User login
AHA challenges diet doctor’s study alleging COVID vax risks
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart Failure Highlights From AHA 2021
Dr Javed Butler, from the University of Mississippi Medical Center, reports on key presentations on heart failure from the 2021 annual meeting of the American Heart Association.
Dr Butler starts with the EMPULSE trial, which looked at the use of empagliflozin in hospitalized patients with acute heart failure. The study found that patients randomly assigned to empagliflozin had a 36% chance of improved outcomes by 3 months.
He next looks at two reports from the EMPEROR-Preserved trials, which examined the effects of empagliflozin on patients with ejection fraction greater than 50%. The study found a 17% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death and a 22% reduction in risk for first heart failure hospitalization. The second EMPEROR report, which examined quality-of-life metrics, found a benefit in favor of empagliflozin over placebo.
Next, Dr Butler discusses the CHIEF-HF trial, in which heart failure patients were randomly assigned to canagliflozin regardless of ejection fraction. Canagliflozin showed benefit in symptom improvement consistently, regardless of patients having diabetes or heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
Finally, Dr Butler examined the results of the FIGARO-DKD trial, which studied finerenone in patients with diabetic kidney disease. The study reported a 32% relative risk reduction in heart failure events, and reduced hospitalization and cardiovascular death in patients who had a history of heart failure events and those who did not.
--
Javed Butler, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
Javed Butler, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Abbott; Amgen; Array; AstraZeneca; Bayer; Boehringer-Ingelheim; Bristol-Myers Squibb; CVRx; Janssen; LivaNova; Luitpold; Medtronic; Merck; Novartis; Novo Nordisk; Vifor
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novartis; Boehringer-Ingelheim; Eli Lilly; Janssen
Dr Javed Butler, from the University of Mississippi Medical Center, reports on key presentations on heart failure from the 2021 annual meeting of the American Heart Association.
Dr Butler starts with the EMPULSE trial, which looked at the use of empagliflozin in hospitalized patients with acute heart failure. The study found that patients randomly assigned to empagliflozin had a 36% chance of improved outcomes by 3 months.
He next looks at two reports from the EMPEROR-Preserved trials, which examined the effects of empagliflozin on patients with ejection fraction greater than 50%. The study found a 17% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death and a 22% reduction in risk for first heart failure hospitalization. The second EMPEROR report, which examined quality-of-life metrics, found a benefit in favor of empagliflozin over placebo.
Next, Dr Butler discusses the CHIEF-HF trial, in which heart failure patients were randomly assigned to canagliflozin regardless of ejection fraction. Canagliflozin showed benefit in symptom improvement consistently, regardless of patients having diabetes or heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
Finally, Dr Butler examined the results of the FIGARO-DKD trial, which studied finerenone in patients with diabetic kidney disease. The study reported a 32% relative risk reduction in heart failure events, and reduced hospitalization and cardiovascular death in patients who had a history of heart failure events and those who did not.
--
Javed Butler, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
Javed Butler, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Abbott; Amgen; Array; AstraZeneca; Bayer; Boehringer-Ingelheim; Bristol-Myers Squibb; CVRx; Janssen; LivaNova; Luitpold; Medtronic; Merck; Novartis; Novo Nordisk; Vifor
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novartis; Boehringer-Ingelheim; Eli Lilly; Janssen
Dr Javed Butler, from the University of Mississippi Medical Center, reports on key presentations on heart failure from the 2021 annual meeting of the American Heart Association.
Dr Butler starts with the EMPULSE trial, which looked at the use of empagliflozin in hospitalized patients with acute heart failure. The study found that patients randomly assigned to empagliflozin had a 36% chance of improved outcomes by 3 months.
He next looks at two reports from the EMPEROR-Preserved trials, which examined the effects of empagliflozin on patients with ejection fraction greater than 50%. The study found a 17% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death and a 22% reduction in risk for first heart failure hospitalization. The second EMPEROR report, which examined quality-of-life metrics, found a benefit in favor of empagliflozin over placebo.
Next, Dr Butler discusses the CHIEF-HF trial, in which heart failure patients were randomly assigned to canagliflozin regardless of ejection fraction. Canagliflozin showed benefit in symptom improvement consistently, regardless of patients having diabetes or heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
Finally, Dr Butler examined the results of the FIGARO-DKD trial, which studied finerenone in patients with diabetic kidney disease. The study reported a 32% relative risk reduction in heart failure events, and reduced hospitalization and cardiovascular death in patients who had a history of heart failure events and those who did not.
--
Javed Butler, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
Javed Butler, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Abbott; Amgen; Array; AstraZeneca; Bayer; Boehringer-Ingelheim; Bristol-Myers Squibb; CVRx; Janssen; LivaNova; Luitpold; Medtronic; Merck; Novartis; Novo Nordisk; Vifor
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novartis; Boehringer-Ingelheim; Eli Lilly; Janssen

SGLT2 inhibitor use tied to fewer atrial arrhythmias
Patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) who received treatment with an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor had significantly fewer atrial arrhythmia events, compared with those who never received such a drug, in a prospective analysis of nearly 14,000 patients with a device who were followed for an average of nearly 2 years.
The findings suggest that use of an agent from the class of SGLT2 inhibitors “is associated with a pronounced reduction in atrial arrhythmia burden and all-cause mortality in patients with a CIED in a real-world setting,” said Ilan Goldenberg, MD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “These data indicate possible antiarrhythmic properties of SGLT2 inhibitors that are incremental to the beneficial effects of the drug on heart failure outcomes,” added Dr. Goldenberg, director of the Clinical Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Rochester (N.Y.).
In a propensity score–matched analysis that included more than 5,000 of the enrolled patients with a CIED, treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor was tied to a significant 23% relative reduction in atrial arrhythmia events and a 44% relative drop in all-cause death, he reported.
Effect mediated by reduced left atrial pressure?
“Other heart failure drugs have shown some decrease in the rate of sudden cardiac death, but this is the first [heart failure] drug to associate with a reduction in atrial arrhythmias,” Dr. Goldenberg noted. “We think that a reduction in left atrial pressure” produced by treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor “may be linked to the reduction in atrial arrhythmias.”
The study did not show an association of SGLT2-inhibitor use and a change in ventricular arrhythmias, compared with patients with CIEDs who did not receive an agent from this class.
The findings suggest “expanding the possible indications for SGLT2 inhibitors,” commented Harriette G.C. Van Spall, MD, a cardiologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who moderated the session where Dr. Goldenberg gave his report.
The study included 13,890 consecutive, prospectively enrolled patients who received a CIED during January 2015–April 2020 at any of five hospitals operated by either of two tertiary health care systems, one run by the University of Rochester and the second based at Sheba Medical Center in Tel HaShomer, Israel. The devices that made patients eligible for the study included permanent pacemakers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, and implantable cardiac monitors. A blinded adjudication committee composed of electrophysiologists identified the arrhythmic episodes.
At entry into the study (the time of device implantation), 12,992 patients were not receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor (94%) and 898 (6%) were receiving a drug from this class. Of those, 39% were on dapagliflozin (Farxiga), 35% were on empagliflozin (Jardiance), and 26% were on canagliflozin (Invokana).
Patients receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline were on average substantially younger than the patients not on this drug class (59 years vs. 69 years); they had a substantially higher prevalence of diabetes (78% vs. 25%), and ischemic cardiomyopathy (63% vs. 39%). Patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline also had more modestly higher prevalence rates of prior heart failure (38% vs. 31%), and hypertension (69% vs. 63%). Prevalence of a history of atrial fibrillation (AFib) was nearly the same in both groups: 31% in patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor and 35% in those not on these drugs.
The study’s primary endpoint was the total number of arrhythmia events during follow-up of 24,442 patient-years, during which patients exhibited 19,633 atrial arrhythmia events and 3,231 ventricular arrhythmia events.
1% absolute reduction in atrial arrhythmias
A multivariate analysis of the entire population – adjusted for baseline differences in age, diabetes, sex, and history of AFib – showed that treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline was linked with a significant 24% relative reduction in incident atrial arrhythmia events, a significant 24% reduction in both atrial and ventricular arrhythmia events, and a 42% relative reduction in all-cause deaths, compared with no SGLT2-inhibitor treatment.
The only analyzed endpoint that showed no significant between-group difference was incidence of ventricular arrhythmias, which was a relative 7% lower in the SGLT2-inhibitor group.
On an absolute basis, treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor was tied to about a 1% lower rate of atrial arrhythmia events per year, a reduction from a 2.5% rate in those not on an SGLT2 inhibitor to about a 1.5% rate in those taking this drug class.
A second, confirmatory analysis used propensity score matching to identify 5,323 patients not on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline who closely matched the 898 patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor. The multivariate modeling for this analysis also adjusted for age, diabetes, sex, and history of AFib.
The results of these analyses closely matched the calculations that used the entire study population. Relative to patients not on an SGLT2 inhibitor those on a drug from this class had 23% fewer atrial arrhythmias, 44% fewer total death, and 22% fewer atrial or ventricular arrhythmias, all significant differences. However, ventricular arrhythmias only reduced by a relative 5%, a nonsignificant difference.
In the propensity score–matched analysis, the absolute reduction in atrial arrhythmias in those on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline was roughly 1.3% fewer per year, compared with those not on this drug class.
The study was funded by an unrestricted grant to the University of Rochester from AstraZeneca, the company that markets the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Goldenberg and Dr. Van Spall had no disclosures.
Patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) who received treatment with an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor had significantly fewer atrial arrhythmia events, compared with those who never received such a drug, in a prospective analysis of nearly 14,000 patients with a device who were followed for an average of nearly 2 years.
The findings suggest that use of an agent from the class of SGLT2 inhibitors “is associated with a pronounced reduction in atrial arrhythmia burden and all-cause mortality in patients with a CIED in a real-world setting,” said Ilan Goldenberg, MD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “These data indicate possible antiarrhythmic properties of SGLT2 inhibitors that are incremental to the beneficial effects of the drug on heart failure outcomes,” added Dr. Goldenberg, director of the Clinical Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Rochester (N.Y.).
In a propensity score–matched analysis that included more than 5,000 of the enrolled patients with a CIED, treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor was tied to a significant 23% relative reduction in atrial arrhythmia events and a 44% relative drop in all-cause death, he reported.
Effect mediated by reduced left atrial pressure?
“Other heart failure drugs have shown some decrease in the rate of sudden cardiac death, but this is the first [heart failure] drug to associate with a reduction in atrial arrhythmias,” Dr. Goldenberg noted. “We think that a reduction in left atrial pressure” produced by treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor “may be linked to the reduction in atrial arrhythmias.”
The study did not show an association of SGLT2-inhibitor use and a change in ventricular arrhythmias, compared with patients with CIEDs who did not receive an agent from this class.
The findings suggest “expanding the possible indications for SGLT2 inhibitors,” commented Harriette G.C. Van Spall, MD, a cardiologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who moderated the session where Dr. Goldenberg gave his report.
The study included 13,890 consecutive, prospectively enrolled patients who received a CIED during January 2015–April 2020 at any of five hospitals operated by either of two tertiary health care systems, one run by the University of Rochester and the second based at Sheba Medical Center in Tel HaShomer, Israel. The devices that made patients eligible for the study included permanent pacemakers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, and implantable cardiac monitors. A blinded adjudication committee composed of electrophysiologists identified the arrhythmic episodes.
At entry into the study (the time of device implantation), 12,992 patients were not receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor (94%) and 898 (6%) were receiving a drug from this class. Of those, 39% were on dapagliflozin (Farxiga), 35% were on empagliflozin (Jardiance), and 26% were on canagliflozin (Invokana).
Patients receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline were on average substantially younger than the patients not on this drug class (59 years vs. 69 years); they had a substantially higher prevalence of diabetes (78% vs. 25%), and ischemic cardiomyopathy (63% vs. 39%). Patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline also had more modestly higher prevalence rates of prior heart failure (38% vs. 31%), and hypertension (69% vs. 63%). Prevalence of a history of atrial fibrillation (AFib) was nearly the same in both groups: 31% in patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor and 35% in those not on these drugs.
The study’s primary endpoint was the total number of arrhythmia events during follow-up of 24,442 patient-years, during which patients exhibited 19,633 atrial arrhythmia events and 3,231 ventricular arrhythmia events.
1% absolute reduction in atrial arrhythmias
A multivariate analysis of the entire population – adjusted for baseline differences in age, diabetes, sex, and history of AFib – showed that treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline was linked with a significant 24% relative reduction in incident atrial arrhythmia events, a significant 24% reduction in both atrial and ventricular arrhythmia events, and a 42% relative reduction in all-cause deaths, compared with no SGLT2-inhibitor treatment.
The only analyzed endpoint that showed no significant between-group difference was incidence of ventricular arrhythmias, which was a relative 7% lower in the SGLT2-inhibitor group.
On an absolute basis, treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor was tied to about a 1% lower rate of atrial arrhythmia events per year, a reduction from a 2.5% rate in those not on an SGLT2 inhibitor to about a 1.5% rate in those taking this drug class.
A second, confirmatory analysis used propensity score matching to identify 5,323 patients not on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline who closely matched the 898 patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor. The multivariate modeling for this analysis also adjusted for age, diabetes, sex, and history of AFib.
The results of these analyses closely matched the calculations that used the entire study population. Relative to patients not on an SGLT2 inhibitor those on a drug from this class had 23% fewer atrial arrhythmias, 44% fewer total death, and 22% fewer atrial or ventricular arrhythmias, all significant differences. However, ventricular arrhythmias only reduced by a relative 5%, a nonsignificant difference.
In the propensity score–matched analysis, the absolute reduction in atrial arrhythmias in those on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline was roughly 1.3% fewer per year, compared with those not on this drug class.
The study was funded by an unrestricted grant to the University of Rochester from AstraZeneca, the company that markets the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Goldenberg and Dr. Van Spall had no disclosures.
Patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) who received treatment with an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor had significantly fewer atrial arrhythmia events, compared with those who never received such a drug, in a prospective analysis of nearly 14,000 patients with a device who were followed for an average of nearly 2 years.
The findings suggest that use of an agent from the class of SGLT2 inhibitors “is associated with a pronounced reduction in atrial arrhythmia burden and all-cause mortality in patients with a CIED in a real-world setting,” said Ilan Goldenberg, MD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “These data indicate possible antiarrhythmic properties of SGLT2 inhibitors that are incremental to the beneficial effects of the drug on heart failure outcomes,” added Dr. Goldenberg, director of the Clinical Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Rochester (N.Y.).
In a propensity score–matched analysis that included more than 5,000 of the enrolled patients with a CIED, treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor was tied to a significant 23% relative reduction in atrial arrhythmia events and a 44% relative drop in all-cause death, he reported.
Effect mediated by reduced left atrial pressure?
“Other heart failure drugs have shown some decrease in the rate of sudden cardiac death, but this is the first [heart failure] drug to associate with a reduction in atrial arrhythmias,” Dr. Goldenberg noted. “We think that a reduction in left atrial pressure” produced by treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor “may be linked to the reduction in atrial arrhythmias.”
