User login
New finasteride lawsuit brings renewed attention to psychiatric, ED adverse event reports
A new merit a closer look and, potentially, better counseling and monitoring from clinicians.
The nonprofit advocacy group Public Citizen filed the suit on behalf of the Post-Finasteride Syndrome Foundation (PFSF) in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia. The PFSF had filed a citizen’s petition in 2017 that requested that the FDA either take the 1-mg formulation off the market, or add warnings about the potential for erectile dysfunction, depression, and suicidal ideation, among other adverse reactions.
The PFSF has alleged that long-term use of Propecia (and its generic equivalents) can lead to postfinasteride syndrome (PFS), characterized by sexual dysfunction and psycho-neurocognitive symptoms. The symptoms may continue long after men stop taking the drug, according to PFSF.
Public Citizen said the FDA needs to take action in part because U.S. prescriptions of the hair loss formulation “more than doubled from 2015 to 2020,” and online and telemedicine companies such as Hims, Roman, and Keeps “aggressively market and sell generic finasteride for hair loss.” According to GoodRx, a 1-month supply of generic 1-mg tablets costs as little as $8-$10.
Both Canadian and British regulatory authorities have added warnings about depression and suicide to the Propecia label but the FDA has not changed its labeling. An agency spokesperson told this news organization that the “FDA does not comment on the status of pending citizen petitions or on pending litigation.”
Propecia’s developer, Merck, has not responded to several requests for comment from this news organization.
Why some patients develop PFS and others do not is still not understood, but some clinicians said they counsel all patients on the risks of severe and persistent side effects that have been associated with Propecia.
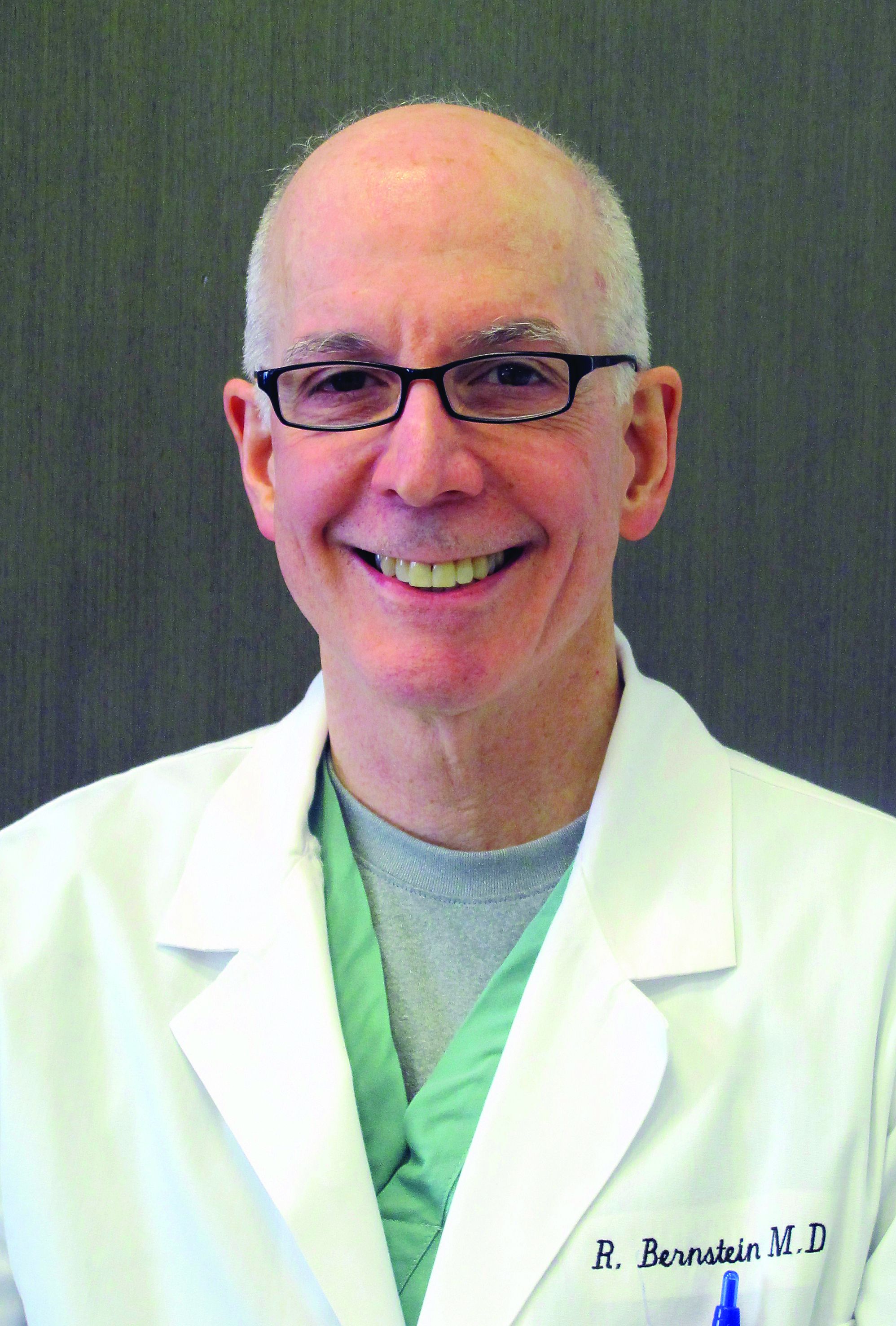
Robert M. Bernstein, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University, New York, and a fellow of the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, said that 2%-4% of his patients have some side effects, similar to the original reported incidence, with sexual dysfunction being the most common.
If a man experiences an adverse effect, the drug should be stopped, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview. He noted that “there seems to be a significant increased risk of persistent side effects in people with certain psychiatric conditions, and those people should be counseled carefully before considering the medication.”
“Everybody should be warned that the risk of persistent side effects is real but in the average person it is quite uncommon,” added Dr. Bernstein, founder of Bernstein Medical, a division of Schweiger Dermatology Group focusing on the diagnosis and treatment of hair loss. “I don’t think it should be withdrawn from the market,” he said.
Alan Jacobs, MD, a Manhattan-based neuroendocrinologist and behavioral neurologist in private practice who said he has treated hundreds of men for PFS, and who is an expert witness for the plaintiff in a suit alleging that finasteride led to a man’s suicide, said that taking the drug off the market would be unfortunate because it helps so many men. “I don’t think you need to get rid of the drug per se,” he said in an interview. “But very rapidly, people need to do clinical research to find out how to predict who’s more at risk,” he added.
Michael S. Irwig, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, who has studied the persistent sexual and nonsexual side effects of finasteride, said he believes there should be a boxed warning on the finasteride label to let the men who take it “know that they can have permanent persistent sexual dysfunction, and/or depression and suicide have been noted with this medicine.
“Those who prescribe it should be having a conversation with patients about the potential risks and benefits so that everybody knows about the potential before they get on the medicine,” said Dr. Irwig, who also is an endocrinologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Other countries warn of psychiatric effects
The FDA approved the 1-mg form of finasteride for male pattern hair loss in 1997.
In 2012, the label and the patient insert were updated to state that side effects included less desire for sex, erectile dysfunction, and a decrease in the amount of semen produced, but that those adverse events occurred in less than 2% of men and generally went away in most men who stopped taking the drug.
That label change unleashed a flood of more than 1,000 lawsuits against Merck. The company reportedly settled at least half of them for $4.3 million in 2018. The Superior Court of New Jersey closed out the consolidated class action against Merck in May 2021, noting that all of the cases had been settled or dismissed.
The suits generally accused Merck of not giving adequate warning about sexual side effects, according to an investigation by Reuters. That 2019 special report found that Merck had understated the number of men who experienced sexual side effects and the duration of those symptoms. The news organization also reported that from 2009 to 2018, the FDA received 5,000 reports of sexual or mental health side effects – and sometimes both – in men who took finasteride. Some 350 of the men reported suicidal thoughts, and there were 50 reports of suicide.
Public Citizen’s lawsuit alleges that VigiBase, which is managed by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for International Drug Monitoring, lists 378 cases of suicidal ideation, 39 cases of suicide attempt, and 88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use. VigiBase collects data from 153 countries on adverse reactions to medications.
In February 2021, more documents from the class action lawsuits were unsealed in response to a Reuters request. According to the news organization, the documents showed that Merck knew of reports of depression, including suicidal thoughts, as early as 2009.
However, according to Reuters, the FDA in 2011 granted Merck’s request to only note depression as a potential side effect, without including the risk of suicidal ideation.
The current FDA label notes a small incidence of sexual dysfunction, including decreased libido (1.8% in trials) and erectile dysfunction (1.3%) and mentions depression as a side effect observed during the postmarketing period.
The Canadian label has the same statistics on sexual side effects but is much stronger on mental adverse effects: “Psychiatric disorders: mood alterations and depression, decreased libido that continued after discontinuation of treatment. Mood alterations including depressed mood and, less frequently, suicidal ideation have been reported in patients treated with finasteride 1 mg. Patients should be monitored for psychiatric symptoms, and if these occur, the patient should be advised to seek medical advice.”
In the United Kingdom, patients prescribed the drug are given a leaflet, which notes that “Mood alterations such as depressed mood, depression and, less frequently, suicidal thoughts have been reported in patients treated with Propecia,” and advises patients to stop taking the drug if they experience any of those symptoms and to discuss it with their physician.
Public Citizen noted in its lawsuit that French and German drug regulators have sent letters to clinicians advising them to inform patients of the risk of suicidal thoughts and anxiety.
Is there biological plausibility?
To bolster its argument that finasteride has dangerous psychiatric side effects, the advocacy organization cited a study first published in JAMA Dermatology in late 2020 that investigated suicidality and psychological adverse events in patients taking finasteride.
David-Dan Nguyen, MPH, and his colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, McGill University, Montreal, and the University of Montreal, examined the VigiBase database and found 356 cases of suicidality and 2,926 psychological adverse events; cases were highest from 2015 to 2019.
They documented what they called a “significant disproportionality signal for suicidality (reporting odds ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 2.90-4.15) and psychological adverse events (ROR, 4.33; 95% CI, 4.17-4.49) with finasteride, especially in younger men and those with alopecia, but not in older men or those with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The study authors noted that some studies have suggested that men with depression have low levels of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone, which is produced by the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor.
According to Public Citizen’s lawsuit, “The product labeling does not disclose important information about finasteride’s mechanism of action,” and “the drug inhibits multiple steroid hormone pathways that are responsible for the formation of brain neurosteroids that regulate many critical functions in the central nervous system, like sexual function, mood, sleep, cognitive function, the stress response, and motivation.”
Dr. Jacobs said that “there’s a lot of good solid high-quality research, mostly in animals, but also some on humans, showing a plausible link between blocking 5-alpha reductase in the brain, deficiency of neuroactive steroids, and depression.”
The author of an accompanying editorial, Roger S. Ho, MD, MPH, an associate professor in the department of dermatology, New York University, was skeptical. “Without a plausible biological hypothesis pharmacodynamically linking the drug and the reported adverse event, this kind of analysis may lead to false findings,” Dr. Ho said in the editorial about the Nguyen study.
Dr. Ho also wrote that he believed that the lack of a suicidality signal for dutasteride, a drug with a similar mechanism of action, but without as much media attention, “hints at a potential reporting bias unique to finasteride.”
He recommended that clinicians “conduct a full evaluation and a detailed, personalized risk-benefit assessment for patients before each prescription of finasteride.”
Important medicine, important caveats
Dr. Jacobs said that many of the men who come to him with side effects after taking finasteride have “been blown off by most of the doctors they go to see.”
Urologists dismiss them because their sexual dysfunction is not a gonad issue. They are told that it’s in their head, said Dr. Jacobs, adding that, “it is in their head, but it’s biological.”
The drug’s label advises that sexual side effects disappear when the drug is stopped. “That’s only true most of the time, not all of the time,” said Dr. Jacobs, adding that the persistence of any side effects impacts what he calls a “small subset” of men who take the drug.
“We have treated tens of thousands of patients who have benefited from the medicine and had no side effects,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But there is a lot that’s still not known about it.”
Even so, “baldness in young people is not a benign condition,” he said, adding that it can be socially debilitating. “An 18-year-old with a full head of thick hair who’s totally bald in 3 or 4 years – that can totally change his psyche,” Dr. Bernstein said. Finasteride may be the best option for those young men, and it is an important medication, he said. Does it need to be used more carefully? “Certainly you can’t argue with that,” he commented.
Dr. Bernstein and Dr. Irwig reported no conflicts. Dr. Jacobs disclosed that he is an expert witness for the plaintiffs in a suit against Propecia maker Merck.
A new merit a closer look and, potentially, better counseling and monitoring from clinicians.
The nonprofit advocacy group Public Citizen filed the suit on behalf of the Post-Finasteride Syndrome Foundation (PFSF) in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia. The PFSF had filed a citizen’s petition in 2017 that requested that the FDA either take the 1-mg formulation off the market, or add warnings about the potential for erectile dysfunction, depression, and suicidal ideation, among other adverse reactions.
The PFSF has alleged that long-term use of Propecia (and its generic equivalents) can lead to postfinasteride syndrome (PFS), characterized by sexual dysfunction and psycho-neurocognitive symptoms. The symptoms may continue long after men stop taking the drug, according to PFSF.
Public Citizen said the FDA needs to take action in part because U.S. prescriptions of the hair loss formulation “more than doubled from 2015 to 2020,” and online and telemedicine companies such as Hims, Roman, and Keeps “aggressively market and sell generic finasteride for hair loss.” According to GoodRx, a 1-month supply of generic 1-mg tablets costs as little as $8-$10.
Both Canadian and British regulatory authorities have added warnings about depression and suicide to the Propecia label but the FDA has not changed its labeling. An agency spokesperson told this news organization that the “FDA does not comment on the status of pending citizen petitions or on pending litigation.”
Propecia’s developer, Merck, has not responded to several requests for comment from this news organization.
Why some patients develop PFS and others do not is still not understood, but some clinicians said they counsel all patients on the risks of severe and persistent side effects that have been associated with Propecia.
Robert M. Bernstein, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University, New York, and a fellow of the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, said that 2%-4% of his patients have some side effects, similar to the original reported incidence, with sexual dysfunction being the most common.
If a man experiences an adverse effect, the drug should be stopped, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview. He noted that “there seems to be a significant increased risk of persistent side effects in people with certain psychiatric conditions, and those people should be counseled carefully before considering the medication.”
“Everybody should be warned that the risk of persistent side effects is real but in the average person it is quite uncommon,” added Dr. Bernstein, founder of Bernstein Medical, a division of Schweiger Dermatology Group focusing on the diagnosis and treatment of hair loss. “I don’t think it should be withdrawn from the market,” he said.
Alan Jacobs, MD, a Manhattan-based neuroendocrinologist and behavioral neurologist in private practice who said he has treated hundreds of men for PFS, and who is an expert witness for the plaintiff in a suit alleging that finasteride led to a man’s suicide, said that taking the drug off the market would be unfortunate because it helps so many men. “I don’t think you need to get rid of the drug per se,” he said in an interview. “But very rapidly, people need to do clinical research to find out how to predict who’s more at risk,” he added.
Michael S. Irwig, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, who has studied the persistent sexual and nonsexual side effects of finasteride, said he believes there should be a boxed warning on the finasteride label to let the men who take it “know that they can have permanent persistent sexual dysfunction, and/or depression and suicide have been noted with this medicine.
“Those who prescribe it should be having a conversation with patients about the potential risks and benefits so that everybody knows about the potential before they get on the medicine,” said Dr. Irwig, who also is an endocrinologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Other countries warn of psychiatric effects
The FDA approved the 1-mg form of finasteride for male pattern hair loss in 1997.
In 2012, the label and the patient insert were updated to state that side effects included less desire for sex, erectile dysfunction, and a decrease in the amount of semen produced, but that those adverse events occurred in less than 2% of men and generally went away in most men who stopped taking the drug.
That label change unleashed a flood of more than 1,000 lawsuits against Merck. The company reportedly settled at least half of them for $4.3 million in 2018. The Superior Court of New Jersey closed out the consolidated class action against Merck in May 2021, noting that all of the cases had been settled or dismissed.
The suits generally accused Merck of not giving adequate warning about sexual side effects, according to an investigation by Reuters. That 2019 special report found that Merck had understated the number of men who experienced sexual side effects and the duration of those symptoms. The news organization also reported that from 2009 to 2018, the FDA received 5,000 reports of sexual or mental health side effects – and sometimes both – in men who took finasteride. Some 350 of the men reported suicidal thoughts, and there were 50 reports of suicide.
Public Citizen’s lawsuit alleges that VigiBase, which is managed by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for International Drug Monitoring, lists 378 cases of suicidal ideation, 39 cases of suicide attempt, and 88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use. VigiBase collects data from 153 countries on adverse reactions to medications.
In February 2021, more documents from the class action lawsuits were unsealed in response to a Reuters request. According to the news organization, the documents showed that Merck knew of reports of depression, including suicidal thoughts, as early as 2009.
However, according to Reuters, the FDA in 2011 granted Merck’s request to only note depression as a potential side effect, without including the risk of suicidal ideation.
The current FDA label notes a small incidence of sexual dysfunction, including decreased libido (1.8% in trials) and erectile dysfunction (1.3%) and mentions depression as a side effect observed during the postmarketing period.
The Canadian label has the same statistics on sexual side effects but is much stronger on mental adverse effects: “Psychiatric disorders: mood alterations and depression, decreased libido that continued after discontinuation of treatment. Mood alterations including depressed mood and, less frequently, suicidal ideation have been reported in patients treated with finasteride 1 mg. Patients should be monitored for psychiatric symptoms, and if these occur, the patient should be advised to seek medical advice.”
In the United Kingdom, patients prescribed the drug are given a leaflet, which notes that “Mood alterations such as depressed mood, depression and, less frequently, suicidal thoughts have been reported in patients treated with Propecia,” and advises patients to stop taking the drug if they experience any of those symptoms and to discuss it with their physician.
Public Citizen noted in its lawsuit that French and German drug regulators have sent letters to clinicians advising them to inform patients of the risk of suicidal thoughts and anxiety.
Is there biological plausibility?
To bolster its argument that finasteride has dangerous psychiatric side effects, the advocacy organization cited a study first published in JAMA Dermatology in late 2020 that investigated suicidality and psychological adverse events in patients taking finasteride.
David-Dan Nguyen, MPH, and his colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, McGill University, Montreal, and the University of Montreal, examined the VigiBase database and found 356 cases of suicidality and 2,926 psychological adverse events; cases were highest from 2015 to 2019.
They documented what they called a “significant disproportionality signal for suicidality (reporting odds ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 2.90-4.15) and psychological adverse events (ROR, 4.33; 95% CI, 4.17-4.49) with finasteride, especially in younger men and those with alopecia, but not in older men or those with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The study authors noted that some studies have suggested that men with depression have low levels of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone, which is produced by the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor.
According to Public Citizen’s lawsuit, “The product labeling does not disclose important information about finasteride’s mechanism of action,” and “the drug inhibits multiple steroid hormone pathways that are responsible for the formation of brain neurosteroids that regulate many critical functions in the central nervous system, like sexual function, mood, sleep, cognitive function, the stress response, and motivation.”
