User login
A Service Evaluation of Acute Neurological Patients Managed on Clinically Inappropriate Wards
From Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Physiotherapy Department, Chichester, UK (Richard J. Holmes), and Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Department of Occupational Therapy, Chichester, UK (Sophie Stratford).
Objective: Despite the benefits of early and frequent input from a neurologist, there is wide variation in the availability of this service, especially in district general hospitals, with many patients managed on clinically inappropriate wards. The purpose of this service evaluation was to explore the impact this had on patient care.
Methods: A retrospective service evaluation was undertaken at a National Health Service hospital by reviewing patient records over a 6-month period. Data related to demographics, processes within the patient’s care, and secondary complications were recorded. Findings were compared with those of stroke patients managed on a specialist stroke ward.
Results: A total of 63 patients were identified, with a mean age of 72 years. The mean length of stay was 25.9 days, with a readmission rate of 16.7%. Only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist. There was a high rate of secondary complications, with a number of patients experiencing falls (11.1%), pressure ulcers (14.3%), and health care–acquired infections (33.3%) during their admission.
Conclusions: The lack of specialist input from a neurologist and the management of patients on clinically inappropriate wards may have negatively impacted length of stay, readmission rates, and the frequency of secondary complications.
Keywords: evaluation; clinical safety; neurology; patient-centered care; clinical outcomes; length of stay.
It is estimated that 10% of acute admissions to district general hospitals (DGHs) of the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom are due to a neurological problem other than stroke.1 In 2011, a joint report from the Royal College of Physicians and the Association of British Neurologists (ABN) recommended that all of these patients should be admitted under the care of a neurologist and be regularly reviewed by a neurologist during their admission.2 The rationale for this recommendation is clear. The involvement of a neurologist has been shown to improve accuracy of the diagnosis3 and significantly reduce length of stay.4,5 Studies have also shown that the involvement of a neurologist has led to a change in the management plan in as high as 79%6 to 89%3 of cases, suggesting that a high proportion of neurological patients not seen by a neurologist are being managed suboptimally.
Despite this, a recent ABN survey of acute neurology services found ongoing wide variations in the availability of this specialist care, with a large proportion of DGHs having limited or no access to a neurologist and very few having dedicated neurology beds.7 While it is recognized that services have been structured in response to the reduced numbers of neurologists within the United Kingdom,8 it is prudent to assess the impact that such services have on patient care.
With this in mind, we planned to evaluate the current provision of care provided to neurological patients in a real-world setting. This was conducted in the context of a neurology liaison service at a DGH with no dedicated neurology beds.
Methods
A retrospective service evaluation was undertaken at a DGH in the southeast of England. The NHS hospital has neurologists on site who provide diagnostic and therapeutic consultations on the wards, but there are no dedicated beds for patients with neurological conditions. Patients requiring neurosurgical input are referred to a tertiary neurosciences center.
Patients were selected from the neurotherapy database if they were referred into the service between August 1, 2019, and January 31, 2020. The neurotherapy database was used as this was the only source that held thorough data on this patient group and allowed for the identification of patients who were not referred into the neurologist’s service. Patients were included if they had a new neurological condition as their primary diagnosis or if they had an exacerbation of an already established neurological condition. If a patient was admitted with more than 1 neurological diagnosis then the primary diagnosis for the admission was to be used in the analysis, though this did not occur during this evaluation. Patients with a primary diagnosis of a stroke were included if they were not managed on the acute stroke ward. Those managed on the stroke ward were excluded so that an analysis of patients managed on wards that were deemed clinically inappropriate could be undertaken. Patients were not included if they had a pre-existing neurological condition (ie, dementia, multiple sclerosis) but were admitted due to a non-neurological cause such as a fall or infection. All patients who met the criteria were included.
A team member independently reviewed each set of patient notes. Demographic data extracted from the medical notes included the patient’s age (on admission), gender, and diagnosis. Medical, nursing, and therapy notes were reviewed to identify secondary complications that arose during the patient’s admission. The secondary complications reviewed were falls (defined as the patient unexpectedly coming to the ground or other lower level), health care–acquired infections (HAIs) (defined as any infection acquired during the hospital admission), and pressure ulcers (defined as injuries to the skin or underlying tissue during the hospital admission). Other details, obtained from the patient administration system, included the length of stay (days), the number of ward moves the patient experienced, the speciality of the consultant responsible for the patient’s care, the discharge destination, and whether the patient was readmitted for any cause within 30 days. All data collected were stored on a password-protected computer and no patient-identifiable data were included.
The results were collated using descriptive statistics. The χ2 test was used to compare categorical data between those patients who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare differences in the length of stay between these 2 groups.
No national data relating to this specific patient group were available within the literature. Therefore, to provide a comparator of neurological patients within the same hospital, data were collected on stroke patients managed on the stroke ward. This group was deemed most appropriate for comparison as they present with similar neurological symptoms but are cared for on a specialist ward. During the evaluation period, 284 stroke patients were admitted to the stroke ward. A sample of 75 patients was randomly selected using a random number generator, and the procedure for data collection was repeated. It was not appropriate to make direct comparative analysis on these 2 groups due to the inherent differences, but it was felt important to provide context with regards to what usual care was like on a specialist ward within the same hospital.
Ethical approval was not required as this was a service evaluation of routinely collected data within a single hospital site.
Results
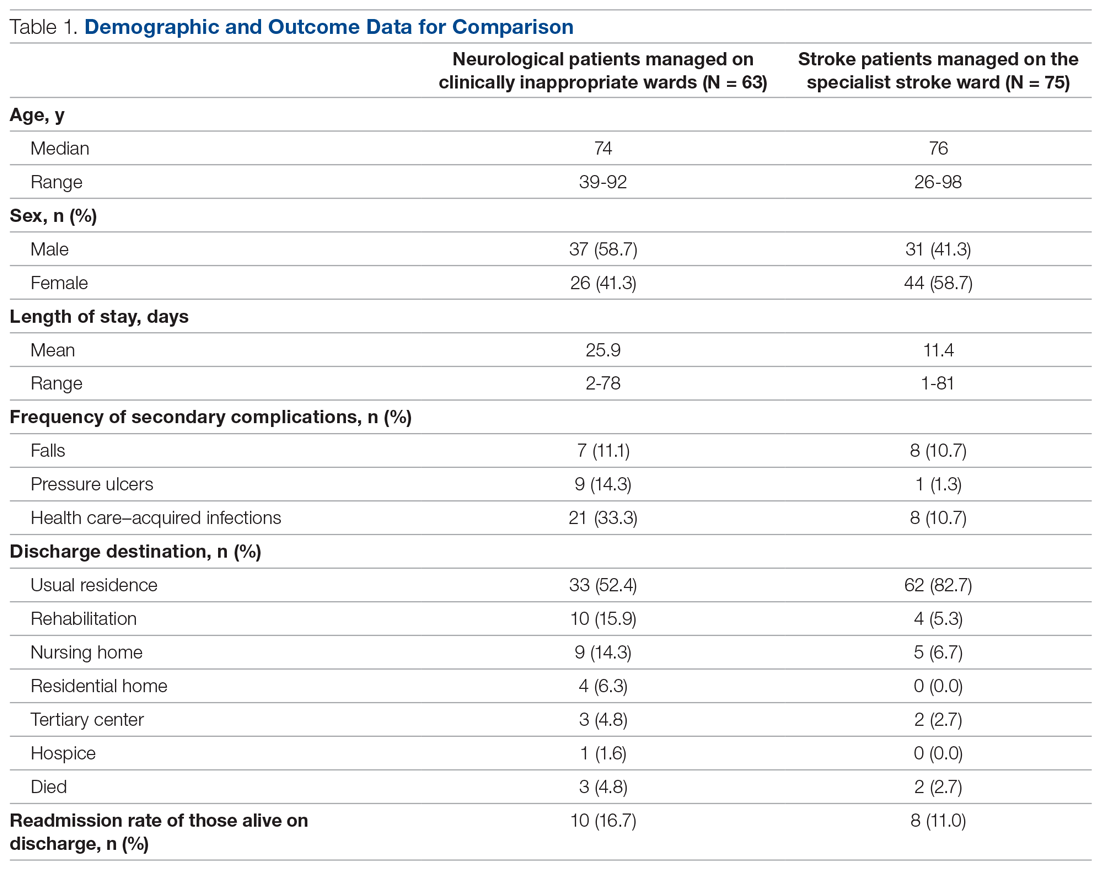
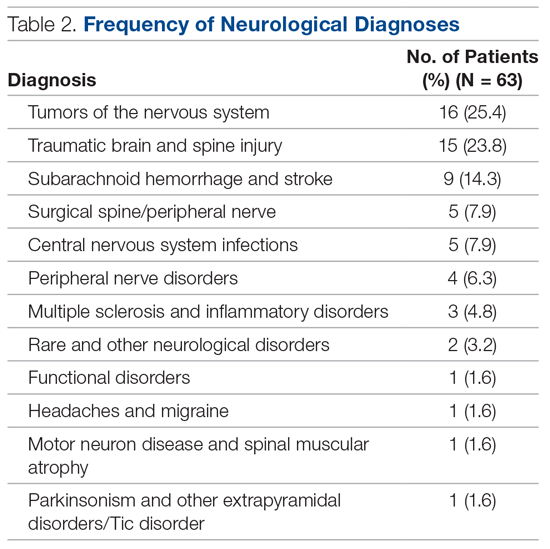
In total, 63 patients were identified: 26 females and 37 males. The median age of patients was 74 years (range, 39-92 years). These demographic details and comparisons to stroke patients managed on a specialist ward can be seen in Table 1. To quantify the range of diagnoses, the condition groups defined by GIRFT Neurology Methodology9 were used. The most common diagnoses were tumors of the nervous system (25.4%) and traumatic brain and spine injury (23.8%). The other conditions included in the analysis can be seen in Table 2.
Despite having a neurological condition as their primary diagnosis, only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist during their hospital admission. Patients were most commonly under the care of a geriatrician (60.3%), but they were also managed by orthopedics (12.6%), acute medicine (7.9%), respiratory (6.3%), cardiology (4.8%), gastroenterology (3.2%), and surgery (3.2%). One patient (1.6%) was managed by intensivists.
The average length of stay was 25.9 days (range, 2-78 days). This was more than double the average length of stay on the stroke ward (11.4 days) (Table 1) and the national average for patients with neurological conditions (9.78 days).10 During their stay, 33% had 2 or more ward moves, with 1 patient moving wards a total of 6 times. Just over half (52.4%) of the patients returned to their usual residence on discharge. The remainder were discharged to rehabilitation units (15.9%), nursing homes (14.3%), residential homes (6.3%), tertiary centers (4.8%), and hospice (1.6%). Unfortunately, 3 patients (4.8%) passed away. Of those still alive (n = 60), 16.7% were readmitted to the hospital within 30 days, compared to a readmission rate of 11% on the stroke ward. None of the patients who were readmitted were seen by a neurologist during their initial admission.
The frequency of secondary complications was reviewed as a measure of the multidisciplinary management of this patient group. It was noted that 11.1% had a fall on the ward, which was similar to a rate of 10.7% on the stroke ward. More striking was the fact that 14.3% of patients developed a pressure ulcer and 33.3% developed an HAI during their admission, compared with rates of 1.3% and 10.7%, respectively, on the stroke ward (Table 1).
There were no significant differences found in length of stay between those who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist (P = .73). This was also true for categorical data, whereby readmission rate (P = .13), frequency of falls (P = .22), frequency of pressure ulcers (P = .67), and HAIs (P = .81) all failed to show a significant difference between groups.
Discussion
The findings of this service evaluation show markedly poorer outcomes for neurological patients compared to stroke patients managed on a specialist stroke ward. It is suggested that these results are in part due to the lack of specialist input from a neurologist in the majority of cases and the fact that all were managed on clinically inappropriate wards. Only 15.9% of neurological patients were seen by a neurologist. This is a slight improvement compared to previous studies in DGHs that showed rates of 10%1 and 11%,11 but it is still a far cry from the goal of 100% set out in recommendations.2 In addition, the increased readmission rate may be suggestive of suboptimal management, especially given that none of those readmitted had been reviewed by a neurologist. There are undoubtedly other factors that may influence readmissions, such as comorbidities, the severity/complexity of the condition, and the strength of community services. However, the impact of a lack of input from a specialist should not be underestimated, and further evaluation of this factor (with confounding factors controlled) would be beneficial.
The result of an extended length of stay was also a predictable outcome based on previous evidence.4,5 With the potential for suboptimal management plans and inaccurate diagnoses, it is inevitable that the patient’s movement through the hospital system will be impeded. In our example, it is possible that the extended length of stay was influenced by the fact that patients included in the evaluation were managed on nonspecialist wards and a large proportion had multiple ward changes.
Given that the evidence clearly shows that stroke patients are most effectively managed by a multidisciplinary team (MDT) with specialist skills,12 it is likely that other neurological patients, who have similar multifactorial needs, would also benefit. The patients in our evaluation were cared for by nursing staff who lacked specific skills and experience in neurology. The allied health professionals involved were specialists in neurotherapy but were not based on the ward and not directly linked to the ward MDT. A review by Epstein found that the benefits of having a MDT, in any speciality, working together on a ward included improved communication, reduced adverse events, and a reduced length of stay.13 This lack of an effective MDT approach may provide some explanation as to why the average length of stay and the rates of some secondary complications were at such elevated levels.
A systematic review exploring the impact of patients admitted to clinically inappropriate wards in a range of specialities found that these patients were associated with worse outcomes.14 This is supported by our findings, in which a higher rate of pressure ulcers and HAIs were observed when compared to rates in the specialist stroke ward. Again, a potential explanation for this is the impact of patients being managed by clinicians who lack the specialist knowledge of the patient group and the risks they face. Another explanation could be due to the high number of ward moves the patients experienced. Blay et al found that ward moves increased length of stay and carried an associated clinical risk, with the odds of falls and HAIs increasing with each move.15 A case example of this is apparent within our analysis in that the patient who experienced 6 ward moves not only had the longest length of stay (78 days), but also developed a pressure ulcer and 2 HAIs during their admission.
This service evaluation had a number of limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, despite including all patients who met the criteria within the stipulated time frame, the sample size was relatively small, making it difficult to identify consistent patterns of behavior within the data.
Furthermore, caution should be applied when interpreting the comparators used, as the patient groups are not equivalent. The use of comparison against a standard is not a prerequisite in a service evaluation of this nature, but comparators were included to help frame the context for the reader. As such, they should only be used in this way rather than to make any firm conclusions.
Finally, as the evaluation was limited to the use of routinely collected data, there are several variables, other than those reported, which may have influenced the results. For example, it was not possible to ascertain certain demographic details, such as body mass index and socioeconomic factors, nor lifestyle factors such as smoking status, alcohol consumption, and exercise levels, all of which could impact negatively on the outcomes of interest. Furthermore, data were not collected on follow-up services after discharge to evaluate whether these had any impact on readmission rates.
Conclusion
This service evaluation highlights the potential impact of managing neurological patients on clinically inappropriate wards with limited input from a neurologist. There is the potential to ameliorate these impacts by cohorting these patients in neurologist-led beds with a specialist MDT. While there are limitations in the design of our study, including the lack of a controlled comparison, the small sample size, and the fact that this is an evaluation of a single service, the negative impacts to patients are concerning and warrant further investigation.
Corresponding author: Richard J. Holmes, MSc, Physiotherapy Department, St. Richard’s Hospital, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 6SE; richard.holmes8@nhs.net.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Kanagaratnam M, Boodhoo A, MacDonald BK, Nitkunan A. Prevalence of acute neurology: a 2-week snapshot in a district general hospital. Clin Med (Lond). 2020;20(2):169-173.
2. Royal College of Physicians. Local adult neurology services for the next decade. Report of a working party. June 2011. Accessed October 29, 2020. https://www.mstrust.org.uk/sites/default/files/files/Local%20adult%20neurology%20services%20for%20the%20next%20decade.pdf
3. McColgan P, Carr AS, McCarron MO. The value of a liaison neurology service in a district general hospital. Postgrad Med J. 2011;87(1025):166-169.
4. Forbes R, Craig J, Callender M, Patterson V. Liaison neurology for acute medical admissions. Clin Med (Lond). 2004;4(3):290.
5. Craig J, Chua R, Russell C, et al. A cohort study of early neurological consultation by telemedicine on the care of neurological inpatients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(7):1031-1035.
6. Ali E, Chaila E, Hutchinson M, Tubridy N. The ‘hidden work’ of a hospital neurologist: 1000 consults later. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(4):e28-e32.
7. Association of British Neurologists. Acute Neurology services survey 2017. Accessed October 29, 2020. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.theabn.org/resource/collection/219B4A48-4D25-4726-97AA-0EB6090769BE/ABN_2017_Acute_Neurology_Survey.pdf
8. Nitkunan A, Lawrence J, Reilly MM. Neurology Workforce Survey. January 28, 2020. Accessed October 28, 2020. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.theabn.org/resource/collection/219B4A48-4D25-4726-97AA-0EB6090769BE/2020_ABN_Neurology_Workforce_Survey_2018-19_28_Jan_2020.pdf
9. Fuller G, Connolly M, Mummery C, Williams A. GIRT Neurology Methodology and Initial Summary of Regional Data. September 2019. Accessed October 26, 2020. https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/GIRFT-neurology-methodology-090919-FINAL.pdf
10. The Neurological Alliance. Neuro Numbers 2019. Accessed October 28, 2020. https://www.neural.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/neuro-numbers-2019.pdf
11. Cai A, Brex P. A survey of acute neurology at a general hospital in the UK. Clin Med (Lond). 2010;10(6):642-643.
12. Langhorne P, Ramachandra S; Stroke Unit Trialists’ Collaboration. Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke: network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;4(4):CD000197.
13. Epstein NE. Multidisciplinary in-hospital teams improve patient outcomes: A review. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5(Suppl 7):S295-S303.
14. La Regina M, Guarneri F, Romano E, et al. What Quality and Safety of Care for Patients Admitted to Clinically Inappropriate Wards: a Systematic Review. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(7):1314-1321.