The study did not show an association of SGLT2-inhibitor use and a change in ventricular arrhythmias, compared with patients with CIEDs who did not receive an agent from this class.
The findings suggest “expanding the possible indications for SGLT2 inhibitors,” commented Harriette G.C. Van Spall, MD, a cardiologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who moderated the session where Dr. Goldenberg gave his report.
The study included 13,890 consecutive, prospectively enrolled patients who received a CIED during January 2015–April 2020 at any of five hospitals operated by either of two tertiary health care systems, one run by the University of Rochester and the second based at Sheba Medical Center in Tel HaShomer, Israel. The devices that made patients eligible for the study included permanent pacemakers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, and implantable cardiac monitors. A blinded adjudication committee composed of electrophysiologists identified the arrhythmic episodes.
At entry into the study (the time of device implantation), 12,992 patients were not receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor (94%) and 898 (6%) were receiving a drug from this class. Of those, 39% were on dapagliflozin (Farxiga), 35% were on empagliflozin (Jardiance), and 26% were on canagliflozin (Invokana).
Patients receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline were on average substantially younger than the patients not on this drug class (59 years vs. 69 years); they had a substantially higher prevalence of diabetes (78% vs. 25%), and ischemic cardiomyopathy (63% vs. 39%). Patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline also had more modestly higher prevalence rates of prior heart failure (38% vs. 31%), and hypertension (69% vs. 63%). Prevalence of a history of atrial fibrillation (AFib) was nearly the same in both groups: 31% in patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor and 35% in those not on these drugs.
The study’s primary endpoint was the total number of arrhythmia events during follow-up of 24,442 patient-years, during which patients exhibited 19,633 atrial arrhythmia events and 3,231 ventricular arrhythmia events.
1% absolute reduction in atrial arrhythmias
A multivariate analysis of the entire population – adjusted for baseline differences in age, diabetes, sex, and history of AFib – showed that treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline was linked with a significant 24% relative reduction in incident atrial arrhythmia events, a significant 24% reduction in both atrial and ventricular arrhythmia events, and a 42% relative reduction in all-cause deaths, compared with no SGLT2-inhibitor treatment.
The only analyzed endpoint that showed no significant between-group difference was incidence of ventricular arrhythmias, which was a relative 7% lower in the SGLT2-inhibitor group.
On an absolute basis, treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor was tied to about a 1% lower rate of atrial arrhythmia events per year, a reduction from a 2.5% rate in those not on an SGLT2 inhibitor to about a 1.5% rate in those taking this drug class.
A second, confirmatory analysis used propensity score matching to identify 5,323 patients not on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline who closely matched the 898 patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor. The multivariate modeling for this analysis also adjusted for age, diabetes, sex, and history of AFib.
The results of these analyses closely matched the calculations that used the entire study population. Relative to patients not on an SGLT2 inhibitor those on a drug from this class had 23% fewer atrial arrhythmias, 44% fewer total death, and 22% fewer atrial or ventricular arrhythmias, all significant differences. However, ventricular arrhythmias only reduced by a relative 5%, a nonsignificant difference.
In the propensity score–matched analysis, the absolute reduction in atrial arrhythmias in those on an SGLT2 inhibitor at baseline was roughly 1.3% fewer per year, compared with those not on this drug class.
The study was funded by an unrestricted grant to the University of Rochester from AstraZeneca, the company that markets the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Goldenberg and Dr. Van Spall had no disclosures.
FROM AHA 2021
Could an oral PCSK9 inhibitor be on the horizon?
The investigational PCSK9 inhibitor that Merck showcased recently would be more than a “me-too” drug if it ultimately wins approval, despite competition from several approved agents that slash elevated cholesterol levels by targeting the same protein.
In fact, it would be something of a breakthrough. The new agent under study – now called MK-0616 – comes in pill form, in contrast to the three currently available PCSK9-lowering drugs that must be given in injections separated by weeks to months.
The drug faces an uncertain road to regulatory review and any approval, but MK-0616 at least seems to be starting out in the right direction.
In two phase 1 studies with a total of 100 participants, plasma PCSK9 levels plunged more than 90% after a single dose of the drug; and low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels dropped about 65% when MK-0616 was given daily for 2 weeks on a background of statin therapy.
Moreover, “MK-0616 was generally well tolerated at up to and including single doses of 300 milligrams,” the maximum tested in the studies, Douglas G. Johns, PhD, reported at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The collective results from the oral agent’s earliest human experience are “definitely encouraging” and support MK-0616 as a potential LDL-lowering agent that would be more convenient and arguably more accessible to patients compared to current injectable PCSK9 inhibitors, proposed Dr. Johns, clinical director of translational medicine for Merck in Kenilworth, N.J.
Available PCSK9-targeting agents include alirocumab (Praluent, Sanofi/Regeneron), Food and Drug Administration–approved in July 2015, and evolocumab (Repatha, Amgen), approved by the agency the following month. Both are monoclonal antibodies with neutralizing specificity for the PCSK9 protein; whereas the third such agent, inclisiran (Leqvio, Novartis) is a small-molecule interfering-RNA that suppresses PCSK9 synthesis. Inclisiran is approved in the European Union but its case to the FDA was turned down in 2020.
Dr. Johns said MK-0616 is a cyclic peptide that is “about one-hundredth the size of a monoclonal antibody, but we’re able to achieve monoclonal antibody-like potency and selectivity with this much smaller footprint.”
Added to statin therapy, the current PCSK9-targeting agents reduce LDL-C by an additional one-half or more, and the two antibody-based agents “also decrease atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. They are, however, expensive and not always available, requiring insurance or other approval,” observed Anne C. Goldberg, MD, as invited discussant after Dr. Johns’ presentation.
“They require every 2- to 4-week injections. They’re generally reserved for secondary prevention, and sometimes primary prevention as in familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Goldberg, of Washington University, St. Louis. Inclisiran, she noted, requires injections every 6 months and has yet to show its mettle in cardiovascular outcomes trials.
“Certainly, an oral form would be easier to use,” she said. “This would be particularly helpful in patients averse to injections,” especially, perhaps, in children. “Children with familial hypercholesterolemia could benefit with greater cholesterol lowering and might be better off with a pill than an injection.” That would be good reason to emphasize the enrollment of children in the drug’s upcoming clinical trials, Dr. Goldberg said.
But cost could potentially become restrictive for MK-0616 as well, should it ever be approved. “If it’s priced too high, then are you really going to see the increased use?” she posed. “Certainly, there’s a high bar for therapies that are add-on to statins in terms of cost effectiveness.”
In the first of the two trials, 60 predominantly White male participants aged 50 or younger were randomly assigned to receive a single dose of MK-0616, at different levels ranging from 10 mg to 300 mg, or placebo. They subsequently crossed over to a different group for a second round of dosing. Both times, three participants took the drug for every one who received placebo.
Participants who took the active drug, regardless of dosage, showed greater than 90% reductions in circulating PCSK9 levels compared to baseline. Six participants discontinued the study before its completion.
In the second trial, 40 White adults aged 65 or younger (mean, 58), including 13 women, with LDL-C of 60 mg/dL to 160 mg/dL (mean, 87 mg/dL) on statin therapy for at least 3 months were randomly assigned 3-to-1 to add-on MK-0616, either 10 mg or 20 mg daily, or placebo for 14 days.
LDL-C levels fell an average of about 65% over the 2 weeks among those taking the active drug; they declined less than 5% for those who took placebo.
There were no deaths or serious adverse events in either trial, Dr. Johns reported. On the other hand, pharmacokinetics studies showed that exposure to the drug fell by “about 50%-60%” when dosing was preceded by food intake within the previous 30 minutes. “However, if a meal is consumed 30 minutes after the dose, this food effect is much, much less prominent, almost negligible.”
These preliminary results show the drug is “orally bioavailable and exerts a clinically meaningful effect,” Dr. Johns said. “However, there’s definitely more to be done. And we are planning the next phase of clinical development, a phase 2 trial, sometime next year.”
The research was funded by Merck. Dr. Johns disclosed employment with and equity ownership in Merck, as did all the study’s coauthors. Dr. Goldberg disclosed holding research contracts through her institution with Regeneron/Sanofi-Aventis, Amarin, Amgen, Pfizer, IONIS/Akcea, Regeneron, Novartis, Arrowroot Pharmaceuticals, and the FH Foundation; and consulting for Novartis, Akcea, Regeneron, and Esperion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational PCSK9 inhibitor that Merck showcased recently would be more than a “me-too” drug if it ultimately wins approval, despite competition from several approved agents that slash elevated cholesterol levels by targeting the same protein.
In fact, it would be something of a breakthrough. The new agent under study – now called MK-0616 – comes in pill form, in contrast to the three currently available PCSK9-lowering drugs that must be given in injections separated by weeks to months.
The drug faces an uncertain road to regulatory review and any approval, but MK-0616 at least seems to be starting out in the right direction.
In two phase 1 studies with a total of 100 participants, plasma PCSK9 levels plunged more than 90% after a single dose of the drug; and low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels dropped about 65% when MK-0616 was given daily for 2 weeks on a background of statin therapy.
Moreover, “MK-0616 was generally well tolerated at up to and including single doses of 300 milligrams,” the maximum tested in the studies, Douglas G. Johns, PhD, reported at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The collective results from the oral agent’s earliest human experience are “definitely encouraging” and support MK-0616 as a potential LDL-lowering agent that would be more convenient and arguably more accessible to patients compared to current injectable PCSK9 inhibitors, proposed Dr. Johns, clinical director of translational medicine for Merck in Kenilworth, N.J.
Available PCSK9-targeting agents include alirocumab (Praluent, Sanofi/Regeneron), Food and Drug Administration–approved in July 2015, and evolocumab (Repatha, Amgen), approved by the agency the following month. Both are monoclonal antibodies with neutralizing specificity for the PCSK9 protein; whereas the third such agent, inclisiran (Leqvio, Novartis) is a small-molecule interfering-RNA that suppresses PCSK9 synthesis. Inclisiran is approved in the European Union but its case to the FDA was turned down in 2020.
Dr. Johns said MK-0616 is a cyclic peptide that is “about one-hundredth the size of a monoclonal antibody, but we’re able to achieve monoclonal antibody-like potency and selectivity with this much smaller footprint.”
Added to statin therapy, the current PCSK9-targeting agents reduce LDL-C by an additional one-half or more, and the two antibody-based agents “also decrease atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. They are, however, expensive and not always available, requiring insurance or other approval,” observed Anne C. Goldberg, MD, as invited discussant after Dr. Johns’ presentation.
“They require every 2- to 4-week injections. They’re generally reserved for secondary prevention, and sometimes primary prevention as in familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Goldberg, of Washington University, St. Louis. Inclisiran, she noted, requires injections every 6 months and has yet to show its mettle in cardiovascular outcomes trials.
“Certainly, an oral form would be easier to use,” she said. “This would be particularly helpful in patients averse to injections,” especially, perhaps, in children. “Children with familial hypercholesterolemia could benefit with greater cholesterol lowering and might be better off with a pill than an injection.” That would be good reason to emphasize the enrollment of children in the drug’s upcoming clinical trials, Dr. Goldberg said.
But cost could potentially become restrictive for MK-0616 as well, should it ever be approved. “If it’s priced too high, then are you really going to see the increased use?” she posed. “Certainly, there’s a high bar for therapies that are add-on to statins in terms of cost effectiveness.”
In the first of the two trials, 60 predominantly White male participants aged 50 or younger were randomly assigned to receive a single dose of MK-0616, at different levels ranging from 10 mg to 300 mg, or placebo. They subsequently crossed over to a different group for a second round of dosing. Both times, three participants took the drug for every one who received placebo.
Participants who took the active drug, regardless of dosage, showed greater than 90% reductions in circulating PCSK9 levels compared to baseline. Six participants discontinued the study before its completion.
In the second trial, 40 White adults aged 65 or younger (mean, 58), including 13 women, with LDL-C of 60 mg/dL to 160 mg/dL (mean, 87 mg/dL) on statin therapy for at least 3 months were randomly assigned 3-to-1 to add-on MK-0616, either 10 mg or 20 mg daily, or placebo for 14 days.
LDL-C levels fell an average of about 65% over the 2 weeks among those taking the active drug; they declined less than 5% for those who took placebo.
There were no deaths or serious adverse events in either trial, Dr. Johns reported. On the other hand, pharmacokinetics studies showed that exposure to the drug fell by “about 50%-60%” when dosing was preceded by food intake within the previous 30 minutes. “However, if a meal is consumed 30 minutes after the dose, this food effect is much, much less prominent, almost negligible.”
These preliminary results show the drug is “orally bioavailable and exerts a clinically meaningful effect,” Dr. Johns said. “However, there’s definitely more to be done. And we are planning the next phase of clinical development, a phase 2 trial, sometime next year.”
The research was funded by Merck. Dr. Johns disclosed employment with and equity ownership in Merck, as did all the study’s coauthors. Dr. Goldberg disclosed holding research contracts through her institution with Regeneron/Sanofi-Aventis, Amarin, Amgen, Pfizer, IONIS/Akcea, Regeneron, Novartis, Arrowroot Pharmaceuticals, and the FH Foundation; and consulting for Novartis, Akcea, Regeneron, and Esperion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational PCSK9 inhibitor that Merck showcased recently would be more than a “me-too” drug if it ultimately wins approval, despite competition from several approved agents that slash elevated cholesterol levels by targeting the same protein.
In fact, it would be something of a breakthrough. The new agent under study – now called MK-0616 – comes in pill form, in contrast to the three currently available PCSK9-lowering drugs that must be given in injections separated by weeks to months.
The drug faces an uncertain road to regulatory review and any approval, but MK-0616 at least seems to be starting out in the right direction.
In two phase 1 studies with a total of 100 participants, plasma PCSK9 levels plunged more than 90% after a single dose of the drug; and low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels dropped about 65% when MK-0616 was given daily for 2 weeks on a background of statin therapy.
Moreover, “MK-0616 was generally well tolerated at up to and including single doses of 300 milligrams,” the maximum tested in the studies, Douglas G. Johns, PhD, reported at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The collective results from the oral agent’s earliest human experience are “definitely encouraging” and support MK-0616 as a potential LDL-lowering agent that would be more convenient and arguably more accessible to patients compared to current injectable PCSK9 inhibitors, proposed Dr. Johns, clinical director of translational medicine for Merck in Kenilworth, N.J.
Available PCSK9-targeting agents include alirocumab (Praluent, Sanofi/Regeneron), Food and Drug Administration–approved in July 2015, and evolocumab (Repatha, Amgen), approved by the agency the following month. Both are monoclonal antibodies with neutralizing specificity for the PCSK9 protein; whereas the third such agent, inclisiran (Leqvio, Novartis) is a small-molecule interfering-RNA that suppresses PCSK9 synthesis. Inclisiran is approved in the European Union but its case to the FDA was turned down in 2020.
Dr. Johns said MK-0616 is a cyclic peptide that is “about one-hundredth the size of a monoclonal antibody, but we’re able to achieve monoclonal antibody-like potency and selectivity with this much smaller footprint.”