Dr. Jacobs said that “there’s a lot of good solid high-quality research, mostly in animals, but also some on humans, showing a plausible link between blocking 5-alpha reductase in the brain, deficiency of neuroactive steroids, and depression.”
The author of an accompanying editorial, Roger S. Ho, MD, MPH, an associate professor in the department of dermatology, New York University, was skeptical. “Without a plausible biological hypothesis pharmacodynamically linking the drug and the reported adverse event, this kind of analysis may lead to false findings,” Dr. Ho said in the editorial about the Nguyen study.
Dr. Ho also wrote that he believed that the lack of a suicidality signal for dutasteride, a drug with a similar mechanism of action, but without as much media attention, “hints at a potential reporting bias unique to finasteride.”
He recommended that clinicians “conduct a full evaluation and a detailed, personalized risk-benefit assessment for patients before each prescription of finasteride.”
Important medicine, important caveats
Dr. Jacobs said that many of the men who come to him with side effects after taking finasteride have “been blown off by most of the doctors they go to see.”
Urologists dismiss them because their sexual dysfunction is not a gonad issue. They are told that it’s in their head, said Dr. Jacobs, adding that, “it is in their head, but it’s biological.”
The drug’s label advises that sexual side effects disappear when the drug is stopped. “That’s only true most of the time, not all of the time,” said Dr. Jacobs, adding that the persistence of any side effects impacts what he calls a “small subset” of men who take the drug.
“We have treated tens of thousands of patients who have benefited from the medicine and had no side effects,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But there is a lot that’s still not known about it.”
Even so, “baldness in young people is not a benign condition,” he said, adding that it can be socially debilitating. “An 18-year-old with a full head of thick hair who’s totally bald in 3 or 4 years – that can totally change his psyche,” Dr. Bernstein said. Finasteride may be the best option for those young men, and it is an important medication, he said. Does it need to be used more carefully? “Certainly you can’t argue with that,” he commented.
Dr. Bernstein and Dr. Irwig reported no conflicts. Dr. Jacobs disclosed that he is an expert witness for the plaintiffs in a suit against Propecia maker Merck.
A new merit a closer look and, potentially, better counseling and monitoring from clinicians.
The nonprofit advocacy group Public Citizen filed the suit on behalf of the Post-Finasteride Syndrome Foundation (PFSF) in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia. The PFSF had filed a citizen’s petition in 2017 that requested that the FDA either take the 1-mg formulation off the market, or add warnings about the potential for erectile dysfunction, depression, and suicidal ideation, among other adverse reactions.
The PFSF has alleged that long-term use of Propecia (and its generic equivalents) can lead to postfinasteride syndrome (PFS), characterized by sexual dysfunction and psycho-neurocognitive symptoms. The symptoms may continue long after men stop taking the drug, according to PFSF.
Public Citizen said the FDA needs to take action in part because U.S. prescriptions of the hair loss formulation “more than doubled from 2015 to 2020,” and online and telemedicine companies such as Hims, Roman, and Keeps “aggressively market and sell generic finasteride for hair loss.” According to GoodRx, a 1-month supply of generic 1-mg tablets costs as little as $8-$10.
Both Canadian and British regulatory authorities have added warnings about depression and suicide to the Propecia label but the FDA has not changed its labeling. An agency spokesperson told this news organization that the “FDA does not comment on the status of pending citizen petitions or on pending litigation.”
Propecia’s developer, Merck, has not responded to several requests for comment from this news organization.
Why some patients develop PFS and others do not is still not understood, but some clinicians said they counsel all patients on the risks of severe and persistent side effects that have been associated with Propecia.
Robert M. Bernstein, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University, New York, and a fellow of the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, said that 2%-4% of his patients have some side effects, similar to the original reported incidence, with sexual dysfunction being the most common.
If a man experiences an adverse effect, the drug should be stopped, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview. He noted that “there seems to be a significant increased risk of persistent side effects in people with certain psychiatric conditions, and those people should be counseled carefully before considering the medication.”
“Everybody should be warned that the risk of persistent side effects is real but in the average person it is quite uncommon,” added Dr. Bernstein, founder of Bernstein Medical, a division of Schweiger Dermatology Group focusing on the diagnosis and treatment of hair loss. “I don’t think it should be withdrawn from the market,” he said.
Alan Jacobs, MD, a Manhattan-based neuroendocrinologist and behavioral neurologist in private practice who said he has treated hundreds of men for PFS, and who is an expert witness for the plaintiff in a suit alleging that finasteride led to a man’s suicide, said that taking the drug off the market would be unfortunate because it helps so many men. “I don’t think you need to get rid of the drug per se,” he said in an interview. “But very rapidly, people need to do clinical research to find out how to predict who’s more at risk,” he added.
Michael S. Irwig, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, who has studied the persistent sexual and nonsexual side effects of finasteride, said he believes there should be a boxed warning on the finasteride label to let the men who take it “know that they can have permanent persistent sexual dysfunction, and/or depression and suicide have been noted with this medicine.
“Those who prescribe it should be having a conversation with patients about the potential risks and benefits so that everybody knows about the potential before they get on the medicine,” said Dr. Irwig, who also is an endocrinologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Other countries warn of psychiatric effects
The FDA approved the 1-mg form of finasteride for male pattern hair loss in 1997.
In 2012, the label and the patient insert were updated to state that side effects included less desire for sex, erectile dysfunction, and a decrease in the amount of semen produced, but that those adverse events occurred in less than 2% of men and generally went away in most men who stopped taking the drug.
That label change unleashed a flood of more than 1,000 lawsuits against Merck. The company reportedly settled at least half of them for $4.3 million in 2018. The Superior Court of New Jersey closed out the consolidated class action against Merck in May 2021, noting that all of the cases had been settled or dismissed.
The suits generally accused Merck of not giving adequate warning about sexual side effects, according to an investigation by Reuters. That 2019 special report found that Merck had understated the number of men who experienced sexual side effects and the duration of those symptoms. The news organization also reported that from 2009 to 2018, the FDA received 5,000 reports of sexual or mental health side effects – and sometimes both – in men who took finasteride. Some 350 of the men reported suicidal thoughts, and there were 50 reports of suicide.
Public Citizen’s lawsuit alleges that VigiBase, which is managed by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for International Drug Monitoring, lists 378 cases of suicidal ideation, 39 cases of suicide attempt, and 88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use. VigiBase collects data from 153 countries on adverse reactions to medications.
In February 2021, more documents from the class action lawsuits were unsealed in response to a Reuters request. According to the news organization, the documents showed that Merck knew of reports of depression, including suicidal thoughts, as early as 2009.
However, according to Reuters, the FDA in 2011 granted Merck’s request to only note depression as a potential side effect, without including the risk of suicidal ideation.
The current FDA label notes a small incidence of sexual dysfunction, including decreased libido (1.8% in trials) and erectile dysfunction (1.3%) and mentions depression as a side effect observed during the postmarketing period.
The Canadian label has the same statistics on sexual side effects but is much stronger on mental adverse effects: “Psychiatric disorders: mood alterations and depression, decreased libido that continued after discontinuation of treatment. Mood alterations including depressed mood and, less frequently, suicidal ideation have been reported in patients treated with finasteride 1 mg. Patients should be monitored for psychiatric symptoms, and if these occur, the patient should be advised to seek medical advice.”
In the United Kingdom, patients prescribed the drug are given a leaflet, which notes that “Mood alterations such as depressed mood, depression and, less frequently, suicidal thoughts have been reported in patients treated with Propecia,” and advises patients to stop taking the drug if they experience any of those symptoms and to discuss it with their physician.
Public Citizen noted in its lawsuit that French and German drug regulators have sent letters to clinicians advising them to inform patients of the risk of suicidal thoughts and anxiety.
Is there biological plausibility?
To bolster its argument that finasteride has dangerous psychiatric side effects, the advocacy organization cited a study first published in JAMA Dermatology in late 2020 that investigated suicidality and psychological adverse events in patients taking finasteride.
David-Dan Nguyen, MPH, and his colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, McGill University, Montreal, and the University of Montreal, examined the VigiBase database and found 356 cases of suicidality and 2,926 psychological adverse events; cases were highest from 2015 to 2019.
They documented what they called a “significant disproportionality signal for suicidality (reporting odds ratio, 1.63; 95% confidence interval, 2.90-4.15) and psychological adverse events (ROR, 4.33; 95% CI, 4.17-4.49) with finasteride, especially in younger men and those with alopecia, but not in older men or those with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The study authors noted that some studies have suggested that men with depression have low levels of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone, which is produced by the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor.
According to Public Citizen’s lawsuit, “The product labeling does not disclose important information about finasteride’s mechanism of action,” and “the drug inhibits multiple steroid hormone pathways that are responsible for the formation of brain neurosteroids that regulate many critical functions in the central nervous system, like sexual function, mood, sleep, cognitive function, the stress response, and motivation.”
Dr. Jacobs said that “there’s a lot of good solid high-quality research, mostly in animals, but also some on humans, showing a plausible link between blocking 5-alpha reductase in the brain, deficiency of neuroactive steroids, and depression.”
The author of an accompanying editorial, Roger S. Ho, MD, MPH, an associate professor in the department of dermatology, New York University, was skeptical. “Without a plausible biological hypothesis pharmacodynamically linking the drug and the reported adverse event, this kind of analysis may lead to false findings,” Dr. Ho said in the editorial about the Nguyen study.
Dr. Ho also wrote that he believed that the lack of a suicidality signal for dutasteride, a drug with a similar mechanism of action, but without as much media attention, “hints at a potential reporting bias unique to finasteride.”
He recommended that clinicians “conduct a full evaluation and a detailed, personalized risk-benefit assessment for patients before each prescription of finasteride.”
Important medicine, important caveats
Dr. Jacobs said that many of the men who come to him with side effects after taking finasteride have “been blown off by most of the doctors they go to see.”
Urologists dismiss them because their sexual dysfunction is not a gonad issue. They are told that it’s in their head, said Dr. Jacobs, adding that, “it is in their head, but it’s biological.”
The drug’s label advises that sexual side effects disappear when the drug is stopped. “That’s only true most of the time, not all of the time,” said Dr. Jacobs, adding that the persistence of any side effects impacts what he calls a “small subset” of men who take the drug.
“We have treated tens of thousands of patients who have benefited from the medicine and had no side effects,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But there is a lot that’s still not known about it.”
Even so, “baldness in young people is not a benign condition,” he said, adding that it can be socially debilitating. “An 18-year-old with a full head of thick hair who’s totally bald in 3 or 4 years – that can totally change his psyche,” Dr. Bernstein said. Finasteride may be the best option for those young men, and it is an important medication, he said. Does it need to be used more carefully? “Certainly you can’t argue with that,” he commented.
Dr. Bernstein and Dr. Irwig reported no conflicts. Dr. Jacobs disclosed that he is an expert witness for the plaintiffs in a suit against Propecia maker Merck.
Baylor gets restraining order against COVID-19 vaccine–skeptic doc
in which he agreed to stop mentioning his prior leadership and academic appointments.
Baylor was the first institution to cut ties with Dr. McCullough, who has promoted the use of therapies seen as unproven for the treatment of COVID-19 and has questioned the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines. Since the Baylor suit, the Texas A&M College of Medicine, and the Texas Christian University (TCU) and University of North Texas Health Science Center (UNTHSC) School of Medicine have both removed Dr. McCullough from their faculties.
Granted by the 191st District Court in Dallas County, Tex., the Baylor restraining order – which is in effect at least until a hearing on the case on September 30 – was sought as part of Baylor Scott & White’s breach of contract suit against McCullough, who had previously been known as a well-respected expert in cardiorenal issues. The suit is seeking $1 million in damages, as well as attorneys’ fees.
The suit seeks to “enforce the terms” of the confidential employment separation agreement signed by Dr. McCullough in February and prevent Dr. McCullough from continuing “improper use of titles and claimed affiliations that have already confused the media, the medical community and the public,” it reads.
“This ongoing confusion regarding [Dr.] McCullough’s affiliations, and whether Plaintiffs support his opinions, is exactly what Plaintiffs bargained to avoid in the Separation Agreement,” and is likely to cause “irreparable reputational and business harm that is incapable of remedy by money damages alone,” the suit states.
One of Dr. McCullough’s attorneys, Clinton Mikel, maintains that all the times the physician was identified in the “thousands of hours of media interviews and countless publications since his departure from Baylor” were “said/printed by a third party with no encouragement from Dr. McCullough,” and that the doctor “does not and cannot control third parties.”
Mr. Mikel said in a statement emailed to this news organization by Dr. McCullough that the suit is “a politically motivated attempt to silence Dr. McCullough,” because it was filed on the same day the organization mandated COVID-19 vaccination for employees.
Dr. McCullough “intends to vigorously defend against Baylor’s unfounded lawsuit,” will seek to dissolve the restraining order, and recover “all payments due him from Baylor under the terms of the settlement agreement,” wrote Mr. Mikel.
The cardiologist’s legal team filed a motion to dismiss the suit on Aug. 9, essentially arguing that Baylor Scott & White’s action restricted Dr. McCullough’s right to free speech under the Texas Citizen’s Participation Act.
COVID-19 vaccines = bioterrorism?
Dr. McCullough accumulated a following in 2020 by promoting early at-home multidrug treatment of COVID-19 in interviews with conservative websites and at a U.S. Senate hearing in November.
Although Dr. McCullough does not appear to have any personal social media accounts, his broadcast and podcast interviews are tweeted by thousands daily around the world and featured on Facebook pages like “Pandemic Debate.”
Some Facebook posts with Dr. McCullough’s pronouncements have been labeled as misinformation or removed. Some of his videos remain on YouTube, where they are posted by the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, a group that believes Dr. McCullough is “under fierce attack for speaking out about COVID-19 early treatment and vaccine safety.”
Dr. McCullough’s March 2021 testimony to the Texas Senate’s Health and Human Services Committee – in which he claimed that COVID-19 patients are being denied what he called proven treatments like hydroxychloroquine – has been viewed more than 3.7 million times on YouTube. The appearance has also been tweeted repeatedly.
Most of Dr. McCullough’s interviews and presentations are aggregated on Rumble, an alternative to YouTube.
In interviews, Dr. McCullough promotes the use of zinc, hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, doxycycline, favipiravir, prednisone, and ivermectin as COVID-19 treatments – based on an outpatient treatment algorithm published in August 2020 in the American Journal of Medicine. The cardiologist was the lead author of that paper, which proposed treating people with COVID-like symptoms whether or not they had confirmed infection.
Dr. McCullough and colleagues published a follow-up paper that added colchicine to the mix in Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine. Dr. McCullough is editor-in-chief of the journal, but this was not noted in the disclosures.
Similarly, Dr. McCullough has not disclosed in his COVID-19 publications or any interviews that he has received consulting fees from a host of pharmaceutical manufacturers that produce COVID-19 drugs and vaccines, including AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Open Payments database, Dr. McCullough was paid about $300,000 annually by drug companies from 2014 to 2019, mostly for consulting on cardiovascular and diabetes medications. His payments dropped to $169,406.06 in 2020.
Dr. McCullough appeared on “The Ingraham Angle” on Fox News in December 2020, claiming that sequential, early treatment with “anti-infectives, corticosteroids, and then antithrombotics” could “reduce [COVID-19] hospitalizations by 85% and cut mortality in half.”
He repeated the claim on the Ingraham show in July and agreed with host Laura Ingraham that the vast majority of healthy people would do fine if they got COVID. He also made the claim that 84% of the COVID-19 cases in Israel were in people who had been vaccinated. “So it’s clear, we can’t vaccinate our way out of this,” he said. An Associated Press “fact check” report has pushed back on similar assertions about vaccine data from Israel.
In a separate interview posted in June, Dr. McCullough called the pandemic the first phase of a bioterrorism event, which was “all about keeping the population in fear and in isolation and preparing them to accept the vaccine, which appears to be phase two of a bioterrorism operation.”
In addition, he said, “good doctors are doing unthinkable things like injecting biologically active messenger RNA that produces this pathogenic spike protein into pregnant women.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the vaccines teach the body to produce the spike protein, which then triggers an immune response that creates antibodies that will attack the virus.
A PolitiFact review debunks the notion that the mRNA vaccines are toxic, cytotoxic, or introduce live, active virus proteins into the body.
FactCheck.org also disputed Dr. McCullough’s claim in a July 13 Ingraham Angle appearance that the mRNA vaccines are ineffective against the Delta variant.
In the FactCheck article, Frederic Bushman, codirector of the University of Pennsylvania’s Center for Research on Coronaviruses and Other Emerging Pathogens, said that people were much better off being vaccinated than not,” adding, “the Delta variant may reduce the effectiveness [of the vaccines] a little, but still, they’re so effective that you get a lot of benefit.”
“The vaccines are failing,” Dr. McCullough asserted in an Aug. 3 video interview posted on Odysee. “As we sit here today, we have 11,000 Americans that the CDC has certified have died after the vaccine,” he said, citing two analyses – one by Jessica Rose, PhD, and another by British researchers.
Similar figures reportedly based on cases reported to the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) were forwarded to this news organization by Dr. McCullough.
The CDC website notes that the agency has received reports of 7,653 deaths in people who received a vaccine as of Sept. 13 (0.0020% of vaccine doses given since Dec. 14, 2020), but it cautions that those deaths do not mean the vaccine was the cause.
Dr. McCullough repeatedly claimed in the Aug. 3 interview that the government has not been transparent on vaccine safety. Since June 2020, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has held 16 public meetings on the COVID-19 vaccines.
To date, the agency has advised clinicians to monitor for rare side effects including Guillain-Barré syndrome and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and myocarditis after mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) vaccines.
Med schools distance themselves
According to the Baylor Scott & White suit, Dr. McCullough agreed on Feb. 24 in a confidential separation agreement that he would no longer use his academic or leadership titles nor hold himself out to be affiliated with Baylor University Medical Center, Baylor Heart and Vascular Institute, the Baylor Research Institute, or any other related institutions.
However, as of August, according to a Baylor spokesperson, McCullough continued to have privileges at Baylor University Medical Center and Baylor Scott & White Heart and Vascular Hospital, Dallas.
The lawsuit points to three interviews posted in June and July where Dr. McCullough is identified as a “vice chief of medicine” or a “vice chief of internal medicine,” both at Baylor University. It also cites a profile at the Cardiometabolic Health Congress website – which this news organization had also viewed – that was still active in late July with a similar title. The profile was later scrubbed from the site.
Social media posts and other media continue to refer to Dr. McCullough’s Baylor credentials. An episode of the Faith and Freedom podcast posted on Aug. 2 identified McCullough as a “professor of medicine at Baylor University Medical Center.”
As of Sept. 16, Dr. McCullough’s bio page at his current practice, Heart Place, lists him as a professor of medicine at Texas A&M College of Medicine. A spokesperson for Texas A&M told this news organization that McCullough is no longer affiliated with the school.
Dr. McCullough acknowledged in the Aug. 3 interview that his Texas A&M title had been “stripped away” at “around the same time this lawsuit was filed.”
He was still a professor of medicine at the TCU and UNTHSC School of Medicine in Fort Worth, but a school spokesperson notified this news organization on Aug. 19 that Dr. McCullough was no longer with the school.