15. Blay N, Roche M, Duffield C, Xu X. Intrahospital transfers and adverse patient outcomes: An analysis of administrative health data. J Clin Nurs. 2017;26(23-24):4927-4935.
From Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Physiotherapy Department, Chichester, UK (Richard J. Holmes), and Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Department of Occupational Therapy, Chichester, UK (Sophie Stratford).
Objective: Despite the benefits of early and frequent input from a neurologist, there is wide variation in the availability of this service, especially in district general hospitals, with many patients managed on clinically inappropriate wards. The purpose of this service evaluation was to explore the impact this had on patient care.
Methods: A retrospective service evaluation was undertaken at a National Health Service hospital by reviewing patient records over a 6-month period. Data related to demographics, processes within the patient’s care, and secondary complications were recorded. Findings were compared with those of stroke patients managed on a specialist stroke ward.
Results: A total of 63 patients were identified, with a mean age of 72 years. The mean length of stay was 25.9 days, with a readmission rate of 16.7%. Only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist. There was a high rate of secondary complications, with a number of patients experiencing falls (11.1%), pressure ulcers (14.3%), and health care–acquired infections (33.3%) during their admission.
Conclusions: The lack of specialist input from a neurologist and the management of patients on clinically inappropriate wards may have negatively impacted length of stay, readmission rates, and the frequency of secondary complications.
Keywords: evaluation; clinical safety; neurology; patient-centered care; clinical outcomes; length of stay.
It is estimated that 10% of acute admissions to district general hospitals (DGHs) of the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom are due to a neurological problem other than stroke.1 In 2011, a joint report from the Royal College of Physicians and the Association of British Neurologists (ABN) recommended that all of these patients should be admitted under the care of a neurologist and be regularly reviewed by a neurologist during their admission.2 The rationale for this recommendation is clear. The involvement of a neurologist has been shown to improve accuracy of the diagnosis3 and significantly reduce length of stay.4,5 Studies have also shown that the involvement of a neurologist has led to a change in the management plan in as high as 79%6 to 89%3 of cases, suggesting that a high proportion of neurological patients not seen by a neurologist are being managed suboptimally.
Despite this, a recent ABN survey of acute neurology services found ongoing wide variations in the availability of this specialist care, with a large proportion of DGHs having limited or no access to a neurologist and very few having dedicated neurology beds.7 While it is recognized that services have been structured in response to the reduced numbers of neurologists within the United Kingdom,8 it is prudent to assess the impact that such services have on patient care.
With this in mind, we planned to evaluate the current provision of care provided to neurological patients in a real-world setting. This was conducted in the context of a neurology liaison service at a DGH with no dedicated neurology beds.
Methods
A retrospective service evaluation was undertaken at a DGH in the southeast of England. The NHS hospital has neurologists on site who provide diagnostic and therapeutic consultations on the wards, but there are no dedicated beds for patients with neurological conditions. Patients requiring neurosurgical input are referred to a tertiary neurosciences center.
Patients were selected from the neurotherapy database if they were referred into the service between August 1, 2019, and January 31, 2020. The neurotherapy database was used as this was the only source that held thorough data on this patient group and allowed for the identification of patients who were not referred into the neurologist’s service. Patients were included if they had a new neurological condition as their primary diagnosis or if they had an exacerbation of an already established neurological condition. If a patient was admitted with more than 1 neurological diagnosis then the primary diagnosis for the admission was to be used in the analysis, though this did not occur during this evaluation. Patients with a primary diagnosis of a stroke were included if they were not managed on the acute stroke ward. Those managed on the stroke ward were excluded so that an analysis of patients managed on wards that were deemed clinically inappropriate could be undertaken. Patients were not included if they had a pre-existing neurological condition (ie, dementia, multiple sclerosis) but were admitted due to a non-neurological cause such as a fall or infection. All patients who met the criteria were included.
A team member independently reviewed each set of patient notes. Demographic data extracted from the medical notes included the patient’s age (on admission), gender, and diagnosis. Medical, nursing, and therapy notes were reviewed to identify secondary complications that arose during the patient’s admission. The secondary complications reviewed were falls (defined as the patient unexpectedly coming to the ground or other lower level), health care–acquired infections (HAIs) (defined as any infection acquired during the hospital admission), and pressure ulcers (defined as injuries to the skin or underlying tissue during the hospital admission). Other details, obtained from the patient administration system, included the length of stay (days), the number of ward moves the patient experienced, the speciality of the consultant responsible for the patient’s care, the discharge destination, and whether the patient was readmitted for any cause within 30 days. All data collected were stored on a password-protected computer and no patient-identifiable data were included.
The results were collated using descriptive statistics. The χ2 test was used to compare categorical data between those patients who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare differences in the length of stay between these 2 groups.
No national data relating to this specific patient group were available within the literature. Therefore, to provide a comparator of neurological patients within the same hospital, data were collected on stroke patients managed on the stroke ward. This group was deemed most appropriate for comparison as they present with similar neurological symptoms but are cared for on a specialist ward. During the evaluation period, 284 stroke patients were admitted to the stroke ward. A sample of 75 patients was randomly selected using a random number generator, and the procedure for data collection was repeated. It was not appropriate to make direct comparative analysis on these 2 groups due to the inherent differences, but it was felt important to provide context with regards to what usual care was like on a specialist ward within the same hospital.
Ethical approval was not required as this was a service evaluation of routinely collected data within a single hospital site.
Results
In total, 63 patients were identified: 26 females and 37 males. The median age of patients was 74 years (range, 39-92 years). These demographic details and comparisons to stroke patients managed on a specialist ward can be seen in Table 1. To quantify the range of diagnoses, the condition groups defined by GIRFT Neurology Methodology9 were used. The most common diagnoses were tumors of the nervous system (25.4%) and traumatic brain and spine injury (23.8%). The other conditions included in the analysis can be seen in Table 2.
Despite having a neurological condition as their primary diagnosis, only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist during their hospital admission. Patients were most commonly under the care of a geriatrician (60.3%), but they were also managed by orthopedics (12.6%), acute medicine (7.9%), respiratory (6.3%), cardiology (4.8%), gastroenterology (3.2%), and surgery (3.2%). One patient (1.6%) was managed by intensivists.
The average length of stay was 25.9 days (range, 2-78 days). This was more than double the average length of stay on the stroke ward (11.4 days) (Table 1) and the national average for patients with neurological conditions (9.78 days).10 During their stay, 33% had 2 or more ward moves, with 1 patient moving wards a total of 6 times. Just over half (52.4%) of the patients returned to their usual residence on discharge. The remainder were discharged to rehabilitation units (15.9%), nursing homes (14.3%), residential homes (6.3%), tertiary centers (4.8%), and hospice (1.6%). Unfortunately, 3 patients (4.8%) passed away. Of those still alive (n = 60), 16.7% were readmitted to the hospital within 30 days, compared to a readmission rate of 11% on the stroke ward. None of the patients who were readmitted were seen by a neurologist during their initial admission.
The frequency of secondary complications was reviewed as a measure of the multidisciplinary management of this patient group. It was noted that 11.1% had a fall on the ward, which was similar to a rate of 10.7% on the stroke ward. More striking was the fact that 14.3% of patients developed a pressure ulcer and 33.3% developed an HAI during their admission, compared with rates of 1.3% and 10.7%, respectively, on the stroke ward (Table 1).
There were no significant differences found in length of stay between those who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist (P = .73). This was also true for categorical data, whereby readmission rate (P = .13), frequency of falls (P = .22), frequency of pressure ulcers (P = .67), and HAIs (P = .81) all failed to show a significant difference between groups.
Discussion
The findings of this service evaluation show markedly poorer outcomes for neurological patients compared to stroke patients managed on a specialist stroke ward. It is suggested that these results are in part due to the lack of specialist input from a neurologist in the majority of cases and the fact that all were managed on clinically inappropriate wards. Only 15.9% of neurological patients were seen by a neurologist. This is a slight improvement compared to previous studies in DGHs that showed rates of 10%1 and 11%,11 but it is still a far cry from the goal of 100% set out in recommendations.2 In addition, the increased readmission rate may be suggestive of suboptimal management, especially given that none of those readmitted had been reviewed by a neurologist. There are undoubtedly other factors that may influence readmissions, such as comorbidities, the severity/complexity of the condition, and the strength of community services. However, the impact of a lack of input from a specialist should not be underestimated, and further evaluation of this factor (with confounding factors controlled) would be beneficial.
The result of an extended length of stay was also a predictable outcome based on previous evidence.4,5 With the potential for suboptimal management plans and inaccurate diagnoses, it is inevitable that the patient’s movement through the hospital system will be impeded. In our example, it is possible that the extended length of stay was influenced by the fact that patients included in the evaluation were managed on nonspecialist wards and a large proportion had multiple ward changes.
Given that the evidence clearly shows that stroke patients are most effectively managed by a multidisciplinary team (MDT) with specialist skills,12 it is likely that other neurological patients, who have similar multifactorial needs, would also benefit. The patients in our evaluation were cared for by nursing staff who lacked specific skills and experience in neurology. The allied health professionals involved were specialists in neurotherapy but were not based on the ward and not directly linked to the ward MDT. A review by Epstein found that the benefits of having a MDT, in any speciality, working together on a ward included improved communication, reduced adverse events, and a reduced length of stay.13 This lack of an effective MDT approach may provide some explanation as to why the average length of stay and the rates of some secondary complications were at such elevated levels.
A systematic review exploring the impact of patients admitted to clinically inappropriate wards in a range of specialities found that these patients were associated with worse outcomes.14 This is supported by our findings, in which a higher rate of pressure ulcers and HAIs were observed when compared to rates in the specialist stroke ward. Again, a potential explanation for this is the impact of patients being managed by clinicians who lack the specialist knowledge of the patient group and the risks they face. Another explanation could be due to the high number of ward moves the patients experienced. Blay et al found that ward moves increased length of stay and carried an associated clinical risk, with the odds of falls and HAIs increasing with each move.15 A case example of this is apparent within our analysis in that the patient who experienced 6 ward moves not only had the longest length of stay (78 days), but also developed a pressure ulcer and 2 HAIs during their admission.
This service evaluation had a number of limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, despite including all patients who met the criteria within the stipulated time frame, the sample size was relatively small, making it difficult to identify consistent patterns of behavior within the data.
Furthermore, caution should be applied when interpreting the comparators used, as the patient groups are not equivalent. The use of comparison against a standard is not a prerequisite in a service evaluation of this nature, but comparators were included to help frame the context for the reader. As such, they should only be used in this way rather than to make any firm conclusions.
Finally, as the evaluation was limited to the use of routinely collected data, there are several variables, other than those reported, which may have influenced the results. For example, it was not possible to ascertain certain demographic details, such as body mass index and socioeconomic factors, nor lifestyle factors such as smoking status, alcohol consumption, and exercise levels, all of which could impact negatively on the outcomes of interest. Furthermore, data were not collected on follow-up services after discharge to evaluate whether these had any impact on readmission rates.
Conclusion
This service evaluation highlights the potential impact of managing neurological patients on clinically inappropriate wards with limited input from a neurologist. There is the potential to ameliorate these impacts by cohorting these patients in neurologist-led beds with a specialist MDT. While there are limitations in the design of our study, including the lack of a controlled comparison, the small sample size, and the fact that this is an evaluation of a single service, the negative impacts to patients are concerning and warrant further investigation.
Corresponding author: Richard J. Holmes, MSc, Physiotherapy Department, St. Richard’s Hospital, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 6SE; richard.holmes8@nhs.net.
Financial disclosures: None.
From Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Physiotherapy Department, Chichester, UK (Richard J. Holmes), and Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Department of Occupational Therapy, Chichester, UK (Sophie Stratford).
Objective: Despite the benefits of early and frequent input from a neurologist, there is wide variation in the availability of this service, especially in district general hospitals, with many patients managed on clinically inappropriate wards. The purpose of this service evaluation was to explore the impact this had on patient care.
Methods: A retrospective service evaluation was undertaken at a National Health Service hospital by reviewing patient records over a 6-month period. Data related to demographics, processes within the patient’s care, and secondary complications were recorded. Findings were compared with those of stroke patients managed on a specialist stroke ward.
Results: A total of 63 patients were identified, with a mean age of 72 years. The mean length of stay was 25.9 days, with a readmission rate of 16.7%. Only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist. There was a high rate of secondary complications, with a number of patients experiencing falls (11.1%), pressure ulcers (14.3%), and health care–acquired infections (33.3%) during their admission.
Conclusions: The lack of specialist input from a neurologist and the management of patients on clinically inappropriate wards may have negatively impacted length of stay, readmission rates, and the frequency of secondary complications.
Keywords: evaluation; clinical safety; neurology; patient-centered care; clinical outcomes; length of stay.
It is estimated that 10% of acute admissions to district general hospitals (DGHs) of the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom are due to a neurological problem other than stroke.1 In 2011, a joint report from the Royal College of Physicians and the Association of British Neurologists (ABN) recommended that all of these patients should be admitted under the care of a neurologist and be regularly reviewed by a neurologist during their admission.2 The rationale for this recommendation is clear. The involvement of a neurologist has been shown to improve accuracy of the diagnosis3 and significantly reduce length of stay.4,5 Studies have also shown that the involvement of a neurologist has led to a change in the management plan in as high as 79%6 to 89%3 of cases, suggesting that a high proportion of neurological patients not seen by a neurologist are being managed suboptimally.
Despite this, a recent ABN survey of acute neurology services found ongoing wide variations in the availability of this specialist care, with a large proportion of DGHs having limited or no access to a neurologist and very few having dedicated neurology beds.7 While it is recognized that services have been structured in response to the reduced numbers of neurologists within the United Kingdom,8 it is prudent to assess the impact that such services have on patient care.
With this in mind, we planned to evaluate the current provision of care provided to neurological patients in a real-world setting. This was conducted in the context of a neurology liaison service at a DGH with no dedicated neurology beds.
Methods
A retrospective service evaluation was undertaken at a DGH in the southeast of England. The NHS hospital has neurologists on site who provide diagnostic and therapeutic consultations on the wards, but there are no dedicated beds for patients with neurological conditions. Patients requiring neurosurgical input are referred to a tertiary neurosciences center.
Patients were selected from the neurotherapy database if they were referred into the service between August 1, 2019, and January 31, 2020. The neurotherapy database was used as this was the only source that held thorough data on this patient group and allowed for the identification of patients who were not referred into the neurologist’s service. Patients were included if they had a new neurological condition as their primary diagnosis or if they had an exacerbation of an already established neurological condition. If a patient was admitted with more than 1 neurological diagnosis then the primary diagnosis for the admission was to be used in the analysis, though this did not occur during this evaluation. Patients with a primary diagnosis of a stroke were included if they were not managed on the acute stroke ward. Those managed on the stroke ward were excluded so that an analysis of patients managed on wards that were deemed clinically inappropriate could be undertaken. Patients were not included if they had a pre-existing neurological condition (ie, dementia, multiple sclerosis) but were admitted due to a non-neurological cause such as a fall or infection. All patients who met the criteria were included.
A team member independently reviewed each set of patient notes. Demographic data extracted from the medical notes included the patient’s age (on admission), gender, and diagnosis. Medical, nursing, and therapy notes were reviewed to identify secondary complications that arose during the patient’s admission. The secondary complications reviewed were falls (defined as the patient unexpectedly coming to the ground or other lower level), health care–acquired infections (HAIs) (defined as any infection acquired during the hospital admission), and pressure ulcers (defined as injuries to the skin or underlying tissue during the hospital admission). Other details, obtained from the patient administration system, included the length of stay (days), the number of ward moves the patient experienced, the speciality of the consultant responsible for the patient’s care, the discharge destination, and whether the patient was readmitted for any cause within 30 days. All data collected were stored on a password-protected computer and no patient-identifiable data were included.
The results were collated using descriptive statistics. The χ2 test was used to compare categorical data between those patients who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare differences in the length of stay between these 2 groups.
No national data relating to this specific patient group were available within the literature. Therefore, to provide a comparator of neurological patients within the same hospital, data were collected on stroke patients managed on the stroke ward. This group was deemed most appropriate for comparison as they present with similar neurological symptoms but are cared for on a specialist ward. During the evaluation period, 284 stroke patients were admitted to the stroke ward. A sample of 75 patients was randomly selected using a random number generator, and the procedure for data collection was repeated. It was not appropriate to make direct comparative analysis on these 2 groups due to the inherent differences, but it was felt important to provide context with regards to what usual care was like on a specialist ward within the same hospital.
Ethical approval was not required as this was a service evaluation of routinely collected data within a single hospital site.
Results
In total, 63 patients were identified: 26 females and 37 males. The median age of patients was 74 years (range, 39-92 years). These demographic details and comparisons to stroke patients managed on a specialist ward can be seen in Table 1. To quantify the range of diagnoses, the condition groups defined by GIRFT Neurology Methodology9 were used. The most common diagnoses were tumors of the nervous system (25.4%) and traumatic brain and spine injury (23.8%). The other conditions included in the analysis can be seen in Table 2.
Despite having a neurological condition as their primary diagnosis, only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist during their hospital admission. Patients were most commonly under the care of a geriatrician (60.3%), but they were also managed by orthopedics (12.6%), acute medicine (7.9%), respiratory (6.3%), cardiology (4.8%), gastroenterology (3.2%), and surgery (3.2%). One patient (1.6%) was managed by intensivists.
The average length of stay was 25.9 days (range, 2-78 days). This was more than double the average length of stay on the stroke ward (11.4 days) (Table 1) and the national average for patients with neurological conditions (9.78 days).10 During their stay, 33% had 2 or more ward moves, with 1 patient moving wards a total of 6 times. Just over half (52.4%) of the patients returned to their usual residence on discharge. The remainder were discharged to rehabilitation units (15.9%), nursing homes (14.3%), residential homes (6.3%), tertiary centers (4.8%), and hospice (1.6%). Unfortunately, 3 patients (4.8%) passed away. Of those still alive (n = 60), 16.7% were readmitted to the hospital within 30 days, compared to a readmission rate of 11% on the stroke ward. None of the patients who were readmitted were seen by a neurologist during their initial admission.