Added to statin therapy, the current PCSK9-targeting agents reduce LDL-C by an additional one-half or more, and the two antibody-based agents “also decrease atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. They are, however, expensive and not always available, requiring insurance or other approval,” observed Anne C. Goldberg, MD, as invited discussant after Dr. Johns’ presentation.
“They require every 2- to 4-week injections. They’re generally reserved for secondary prevention, and sometimes primary prevention as in familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Goldberg, of Washington University, St. Louis. Inclisiran, she noted, requires injections every 6 months and has yet to show its mettle in cardiovascular outcomes trials.
“Certainly, an oral form would be easier to use,” she said. “This would be particularly helpful in patients averse to injections,” especially, perhaps, in children. “Children with familial hypercholesterolemia could benefit with greater cholesterol lowering and might be better off with a pill than an injection.” That would be good reason to emphasize the enrollment of children in the drug’s upcoming clinical trials, Dr. Goldberg said.
But cost could potentially become restrictive for MK-0616 as well, should it ever be approved. “If it’s priced too high, then are you really going to see the increased use?” she posed. “Certainly, there’s a high bar for therapies that are add-on to statins in terms of cost effectiveness.”
In the first of the two trials, 60 predominantly White male participants aged 50 or younger were randomly assigned to receive a single dose of MK-0616, at different levels ranging from 10 mg to 300 mg, or placebo. They subsequently crossed over to a different group for a second round of dosing. Both times, three participants took the drug for every one who received placebo.
Participants who took the active drug, regardless of dosage, showed greater than 90% reductions in circulating PCSK9 levels compared to baseline. Six participants discontinued the study before its completion.
In the second trial, 40 White adults aged 65 or younger (mean, 58), including 13 women, with LDL-C of 60 mg/dL to 160 mg/dL (mean, 87 mg/dL) on statin therapy for at least 3 months were randomly assigned 3-to-1 to add-on MK-0616, either 10 mg or 20 mg daily, or placebo for 14 days.
LDL-C levels fell an average of about 65% over the 2 weeks among those taking the active drug; they declined less than 5% for those who took placebo.
There were no deaths or serious adverse events in either trial, Dr. Johns reported. On the other hand, pharmacokinetics studies showed that exposure to the drug fell by “about 50%-60%” when dosing was preceded by food intake within the previous 30 minutes. “However, if a meal is consumed 30 minutes after the dose, this food effect is much, much less prominent, almost negligible.”
These preliminary results show the drug is “orally bioavailable and exerts a clinically meaningful effect,” Dr. Johns said. “However, there’s definitely more to be done. And we are planning the next phase of clinical development, a phase 2 trial, sometime next year.”
The research was funded by Merck. Dr. Johns disclosed employment with and equity ownership in Merck, as did all the study’s coauthors. Dr. Goldberg disclosed holding research contracts through her institution with Regeneron/Sanofi-Aventis, Amarin, Amgen, Pfizer, IONIS/Akcea, Regeneron, Novartis, Arrowroot Pharmaceuticals, and the FH Foundation; and consulting for Novartis, Akcea, Regeneron, and Esperion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2021
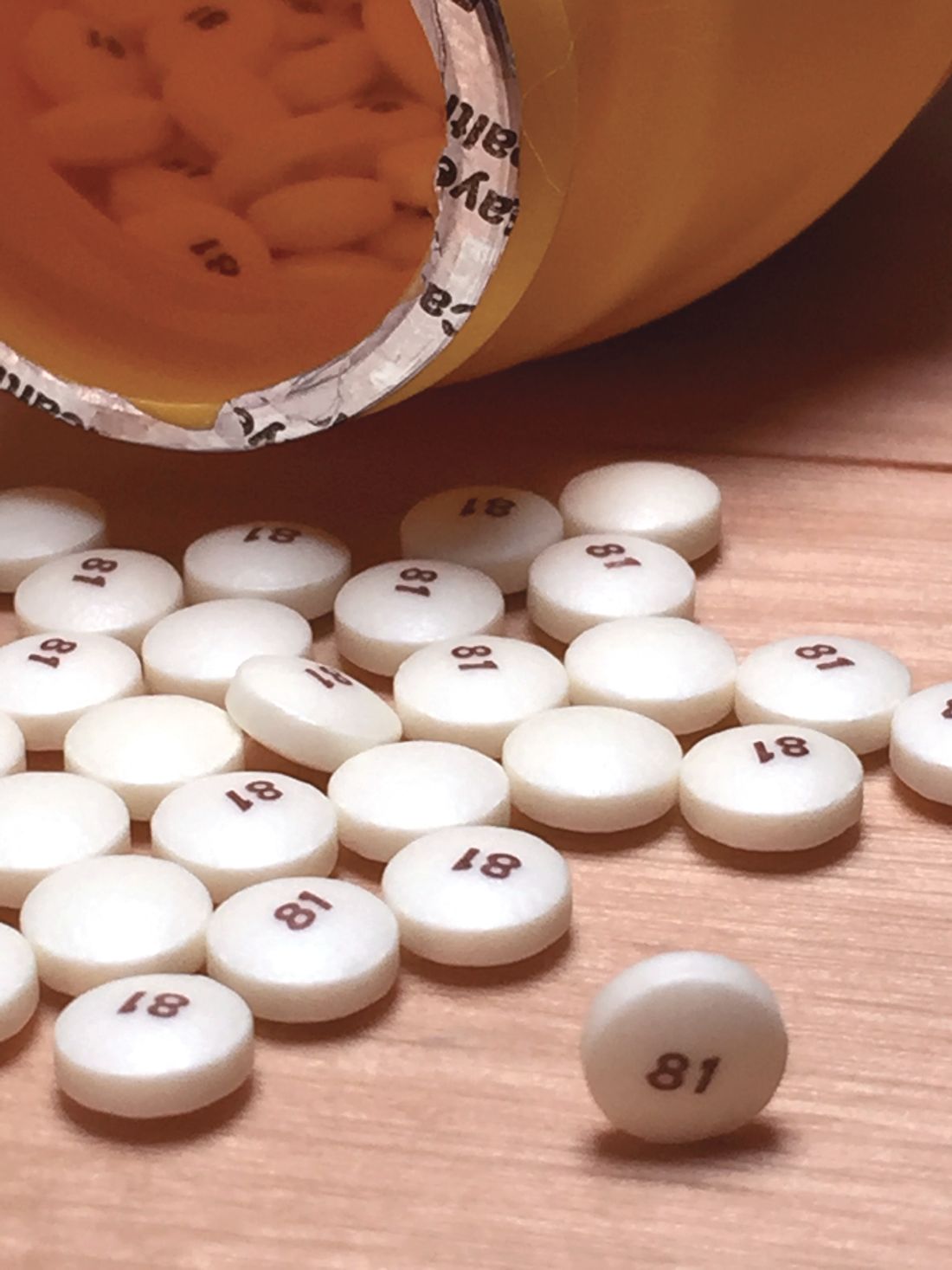
Daily aspirin linked to increased risk of heart failure
Daily aspirin is associated with new onset heart failure independent of other risk factors, according to data derived from a database with follow-up from more than 30,000 patients who did not have HF when they were enrolled.
These data are not relevant to primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular events but “refer only to starting aspirin for secondary prevention of HF in patients at high risk of HF or with symptomatic HF,” according to the senior investigator, Jan A. Staessen, MD, PhD, professor emeritus at the University of Leuven (Belgium).
In data from 30,827 patients at risk for HF enrolled in six observational studies, the hazard ratio (HR) for developing HF among those taking daily aspirin at baseline relative to those who were not was 1.26 (P ≤ .001) over 5.3 years of follow-up. In the 22,690 patients without a prior history cardiovascular disease (CVD), the HF risk increase for exposure to daily aspirin was about the same (HR 1.27; P = .001).
This study was launched because multiple conflicting studies have made the relationship between aspirin and HF risk unclear, according to the multinational team of authors, whose finding were published in ESC Heart Failure.
In principle, HF is recognized as a prothrombotic condition for which an antithrombotic therapy such as aspirin would be expected to have a protective role, but the investigators pointed out that the evidence is mixed. In a population-based Danish study of 12,277 patients with new-onset HF, for example, there was no relationship seen between aspirin use and a reduction in the composite outcome of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Aspirin use linked to HF admissions
“Interestingly, this study reported that aspirin use was associated with an increased risk of readmissions for HF,” wrote the authors of the newly published data. “Uncertainty on aspirin use has been reflected in current guideline recommendations,” they added.
The population studied was drawn from the HOMAGE database, which has collated data on 46,437 participants in 21 studies. After the exclusion of studies with patients who already had HF as well as studies without information on HF incidence over time, six studies with 30,827 participants provided the basis for this analysis.
One study, ASCOT, which was randomized and blinded, served as the derivation data set. The remaining five studies, FLEMENGHO, HEALTH ABC, HULL LIFE LAB, PREDICTOR, and PROSPER, served as the validation data set.
In addition to identifying participants as aspirin users or nonusers at baseline, all of the studies had detailed baseline data on a wide variety of patient characteristics and risk factors, such as body mass index, blood cholesterol levels, blood glucose concentrations, blood pressure, and creatinine.
No patient in any trial was on an antithrombotic therapy other than aspirin at baseline.
Of the minority of patients with CVD at baseline, more than 80% had coronary heart disease. Only 2.8% of the total population had a prior myocardial infarction. In the study population overall, most (86%) had hypertension, and there was a sizeable proportion with diabetes (22%). The average age was 67 years, and 34% were women.
HF incidence on aspirin: 14.5/1000 person-years
Overall, the incidence rate of HF per 1,000 person-years for the entire population before adjustment was 14.5 in the group on daily aspirin versus 5.9 in the non-aspirin group. These absolute rates were lower in the discovery data set than in the validation set, but the relative differences in HF incidence rates for those who were versus those who were not on aspirin at baseline were similar.
Numerous sensitivity analyses supported the basic conclusions. This not only included one omitting patients with a history of CVD, but another that excluded patients who developed HF within the first 2 years. Stratified analyses looking for overall consistency across variables showed increased risk of new onset heart failure among those taking daily aspirin regardless of relative age, body weight, or blood pressure levels.
The most important limitation of this study was that it evaluated data taken from studies not originally designed to test the study hypothesis. In addition, only baseline data were available, so the drugs that patients took over the course of follow-up are unknown. However, the authors believe these data have a clinical message.
Given the consistency of these results, “our observations suggest that aspirin should be prescribed with caution in patients at risk of HF or having HF,” the investigators concluded.
“If such treatment is initiated in these patients, use low-dose aspirin,” Dr. Staessen told this news organization.
Aspirin for CVD versus HF risk
Many patients take low-dose aspirin to prevent the types of cardiovascular events, such as MI, that lead to heart failure. In attempting to address a controversy regarding aspirin and risk of new onset heart failure, it appears to create another regarding CVD risk reduction.
Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Health, Boston, expressed some reluctance in applying these data to routine practice.
“It is important to emphasize that this pooled analysis draws upon six observational studies, not randomized trials of aspirin,” Dr. Bhatt said.
He called these findings “provocative,” but he said they “would need to be confirmed in databases of already completed randomized trials of aspirin versus a control before being actionable.” For Dr. Bhatt, one obstacle to a change in practice based on these data is that, “to my knowledge, no such signal [of a relationship between aspirin and incident heart failure] exists in the cumulative randomized data.”
Dr. Staessen reports no potential conflicts of interest for this study. Dr. Bhatt has a financial relationship with a large number of pharmaceutical companies, including PLx Pharma, for which he performs aspirin-related research.
Daily aspirin is associated with new onset heart failure independent of other risk factors, according to data derived from a database with follow-up from more than 30,000 patients who did not have HF when they were enrolled.
These data are not relevant to primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular events but “refer only to starting aspirin for secondary prevention of HF in patients at high risk of HF or with symptomatic HF,” according to the senior investigator, Jan A. Staessen, MD, PhD, professor emeritus at the University of Leuven (Belgium).
In data from 30,827 patients at risk for HF enrolled in six observational studies, the hazard ratio (HR) for developing HF among those taking daily aspirin at baseline relative to those who were not was 1.26 (P ≤ .001) over 5.3 years of follow-up. In the 22,690 patients without a prior history cardiovascular disease (CVD), the HF risk increase for exposure to daily aspirin was about the same (HR 1.27; P = .001).
This study was launched because multiple conflicting studies have made the relationship between aspirin and HF risk unclear, according to the multinational team of authors, whose finding were published in ESC Heart Failure.
In principle, HF is recognized as a prothrombotic condition for which an antithrombotic therapy such as aspirin would be expected to have a protective role, but the investigators pointed out that the evidence is mixed. In a population-based Danish study of 12,277 patients with new-onset HF, for example, there was no relationship seen between aspirin use and a reduction in the composite outcome of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Aspirin use linked to HF admissions
“Interestingly, this study reported that aspirin use was associated with an increased risk of readmissions for HF,” wrote the authors of the newly published data. “Uncertainty on aspirin use has been reflected in current guideline recommendations,” they added.
The population studied was drawn from the HOMAGE database, which has collated data on 46,437 participants in 21 studies. After the exclusion of studies with patients who already had HF as well as studies without information on HF incidence over time, six studies with 30,827 participants provided the basis for this analysis.
One study, ASCOT, which was randomized and blinded, served as the derivation data set. The remaining five studies, FLEMENGHO, HEALTH ABC, HULL LIFE LAB, PREDICTOR, and PROSPER, served as the validation data set.
In addition to identifying participants as aspirin users or nonusers at baseline, all of the studies had detailed baseline data on a wide variety of patient characteristics and risk factors, such as body mass index, blood cholesterol levels, blood glucose concentrations, blood pressure, and creatinine.
No patient in any trial was on an antithrombotic therapy other than aspirin at baseline.
Of the minority of patients with CVD at baseline, more than 80% had coronary heart disease. Only 2.8% of the total population had a prior myocardial infarction. In the study population overall, most (86%) had hypertension, and there was a sizeable proportion with diabetes (22%). The average age was 67 years, and 34% were women.
HF incidence on aspirin: 14.5/1000 person-years
Overall, the incidence rate of HF per 1,000 person-years for the entire population before adjustment was 14.5 in the group on daily aspirin versus 5.9 in the non-aspirin group. These absolute rates were lower in the discovery data set than in the validation set, but the relative differences in HF incidence rates for those who were versus those who were not on aspirin at baseline were similar.
Numerous sensitivity analyses supported the basic conclusions. This not only included one omitting patients with a history of CVD, but another that excluded patients who developed HF within the first 2 years. Stratified analyses looking for overall consistency across variables showed increased risk of new onset heart failure among those taking daily aspirin regardless of relative age, body weight, or blood pressure levels.
The most important limitation of this study was that it evaluated data taken from studies not originally designed to test the study hypothesis. In addition, only baseline data were available, so the drugs that patients took over the course of follow-up are unknown. However, the authors believe these data have a clinical message.
Given the consistency of these results, “our observations suggest that aspirin should be prescribed with caution in patients at risk of HF or having HF,” the investigators concluded.
“If such treatment is initiated in these patients, use low-dose aspirin,” Dr. Staessen told this news organization.