Dr. McCullough has portrayed himself as both a victim and a truth-teller, a “concerned physician” warning the world about the dangers of COVID-19 vaccines. The Baylor Scott & White lawsuit “is really a strong-armed tactic,” he said in the Aug. 3 interview. “I’m just a little guy, so I have to hire my legal teams, and in a sense be drained dry on legal fees,” he said.
But Dr. McCullough apparently has a plan for helping to defray his legal costs. In the Aug. 3 interview, he said a foundation he helped start, Truth for Health, has a “donation side to it,” adding “some of that may be used for legal expense.”
Cheryl Jones, an attorney with PK Law in Towson, Md., said that might draw interest from the Internal Revenue Service. “I would expect IRS scrutiny if contributions to the Medical Censorship Defense Fund are used to defend Dr McCullough in his personal breach of contract lawsuit,” she told this news organization.
The IRS generally recognizes defending “human and civil rights secured by law” as a legitimate charitable purpose for a legal defense fund, she said, adding that such a fund “must serve only public, rather than private, interests.”
Misinformation from a physician more damaging?
Some in the medical field have refuted Dr. McCullough’s pronouncements on how to treat COVID-19, including two infectious disease specialists with Monash University, Melbourne, who responded to the cardiologist’s original paper in the American Journal of Medicine.
Tony Korman, MBBS, a professor at the Centre for Inflammatory Diseases at Monash, told this news organization, “we had concerns that reputable medical journals would accept and publish papers proposing treatment of COVID-19 which was not supported by evidence.”
The website Healthfeedback.org has also challenged McCullough’s and his supporters’ claims, including that the American Journal of Medicine endorsed the use of hydroxychloroquine and that the COVID-19 vaccines have caused thousands of deaths.
David Broniatowski, PhD, associate director for the Institute for Data, Democracy and Politics at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview that Dr. McCullough’s casting himself as a “rebel doctor” is a well-known trope in the vaccine misinformation universe.
Although he was not familiar with Dr. McCullough, Dr. Broniatowski said the cardiologist’s claims are not unique – they’ve been circulating among antivaccine and conspiracy-oriented groups for months.
For instance, Dr. McCullough has claimed in interviews that a whistleblower within the CDC knows of 50,000 vaccine-related deaths. Using data from the supposed whistleblower, the group America’s Frontline Doctors sued the federal government in July to stop the administration of COVID-19 vaccines to those under 18, people who have already had COVID, and individuals who the group said have not been adequately informed about the risks.
The idea of a whistleblower inside the CDC is recycled from antivaccine claims from decades ago, Dr. Broniatowski said.
But, he added, “somebody who speaks with the credibility of a major institution will be more likely to be listened to by some people.” That vulnerable group is “being taken advantage of by a relatively small number of disinformation purveyors, who, in some cases, profit from that disinformation,” said Dr. Broniatowski.
“We rely on our doctors because we trust them,” he said. “And we trust them because we believe that as physicians, their value system places the patient’s best interests first. That’s why it’s so much of a disappointment when you have a physician that appears to be exercising this sort of bad judgment.”
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, also said that he was not familiar with Dr. McCullough. But apprised of his claims, Dr. Offit told this news organization, “Peter McCullough is a friend of the virus.”
“The kind of information he promotes allows the virus to continue to spread, continue to do an enormous amount of harm, and continue to mutate and create variants that have become more contagious and more resistant to vaccine-induced immunity,” said Dr. Offit, the Maurice R. Hilleman professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Offit added that the war should be against SARS-CoV-2, but “because this virus has so many supporters, the war in essence becomes a war against ourselves, which is much harder.”
Dr. McCullough maintains he is doing a service to his patients. “I’m just giving and trying to help America understand the pandemic,” he told Ms. Ingraham on Fox News on July 29.
But he acknowledged concern about the Federation of State Medical Board’s announcement that physicians who spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation risk suspension or revocation of their license.
“I have to tell you I’m worried – that no matter what I do and how careful I am to cite the scientific studies, I’m still gonna be hunted down for quote, misinformation,” he said in the Aug. 3 interview.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in which he agreed to stop mentioning his prior leadership and academic appointments.
Baylor was the first institution to cut ties with Dr. McCullough, who has promoted the use of therapies seen as unproven for the treatment of COVID-19 and has questioned the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines. Since the Baylor suit, the Texas A&M College of Medicine, and the Texas Christian University (TCU) and University of North Texas Health Science Center (UNTHSC) School of Medicine have both removed Dr. McCullough from their faculties.
Granted by the 191st District Court in Dallas County, Tex., the Baylor restraining order – which is in effect at least until a hearing on the case on September 30 – was sought as part of Baylor Scott & White’s breach of contract suit against McCullough, who had previously been known as a well-respected expert in cardiorenal issues. The suit is seeking $1 million in damages, as well as attorneys’ fees.
The suit seeks to “enforce the terms” of the confidential employment separation agreement signed by Dr. McCullough in February and prevent Dr. McCullough from continuing “improper use of titles and claimed affiliations that have already confused the media, the medical community and the public,” it reads.
“This ongoing confusion regarding [Dr.] McCullough’s affiliations, and whether Plaintiffs support his opinions, is exactly what Plaintiffs bargained to avoid in the Separation Agreement,” and is likely to cause “irreparable reputational and business harm that is incapable of remedy by money damages alone,” the suit states.
One of Dr. McCullough’s attorneys, Clinton Mikel, maintains that all the times the physician was identified in the “thousands of hours of media interviews and countless publications since his departure from Baylor” were “said/printed by a third party with no encouragement from Dr. McCullough,” and that the doctor “does not and cannot control third parties.”
Mr. Mikel said in a statement emailed to this news organization by Dr. McCullough that the suit is “a politically motivated attempt to silence Dr. McCullough,” because it was filed on the same day the organization mandated COVID-19 vaccination for employees.
Dr. McCullough “intends to vigorously defend against Baylor’s unfounded lawsuit,” will seek to dissolve the restraining order, and recover “all payments due him from Baylor under the terms of the settlement agreement,” wrote Mr. Mikel.
The cardiologist’s legal team filed a motion to dismiss the suit on Aug. 9, essentially arguing that Baylor Scott & White’s action restricted Dr. McCullough’s right to free speech under the Texas Citizen’s Participation Act.
COVID-19 vaccines = bioterrorism?
Dr. McCullough accumulated a following in 2020 by promoting early at-home multidrug treatment of COVID-19 in interviews with conservative websites and at a U.S. Senate hearing in November.
Although Dr. McCullough does not appear to have any personal social media accounts, his broadcast and podcast interviews are tweeted by thousands daily around the world and featured on Facebook pages like “Pandemic Debate.”
Some Facebook posts with Dr. McCullough’s pronouncements have been labeled as misinformation or removed. Some of his videos remain on YouTube, where they are posted by the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, a group that believes Dr. McCullough is “under fierce attack for speaking out about COVID-19 early treatment and vaccine safety.”
Dr. McCullough’s March 2021 testimony to the Texas Senate’s Health and Human Services Committee – in which he claimed that COVID-19 patients are being denied what he called proven treatments like hydroxychloroquine – has been viewed more than 3.7 million times on YouTube. The appearance has also been tweeted repeatedly.
Most of Dr. McCullough’s interviews and presentations are aggregated on Rumble, an alternative to YouTube.
In interviews, Dr. McCullough promotes the use of zinc, hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, doxycycline, favipiravir, prednisone, and ivermectin as COVID-19 treatments – based on an outpatient treatment algorithm published in August 2020 in the American Journal of Medicine. The cardiologist was the lead author of that paper, which proposed treating people with COVID-like symptoms whether or not they had confirmed infection.
Dr. McCullough and colleagues published a follow-up paper that added colchicine to the mix in Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine. Dr. McCullough is editor-in-chief of the journal, but this was not noted in the disclosures.
Similarly, Dr. McCullough has not disclosed in his COVID-19 publications or any interviews that he has received consulting fees from a host of pharmaceutical manufacturers that produce COVID-19 drugs and vaccines, including AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Open Payments database, Dr. McCullough was paid about $300,000 annually by drug companies from 2014 to 2019, mostly for consulting on cardiovascular and diabetes medications. His payments dropped to $169,406.06 in 2020.
Dr. McCullough appeared on “The Ingraham Angle” on Fox News in December 2020, claiming that sequential, early treatment with “anti-infectives, corticosteroids, and then antithrombotics” could “reduce [COVID-19] hospitalizations by 85% and cut mortality in half.”
He repeated the claim on the Ingraham show in July and agreed with host Laura Ingraham that the vast majority of healthy people would do fine if they got COVID. He also made the claim that 84% of the COVID-19 cases in Israel were in people who had been vaccinated. “So it’s clear, we can’t vaccinate our way out of this,” he said. An Associated Press “fact check” report has pushed back on similar assertions about vaccine data from Israel.
In a separate interview posted in June, Dr. McCullough called the pandemic the first phase of a bioterrorism event, which was “all about keeping the population in fear and in isolation and preparing them to accept the vaccine, which appears to be phase two of a bioterrorism operation.”
In addition, he said, “good doctors are doing unthinkable things like injecting biologically active messenger RNA that produces this pathogenic spike protein into pregnant women.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the vaccines teach the body to produce the spike protein, which then triggers an immune response that creates antibodies that will attack the virus.
A PolitiFact review debunks the notion that the mRNA vaccines are toxic, cytotoxic, or introduce live, active virus proteins into the body.
FactCheck.org also disputed Dr. McCullough’s claim in a July 13 Ingraham Angle appearance that the mRNA vaccines are ineffective against the Delta variant.
In the FactCheck article, Frederic Bushman, codirector of the University of Pennsylvania’s Center for Research on Coronaviruses and Other Emerging Pathogens, said that people were much better off being vaccinated than not,” adding, “the Delta variant may reduce the effectiveness [of the vaccines] a little, but still, they’re so effective that you get a lot of benefit.”
“The vaccines are failing,” Dr. McCullough asserted in an Aug. 3 video interview posted on Odysee. “As we sit here today, we have 11,000 Americans that the CDC has certified have died after the vaccine,” he said, citing two analyses – one by Jessica Rose, PhD, and another by British researchers.
Similar figures reportedly based on cases reported to the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) were forwarded to this news organization by Dr. McCullough.
The CDC website notes that the agency has received reports of 7,653 deaths in people who received a vaccine as of Sept. 13 (0.0020% of vaccine doses given since Dec. 14, 2020), but it cautions that those deaths do not mean the vaccine was the cause.
Dr. McCullough repeatedly claimed in the Aug. 3 interview that the government has not been transparent on vaccine safety. Since June 2020, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has held 16 public meetings on the COVID-19 vaccines.
To date, the agency has advised clinicians to monitor for rare side effects including Guillain-Barré syndrome and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and myocarditis after mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) vaccines.
Med schools distance themselves
According to the Baylor Scott & White suit, Dr. McCullough agreed on Feb. 24 in a confidential separation agreement that he would no longer use his academic or leadership titles nor hold himself out to be affiliated with Baylor University Medical Center, Baylor Heart and Vascular Institute, the Baylor Research Institute, or any other related institutions.
However, as of August, according to a Baylor spokesperson, McCullough continued to have privileges at Baylor University Medical Center and Baylor Scott & White Heart and Vascular Hospital, Dallas.
The lawsuit points to three interviews posted in June and July where Dr. McCullough is identified as a “vice chief of medicine” or a “vice chief of internal medicine,” both at Baylor University. It also cites a profile at the Cardiometabolic Health Congress website – which this news organization had also viewed – that was still active in late July with a similar title. The profile was later scrubbed from the site.
Social media posts and other media continue to refer to Dr. McCullough’s Baylor credentials. An episode of the Faith and Freedom podcast posted on Aug. 2 identified McCullough as a “professor of medicine at Baylor University Medical Center.”
As of Sept. 16, Dr. McCullough’s bio page at his current practice, Heart Place, lists him as a professor of medicine at Texas A&M College of Medicine. A spokesperson for Texas A&M told this news organization that McCullough is no longer affiliated with the school.
Dr. McCullough acknowledged in the Aug. 3 interview that his Texas A&M title had been “stripped away” at “around the same time this lawsuit was filed.”
He was still a professor of medicine at the TCU and UNTHSC School of Medicine in Fort Worth, but a school spokesperson notified this news organization on Aug. 19 that Dr. McCullough was no longer with the school.
Dr. McCullough has portrayed himself as both a victim and a truth-teller, a “concerned physician” warning the world about the dangers of COVID-19 vaccines. The Baylor Scott & White lawsuit “is really a strong-armed tactic,” he said in the Aug. 3 interview. “I’m just a little guy, so I have to hire my legal teams, and in a sense be drained dry on legal fees,” he said.
But Dr. McCullough apparently has a plan for helping to defray his legal costs. In the Aug. 3 interview, he said a foundation he helped start, Truth for Health, has a “donation side to it,” adding “some of that may be used for legal expense.”
Cheryl Jones, an attorney with PK Law in Towson, Md., said that might draw interest from the Internal Revenue Service. “I would expect IRS scrutiny if contributions to the Medical Censorship Defense Fund are used to defend Dr McCullough in his personal breach of contract lawsuit,” she told this news organization.
The IRS generally recognizes defending “human and civil rights secured by law” as a legitimate charitable purpose for a legal defense fund, she said, adding that such a fund “must serve only public, rather than private, interests.”
Misinformation from a physician more damaging?
Some in the medical field have refuted Dr. McCullough’s pronouncements on how to treat COVID-19, including two infectious disease specialists with Monash University, Melbourne, who responded to the cardiologist’s original paper in the American Journal of Medicine.
Tony Korman, MBBS, a professor at the Centre for Inflammatory Diseases at Monash, told this news organization, “we had concerns that reputable medical journals would accept and publish papers proposing treatment of COVID-19 which was not supported by evidence.”
The website Healthfeedback.org has also challenged McCullough’s and his supporters’ claims, including that the American Journal of Medicine endorsed the use of hydroxychloroquine and that the COVID-19 vaccines have caused thousands of deaths.
David Broniatowski, PhD, associate director for the Institute for Data, Democracy and Politics at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview that Dr. McCullough’s casting himself as a “rebel doctor” is a well-known trope in the vaccine misinformation universe.
Although he was not familiar with Dr. McCullough, Dr. Broniatowski said the cardiologist’s claims are not unique – they’ve been circulating among antivaccine and conspiracy-oriented groups for months.
For instance, Dr. McCullough has claimed in interviews that a whistleblower within the CDC knows of 50,000 vaccine-related deaths. Using data from the supposed whistleblower, the group America’s Frontline Doctors sued the federal government in July to stop the administration of COVID-19 vaccines to those under 18, people who have already had COVID, and individuals who the group said have not been adequately informed about the risks.
The idea of a whistleblower inside the CDC is recycled from antivaccine claims from decades ago, Dr. Broniatowski said.
But, he added, “somebody who speaks with the credibility of a major institution will be more likely to be listened to by some people.” That vulnerable group is “being taken advantage of by a relatively small number of disinformation purveyors, who, in some cases, profit from that disinformation,” said Dr. Broniatowski.
“We rely on our doctors because we trust them,” he said. “And we trust them because we believe that as physicians, their value system places the patient’s best interests first. That’s why it’s so much of a disappointment when you have a physician that appears to be exercising this sort of bad judgment.”
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, also said that he was not familiar with Dr. McCullough. But apprised of his claims, Dr. Offit told this news organization, “Peter McCullough is a friend of the virus.”
“The kind of information he promotes allows the virus to continue to spread, continue to do an enormous amount of harm, and continue to mutate and create variants that have become more contagious and more resistant to vaccine-induced immunity,” said Dr. Offit, the Maurice R. Hilleman professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Offit added that the war should be against SARS-CoV-2, but “because this virus has so many supporters, the war in essence becomes a war against ourselves, which is much harder.”
Dr. McCullough maintains he is doing a service to his patients. “I’m just giving and trying to help America understand the pandemic,” he told Ms. Ingraham on Fox News on July 29.
But he acknowledged concern about the Federation of State Medical Board’s announcement that physicians who spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation risk suspension or revocation of their license.
“I have to tell you I’m worried – that no matter what I do and how careful I am to cite the scientific studies, I’m still gonna be hunted down for quote, misinformation,” he said in the Aug. 3 interview.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in which he agreed to stop mentioning his prior leadership and academic appointments.
Baylor was the first institution to cut ties with Dr. McCullough, who has promoted the use of therapies seen as unproven for the treatment of COVID-19 and has questioned the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines. Since the Baylor suit, the Texas A&M College of Medicine, and the Texas Christian University (TCU) and University of North Texas Health Science Center (UNTHSC) School of Medicine have both removed Dr. McCullough from their faculties.
Granted by the 191st District Court in Dallas County, Tex., the Baylor restraining order – which is in effect at least until a hearing on the case on September 30 – was sought as part of Baylor Scott & White’s breach of contract suit against McCullough, who had previously been known as a well-respected expert in cardiorenal issues. The suit is seeking $1 million in damages, as well as attorneys’ fees.
The suit seeks to “enforce the terms” of the confidential employment separation agreement signed by Dr. McCullough in February and prevent Dr. McCullough from continuing “improper use of titles and claimed affiliations that have already confused the media, the medical community and the public,” it reads.
“This ongoing confusion regarding [Dr.] McCullough’s affiliations, and whether Plaintiffs support his opinions, is exactly what Plaintiffs bargained to avoid in the Separation Agreement,” and is likely to cause “irreparable reputational and business harm that is incapable of remedy by money damages alone,” the suit states.
One of Dr. McCullough’s attorneys, Clinton Mikel, maintains that all the times the physician was identified in the “thousands of hours of media interviews and countless publications since his departure from Baylor” were “said/printed by a third party with no encouragement from Dr. McCullough,” and that the doctor “does not and cannot control third parties.”
Mr. Mikel said in a statement emailed to this news organization by Dr. McCullough that the suit is “a politically motivated attempt to silence Dr. McCullough,” because it was filed on the same day the organization mandated COVID-19 vaccination for employees.
Dr. McCullough “intends to vigorously defend against Baylor’s unfounded lawsuit,” will seek to dissolve the restraining order, and recover “all payments due him from Baylor under the terms of the settlement agreement,” wrote Mr. Mikel.
The cardiologist’s legal team filed a motion to dismiss the suit on Aug. 9, essentially arguing that Baylor Scott & White’s action restricted Dr. McCullough’s right to free speech under the Texas Citizen’s Participation Act.
COVID-19 vaccines = bioterrorism?
Dr. McCullough accumulated a following in 2020 by promoting early at-home multidrug treatment of COVID-19 in interviews with conservative websites and at a U.S. Senate hearing in November.
Although Dr. McCullough does not appear to have any personal social media accounts, his broadcast and podcast interviews are tweeted by thousands daily around the world and featured on Facebook pages like “Pandemic Debate.”
Some Facebook posts with Dr. McCullough’s pronouncements have been labeled as misinformation or removed. Some of his videos remain on YouTube, where they are posted by the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, a group that believes Dr. McCullough is “under fierce attack for speaking out about COVID-19 early treatment and vaccine safety.”
Dr. McCullough’s March 2021 testimony to the Texas Senate’s Health and Human Services Committee – in which he claimed that COVID-19 patients are being denied what he called proven treatments like hydroxychloroquine – has been viewed more than 3.7 million times on YouTube. The appearance has also been tweeted repeatedly.
Most of Dr. McCullough’s interviews and presentations are aggregated on Rumble, an alternative to YouTube.
