User login
Two Techniques to Avoid Cyst Spray During Excision
Practice Gap
Epidermoid cysts are asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, mobile, subcutaneous masses that elevate the skin. Also known as epidermal, keratin, or infundibular cysts, epidermoid cysts are caused by proliferation of surface epidermoid cells within the dermis and can arise anywhere on the body, most commonly on the face, neck, and trunk.1 Cutaneous cysts often contain fluid or semifluid contents and can be aesthetically displeasing or cause mild pain, prompting patients to seek removal. Definitive treatment of epidermoid cysts is complete surgical removal,2 which can be performed in office in a sterile or clean manner by either dermatologists or primary care providers.
Prior to incision, a local anesthetic—commonly lidocaine with epinephrine—is injected in the region surrounding the cyst sac so as not to rupture the cyst wall. Maintaining the cyst wall throughout the procedure ensures total cyst removal and minimizes the risk for recurrence. However, it often is difficult to approximate the cyst border because it cannot be visualized prior to incision.
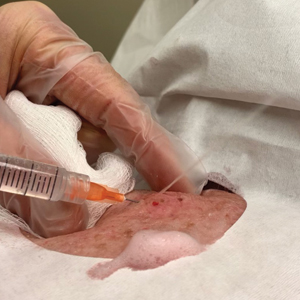
Throughout the duration of the procedure, cyst contents may suddenly spray out of the area and pose a risk to providers and their staff (Figure, A). Even with careful application around the periphery, either puncture or pericystic anesthesia between the cyst wall and the dermis can lead to splatter. Larger and wider peripheral anesthesia may not be possible given a shortage of lidocaine and a desire to minimize injection. Even with meticulous use of personal protective equipment in cutaneous surgery, infectious organisms found in ruptured cysts and abscesses may spray the surgical field.3 Therefore, it is in our best interest to minimize the trajectory of cyst spray contents.
The Tools
We have employed 2 simple techniques using equipment normally found on a standard surgical tray for easy safe injection of cysts. Supplies needed include 4×4-inch gauze pads, alcohol and chlorhexidine, a marker, all instruments necessary for cyst excision, and a small clear biohazard bag.
The Technique
Prior to covering the cyst, care is taken to locate the cyst opening. At times, a comedo or punctum can be seen overlying the cyst bulge. We mark the lumen and cyst opening with a surgical marker. If the pore is not easily identified, we draw an 8-mm circle around the mound of the cyst.
One option is to apply a gauze pad over the cyst to allow for stabilization of the surgical field and blanket the area from splatter (Figure, B). Then we cover the cyst using antiseptic-soaked gauze as a protective barrier to avoid potentially contaminated spray. This tool can be constructed from a 4×4-inch gauze pad with the addition of alcohol and chlorhexidine. When the cyst is covered, the surgeon can inject the lesion and surrounding tissue without biohazard splatter.
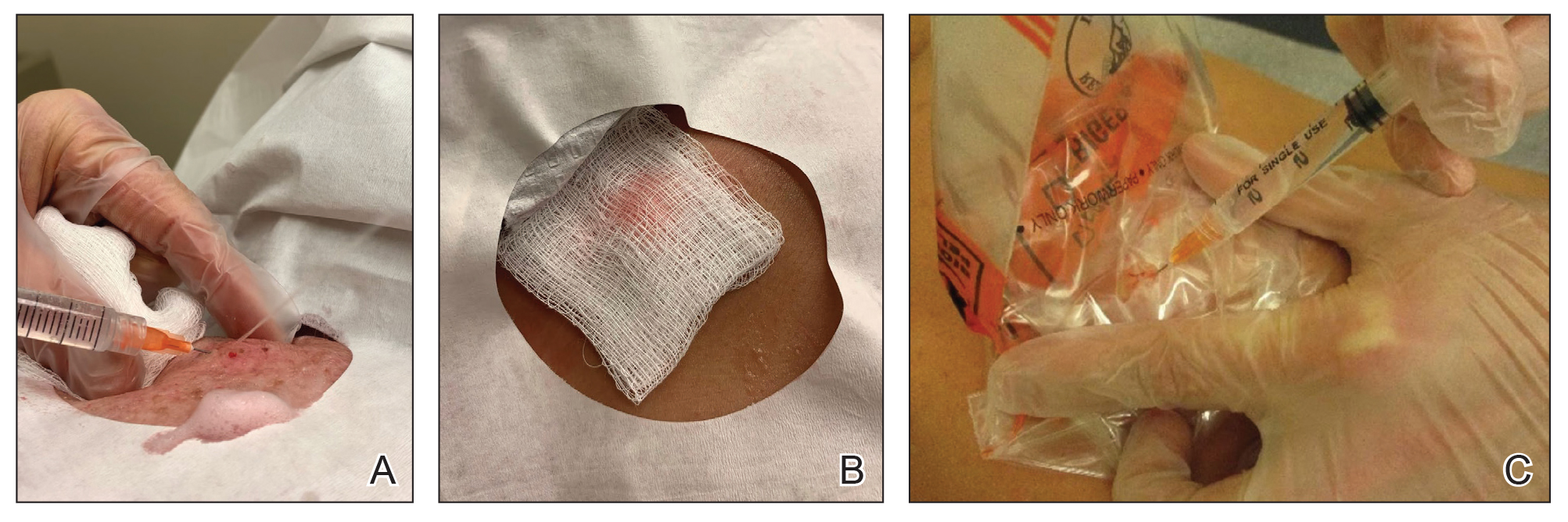
Another method is to cover the cyst with a small clear biohazard bag (Figure, C). When injecting anesthetic through the bag, the spray is captured by the bag and does not reach the surgeon or staff. This method is potentially more effective given that the cyst can still be visualized fully for more accurate injection.
Practice Implications
Outpatient surgical excision is a common effective procedure for epidermoid cysts. However, it is not uncommon for cyst contents to spray during the injection of anesthetic, posing a nuisance to the surgeon, health care staff, and patient. The technique of covering the lesion with antiseptic-soaked gauze or a small clear biohazard bag prevents cyst contents from spraying and reduces risk for contamination. In addition to these protective benefits, the use of readily available items replaces the need to order a splatter control shield.
Limitations—Although we seldom see spray using our technique, covering the cyst with gauze may disguise the region of interest and interfere with accurate incision. Marking the lesion prior to anesthesia administration or using a clear biohazard bag minimizes difficulty visualizing the cyst opening.
- Zito PM, Scharf R. Epidermoid cyst. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June 13, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499974
- Weir CB, St. Hilaire NJ. Epidermal inclusion cyst. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June3, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532310/
- Kuniyuki S, Yoshida Y, Maekawa N, et al. Bacteriological study of epidermal cysts. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;88:23-25. doi:10.2340/00015555-0348
Practice Gap
Epidermoid cysts are asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, mobile, subcutaneous masses that elevate the skin. Also known as epidermal, keratin, or infundibular cysts, epidermoid cysts are caused by proliferation of surface epidermoid cells within the dermis and can arise anywhere on the body, most commonly on the face, neck, and trunk.1 Cutaneous cysts often contain fluid or semifluid contents and can be aesthetically displeasing or cause mild pain, prompting patients to seek removal. Definitive treatment of epidermoid cysts is complete surgical removal,2 which can be performed in office in a sterile or clean manner by either dermatologists or primary care providers.
Prior to incision, a local anesthetic—commonly lidocaine with epinephrine—is injected in the region surrounding the cyst sac so as not to rupture the cyst wall. Maintaining the cyst wall throughout the procedure ensures total cyst removal and minimizes the risk for recurrence. However, it often is difficult to approximate the cyst border because it cannot be visualized prior to incision.
Throughout the duration of the procedure, cyst contents may suddenly spray out of the area and pose a risk to providers and their staff (Figure, A). Even with careful application around the periphery, either puncture or pericystic anesthesia between the cyst wall and the dermis can lead to splatter. Larger and wider peripheral anesthesia may not be possible given a shortage of lidocaine and a desire to minimize injection. Even with meticulous use of personal protective equipment in cutaneous surgery, infectious organisms found in ruptured cysts and abscesses may spray the surgical field.3 Therefore, it is in our best interest to minimize the trajectory of cyst spray contents.
The Tools
We have employed 2 simple techniques using equipment normally found on a standard surgical tray for easy safe injection of cysts. Supplies needed include 4×4-inch gauze pads, alcohol and chlorhexidine, a marker, all instruments necessary for cyst excision, and a small clear biohazard bag.
The Technique
Prior to covering the cyst, care is taken to locate the cyst opening. At times, a comedo or punctum can be seen overlying the cyst bulge. We mark the lumen and cyst opening with a surgical marker. If the pore is not easily identified, we draw an 8-mm circle around the mound of the cyst.
One option is to apply a gauze pad over the cyst to allow for stabilization of the surgical field and blanket the area from splatter (Figure, B). Then we cover the cyst using antiseptic-soaked gauze as a protective barrier to avoid potentially contaminated spray. This tool can be constructed from a 4×4-inch gauze pad with the addition of alcohol and chlorhexidine. When the cyst is covered, the surgeon can inject the lesion and surrounding tissue without biohazard splatter.

Another method is to cover the cyst with a small clear biohazard bag (Figure, C). When injecting anesthetic through the bag, the spray is captured by the bag and does not reach the surgeon or staff. This method is potentially more effective given that the cyst can still be visualized fully for more accurate injection.
Practice Implications
Outpatient surgical excision is a common effective procedure for epidermoid cysts. However, it is not uncommon for cyst contents to spray during the injection of anesthetic, posing a nuisance to the surgeon, health care staff, and patient. The technique of covering the lesion with antiseptic-soaked gauze or a small clear biohazard bag prevents cyst contents from spraying and reduces risk for contamination. In addition to these protective benefits, the use of readily available items replaces the need to order a splatter control shield.
Limitations—Although we seldom see spray using our technique, covering the cyst with gauze may disguise the region of interest and interfere with accurate incision. Marking the lesion prior to anesthesia administration or using a clear biohazard bag minimizes difficulty visualizing the cyst opening.
Practice Gap
Epidermoid cysts are asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, mobile, subcutaneous masses that elevate the skin. Also known as epidermal, keratin, or infundibular cysts, epidermoid cysts are caused by proliferation of surface epidermoid cells within the dermis and can arise anywhere on the body, most commonly on the face, neck, and trunk.1 Cutaneous cysts often contain fluid or semifluid contents and can be aesthetically displeasing or cause mild pain, prompting patients to seek removal. Definitive treatment of epidermoid cysts is complete surgical removal,2 which can be performed in office in a sterile or clean manner by either dermatologists or primary care providers.
Prior to incision, a local anesthetic—commonly lidocaine with epinephrine—is injected in the region surrounding the cyst sac so as not to rupture the cyst wall. Maintaining the cyst wall throughout the procedure ensures total cyst removal and minimizes the risk for recurrence. However, it often is difficult to approximate the cyst border because it cannot be visualized prior to incision.
Throughout the duration of the procedure, cyst contents may suddenly spray out of the area and pose a risk to providers and their staff (Figure, A). Even with careful application around the periphery, either puncture or pericystic anesthesia between the cyst wall and the dermis can lead to splatter. Larger and wider peripheral anesthesia may not be possible given a shortage of lidocaine and a desire to minimize injection. Even with meticulous use of personal protective equipment in cutaneous surgery, infectious organisms found in ruptured cysts and abscesses may spray the surgical field.3 Therefore, it is in our best interest to minimize the trajectory of cyst spray contents.
The Tools
We have employed 2 simple techniques using equipment normally found on a standard surgical tray for easy safe injection of cysts. Supplies needed include 4×4-inch gauze pads, alcohol and chlorhexidine, a marker, all instruments necessary for cyst excision, and a small clear biohazard bag.
The Technique
Prior to covering the cyst, care is taken to locate the cyst opening. At times, a comedo or punctum can be seen overlying the cyst bulge. We mark the lumen and cyst opening with a surgical marker. If the pore is not easily identified, we draw an 8-mm circle around the mound of the cyst.
One option is to apply a gauze pad over the cyst to allow for stabilization of the surgical field and blanket the area from splatter (Figure, B). Then we cover the cyst using antiseptic-soaked gauze as a protective barrier to avoid potentially contaminated spray. This tool can be constructed from a 4×4-inch gauze pad with the addition of alcohol and chlorhexidine. When the cyst is covered, the surgeon can inject the lesion and surrounding tissue without biohazard splatter.

Another method is to cover the cyst with a small clear biohazard bag (Figure, C). When injecting anesthetic through the bag, the spray is captured by the bag and does not reach the surgeon or staff. This method is potentially more effective given that the cyst can still be visualized fully for more accurate injection.
Practice Implications
Outpatient surgical excision is a common effective procedure for epidermoid cysts. However, it is not uncommon for cyst contents to spray during the injection of anesthetic, posing a nuisance to the surgeon, health care staff, and patient. The technique of covering the lesion with antiseptic-soaked gauze or a small clear biohazard bag prevents cyst contents from spraying and reduces risk for contamination. In addition to these protective benefits, the use of readily available items replaces the need to order a splatter control shield.
Limitations—Although we seldom see spray using our technique, covering the cyst with gauze may disguise the region of interest and interfere with accurate incision. Marking the lesion prior to anesthesia administration or using a clear biohazard bag minimizes difficulty visualizing the cyst opening.
- Zito PM, Scharf R. Epidermoid cyst. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June 13, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499974
- Weir CB, St. Hilaire NJ. Epidermal inclusion cyst. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June3, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532310/
- Kuniyuki S, Yoshida Y, Maekawa N, et al. Bacteriological study of epidermal cysts. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;88:23-25. doi:10.2340/00015555-0348
- Zito PM, Scharf R. Epidermoid cyst. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June 13, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499974
- Weir CB, St. Hilaire NJ. Epidermal inclusion cyst. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June3, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532310/
- Kuniyuki S, Yoshida Y, Maekawa N, et al. Bacteriological study of epidermal cysts. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;88:23-25. doi:10.2340/00015555-0348
Coding & billing: A look into G2211 for visit complexities
This add-on code is for new (99202-99205) and established (99212-99215) office visits. CMS created this add-on code to address the additional costs and resources associated with providing longitudinal care.
G2211 – Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management (E/M) associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or a complex condition (Add-on code; list separately in addition to office/outpatient (O/O) E/M visit, new or established)
The documentation should demonstrate the intent and need for ongoing care. Otherwise, no additional documentation is required. CMS pays $16.04 for each service (wRVU = 0.33). It may be reported each time the patient is seen, and there is currently no limit to how often it may be used. Also, there is no additional copay requirement for patients.
Do’s and don’ts
Do report in the following situations when longitudinal care is provided:
- The provider has or intends to have a long-term, ongoing relationship with the patient (ie, G2211 can be used for a new patient visit)
- Audio/video virtual visits
- May be reported with Prolonged Care Services G2212
- When advanced practice providers or physician colleagues in the same specialty practice see the patient (ie, if you see the patient for an urgent visit, but the patient is usually followed by your partner, you can still use G2211)
- When working with graduate medical education trainees (along with the -GC modifier), and as long as the conditions described in the description of G2211 are met
Do NOT report in the following situations:
- If modifier -25 is appended to the E/M service when another service is provided on the same day (eg, pulmonary function tests, 6-minute walk tests, immunization)
- Audio-only virtual visits, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or long-term acute care hospital
- If the patient is not expected to return for ongoing care
- If the reason for longitudinal care does not include a “single, serious condition or a complex condition” (eg, annual visits for a stable 6 mm lung nodule)
CMS expects that this will be billed with 38% of all E/M services initially and potentially up to 54% over time. We feel this is reimbursement for the work being done to care for our patients with single, serious, or complex conditions. Both Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans are expected to reimburse for this service. Whether other payers will do the same is unclear, but it will become clear with time and further negotiation at the local level. In the meantime, members are encouraged to report this code for all appropriate patient encounters.
Questions and answers — G2211
Question: What private insurances cover G2211?
Answer: As of March 1, 2024, four national payers have confirmed coverage of G2211:
- Cigna (Medicare Advantage only),
- Humana (commercial and Medicare Advantage),
- United Healthcare (commercial and Medicare Advantage), and
- Aetna (Medicare Advantage).
Question: What needs to be documented for G2211?
Answer: CMS states, “You must document the reason for billing the office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M). The visits themselves would need to be medically reasonable and necessary for the practitioner to report G2211. In addition, the documentation would need to illustrate medical necessity of the O/O E/M visit. We [CMS] haven’t required additional documentation.”
American Thoracic Society (ATS) and CHEST also recommend including a detailed assessment and plan for the visit, as well as any follow-up. The complexity of the visit should be clear in your documentation to support the medical necessity for reporting the G2211.
Question: How can a provider show that a new patient visit (99202-99205) is part of continuing care?
Answer: The treating practitioner should make sure their documentation supports their intent to provide ongoing care to the patient. Establishing such intent goes beyond a statement that the provider plans to provide ongoing care or schedule a follow-up visit. The circumstances of the visit should support the extra work involved in becoming the focal point of the patient’s care or providing ongoing care for a serious or complex condition.
Question: Dr. Red works at a primary care practice, is the focal point for a patient’s care, and has reported G2211. If Dr. Yellow, who is in the same specialty, or Mr. Green, a nurse practitioner, is covering for Dr. Red, and the patient comes in for a visit, can they report G2211 for that visit?
Answer: Yes. The same specialty/same provider rules would apply in this situation. But remember that Dr. Yellow’s or Mr. Green’s documentation for that encounter must support the code.
Question: Can a resident report G2211 under the primary care exemption?
Answer: Yes, according to CMS staff, so long as the service and the documentation meet all the requirements for the exemption and the visit complexity code. For example, the resident can only report low-level E/M codes, and the resident must be “the focal point for that person’s care.”
Question: Are there frequency limits for how often we can report G2211, either for a single patient in a given time period or by a provider or a practice?
Answer: Not at this time, but make sure your providers are following the rules for reporting the code. “There’s got to be documentation that suggests why the practitioner believes they are treating the patient on this long-standing, longitudinal trajectory, and we’ll be able to see how that interaction is happening,” senior CMS staff said. CMS staff further issued a subtle warning to providers by reminding them that CMS has a very strong integrity program. Your practice can avoid problems with thorough training, frequent chart review, and encouraging the team to ask questions until you feel that everyone is comfortable with the code.
Question: Are there any limits on the specialties that can report the code? Is it just for primary care providers?
Answer: No. Remember that a provider who is managing a single serious or complex condition can also report the code. But CMS expects the documentation to support the ongoing nature of the treatment. If a patient sees a provider as a one-off encounter, perhaps to manage an acute problem, that visit wouldn’t qualify. But if the provider clearly documents that they are actively managing the patient’s condition, the encounters could qualify.
Question: Will CMS issue a list of conditions that meet the code’s serious or complex condition requirement?
Answer: CMS has included the examples of HIV and sickle cell anemia in existing guidance, and it plans to issue a few more examples “that help folks understand what is expected.” However, it won’t be a complete list of every condition that might qualify.
Originally published in the May 2023 issue of the American Thoracic Society’s ATS Coding & Billing Quarterly. Republished with permission from the American Thoracic Society.
This add-on code is for new (99202-99205) and established (99212-99215) office visits. CMS created this add-on code to address the additional costs and resources associated with providing longitudinal care.
G2211 – Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management (E/M) associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or a complex condition (Add-on code; list separately in addition to office/outpatient (O/O) E/M visit, new or established)
The documentation should demonstrate the intent and need for ongoing care. Otherwise, no additional documentation is required. CMS pays $16.04 for each service (wRVU = 0.33). It may be reported each time the patient is seen, and there is currently no limit to how often it may be used. Also, there is no additional copay requirement for patients.
Do’s and don’ts
Do report in the following situations when longitudinal care is provided:
- The provider has or intends to have a long-term, ongoing relationship with the patient (ie, G2211 can be used for a new patient visit)
- Audio/video virtual visits
- May be reported with Prolonged Care Services G2212
- When advanced practice providers or physician colleagues in the same specialty practice see the patient (ie, if you see the patient for an urgent visit, but the patient is usually followed by your partner, you can still use G2211)
- When working with graduate medical education trainees (along with the -GC modifier), and as long as the conditions described in the description of G2211 are met
Do NOT report in the following situations:
- If modifier -25 is appended to the E/M service when another service is provided on the same day (eg, pulmonary function tests, 6-minute walk tests, immunization)
- Audio-only virtual visits, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or long-term acute care hospital
- If the patient is not expected to return for ongoing care
- If the reason for longitudinal care does not include a “single, serious condition or a complex condition” (eg, annual visits for a stable 6 mm lung nodule)
CMS expects that this will be billed with 38% of all E/M services initially and potentially up to 54% over time. We feel this is reimbursement for the work being done to care for our patients with single, serious, or complex conditions. Both Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans are expected to reimburse for this service. Whether other payers will do the same is unclear, but it will become clear with time and further negotiation at the local level. In the meantime, members are encouraged to report this code for all appropriate patient encounters.
Questions and answers — G2211
Question: What private insurances cover G2211?
Answer: As of March 1, 2024, four national payers have confirmed coverage of G2211:
- Cigna (Medicare Advantage only),
- Humana (commercial and Medicare Advantage),
- United Healthcare (commercial and Medicare Advantage), and
- Aetna (Medicare Advantage).
Question: What needs to be documented for G2211?
Answer: CMS states, “You must document the reason for billing the office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M). The visits themselves would need to be medically reasonable and necessary for the practitioner to report G2211. In addition, the documentation would need to illustrate medical necessity of the O/O E/M visit. We [CMS] haven’t required additional documentation.”