Aspirin for CVD versus HF risk
Many patients take low-dose aspirin to prevent the types of cardiovascular events, such as MI, that lead to heart failure. In attempting to address a controversy regarding aspirin and risk of new onset heart failure, it appears to create another regarding CVD risk reduction.
Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Health, Boston, expressed some reluctance in applying these data to routine practice.
“It is important to emphasize that this pooled analysis draws upon six observational studies, not randomized trials of aspirin,” Dr. Bhatt said.
He called these findings “provocative,” but he said they “would need to be confirmed in databases of already completed randomized trials of aspirin versus a control before being actionable.” For Dr. Bhatt, one obstacle to a change in practice based on these data is that, “to my knowledge, no such signal [of a relationship between aspirin and incident heart failure] exists in the cumulative randomized data.”
Dr. Staessen reports no potential conflicts of interest for this study. Dr. Bhatt has a financial relationship with a large number of pharmaceutical companies, including PLx Pharma, for which he performs aspirin-related research.
Daily aspirin is associated with new onset heart failure independent of other risk factors, according to data derived from a database with follow-up from more than 30,000 patients who did not have HF when they were enrolled.
These data are not relevant to primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular events but “refer only to starting aspirin for secondary prevention of HF in patients at high risk of HF or with symptomatic HF,” according to the senior investigator, Jan A. Staessen, MD, PhD, professor emeritus at the University of Leuven (Belgium).
In data from 30,827 patients at risk for HF enrolled in six observational studies, the hazard ratio (HR) for developing HF among those taking daily aspirin at baseline relative to those who were not was 1.26 (P ≤ .001) over 5.3 years of follow-up. In the 22,690 patients without a prior history cardiovascular disease (CVD), the HF risk increase for exposure to daily aspirin was about the same (HR 1.27; P = .001).
This study was launched because multiple conflicting studies have made the relationship between aspirin and HF risk unclear, according to the multinational team of authors, whose finding were published in ESC Heart Failure.
In principle, HF is recognized as a prothrombotic condition for which an antithrombotic therapy such as aspirin would be expected to have a protective role, but the investigators pointed out that the evidence is mixed. In a population-based Danish study of 12,277 patients with new-onset HF, for example, there was no relationship seen between aspirin use and a reduction in the composite outcome of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Aspirin use linked to HF admissions
“Interestingly, this study reported that aspirin use was associated with an increased risk of readmissions for HF,” wrote the authors of the newly published data. “Uncertainty on aspirin use has been reflected in current guideline recommendations,” they added.
The population studied was drawn from the HOMAGE database, which has collated data on 46,437 participants in 21 studies. After the exclusion of studies with patients who already had HF as well as studies without information on HF incidence over time, six studies with 30,827 participants provided the basis for this analysis.
One study, ASCOT, which was randomized and blinded, served as the derivation data set. The remaining five studies, FLEMENGHO, HEALTH ABC, HULL LIFE LAB, PREDICTOR, and PROSPER, served as the validation data set.
In addition to identifying participants as aspirin users or nonusers at baseline, all of the studies had detailed baseline data on a wide variety of patient characteristics and risk factors, such as body mass index, blood cholesterol levels, blood glucose concentrations, blood pressure, and creatinine.
No patient in any trial was on an antithrombotic therapy other than aspirin at baseline.
Of the minority of patients with CVD at baseline, more than 80% had coronary heart disease. Only 2.8% of the total population had a prior myocardial infarction. In the study population overall, most (86%) had hypertension, and there was a sizeable proportion with diabetes (22%). The average age was 67 years, and 34% were women.
HF incidence on aspirin: 14.5/1000 person-years
Overall, the incidence rate of HF per 1,000 person-years for the entire population before adjustment was 14.5 in the group on daily aspirin versus 5.9 in the non-aspirin group. These absolute rates were lower in the discovery data set than in the validation set, but the relative differences in HF incidence rates for those who were versus those who were not on aspirin at baseline were similar.
Numerous sensitivity analyses supported the basic conclusions. This not only included one omitting patients with a history of CVD, but another that excluded patients who developed HF within the first 2 years. Stratified analyses looking for overall consistency across variables showed increased risk of new onset heart failure among those taking daily aspirin regardless of relative age, body weight, or blood pressure levels.
The most important limitation of this study was that it evaluated data taken from studies not originally designed to test the study hypothesis. In addition, only baseline data were available, so the drugs that patients took over the course of follow-up are unknown. However, the authors believe these data have a clinical message.
Given the consistency of these results, “our observations suggest that aspirin should be prescribed with caution in patients at risk of HF or having HF,” the investigators concluded.
“If such treatment is initiated in these patients, use low-dose aspirin,” Dr. Staessen told this news organization.
Aspirin for CVD versus HF risk
Many patients take low-dose aspirin to prevent the types of cardiovascular events, such as MI, that lead to heart failure. In attempting to address a controversy regarding aspirin and risk of new onset heart failure, it appears to create another regarding CVD risk reduction.
Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Health, Boston, expressed some reluctance in applying these data to routine practice.
“It is important to emphasize that this pooled analysis draws upon six observational studies, not randomized trials of aspirin,” Dr. Bhatt said.
He called these findings “provocative,” but he said they “would need to be confirmed in databases of already completed randomized trials of aspirin versus a control before being actionable.” For Dr. Bhatt, one obstacle to a change in practice based on these data is that, “to my knowledge, no such signal [of a relationship between aspirin and incident heart failure] exists in the cumulative randomized data.”
Dr. Staessen reports no potential conflicts of interest for this study. Dr. Bhatt has a financial relationship with a large number of pharmaceutical companies, including PLx Pharma, for which he performs aspirin-related research.
FROM JACC HEART FAILURE
Advanced CKD doesn’t derail empagliflozin in EMPEROR-preserved
More than half of the nearly 6,000 patients with heart failure and HFpEF enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had CKD (although renal function was not an enrollment criterion), including 10% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that fell in the range of 20-29 mL/min/1.73 m2, which categorized them as having stage 4 CKD.
The results showed, in a prespecified analysis, that treatment with empagliflozin led to a consistent, significant relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure “across the full spectrum of kidney function, down to an eGFR of 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” said Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Among the 46.5% of enrolled patients without CKD, empagliflozin produced a significant 20% drop in the primary outcome relative to those who received placebo. Among the 53.5% of patients with CKD at time of randomization (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1/73 m2 or a urinary albumin to creatinine ratio >300 mg/g), treatment with empagliflozin was associated with a significant 25% cut in the primary endpoint compared with placebo.
Empagliflozin was also “well tolerated” by patients with HFpEF, whether or not they also had CKD, “including patients with severely impaired kidney function,” said Dr. Zannad, a professor of cardiology therapeutics at the University of Lorraine in Nancy, France, at the virtual meeting.
An end to ‘renalism’
“This is a nail in the coffin for the concept of ‘renalism,’” the erroneous notion held by many clinicians and researchers that various treatments are not as effective and potentially more likely to cause adverse effects in patients with CKD compared with those with better renal function, commented Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist who is a professor and director of the cardiorenal program at George Washington University, Washington, D.C.
In addition to EMPEROR-Preserved, other large trials of agents from the SGLT2 inhibitor class bucked the premise of renalism and took the “groundbreaking step” of enrolling patients with moderate-severe CKD, noted Dr. Rangaswami in an interview. In particular, two trials took this approach when enrolling patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), EMPEROR-Reduced (which also tested empagliflozin and matched the design of EMPEROR-Preserved) and DAPA-HF (which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin [Farxiga, AstraZeneca]).
“It was a huge, bold step, especially in EMPEROR-Preserved and in EMPEROR-Reduced, which both enrolled patients with eGFRs as low as 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” Dr. Rangaswami said. DAPA-HF included patients with eGFRs as low as 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF – published earlier this year – both had similar findings as EMPEROR-Preserved as reported by Dr. Zannad: consistent benefit from empagliflozin or dapagliflozin regardless of eGFR level and no signal of increased adverse events from treatment.
In fact, all three analyses show that patients with worse renal function had the highest risk for cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure; hence, the beneficial impact from SGLT2 inhibitors is greatest in these patients.
These observations “make it easier to focus on the group with moderate-to-severe CKD,” both in the routine care setting as well as in future trials, said Dr. Rangaswami.
“This is a welcome trend that paves the way to test more treatments in patients with stage 4 and even stage 5 CKD, patients ... excluded from trials in the past,” she said.
In addition, the consistent benefit from SGLT2 inhibitors in these three heart failure trials regardless of CKD “means there is simply no room for renalism. There is no room for clinicians to say that because a patient’s eGFR is 30 mL/min/1.73m2 they are worried about starting an SGLT2 inhibitor,” she stressed.
More CKD-independent effects of empagliflozin
Results of other new analyses from EMPEROR-Preserved, also reported by Dr. Zannad, included the finding that empagliflozin was associated with a similar slowing of loss of renal function over time compared with placebo, regardless of CKD status.
In patients with CKD, empagliflozin slowed eGFR loss by 1.4 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, and in those without CKD, by 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, relative to placebo.
“Even in patients without CKD, there was a relevant eGFR decline in the placebo group that was attenuated by empagliflozin,” Dr. Zannad said.
At the end of the study, when empagliflozin was stopped, patients with or without CKD had their eGFR bounce back by an identical 2.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 relative to placebo.
Empagliflozin slowed progression to macroalbuminuria and significantly reduced the incidence of acute kidney injury by a similar amount regardless of CKD status compared with placebo.
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with function-limiting HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction >40%, and a minimum level of a reliable serum marker of heart failure, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Compared with placebo, empagliflozin reduced the trial’s primary outcome by an absolute 3.3 percentage points and by a significant relative risk reduction of 21% after a median 26 months of follow-up, according to a report published in October 2021.
EMPEROR-Preserved is the first prospective, randomized trial to unequivocally show the efficacy and safety of a drug for improving outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Lilly, which market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Zannad has reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as other companies. Dr. Rangaswami has reported being a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than half of the nearly 6,000 patients with heart failure and HFpEF enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had CKD (although renal function was not an enrollment criterion), including 10% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that fell in the range of 20-29 mL/min/1.73 m2, which categorized them as having stage 4 CKD.
The results showed, in a prespecified analysis, that treatment with empagliflozin led to a consistent, significant relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure “across the full spectrum of kidney function, down to an eGFR of 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” said Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Among the 46.5% of enrolled patients without CKD, empagliflozin produced a significant 20% drop in the primary outcome relative to those who received placebo. Among the 53.5% of patients with CKD at time of randomization (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1/73 m2 or a urinary albumin to creatinine ratio >300 mg/g), treatment with empagliflozin was associated with a significant 25% cut in the primary endpoint compared with placebo.
Empagliflozin was also “well tolerated” by patients with HFpEF, whether or not they also had CKD, “including patients with severely impaired kidney function,” said Dr. Zannad, a professor of cardiology therapeutics at the University of Lorraine in Nancy, France, at the virtual meeting.
An end to ‘renalism’
“This is a nail in the coffin for the concept of ‘renalism,’” the erroneous notion held by many clinicians and researchers that various treatments are not as effective and potentially more likely to cause adverse effects in patients with CKD compared with those with better renal function, commented Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist who is a professor and director of the cardiorenal program at George Washington University, Washington, D.C.
In addition to EMPEROR-Preserved, other large trials of agents from the SGLT2 inhibitor class bucked the premise of renalism and took the “groundbreaking step” of enrolling patients with moderate-severe CKD, noted Dr. Rangaswami in an interview. In particular, two trials took this approach when enrolling patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), EMPEROR-Reduced (which also tested empagliflozin and matched the design of EMPEROR-Preserved) and DAPA-HF (which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin [Farxiga, AstraZeneca]).
“It was a huge, bold step, especially in EMPEROR-Preserved and in EMPEROR-Reduced, which both enrolled patients with eGFRs as low as 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” Dr. Rangaswami said. DAPA-HF included patients with eGFRs as low as 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF – published earlier this year – both had similar findings as EMPEROR-Preserved as reported by Dr. Zannad: consistent benefit from empagliflozin or dapagliflozin regardless of eGFR level and no signal of increased adverse events from treatment.
In fact, all three analyses show that patients with worse renal function had the highest risk for cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure; hence, the beneficial impact from SGLT2 inhibitors is greatest in these patients.
These observations “make it easier to focus on the group with moderate-to-severe CKD,” both in the routine care setting as well as in future trials, said Dr. Rangaswami.
“This is a welcome trend that paves the way to test more treatments in patients with stage 4 and even stage 5 CKD, patients ... excluded from trials in the past,” she said.
In addition, the consistent benefit from SGLT2 inhibitors in these three heart failure trials regardless of CKD “means there is simply no room for renalism. There is no room for clinicians to say that because a patient’s eGFR is 30 mL/min/1.73m2 they are worried about starting an SGLT2 inhibitor,” she stressed.
More CKD-independent effects of empagliflozin
Results of other new analyses from EMPEROR-Preserved, also reported by Dr. Zannad, included the finding that empagliflozin was associated with a similar slowing of loss of renal function over time compared with placebo, regardless of CKD status.
In patients with CKD, empagliflozin slowed eGFR loss by 1.4 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, and in those without CKD, by 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, relative to placebo.
“Even in patients without CKD, there was a relevant eGFR decline in the placebo group that was attenuated by empagliflozin,” Dr. Zannad said.
At the end of the study, when empagliflozin was stopped, patients with or without CKD had their eGFR bounce back by an identical 2.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 relative to placebo.
Empagliflozin slowed progression to macroalbuminuria and significantly reduced the incidence of acute kidney injury by a similar amount regardless of CKD status compared with placebo.
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with function-limiting HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction >40%, and a minimum level of a reliable serum marker of heart failure, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Compared with placebo, empagliflozin reduced the trial’s primary outcome by an absolute 3.3 percentage points and by a significant relative risk reduction of 21% after a median 26 months of follow-up, according to a report published in October 2021.
EMPEROR-Preserved is the first prospective, randomized trial to unequivocally show the efficacy and safety of a drug for improving outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Lilly, which market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Zannad has reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as other companies. Dr. Rangaswami has reported being a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than half of the nearly 6,000 patients with heart failure and HFpEF enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had CKD (although renal function was not an enrollment criterion), including 10% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that fell in the range of 20-29 mL/min/1.73 m2, which categorized them as having stage 4 CKD.
The results showed, in a prespecified analysis, that treatment with empagliflozin led to a consistent, significant relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure “across the full spectrum of kidney function, down to an eGFR of 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” said Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Among the 46.5% of enrolled patients without CKD, empagliflozin produced a significant 20% drop in the primary outcome relative to those who received placebo. Among the 53.5% of patients with CKD at time of randomization (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1/73 m2 or a urinary albumin to creatinine ratio >300 mg/g), treatment with empagliflozin was associated with a significant 25% cut in the primary endpoint compared with placebo.
Empagliflozin was also “well tolerated” by patients with HFpEF, whether or not they also had CKD, “including patients with severely impaired kidney function,” said Dr. Zannad, a professor of cardiology therapeutics at the University of Lorraine in Nancy, France, at the virtual meeting.