In interviews, Dr. McCullough promotes the use of zinc, hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, doxycycline, favipiravir, prednisone, and ivermectin as COVID-19 treatments – based on an outpatient treatment algorithm published in August 2020 in the American Journal of Medicine. The cardiologist was the lead author of that paper, which proposed treating people with COVID-like symptoms whether or not they had confirmed infection.
Dr. McCullough and colleagues published a follow-up paper that added colchicine to the mix in Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine. Dr. McCullough is editor-in-chief of the journal, but this was not noted in the disclosures.
Similarly, Dr. McCullough has not disclosed in his COVID-19 publications or any interviews that he has received consulting fees from a host of pharmaceutical manufacturers that produce COVID-19 drugs and vaccines, including AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Open Payments database, Dr. McCullough was paid about $300,000 annually by drug companies from 2014 to 2019, mostly for consulting on cardiovascular and diabetes medications. His payments dropped to $169,406.06 in 2020.
Dr. McCullough appeared on “The Ingraham Angle” on Fox News in December 2020, claiming that sequential, early treatment with “anti-infectives, corticosteroids, and then antithrombotics” could “reduce [COVID-19] hospitalizations by 85% and cut mortality in half.”
He repeated the claim on the Ingraham show in July and agreed with host Laura Ingraham that the vast majority of healthy people would do fine if they got COVID. He also made the claim that 84% of the COVID-19 cases in Israel were in people who had been vaccinated. “So it’s clear, we can’t vaccinate our way out of this,” he said. An Associated Press “fact check” report has pushed back on similar assertions about vaccine data from Israel.
In a separate interview posted in June, Dr. McCullough called the pandemic the first phase of a bioterrorism event, which was “all about keeping the population in fear and in isolation and preparing them to accept the vaccine, which appears to be phase two of a bioterrorism operation.”
In addition, he said, “good doctors are doing unthinkable things like injecting biologically active messenger RNA that produces this pathogenic spike protein into pregnant women.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the vaccines teach the body to produce the spike protein, which then triggers an immune response that creates antibodies that will attack the virus.
A PolitiFact review debunks the notion that the mRNA vaccines are toxic, cytotoxic, or introduce live, active virus proteins into the body.
FactCheck.org also disputed Dr. McCullough’s claim in a July 13 Ingraham Angle appearance that the mRNA vaccines are ineffective against the Delta variant.
In the FactCheck article, Frederic Bushman, codirector of the University of Pennsylvania’s Center for Research on Coronaviruses and Other Emerging Pathogens, said that people were much better off being vaccinated than not,” adding, “the Delta variant may reduce the effectiveness [of the vaccines] a little, but still, they’re so effective that you get a lot of benefit.”
“The vaccines are failing,” Dr. McCullough asserted in an Aug. 3 video interview posted on Odysee. “As we sit here today, we have 11,000 Americans that the CDC has certified have died after the vaccine,” he said, citing two analyses – one by Jessica Rose, PhD, and another by British researchers.
Similar figures reportedly based on cases reported to the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) were forwarded to this news organization by Dr. McCullough.
The CDC website notes that the agency has received reports of 7,653 deaths in people who received a vaccine as of Sept. 13 (0.0020% of vaccine doses given since Dec. 14, 2020), but it cautions that those deaths do not mean the vaccine was the cause.
Dr. McCullough repeatedly claimed in the Aug. 3 interview that the government has not been transparent on vaccine safety. Since June 2020, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has held 16 public meetings on the COVID-19 vaccines.
To date, the agency has advised clinicians to monitor for rare side effects including Guillain-Barré syndrome and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and myocarditis after mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) vaccines.
Med schools distance themselves
According to the Baylor Scott & White suit, Dr. McCullough agreed on Feb. 24 in a confidential separation agreement that he would no longer use his academic or leadership titles nor hold himself out to be affiliated with Baylor University Medical Center, Baylor Heart and Vascular Institute, the Baylor Research Institute, or any other related institutions.
However, as of August, according to a Baylor spokesperson, McCullough continued to have privileges at Baylor University Medical Center and Baylor Scott & White Heart and Vascular Hospital, Dallas.
The lawsuit points to three interviews posted in June and July where Dr. McCullough is identified as a “vice chief of medicine” or a “vice chief of internal medicine,” both at Baylor University. It also cites a profile at the Cardiometabolic Health Congress website – which this news organization had also viewed – that was still active in late July with a similar title. The profile was later scrubbed from the site.
Social media posts and other media continue to refer to Dr. McCullough’s Baylor credentials. An episode of the Faith and Freedom podcast posted on Aug. 2 identified McCullough as a “professor of medicine at Baylor University Medical Center.”
As of Sept. 16, Dr. McCullough’s bio page at his current practice, Heart Place, lists him as a professor of medicine at Texas A&M College of Medicine. A spokesperson for Texas A&M told this news organization that McCullough is no longer affiliated with the school.
Dr. McCullough acknowledged in the Aug. 3 interview that his Texas A&M title had been “stripped away” at “around the same time this lawsuit was filed.”
He was still a professor of medicine at the TCU and UNTHSC School of Medicine in Fort Worth, but a school spokesperson notified this news organization on Aug. 19 that Dr. McCullough was no longer with the school.
Dr. McCullough has portrayed himself as both a victim and a truth-teller, a “concerned physician” warning the world about the dangers of COVID-19 vaccines. The Baylor Scott & White lawsuit “is really a strong-armed tactic,” he said in the Aug. 3 interview. “I’m just a little guy, so I have to hire my legal teams, and in a sense be drained dry on legal fees,” he said.
But Dr. McCullough apparently has a plan for helping to defray his legal costs. In the Aug. 3 interview, he said a foundation he helped start, Truth for Health, has a “donation side to it,” adding “some of that may be used for legal expense.”
Cheryl Jones, an attorney with PK Law in Towson, Md., said that might draw interest from the Internal Revenue Service. “I would expect IRS scrutiny if contributions to the Medical Censorship Defense Fund are used to defend Dr McCullough in his personal breach of contract lawsuit,” she told this news organization.
The IRS generally recognizes defending “human and civil rights secured by law” as a legitimate charitable purpose for a legal defense fund, she said, adding that such a fund “must serve only public, rather than private, interests.”
Misinformation from a physician more damaging?
Some in the medical field have refuted Dr. McCullough’s pronouncements on how to treat COVID-19, including two infectious disease specialists with Monash University, Melbourne, who responded to the cardiologist’s original paper in the American Journal of Medicine.
Tony Korman, MBBS, a professor at the Centre for Inflammatory Diseases at Monash, told this news organization, “we had concerns that reputable medical journals would accept and publish papers proposing treatment of COVID-19 which was not supported by evidence.”
The website Healthfeedback.org has also challenged McCullough’s and his supporters’ claims, including that the American Journal of Medicine endorsed the use of hydroxychloroquine and that the COVID-19 vaccines have caused thousands of deaths.
David Broniatowski, PhD, associate director for the Institute for Data, Democracy and Politics at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview that Dr. McCullough’s casting himself as a “rebel doctor” is a well-known trope in the vaccine misinformation universe.
Although he was not familiar with Dr. McCullough, Dr. Broniatowski said the cardiologist’s claims are not unique – they’ve been circulating among antivaccine and conspiracy-oriented groups for months.
For instance, Dr. McCullough has claimed in interviews that a whistleblower within the CDC knows of 50,000 vaccine-related deaths. Using data from the supposed whistleblower, the group America’s Frontline Doctors sued the federal government in July to stop the administration of COVID-19 vaccines to those under 18, people who have already had COVID, and individuals who the group said have not been adequately informed about the risks.
The idea of a whistleblower inside the CDC is recycled from antivaccine claims from decades ago, Dr. Broniatowski said.
But, he added, “somebody who speaks with the credibility of a major institution will be more likely to be listened to by some people.” That vulnerable group is “being taken advantage of by a relatively small number of disinformation purveyors, who, in some cases, profit from that disinformation,” said Dr. Broniatowski.
“We rely on our doctors because we trust them,” he said. “And we trust them because we believe that as physicians, their value system places the patient’s best interests first. That’s why it’s so much of a disappointment when you have a physician that appears to be exercising this sort of bad judgment.”
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, also said that he was not familiar with Dr. McCullough. But apprised of his claims, Dr. Offit told this news organization, “Peter McCullough is a friend of the virus.”
“The kind of information he promotes allows the virus to continue to spread, continue to do an enormous amount of harm, and continue to mutate and create variants that have become more contagious and more resistant to vaccine-induced immunity,” said Dr. Offit, the Maurice R. Hilleman professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Offit added that the war should be against SARS-CoV-2, but “because this virus has so many supporters, the war in essence becomes a war against ourselves, which is much harder.”
Dr. McCullough maintains he is doing a service to his patients. “I’m just giving and trying to help America understand the pandemic,” he told Ms. Ingraham on Fox News on July 29.
But he acknowledged concern about the Federation of State Medical Board’s announcement that physicians who spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation risk suspension or revocation of their license.
“I have to tell you I’m worried – that no matter what I do and how careful I am to cite the scientific studies, I’m still gonna be hunted down for quote, misinformation,” he said in the Aug. 3 interview.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccine preprint study prompts Twitter outrage
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Will interchangeable insulin be more affordable in the U.S.?
When the Food and Drug Administration approved Semglee, the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, the agency pitched it as having the potential to be less costly than insulins currently on the market, but lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing has left analysts and advocates guessing whether it will indeed be a source of relief.
Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals), first approved as a biosimilar in June 2020, costs about $100 a vial.
But receiving the “interchangeable designation” in July 2021, the first for any insulin, now allows Semglee to be substituted for the branded Lantus (insulin glargine, Sanofi) at the pharmacy without the need for a separate prescription, the same way as generic medicines.
A spokesperson for Viatris – Mylan’s parent company told this news organization that the interchangeable, with its new labeling, will be “introduced before the end of the year,” but it would not give any more details.
“Additional information, including pricing information, for interchangeable biosimilar Semglee will be provided at the time of product launch,” said the spokesperson.
Even at $100 a vial, it is not cheap
Ian Devaney, a spokesman for the advocacy group T1 International, said the organization is optimistic, given that “another player has been able to enter into a space that has for so long been dominated by Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.” Increased competition “will help drive down the overall costs of insulin,” Mr. Devaney said in an interview. But, he added, for many people, especially in low-income countries, Semglee’s launch will have little to no impact on price.
Even at $100 a vial in the United States, “this is not an insignificant amount of money and presents a very difficult financial challenge for those dependent on insulin to survive,” he said.
A current Semglee user agreed, sharing her story with this news organization via T1 International. “My son uses three to five vials of long-acting insulin per month, and I use one to three vials per month,” said the woman, who prefers to remain anonymous. “If we were to lose Medicaid, we would still be paying up to $800 out of pocket monthly to survive, and that’s not even counting fast-acting insulin or other supplies. While $100 a vial may be cheaper, these costs are still outrageous.”
The woman also noted that, while new competitors are welcome, they also have been disruptive. After her doctor switched her to Semglee, she was notified that it was on back order. “It took a week to get it filled, and when it finally came in, it was in short supply,” she said, noting that she and her son received one Semglee pen each, “well short of the three and five each we were expecting.”
U.S. pricing is all ‘smoke and mirrors’
Sara W. Koblitz, a food and drug law attorney with Hyman Phelps in Washington, D.C., noted in a blog post that interchangeable Semglee will likely be awarded a year of marketing exclusivity, which will block other interchangeable competitors from entering the market during that time.
With no competition, “Mylan can price Semglee only slightly less than Lantus and still take market share, only marginally reducing costs to consumers,” she wrote.
Jing Luo, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, who has studied insulin access and costs, said that having just one interchangeable on the market might not be enough to drive insulin costs down.
And, he told this news organization, “there’s even a possibility that Semglee prices will go up, but hopefully that will not be the case.”
Manufacturers like Mylan can also offer confidential discounts and rebates to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), health plans, and health plan sponsors (usually large companies that are self-insured) that make it difficult to assess the true cost, said David Steinberg, PharmD, director of pharmacy insights at Scripta Insights. The Wellesley, Mass.–based company advises self-insured employers on how to optimize pharmacy benefits.
When it comes to pricing, “it’s a lot of smoke and mirrors,” Dr. Steinberg said in an interview.
Dr. Steinberg also noted that some PBMs might choose to continue contracts with Sanofi that offer rebates for Lantus, leaving Semglee in a less-preferred position on a formulary, which could increase how much the patient pays at the pharmacy counter.
Medicare and Medicaid, however, can put Semglee in the top-tier preferred formulary position. Most Medicaid plans cover Semglee, but it appears that Medicare has not added coverage yet.
Does current pricing predict the future?
The currently marketed Semglee has an average wholesale price (AWP) that is one third of Lantus’, and about half of what is published for Basaglar (insulin glargine, Eli Lilly), a “follow-on biologic” approved in 2015 that is similar to Lantus, Dr. Steinberg said.
The AWP is often cited by analysts when talking about costs. The AWP of the current Semglee 10-mL vial is $118.38; the Lantus 10-mL vial is $340.27, said Steinberg.
Five prefilled Semglee pens (each 3 mL) are $177.58; for Lantus, the AWP for five 3-mL pens is $510.37.
Dr. Luo said he has seen a box of Semglee pens retail between $177 and $195, compared with about $500 retail for the Lantus pens.
Currently, people with commercial insurance can get Semglee for $0-75 a month, for up to a year, using the company’s savings program.
Steinberg said it’s possible that Mylan could increase the list price for the interchangeable Semglee, but that move could backfire. “I think their goal initially is to get market share,” he said.
After Basaglar came on the market – in late 2016 – the price of Lantus came down significantly over the next few years, according to a 2019 study by Dr. Luo’s colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh.
But Basaglar has not hung on to market share, according to Scott Strumello, a person with autoimmune type 1 diabetes who tweets and blogs about insulin and other issues.
In early August, Mr. Strumello tweeted some Lilly data that showed U.S. sales of Basaglar declined 42% in the first two quarters of 2021, compared with the same period in 2020.
Dr. Steinberg noted that the decline may have to do with rebates being given to PBMs by competitors Sanofi and Novo Nordisk. Sanofi “is very aggressive when it comes to pricing with their PBM partners,” he said.
While Mr. Devaney said people with diabetes are hopeful that Semglee can break the big three manufacturers’ monopoly, he added: “We don’t see Semglee as something that is solving the root cause of the insulin price crisis, which is high list prices and pharmaceutical industry greed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the Food and Drug Administration approved Semglee, the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, the agency pitched it as having the potential to be less costly than insulins currently on the market, but lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing has left analysts and advocates guessing whether it will indeed be a source of relief.
Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals), first approved as a biosimilar in June 2020, costs about $100 a vial.
But receiving the “interchangeable designation” in July 2021, the first for any insulin, now allows Semglee to be substituted for the branded Lantus (insulin glargine, Sanofi) at the pharmacy without the need for a separate prescription, the same way as generic medicines.
A spokesperson for Viatris – Mylan’s parent company told this news organization that the interchangeable, with its new labeling, will be “introduced before the end of the year,” but it would not give any more details.
“Additional information, including pricing information, for interchangeable biosimilar Semglee will be provided at the time of product launch,” said the spokesperson.
Even at $100 a vial, it is not cheap
Ian Devaney, a spokesman for the advocacy group T1 International, said the organization is optimistic, given that “another player has been able to enter into a space that has for so long been dominated by Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.” Increased competition “will help drive down the overall costs of insulin,” Mr. Devaney said in an interview. But, he added, for many people, especially in low-income countries, Semglee’s launch will have little to no impact on price.
Even at $100 a vial in the United States, “this is not an insignificant amount of money and presents a very difficult financial challenge for those dependent on insulin to survive,” he said.
A current Semglee user agreed, sharing her story with this news organization via T1 International. “My son uses three to five vials of long-acting insulin per month, and I use one to three vials per month,” said the woman, who prefers to remain anonymous. “If we were to lose Medicaid, we would still be paying up to $800 out of pocket monthly to survive, and that’s not even counting fast-acting insulin or other supplies. While $100 a vial may be cheaper, these costs are still outrageous.”
The woman also noted that, while new competitors are welcome, they also have been disruptive. After her doctor switched her to Semglee, she was notified that it was on back order. “It took a week to get it filled, and when it finally came in, it was in short supply,” she said, noting that she and her son received one Semglee pen each, “well short of the three and five each we were expecting.”
U.S. pricing is all ‘smoke and mirrors’
Sara W. Koblitz, a food and drug law attorney with Hyman Phelps in Washington, D.C., noted in a blog post that interchangeable Semglee will likely be awarded a year of marketing exclusivity, which will block other interchangeable competitors from entering the market during that time.
With no competition, “Mylan can price Semglee only slightly less than Lantus and still take market share, only marginally reducing costs to consumers,” she wrote.
Jing Luo, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, who has studied insulin access and costs, said that having just one interchangeable on the market might not be enough to drive insulin costs down.
And, he told this news organization, “there’s even a possibility that Semglee prices will go up, but hopefully that will not be the case.”
Manufacturers like Mylan can also offer confidential discounts and rebates to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), health plans, and health plan sponsors (usually large companies that are self-insured) that make it difficult to assess the true cost, said David Steinberg, PharmD, director of pharmacy insights at Scripta Insights. The Wellesley, Mass.–based company advises self-insured employers on how to optimize pharmacy benefits.
When it comes to pricing, “it’s a lot of smoke and mirrors,” Dr. Steinberg said in an interview.
Dr. Steinberg also noted that some PBMs might choose to continue contracts with Sanofi that offer rebates for Lantus, leaving Semglee in a less-preferred position on a formulary, which could increase how much the patient pays at the pharmacy counter.
Medicare and Medicaid, however, can put Semglee in the top-tier preferred formulary position. Most Medicaid plans cover Semglee, but it appears that Medicare has not added coverage yet.
Does current pricing predict the future?
The currently marketed Semglee has an average wholesale price (AWP) that is one third of Lantus’, and about half of what is published for Basaglar (insulin glargine, Eli Lilly), a “follow-on biologic” approved in 2015 that is similar to Lantus, Dr. Steinberg said.
The AWP is often cited by analysts when talking about costs. The AWP of the current Semglee 10-mL vial is $118.38; the Lantus 10-mL vial is $340.27, said Steinberg.
Five prefilled Semglee pens (each 3 mL) are $177.58; for Lantus, the AWP for five 3-mL pens is $510.37.
Dr. Luo said he has seen a box of Semglee pens retail between $177 and $195, compared with about $500 retail for the Lantus pens.
Currently, people with commercial insurance can get Semglee for $0-75 a month, for up to a year, using the company’s savings program.
Steinberg said it’s possible that Mylan could increase the list price for the interchangeable Semglee, but that move could backfire. “I think their goal initially is to get market share,” he said.
After Basaglar came on the market – in late 2016 – the price of Lantus came down significantly over the next few years, according to a 2019 study by Dr. Luo’s colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh.
But Basaglar has not hung on to market share, according to Scott Strumello, a person with autoimmune type 1 diabetes who tweets and blogs about insulin and other issues.
In early August, Mr. Strumello tweeted some Lilly data that showed U.S. sales of Basaglar declined 42% in the first two quarters of 2021, compared with the same period in 2020.
