User login
Therapy ups breast cancer survivors’ cardiac risks
WASHINGTON – Oncologists and cardiologists need to work hand-in-hand when managing the care of women with breast cancer whose treatment plan includes cardiotoxic therapies and breast irradiation, reported specialists.
Depending on the cancer subtype, women with breast cancer may receive chemotherapy with a cardiotoxic anthracycline such as doxorubicin or epirubicin, or a HER2-targeted agent such as trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab (Perjeta), or ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla).
“The cardiotoxicity related to breast cancer has been a well publicized issue, and chances are your patients know about it and are concerned as well,” Jennifer E. Liu, MD, director of cardiovascular laboratories at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
Anthracyclines, trastuzumab, and HF
In large adjuvant therapy trials of anthracyclines and trastuzumab in women with breast cancer, doxorubicin alone was associated with an asymptomatic decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 4% to 11%, and a less than 1% incidence of heart failure (HF), Dr. Liu noted.
When patients received an anthracycline followed by trastuzumab, the incidence of asymptomatic LVEF decline ranged from 4% to 19%, the incidence of clinical HF was 2% to 4%, and the rate of trastuzumab interruption for cardiac adverse events ranged from 5% to 18%.
In comparison, in trials with trastuzumab in combination therapy that did not contain an anthracycline, the risk of cardiovascular complications was lower, with asymptomatic decline in LVEF ranging from 3.2% to 9.4%, and class III/IV HF occurring in just 0.5% of patients. In trials combining trastuzumab and pertuzumab, there were no increases in cardiac toxicity over trastuzumab alone.
Although with longer follow-up, the approximately 4% rate of HF in patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, paclitaxel, and trastuzumab in the NSABP B-31 trial has not changed significantly; retrospective claims-based studies reflecting daily practice have shown significantly higher rates of HF and or cardiomyopathy, Dr. Liu said.
She cited a 2012 study showing that among 45,537 women with a mean age of 76 years who were treated for breast cancer, the 3-year incidence rates of HF and/or cardiomyopathy were 32% for patients treated with trastuzumab alone, and 41.9% for those treated with an anthracycline followed by trastuzumab. Other, smaller studies also showed lower but significantly elevated risks for the drugs.
The discrepancy between clinical trial and “real world” results may be chalked up to the fact that claims-based data rely on diagnostic codes that may not accurately reflect the actual cardiac diagnosis, and by the fact that clinical trials have strict entry criteria that exclude patients with cardiovascular disease, she said.
Radiation risks
Radiation therapy is associated with a more than 7% increase in major coronary events per Gy of mean heart dose, Dr. Liu noted, citing a 2013 study (N Engl J Med. 2013;368:987-98).
Paul Nguyen, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center in Boston, said that risk factors for radiation-induced heart disease include anterior or left chest irradiation, cumulative doses above 30 Gy, patient age younger than 50 years, doses of more than 2 Gy per fraction, presence and extent of tumor in or near the heart, lack of radiation shielding, concomitant chemotherapy (especially with anthracyclines), and preexisting cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
For patients with breast cancer, the risk of developing radiation-induced heart disease has diminished considerably with the adoption of heart-sparing techniques over the last several decades, including 3-D conformal techniques, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, proton beam therapy, novel patient positioning techniques that allow radiation only to the cancer-involved breast, and deep inspiration breath holds in which the radiation beam is gated to turn on only when the patient is holding a deep breath, Dr. Nguyen noted.
Treatment options for LVEF decline
The package insert for trastuzumab recommends withholding the drug for a minimum of 4 weeks if the patient has a 16% or greater decline in LVEF from baseline, or a 10% or greater decline from baseline to below the lower limit of normal. The insert recommends LVEF monitoring every 3 or 4 weeks, and says that trastuzumab can be resumed if LVEF improves to above the lower limit of normal with an absolute decrease from baseline of not more than 15%. The insert also states, however, that “the safety of continuation or resumption of trastuzumab in patients with trastuzumab induced LV dysfunction has never been studied, “ Dr. Liu noted.
She cited an American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline on the prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers, which states in part that the decision to continue or discontinue cancer therapy in patients with evidence of cardiac dysfunction “made by the oncologist, should be informed by close collaboration with a cardiologist, fully evaluating the clinical circumstances and considering the risks and benefits of continuation of therapy responsible for the cardiac dysfunction.”
“I want to emphasize the importance of accepting and managing cardiovascular risk in patients priors to and during potentially cardiotoxic therapy. To optimize cardiologic and oncologic outcomes, we need to avoid or minimize treatment interruptions of life-saving therapy, and mitigate cardiac events with aggressive cardiovascular risk-factor modification,” Dr. Liu said.
She called for development of better risk stratification tools to tailor cardiac surveillance during therapy, based on both patient-specific and treatment-specific risk factors.
Dr. Liu reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Nguyen reported consulting fees/honoraria from Astellas, Augmenix, Blue Earth Diagnostics. Cota, Dendreon, Ferring Pharmaceuticals. GenomeDx, Janssen, and Nanobiotix.
WASHINGTON – Oncologists and cardiologists need to work hand-in-hand when managing the care of women with breast cancer whose treatment plan includes cardiotoxic therapies and breast irradiation, reported specialists.
Depending on the cancer subtype, women with breast cancer may receive chemotherapy with a cardiotoxic anthracycline such as doxorubicin or epirubicin, or a HER2-targeted agent such as trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab (Perjeta), or ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla).
“The cardiotoxicity related to breast cancer has been a well publicized issue, and chances are your patients know about it and are concerned as well,” Jennifer E. Liu, MD, director of cardiovascular laboratories at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
Anthracyclines, trastuzumab, and HF
In large adjuvant therapy trials of anthracyclines and trastuzumab in women with breast cancer, doxorubicin alone was associated with an asymptomatic decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 4% to 11%, and a less than 1% incidence of heart failure (HF), Dr. Liu noted.
When patients received an anthracycline followed by trastuzumab, the incidence of asymptomatic LVEF decline ranged from 4% to 19%, the incidence of clinical HF was 2% to 4%, and the rate of trastuzumab interruption for cardiac adverse events ranged from 5% to 18%.
In comparison, in trials with trastuzumab in combination therapy that did not contain an anthracycline, the risk of cardiovascular complications was lower, with asymptomatic decline in LVEF ranging from 3.2% to 9.4%, and class III/IV HF occurring in just 0.5% of patients. In trials combining trastuzumab and pertuzumab, there were no increases in cardiac toxicity over trastuzumab alone.
Although with longer follow-up, the approximately 4% rate of HF in patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, paclitaxel, and trastuzumab in the NSABP B-31 trial has not changed significantly; retrospective claims-based studies reflecting daily practice have shown significantly higher rates of HF and or cardiomyopathy, Dr. Liu said.
She cited a 2012 study showing that among 45,537 women with a mean age of 76 years who were treated for breast cancer, the 3-year incidence rates of HF and/or cardiomyopathy were 32% for patients treated with trastuzumab alone, and 41.9% for those treated with an anthracycline followed by trastuzumab. Other, smaller studies also showed lower but significantly elevated risks for the drugs.
The discrepancy between clinical trial and “real world” results may be chalked up to the fact that claims-based data rely on diagnostic codes that may not accurately reflect the actual cardiac diagnosis, and by the fact that clinical trials have strict entry criteria that exclude patients with cardiovascular disease, she said.
Radiation risks
Radiation therapy is associated with a more than 7% increase in major coronary events per Gy of mean heart dose, Dr. Liu noted, citing a 2013 study (N Engl J Med. 2013;368:987-98).
Paul Nguyen, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center in Boston, said that risk factors for radiation-induced heart disease include anterior or left chest irradiation, cumulative doses above 30 Gy, patient age younger than 50 years, doses of more than 2 Gy per fraction, presence and extent of tumor in or near the heart, lack of radiation shielding, concomitant chemotherapy (especially with anthracyclines), and preexisting cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
For patients with breast cancer, the risk of developing radiation-induced heart disease has diminished considerably with the adoption of heart-sparing techniques over the last several decades, including 3-D conformal techniques, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, proton beam therapy, novel patient positioning techniques that allow radiation only to the cancer-involved breast, and deep inspiration breath holds in which the radiation beam is gated to turn on only when the patient is holding a deep breath, Dr. Nguyen noted.
Treatment options for LVEF decline
The package insert for trastuzumab recommends withholding the drug for a minimum of 4 weeks if the patient has a 16% or greater decline in LVEF from baseline, or a 10% or greater decline from baseline to below the lower limit of normal. The insert recommends LVEF monitoring every 3 or 4 weeks, and says that trastuzumab can be resumed if LVEF improves to above the lower limit of normal with an absolute decrease from baseline of not more than 15%. The insert also states, however, that “the safety of continuation or resumption of trastuzumab in patients with trastuzumab induced LV dysfunction has never been studied, “ Dr. Liu noted.
She cited an American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline on the prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers, which states in part that the decision to continue or discontinue cancer therapy in patients with evidence of cardiac dysfunction “made by the oncologist, should be informed by close collaboration with a cardiologist, fully evaluating the clinical circumstances and considering the risks and benefits of continuation of therapy responsible for the cardiac dysfunction.”
“I want to emphasize the importance of accepting and managing cardiovascular risk in patients priors to and during potentially cardiotoxic therapy. To optimize cardiologic and oncologic outcomes, we need to avoid or minimize treatment interruptions of life-saving therapy, and mitigate cardiac events with aggressive cardiovascular risk-factor modification,” Dr. Liu said.
She called for development of better risk stratification tools to tailor cardiac surveillance during therapy, based on both patient-specific and treatment-specific risk factors.
Dr. Liu reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Nguyen reported consulting fees/honoraria from Astellas, Augmenix, Blue Earth Diagnostics. Cota, Dendreon, Ferring Pharmaceuticals. GenomeDx, Janssen, and Nanobiotix.
WASHINGTON – Oncologists and cardiologists need to work hand-in-hand when managing the care of women with breast cancer whose treatment plan includes cardiotoxic therapies and breast irradiation, reported specialists.
Depending on the cancer subtype, women with breast cancer may receive chemotherapy with a cardiotoxic anthracycline such as doxorubicin or epirubicin, or a HER2-targeted agent such as trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab (Perjeta), or ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla).
“The cardiotoxicity related to breast cancer has been a well publicized issue, and chances are your patients know about it and are concerned as well,” Jennifer E. Liu, MD, director of cardiovascular laboratories at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
Anthracyclines, trastuzumab, and HF
In large adjuvant therapy trials of anthracyclines and trastuzumab in women with breast cancer, doxorubicin alone was associated with an asymptomatic decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 4% to 11%, and a less than 1% incidence of heart failure (HF), Dr. Liu noted.
When patients received an anthracycline followed by trastuzumab, the incidence of asymptomatic LVEF decline ranged from 4% to 19%, the incidence of clinical HF was 2% to 4%, and the rate of trastuzumab interruption for cardiac adverse events ranged from 5% to 18%.
In comparison, in trials with trastuzumab in combination therapy that did not contain an anthracycline, the risk of cardiovascular complications was lower, with asymptomatic decline in LVEF ranging from 3.2% to 9.4%, and class III/IV HF occurring in just 0.5% of patients. In trials combining trastuzumab and pertuzumab, there were no increases in cardiac toxicity over trastuzumab alone.
Although with longer follow-up, the approximately 4% rate of HF in patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, paclitaxel, and trastuzumab in the NSABP B-31 trial has not changed significantly; retrospective claims-based studies reflecting daily practice have shown significantly higher rates of HF and or cardiomyopathy, Dr. Liu said.
She cited a 2012 study showing that among 45,537 women with a mean age of 76 years who were treated for breast cancer, the 3-year incidence rates of HF and/or cardiomyopathy were 32% for patients treated with trastuzumab alone, and 41.9% for those treated with an anthracycline followed by trastuzumab. Other, smaller studies also showed lower but significantly elevated risks for the drugs.
The discrepancy between clinical trial and “real world” results may be chalked up to the fact that claims-based data rely on diagnostic codes that may not accurately reflect the actual cardiac diagnosis, and by the fact that clinical trials have strict entry criteria that exclude patients with cardiovascular disease, she said.
Radiation risks
Radiation therapy is associated with a more than 7% increase in major coronary events per Gy of mean heart dose, Dr. Liu noted, citing a 2013 study (N Engl J Med. 2013;368:987-98).
Paul Nguyen, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center in Boston, said that risk factors for radiation-induced heart disease include anterior or left chest irradiation, cumulative doses above 30 Gy, patient age younger than 50 years, doses of more than 2 Gy per fraction, presence and extent of tumor in or near the heart, lack of radiation shielding, concomitant chemotherapy (especially with anthracyclines), and preexisting cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
For patients with breast cancer, the risk of developing radiation-induced heart disease has diminished considerably with the adoption of heart-sparing techniques over the last several decades, including 3-D conformal techniques, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, proton beam therapy, novel patient positioning techniques that allow radiation only to the cancer-involved breast, and deep inspiration breath holds in which the radiation beam is gated to turn on only when the patient is holding a deep breath, Dr. Nguyen noted.
Treatment options for LVEF decline
The package insert for trastuzumab recommends withholding the drug for a minimum of 4 weeks if the patient has a 16% or greater decline in LVEF from baseline, or a 10% or greater decline from baseline to below the lower limit of normal. The insert recommends LVEF monitoring every 3 or 4 weeks, and says that trastuzumab can be resumed if LVEF improves to above the lower limit of normal with an absolute decrease from baseline of not more than 15%. The insert also states, however, that “the safety of continuation or resumption of trastuzumab in patients with trastuzumab induced LV dysfunction has never been studied, “ Dr. Liu noted.
She cited an American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline on the prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers, which states in part that the decision to continue or discontinue cancer therapy in patients with evidence of cardiac dysfunction “made by the oncologist, should be informed by close collaboration with a cardiologist, fully evaluating the clinical circumstances and considering the risks and benefits of continuation of therapy responsible for the cardiac dysfunction.”
“I want to emphasize the importance of accepting and managing cardiovascular risk in patients priors to and during potentially cardiotoxic therapy. To optimize cardiologic and oncologic outcomes, we need to avoid or minimize treatment interruptions of life-saving therapy, and mitigate cardiac events with aggressive cardiovascular risk-factor modification,” Dr. Liu said.
She called for development of better risk stratification tools to tailor cardiac surveillance during therapy, based on both patient-specific and treatment-specific risk factors.
Dr. Liu reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Nguyen reported consulting fees/honoraria from Astellas, Augmenix, Blue Earth Diagnostics. Cota, Dendreon, Ferring Pharmaceuticals. GenomeDx, Janssen, and Nanobiotix.
REPORTING FROM ACC CARDIO-ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Oncologists should work with cardiologists to mitigate heart disease risk.
Major finding: Anthracyclines followed by trastuzumab significantly increase risk of HF.
Study details: Review of risk for heart disease in breast cancer survivors.
Disclosures: Dr. Liu reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Nguyen reported consulting fees/honoraria from Astellas, Augmenix, Blue Earth Diagnostics, Cota, Dendreon, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, GenomeDx, Janssen, and Nanobiotix.