An end to ‘renalism’
“This is a nail in the coffin for the concept of ‘renalism,’” the erroneous notion held by many clinicians and researchers that various treatments are not as effective and potentially more likely to cause adverse effects in patients with CKD compared with those with better renal function, commented Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist who is a professor and director of the cardiorenal program at George Washington University, Washington, D.C.
In addition to EMPEROR-Preserved, other large trials of agents from the SGLT2 inhibitor class bucked the premise of renalism and took the “groundbreaking step” of enrolling patients with moderate-severe CKD, noted Dr. Rangaswami in an interview. In particular, two trials took this approach when enrolling patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), EMPEROR-Reduced (which also tested empagliflozin and matched the design of EMPEROR-Preserved) and DAPA-HF (which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin [Farxiga, AstraZeneca]).
“It was a huge, bold step, especially in EMPEROR-Preserved and in EMPEROR-Reduced, which both enrolled patients with eGFRs as low as 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” Dr. Rangaswami said. DAPA-HF included patients with eGFRs as low as 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF – published earlier this year – both had similar findings as EMPEROR-Preserved as reported by Dr. Zannad: consistent benefit from empagliflozin or dapagliflozin regardless of eGFR level and no signal of increased adverse events from treatment.
In fact, all three analyses show that patients with worse renal function had the highest risk for cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure; hence, the beneficial impact from SGLT2 inhibitors is greatest in these patients.
These observations “make it easier to focus on the group with moderate-to-severe CKD,” both in the routine care setting as well as in future trials, said Dr. Rangaswami.
“This is a welcome trend that paves the way to test more treatments in patients with stage 4 and even stage 5 CKD, patients ... excluded from trials in the past,” she said.
In addition, the consistent benefit from SGLT2 inhibitors in these three heart failure trials regardless of CKD “means there is simply no room for renalism. There is no room for clinicians to say that because a patient’s eGFR is 30 mL/min/1.73m2 they are worried about starting an SGLT2 inhibitor,” she stressed.
More CKD-independent effects of empagliflozin
Results of other new analyses from EMPEROR-Preserved, also reported by Dr. Zannad, included the finding that empagliflozin was associated with a similar slowing of loss of renal function over time compared with placebo, regardless of CKD status.
In patients with CKD, empagliflozin slowed eGFR loss by 1.4 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, and in those without CKD, by 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, relative to placebo.
“Even in patients without CKD, there was a relevant eGFR decline in the placebo group that was attenuated by empagliflozin,” Dr. Zannad said.
At the end of the study, when empagliflozin was stopped, patients with or without CKD had their eGFR bounce back by an identical 2.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 relative to placebo.
Empagliflozin slowed progression to macroalbuminuria and significantly reduced the incidence of acute kidney injury by a similar amount regardless of CKD status compared with placebo.
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with function-limiting HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction >40%, and a minimum level of a reliable serum marker of heart failure, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Compared with placebo, empagliflozin reduced the trial’s primary outcome by an absolute 3.3 percentage points and by a significant relative risk reduction of 21% after a median 26 months of follow-up, according to a report published in October 2021.
EMPEROR-Preserved is the first prospective, randomized trial to unequivocally show the efficacy and safety of a drug for improving outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Lilly, which market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Zannad has reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as other companies. Dr. Rangaswami has reported being a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM KIDNEY WEEK 2021
Empagliflozin a winner in challenging arena of stabilized acute HF
The sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors, relative newcomers among first-line agents for chronic heart failure (HF), could well attain the same go-to status in patients hospitalized with acute HF if the EMPULSE trial has anything to say about it.
Of the study’s 530 such patients, those started on daily empagliflozin (Jardiance) soon after they were stabilized, compared with a control group, were less likely to die or be rehospitalized for HF over the next 3 months.
Also, “we saw an improvement in quality of life, we saw a greater reduction in body weight, and we didn’t see any safety concerns in this very vulnerable and sick patient population,” Adriaan A. Voors, MD, University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), said when presenting the trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Patients assigned to empagliflozin had a 36% greater likelihood of showing a benefit as reflected in the treatment’s win ratio when opposed by placebo, an emerging way to express outcomes in cardiovascular clinical trials. The SGLT2 inhibitor’s win ratio for the primary endpoint was 1.36 (95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.68, P = .0054), Dr. Voors reported. The outcome consisted of death, number of HF events, time to first HF event, and 90-day change in quality of life scores.
There is reluctance in practice to start patients that early after decompensation on drugs used in chronic HF, Dr. Voors said in an interview. Empagliflozin in the trial was initiated in the stabilized setting an average of 3 days after hospital admission, he said. The trial should reassure physicians that the drug “is not only safe to start early in hospital, but it’s also beneficial to start early in hospital.”
EMPULSE, combined with support from other recent trials, “should be clinical practice changing, with early in-hospital initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with HF being the expectation, along with clear recognition that delaying SGLT2 inhibitor initiation may expose patients to unnecessary harms and delays in improved health status,” Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, told this news organization.
“For patients with HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, early in-hospital initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors – once stabilized and in the absence of contraindications – should be considered a new standard of care,” said Fonarow, who was not part of EMPULSE.
The trial also lends new weight to the strategy of “simultaneous or rapid-sequence initiation” of the so-called four pillars of guideline-directed medical therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction in patients hospitalized with HFrEF, once they are stabilized, Dr. Fonarow said. The four-pronged approach, he noted, consists of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Indeed, the new findings “fill an important gap and are clearly practice changing,” agreed Nancy K. Sweitzer, MD, PhD, University of Arizona Sarver Heart Center, Tucson, as an invited discussant following Dr. Voors’ presentation. “Few therapies have been shown to impact the course of those hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure.”
Of note in the trial, Dr. Sweitzer continued, patients were started on empagliflozin regardless of any drug therapy they might already be on for chronic HF. “Because patients in the EMPULSE trial could be enrolled with a new diagnosis of heart failure, they were, by definition, not all on chronic guideline-directed heart failure therapy. Nevertheless, such patients benefited equally from the study intervention,” she said.
“This is crucial, as it tells us these drugs have immediate and important effects and should not be withheld while other drug classes are initiated and optimized.”
EMPULSE entered patients hospitalized for acute HF, which could be de novo or a decompensation of chronic HF, without regard to ejection fraction or whether they had diabetes, and who were clinically stable after at least one dose of loop diuretics. Their ejection fractions averaged 35% and exceeded 40% in about one-third of the total cohort.
At 90 days in the win ratio analysis, the 265 patients assigned to empagliflozin 10 mg once daily were the “winners”; that is, they were more likely to show a clinical benefit about 54% of the time in paired match-ups of patient outcomes, compared with about 40% for the 265 in the control group. The match-ups were a tie 6.4% of the time.
The empagliflozin group also benefited significantly for the endpoint of death from any cause or first HF event, with a hazard ratio of 0.65 (95% CI, 0.43-0.99; P = .042). They also were less likely to experience acute renal failure (7.7% vs. 12.1% for the control group) or serious adverse events (32.3% vs. 43.6%), Dr. Voors reported.
Tempting as it might be, the findings can’t necessarily be generalized to other SGLT2 inhibitors without an evidence base. But as Dr. Voors observed, several ongoing trials are exploring dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in a similar clinical setting.
They include DICTATE-AHF in patients with diabetes admitted with acute HF, and DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68, which is entering patients stabilized during hospitalization with acute decompensated HFrEF. The trials are scheduled for completion in 2022 and 2023, respectively.
EMPULSE was supported by the Boehringer Ingelheim–Eli Lilly Diabetes Alliance. Dr. Voors disclosed research support and consulting for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Merck, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Sweitzer disclosed honoraria from Acorda and Myokardia, and reported receiving research support from Novartis and Merck. Dr. Fonarow cited honoraria from Abbott, Amgen, Janssen, Medtronic, Bayer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Cytokinetics, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors, relative newcomers among first-line agents for chronic heart failure (HF), could well attain the same go-to status in patients hospitalized with acute HF if the EMPULSE trial has anything to say about it.
Of the study’s 530 such patients, those started on daily empagliflozin (Jardiance) soon after they were stabilized, compared with a control group, were less likely to die or be rehospitalized for HF over the next 3 months.
Also, “we saw an improvement in quality of life, we saw a greater reduction in body weight, and we didn’t see any safety concerns in this very vulnerable and sick patient population,” Adriaan A. Voors, MD, University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), said when presenting the trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Patients assigned to empagliflozin had a 36% greater likelihood of showing a benefit as reflected in the treatment’s win ratio when opposed by placebo, an emerging way to express outcomes in cardiovascular clinical trials. The SGLT2 inhibitor’s win ratio for the primary endpoint was 1.36 (95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.68, P = .0054), Dr. Voors reported. The outcome consisted of death, number of HF events, time to first HF event, and 90-day change in quality of life scores.
There is reluctance in practice to start patients that early after decompensation on drugs used in chronic HF, Dr. Voors said in an interview. Empagliflozin in the trial was initiated in the stabilized setting an average of 3 days after hospital admission, he said. The trial should reassure physicians that the drug “is not only safe to start early in hospital, but it’s also beneficial to start early in hospital.”
EMPULSE, combined with support from other recent trials, “should be clinical practice changing, with early in-hospital initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with HF being the expectation, along with clear recognition that delaying SGLT2 inhibitor initiation may expose patients to unnecessary harms and delays in improved health status,” Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, told this news organization.
“For patients with HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, early in-hospital initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors – once stabilized and in the absence of contraindications – should be considered a new standard of care,” said Fonarow, who was not part of EMPULSE.
The trial also lends new weight to the strategy of “simultaneous or rapid-sequence initiation” of the so-called four pillars of guideline-directed medical therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction in patients hospitalized with HFrEF, once they are stabilized, Dr. Fonarow said. The four-pronged approach, he noted, consists of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Indeed, the new findings “fill an important gap and are clearly practice changing,” agreed Nancy K. Sweitzer, MD, PhD, University of Arizona Sarver Heart Center, Tucson, as an invited discussant following Dr. Voors’ presentation. “Few therapies have been shown to impact the course of those hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure.”
Of note in the trial, Dr. Sweitzer continued, patients were started on empagliflozin regardless of any drug therapy they might already be on for chronic HF. “Because patients in the EMPULSE trial could be enrolled with a new diagnosis of heart failure, they were, by definition, not all on chronic guideline-directed heart failure therapy. Nevertheless, such patients benefited equally from the study intervention,” she said.
“This is crucial, as it tells us these drugs have immediate and important effects and should not be withheld while other drug classes are initiated and optimized.”
EMPULSE entered patients hospitalized for acute HF, which could be de novo or a decompensation of chronic HF, without regard to ejection fraction or whether they had diabetes, and who were clinically stable after at least one dose of loop diuretics. Their ejection fractions averaged 35% and exceeded 40% in about one-third of the total cohort.
At 90 days in the win ratio analysis, the 265 patients assigned to empagliflozin 10 mg once daily were the “winners”; that is, they were more likely to show a clinical benefit about 54% of the time in paired match-ups of patient outcomes, compared with about 40% for the 265 in the control group. The match-ups were a tie 6.4% of the time.
The empagliflozin group also benefited significantly for the endpoint of death from any cause or first HF event, with a hazard ratio of 0.65 (95% CI, 0.43-0.99; P = .042). They also were less likely to experience acute renal failure (7.7% vs. 12.1% for the control group) or serious adverse events (32.3% vs. 43.6%), Dr. Voors reported.
Tempting as it might be, the findings can’t necessarily be generalized to other SGLT2 inhibitors without an evidence base. But as Dr. Voors observed, several ongoing trials are exploring dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in a similar clinical setting.
They include DICTATE-AHF in patients with diabetes admitted with acute HF, and DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68, which is entering patients stabilized during hospitalization with acute decompensated HFrEF. The trials are scheduled for completion in 2022 and 2023, respectively.
EMPULSE was supported by the Boehringer Ingelheim–Eli Lilly Diabetes Alliance. Dr. Voors disclosed research support and consulting for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Merck, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Sweitzer disclosed honoraria from Acorda and Myokardia, and reported receiving research support from Novartis and Merck. Dr. Fonarow cited honoraria from Abbott, Amgen, Janssen, Medtronic, Bayer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Cytokinetics, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors, relative newcomers among first-line agents for chronic heart failure (HF), could well attain the same go-to status in patients hospitalized with acute HF if the EMPULSE trial has anything to say about it.
Of the study’s 530 such patients, those started on daily empagliflozin (Jardiance) soon after they were stabilized, compared with a control group, were less likely to die or be rehospitalized for HF over the next 3 months.
Also, “we saw an improvement in quality of life, we saw a greater reduction in body weight, and we didn’t see any safety concerns in this very vulnerable and sick patient population,” Adriaan A. Voors, MD, University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), said when presenting the trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Patients assigned to empagliflozin had a 36% greater likelihood of showing a benefit as reflected in the treatment’s win ratio when opposed by placebo, an emerging way to express outcomes in cardiovascular clinical trials. The SGLT2 inhibitor’s win ratio for the primary endpoint was 1.36 (95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.68, P = .0054), Dr. Voors reported. The outcome consisted of death, number of HF events, time to first HF event, and 90-day change in quality of life scores.
There is reluctance in practice to start patients that early after decompensation on drugs used in chronic HF, Dr. Voors said in an interview. Empagliflozin in the trial was initiated in the stabilized setting an average of 3 days after hospital admission, he said. The trial should reassure physicians that the drug “is not only safe to start early in hospital, but it’s also beneficial to start early in hospital.”
EMPULSE, combined with support from other recent trials, “should be clinical practice changing, with early in-hospital initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with HF being the expectation, along with clear recognition that delaying SGLT2 inhibitor initiation may expose patients to unnecessary harms and delays in improved health status,” Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, told this news organization.
“For patients with HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, early in-hospital initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors – once stabilized and in the absence of contraindications – should be considered a new standard of care,” said Fonarow, who was not part of EMPULSE.
The trial also lends new weight to the strategy of “simultaneous or rapid-sequence initiation” of the so-called four pillars of guideline-directed medical therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction in patients hospitalized with HFrEF, once they are stabilized, Dr. Fonarow said. The four-pronged approach, he noted, consists of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Indeed, the new findings “fill an important gap and are clearly practice changing,” agreed Nancy K. Sweitzer, MD, PhD, University of Arizona Sarver Heart Center, Tucson, as an invited discussant following Dr. Voors’ presentation. “Few therapies have been shown to impact the course of those hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure.”
Of note in the trial, Dr. Sweitzer continued, patients were started on empagliflozin regardless of any drug therapy they might already be on for chronic HF. “Because patients in the EMPULSE trial could be enrolled with a new diagnosis of heart failure, they were, by definition, not all on chronic guideline-directed heart failure therapy. Nevertheless, such patients benefited equally from the study intervention,” she said.
“This is crucial, as it tells us these drugs have immediate and important effects and should not be withheld while other drug classes are initiated and optimized.”
EMPULSE entered patients hospitalized for acute HF, which could be de novo or a decompensation of chronic HF, without regard to ejection fraction or whether they had diabetes, and who were clinically stable after at least one dose of loop diuretics. Their ejection fractions averaged 35% and exceeded 40% in about one-third of the total cohort.