Dr. Steinberg noted that the decline may have to do with rebates being given to PBMs by competitors Sanofi and Novo Nordisk. Sanofi “is very aggressive when it comes to pricing with their PBM partners,” he said.
While Mr. Devaney said people with diabetes are hopeful that Semglee can break the big three manufacturers’ monopoly, he added: “We don’t see Semglee as something that is solving the root cause of the insulin price crisis, which is high list prices and pharmaceutical industry greed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the Food and Drug Administration approved Semglee, the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, the agency pitched it as having the potential to be less costly than insulins currently on the market, but lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing has left analysts and advocates guessing whether it will indeed be a source of relief.
Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals), first approved as a biosimilar in June 2020, costs about $100 a vial.
But receiving the “interchangeable designation” in July 2021, the first for any insulin, now allows Semglee to be substituted for the branded Lantus (insulin glargine, Sanofi) at the pharmacy without the need for a separate prescription, the same way as generic medicines.
A spokesperson for Viatris – Mylan’s parent company told this news organization that the interchangeable, with its new labeling, will be “introduced before the end of the year,” but it would not give any more details.
“Additional information, including pricing information, for interchangeable biosimilar Semglee will be provided at the time of product launch,” said the spokesperson.
Even at $100 a vial, it is not cheap
Ian Devaney, a spokesman for the advocacy group T1 International, said the organization is optimistic, given that “another player has been able to enter into a space that has for so long been dominated by Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.” Increased competition “will help drive down the overall costs of insulin,” Mr. Devaney said in an interview. But, he added, for many people, especially in low-income countries, Semglee’s launch will have little to no impact on price.
Even at $100 a vial in the United States, “this is not an insignificant amount of money and presents a very difficult financial challenge for those dependent on insulin to survive,” he said.
A current Semglee user agreed, sharing her story with this news organization via T1 International. “My son uses three to five vials of long-acting insulin per month, and I use one to three vials per month,” said the woman, who prefers to remain anonymous. “If we were to lose Medicaid, we would still be paying up to $800 out of pocket monthly to survive, and that’s not even counting fast-acting insulin or other supplies. While $100 a vial may be cheaper, these costs are still outrageous.”
The woman also noted that, while new competitors are welcome, they also have been disruptive. After her doctor switched her to Semglee, she was notified that it was on back order. “It took a week to get it filled, and when it finally came in, it was in short supply,” she said, noting that she and her son received one Semglee pen each, “well short of the three and five each we were expecting.”
U.S. pricing is all ‘smoke and mirrors’
Sara W. Koblitz, a food and drug law attorney with Hyman Phelps in Washington, D.C., noted in a blog post that interchangeable Semglee will likely be awarded a year of marketing exclusivity, which will block other interchangeable competitors from entering the market during that time.
With no competition, “Mylan can price Semglee only slightly less than Lantus and still take market share, only marginally reducing costs to consumers,” she wrote.
Jing Luo, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, who has studied insulin access and costs, said that having just one interchangeable on the market might not be enough to drive insulin costs down.
And, he told this news organization, “there’s even a possibility that Semglee prices will go up, but hopefully that will not be the case.”
Manufacturers like Mylan can also offer confidential discounts and rebates to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), health plans, and health plan sponsors (usually large companies that are self-insured) that make it difficult to assess the true cost, said David Steinberg, PharmD, director of pharmacy insights at Scripta Insights. The Wellesley, Mass.–based company advises self-insured employers on how to optimize pharmacy benefits.
When it comes to pricing, “it’s a lot of smoke and mirrors,” Dr. Steinberg said in an interview.
Dr. Steinberg also noted that some PBMs might choose to continue contracts with Sanofi that offer rebates for Lantus, leaving Semglee in a less-preferred position on a formulary, which could increase how much the patient pays at the pharmacy counter.
Medicare and Medicaid, however, can put Semglee in the top-tier preferred formulary position. Most Medicaid plans cover Semglee, but it appears that Medicare has not added coverage yet.
Does current pricing predict the future?
The currently marketed Semglee has an average wholesale price (AWP) that is one third of Lantus’, and about half of what is published for Basaglar (insulin glargine, Eli Lilly), a “follow-on biologic” approved in 2015 that is similar to Lantus, Dr. Steinberg said.
The AWP is often cited by analysts when talking about costs. The AWP of the current Semglee 10-mL vial is $118.38; the Lantus 10-mL vial is $340.27, said Steinberg.
Five prefilled Semglee pens (each 3 mL) are $177.58; for Lantus, the AWP for five 3-mL pens is $510.37.
Dr. Luo said he has seen a box of Semglee pens retail between $177 and $195, compared with about $500 retail for the Lantus pens.
Currently, people with commercial insurance can get Semglee for $0-75 a month, for up to a year, using the company’s savings program.
Steinberg said it’s possible that Mylan could increase the list price for the interchangeable Semglee, but that move could backfire. “I think their goal initially is to get market share,” he said.
After Basaglar came on the market – in late 2016 – the price of Lantus came down significantly over the next few years, according to a 2019 study by Dr. Luo’s colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh.
But Basaglar has not hung on to market share, according to Scott Strumello, a person with autoimmune type 1 diabetes who tweets and blogs about insulin and other issues.
In early August, Mr. Strumello tweeted some Lilly data that showed U.S. sales of Basaglar declined 42% in the first two quarters of 2021, compared with the same period in 2020.
Dr. Steinberg noted that the decline may have to do with rebates being given to PBMs by competitors Sanofi and Novo Nordisk. Sanofi “is very aggressive when it comes to pricing with their PBM partners,” he said.
While Mr. Devaney said people with diabetes are hopeful that Semglee can break the big three manufacturers’ monopoly, he added: “We don’t see Semglee as something that is solving the root cause of the insulin price crisis, which is high list prices and pharmaceutical industry greed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
United Healthcare settles claims it violated mental health parity
The nation’s largest health care insurer has agreed to pay $16 million in restitution and penalties to consumers, the federal government, and the state of New York to settle complaints that it illegally limited outpatient psychotherapy.
The settlement resolves a joint U.S. Department of Labor and New York Attorney General investigation and lawsuit that found that United Healthcare and United Behavioral Health (UBH) had, since at least 2013, violated the federal Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008.
United Healthcare and UBH are fighting similar claims in Wit v United Behavioral Health, which is currently on appeal at the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. If that complaint is decided against UBH, the insurer might have to reprocess more than 67,000 claims.
The joint New York–federal investigation determined that United Healthcare reduced reimbursement rates for out-of-network mental health services and denied payment for many services using its Algorithms for Effective Reporting and Treatment (ALERT) utilization review program.
All outpatient psychotherapy was subjected to review; by comparison, only a handful of medical and surgical services were. That violated parity laws, the New York Attorney General’s office said in a statement.
“United’s denial of these vital services was both unlawful and dangerous,” New York Attorney General Letitia James said in the statement.
“Protecting access to mental health and substance disorder treatment is a priority for the Department of Labor and something I believe in strongly as a person in long-term recovery,” U.S. Secretary of Labor Marty Walsh said in another statement.
Mr. Walsh added that the settlement “provides compensation for many people who were denied full benefits and equitable treatment.”
‘Investigations change behavior’
Commenting for this news organization, Joe Parks, MD, medical director of the National Council for Mental Wellbeing, applauded the settlement.
“These kinds of investigations change behavior, and people get better coverage,” Dr. Parks said.
He also applauded New York, saying that it “has been one of the more assertive states in expecting companies to comply with parity requirements. They should be emulated by other states.”
Dr. Parks noted that a 2019 U.S. Government Accountability Office report showed that only 20 states routinely conducted parity compliance reviews.
A spokesperson for the American Psychiatric Association said it was notable that the Department of Labor focused on three issues that it had not publicly investigated before.
These were payment parity, the use of algorithms in mental health to identify practitioners and patients who use more health care than expected of the “average” person, and requiring disclosure of how the insurer set rates, guidelines, and medical necessity standards.
The American Psychological Association’s chief of psychological practice, Jared L. Skillings, PhD, said the group was gratified that the Department of Labor and New York took complaints seriously and that it “is encouraged that United Behavioral Health and United Healthcare have agreed to change their unfair procedures regarding reimbursement and denial of psychological care.”
The association “will monitor implementation of the settlement with high hopes for fair treatment for patients with mental health needs,” Dr. Skillings said in an interview.
Across-the-board cuts for therapy
The investigation found that United Healthcare reduced the allowable reimbursement amount for all nonphysicians across the board for psychotherapy – by 25% for PhD-level psychologists and by 35% for all MA-level therapists.
The company’s ALERT system used arbitrary thresholds to trigger utilization review, which “often led to denials of coverage when providers could not justify continued treatment after 20 sessions,” said the New York attorney general.
Beneficiaries had to figure out how to pay for continuing services or abruptly end necessary treatment.
United Healthcare agreed to stop reducing reimbursement and to not employ a similar policy in New York for at least 2 years. It will stop using ALERT and stop issuing denials for psychotherapy through at least 2023.
In addition, “We are committed to ensuring all our members have access to care and to reimbursing providers consistent with the terms of the member’s health plan and state and federal rules,” United Healthcare said.
Dr. Parks noted that United Healthcare had stopped using ALERT long before the settlement and was instead employing Level of Care Utilization System for Psychiatric and Addiction Services (LOCUS) and American Society of Addiction Medicine criteria, which he called “a good step forward.”
‘Meaningful’ payout
United Healthcare will pay $14.3 million in restitution to consumers, including $9 million to 20,000 New Yorkers who received denials of or reductions in reimbursement. The company will also pay more than $2 million in penalties, with $1.3 million going to New York.
The insurer has annual revenues of some $250 billion.
“It’s not a large amount of money in United’s overall business operation,” said Dr. Parks.
However, “It certainly could be a meaningful amount of money for the individuals that didn’t get coverage that paid out of pocket,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The nation’s largest health care insurer has agreed to pay $16 million in restitution and penalties to consumers, the federal government, and the state of New York to settle complaints that it illegally limited outpatient psychotherapy.
The settlement resolves a joint U.S. Department of Labor and New York Attorney General investigation and lawsuit that found that United Healthcare and United Behavioral Health (UBH) had, since at least 2013, violated the federal Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008.
United Healthcare and UBH are fighting similar claims in Wit v United Behavioral Health, which is currently on appeal at the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. If that complaint is decided against UBH, the insurer might have to reprocess more than 67,000 claims.
The joint New York–federal investigation determined that United Healthcare reduced reimbursement rates for out-of-network mental health services and denied payment for many services using its Algorithms for Effective Reporting and Treatment (ALERT) utilization review program.
All outpatient psychotherapy was subjected to review; by comparison, only a handful of medical and surgical services were. That violated parity laws, the New York Attorney General’s office said in a statement.
“United’s denial of these vital services was both unlawful and dangerous,” New York Attorney General Letitia James said in the statement.
“Protecting access to mental health and substance disorder treatment is a priority for the Department of Labor and something I believe in strongly as a person in long-term recovery,” U.S. Secretary of Labor Marty Walsh said in another statement.
Mr. Walsh added that the settlement “provides compensation for many people who were denied full benefits and equitable treatment.”
‘Investigations change behavior’
Commenting for this news organization, Joe Parks, MD, medical director of the National Council for Mental Wellbeing, applauded the settlement.
“These kinds of investigations change behavior, and people get better coverage,” Dr. Parks said.
He also applauded New York, saying that it “has been one of the more assertive states in expecting companies to comply with parity requirements. They should be emulated by other states.”
Dr. Parks noted that a 2019 U.S. Government Accountability Office report showed that only 20 states routinely conducted parity compliance reviews.
A spokesperson for the American Psychiatric Association said it was notable that the Department of Labor focused on three issues that it had not publicly investigated before.
These were payment parity, the use of algorithms in mental health to identify practitioners and patients who use more health care than expected of the “average” person, and requiring disclosure of how the insurer set rates, guidelines, and medical necessity standards.
The American Psychological Association’s chief of psychological practice, Jared L. Skillings, PhD, said the group was gratified that the Department of Labor and New York took complaints seriously and that it “is encouraged that United Behavioral Health and United Healthcare have agreed to change their unfair procedures regarding reimbursement and denial of psychological care.”
The association “will monitor implementation of the settlement with high hopes for fair treatment for patients with mental health needs,” Dr. Skillings said in an interview.
Across-the-board cuts for therapy
The investigation found that United Healthcare reduced the allowable reimbursement amount for all nonphysicians across the board for psychotherapy – by 25% for PhD-level psychologists and by 35% for all MA-level therapists.
The company’s ALERT system used arbitrary thresholds to trigger utilization review, which “often led to denials of coverage when providers could not justify continued treatment after 20 sessions,” said the New York attorney general.
Beneficiaries had to figure out how to pay for continuing services or abruptly end necessary treatment.
United Healthcare agreed to stop reducing reimbursement and to not employ a similar policy in New York for at least 2 years. It will stop using ALERT and stop issuing denials for psychotherapy through at least 2023.
In addition, “We are committed to ensuring all our members have access to care and to reimbursing providers consistent with the terms of the member’s health plan and state and federal rules,” United Healthcare said.
Dr. Parks noted that United Healthcare had stopped using ALERT long before the settlement and was instead employing Level of Care Utilization System for Psychiatric and Addiction Services (LOCUS) and American Society of Addiction Medicine criteria, which he called “a good step forward.”
‘Meaningful’ payout
United Healthcare will pay $14.3 million in restitution to consumers, including $9 million to 20,000 New Yorkers who received denials of or reductions in reimbursement. The company will also pay more than $2 million in penalties, with $1.3 million going to New York.
The insurer has annual revenues of some $250 billion.
“It’s not a large amount of money in United’s overall business operation,” said Dr. Parks.
However, “It certainly could be a meaningful amount of money for the individuals that didn’t get coverage that paid out of pocket,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The nation’s largest health care insurer has agreed to pay $16 million in restitution and penalties to consumers, the federal government, and the state of New York to settle complaints that it illegally limited outpatient psychotherapy.
The settlement resolves a joint U.S. Department of Labor and New York Attorney General investigation and lawsuit that found that United Healthcare and United Behavioral Health (UBH) had, since at least 2013, violated the federal Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008.
United Healthcare and UBH are fighting similar claims in Wit v United Behavioral Health, which is currently on appeal at the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. If that complaint is decided against UBH, the insurer might have to reprocess more than 67,000 claims.
The joint New York–federal investigation determined that United Healthcare reduced reimbursement rates for out-of-network mental health services and denied payment for many services using its Algorithms for Effective Reporting and Treatment (ALERT) utilization review program.
All outpatient psychotherapy was subjected to review; by comparison, only a handful of medical and surgical services were. That violated parity laws, the New York Attorney General’s office said in a statement.
“United’s denial of these vital services was both unlawful and dangerous,” New York Attorney General Letitia James said in the statement.
“Protecting access to mental health and substance disorder treatment is a priority for the Department of Labor and something I believe in strongly as a person in long-term recovery,” U.S. Secretary of Labor Marty Walsh said in another statement.
Mr. Walsh added that the settlement “provides compensation for many people who were denied full benefits and equitable treatment.”
‘Investigations change behavior’
Commenting for this news organization, Joe Parks, MD, medical director of the National Council for Mental Wellbeing, applauded the settlement.
“These kinds of investigations change behavior, and people get better coverage,” Dr. Parks said.
He also applauded New York, saying that it “has been one of the more assertive states in expecting companies to comply with parity requirements. They should be emulated by other states.”
Dr. Parks noted that a 2019 U.S. Government Accountability Office report showed that only 20 states routinely conducted parity compliance reviews.
A spokesperson for the American Psychiatric Association said it was notable that the Department of Labor focused on three issues that it had not publicly investigated before.
These were payment parity, the use of algorithms in mental health to identify practitioners and patients who use more health care than expected of the “average” person, and requiring disclosure of how the insurer set rates, guidelines, and medical necessity standards.
The American Psychological Association’s chief of psychological practice, Jared L. Skillings, PhD, said the group was gratified that the Department of Labor and New York took complaints seriously and that it “is encouraged that United Behavioral Health and United Healthcare have agreed to change their unfair procedures regarding reimbursement and denial of psychological care.”
The association “will monitor implementation of the settlement with high hopes for fair treatment for patients with mental health needs,” Dr. Skillings said in an interview.
Across-the-board cuts for therapy
The investigation found that United Healthcare reduced the allowable reimbursement amount for all nonphysicians across the board for psychotherapy – by 25% for PhD-level psychologists and by 35% for all MA-level therapists.
The company’s ALERT system used arbitrary thresholds to trigger utilization review, which “often led to denials of coverage when providers could not justify continued treatment after 20 sessions,” said the New York attorney general.
Beneficiaries had to figure out how to pay for continuing services or abruptly end necessary treatment.
United Healthcare agreed to stop reducing reimbursement and to not employ a similar policy in New York for at least 2 years. It will stop using ALERT and stop issuing denials for psychotherapy through at least 2023.
In addition, “We are committed to ensuring all our members have access to care and to reimbursing providers consistent with the terms of the member’s health plan and state and federal rules,” United Healthcare said.
Dr. Parks noted that United Healthcare had stopped using ALERT long before the settlement and was instead employing Level of Care Utilization System for Psychiatric and Addiction Services (LOCUS) and American Society of Addiction Medicine criteria, which he called “a good step forward.”
‘Meaningful’ payout
United Healthcare will pay $14.3 million in restitution to consumers, including $9 million to 20,000 New Yorkers who received denials of or reductions in reimbursement. The company will also pay more than $2 million in penalties, with $1.3 million going to New York.
The insurer has annual revenues of some $250 billion.
“It’s not a large amount of money in United’s overall business operation,” said Dr. Parks.
However, “It certainly could be a meaningful amount of money for the individuals that didn’t get coverage that paid out of pocket,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Deeper dive’ into opioid overdose deaths during COVID pandemic
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pups for veterans with PTSD: Biden signs PAWS act into law
Service members with posttraumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions may eventually have expanded access to service dogs through legislation recently signed into law by President Joseph R. Biden.
The Puppies Assisting Wounded Servicemembers (PAWS) for Veterans Therapy Act (HR 1448) orders the Department of Veterans Affairs to begin a pilot program that over the course of 5 years will examine the utility and effectiveness of service dogs for improving the mental health of military veterans.
The legislation does not set a specific start date for the pilot program, but Rory Diamond, CEO of K9s for Warriors, a nonprofit organization based in Ponte Vedra, Fla., noted that K9s for Warriors and other organizations will be pushing the VA to start in 2022.
“We commend the White House for supporting this bill as a critical step in combating veteran suicide, and we’re confident in the path ahead for service dogs ultimately becoming a covered VA benefit to veterans with PTSD,” Mr. Diamond said in a statement provided to this news organization.
“For servicemembers relying on task-trained service dogs for PTSD, the HR 1448 is a giant leap towards supporting veterans and their service dogs in an equitable way,” Canine Companions, a national nonprofit organization that trains and provides service dogs, said in its own statement.
“It might mean the difference between having a veteran who won’t be here tomorrow and having one that will,” the group added.
Invisible wounds of war
In another statement, Bill McCabe, legislative affairs director at the Enlisted Association, said that “now, more than ever, veterans suffering from invisible wounds of war need access to trained service dogs, which have been scientifically proven to help alleviate symptoms of posttraumatic stress,” as well as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and military sexual trauma.
