharge or to return to normal activity level) was 31% faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo (P < .001).
The median time to recovery was 11 days for patients treated with remdesivir, compared with 15 days for those who received placebo. Results also suggested a survival benefit, with a mortality rate of 8.0% for the group receiving remdesivir and 11.6% for the patients who received placebo (P = .059).
The study, known as the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT), is the first clinical trial launched in the United States to evaluate an experimental treatment for COVID-19. It is being conducted at 68 sites – 47 in the United States and 21 in countries in Europe and Asia.
The data are being released after an interim review by the independent data safety monitoring board found significant benefit with the drug, Dr. Fauci said.
“The reason we are making the announcement now is something that people don’t fully appreciate: Whenever you have clear-cut evidence that a drug works, you have an ethical obligation to let the people in the placebo group know so they could have access,” he explained.
“When I was looking at the data with our team the other night, it was reminiscent of 34 years ago in 1986 when we were struggling for drugs for HIV,” said Dr. Fauci, who was a key figure in HIV/AIDS research. “We did the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial with AZT. It turned out to have an effect that was modest but that was not the endgame because, building on that, every year after, we did better and better.”
Similarly, new trials of drugs for COVID-19 will build on remdesivir, with other agents being added to block other pathways or viral enzymes, Dr. Fauci said.
The study will be submitted to a journal for peer review, he noted, but the New York Times is reporting that the Food and Drug Administration will approve remdesivir for emergency use soon.
In contrast to the positive results Dr. Fauci described from the NIAID-sponsored trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of remdesivir among hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in China was inconclusive.
The study, published online in The Lancet, showed some nonsignificant trends toward benefit but did not meet its primary endpoint.
The study was stopped early after 237 of the intended 453 patients were enrolled, owing to a lack of additional patients who met the eligibility criteria. The trial was thus underpowered.
Results showed that treatment with remdesivir did not significantly speed recovery or reduce deaths from COVID-19, but with regard to prespecified secondary outcomes, time to clinical improvement and duration of invasive mechanical ventilation were shorter among a subgroup of patients who began undergoing treatment with remdesivir within 10 days of showing symptoms, in comparison with patients who received standard care.
“To me, the studies reported here in The Lancet appear to be less promising than some statements released today from the NIH, so the situation is a bit puzzling to me,” said Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not involved in the study. “I would need to look more closely at the data which NIH is looking at to understand the differences.”
Trial details
The published trial was conducted at 10 hospitals in Hubei, China. Enrollment criteria included being admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 12 days of symptom onset, having oxygen saturation of 94% or less, and having radiologically confirmed pneumonia.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive intravenous remdesivir (200 mg on day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2–10 in single daily infusions) or placebo infusions for 10 days. Patients were permitted concomitant use of lopinavir-ritonavir, interferons, and corticosteroids.
The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement to day 28, defined as the time (in days) from randomization to the point of a decline of two levels on a six-point ordinal scale of clinical status (on that scale, 1 indicated that the patient was discharged, and 6 indicated death) or to the patient’s being discharged alive from hospital, whichever came first.
The trial was stopped early because stringent public health measures used in Wuhan led to marked reductions in new patient presentations and because lack of available hospital beds resulted in most patients being enrolled later in the course of disease.
Between Feb. 6, 2020, and March 12, 2020, 237 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (n = 158) or placebo (n = 79).
Results showed that use of remdesivir was not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-1.75).
Although not statistically significant, time to clinical improvement was numerically faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo among patients with symptom duration of 10 days or less (median, 18 days vs. 23 days; HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.95-2.43).
The mortality rates were similar for the two groups (14% of patients who received remdesivir died vs. 13% of those who received placebo). There was no signal that viral load decreased differentially over time between the two groups.
Adverse events were reported in 66% of remdesivir recipients, vs. 64% of those who received placebo. Remdesivir was stopped early because of adverse events in 12% of patients; it was stopped early for 5% of those who received placebo.
The authors, led by Yeming Wang, MD, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, noted that compared with a previous study of compassionate use of remdesivir, the population in the current study was less ill and was treated somewhat earlier in the disease course (median, 10 days vs. 12 days).
Because the study was terminated early, the researchers said they could not adequately assess whether earlier treatment with remdesivir might have provided clinical benefit.
“However, among patients who were treated within 10 days of symptom onset, remdesivir was not a significant factor but was associated with a numerical reduction of 5 days in median time to clinical improvement,” they stated.
They added that remdesivir was adequately tolerated and that no new safety concerns were identified.
In an accompanying comment in The Lancet, John David Norrie, MD, Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, United Kingdom, pointed out that this study “has not shown a statistically significant finding that confirms a remdesivir treatment benefit of at least the minimally clinically important difference, nor has it ruled such a benefit out.”