American Thoracic Society (ATS) and CHEST also recommend including a detailed assessment and plan for the visit, as well as any follow-up. The complexity of the visit should be clear in your documentation to support the medical necessity for reporting the G2211.
Question: How can a provider show that a new patient visit (99202-99205) is part of continuing care?
Answer: The treating practitioner should make sure their documentation supports their intent to provide ongoing care to the patient. Establishing such intent goes beyond a statement that the provider plans to provide ongoing care or schedule a follow-up visit. The circumstances of the visit should support the extra work involved in becoming the focal point of the patient’s care or providing ongoing care for a serious or complex condition.
Question: Dr. Red works at a primary care practice, is the focal point for a patient’s care, and has reported G2211. If Dr. Yellow, who is in the same specialty, or Mr. Green, a nurse practitioner, is covering for Dr. Red, and the patient comes in for a visit, can they report G2211 for that visit?
Answer: Yes. The same specialty/same provider rules would apply in this situation. But remember that Dr. Yellow’s or Mr. Green’s documentation for that encounter must support the code.
Question: Can a resident report G2211 under the primary care exemption?
Answer: Yes, according to CMS staff, so long as the service and the documentation meet all the requirements for the exemption and the visit complexity code. For example, the resident can only report low-level E/M codes, and the resident must be “the focal point for that person’s care.”
Question: Are there frequency limits for how often we can report G2211, either for a single patient in a given time period or by a provider or a practice?
Answer: Not at this time, but make sure your providers are following the rules for reporting the code. “There’s got to be documentation that suggests why the practitioner believes they are treating the patient on this long-standing, longitudinal trajectory, and we’ll be able to see how that interaction is happening,” senior CMS staff said. CMS staff further issued a subtle warning to providers by reminding them that CMS has a very strong integrity program. Your practice can avoid problems with thorough training, frequent chart review, and encouraging the team to ask questions until you feel that everyone is comfortable with the code.
Question: Are there any limits on the specialties that can report the code? Is it just for primary care providers?
Answer: No. Remember that a provider who is managing a single serious or complex condition can also report the code. But CMS expects the documentation to support the ongoing nature of the treatment. If a patient sees a provider as a one-off encounter, perhaps to manage an acute problem, that visit wouldn’t qualify. But if the provider clearly documents that they are actively managing the patient’s condition, the encounters could qualify.
Question: Will CMS issue a list of conditions that meet the code’s serious or complex condition requirement?
Answer: CMS has included the examples of HIV and sickle cell anemia in existing guidance, and it plans to issue a few more examples “that help folks understand what is expected.” However, it won’t be a complete list of every condition that might qualify.
Originally published in the May 2023 issue of the American Thoracic Society’s ATS Coding & Billing Quarterly. Republished with permission from the American Thoracic Society.
This add-on code is for new (99202-99205) and established (99212-99215) office visits. CMS created this add-on code to address the additional costs and resources associated with providing longitudinal care.
G2211 – Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management (E/M) associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or a complex condition (Add-on code; list separately in addition to office/outpatient (O/O) E/M visit, new or established)
The documentation should demonstrate the intent and need for ongoing care. Otherwise, no additional documentation is required. CMS pays $16.04 for each service (wRVU = 0.33). It may be reported each time the patient is seen, and there is currently no limit to how often it may be used. Also, there is no additional copay requirement for patients.
Do’s and don’ts
Do report in the following situations when longitudinal care is provided:
- The provider has or intends to have a long-term, ongoing relationship with the patient (ie, G2211 can be used for a new patient visit)
- Audio/video virtual visits
- May be reported with Prolonged Care Services G2212
- When advanced practice providers or physician colleagues in the same specialty practice see the patient (ie, if you see the patient for an urgent visit, but the patient is usually followed by your partner, you can still use G2211)
- When working with graduate medical education trainees (along with the -GC modifier), and as long as the conditions described in the description of G2211 are met
Do NOT report in the following situations:
- If modifier -25 is appended to the E/M service when another service is provided on the same day (eg, pulmonary function tests, 6-minute walk tests, immunization)
- Audio-only virtual visits, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or long-term acute care hospital
- If the patient is not expected to return for ongoing care
- If the reason for longitudinal care does not include a “single, serious condition or a complex condition” (eg, annual visits for a stable 6 mm lung nodule)
CMS expects that this will be billed with 38% of all E/M services initially and potentially up to 54% over time. We feel this is reimbursement for the work being done to care for our patients with single, serious, or complex conditions. Both Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans are expected to reimburse for this service. Whether other payers will do the same is unclear, but it will become clear with time and further negotiation at the local level. In the meantime, members are encouraged to report this code for all appropriate patient encounters.
Questions and answers — G2211
Question: What private insurances cover G2211?
Answer: As of March 1, 2024, four national payers have confirmed coverage of G2211:
- Cigna (Medicare Advantage only),
- Humana (commercial and Medicare Advantage),
- United Healthcare (commercial and Medicare Advantage), and
- Aetna (Medicare Advantage).
Question: What needs to be documented for G2211?
Answer: CMS states, “You must document the reason for billing the office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M). The visits themselves would need to be medically reasonable and necessary for the practitioner to report G2211. In addition, the documentation would need to illustrate medical necessity of the O/O E/M visit. We [CMS] haven’t required additional documentation.”
American Thoracic Society (ATS) and CHEST also recommend including a detailed assessment and plan for the visit, as well as any follow-up. The complexity of the visit should be clear in your documentation to support the medical necessity for reporting the G2211.
Question: How can a provider show that a new patient visit (99202-99205) is part of continuing care?
Answer: The treating practitioner should make sure their documentation supports their intent to provide ongoing care to the patient. Establishing such intent goes beyond a statement that the provider plans to provide ongoing care or schedule a follow-up visit. The circumstances of the visit should support the extra work involved in becoming the focal point of the patient’s care or providing ongoing care for a serious or complex condition.
Question: Dr. Red works at a primary care practice, is the focal point for a patient’s care, and has reported G2211. If Dr. Yellow, who is in the same specialty, or Mr. Green, a nurse practitioner, is covering for Dr. Red, and the patient comes in for a visit, can they report G2211 for that visit?
Answer: Yes. The same specialty/same provider rules would apply in this situation. But remember that Dr. Yellow’s or Mr. Green’s documentation for that encounter must support the code.
Question: Can a resident report G2211 under the primary care exemption?
Answer: Yes, according to CMS staff, so long as the service and the documentation meet all the requirements for the exemption and the visit complexity code. For example, the resident can only report low-level E/M codes, and the resident must be “the focal point for that person’s care.”
Question: Are there frequency limits for how often we can report G2211, either for a single patient in a given time period or by a provider or a practice?
Answer: Not at this time, but make sure your providers are following the rules for reporting the code. “There’s got to be documentation that suggests why the practitioner believes they are treating the patient on this long-standing, longitudinal trajectory, and we’ll be able to see how that interaction is happening,” senior CMS staff said. CMS staff further issued a subtle warning to providers by reminding them that CMS has a very strong integrity program. Your practice can avoid problems with thorough training, frequent chart review, and encouraging the team to ask questions until you feel that everyone is comfortable with the code.
Question: Are there any limits on the specialties that can report the code? Is it just for primary care providers?
Answer: No. Remember that a provider who is managing a single serious or complex condition can also report the code. But CMS expects the documentation to support the ongoing nature of the treatment. If a patient sees a provider as a one-off encounter, perhaps to manage an acute problem, that visit wouldn’t qualify. But if the provider clearly documents that they are actively managing the patient’s condition, the encounters could qualify.
Question: Will CMS issue a list of conditions that meet the code’s serious or complex condition requirement?
Answer: CMS has included the examples of HIV and sickle cell anemia in existing guidance, and it plans to issue a few more examples “that help folks understand what is expected.” However, it won’t be a complete list of every condition that might qualify.
Originally published in the May 2023 issue of the American Thoracic Society’s ATS Coding & Billing Quarterly. Republished with permission from the American Thoracic Society.
For One Colorado GI, Private Practice Is Anything But Routine
Lisa Mathew, MD, wants to quell any misconceptions that private practice is dull or routine. “That has not been my experience at all,” says Dr. Mathew, a partner with South Denver Gastroenterology in the suburbs of Denver, Colorado.
“It’s an area within GI where we can be quite nimble in trialing new technologies, optimizing patients’ access to care and working to ensure a positive patient experience,” she said.
Nationwide, a flourishing GI private practice community engages in ongoing dialogue about improvements, navigating a changing healthcare environment, and innovation. “That has been a surprising and wonderful twist in my career,” she added.
Dr. Mathew fosters that dialogue through Gastro Broadcast, a podcast she shares with several other GI physicians. Targeted toward private GI practice, it highlights innovations within the community, providing updates on practice management and other technological advances.
In an interview, she spoke frankly about her favorite recent podcast guest, the challenges she’s faced in her career, and why her fellow GI specialists are her “tribe.”
Q: Why did you choose GI?
Dr. Mathew: In medical school at Duke University, I was considering going into ob.gyn., but academically I was a little more drawn toward internal medicine. While I was in my residency at the University of Pennsylvania, I really clicked with the gastroenterologists. I enjoyed their sense of humor. They were dealing with complex medical issues but doing so with a sense of levity and enjoyment in their work. When I entered fellowship at the University of Washington, I felt like I found my tribe. This was a group of people who really love their work, love medicine, love being able to develop their procedural skills, and keep a sense of humor about themselves. I married a cardiologist (and he’s a hilarious cardiologist), but the world of cardiology is a little more buttoned up. I like that GI is a little more relaxed.
Q: What gives you the most joy in your day-to-day practice?
Dr. Mathew: My patients. They are funny and genuine, and they allow you into these moments of vulnerability — it’s an honor to walk through that together. I’m always so grateful for the trust they put in me in those moments. As my practice has matured, it’s been incredible to watch those relationships grow, as well as begin caring for husbands, wives, sons and daughters of my patients. I enjoy being a part of my community.
Q: Can you talk about an interesting recent guest you had on your podcast? Who was it and why did he or she stand out?
Dr. Mathew: Russ Arjal, MD, AGAF, cofounder, chief medical officer and president of Telebelly Health. He’s been working on a platform for exclusively telehealth services that improves access to care; pairing patients with brick-and-mortar gastroenterology to provide any necessary procedural care, such as colonoscopy and upper endoscopy. It was a fantastic interview. I think it’s so refreshing and inspiring to see how people innovate within the field of GI. On the procedural side, you see this all the time. With my advanced endoscopy colleagues, they’re constantly pushing the boundaries of what we can do procedurally. My academic colleagues are constantly thinking through what the next best treatment is or how best can we optimize care. And, in the world of private practice, we’re thinking about practice care delivery — how to improve access and make the experience of being a patient better, with the ultimate goal of improving health outcomes.
Q: What fears did you have to push past to get to where you are in your career?
Dr. Mathew: Imposter Syndrome is a very, very common issue, maybe somewhat more for women in GI. I think it’s something that everybody wrestles with to some degree. For me, it was developing confidence not just in my clinical skills, but in learning all the complexities of running a small business. It takes time to develop confidence in your abilities and judgment. I think to some degree, that’s normal. It just takes a while to settle into whatever your chosen career path is. Having a community and strong mentors to support me has made all the difference.
Q: Describe your biggest practice-related challenge and what you are doing to address it.
Dr. Mathew: One of the greatest challenges in my career has been navigating COVID — both with just the tremendous sea change it had on our ability to practice, as well as the financial consequences to someone in private practice. Those were very challenging times to deliver the care that was needed, protect staff, and to maintain a small business. Fortunately, as with many practices across the nation, we’ve emerged through that.
We pivoted, we innovated with telehealth and other services that allowed us to care for our patients. But there were a lot of lessons learned and a lot of difficult moments.
Q: What teacher or mentor had the greatest impact on you?
Dr. Mathew: My dad has taught me the value of hard work. Being a physician just comes in tandem with hard work. And my mom, who is a nurse, has always shown the importance of empathy. Without it, everything else is a little empty. Medicine is a combination of skill and hard work, but also an ability to connect with other people. Empathy is essential to that.
Q: Describe how you would spend a free Saturday afternoon.
Dr. Mathew: We have three children who are native Coloradans so skiing is their birthright. Our entire family are diehard skiers. This is our joy. When you talk about the beach versus mountains debate, we are firmly team mountains. On a perfect Saturday afternoon, I’m on the slopes with my little crew, just tearing it up, having a great time.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Texting
Favorite city in U.S. besides the one you live in?
Washington, D.C.
Favorite breakfast?
Avocado toast
Place you most want to travel to?
South America
Favorite junk food?
Candy
Favorite season?
Winter
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
2 or 3
If you weren’t a gastroenterologist, what would you be?
Ski coach
Best Halloween costume you ever wore?
Bunch of grapes
Favorite type of music?
Indie folk
Favorite movie genre?
Books, not into movies
Cat person or dog person?
Neither, but I am a certified beekeeper
What song do you have to sing along with when you hear it?
Anything by Queen
Introvert or extrovert?
Extrovert with introverted tendencies
Favorite holiday?
Thanksgiving
Optimist or pessimist?
100% glass half full
Lisa Mathew, MD, wants to quell any misconceptions that private practice is dull or routine. “That has not been my experience at all,” says Dr. Mathew, a partner with South Denver Gastroenterology in the suburbs of Denver, Colorado.
“It’s an area within GI where we can be quite nimble in trialing new technologies, optimizing patients’ access to care and working to ensure a positive patient experience,” she said.
Nationwide, a flourishing GI private practice community engages in ongoing dialogue about improvements, navigating a changing healthcare environment, and innovation. “That has been a surprising and wonderful twist in my career,” she added.
Dr. Mathew fosters that dialogue through Gastro Broadcast, a podcast she shares with several other GI physicians. Targeted toward private GI practice, it highlights innovations within the community, providing updates on practice management and other technological advances.
In an interview, she spoke frankly about her favorite recent podcast guest, the challenges she’s faced in her career, and why her fellow GI specialists are her “tribe.”
Q: Why did you choose GI?
Dr. Mathew: In medical school at Duke University, I was considering going into ob.gyn., but academically I was a little more drawn toward internal medicine. While I was in my residency at the University of Pennsylvania, I really clicked with the gastroenterologists. I enjoyed their sense of humor. They were dealing with complex medical issues but doing so with a sense of levity and enjoyment in their work. When I entered fellowship at the University of Washington, I felt like I found my tribe. This was a group of people who really love their work, love medicine, love being able to develop their procedural skills, and keep a sense of humor about themselves. I married a cardiologist (and he’s a hilarious cardiologist), but the world of cardiology is a little more buttoned up. I like that GI is a little more relaxed.
Q: What gives you the most joy in your day-to-day practice?
Dr. Mathew: My patients. They are funny and genuine, and they allow you into these moments of vulnerability — it’s an honor to walk through that together. I’m always so grateful for the trust they put in me in those moments. As my practice has matured, it’s been incredible to watch those relationships grow, as well as begin caring for husbands, wives, sons and daughters of my patients. I enjoy being a part of my community.
Q: Can you talk about an interesting recent guest you had on your podcast? Who was it and why did he or she stand out?
Dr. Mathew: Russ Arjal, MD, AGAF, cofounder, chief medical officer and president of Telebelly Health. He’s been working on a platform for exclusively telehealth services that improves access to care; pairing patients with brick-and-mortar gastroenterology to provide any necessary procedural care, such as colonoscopy and upper endoscopy. It was a fantastic interview. I think it’s so refreshing and inspiring to see how people innovate within the field of GI. On the procedural side, you see this all the time. With my advanced endoscopy colleagues, they’re constantly pushing the boundaries of what we can do procedurally. My academic colleagues are constantly thinking through what the next best treatment is or how best can we optimize care. And, in the world of private practice, we’re thinking about practice care delivery — how to improve access and make the experience of being a patient better, with the ultimate goal of improving health outcomes.
Q: What fears did you have to push past to get to where you are in your career?
Dr. Mathew: Imposter Syndrome is a very, very common issue, maybe somewhat more for women in GI. I think it’s something that everybody wrestles with to some degree. For me, it was developing confidence not just in my clinical skills, but in learning all the complexities of running a small business. It takes time to develop confidence in your abilities and judgment. I think to some degree, that’s normal. It just takes a while to settle into whatever your chosen career path is. Having a community and strong mentors to support me has made all the difference.
Q: Describe your biggest practice-related challenge and what you are doing to address it.
Dr. Mathew: One of the greatest challenges in my career has been navigating COVID — both with just the tremendous sea change it had on our ability to practice, as well as the financial consequences to someone in private practice. Those were very challenging times to deliver the care that was needed, protect staff, and to maintain a small business. Fortunately, as with many practices across the nation, we’ve emerged through that.
We pivoted, we innovated with telehealth and other services that allowed us to care for our patients. But there were a lot of lessons learned and a lot of difficult moments.
Q: What teacher or mentor had the greatest impact on you?
Dr. Mathew: My dad has taught me the value of hard work. Being a physician just comes in tandem with hard work. And my mom, who is a nurse, has always shown the importance of empathy. Without it, everything else is a little empty. Medicine is a combination of skill and hard work, but also an ability to connect with other people. Empathy is essential to that.
Q: Describe how you would spend a free Saturday afternoon.
Dr. Mathew: We have three children who are native Coloradans so skiing is their birthright. Our entire family are diehard skiers. This is our joy. When you talk about the beach versus mountains debate, we are firmly team mountains. On a perfect Saturday afternoon, I’m on the slopes with my little crew, just tearing it up, having a great time.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Texting
Favorite city in U.S. besides the one you live in?
Washington, D.C.
Favorite breakfast?
Avocado toast
Place you most want to travel to?
South America
Favorite junk food?
Candy
Favorite season?
Winter
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
2 or 3
If you weren’t a gastroenterologist, what would you be?
Ski coach
Best Halloween costume you ever wore?
Bunch of grapes
Favorite type of music?
Indie folk
Favorite movie genre?
Books, not into movies
Cat person or dog person?
Neither, but I am a certified beekeeper
What song do you have to sing along with when you hear it?
Anything by Queen
Introvert or extrovert?
Extrovert with introverted tendencies
Favorite holiday?
Thanksgiving
Optimist or pessimist?
100% glass half full
Lisa Mathew, MD, wants to quell any misconceptions that private practice is dull or routine. “That has not been my experience at all,” says Dr. Mathew, a partner with South Denver Gastroenterology in the suburbs of Denver, Colorado.
“It’s an area within GI where we can be quite nimble in trialing new technologies, optimizing patients’ access to care and working to ensure a positive patient experience,” she said.
Nationwide, a flourishing GI private practice community engages in ongoing dialogue about improvements, navigating a changing healthcare environment, and innovation. “That has been a surprising and wonderful twist in my career,” she added.
Dr. Mathew fosters that dialogue through Gastro Broadcast, a podcast she shares with several other GI physicians. Targeted toward private GI practice, it highlights innovations within the community, providing updates on practice management and other technological advances.
In an interview, she spoke frankly about her favorite recent podcast guest, the challenges she’s faced in her career, and why her fellow GI specialists are her “tribe.”
Q: Why did you choose GI?
Dr. Mathew: In medical school at Duke University, I was considering going into ob.gyn., but academically I was a little more drawn toward internal medicine. While I was in my residency at the University of Pennsylvania, I really clicked with the gastroenterologists. I enjoyed their sense of humor. They were dealing with complex medical issues but doing so with a sense of levity and enjoyment in their work. When I entered fellowship at the University of Washington, I felt like I found my tribe. This was a group of people who really love their work, love medicine, love being able to develop their procedural skills, and keep a sense of humor about themselves. I married a cardiologist (and he’s a hilarious cardiologist), but the world of cardiology is a little more buttoned up. I like that GI is a little more relaxed.
Q: What gives you the most joy in your day-to-day practice?
Dr. Mathew: My patients. They are funny and genuine, and they allow you into these moments of vulnerability — it’s an honor to walk through that together. I’m always so grateful for the trust they put in me in those moments. As my practice has matured, it’s been incredible to watch those relationships grow, as well as begin caring for husbands, wives, sons and daughters of my patients. I enjoy being a part of my community.
Q: Can you talk about an interesting recent guest you had on your podcast? Who was it and why did he or she stand out?
Dr. Mathew: Russ Arjal, MD, AGAF, cofounder, chief medical officer and president of Telebelly Health. He’s been working on a platform for exclusively telehealth services that improves access to care; pairing patients with brick-and-mortar gastroenterology to provide any necessary procedural care, such as colonoscopy and upper endoscopy. It was a fantastic interview. I think it’s so refreshing and inspiring to see how people innovate within the field of GI. On the procedural side, you see this all the time. With my advanced endoscopy colleagues, they’re constantly pushing the boundaries of what we can do procedurally. My academic colleagues are constantly thinking through what the next best treatment is or how best can we optimize care. And, in the world of private practice, we’re thinking about practice care delivery — how to improve access and make the experience of being a patient better, with the ultimate goal of improving health outcomes.
Q: What fears did you have to push past to get to where you are in your career?
Dr. Mathew: Imposter Syndrome is a very, very common issue, maybe somewhat more for women in GI. I think it’s something that everybody wrestles with to some degree. For me, it was developing confidence not just in my clinical skills, but in learning all the complexities of running a small business. It takes time to develop confidence in your abilities and judgment. I think to some degree, that’s normal. It just takes a while to settle into whatever your chosen career path is. Having a community and strong mentors to support me has made all the difference.
Q: Describe your biggest practice-related challenge and what you are doing to address it.