“We thank President Biden for recognizing veterans need every possible option when seeking mental health treatments, and look forward to working with the Department of Veterans Affairs to implement this important program,” Mr. McCabe said.
A recent VA report showed that in 2014, 40% of veterans had mental health conditions such as PTSD and substance use. An average of 20 veterans per day died by suicide that year.
Veterans with problems regarding mobility, hearing, and sight, as well as some mental health problems, have been eligible to have costs of veterinary care for service dogs paid by the VA, although the VA has not paid for the training of the animals.
The PAWS Act, which was bipartisan legislation introduced by U.S. Senators Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Kyrsten Sinema (D-Ariz.), Kevin Cramer (R-N.D.), and Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), aims to expand eligibility to those with any mental health problems.
For at least a decade, various service dog and veterans’ organizations have pushed to have the VA expand the service dog benefit. This new law is a “first step,” said Mr. Diamond. “We had to kick open the door,” he said, adding that “the VA has essentially said no for almost 15 years.”
Mr. Diamond noted that there is “overwhelming” evidence showing that service dogs improve quality of life and reduce distress for veterans with PTSD and other diagnoses.
‘No excuse’
Results from a VA study showed that suicidal ideation was reduced in veterans who were paired with service dogs, compared with veterans paired with emotional support dogs. The study, which was made public in March, found no reduction in overall disability, according to a report by Military.com.
K9s for Warriors cites numerous other studies, published in peer-reviewed journals, that have shown that service dogs reduce PTSD symptoms, especially hypervigilance.
“There really is no excuse not to have the VA engaged in helping veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress who are extremely high risk of suicide to get a lifesaving service dog,” Mr. Diamond said.
His organization has paired 700 veterans suffering from TBI, PTSD, or military sexual trauma with a service dog. The organization provides a 3-week training program for the veteran and his or her dog.
Although about 200 of the graduates have been eligible to receive coverage from the VA for veterinary care for the dogs, it requires a lot of paperwork, and the criteria for who can be certified to receive that benefit are somewhat vague, Mr. Diamond noted.
Under current policy, the dog and veteran must have successfully completed a training program offered by an organization accredited by Assistance Dogs International or the International Guide Dog Federation.
The new pilot program will enable eligible veterans to receive dog training instruction from accredited nonprofit service dog training organizations, and it will give them the opportunity to adopt a dog that they actively assisted in training.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Service members with posttraumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions may eventually have expanded access to service dogs through legislation recently signed into law by President Joseph R. Biden.
The Puppies Assisting Wounded Servicemembers (PAWS) for Veterans Therapy Act (HR 1448) orders the Department of Veterans Affairs to begin a pilot program that over the course of 5 years will examine the utility and effectiveness of service dogs for improving the mental health of military veterans.
The legislation does not set a specific start date for the pilot program, but Rory Diamond, CEO of K9s for Warriors, a nonprofit organization based in Ponte Vedra, Fla., noted that K9s for Warriors and other organizations will be pushing the VA to start in 2022.
“We commend the White House for supporting this bill as a critical step in combating veteran suicide, and we’re confident in the path ahead for service dogs ultimately becoming a covered VA benefit to veterans with PTSD,” Mr. Diamond said in a statement provided to this news organization.
“For servicemembers relying on task-trained service dogs for PTSD, the HR 1448 is a giant leap towards supporting veterans and their service dogs in an equitable way,” Canine Companions, a national nonprofit organization that trains and provides service dogs, said in its own statement.
“It might mean the difference between having a veteran who won’t be here tomorrow and having one that will,” the group added.
Invisible wounds of war
In another statement, Bill McCabe, legislative affairs director at the Enlisted Association, said that “now, more than ever, veterans suffering from invisible wounds of war need access to trained service dogs, which have been scientifically proven to help alleviate symptoms of posttraumatic stress,” as well as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and military sexual trauma.
“We thank President Biden for recognizing veterans need every possible option when seeking mental health treatments, and look forward to working with the Department of Veterans Affairs to implement this important program,” Mr. McCabe said.
A recent VA report showed that in 2014, 40% of veterans had mental health conditions such as PTSD and substance use. An average of 20 veterans per day died by suicide that year.
Veterans with problems regarding mobility, hearing, and sight, as well as some mental health problems, have been eligible to have costs of veterinary care for service dogs paid by the VA, although the VA has not paid for the training of the animals.
The PAWS Act, which was bipartisan legislation introduced by U.S. Senators Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Kyrsten Sinema (D-Ariz.), Kevin Cramer (R-N.D.), and Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), aims to expand eligibility to those with any mental health problems.
For at least a decade, various service dog and veterans’ organizations have pushed to have the VA expand the service dog benefit. This new law is a “first step,” said Mr. Diamond. “We had to kick open the door,” he said, adding that “the VA has essentially said no for almost 15 years.”
Mr. Diamond noted that there is “overwhelming” evidence showing that service dogs improve quality of life and reduce distress for veterans with PTSD and other diagnoses.
‘No excuse’
Results from a VA study showed that suicidal ideation was reduced in veterans who were paired with service dogs, compared with veterans paired with emotional support dogs. The study, which was made public in March, found no reduction in overall disability, according to a report by Military.com.
K9s for Warriors cites numerous other studies, published in peer-reviewed journals, that have shown that service dogs reduce PTSD symptoms, especially hypervigilance.
“There really is no excuse not to have the VA engaged in helping veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress who are extremely high risk of suicide to get a lifesaving service dog,” Mr. Diamond said.
His organization has paired 700 veterans suffering from TBI, PTSD, or military sexual trauma with a service dog. The organization provides a 3-week training program for the veteran and his or her dog.
Although about 200 of the graduates have been eligible to receive coverage from the VA for veterinary care for the dogs, it requires a lot of paperwork, and the criteria for who can be certified to receive that benefit are somewhat vague, Mr. Diamond noted.
Under current policy, the dog and veteran must have successfully completed a training program offered by an organization accredited by Assistance Dogs International or the International Guide Dog Federation.
The new pilot program will enable eligible veterans to receive dog training instruction from accredited nonprofit service dog training organizations, and it will give them the opportunity to adopt a dog that they actively assisted in training.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Service members with posttraumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions may eventually have expanded access to service dogs through legislation recently signed into law by President Joseph R. Biden.
The Puppies Assisting Wounded Servicemembers (PAWS) for Veterans Therapy Act (HR 1448) orders the Department of Veterans Affairs to begin a pilot program that over the course of 5 years will examine the utility and effectiveness of service dogs for improving the mental health of military veterans.
The legislation does not set a specific start date for the pilot program, but Rory Diamond, CEO of K9s for Warriors, a nonprofit organization based in Ponte Vedra, Fla., noted that K9s for Warriors and other organizations will be pushing the VA to start in 2022.
“We commend the White House for supporting this bill as a critical step in combating veteran suicide, and we’re confident in the path ahead for service dogs ultimately becoming a covered VA benefit to veterans with PTSD,” Mr. Diamond said in a statement provided to this news organization.
“For servicemembers relying on task-trained service dogs for PTSD, the HR 1448 is a giant leap towards supporting veterans and their service dogs in an equitable way,” Canine Companions, a national nonprofit organization that trains and provides service dogs, said in its own statement.
“It might mean the difference between having a veteran who won’t be here tomorrow and having one that will,” the group added.
Invisible wounds of war
In another statement, Bill McCabe, legislative affairs director at the Enlisted Association, said that “now, more than ever, veterans suffering from invisible wounds of war need access to trained service dogs, which have been scientifically proven to help alleviate symptoms of posttraumatic stress,” as well as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and military sexual trauma.
“We thank President Biden for recognizing veterans need every possible option when seeking mental health treatments, and look forward to working with the Department of Veterans Affairs to implement this important program,” Mr. McCabe said.
A recent VA report showed that in 2014, 40% of veterans had mental health conditions such as PTSD and substance use. An average of 20 veterans per day died by suicide that year.
Veterans with problems regarding mobility, hearing, and sight, as well as some mental health problems, have been eligible to have costs of veterinary care for service dogs paid by the VA, although the VA has not paid for the training of the animals.
The PAWS Act, which was bipartisan legislation introduced by U.S. Senators Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Kyrsten Sinema (D-Ariz.), Kevin Cramer (R-N.D.), and Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), aims to expand eligibility to those with any mental health problems.
For at least a decade, various service dog and veterans’ organizations have pushed to have the VA expand the service dog benefit. This new law is a “first step,” said Mr. Diamond. “We had to kick open the door,” he said, adding that “the VA has essentially said no for almost 15 years.”
Mr. Diamond noted that there is “overwhelming” evidence showing that service dogs improve quality of life and reduce distress for veterans with PTSD and other diagnoses.
‘No excuse’
Results from a VA study showed that suicidal ideation was reduced in veterans who were paired with service dogs, compared with veterans paired with emotional support dogs. The study, which was made public in March, found no reduction in overall disability, according to a report by Military.com.
K9s for Warriors cites numerous other studies, published in peer-reviewed journals, that have shown that service dogs reduce PTSD symptoms, especially hypervigilance.
“There really is no excuse not to have the VA engaged in helping veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress who are extremely high risk of suicide to get a lifesaving service dog,” Mr. Diamond said.
His organization has paired 700 veterans suffering from TBI, PTSD, or military sexual trauma with a service dog. The organization provides a 3-week training program for the veteran and his or her dog.
Although about 200 of the graduates have been eligible to receive coverage from the VA for veterinary care for the dogs, it requires a lot of paperwork, and the criteria for who can be certified to receive that benefit are somewhat vague, Mr. Diamond noted.
Under current policy, the dog and veteran must have successfully completed a training program offered by an organization accredited by Assistance Dogs International or the International Guide Dog Federation.
The new pilot program will enable eligible veterans to receive dog training instruction from accredited nonprofit service dog training organizations, and it will give them the opportunity to adopt a dog that they actively assisted in training.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Munchausen by Internet’ crises a warning for all HCPs
A new study documents a handful of cases of women with Munchausen syndrome by Internet who targeted doulas in the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 lockdown.
The five cases were investigated by Kathryn Newns, MSc, DClinPsy, a clinical psychologist in Cambridge, England, who said the cases were brought to her attention by a doula she herself had used for the birth of her own child a decade earlier.
Dr. Newns said she believes these are not isolated cases – either geographically or in terms of the specialty involved.
“I don’t think it is likely that this is only happening in the United Kingdom. And I’m sure it’s not just happening in the doula world,” Dr. Newns told this news organization.
Coinvestigator Marc Feldman, MD, a clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, coined the term “Munchausen by Internet” in a 2000 article. The expression refers to use of electronic media to perpetrate hoaxes that reward posers with sympathy, control, or emotional gratification. The hoaxers do not seek financial gain.
“The ease of carrying out Munchausen behaviors makes me think that it must be much more common than it ever was,” Dr. Feldman said in an interview.
He noted that the new DSM-5 will eliminate the terms “Munchausen” and “Munchausen by Internet” and will clarify that “factitious disorder” can be partly or wholly carried out online.
The study was published in the May issue of the Annals of Clinical Psychiatry.
A warning for others
In the past, those with factitious disorder had to go to medical libraries to study up on the ailment they wanted to feign. They would then present to an emergency department or a doctor’s office and act convincingly, Dr. Feldman said.
“Now all you have to do is go to Wikipedia and you can become an expert on a medical ailment within a few minutes,” he added.
In the five cases described in the study, the hoaxers created rich stories, especially in cases 1 and 2. In those cases, the perpetrator turned out to be the same person. Subterfuge “obviously made it much harder to know she wasn’t who she purported to be,” said Dr. Newns.
Dr. Feldman noted that in Munchausen by Internet, there may be some element of truth within the stories.
For health care professionals, “it takes a considerable leap to assume that somebody who’s talking about some dreaded ailment is in fact exaggerating or outright lying,” he said.
In the five cases described in the study, persons contacted doulas, then related traumatic stories and described dramatic, immediate needs. All of the doulas were working remotely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. This likely made it easier for the perpetrators to pull off the hoaxes. The health care professionals agreed to share their experiences in the hopes of warning others.
Elaborate scenarios
The first two cases were ultimately determined to involve one person who had created elaborate scenarios.
In case 1, the hoaxer, who called herself “Jessica,” texted the doula “Charlotte” when she was allegedly 39 weeks’ pregnant. She said she was unable to go to the hospital because of the COVID-19 risks to her husband, who had cystic fibrosis and had recently undergone a heart and lung transplant.
The husband “Jordan” took over communications, using the same WhatsApp number as Jessica, as Jessica went into labor.
Ostensibly, a midwife team had come to Jessica’s and Jordan’s house. When the doula was on the phone with Jordan, she heard Jessica crying, grunting, and screaming, and then, at 2:00 a.m., she heard the sound of a baby crying. A photo of the baby was texted to Charlotte.
Soon, there were many problems. Jessica allegedly had a postpartum hemorrhage, and mother and baby were taken to separate hospitals. The baby was then diagnosed with congenital heart disease.
Over the next week, “midwives” started texting back and forth with Charlotte. The doula began to have doubts and asked a midwife to share a visual communication.
After receiving no response, Charlotte used a video call, got Jessica on screen, and told her she thought there was no baby. Jessica said the baby was real and showed a “growth chart” as proof of the 5-day-old baby’s existence. The birth and baby noises were later determined to be recordings.
Child deaths
After sharing information among themselves on a private Facebook group, the doulas determined that the person in case 2, “Dakota,” was the same woman who was involved in case 1.
In case 2, a doula had spent 2 years supporting Dakota through the deaths of a parent and her baby, who had a congenital defect. A baby-loss charity had also worked with Dakota but could not confirm the baby’s existence.
Dakota had gone so far as to make a video for the doula that showed a hospital room. In a voice-over, Dakota thanks everyone for the support she received as the baby died.
In case 3, “Hannah” texted a doula seeking emotional but not birth support. The doula, Nikki Barrow, has recounted the case on her own blog.
Hannah became desperate when she went into labor. Ms. Barrow remained close via texts, phone, and video calls, even as the baby supposedly died after 3 days. The doula lit a candle for the baby and cried with Hannah.
Ms. Barrow was eventually able to break away from Hannah, saying she was not a bereavement specialist. However, days later, Hannah tracked her down and claimed she had an infection in her heart and did not have much time to live. At that point, Ms. Barrow stopped all contact.
She determined from other doulas that Hannah had been hoaxing doulas for 4 or 5 years. Some had offered to get her help, but she refused and ended all contact.
Multiple COVID crises?
In case 4, a woman sought support on a doula-centered Facebook page and said her partner “Jack” would be in touch. Jack sent the doula hundreds of emails, texts, and WhatsApp messages and then said he was hospitalized with COVID. The woman, “Hayley,” was also soon diagnosed with COVID.
Hayley refused video contact and did not share photos. Drama continued to unfold. She reported that her baby was breach, that she had a second uterus with a second pregnancy simultaneously, and that the baby had COVID.
Hayley also claimed that her partner had come to the hospital, had raped her, and had brandished a gun. When the doula called the police, they did not find Hayley at the hospital or elsewhere.
In case 5, a “grandmother” contacted “Lisa” to find a doula for her daughter-in-law, “Anna.” Hours later, Anna was giving birth, and the baby had to be taken to the hospital because of cardiac and breathing problems. The doula heard nothing more after a few weeks.
However, at least three other doulas said they had supported the same “family.”
Online training program
In all cases, the doulas were not paid for their time. Reports to the police prompted no action because no money had changed hands. Some doulas said they felt bereaved, angry, or “silly” that they had been hoodwinked. All noted how difficult it was to disengage from clients who seemed to be in peril.
Ms. Barrow decided to create an online training program in which doulas are advised on how to stay safe while working online.
DoulaMatch, which matches birth support specialists with women in the United States and Canada, offers tips to help protect doulas from hoaxes.
Kim James, BDT(DONA), ICCE, LCCE, CLE, the owner and operator of DoulaMatch, said the organization is aware of “scammers who waste everyone’s time and have found doulas to be the latest easy targets.”
However, she noted, “I’ve only very occasionally and anecdotally heard about people fabricating a pregnancy for emotional gratification.”
In his 2000 article, Dr. Feldman offers clues to help detect hoaxers. He advises clinicians to be wary of the following:
- Cases in which the length, frequency, and duration of posts are incongruous with the severity of the illness the person is claiming to have; for example, someone who claims to be in submitting detailed posts.
- Near-fatal exacerbations of illness alternating with miraculous recoveries.
- Personal claims that are fantastic, are contradicted by later posts, or are disproved.
- Continual dramatic events occurring in the person’s life, especially when others in a group become the focus of attention.
- Others ostensibly posting on behalf of the individual who have identical patterns of writing, such as making grammatical errors, misspellings, and using stylistic idiosyncrasies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study documents a handful of cases of women with Munchausen syndrome by Internet who targeted doulas in the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 lockdown.
The five cases were investigated by Kathryn Newns, MSc, DClinPsy, a clinical psychologist in Cambridge, England, who said the cases were brought to her attention by a doula she herself had used for the birth of her own child a decade earlier.
Dr. Newns said she believes these are not isolated cases – either geographically or in terms of the specialty involved.
“I don’t think it is likely that this is only happening in the United Kingdom. And I’m sure it’s not just happening in the doula world,” Dr. Newns told this news organization.
Coinvestigator Marc Feldman, MD, a clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, coined the term “Munchausen by Internet” in a 2000 article. The expression refers to use of electronic media to perpetrate hoaxes that reward posers with sympathy, control, or emotional gratification. The hoaxers do not seek financial gain.
“The ease of carrying out Munchausen behaviors makes me think that it must be much more common than it ever was,” Dr. Feldman said in an interview.
He noted that the new DSM-5 will eliminate the terms “Munchausen” and “Munchausen by Internet” and will clarify that “factitious disorder” can be partly or wholly carried out online.
The study was published in the May issue of the Annals of Clinical Psychiatry.
A warning for others
In the past, those with factitious disorder had to go to medical libraries to study up on the ailment they wanted to feign. They would then present to an emergency department or a doctor’s office and act convincingly, Dr. Feldman said.
“Now all you have to do is go to Wikipedia and you can become an expert on a medical ailment within a few minutes,” he added.
In the five cases described in the study, the hoaxers created rich stories, especially in cases 1 and 2. In those cases, the perpetrator turned out to be the same person. Subterfuge “obviously made it much harder to know she wasn’t who she purported to be,” said Dr. Newns.
Dr. Feldman noted that in Munchausen by Internet, there may be some element of truth within the stories.
For health care professionals, “it takes a considerable leap to assume that somebody who’s talking about some dreaded ailment is in fact exaggerating or outright lying,” he said.
In the five cases described in the study, persons contacted doulas, then related traumatic stories and described dramatic, immediate needs. All of the doulas were working remotely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. This likely made it easier for the perpetrators to pull off the hoaxes. The health care professionals agreed to share their experiences in the hopes of warning others.
Elaborate scenarios
The first two cases were ultimately determined to involve one person who had created elaborate scenarios.
In case 1, the hoaxer, who called herself “Jessica,” texted the doula “Charlotte” when she was allegedly 39 weeks’ pregnant. She said she was unable to go to the hospital because of the COVID-19 risks to her husband, who had cystic fibrosis and had recently undergone a heart and lung transplant.
The husband “Jordan” took over communications, using the same WhatsApp number as Jessica, as Jessica went into labor.