Impella RP shows higher mortality in postapproval study
The Food and Drug Administration issued a letter on Feb. 4, 2019, to health care providers regarding interim results from a postapproval study for Abiomed’s Impella RP System because these results appear to have a higher mortality rate than was seen in premarket clinical studies.
As a condition of its approval, the FDA mandated Abiomed to perform a postapproval study (PAS); this study reflects use in a broader population than the premarket studies, which adhered to stricter inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Earlier in January, Abiomed submitted data to the FDA suggesting that differences in preimplant characteristics between patients in the PAS and those in the premarket clinical studies may explain the difference in mortality. Specifically, 16 of the 23 patients enrolled in the PAS would not have met the enrollment criteria for the premarket clinical studies because they were in cardiogenic shock for longer than 48 hours, experienced an in-hospital cardiac arrest, were treated with an intra-aortic balloon pump, or suffered a preimplant hypoxic or ischemic neurologic event.
“Although the FDA is concerned about the high mortality rate from the interim PAS results,” they wrote in the letter, which is available on the FDA website, “we believe that, when the device is used for the currently approved indication in appropriately selected patients, the benefits of the Impella RP system continue to outweigh the risks.”
The Food and Drug Administration issued a letter on Feb. 4, 2019, to health care providers regarding interim results from a postapproval study for Abiomed’s Impella RP System because these results appear to have a higher mortality rate than was seen in premarket clinical studies.
As a condition of its approval, the FDA mandated Abiomed to perform a postapproval study (PAS); this study reflects use in a broader population than the premarket studies, which adhered to stricter inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Earlier in January, Abiomed submitted data to the FDA suggesting that differences in preimplant characteristics between patients in the PAS and those in the premarket clinical studies may explain the difference in mortality. Specifically, 16 of the 23 patients enrolled in the PAS would not have met the enrollment criteria for the premarket clinical studies because they were in cardiogenic shock for longer than 48 hours, experienced an in-hospital cardiac arrest, were treated with an intra-aortic balloon pump, or suffered a preimplant hypoxic or ischemic neurologic event.
“Although the FDA is concerned about the high mortality rate from the interim PAS results,” they wrote in the letter, which is available on the FDA website, “we believe that, when the device is used for the currently approved indication in appropriately selected patients, the benefits of the Impella RP system continue to outweigh the risks.”
The Food and Drug Administration issued a letter on Feb. 4, 2019, to health care providers regarding interim results from a postapproval study for Abiomed’s Impella RP System because these results appear to have a higher mortality rate than was seen in premarket clinical studies.
As a condition of its approval, the FDA mandated Abiomed to perform a postapproval study (PAS); this study reflects use in a broader population than the premarket studies, which adhered to stricter inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Earlier in January, Abiomed submitted data to the FDA suggesting that differences in preimplant characteristics between patients in the PAS and those in the premarket clinical studies may explain the difference in mortality. Specifically, 16 of the 23 patients enrolled in the PAS would not have met the enrollment criteria for the premarket clinical studies because they were in cardiogenic shock for longer than 48 hours, experienced an in-hospital cardiac arrest, were treated with an intra-aortic balloon pump, or suffered a preimplant hypoxic or ischemic neurologic event.
“Although the FDA is concerned about the high mortality rate from the interim PAS results,” they wrote in the letter, which is available on the FDA website, “we believe that, when the device is used for the currently approved indication in appropriately selected patients, the benefits of the Impella RP system continue to outweigh the risks.”
Immunotherapy’s cardiac effects require early monitoring, management
WASHINGTON – Unquestionably, immunotherapy is revolutionizing the care of patients with various solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.
But it’s equally true that there’s no such thing as either a free lunch or a cancer therapy free of side effects, whether it’s increased risk for heart failure associated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, or inflammatory conditions, arrhythmias, and thromboembolic events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, said R. Frank Cornell, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
“Early awareness and intervention is critical for improved outcomes, and a multidisciplinary approach between oncology, cardiology, the clinic nurse, and other health care providers is critical in managing these patients with these complicated therapies,” he said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
Checkpoint inhibitors and the heart
Toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as the programmed death 1/ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 antibody ipilimumab (Yervoy) tend to mimic autoimmune conditions, Dr. Cornell said.
Cardiovascular events associated with these agents, while uncommon, include myocarditis, pericarditis, arrhythmias, impaired ventricular function with heart failure, vasculitis, and venous thromboembolism, he said, citing an American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) clinical practice guideline (J Clin Oncol 2018;36[17]:1714-68).
Dr. Cornell described the case of a 63-year-old woman with disseminated metastatic melanoma who presented to the emergency department 10 days after starting on combination therapy with ipilimumab and nivolumab. She had developed shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, and a mild cough for 1 or 2 days.
Her cardiac laboratory markers had been normal at baseline, but were markedly elevated on presentation, and electrocardiograms showed complete heart block and subsequent ventricular tachycardia.
The patient was started on high-dose prednisone, but she died in hospital, and an autopsy showed that the cause of death was infiltration into the myocardium of CD3-positive and CD8-positive T lymphocytes.
“So how do we manage this? This is a good opportunity, I think, for further cardiology and oncology collaboration to develop more robust guidelines for what we can do to best prevent this,” Dr. Cornell said.
Patients started on the ipilimumab/nivolumab combination should be tested weekly for cardiac troponin, creatine kinase (CK) and CK-muscle/brain (CK-MB) weekly for the first 3-4 weeks of therapy. Therapy should be stopped if troponin levels continue to rise, and the patient should be started on high-dose steroids, he said.
The role of other anti-inflammatory agents such as infliximab (Remicade and biosimilars) is unclear and needs further study, he added.
Dr. Cornell cited a 2018 letter to The Lancet by Javid J. Moslehi, MD, and colleagues from Vanderbilt describing an increase in reports of fatal myocarditis among patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
“We highlight the high mortality rate with severe immune checkpoint inhibitor–related myocarditis, which is more frequent with combination PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade, but can also occur with monotherapy. Myocarditis was observed across immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens, although it remains too early to determine whether the incidence differs between use of anti-PD1 and anti-PD-L1 drugs. Furthermore, this condition occurs early on during therapy and across cancer types,” they wrote.
Most of the patients had no preexisting cardiovascular disease, and most were not taking medications for hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or diabetes.
CAR-T cells and cardiac disease
The primary cardiac complications associated with CAR-T cell therapy are related to the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a condition marked by progressive elevation in inflammatory cytokines that in turn leads to marked elevations in C-reactive protein (CRP), interferon gamma, tumor necrosis factor al, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL) 6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-1 beta.
In rare instances, CRS can lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), capillary leak syndrome, and a hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like (HLH) syndrome, Dr. Cornell said.
Package inserts for the two Food and Drug Administration–approved CAR-T cell products, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) and tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) show that each was associated in clinical trials with a high incidence of CRS.
Among patients treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel, 94% developed CRS, which was grade 3 or greater in severity in 13%. The median time to onset was 2 days, and the median duration was 7 days. Cardiovascular adverse events included grade 3 or greater tachycardia in 2%, arrhythmias in 7%, edema in 1%, dyspnea in 3%, pleural effusion in 2%, hypotension in 15%, hypertension in 6%, and thrombosis in 1%.
Among patients treated with tisagenlecleucel, 79% treated for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and 74% treated for diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) developed CRS, which was grade 3 or greater in 49% and 23% of patients, respectively. The median time to onset was 3 days, and the median duration of CRS was 8 days.
Cardiovascular adverse events of grade 3 or greater among these patients included tachycardia in 4%, fluid overload in 7%, edema in 1%, dyspnea in 12%, pulmonary edema in 4%, hypotension in 22%, and hypertension in 6%.
Risk factors for CRS include high pre-infusion tumor burden, active infections, and concurrent inflammatory processes, Dr. Cornell said.
Prevention of cardiovascular complications of CAR-T cell therapy requires management of CRS. Patients with grade 2 or greater CRS should receive the anti-IL-6 agent tocilizumab (Actemra) 8 mg/kg intravenously over 1 hour to a maximum dose of 800 mg. Tocilizumab infusions can be repeated every 8 hours as needed if the patient is not responsive to intravenous fluids or increasing supplement oxygen, but should be limited to a maximum of three doses over 24 hours, and a maximum total of four doses.
Patients with grade 3 CRS should also receive intravenous methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg twice daily or the equivalent amount of dexamethasone, with corticosteroids continued until the severity of CRS is grade 1 or less, then tapered over 3 days,
Patients with grade 4 CRS should also receive IV methylprednisolone 1,000 mg per day for 3 days, and if symptoms improve, continue management as per grade 3, Dr. Cornell said.
Dr. Cornell reported having nothing to disclose.
WASHINGTON – Unquestionably, immunotherapy is revolutionizing the care of patients with various solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.
But it’s equally true that there’s no such thing as either a free lunch or a cancer therapy free of side effects, whether it’s increased risk for heart failure associated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, or inflammatory conditions, arrhythmias, and thromboembolic events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, said R. Frank Cornell, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
“Early awareness and intervention is critical for improved outcomes, and a multidisciplinary approach between oncology, cardiology, the clinic nurse, and other health care providers is critical in managing these patients with these complicated therapies,” he said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
Checkpoint inhibitors and the heart
Toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as the programmed death 1/ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 antibody ipilimumab (Yervoy) tend to mimic autoimmune conditions, Dr. Cornell said.
Cardiovascular events associated with these agents, while uncommon, include myocarditis, pericarditis, arrhythmias, impaired ventricular function with heart failure, vasculitis, and venous thromboembolism, he said, citing an American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) clinical practice guideline (J Clin Oncol 2018;36[17]:1714-68).
Dr. Cornell described the case of a 63-year-old woman with disseminated metastatic melanoma who presented to the emergency department 10 days after starting on combination therapy with ipilimumab and nivolumab. She had developed shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, and a mild cough for 1 or 2 days.
Her cardiac laboratory markers had been normal at baseline, but were markedly elevated on presentation, and electrocardiograms showed complete heart block and subsequent ventricular tachycardia.
The patient was started on high-dose prednisone, but she died in hospital, and an autopsy showed that the cause of death was infiltration into the myocardium of CD3-positive and CD8-positive T lymphocytes.
“So how do we manage this? This is a good opportunity, I think, for further cardiology and oncology collaboration to develop more robust guidelines for what we can do to best prevent this,” Dr. Cornell said.
Patients started on the ipilimumab/nivolumab combination should be tested weekly for cardiac troponin, creatine kinase (CK) and CK-muscle/brain (CK-MB) weekly for the first 3-4 weeks of therapy. Therapy should be stopped if troponin levels continue to rise, and the patient should be started on high-dose steroids, he said.
The role of other anti-inflammatory agents such as infliximab (Remicade and biosimilars) is unclear and needs further study, he added.
Dr. Cornell cited a 2018 letter to The Lancet by Javid J. Moslehi, MD, and colleagues from Vanderbilt describing an increase in reports of fatal myocarditis among patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
“We highlight the high mortality rate with severe immune checkpoint inhibitor–related myocarditis, which is more frequent with combination PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade, but can also occur with monotherapy. Myocarditis was observed across immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens, although it remains too early to determine whether the incidence differs between use of anti-PD1 and anti-PD-L1 drugs. Furthermore, this condition occurs early on during therapy and across cancer types,” they wrote.
Most of the patients had no preexisting cardiovascular disease, and most were not taking medications for hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or diabetes.
CAR-T cells and cardiac disease
The primary cardiac complications associated with CAR-T cell therapy are related to the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a condition marked by progressive elevation in inflammatory cytokines that in turn leads to marked elevations in C-reactive protein (CRP), interferon gamma, tumor necrosis factor al, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL) 6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-1 beta.
In rare instances, CRS can lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), capillary leak syndrome, and a hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like (HLH) syndrome, Dr. Cornell said.
Package inserts for the two Food and Drug Administration–approved CAR-T cell products, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) and tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) show that each was associated in clinical trials with a high incidence of CRS.
Among patients treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel, 94% developed CRS, which was grade 3 or greater in severity in 13%. The median time to onset was 2 days, and the median duration was 7 days. Cardiovascular adverse events included grade 3 or greater tachycardia in 2%, arrhythmias in 7%, edema in 1%, dyspnea in 3%, pleural effusion in 2%, hypotension in 15%, hypertension in 6%, and thrombosis in 1%.
Among patients treated with tisagenlecleucel, 79% treated for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and 74% treated for diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) developed CRS, which was grade 3 or greater in 49% and 23% of patients, respectively. The median time to onset was 3 days, and the median duration of CRS was 8 days.
Cardiovascular adverse events of grade 3 or greater among these patients included tachycardia in 4%, fluid overload in 7%, edema in 1%, dyspnea in 12%, pulmonary edema in 4%, hypotension in 22%, and hypertension in 6%.
Risk factors for CRS include high pre-infusion tumor burden, active infections, and concurrent inflammatory processes, Dr. Cornell said.
Prevention of cardiovascular complications of CAR-T cell therapy requires management of CRS. Patients with grade 2 or greater CRS should receive the anti-IL-6 agent tocilizumab (Actemra) 8 mg/kg intravenously over 1 hour to a maximum dose of 800 mg. Tocilizumab infusions can be repeated every 8 hours as needed if the patient is not responsive to intravenous fluids or increasing supplement oxygen, but should be limited to a maximum of three doses over 24 hours, and a maximum total of four doses.
Patients with grade 3 CRS should also receive intravenous methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg twice daily or the equivalent amount of dexamethasone, with corticosteroids continued until the severity of CRS is grade 1 or less, then tapered over 3 days,
Patients with grade 4 CRS should also receive IV methylprednisolone 1,000 mg per day for 3 days, and if symptoms improve, continue management as per grade 3, Dr. Cornell said.
Dr. Cornell reported having nothing to disclose.
WASHINGTON – Unquestionably, immunotherapy is revolutionizing the care of patients with various solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.
But it’s equally true that there’s no such thing as either a free lunch or a cancer therapy free of side effects, whether it’s increased risk for heart failure associated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy, or inflammatory conditions, arrhythmias, and thromboembolic events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, said R. Frank Cornell, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
“Early awareness and intervention is critical for improved outcomes, and a multidisciplinary approach between oncology, cardiology, the clinic nurse, and other health care providers is critical in managing these patients with these complicated therapies,” he said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
Checkpoint inhibitors and the heart
Toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as the programmed death 1/ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 antibody ipilimumab (Yervoy) tend to mimic autoimmune conditions, Dr. Cornell said.
Cardiovascular events associated with these agents, while uncommon, include myocarditis, pericarditis, arrhythmias, impaired ventricular function with heart failure, vasculitis, and venous thromboembolism, he said, citing an American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) clinical practice guideline (J Clin Oncol 2018;36[17]:1714-68).
Dr. Cornell described the case of a 63-year-old woman with disseminated metastatic melanoma who presented to the emergency department 10 days after starting on combination therapy with ipilimumab and nivolumab. She had developed shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, and a mild cough for 1 or 2 days.
Her cardiac laboratory markers had been normal at baseline, but were markedly elevated on presentation, and electrocardiograms showed complete heart block and subsequent ventricular tachycardia.