The frequency of secondary complications was reviewed as a measure of the multidisciplinary management of this patient group. It was noted that 11.1% had a fall on the ward, which was similar to a rate of 10.7% on the stroke ward. More striking was the fact that 14.3% of patients developed a pressure ulcer and 33.3% developed an HAI during their admission, compared with rates of 1.3% and 10.7%, respectively, on the stroke ward (Table 1).
There were no significant differences found in length of stay between those who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist (P = .73). This was also true for categorical data, whereby readmission rate (P = .13), frequency of falls (P = .22), frequency of pressure ulcers (P = .67), and HAIs (P = .81) all failed to show a significant difference between groups.
Discussion
The findings of this service evaluation show markedly poorer outcomes for neurological patients compared to stroke patients managed on a specialist stroke ward. It is suggested that these results are in part due to the lack of specialist input from a neurologist in the majority of cases and the fact that all were managed on clinically inappropriate wards. Only 15.9% of neurological patients were seen by a neurologist. This is a slight improvement compared to previous studies in DGHs that showed rates of 10%1 and 11%,11 but it is still a far cry from the goal of 100% set out in recommendations.2 In addition, the increased readmission rate may be suggestive of suboptimal management, especially given that none of those readmitted had been reviewed by a neurologist. There are undoubtedly other factors that may influence readmissions, such as comorbidities, the severity/complexity of the condition, and the strength of community services. However, the impact of a lack of input from a specialist should not be underestimated, and further evaluation of this factor (with confounding factors controlled) would be beneficial.
The result of an extended length of stay was also a predictable outcome based on previous evidence.4,5 With the potential for suboptimal management plans and inaccurate diagnoses, it is inevitable that the patient’s movement through the hospital system will be impeded. In our example, it is possible that the extended length of stay was influenced by the fact that patients included in the evaluation were managed on nonspecialist wards and a large proportion had multiple ward changes.
Given that the evidence clearly shows that stroke patients are most effectively managed by a multidisciplinary team (MDT) with specialist skills,12 it is likely that other neurological patients, who have similar multifactorial needs, would also benefit. The patients in our evaluation were cared for by nursing staff who lacked specific skills and experience in neurology. The allied health professionals involved were specialists in neurotherapy but were not based on the ward and not directly linked to the ward MDT. A review by Epstein found that the benefits of having a MDT, in any speciality, working together on a ward included improved communication, reduced adverse events, and a reduced length of stay.13 This lack of an effective MDT approach may provide some explanation as to why the average length of stay and the rates of some secondary complications were at such elevated levels.
A systematic review exploring the impact of patients admitted to clinically inappropriate wards in a range of specialities found that these patients were associated with worse outcomes.14 This is supported by our findings, in which a higher rate of pressure ulcers and HAIs were observed when compared to rates in the specialist stroke ward. Again, a potential explanation for this is the impact of patients being managed by clinicians who lack the specialist knowledge of the patient group and the risks they face. Another explanation could be due to the high number of ward moves the patients experienced. Blay et al found that ward moves increased length of stay and carried an associated clinical risk, with the odds of falls and HAIs increasing with each move.15 A case example of this is apparent within our analysis in that the patient who experienced 6 ward moves not only had the longest length of stay (78 days), but also developed a pressure ulcer and 2 HAIs during their admission.
This service evaluation had a number of limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, despite including all patients who met the criteria within the stipulated time frame, the sample size was relatively small, making it difficult to identify consistent patterns of behavior within the data.
Furthermore, caution should be applied when interpreting the comparators used, as the patient groups are not equivalent. The use of comparison against a standard is not a prerequisite in a service evaluation of this nature, but comparators were included to help frame the context for the reader. As such, they should only be used in this way rather than to make any firm conclusions.
Finally, as the evaluation was limited to the use of routinely collected data, there are several variables, other than those reported, which may have influenced the results. For example, it was not possible to ascertain certain demographic details, such as body mass index and socioeconomic factors, nor lifestyle factors such as smoking status, alcohol consumption, and exercise levels, all of which could impact negatively on the outcomes of interest. Furthermore, data were not collected on follow-up services after discharge to evaluate whether these had any impact on readmission rates.
Conclusion
This service evaluation highlights the potential impact of managing neurological patients on clinically inappropriate wards with limited input from a neurologist. There is the potential to ameliorate these impacts by cohorting these patients in neurologist-led beds with a specialist MDT. While there are limitations in the design of our study, including the lack of a controlled comparison, the small sample size, and the fact that this is an evaluation of a single service, the negative impacts to patients are concerning and warrant further investigation.
Corresponding author: Richard J. Holmes, MSc, Physiotherapy Department, St. Richard’s Hospital, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 6SE; richard.holmes8@nhs.net.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Kanagaratnam M, Boodhoo A, MacDonald BK, Nitkunan A. Prevalence of acute neurology: a 2-week snapshot in a district general hospital. Clin Med (Lond). 2020;20(2):169-173.
2. Royal College of Physicians. Local adult neurology services for the next decade. Report of a working party. June 2011. Accessed October 29, 2020. https://www.mstrust.org.uk/sites/default/files/files/Local%20adult%20neurology%20services%20for%20the%20next%20decade.pdf
3. McColgan P, Carr AS, McCarron MO. The value of a liaison neurology service in a district general hospital. Postgrad Med J. 2011;87(1025):166-169.
4. Forbes R, Craig J, Callender M, Patterson V. Liaison neurology for acute medical admissions. Clin Med (Lond). 2004;4(3):290.
5. Craig J, Chua R, Russell C, et al. A cohort study of early neurological consultation by telemedicine on the care of neurological inpatients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(7):1031-1035.
6. Ali E, Chaila E, Hutchinson M, Tubridy N. The ‘hidden work’ of a hospital neurologist: 1000 consults later. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(4):e28-e32.
7. Association of British Neurologists. Acute Neurology services survey 2017. Accessed October 29, 2020. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.theabn.org/resource/collection/219B4A48-4D25-4726-97AA-0EB6090769BE/ABN_2017_Acute_Neurology_Survey.pdf
8. Nitkunan A, Lawrence J, Reilly MM. Neurology Workforce Survey. January 28, 2020. Accessed October 28, 2020. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.theabn.org/resource/collection/219B4A48-4D25-4726-97AA-0EB6090769BE/2020_ABN_Neurology_Workforce_Survey_2018-19_28_Jan_2020.pdf
9. Fuller G, Connolly M, Mummery C, Williams A. GIRT Neurology Methodology and Initial Summary of Regional Data. September 2019. Accessed October 26, 2020. https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/GIRFT-neurology-methodology-090919-FINAL.pdf
10. The Neurological Alliance. Neuro Numbers 2019. Accessed October 28, 2020. https://www.neural.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/neuro-numbers-2019.pdf
11. Cai A, Brex P. A survey of acute neurology at a general hospital in the UK. Clin Med (Lond). 2010;10(6):642-643.
12. Langhorne P, Ramachandra S; Stroke Unit Trialists’ Collaboration. Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke: network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;4(4):CD000197.
13. Epstein NE. Multidisciplinary in-hospital teams improve patient outcomes: A review. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5(Suppl 7):S295-S303.
14. La Regina M, Guarneri F, Romano E, et al. What Quality and Safety of Care for Patients Admitted to Clinically Inappropriate Wards: a Systematic Review. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(7):1314-1321.
15. Blay N, Roche M, Duffield C, Xu X. Intrahospital transfers and adverse patient outcomes: An analysis of administrative health data. J Clin Nurs. 2017;26(23-24):4927-4935.
1. Kanagaratnam M, Boodhoo A, MacDonald BK, Nitkunan A. Prevalence of acute neurology: a 2-week snapshot in a district general hospital. Clin Med (Lond). 2020;20(2):169-173.
2. Royal College of Physicians. Local adult neurology services for the next decade. Report of a working party. June 2011. Accessed October 29, 2020. https://www.mstrust.org.uk/sites/default/files/files/Local%20adult%20neurology%20services%20for%20the%20next%20decade.pdf
3. McColgan P, Carr AS, McCarron MO. The value of a liaison neurology service in a district general hospital. Postgrad Med J. 2011;87(1025):166-169.
4. Forbes R, Craig J, Callender M, Patterson V. Liaison neurology for acute medical admissions. Clin Med (Lond). 2004;4(3):290.
5. Craig J, Chua R, Russell C, et al. A cohort study of early neurological consultation by telemedicine on the care of neurological inpatients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(7):1031-1035.
6. Ali E, Chaila E, Hutchinson M, Tubridy N. The ‘hidden work’ of a hospital neurologist: 1000 consults later. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(4):e28-e32.
7. Association of British Neurologists. Acute Neurology services survey 2017. Accessed October 29, 2020. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.theabn.org/resource/collection/219B4A48-4D25-4726-97AA-0EB6090769BE/ABN_2017_Acute_Neurology_Survey.pdf
8. Nitkunan A, Lawrence J, Reilly MM. Neurology Workforce Survey. January 28, 2020. Accessed October 28, 2020. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.theabn.org/resource/collection/219B4A48-4D25-4726-97AA-0EB6090769BE/2020_ABN_Neurology_Workforce_Survey_2018-19_28_Jan_2020.pdf
9. Fuller G, Connolly M, Mummery C, Williams A. GIRT Neurology Methodology and Initial Summary of Regional Data. September 2019. Accessed October 26, 2020. https://gettingitrightfirsttime.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/GIRFT-neurology-methodology-090919-FINAL.pdf
10. The Neurological Alliance. Neuro Numbers 2019. Accessed October 28, 2020. https://www.neural.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/neuro-numbers-2019.pdf
11. Cai A, Brex P. A survey of acute neurology at a general hospital in the UK. Clin Med (Lond). 2010;10(6):642-643.
12. Langhorne P, Ramachandra S; Stroke Unit Trialists’ Collaboration. Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke: network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;4(4):CD000197.
13. Epstein NE. Multidisciplinary in-hospital teams improve patient outcomes: A review. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5(Suppl 7):S295-S303.
14. La Regina M, Guarneri F, Romano E, et al. What Quality and Safety of Care for Patients Admitted to Clinically Inappropriate Wards: a Systematic Review. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(7):1314-1321.
15. Blay N, Roche M, Duffield C, Xu X. Intrahospital transfers and adverse patient outcomes: An analysis of administrative health data. J Clin Nurs. 2017;26(23-24):4927-4935.
HHS to inject billions into mental health, substance use disorders
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services will inject billions of dollars into programs designed to address mental health and substance use disorders, including $3 billion released to states as of May 18, said federal officials.
The American Rescue Plan, a COVID-relief package signed into law in March, contained the money, which will be divided equally between the Community Mental Health Services Block Grant Program and the Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment Block Grant Program, said Tom Coderre, Acting Assistant Secretary for Mental Health and Substance Use, in a call with reporters.
The award amounts will vary by state.
The mental health program helps states and territories provide services for children with serious emotional issues and adults with serious mental illness.
The substance use program provides money to plan, implement, and evaluate prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery services.
, which fueled an increase in anxiety, depression, and overdose, said Assistant Secretary for Health Rachel Levine, MD, on the call.
“We know multiple stressors during the pandemic – isolation, sickness, grief, job loss, food instability, and loss of routines – have devastated many Americans and presented the unprecedented behavioral health challenges across the nation,” said Dr. Levine.
The HHS also announced that it is re-establishing a Behavioral Health Coordinating Council (BHCC). Dr. Levine and Mr. Coderre will serve as cochairs of the Council, which will coordinate action-oriented approaches to addressing the HHS’s behavioral health efforts.
However, in 2014, the U.S. Government Accountability Office criticized the BHCC for only focusing on the HHS, and noted the lack of coordination across the federal government’s various efforts to address mental health.
‘A huge step forward’
The American Psychiatric Association welcomed the new money and the return of the council.
“In the wake of the pandemic an unprecedented, and as of yet untold, number of Americans are faced with mental health and substance use disorders, particularly in communities impacted by structural racism,” said APA President Vivian Pender, MD, in a statement. “With the creation of this Council and this investment in mental health, the administration is taking a huge step forward.”
APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, added: “This Council has great potential to ease the challenges we face as we begin to recover from the pandemic’s impact on our society, and [the] APA looks forward to assisting in their efforts.”
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra noted in a statement that the COVID-19 pandemic “has made clear the need to invest resources in our nation’s mental health and address the inequities that still exist around behavioral health care.” He added, “This national problem calls for department-wide coordination to address the issue.”
Dr. Levine said the Council “will assure the right prioritization and guidelines are in place to provide pathways to prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery services.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services will inject billions of dollars into programs designed to address mental health and substance use disorders, including $3 billion released to states as of May 18, said federal officials.
The American Rescue Plan, a COVID-relief package signed into law in March, contained the money, which will be divided equally between the Community Mental Health Services Block Grant Program and the Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment Block Grant Program, said Tom Coderre, Acting Assistant Secretary for Mental Health and Substance Use, in a call with reporters.
The award amounts will vary by state.
The mental health program helps states and territories provide services for children with serious emotional issues and adults with serious mental illness.
The substance use program provides money to plan, implement, and evaluate prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery services.
, which fueled an increase in anxiety, depression, and overdose, said Assistant Secretary for Health Rachel Levine, MD, on the call.
“We know multiple stressors during the pandemic – isolation, sickness, grief, job loss, food instability, and loss of routines – have devastated many Americans and presented the unprecedented behavioral health challenges across the nation,” said Dr. Levine.
The HHS also announced that it is re-establishing a Behavioral Health Coordinating Council (BHCC). Dr. Levine and Mr. Coderre will serve as cochairs of the Council, which will coordinate action-oriented approaches to addressing the HHS’s behavioral health efforts.
However, in 2014, the U.S. Government Accountability Office criticized the BHCC for only focusing on the HHS, and noted the lack of coordination across the federal government’s various efforts to address mental health.
‘A huge step forward’
The American Psychiatric Association welcomed the new money and the return of the council.
“In the wake of the pandemic an unprecedented, and as of yet untold, number of Americans are faced with mental health and substance use disorders, particularly in communities impacted by structural racism,” said APA President Vivian Pender, MD, in a statement. “With the creation of this Council and this investment in mental health, the administration is taking a huge step forward.”
APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, added: “This Council has great potential to ease the challenges we face as we begin to recover from the pandemic’s impact on our society, and [the] APA looks forward to assisting in their efforts.”
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra noted in a statement that the COVID-19 pandemic “has made clear the need to invest resources in our nation’s mental health and address the inequities that still exist around behavioral health care.” He added, “This national problem calls for department-wide coordination to address the issue.”
Dr. Levine said the Council “will assure the right prioritization and guidelines are in place to provide pathways to prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery services.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services will inject billions of dollars into programs designed to address mental health and substance use disorders, including $3 billion released to states as of May 18, said federal officials.
The American Rescue Plan, a COVID-relief package signed into law in March, contained the money, which will be divided equally between the Community Mental Health Services Block Grant Program and the Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment Block Grant Program, said Tom Coderre, Acting Assistant Secretary for Mental Health and Substance Use, in a call with reporters.
The award amounts will vary by state.
The mental health program helps states and territories provide services for children with serious emotional issues and adults with serious mental illness.
The substance use program provides money to plan, implement, and evaluate prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery services.
, which fueled an increase in anxiety, depression, and overdose, said Assistant Secretary for Health Rachel Levine, MD, on the call.
“We know multiple stressors during the pandemic – isolation, sickness, grief, job loss, food instability, and loss of routines – have devastated many Americans and presented the unprecedented behavioral health challenges across the nation,” said Dr. Levine.
The HHS also announced that it is re-establishing a Behavioral Health Coordinating Council (BHCC). Dr. Levine and Mr. Coderre will serve as cochairs of the Council, which will coordinate action-oriented approaches to addressing the HHS’s behavioral health efforts.
However, in 2014, the U.S. Government Accountability Office criticized the BHCC for only focusing on the HHS, and noted the lack of coordination across the federal government’s various efforts to address mental health.
‘A huge step forward’
The American Psychiatric Association welcomed the new money and the return of the council.
“In the wake of the pandemic an unprecedented, and as of yet untold, number of Americans are faced with mental health and substance use disorders, particularly in communities impacted by structural racism,” said APA President Vivian Pender, MD, in a statement. “With the creation of this Council and this investment in mental health, the administration is taking a huge step forward.”
APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, added: “This Council has great potential to ease the challenges we face as we begin to recover from the pandemic’s impact on our society, and [the] APA looks forward to assisting in their efforts.”
HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra noted in a statement that the COVID-19 pandemic “has made clear the need to invest resources in our nation’s mental health and address the inequities that still exist around behavioral health care.” He added, “This national problem calls for department-wide coordination to address the issue.”
Dr. Levine said the Council “will assure the right prioritization and guidelines are in place to provide pathways to prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery services.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC: Vaccinated? You don’t need a mask indoors
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HHS prohibits discrimination against LGBTQ patients: Action reverses Trump-era policy
The Biden administration is reversing a Trump-era policy that allowed health care providers to bar services to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or queer (LGBTQ) patients.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services gave notice on Monday that it would interpret the Affordable Care Act’s Section 1557 – which bars discrimination on the basis of sex – to include discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity. The department said its position is consistent with a June 2020 U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Bostock v. Clayton County, GA. The ruling determined that the Civil Rights Act’s prohibition of employment discrimination on the basis of sex includes sexual orientation and gender identity.
“The mission of our Department is to enhance the health and well-being of all Americans, no matter their gender identity or sexual orientation,” said HHS Assistant Secretary for Health Rachel Levine, MD, in a statement released Monday.
“All people need access to health care services to fix a broken bone, protect their heart health, and screen for cancer risk,” she said. “No one should be discriminated against when seeking medical services because of who they are.”
Many physician organizations applauded the decision.
“The Biden administration did the right thing by terminating a short-lived effort to allow discrimination based on gender or sexual orientation when seeking health care,” said Susan R. Bailey, MD, president of the American Medical Association, in a statement.