Dr. Mathew: One of the greatest challenges in my career has been navigating COVID — both with just the tremendous sea change it had on our ability to practice, as well as the financial consequences to someone in private practice. Those were very challenging times to deliver the care that was needed, protect staff, and to maintain a small business. Fortunately, as with many practices across the nation, we’ve emerged through that.
We pivoted, we innovated with telehealth and other services that allowed us to care for our patients. But there were a lot of lessons learned and a lot of difficult moments.
Q: What teacher or mentor had the greatest impact on you?
Dr. Mathew: My dad has taught me the value of hard work. Being a physician just comes in tandem with hard work. And my mom, who is a nurse, has always shown the importance of empathy. Without it, everything else is a little empty. Medicine is a combination of skill and hard work, but also an ability to connect with other people. Empathy is essential to that.
Q: Describe how you would spend a free Saturday afternoon.
Dr. Mathew: We have three children who are native Coloradans so skiing is their birthright. Our entire family are diehard skiers. This is our joy. When you talk about the beach versus mountains debate, we are firmly team mountains. On a perfect Saturday afternoon, I’m on the slopes with my little crew, just tearing it up, having a great time.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Texting
Favorite city in U.S. besides the one you live in?
Washington, D.C.
Favorite breakfast?
Avocado toast
Place you most want to travel to?
South America
Favorite junk food?
Candy
Favorite season?
Winter
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
2 or 3
If you weren’t a gastroenterologist, what would you be?
Ski coach
Best Halloween costume you ever wore?
Bunch of grapes
Favorite type of music?
Indie folk
Favorite movie genre?
Books, not into movies
Cat person or dog person?
Neither, but I am a certified beekeeper
What song do you have to sing along with when you hear it?
Anything by Queen
Introvert or extrovert?
Extrovert with introverted tendencies
Favorite holiday?
Thanksgiving
Optimist or pessimist?
100% glass half full
Scope of Practice Concerns Lead to Hospital’s Temp Ban on CRNAs
Two hospitals in California in recent months have been cited by state inspectors for allowing certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) to practice beyond their scope, leading to one hospital temporarily stopping use of CRNAs in surgeries.
In one case, a CRNA changed a physician’s order from general anesthesia to spinal anesthesia for a patient who later became unresponsive and had to be transferred to another hospital, according to The Modesto Bee.
The unusual situation highlights the ongoing, often contentious debate about the proper role of CRNAs in surgery amid widely varying state scope of practice laws.
Elizabeth Bamgbose, CRNA, past president of the California Association of Nurse Anesthetists (CANA), said that the absence of CRNAs at Doctors Medical Center (DMC) in Modesto, California, had led to the cancellation of hundreds of procedures. It was an unnecessary step, she said.
“It’s unfortunate that a single surveyor has taken it upon themselves to reinterpret state regulations and redefine a practice that was efficient and safe,” said Ms. Bamgbose, a member of the CANA practice committee.
In late May, the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) issued an “immediate jeopardy” warning about DMC of Modesto. The state agency, like its counterparts in other states, acts on behalf of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in surveying healthcare facilities. CMS defines immediate jeopardy as “a situation in which entity noncompliance has placed the health and safety of recipients in its care at risk for serious injury, serious harm, serious impairment, or death.”
The administrative warning comes with fines and requires the facility to submit an action plan to remediate the situation. The state determines through a follow-up survey whether the plan is sufficient for the facility to avoid being dropped from participation in Medicare and Medicaid.
Before the immediate jeopardy action was taken against DMC, the state had issued three previous such warnings in 2024, according to the CDPH enforcement actions dashboard.
CRNA Claims to Be in Charge
Stanislaus Surgical Hospital in Modesto, California, was the first facility to attract CDPH attention. It reportedly was cited in August 2023 and January 2024 surveys for a number of violations of the CMS conditions of participation, including allowing nurse anesthetists to practice beyond their scope.
According to The Modesto Bee, CDPH issued an “immediate jeopardy” order for Stanislaus in January.
The paper reported that state regulators took issue with a CRNA claiming to be the lead manager of the hospital’s anesthesia group, referring to herself as the “chief CRNA.”
Jennifer Banek, MSN, CRNA, a member of the American Association of Nurse Anesthesiology board, declined comment on the Stanislaus hospital but said that “it would not be unusual for a nurse anesthetist to serve as a leader, especially (for a) rural or underserved population.”
In April, CMS informed Stanislaus it was being terminated from Medicare, but several Congressional representatives from the Modesto area asked CMS to reconsider. The agency eventually reversed the sanction, The Modesto Bee reported.
CDPH subsequently cited DMC for CRNA scope of practice issues. A department spokesman said that CDPH teams went to DMC “to investigate practices that may not be compliant with state and federal requirements.” The agency declined to comment further until its investigations were complete.
CDPH is monitoring DMC to ensure the hospital complies with state requirements and will return for an unannounced follow-up survey “so it can provide safe, high-quality care to patients that need it,” the spokesperson said.
Although DMC would not confirm it on the record, the immediate jeopardy order led to the removal of all CRNAs, according to Ms. Banek, Ms. Bamgbose, and The Modesto Bee.
The hospital said in a statement that it is working with CDPH to address its concerns and will await a follow-up survey. “Our hospital will continue to fully participate in the Medicare and Medicaid programs during this process.”
Scope of Practice Confusion?
But that does not supersede state laws or hospital bylaws governing practice, said American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) president Ronald Harter, MD.
Five states — Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon — have laws that allow nurse anesthetists to practice without physician oversight or involvement, said Dr. Harter, professor of anesthesiology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio.
“There’s a lot of various opinions on what exactly constitutes scope of practice of a nurse anesthetist,” Dr. Harter said. “The vast majority of them work under the direction of an anesthesiologist, and in those settings, it’s typically very clear to everybody who performs what tasks within the care team,” he said.
It’s less common for nurse anesthetists to work totally independent of physician oversight, he said.
Ms. Bamgbose, however, said there is no California statute requiring physician supervision of CRNAs.
The ASA maintains that CRNAs should always be under the supervision of a physician, which can be an anesthesiologist, obstetrician, gastroenterologist, surgeon, or other physician conducting a procedure. An anesthesiologist does not necessarily have to be physically on site, but in those circumstances, the physician conducting the procedure would be, said Dr. Harter.
Nurse anesthetists are “excellent advanced practice nurses,” Dr. Harter said. “But they haven’t been to medical school; they haven’t conducted a residency in anesthesiology. [They] don’t have the medical knowledge and skills that are required to manage the medical problems that patients either bring to the OR with them or that can arise during the time that they’re under anesthesia.”
Filling a Gap
Nurse anesthetists see things differently.
CRNAs, by virtue of their certification, can “practice to the full extent and to the full scope, which is complete service of anesthesia,” said Ms. Bamgbose. “You can practice independently of anyone, any type of supervision,” she said.
She acknowledges that “the bylaws of any institution will govern the scope at which any healthcare professional can practice at that institution.”
Most nurse anesthetists see themselves as independent practitioners.
Seventy-five percent of CRNAs who responded to a 2023 Medscape Medical News survey said they practice independently. But even Ms. Banek said that often, the meaning of “independent” is in the eye of the beholder. “It could mean different things to various providers, especially depending on the state that they are residing in,” she said.
Ms. Banek and Ms. Bamgbose said that CRNAs can help fill a gap in anesthesiology services in underserved areas.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates there are currently 32,530 anesthesiologists in the United States, with California employing the largest number, at about 5300. The Association of American Medical Colleges estimated the number at 42,263 in 2022. But the federal Health Resources and Services Administration projects a shortage of 6300 anesthesiologists over the next 15 years.
Some 61,000 CRNAs are currently practicing, with 2400 graduating each year. They are required to be board-certified and are recredentialed every 4 years. By 2025, all will be required to have a doctoral degree. Most have already achieved that status, said Ms. Banek.
“Nurse anesthetists provide care predominantly to rural and underserved areas,” she said, adding, “In many rural hospitals across the country and in all three branches of the military, CRNAs practice autonomously.”
There are 3000 CRNAs in California, said Ms. Bamgbose. Nurse anesthetists are the only anesthesiology professionals in four of 58 California counties, she said.
Ms. Banek said she had heard that some 200 cases were canceled in 1 week at DMC due to the lack of CRNAs. Having physician supervision, which she called redundant, “is really creating a barrier to care,” she said.
“We have countless state and national studies that show the safety and efficacy of our practice,” said Ms. Bamgbose. “To interrupt that care ... is incredibly disruptive to the system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two hospitals in California in recent months have been cited by state inspectors for allowing certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) to practice beyond their scope, leading to one hospital temporarily stopping use of CRNAs in surgeries.
In one case, a CRNA changed a physician’s order from general anesthesia to spinal anesthesia for a patient who later became unresponsive and had to be transferred to another hospital, according to The Modesto Bee.
The unusual situation highlights the ongoing, often contentious debate about the proper role of CRNAs in surgery amid widely varying state scope of practice laws.
Elizabeth Bamgbose, CRNA, past president of the California Association of Nurse Anesthetists (CANA), said that the absence of CRNAs at Doctors Medical Center (DMC) in Modesto, California, had led to the cancellation of hundreds of procedures. It was an unnecessary step, she said.
“It’s unfortunate that a single surveyor has taken it upon themselves to reinterpret state regulations and redefine a practice that was efficient and safe,” said Ms. Bamgbose, a member of the CANA practice committee.
In late May, the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) issued an “immediate jeopardy” warning about DMC of Modesto. The state agency, like its counterparts in other states, acts on behalf of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in surveying healthcare facilities. CMS defines immediate jeopardy as “a situation in which entity noncompliance has placed the health and safety of recipients in its care at risk for serious injury, serious harm, serious impairment, or death.”
The administrative warning comes with fines and requires the facility to submit an action plan to remediate the situation. The state determines through a follow-up survey whether the plan is sufficient for the facility to avoid being dropped from participation in Medicare and Medicaid.
Before the immediate jeopardy action was taken against DMC, the state had issued three previous such warnings in 2024, according to the CDPH enforcement actions dashboard.
CRNA Claims to Be in Charge
Stanislaus Surgical Hospital in Modesto, California, was the first facility to attract CDPH attention. It reportedly was cited in August 2023 and January 2024 surveys for a number of violations of the CMS conditions of participation, including allowing nurse anesthetists to practice beyond their scope.
According to The Modesto Bee, CDPH issued an “immediate jeopardy” order for Stanislaus in January.
The paper reported that state regulators took issue with a CRNA claiming to be the lead manager of the hospital’s anesthesia group, referring to herself as the “chief CRNA.”
Jennifer Banek, MSN, CRNA, a member of the American Association of Nurse Anesthesiology board, declined comment on the Stanislaus hospital but said that “it would not be unusual for a nurse anesthetist to serve as a leader, especially (for a) rural or underserved population.”
In April, CMS informed Stanislaus it was being terminated from Medicare, but several Congressional representatives from the Modesto area asked CMS to reconsider. The agency eventually reversed the sanction, The Modesto Bee reported.
CDPH subsequently cited DMC for CRNA scope of practice issues. A department spokesman said that CDPH teams went to DMC “to investigate practices that may not be compliant with state and federal requirements.” The agency declined to comment further until its investigations were complete.
CDPH is monitoring DMC to ensure the hospital complies with state requirements and will return for an unannounced follow-up survey “so it can provide safe, high-quality care to patients that need it,” the spokesperson said.
Although DMC would not confirm it on the record, the immediate jeopardy order led to the removal of all CRNAs, according to Ms. Banek, Ms. Bamgbose, and The Modesto Bee.
The hospital said in a statement that it is working with CDPH to address its concerns and will await a follow-up survey. “Our hospital will continue to fully participate in the Medicare and Medicaid programs during this process.”
Scope of Practice Confusion?
But that does not supersede state laws or hospital bylaws governing practice, said American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) president Ronald Harter, MD.
Five states — Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon — have laws that allow nurse anesthetists to practice without physician oversight or involvement, said Dr. Harter, professor of anesthesiology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio.
“There’s a lot of various opinions on what exactly constitutes scope of practice of a nurse anesthetist,” Dr. Harter said. “The vast majority of them work under the direction of an anesthesiologist, and in those settings, it’s typically very clear to everybody who performs what tasks within the care team,” he said.
It’s less common for nurse anesthetists to work totally independent of physician oversight, he said.
Ms. Bamgbose, however, said there is no California statute requiring physician supervision of CRNAs.
The ASA maintains that CRNAs should always be under the supervision of a physician, which can be an anesthesiologist, obstetrician, gastroenterologist, surgeon, or other physician conducting a procedure. An anesthesiologist does not necessarily have to be physically on site, but in those circumstances, the physician conducting the procedure would be, said Dr. Harter.
Nurse anesthetists are “excellent advanced practice nurses,” Dr. Harter said. “But they haven’t been to medical school; they haven’t conducted a residency in anesthesiology. [They] don’t have the medical knowledge and skills that are required to manage the medical problems that patients either bring to the OR with them or that can arise during the time that they’re under anesthesia.”
Filling a Gap
Nurse anesthetists see things differently.
CRNAs, by virtue of their certification, can “practice to the full extent and to the full scope, which is complete service of anesthesia,” said Ms. Bamgbose. “You can practice independently of anyone, any type of supervision,” she said.
She acknowledges that “the bylaws of any institution will govern the scope at which any healthcare professional can practice at that institution.”
Most nurse anesthetists see themselves as independent practitioners.
Seventy-five percent of CRNAs who responded to a 2023 Medscape Medical News survey said they practice independently. But even Ms. Banek said that often, the meaning of “independent” is in the eye of the beholder. “It could mean different things to various providers, especially depending on the state that they are residing in,” she said.
Ms. Banek and Ms. Bamgbose said that CRNAs can help fill a gap in anesthesiology services in underserved areas.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates there are currently 32,530 anesthesiologists in the United States, with California employing the largest number, at about 5300. The Association of American Medical Colleges estimated the number at 42,263 in 2022. But the federal Health Resources and Services Administration projects a shortage of 6300 anesthesiologists over the next 15 years.
Some 61,000 CRNAs are currently practicing, with 2400 graduating each year. They are required to be board-certified and are recredentialed every 4 years. By 2025, all will be required to have a doctoral degree. Most have already achieved that status, said Ms. Banek.
“Nurse anesthetists provide care predominantly to rural and underserved areas,” she said, adding, “In many rural hospitals across the country and in all three branches of the military, CRNAs practice autonomously.”
There are 3000 CRNAs in California, said Ms. Bamgbose. Nurse anesthetists are the only anesthesiology professionals in four of 58 California counties, she said.
Ms. Banek said she had heard that some 200 cases were canceled in 1 week at DMC due to the lack of CRNAs. Having physician supervision, which she called redundant, “is really creating a barrier to care,” she said.
“We have countless state and national studies that show the safety and efficacy of our practice,” said Ms. Bamgbose. “To interrupt that care ... is incredibly disruptive to the system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two hospitals in California in recent months have been cited by state inspectors for allowing certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) to practice beyond their scope, leading to one hospital temporarily stopping use of CRNAs in surgeries.
In one case, a CRNA changed a physician’s order from general anesthesia to spinal anesthesia for a patient who later became unresponsive and had to be transferred to another hospital, according to The Modesto Bee.
The unusual situation highlights the ongoing, often contentious debate about the proper role of CRNAs in surgery amid widely varying state scope of practice laws.
Elizabeth Bamgbose, CRNA, past president of the California Association of Nurse Anesthetists (CANA), said that the absence of CRNAs at Doctors Medical Center (DMC) in Modesto, California, had led to the cancellation of hundreds of procedures. It was an unnecessary step, she said.
“It’s unfortunate that a single surveyor has taken it upon themselves to reinterpret state regulations and redefine a practice that was efficient and safe,” said Ms. Bamgbose, a member of the CANA practice committee.
In late May, the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) issued an “immediate jeopardy” warning about DMC of Modesto. The state agency, like its counterparts in other states, acts on behalf of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in surveying healthcare facilities. CMS defines immediate jeopardy as “a situation in which entity noncompliance has placed the health and safety of recipients in its care at risk for serious injury, serious harm, serious impairment, or death.”
The administrative warning comes with fines and requires the facility to submit an action plan to remediate the situation. The state determines through a follow-up survey whether the plan is sufficient for the facility to avoid being dropped from participation in Medicare and Medicaid.
Before the immediate jeopardy action was taken against DMC, the state had issued three previous such warnings in 2024, according to the CDPH enforcement actions dashboard.
CRNA Claims to Be in Charge
Stanislaus Surgical Hospital in Modesto, California, was the first facility to attract CDPH attention. It reportedly was cited in August 2023 and January 2024 surveys for a number of violations of the CMS conditions of participation, including allowing nurse anesthetists to practice beyond their scope.
According to The Modesto Bee, CDPH issued an “immediate jeopardy” order for Stanislaus in January.
The paper reported that state regulators took issue with a CRNA claiming to be the lead manager of the hospital’s anesthesia group, referring to herself as the “chief CRNA.”
Jennifer Banek, MSN, CRNA, a member of the American Association of Nurse Anesthesiology board, declined comment on the Stanislaus hospital but said that “it would not be unusual for a nurse anesthetist to serve as a leader, especially (for a) rural or underserved population.”
In April, CMS informed Stanislaus it was being terminated from Medicare, but several Congressional representatives from the Modesto area asked CMS to reconsider. The agency eventually reversed the sanction, The Modesto Bee reported.
CDPH subsequently cited DMC for CRNA scope of practice issues. A department spokesman said that CDPH teams went to DMC “to investigate practices that may not be compliant with state and federal requirements.” The agency declined to comment further until its investigations were complete.
CDPH is monitoring DMC to ensure the hospital complies with state requirements and will return for an unannounced follow-up survey “so it can provide safe, high-quality care to patients that need it,” the spokesperson said.
Although DMC would not confirm it on the record, the immediate jeopardy order led to the removal of all CRNAs, according to Ms. Banek, Ms. Bamgbose, and The Modesto Bee.
The hospital said in a statement that it is working with CDPH to address its concerns and will await a follow-up survey. “Our hospital will continue to fully participate in the Medicare and Medicaid programs during this process.”
Scope of Practice Confusion?
But that does not supersede state laws or hospital bylaws governing practice, said American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) president Ronald Harter, MD.
Five states — Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon — have laws that allow nurse anesthetists to practice without physician oversight or involvement, said Dr. Harter, professor of anesthesiology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio.
“There’s a lot of various opinions on what exactly constitutes scope of practice of a nurse anesthetist,” Dr. Harter said. “The vast majority of them work under the direction of an anesthesiologist, and in those settings, it’s typically very clear to everybody who performs what tasks within the care team,” he said.
It’s less common for nurse anesthetists to work totally independent of physician oversight, he said.
Ms. Bamgbose, however, said there is no California statute requiring physician supervision of CRNAs.
The ASA maintains that CRNAs should always be under the supervision of a physician, which can be an anesthesiologist, obstetrician, gastroenterologist, surgeon, or other physician conducting a procedure. An anesthesiologist does not necessarily have to be physically on site, but in those circumstances, the physician conducting the procedure would be, said Dr. Harter.
Nurse anesthetists are “excellent advanced practice nurses,” Dr. Harter said. “But they haven’t been to medical school; they haven’t conducted a residency in anesthesiology. [They] don’t have the medical knowledge and skills that are required to manage the medical problems that patients either bring to the OR with them or that can arise during the time that they’re under anesthesia.”
Filling a Gap
Nurse anesthetists see things differently.
CRNAs, by virtue of their certification, can “practice to the full extent and to the full scope, which is complete service of anesthesia,” said Ms. Bamgbose. “You can practice independently of anyone, any type of supervision,” she said.
She acknowledges that “the bylaws of any institution will govern the scope at which any healthcare professional can practice at that institution.”
Most nurse anesthetists see themselves as independent practitioners.
Seventy-five percent of CRNAs who responded to a 2023 Medscape Medical News survey said they practice independently. But even Ms. Banek said that often, the meaning of “independent” is in the eye of the beholder. “It could mean different things to various providers, especially depending on the state that they are residing in,” she said.
Ms. Banek and Ms. Bamgbose said that CRNAs can help fill a gap in anesthesiology services in underserved areas.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates there are currently 32,530 anesthesiologists in the United States, with California employing the largest number, at about 5300. The Association of American Medical Colleges estimated the number at 42,263 in 2022. But the federal Health Resources and Services Administration projects a shortage of 6300 anesthesiologists over the next 15 years.
Some 61,000 CRNAs are currently practicing, with 2400 graduating each year. They are required to be board-certified and are recredentialed every 4 years. By 2025, all will be required to have a doctoral degree. Most have already achieved that status, said Ms. Banek.
“Nurse anesthetists provide care predominantly to rural and underserved areas,” she said, adding, “In many rural hospitals across the country and in all three branches of the military, CRNAs practice autonomously.”
There are 3000 CRNAs in California, said Ms. Bamgbose. Nurse anesthetists are the only anesthesiology professionals in four of 58 California counties, she said.
Ms. Banek said she had heard that some 200 cases were canceled in 1 week at DMC due to the lack of CRNAs. Having physician supervision, which she called redundant, “is really creating a barrier to care,” she said.
“We have countless state and national studies that show the safety and efficacy of our practice,” said Ms. Bamgbose. “To interrupt that care ... is incredibly disruptive to the system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CMS Announces End to Cyberattack Relief Program
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has announced the conclusion of a program that provided billions in early Medicare payments to those affected by the Change Healthcare/UnitedHealth Group cyberattack last winter.
CMS reported that the program advanced more than $2.55 billion in Medicare payments to > 4200 Part A providers, including hospitals, and more than $717.18 million in payments to Part B suppliers such as physicians, nonphysician practitioners, and durable medical equipment suppliers.