Dr. Norrie was cautious about the fact that the subgroup analysis suggested possible benefit for those treated within 10 days.
Although he said it seems biologically plausible that treating patients earlier could be more effective, he added that “as well as being vigilant against overinterpretation, we need to ensure that hypotheses generated in efficacy-based trials, even in subgroups, are confirmed or refuted in subsequent adequately powered trials or meta-analyses.”
Noting that several other trials of remdesivir are underway, he concluded: “With each individual study at heightened risk of being incomplete, pooling data across possibly several underpowered but high-quality studies looks like our best way to obtain robust insights into what works, safely, and on whom.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Standing orders for vaccines may improve pediatric vaccination rates
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Two rare neurologic conditions linked to COVID-19
A 50-year-old man developed Miller Fisher syndrome and a 39-year-old man developed polyneuritis cranialis. Both are variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which physicians in China and Italy also linked to COVID-19 infection, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
In both cases, physicians made the diagnoses based on abnormal eye examinations. The two patients responded to treatment and improved over 2 weeks, with only the 50-year-old featuring residual symptoms of anosmia and ageusia.
The report was published online April 17 in Neurology.
The 50-year-old man was admitted to an emergency room with a temperature of 99.9°F (37.7°C). He reported 2 days of vertical diplopia, perioral paresthesias, and gait instability. His neurologic examination showed intact cognitive function and language.
Five days earlier he developed a cough, malaise, headache, low back pain, fever, anosmia, and ageusia.
His neuro-ophthalmologic examination showed right hypertropia in all fields of gaze, severe limitations to the adduction and downgaze movements of his right eye, and left eye nystagmus on left gaze. These findings were consistent with right internuclear ophthalmoparesis and right fascicular oculomotor palsy.
He responded to intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin therapy and was discharged home 2 weeks after admission.
The 39-year-old man was admitted to the emergency room with acute onset diplopia and ageusia. Three days earlier he had presented with diarrhea, a low-grade fever and in generally poor condition, without any headache, respiratory symptoms, or dyspnea.
He showed esotropia of 10 prism diopters at distance and 4 prism diopters at near, severe abduction deficits in both eyes, and fixation nystagmus, with the upper gaze more impaired, all consistent with bilateral abducens palsy.
The patient was discharged home and treated symptomatically with acetaminophen and telemedicine monitoring “due to a complete hospital saturation with COVID-19 patients,” wrote the researchers, led by Consuelo Gutiérrez-Ortiz, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain.
Two weeks later, he had made a complete neurologic recovery with no ageusia, complete eye movements, and normal deep tendon reflexes.
“Fisher syndrome and polyneuritis cranialis in these two patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be simply coincidental. However, taking into account the temporal relationship, we feel that COVID-19 might have been responsible for the development of these two neurological pictures,” the authors noted.
European Regional Development Funds (FEDER) supported this research.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 50-year-old man developed Miller Fisher syndrome and a 39-year-old man developed polyneuritis cranialis. Both are variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which physicians in China and Italy also linked to COVID-19 infection, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
In both cases, physicians made the diagnoses based on abnormal eye examinations. The two patients responded to treatment and improved over 2 weeks, with only the 50-year-old featuring residual symptoms of anosmia and ageusia.
The report was published online April 17 in Neurology.
The 50-year-old man was admitted to an emergency room with a temperature of 99.9°F (37.7°C). He reported 2 days of vertical diplopia, perioral paresthesias, and gait instability. His neurologic examination showed intact cognitive function and language.
Five days earlier he developed a cough, malaise, headache, low back pain, fever, anosmia, and ageusia.
His neuro-ophthalmologic examination showed right hypertropia in all fields of gaze, severe limitations to the adduction and downgaze movements of his right eye, and left eye nystagmus on left gaze. These findings were consistent with right internuclear ophthalmoparesis and right fascicular oculomotor palsy.
He responded to intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin therapy and was discharged home 2 weeks after admission.
The 39-year-old man was admitted to the emergency room with acute onset diplopia and ageusia. Three days earlier he had presented with diarrhea, a low-grade fever and in generally poor condition, without any headache, respiratory symptoms, or dyspnea.
He showed esotropia of 10 prism diopters at distance and 4 prism diopters at near, severe abduction deficits in both eyes, and fixation nystagmus, with the upper gaze more impaired, all consistent with bilateral abducens palsy.
The patient was discharged home and treated symptomatically with acetaminophen and telemedicine monitoring “due to a complete hospital saturation with COVID-19 patients,” wrote the researchers, led by Consuelo Gutiérrez-Ortiz, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain.