When, in 2019, the Trump administration proposed to allow providers to deny care to LGBTQ people, the AMA said in a letter to the HHS that its interpretation “was contrary to the intent and the plain language of the law.”
Now, said Bailey, the AMA welcomes the Biden administration’s interpretation. It “is a victory for health equity and ends a dismal chapter in which a federal agency sought to remove civil rights protections,” she said.
An alliance of patient groups – including the American Cancer Society, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the American Heart Association, the American Lung Association, the Epilepsy Foundation, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, and the National Organization for Rare Disorders – also applauded the new policy. “This community already faces significant health disparities,” the groups noted in a statement. People with chronic illness such as HIV and cancer “need to be able to access care quickly and without fear of discrimination,” they said.
The groups had filed a friend of the court brief in a case against the Trump administration rule.
“We welcome this positive step to ensure access is preserved without hindrance, as intended by the health care law,” they said.
Twenty-two states and Washington, D.C. – led by former California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who is now HHS secretary – sued the Trump administration in July 2020, aiming to overturn the rule.
Chase Strangio, deputy director for Trans Justice with the American Civil Liberties Union LGBTQ & HIV Project, noted that the HHS announcement was crucial in the face of efforts in multiple states to bar health care for transgender youth. “The Biden administration has affirmed what courts have said for decades: Discrimination against LGBTQ people is against the law. It also affirms what transgender people have long said: Gender-affirming care is life-saving care,” he said in a statement.
Lambda Legal, which led another lawsuit against the Trump administration rule, said it welcomed the HHS action but noted in a statement by the organization’s senior attorney, Omar Gonzalez-Pagan, that it “does not address significant aspects of the Trump-era rule that we and others have challenged in court.”
The Trump rule also “limited the remedies available to people who face health disparities, limited access to health care for people with Limited English Proficiency, unlawfully incorporated religious exemptions, and dramatically reduced the number of health care entities and insurance subject to the rule, all of which today’s action does not address,” said Gonzalez-Pagan.
“We encourage Secretary Xavier Becerra and the Biden administration to take additional steps to ensure that all LGBTQ people are completely covered wherever and whenever they may encounter discrimination during some of the most delicate and precarious moments of their lives: When seeking health care,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Biden administration is reversing a Trump-era policy that allowed health care providers to bar services to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or queer (LGBTQ) patients.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services gave notice on Monday that it would interpret the Affordable Care Act’s Section 1557 – which bars discrimination on the basis of sex – to include discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity. The department said its position is consistent with a June 2020 U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Bostock v. Clayton County, GA. The ruling determined that the Civil Rights Act’s prohibition of employment discrimination on the basis of sex includes sexual orientation and gender identity.
“The mission of our Department is to enhance the health and well-being of all Americans, no matter their gender identity or sexual orientation,” said HHS Assistant Secretary for Health Rachel Levine, MD, in a statement released Monday.
“All people need access to health care services to fix a broken bone, protect their heart health, and screen for cancer risk,” she said. “No one should be discriminated against when seeking medical services because of who they are.”
Many physician organizations applauded the decision.
“The Biden administration did the right thing by terminating a short-lived effort to allow discrimination based on gender or sexual orientation when seeking health care,” said Susan R. Bailey, MD, president of the American Medical Association, in a statement.
When, in 2019, the Trump administration proposed to allow providers to deny care to LGBTQ people, the AMA said in a letter to the HHS that its interpretation “was contrary to the intent and the plain language of the law.”
Now, said Bailey, the AMA welcomes the Biden administration’s interpretation. It “is a victory for health equity and ends a dismal chapter in which a federal agency sought to remove civil rights protections,” she said.
An alliance of patient groups – including the American Cancer Society, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the American Heart Association, the American Lung Association, the Epilepsy Foundation, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, and the National Organization for Rare Disorders – also applauded the new policy. “This community already faces significant health disparities,” the groups noted in a statement. People with chronic illness such as HIV and cancer “need to be able to access care quickly and without fear of discrimination,” they said.
The groups had filed a friend of the court brief in a case against the Trump administration rule.
“We welcome this positive step to ensure access is preserved without hindrance, as intended by the health care law,” they said.
Twenty-two states and Washington, D.C. – led by former California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who is now HHS secretary – sued the Trump administration in July 2020, aiming to overturn the rule.
Chase Strangio, deputy director for Trans Justice with the American Civil Liberties Union LGBTQ & HIV Project, noted that the HHS announcement was crucial in the face of efforts in multiple states to bar health care for transgender youth. “The Biden administration has affirmed what courts have said for decades: Discrimination against LGBTQ people is against the law. It also affirms what transgender people have long said: Gender-affirming care is life-saving care,” he said in a statement.
Lambda Legal, which led another lawsuit against the Trump administration rule, said it welcomed the HHS action but noted in a statement by the organization’s senior attorney, Omar Gonzalez-Pagan, that it “does not address significant aspects of the Trump-era rule that we and others have challenged in court.”
The Trump rule also “limited the remedies available to people who face health disparities, limited access to health care for people with Limited English Proficiency, unlawfully incorporated religious exemptions, and dramatically reduced the number of health care entities and insurance subject to the rule, all of which today’s action does not address,” said Gonzalez-Pagan.
“We encourage Secretary Xavier Becerra and the Biden administration to take additional steps to ensure that all LGBTQ people are completely covered wherever and whenever they may encounter discrimination during some of the most delicate and precarious moments of their lives: When seeking health care,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Biden administration is reversing a Trump-era policy that allowed health care providers to bar services to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or queer (LGBTQ) patients.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services gave notice on Monday that it would interpret the Affordable Care Act’s Section 1557 – which bars discrimination on the basis of sex – to include discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity. The department said its position is consistent with a June 2020 U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Bostock v. Clayton County, GA. The ruling determined that the Civil Rights Act’s prohibition of employment discrimination on the basis of sex includes sexual orientation and gender identity.
“The mission of our Department is to enhance the health and well-being of all Americans, no matter their gender identity or sexual orientation,” said HHS Assistant Secretary for Health Rachel Levine, MD, in a statement released Monday.
“All people need access to health care services to fix a broken bone, protect their heart health, and screen for cancer risk,” she said. “No one should be discriminated against when seeking medical services because of who they are.”
Many physician organizations applauded the decision.
“The Biden administration did the right thing by terminating a short-lived effort to allow discrimination based on gender or sexual orientation when seeking health care,” said Susan R. Bailey, MD, president of the American Medical Association, in a statement.
When, in 2019, the Trump administration proposed to allow providers to deny care to LGBTQ people, the AMA said in a letter to the HHS that its interpretation “was contrary to the intent and the plain language of the law.”
Now, said Bailey, the AMA welcomes the Biden administration’s interpretation. It “is a victory for health equity and ends a dismal chapter in which a federal agency sought to remove civil rights protections,” she said.
An alliance of patient groups – including the American Cancer Society, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the American Heart Association, the American Lung Association, the Epilepsy Foundation, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, and the National Organization for Rare Disorders – also applauded the new policy. “This community already faces significant health disparities,” the groups noted in a statement. People with chronic illness such as HIV and cancer “need to be able to access care quickly and without fear of discrimination,” they said.
The groups had filed a friend of the court brief in a case against the Trump administration rule.
“We welcome this positive step to ensure access is preserved without hindrance, as intended by the health care law,” they said.
Twenty-two states and Washington, D.C. – led by former California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who is now HHS secretary – sued the Trump administration in July 2020, aiming to overturn the rule.
Chase Strangio, deputy director for Trans Justice with the American Civil Liberties Union LGBTQ & HIV Project, noted that the HHS announcement was crucial in the face of efforts in multiple states to bar health care for transgender youth. “The Biden administration has affirmed what courts have said for decades: Discrimination against LGBTQ people is against the law. It also affirms what transgender people have long said: Gender-affirming care is life-saving care,” he said in a statement.
Lambda Legal, which led another lawsuit against the Trump administration rule, said it welcomed the HHS action but noted in a statement by the organization’s senior attorney, Omar Gonzalez-Pagan, that it “does not address significant aspects of the Trump-era rule that we and others have challenged in court.”
The Trump rule also “limited the remedies available to people who face health disparities, limited access to health care for people with Limited English Proficiency, unlawfully incorporated religious exemptions, and dramatically reduced the number of health care entities and insurance subject to the rule, all of which today’s action does not address,” said Gonzalez-Pagan.
“We encourage Secretary Xavier Becerra and the Biden administration to take additional steps to ensure that all LGBTQ people are completely covered wherever and whenever they may encounter discrimination during some of the most delicate and precarious moments of their lives: When seeking health care,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA blazes path for ‘real-world’ evidence as proof of efficacy
In 2016, results from the LEADER trial of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes helped jump-start awareness of the potential role of this new class of drugs, the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists, for reducing cardiovascular events. The randomized, placebo-controlled trial enrolled more than 9000 patients at more than 400 sites in over 30 countries, and took nearly 6 years from the start of patient enrollment to publication of the landmark results.
In December 2020, an independent team of researchers published results from a study with a design identical to LEADER, but used data that came not from a massive, global, years-long trial but from already-existing numbers culled from three large U.S. insurance claim databases. The result of this emulation using real-world data was virtually identical to what the actual trial showed, replicating both the direction and statistical significance of the original finding of the randomized, controlled trial (RCT).
What if research proved that this sort of RCT emulation could reliably be done on a regular basis? What might it mean for regulatory decisions on drugs and devices that historically have been based entirely on efficacy evidence from RCTs?
Making the most of a sea of observational data
Medicine in the United States has become increasingly awash in a sea of observational data collected from sources that include electronic health records, insurance claims, and increasingly, personal-health monitoring devices.
The Food and Drug Administration is now in the process of trying to figure out how it can legitimately harness this tsunami of real-world data to make efficacy decisions, essentially creating a new category of evidence to complement traditional data from randomized trials. It’s an opportunity that agency staff and their outside advisors have been keen to seize, especially given the soaring cost of prospective, randomized trials.
Recognition of this untapped resource in part led to a key initiative, among many others, included in the 21st Century Cures Act, passed in December 2016. Among the Act’s mandates was that, by the end of 2021, the FDA would issue guidance on when drug sponsors could use real-world evidence (RWE) to either help support a new indication for an already approved drug or help satisfy postapproval study requirements.
The initiative recognizes that this approach is not appropriate for initial drug approvals, which remain exclusively reliant on evidence from RCTs. Instead, it seems best suited to support expanding indications for already approved drugs.
Although FDA staff have made progress in identifying the challenges and broadening their understanding of how to best handle real-world data that come from observing patients in routine practice, agency leaders stress that this complex issue will likely not be fully resolved by their guidance to be published later this year. The FDA released a draft of the guidance in May 2019.
Can RWE be ‘credible and reliable?’
“Whether observational, nonrandomized data can become credible enough to use is what we’re talking about. These are possibilities that need to be explained and better understood,” said Robert Temple, MD, deputy director for clinical science of the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Since the 1970s, the FDA has recognized historical controls as legitimate, so it’s possible [for RWE] to be credible. The big test is when is it credible and reliable enough [to assess efficacy]?” wondered Dr. Temple during a 2-day workshop on the topic held mid-February and organized by Duke University’s Margolis Center for Health Policy.
“We’re approaching an inflection point regarding how observational studies are generated and used, but our evidentiary standards will not lower, and it will be a case-by-case decision” by the agency as they review future RWE submissions, said John Concato, MD, the FDA’s associate director for real-world evidence, during the workshop.
“We are working toward guidance development, but also looking down the road to what we need to do to enable this,” said Dr. Concato. “It’s a complicated issue. If it was easy, it would have already been fixed.” He added that the agency will likely release a “portfolio” of guidance for submitting real-world data and RWE. Real-world data are raw information that, when analyzed, become RWE.
In short, the FDA seems headed toward guidance that won’t spell out a pathway that guarantees success using RWE but will at least open the door to consideration of this unprecedented application.
Not like flipping a switch
The guidance will not activate acceptance of RWE all at once. “It’s not like a light switch,” cautioned Adam Kroetsch, MPP, research director for biomedical innovation and regulatory policy at Duke-Margolis in Washington, D.C. “It’s an evolutionary process,” and the upcoming guidance will provide “just a little more clarity” on what sorts of best practices using RWE the FDA will find persuasive. “It’s hard for the FDA to clearly say what it’s looking for until they see some good examples,” Dr. Kroetsch said in an interview.
What will change is that drug sponsors can submit using RWE, and the FDA “will have a more open-minded view,” predicted Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, ScD, a workshop participant and chief of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “For the first time, a law required [the FDA] to take a serious look” at observational data for efficacy assessment.
“The FDA has had a bias against using RWE for evidence of efficacy but has long used it to understand drug safety. Now the FDA is trying to wrap its arms around how to best use RWE” for efficacy decisions, said Joseph S. Ross, MD, another workshop participant and professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The agency’s cautious approach is reassuring, Dr. Ross noted in an interview. “There was worry that the 21st Century Cures Act would open the door to allowing real-world data to be used in ways that weren’t very reliable. Very quickly, the FDA started trying to figure out the best ways to use these data in reasonable ways.”
Duplicating RCTs with RWE
To help better understand the potential use of RWE, the FDA sponsored several demonstration projects. Researchers presented results from three of these projects during the workshop in February. All three examined whether RWE, plugged into the design of an actual RCT, can produce roughly similar results when similar patients are used.
A generally consistent finding from the three demonstration projects was that “when the data are fit for purpose” the emulated or duplicated analyses with RWE “can come to similar conclusions” as the actual RCTs, said Dr. Schneeweiss, who leads one of the demonstration projects, RCT DUPLICATE.
At the workshop he reported results from RWE duplications of 20 different RCTs using insurance claims data from U.S. patients. The findings came from 10 duplications already reported in Circulation in December 2020 (including a duplication of the LEADER trial), and an additional 10 as yet unpublished RCT duplications. In the next few months, the researchers intend to assess a final group of 10 more RCT duplications.
Workshop participants also presented results from two other FDA demonstration projects: the OPERAND program run by the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials Center of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard; and the CERSI program based at Yale and the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. Both are smaller in scale than RCT DUPLICATE, incorporate lab data in addition to claims data, and in some cases test how well RWE can emulate RCTs that are not yet completed.
Collectively, results from these demonstration projects suggest that RWE can successfully emulate the results of an RCT, said Dr. Ross, a coinvestigator on the CERSI study. But the CERSI findings also highlighted how an RCT can fall short of clinical relevance.
“One of our most important findings was that RCTs don’t always represent real-world practice,” he said. His group attempted to replicate the 5,000-patient GRADE trial of four different drug options added to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. One of the four options included insulin glargine (Lantus), and the attempt to emulate the study with RWE hit the bump that no relevant real-world patients in their US claims database actually received the formulation.
That means the GRADE trial “is almost meaningless. It doesn’t reflect real-world practice,” Dr. Ross noted.
Results from the three demonstration projects “highlight the gaps we still have,” summed up Dr. Kroetsch. “They show where we need better data” from observational sources that function as well as data from RCTs.
Still, the demonstration project results are “an important step forward in establishing the validity of real-world evidence,” commented David Kerr, MBChB, an endocrinologist and director of research and innovation at the Sansum Diabetes Research Institute in Santa Barbara, Calif.
‘Target trials’ tether RWE
The target trial approach to designing an observational study is a key tool for boosting reliability and applicability of the results. The idea is to create a well-designed trial that could be the basis for a conventional RCT, and then use observational data to flesh out the target trial instead of collecting data from prospectively enrolled patients.
Designing observational studies that emulate target trials allows causal inferences, said Miguel A. Hernán, MD, DrPH, a professor of biostatistics and epidemiology at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston. Plugging real-world data into the framework of an appropriately designed target trial substantially cuts the risk of a biased analysis, he explained during the workshop.
However, the approach has limitations. The target trial must be a pragmatic trial, and the approach does not work for placebo-controlled trials, although it can accommodate a usual-care control arm. It also usually precludes patient blinding, testing treatments not used in routine practice, and close monitoring of patients in ways that are uncommon in usual care.
The target trial approach received broad endorsement during the workshop as the future for observational studies destined for efficacy consideration by the FDA.
“The idea of prespecifying a target trial is a really fantastic place to start,” commented Robert Ball, MD, deputy director of the FDA Office of Surveillance and Epidemiology. “There is still a whole set of questions once the trial is prespecified, but prespecification would be a fantastic step forward,” he said during the workshop.
Participants also endorsed other important steps to boost the value of observational studies for regulatory reviews, including preregistering the study on a site such as clinicaltrials.gov; being fully transparent about the origins of observational data; using data that match the needs of the target trial; not reviewing the data in advance to avoid cherry picking and gaming the analysis; and reporting neutral or negative results when they occur, something often not currently done for observational analyses.
But although there was clear progress and much agreement among thought leaders at the workshop, FDA representatives stressed caution in moving forward.
“No easy answer”
“With more experience, we can learn what works and what doesn’t work in generating valid results from observational studies,” said Dr. Concato. “Although the observational results have upside potential, we need to learn more. There is no easy answer, no checklist for fit-for-use data, no off-the-shelf study design, and no ideal analytic method.”
Dr. Concato acknowledged that the FDA’s goal is clear given the 2016 legislation. “The FDA is embracing our obligations under the 21st Century Cures Act to evaluate use of real-world data and real-world evidence.”
He also suggested that researchers “shy away from a false dichotomy of RCTs or observational studies and instead think about how and when RCTs and observational studies can be designed and conducted to yield trustworthy results.” Dr. Concato’s solution: “a taxonomy of interventional or noninterventional studies.”
“The FDA is under enormous pressure to embrace real-world evidence, both because of the economics of running RCTs and because of the availability of new observational data from electronic health records, wearable devices, claims, etc.,” said Dr. Kerr, who did not participate in the workshop but coauthored an editorial that calls for using real-world data in regulatory decisions for drugs and devices for diabetes. These factors create an “irresistible force” spurring the FDA to consider observational, noninterventional data.
“I think the FDA really wants this to go forward,” Dr. Kerr added in an interview. “The FDA keeps telling us that clinical trials do not have enough women or patients from minority groups. Real-world data is a way to address that. This will not be the death of RCTs, but this work shines a light on the deficiencies of RCTs and how the deficiencies can be dealt with.”