At 90 days in the win ratio analysis, the 265 patients assigned to empagliflozin 10 mg once daily were the “winners”; that is, they were more likely to show a clinical benefit about 54% of the time in paired match-ups of patient outcomes, compared with about 40% for the 265 in the control group. The match-ups were a tie 6.4% of the time.
The empagliflozin group also benefited significantly for the endpoint of death from any cause or first HF event, with a hazard ratio of 0.65 (95% CI, 0.43-0.99; P = .042). They also were less likely to experience acute renal failure (7.7% vs. 12.1% for the control group) or serious adverse events (32.3% vs. 43.6%), Dr. Voors reported.
Tempting as it might be, the findings can’t necessarily be generalized to other SGLT2 inhibitors without an evidence base. But as Dr. Voors observed, several ongoing trials are exploring dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in a similar clinical setting.
They include DICTATE-AHF in patients with diabetes admitted with acute HF, and DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68, which is entering patients stabilized during hospitalization with acute decompensated HFrEF. The trials are scheduled for completion in 2022 and 2023, respectively.
EMPULSE was supported by the Boehringer Ingelheim–Eli Lilly Diabetes Alliance. Dr. Voors disclosed research support and consulting for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Merck, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Sweitzer disclosed honoraria from Acorda and Myokardia, and reported receiving research support from Novartis and Merck. Dr. Fonarow cited honoraria from Abbott, Amgen, Janssen, Medtronic, Bayer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Cytokinetics, and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2021
EMPEROR-Preserved findings confirmed in ‘true’ HFpEF patients
Main results from the landmark EMPEROR-Preserved trial, reported in August, established for the first time that treatment with a drug, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin, could clearly benefit patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The only caveat was that EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 41%, while “true” HFpEF means patients with heart failure and an LVEF of at least 50%, according to recent definitions. About one-third of the 5,988 patients enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had an LVEF of 41%-49%, heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction.
Secondary analysis from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial has now resolved this ambiguity by showing that, among the 4,005 patients (67%) enrolled in the trial with an LVEF of at least 50%, treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) reduced the study’s primary endpoint – cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for heart failure – by a significant 17%, relative to patients who received placebo, dismissing any doubt about the relevance of the overall finding to the subgroup of patients with unmitigated HFpEF.
“This is the first large-scale trial to document meaningful and significant improvements associated with drug therapy in patients with ‘true’ HFpEF,” Stefan D. Anker, MD, said in presenting the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Streamlining heart failure treatment
The demonstration that empagliflozin is an effective – and safe – treatment for patients with HFpEF not only provides a new treatment for a disorder that until now had no evidence-based intervention, but also streamlines the management approach for treating patients with heart failure with an agent from empagliflozin’s class, the SGLT2 inhibitors, commented Mary Norine Walsh, MD, medical director of the heart failure and cardiac transplantation programs at Ascension St. Vincent Heart Center in Indianapolis.
That’s because empagliflozin has shown significant and consistent benefit across essentially the full range of LVEFs seen in patients with heart failure based on its performance in EMPEROR-Preserved as well as in a mirror-image trial, EMPEROR-Reduced, run in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
“Clinicians do not need to stop and assess LVEF with echocardiography or other imaging before they decide on how to treat heart failure patients” with an SGLT2 inhibitor, noted Dr. Walsh, a designated discussant for the report. “Clinicians who are busy can now refer less to LVEF than to the patient’s phenotype.”
Treatment prevents hospitalization for heart failure
The more-detailed data reported by Dr. Anker also strengthened the case that the benefit from empagliflozin in patients with an LVEF of at least 50% mostly came from a reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure (HHF), which dropped following start of empagliflozin treatment by a relative 22%, compared with placebo for first HHF, a significant decline, and by a relative 17% for total HHF, a reduction that missed significance in this secondary analysis. The other half of the primary endpoint, cardiovascular death, declined by a nonsignificant 11% with empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in patients with clear-cut HFpEF.
The significant reduction in first HHF is, by itself, sufficient reason to use empagliflozin (or possibly a different SGLT2 inhibitor) in patients with HFpEF, maintained Clyde W. Yancy, MD, professor and chief of cardiology at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“Attenuated HHF is a meaningful outcome,” stressed Dr. Yancy, also a discussant for the study. “This is the first time we’ve had evidence supporting that we can change the natural history of patients with HFpEF. While we still need to find interventions that save lives, we cannot overlook that this treatment can improve morbidity, and we cannot overlook that patient quality of life is better.”
Further benefits in patients with an LVEF of at least 50%
Dr. Anker, professor of cardiology and metabolism at Charité Medical University in Berlin, also reported results from several other analyses that further defined the effect of empagliflozin on clinical outcomes of patients with “true” HFpEF:
- The impact of empagliflozin, compared with placebo, for reducing both the study’s combined, primary outcome as well as total HHF was statistically consistent across all strata of LVEF, from 50% to greater than 70%. However, both outcome measures also showed a puzzling loss of benefit among patients with an LVEF of 65%-69%. In prior reports, a researcher on the EMPEROR-Preserved team, Milton Packer, MD, speculated that some patients in this LVEF stratum might not actually have had heart failure but instead had a different disorder that mimicked heart failure in clinical presentation, such as atrial fibrillation.
- Patients’ quality of life as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire showed a consistent benefit from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, both in patients with an LVEF of at least 50% as well as in those with an LVEF of 41%-49%. In both subgroups the adjusted mean difference from placebo was significant and about 1.5 points.
- Patients showed a significant improvement in average New York Heart Association functional class while on treatment, and a strong trend toward less deterioration in functional class while on treatment.
- Deterioration of renal function on treatment slowed by an average 1.24 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, in the subgroup with an LVEF of at least 50%.
Dr. Anker also reported the primary outcome and component results for the subgroup of patients with a baseline LVEF of 41%-49%. These patients had what looked like a “bigger magnitude” of effect from treatment, he noted, showing a significant 29% relative decline in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo-treated patients, and a significant 42% relative drop in first HHF and a significant 43% relative decline in total HHF, compared with placebo.
The primary analysis from EMPEROR-Preserved, which included all 5,988 randomized patients with heart failure and an LVEF of 41% or greater, showed a significant reduction in the combined, primary endpoint with empagliflozin treatment of 21%, compared with control patients during a median follow-up of about 26 months. The absolute rate reduction of the combined primary endpoint was 3.3% during 26-months’ follow-up. Statistical tests have shown no heterogeneity of this effect by diabetes status (49% of patients had diabetes), nor by renal function down to an estimated glomerular filtration rate at entry as low as 20 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, the two companies that market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Anker has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim as well as to Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Brahms, Cardiac Dimensions, Cordio, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Yancy had no disclosures.
Main results from the landmark EMPEROR-Preserved trial, reported in August, established for the first time that treatment with a drug, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin, could clearly benefit patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The only caveat was that EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 41%, while “true” HFpEF means patients with heart failure and an LVEF of at least 50%, according to recent definitions. About one-third of the 5,988 patients enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had an LVEF of 41%-49%, heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction.
Secondary analysis from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial has now resolved this ambiguity by showing that, among the 4,005 patients (67%) enrolled in the trial with an LVEF of at least 50%, treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) reduced the study’s primary endpoint – cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for heart failure – by a significant 17%, relative to patients who received placebo, dismissing any doubt about the relevance of the overall finding to the subgroup of patients with unmitigated HFpEF.
“This is the first large-scale trial to document meaningful and significant improvements associated with drug therapy in patients with ‘true’ HFpEF,” Stefan D. Anker, MD, said in presenting the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Streamlining heart failure treatment
The demonstration that empagliflozin is an effective – and safe – treatment for patients with HFpEF not only provides a new treatment for a disorder that until now had no evidence-based intervention, but also streamlines the management approach for treating patients with heart failure with an agent from empagliflozin’s class, the SGLT2 inhibitors, commented Mary Norine Walsh, MD, medical director of the heart failure and cardiac transplantation programs at Ascension St. Vincent Heart Center in Indianapolis.
That’s because empagliflozin has shown significant and consistent benefit across essentially the full range of LVEFs seen in patients with heart failure based on its performance in EMPEROR-Preserved as well as in a mirror-image trial, EMPEROR-Reduced, run in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
“Clinicians do not need to stop and assess LVEF with echocardiography or other imaging before they decide on how to treat heart failure patients” with an SGLT2 inhibitor, noted Dr. Walsh, a designated discussant for the report. “Clinicians who are busy can now refer less to LVEF than to the patient’s phenotype.”
Treatment prevents hospitalization for heart failure
The more-detailed data reported by Dr. Anker also strengthened the case that the benefit from empagliflozin in patients with an LVEF of at least 50% mostly came from a reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure (HHF), which dropped following start of empagliflozin treatment by a relative 22%, compared with placebo for first HHF, a significant decline, and by a relative 17% for total HHF, a reduction that missed significance in this secondary analysis. The other half of the primary endpoint, cardiovascular death, declined by a nonsignificant 11% with empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in patients with clear-cut HFpEF.
The significant reduction in first HHF is, by itself, sufficient reason to use empagliflozin (or possibly a different SGLT2 inhibitor) in patients with HFpEF, maintained Clyde W. Yancy, MD, professor and chief of cardiology at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“Attenuated HHF is a meaningful outcome,” stressed Dr. Yancy, also a discussant for the study. “This is the first time we’ve had evidence supporting that we can change the natural history of patients with HFpEF. While we still need to find interventions that save lives, we cannot overlook that this treatment can improve morbidity, and we cannot overlook that patient quality of life is better.”
Further benefits in patients with an LVEF of at least 50%
Dr. Anker, professor of cardiology and metabolism at Charité Medical University in Berlin, also reported results from several other analyses that further defined the effect of empagliflozin on clinical outcomes of patients with “true” HFpEF:
- The impact of empagliflozin, compared with placebo, for reducing both the study’s combined, primary outcome as well as total HHF was statistically consistent across all strata of LVEF, from 50% to greater than 70%. However, both outcome measures also showed a puzzling loss of benefit among patients with an LVEF of 65%-69%. In prior reports, a researcher on the EMPEROR-Preserved team, Milton Packer, MD, speculated that some patients in this LVEF stratum might not actually have had heart failure but instead had a different disorder that mimicked heart failure in clinical presentation, such as atrial fibrillation.
- Patients’ quality of life as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire showed a consistent benefit from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, both in patients with an LVEF of at least 50% as well as in those with an LVEF of 41%-49%. In both subgroups the adjusted mean difference from placebo was significant and about 1.5 points.
- Patients showed a significant improvement in average New York Heart Association functional class while on treatment, and a strong trend toward less deterioration in functional class while on treatment.
- Deterioration of renal function on treatment slowed by an average 1.24 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, in the subgroup with an LVEF of at least 50%.
Dr. Anker also reported the primary outcome and component results for the subgroup of patients with a baseline LVEF of 41%-49%. These patients had what looked like a “bigger magnitude” of effect from treatment, he noted, showing a significant 29% relative decline in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo-treated patients, and a significant 42% relative drop in first HHF and a significant 43% relative decline in total HHF, compared with placebo.
The primary analysis from EMPEROR-Preserved, which included all 5,988 randomized patients with heart failure and an LVEF of 41% or greater, showed a significant reduction in the combined, primary endpoint with empagliflozin treatment of 21%, compared with control patients during a median follow-up of about 26 months. The absolute rate reduction of the combined primary endpoint was 3.3% during 26-months’ follow-up. Statistical tests have shown no heterogeneity of this effect by diabetes status (49% of patients had diabetes), nor by renal function down to an estimated glomerular filtration rate at entry as low as 20 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, the two companies that market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Anker has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim as well as to Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Brahms, Cardiac Dimensions, Cordio, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Yancy had no disclosures.
Main results from the landmark EMPEROR-Preserved trial, reported in August, established for the first time that treatment with a drug, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin, could clearly benefit patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The only caveat was that EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 41%, while “true” HFpEF means patients with heart failure and an LVEF of at least 50%, according to recent definitions. About one-third of the 5,988 patients enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had an LVEF of 41%-49%, heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction.
Secondary analysis from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial has now resolved this ambiguity by showing that, among the 4,005 patients (67%) enrolled in the trial with an LVEF of at least 50%, treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) reduced the study’s primary endpoint – cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for heart failure – by a significant 17%, relative to patients who received placebo, dismissing any doubt about the relevance of the overall finding to the subgroup of patients with unmitigated HFpEF.
“This is the first large-scale trial to document meaningful and significant improvements associated with drug therapy in patients with ‘true’ HFpEF,” Stefan D. Anker, MD, said in presenting the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Streamlining heart failure treatment
The demonstration that empagliflozin is an effective – and safe – treatment for patients with HFpEF not only provides a new treatment for a disorder that until now had no evidence-based intervention, but also streamlines the management approach for treating patients with heart failure with an agent from empagliflozin’s class, the SGLT2 inhibitors, commented Mary Norine Walsh, MD, medical director of the heart failure and cardiac transplantation programs at Ascension St. Vincent Heart Center in Indianapolis.
That’s because empagliflozin has shown significant and consistent benefit across essentially the full range of LVEFs seen in patients with heart failure based on its performance in EMPEROR-Preserved as well as in a mirror-image trial, EMPEROR-Reduced, run in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
“Clinicians do not need to stop and assess LVEF with echocardiography or other imaging before they decide on how to treat heart failure patients” with an SGLT2 inhibitor, noted Dr. Walsh, a designated discussant for the report. “Clinicians who are busy can now refer less to LVEF than to the patient’s phenotype.”
Treatment prevents hospitalization for heart failure
The more-detailed data reported by Dr. Anker also strengthened the case that the benefit from empagliflozin in patients with an LVEF of at least 50% mostly came from a reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure (HHF), which dropped following start of empagliflozin treatment by a relative 22%, compared with placebo for first HHF, a significant decline, and by a relative 17% for total HHF, a reduction that missed significance in this secondary analysis. The other half of the primary endpoint, cardiovascular death, declined by a nonsignificant 11% with empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in patients with clear-cut HFpEF.
The significant reduction in first HHF is, by itself, sufficient reason to use empagliflozin (or possibly a different SGLT2 inhibitor) in patients with HFpEF, maintained Clyde W. Yancy, MD, professor and chief of cardiology at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“Attenuated HHF is a meaningful outcome,” stressed Dr. Yancy, also a discussant for the study. “This is the first time we’ve had evidence supporting that we can change the natural history of patients with HFpEF. While we still need to find interventions that save lives, we cannot overlook that this treatment can improve morbidity, and we cannot overlook that patient quality of life is better.”
Further benefits in patients with an LVEF of at least 50%
Dr. Anker, professor of cardiology and metabolism at Charité Medical University in Berlin, also reported results from several other analyses that further defined the effect of empagliflozin on clinical outcomes of patients with “true” HFpEF:
- The impact of empagliflozin, compared with placebo, for reducing both the study’s combined, primary outcome as well as total HHF was statistically consistent across all strata of LVEF, from 50% to greater than 70%. However, both outcome measures also showed a puzzling loss of benefit among patients with an LVEF of 65%-69%. In prior reports, a researcher on the EMPEROR-Preserved team, Milton Packer, MD, speculated that some patients in this LVEF stratum might not actually have had heart failure but instead had a different disorder that mimicked heart failure in clinical presentation, such as atrial fibrillation.