According to CMS, the Medicare billing system is now functioning properly, and 96% of the early payments have been recovered. The advances were to represent ≤ 30 days of typical claims payments in a 3-month period of 2023, with full repayment expected within 90 days through “automatic recoupment from Medicare claims” — no extensions allowed.
The agency took a victory lap regarding its response. “In the face of one of the most widespread cyberattacks on the US health care industry, CMS promptly took action to get providers and suppliers access to the funds they needed to continue providing patients with vital care,” CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure said in a statement. “Our efforts helped minimize the disruptive fallout from this incident, and we will remain vigilant to be ready to address future events.”
Ongoing Concerns from Health Care Organizations
Ben Teicher, an American Hospital Association spokesman, said that the organization hopes that CMS will be responsive if there’s more need for action after the advance payment program expires. The organization represents about 5000 hospitals, health care systems, and other providers.
“Our members report that the aftereffects of this event will likely be felt throughout the remainder of the year,” he said. According to Teicher, hospitals remain concerned about their ability to process claims and appeal denials, the safety of reconnecting to cyber services, and access to information needed to bill patients and reconcile payments.
In addition, hospitals are concerned about “financial support to mitigate the considerable costs incurred as a result of the cyberattack,” he said.
Charlene MacDonald, executive vice-president of public affairs at the Federation of American Hospitals, which represents more than 1000 for-profit hospitals, sent a statement to this news organization that said some providers “are still feeling the effects of care denials and delays caused by insurer inaction.
“We appreciate that the Administration acted within its authority to support providers during this unprecedented crisis and blunt these devastating impacts, especially because a vast majority of managed care companies failed to step up to the plate,” she said. “It is now time to shift our focus to holding plans accountable for using tactics to delay and deny needed patient care.”
Cyberattack Impact and Response
The ransom-based cyberattack against Change Healthcare/UnitedHealth Group targeted an electronic data interchange clearing house processing payer reimbursement systems, disrupting cash flows at hospitals and medical practices, and affecting patient access to prescriptions and life-saving therapy.
Change Healthcare — part of the UnitedHealth Group subsidiary Optum — processes half of all medical claims, according to a Department of Justice lawsuit. The American Hospital Association described the cyberattack as “the most significant and consequential incident of its kind” in US history.
By late March, UnitedHealth Group said nearly all medical and pharmacy claims were processing properly, while a deputy secretary of the US Department of Health & Human Services told clinicians that officials were focusing on the last group of clinicians who were facing cash-flow problems.
Still, a senior advisor with CMS told providers at that time that “we have heard from so many providers over the last several weeks who are really struggling to make ends meet right now or who are worried that they will not be able to make payroll in the weeks to come.”
Randy Dotinga is a freelance health/medical reporter and board member of the Association of Health Care Journalists.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has announced the conclusion of a program that provided billions in early Medicare payments to those affected by the Change Healthcare/UnitedHealth Group cyberattack last winter.
CMS reported that the program advanced more than $2.55 billion in Medicare payments to > 4200 Part A providers, including hospitals, and more than $717.18 million in payments to Part B suppliers such as physicians, nonphysician practitioners, and durable medical equipment suppliers.
According to CMS, the Medicare billing system is now functioning properly, and 96% of the early payments have been recovered. The advances were to represent ≤ 30 days of typical claims payments in a 3-month period of 2023, with full repayment expected within 90 days through “automatic recoupment from Medicare claims” — no extensions allowed.
The agency took a victory lap regarding its response. “In the face of one of the most widespread cyberattacks on the US health care industry, CMS promptly took action to get providers and suppliers access to the funds they needed to continue providing patients with vital care,” CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure said in a statement. “Our efforts helped minimize the disruptive fallout from this incident, and we will remain vigilant to be ready to address future events.”
Ongoing Concerns from Health Care Organizations
Ben Teicher, an American Hospital Association spokesman, said that the organization hopes that CMS will be responsive if there’s more need for action after the advance payment program expires. The organization represents about 5000 hospitals, health care systems, and other providers.
“Our members report that the aftereffects of this event will likely be felt throughout the remainder of the year,” he said. According to Teicher, hospitals remain concerned about their ability to process claims and appeal denials, the safety of reconnecting to cyber services, and access to information needed to bill patients and reconcile payments.
In addition, hospitals are concerned about “financial support to mitigate the considerable costs incurred as a result of the cyberattack,” he said.
Charlene MacDonald, executive vice-president of public affairs at the Federation of American Hospitals, which represents more than 1000 for-profit hospitals, sent a statement to this news organization that said some providers “are still feeling the effects of care denials and delays caused by insurer inaction.
“We appreciate that the Administration acted within its authority to support providers during this unprecedented crisis and blunt these devastating impacts, especially because a vast majority of managed care companies failed to step up to the plate,” she said. “It is now time to shift our focus to holding plans accountable for using tactics to delay and deny needed patient care.”
Cyberattack Impact and Response
The ransom-based cyberattack against Change Healthcare/UnitedHealth Group targeted an electronic data interchange clearing house processing payer reimbursement systems, disrupting cash flows at hospitals and medical practices, and affecting patient access to prescriptions and life-saving therapy.
Change Healthcare — part of the UnitedHealth Group subsidiary Optum — processes half of all medical claims, according to a Department of Justice lawsuit. The American Hospital Association described the cyberattack as “the most significant and consequential incident of its kind” in US history.
By late March, UnitedHealth Group said nearly all medical and pharmacy claims were processing properly, while a deputy secretary of the US Department of Health & Human Services told clinicians that officials were focusing on the last group of clinicians who were facing cash-flow problems.
Still, a senior advisor with CMS told providers at that time that “we have heard from so many providers over the last several weeks who are really struggling to make ends meet right now or who are worried that they will not be able to make payroll in the weeks to come.”
Randy Dotinga is a freelance health/medical reporter and board member of the Association of Health Care Journalists.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has announced the conclusion of a program that provided billions in early Medicare payments to those affected by the Change Healthcare/UnitedHealth Group cyberattack last winter.
CMS reported that the program advanced more than $2.55 billion in Medicare payments to > 4200 Part A providers, including hospitals, and more than $717.18 million in payments to Part B suppliers such as physicians, nonphysician practitioners, and durable medical equipment suppliers.
According to CMS, the Medicare billing system is now functioning properly, and 96% of the early payments have been recovered. The advances were to represent ≤ 30 days of typical claims payments in a 3-month period of 2023, with full repayment expected within 90 days through “automatic recoupment from Medicare claims” — no extensions allowed.
The agency took a victory lap regarding its response. “In the face of one of the most widespread cyberattacks on the US health care industry, CMS promptly took action to get providers and suppliers access to the funds they needed to continue providing patients with vital care,” CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure said in a statement. “Our efforts helped minimize the disruptive fallout from this incident, and we will remain vigilant to be ready to address future events.”
Ongoing Concerns from Health Care Organizations
Ben Teicher, an American Hospital Association spokesman, said that the organization hopes that CMS will be responsive if there’s more need for action after the advance payment program expires. The organization represents about 5000 hospitals, health care systems, and other providers.
“Our members report that the aftereffects of this event will likely be felt throughout the remainder of the year,” he said. According to Teicher, hospitals remain concerned about their ability to process claims and appeal denials, the safety of reconnecting to cyber services, and access to information needed to bill patients and reconcile payments.
In addition, hospitals are concerned about “financial support to mitigate the considerable costs incurred as a result of the cyberattack,” he said.
Charlene MacDonald, executive vice-president of public affairs at the Federation of American Hospitals, which represents more than 1000 for-profit hospitals, sent a statement to this news organization that said some providers “are still feeling the effects of care denials and delays caused by insurer inaction.
“We appreciate that the Administration acted within its authority to support providers during this unprecedented crisis and blunt these devastating impacts, especially because a vast majority of managed care companies failed to step up to the plate,” she said. “It is now time to shift our focus to holding plans accountable for using tactics to delay and deny needed patient care.”
Cyberattack Impact and Response
The ransom-based cyberattack against Change Healthcare/UnitedHealth Group targeted an electronic data interchange clearing house processing payer reimbursement systems, disrupting cash flows at hospitals and medical practices, and affecting patient access to prescriptions and life-saving therapy.
Change Healthcare — part of the UnitedHealth Group subsidiary Optum — processes half of all medical claims, according to a Department of Justice lawsuit. The American Hospital Association described the cyberattack as “the most significant and consequential incident of its kind” in US history.
By late March, UnitedHealth Group said nearly all medical and pharmacy claims were processing properly, while a deputy secretary of the US Department of Health & Human Services told clinicians that officials were focusing on the last group of clinicians who were facing cash-flow problems.
Still, a senior advisor with CMS told providers at that time that “we have heard from so many providers over the last several weeks who are really struggling to make ends meet right now or who are worried that they will not be able to make payroll in the weeks to come.”
Randy Dotinga is a freelance health/medical reporter and board member of the Association of Health Care Journalists.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is This Journal Legit? Predatory Publishers
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: My guest today is Dr. Jose Merino, editor in chief of the Neurology family of journals and professor of neurology and co-vice chair of education at Georgetown University in Washington, DC.
Our program today is a follow-up of Dr. Merino’s presentation at the recent American Academy of Neurology meeting in Denver, Colorado. Along with two other panelists, Dr. Merino discussed the role of open-access publication and the dangers of predatory journals.
Jose G. Merino, MD, MPhil: Thank you for having me here. It’s a pleasure.
Open Access Defined
Dr. Wilner: I remember when publication in neurology was pretty straightforward. It was either the green journal or the blue journal, but things have certainly changed. I think one topic that is not clear to everyone is this concept of open access. Could you define that for us?
Dr. Merino: Sure. Open access is a mode of publication that fosters more open or accessible science. The idea of open access is that it combines two main elements. One is that the papers that are published become immediately available to anybody with an internet connection anywhere in the world without any restrictions.
The second important element from open access, which makes it different from other models we can talk about, is the fact that the authors retain the copyright of their work, but they give the journal and readers a license to use, reproduce, and modify the content.
This is different, for example, from instances where we have funder mandates. For example, NIH papers have to become available 6 months after publication, so they’re available to everybody but not immediately.
Dr. Wilner: I remember that when a journal article was published, say, in Neurology, if you didn’t have a subscription to Neurology, you went to the library that hopefully had a subscription.
If they didn’t have it, you would write to the author and say, “Hey, I heard you have this great paper because the abstract was out there. Could you send me a reprint?” Has that whole universe evaporated?
Dr. Merino: It depends on how the paper is published. For example, in Neurology, some of the research we publish is open access. Basically, if you have an internet connection, you can access the paper.
That’s the case for papers published in our wholly open-access journals in the Neurology family like Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, Neurology Genetics, or Neurology Education.
For other papers that are published in Neurology, not under open access, there is a paywall. For some of them, the paywall comes down after a few months based on funder mandates and so on. As I was mentioning, the NIH-funded papers are available 6 months later.
In the first 6 months, you may have to go to your library, and if your library has a subscription, you can download it directly. [This is also true for] those that always stay behind the paywall, where you have to have a subscription or your library has to have a subscription.
Is Pay to Publish a Red Flag?
Dr. Wilner: I’m a professional writer. With any luck, when I write something, I get paid to write it. There’s been a long tradition in academic medicine that when you submit an article to, say, Neurology, you don’t get paid as an author for the publication. Your reward is the honor of it being published.
Neurology supports itself in various ways, including advertising and so on. That’s been the contract: free publication for work that merits it, and the journal survives on its own.
With open access, one of the things that’s happened is that — and I’ve published open access myself — is that I get a notification that I need to pay to have my article that I’ve slaved over published. Explain that, please.
Dr. Merino: This is the issue with open access. As I mentioned, the paper gets published. You’re giving the journal a license to publish it. You’re retaining the copyright of your work. That means that the journal cannot make money or support itself by just publishing open access because they belong to you.
Typically, open-access journals are not in print and don’t have much in terms of advertising. The contract is you’re giving me a license to publish it, but it’s your journal, so you’re paying a fee for the journal expenses to basically produce your paper. That’s what’s happening with open access.
That’s been recognized with many funders, for example, with NIH funding or many of the European funders, they’re including open-access fees as part of their funding for research. Now, of course, this doesn’t help if you’re not a funded researcher or if you’re a fellow who’s doing work and so on.
Typically, most journals will have waived fees or lower fees for these situations. The reason for the open-access fee is the fact that you’re retaining the copyright. You’re not giving it to the journal who can then use it to generate its revenue for supporting itself, the editorial staff, and so on.
Dr. Wilner: This idea of charging for publication has created a satellite business of what are called predatory journals. How does one know if the open-access journal that I’m submitting to is really just in the business of wanting my $300 or my $900 to get published? How do I know if that’s a reasonable place to publish?
Predatory Journals
Dr. Merino: That’s a big challenge that has come with this whole idea of open access and the fact that now, many journals are online only, so you’re no longer seeing a physical copy. That has given rise to the predatory journals.
The predatory journal, by definition, is a journal that claims to be open access. They’ll take your paper and publish it, but they don’t provide all the other services that you would typically expect from the fact that you’re paying an open-access fee. This includes getting appropriate peer review, production of the manuscript, and long-term curation and storage of the manuscript.
Many predatory journals will take your open-access fee, accept any paper that you submit, regardless of the quality, because they’re charging the fees for that. They don’t send it to real peer review, and then in a few months, the journal disappears so there’s no way for anybody to actually find your paper anymore.
There are certain checklists. Dr. David Moher at the University of Toronto has produced some work trying to help us identify predatory journals.
One thing I typically suggest to people who ask me this question is: Have you ever heard of this journal before? Does the journal have a track record? How far back does the story of the journal go? Is it supported by a publisher that you know? Do you know anybody who has published there? Is it something you can easily access?
If in doubt, always ask your friendly medical librarian. There used to be lists that were kept in terms of predatory journals that were being constantly updated, but those had to be shut down. As far as I understand, there were legal issues in terms of how things got on that list.
I think that overall, if you’ve heard of it, if it’s relevant, if it’s known in your field, and if your librarian knows it, it’s probably a good legitimate open-access journal. There are many very good legitimate open-access journals.
I mentioned the two that we have in our family, but all the other major journals have their own open-access journal within their family. There are some, like BMC or PLOS, that are completely open-access and legitimate journals.
Impact Factor
Dr. Wilner: What about impact factor? Many journals boast about their impact factor. I’m not sure how to interpret that number.
Dr. Merino: Impact factor is very interesting. The impact factor was developed by medical librarians to try to identify the journals they should be subscribing to. It’s a measure of the average citations to an average paper in the journal.
It doesn’t tell you about specific papers. It tells you, on average, how many of the papers in this journal get cited so many times. It’s calculated by the number of articles that were cited divided by the number of articles that were published. Journals that publish many papers, like Neurology, have a hard time bringing up their impact factor beyond a certain level.
Similarly, very small journals with one or two very highly cited papers have a very high impact factor. It’s being used as a measure, perhaps inappropriately, of how good or how reputable a journal is. We all say we don’t care about journal impact factors, but we all know our journal impact factor and we used to know it to three decimals. Now, they changed the system, and there’s only one decimal point, which makes more sense.
This is more important, for example, for authors when deciding where to submit papers. I know that in some countries, particularly in Europe, the impact factor of the journal where you publish has an impact on your promotion decisions.
I would say what’s even more important than the impact factor, is to say, “Well, is this the journal that fits the scope of my paper? Is this the journal that reaches the audience that I want to reach when I write my paper?”
There are some papers, for example, that are very influential. The impact factor just captures citations. There are some papers that are very influential that may not get cited very often. There may be papers that change clinical practice.
If you read a paper that tells you that you should be changing how you treat your patients with myasthenia based on this paper, that may not get cited. It’s a very clinically focused paper, but it’s probably more impactful than one that gets cited very much in some respect, or they make it to public policy decisions, and so on.
I think it’s important to look more at the audience and the journal scope when you submit your papers.
Dr. Wilner: One other technical question. The journals also say they’re indexed in PubMed or Google Scholar. If I want to publish my paper and I want it indexed where the right people are going to find it, where does it need to be indexed?
Dr. Merino: I grew up using Index Medicus, MedlinePlus, and the Library of Science. I still do. If I need to find something, I go to PubMed. Ideally, papers are listed in MedlinePlus or can be found in PubMed. They’re not the same thing, but you can find them through them.
That would be an important thing. Nowadays, a lot more people are using Google Scholar or Google just to identify papers. It may be a little bit less relevant, but it’s still a measure of the quality of the journal before they get indexed in some of these. For example, if you get listed in MedlinePlus, it has gone through certain quality checks by the index itself to see whether they would accept the journal or not. That’s something you want to check.
Typically, most of the large journals or the journals you and I know about are listed in more than one place, right? They’re listed in Scopus and Web of Science. They’re listed in MedlinePlus and so on. Again, if you’re submitting your paper, go somewhere where you know the journal and you’ve heard about it.
Dr. Wilner: I’m not going to ask you about artificial intelligence. We can do that another time. I want to ask something closer to me, which is this question of publish or perish.
There seems to be, in academics, more emphasis on the number of papers that one has published rather than their quality. How does a younger academician or one who really needs to publish cope with that?
Dr. Merino: Many people are writing up research that may not be relevant or that may not be high quality just because you need to have a long list of papers to get promoted, for example, if you’re an academician.
Doug Altman, who was a very influential person in the field quality of not only medical statistics but also medical publishing, had the idea that we need less research, but we need better research.
We often receive papers where you say, well, what’s the rationale behind the question in this paper? It’s like they had a large amount of data and were trying to squeeze as much as they could out of that. I think, as a young academician, the important thing to think about is whether it is an important question that matters to you and to the field, from whatever perspective, whether it’s going to advance research, advance clinical care, or have public policy implications.
Is this one where the answer will be important no matter what the answer is? If you’re thinking of that, your work will be well recognized, people will know you, and you’ll get invited to collaborate. I think that’s the most important thing rather than just churning out a large number of papers.
The productivity will come from the fact that you start by saying, let me ask something that’s really meaningful to me and to the field, with a good question and using strong research methodology.
Dr. Wilner: Thanks for that, Dr. Merino. I think that’s very valuable for all of us. This has been a great discussion. Do you have any final comments before we wrap up?
Dr. Merino: I want to encourage people to continue reading medical journals all the time and submitting to us, again, good research and important questions with robust methodology. That’s what we’re looking for in Neurology and most serious medical journals.
Dr. Wilner is an associate professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. Dr. Merino is a professor in the department of neurology at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC. Dr. Wilner reported conflicts of interest with Accordant Health Services and Lulu Publishing. Dr. Merino reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: My guest today is Dr. Jose Merino, editor in chief of the Neurology family of journals and professor of neurology and co-vice chair of education at Georgetown University in Washington, DC.
Our program today is a follow-up of Dr. Merino’s presentation at the recent American Academy of Neurology meeting in Denver, Colorado. Along with two other panelists, Dr. Merino discussed the role of open-access publication and the dangers of predatory journals.
Jose G. Merino, MD, MPhil: Thank you for having me here. It’s a pleasure.
Open Access Defined
Dr. Wilner: I remember when publication in neurology was pretty straightforward. It was either the green journal or the blue journal, but things have certainly changed. I think one topic that is not clear to everyone is this concept of open access. Could you define that for us?
Dr. Merino: Sure. Open access is a mode of publication that fosters more open or accessible science. The idea of open access is that it combines two main elements. One is that the papers that are published become immediately available to anybody with an internet connection anywhere in the world without any restrictions.
The second important element from open access, which makes it different from other models we can talk about, is the fact that the authors retain the copyright of their work, but they give the journal and readers a license to use, reproduce, and modify the content.
This is different, for example, from instances where we have funder mandates. For example, NIH papers have to become available 6 months after publication, so they’re available to everybody but not immediately.
Dr. Wilner: I remember that when a journal article was published, say, in Neurology, if you didn’t have a subscription to Neurology, you went to the library that hopefully had a subscription.
If they didn’t have it, you would write to the author and say, “Hey, I heard you have this great paper because the abstract was out there. Could you send me a reprint?” Has that whole universe evaporated?
Dr. Merino: It depends on how the paper is published. For example, in Neurology, some of the research we publish is open access. Basically, if you have an internet connection, you can access the paper.
That’s the case for papers published in our wholly open-access journals in the Neurology family like Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, Neurology Genetics, or Neurology Education.
For other papers that are published in Neurology, not under open access, there is a paywall. For some of them, the paywall comes down after a few months based on funder mandates and so on. As I was mentioning, the NIH-funded papers are available 6 months later.
In the first 6 months, you may have to go to your library, and if your library has a subscription, you can download it directly. [This is also true for] those that always stay behind the paywall, where you have to have a subscription or your library has to have a subscription.
Is Pay to Publish a Red Flag?
Dr. Wilner: I’m a professional writer. With any luck, when I write something, I get paid to write it. There’s been a long tradition in academic medicine that when you submit an article to, say, Neurology, you don’t get paid as an author for the publication. Your reward is the honor of it being published.
Neurology supports itself in various ways, including advertising and so on. That’s been the contract: free publication for work that merits it, and the journal survives on its own.
With open access, one of the things that’s happened is that — and I’ve published open access myself — is that I get a notification that I need to pay to have my article that I’ve slaved over published. Explain that, please.
Dr. Merino: This is the issue with open access. As I mentioned, the paper gets published. You’re giving the journal a license to publish it. You’re retaining the copyright of your work. That means that the journal cannot make money or support itself by just publishing open access because they belong to you.
Typically, open-access journals are not in print and don’t have much in terms of advertising. The contract is you’re giving me a license to publish it, but it’s your journal, so you’re paying a fee for the journal expenses to basically produce your paper. That’s what’s happening with open access.