Dr. Kroetsch has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Schneeweiss has reported being a consultant to and holding equity in Aetion and receiving research funding from the FDA. Dr. Ross has reported receiving research funding from the FDA, Johnson & Johnson, and Medtronic. Dr. Hernán has reported being a consultant for Cytel. Dr. Kerr has reported being a consultant for Ascensia, EOFlow, Lifecare, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, and Voluntis. Dr. Temple, Dr. Concato, and Dr. Ball are FDA employees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2016, results from the LEADER trial of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes helped jump-start awareness of the potential role of this new class of drugs, the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists, for reducing cardiovascular events. The randomized, placebo-controlled trial enrolled more than 9000 patients at more than 400 sites in over 30 countries, and took nearly 6 years from the start of patient enrollment to publication of the landmark results.
In December 2020, an independent team of researchers published results from a study with a design identical to LEADER, but used data that came not from a massive, global, years-long trial but from already-existing numbers culled from three large U.S. insurance claim databases. The result of this emulation using real-world data was virtually identical to what the actual trial showed, replicating both the direction and statistical significance of the original finding of the randomized, controlled trial (RCT).
What if research proved that this sort of RCT emulation could reliably be done on a regular basis? What might it mean for regulatory decisions on drugs and devices that historically have been based entirely on efficacy evidence from RCTs?
Making the most of a sea of observational data
Medicine in the United States has become increasingly awash in a sea of observational data collected from sources that include electronic health records, insurance claims, and increasingly, personal-health monitoring devices.
The Food and Drug Administration is now in the process of trying to figure out how it can legitimately harness this tsunami of real-world data to make efficacy decisions, essentially creating a new category of evidence to complement traditional data from randomized trials. It’s an opportunity that agency staff and their outside advisors have been keen to seize, especially given the soaring cost of prospective, randomized trials.
Recognition of this untapped resource in part led to a key initiative, among many others, included in the 21st Century Cures Act, passed in December 2016. Among the Act’s mandates was that, by the end of 2021, the FDA would issue guidance on when drug sponsors could use real-world evidence (RWE) to either help support a new indication for an already approved drug or help satisfy postapproval study requirements.
The initiative recognizes that this approach is not appropriate for initial drug approvals, which remain exclusively reliant on evidence from RCTs. Instead, it seems best suited to support expanding indications for already approved drugs.
Although FDA staff have made progress in identifying the challenges and broadening their understanding of how to best handle real-world data that come from observing patients in routine practice, agency leaders stress that this complex issue will likely not be fully resolved by their guidance to be published later this year. The FDA released a draft of the guidance in May 2019.
Can RWE be ‘credible and reliable?’
“Whether observational, nonrandomized data can become credible enough to use is what we’re talking about. These are possibilities that need to be explained and better understood,” said Robert Temple, MD, deputy director for clinical science of the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Since the 1970s, the FDA has recognized historical controls as legitimate, so it’s possible [for RWE] to be credible. The big test is when is it credible and reliable enough [to assess efficacy]?” wondered Dr. Temple during a 2-day workshop on the topic held mid-February and organized by Duke University’s Margolis Center for Health Policy.
“We’re approaching an inflection point regarding how observational studies are generated and used, but our evidentiary standards will not lower, and it will be a case-by-case decision” by the agency as they review future RWE submissions, said John Concato, MD, the FDA’s associate director for real-world evidence, during the workshop.
“We are working toward guidance development, but also looking down the road to what we need to do to enable this,” said Dr. Concato. “It’s a complicated issue. If it was easy, it would have already been fixed.” He added that the agency will likely release a “portfolio” of guidance for submitting real-world data and RWE. Real-world data are raw information that, when analyzed, become RWE.
In short, the FDA seems headed toward guidance that won’t spell out a pathway that guarantees success using RWE but will at least open the door to consideration of this unprecedented application.
Not like flipping a switch
The guidance will not activate acceptance of RWE all at once. “It’s not like a light switch,” cautioned Adam Kroetsch, MPP, research director for biomedical innovation and regulatory policy at Duke-Margolis in Washington, D.C. “It’s an evolutionary process,” and the upcoming guidance will provide “just a little more clarity” on what sorts of best practices using RWE the FDA will find persuasive. “It’s hard for the FDA to clearly say what it’s looking for until they see some good examples,” Dr. Kroetsch said in an interview.
What will change is that drug sponsors can submit using RWE, and the FDA “will have a more open-minded view,” predicted Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, ScD, a workshop participant and chief of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “For the first time, a law required [the FDA] to take a serious look” at observational data for efficacy assessment.
“The FDA has had a bias against using RWE for evidence of efficacy but has long used it to understand drug safety. Now the FDA is trying to wrap its arms around how to best use RWE” for efficacy decisions, said Joseph S. Ross, MD, another workshop participant and professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The agency’s cautious approach is reassuring, Dr. Ross noted in an interview. “There was worry that the 21st Century Cures Act would open the door to allowing real-world data to be used in ways that weren’t very reliable. Very quickly, the FDA started trying to figure out the best ways to use these data in reasonable ways.”
Duplicating RCTs with RWE
To help better understand the potential use of RWE, the FDA sponsored several demonstration projects. Researchers presented results from three of these projects during the workshop in February. All three examined whether RWE, plugged into the design of an actual RCT, can produce roughly similar results when similar patients are used.
A generally consistent finding from the three demonstration projects was that “when the data are fit for purpose” the emulated or duplicated analyses with RWE “can come to similar conclusions” as the actual RCTs, said Dr. Schneeweiss, who leads one of the demonstration projects, RCT DUPLICATE.
At the workshop he reported results from RWE duplications of 20 different RCTs using insurance claims data from U.S. patients. The findings came from 10 duplications already reported in Circulation in December 2020 (including a duplication of the LEADER trial), and an additional 10 as yet unpublished RCT duplications. In the next few months, the researchers intend to assess a final group of 10 more RCT duplications.
Workshop participants also presented results from two other FDA demonstration projects: the OPERAND program run by the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials Center of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard; and the CERSI program based at Yale and the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. Both are smaller in scale than RCT DUPLICATE, incorporate lab data in addition to claims data, and in some cases test how well RWE can emulate RCTs that are not yet completed.
Collectively, results from these demonstration projects suggest that RWE can successfully emulate the results of an RCT, said Dr. Ross, a coinvestigator on the CERSI study. But the CERSI findings also highlighted how an RCT can fall short of clinical relevance.
“One of our most important findings was that RCTs don’t always represent real-world practice,” he said. His group attempted to replicate the 5,000-patient GRADE trial of four different drug options added to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. One of the four options included insulin glargine (Lantus), and the attempt to emulate the study with RWE hit the bump that no relevant real-world patients in their US claims database actually received the formulation.
That means the GRADE trial “is almost meaningless. It doesn’t reflect real-world practice,” Dr. Ross noted.
Results from the three demonstration projects “highlight the gaps we still have,” summed up Dr. Kroetsch. “They show where we need better data” from observational sources that function as well as data from RCTs.
Still, the demonstration project results are “an important step forward in establishing the validity of real-world evidence,” commented David Kerr, MBChB, an endocrinologist and director of research and innovation at the Sansum Diabetes Research Institute in Santa Barbara, Calif.
‘Target trials’ tether RWE
The target trial approach to designing an observational study is a key tool for boosting reliability and applicability of the results. The idea is to create a well-designed trial that could be the basis for a conventional RCT, and then use observational data to flesh out the target trial instead of collecting data from prospectively enrolled patients.
Designing observational studies that emulate target trials allows causal inferences, said Miguel A. Hernán, MD, DrPH, a professor of biostatistics and epidemiology at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston. Plugging real-world data into the framework of an appropriately designed target trial substantially cuts the risk of a biased analysis, he explained during the workshop.
However, the approach has limitations. The target trial must be a pragmatic trial, and the approach does not work for placebo-controlled trials, although it can accommodate a usual-care control arm. It also usually precludes patient blinding, testing treatments not used in routine practice, and close monitoring of patients in ways that are uncommon in usual care.
The target trial approach received broad endorsement during the workshop as the future for observational studies destined for efficacy consideration by the FDA.
“The idea of prespecifying a target trial is a really fantastic place to start,” commented Robert Ball, MD, deputy director of the FDA Office of Surveillance and Epidemiology. “There is still a whole set of questions once the trial is prespecified, but prespecification would be a fantastic step forward,” he said during the workshop.
Participants also endorsed other important steps to boost the value of observational studies for regulatory reviews, including preregistering the study on a site such as clinicaltrials.gov; being fully transparent about the origins of observational data; using data that match the needs of the target trial; not reviewing the data in advance to avoid cherry picking and gaming the analysis; and reporting neutral or negative results when they occur, something often not currently done for observational analyses.
But although there was clear progress and much agreement among thought leaders at the workshop, FDA representatives stressed caution in moving forward.
“No easy answer”
“With more experience, we can learn what works and what doesn’t work in generating valid results from observational studies,” said Dr. Concato. “Although the observational results have upside potential, we need to learn more. There is no easy answer, no checklist for fit-for-use data, no off-the-shelf study design, and no ideal analytic method.”
Dr. Concato acknowledged that the FDA’s goal is clear given the 2016 legislation. “The FDA is embracing our obligations under the 21st Century Cures Act to evaluate use of real-world data and real-world evidence.”
He also suggested that researchers “shy away from a false dichotomy of RCTs or observational studies and instead think about how and when RCTs and observational studies can be designed and conducted to yield trustworthy results.” Dr. Concato’s solution: “a taxonomy of interventional or noninterventional studies.”
“The FDA is under enormous pressure to embrace real-world evidence, both because of the economics of running RCTs and because of the availability of new observational data from electronic health records, wearable devices, claims, etc.,” said Dr. Kerr, who did not participate in the workshop but coauthored an editorial that calls for using real-world data in regulatory decisions for drugs and devices for diabetes. These factors create an “irresistible force” spurring the FDA to consider observational, noninterventional data.
“I think the FDA really wants this to go forward,” Dr. Kerr added in an interview. “The FDA keeps telling us that clinical trials do not have enough women or patients from minority groups. Real-world data is a way to address that. This will not be the death of RCTs, but this work shines a light on the deficiencies of RCTs and how the deficiencies can be dealt with.”
Dr. Kroetsch has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Schneeweiss has reported being a consultant to and holding equity in Aetion and receiving research funding from the FDA. Dr. Ross has reported receiving research funding from the FDA, Johnson & Johnson, and Medtronic. Dr. Hernán has reported being a consultant for Cytel. Dr. Kerr has reported being a consultant for Ascensia, EOFlow, Lifecare, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, and Voluntis. Dr. Temple, Dr. Concato, and Dr. Ball are FDA employees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2016, results from the LEADER trial of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes helped jump-start awareness of the potential role of this new class of drugs, the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists, for reducing cardiovascular events. The randomized, placebo-controlled trial enrolled more than 9000 patients at more than 400 sites in over 30 countries, and took nearly 6 years from the start of patient enrollment to publication of the landmark results.
In December 2020, an independent team of researchers published results from a study with a design identical to LEADER, but used data that came not from a massive, global, years-long trial but from already-existing numbers culled from three large U.S. insurance claim databases. The result of this emulation using real-world data was virtually identical to what the actual trial showed, replicating both the direction and statistical significance of the original finding of the randomized, controlled trial (RCT).
What if research proved that this sort of RCT emulation could reliably be done on a regular basis? What might it mean for regulatory decisions on drugs and devices that historically have been based entirely on efficacy evidence from RCTs?
Making the most of a sea of observational data
Medicine in the United States has become increasingly awash in a sea of observational data collected from sources that include electronic health records, insurance claims, and increasingly, personal-health monitoring devices.
The Food and Drug Administration is now in the process of trying to figure out how it can legitimately harness this tsunami of real-world data to make efficacy decisions, essentially creating a new category of evidence to complement traditional data from randomized trials. It’s an opportunity that agency staff and their outside advisors have been keen to seize, especially given the soaring cost of prospective, randomized trials.
Recognition of this untapped resource in part led to a key initiative, among many others, included in the 21st Century Cures Act, passed in December 2016. Among the Act’s mandates was that, by the end of 2021, the FDA would issue guidance on when drug sponsors could use real-world evidence (RWE) to either help support a new indication for an already approved drug or help satisfy postapproval study requirements.
The initiative recognizes that this approach is not appropriate for initial drug approvals, which remain exclusively reliant on evidence from RCTs. Instead, it seems best suited to support expanding indications for already approved drugs.
Although FDA staff have made progress in identifying the challenges and broadening their understanding of how to best handle real-world data that come from observing patients in routine practice, agency leaders stress that this complex issue will likely not be fully resolved by their guidance to be published later this year. The FDA released a draft of the guidance in May 2019.
Can RWE be ‘credible and reliable?’
“Whether observational, nonrandomized data can become credible enough to use is what we’re talking about. These are possibilities that need to be explained and better understood,” said Robert Temple, MD, deputy director for clinical science of the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Since the 1970s, the FDA has recognized historical controls as legitimate, so it’s possible [for RWE] to be credible. The big test is when is it credible and reliable enough [to assess efficacy]?” wondered Dr. Temple during a 2-day workshop on the topic held mid-February and organized by Duke University’s Margolis Center for Health Policy.
“We’re approaching an inflection point regarding how observational studies are generated and used, but our evidentiary standards will not lower, and it will be a case-by-case decision” by the agency as they review future RWE submissions, said John Concato, MD, the FDA’s associate director for real-world evidence, during the workshop.
“We are working toward guidance development, but also looking down the road to what we need to do to enable this,” said Dr. Concato. “It’s a complicated issue. If it was easy, it would have already been fixed.” He added that the agency will likely release a “portfolio” of guidance for submitting real-world data and RWE. Real-world data are raw information that, when analyzed, become RWE.
In short, the FDA seems headed toward guidance that won’t spell out a pathway that guarantees success using RWE but will at least open the door to consideration of this unprecedented application.
Not like flipping a switch
The guidance will not activate acceptance of RWE all at once. “It’s not like a light switch,” cautioned Adam Kroetsch, MPP, research director for biomedical innovation and regulatory policy at Duke-Margolis in Washington, D.C. “It’s an evolutionary process,” and the upcoming guidance will provide “just a little more clarity” on what sorts of best practices using RWE the FDA will find persuasive. “It’s hard for the FDA to clearly say what it’s looking for until they see some good examples,” Dr. Kroetsch said in an interview.
What will change is that drug sponsors can submit using RWE, and the FDA “will have a more open-minded view,” predicted Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, ScD, a workshop participant and chief of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “For the first time, a law required [the FDA] to take a serious look” at observational data for efficacy assessment.
“The FDA has had a bias against using RWE for evidence of efficacy but has long used it to understand drug safety. Now the FDA is trying to wrap its arms around how to best use RWE” for efficacy decisions, said Joseph S. Ross, MD, another workshop participant and professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The agency’s cautious approach is reassuring, Dr. Ross noted in an interview. “There was worry that the 21st Century Cures Act would open the door to allowing real-world data to be used in ways that weren’t very reliable. Very quickly, the FDA started trying to figure out the best ways to use these data in reasonable ways.”
Duplicating RCTs with RWE
To help better understand the potential use of RWE, the FDA sponsored several demonstration projects. Researchers presented results from three of these projects during the workshop in February. All three examined whether RWE, plugged into the design of an actual RCT, can produce roughly similar results when similar patients are used.
A generally consistent finding from the three demonstration projects was that “when the data are fit for purpose” the emulated or duplicated analyses with RWE “can come to similar conclusions” as the actual RCTs, said Dr. Schneeweiss, who leads one of the demonstration projects, RCT DUPLICATE.
At the workshop he reported results from RWE duplications of 20 different RCTs using insurance claims data from U.S. patients. The findings came from 10 duplications already reported in Circulation in December 2020 (including a duplication of the LEADER trial), and an additional 10 as yet unpublished RCT duplications. In the next few months, the researchers intend to assess a final group of 10 more RCT duplications.
Workshop participants also presented results from two other FDA demonstration projects: the OPERAND program run by the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials Center of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard; and the CERSI program based at Yale and the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. Both are smaller in scale than RCT DUPLICATE, incorporate lab data in addition to claims data, and in some cases test how well RWE can emulate RCTs that are not yet completed.
Collectively, results from these demonstration projects suggest that RWE can successfully emulate the results of an RCT, said Dr. Ross, a coinvestigator on the CERSI study. But the CERSI findings also highlighted how an RCT can fall short of clinical relevance.
“One of our most important findings was that RCTs don’t always represent real-world practice,” he said. His group attempted to replicate the 5,000-patient GRADE trial of four different drug options added to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. One of the four options included insulin glargine (Lantus), and the attempt to emulate the study with RWE hit the bump that no relevant real-world patients in their US claims database actually received the formulation.
That means the GRADE trial “is almost meaningless. It doesn’t reflect real-world practice,” Dr. Ross noted.
Results from the three demonstration projects “highlight the gaps we still have,” summed up Dr. Kroetsch. “They show where we need better data” from observational sources that function as well as data from RCTs.
Still, the demonstration project results are “an important step forward in establishing the validity of real-world evidence,” commented David Kerr, MBChB, an endocrinologist and director of research and innovation at the Sansum Diabetes Research Institute in Santa Barbara, Calif.
‘Target trials’ tether RWE
The target trial approach to designing an observational study is a key tool for boosting reliability and applicability of the results. The idea is to create a well-designed trial that could be the basis for a conventional RCT, and then use observational data to flesh out the target trial instead of collecting data from prospectively enrolled patients.
Designing observational studies that emulate target trials allows causal inferences, said Miguel A. Hernán, MD, DrPH, a professor of biostatistics and epidemiology at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston. Plugging real-world data into the framework of an appropriately designed target trial substantially cuts the risk of a biased analysis, he explained during the workshop.
However, the approach has limitations. The target trial must be a pragmatic trial, and the approach does not work for placebo-controlled trials, although it can accommodate a usual-care control arm. It also usually precludes patient blinding, testing treatments not used in routine practice, and close monitoring of patients in ways that are uncommon in usual care.