Two weeks later, he had made a complete neurologic recovery with no ageusia, complete eye movements, and normal deep tendon reflexes.
“Fisher syndrome and polyneuritis cranialis in these two patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be simply coincidental. However, taking into account the temporal relationship, we feel that COVID-19 might have been responsible for the development of these two neurological pictures,” the authors noted.
European Regional Development Funds (FEDER) supported this research.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 50-year-old man developed Miller Fisher syndrome and a 39-year-old man developed polyneuritis cranialis. Both are variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which physicians in China and Italy also linked to COVID-19 infection, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
In both cases, physicians made the diagnoses based on abnormal eye examinations. The two patients responded to treatment and improved over 2 weeks, with only the 50-year-old featuring residual symptoms of anosmia and ageusia.
The report was published online April 17 in Neurology.
The 50-year-old man was admitted to an emergency room with a temperature of 99.9°F (37.7°C). He reported 2 days of vertical diplopia, perioral paresthesias, and gait instability. His neurologic examination showed intact cognitive function and language.
Five days earlier he developed a cough, malaise, headache, low back pain, fever, anosmia, and ageusia.
His neuro-ophthalmologic examination showed right hypertropia in all fields of gaze, severe limitations to the adduction and downgaze movements of his right eye, and left eye nystagmus on left gaze. These findings were consistent with right internuclear ophthalmoparesis and right fascicular oculomotor palsy.
He responded to intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin therapy and was discharged home 2 weeks after admission.
The 39-year-old man was admitted to the emergency room with acute onset diplopia and ageusia. Three days earlier he had presented with diarrhea, a low-grade fever and in generally poor condition, without any headache, respiratory symptoms, or dyspnea.
He showed esotropia of 10 prism diopters at distance and 4 prism diopters at near, severe abduction deficits in both eyes, and fixation nystagmus, with the upper gaze more impaired, all consistent with bilateral abducens palsy.
The patient was discharged home and treated symptomatically with acetaminophen and telemedicine monitoring “due to a complete hospital saturation with COVID-19 patients,” wrote the researchers, led by Consuelo Gutiérrez-Ortiz, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain.
Two weeks later, he had made a complete neurologic recovery with no ageusia, complete eye movements, and normal deep tendon reflexes.
“Fisher syndrome and polyneuritis cranialis in these two patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be simply coincidental. However, taking into account the temporal relationship, we feel that COVID-19 might have been responsible for the development of these two neurological pictures,” the authors noted.
European Regional Development Funds (FEDER) supported this research.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Survey: Hydroxychloroquine use fairly common in COVID-19
One of five physicians in front-line treatment roles has prescribed hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19, according to a new survey from health care market research company InCrowd.
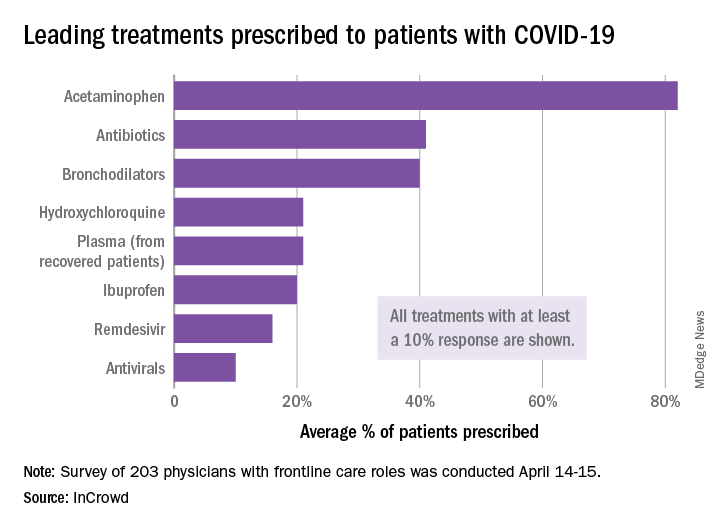
The most common treatments were acetaminophen, prescribed to 82% of patients, antibiotics (41%), and bronchodilators (40%), InCrowd said after surveying 203 primary care physicians, pediatricians, and emergency medicine or critical care physicians who are treating at least 20 patients with flulike symptoms.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine outside of hospitals and clinical trials.
The InCrowd survey, which took place April 14-15 and is the fourth in a series investigating COVID-19’s impact on physicians, showed that access to testing was up to 82% in mid-April, compared with 67% in March and 20% in late February. The April respondents also were twice as likely (59% vs. 24% in March) to say that their facilities were prepared to treat patients, InCrowd reported.
“U.S. physicians report sluggish optimism around preparedness, safety, and institutional efforts, while many worry about the future, including a second outbreak and job security,” the company said in a separate written statement.