That’s been recognized with many funders, for example, with NIH funding or many of the European funders, they’re including open-access fees as part of their funding for research. Now, of course, this doesn’t help if you’re not a funded researcher or if you’re a fellow who’s doing work and so on.
Typically, most journals will have waived fees or lower fees for these situations. The reason for the open-access fee is the fact that you’re retaining the copyright. You’re not giving it to the journal who can then use it to generate its revenue for supporting itself, the editorial staff, and so on.
Dr. Wilner: This idea of charging for publication has created a satellite business of what are called predatory journals. How does one know if the open-access journal that I’m submitting to is really just in the business of wanting my $300 or my $900 to get published? How do I know if that’s a reasonable place to publish?
Predatory Journals
Dr. Merino: That’s a big challenge that has come with this whole idea of open access and the fact that now, many journals are online only, so you’re no longer seeing a physical copy. That has given rise to the predatory journals.
The predatory journal, by definition, is a journal that claims to be open access. They’ll take your paper and publish it, but they don’t provide all the other services that you would typically expect from the fact that you’re paying an open-access fee. This includes getting appropriate peer review, production of the manuscript, and long-term curation and storage of the manuscript.
Many predatory journals will take your open-access fee, accept any paper that you submit, regardless of the quality, because they’re charging the fees for that. They don’t send it to real peer review, and then in a few months, the journal disappears so there’s no way for anybody to actually find your paper anymore.
There are certain checklists. Dr. David Moher at the University of Toronto has produced some work trying to help us identify predatory journals.
One thing I typically suggest to people who ask me this question is: Have you ever heard of this journal before? Does the journal have a track record? How far back does the story of the journal go? Is it supported by a publisher that you know? Do you know anybody who has published there? Is it something you can easily access?
If in doubt, always ask your friendly medical librarian. There used to be lists that were kept in terms of predatory journals that were being constantly updated, but those had to be shut down. As far as I understand, there were legal issues in terms of how things got on that list.
I think that overall, if you’ve heard of it, if it’s relevant, if it’s known in your field, and if your librarian knows it, it’s probably a good legitimate open-access journal. There are many very good legitimate open-access journals.
I mentioned the two that we have in our family, but all the other major journals have their own open-access journal within their family. There are some, like BMC or PLOS, that are completely open-access and legitimate journals.
Impact Factor
Dr. Wilner: What about impact factor? Many journals boast about their impact factor. I’m not sure how to interpret that number.
Dr. Merino: Impact factor is very interesting. The impact factor was developed by medical librarians to try to identify the journals they should be subscribing to. It’s a measure of the average citations to an average paper in the journal.
It doesn’t tell you about specific papers. It tells you, on average, how many of the papers in this journal get cited so many times. It’s calculated by the number of articles that were cited divided by the number of articles that were published. Journals that publish many papers, like Neurology, have a hard time bringing up their impact factor beyond a certain level.
Similarly, very small journals with one or two very highly cited papers have a very high impact factor. It’s being used as a measure, perhaps inappropriately, of how good or how reputable a journal is. We all say we don’t care about journal impact factors, but we all know our journal impact factor and we used to know it to three decimals. Now, they changed the system, and there’s only one decimal point, which makes more sense.
This is more important, for example, for authors when deciding where to submit papers. I know that in some countries, particularly in Europe, the impact factor of the journal where you publish has an impact on your promotion decisions.
I would say what’s even more important than the impact factor, is to say, “Well, is this the journal that fits the scope of my paper? Is this the journal that reaches the audience that I want to reach when I write my paper?”
There are some papers, for example, that are very influential. The impact factor just captures citations. There are some papers that are very influential that may not get cited very often. There may be papers that change clinical practice.
If you read a paper that tells you that you should be changing how you treat your patients with myasthenia based on this paper, that may not get cited. It’s a very clinically focused paper, but it’s probably more impactful than one that gets cited very much in some respect, or they make it to public policy decisions, and so on.
I think it’s important to look more at the audience and the journal scope when you submit your papers.
Dr. Wilner: One other technical question. The journals also say they’re indexed in PubMed or Google Scholar. If I want to publish my paper and I want it indexed where the right people are going to find it, where does it need to be indexed?
Dr. Merino: I grew up using Index Medicus, MedlinePlus, and the Library of Science. I still do. If I need to find something, I go to PubMed. Ideally, papers are listed in MedlinePlus or can be found in PubMed. They’re not the same thing, but you can find them through them.
That would be an important thing. Nowadays, a lot more people are using Google Scholar or Google just to identify papers. It may be a little bit less relevant, but it’s still a measure of the quality of the journal before they get indexed in some of these. For example, if you get listed in MedlinePlus, it has gone through certain quality checks by the index itself to see whether they would accept the journal or not. That’s something you want to check.
Typically, most of the large journals or the journals you and I know about are listed in more than one place, right? They’re listed in Scopus and Web of Science. They’re listed in MedlinePlus and so on. Again, if you’re submitting your paper, go somewhere where you know the journal and you’ve heard about it.
Dr. Wilner: I’m not going to ask you about artificial intelligence. We can do that another time. I want to ask something closer to me, which is this question of publish or perish.
There seems to be, in academics, more emphasis on the number of papers that one has published rather than their quality. How does a younger academician or one who really needs to publish cope with that?
Dr. Merino: Many people are writing up research that may not be relevant or that may not be high quality just because you need to have a long list of papers to get promoted, for example, if you’re an academician.
Doug Altman, who was a very influential person in the field quality of not only medical statistics but also medical publishing, had the idea that we need less research, but we need better research.
We often receive papers where you say, well, what’s the rationale behind the question in this paper? It’s like they had a large amount of data and were trying to squeeze as much as they could out of that. I think, as a young academician, the important thing to think about is whether it is an important question that matters to you and to the field, from whatever perspective, whether it’s going to advance research, advance clinical care, or have public policy implications.
Is this one where the answer will be important no matter what the answer is? If you’re thinking of that, your work will be well recognized, people will know you, and you’ll get invited to collaborate. I think that’s the most important thing rather than just churning out a large number of papers.
The productivity will come from the fact that you start by saying, let me ask something that’s really meaningful to me and to the field, with a good question and using strong research methodology.
Dr. Wilner: Thanks for that, Dr. Merino. I think that’s very valuable for all of us. This has been a great discussion. Do you have any final comments before we wrap up?
Dr. Merino: I want to encourage people to continue reading medical journals all the time and submitting to us, again, good research and important questions with robust methodology. That’s what we’re looking for in Neurology and most serious medical journals.
Dr. Wilner is an associate professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. Dr. Merino is a professor in the department of neurology at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC. Dr. Wilner reported conflicts of interest with Accordant Health Services and Lulu Publishing. Dr. Merino reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: My guest today is Dr. Jose Merino, editor in chief of the Neurology family of journals and professor of neurology and co-vice chair of education at Georgetown University in Washington, DC.
Our program today is a follow-up of Dr. Merino’s presentation at the recent American Academy of Neurology meeting in Denver, Colorado. Along with two other panelists, Dr. Merino discussed the role of open-access publication and the dangers of predatory journals.
Jose G. Merino, MD, MPhil: Thank you for having me here. It’s a pleasure.
Open Access Defined
Dr. Wilner: I remember when publication in neurology was pretty straightforward. It was either the green journal or the blue journal, but things have certainly changed. I think one topic that is not clear to everyone is this concept of open access. Could you define that for us?
Dr. Merino: Sure. Open access is a mode of publication that fosters more open or accessible science. The idea of open access is that it combines two main elements. One is that the papers that are published become immediately available to anybody with an internet connection anywhere in the world without any restrictions.
The second important element from open access, which makes it different from other models we can talk about, is the fact that the authors retain the copyright of their work, but they give the journal and readers a license to use, reproduce, and modify the content.
This is different, for example, from instances where we have funder mandates. For example, NIH papers have to become available 6 months after publication, so they’re available to everybody but not immediately.
Dr. Wilner: I remember that when a journal article was published, say, in Neurology, if you didn’t have a subscription to Neurology, you went to the library that hopefully had a subscription.
If they didn’t have it, you would write to the author and say, “Hey, I heard you have this great paper because the abstract was out there. Could you send me a reprint?” Has that whole universe evaporated?
Dr. Merino: It depends on how the paper is published. For example, in Neurology, some of the research we publish is open access. Basically, if you have an internet connection, you can access the paper.
That’s the case for papers published in our wholly open-access journals in the Neurology family like Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, Neurology Genetics, or Neurology Education.
For other papers that are published in Neurology, not under open access, there is a paywall. For some of them, the paywall comes down after a few months based on funder mandates and so on. As I was mentioning, the NIH-funded papers are available 6 months later.
In the first 6 months, you may have to go to your library, and if your library has a subscription, you can download it directly. [This is also true for] those that always stay behind the paywall, where you have to have a subscription or your library has to have a subscription.
Is Pay to Publish a Red Flag?
Dr. Wilner: I’m a professional writer. With any luck, when I write something, I get paid to write it. There’s been a long tradition in academic medicine that when you submit an article to, say, Neurology, you don’t get paid as an author for the publication. Your reward is the honor of it being published.
Neurology supports itself in various ways, including advertising and so on. That’s been the contract: free publication for work that merits it, and the journal survives on its own.
With open access, one of the things that’s happened is that — and I’ve published open access myself — is that I get a notification that I need to pay to have my article that I’ve slaved over published. Explain that, please.
Dr. Merino: This is the issue with open access. As I mentioned, the paper gets published. You’re giving the journal a license to publish it. You’re retaining the copyright of your work. That means that the journal cannot make money or support itself by just publishing open access because they belong to you.
Typically, open-access journals are not in print and don’t have much in terms of advertising. The contract is you’re giving me a license to publish it, but it’s your journal, so you’re paying a fee for the journal expenses to basically produce your paper. That’s what’s happening with open access.
That’s been recognized with many funders, for example, with NIH funding or many of the European funders, they’re including open-access fees as part of their funding for research. Now, of course, this doesn’t help if you’re not a funded researcher or if you’re a fellow who’s doing work and so on.
Typically, most journals will have waived fees or lower fees for these situations. The reason for the open-access fee is the fact that you’re retaining the copyright. You’re not giving it to the journal who can then use it to generate its revenue for supporting itself, the editorial staff, and so on.
Dr. Wilner: This idea of charging for publication has created a satellite business of what are called predatory journals. How does one know if the open-access journal that I’m submitting to is really just in the business of wanting my $300 or my $900 to get published? How do I know if that’s a reasonable place to publish?
Predatory Journals
Dr. Merino: That’s a big challenge that has come with this whole idea of open access and the fact that now, many journals are online only, so you’re no longer seeing a physical copy. That has given rise to the predatory journals.
The predatory journal, by definition, is a journal that claims to be open access. They’ll take your paper and publish it, but they don’t provide all the other services that you would typically expect from the fact that you’re paying an open-access fee. This includes getting appropriate peer review, production of the manuscript, and long-term curation and storage of the manuscript.
Many predatory journals will take your open-access fee, accept any paper that you submit, regardless of the quality, because they’re charging the fees for that. They don’t send it to real peer review, and then in a few months, the journal disappears so there’s no way for anybody to actually find your paper anymore.
There are certain checklists. Dr. David Moher at the University of Toronto has produced some work trying to help us identify predatory journals.
One thing I typically suggest to people who ask me this question is: Have you ever heard of this journal before? Does the journal have a track record? How far back does the story of the journal go? Is it supported by a publisher that you know? Do you know anybody who has published there? Is it something you can easily access?
If in doubt, always ask your friendly medical librarian. There used to be lists that were kept in terms of predatory journals that were being constantly updated, but those had to be shut down. As far as I understand, there were legal issues in terms of how things got on that list.
I think that overall, if you’ve heard of it, if it’s relevant, if it’s known in your field, and if your librarian knows it, it’s probably a good legitimate open-access journal. There are many very good legitimate open-access journals.
I mentioned the two that we have in our family, but all the other major journals have their own open-access journal within their family. There are some, like BMC or PLOS, that are completely open-access and legitimate journals.
Impact Factor
Dr. Wilner: What about impact factor? Many journals boast about their impact factor. I’m not sure how to interpret that number.
Dr. Merino: Impact factor is very interesting. The impact factor was developed by medical librarians to try to identify the journals they should be subscribing to. It’s a measure of the average citations to an average paper in the journal.
It doesn’t tell you about specific papers. It tells you, on average, how many of the papers in this journal get cited so many times. It’s calculated by the number of articles that were cited divided by the number of articles that were published. Journals that publish many papers, like Neurology, have a hard time bringing up their impact factor beyond a certain level.
Similarly, very small journals with one or two very highly cited papers have a very high impact factor. It’s being used as a measure, perhaps inappropriately, of how good or how reputable a journal is. We all say we don’t care about journal impact factors, but we all know our journal impact factor and we used to know it to three decimals. Now, they changed the system, and there’s only one decimal point, which makes more sense.
This is more important, for example, for authors when deciding where to submit papers. I know that in some countries, particularly in Europe, the impact factor of the journal where you publish has an impact on your promotion decisions.
I would say what’s even more important than the impact factor, is to say, “Well, is this the journal that fits the scope of my paper? Is this the journal that reaches the audience that I want to reach when I write my paper?”
There are some papers, for example, that are very influential. The impact factor just captures citations. There are some papers that are very influential that may not get cited very often. There may be papers that change clinical practice.
If you read a paper that tells you that you should be changing how you treat your patients with myasthenia based on this paper, that may not get cited. It’s a very clinically focused paper, but it’s probably more impactful than one that gets cited very much in some respect, or they make it to public policy decisions, and so on.
I think it’s important to look more at the audience and the journal scope when you submit your papers.
Dr. Wilner: One other technical question. The journals also say they’re indexed in PubMed or Google Scholar. If I want to publish my paper and I want it indexed where the right people are going to find it, where does it need to be indexed?
Dr. Merino: I grew up using Index Medicus, MedlinePlus, and the Library of Science. I still do. If I need to find something, I go to PubMed. Ideally, papers are listed in MedlinePlus or can be found in PubMed. They’re not the same thing, but you can find them through them.
That would be an important thing. Nowadays, a lot more people are using Google Scholar or Google just to identify papers. It may be a little bit less relevant, but it’s still a measure of the quality of the journal before they get indexed in some of these. For example, if you get listed in MedlinePlus, it has gone through certain quality checks by the index itself to see whether they would accept the journal or not. That’s something you want to check.
Typically, most of the large journals or the journals you and I know about are listed in more than one place, right? They’re listed in Scopus and Web of Science. They’re listed in MedlinePlus and so on. Again, if you’re submitting your paper, go somewhere where you know the journal and you’ve heard about it.
Dr. Wilner: I’m not going to ask you about artificial intelligence. We can do that another time. I want to ask something closer to me, which is this question of publish or perish.
There seems to be, in academics, more emphasis on the number of papers that one has published rather than their quality. How does a younger academician or one who really needs to publish cope with that?
Dr. Merino: Many people are writing up research that may not be relevant or that may not be high quality just because you need to have a long list of papers to get promoted, for example, if you’re an academician.
Doug Altman, who was a very influential person in the field quality of not only medical statistics but also medical publishing, had the idea that we need less research, but we need better research.
We often receive papers where you say, well, what’s the rationale behind the question in this paper? It’s like they had a large amount of data and were trying to squeeze as much as they could out of that. I think, as a young academician, the important thing to think about is whether it is an important question that matters to you and to the field, from whatever perspective, whether it’s going to advance research, advance clinical care, or have public policy implications.
Is this one where the answer will be important no matter what the answer is? If you’re thinking of that, your work will be well recognized, people will know you, and you’ll get invited to collaborate. I think that’s the most important thing rather than just churning out a large number of papers.
The productivity will come from the fact that you start by saying, let me ask something that’s really meaningful to me and to the field, with a good question and using strong research methodology.
Dr. Wilner: Thanks for that, Dr. Merino. I think that’s very valuable for all of us. This has been a great discussion. Do you have any final comments before we wrap up?
Dr. Merino: I want to encourage people to continue reading medical journals all the time and submitting to us, again, good research and important questions with robust methodology. That’s what we’re looking for in Neurology and most serious medical journals.
Dr. Wilner is an associate professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. Dr. Merino is a professor in the department of neurology at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC. Dr. Wilner reported conflicts of interest with Accordant Health Services and Lulu Publishing. Dr. Merino reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncology Mergers Are on the Rise. How Can Independent Practices Survive?
When he completed his fellowship at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, Moshe Chasky, MD, joined a small five-person practice that rented space from the city’s Jefferson Hospital in Philadelphia. The arrangement seemed to work well for the hospital and the small practice, which remained independent.
Within 10 years, the hospital sought to buy the practice, Alliance Cancer Specialists.
But the oncologists at Alliance did not want to join Jefferson.
The hospital eventually entered into an exclusive agreement with its own medical group to provide inpatient oncology/hematology services at three Jefferson Health–Northeast hospitals and stripped Dr. Chasky and his colleagues of their privileges at those facilities, Medscape Medical News reported last year.
said Jeff Patton, MD, CEO of OneOncology, a management services organization.
A 2020 report from the Community Oncology Alliance (COA), for instance, tracked mergers, acquisitions, and closures in the community oncology setting and found the number of practices acquired by hospitals, known as vertical integration, nearly tripled from 2010 to 2020.
“Some hospitals are pretty predatory in their approach,” Dr. Patton said. If hospitals have their own oncology program, “they’ll employ the referring doctors and then discourage them or prevent them from referring patients to our independent practices that are not owned by the hospital.”
Still, in the face of growing pressure to join hospitals, some community oncology practices are finding ways to survive and maintain their independence.
A Growing Trend
The latest data continue to show a clear trend: Consolidation in oncology is on the rise.
A 2024 study revealed that the pace of consolidation seems to be increasing.
The analysis found that, between 2015 and 2022, the number of medical oncologists increased by 14% and the number of medical oncologists per practice increased by 40%, while the number of practices decreased by 18%.
While about 44% of practices remain independent, the percentage of medical oncologists working in practices with more than 25 clinicians has increased from 34% in 2015 to 44% in 2022. By 2022, the largest 102 practices in the United States employed more than 40% of all medical oncologists.
“The rate of consolidation seems to be rapid,” study coauthor Parsa Erfani, MD, an internal medicine resident at Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, explained.
Consolidation appears to breed more consolidation. The researchers found, for instance, that markets with greater hospital consolidation and more hospital beds per capita were more likely to undergo consolidation in oncology.
Consolidation may be higher in these markets “because hospitals or health systems are buying up oncology practices or conversely because oncology practices are merging to compete more effectively with larger hospitals in the area,” Dr. Erfani told this news organization.
Mergers among independent practices, known as horizontal integration, have also been on the rise, according to the 2020 COA report. These mergers can help counter pressures from hospitals seeking to acquire community practices as well as prevent practices and their clinics from closing.
Although Dr. Erfani’s research wasn’t designed to determine the factors behind consolidation, he and his colleagues point to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the federal 340B Drug Pricing Program as potential drivers of this trend.
The ACA encouraged consolidation as a way to improve efficiency and created the need for ever-larger information systems to collect and report quality data. But these data collection and reporting requirements have become increasingly difficult for smaller practices to take on.
The 340B Program, however, may be a bigger contributing factor to consolidation. Created in 1992, the 340B Program allows qualifying hospitals and clinics that treat low-income and uninsured patients to buy outpatient prescription drugs at a 25%-50% discount.
Hospitals seeking to capitalize on the margins possible under the 340B Program will “buy all the referring physicians in a market so that the medical oncology group is left with little choice but to sell to the hospital,” said Dr. Patton.
“Those 340B dollars are worth a lot to hospitals,” said David A. Eagle, MD, a hematologist/oncologist with New York Cancer & Blood Specialists and past president of COA. The program “creates an appetite for nonprofit hospitals to want to grow their medical oncology programs,” he told this news organization.
Declining Medicare reimbursement has also hit independent practices hard.
Over the past 15 years, compared with inflation, physicians have gotten “a pay rate decrease from Medicare,” said Dr. Patton. Payers have followed that lead and tried to cut pay for clinicians, especially those who do not have market share, he said. Paying them less is “disingenuous knowing that our costs of providing care are going up,” he said.
Less Access, Higher Costs, Worse Care?
Many studies have demonstrated that, when hospitals become behemoths in a given market, healthcare costs go up.
“There are robust data showing that consolidation increases healthcare costs by reducing competition, including in oncology,” wrote Dr. Erfani and colleagues.
Oncology practices that are owned by hospitals bill facility fees for outpatient chemotherapy treatment, adding another layer of cost, the researchers explained, citing a 2019 Health Economics study.
Another analysis, published in 2020, found that hospital prices for the top 37 infused cancer drugs averaged 86% more per unit than the price charged by physician offices. Hospital outpatient departments charged even more, on average, for drugs — 128% more for nivolumab and 428% more for fluorouracil, for instance.
In their 2024 analysis, Dr. Erfani and colleagues also found that increased hospital market concentration was associated with worse quality of care, across all assessed patient satisfaction measures, and may result in worse access to care as well.
Overall, these consolidation “trends have important implications for cancer care cost, quality, and access,” the authors concluded.
Navigating the Consolidation Trend
In the face of mounting pressure to join hospitals, community oncology practices have typically relied on horizontal mergers to maintain their independence. An increasing number of practices, however, are now turning to another strategy: Management services organizations.
According to some oncologists, a core benefit of joining a management services organization is their community practices can maintain autonomy, hold on to referrals, and benefit from access to a wider network of peers and recently approved treatments such as chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies.