The patient was started on high-dose prednisone, but she died in hospital, and an autopsy showed that the cause of death was infiltration into the myocardium of CD3-positive and CD8-positive T lymphocytes.
“So how do we manage this? This is a good opportunity, I think, for further cardiology and oncology collaboration to develop more robust guidelines for what we can do to best prevent this,” Dr. Cornell said.
Patients started on the ipilimumab/nivolumab combination should be tested weekly for cardiac troponin, creatine kinase (CK) and CK-muscle/brain (CK-MB) weekly for the first 3-4 weeks of therapy. Therapy should be stopped if troponin levels continue to rise, and the patient should be started on high-dose steroids, he said.
The role of other anti-inflammatory agents such as infliximab (Remicade and biosimilars) is unclear and needs further study, he added.
Dr. Cornell cited a 2018 letter to The Lancet by Javid J. Moslehi, MD, and colleagues from Vanderbilt describing an increase in reports of fatal myocarditis among patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
“We highlight the high mortality rate with severe immune checkpoint inhibitor–related myocarditis, which is more frequent with combination PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade, but can also occur with monotherapy. Myocarditis was observed across immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens, although it remains too early to determine whether the incidence differs between use of anti-PD1 and anti-PD-L1 drugs. Furthermore, this condition occurs early on during therapy and across cancer types,” they wrote.
Most of the patients had no preexisting cardiovascular disease, and most were not taking medications for hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or diabetes.
CAR-T cells and cardiac disease
The primary cardiac complications associated with CAR-T cell therapy are related to the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a condition marked by progressive elevation in inflammatory cytokines that in turn leads to marked elevations in C-reactive protein (CRP), interferon gamma, tumor necrosis factor al, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL) 6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-1 beta.
In rare instances, CRS can lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), capillary leak syndrome, and a hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like (HLH) syndrome, Dr. Cornell said.
Package inserts for the two Food and Drug Administration–approved CAR-T cell products, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) and tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) show that each was associated in clinical trials with a high incidence of CRS.
Among patients treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel, 94% developed CRS, which was grade 3 or greater in severity in 13%. The median time to onset was 2 days, and the median duration was 7 days. Cardiovascular adverse events included grade 3 or greater tachycardia in 2%, arrhythmias in 7%, edema in 1%, dyspnea in 3%, pleural effusion in 2%, hypotension in 15%, hypertension in 6%, and thrombosis in 1%.
Among patients treated with tisagenlecleucel, 79% treated for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and 74% treated for diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) developed CRS, which was grade 3 or greater in 49% and 23% of patients, respectively. The median time to onset was 3 days, and the median duration of CRS was 8 days.
Cardiovascular adverse events of grade 3 or greater among these patients included tachycardia in 4%, fluid overload in 7%, edema in 1%, dyspnea in 12%, pulmonary edema in 4%, hypotension in 22%, and hypertension in 6%.
Risk factors for CRS include high pre-infusion tumor burden, active infections, and concurrent inflammatory processes, Dr. Cornell said.
Prevention of cardiovascular complications of CAR-T cell therapy requires management of CRS. Patients with grade 2 or greater CRS should receive the anti-IL-6 agent tocilizumab (Actemra) 8 mg/kg intravenously over 1 hour to a maximum dose of 800 mg. Tocilizumab infusions can be repeated every 8 hours as needed if the patient is not responsive to intravenous fluids or increasing supplement oxygen, but should be limited to a maximum of three doses over 24 hours, and a maximum total of four doses.
Patients with grade 3 CRS should also receive intravenous methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg twice daily or the equivalent amount of dexamethasone, with corticosteroids continued until the severity of CRS is grade 1 or less, then tapered over 3 days,
Patients with grade 4 CRS should also receive IV methylprednisolone 1,000 mg per day for 3 days, and if symptoms improve, continue management as per grade 3, Dr. Cornell said.
Dr. Cornell reported having nothing to disclose.
REPORTING FROM ACC CARDIO-ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Monitor for cardiac symptoms and treat or interrupt immunotherapy as needed.
Major finding: Immune checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapies are associated with distinct cardiovascular adverse events.
Study details: Review of strategies for managing the cardiovascular consequences of cancer immunotherapies.
Disclosures: Dr. Cornell reported having nothing to disclose.
Atrial fib guidelines updated, SPRINT MIND published, and more
This week in cardiology news, revised atrial fibrillation guidelines revamp anticoagulation, the SPRINT MIND results showing that tight BP control staves off mild cognitive impairment are published, the FDA discovers that nitrosamine-contaminated ARBs have been on the market for years, and subclinical hypothyroidism boosts the immediate risk of heart failure.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
TuneIn
This week in cardiology news, revised atrial fibrillation guidelines revamp anticoagulation, the SPRINT MIND results showing that tight BP control staves off mild cognitive impairment are published, the FDA discovers that nitrosamine-contaminated ARBs have been on the market for years, and subclinical hypothyroidism boosts the immediate risk of heart failure.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
TuneIn
This week in cardiology news, revised atrial fibrillation guidelines revamp anticoagulation, the SPRINT MIND results showing that tight BP control staves off mild cognitive impairment are published, the FDA discovers that nitrosamine-contaminated ARBs have been on the market for years, and subclinical hypothyroidism boosts the immediate risk of heart failure.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
TuneIn
Subclinical hypothyroidism boosts immediate risk of heart failure
CHICAGO – The short-term risk of developing heart failure in patients with newly identified hypothyroidism, be it overt or subclinical, is double that of euthyroid individuals, Caroline H. Noergaard, MD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“This is really important clinically. The association with heart failure has previously been shown in both overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism, but it’s actually new knowledge that hypothyroidism is associated with immediate risk of heart failure. And a lot of people have subclinical hypothyroidism,” said Dr. Noergaard, a PhD student in epidemiology at Aalborg (Denmark) University.
Also at the meeting, Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, reported that free thyroxine levels within the normal reference range were associated in graded fashion with an increased prevalence and incidence of atrial fibrillation in a large Utah study, a finding that provides independent confirmation of an earlier report by investigators from the population-based Rotterdam Study.
“These findings validate those of the Rotterdam Study in a much larger dataset and may have important clinical implications, including a redefinition of the reference range and the target-free T4 levels for thyroxine replacement therapy,” observed Dr. Anderson, professor of internal medicine at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and a research cardiologist at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute.
Hypothyroidism and heart failure
Dr. Noergaard presented a retrospective study of over 1 million Copenhagen-area adults (mean age, 50 years) with no history of heart failure, who had their first thyroid function test. She and her coinvestigators turned to comprehensive Danish national health care registries to determine how many of these individuals were diagnosed with new-onset heart failure within 90 days after their thyroid function test.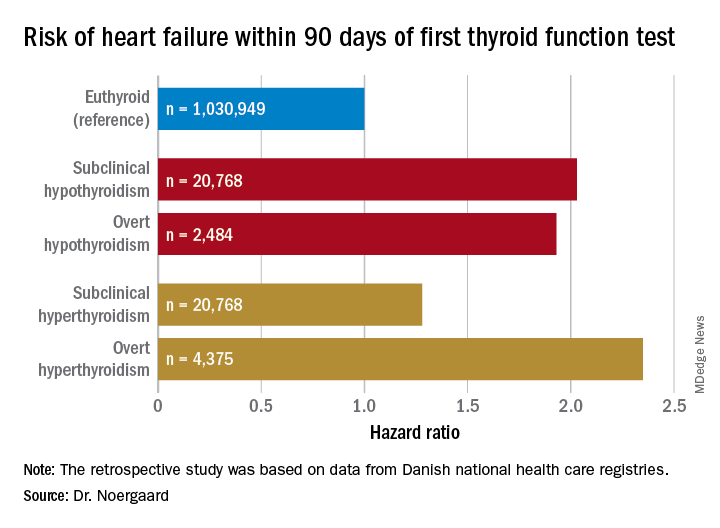
Subclinical hypothyroidism was defined by a thyroid-stimulating hormone level greater than 5 mIU/L and a free T4 of 9-22 pmol/L. Overt hypothyroidism required a TSH greater than 5 mIU/L with a free T4 less than 9 pmol/L.
Free T4 predicts atrial fibrillation risk
Dr. Anderson presented a retrospective analysis of 174,914 adult patients in the Intermountain Healthcare EMR database, none of whom were on thyroid replacement at entry. The patients, who were a mean age of 64 years and 65% women, were followed for an average of 6.3 years. Of these, 88.4% had a free T4 within the normal reference range of 0.75-1.5 ng/dL, 7.4% had a value below the cutoff for normal, and 4.2% had a free T4 above the reference range.
Upon dividing the patients within the normal range into quartiles based upon their free T4 level, he and his coinvestigators found that the baseline prevalence of atrial fibrillation was 8.7% in those in quartile 1, 9.3% in quartile 2, 10.5% in quartile 3, and 12.6% in quartile 4. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for potential confounders, the risk of prevalent atrial fibrillation was increased by 11% for patients in quartile 2, compared with those in the first quartile, by 22% in quartile 3, and by 40% in quartile 4.
The incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation during 3 years of follow-up was 4.1% in patients in normal-range quartile 1, 4.3% in quartile 2, 4.5% in quartile 3, and 5.2% in the top normal-range quartile. The odds of developing atrial fibrillation were increased by 8% and 16% in quartiles 3 and 4, compared with quartile 1.
Serum TSH and free T3 levels showed no consistent relationship with atrial fibrillation.
The Utah findings confirm in a large U.S. population the earlier report from the Rotterdam Study (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Oct;100(10):3718-24).
Dr. Noergaard and Dr. Anderson reported having no financial conflicts regarding their studies, which were carried out free of commercial support.
CHICAGO – The short-term risk of developing heart failure in patients with newly identified hypothyroidism, be it overt or subclinical, is double that of euthyroid individuals, Caroline H. Noergaard, MD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“This is really important clinically. The association with heart failure has previously been shown in both overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism, but it’s actually new knowledge that hypothyroidism is associated with immediate risk of heart failure. And a lot of people have subclinical hypothyroidism,” said Dr. Noergaard, a PhD student in epidemiology at Aalborg (Denmark) University.
Also at the meeting, Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, reported that free thyroxine levels within the normal reference range were associated in graded fashion with an increased prevalence and incidence of atrial fibrillation in a large Utah study, a finding that provides independent confirmation of an earlier report by investigators from the population-based Rotterdam Study.
“These findings validate those of the Rotterdam Study in a much larger dataset and may have important clinical implications, including a redefinition of the reference range and the target-free T4 levels for thyroxine replacement therapy,” observed Dr. Anderson, professor of internal medicine at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and a research cardiologist at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute.
Hypothyroidism and heart failure
Dr. Noergaard presented a retrospective study of over 1 million Copenhagen-area adults (mean age, 50 years) with no history of heart failure, who had their first thyroid function test. She and her coinvestigators turned to comprehensive Danish national health care registries to determine how many of these individuals were diagnosed with new-onset heart failure within 90 days after their thyroid function test.
Subclinical hypothyroidism was defined by a thyroid-stimulating hormone level greater than 5 mIU/L and a free T4 of 9-22 pmol/L. Overt hypothyroidism required a TSH greater than 5 mIU/L with a free T4 less than 9 pmol/L.
Free T4 predicts atrial fibrillation risk
Dr. Anderson presented a retrospective analysis of 174,914 adult patients in the Intermountain Healthcare EMR database, none of whom were on thyroid replacement at entry. The patients, who were a mean age of 64 years and 65% women, were followed for an average of 6.3 years. Of these, 88.4% had a free T4 within the normal reference range of 0.75-1.5 ng/dL, 7.4% had a value below the cutoff for normal, and 4.2% had a free T4 above the reference range.
Upon dividing the patients within the normal range into quartiles based upon their free T4 level, he and his coinvestigators found that the baseline prevalence of atrial fibrillation was 8.7% in those in quartile 1, 9.3% in quartile 2, 10.5% in quartile 3, and 12.6% in quartile 4. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for potential confounders, the risk of prevalent atrial fibrillation was increased by 11% for patients in quartile 2, compared with those in the first quartile, by 22% in quartile 3, and by 40% in quartile 4.
The incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation during 3 years of follow-up was 4.1% in patients in normal-range quartile 1, 4.3% in quartile 2, 4.5% in quartile 3, and 5.2% in the top normal-range quartile. The odds of developing atrial fibrillation were increased by 8% and 16% in quartiles 3 and 4, compared with quartile 1.
Serum TSH and free T3 levels showed no consistent relationship with atrial fibrillation.
The Utah findings confirm in a large U.S. population the earlier report from the Rotterdam Study (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Oct;100(10):3718-24).
Dr. Noergaard and Dr. Anderson reported having no financial conflicts regarding their studies, which were carried out free of commercial support.
CHICAGO – The short-term risk of developing heart failure in patients with newly identified hypothyroidism, be it overt or subclinical, is double that of euthyroid individuals, Caroline H. Noergaard, MD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“This is really important clinically. The association with heart failure has previously been shown in both overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism, but it’s actually new knowledge that hypothyroidism is associated with immediate risk of heart failure. And a lot of people have subclinical hypothyroidism,” said Dr. Noergaard, a PhD student in epidemiology at Aalborg (Denmark) University.
Also at the meeting, Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, reported that free thyroxine levels within the normal reference range were associated in graded fashion with an increased prevalence and incidence of atrial fibrillation in a large Utah study, a finding that provides independent confirmation of an earlier report by investigators from the population-based Rotterdam Study.
“These findings validate those of the Rotterdam Study in a much larger dataset and may have important clinical implications, including a redefinition of the reference range and the target-free T4 levels for thyroxine replacement therapy,” observed Dr. Anderson, professor of internal medicine at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and a research cardiologist at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute.
Hypothyroidism and heart failure
Dr. Noergaard presented a retrospective study of over 1 million Copenhagen-area adults (mean age, 50 years) with no history of heart failure, who had their first thyroid function test. She and her coinvestigators turned to comprehensive Danish national health care registries to determine how many of these individuals were diagnosed with new-onset heart failure within 90 days after their thyroid function test.
Subclinical hypothyroidism was defined by a thyroid-stimulating hormone level greater than 5 mIU/L and a free T4 of 9-22 pmol/L. Overt hypothyroidism required a TSH greater than 5 mIU/L with a free T4 less than 9 pmol/L.
Free T4 predicts atrial fibrillation risk
Dr. Anderson presented a retrospective analysis of 174,914 adult patients in the Intermountain Healthcare EMR database, none of whom were on thyroid replacement at entry. The patients, who were a mean age of 64 years and 65% women, were followed for an average of 6.3 years. Of these, 88.4% had a free T4 within the normal reference range of 0.75-1.5 ng/dL, 7.4% had a value below the cutoff for normal, and 4.2% had a free T4 above the reference range.
Upon dividing the patients within the normal range into quartiles based upon their free T4 level, he and his coinvestigators found that the baseline prevalence of atrial fibrillation was 8.7% in those in quartile 1, 9.3% in quartile 2, 10.5% in quartile 3, and 12.6% in quartile 4. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for potential confounders, the risk of prevalent atrial fibrillation was increased by 11% for patients in quartile 2, compared with those in the first quartile, by 22% in quartile 3, and by 40% in quartile 4.
The incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation during 3 years of follow-up was 4.1% in patients in normal-range quartile 1, 4.3% in quartile 2, 4.5% in quartile 3, and 5.2% in the top normal-range quartile. The odds of developing atrial fibrillation were increased by 8% and 16% in quartiles 3 and 4, compared with quartile 1.
Serum TSH and free T3 levels showed no consistent relationship with atrial fibrillation.
The Utah findings confirm in a large U.S. population the earlier report from the Rotterdam Study (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Oct;100(10):3718-24).
Dr. Noergaard and Dr. Anderson reported having no financial conflicts regarding their studies, which were carried out free of commercial support.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Both subclinical and overt hypothyroidism are associated with a 100% increased risk of being diagnosed with heart failure, compared with euthyroid individuals.
Study details: This was a retrospective study of the association between free thyroxine levels and short-term risk of developing heart failure in more than 1 million Copenhagen-area patients.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the Danish study, conducted free of commercial support.
HDL-P subfractions may be prognostic in heart failure
In heart failure, derangements in HDL cholesterol particle (HDL-P) subfractions have prognostic implications beyond those of conventional cardiovascular risk factors, according to investigators who analyzed plasma samples from more than 6,500 patients.
The study revealed derangements that were shared and more severe in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) as compared to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), according to the researchers, who said their study is the largest to date of HDL-P subfractions in heart failure.
Both total HDL-P and small HDL-P had a strong inverse association with adverse outcomes, consistent with the conclusions of previous studies, they said in a report on their study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Altogether, our findings support total and small HDL-P as important markers of residual risk in both HFrEF and HFpEF,” said the investigators, led by Wynn G. Hunter, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Dr. Hunter and colleagues used the CATHGEN (Catheterization Genetics) biorepository to identify plasma samples obtained at catheterization for 782 patients with HFrEF, 1,004 with HFpEF, and 4,742 with no heart failure.
Lipoprotein profiling of the samples revealed that mean HDL-P size was greater in HFrEF than in HFpEF, and in both of those cases, mean HDL-P size was greater than in patients with no heart failure (P less than .0001), investigators reported.
Concentrations of small HDL-P and total HDL-P were by contrast lower in HFrEF versus HFpEF, and again, the values for both HFrEF and HFpEF were lower than in patients without heart failure (P less than .0001), they added.
Small HDL-P and total HDL-P had an inverse association with time to adverse events and all-cause mortality for both the HFrEF and HFpEF groups, according to investigators, who said those links remained robust even after multivariate adjustment for 14 cardiovascular risk factors, including diabetes, LDL particle, and GlycA, a marker of inflammation.
For example, small HDL-P and total HDL-P were inversely associated with all-cause mortality risk, with adjusted hazard ratios of 0.69-0.79 (P less than .0001), they reported. Similarly, a greater mean HDL-P size was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality, yielding adjusted hazard ratios of 1.23-1.46 (P less than .0001).
Further studies are needed to clarify the role of HDL-P in the pathophysiology of heart failure, and to identify treatments that might increase total and small HDL-P in heart failure patients, Dr. Hunter and coauthors concluded.
Dr. Hunter reported no disclosures related to the study. Coauthors provided disclosures related to Amgen, Ostuka, Roche Diagnostics, Novartis, Trevena, Singulex, Medtronic, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Portola, Boston Scientific, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Alnylam, Ikaria Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Philips, LipoScience, and Pfizer, among others.
SOURCE: Hunter WG et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jan 22;73(2):177-86.
Although the study by Dr. Hunter and colleagues confirms the role of HDL cholesterol and HDL-P subfractions in heart failure, the immediate clinical implications of their findings are uncertain.
However, clinical use as a biomarker remains a “distant vision,” in part because a useful biomarker must be proven to provide an incremental benefit in terms of reducing disease-associated morbidity or mortality.
Even so, the present study could begin to inform future therapeutic studies looking at increasing specific HDL-P subfractions, rather than increasing HDL cholesterol across the board.
“Perhaps, this study will possibly serve to spur investigation into therapies designed to reduce derangements of [HDL cholesterol] metabolism and primarily target HDL-P as a regulator molecule, a promise that may keep the HDL story alive into the near future of scientific excursion.”
These comments were taken from an accompanying editorial by Hector O. Ventura, MD, and Carl J. Lavie, MD, of the University of Queensland Ochsner Clinical School, Brisbane, Australia, and New Orleans; and Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, of the Center of Advanced Heart Disease, Harvard University, Boston (J Am Coll Cardiol 2019 Jan 22;73[2]:187-9). Dr. Mehra reported that he is a consultant for Abbott, Medtronic, nupulseCV, Portola, Bayer, and FineHeart.
Although the study by Dr. Hunter and colleagues confirms the role of HDL cholesterol and HDL-P subfractions in heart failure, the immediate clinical implications of their findings are uncertain.
However, clinical use as a biomarker remains a “distant vision,” in part because a useful biomarker must be proven to provide an incremental benefit in terms of reducing disease-associated morbidity or mortality.
Even so, the present study could begin to inform future therapeutic studies looking at increasing specific HDL-P subfractions, rather than increasing HDL cholesterol across the board.
“Perhaps, this study will possibly serve to spur investigation into therapies designed to reduce derangements of [HDL cholesterol] metabolism and primarily target HDL-P as a regulator molecule, a promise that may keep the HDL story alive into the near future of scientific excursion.”
These comments were taken from an accompanying editorial by Hector O. Ventura, MD, and Carl J. Lavie, MD, of the University of Queensland Ochsner Clinical School, Brisbane, Australia, and New Orleans; and Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, of the Center of Advanced Heart Disease, Harvard University, Boston (J Am Coll Cardiol 2019 Jan 22;73[2]:187-9). Dr. Mehra reported that he is a consultant for Abbott, Medtronic, nupulseCV, Portola, Bayer, and FineHeart.
Although the study by Dr. Hunter and colleagues confirms the role of HDL cholesterol and HDL-P subfractions in heart failure, the immediate clinical implications of their findings are uncertain.
However, clinical use as a biomarker remains a “distant vision,” in part because a useful biomarker must be proven to provide an incremental benefit in terms of reducing disease-associated morbidity or mortality.
Even so, the present study could begin to inform future therapeutic studies looking at increasing specific HDL-P subfractions, rather than increasing HDL cholesterol across the board.
“Perhaps, this study will possibly serve to spur investigation into therapies designed to reduce derangements of [HDL cholesterol] metabolism and primarily target HDL-P as a regulator molecule, a promise that may keep the HDL story alive into the near future of scientific excursion.”
These comments were taken from an accompanying editorial by Hector O. Ventura, MD, and Carl J. Lavie, MD, of the University of Queensland Ochsner Clinical School, Brisbane, Australia, and New Orleans; and Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, of the Center of Advanced Heart Disease, Harvard University, Boston (J Am Coll Cardiol 2019 Jan 22;73[2]:187-9). Dr. Mehra reported that he is a consultant for Abbott, Medtronic, nupulseCV, Portola, Bayer, and FineHeart.
In heart failure, derangements in HDL cholesterol particle (HDL-P) subfractions have prognostic implications beyond those of conventional cardiovascular risk factors, according to investigators who analyzed plasma samples from more than 6,500 patients.
The study revealed derangements that were shared and more severe in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) as compared to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), according to the researchers, who said their study is the largest to date of HDL-P subfractions in heart failure.
Both total HDL-P and small HDL-P had a strong inverse association with adverse outcomes, consistent with the conclusions of previous studies, they said in a report on their study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Altogether, our findings support total and small HDL-P as important markers of residual risk in both HFrEF and HFpEF,” said the investigators, led by Wynn G. Hunter, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Dr. Hunter and colleagues used the CATHGEN (Catheterization Genetics) biorepository to identify plasma samples obtained at catheterization for 782 patients with HFrEF, 1,004 with HFpEF, and 4,742 with no heart failure.
Lipoprotein profiling of the samples revealed that mean HDL-P size was greater in HFrEF than in HFpEF, and in both of those cases, mean HDL-P size was greater than in patients with no heart failure (P less than .0001), investigators reported.
Concentrations of small HDL-P and total HDL-P were by contrast lower in HFrEF versus HFpEF, and again, the values for both HFrEF and HFpEF were lower than in patients without heart failure (P less than .0001), they added.
Small HDL-P and total HDL-P had an inverse association with time to adverse events and all-cause mortality for both the HFrEF and HFpEF groups, according to investigators, who said those links remained robust even after multivariate adjustment for 14 cardiovascular risk factors, including diabetes, LDL particle, and GlycA, a marker of inflammation.
For example, small HDL-P and total HDL-P were inversely associated with all-cause mortality risk, with adjusted hazard ratios of 0.69-0.79 (P less than .0001), they reported. Similarly, a greater mean HDL-P size was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality, yielding adjusted hazard ratios of 1.23-1.46 (P less than .0001).
Further studies are needed to clarify the role of HDL-P in the pathophysiology of heart failure, and to identify treatments that might increase total and small HDL-P in heart failure patients, Dr. Hunter and coauthors concluded.
Dr. Hunter reported no disclosures related to the study. Coauthors provided disclosures related to Amgen, Ostuka, Roche Diagnostics, Novartis, Trevena, Singulex, Medtronic, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Portola, Boston Scientific, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Alnylam, Ikaria Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Philips, LipoScience, and Pfizer, among others.
SOURCE: Hunter WG et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jan 22;73(2):177-86.
In heart failure, derangements in HDL cholesterol particle (HDL-P) subfractions have prognostic implications beyond those of conventional cardiovascular risk factors, according to investigators who analyzed plasma samples from more than 6,500 patients.
The study revealed derangements that were shared and more severe in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) as compared to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), according to the researchers, who said their study is the largest to date of HDL-P subfractions in heart failure.
Both total HDL-P and small HDL-P had a strong inverse association with adverse outcomes, consistent with the conclusions of previous studies, they said in a report on their study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Altogether, our findings support total and small HDL-P as important markers of residual risk in both HFrEF and HFpEF,” said the investigators, led by Wynn G. Hunter, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Dr. Hunter and colleagues used the CATHGEN (Catheterization Genetics) biorepository to identify plasma samples obtained at catheterization for 782 patients with HFrEF, 1,004 with HFpEF, and 4,742 with no heart failure.
Lipoprotein profiling of the samples revealed that mean HDL-P size was greater in HFrEF than in HFpEF, and in both of those cases, mean HDL-P size was greater than in patients with no heart failure (P less than .0001), investigators reported.
Concentrations of small HDL-P and total HDL-P were by contrast lower in HFrEF versus HFpEF, and again, the values for both HFrEF and HFpEF were lower than in patients without heart failure (P less than .0001), they added.
Small HDL-P and total HDL-P had an inverse association with time to adverse events and all-cause mortality for both the HFrEF and HFpEF groups, according to investigators, who said those links remained robust even after multivariate adjustment for 14 cardiovascular risk factors, including diabetes, LDL particle, and GlycA, a marker of inflammation.
For example, small HDL-P and total HDL-P were inversely associated with all-cause mortality risk, with adjusted hazard ratios of 0.69-0.79 (P less than .0001), they reported. Similarly, a greater mean HDL-P size was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality, yielding adjusted hazard ratios of 1.23-1.46 (P less than .0001).
Further studies are needed to clarify the role of HDL-P in the pathophysiology of heart failure, and to identify treatments that might increase total and small HDL-P in heart failure patients, Dr. Hunter and coauthors concluded.
Dr. Hunter reported no disclosures related to the study. Coauthors provided disclosures related to Amgen, Ostuka, Roche Diagnostics, Novartis, Trevena, Singulex, Medtronic, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Portola, Boston Scientific, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Alnylam, Ikaria Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Philips, LipoScience, and Pfizer, among others.
SOURCE: Hunter WG et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jan 22;73(2):177-86.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Key clinical point: Derangements in HDL particle (HDL-P) subfractions may have prognostic implications in patients with heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
Major finding: (P less than .0001).
Study details: Study based on lipid profiling of more than 6,500 plasma samples obtained at catheterization.
Disclosures: Study authors provided disclosures related to Amgen, Ostuka, Roche Diagnostics, Novartis, Medtronic, and others.
Source: Hunter WG et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jan 22;73(2):177-86.
SGLT-2 inhibitors promising for heart failure prevention, not treatment
LOS ANGELES –
They also may play a role in the treatment of patients with known heart failure (HF), but further studies are required to prove definite treatment benefit.
“These trials enrolled a minority of patients with known heart failure, and, in those subgroups, the drugs seems to reduce the risk for hospitalization, opening the possibility of treatment benefit,” Javed Butler, MD, said at the World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease. “But there were not enough patients to conclude this. If you are treating diabetes with these agents in patients with heart failure, more power to you. But don’t think you are treating heart failure per se until the results of the dedicated heart failure trials come out.”
Good glycemic control has not been shown to affect heart failure outcomes per se, said Dr. Butler, professor and chairman of the department of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson.
“People seem to mix the concepts of prevention and treatment together,” he said. “We have now very good evidence across all trials with SGLT-2 inhibitors for prevention of heart failure. But for treatment, we need more data despite favorable early signals.
“Also, these trials include most patients with ischemic heart disease, but we don’t have data on nonischemic etiology for the development of heart failure from these trials,” Dr. Butler added.
The best available data from clinical trials suggest that patients with American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association heart failure classification stages A and B benefit the most from aggressive treatment to prevent HF.
“Either they have diseases like high blood pressure or diabetes, but their hearts are normal, or, perhaps, their hearts are abnormal, and they develop left ventricular hypertrophy or atrial fibrillation,” he said. “However, if someone is stage C – manifest heart failure – or stage D – advanced heart failure – we need further data on novel therapies to improve their outcomes.”
Dr. Butler emphasized that not all heart failure is associated with atherosclerotic vascular disease. In fact, the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study showed that the incidence of heart failure increased progressively across age groups, both for those with and without a preceding vascular event (P = .03 and P less than .001, respectively; Eur J Heart Fail. 2014 May;16[5]:526-34). “There’s a whole other world of nonischemic heart failure that we also need to worry about,” he said. “There is a lot of microvascular endothelial dysfunction.”
The combination of heart failure and diabetes is especially lethal. “If you put them together, you’re looking at about a 10-fold higher risk of mortality, which is a horrible prognosis,” Dr. Butler said. “That means that we need to think about prevention and treatment separately.”
Data from the SAVOR-TIMI 53, EXAMINE, and TECOS trials show there is no protective effect of dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors when it comes to hospitalization for heart failure.
“The other classes of drugs either increase the risk, or we don’t have very good data,” Dr. Butler said. “So far, across the spectrum of therapies for diabetes, the effect on heart failure is neutral and perhaps confers some risk.”
SGLT-2 inhibitors convey a different story.
In the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial, one inclusion criterion was established cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the form of a prior MI, coronary artery disease, stroke, unstable angina, or occlusive peripheral artery disease, but not heart failure alone (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26; 373[22]:2117-28). “This was not a heart failure study, so we don’t know what their New York Heart Association class was, or the details of their baseline HF treatment in the minority of patients who were enrolled who had a history of HF,” Dr. Butler cautioned.