The target trial approach received broad endorsement during the workshop as the future for observational studies destined for efficacy consideration by the FDA.
“The idea of prespecifying a target trial is a really fantastic place to start,” commented Robert Ball, MD, deputy director of the FDA Office of Surveillance and Epidemiology. “There is still a whole set of questions once the trial is prespecified, but prespecification would be a fantastic step forward,” he said during the workshop.
Participants also endorsed other important steps to boost the value of observational studies for regulatory reviews, including preregistering the study on a site such as clinicaltrials.gov; being fully transparent about the origins of observational data; using data that match the needs of the target trial; not reviewing the data in advance to avoid cherry picking and gaming the analysis; and reporting neutral or negative results when they occur, something often not currently done for observational analyses.
But although there was clear progress and much agreement among thought leaders at the workshop, FDA representatives stressed caution in moving forward.
“No easy answer”
“With more experience, we can learn what works and what doesn’t work in generating valid results from observational studies,” said Dr. Concato. “Although the observational results have upside potential, we need to learn more. There is no easy answer, no checklist for fit-for-use data, no off-the-shelf study design, and no ideal analytic method.”
Dr. Concato acknowledged that the FDA’s goal is clear given the 2016 legislation. “The FDA is embracing our obligations under the 21st Century Cures Act to evaluate use of real-world data and real-world evidence.”
He also suggested that researchers “shy away from a false dichotomy of RCTs or observational studies and instead think about how and when RCTs and observational studies can be designed and conducted to yield trustworthy results.” Dr. Concato’s solution: “a taxonomy of interventional or noninterventional studies.”
“The FDA is under enormous pressure to embrace real-world evidence, both because of the economics of running RCTs and because of the availability of new observational data from electronic health records, wearable devices, claims, etc.,” said Dr. Kerr, who did not participate in the workshop but coauthored an editorial that calls for using real-world data in regulatory decisions for drugs and devices for diabetes. These factors create an “irresistible force” spurring the FDA to consider observational, noninterventional data.
“I think the FDA really wants this to go forward,” Dr. Kerr added in an interview. “The FDA keeps telling us that clinical trials do not have enough women or patients from minority groups. Real-world data is a way to address that. This will not be the death of RCTs, but this work shines a light on the deficiencies of RCTs and how the deficiencies can be dealt with.”
Dr. Kroetsch has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Schneeweiss has reported being a consultant to and holding equity in Aetion and receiving research funding from the FDA. Dr. Ross has reported receiving research funding from the FDA, Johnson & Johnson, and Medtronic. Dr. Hernán has reported being a consultant for Cytel. Dr. Kerr has reported being a consultant for Ascensia, EOFlow, Lifecare, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, and Voluntis. Dr. Temple, Dr. Concato, and Dr. Ball are FDA employees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Fauci: Feds may ease indoor mask mandates soon
Federal guidance on indoor mask use may change soon, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said on May 9.
He was asked whether it’s time to start relaxing indoor mask requirements.
“I think so, and I think you’re going to probably be seeing that as we go along and as more people get vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said on ABC News’s This Week.Nearly 150 million adults in the United States – or about 58% of the adult population – have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the latest CDC tally. About 113 million adults, or 44%, are considered fully vaccinated.
“The CDC will be, you know, almost in real time … updating their recommendations and their guidelines,” Dr. Fauci said.
In April, the CDC relaxed its guidance for those who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Those who have gotten a shot don’t need to wear a mask outdoors or in small indoor gatherings with other vaccinated people, but both vaccinated and unvaccinated people are still advised to wear masks in indoor public spaces.
“We do need to start being more liberal as we get more people vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said. “As you get more people vaccinated, the number of cases per day will absolutely go down.”
The United States is averaging about 43,000 cases per day, he said, adding that the cases need to be “much, much lower.” When the case numbers drop and vaccination numbers increase, the risk of infection will fall dramatically indoors and outdoors, he said.
Even after the pandemic, though, wearing masks could become a seasonal habit, Dr. Fauci said May 9 on NBC News’s Meet the Press.“I think people have gotten used to the fact that wearing masks, clearly if you look at the data, it diminishes respiratory diseases. We’ve had practically a nonexistent flu season this year,” he said.
“So it is conceivable that as we go on, a year or 2 or more from now, that during certain seasonal periods when you have respiratory-borne viruses like the flu, people might actually elect to wear masks to diminish the likelihood that you’ll spread these respiratory-borne diseases,” he said.
Dr. Fauci was asked about indoor mask guidelines on May 9 after former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said face mask requirements should be relaxed.
“Certainly outdoors, we shouldn’t be putting limits on gatherings anymore,” Dr. Gottlieb said on CBS News’s Face the Nation.“The states where prevalence is low, vaccination rates are high, we have good testing in place, and we’re identifying infections, I think we could start lifting these restrictions indoors as well, on a broad basis,” he said.
Lifting pandemic-related restrictions in areas where they’re no longer necessary could also encourage people to implement them again if cases increase during future surges, such as this fall or winter, Dr. Gottlieb said.
At the same time, Americans should continue to follow CDC guidance and wait for new guidelines before changing their indoor mask use, Jeffrey Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said on CNN’s State of the Union on May 9.
“We all want to get back to a normal lifestyle,” he said. “I think we’re on the path to do that, but stay disciplined, and let’s take advantage of the new privilege of being vaccinated and not wearing masks outdoors, for example, unless you’re in a crowded place.”
Mr. Zients pointed to President Joe Biden’s goal for 70% of adults to receive at least one vaccine dose by July 4.
“As we all move toward that 70% goal, there will be more and more advantages to being vaccinated,” he said. “And if you’re not vaccinated, you’re not protected.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Federal guidance on indoor mask use may change soon, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said on May 9.
He was asked whether it’s time to start relaxing indoor mask requirements.
“I think so, and I think you’re going to probably be seeing that as we go along and as more people get vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said on ABC News’s This Week.Nearly 150 million adults in the United States – or about 58% of the adult population – have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the latest CDC tally. About 113 million adults, or 44%, are considered fully vaccinated.
“The CDC will be, you know, almost in real time … updating their recommendations and their guidelines,” Dr. Fauci said.
In April, the CDC relaxed its guidance for those who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Those who have gotten a shot don’t need to wear a mask outdoors or in small indoor gatherings with other vaccinated people, but both vaccinated and unvaccinated people are still advised to wear masks in indoor public spaces.
“We do need to start being more liberal as we get more people vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said. “As you get more people vaccinated, the number of cases per day will absolutely go down.”
The United States is averaging about 43,000 cases per day, he said, adding that the cases need to be “much, much lower.” When the case numbers drop and vaccination numbers increase, the risk of infection will fall dramatically indoors and outdoors, he said.
Even after the pandemic, though, wearing masks could become a seasonal habit, Dr. Fauci said May 9 on NBC News’s Meet the Press.“I think people have gotten used to the fact that wearing masks, clearly if you look at the data, it diminishes respiratory diseases. We’ve had practically a nonexistent flu season this year,” he said.
“So it is conceivable that as we go on, a year or 2 or more from now, that during certain seasonal periods when you have respiratory-borne viruses like the flu, people might actually elect to wear masks to diminish the likelihood that you’ll spread these respiratory-borne diseases,” he said.
Dr. Fauci was asked about indoor mask guidelines on May 9 after former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said face mask requirements should be relaxed.
“Certainly outdoors, we shouldn’t be putting limits on gatherings anymore,” Dr. Gottlieb said on CBS News’s Face the Nation.“The states where prevalence is low, vaccination rates are high, we have good testing in place, and we’re identifying infections, I think we could start lifting these restrictions indoors as well, on a broad basis,” he said.
Lifting pandemic-related restrictions in areas where they’re no longer necessary could also encourage people to implement them again if cases increase during future surges, such as this fall or winter, Dr. Gottlieb said.
At the same time, Americans should continue to follow CDC guidance and wait for new guidelines before changing their indoor mask use, Jeffrey Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said on CNN’s State of the Union on May 9.
“We all want to get back to a normal lifestyle,” he said. “I think we’re on the path to do that, but stay disciplined, and let’s take advantage of the new privilege of being vaccinated and not wearing masks outdoors, for example, unless you’re in a crowded place.”
Mr. Zients pointed to President Joe Biden’s goal for 70% of adults to receive at least one vaccine dose by July 4.
“As we all move toward that 70% goal, there will be more and more advantages to being vaccinated,” he said. “And if you’re not vaccinated, you’re not protected.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Federal guidance on indoor mask use may change soon, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said on May 9.
He was asked whether it’s time to start relaxing indoor mask requirements.
“I think so, and I think you’re going to probably be seeing that as we go along and as more people get vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said on ABC News’s This Week.Nearly 150 million adults in the United States – or about 58% of the adult population – have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the latest CDC tally. About 113 million adults, or 44%, are considered fully vaccinated.
“The CDC will be, you know, almost in real time … updating their recommendations and their guidelines,” Dr. Fauci said.
In April, the CDC relaxed its guidance for those who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Those who have gotten a shot don’t need to wear a mask outdoors or in small indoor gatherings with other vaccinated people, but both vaccinated and unvaccinated people are still advised to wear masks in indoor public spaces.
“We do need to start being more liberal as we get more people vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said. “As you get more people vaccinated, the number of cases per day will absolutely go down.”
The United States is averaging about 43,000 cases per day, he said, adding that the cases need to be “much, much lower.” When the case numbers drop and vaccination numbers increase, the risk of infection will fall dramatically indoors and outdoors, he said.
Even after the pandemic, though, wearing masks could become a seasonal habit, Dr. Fauci said May 9 on NBC News’s Meet the Press.“I think people have gotten used to the fact that wearing masks, clearly if you look at the data, it diminishes respiratory diseases. We’ve had practically a nonexistent flu season this year,” he said.
“So it is conceivable that as we go on, a year or 2 or more from now, that during certain seasonal periods when you have respiratory-borne viruses like the flu, people might actually elect to wear masks to diminish the likelihood that you’ll spread these respiratory-borne diseases,” he said.
Dr. Fauci was asked about indoor mask guidelines on May 9 after former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said face mask requirements should be relaxed.
“Certainly outdoors, we shouldn’t be putting limits on gatherings anymore,” Dr. Gottlieb said on CBS News’s Face the Nation.“The states where prevalence is low, vaccination rates are high, we have good testing in place, and we’re identifying infections, I think we could start lifting these restrictions indoors as well, on a broad basis,” he said.
Lifting pandemic-related restrictions in areas where they’re no longer necessary could also encourage people to implement them again if cases increase during future surges, such as this fall or winter, Dr. Gottlieb said.
At the same time, Americans should continue to follow CDC guidance and wait for new guidelines before changing their indoor mask use, Jeffrey Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said on CNN’s State of the Union on May 9.
“We all want to get back to a normal lifestyle,” he said. “I think we’re on the path to do that, but stay disciplined, and let’s take advantage of the new privilege of being vaccinated and not wearing masks outdoors, for example, unless you’re in a crowded place.”
Mr. Zients pointed to President Joe Biden’s goal for 70% of adults to receive at least one vaccine dose by July 4.
“As we all move toward that 70% goal, there will be more and more advantages to being vaccinated,” he said. “And if you’re not vaccinated, you’re not protected.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA moves to ban menthol in cigarettes
The Food and Drug Administration said that within a year it will ban menthol in cigarettes and ban all flavors including menthol in cigars.
Menthol makes it easier to start smoking, and also enhances the effects of nicotine, making it more addictive and harder to quit, the FDA said in announcing its actions on Thursday.
Nineteen organizations – including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, American Medical Association, American Heart Association, and the National Medical Association – have pushed the FDA to ban menthol for years. The agency banned all flavors in cigarettes in 2009 but did not take any action against menthol. In 2013, the groups filed a petition demanding that the FDA ban menthol, too. The agency responded months later with a notice that it would start the process.
But it never took any action. Action on Smoking and Health and the African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council, later joined by the AMA and the NMA, sued in 2020 to compel the agency to do something. Now it has finally agreed to act.
The African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council welcomed the move but said the fight is not over and encouraged tobacco control activists to fight to ban menthol tobacco products at the local, state and federal level. “We know that this rule-making process could take years and we know that the tobacco industry will continue to do everything in their power to derail any attempt to remove their deadly products from the market,” Phillip Gardiner, MD, council cochair, said in a statement.
The AMA is urging the FDA to quickly implement the ban and remove the products “without further delay,” AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement.
“FDA’s long-awaited decision to take action to eliminate menthol flavoring in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars ends a decades-long deference to the tobacco industry, which has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to profit from products that result in death,” Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, said in her own statement.
Ms. Lacasse said banning menthol will help eliminate health disparities. She said 86% of Black people who smoke use menthol cigarettes, compared with 46% of Hispanic people who smoke, 39% of Asian people who smoke, and 29% of White people who smoke. “FDA’s actions today send a clear message that Big Tobacco’s strategy to profit off addicting Black communities will no longer be tolerated,” she said.
Not all groups are on board, however. The American Civil Liberties Union and several other organizations wrote to the country’s top health officials urging them to reconsider.
“Such a ban will trigger criminal penalties which will disproportionately impact people of color, as well as prioritize criminalization over public health and harm reduction,” the letter says. “A ban will also lead to unconstitutional policing and other negative interactions with local law enforcement.”
The letter calls the proposed ban “well intentioned,” but said any effort to reduce death and disease from tobacco “must avoid solutions that will create yet another reason for armed police to engage citizens on the street based on pretext or conduct that does not pose a threat to public safety.”
Instead of a ban, the organizations said, policy makers should consider increased education for adults and minors, stop-smoking programs, and increased funding for health centers in communities of color.
The Biden administration, however, pressed the point that banning menthol will bring many positives. Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD said in a statement that banning menthol “will help significantly reduce youth initiation, increase the chances of smoking cessation among current smokers, and address health disparities experienced by communities of color, low-income populations, and LGBTQ-plus individuals, all of whom are far more likely to use these tobacco products.”
The FDA cited data showing that, in the first year or so after a ban goes into effect, an additional 923,000 smokers would quit, including 230,000 African Americans. Another study suggests that 633,000 deaths would be averted, including 237,000 Black Americans.
Dr. Woodcock added that, “armed with strong scientific evidence, and with full support from the [Biden] administration, we believe these actions will launch us on a trajectory toward ending tobacco-related disease and death in the U.S.”
The FDA estimates that 18.6 million Americans who are current smokers use menthol cigarettes, with a disproportionately high number being Black people. Menthol cigarette use among Black and Hispanic youth increased from 2011 to 2018, but declined for non-Hispanic White youth.
Flavored mass-produced cigars and cigarillos are disproportionately popular among youth, especially non-Hispanic Black high school students, who in 2020 reported past 30-day cigar smoking at levels twice as high as their White counterparts, said the FDA. Three-quarters of 12- to 17-year-olds reported they smoke cigars because they like the flavors. In 2020, more young people tried a cigar every day than tried a cigarette, reports the agency.
“This long-overdue decision will protect future generations of young people from nicotine addiction, especially Black children and communities, which have disproportionately suffered from menthol tobacco use due to targeted efforts from the tobacco industry,” Lee Savio Beers, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a statement.
The FDA’s announcement “is only a first step that must be followed with urgent, comprehensive action to remove these flavored products from the market,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration said that within a year it will ban menthol in cigarettes and ban all flavors including menthol in cigars.
Menthol makes it easier to start smoking, and also enhances the effects of nicotine, making it more addictive and harder to quit, the FDA said in announcing its actions on Thursday.
Nineteen organizations – including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, American Medical Association, American Heart Association, and the National Medical Association – have pushed the FDA to ban menthol for years. The agency banned all flavors in cigarettes in 2009 but did not take any action against menthol. In 2013, the groups filed a petition demanding that the FDA ban menthol, too. The agency responded months later with a notice that it would start the process.
But it never took any action. Action on Smoking and Health and the African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council, later joined by the AMA and the NMA, sued in 2020 to compel the agency to do something. Now it has finally agreed to act.
The African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council welcomed the move but said the fight is not over and encouraged tobacco control activists to fight to ban menthol tobacco products at the local, state and federal level. “We know that this rule-making process could take years and we know that the tobacco industry will continue to do everything in their power to derail any attempt to remove their deadly products from the market,” Phillip Gardiner, MD, council cochair, said in a statement.
The AMA is urging the FDA to quickly implement the ban and remove the products “without further delay,” AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement.
“FDA’s long-awaited decision to take action to eliminate menthol flavoring in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars ends a decades-long deference to the tobacco industry, which has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to profit from products that result in death,” Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, said in her own statement.
Ms. Lacasse said banning menthol will help eliminate health disparities. She said 86% of Black people who smoke use menthol cigarettes, compared with 46% of Hispanic people who smoke, 39% of Asian people who smoke, and 29% of White people who smoke. “FDA’s actions today send a clear message that Big Tobacco’s strategy to profit off addicting Black communities will no longer be tolerated,” she said.
Not all groups are on board, however. The American Civil Liberties Union and several other organizations wrote to the country’s top health officials urging them to reconsider.
“Such a ban will trigger criminal penalties which will disproportionately impact people of color, as well as prioritize criminalization over public health and harm reduction,” the letter says. “A ban will also lead to unconstitutional policing and other negative interactions with local law enforcement.”
The letter calls the proposed ban “well intentioned,” but said any effort to reduce death and disease from tobacco “must avoid solutions that will create yet another reason for armed police to engage citizens on the street based on pretext or conduct that does not pose a threat to public safety.”
Instead of a ban, the organizations said, policy makers should consider increased education for adults and minors, stop-smoking programs, and increased funding for health centers in communities of color.
The Biden administration, however, pressed the point that banning menthol will bring many positives. Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD said in a statement that banning menthol “will help significantly reduce youth initiation, increase the chances of smoking cessation among current smokers, and address health disparities experienced by communities of color, low-income populations, and LGBTQ-plus individuals, all of whom are far more likely to use these tobacco products.”