In these arrangements, the management company also provides business assistance to practices, including help with billing and collection, payer negotiations, supply chain issues, and credentialing, as well as recruiting, hiring, and marketing.
These management organizations, which include American Oncology Network, Integrated Oncology Network, OneOncology, and Verdi Oncology, are, however, backed by private equity. According to a 2022 report, private equity–backed management organizations have ramped up arrangements with community oncology practices over the past few years — a trend that has concerned some experts.
The authors of a recent analysis in JAMA Internal Medicine explained that, although private equity involvement in physician practices may enable operational efficiencies, “critics point to potential conflicts of interest” and highlight concerns that patients “may face additional barriers to both accessibility and affordability of care.”
The difference, according to some oncologists, is their practices are not owned by the management services organization; instead, the practices enter contracts that outline the boundaries of the relationship and stipulate fees to the management organizations.
In 2020, Dr. Chasky’s practice, Alliance Cancer Specialists, joined The US Oncology Network, a management services organization wholly owned by McKesson. The organization provides the practice with capital and other resources, as well as access to the Sarah Cannon Research Institute, so patients can participate in clinical trials.
“We totally function as an independent practice,” said Dr. Chasky. “We make our own management decisions,” he said. For instance, if Alliance wants to hire a new clinician, US Oncology helps with the recruitment. “But at the end of the day, it’s our practice,” he said.
Davey Daniel, MD — whose community practice joined the management services organization OneOncology — has seen the benefits of being part of a larger network. For instance, bispecific therapies for leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma are typically administered at academic centers because of the risk for cytokine release syndrome.
However, physician leaders in the OneOncology network “came up with a playbook on how to do it safely” in the community setting, said Dr. Daniel. “It meant that we were adopting FDA newly approved therapies in a very short course.”
Being able to draw from a wider pool of expertise has had other advantages. Dr. Daniel can lean on pathologists and research scientists in the network for advice on targeted therapy use. “We’re actually bringing precision medicine expertise to the community,” Dr. Daniel said.
Dr. Chasky and Dr. Eagle, whose practice is also part of OneOncology, said that continuing to work in the community setting has allowed them greater flexibility.
Dr. Eagle explained that New York Cancer & Blood Specialists tries to offer patients an appointment within 2 days of a referral, and it allows walk-in visits.
Dr. Chasky leans into the flexibility by having staff stay late, when needed, to ensure that all patients are seen. “We’re there for our patients at all hours,” Dr. Chasky said, adding that often “you don’t have that flexibility when you work for a big hospital system.”
The bottom line is community oncology can still thrive, said Nick Ferreyros, managing director of COA, “as long as we have a healthy competitive ecosystem where [we] are valued and seen as an important part of our cancer care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When he completed his fellowship at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, Moshe Chasky, MD, joined a small five-person practice that rented space from the city’s Jefferson Hospital in Philadelphia. The arrangement seemed to work well for the hospital and the small practice, which remained independent.
Within 10 years, the hospital sought to buy the practice, Alliance Cancer Specialists.
But the oncologists at Alliance did not want to join Jefferson.
The hospital eventually entered into an exclusive agreement with its own medical group to provide inpatient oncology/hematology services at three Jefferson Health–Northeast hospitals and stripped Dr. Chasky and his colleagues of their privileges at those facilities, Medscape Medical News reported last year.
said Jeff Patton, MD, CEO of OneOncology, a management services organization.
A 2020 report from the Community Oncology Alliance (COA), for instance, tracked mergers, acquisitions, and closures in the community oncology setting and found the number of practices acquired by hospitals, known as vertical integration, nearly tripled from 2010 to 2020.
“Some hospitals are pretty predatory in their approach,” Dr. Patton said. If hospitals have their own oncology program, “they’ll employ the referring doctors and then discourage them or prevent them from referring patients to our independent practices that are not owned by the hospital.”
Still, in the face of growing pressure to join hospitals, some community oncology practices are finding ways to survive and maintain their independence.
A Growing Trend
The latest data continue to show a clear trend: Consolidation in oncology is on the rise.
A 2024 study revealed that the pace of consolidation seems to be increasing.
The analysis found that, between 2015 and 2022, the number of medical oncologists increased by 14% and the number of medical oncologists per practice increased by 40%, while the number of practices decreased by 18%.
While about 44% of practices remain independent, the percentage of medical oncologists working in practices with more than 25 clinicians has increased from 34% in 2015 to 44% in 2022. By 2022, the largest 102 practices in the United States employed more than 40% of all medical oncologists.
“The rate of consolidation seems to be rapid,” study coauthor Parsa Erfani, MD, an internal medicine resident at Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, explained.
Consolidation appears to breed more consolidation. The researchers found, for instance, that markets with greater hospital consolidation and more hospital beds per capita were more likely to undergo consolidation in oncology.
Consolidation may be higher in these markets “because hospitals or health systems are buying up oncology practices or conversely because oncology practices are merging to compete more effectively with larger hospitals in the area,” Dr. Erfani told this news organization.
Mergers among independent practices, known as horizontal integration, have also been on the rise, according to the 2020 COA report. These mergers can help counter pressures from hospitals seeking to acquire community practices as well as prevent practices and their clinics from closing.
Although Dr. Erfani’s research wasn’t designed to determine the factors behind consolidation, he and his colleagues point to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the federal 340B Drug Pricing Program as potential drivers of this trend.
The ACA encouraged consolidation as a way to improve efficiency and created the need for ever-larger information systems to collect and report quality data. But these data collection and reporting requirements have become increasingly difficult for smaller practices to take on.
The 340B Program, however, may be a bigger contributing factor to consolidation. Created in 1992, the 340B Program allows qualifying hospitals and clinics that treat low-income and uninsured patients to buy outpatient prescription drugs at a 25%-50% discount.
Hospitals seeking to capitalize on the margins possible under the 340B Program will “buy all the referring physicians in a market so that the medical oncology group is left with little choice but to sell to the hospital,” said Dr. Patton.
“Those 340B dollars are worth a lot to hospitals,” said David A. Eagle, MD, a hematologist/oncologist with New York Cancer & Blood Specialists and past president of COA. The program “creates an appetite for nonprofit hospitals to want to grow their medical oncology programs,” he told this news organization.
Declining Medicare reimbursement has also hit independent practices hard.
Over the past 15 years, compared with inflation, physicians have gotten “a pay rate decrease from Medicare,” said Dr. Patton. Payers have followed that lead and tried to cut pay for clinicians, especially those who do not have market share, he said. Paying them less is “disingenuous knowing that our costs of providing care are going up,” he said.
Less Access, Higher Costs, Worse Care?
Many studies have demonstrated that, when hospitals become behemoths in a given market, healthcare costs go up.
“There are robust data showing that consolidation increases healthcare costs by reducing competition, including in oncology,” wrote Dr. Erfani and colleagues.
Oncology practices that are owned by hospitals bill facility fees for outpatient chemotherapy treatment, adding another layer of cost, the researchers explained, citing a 2019 Health Economics study.
Another analysis, published in 2020, found that hospital prices for the top 37 infused cancer drugs averaged 86% more per unit than the price charged by physician offices. Hospital outpatient departments charged even more, on average, for drugs — 128% more for nivolumab and 428% more for fluorouracil, for instance.
In their 2024 analysis, Dr. Erfani and colleagues also found that increased hospital market concentration was associated with worse quality of care, across all assessed patient satisfaction measures, and may result in worse access to care as well.
Overall, these consolidation “trends have important implications for cancer care cost, quality, and access,” the authors concluded.
Navigating the Consolidation Trend
In the face of mounting pressure to join hospitals, community oncology practices have typically relied on horizontal mergers to maintain their independence. An increasing number of practices, however, are now turning to another strategy: Management services organizations.
According to some oncologists, a core benefit of joining a management services organization is their community practices can maintain autonomy, hold on to referrals, and benefit from access to a wider network of peers and recently approved treatments such as chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies.
In these arrangements, the management company also provides business assistance to practices, including help with billing and collection, payer negotiations, supply chain issues, and credentialing, as well as recruiting, hiring, and marketing.
These management organizations, which include American Oncology Network, Integrated Oncology Network, OneOncology, and Verdi Oncology, are, however, backed by private equity. According to a 2022 report, private equity–backed management organizations have ramped up arrangements with community oncology practices over the past few years — a trend that has concerned some experts.
The authors of a recent analysis in JAMA Internal Medicine explained that, although private equity involvement in physician practices may enable operational efficiencies, “critics point to potential conflicts of interest” and highlight concerns that patients “may face additional barriers to both accessibility and affordability of care.”
The difference, according to some oncologists, is their practices are not owned by the management services organization; instead, the practices enter contracts that outline the boundaries of the relationship and stipulate fees to the management organizations.
In 2020, Dr. Chasky’s practice, Alliance Cancer Specialists, joined The US Oncology Network, a management services organization wholly owned by McKesson. The organization provides the practice with capital and other resources, as well as access to the Sarah Cannon Research Institute, so patients can participate in clinical trials.
“We totally function as an independent practice,” said Dr. Chasky. “We make our own management decisions,” he said. For instance, if Alliance wants to hire a new clinician, US Oncology helps with the recruitment. “But at the end of the day, it’s our practice,” he said.
Davey Daniel, MD — whose community practice joined the management services organization OneOncology — has seen the benefits of being part of a larger network. For instance, bispecific therapies for leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma are typically administered at academic centers because of the risk for cytokine release syndrome.
However, physician leaders in the OneOncology network “came up with a playbook on how to do it safely” in the community setting, said Dr. Daniel. “It meant that we were adopting FDA newly approved therapies in a very short course.”
Being able to draw from a wider pool of expertise has had other advantages. Dr. Daniel can lean on pathologists and research scientists in the network for advice on targeted therapy use. “We’re actually bringing precision medicine expertise to the community,” Dr. Daniel said.
Dr. Chasky and Dr. Eagle, whose practice is also part of OneOncology, said that continuing to work in the community setting has allowed them greater flexibility.
Dr. Eagle explained that New York Cancer & Blood Specialists tries to offer patients an appointment within 2 days of a referral, and it allows walk-in visits.
Dr. Chasky leans into the flexibility by having staff stay late, when needed, to ensure that all patients are seen. “We’re there for our patients at all hours,” Dr. Chasky said, adding that often “you don’t have that flexibility when you work for a big hospital system.”
The bottom line is community oncology can still thrive, said Nick Ferreyros, managing director of COA, “as long as we have a healthy competitive ecosystem where [we] are valued and seen as an important part of our cancer care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When he completed his fellowship at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, Moshe Chasky, MD, joined a small five-person practice that rented space from the city’s Jefferson Hospital in Philadelphia. The arrangement seemed to work well for the hospital and the small practice, which remained independent.
Within 10 years, the hospital sought to buy the practice, Alliance Cancer Specialists.
But the oncologists at Alliance did not want to join Jefferson.
The hospital eventually entered into an exclusive agreement with its own medical group to provide inpatient oncology/hematology services at three Jefferson Health–Northeast hospitals and stripped Dr. Chasky and his colleagues of their privileges at those facilities, Medscape Medical News reported last year.
said Jeff Patton, MD, CEO of OneOncology, a management services organization.
A 2020 report from the Community Oncology Alliance (COA), for instance, tracked mergers, acquisitions, and closures in the community oncology setting and found the number of practices acquired by hospitals, known as vertical integration, nearly tripled from 2010 to 2020.
“Some hospitals are pretty predatory in their approach,” Dr. Patton said. If hospitals have their own oncology program, “they’ll employ the referring doctors and then discourage them or prevent them from referring patients to our independent practices that are not owned by the hospital.”
Still, in the face of growing pressure to join hospitals, some community oncology practices are finding ways to survive and maintain their independence.
A Growing Trend
The latest data continue to show a clear trend: Consolidation in oncology is on the rise.
A 2024 study revealed that the pace of consolidation seems to be increasing.
The analysis found that, between 2015 and 2022, the number of medical oncologists increased by 14% and the number of medical oncologists per practice increased by 40%, while the number of practices decreased by 18%.
While about 44% of practices remain independent, the percentage of medical oncologists working in practices with more than 25 clinicians has increased from 34% in 2015 to 44% in 2022. By 2022, the largest 102 practices in the United States employed more than 40% of all medical oncologists.
“The rate of consolidation seems to be rapid,” study coauthor Parsa Erfani, MD, an internal medicine resident at Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, explained.
Consolidation appears to breed more consolidation. The researchers found, for instance, that markets with greater hospital consolidation and more hospital beds per capita were more likely to undergo consolidation in oncology.
Consolidation may be higher in these markets “because hospitals or health systems are buying up oncology practices or conversely because oncology practices are merging to compete more effectively with larger hospitals in the area,” Dr. Erfani told this news organization.
Mergers among independent practices, known as horizontal integration, have also been on the rise, according to the 2020 COA report. These mergers can help counter pressures from hospitals seeking to acquire community practices as well as prevent practices and their clinics from closing.
Although Dr. Erfani’s research wasn’t designed to determine the factors behind consolidation, he and his colleagues point to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the federal 340B Drug Pricing Program as potential drivers of this trend.
The ACA encouraged consolidation as a way to improve efficiency and created the need for ever-larger information systems to collect and report quality data. But these data collection and reporting requirements have become increasingly difficult for smaller practices to take on.
The 340B Program, however, may be a bigger contributing factor to consolidation. Created in 1992, the 340B Program allows qualifying hospitals and clinics that treat low-income and uninsured patients to buy outpatient prescription drugs at a 25%-50% discount.
Hospitals seeking to capitalize on the margins possible under the 340B Program will “buy all the referring physicians in a market so that the medical oncology group is left with little choice but to sell to the hospital,” said Dr. Patton.
“Those 340B dollars are worth a lot to hospitals,” said David A. Eagle, MD, a hematologist/oncologist with New York Cancer & Blood Specialists and past president of COA. The program “creates an appetite for nonprofit hospitals to want to grow their medical oncology programs,” he told this news organization.
Declining Medicare reimbursement has also hit independent practices hard.
Over the past 15 years, compared with inflation, physicians have gotten “a pay rate decrease from Medicare,” said Dr. Patton. Payers have followed that lead and tried to cut pay for clinicians, especially those who do not have market share, he said. Paying them less is “disingenuous knowing that our costs of providing care are going up,” he said.
Less Access, Higher Costs, Worse Care?
Many studies have demonstrated that, when hospitals become behemoths in a given market, healthcare costs go up.
“There are robust data showing that consolidation increases healthcare costs by reducing competition, including in oncology,” wrote Dr. Erfani and colleagues.
Oncology practices that are owned by hospitals bill facility fees for outpatient chemotherapy treatment, adding another layer of cost, the researchers explained, citing a 2019 Health Economics study.
Another analysis, published in 2020, found that hospital prices for the top 37 infused cancer drugs averaged 86% more per unit than the price charged by physician offices. Hospital outpatient departments charged even more, on average, for drugs — 128% more for nivolumab and 428% more for fluorouracil, for instance.
In their 2024 analysis, Dr. Erfani and colleagues also found that increased hospital market concentration was associated with worse quality of care, across all assessed patient satisfaction measures, and may result in worse access to care as well.
Overall, these consolidation “trends have important implications for cancer care cost, quality, and access,” the authors concluded.
Navigating the Consolidation Trend
In the face of mounting pressure to join hospitals, community oncology practices have typically relied on horizontal mergers to maintain their independence. An increasing number of practices, however, are now turning to another strategy: Management services organizations.
According to some oncologists, a core benefit of joining a management services organization is their community practices can maintain autonomy, hold on to referrals, and benefit from access to a wider network of peers and recently approved treatments such as chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies.
In these arrangements, the management company also provides business assistance to practices, including help with billing and collection, payer negotiations, supply chain issues, and credentialing, as well as recruiting, hiring, and marketing.
These management organizations, which include American Oncology Network, Integrated Oncology Network, OneOncology, and Verdi Oncology, are, however, backed by private equity. According to a 2022 report, private equity–backed management organizations have ramped up arrangements with community oncology practices over the past few years — a trend that has concerned some experts.
The authors of a recent analysis in JAMA Internal Medicine explained that, although private equity involvement in physician practices may enable operational efficiencies, “critics point to potential conflicts of interest” and highlight concerns that patients “may face additional barriers to both accessibility and affordability of care.”
The difference, according to some oncologists, is their practices are not owned by the management services organization; instead, the practices enter contracts that outline the boundaries of the relationship and stipulate fees to the management organizations.
In 2020, Dr. Chasky’s practice, Alliance Cancer Specialists, joined The US Oncology Network, a management services organization wholly owned by McKesson. The organization provides the practice with capital and other resources, as well as access to the Sarah Cannon Research Institute, so patients can participate in clinical trials.
“We totally function as an independent practice,” said Dr. Chasky. “We make our own management decisions,” he said. For instance, if Alliance wants to hire a new clinician, US Oncology helps with the recruitment. “But at the end of the day, it’s our practice,” he said.
Davey Daniel, MD — whose community practice joined the management services organization OneOncology — has seen the benefits of being part of a larger network. For instance, bispecific therapies for leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma are typically administered at academic centers because of the risk for cytokine release syndrome.
However, physician leaders in the OneOncology network “came up with a playbook on how to do it safely” in the community setting, said Dr. Daniel. “It meant that we were adopting FDA newly approved therapies in a very short course.”
Being able to draw from a wider pool of expertise has had other advantages. Dr. Daniel can lean on pathologists and research scientists in the network for advice on targeted therapy use. “We’re actually bringing precision medicine expertise to the community,” Dr. Daniel said.
Dr. Chasky and Dr. Eagle, whose practice is also part of OneOncology, said that continuing to work in the community setting has allowed them greater flexibility.
Dr. Eagle explained that New York Cancer & Blood Specialists tries to offer patients an appointment within 2 days of a referral, and it allows walk-in visits.
Dr. Chasky leans into the flexibility by having staff stay late, when needed, to ensure that all patients are seen. “We’re there for our patients at all hours,” Dr. Chasky said, adding that often “you don’t have that flexibility when you work for a big hospital system.”
The bottom line is community oncology can still thrive, said Nick Ferreyros, managing director of COA, “as long as we have a healthy competitive ecosystem where [we] are valued and seen as an important part of our cancer care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicare Advantage Plans Not Always Advantageous
While Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are marketed as providing more generous benefits than traditional Medicare (TM), differences in the financial burden between beneficiaries switching to MA and staying with TM, are minimal, a longitudinal cohort analysis found.
In fact, according to a study by Sungchul Park, PhD, a health economist at Korea University in Seoul, and colleagues, the estimated annual out-of-pocket spending when switching to MA was $168 higher than staying in TM. That amounted to a 10.5% relative increase based on baseline out-of-pocket spending of $1597 annually among switchers, ranging widely, however, from a $133 decrease to a $469 increase. And for some, MA enrollment was associated with a higher likelihood of catastrophic financial burden.
“Our findings contrast with the notion that MA’s apparently more generous health insurance benefits lead to financial savings for enrollees,” Dr. Park and associates wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The study
The analysis looked at costs for 7054 TM stayers and 1544 TM-to-MA switchers from the 2014-2020 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, focusing on a cohort in which 18% of TM-covered individuals in year 1 switched to MA in year 2.
Comparative financial outcome measures included individual healthcare costs (out-of-pocket spending/cost sharing), financial burden (high/catastrophic), and subjective financial hardship (difficulty paying medical bills).
Although the overall out-of-pocket differences for MA were minimal and amounted to less than 1% of total healthcare expenses, MA was associated with a greater financial burden in vulnerable, especially in low-income populations. For every 100 beneficiaries with family incomes below 200% of the federal poverty level, one to six more switchers faced a catastrophic financial burden, with their out-of-pocket costs consuming more than 40% of household income in the year after switching.
The gap between the perception of lower costs and reality may be caused by a substantially heavier cost-sharing burden for certain services in MA plans, Dr. Park and associates pointed out. While MA enrollees generally paid less in some studies than the Part A hospital deductible for TM for inpatient stays of 3 days, they were more likely to face higher cost sharing for stays exceeding 7 days
Furthermore, whereas TM covers home health services without cost sharing, some MA plans have copayments. In addition, out-of-network health services can cost more. MA enrollees paid an average of $9 more for mental health services than for other in-network services and often encountered limited access to in-network providers. According to a 2021 study, only 18.2% of mental health professionals, 34.4% of cardiologists, 50.0% of psychiatrists, and 57.9% of primary care providers were included in MA networks,
An accompanying editorial noted that private MA plans will reap $83 billion in overpayments from U.S. taxpayers this year, according to Congress’s Medicare Payment Advisory Commission.
And as the data from Dr. Park and colleagues reveal, switchers don’t get much financial protection, according to primary care physician and healthcare researcher Steffi J. Woolhandler, MD, MPH, and internist David U. Himmelstein, MD, both of City University of New York at Hunter College in New York City.
“Medicare Advantage looks good when you’re healthy and don’t need much care. But when you need coverage, it often fails, leaving you with big bills and narrow choices for care,” Dr. Woolhandler said in an interview.
So how do these findings square with insurers’ hard-sell claims and enrollees’ perceptions that MA cuts out-of-pocket costs? “The likeliest explanation is that MA insurers have structured their benefits to advantage low-cost (that is, profitable) enrollees and disadvantage those requiring expensive care,” the editorial commentators wrote. For beneficiaries on inexpensive medications, MA plans would be a financial win. “But for patients requiring expensive chemotherapies, the 20% coinsurance that most MA plans charge could be financially ruinous.”