- Patients’ quality of life as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire showed a consistent benefit from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, both in patients with an LVEF of at least 50% as well as in those with an LVEF of 41%-49%. In both subgroups the adjusted mean difference from placebo was significant and about 1.5 points.
- Patients showed a significant improvement in average New York Heart Association functional class while on treatment, and a strong trend toward less deterioration in functional class while on treatment.
- Deterioration of renal function on treatment slowed by an average 1.24 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, in the subgroup with an LVEF of at least 50%.
Dr. Anker also reported the primary outcome and component results for the subgroup of patients with a baseline LVEF of 41%-49%. These patients had what looked like a “bigger magnitude” of effect from treatment, he noted, showing a significant 29% relative decline in the primary endpoint, compared with placebo-treated patients, and a significant 42% relative drop in first HHF and a significant 43% relative decline in total HHF, compared with placebo.
The primary analysis from EMPEROR-Preserved, which included all 5,988 randomized patients with heart failure and an LVEF of 41% or greater, showed a significant reduction in the combined, primary endpoint with empagliflozin treatment of 21%, compared with control patients during a median follow-up of about 26 months. The absolute rate reduction of the combined primary endpoint was 3.3% during 26-months’ follow-up. Statistical tests have shown no heterogeneity of this effect by diabetes status (49% of patients had diabetes), nor by renal function down to an estimated glomerular filtration rate at entry as low as 20 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, the two companies that market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Anker has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim as well as to Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Brahms, Cardiac Dimensions, Cordio, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Yancy had no disclosures.
FROM AHA2021
DREAM-HF: Negative stem cell trial in heart failure may still offer promise
A large, multicenter, sham-controlled trial in heart failure showed no benefit at all from stem cell delivery on the primary outcome of recurrent nonfatal decompensated HF events, but the results were still promising, according to the DREAM-HF study’s principal investigator.
When added to guideline-directed medical therapy in patients with HF, a single dose of mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC) significantly reduced major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) – a composite of cardiac death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke – and all-cause death in New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II (but not class III patients), reported Emerson C. Perin, MD, PhD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The problem is that none of these outcomes were included in the primary endpoint, which was recurrent events because of nonfatal decompensated heart failure. On this endpoint, the hazard ratio for events by the end of follow-up was nonsignificantly but slightly increased among those randomized to MPCs rather than sham control (HR, 1.2; P = .406).
“We learned a lot in this trial,” said Dr. Perin, who is medical director of the Texas Heart Institute in Houston, acknowledging that the expectation of benefit on the primary endpoint now appears to have been misplaced, but the positive result on other outcomes opens a new research direction.
With a negative result on the primary endpoint, a benefit on secondary endpoints is considered hypothesis generating. But Dr. Perin defended his sense of overall optimism about the results, because all of the endpoints on which benefit was demonstrated were prespecified. The positive findings “are not from a post hoc analyses,” he emphasized.
DREAM-HF
In the trial, 537 patients with chronic ischemic or nonischemic heart failure with NYHA class II or III symptoms and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or lower were randomized at 51 sites in the United States and Canada. Patients were required to have elevated N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels, at least one prior hospitalization for heart failure, and have been on positive inotropic therapy for more than 1 month (but less than 9 months).
The intracardiac administration of MPCs, which are derived from adult human bone marrow, were delivered by injection guided with the NOGA left ventricular electromechanical mapping system. Multiple transendocardial injections were delivered, all in a single session.
There were no differences in baseline characteristics between those receiving MPCs and those who underwent a sham procedure. In both groups, more than half of patients had a previous MI and a coronary revascularization. Nearly 85% had an implanted defibrillator. Roughly two-thirds were in NYHA class III HF and the remaining were in class II.
Over the follow-up, the lines on a graph documenting nonfatal decompensated heart failure events were largely superimposed for the MPC-treated and sham-treated patients, with no significant differences seen over time.
However, the differences on the secondary events were sizable. For the composite outcome of nonfatal MI and nonfatal stroke over a mean follow-up of about 30 months, the rate of events was less than half as great in those randomized to MPCs (4.6% vs. 13.0%). This translated into about 65% reduction in risk (HR, 0.346; P = .001) overall, and the reduction was about the same in class II or III patients.
For a composite endpoint of MACE, events in the group treated with MPCs were about one-third lower than in the sham procedure group (20.3% vs. 30.1%), a difference that also reached significance (HR, 0.667; P = .021).
For this MACE endpoint, response was evaluated by systemic inflammation. For those with a high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) level of less than 2 mg/L, the risk reduction was small and not significant (HR, 0.843; P = .519). Conversely, there was a large risk reduction in those with hsCRP of at least 2 mg/L that did reach statistical significance (HR, 0.551; P = .012).
Inflammation was also found to be a discriminator for time to cardiac death among the patients with NYHA class II HF. Again, there was no benefit among those with hsCRP below 2 mg/L (HR, 1.355; P = .672), but an 80% risk reduction for those with hsCRP of at least 2 mg/L (HR, 0.204; P = .005).
In class II patients with hsCRP at least 2 mg/L, there was also a 60% reduction in all-cause death (HR, 0.401; P = .027). Neither the reduction in cardiac death nor all-cause death was observed in class III HF patients whether or not they had elevated hsCRP.
These signals of benefit provide a direction for a new set of studies, but Dr. Perin said that safety analyses from the DREAM-HF trial are reassuring for further clinical development.
In addition to the fact that “treatment-emergent adverse events and serious adverse events were similar in the MPC-treated and control patients,” Dr. Perin said that MPC administration was not associated with any clinically meaningful immune responses.
MPCs were first injected into a human 15 years ago, according to Dr. Perin. While a phase 2 trial published several years ago did show an association of MPC administration with a reduction in HF-associated events as well as a reduction in adverse ventricular remodeling, the ischemic benefits observed in this trial, particularly in those with elevated hsCRP, provide a new direction for future trials.
“This turns the page in heart failure research. We now have a new mechanism to consider,” Dr. Perin said.
Not so fast, expert says
This might be a reasonable conclusion, but the AHA-invited discussant, Larry Allen, MD, believes there is essentially no clinical message from this trial. He reiterated multiple times that this trial was neutral with no trend for benefit on the primary outcome.
“There was benefit on the secondary outcomes of nonfatal MI or stroke, but these are not the outcomes we follow in heart failure patients,” he said, noting that benefit from regenerative therapy on ischemic events has not been a major focus of the trials that preceded DREAM-HF.
Despite these intriguing results, “patients should understand that stem cells remain experimental,” he said. For the patient, it is “more important to double down on the importance of guideline directed medical therapy,” which is still being administered at levels that are suboptimal, according to Dr. Allen, medical director of advanced heart failure at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
“Keep up the investment” in the promise of stem cell therapy, he said, but he cautioned that some of the secondary benefits observed in DREAM-HF, such as the greater response in patients with elevated hsCRP, appear to be new observations that will require a great deal more study to validate.
Dr. Perin has a financial relationship with Mesoblast, which provided funding for the DREAM-HF trial. Dr. Allen reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A large, multicenter, sham-controlled trial in heart failure showed no benefit at all from stem cell delivery on the primary outcome of recurrent nonfatal decompensated HF events, but the results were still promising, according to the DREAM-HF study’s principal investigator.
When added to guideline-directed medical therapy in patients with HF, a single dose of mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC) significantly reduced major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) – a composite of cardiac death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke – and all-cause death in New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II (but not class III patients), reported Emerson C. Perin, MD, PhD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The problem is that none of these outcomes were included in the primary endpoint, which was recurrent events because of nonfatal decompensated heart failure. On this endpoint, the hazard ratio for events by the end of follow-up was nonsignificantly but slightly increased among those randomized to MPCs rather than sham control (HR, 1.2; P = .406).
“We learned a lot in this trial,” said Dr. Perin, who is medical director of the Texas Heart Institute in Houston, acknowledging that the expectation of benefit on the primary endpoint now appears to have been misplaced, but the positive result on other outcomes opens a new research direction.
With a negative result on the primary endpoint, a benefit on secondary endpoints is considered hypothesis generating. But Dr. Perin defended his sense of overall optimism about the results, because all of the endpoints on which benefit was demonstrated were prespecified. The positive findings “are not from a post hoc analyses,” he emphasized.
DREAM-HF
In the trial, 537 patients with chronic ischemic or nonischemic heart failure with NYHA class II or III symptoms and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or lower were randomized at 51 sites in the United States and Canada. Patients were required to have elevated N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels, at least one prior hospitalization for heart failure, and have been on positive inotropic therapy for more than 1 month (but less than 9 months).
The intracardiac administration of MPCs, which are derived from adult human bone marrow, were delivered by injection guided with the NOGA left ventricular electromechanical mapping system. Multiple transendocardial injections were delivered, all in a single session.
There were no differences in baseline characteristics between those receiving MPCs and those who underwent a sham procedure. In both groups, more than half of patients had a previous MI and a coronary revascularization. Nearly 85% had an implanted defibrillator. Roughly two-thirds were in NYHA class III HF and the remaining were in class II.
Over the follow-up, the lines on a graph documenting nonfatal decompensated heart failure events were largely superimposed for the MPC-treated and sham-treated patients, with no significant differences seen over time.
However, the differences on the secondary events were sizable. For the composite outcome of nonfatal MI and nonfatal stroke over a mean follow-up of about 30 months, the rate of events was less than half as great in those randomized to MPCs (4.6% vs. 13.0%). This translated into about 65% reduction in risk (HR, 0.346; P = .001) overall, and the reduction was about the same in class II or III patients.
For a composite endpoint of MACE, events in the group treated with MPCs were about one-third lower than in the sham procedure group (20.3% vs. 30.1%), a difference that also reached significance (HR, 0.667; P = .021).
For this MACE endpoint, response was evaluated by systemic inflammation. For those with a high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) level of less than 2 mg/L, the risk reduction was small and not significant (HR, 0.843; P = .519). Conversely, there was a large risk reduction in those with hsCRP of at least 2 mg/L that did reach statistical significance (HR, 0.551; P = .012).
Inflammation was also found to be a discriminator for time to cardiac death among the patients with NYHA class II HF. Again, there was no benefit among those with hsCRP below 2 mg/L (HR, 1.355; P = .672), but an 80% risk reduction for those with hsCRP of at least 2 mg/L (HR, 0.204; P = .005).
In class II patients with hsCRP at least 2 mg/L, there was also a 60% reduction in all-cause death (HR, 0.401; P = .027). Neither the reduction in cardiac death nor all-cause death was observed in class III HF patients whether or not they had elevated hsCRP.
These signals of benefit provide a direction for a new set of studies, but Dr. Perin said that safety analyses from the DREAM-HF trial are reassuring for further clinical development.
In addition to the fact that “treatment-emergent adverse events and serious adverse events were similar in the MPC-treated and control patients,” Dr. Perin said that MPC administration was not associated with any clinically meaningful immune responses.
MPCs were first injected into a human 15 years ago, according to Dr. Perin. While a phase 2 trial published several years ago did show an association of MPC administration with a reduction in HF-associated events as well as a reduction in adverse ventricular remodeling, the ischemic benefits observed in this trial, particularly in those with elevated hsCRP, provide a new direction for future trials.
“This turns the page in heart failure research. We now have a new mechanism to consider,” Dr. Perin said.
Not so fast, expert says
This might be a reasonable conclusion, but the AHA-invited discussant, Larry Allen, MD, believes there is essentially no clinical message from this trial. He reiterated multiple times that this trial was neutral with no trend for benefit on the primary outcome.
“There was benefit on the secondary outcomes of nonfatal MI or stroke, but these are not the outcomes we follow in heart failure patients,” he said, noting that benefit from regenerative therapy on ischemic events has not been a major focus of the trials that preceded DREAM-HF.
Despite these intriguing results, “patients should understand that stem cells remain experimental,” he said. For the patient, it is “more important to double down on the importance of guideline directed medical therapy,” which is still being administered at levels that are suboptimal, according to Dr. Allen, medical director of advanced heart failure at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
“Keep up the investment” in the promise of stem cell therapy, he said, but he cautioned that some of the secondary benefits observed in DREAM-HF, such as the greater response in patients with elevated hsCRP, appear to be new observations that will require a great deal more study to validate.
Dr. Perin has a financial relationship with Mesoblast, which provided funding for the DREAM-HF trial. Dr. Allen reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A large, multicenter, sham-controlled trial in heart failure showed no benefit at all from stem cell delivery on the primary outcome of recurrent nonfatal decompensated HF events, but the results were still promising, according to the DREAM-HF study’s principal investigator.
When added to guideline-directed medical therapy in patients with HF, a single dose of mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC) significantly reduced major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) – a composite of cardiac death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke – and all-cause death in New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II (but not class III patients), reported Emerson C. Perin, MD, PhD, at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The problem is that none of these outcomes were included in the primary endpoint, which was recurrent events because of nonfatal decompensated heart failure. On this endpoint, the hazard ratio for events by the end of follow-up was nonsignificantly but slightly increased among those randomized to MPCs rather than sham control (HR, 1.2; P = .406).
“We learned a lot in this trial,” said Dr. Perin, who is medical director of the Texas Heart Institute in Houston, acknowledging that the expectation of benefit on the primary endpoint now appears to have been misplaced, but the positive result on other outcomes opens a new research direction.
With a negative result on the primary endpoint, a benefit on secondary endpoints is considered hypothesis generating. But Dr. Perin defended his sense of overall optimism about the results, because all of the endpoints on which benefit was demonstrated were prespecified. The positive findings “are not from a post hoc analyses,” he emphasized.
DREAM-HF
In the trial, 537 patients with chronic ischemic or nonischemic heart failure with NYHA class II or III symptoms and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or lower were randomized at 51 sites in the United States and Canada. Patients were required to have elevated N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels, at least one prior hospitalization for heart failure, and have been on positive inotropic therapy for more than 1 month (but less than 9 months).
The intracardiac administration of MPCs, which are derived from adult human bone marrow, were delivered by injection guided with the NOGA left ventricular electromechanical mapping system. Multiple transendocardial injections were delivered, all in a single session.
There were no differences in baseline characteristics between those receiving MPCs and those who underwent a sham procedure. In both groups, more than half of patients had a previous MI and a coronary revascularization. Nearly 85% had an implanted defibrillator. Roughly two-thirds were in NYHA class III HF and the remaining were in class II.
Over the follow-up, the lines on a graph documenting nonfatal decompensated heart failure events were largely superimposed for the MPC-treated and sham-treated patients, with no significant differences seen over time.
However, the differences on the secondary events were sizable. For the composite outcome of nonfatal MI and nonfatal stroke over a mean follow-up of about 30 months, the rate of events was less than half as great in those randomized to MPCs (4.6% vs. 13.0%). This translated into about 65% reduction in risk (HR, 0.346; P = .001) overall, and the reduction was about the same in class II or III patients.