The FDA cited data showing that, in the first year or so after a ban goes into effect, an additional 923,000 smokers would quit, including 230,000 African Americans. Another study suggests that 633,000 deaths would be averted, including 237,000 Black Americans.
Dr. Woodcock added that, “armed with strong scientific evidence, and with full support from the [Biden] administration, we believe these actions will launch us on a trajectory toward ending tobacco-related disease and death in the U.S.”
The FDA estimates that 18.6 million Americans who are current smokers use menthol cigarettes, with a disproportionately high number being Black people. Menthol cigarette use among Black and Hispanic youth increased from 2011 to 2018, but declined for non-Hispanic White youth.
Flavored mass-produced cigars and cigarillos are disproportionately popular among youth, especially non-Hispanic Black high school students, who in 2020 reported past 30-day cigar smoking at levels twice as high as their White counterparts, said the FDA. Three-quarters of 12- to 17-year-olds reported they smoke cigars because they like the flavors. In 2020, more young people tried a cigar every day than tried a cigarette, reports the agency.
“This long-overdue decision will protect future generations of young people from nicotine addiction, especially Black children and communities, which have disproportionately suffered from menthol tobacco use due to targeted efforts from the tobacco industry,” Lee Savio Beers, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a statement.
The FDA’s announcement “is only a first step that must be followed with urgent, comprehensive action to remove these flavored products from the market,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration said that within a year it will ban menthol in cigarettes and ban all flavors including menthol in cigars.
Menthol makes it easier to start smoking, and also enhances the effects of nicotine, making it more addictive and harder to quit, the FDA said in announcing its actions on Thursday.
Nineteen organizations – including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, American Medical Association, American Heart Association, and the National Medical Association – have pushed the FDA to ban menthol for years. The agency banned all flavors in cigarettes in 2009 but did not take any action against menthol. In 2013, the groups filed a petition demanding that the FDA ban menthol, too. The agency responded months later with a notice that it would start the process.
But it never took any action. Action on Smoking and Health and the African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council, later joined by the AMA and the NMA, sued in 2020 to compel the agency to do something. Now it has finally agreed to act.
The African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council welcomed the move but said the fight is not over and encouraged tobacco control activists to fight to ban menthol tobacco products at the local, state and federal level. “We know that this rule-making process could take years and we know that the tobacco industry will continue to do everything in their power to derail any attempt to remove their deadly products from the market,” Phillip Gardiner, MD, council cochair, said in a statement.
The AMA is urging the FDA to quickly implement the ban and remove the products “without further delay,” AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement.
“FDA’s long-awaited decision to take action to eliminate menthol flavoring in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars ends a decades-long deference to the tobacco industry, which has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to profit from products that result in death,” Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, said in her own statement.
Ms. Lacasse said banning menthol will help eliminate health disparities. She said 86% of Black people who smoke use menthol cigarettes, compared with 46% of Hispanic people who smoke, 39% of Asian people who smoke, and 29% of White people who smoke. “FDA’s actions today send a clear message that Big Tobacco’s strategy to profit off addicting Black communities will no longer be tolerated,” she said.
Not all groups are on board, however. The American Civil Liberties Union and several other organizations wrote to the country’s top health officials urging them to reconsider.
“Such a ban will trigger criminal penalties which will disproportionately impact people of color, as well as prioritize criminalization over public health and harm reduction,” the letter says. “A ban will also lead to unconstitutional policing and other negative interactions with local law enforcement.”
The letter calls the proposed ban “well intentioned,” but said any effort to reduce death and disease from tobacco “must avoid solutions that will create yet another reason for armed police to engage citizens on the street based on pretext or conduct that does not pose a threat to public safety.”
Instead of a ban, the organizations said, policy makers should consider increased education for adults and minors, stop-smoking programs, and increased funding for health centers in communities of color.
The Biden administration, however, pressed the point that banning menthol will bring many positives. Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD said in a statement that banning menthol “will help significantly reduce youth initiation, increase the chances of smoking cessation among current smokers, and address health disparities experienced by communities of color, low-income populations, and LGBTQ-plus individuals, all of whom are far more likely to use these tobacco products.”
The FDA cited data showing that, in the first year or so after a ban goes into effect, an additional 923,000 smokers would quit, including 230,000 African Americans. Another study suggests that 633,000 deaths would be averted, including 237,000 Black Americans.
Dr. Woodcock added that, “armed with strong scientific evidence, and with full support from the [Biden] administration, we believe these actions will launch us on a trajectory toward ending tobacco-related disease and death in the U.S.”
The FDA estimates that 18.6 million Americans who are current smokers use menthol cigarettes, with a disproportionately high number being Black people. Menthol cigarette use among Black and Hispanic youth increased from 2011 to 2018, but declined for non-Hispanic White youth.
Flavored mass-produced cigars and cigarillos are disproportionately popular among youth, especially non-Hispanic Black high school students, who in 2020 reported past 30-day cigar smoking at levels twice as high as their White counterparts, said the FDA. Three-quarters of 12- to 17-year-olds reported they smoke cigars because they like the flavors. In 2020, more young people tried a cigar every day than tried a cigarette, reports the agency.
“This long-overdue decision will protect future generations of young people from nicotine addiction, especially Black children and communities, which have disproportionately suffered from menthol tobacco use due to targeted efforts from the tobacco industry,” Lee Savio Beers, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a statement.
The FDA’s announcement “is only a first step that must be followed with urgent, comprehensive action to remove these flavored products from the market,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC guidelines coming on long COVID
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is finalizing new guidelines to help clinicians diagnose and manage long COVID, or postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a day-long congressional hearing on April 28, John Brooks, MD, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention, testified that the guidelines were going through the clearance process at the agency, but would be forthcoming.
“They should be coming out very shortly,” Dr. Brooks said.
The guidelines, which were developed in collaboration with newly established long-COVID clinics and patient advocacy groups, will “illustrate how to diagnose and begin to pull together what we know about management,” of the complex condition, he said.
For many doctors and patients who are struggling to understand symptoms that persist for months after the initial viral infection, the guidelines can’t come soon enough.
National Institutes of Health Director Francis Collins, MD, PhD, who also testified at the hearing, estimated that as many as 3 million people could be left with chronic health problems after even mild COVID infections.
“I can’t overstate how serious this issue is for the health of our nation,” he said.
Dr. Collins said his estimate was based on studies showing that roughly 10% of people who get COVID could be affected by this and whose “long-term course is uncertain,” he said. So far, more than 32 million Americans are known to have been infected with the new coronavirus.
“We need to make sure we put our arms around them and bring answers and care to them,” said Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.), chairwoman of the Subcommittee on Health.
Jennifer Possick, MD, who directs the post-COVID recovery program at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital, testified that the tidal wave of patients she and her colleagues were seeing was overwhelming.
“We are a well-resourced program at an academic medical center, but we are swamped by the need in our community. This year, we have seen more patients with post COVID-19 conditions in our clinic alone than we have new cases of asthma and COPD combined,” she said. “The magnitude of the challenge is daunting.”
Dr. Possick estimated that there are “over 60” clinics in the United States that have started to treat long-COVID patients, but said they are grassroots efforts and all very different from each other.
“Whoever had the resources, had the time, [and] was able to take the initiative and forge to the relationships because most of them are multidisciplinary, did so,” she said.
Patients testify
Several representatives shared moving personal stories of loved ones or staffers who remained ill months after a COVID diagnosis.
Rep. Ann Kuster, from New Hampshire, talked about her 34-year-old niece, a member of the U.S. Ski Team, who had COVID just over a year ago and “continues to struggle with everything, even the simplest activities of daily living” she said. “She has to choose between taking a shower or making dinner. I’m so proud of her for hanging in there.”
Long-COVID patients invited to testify by the subcommittee described months of disability that left them with soaring medical bills and no ability to work to pay them.
“I am now a poor, Black, disabled woman, living with long COVID,” said Chimere Smith, who said she had been a school teacher in Baltimore. “Saying it aloud makes it no more easy to accept.”
She said COVID had affected her ability to think clearly and caused debilitating fatigue, which prevented her from working. She said she lost her vision for almost 5 months because doctors misdiagnosed a cataract caused by long COVID as dry eye.
“If I did not have a loving family, I [would] be speaking to you today [from] my car, the only property I now own.”
Ms. Smith said that long-COVID clinics, which are mostly housed within academic medical centers, were not going to be accessible for all long-haulers, who are disproportionately women of color. She has started a clinic, based out of her church, to help other patients from her community.
“No one wants to hear that long COVID has decimated my life or the lives of other black women in less than a year,” Ms. Smith said. “We’ve just been waiting and hoping for compassionate doctors and politicians who would acknowledge us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is finalizing new guidelines to help clinicians diagnose and manage long COVID, or postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a day-long congressional hearing on April 28, John Brooks, MD, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention, testified that the guidelines were going through the clearance process at the agency, but would be forthcoming.
“They should be coming out very shortly,” Dr. Brooks said.
The guidelines, which were developed in collaboration with newly established long-COVID clinics and patient advocacy groups, will “illustrate how to diagnose and begin to pull together what we know about management,” of the complex condition, he said.
For many doctors and patients who are struggling to understand symptoms that persist for months after the initial viral infection, the guidelines can’t come soon enough.
National Institutes of Health Director Francis Collins, MD, PhD, who also testified at the hearing, estimated that as many as 3 million people could be left with chronic health problems after even mild COVID infections.
“I can’t overstate how serious this issue is for the health of our nation,” he said.
Dr. Collins said his estimate was based on studies showing that roughly 10% of people who get COVID could be affected by this and whose “long-term course is uncertain,” he said. So far, more than 32 million Americans are known to have been infected with the new coronavirus.
“We need to make sure we put our arms around them and bring answers and care to them,” said Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.), chairwoman of the Subcommittee on Health.
Jennifer Possick, MD, who directs the post-COVID recovery program at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital, testified that the tidal wave of patients she and her colleagues were seeing was overwhelming.
“We are a well-resourced program at an academic medical center, but we are swamped by the need in our community. This year, we have seen more patients with post COVID-19 conditions in our clinic alone than we have new cases of asthma and COPD combined,” she said. “The magnitude of the challenge is daunting.”
Dr. Possick estimated that there are “over 60” clinics in the United States that have started to treat long-COVID patients, but said they are grassroots efforts and all very different from each other.
“Whoever had the resources, had the time, [and] was able to take the initiative and forge to the relationships because most of them are multidisciplinary, did so,” she said.
Patients testify
Several representatives shared moving personal stories of loved ones or staffers who remained ill months after a COVID diagnosis.
Rep. Ann Kuster, from New Hampshire, talked about her 34-year-old niece, a member of the U.S. Ski Team, who had COVID just over a year ago and “continues to struggle with everything, even the simplest activities of daily living” she said. “She has to choose between taking a shower or making dinner. I’m so proud of her for hanging in there.”
Long-COVID patients invited to testify by the subcommittee described months of disability that left them with soaring medical bills and no ability to work to pay them.
“I am now a poor, Black, disabled woman, living with long COVID,” said Chimere Smith, who said she had been a school teacher in Baltimore. “Saying it aloud makes it no more easy to accept.”
She said COVID had affected her ability to think clearly and caused debilitating fatigue, which prevented her from working. She said she lost her vision for almost 5 months because doctors misdiagnosed a cataract caused by long COVID as dry eye.
“If I did not have a loving family, I [would] be speaking to you today [from] my car, the only property I now own.”
Ms. Smith said that long-COVID clinics, which are mostly housed within academic medical centers, were not going to be accessible for all long-haulers, who are disproportionately women of color. She has started a clinic, based out of her church, to help other patients from her community.
“No one wants to hear that long COVID has decimated my life or the lives of other black women in less than a year,” Ms. Smith said. “We’ve just been waiting and hoping for compassionate doctors and politicians who would acknowledge us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is finalizing new guidelines to help clinicians diagnose and manage long COVID, or postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a day-long congressional hearing on April 28, John Brooks, MD, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention, testified that the guidelines were going through the clearance process at the agency, but would be forthcoming.
“They should be coming out very shortly,” Dr. Brooks said.
The guidelines, which were developed in collaboration with newly established long-COVID clinics and patient advocacy groups, will “illustrate how to diagnose and begin to pull together what we know about management,” of the complex condition, he said.
For many doctors and patients who are struggling to understand symptoms that persist for months after the initial viral infection, the guidelines can’t come soon enough.
National Institutes of Health Director Francis Collins, MD, PhD, who also testified at the hearing, estimated that as many as 3 million people could be left with chronic health problems after even mild COVID infections.
“I can’t overstate how serious this issue is for the health of our nation,” he said.
Dr. Collins said his estimate was based on studies showing that roughly 10% of people who get COVID could be affected by this and whose “long-term course is uncertain,” he said. So far, more than 32 million Americans are known to have been infected with the new coronavirus.
“We need to make sure we put our arms around them and bring answers and care to them,” said Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.), chairwoman of the Subcommittee on Health.
Jennifer Possick, MD, who directs the post-COVID recovery program at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital, testified that the tidal wave of patients she and her colleagues were seeing was overwhelming.
“We are a well-resourced program at an academic medical center, but we are swamped by the need in our community. This year, we have seen more patients with post COVID-19 conditions in our clinic alone than we have new cases of asthma and COPD combined,” she said. “The magnitude of the challenge is daunting.”
Dr. Possick estimated that there are “over 60” clinics in the United States that have started to treat long-COVID patients, but said they are grassroots efforts and all very different from each other.
“Whoever had the resources, had the time, [and] was able to take the initiative and forge to the relationships because most of them are multidisciplinary, did so,” she said.
Patients testify
Several representatives shared moving personal stories of loved ones or staffers who remained ill months after a COVID diagnosis.
Rep. Ann Kuster, from New Hampshire, talked about her 34-year-old niece, a member of the U.S. Ski Team, who had COVID just over a year ago and “continues to struggle with everything, even the simplest activities of daily living” she said. “She has to choose between taking a shower or making dinner. I’m so proud of her for hanging in there.”
Long-COVID patients invited to testify by the subcommittee described months of disability that left them with soaring medical bills and no ability to work to pay them.
“I am now a poor, Black, disabled woman, living with long COVID,” said Chimere Smith, who said she had been a school teacher in Baltimore. “Saying it aloud makes it no more easy to accept.”
She said COVID had affected her ability to think clearly and caused debilitating fatigue, which prevented her from working. She said she lost her vision for almost 5 months because doctors misdiagnosed a cataract caused by long COVID as dry eye.
“If I did not have a loving family, I [would] be speaking to you today [from] my car, the only property I now own.”
Ms. Smith said that long-COVID clinics, which are mostly housed within academic medical centers, were not going to be accessible for all long-haulers, who are disproportionately women of color. She has started a clinic, based out of her church, to help other patients from her community.
“No one wants to hear that long COVID has decimated my life or the lives of other black women in less than a year,” Ms. Smith said. “We’ve just been waiting and hoping for compassionate doctors and politicians who would acknowledge us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feds lift pause of J&J COVID vaccine, add new warning
Use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should resume in the United States for all adults, the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Contol and Prevention said April 23, although health care providers should warn patients of the risk of developing the rare and serious blood clots that caused the agencies to pause the vaccine’s distribution earlier this month.
“What we are seeing is the overall rate of events was 1.9 cases per million people. In women 18 to 29 years there was an approximate 7 cases per million. The risk is even lower in women over the age of 50 at .9 cases per million,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a news briefing the same day.
In the end, the potential benefits of the vaccine far outweighed its risks.
“In terms of benefits, we found that for every 1 million doses of this vaccine, the J&J vaccine could prevent over 650 hospitalizations and 12 deaths among women ages 18-49,” Dr. Walensky said. The potential benefits to women over 50 were even greater: It could prevent 4,700 hospitalizations and 650 deaths.
“In the end, this vaccine was shown to be safe and effective for the vast majority of people,” Dr. Walensky said.
The recommendation to continue the vaccine’s rollout came barely 2 hours after a CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend the pause be lifted. The vote was 10-4 with one abstention.
The decision also includes instructions for the warning directed at women under 50 who have an increased risk of a rare but serious blood clot disorder called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS).
As of April 21, 15 cases of TTS, all in women and 13 of them in women under 50, have been confirmed among 7.98 million doses of the J&J vaccine administered in the United States. Three women have died.
The FDA and CDC recommended the pause on April 13 after reports that 6 women developed a blood clotting disorder 6 to 13 days after they received the J&J vaccine.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and a non-voting ACIP member, said in an interview the panel made the right recommendation.
He applauded both the decision to restart the vaccine and the updated warning information that “will explain [TTS] more fully to people, particularly women, who are coming to be vaccinated.”
As to women in the risk group needing to have a choice of vaccines, Dr. Schaffner said that will be addressed differently across the country.
“Every provider will not have alternative vaccines in their location so there will be many different ways to do this. You may have to get this information and select which site you’re going to depending on which vaccine is available if this matter is important to you,” he noted.
ACIP made the decision after a 6-hour emergency meeting to hear evidence on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine's protective benefits against COVID-19 vs. risk of TTS.
In the CDC-FDA press briefing, Dr. Walensky pointed out that over the past few days, as regulators have reviewed the rare events, newly identified patients had been treated appropriately, without the use of heparin, which is not advised for treating TTS.
As a result, regulators felt as if their messages had gotten out to doctors who now knew how to take special precautions when treating patients with the disorder.
She said the Johnson & Johnson shot remained an important option because it was convenient to give and easier to store than the other vaccines currently authorized in the United States.
Peter Marks, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had already added information describing the risk of the rare clotting disorder to its fact sheets for patients and doctors.
Janet Woodcock, MD, acting commissioner of the FDA, said vaccination centers could resume giving the “one and done” shots as early as April 24.
This article was updated April 24, 2021, and first appeared on WebMD.com.
Use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should resume in the United States for all adults, the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Contol and Prevention said April 23, although health care providers should warn patients of the risk of developing the rare and serious blood clots that caused the agencies to pause the vaccine’s distribution earlier this month.
“What we are seeing is the overall rate of events was 1.9 cases per million people. In women 18 to 29 years there was an approximate 7 cases per million. The risk is even lower in women over the age of 50 at .9 cases per million,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a news briefing the same day.