However, the trial found that empagliflozin conferred an overall cardiovascular death risk reduction of 38%, compared with placebo. When the researchers assessed the impact of treatment on all modes of cardiovascular death, they found that death from heart failure benefited the most (hazard ratio, 0.32; P = .0008), while sudden death benefited as well. Empagliflozin also had a significant impact on reduced hospitalization for heart failure, compared with placebo (HR, 0.65).
“This is a large enough cohort that you should feel comfortable that this drug is preventing heart failure in those with HF at baseline,” said Dr. Butler, who was not involved with the study. “We can have a debate about whether this is a treatment for heart failure or not, but for prevention of heart failure, I feel comfortable that these drugs do that.”
A subsequent study of canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes showed the same result (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17; 377[7]:644-57). It reduced hospitalization for heart failure by 33% (HR, 0.67).
Then came the CVD-REAL study, which found low rates of hospitalization for heart failure and all-cause death in new users of SGLT-2 inhibitors. More recently, DECLARE-TIMI 58 yielded similar results.
“One of the criticisms of these findings is that heart failure characteristics were not well phenotyped in these studies,” Dr. Butler said. “I say it really does not matter. Heart failure hospitalizations are associated with a poor prognosis irrespective of whether the hospitalization occurred in patients without heart failure or in a patient with previously diagnosed heart failure, or whether the patient has reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
“Framingham and other classic studies show us that 5-year mortality for heart failure is about 50%,” he noted. “If you can prevent a disease that has a 5-year mortality of 50%, doesn’t that sound like a really good deal?”
A contemporary appraisal of the heart failure epidemic in Olmstead County, Minn., during 2000-2010 found that the mortality was 20.2% at 1 year after diagnosis, and 52.6% at 5 years after diagnosis. The data include new-onset HF in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Specifically, new-onset HF hospitalization was associated with a 1-year post discharge mortality of 21.1% (JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175[6]:996-1004). “We cannot ignore prevention of heart failure,” Dr. Butler said. “Also, for treatment, once you get hospitalized for heart failure, the fundamental natural history of the disease changes. There is a 30% cumulative incremental death risk between the second and third hospitalizations.”
Dr. Butler concluded his presentation by noting that five randomized, controlled trials evaluating SGLT-2 inhibitors in HF have been launched, and should help elucidate any effects the drugs may have in treating the condition. They include EMPEROR-Preserved (NCT03057951), EMPEROR-Reduced (NCT03057977), Dapa-HF (NCT03036124), and SOLOIST-WHF (NCT03521934) and DELIVER (NCT03619213).
Dr. Butler disclosed that he has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the European Union, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. He has also been a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies, including Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, and AstraZeneca, which sponsored the EMPA-REG, CANVAS, and DECLARE TIMI 58 trials.
LOS ANGELES –
They also may play a role in the treatment of patients with known heart failure (HF), but further studies are required to prove definite treatment benefit.
“These trials enrolled a minority of patients with known heart failure, and, in those subgroups, the drugs seems to reduce the risk for hospitalization, opening the possibility of treatment benefit,” Javed Butler, MD, said at the World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease. “But there were not enough patients to conclude this. If you are treating diabetes with these agents in patients with heart failure, more power to you. But don’t think you are treating heart failure per se until the results of the dedicated heart failure trials come out.”
Good glycemic control has not been shown to affect heart failure outcomes per se, said Dr. Butler, professor and chairman of the department of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson.
“People seem to mix the concepts of prevention and treatment together,” he said. “We have now very good evidence across all trials with SGLT-2 inhibitors for prevention of heart failure. But for treatment, we need more data despite favorable early signals.
“Also, these trials include most patients with ischemic heart disease, but we don’t have data on nonischemic etiology for the development of heart failure from these trials,” Dr. Butler added.
The best available data from clinical trials suggest that patients with American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association heart failure classification stages A and B benefit the most from aggressive treatment to prevent HF.
“Either they have diseases like high blood pressure or diabetes, but their hearts are normal, or, perhaps, their hearts are abnormal, and they develop left ventricular hypertrophy or atrial fibrillation,” he said. “However, if someone is stage C – manifest heart failure – or stage D – advanced heart failure – we need further data on novel therapies to improve their outcomes.”
Dr. Butler emphasized that not all heart failure is associated with atherosclerotic vascular disease. In fact, the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study showed that the incidence of heart failure increased progressively across age groups, both for those with and without a preceding vascular event (P = .03 and P less than .001, respectively; Eur J Heart Fail. 2014 May;16[5]:526-34). “There’s a whole other world of nonischemic heart failure that we also need to worry about,” he said. “There is a lot of microvascular endothelial dysfunction.”
The combination of heart failure and diabetes is especially lethal. “If you put them together, you’re looking at about a 10-fold higher risk of mortality, which is a horrible prognosis,” Dr. Butler said. “That means that we need to think about prevention and treatment separately.”
Data from the SAVOR-TIMI 53, EXAMINE, and TECOS trials show there is no protective effect of dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors when it comes to hospitalization for heart failure.
“The other classes of drugs either increase the risk, or we don’t have very good data,” Dr. Butler said. “So far, across the spectrum of therapies for diabetes, the effect on heart failure is neutral and perhaps confers some risk.”
SGLT-2 inhibitors convey a different story.
In the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial, one inclusion criterion was established cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the form of a prior MI, coronary artery disease, stroke, unstable angina, or occlusive peripheral artery disease, but not heart failure alone (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26; 373[22]:2117-28). “This was not a heart failure study, so we don’t know what their New York Heart Association class was, or the details of their baseline HF treatment in the minority of patients who were enrolled who had a history of HF,” Dr. Butler cautioned.
However, the trial found that empagliflozin conferred an overall cardiovascular death risk reduction of 38%, compared with placebo. When the researchers assessed the impact of treatment on all modes of cardiovascular death, they found that death from heart failure benefited the most (hazard ratio, 0.32; P = .0008), while sudden death benefited as well. Empagliflozin also had a significant impact on reduced hospitalization for heart failure, compared with placebo (HR, 0.65).
“This is a large enough cohort that you should feel comfortable that this drug is preventing heart failure in those with HF at baseline,” said Dr. Butler, who was not involved with the study. “We can have a debate about whether this is a treatment for heart failure or not, but for prevention of heart failure, I feel comfortable that these drugs do that.”
A subsequent study of canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes showed the same result (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17; 377[7]:644-57). It reduced hospitalization for heart failure by 33% (HR, 0.67).
Then came the CVD-REAL study, which found low rates of hospitalization for heart failure and all-cause death in new users of SGLT-2 inhibitors. More recently, DECLARE-TIMI 58 yielded similar results.
“One of the criticisms of these findings is that heart failure characteristics were not well phenotyped in these studies,” Dr. Butler said. “I say it really does not matter. Heart failure hospitalizations are associated with a poor prognosis irrespective of whether the hospitalization occurred in patients without heart failure or in a patient with previously diagnosed heart failure, or whether the patient has reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
“Framingham and other classic studies show us that 5-year mortality for heart failure is about 50%,” he noted. “If you can prevent a disease that has a 5-year mortality of 50%, doesn’t that sound like a really good deal?”
A contemporary appraisal of the heart failure epidemic in Olmstead County, Minn., during 2000-2010 found that the mortality was 20.2% at 1 year after diagnosis, and 52.6% at 5 years after diagnosis. The data include new-onset HF in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Specifically, new-onset HF hospitalization was associated with a 1-year post discharge mortality of 21.1% (JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175[6]:996-1004). “We cannot ignore prevention of heart failure,” Dr. Butler said. “Also, for treatment, once you get hospitalized for heart failure, the fundamental natural history of the disease changes. There is a 30% cumulative incremental death risk between the second and third hospitalizations.”
Dr. Butler concluded his presentation by noting that five randomized, controlled trials evaluating SGLT-2 inhibitors in HF have been launched, and should help elucidate any effects the drugs may have in treating the condition. They include EMPEROR-Preserved (NCT03057951), EMPEROR-Reduced (NCT03057977), Dapa-HF (NCT03036124), and SOLOIST-WHF (NCT03521934) and DELIVER (NCT03619213).
Dr. Butler disclosed that he has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the European Union, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. He has also been a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies, including Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, and AstraZeneca, which sponsored the EMPA-REG, CANVAS, and DECLARE TIMI 58 trials.
LOS ANGELES –
They also may play a role in the treatment of patients with known heart failure (HF), but further studies are required to prove definite treatment benefit.
“These trials enrolled a minority of patients with known heart failure, and, in those subgroups, the drugs seems to reduce the risk for hospitalization, opening the possibility of treatment benefit,” Javed Butler, MD, said at the World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease. “But there were not enough patients to conclude this. If you are treating diabetes with these agents in patients with heart failure, more power to you. But don’t think you are treating heart failure per se until the results of the dedicated heart failure trials come out.”
Good glycemic control has not been shown to affect heart failure outcomes per se, said Dr. Butler, professor and chairman of the department of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson.
“People seem to mix the concepts of prevention and treatment together,” he said. “We have now very good evidence across all trials with SGLT-2 inhibitors for prevention of heart failure. But for treatment, we need more data despite favorable early signals.
“Also, these trials include most patients with ischemic heart disease, but we don’t have data on nonischemic etiology for the development of heart failure from these trials,” Dr. Butler added.
The best available data from clinical trials suggest that patients with American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association heart failure classification stages A and B benefit the most from aggressive treatment to prevent HF.
“Either they have diseases like high blood pressure or diabetes, but their hearts are normal, or, perhaps, their hearts are abnormal, and they develop left ventricular hypertrophy or atrial fibrillation,” he said. “However, if someone is stage C – manifest heart failure – or stage D – advanced heart failure – we need further data on novel therapies to improve their outcomes.”
Dr. Butler emphasized that not all heart failure is associated with atherosclerotic vascular disease. In fact, the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study showed that the incidence of heart failure increased progressively across age groups, both for those with and without a preceding vascular event (P = .03 and P less than .001, respectively; Eur J Heart Fail. 2014 May;16[5]:526-34). “There’s a whole other world of nonischemic heart failure that we also need to worry about,” he said. “There is a lot of microvascular endothelial dysfunction.”
The combination of heart failure and diabetes is especially lethal. “If you put them together, you’re looking at about a 10-fold higher risk of mortality, which is a horrible prognosis,” Dr. Butler said. “That means that we need to think about prevention and treatment separately.”
Data from the SAVOR-TIMI 53, EXAMINE, and TECOS trials show there is no protective effect of dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors when it comes to hospitalization for heart failure.
“The other classes of drugs either increase the risk, or we don’t have very good data,” Dr. Butler said. “So far, across the spectrum of therapies for diabetes, the effect on heart failure is neutral and perhaps confers some risk.”
SGLT-2 inhibitors convey a different story.
In the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial, one inclusion criterion was established cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the form of a prior MI, coronary artery disease, stroke, unstable angina, or occlusive peripheral artery disease, but not heart failure alone (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26; 373[22]:2117-28). “This was not a heart failure study, so we don’t know what their New York Heart Association class was, or the details of their baseline HF treatment in the minority of patients who were enrolled who had a history of HF,” Dr. Butler cautioned.
However, the trial found that empagliflozin conferred an overall cardiovascular death risk reduction of 38%, compared with placebo. When the researchers assessed the impact of treatment on all modes of cardiovascular death, they found that death from heart failure benefited the most (hazard ratio, 0.32; P = .0008), while sudden death benefited as well. Empagliflozin also had a significant impact on reduced hospitalization for heart failure, compared with placebo (HR, 0.65).
“This is a large enough cohort that you should feel comfortable that this drug is preventing heart failure in those with HF at baseline,” said Dr. Butler, who was not involved with the study. “We can have a debate about whether this is a treatment for heart failure or not, but for prevention of heart failure, I feel comfortable that these drugs do that.”
A subsequent study of canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes showed the same result (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17; 377[7]:644-57). It reduced hospitalization for heart failure by 33% (HR, 0.67).
Then came the CVD-REAL study, which found low rates of hospitalization for heart failure and all-cause death in new users of SGLT-2 inhibitors. More recently, DECLARE-TIMI 58 yielded similar results.
“One of the criticisms of these findings is that heart failure characteristics were not well phenotyped in these studies,” Dr. Butler said. “I say it really does not matter. Heart failure hospitalizations are associated with a poor prognosis irrespective of whether the hospitalization occurred in patients without heart failure or in a patient with previously diagnosed heart failure, or whether the patient has reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
“Framingham and other classic studies show us that 5-year mortality for heart failure is about 50%,” he noted. “If you can prevent a disease that has a 5-year mortality of 50%, doesn’t that sound like a really good deal?”
A contemporary appraisal of the heart failure epidemic in Olmstead County, Minn., during 2000-2010 found that the mortality was 20.2% at 1 year after diagnosis, and 52.6% at 5 years after diagnosis. The data include new-onset HF in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Specifically, new-onset HF hospitalization was associated with a 1-year post discharge mortality of 21.1% (JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175[6]:996-1004). “We cannot ignore prevention of heart failure,” Dr. Butler said. “Also, for treatment, once you get hospitalized for heart failure, the fundamental natural history of the disease changes. There is a 30% cumulative incremental death risk between the second and third hospitalizations.”
Dr. Butler concluded his presentation by noting that five randomized, controlled trials evaluating SGLT-2 inhibitors in HF have been launched, and should help elucidate any effects the drugs may have in treating the condition. They include EMPEROR-Preserved (NCT03057951), EMPEROR-Reduced (NCT03057977), Dapa-HF (NCT03036124), and SOLOIST-WHF (NCT03521934) and DELIVER (NCT03619213).
Dr. Butler disclosed that he has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the European Union, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. He has also been a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies, including Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, and AstraZeneca, which sponsored the EMPA-REG, CANVAS, and DECLARE TIMI 58 trials.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM WCIRDC 2018
New diabetes drugs solidify their cardiovascular and renal benefits
CHICAGO – When the first results from a large trial that showed profound and unexpected benefits for preventing heart failure hospitalizations associated with use of the antihyperglycemic sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin came out – a little over 3 years ago – the general reaction from clinicians was some variant of “Could this be real?”
Since then, as results from some five other large, international trials have come out showing both similar benefits from two other drugs in the same SGLT2 inhibitor class, canagliflozin and dapagliflozin, as well as results showing clear cardiovascular disease benefits from three drugs in a second class of antihyperglycemics, the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), the general consensus among cardiologists became: “The cardiovascular and renal benefits are real. How can we now best use these drugs to help patients?”
This change increasingly forces cardiologists, as well as the primary care physicians who often manage patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, to become more comfortable prescribing these two classes of antihyperglycemic drugs. During a talk at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, Eugene Braunwald, MD, arguably the top thought leader in cardiology, coined a new name for the medical subspecialty that he foresees navigating this overlap between diabetes care and cardiovascular disease prevention: diabetocardiology (although a more euphonic alternative might be cardiodiabetology, while the more comprehensive name could be cardionephrodiabetology).
“I was certainly surprised” by the first report in 2015 from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28), said Dr. Braunwald, who is professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. A lot of his colleagues were surprised and said, “It’s just one trial.”
“Now we have three trials,” with the addition of the CANVAS trial for canagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[7]:644-57) and the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial (N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 10. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1812389) for dapagliflozin reported at the AHA meeting in November.