For a composite endpoint of MACE, events in the group treated with MPCs were about one-third lower than in the sham procedure group (20.3% vs. 30.1%), a difference that also reached significance (HR, 0.667; P = .021).
For this MACE endpoint, response was evaluated by systemic inflammation. For those with a high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) level of less than 2 mg/L, the risk reduction was small and not significant (HR, 0.843; P = .519). Conversely, there was a large risk reduction in those with hsCRP of at least 2 mg/L that did reach statistical significance (HR, 0.551; P = .012).
Inflammation was also found to be a discriminator for time to cardiac death among the patients with NYHA class II HF. Again, there was no benefit among those with hsCRP below 2 mg/L (HR, 1.355; P = .672), but an 80% risk reduction for those with hsCRP of at least 2 mg/L (HR, 0.204; P = .005).
In class II patients with hsCRP at least 2 mg/L, there was also a 60% reduction in all-cause death (HR, 0.401; P = .027). Neither the reduction in cardiac death nor all-cause death was observed in class III HF patients whether or not they had elevated hsCRP.
These signals of benefit provide a direction for a new set of studies, but Dr. Perin said that safety analyses from the DREAM-HF trial are reassuring for further clinical development.
In addition to the fact that “treatment-emergent adverse events and serious adverse events were similar in the MPC-treated and control patients,” Dr. Perin said that MPC administration was not associated with any clinically meaningful immune responses.
MPCs were first injected into a human 15 years ago, according to Dr. Perin. While a phase 2 trial published several years ago did show an association of MPC administration with a reduction in HF-associated events as well as a reduction in adverse ventricular remodeling, the ischemic benefits observed in this trial, particularly in those with elevated hsCRP, provide a new direction for future trials.
“This turns the page in heart failure research. We now have a new mechanism to consider,” Dr. Perin said.
Not so fast, expert says
This might be a reasonable conclusion, but the AHA-invited discussant, Larry Allen, MD, believes there is essentially no clinical message from this trial. He reiterated multiple times that this trial was neutral with no trend for benefit on the primary outcome.
“There was benefit on the secondary outcomes of nonfatal MI or stroke, but these are not the outcomes we follow in heart failure patients,” he said, noting that benefit from regenerative therapy on ischemic events has not been a major focus of the trials that preceded DREAM-HF.
Despite these intriguing results, “patients should understand that stem cells remain experimental,” he said. For the patient, it is “more important to double down on the importance of guideline directed medical therapy,” which is still being administered at levels that are suboptimal, according to Dr. Allen, medical director of advanced heart failure at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
“Keep up the investment” in the promise of stem cell therapy, he said, but he cautioned that some of the secondary benefits observed in DREAM-HF, such as the greater response in patients with elevated hsCRP, appear to be new observations that will require a great deal more study to validate.
Dr. Perin has a financial relationship with Mesoblast, which provided funding for the DREAM-HF trial. Dr. Allen reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM AHA 2021
EHRs have no impact on inpatient heart failure clinical choices or outcomes
When provided at the bedside of patients hospitalized for heart failure, an electronic health record (EHR) alert with prognostic information did not improve outcomes or appear to have any impact on what treatments were offered.
There was no signal that the EHR prognostic alerts, which identified the 12-month risk of mortality, had any impact on any of a variety of clinical-decision-making metrics or on any of the primary or secondary outcomes, according to Tariq Ahmad, MD, who reported results of the randomized REVEAL-HF trial, presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“These results call into question the hypothesis that accurate prognostic information alone will lead to better clinical decision-making,” said Dr. Ahmad, medical director of the Heart Transplant and Mechanical Circulatory Support Program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and principal investigator of REVEAL-HF.
He acknowledged that the possibility that many clinicians pay little or no attention to EHR alert might have played a role in the negative results.
At four participating Yale-affiliated clinical centers, all patients hospitalized for acute heart failure were randomized as long as they were over the age of 18, had an N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level above 500 pg/mL, and had been placed on IV diuretics within 24 hours of admission. In the experimental arm, the provider at the time of entering orders received an EHR alert with an estimate of the risk of all-cause mortality at 12 months. There was no such alert for patients managed in the control arm.
Twelve-month mortality estimates calculated
The all-cause mortality risk was calculated on a sizeable list of variables that included laboratory results, such as cell counts, and patient characteristics, such as weight and age. The risk estimate was displayed along with a five-category color-coded bar to provide context for the risk in the spectrum of very low, low, medium, high, and very high likelihood of death within 12 months.
The 1,590 patients randomized to the experimental arm and the 1,534 patients randomized to the usual care arm did not differ significantly in any baseline characteristics. The median age was about 77 years, the mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 55%. About 29% had an LVEF below 40%, about 40% had chronic kidney disease, and about 30% had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The composite primary outcome of all-cause mortality or rehospitalization within 12 months was reached by 38.9% and 39.3% (P = 0.82) of the intervention and control arms, respectively. The components of the primary outcome were also nearly identical, as was inpatient mortality (8.4% vs. 8.8%; P = 0.72).
There were no significant differences in any of the secondary outcomes, which included rates of 30-day rehospitalizations, discharge on guideline-recommended heart failure therapies, implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator, use of a left ventricular assist device, or heart transplant.
The proportion of patients referred for palliative care was almost identical in the very low, low, and medium risk groups. In the high (23.4 vs. 15.6; P = 0.19) and very high (50% vs. 40%; P = 0.92) groups, there were numerically more referrals in the group randomized to usual care, but these rates did not reach significance.
No differences seen in discharge meds
There was essentially no difference between groups in the rates at which patients were discharged on beta-blockers, renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or mineralocorticoid antagonists.
When prespecified subgroups, such as those older than age 75 years relative to those younger, males relative to females, Black versus White participants, patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) relative to preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), and intensive care unit versus non-ICU patients, were compared, there were no indications that the EHR alert improved outcomes.
Invited discussant Harriette G. C. Van Spall, MD, director of digital health and virtual care and associate professor of cardiology at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., did not dispute the conclusions, but she pointed out several potential explanations for the neutral result.
Not least, nearly 75% of those enrolled had low risk or very low risk for adverse outcomes within 1 year, so the opportunity to show a reduction in events, including all-cause mortality, was limited.
“This was largely a HFpEF population, for which there are no treatments for which a risk score would change therapy,” she said.
EHR alert efficacy questioned
There is considerable evidence that risk prediction tools “are common but underutilized in HF,” Dr. Van Spall added. She noted that many clinicians find alerts in the EHR more annoying than informative, and it remains unknown what proportion of clinicians pay attention to them, particularly in the absence of evidence that they lead to meaningful improvements in care over their own clinical judgment.
Dr. Ahmad agreed.
“I think that we need to study these alerts in a clinical trial format,” he said. Acknowledging that alerts have been poorly received by many clinicians, Dr. Ahmad said that trials to validate the impact of any specific alert are needed to improve their credibility. If a positive impact cannot be shown, he said the alert should be eliminated, leaving only the alerts with proven clinical value.
Dr. Ahmad reported financial relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Novartis, and Relypsa. Dr. Van Spall reports no potential conflicts of interest.
When provided at the bedside of patients hospitalized for heart failure, an electronic health record (EHR) alert with prognostic information did not improve outcomes or appear to have any impact on what treatments were offered.
There was no signal that the EHR prognostic alerts, which identified the 12-month risk of mortality, had any impact on any of a variety of clinical-decision-making metrics or on any of the primary or secondary outcomes, according to Tariq Ahmad, MD, who reported results of the randomized REVEAL-HF trial, presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“These results call into question the hypothesis that accurate prognostic information alone will lead to better clinical decision-making,” said Dr. Ahmad, medical director of the Heart Transplant and Mechanical Circulatory Support Program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and principal investigator of REVEAL-HF.
He acknowledged that the possibility that many clinicians pay little or no attention to EHR alert might have played a role in the negative results.
At four participating Yale-affiliated clinical centers, all patients hospitalized for acute heart failure were randomized as long as they were over the age of 18, had an N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level above 500 pg/mL, and had been placed on IV diuretics within 24 hours of admission. In the experimental arm, the provider at the time of entering orders received an EHR alert with an estimate of the risk of all-cause mortality at 12 months. There was no such alert for patients managed in the control arm.
Twelve-month mortality estimates calculated
The all-cause mortality risk was calculated on a sizeable list of variables that included laboratory results, such as cell counts, and patient characteristics, such as weight and age. The risk estimate was displayed along with a five-category color-coded bar to provide context for the risk in the spectrum of very low, low, medium, high, and very high likelihood of death within 12 months.
The 1,590 patients randomized to the experimental arm and the 1,534 patients randomized to the usual care arm did not differ significantly in any baseline characteristics. The median age was about 77 years, the mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 55%. About 29% had an LVEF below 40%, about 40% had chronic kidney disease, and about 30% had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The composite primary outcome of all-cause mortality or rehospitalization within 12 months was reached by 38.9% and 39.3% (P = 0.82) of the intervention and control arms, respectively. The components of the primary outcome were also nearly identical, as was inpatient mortality (8.4% vs. 8.8%; P = 0.72).
There were no significant differences in any of the secondary outcomes, which included rates of 30-day rehospitalizations, discharge on guideline-recommended heart failure therapies, implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator, use of a left ventricular assist device, or heart transplant.
The proportion of patients referred for palliative care was almost identical in the very low, low, and medium risk groups. In the high (23.4 vs. 15.6; P = 0.19) and very high (50% vs. 40%; P = 0.92) groups, there were numerically more referrals in the group randomized to usual care, but these rates did not reach significance.
No differences seen in discharge meds
There was essentially no difference between groups in the rates at which patients were discharged on beta-blockers, renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or mineralocorticoid antagonists.
When prespecified subgroups, such as those older than age 75 years relative to those younger, males relative to females, Black versus White participants, patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) relative to preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), and intensive care unit versus non-ICU patients, were compared, there were no indications that the EHR alert improved outcomes.
Invited discussant Harriette G. C. Van Spall, MD, director of digital health and virtual care and associate professor of cardiology at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., did not dispute the conclusions, but she pointed out several potential explanations for the neutral result.
Not least, nearly 75% of those enrolled had low risk or very low risk for adverse outcomes within 1 year, so the opportunity to show a reduction in events, including all-cause mortality, was limited.
“This was largely a HFpEF population, for which there are no treatments for which a risk score would change therapy,” she said.
EHR alert efficacy questioned
There is considerable evidence that risk prediction tools “are common but underutilized in HF,” Dr. Van Spall added. She noted that many clinicians find alerts in the EHR more annoying than informative, and it remains unknown what proportion of clinicians pay attention to them, particularly in the absence of evidence that they lead to meaningful improvements in care over their own clinical judgment.
Dr. Ahmad agreed.
“I think that we need to study these alerts in a clinical trial format,” he said. Acknowledging that alerts have been poorly received by many clinicians, Dr. Ahmad said that trials to validate the impact of any specific alert are needed to improve their credibility. If a positive impact cannot be shown, he said the alert should be eliminated, leaving only the alerts with proven clinical value.
Dr. Ahmad reported financial relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Novartis, and Relypsa. Dr. Van Spall reports no potential conflicts of interest.
When provided at the bedside of patients hospitalized for heart failure, an electronic health record (EHR) alert with prognostic information did not improve outcomes or appear to have any impact on what treatments were offered.
There was no signal that the EHR prognostic alerts, which identified the 12-month risk of mortality, had any impact on any of a variety of clinical-decision-making metrics or on any of the primary or secondary outcomes, according to Tariq Ahmad, MD, who reported results of the randomized REVEAL-HF trial, presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“These results call into question the hypothesis that accurate prognostic information alone will lead to better clinical decision-making,” said Dr. Ahmad, medical director of the Heart Transplant and Mechanical Circulatory Support Program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and principal investigator of REVEAL-HF.
He acknowledged that the possibility that many clinicians pay little or no attention to EHR alert might have played a role in the negative results.
At four participating Yale-affiliated clinical centers, all patients hospitalized for acute heart failure were randomized as long as they were over the age of 18, had an N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level above 500 pg/mL, and had been placed on IV diuretics within 24 hours of admission. In the experimental arm, the provider at the time of entering orders received an EHR alert with an estimate of the risk of all-cause mortality at 12 months. There was no such alert for patients managed in the control arm.
Twelve-month mortality estimates calculated
The all-cause mortality risk was calculated on a sizeable list of variables that included laboratory results, such as cell counts, and patient characteristics, such as weight and age. The risk estimate was displayed along with a five-category color-coded bar to provide context for the risk in the spectrum of very low, low, medium, high, and very high likelihood of death within 12 months.
The 1,590 patients randomized to the experimental arm and the 1,534 patients randomized to the usual care arm did not differ significantly in any baseline characteristics. The median age was about 77 years, the mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 55%. About 29% had an LVEF below 40%, about 40% had chronic kidney disease, and about 30% had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The composite primary outcome of all-cause mortality or rehospitalization within 12 months was reached by 38.9% and 39.3% (P = 0.82) of the intervention and control arms, respectively. The components of the primary outcome were also nearly identical, as was inpatient mortality (8.4% vs. 8.8%; P = 0.72).
There were no significant differences in any of the secondary outcomes, which included rates of 30-day rehospitalizations, discharge on guideline-recommended heart failure therapies, implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator, use of a left ventricular assist device, or heart transplant.
The proportion of patients referred for palliative care was almost identical in the very low, low, and medium risk groups. In the high (23.4 vs. 15.6; P = 0.19) and very high (50% vs. 40%; P = 0.92) groups, there were numerically more referrals in the group randomized to usual care, but these rates did not reach significance.
No differences seen in discharge meds
There was essentially no difference between groups in the rates at which patients were discharged on beta-blockers, renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or mineralocorticoid antagonists.
When prespecified subgroups, such as those older than age 75 years relative to those younger, males relative to females, Black versus White participants, patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) relative to preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), and intensive care unit versus non-ICU patients, were compared, there were no indications that the EHR alert improved outcomes.
Invited discussant Harriette G. C. Van Spall, MD, director of digital health and virtual care and associate professor of cardiology at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., did not dispute the conclusions, but she pointed out several potential explanations for the neutral result.
Not least, nearly 75% of those enrolled had low risk or very low risk for adverse outcomes within 1 year, so the opportunity to show a reduction in events, including all-cause mortality, was limited.
“This was largely a HFpEF population, for which there are no treatments for which a risk score would change therapy,” she said.
EHR alert efficacy questioned
There is considerable evidence that risk prediction tools “are common but underutilized in HF,” Dr. Van Spall added. She noted that many clinicians find alerts in the EHR more annoying than informative, and it remains unknown what proportion of clinicians pay attention to them, particularly in the absence of evidence that they lead to meaningful improvements in care over their own clinical judgment.
Dr. Ahmad agreed.
“I think that we need to study these alerts in a clinical trial format,” he said. Acknowledging that alerts have been poorly received by many clinicians, Dr. Ahmad said that trials to validate the impact of any specific alert are needed to improve their credibility. If a positive impact cannot be shown, he said the alert should be eliminated, leaving only the alerts with proven clinical value.
Dr. Ahmad reported financial relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Novartis, and Relypsa. Dr. Van Spall reports no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM AHA 2021