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, David A. Lipschutz, JD, LLB, associate director of the Center for Medicare Advocacy in Washington, DC, called the study an important one that provides more evidence that significant overpayments to MA plans don’t translate to better financial protections for plan enrollees, particularly lower-income individuals. “While there has been some recent movement to hold plans more accountable for providing necessary care, much more impactful action by policymakers is required to mitigate the harms of the growing privatization of the Medicare program,” he said. “MA overpayments could be redistributed to traditional Medicare in order to enrich all Medicare beneficiaries instead of just insurance companies.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea. Dr. Park disclosed no competing interests. One study coauthor reported support from government and not-for-profit research-funding bodies. Editorialists Dr. Woolhandler and Dr. Himmelstein had no competing interests to declare. Dr. Lipschutz disclosed Medicare advocacy work.
While Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are marketed as providing more generous benefits than traditional Medicare (TM), differences in the financial burden between beneficiaries switching to MA and staying with TM, are minimal, a longitudinal cohort analysis found.
In fact, according to a study by Sungchul Park, PhD, a health economist at Korea University in Seoul, and colleagues, the estimated annual out-of-pocket spending when switching to MA was $168 higher than staying in TM. That amounted to a 10.5% relative increase based on baseline out-of-pocket spending of $1597 annually among switchers, ranging widely, however, from a $133 decrease to a $469 increase. And for some, MA enrollment was associated with a higher likelihood of catastrophic financial burden.
“Our findings contrast with the notion that MA’s apparently more generous health insurance benefits lead to financial savings for enrollees,” Dr. Park and associates wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The study
The analysis looked at costs for 7054 TM stayers and 1544 TM-to-MA switchers from the 2014-2020 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, focusing on a cohort in which 18% of TM-covered individuals in year 1 switched to MA in year 2.
Comparative financial outcome measures included individual healthcare costs (out-of-pocket spending/cost sharing), financial burden (high/catastrophic), and subjective financial hardship (difficulty paying medical bills).
Although the overall out-of-pocket differences for MA were minimal and amounted to less than 1% of total healthcare expenses, MA was associated with a greater financial burden in vulnerable, especially in low-income populations. For every 100 beneficiaries with family incomes below 200% of the federal poverty level, one to six more switchers faced a catastrophic financial burden, with their out-of-pocket costs consuming more than 40% of household income in the year after switching.
The gap between the perception of lower costs and reality may be caused by a substantially heavier cost-sharing burden for certain services in MA plans, Dr. Park and associates pointed out. While MA enrollees generally paid less in some studies than the Part A hospital deductible for TM for inpatient stays of 3 days, they were more likely to face higher cost sharing for stays exceeding 7 days
Furthermore, whereas TM covers home health services without cost sharing, some MA plans have copayments. In addition, out-of-network health services can cost more. MA enrollees paid an average of $9 more for mental health services than for other in-network services and often encountered limited access to in-network providers. According to a 2021 study, only 18.2% of mental health professionals, 34.4% of cardiologists, 50.0% of psychiatrists, and 57.9% of primary care providers were included in MA networks,
An accompanying editorial noted that private MA plans will reap $83 billion in overpayments from U.S. taxpayers this year, according to Congress’s Medicare Payment Advisory Commission.
And as the data from Dr. Park and colleagues reveal, switchers don’t get much financial protection, according to primary care physician and healthcare researcher Steffi J. Woolhandler, MD, MPH, and internist David U. Himmelstein, MD, both of City University of New York at Hunter College in New York City.
“Medicare Advantage looks good when you’re healthy and don’t need much care. But when you need coverage, it often fails, leaving you with big bills and narrow choices for care,” Dr. Woolhandler said in an interview.
So how do these findings square with insurers’ hard-sell claims and enrollees’ perceptions that MA cuts out-of-pocket costs? “The likeliest explanation is that MA insurers have structured their benefits to advantage low-cost (that is, profitable) enrollees and disadvantage those requiring expensive care,” the editorial commentators wrote. For beneficiaries on inexpensive medications, MA plans would be a financial win. “But for patients requiring expensive chemotherapies, the 20% coinsurance that most MA plans charge could be financially ruinous.”
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, David A. Lipschutz, JD, LLB, associate director of the Center for Medicare Advocacy in Washington, DC, called the study an important one that provides more evidence that significant overpayments to MA plans don’t translate to better financial protections for plan enrollees, particularly lower-income individuals. “While there has been some recent movement to hold plans more accountable for providing necessary care, much more impactful action by policymakers is required to mitigate the harms of the growing privatization of the Medicare program,” he said. “MA overpayments could be redistributed to traditional Medicare in order to enrich all Medicare beneficiaries instead of just insurance companies.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea. Dr. Park disclosed no competing interests. One study coauthor reported support from government and not-for-profit research-funding bodies. Editorialists Dr. Woolhandler and Dr. Himmelstein had no competing interests to declare. Dr. Lipschutz disclosed Medicare advocacy work.
While Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are marketed as providing more generous benefits than traditional Medicare (TM), differences in the financial burden between beneficiaries switching to MA and staying with TM, are minimal, a longitudinal cohort analysis found.
In fact, according to a study by Sungchul Park, PhD, a health economist at Korea University in Seoul, and colleagues, the estimated annual out-of-pocket spending when switching to MA was $168 higher than staying in TM. That amounted to a 10.5% relative increase based on baseline out-of-pocket spending of $1597 annually among switchers, ranging widely, however, from a $133 decrease to a $469 increase. And for some, MA enrollment was associated with a higher likelihood of catastrophic financial burden.
“Our findings contrast with the notion that MA’s apparently more generous health insurance benefits lead to financial savings for enrollees,” Dr. Park and associates wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The study
The analysis looked at costs for 7054 TM stayers and 1544 TM-to-MA switchers from the 2014-2020 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, focusing on a cohort in which 18% of TM-covered individuals in year 1 switched to MA in year 2.
Comparative financial outcome measures included individual healthcare costs (out-of-pocket spending/cost sharing), financial burden (high/catastrophic), and subjective financial hardship (difficulty paying medical bills).
Although the overall out-of-pocket differences for MA were minimal and amounted to less than 1% of total healthcare expenses, MA was associated with a greater financial burden in vulnerable, especially in low-income populations. For every 100 beneficiaries with family incomes below 200% of the federal poverty level, one to six more switchers faced a catastrophic financial burden, with their out-of-pocket costs consuming more than 40% of household income in the year after switching.
The gap between the perception of lower costs and reality may be caused by a substantially heavier cost-sharing burden for certain services in MA plans, Dr. Park and associates pointed out. While MA enrollees generally paid less in some studies than the Part A hospital deductible for TM for inpatient stays of 3 days, they were more likely to face higher cost sharing for stays exceeding 7 days
Furthermore, whereas TM covers home health services without cost sharing, some MA plans have copayments. In addition, out-of-network health services can cost more. MA enrollees paid an average of $9 more for mental health services than for other in-network services and often encountered limited access to in-network providers. According to a 2021 study, only 18.2% of mental health professionals, 34.4% of cardiologists, 50.0% of psychiatrists, and 57.9% of primary care providers were included in MA networks,
An accompanying editorial noted that private MA plans will reap $83 billion in overpayments from U.S. taxpayers this year, according to Congress’s Medicare Payment Advisory Commission.
And as the data from Dr. Park and colleagues reveal, switchers don’t get much financial protection, according to primary care physician and healthcare researcher Steffi J. Woolhandler, MD, MPH, and internist David U. Himmelstein, MD, both of City University of New York at Hunter College in New York City.
“Medicare Advantage looks good when you’re healthy and don’t need much care. But when you need coverage, it often fails, leaving you with big bills and narrow choices for care,” Dr. Woolhandler said in an interview.
So how do these findings square with insurers’ hard-sell claims and enrollees’ perceptions that MA cuts out-of-pocket costs? “The likeliest explanation is that MA insurers have structured their benefits to advantage low-cost (that is, profitable) enrollees and disadvantage those requiring expensive care,” the editorial commentators wrote. For beneficiaries on inexpensive medications, MA plans would be a financial win. “But for patients requiring expensive chemotherapies, the 20% coinsurance that most MA plans charge could be financially ruinous.”
Commenting on the study but not involved in it, David A. Lipschutz, JD, LLB, associate director of the Center for Medicare Advocacy in Washington, DC, called the study an important one that provides more evidence that significant overpayments to MA plans don’t translate to better financial protections for plan enrollees, particularly lower-income individuals. “While there has been some recent movement to hold plans more accountable for providing necessary care, much more impactful action by policymakers is required to mitigate the harms of the growing privatization of the Medicare program,” he said. “MA overpayments could be redistributed to traditional Medicare in order to enrich all Medicare beneficiaries instead of just insurance companies.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea. Dr. Park disclosed no competing interests. One study coauthor reported support from government and not-for-profit research-funding bodies. Editorialists Dr. Woolhandler and Dr. Himmelstein had no competing interests to declare. Dr. Lipschutz disclosed Medicare advocacy work.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
US Hospitals Prone to Cyberattacks Like One That Impacted Patient Care at Ascension, Experts Say
In the wake of a debilitating cyberattack against one of the nation’s largest health care systems, Marvin Ruckle, a nurse at an Ascension hospital in Wichita, Kansas, said he had a frightening experience: He nearly gave a baby “the wrong dose of narcotic” because of confusing paperwork.
A May 8 ransomware attack against Ascension, a Catholic health system with 140 hospitals in at least 10 states, locked providers out of systems that track and coordinate nearly every aspect of patient care. They include its systems for electronic health records, some phones, and ones “utilized to order certain tests, procedures and medications,” the company said in a May 9 statement.
More than a dozen doctors and nurses who work for the sprawling health system told Michigan Public and KFF Health News that patient care at its hospitals across the nation was compromised in the fallout of the cyberattack over the past several weeks. Clinicians working for hospitals in three states described harrowing lapses, including delayed or lost lab results, medication errors, and an absence of routine safety checks via technology to prevent potentially fatal mistakes.
Despite a precipitous rise in cyberattacks against the health sector in recent years, a weeks-long disruption of this magnitude is beyond what most health systems are prepared for, said John S. Clark, an associate chief pharmacy officer at the University of Michigan health system.
“I don’t believe that anyone is fully prepared,” he said. Most emergency management plans “are designed around long-term downtimes that are into one, two, or three days.”
Ascension in a public statement May 9 said its care teams were “trained for these kinds of disruptions,” but did not respond to questions in early June about whether it had prepared for longer periods of downtime. Ascension said June 14 it had restored access to electronic health records across its network, but that patient “medical records and other information collected between May 8” and when the service was restored “may be temporarily inaccessible as we work to update the portal with information collected during the system downtime.”
Ruckle said he “had no training” for the cyberattack.
Back to Paper
Lisa Watson, an intensive care unit nurse at Ascension Via Christi St. Francis hospital in Wichita, described her own close call. She said she nearly administered the wrong medication to a critically ill patient because she couldn’t scan it as she normally would. “My patient probably would have passed away had I not caught it,” she said.
Watson is no stranger to using paper for patients’ medical charts, saying she did so “for probably half of my career,” before electronic health records became ubiquitous in hospitals. What happened after the cyberattack was “by no means the same.”
“When we paper-charted, we had systems in place to get those orders to other departments in a timely manner,” she said, “and those have all gone away.”
Melissa LaRue, an ICU nurse at Ascension Saint Agnes Hospital in Baltimore, described a close call with “administering the wrong dosage” of a patient’s blood pressure medication. “Luckily,” she said, it was “triple-checked and remedied before that could happen. But I think the potential for harm is there when you have so much information and paperwork that you have to go through.”
Clinicians say their hospitals have relied on slapdash workarounds, using handwritten notes, faxes, sticky notes, and basic computer spreadsheets — many devised on the fly by doctors and nurses — to care for patients.
More than a dozen other nurses and doctors, some of them without union protections, at Ascension hospitals in Michigan recounted situations in which they say patient care was compromised. Those clinicians spoke on the condition that they not be named for fear of retaliation by their employer.
An Ascension hospital emergency room doctor in Detroit said a man on the city’s east side was given a dangerous narcotic intended for another patient because of a paperwork mix-up. As a result, the patient’s breathing slowed to the point that he had to be put on a ventilator. “We intubated him and we sent him to the ICU because he got the wrong medication.”
A nurse in a Michigan Ascension hospital ER said a woman with low blood sugar and “altered mental status” went into cardiac arrest and died after staff said they waited four hours for lab results they needed to determine how to treat her, but never received. “If I started having crushing chest pain in the middle of work and thought I was having a big one, I would grab someone to drive me down the street to another hospital,” the same ER nurse said.
Similar concerns reportedly led a travel nurse at an Ascension hospital in Indiana to quit. “I just want to warn those patients that are coming to any of the Ascension facilities that there will be delays in care. There is potential for error and for harm,” Justin Neisser told CBS4 in Indianapolis in May.
Several nurses and doctors at Ascension hospitals said they feared the errors they’ve witnessed since the cyberattack began could threaten their professional licenses. “This is how a RaDonda Vaught happens,” one nurse said, referring to the Tennessee nurse who was convicted of criminally negligent homicide in 2022 for a fatal drug error.
Reporters were not able to review records to verify clinicians’ claims because of privacy laws surrounding patients’ medical information that apply to health care professionals.
Ascension declined to answer questions about claims that care has been affected by the ransomware attack. “As we have made clear throughout this cyber attack which has impacted our system and our dedicated clinical providers, caring for our patients is our highest priority,” Sean Fitzpatrick, Ascension’s vice president of external communications, said via email on June 3. “We are confident that our care providers in our hospitals and facilities continue to provide quality medical care.”
The federal government requires hospitals to protect patients’ sensitive health data, according to cybersecurity experts. However, there are no federal requirements for hospitals to prevent or prepare for cyberattacks that could compromise their electronic systems.
Hospitals: ‘The No.1 Target of Ransomware’
“We’ve started to think about these as public health issues and disasters on the scale of earthquakes or hurricanes,” said Jeff Tully, a co-director of the Center for Healthcare Cybersecurity at the University of California-San Diego. “These types of cybersecurity incidents should be thought of as a matter of when, and not if.”
Josh Corman, a cybersecurity expert and advocate, said ransom crews regard hospitals as the perfect prey: “They have terrible security and they’ll pay. So almost immediately, hospitals went to the No. 1 target of ransomware.”
In 2023, the health sector experienced the largest share of ransomware attacks of 16 infrastructure sectors considered vital to national security or safety, according to an FBI report on internet crimes. In March, the federal Department of Health and Human Services said reported large breaches involving ransomware had jumped by 264% over the past five years.
A cyberattack this year on Change Healthcare, a unit of UnitedHealth Group’s Optum division that processes billions of health care transactions every year, crippled the business of providers, pharmacies, and hospitals.
In May, UnitedHealth Group CEO Andrew Witty told lawmakers the company paid a $22 million ransom as a result of the Change Healthcare attack — which occurred after hackers accessed a company portal that didn’t have multifactor authentication, a basic cybersecurity tool.
The Biden administration in recent months has pushed to bolster health care cybersecurity standards, but it’s not clear which new measures will be required.
In January, HHS nudged companies to improve email security, add multifactor authentication, and institute cybersecurity training and testing, among other voluntary measures. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is expected to release new requirements for hospitals, but the scope and timing are unclear. The same is true of an update HHS is expected to make to patient privacy regulations.
HHS said the voluntary measures “will inform the creation of new enforceable cybersecurity standards,” department spokesperson Jeff Nesbit said in a statement.
“The recent cyberattack at Ascension only underscores the need for everyone in the health care ecosystem to do their part to secure their systems and protect patients,” Nesbit said.
Meanwhile, lobbyists for the hospital industry contend cybersecurity mandates or penalties are misplaced and would curtail hospitals’ resources to fend off attacks.
“Hospitals and health systems are not the primary source of cyber risk exposure facing the health care sector,” the American Hospital Association, the largest lobbying group for U.S. hospitals, said in an April statement prepared for U.S. House lawmakers. Most large data breaches that hit hospitals in 2023 originated with third-party “business associates” or other health entities, including CMS itself, the AHA statement said.
Hospitals consolidating into large multistate health systems face increased risk of data breaches and ransomware attacks, according to one study. Ascension in 2022 was the third-largest hospital chain in the U.S. by number of beds, according to the most recent data from the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
And while cybersecurity regulations can quickly become outdated, they can at least make it clear that if health systems fail to implement basic protections there “should be consequences for that,” Jim Bagian, a former director of the National Center for Patient Safety at the Veterans Health Administration, told Michigan Public’s Stateside.
Patients can pay the price when lapses occur. Those in hospital care face a greater likelihood of death during a cyberattack, according to researchers at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health.
Workers concerned about patient safety at Ascension hospitals in Michigan have called for the company to make changes.
“We implore Ascension to recognize the internal problems that continue to plague its hospitals, both publicly and transparently,” said Dina Carlisle, a nurse and the president of the OPEIU Local 40 union, which represents nurses at Ascension Providence Rochester. At least 125 staff members at that Ascension hospital have signed a petition asking administrators to temporarily reduce elective surgeries and nonemergency patient admissions, like under the protocols many hospitals adopted early in the covid-19 pandemic.
Watson, the Kansas ICU nurse, said in late May that nurses had urged management to bring in more nurses to help manage the workflow. “Everything that we say has fallen on deaf ears,” she said.
“It is very hard to be a nurse at Ascension right now,” Watson said in late May. “It is very hard to be a patient at Ascension right now.”
If you’re a patient or worker at an Ascension hospital and would like to tell KFF Health News about your experiences, click here to share your story with us.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
In the wake of a debilitating cyberattack against one of the nation’s largest health care systems, Marvin Ruckle, a nurse at an Ascension hospital in Wichita, Kansas, said he had a frightening experience: He nearly gave a baby “the wrong dose of narcotic” because of confusing paperwork.
A May 8 ransomware attack against Ascension, a Catholic health system with 140 hospitals in at least 10 states, locked providers out of systems that track and coordinate nearly every aspect of patient care. They include its systems for electronic health records, some phones, and ones “utilized to order certain tests, procedures and medications,” the company said in a May 9 statement.
More than a dozen doctors and nurses who work for the sprawling health system told Michigan Public and KFF Health News that patient care at its hospitals across the nation was compromised in the fallout of the cyberattack over the past several weeks. Clinicians working for hospitals in three states described harrowing lapses, including delayed or lost lab results, medication errors, and an absence of routine safety checks via technology to prevent potentially fatal mistakes.
Despite a precipitous rise in cyberattacks against the health sector in recent years, a weeks-long disruption of this magnitude is beyond what most health systems are prepared for, said John S. Clark, an associate chief pharmacy officer at the University of Michigan health system.
“I don’t believe that anyone is fully prepared,” he said. Most emergency management plans “are designed around long-term downtimes that are into one, two, or three days.”
Ascension in a public statement May 9 said its care teams were “trained for these kinds of disruptions,” but did not respond to questions in early June about whether it had prepared for longer periods of downtime. Ascension said June 14 it had restored access to electronic health records across its network, but that patient “medical records and other information collected between May 8” and when the service was restored “may be temporarily inaccessible as we work to update the portal with information collected during the system downtime.”
Ruckle said he “had no training” for the cyberattack.
Back to Paper
Lisa Watson, an intensive care unit nurse at Ascension Via Christi St. Francis hospital in Wichita, described her own close call. She said she nearly administered the wrong medication to a critically ill patient because she couldn’t scan it as she normally would. “My patient probably would have passed away had I not caught it,” she said.
Watson is no stranger to using paper for patients’ medical charts, saying she did so “for probably half of my career,” before electronic health records became ubiquitous in hospitals. What happened after the cyberattack was “by no means the same.”
“When we paper-charted, we had systems in place to get those orders to other departments in a timely manner,” she said, “and those have all gone away.”
Melissa LaRue, an ICU nurse at Ascension Saint Agnes Hospital in Baltimore, described a close call with “administering the wrong dosage” of a patient’s blood pressure medication. “Luckily,” she said, it was “triple-checked and remedied before that could happen. But I think the potential for harm is there when you have so much information and paperwork that you have to go through.”
Clinicians say their hospitals have relied on slapdash workarounds, using handwritten notes, faxes, sticky notes, and basic computer spreadsheets — many devised on the fly by doctors and nurses — to care for patients.
More than a dozen other nurses and doctors, some of them without union protections, at Ascension hospitals in Michigan recounted situations in which they say patient care was compromised. Those clinicians spoke on the condition that they not be named for fear of retaliation by their employer.
An Ascension hospital emergency room doctor in Detroit said a man on the city’s east side was given a dangerous narcotic intended for another patient because of a paperwork mix-up. As a result, the patient’s breathing slowed to the point that he had to be put on a ventilator. “We intubated him and we sent him to the ICU because he got the wrong medication.”
A nurse in a Michigan Ascension hospital ER said a woman with low blood sugar and “altered mental status” went into cardiac arrest and died after staff said they waited four hours for lab results they needed to determine how to treat her, but never received. “If I started having crushing chest pain in the middle of work and thought I was having a big one, I would grab someone to drive me down the street to another hospital,” the same ER nurse said.
Similar concerns reportedly led a travel nurse at an Ascension hospital in Indiana to quit. “I just want to warn those patients that are coming to any of the Ascension facilities that there will be delays in care. There is potential for error and for harm,” Justin Neisser told CBS4 in Indianapolis in May.
Several nurses and doctors at Ascension hospitals said they feared the errors they’ve witnessed since the cyberattack began could threaten their professional licenses. “This is how a RaDonda Vaught happens,” one nurse said, referring to the Tennessee nurse who was convicted of criminally negligent homicide in 2022 for a fatal drug error.
Reporters were not able to review records to verify clinicians’ claims because of privacy laws surrounding patients’ medical information that apply to health care professionals.