“We are in the midst of two pandemics: heart failure and type 2 diabetes. As cardiologists, we have to learn how to deal with this,” said Dr. Braunwald, and the evidence now clearly shows that these drugs can help with that.
As another speaker at the meeting, Javed Butler, MD, a heart failure specialist, observed in a separate talk at the meeting, “Heart failure is one of the most common, if not the most common complication, of patients with diabetes.” This tight link between heart failure and diabetes helps make cardiovascular mortality “the number one cause of death” in patients with diabetes, said Dr. Butler, professor and chairman of medicine at the University of Mississippi in Jackson.
“Thanks to the cardiovascular outcome trials, we now have a much broader and deeper appreciation of heart failure and renal disease as integral components of the cardiovascular-renal spectrum in people with diabetes,” said Subodh Verma, MD, a professor at the University of Toronto and cardiac surgeon at St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto. Dr. Braunwald spelled out in his talk some of the interrelationships of diabetes, heart failure, and renal dysfunction that together produce a downward-spiraling vicious circle for patients, a pathophysiological process that clinicians can now short-circuit by treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor.
Cardiovascular outcome trials show the way
In the context of antihyperglycemic drugs, the “cardiovascular outcome trials” refers to a series of large trials mandated by the Food and Drug Administration in 2008 to assess the cardiovascular disease effects of new agents coming onto the U.S. market to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). By the time Dr. Verma spoke at the AHA meeting, he could cite reported results from 12 of these trials: 5 different drugs in the GLP-1 RA class, 4 drugs in the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class, and 3 drugs from the SGLT2 inhibitor class. Dr. Verma summed what the findings have shown.
The four tested DDP-4 inhibitors (alogliptin, linagliptin, saxagliptin, and sitagliptin) consistently showed neutrality for the primary outcome of major adverse cardiovascular disease events (MACE), constituted by cardiovascular disease death, MI, or stroke.
The five tested GLP-1 RAs (albiglutide, exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, and semaglutide) showed a mixed pattern of MACE results that seemed to be linked with the subclass the drug fell into. The two exedin-4–based drugs, exenatide and lixisenatide, each showed a statistically neutral effect for MACE, as well as collectively in a combined analysis. In contrast, three human GLP-1–based drugs, albiglutide, liraglutide, and semaglutide, each showed a consistent, statistically-significant MACE reduction in their respective outcome trials, and collectively they showed a highly significant 18% reduction in MACE, compared with placebo, Dr. Verma said. Further, recent analysis by Dr. Verma that used data from liraglutide treatment in the LEADER trial showed the MACE benefit occurred only among enrolled patients treated with liraglutide who had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Patients enrolled in the trial with only multiple risk factors (in addition to having T2DM) but without established ASCVD showed no significant benefit from liraglutide treatment for the MACE endpoint, compared with control patients.
Recently a press-release announcement of results from a sixth GLP-1 RA, dulaglutide, in the REWIND trial of MACE outcomes suggested that a drug in this class could have broader effect. The majority, 69%, of the 9,901 patients with T2DM enrolled in REWIND had risk factors but not established ASCVD at enrollment. A Nov. 5, 2018, statement from the company developing this drug, Lilly, reported that the study overall produced a statistically significant reduction in MACE, although it provided no additional details. As the released noted, this made REWIND the first trial to show a MACE benefit from a drug in the GLP-1 RA class in patients without established ASCVD.
The MACE outcome results from the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials showed a similar pattern as liraglutide: In patients with established ASCVD, the drugs individually each produced a MACE reduction, although dapagliflozin just missed having a statistically significant reduction. Collectively, the three drugs showed a statistically significant, 14% relative risk reduction for MACE, compared with control patients. But among patients with multiple risk factors only, but without established ASCVD, included in two of the three trials (CANVAS and DECLARE-TIMI 58), the results showed both individually and collectively a neutral MACE effect.
But unlike the other antihyperglycemic drugs tested in the cardiovascular outcome trials, the SGLT2 inhibitors have shown two additional, highly important secondary outcomes: a consistent reduction in hospitalization for heart failure and a consistent reduction in renal-disease progression.
A meta-analysis of the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials published coincident with the release of the DECLARE-TIMI 58 results showed that, for the outcome of either cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure, the SGLT2 inhibitors collectively showed a significant 29% relative decrease in this incidence among patients with a history of heart failure, and a significant 21% relative decrease among patients without history of heart failure (Lancet. 2018 Nov 10. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X). Among the subset of patients with established ASCVD, treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor across all three trials showed a significant 16% relative risk reduction, and in the subset with multiple risk factors but no established ASCVD, the two SGLT2 inhibitors collectively produced a 16% relative cut in cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization with a P value of .06. Finally, the Lancet meta-analysis showed that, for a combined endpoint that reflected renal worsening, the SGLT2 inhibitors showed a significant relative reduction of about 45% in both the subgroup of patients with established ASCVD and in the subgroup of those with just risk factors.
“This is a big step forward for patients with multiple risk factors and diabetes but without ASCVD, that both renal disease and hospitalization for heart failure are sensitive” to the SGLT2 inhibitors, Dr. Verma noted. “We see renal protection and reduction of heart failure hospitalization across both primary and secondary prevention patients, with no need to distinguish them based on ASCVD.” In contrast, he noted, the MACE benefit from the SGLT2 inhibitors seems limited to patients with ASCVD. The day before making this point in a talk during the meeting, Dr. Verma had published the same message in a commentary (Lancet. 2018 Nov 10. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32824-1).
Although the “nomenclature of primary versus secondary prevention is appropriate for atherosclerotic outcomes, it is likely to be inappropriate for a person with type 2 diabetes who is at risk of hospitalization for heart failure and renal disease,” Dr. Verma wrote with his associates in the commentary.
What it means for clinicians
The upshot of all of these cardiovascular outcome trial results that came out over the past 3 years has been a new appreciation of how antihyperglycemic drugs can have cardiovascular and renal benefits that transcend their effects on glycemia. The evidence has put the SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 RAs on track to challenge, and potentially displace, metformin as the top drug to prescribe for patients with T2DM.
Clinicians should realize that they should prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors and selected GLP-1 RAs “as early as metformin in patients with established ASCVD,” said Dr. Verma. “For patients with recalcitrant atherosclerotic disease and a history of MI and ischemia, I’d primarily treat with a GLP-1 RA. In a patient with left ventricular dysfunction or evidence of heart failure, I’d use an SGLT2 inhibitor. But it’s not a fight between these two. You could treat a patients with type 2 diabetes with both classes,” although the practicality of this approach is limited by the high cost of these drugs.
The SGLT2 inhibitors “should now be considered as first-line therapy after metformin in most people with type 2 diabetes, irrespective of whether or not they have established atherosclerotic vascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or heart failure,” he and his associates wrote in their recent commentary.
“What I struggle with the most is how we prioritize and individualize secondary-prevention therapies based on risk for ischemia and heart failure. Some therapies [the SGLT2 inhibitors] are predominantly for heart failure prevention, and some [the GLP-1 RAs] are primarily for ischemia. How do we choose when a patient cannot afford to take both? Does a combination of a SGLT2 inhibitor and a GLP-1 RA offer the greatest CVD benefit? We need to test this in a trial. And will metformin be displaced as first-line treatment?” Dr. Verma asked.
“The day will probably come when, for maximal protection, you treat with both classes. But right now we’re forced to choose because of the cost,” said John McMurray, MD, professor of cardiology at the University of Glasgow, in a talk during the meeting.
As to specifically which SGLT2 inhibitor to prescribe, “they all look pretty much the same” in the newly published meta-analysis, Dr. McMurray said, although he noted that safety differences among agents in the class remain possible.
“For patients similar to those studied in the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials, clinicians should use one of these drugs to reduce the risk for incident heart failure, irrespective of their effect on MACE,” said Dr. Butler. Reducing the risk for incident heart failure and of progressive renal dysfunction are two new goals for antihyperglycemic therapy that now overlay the long-standing goals of controlling glycemia and reducing cardiovascular disease risk and the more recent goals of cutting cardiovascular disease mortality and cutting the risk for a MACE event.
A current limitation for practice is that the none of the three drug companies that market the tested SGLT2 inhibitor drugs has sought regulatory approval for an indication of reducing the risk for heart failure hospitalization. Despite that, “these drugs should be used for renal protection and reducing heart failure hospitalizations,” Dr. Butler said. “We need to start thinking about this and not get lost thinking about only their MACE effect because, when you focus on MACE, there is a competition between the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 RA. If we think of GLP-1 RAs as drugs to prevent MACE, and SGLT2 inhibitors as drugs that primarily prevent heart failure and renal dysfunction, then there is no competition. Perhaps combined treatment is where we need to go,” he said in an interview.
But the enthusiasm that experts like Dr. Butler, Dr. McMurray, and Dr. Verma have for wider use of both classes of drugs in appropriate patients is not necessarily matched right now among many community physicians. Cardiologist David J. Becker, MD, is an example of the clinicians who appreciate the growing evidence that supports wider use of these antihyperglycemic drugs but remain uneasy about applying this evidence in their practice.
Dr. Becker, associate director of the Preventive and Integrative Heart Health Program of the Temple Heart and Vascular Institute in Philadelphia, writes a column for the Philadelphia Inquirer on medical care. In a December 2018 piece, he said “like most cardiologists, I ‘don’t do diabetes’ – because it’s not my expertise. The new drugs, however, mean I need to learn more” about treating these patients. “The problem: There are so many of these medications that they present a bewildering choice for patients and doctors.”
Dr. Becker cited several barriers he sees for himself and his nonendocrinologist colleagues to prescribe these drugs – and for patients to take them:
- High cost, with prices that run close to $20/day for each medication.
- A thicket of names and choices that “lead to confusion and paralysis,” which has been exacerbated by “advertising wars” among competing drug companies.
- Cardiologists and primary care physicians usually defer to endocrinologists to prescribe these drugs, but most patients with T2DM aren’t seen by endocrinologists. The result: “Few doctors prescribe them.”
The cardiovascular disease benefits of these drugs have not been adequately promoted. Until that changes, “cardiologists like me will not realize their importance,” Dr. Becker concluded.
While christening the new diabetocardiology subspecialty, Dr. Braunwald placed the onus for managing this emerging facet of diabetes largely outside the scope of endocrinology.
“We can’t call in a consultant every time we have a patient with diabetes; it would bankrupt the system,” he said. Training of cardiologists now needs to include several months of treating patients with diabetes, Dr. Braunwald advised, just like 30 or so years ago when cardiologists like himself had to become more familiar with blood clotting to better manage thrombotic disease.
Dr. Braunwald has been a consultant to Cardurion, Myokardia, and Sanofi; an advisor to Endcardia; and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Daiishi Sankyo, and Novartis. Dr. Butler has been a consultant or advisor to AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi. Dr. Verma has received honoraria and research funding from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, NovoNordisk, Sanofi, and Valeant. Dr. McMurray has received research funding from 12 companies. Dr. Becker had no disclosures.
CHICAGO – When the first results from a large trial that showed profound and unexpected benefits for preventing heart failure hospitalizations associated with use of the antihyperglycemic sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin came out – a little over 3 years ago – the general reaction from clinicians was some variant of “Could this be real?”
Since then, as results from some five other large, international trials have come out showing both similar benefits from two other drugs in the same SGLT2 inhibitor class, canagliflozin and dapagliflozin, as well as results showing clear cardiovascular disease benefits from three drugs in a second class of antihyperglycemics, the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), the general consensus among cardiologists became: “The cardiovascular and renal benefits are real. How can we now best use these drugs to help patients?”
This change increasingly forces cardiologists, as well as the primary care physicians who often manage patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, to become more comfortable prescribing these two classes of antihyperglycemic drugs. During a talk at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, Eugene Braunwald, MD, arguably the top thought leader in cardiology, coined a new name for the medical subspecialty that he foresees navigating this overlap between diabetes care and cardiovascular disease prevention: diabetocardiology (although a more euphonic alternative might be cardiodiabetology, while the more comprehensive name could be cardionephrodiabetology).
“I was certainly surprised” by the first report in 2015 from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28), said Dr. Braunwald, who is professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. A lot of his colleagues were surprised and said, “It’s just one trial.”
“Now we have three trials,” with the addition of the CANVAS trial for canagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[7]:644-57) and the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial (N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 10. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1812389) for dapagliflozin reported at the AHA meeting in November.
“We are in the midst of two pandemics: heart failure and type 2 diabetes. As cardiologists, we have to learn how to deal with this,” said Dr. Braunwald, and the evidence now clearly shows that these drugs can help with that.
As another speaker at the meeting, Javed Butler, MD, a heart failure specialist, observed in a separate talk at the meeting, “Heart failure is one of the most common, if not the most common complication, of patients with diabetes.” This tight link between heart failure and diabetes helps make cardiovascular mortality “the number one cause of death” in patients with diabetes, said Dr. Butler, professor and chairman of medicine at the University of Mississippi in Jackson.
“Thanks to the cardiovascular outcome trials, we now have a much broader and deeper appreciation of heart failure and renal disease as integral components of the cardiovascular-renal spectrum in people with diabetes,” said Subodh Verma, MD, a professor at the University of Toronto and cardiac surgeon at St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto. Dr. Braunwald spelled out in his talk some of the interrelationships of diabetes, heart failure, and renal dysfunction that together produce a downward-spiraling vicious circle for patients, a pathophysiological process that clinicians can now short-circuit by treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor.
Cardiovascular outcome trials show the way
In the context of antihyperglycemic drugs, the “cardiovascular outcome trials” refers to a series of large trials mandated by the Food and Drug Administration in 2008 to assess the cardiovascular disease effects of new agents coming onto the U.S. market to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). By the time Dr. Verma spoke at the AHA meeting, he could cite reported results from 12 of these trials: 5 different drugs in the GLP-1 RA class, 4 drugs in the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class, and 3 drugs from the SGLT2 inhibitor class. Dr. Verma summed what the findings have shown.
The four tested DDP-4 inhibitors (alogliptin, linagliptin, saxagliptin, and sitagliptin) consistently showed neutrality for the primary outcome of major adverse cardiovascular disease events (MACE), constituted by cardiovascular disease death, MI, or stroke.
The five tested GLP-1 RAs (albiglutide, exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, and semaglutide) showed a mixed pattern of MACE results that seemed to be linked with the subclass the drug fell into. The two exedin-4–based drugs, exenatide and lixisenatide, each showed a statistically neutral effect for MACE, as well as collectively in a combined analysis. In contrast, three human GLP-1–based drugs, albiglutide, liraglutide, and semaglutide, each showed a consistent, statistically-significant MACE reduction in their respective outcome trials, and collectively they showed a highly significant 18% reduction in MACE, compared with placebo, Dr. Verma said. Further, recent analysis by Dr. Verma that used data from liraglutide treatment in the LEADER trial showed the MACE benefit occurred only among enrolled patients treated with liraglutide who had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Patients enrolled in the trial with only multiple risk factors (in addition to having T2DM) but without established ASCVD showed no significant benefit from liraglutide treatment for the MACE endpoint, compared with control patients.