The average estimate for a return to normal was just over 6 months among respondents, and only 28% believed that their facility was prepared for a second outbreak later in the year, InCrowd noted.
On a personal level, 45% of the respondents were concerned about the safety of their job. An emergency/critical care physician from Tennessee said, “We’ve been cutting back on staff due to overall revenue reductions, but have increased acuity and complexity which requires more staffing. This puts even more of a burden on those of us still here.”
Support for institutional responses to slow the pandemic was strongest for state governments, which gained approval from 54% of front-line physicians, up from 33% in March. Actions taken by the federal government were supported by 21% of respondents, compared with 38% for the World Health Organization and 46% for governments outside the United States, InCrowd reported.
Suggestions for further actions by state and local authorities included this comment from an emergency/critical care physician in Florida: “Continued, broad and properly enforced stay at home and social distancing measures MUST remain in place to keep citizens and healthcare workers safe, and the latter alive and in adequate supply.”
One of five physicians in front-line treatment roles has prescribed hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19, according to a new survey from health care market research company InCrowd.

The most common treatments were acetaminophen, prescribed to 82% of patients, antibiotics (41%), and bronchodilators (40%), InCrowd said after surveying 203 primary care physicians, pediatricians, and emergency medicine or critical care physicians who are treating at least 20 patients with flulike symptoms.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine outside of hospitals and clinical trials.
The InCrowd survey, which took place April 14-15 and is the fourth in a series investigating COVID-19’s impact on physicians, showed that access to testing was up to 82% in mid-April, compared with 67% in March and 20% in late February. The April respondents also were twice as likely (59% vs. 24% in March) to say that their facilities were prepared to treat patients, InCrowd reported.
“U.S. physicians report sluggish optimism around preparedness, safety, and institutional efforts, while many worry about the future, including a second outbreak and job security,” the company said in a separate written statement.
The average estimate for a return to normal was just over 6 months among respondents, and only 28% believed that their facility was prepared for a second outbreak later in the year, InCrowd noted.
On a personal level, 45% of the respondents were concerned about the safety of their job. An emergency/critical care physician from Tennessee said, “We’ve been cutting back on staff due to overall revenue reductions, but have increased acuity and complexity which requires more staffing. This puts even more of a burden on those of us still here.”
Support for institutional responses to slow the pandemic was strongest for state governments, which gained approval from 54% of front-line physicians, up from 33% in March. Actions taken by the federal government were supported by 21% of respondents, compared with 38% for the World Health Organization and 46% for governments outside the United States, InCrowd reported.
Suggestions for further actions by state and local authorities included this comment from an emergency/critical care physician in Florida: “Continued, broad and properly enforced stay at home and social distancing measures MUST remain in place to keep citizens and healthcare workers safe, and the latter alive and in adequate supply.”
One of five physicians in front-line treatment roles has prescribed hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19, according to a new survey from health care market research company InCrowd.

The most common treatments were acetaminophen, prescribed to 82% of patients, antibiotics (41%), and bronchodilators (40%), InCrowd said after surveying 203 primary care physicians, pediatricians, and emergency medicine or critical care physicians who are treating at least 20 patients with flulike symptoms.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine outside of hospitals and clinical trials.
The InCrowd survey, which took place April 14-15 and is the fourth in a series investigating COVID-19’s impact on physicians, showed that access to testing was up to 82% in mid-April, compared with 67% in March and 20% in late February. The April respondents also were twice as likely (59% vs. 24% in March) to say that their facilities were prepared to treat patients, InCrowd reported.
“U.S. physicians report sluggish optimism around preparedness, safety, and institutional efforts, while many worry about the future, including a second outbreak and job security,” the company said in a separate written statement.
The average estimate for a return to normal was just over 6 months among respondents, and only 28% believed that their facility was prepared for a second outbreak later in the year, InCrowd noted.
On a personal level, 45% of the respondents were concerned about the safety of their job. An emergency/critical care physician from Tennessee said, “We’ve been cutting back on staff due to overall revenue reductions, but have increased acuity and complexity which requires more staffing. This puts even more of a burden on those of us still here.”
Support for institutional responses to slow the pandemic was strongest for state governments, which gained approval from 54% of front-line physicians, up from 33% in March. Actions taken by the federal government were supported by 21% of respondents, compared with 38% for the World Health Organization and 46% for governments outside the United States, InCrowd reported.
Suggestions for further actions by state and local authorities included this comment from an emergency/critical care physician in Florida: “Continued, broad and properly enforced stay at home and social distancing measures MUST remain in place to keep citizens and healthcare workers safe, and the latter alive and in adequate supply.”