Ostensibly, a midwife team had come to Jessica’s and Jordan’s house. When the doula was on the phone with Jordan, she heard Jessica crying, grunting, and screaming, and then, at 2:00 a.m., she heard the sound of a baby crying. A photo of the baby was texted to Charlotte.
Soon, there were many problems. Jessica allegedly had a postpartum hemorrhage, and mother and baby were taken to separate hospitals. The baby was then diagnosed with congenital heart disease.
Over the next week, “midwives” started texting back and forth with Charlotte. The doula began to have doubts and asked a midwife to share a visual communication.
After receiving no response, Charlotte used a video call, got Jessica on screen, and told her she thought there was no baby. Jessica said the baby was real and showed a “growth chart” as proof of the 5-day-old baby’s existence. The birth and baby noises were later determined to be recordings.
Child deaths
After sharing information among themselves on a private Facebook group, the doulas determined that the person in case 2, “Dakota,” was the same woman who was involved in case 1.
In case 2, a doula had spent 2 years supporting Dakota through the deaths of a parent and her baby, who had a congenital defect. A baby-loss charity had also worked with Dakota but could not confirm the baby’s existence.
Dakota had gone so far as to make a video for the doula that showed a hospital room. In a voice-over, Dakota thanks everyone for the support she received as the baby died.
In case 3, “Hannah” texted a doula seeking emotional but not birth support. The doula, Nikki Barrow, has recounted the case on her own blog.
Hannah became desperate when she went into labor. Ms. Barrow remained close via texts, phone, and video calls, even as the baby supposedly died after 3 days. The doula lit a candle for the baby and cried with Hannah.
Ms. Barrow was eventually able to break away from Hannah, saying she was not a bereavement specialist. However, days later, Hannah tracked her down and claimed she had an infection in her heart and did not have much time to live. At that point, Ms. Barrow stopped all contact.
She determined from other doulas that Hannah had been hoaxing doulas for 4 or 5 years. Some had offered to get her help, but she refused and ended all contact.
Multiple COVID crises?
In case 4, a woman sought support on a doula-centered Facebook page and said her partner “Jack” would be in touch. Jack sent the doula hundreds of emails, texts, and WhatsApp messages and then said he was hospitalized with COVID. The woman, “Hayley,” was also soon diagnosed with COVID.
Hayley refused video contact and did not share photos. Drama continued to unfold. She reported that her baby was breach, that she had a second uterus with a second pregnancy simultaneously, and that the baby had COVID.
Hayley also claimed that her partner had come to the hospital, had raped her, and had brandished a gun. When the doula called the police, they did not find Hayley at the hospital or elsewhere.
In case 5, a “grandmother” contacted “Lisa” to find a doula for her daughter-in-law, “Anna.” Hours later, Anna was giving birth, and the baby had to be taken to the hospital because of cardiac and breathing problems. The doula heard nothing more after a few weeks.
However, at least three other doulas said they had supported the same “family.”
Online training program
In all cases, the doulas were not paid for their time. Reports to the police prompted no action because no money had changed hands. Some doulas said they felt bereaved, angry, or “silly” that they had been hoodwinked. All noted how difficult it was to disengage from clients who seemed to be in peril.
Ms. Barrow decided to create an online training program in which doulas are advised on how to stay safe while working online.
DoulaMatch, which matches birth support specialists with women in the United States and Canada, offers tips to help protect doulas from hoaxes.
Kim James, BDT(DONA), ICCE, LCCE, CLE, the owner and operator of DoulaMatch, said the organization is aware of “scammers who waste everyone’s time and have found doulas to be the latest easy targets.”
However, she noted, “I’ve only very occasionally and anecdotally heard about people fabricating a pregnancy for emotional gratification.”
In his 2000 article, Dr. Feldman offers clues to help detect hoaxers. He advises clinicians to be wary of the following:
- Cases in which the length, frequency, and duration of posts are incongruous with the severity of the illness the person is claiming to have; for example, someone who claims to be in submitting detailed posts.
- Near-fatal exacerbations of illness alternating with miraculous recoveries.
- Personal claims that are fantastic, are contradicted by later posts, or are disproved.
- Continual dramatic events occurring in the person’s life, especially when others in a group become the focus of attention.
- Others ostensibly posting on behalf of the individual who have identical patterns of writing, such as making grammatical errors, misspellings, and using stylistic idiosyncrasies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study documents a handful of cases of women with Munchausen syndrome by Internet who targeted doulas in the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 lockdown.
The five cases were investigated by Kathryn Newns, MSc, DClinPsy, a clinical psychologist in Cambridge, England, who said the cases were brought to her attention by a doula she herself had used for the birth of her own child a decade earlier.
Dr. Newns said she believes these are not isolated cases – either geographically or in terms of the specialty involved.
“I don’t think it is likely that this is only happening in the United Kingdom. And I’m sure it’s not just happening in the doula world,” Dr. Newns told this news organization.
Coinvestigator Marc Feldman, MD, a clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, coined the term “Munchausen by Internet” in a 2000 article. The expression refers to use of electronic media to perpetrate hoaxes that reward posers with sympathy, control, or emotional gratification. The hoaxers do not seek financial gain.
“The ease of carrying out Munchausen behaviors makes me think that it must be much more common than it ever was,” Dr. Feldman said in an interview.
He noted that the new DSM-5 will eliminate the terms “Munchausen” and “Munchausen by Internet” and will clarify that “factitious disorder” can be partly or wholly carried out online.
The study was published in the May issue of the Annals of Clinical Psychiatry.
A warning for others
In the past, those with factitious disorder had to go to medical libraries to study up on the ailment they wanted to feign. They would then present to an emergency department or a doctor’s office and act convincingly, Dr. Feldman said.
“Now all you have to do is go to Wikipedia and you can become an expert on a medical ailment within a few minutes,” he added.
In the five cases described in the study, the hoaxers created rich stories, especially in cases 1 and 2. In those cases, the perpetrator turned out to be the same person. Subterfuge “obviously made it much harder to know she wasn’t who she purported to be,” said Dr. Newns.
Dr. Feldman noted that in Munchausen by Internet, there may be some element of truth within the stories.
For health care professionals, “it takes a considerable leap to assume that somebody who’s talking about some dreaded ailment is in fact exaggerating or outright lying,” he said.
In the five cases described in the study, persons contacted doulas, then related traumatic stories and described dramatic, immediate needs. All of the doulas were working remotely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. This likely made it easier for the perpetrators to pull off the hoaxes. The health care professionals agreed to share their experiences in the hopes of warning others.
Elaborate scenarios
The first two cases were ultimately determined to involve one person who had created elaborate scenarios.
In case 1, the hoaxer, who called herself “Jessica,” texted the doula “Charlotte” when she was allegedly 39 weeks’ pregnant. She said she was unable to go to the hospital because of the COVID-19 risks to her husband, who had cystic fibrosis and had recently undergone a heart and lung transplant.
The husband “Jordan” took over communications, using the same WhatsApp number as Jessica, as Jessica went into labor.
Ostensibly, a midwife team had come to Jessica’s and Jordan’s house. When the doula was on the phone with Jordan, she heard Jessica crying, grunting, and screaming, and then, at 2:00 a.m., she heard the sound of a baby crying. A photo of the baby was texted to Charlotte.
Soon, there were many problems. Jessica allegedly had a postpartum hemorrhage, and mother and baby were taken to separate hospitals. The baby was then diagnosed with congenital heart disease.
Over the next week, “midwives” started texting back and forth with Charlotte. The doula began to have doubts and asked a midwife to share a visual communication.
After receiving no response, Charlotte used a video call, got Jessica on screen, and told her she thought there was no baby. Jessica said the baby was real and showed a “growth chart” as proof of the 5-day-old baby’s existence. The birth and baby noises were later determined to be recordings.
Child deaths
After sharing information among themselves on a private Facebook group, the doulas determined that the person in case 2, “Dakota,” was the same woman who was involved in case 1.
In case 2, a doula had spent 2 years supporting Dakota through the deaths of a parent and her baby, who had a congenital defect. A baby-loss charity had also worked with Dakota but could not confirm the baby’s existence.
Dakota had gone so far as to make a video for the doula that showed a hospital room. In a voice-over, Dakota thanks everyone for the support she received as the baby died.
In case 3, “Hannah” texted a doula seeking emotional but not birth support. The doula, Nikki Barrow, has recounted the case on her own blog.
Hannah became desperate when she went into labor. Ms. Barrow remained close via texts, phone, and video calls, even as the baby supposedly died after 3 days. The doula lit a candle for the baby and cried with Hannah.
Ms. Barrow was eventually able to break away from Hannah, saying she was not a bereavement specialist. However, days later, Hannah tracked her down and claimed she had an infection in her heart and did not have much time to live. At that point, Ms. Barrow stopped all contact.
She determined from other doulas that Hannah had been hoaxing doulas for 4 or 5 years. Some had offered to get her help, but she refused and ended all contact.
Multiple COVID crises?
In case 4, a woman sought support on a doula-centered Facebook page and said her partner “Jack” would be in touch. Jack sent the doula hundreds of emails, texts, and WhatsApp messages and then said he was hospitalized with COVID. The woman, “Hayley,” was also soon diagnosed with COVID.
Hayley refused video contact and did not share photos. Drama continued to unfold. She reported that her baby was breach, that she had a second uterus with a second pregnancy simultaneously, and that the baby had COVID.
Hayley also claimed that her partner had come to the hospital, had raped her, and had brandished a gun. When the doula called the police, they did not find Hayley at the hospital or elsewhere.
In case 5, a “grandmother” contacted “Lisa” to find a doula for her daughter-in-law, “Anna.” Hours later, Anna was giving birth, and the baby had to be taken to the hospital because of cardiac and breathing problems. The doula heard nothing more after a few weeks.
However, at least three other doulas said they had supported the same “family.”
Online training program
In all cases, the doulas were not paid for their time. Reports to the police prompted no action because no money had changed hands. Some doulas said they felt bereaved, angry, or “silly” that they had been hoodwinked. All noted how difficult it was to disengage from clients who seemed to be in peril.
Ms. Barrow decided to create an online training program in which doulas are advised on how to stay safe while working online.
DoulaMatch, which matches birth support specialists with women in the United States and Canada, offers tips to help protect doulas from hoaxes.
Kim James, BDT(DONA), ICCE, LCCE, CLE, the owner and operator of DoulaMatch, said the organization is aware of “scammers who waste everyone’s time and have found doulas to be the latest easy targets.”
However, she noted, “I’ve only very occasionally and anecdotally heard about people fabricating a pregnancy for emotional gratification.”
In his 2000 article, Dr. Feldman offers clues to help detect hoaxers. He advises clinicians to be wary of the following:
- Cases in which the length, frequency, and duration of posts are incongruous with the severity of the illness the person is claiming to have; for example, someone who claims to be in submitting detailed posts.
- Near-fatal exacerbations of illness alternating with miraculous recoveries.
- Personal claims that are fantastic, are contradicted by later posts, or are disproved.
- Continual dramatic events occurring in the person’s life, especially when others in a group become the focus of attention.
- Others ostensibly posting on behalf of the individual who have identical patterns of writing, such as making grammatical errors, misspellings, and using stylistic idiosyncrasies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Are you at legal risk for speaking at conferences?
When Jerry Gardner, MD, and a junior colleague received the acceptance notification for their abstract to be presented at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2021, a clause in the mandatory participation agreement gave Dr. Gardner pause. It required his colleague, as the submitting author, to completely accept any and all legal responsibility for any claims that might arise out of their presentation.
The clause was a red flag to Dr. Gardner, president of Science for Organizations, a Mill Valley, Calif.–based consulting firm. The gastroenterologist and former head of the digestive diseases branch at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – who has made hundreds of presentations and had participated in DDW for 40 years – had never encountered such a broad indemnity clause.
This news organization investigated just how risky it is to make a presentation at a conference – more than a dozen professional societies were contacted. Although DDW declined to discuss its agreement, Houston health care attorney Rachel V. Rose said that Dr. Gardner was smart to be cautious. “I would not sign that agreement. I have never seen anything that broad and all encompassing,” she said.
The DDW requirement “means that participants must put themselves at great potential financial risk in order to present their work,” Dr. Gardner said. He added that he and his colleague would not have submitted an abstract had they known about the indemnification clause up front.
Dr. Gardner advised his colleague not to sign the DDW agreement. She did not, and both missed the meeting.
Speakers ‘have to be careful’
Dr. Gardner may be an exception. How many doctors are willing to forgo a presentation because of a concern about something in an agreement?
John Mandrola, MD, said he operates under the assumption that if he does not sign the agreement, then he won’t be able to give his presentation. He admits that he generally just signs them and is careful with his presentations. “I’ve never really paid much attention to them,” said Dr. Mandrola, a cardiac electrophysiologist in Louisville, Ky., and chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.
Not everyone takes that approach. “I do think that people read them, but they also take them with a grain of salt,” said E. Magnus Ohman, MBBS, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. He said he’s pragmatic and regards the agreements as a necessary evil in a litigious nation. Speakers “have to be careful, obviously,” Dr. Ohman said in an interview.
Some argue that the requirements are not only fair but also understandable. David Johnson, MD, a former president of the American College of Gastroenterology, said he has never had questions about agreements for meetings he has been involved with. “To me, this is not anything other than standard operating procedure,” he said.
Presenters participate by invitation, noted Dr. Johnson, a professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, who is a contributor to this news organization. “If they stand up and do something egregious, I would concur that the society should not be liable,” he said.
Big asks, big secrecy
Even for those who generally agree with Dr. Johnson’s position, it may be hard to completely understand what’s at stake without an attorney.
Although many declined to discuss their policies, a handful of professional societies provided their agreements for review. In general, the agreements appear to offer broad protection and rights to the organizers and large liability exposure for the participants. Participants are charged with a wide range of responsibilities, such as ensuring against copyright violations and intellectual property infringement, and that they also agree to unlimited use of their presentations and their name and likeness.
The American Academy of Neurology, which held its meeting virtually in 2021, required participants to indemnify the organization against all “losses, expenses, damages, or liabilities,” including “reasonable attorneys’ fees.” Federal employees, however, could opt out of indemnification.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology said that it does not usually require indemnification from its meeting participants. However, a spokesperson noted that ASCO did require participants at its 2021 virtual meeting to abide by the terms of use for content posted to the ASCO website. Those terms specify that users agree to indemnify ASCO from damages related to posts.
The American Psychiatric Association said it does not require any indemnification but did not make its agreement available. The American Academy of Pediatrics also said it did not require indemnification but would not share its agreement.
An American Diabetes Association spokesperson said that “every association is different in what they ask or require from speakers,” but would not share its requirements.
The American Academy of Family Physicians, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the American College of Physicians, and the Endocrine Society all declined to participate.
The organizations that withheld agreements “probably don’t want anybody picking apart their documents,” said Kyle Claussen, CEO of the Resolve Physician Agency, which reviews employment contracts and other contracts for physicians. “The more fair a document, the more likely they would be willing to disclose that, because they have nothing to hide,” he said.
‘It’s all on you’
Requiring indemnification for any and all aspects of a presentation appears to be increasingly common, said the attorneys interviewed for this article. As organizations repackage meeting presentations for sale, they put the content further out into the world and for a longer period, which increases liability exposure.
“If I’m the attorney for DDW, I certainly think I’d want to have this in place,” said Mr. Claussen.
“It’s good business sense for them because it reduces their risk,” said Courtney H. A. Thompson, an attorney with Fredrikson & Byron in Minneapolis, who advises regional and national corporations and ad agencies on advertising, marketing, and trademark law. She also works with clients who speak at meetings and who thus encounter meeting agreements.
Ms. Thompson said indemnity clauses have become fairly common over the past decade, especially as more companies and organizations have sought to protect trademarks, copyrights, and intellectual property and to minimize litigation costs.
A conference organizer “doesn’t want a third party to come after them for intellectual property, privacy, or publicity right infringement based on the participation of the customer or, in this case, the speaker,” said Ms. Thompson.
The agreements also reflect America’s litigation-prone culture.
Dean Fanelli, a patent attorney in the Washington, D.C., office of Cooley LLP, said the agreements he’s been asked to sign as a speaker increasingly seem “overly lawyerly.”
Two decades ago, a speaker might have been asked to sign a paragraph or a one-page form. Now “they often look more like formalized legal agreements,” Mr. Fanelli told this news organization.
The DDW agreement, for instance, ran four pages and contained 21 detailed clauses.
The increasingly complicated agreements “are a little over the top,” said Mr. Fanelli. But as an attorney who works with clients in the pharmaceutical industry, he said he understands that meeting organizers want to protect their rights.
DDW’s main indemnification clause requires the participant to indemnify DDW and its agents, directors, and employees “against any and all claims, demands, causes of action, losses, damages, liabilities, costs, and expenses,” including attorneys’ fees “arising out of a claim, action or proceeding” based on a breach or “alleged breach” by the participant.
“You’re releasing this information to them and then you’re also giving them blanket indemnity back, saying if there’s any type of intellectual property violation on your end – if you’ve included any type of work that’s protected, if this causes any problems – it’s all on you,” said Mr. Claussen.
Other potential pitfalls
Aside from indemnification, participation agreements can contain other potentially worrisome clauses, including onerous terms for cancellation and reuse of content without remuneration.
DDW requires royalty-free licensing of a speaker’s content; the organization can reproduce it in perpetuity without royalties. Many organizations have such a clause in their agreements, including the AAN and the American College of Cardiology.
ASCO’s general authorization form for meeting participants requires that they assign to ASCO rights to their content “perpetually, irrevocably, worldwide and royalty free.” Participants can contact the organization if they seek to opt out, but it’s not clear whether ASCO grants such requests.
Participants in the upcoming American Heart Association annual meeting can deny permission to record their presentation. But if they allow recording and do not agree to assign all rights and copyright ownership to the AHA, the work will be excluded from publication in the meeting program, e-posters, and the meeting supplement in Circulation.
Mr. Claussen said granting royalty-free rights presents a conundrum. Having content reproduced in various formats “might be better for your personal brand,” but it’s not likely to result in any direct compensation and could increase liability exposure, he said.
How presenters must prepare
Mr. Claussen and Ms. Rose said speakers should be vigilant about their own rights and responsibilities, including ensuring that they do not violate copyrights or infringe on intellectual property rights.
“I would recommend that folks be meticulous about what is in their slide deck and materials,” said Ms. Thompson. He said that presenters should be sure they have the right to share material. Technologies crawl the internet seeking out infringement, which often leads to cease and desist letters from attorneys, she said.
It’s better to head off such a letter, Ms. Thompson said. “You need to defend it whether or not it’s a viable claim,” and that can be costly, she said.
Both Ms. Thompson and Mr. Fanelli also warn about disclosing anything that might be considered a trade secret. Many agreements prohibit presenters from engaging in commercial promotion, but if a talk includes information about a drug or device, the manufacturer will want to review the presentation before it’s made public, said Mr. Fanelli.
Many organizations prohibit attendees from photographing, recording, or tweeting at meetings and often require speakers to warn the audience about doing so. DDW goes further by holding presenters liable if someone violates the rule.
“That’s a huge problem,” said Dr. Mandrola. He noted that although it might be easy to police journalists attending a meeting, “it seems hard to enforce that rule amongst just regular attendees.”
Accept or negotiate?