Recently a press-release announcement of results from a sixth GLP-1 RA, dulaglutide, in the REWIND trial of MACE outcomes suggested that a drug in this class could have broader effect. The majority, 69%, of the 9,901 patients with T2DM enrolled in REWIND had risk factors but not established ASCVD at enrollment. A Nov. 5, 2018, statement from the company developing this drug, Lilly, reported that the study overall produced a statistically significant reduction in MACE, although it provided no additional details. As the released noted, this made REWIND the first trial to show a MACE benefit from a drug in the GLP-1 RA class in patients without established ASCVD.
The MACE outcome results from the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials showed a similar pattern as liraglutide: In patients with established ASCVD, the drugs individually each produced a MACE reduction, although dapagliflozin just missed having a statistically significant reduction. Collectively, the three drugs showed a statistically significant, 14% relative risk reduction for MACE, compared with control patients. But among patients with multiple risk factors only, but without established ASCVD, included in two of the three trials (CANVAS and DECLARE-TIMI 58), the results showed both individually and collectively a neutral MACE effect.
But unlike the other antihyperglycemic drugs tested in the cardiovascular outcome trials, the SGLT2 inhibitors have shown two additional, highly important secondary outcomes: a consistent reduction in hospitalization for heart failure and a consistent reduction in renal-disease progression.
A meta-analysis of the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials published coincident with the release of the DECLARE-TIMI 58 results showed that, for the outcome of either cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure, the SGLT2 inhibitors collectively showed a significant 29% relative decrease in this incidence among patients with a history of heart failure, and a significant 21% relative decrease among patients without history of heart failure (Lancet. 2018 Nov 10. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X). Among the subset of patients with established ASCVD, treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor across all three trials showed a significant 16% relative risk reduction, and in the subset with multiple risk factors but no established ASCVD, the two SGLT2 inhibitors collectively produced a 16% relative cut in cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization with a P value of .06. Finally, the Lancet meta-analysis showed that, for a combined endpoint that reflected renal worsening, the SGLT2 inhibitors showed a significant relative reduction of about 45% in both the subgroup of patients with established ASCVD and in the subgroup of those with just risk factors.
“This is a big step forward for patients with multiple risk factors and diabetes but without ASCVD, that both renal disease and hospitalization for heart failure are sensitive” to the SGLT2 inhibitors, Dr. Verma noted. “We see renal protection and reduction of heart failure hospitalization across both primary and secondary prevention patients, with no need to distinguish them based on ASCVD.” In contrast, he noted, the MACE benefit from the SGLT2 inhibitors seems limited to patients with ASCVD. The day before making this point in a talk during the meeting, Dr. Verma had published the same message in a commentary (Lancet. 2018 Nov 10. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32824-1).
Although the “nomenclature of primary versus secondary prevention is appropriate for atherosclerotic outcomes, it is likely to be inappropriate for a person with type 2 diabetes who is at risk of hospitalization for heart failure and renal disease,” Dr. Verma wrote with his associates in the commentary.
What it means for clinicians
The upshot of all of these cardiovascular outcome trial results that came out over the past 3 years has been a new appreciation of how antihyperglycemic drugs can have cardiovascular and renal benefits that transcend their effects on glycemia. The evidence has put the SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 RAs on track to challenge, and potentially displace, metformin as the top drug to prescribe for patients with T2DM.
Clinicians should realize that they should prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors and selected GLP-1 RAs “as early as metformin in patients with established ASCVD,” said Dr. Verma. “For patients with recalcitrant atherosclerotic disease and a history of MI and ischemia, I’d primarily treat with a GLP-1 RA. In a patient with left ventricular dysfunction or evidence of heart failure, I’d use an SGLT2 inhibitor. But it’s not a fight between these two. You could treat a patients with type 2 diabetes with both classes,” although the practicality of this approach is limited by the high cost of these drugs.
The SGLT2 inhibitors “should now be considered as first-line therapy after metformin in most people with type 2 diabetes, irrespective of whether or not they have established atherosclerotic vascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or heart failure,” he and his associates wrote in their recent commentary.
“What I struggle with the most is how we prioritize and individualize secondary-prevention therapies based on risk for ischemia and heart failure. Some therapies [the SGLT2 inhibitors] are predominantly for heart failure prevention, and some [the GLP-1 RAs] are primarily for ischemia. How do we choose when a patient cannot afford to take both? Does a combination of a SGLT2 inhibitor and a GLP-1 RA offer the greatest CVD benefit? We need to test this in a trial. And will metformin be displaced as first-line treatment?” Dr. Verma asked.
“The day will probably come when, for maximal protection, you treat with both classes. But right now we’re forced to choose because of the cost,” said John McMurray, MD, professor of cardiology at the University of Glasgow, in a talk during the meeting.
As to specifically which SGLT2 inhibitor to prescribe, “they all look pretty much the same” in the newly published meta-analysis, Dr. McMurray said, although he noted that safety differences among agents in the class remain possible.
“For patients similar to those studied in the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials, clinicians should use one of these drugs to reduce the risk for incident heart failure, irrespective of their effect on MACE,” said Dr. Butler. Reducing the risk for incident heart failure and of progressive renal dysfunction are two new goals for antihyperglycemic therapy that now overlay the long-standing goals of controlling glycemia and reducing cardiovascular disease risk and the more recent goals of cutting cardiovascular disease mortality and cutting the risk for a MACE event.
A current limitation for practice is that the none of the three drug companies that market the tested SGLT2 inhibitor drugs has sought regulatory approval for an indication of reducing the risk for heart failure hospitalization. Despite that, “these drugs should be used for renal protection and reducing heart failure hospitalizations,” Dr. Butler said. “We need to start thinking about this and not get lost thinking about only their MACE effect because, when you focus on MACE, there is a competition between the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 RA. If we think of GLP-1 RAs as drugs to prevent MACE, and SGLT2 inhibitors as drugs that primarily prevent heart failure and renal dysfunction, then there is no competition. Perhaps combined treatment is where we need to go,” he said in an interview.
But the enthusiasm that experts like Dr. Butler, Dr. McMurray, and Dr. Verma have for wider use of both classes of drugs in appropriate patients is not necessarily matched right now among many community physicians. Cardiologist David J. Becker, MD, is an example of the clinicians who appreciate the growing evidence that supports wider use of these antihyperglycemic drugs but remain uneasy about applying this evidence in their practice.
Dr. Becker, associate director of the Preventive and Integrative Heart Health Program of the Temple Heart and Vascular Institute in Philadelphia, writes a column for the Philadelphia Inquirer on medical care. In a December 2018 piece, he said “like most cardiologists, I ‘don’t do diabetes’ – because it’s not my expertise. The new drugs, however, mean I need to learn more” about treating these patients. “The problem: There are so many of these medications that they present a bewildering choice for patients and doctors.”
Dr. Becker cited several barriers he sees for himself and his nonendocrinologist colleagues to prescribe these drugs – and for patients to take them:
- High cost, with prices that run close to $20/day for each medication.
- A thicket of names and choices that “lead to confusion and paralysis,” which has been exacerbated by “advertising wars” among competing drug companies.
- Cardiologists and primary care physicians usually defer to endocrinologists to prescribe these drugs, but most patients with T2DM aren’t seen by endocrinologists. The result: “Few doctors prescribe them.”
The cardiovascular disease benefits of these drugs have not been adequately promoted. Until that changes, “cardiologists like me will not realize their importance,” Dr. Becker concluded.
While christening the new diabetocardiology subspecialty, Dr. Braunwald placed the onus for managing this emerging facet of diabetes largely outside the scope of endocrinology.
“We can’t call in a consultant every time we have a patient with diabetes; it would bankrupt the system,” he said. Training of cardiologists now needs to include several months of treating patients with diabetes, Dr. Braunwald advised, just like 30 or so years ago when cardiologists like himself had to become more familiar with blood clotting to better manage thrombotic disease.
Dr. Braunwald has been a consultant to Cardurion, Myokardia, and Sanofi; an advisor to Endcardia; and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Daiishi Sankyo, and Novartis. Dr. Butler has been a consultant or advisor to AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi. Dr. Verma has received honoraria and research funding from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, NovoNordisk, Sanofi, and Valeant. Dr. McMurray has received research funding from 12 companies. Dr. Becker had no disclosures.
CHICAGO – When the first results from a large trial that showed profound and unexpected benefits for preventing heart failure hospitalizations associated with use of the antihyperglycemic sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin came out – a little over 3 years ago – the general reaction from clinicians was some variant of “Could this be real?”
Since then, as results from some five other large, international trials have come out showing both similar benefits from two other drugs in the same SGLT2 inhibitor class, canagliflozin and dapagliflozin, as well as results showing clear cardiovascular disease benefits from three drugs in a second class of antihyperglycemics, the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), the general consensus among cardiologists became: “The cardiovascular and renal benefits are real. How can we now best use these drugs to help patients?”
This change increasingly forces cardiologists, as well as the primary care physicians who often manage patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, to become more comfortable prescribing these two classes of antihyperglycemic drugs. During a talk at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, Eugene Braunwald, MD, arguably the top thought leader in cardiology, coined a new name for the medical subspecialty that he foresees navigating this overlap between diabetes care and cardiovascular disease prevention: diabetocardiology (although a more euphonic alternative might be cardiodiabetology, while the more comprehensive name could be cardionephrodiabetology).
“I was certainly surprised” by the first report in 2015 from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28), said Dr. Braunwald, who is professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. A lot of his colleagues were surprised and said, “It’s just one trial.”
“Now we have three trials,” with the addition of the CANVAS trial for canagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[7]:644-57) and the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial (N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 10. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1812389) for dapagliflozin reported at the AHA meeting in November.
“We are in the midst of two pandemics: heart failure and type 2 diabetes. As cardiologists, we have to learn how to deal with this,” said Dr. Braunwald, and the evidence now clearly shows that these drugs can help with that.
As another speaker at the meeting, Javed Butler, MD, a heart failure specialist, observed in a separate talk at the meeting, “Heart failure is one of the most common, if not the most common complication, of patients with diabetes.” This tight link between heart failure and diabetes helps make cardiovascular mortality “the number one cause of death” in patients with diabetes, said Dr. Butler, professor and chairman of medicine at the University of Mississippi in Jackson.
“Thanks to the cardiovascular outcome trials, we now have a much broader and deeper appreciation of heart failure and renal disease as integral components of the cardiovascular-renal spectrum in people with diabetes,” said Subodh Verma, MD, a professor at the University of Toronto and cardiac surgeon at St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto. Dr. Braunwald spelled out in his talk some of the interrelationships of diabetes, heart failure, and renal dysfunction that together produce a downward-spiraling vicious circle for patients, a pathophysiological process that clinicians can now short-circuit by treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor.
Cardiovascular outcome trials show the way
In the context of antihyperglycemic drugs, the “cardiovascular outcome trials” refers to a series of large trials mandated by the Food and Drug Administration in 2008 to assess the cardiovascular disease effects of new agents coming onto the U.S. market to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). By the time Dr. Verma spoke at the AHA meeting, he could cite reported results from 12 of these trials: 5 different drugs in the GLP-1 RA class, 4 drugs in the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class, and 3 drugs from the SGLT2 inhibitor class. Dr. Verma summed what the findings have shown.
The four tested DDP-4 inhibitors (alogliptin, linagliptin, saxagliptin, and sitagliptin) consistently showed neutrality for the primary outcome of major adverse cardiovascular disease events (MACE), constituted by cardiovascular disease death, MI, or stroke.
The five tested GLP-1 RAs (albiglutide, exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, and semaglutide) showed a mixed pattern of MACE results that seemed to be linked with the subclass the drug fell into. The two exedin-4–based drugs, exenatide and lixisenatide, each showed a statistically neutral effect for MACE, as well as collectively in a combined analysis. In contrast, three human GLP-1–based drugs, albiglutide, liraglutide, and semaglutide, each showed a consistent, statistically-significant MACE reduction in their respective outcome trials, and collectively they showed a highly significant 18% reduction in MACE, compared with placebo, Dr. Verma said. Further, recent analysis by Dr. Verma that used data from liraglutide treatment in the LEADER trial showed the MACE benefit occurred only among enrolled patients treated with liraglutide who had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Patients enrolled in the trial with only multiple risk factors (in addition to having T2DM) but without established ASCVD showed no significant benefit from liraglutide treatment for the MACE endpoint, compared with control patients.
Recently a press-release announcement of results from a sixth GLP-1 RA, dulaglutide, in the REWIND trial of MACE outcomes suggested that a drug in this class could have broader effect. The majority, 69%, of the 9,901 patients with T2DM enrolled in REWIND had risk factors but not established ASCVD at enrollment. A Nov. 5, 2018, statement from the company developing this drug, Lilly, reported that the study overall produced a statistically significant reduction in MACE, although it provided no additional details. As the released noted, this made REWIND the first trial to show a MACE benefit from a drug in the GLP-1 RA class in patients without established ASCVD.
The MACE outcome results from the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials showed a similar pattern as liraglutide: In patients with established ASCVD, the drugs individually each produced a MACE reduction, although dapagliflozin just missed having a statistically significant reduction. Collectively, the three drugs showed a statistically significant, 14% relative risk reduction for MACE, compared with control patients. But among patients with multiple risk factors only, but without established ASCVD, included in two of the three trials (CANVAS and DECLARE-TIMI 58), the results showed both individually and collectively a neutral MACE effect.
But unlike the other antihyperglycemic drugs tested in the cardiovascular outcome trials, the SGLT2 inhibitors have shown two additional, highly important secondary outcomes: a consistent reduction in hospitalization for heart failure and a consistent reduction in renal-disease progression.
A meta-analysis of the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials published coincident with the release of the DECLARE-TIMI 58 results showed that, for the outcome of either cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure, the SGLT2 inhibitors collectively showed a significant 29% relative decrease in this incidence among patients with a history of heart failure, and a significant 21% relative decrease among patients without history of heart failure (Lancet. 2018 Nov 10. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X). Among the subset of patients with established ASCVD, treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor across all three trials showed a significant 16% relative risk reduction, and in the subset with multiple risk factors but no established ASCVD, the two SGLT2 inhibitors collectively produced a 16% relative cut in cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization with a P value of .06. Finally, the Lancet meta-analysis showed that, for a combined endpoint that reflected renal worsening, the SGLT2 inhibitors showed a significant relative reduction of about 45% in both the subgroup of patients with established ASCVD and in the subgroup of those with just risk factors.
“This is a big step forward for patients with multiple risk factors and diabetes but without ASCVD, that both renal disease and hospitalization for heart failure are sensitive” to the SGLT2 inhibitors, Dr. Verma noted. “We see renal protection and reduction of heart failure hospitalization across both primary and secondary prevention patients, with no need to distinguish them based on ASCVD.” In contrast, he noted, the MACE benefit from the SGLT2 inhibitors seems limited to patients with ASCVD. The day before making this point in a talk during the meeting, Dr. Verma had published the same message in a commentary (Lancet. 2018 Nov 10. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32824-1).
Although the “nomenclature of primary versus secondary prevention is appropriate for atherosclerotic outcomes, it is likely to be inappropriate for a person with type 2 diabetes who is at risk of hospitalization for heart failure and renal disease,” Dr. Verma wrote with his associates in the commentary.