In the end, the potential benefits of the vaccine far outweighed its risks.
“In terms of benefits, we found that for every 1 million doses of this vaccine, the J&J vaccine could prevent over 650 hospitalizations and 12 deaths among women ages 18-49,” Dr. Walensky said. The potential benefits to women over 50 were even greater: It could prevent 4,700 hospitalizations and 650 deaths.
“In the end, this vaccine was shown to be safe and effective for the vast majority of people,” Dr. Walensky said.
The recommendation to continue the vaccine’s rollout came barely 2 hours after a CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend the pause be lifted. The vote was 10-4 with one abstention.
The decision also includes instructions for the warning directed at women under 50 who have an increased risk of a rare but serious blood clot disorder called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS).
As of April 21, 15 cases of TTS, all in women and 13 of them in women under 50, have been confirmed among 7.98 million doses of the J&J vaccine administered in the United States. Three women have died.
The FDA and CDC recommended the pause on April 13 after reports that 6 women developed a blood clotting disorder 6 to 13 days after they received the J&J vaccine.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and a non-voting ACIP member, said in an interview the panel made the right recommendation.
He applauded both the decision to restart the vaccine and the updated warning information that “will explain [TTS] more fully to people, particularly women, who are coming to be vaccinated.”
As to women in the risk group needing to have a choice of vaccines, Dr. Schaffner said that will be addressed differently across the country.
“Every provider will not have alternative vaccines in their location so there will be many different ways to do this. You may have to get this information and select which site you’re going to depending on which vaccine is available if this matter is important to you,” he noted.
ACIP made the decision after a 6-hour emergency meeting to hear evidence on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine's protective benefits against COVID-19 vs. risk of TTS.
In the CDC-FDA press briefing, Dr. Walensky pointed out that over the past few days, as regulators have reviewed the rare events, newly identified patients had been treated appropriately, without the use of heparin, which is not advised for treating TTS.
As a result, regulators felt as if their messages had gotten out to doctors who now knew how to take special precautions when treating patients with the disorder.
She said the Johnson & Johnson shot remained an important option because it was convenient to give and easier to store than the other vaccines currently authorized in the United States.
Peter Marks, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had already added information describing the risk of the rare clotting disorder to its fact sheets for patients and doctors.
Janet Woodcock, MD, acting commissioner of the FDA, said vaccination centers could resume giving the “one and done” shots as early as April 24.
This article was updated April 24, 2021, and first appeared on WebMD.com.
Use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should resume in the United States for all adults, the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Contol and Prevention said April 23, although health care providers should warn patients of the risk of developing the rare and serious blood clots that caused the agencies to pause the vaccine’s distribution earlier this month.
“What we are seeing is the overall rate of events was 1.9 cases per million people. In women 18 to 29 years there was an approximate 7 cases per million. The risk is even lower in women over the age of 50 at .9 cases per million,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a news briefing the same day.
In the end, the potential benefits of the vaccine far outweighed its risks.
“In terms of benefits, we found that for every 1 million doses of this vaccine, the J&J vaccine could prevent over 650 hospitalizations and 12 deaths among women ages 18-49,” Dr. Walensky said. The potential benefits to women over 50 were even greater: It could prevent 4,700 hospitalizations and 650 deaths.
“In the end, this vaccine was shown to be safe and effective for the vast majority of people,” Dr. Walensky said.
The recommendation to continue the vaccine’s rollout came barely 2 hours after a CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend the pause be lifted. The vote was 10-4 with one abstention.
The decision also includes instructions for the warning directed at women under 50 who have an increased risk of a rare but serious blood clot disorder called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS).
As of April 21, 15 cases of TTS, all in women and 13 of them in women under 50, have been confirmed among 7.98 million doses of the J&J vaccine administered in the United States. Three women have died.
The FDA and CDC recommended the pause on April 13 after reports that 6 women developed a blood clotting disorder 6 to 13 days after they received the J&J vaccine.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and a non-voting ACIP member, said in an interview the panel made the right recommendation.
He applauded both the decision to restart the vaccine and the updated warning information that “will explain [TTS] more fully to people, particularly women, who are coming to be vaccinated.”
As to women in the risk group needing to have a choice of vaccines, Dr. Schaffner said that will be addressed differently across the country.
“Every provider will not have alternative vaccines in their location so there will be many different ways to do this. You may have to get this information and select which site you’re going to depending on which vaccine is available if this matter is important to you,” he noted.
ACIP made the decision after a 6-hour emergency meeting to hear evidence on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine's protective benefits against COVID-19 vs. risk of TTS.
In the CDC-FDA press briefing, Dr. Walensky pointed out that over the past few days, as regulators have reviewed the rare events, newly identified patients had been treated appropriately, without the use of heparin, which is not advised for treating TTS.
As a result, regulators felt as if their messages had gotten out to doctors who now knew how to take special precautions when treating patients with the disorder.
She said the Johnson & Johnson shot remained an important option because it was convenient to give and easier to store than the other vaccines currently authorized in the United States.
Peter Marks, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had already added information describing the risk of the rare clotting disorder to its fact sheets for patients and doctors.
Janet Woodcock, MD, acting commissioner of the FDA, said vaccination centers could resume giving the “one and done” shots as early as April 24.
This article was updated April 24, 2021, and first appeared on WebMD.com.
HHS proposes overturning Title X ‘gag’ rule
The Department of Health & Human Services has proposed overturning rules issued during the Trump administration that effectively prohibit clinicians at Title X–funded health clinics from discussing abortion or referring patients for abortions.
HHS proposed the overhaul of the Title X regulations on April 14. The previous administration’s 2019 rules “have undermined the public health of the population the program is meant to serve,” HHS said in the introduction to its proposal.
Medical organizations and reproductive health specialists lauded the move.
“Clinicians providing care to patients must be empowered to share the full spectrum of accurate medical information necessary to ensure that their patients are able to make timely, fully informed medical decisions,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in a statement. “This means transparent, respectful, evidence-based conversations about contraception and abortion care. The proposed rule will ensure that those conversations can once again happen without restrictions, interference, or threat of financial loss.”
“Providers of comprehensive reproductive health care, including abortion care, base their relationships with their patients on trust,” Physicians for Reproductive Health President and CEO Jamila Perritt, MD, said in a statement. “The Title X gag rule went against everything we knew as providers of ethical, evidence-based health care by forcing providers at Title X funded clinics to withhold information that their patients needed and requested.”
HHS said that, since 2019, more than 1,000 Title X–funded service sites (25% of the total) have withdrawn from the program. Currently, Title X services – which include family planning, STI testing, cancer screening, and HIV testing and treatment – are not available in six states and are only available on a limited basis in six additional states. Planned Parenthood fully withdrew from Title X.
HHS said that tens of thousands fewer birth control implant procedures have been performed and that hundreds of thousands fewer Pap tests and a half-million or more fewer tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea have been conducted. In addition, the reduction in services may have led to up to 181,477 unintended pregnancies, HHS said.
The closure of sites and decreased availability of services have also exacerbated health inequities, according to the department.
The loss of services “has been especially felt by those already facing disproportionate barriers to accessing care, including the Black, Latinx and Indigenous communities that have also suffered the most harm during the COVID-19 pandemic,” agreed Dr. Phipps.
The new regulation proposes to “ensure access to equitable, affordable, client-centered, quality family-planning services for all clients, especially for low-income clients,” HHS said.
The proposed change in the rules “brings us one step closer to restoring access to necessary care for millions of low-income and uninsured patients who depend on Title X for family planning services,” American Medical Association President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement. “We are pleased that the Biden administration shares our commitment to undoing this dangerous and discriminatory ‘gag rule,’ and look forward to its elimination through any means necessary to achieve the best outcome for patients and physicians – improving the health of our nation.”
Planned Parenthood also applauded the move, and the HIV Medicine Association thanked the Biden administration for its proposal, which it called “a major step to improve #HealthEquity for all people in this country,” in a tweet.
March for Life, an antiabortion group, however, said it strongly opposed the HHS proposal. The rules “appear specifically designed to bring America’s largest abortion provider, Planned Parenthood, back into the taxpayer-funded program and keep prolife organizations out,” said the group in a tweet.
“Abortion is neither health care nor family planning, and the Title X program should not be funding it,” said the group.
The Title X program does not pay for abortions, however.
The Trump administration rules prohibit abortion referrals and impose counseling standards for pregnant patients and what the Guttmacher Institute called “unnecessary and stringent requirements for the physical and financial separation of Title X–funded activities from a range of abortion-related activities.”
The new rules would reestablish regulations from 2000, with some new additions. For instance, the program will “formally integrate elements of quality family-planning services guidelines developed by [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and Office of Population Affairs,” tweeted Alina Salganicoff, director of women’s health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “That means that higher standards for providing family planning will be required,” she tweeted. In addition, sites that offer natural family planning and abstinence “will only be able to participate if they offer referrals to other providers that offer clients access to the contraceptive of their choice.”
The proposed rules are open for public comment for 30 days. They could be made final by the fall. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that many sites could be ready to return to the program by then, especially since the recently passed coronavirus relief package, the American Rescue Plan, included a $50 million supplemental appropriation for Title X.
The 2019 rules remain in effect in the meantime, although the U.S. Supreme Court agreed in February to hear a challenge mounted by 21 states, the city of Baltimore, and organizations that included the AMA and Planned Parenthood. Those plaintiffs have requested that the case be dismissed, but it currently remains on the docket.
Not all medical providers are likely to support the new rules if they go into effect. The American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Christian Medical and Dental Associations, and the Catholic Medical Association filed motions in the Supreme Court case to defend the Trump regulations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Department of Health & Human Services has proposed overturning rules issued during the Trump administration that effectively prohibit clinicians at Title X–funded health clinics from discussing abortion or referring patients for abortions.
HHS proposed the overhaul of the Title X regulations on April 14. The previous administration’s 2019 rules “have undermined the public health of the population the program is meant to serve,” HHS said in the introduction to its proposal.
Medical organizations and reproductive health specialists lauded the move.
“Clinicians providing care to patients must be empowered to share the full spectrum of accurate medical information necessary to ensure that their patients are able to make timely, fully informed medical decisions,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in a statement. “This means transparent, respectful, evidence-based conversations about contraception and abortion care. The proposed rule will ensure that those conversations can once again happen without restrictions, interference, or threat of financial loss.”
“Providers of comprehensive reproductive health care, including abortion care, base their relationships with their patients on trust,” Physicians for Reproductive Health President and CEO Jamila Perritt, MD, said in a statement. “The Title X gag rule went against everything we knew as providers of ethical, evidence-based health care by forcing providers at Title X funded clinics to withhold information that their patients needed and requested.”
HHS said that, since 2019, more than 1,000 Title X–funded service sites (25% of the total) have withdrawn from the program. Currently, Title X services – which include family planning, STI testing, cancer screening, and HIV testing and treatment – are not available in six states and are only available on a limited basis in six additional states. Planned Parenthood fully withdrew from Title X.
HHS said that tens of thousands fewer birth control implant procedures have been performed and that hundreds of thousands fewer Pap tests and a half-million or more fewer tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea have been conducted. In addition, the reduction in services may have led to up to 181,477 unintended pregnancies, HHS said.
The closure of sites and decreased availability of services have also exacerbated health inequities, according to the department.
The loss of services “has been especially felt by those already facing disproportionate barriers to accessing care, including the Black, Latinx and Indigenous communities that have also suffered the most harm during the COVID-19 pandemic,” agreed Dr. Phipps.
The new regulation proposes to “ensure access to equitable, affordable, client-centered, quality family-planning services for all clients, especially for low-income clients,” HHS said.
The proposed change in the rules “brings us one step closer to restoring access to necessary care for millions of low-income and uninsured patients who depend on Title X for family planning services,” American Medical Association President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement. “We are pleased that the Biden administration shares our commitment to undoing this dangerous and discriminatory ‘gag rule,’ and look forward to its elimination through any means necessary to achieve the best outcome for patients and physicians – improving the health of our nation.”
Planned Parenthood also applauded the move, and the HIV Medicine Association thanked the Biden administration for its proposal, which it called “a major step to improve #HealthEquity for all people in this country,” in a tweet.
March for Life, an antiabortion group, however, said it strongly opposed the HHS proposal. The rules “appear specifically designed to bring America’s largest abortion provider, Planned Parenthood, back into the taxpayer-funded program and keep prolife organizations out,” said the group in a tweet.
“Abortion is neither health care nor family planning, and the Title X program should not be funding it,” said the group.
The Title X program does not pay for abortions, however.
The Trump administration rules prohibit abortion referrals and impose counseling standards for pregnant patients and what the Guttmacher Institute called “unnecessary and stringent requirements for the physical and financial separation of Title X–funded activities from a range of abortion-related activities.”
The new rules would reestablish regulations from 2000, with some new additions. For instance, the program will “formally integrate elements of quality family-planning services guidelines developed by [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and Office of Population Affairs,” tweeted Alina Salganicoff, director of women’s health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “That means that higher standards for providing family planning will be required,” she tweeted. In addition, sites that offer natural family planning and abstinence “will only be able to participate if they offer referrals to other providers that offer clients access to the contraceptive of their choice.”
The proposed rules are open for public comment for 30 days. They could be made final by the fall. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that many sites could be ready to return to the program by then, especially since the recently passed coronavirus relief package, the American Rescue Plan, included a $50 million supplemental appropriation for Title X.
The 2019 rules remain in effect in the meantime, although the U.S. Supreme Court agreed in February to hear a challenge mounted by 21 states, the city of Baltimore, and organizations that included the AMA and Planned Parenthood. Those plaintiffs have requested that the case be dismissed, but it currently remains on the docket.
Not all medical providers are likely to support the new rules if they go into effect. The American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Christian Medical and Dental Associations, and the Catholic Medical Association filed motions in the Supreme Court case to defend the Trump regulations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Department of Health & Human Services has proposed overturning rules issued during the Trump administration that effectively prohibit clinicians at Title X–funded health clinics from discussing abortion or referring patients for abortions.
HHS proposed the overhaul of the Title X regulations on April 14. The previous administration’s 2019 rules “have undermined the public health of the population the program is meant to serve,” HHS said in the introduction to its proposal.
Medical organizations and reproductive health specialists lauded the move.
“Clinicians providing care to patients must be empowered to share the full spectrum of accurate medical information necessary to ensure that their patients are able to make timely, fully informed medical decisions,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in a statement. “This means transparent, respectful, evidence-based conversations about contraception and abortion care. The proposed rule will ensure that those conversations can once again happen without restrictions, interference, or threat of financial loss.”
“Providers of comprehensive reproductive health care, including abortion care, base their relationships with their patients on trust,” Physicians for Reproductive Health President and CEO Jamila Perritt, MD, said in a statement. “The Title X gag rule went against everything we knew as providers of ethical, evidence-based health care by forcing providers at Title X funded clinics to withhold information that their patients needed and requested.”
HHS said that, since 2019, more than 1,000 Title X–funded service sites (25% of the total) have withdrawn from the program. Currently, Title X services – which include family planning, STI testing, cancer screening, and HIV testing and treatment – are not available in six states and are only available on a limited basis in six additional states. Planned Parenthood fully withdrew from Title X.
HHS said that tens of thousands fewer birth control implant procedures have been performed and that hundreds of thousands fewer Pap tests and a half-million or more fewer tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea have been conducted. In addition, the reduction in services may have led to up to 181,477 unintended pregnancies, HHS said.
The closure of sites and decreased availability of services have also exacerbated health inequities, according to the department.
The loss of services “has been especially felt by those already facing disproportionate barriers to accessing care, including the Black, Latinx and Indigenous communities that have also suffered the most harm during the COVID-19 pandemic,” agreed Dr. Phipps.
The new regulation proposes to “ensure access to equitable, affordable, client-centered, quality family-planning services for all clients, especially for low-income clients,” HHS said.
The proposed change in the rules “brings us one step closer to restoring access to necessary care for millions of low-income and uninsured patients who depend on Title X for family planning services,” American Medical Association President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement. “We are pleased that the Biden administration shares our commitment to undoing this dangerous and discriminatory ‘gag rule,’ and look forward to its elimination through any means necessary to achieve the best outcome for patients and physicians – improving the health of our nation.”
Planned Parenthood also applauded the move, and the HIV Medicine Association thanked the Biden administration for its proposal, which it called “a major step to improve #HealthEquity for all people in this country,” in a tweet.
March for Life, an antiabortion group, however, said it strongly opposed the HHS proposal. The rules “appear specifically designed to bring America’s largest abortion provider, Planned Parenthood, back into the taxpayer-funded program and keep prolife organizations out,” said the group in a tweet.
“Abortion is neither health care nor family planning, and the Title X program should not be funding it,” said the group.
The Title X program does not pay for abortions, however.
The Trump administration rules prohibit abortion referrals and impose counseling standards for pregnant patients and what the Guttmacher Institute called “unnecessary and stringent requirements for the physical and financial separation of Title X–funded activities from a range of abortion-related activities.”
The new rules would reestablish regulations from 2000, with some new additions. For instance, the program will “formally integrate elements of quality family-planning services guidelines developed by [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and Office of Population Affairs,” tweeted Alina Salganicoff, director of women’s health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “That means that higher standards for providing family planning will be required,” she tweeted. In addition, sites that offer natural family planning and abstinence “will only be able to participate if they offer referrals to other providers that offer clients access to the contraceptive of their choice.”
The proposed rules are open for public comment for 30 days. They could be made final by the fall. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that many sites could be ready to return to the program by then, especially since the recently passed coronavirus relief package, the American Rescue Plan, included a $50 million supplemental appropriation for Title X.
The 2019 rules remain in effect in the meantime, although the U.S. Supreme Court agreed in February to hear a challenge mounted by 21 states, the city of Baltimore, and organizations that included the AMA and Planned Parenthood. Those plaintiffs have requested that the case be dismissed, but it currently remains on the docket.
Not all medical providers are likely to support the new rules if they go into effect. The American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Christian Medical and Dental Associations, and the Catholic Medical Association filed motions in the Supreme Court case to defend the Trump regulations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.