Ascension declined to answer questions about claims that care has been affected by the ransomware attack. “As we have made clear throughout this cyber attack which has impacted our system and our dedicated clinical providers, caring for our patients is our highest priority,” Sean Fitzpatrick, Ascension’s vice president of external communications, said via email on June 3. “We are confident that our care providers in our hospitals and facilities continue to provide quality medical care.”
The federal government requires hospitals to protect patients’ sensitive health data, according to cybersecurity experts. However, there are no federal requirements for hospitals to prevent or prepare for cyberattacks that could compromise their electronic systems.
Hospitals: ‘The No.1 Target of Ransomware’
“We’ve started to think about these as public health issues and disasters on the scale of earthquakes or hurricanes,” said Jeff Tully, a co-director of the Center for Healthcare Cybersecurity at the University of California-San Diego. “These types of cybersecurity incidents should be thought of as a matter of when, and not if.”
Josh Corman, a cybersecurity expert and advocate, said ransom crews regard hospitals as the perfect prey: “They have terrible security and they’ll pay. So almost immediately, hospitals went to the No. 1 target of ransomware.”
In 2023, the health sector experienced the largest share of ransomware attacks of 16 infrastructure sectors considered vital to national security or safety, according to an FBI report on internet crimes. In March, the federal Department of Health and Human Services said reported large breaches involving ransomware had jumped by 264% over the past five years.
A cyberattack this year on Change Healthcare, a unit of UnitedHealth Group’s Optum division that processes billions of health care transactions every year, crippled the business of providers, pharmacies, and hospitals.
In May, UnitedHealth Group CEO Andrew Witty told lawmakers the company paid a $22 million ransom as a result of the Change Healthcare attack — which occurred after hackers accessed a company portal that didn’t have multifactor authentication, a basic cybersecurity tool.
The Biden administration in recent months has pushed to bolster health care cybersecurity standards, but it’s not clear which new measures will be required.
In January, HHS nudged companies to improve email security, add multifactor authentication, and institute cybersecurity training and testing, among other voluntary measures. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is expected to release new requirements for hospitals, but the scope and timing are unclear. The same is true of an update HHS is expected to make to patient privacy regulations.
HHS said the voluntary measures “will inform the creation of new enforceable cybersecurity standards,” department spokesperson Jeff Nesbit said in a statement.
“The recent cyberattack at Ascension only underscores the need for everyone in the health care ecosystem to do their part to secure their systems and protect patients,” Nesbit said.
Meanwhile, lobbyists for the hospital industry contend cybersecurity mandates or penalties are misplaced and would curtail hospitals’ resources to fend off attacks.
“Hospitals and health systems are not the primary source of cyber risk exposure facing the health care sector,” the American Hospital Association, the largest lobbying group for U.S. hospitals, said in an April statement prepared for U.S. House lawmakers. Most large data breaches that hit hospitals in 2023 originated with third-party “business associates” or other health entities, including CMS itself, the AHA statement said.
Hospitals consolidating into large multistate health systems face increased risk of data breaches and ransomware attacks, according to one study. Ascension in 2022 was the third-largest hospital chain in the U.S. by number of beds, according to the most recent data from the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
And while cybersecurity regulations can quickly become outdated, they can at least make it clear that if health systems fail to implement basic protections there “should be consequences for that,” Jim Bagian, a former director of the National Center for Patient Safety at the Veterans Health Administration, told Michigan Public’s Stateside.
Patients can pay the price when lapses occur. Those in hospital care face a greater likelihood of death during a cyberattack, according to researchers at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health.
Workers concerned about patient safety at Ascension hospitals in Michigan have called for the company to make changes.
“We implore Ascension to recognize the internal problems that continue to plague its hospitals, both publicly and transparently,” said Dina Carlisle, a nurse and the president of the OPEIU Local 40 union, which represents nurses at Ascension Providence Rochester. At least 125 staff members at that Ascension hospital have signed a petition asking administrators to temporarily reduce elective surgeries and nonemergency patient admissions, like under the protocols many hospitals adopted early in the covid-19 pandemic.
Watson, the Kansas ICU nurse, said in late May that nurses had urged management to bring in more nurses to help manage the workflow. “Everything that we say has fallen on deaf ears,” she said.
“It is very hard to be a nurse at Ascension right now,” Watson said in late May. “It is very hard to be a patient at Ascension right now.”
If you’re a patient or worker at an Ascension hospital and would like to tell KFF Health News about your experiences, click here to share your story with us.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
In the wake of a debilitating cyberattack against one of the nation’s largest health care systems, Marvin Ruckle, a nurse at an Ascension hospital in Wichita, Kansas, said he had a frightening experience: He nearly gave a baby “the wrong dose of narcotic” because of confusing paperwork.
A May 8 ransomware attack against Ascension, a Catholic health system with 140 hospitals in at least 10 states, locked providers out of systems that track and coordinate nearly every aspect of patient care. They include its systems for electronic health records, some phones, and ones “utilized to order certain tests, procedures and medications,” the company said in a May 9 statement.
More than a dozen doctors and nurses who work for the sprawling health system told Michigan Public and KFF Health News that patient care at its hospitals across the nation was compromised in the fallout of the cyberattack over the past several weeks. Clinicians working for hospitals in three states described harrowing lapses, including delayed or lost lab results, medication errors, and an absence of routine safety checks via technology to prevent potentially fatal mistakes.
Despite a precipitous rise in cyberattacks against the health sector in recent years, a weeks-long disruption of this magnitude is beyond what most health systems are prepared for, said John S. Clark, an associate chief pharmacy officer at the University of Michigan health system.
“I don’t believe that anyone is fully prepared,” he said. Most emergency management plans “are designed around long-term downtimes that are into one, two, or three days.”
Ascension in a public statement May 9 said its care teams were “trained for these kinds of disruptions,” but did not respond to questions in early June about whether it had prepared for longer periods of downtime. Ascension said June 14 it had restored access to electronic health records across its network, but that patient “medical records and other information collected between May 8” and when the service was restored “may be temporarily inaccessible as we work to update the portal with information collected during the system downtime.”
Ruckle said he “had no training” for the cyberattack.
Back to Paper
Lisa Watson, an intensive care unit nurse at Ascension Via Christi St. Francis hospital in Wichita, described her own close call. She said she nearly administered the wrong medication to a critically ill patient because she couldn’t scan it as she normally would. “My patient probably would have passed away had I not caught it,” she said.
Watson is no stranger to using paper for patients’ medical charts, saying she did so “for probably half of my career,” before electronic health records became ubiquitous in hospitals. What happened after the cyberattack was “by no means the same.”
“When we paper-charted, we had systems in place to get those orders to other departments in a timely manner,” she said, “and those have all gone away.”
Melissa LaRue, an ICU nurse at Ascension Saint Agnes Hospital in Baltimore, described a close call with “administering the wrong dosage” of a patient’s blood pressure medication. “Luckily,” she said, it was “triple-checked and remedied before that could happen. But I think the potential for harm is there when you have so much information and paperwork that you have to go through.”
Clinicians say their hospitals have relied on slapdash workarounds, using handwritten notes, faxes, sticky notes, and basic computer spreadsheets — many devised on the fly by doctors and nurses — to care for patients.
More than a dozen other nurses and doctors, some of them without union protections, at Ascension hospitals in Michigan recounted situations in which they say patient care was compromised. Those clinicians spoke on the condition that they not be named for fear of retaliation by their employer.
An Ascension hospital emergency room doctor in Detroit said a man on the city’s east side was given a dangerous narcotic intended for another patient because of a paperwork mix-up. As a result, the patient’s breathing slowed to the point that he had to be put on a ventilator. “We intubated him and we sent him to the ICU because he got the wrong medication.”
A nurse in a Michigan Ascension hospital ER said a woman with low blood sugar and “altered mental status” went into cardiac arrest and died after staff said they waited four hours for lab results they needed to determine how to treat her, but never received. “If I started having crushing chest pain in the middle of work and thought I was having a big one, I would grab someone to drive me down the street to another hospital,” the same ER nurse said.
Similar concerns reportedly led a travel nurse at an Ascension hospital in Indiana to quit. “I just want to warn those patients that are coming to any of the Ascension facilities that there will be delays in care. There is potential for error and for harm,” Justin Neisser told CBS4 in Indianapolis in May.
Several nurses and doctors at Ascension hospitals said they feared the errors they’ve witnessed since the cyberattack began could threaten their professional licenses. “This is how a RaDonda Vaught happens,” one nurse said, referring to the Tennessee nurse who was convicted of criminally negligent homicide in 2022 for a fatal drug error.
Reporters were not able to review records to verify clinicians’ claims because of privacy laws surrounding patients’ medical information that apply to health care professionals.
Ascension declined to answer questions about claims that care has been affected by the ransomware attack. “As we have made clear throughout this cyber attack which has impacted our system and our dedicated clinical providers, caring for our patients is our highest priority,” Sean Fitzpatrick, Ascension’s vice president of external communications, said via email on June 3. “We are confident that our care providers in our hospitals and facilities continue to provide quality medical care.”
The federal government requires hospitals to protect patients’ sensitive health data, according to cybersecurity experts. However, there are no federal requirements for hospitals to prevent or prepare for cyberattacks that could compromise their electronic systems.
Hospitals: ‘The No.1 Target of Ransomware’
“We’ve started to think about these as public health issues and disasters on the scale of earthquakes or hurricanes,” said Jeff Tully, a co-director of the Center for Healthcare Cybersecurity at the University of California-San Diego. “These types of cybersecurity incidents should be thought of as a matter of when, and not if.”
Josh Corman, a cybersecurity expert and advocate, said ransom crews regard hospitals as the perfect prey: “They have terrible security and they’ll pay. So almost immediately, hospitals went to the No. 1 target of ransomware.”
In 2023, the health sector experienced the largest share of ransomware attacks of 16 infrastructure sectors considered vital to national security or safety, according to an FBI report on internet crimes. In March, the federal Department of Health and Human Services said reported large breaches involving ransomware had jumped by 264% over the past five years.
A cyberattack this year on Change Healthcare, a unit of UnitedHealth Group’s Optum division that processes billions of health care transactions every year, crippled the business of providers, pharmacies, and hospitals.
In May, UnitedHealth Group CEO Andrew Witty told lawmakers the company paid a $22 million ransom as a result of the Change Healthcare attack — which occurred after hackers accessed a company portal that didn’t have multifactor authentication, a basic cybersecurity tool.
The Biden administration in recent months has pushed to bolster health care cybersecurity standards, but it’s not clear which new measures will be required.
In January, HHS nudged companies to improve email security, add multifactor authentication, and institute cybersecurity training and testing, among other voluntary measures. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is expected to release new requirements for hospitals, but the scope and timing are unclear. The same is true of an update HHS is expected to make to patient privacy regulations.
HHS said the voluntary measures “will inform the creation of new enforceable cybersecurity standards,” department spokesperson Jeff Nesbit said in a statement.
“The recent cyberattack at Ascension only underscores the need for everyone in the health care ecosystem to do their part to secure their systems and protect patients,” Nesbit said.
Meanwhile, lobbyists for the hospital industry contend cybersecurity mandates or penalties are misplaced and would curtail hospitals’ resources to fend off attacks.
“Hospitals and health systems are not the primary source of cyber risk exposure facing the health care sector,” the American Hospital Association, the largest lobbying group for U.S. hospitals, said in an April statement prepared for U.S. House lawmakers. Most large data breaches that hit hospitals in 2023 originated with third-party “business associates” or other health entities, including CMS itself, the AHA statement said.
Hospitals consolidating into large multistate health systems face increased risk of data breaches and ransomware attacks, according to one study. Ascension in 2022 was the third-largest hospital chain in the U.S. by number of beds, according to the most recent data from the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
And while cybersecurity regulations can quickly become outdated, they can at least make it clear that if health systems fail to implement basic protections there “should be consequences for that,” Jim Bagian, a former director of the National Center for Patient Safety at the Veterans Health Administration, told Michigan Public’s Stateside.
Patients can pay the price when lapses occur. Those in hospital care face a greater likelihood of death during a cyberattack, according to researchers at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health.
Workers concerned about patient safety at Ascension hospitals in Michigan have called for the company to make changes.
“We implore Ascension to recognize the internal problems that continue to plague its hospitals, both publicly and transparently,” said Dina Carlisle, a nurse and the president of the OPEIU Local 40 union, which represents nurses at Ascension Providence Rochester. At least 125 staff members at that Ascension hospital have signed a petition asking administrators to temporarily reduce elective surgeries and nonemergency patient admissions, like under the protocols many hospitals adopted early in the covid-19 pandemic.
Watson, the Kansas ICU nurse, said in late May that nurses had urged management to bring in more nurses to help manage the workflow. “Everything that we say has fallen on deaf ears,” she said.
“It is very hard to be a nurse at Ascension right now,” Watson said in late May. “It is very hard to be a patient at Ascension right now.”
If you’re a patient or worker at an Ascension hospital and would like to tell KFF Health News about your experiences, click here to share your story with us.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Doctors Endorsing Products on X May Not Disclose Company Ties
Lead author Aaron Mitchell, MD, MPH, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, told this news organization that he and his colleagues undertook the study in part to see whether physicians were adhering to professional and industry guidelines regarding marketing communications.
The team reviewed posts by physicians on X during 2022, looking for key words that might indicate that the posts were intended as endorsements of a product. The researchers then delved into the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments database to see how many of those identified as having endorsed a product were paid by the manufacturers.
What Dr. Mitchell found concerned him, he said.
Overall, the researchers identified 28 physician endorsers who received a total of $1.4 million from sponsors in 2022. Among these, 26 physicians (93%) received payments from the product’s manufacturer, totaling $713,976, and 24 physicians (86%) accepted payments related to the endorsed drug or device, totaling $492,098.
While most did disclose that the posts were sponsored — by adding the word “sponsored” or using #sponsored — nine physicians did not.
Although 28 physician endorsers represent a “small fraction” of the overall number of physicians who use X, each endorsement was ultimately posted dozens, if not hundreds of times, said Dr. Mitchell. In fact, he said he saw the same particular endorsement post every time he opened his X app for months.
Overall, Dr. Mitchell noted that it’s less about the fact that the endorsements are occurring on social media and more that there are these paid endorsements taking place at all.
Among the physician specialties promoting a product, urologists and oncologists dominated. Almost one third were urologists, and 57% were oncologists — six medical oncologists, six radiation oncologists, and four gynecologic oncologists. Of the remaining three physicians, two were internists and one was a pulmonary and critical care medicine specialist.
The authors tracked posts from physicians and industry accounts. Many of the posts on industry accounts were physician testimonials, usually videos. Almost half — 8 of 17 — of those testimonials did not disclose that the doctor was being paid by the manufacturer. In another case, a physician did not disclose that they were paid to endorse a white paper.
Fifteen promotional posts were for a Boston Scientific product, followed by six for GlaxoSmithKline, two for Eisai, two for Exelixis, and one each for AstraZeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer.
In general, Dr. Mitchell said, industry guidelines suggest that manufacturer-paid speakers or consultants should have well-regarded expertise in the area they are being asked to weigh in on, but most physician endorsers in the study were not key opinion leaders or experts.
The authors examined the paid endorsers’ H-index — a measure of academic productivity provided by Scopus. Overall, 19 of the 28 physicians had an H-index below 20, which is considered less accomplished, and 14 had no published research related to the endorsed product.
Ten received payments from manufacturers for research purposes, and only one received research payments related to the endorsed product ($224,577).
“Physicians’ participation in industry marketing raises questions regarding professionalism and their responsibilities as patient advocates,” the JAMA authors wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Coauthors Samer Al Hadidi, MD, reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer, Sanofi, and Janssen during the conduct of the study, and Timothy S. Anderson, MD, reported receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging, the American Heart Association, and the American College of Cardiology, and receiving consulting fees from the American Medical Student Association. Dr. Anderson is also an associate editor of JAMA Internal Medicine.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lead author Aaron Mitchell, MD, MPH, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, told this news organization that he and his colleagues undertook the study in part to see whether physicians were adhering to professional and industry guidelines regarding marketing communications.
The team reviewed posts by physicians on X during 2022, looking for key words that might indicate that the posts were intended as endorsements of a product. The researchers then delved into the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments database to see how many of those identified as having endorsed a product were paid by the manufacturers.
What Dr. Mitchell found concerned him, he said.
Overall, the researchers identified 28 physician endorsers who received a total of $1.4 million from sponsors in 2022. Among these, 26 physicians (93%) received payments from the product’s manufacturer, totaling $713,976, and 24 physicians (86%) accepted payments related to the endorsed drug or device, totaling $492,098.
While most did disclose that the posts were sponsored — by adding the word “sponsored” or using #sponsored — nine physicians did not.
Although 28 physician endorsers represent a “small fraction” of the overall number of physicians who use X, each endorsement was ultimately posted dozens, if not hundreds of times, said Dr. Mitchell. In fact, he said he saw the same particular endorsement post every time he opened his X app for months.
Overall, Dr. Mitchell noted that it’s less about the fact that the endorsements are occurring on social media and more that there are these paid endorsements taking place at all.
Among the physician specialties promoting a product, urologists and oncologists dominated. Almost one third were urologists, and 57% were oncologists — six medical oncologists, six radiation oncologists, and four gynecologic oncologists. Of the remaining three physicians, two were internists and one was a pulmonary and critical care medicine specialist.
The authors tracked posts from physicians and industry accounts. Many of the posts on industry accounts were physician testimonials, usually videos. Almost half — 8 of 17 — of those testimonials did not disclose that the doctor was being paid by the manufacturer. In another case, a physician did not disclose that they were paid to endorse a white paper.
Fifteen promotional posts were for a Boston Scientific product, followed by six for GlaxoSmithKline, two for Eisai, two for Exelixis, and one each for AstraZeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer.
In general, Dr. Mitchell said, industry guidelines suggest that manufacturer-paid speakers or consultants should have well-regarded expertise in the area they are being asked to weigh in on, but most physician endorsers in the study were not key opinion leaders or experts.
The authors examined the paid endorsers’ H-index — a measure of academic productivity provided by Scopus. Overall, 19 of the 28 physicians had an H-index below 20, which is considered less accomplished, and 14 had no published research related to the endorsed product.
Ten received payments from manufacturers for research purposes, and only one received research payments related to the endorsed product ($224,577).
“Physicians’ participation in industry marketing raises questions regarding professionalism and their responsibilities as patient advocates,” the JAMA authors wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Coauthors Samer Al Hadidi, MD, reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer, Sanofi, and Janssen during the conduct of the study, and Timothy S. Anderson, MD, reported receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging, the American Heart Association, and the American College of Cardiology, and receiving consulting fees from the American Medical Student Association. Dr. Anderson is also an associate editor of JAMA Internal Medicine.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lead author Aaron Mitchell, MD, MPH, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, told this news organization that he and his colleagues undertook the study in part to see whether physicians were adhering to professional and industry guidelines regarding marketing communications.
The team reviewed posts by physicians on X during 2022, looking for key words that might indicate that the posts were intended as endorsements of a product. The researchers then delved into the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments database to see how many of those identified as having endorsed a product were paid by the manufacturers.
What Dr. Mitchell found concerned him, he said.
Overall, the researchers identified 28 physician endorsers who received a total of $1.4 million from sponsors in 2022. Among these, 26 physicians (93%) received payments from the product’s manufacturer, totaling $713,976, and 24 physicians (86%) accepted payments related to the endorsed drug or device, totaling $492,098.
While most did disclose that the posts were sponsored — by adding the word “sponsored” or using #sponsored — nine physicians did not.
Although 28 physician endorsers represent a “small fraction” of the overall number of physicians who use X, each endorsement was ultimately posted dozens, if not hundreds of times, said Dr. Mitchell. In fact, he said he saw the same particular endorsement post every time he opened his X app for months.
Overall, Dr. Mitchell noted that it’s less about the fact that the endorsements are occurring on social media and more that there are these paid endorsements taking place at all.
Among the physician specialties promoting a product, urologists and oncologists dominated. Almost one third were urologists, and 57% were oncologists — six medical oncologists, six radiation oncologists, and four gynecologic oncologists. Of the remaining three physicians, two were internists and one was a pulmonary and critical care medicine specialist.
The authors tracked posts from physicians and industry accounts. Many of the posts on industry accounts were physician testimonials, usually videos. Almost half — 8 of 17 — of those testimonials did not disclose that the doctor was being paid by the manufacturer. In another case, a physician did not disclose that they were paid to endorse a white paper.
Fifteen promotional posts were for a Boston Scientific product, followed by six for GlaxoSmithKline, two for Eisai, two for Exelixis, and one each for AstraZeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer.
In general, Dr. Mitchell said, industry guidelines suggest that manufacturer-paid speakers or consultants should have well-regarded expertise in the area they are being asked to weigh in on, but most physician endorsers in the study were not key opinion leaders or experts.
The authors examined the paid endorsers’ H-index — a measure of academic productivity provided by Scopus. Overall, 19 of the 28 physicians had an H-index below 20, which is considered less accomplished, and 14 had no published research related to the endorsed product.
Ten received payments from manufacturers for research purposes, and only one received research payments related to the endorsed product ($224,577).
“Physicians’ participation in industry marketing raises questions regarding professionalism and their responsibilities as patient advocates,” the JAMA authors wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Coauthors Samer Al Hadidi, MD, reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer, Sanofi, and Janssen during the conduct of the study, and Timothy S. Anderson, MD, reported receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging, the American Heart Association, and the American College of Cardiology, and receiving consulting fees from the American Medical Student Association. Dr. Anderson is also an associate editor of JAMA Internal Medicine.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.