What it means for clinicians
The upshot of all of these cardiovascular outcome trial results that came out over the past 3 years has been a new appreciation of how antihyperglycemic drugs can have cardiovascular and renal benefits that transcend their effects on glycemia. The evidence has put the SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 RAs on track to challenge, and potentially displace, metformin as the top drug to prescribe for patients with T2DM.
Clinicians should realize that they should prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors and selected GLP-1 RAs “as early as metformin in patients with established ASCVD,” said Dr. Verma. “For patients with recalcitrant atherosclerotic disease and a history of MI and ischemia, I’d primarily treat with a GLP-1 RA. In a patient with left ventricular dysfunction or evidence of heart failure, I’d use an SGLT2 inhibitor. But it’s not a fight between these two. You could treat a patients with type 2 diabetes with both classes,” although the practicality of this approach is limited by the high cost of these drugs.
The SGLT2 inhibitors “should now be considered as first-line therapy after metformin in most people with type 2 diabetes, irrespective of whether or not they have established atherosclerotic vascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or heart failure,” he and his associates wrote in their recent commentary.
“What I struggle with the most is how we prioritize and individualize secondary-prevention therapies based on risk for ischemia and heart failure. Some therapies [the SGLT2 inhibitors] are predominantly for heart failure prevention, and some [the GLP-1 RAs] are primarily for ischemia. How do we choose when a patient cannot afford to take both? Does a combination of a SGLT2 inhibitor and a GLP-1 RA offer the greatest CVD benefit? We need to test this in a trial. And will metformin be displaced as first-line treatment?” Dr. Verma asked.
“The day will probably come when, for maximal protection, you treat with both classes. But right now we’re forced to choose because of the cost,” said John McMurray, MD, professor of cardiology at the University of Glasgow, in a talk during the meeting.
As to specifically which SGLT2 inhibitor to prescribe, “they all look pretty much the same” in the newly published meta-analysis, Dr. McMurray said, although he noted that safety differences among agents in the class remain possible.
“For patients similar to those studied in the three SGLT2 inhibitor trials, clinicians should use one of these drugs to reduce the risk for incident heart failure, irrespective of their effect on MACE,” said Dr. Butler. Reducing the risk for incident heart failure and of progressive renal dysfunction are two new goals for antihyperglycemic therapy that now overlay the long-standing goals of controlling glycemia and reducing cardiovascular disease risk and the more recent goals of cutting cardiovascular disease mortality and cutting the risk for a MACE event.
A current limitation for practice is that the none of the three drug companies that market the tested SGLT2 inhibitor drugs has sought regulatory approval for an indication of reducing the risk for heart failure hospitalization. Despite that, “these drugs should be used for renal protection and reducing heart failure hospitalizations,” Dr. Butler said. “We need to start thinking about this and not get lost thinking about only their MACE effect because, when you focus on MACE, there is a competition between the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 RA. If we think of GLP-1 RAs as drugs to prevent MACE, and SGLT2 inhibitors as drugs that primarily prevent heart failure and renal dysfunction, then there is no competition. Perhaps combined treatment is where we need to go,” he said in an interview.
But the enthusiasm that experts like Dr. Butler, Dr. McMurray, and Dr. Verma have for wider use of both classes of drugs in appropriate patients is not necessarily matched right now among many community physicians. Cardiologist David J. Becker, MD, is an example of the clinicians who appreciate the growing evidence that supports wider use of these antihyperglycemic drugs but remain uneasy about applying this evidence in their practice.
Dr. Becker, associate director of the Preventive and Integrative Heart Health Program of the Temple Heart and Vascular Institute in Philadelphia, writes a column for the Philadelphia Inquirer on medical care. In a December 2018 piece, he said “like most cardiologists, I ‘don’t do diabetes’ – because it’s not my expertise. The new drugs, however, mean I need to learn more” about treating these patients. “The problem: There are so many of these medications that they present a bewildering choice for patients and doctors.”
Dr. Becker cited several barriers he sees for himself and his nonendocrinologist colleagues to prescribe these drugs – and for patients to take them:
- High cost, with prices that run close to $20/day for each medication.
- A thicket of names and choices that “lead to confusion and paralysis,” which has been exacerbated by “advertising wars” among competing drug companies.
- Cardiologists and primary care physicians usually defer to endocrinologists to prescribe these drugs, but most patients with T2DM aren’t seen by endocrinologists. The result: “Few doctors prescribe them.”
The cardiovascular disease benefits of these drugs have not been adequately promoted. Until that changes, “cardiologists like me will not realize their importance,” Dr. Becker concluded.
While christening the new diabetocardiology subspecialty, Dr. Braunwald placed the onus for managing this emerging facet of diabetes largely outside the scope of endocrinology.
“We can’t call in a consultant every time we have a patient with diabetes; it would bankrupt the system,” he said. Training of cardiologists now needs to include several months of treating patients with diabetes, Dr. Braunwald advised, just like 30 or so years ago when cardiologists like himself had to become more familiar with blood clotting to better manage thrombotic disease.
Dr. Braunwald has been a consultant to Cardurion, Myokardia, and Sanofi; an advisor to Endcardia; and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Daiishi Sankyo, and Novartis. Dr. Butler has been a consultant or advisor to AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi. Dr. Verma has received honoraria and research funding from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, NovoNordisk, Sanofi, and Valeant. Dr. McMurray has received research funding from 12 companies. Dr. Becker had no disclosures.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program may be doing more harm than good
A Medicare program aimed at lowering readmissions to hospitals could be having an adverse effect on mortality.
Results from a retrospective cohort study of hospitalizations for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia among Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older between April 1, 2005 and March 31, 2015 (covering the period before and after the Medicare Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program was announced in April 2010 and implemented in October 2012) found a significant increase in 30-day post discharge mortality among heart failure and pneumonia patients.
“Most concerning, however, is the possibility that the relationship between the HRRP and postdischarge mortality for heart failure and pneumonia is causal, indicating that the HRRP led to changes in quality of care that adversely affected patients,” Rishi Wadhera, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and his colleagues wrote in a report published Dec. 25, 2018, in JAMA.
They looked at 8.3 million hospitalizations for heart failure, acute MI, and pneumonia, among whom 7.9 million were alive at the time of discharge. There were roughly 270,000 deaths within 30 days of discharge for heart failure; 128,000 for acute MI; and 246,000 for pneumonia.
To examine trends, the timing was divided into four periods: two prior to the announcement of the HRRP (April 2005–September 2007 and October 2007–March 2010); a third covering the time when the HRRP was announced (April 2010–September 2012); and the fourth when HRRP was implemented (October 2012–March 2015).
They found that among patients discharged with heart failure, 30-day mortality was rising even before the announcement of the HRRP, by 0.27% from the first period to the second period. That baseline trend continued when the HRRP was announced, by 0.49%, from second period to third. The difference in change between those periods was 0.22%. After implementation, 30-day mortality increased by 0.52%, with a difference in change from the third period of 0.25%. Both changes were statistically significant.
Among pneumonia patients, postdischarge mortality was stable before HRRP, but significantly increased after HRRP announcement, by 0.26%, with a difference in change from the second period to the third period of 0.22%. After implementation, the 30-day postdischarge mortality was 0.44%, with a significant difference in change of 0.40%.
Acute MI was a different story. Postdischarge mortality decreased significantly after the implementation of the HRRP, by 0.22%. The difference in change was –0.26%.
The authors suggested that “some hospitals may have focused more resources and efforts on reducing or avoiding readmissions than on prioritizing survival.” They add that the increases in heart failure morbidity could be related to patients with more severe heart conditions.
They noted that “although hospitals that reduce readmissions also appear to reduce mortality, this hospital-level concordance does not reflect the change in readmissions and mortality at the level of the patient population, which is arguably of greater importance to individual patients and to public health.”
Further research is needed to understand whether the increase in 30-day postdischarge mortality is a result of the HRRP, the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Wadhera R et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19232.
Evidence in this study shows that while the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program my be succeeding in reducing hospital admissions, little evidence is available to show that it is having a positive effect on patient outcomes.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services needs to reexamine the program and find alternative methods that are both effective at reducing hospital readmissions while at the same time protect patients from unintentional harm, including death.
Gregg C. Fonarow, MD , University of California Medical Center, Los Angeles, in an editorial published in JAMA, Dec. 25, 2018. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19325 .
Evidence in this study shows that while the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program my be succeeding in reducing hospital admissions, little evidence is available to show that it is having a positive effect on patient outcomes.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services needs to reexamine the program and find alternative methods that are both effective at reducing hospital readmissions while at the same time protect patients from unintentional harm, including death.
Gregg C. Fonarow, MD , University of California Medical Center, Los Angeles, in an editorial published in JAMA, Dec. 25, 2018. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19325 .
Evidence in this study shows that while the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program my be succeeding in reducing hospital admissions, little evidence is available to show that it is having a positive effect on patient outcomes.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services needs to reexamine the program and find alternative methods that are both effective at reducing hospital readmissions while at the same time protect patients from unintentional harm, including death.
Gregg C. Fonarow, MD , University of California Medical Center, Los Angeles, in an editorial published in JAMA, Dec. 25, 2018. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19325 .
A Medicare program aimed at lowering readmissions to hospitals could be having an adverse effect on mortality.
Results from a retrospective cohort study of hospitalizations for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia among Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older between April 1, 2005 and March 31, 2015 (covering the period before and after the Medicare Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program was announced in April 2010 and implemented in October 2012) found a significant increase in 30-day post discharge mortality among heart failure and pneumonia patients.
“Most concerning, however, is the possibility that the relationship between the HRRP and postdischarge mortality for heart failure and pneumonia is causal, indicating that the HRRP led to changes in quality of care that adversely affected patients,” Rishi Wadhera, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and his colleagues wrote in a report published Dec. 25, 2018, in JAMA.
They looked at 8.3 million hospitalizations for heart failure, acute MI, and pneumonia, among whom 7.9 million were alive at the time of discharge. There were roughly 270,000 deaths within 30 days of discharge for heart failure; 128,000 for acute MI; and 246,000 for pneumonia.
To examine trends, the timing was divided into four periods: two prior to the announcement of the HRRP (April 2005–September 2007 and October 2007–March 2010); a third covering the time when the HRRP was announced (April 2010–September 2012); and the fourth when HRRP was implemented (October 2012–March 2015).
They found that among patients discharged with heart failure, 30-day mortality was rising even before the announcement of the HRRP, by 0.27% from the first period to the second period. That baseline trend continued when the HRRP was announced, by 0.49%, from second period to third. The difference in change between those periods was 0.22%. After implementation, 30-day mortality increased by 0.52%, with a difference in change from the third period of 0.25%. Both changes were statistically significant.
Among pneumonia patients, postdischarge mortality was stable before HRRP, but significantly increased after HRRP announcement, by 0.26%, with a difference in change from the second period to the third period of 0.22%. After implementation, the 30-day postdischarge mortality was 0.44%, with a significant difference in change of 0.40%.
Acute MI was a different story. Postdischarge mortality decreased significantly after the implementation of the HRRP, by 0.22%. The difference in change was –0.26%.
The authors suggested that “some hospitals may have focused more resources and efforts on reducing or avoiding readmissions than on prioritizing survival.” They add that the increases in heart failure morbidity could be related to patients with more severe heart conditions.
They noted that “although hospitals that reduce readmissions also appear to reduce mortality, this hospital-level concordance does not reflect the change in readmissions and mortality at the level of the patient population, which is arguably of greater importance to individual patients and to public health.”
Further research is needed to understand whether the increase in 30-day postdischarge mortality is a result of the HRRP, the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Wadhera R et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19232.
A Medicare program aimed at lowering readmissions to hospitals could be having an adverse effect on mortality.
Results from a retrospective cohort study of hospitalizations for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia among Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older between April 1, 2005 and March 31, 2015 (covering the period before and after the Medicare Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program was announced in April 2010 and implemented in October 2012) found a significant increase in 30-day post discharge mortality among heart failure and pneumonia patients.
“Most concerning, however, is the possibility that the relationship between the HRRP and postdischarge mortality for heart failure and pneumonia is causal, indicating that the HRRP led to changes in quality of care that adversely affected patients,” Rishi Wadhera, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and his colleagues wrote in a report published Dec. 25, 2018, in JAMA.
They looked at 8.3 million hospitalizations for heart failure, acute MI, and pneumonia, among whom 7.9 million were alive at the time of discharge. There were roughly 270,000 deaths within 30 days of discharge for heart failure; 128,000 for acute MI; and 246,000 for pneumonia.
To examine trends, the timing was divided into four periods: two prior to the announcement of the HRRP (April 2005–September 2007 and October 2007–March 2010); a third covering the time when the HRRP was announced (April 2010–September 2012); and the fourth when HRRP was implemented (October 2012–March 2015).
They found that among patients discharged with heart failure, 30-day mortality was rising even before the announcement of the HRRP, by 0.27% from the first period to the second period. That baseline trend continued when the HRRP was announced, by 0.49%, from second period to third. The difference in change between those periods was 0.22%. After implementation, 30-day mortality increased by 0.52%, with a difference in change from the third period of 0.25%. Both changes were statistically significant.
Among pneumonia patients, postdischarge mortality was stable before HRRP, but significantly increased after HRRP announcement, by 0.26%, with a difference in change from the second period to the third period of 0.22%. After implementation, the 30-day postdischarge mortality was 0.44%, with a significant difference in change of 0.40%.
Acute MI was a different story. Postdischarge mortality decreased significantly after the implementation of the HRRP, by 0.22%. The difference in change was –0.26%.
The authors suggested that “some hospitals may have focused more resources and efforts on reducing or avoiding readmissions than on prioritizing survival.” They add that the increases in heart failure morbidity could be related to patients with more severe heart conditions.
They noted that “although hospitals that reduce readmissions also appear to reduce mortality, this hospital-level concordance does not reflect the change in readmissions and mortality at the level of the patient population, which is arguably of greater importance to individual patients and to public health.”
Further research is needed to understand whether the increase in 30-day postdischarge mortality is a result of the HRRP, the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Wadhera R et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19232.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Heart failure patients saw mortality increase 0.52% after HRRP launched.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study across 10 years, including time before and after the implementation of the HRRP.
Disclosures: The Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology funded the study. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Source: Wadhera R et al. JAMA 2018 Dec 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19232.
Reducing heart failure readmissions raises mortality
This week from MDedge Cardiology, the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program may be doing more harm than good, ticagrelor holds no edge over aspirin in CABG patients, weight-loss apps lack evidence, and the Surgeon General sends out an alarm.
Subscribe to Cardiocast wherever you get your podcasts.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
This week from MDedge Cardiology, the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program may be doing more harm than good, ticagrelor holds no edge over aspirin in CABG patients, weight-loss apps lack evidence, and the Surgeon General sends out an alarm.
Subscribe to Cardiocast wherever you get your podcasts.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
This week from MDedge Cardiology, the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program may be doing more harm than good, ticagrelor holds no edge over aspirin in CABG patients, weight-loss apps lack evidence, and the Surgeon General sends out an alarm.
Subscribe to Cardiocast wherever you get your podcasts.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts





