Individuals who submit work to an organization might feel they must sign an agreement as is, especially if they are looking to advance their career or expand knowledge by presenting work at a meeting. But some attorneys said it might be possible to negotiate with meeting organizers.
“My personal opinion is that it never hurts to ask,” said Ms. Thompson. If she were speaking at a legal conference, she would mark up a contract and “see what happens.” The more times pushback is accepted – say, if it works with three out of five speaking engagements – the more it reduces overall liability exposure.
Mr. Fanelli, however, said that although he always reads over an agreement, he typically signs without negotiating. “I don’t usually worry about it because I’m just trying to talk at a particular seminar,” he said.
Prospective presenters “have to weigh that balance – do you want to talk at a seminar, or are you concerned about the legal issues?” said Mr. Fanelli.
If in doubt, talk with a lawyer.
“If you ever have a question on whether or not you should consult an attorney, the answer is always yes,” said Mr. Claussen. It would be “an ounce of prevention,” especially if it’s just a short agreement, he said.
Dr. Ohman, however, said that he believed “it would be fairly costly” and potentially unwieldy. “You can’t litigate everything in life,” he added.
As for Dr. Gardner, he said he would not be as likely to attend DDW in the future if he has to agree to cover any and all liability. “I can’t conceive of ever agreeing to personally indemnify DDW in order to make a presentation at the annual meeting,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Jerry Gardner, MD, and a junior colleague received the acceptance notification for their abstract to be presented at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2021, a clause in the mandatory participation agreement gave Dr. Gardner pause. It required his colleague, as the submitting author, to completely accept any and all legal responsibility for any claims that might arise out of their presentation.
The clause was a red flag to Dr. Gardner, president of Science for Organizations, a Mill Valley, Calif.–based consulting firm. The gastroenterologist and former head of the digestive diseases branch at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – who has made hundreds of presentations and had participated in DDW for 40 years – had never encountered such a broad indemnity clause.
This news organization investigated just how risky it is to make a presentation at a conference – more than a dozen professional societies were contacted. Although DDW declined to discuss its agreement, Houston health care attorney Rachel V. Rose said that Dr. Gardner was smart to be cautious. “I would not sign that agreement. I have never seen anything that broad and all encompassing,” she said.
The DDW requirement “means that participants must put themselves at great potential financial risk in order to present their work,” Dr. Gardner said. He added that he and his colleague would not have submitted an abstract had they known about the indemnification clause up front.
Dr. Gardner advised his colleague not to sign the DDW agreement. She did not, and both missed the meeting.
Speakers ‘have to be careful’
Dr. Gardner may be an exception. How many doctors are willing to forgo a presentation because of a concern about something in an agreement?
John Mandrola, MD, said he operates under the assumption that if he does not sign the agreement, then he won’t be able to give his presentation. He admits that he generally just signs them and is careful with his presentations. “I’ve never really paid much attention to them,” said Dr. Mandrola, a cardiac electrophysiologist in Louisville, Ky., and chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.
Not everyone takes that approach. “I do think that people read them, but they also take them with a grain of salt,” said E. Magnus Ohman, MBBS, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. He said he’s pragmatic and regards the agreements as a necessary evil in a litigious nation. Speakers “have to be careful, obviously,” Dr. Ohman said in an interview.
Some argue that the requirements are not only fair but also understandable. David Johnson, MD, a former president of the American College of Gastroenterology, said he has never had questions about agreements for meetings he has been involved with. “To me, this is not anything other than standard operating procedure,” he said.
Presenters participate by invitation, noted Dr. Johnson, a professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, who is a contributor to this news organization. “If they stand up and do something egregious, I would concur that the society should not be liable,” he said.
Big asks, big secrecy
Even for those who generally agree with Dr. Johnson’s position, it may be hard to completely understand what’s at stake without an attorney.
Although many declined to discuss their policies, a handful of professional societies provided their agreements for review. In general, the agreements appear to offer broad protection and rights to the organizers and large liability exposure for the participants. Participants are charged with a wide range of responsibilities, such as ensuring against copyright violations and intellectual property infringement, and that they also agree to unlimited use of their presentations and their name and likeness.
The American Academy of Neurology, which held its meeting virtually in 2021, required participants to indemnify the organization against all “losses, expenses, damages, or liabilities,” including “reasonable attorneys’ fees.” Federal employees, however, could opt out of indemnification.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology said that it does not usually require indemnification from its meeting participants. However, a spokesperson noted that ASCO did require participants at its 2021 virtual meeting to abide by the terms of use for content posted to the ASCO website. Those terms specify that users agree to indemnify ASCO from damages related to posts.
The American Psychiatric Association said it does not require any indemnification but did not make its agreement available. The American Academy of Pediatrics also said it did not require indemnification but would not share its agreement.
An American Diabetes Association spokesperson said that “every association is different in what they ask or require from speakers,” but would not share its requirements.
The American Academy of Family Physicians, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the American College of Physicians, and the Endocrine Society all declined to participate.
The organizations that withheld agreements “probably don’t want anybody picking apart their documents,” said Kyle Claussen, CEO of the Resolve Physician Agency, which reviews employment contracts and other contracts for physicians. “The more fair a document, the more likely they would be willing to disclose that, because they have nothing to hide,” he said.
‘It’s all on you’
Requiring indemnification for any and all aspects of a presentation appears to be increasingly common, said the attorneys interviewed for this article. As organizations repackage meeting presentations for sale, they put the content further out into the world and for a longer period, which increases liability exposure.
“If I’m the attorney for DDW, I certainly think I’d want to have this in place,” said Mr. Claussen.
“It’s good business sense for them because it reduces their risk,” said Courtney H. A. Thompson, an attorney with Fredrikson & Byron in Minneapolis, who advises regional and national corporations and ad agencies on advertising, marketing, and trademark law. She also works with clients who speak at meetings and who thus encounter meeting agreements.
Ms. Thompson said indemnity clauses have become fairly common over the past decade, especially as more companies and organizations have sought to protect trademarks, copyrights, and intellectual property and to minimize litigation costs.
A conference organizer “doesn’t want a third party to come after them for intellectual property, privacy, or publicity right infringement based on the participation of the customer or, in this case, the speaker,” said Ms. Thompson.
The agreements also reflect America’s litigation-prone culture.
Dean Fanelli, a patent attorney in the Washington, D.C., office of Cooley LLP, said the agreements he’s been asked to sign as a speaker increasingly seem “overly lawyerly.”
Two decades ago, a speaker might have been asked to sign a paragraph or a one-page form. Now “they often look more like formalized legal agreements,” Mr. Fanelli told this news organization.
The DDW agreement, for instance, ran four pages and contained 21 detailed clauses.
The increasingly complicated agreements “are a little over the top,” said Mr. Fanelli. But as an attorney who works with clients in the pharmaceutical industry, he said he understands that meeting organizers want to protect their rights.
DDW’s main indemnification clause requires the participant to indemnify DDW and its agents, directors, and employees “against any and all claims, demands, causes of action, losses, damages, liabilities, costs, and expenses,” including attorneys’ fees “arising out of a claim, action or proceeding” based on a breach or “alleged breach” by the participant.
“You’re releasing this information to them and then you’re also giving them blanket indemnity back, saying if there’s any type of intellectual property violation on your end – if you’ve included any type of work that’s protected, if this causes any problems – it’s all on you,” said Mr. Claussen.
Other potential pitfalls
Aside from indemnification, participation agreements can contain other potentially worrisome clauses, including onerous terms for cancellation and reuse of content without remuneration.
DDW requires royalty-free licensing of a speaker’s content; the organization can reproduce it in perpetuity without royalties. Many organizations have such a clause in their agreements, including the AAN and the American College of Cardiology.
ASCO’s general authorization form for meeting participants requires that they assign to ASCO rights to their content “perpetually, irrevocably, worldwide and royalty free.” Participants can contact the organization if they seek to opt out, but it’s not clear whether ASCO grants such requests.
Participants in the upcoming American Heart Association annual meeting can deny permission to record their presentation. But if they allow recording and do not agree to assign all rights and copyright ownership to the AHA, the work will be excluded from publication in the meeting program, e-posters, and the meeting supplement in Circulation.
Mr. Claussen said granting royalty-free rights presents a conundrum. Having content reproduced in various formats “might be better for your personal brand,” but it’s not likely to result in any direct compensation and could increase liability exposure, he said.
How presenters must prepare
Mr. Claussen and Ms. Rose said speakers should be vigilant about their own rights and responsibilities, including ensuring that they do not violate copyrights or infringe on intellectual property rights.
“I would recommend that folks be meticulous about what is in their slide deck and materials,” said Ms. Thompson. He said that presenters should be sure they have the right to share material. Technologies crawl the internet seeking out infringement, which often leads to cease and desist letters from attorneys, she said.
It’s better to head off such a letter, Ms. Thompson said. “You need to defend it whether or not it’s a viable claim,” and that can be costly, she said.
Both Ms. Thompson and Mr. Fanelli also warn about disclosing anything that might be considered a trade secret. Many agreements prohibit presenters from engaging in commercial promotion, but if a talk includes information about a drug or device, the manufacturer will want to review the presentation before it’s made public, said Mr. Fanelli.
Many organizations prohibit attendees from photographing, recording, or tweeting at meetings and often require speakers to warn the audience about doing so. DDW goes further by holding presenters liable if someone violates the rule.
“That’s a huge problem,” said Dr. Mandrola. He noted that although it might be easy to police journalists attending a meeting, “it seems hard to enforce that rule amongst just regular attendees.”
Accept or negotiate?
Individuals who submit work to an organization might feel they must sign an agreement as is, especially if they are looking to advance their career or expand knowledge by presenting work at a meeting. But some attorneys said it might be possible to negotiate with meeting organizers.
“My personal opinion is that it never hurts to ask,” said Ms. Thompson. If she were speaking at a legal conference, she would mark up a contract and “see what happens.” The more times pushback is accepted – say, if it works with three out of five speaking engagements – the more it reduces overall liability exposure.
Mr. Fanelli, however, said that although he always reads over an agreement, he typically signs without negotiating. “I don’t usually worry about it because I’m just trying to talk at a particular seminar,” he said.
Prospective presenters “have to weigh that balance – do you want to talk at a seminar, or are you concerned about the legal issues?” said Mr. Fanelli.
If in doubt, talk with a lawyer.
“If you ever have a question on whether or not you should consult an attorney, the answer is always yes,” said Mr. Claussen. It would be “an ounce of prevention,” especially if it’s just a short agreement, he said.
Dr. Ohman, however, said that he believed “it would be fairly costly” and potentially unwieldy. “You can’t litigate everything in life,” he added.
As for Dr. Gardner, he said he would not be as likely to attend DDW in the future if he has to agree to cover any and all liability. “I can’t conceive of ever agreeing to personally indemnify DDW in order to make a presentation at the annual meeting,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Jerry Gardner, MD, and a junior colleague received the acceptance notification for their abstract to be presented at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2021, a clause in the mandatory participation agreement gave Dr. Gardner pause. It required his colleague, as the submitting author, to completely accept any and all legal responsibility for any claims that might arise out of their presentation.
The clause was a red flag to Dr. Gardner, president of Science for Organizations, a Mill Valley, Calif.–based consulting firm. The gastroenterologist and former head of the digestive diseases branch at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – who has made hundreds of presentations and had participated in DDW for 40 years – had never encountered such a broad indemnity clause.
This news organization investigated just how risky it is to make a presentation at a conference – more than a dozen professional societies were contacted. Although DDW declined to discuss its agreement, Houston health care attorney Rachel V. Rose said that Dr. Gardner was smart to be cautious. “I would not sign that agreement. I have never seen anything that broad and all encompassing,” she said.
The DDW requirement “means that participants must put themselves at great potential financial risk in order to present their work,” Dr. Gardner said. He added that he and his colleague would not have submitted an abstract had they known about the indemnification clause up front.
Dr. Gardner advised his colleague not to sign the DDW agreement. She did not, and both missed the meeting.
Speakers ‘have to be careful’
Dr. Gardner may be an exception. How many doctors are willing to forgo a presentation because of a concern about something in an agreement?
John Mandrola, MD, said he operates under the assumption that if he does not sign the agreement, then he won’t be able to give his presentation. He admits that he generally just signs them and is careful with his presentations. “I’ve never really paid much attention to them,” said Dr. Mandrola, a cardiac electrophysiologist in Louisville, Ky., and chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.
Not everyone takes that approach. “I do think that people read them, but they also take them with a grain of salt,” said E. Magnus Ohman, MBBS, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C. He said he’s pragmatic and regards the agreements as a necessary evil in a litigious nation. Speakers “have to be careful, obviously,” Dr. Ohman said in an interview.
Some argue that the requirements are not only fair but also understandable. David Johnson, MD, a former president of the American College of Gastroenterology, said he has never had questions about agreements for meetings he has been involved with. “To me, this is not anything other than standard operating procedure,” he said.
Presenters participate by invitation, noted Dr. Johnson, a professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, who is a contributor to this news organization. “If they stand up and do something egregious, I would concur that the society should not be liable,” he said.
Big asks, big secrecy
Even for those who generally agree with Dr. Johnson’s position, it may be hard to completely understand what’s at stake without an attorney.
Although many declined to discuss their policies, a handful of professional societies provided their agreements for review. In general, the agreements appear to offer broad protection and rights to the organizers and large liability exposure for the participants. Participants are charged with a wide range of responsibilities, such as ensuring against copyright violations and intellectual property infringement, and that they also agree to unlimited use of their presentations and their name and likeness.
The American Academy of Neurology, which held its meeting virtually in 2021, required participants to indemnify the organization against all “losses, expenses, damages, or liabilities,” including “reasonable attorneys’ fees.” Federal employees, however, could opt out of indemnification.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology said that it does not usually require indemnification from its meeting participants. However, a spokesperson noted that ASCO did require participants at its 2021 virtual meeting to abide by the terms of use for content posted to the ASCO website. Those terms specify that users agree to indemnify ASCO from damages related to posts.
The American Psychiatric Association said it does not require any indemnification but did not make its agreement available. The American Academy of Pediatrics also said it did not require indemnification but would not share its agreement.
An American Diabetes Association spokesperson said that “every association is different in what they ask or require from speakers,” but would not share its requirements.
The American Academy of Family Physicians, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the American College of Physicians, and the Endocrine Society all declined to participate.
The organizations that withheld agreements “probably don’t want anybody picking apart their documents,” said Kyle Claussen, CEO of the Resolve Physician Agency, which reviews employment contracts and other contracts for physicians. “The more fair a document, the more likely they would be willing to disclose that, because they have nothing to hide,” he said.
‘It’s all on you’
Requiring indemnification for any and all aspects of a presentation appears to be increasingly common, said the attorneys interviewed for this article. As organizations repackage meeting presentations for sale, they put the content further out into the world and for a longer period, which increases liability exposure.
“If I’m the attorney for DDW, I certainly think I’d want to have this in place,” said Mr. Claussen.
“It’s good business sense for them because it reduces their risk,” said Courtney H. A. Thompson, an attorney with Fredrikson & Byron in Minneapolis, who advises regional and national corporations and ad agencies on advertising, marketing, and trademark law. She also works with clients who speak at meetings and who thus encounter meeting agreements.
Ms. Thompson said indemnity clauses have become fairly common over the past decade, especially as more companies and organizations have sought to protect trademarks, copyrights, and intellectual property and to minimize litigation costs.
A conference organizer “doesn’t want a third party to come after them for intellectual property, privacy, or publicity right infringement based on the participation of the customer or, in this case, the speaker,” said Ms. Thompson.
The agreements also reflect America’s litigation-prone culture.
Dean Fanelli, a patent attorney in the Washington, D.C., office of Cooley LLP, said the agreements he’s been asked to sign as a speaker increasingly seem “overly lawyerly.”
Two decades ago, a speaker might have been asked to sign a paragraph or a one-page form. Now “they often look more like formalized legal agreements,” Mr. Fanelli told this news organization.
The DDW agreement, for instance, ran four pages and contained 21 detailed clauses.
The increasingly complicated agreements “are a little over the top,” said Mr. Fanelli. But as an attorney who works with clients in the pharmaceutical industry, he said he understands that meeting organizers want to protect their rights.
DDW’s main indemnification clause requires the participant to indemnify DDW and its agents, directors, and employees “against any and all claims, demands, causes of action, losses, damages, liabilities, costs, and expenses,” including attorneys’ fees “arising out of a claim, action or proceeding” based on a breach or “alleged breach” by the participant.
“You’re releasing this information to them and then you’re also giving them blanket indemnity back, saying if there’s any type of intellectual property violation on your end – if you’ve included any type of work that’s protected, if this causes any problems – it’s all on you,” said Mr. Claussen.
Other potential pitfalls
Aside from indemnification, participation agreements can contain other potentially worrisome clauses, including onerous terms for cancellation and reuse of content without remuneration.
DDW requires royalty-free licensing of a speaker’s content; the organization can reproduce it in perpetuity without royalties. Many organizations have such a clause in their agreements, including the AAN and the American College of Cardiology.
ASCO’s general authorization form for meeting participants requires that they assign to ASCO rights to their content “perpetually, irrevocably, worldwide and royalty free.” Participants can contact the organization if they seek to opt out, but it’s not clear whether ASCO grants such requests.
Participants in the upcoming American Heart Association annual meeting can deny permission to record their presentation. But if they allow recording and do not agree to assign all rights and copyright ownership to the AHA, the work will be excluded from publication in the meeting program, e-posters, and the meeting supplement in Circulation.
Mr. Claussen said granting royalty-free rights presents a conundrum. Having content reproduced in various formats “might be better for your personal brand,” but it’s not likely to result in any direct compensation and could increase liability exposure, he said.
How presenters must prepare
Mr. Claussen and Ms. Rose said speakers should be vigilant about their own rights and responsibilities, including ensuring that they do not violate copyrights or infringe on intellectual property rights.
“I would recommend that folks be meticulous about what is in their slide deck and materials,” said Ms. Thompson. He said that presenters should be sure they have the right to share material. Technologies crawl the internet seeking out infringement, which often leads to cease and desist letters from attorneys, she said.
It’s better to head off such a letter, Ms. Thompson said. “You need to defend it whether or not it’s a viable claim,” and that can be costly, she said.
Both Ms. Thompson and Mr. Fanelli also warn about disclosing anything that might be considered a trade secret. Many agreements prohibit presenters from engaging in commercial promotion, but if a talk includes information about a drug or device, the manufacturer will want to review the presentation before it’s made public, said Mr. Fanelli.
Many organizations prohibit attendees from photographing, recording, or tweeting at meetings and often require speakers to warn the audience about doing so. DDW goes further by holding presenters liable if someone violates the rule.
“That’s a huge problem,” said Dr. Mandrola. He noted that although it might be easy to police journalists attending a meeting, “it seems hard to enforce that rule amongst just regular attendees.”
Accept or negotiate?
Individuals who submit work to an organization might feel they must sign an agreement as is, especially if they are looking to advance their career or expand knowledge by presenting work at a meeting. But some attorneys said it might be possible to negotiate with meeting organizers.
“My personal opinion is that it never hurts to ask,” said Ms. Thompson. If she were speaking at a legal conference, she would mark up a contract and “see what happens.” The more times pushback is accepted – say, if it works with three out of five speaking engagements – the more it reduces overall liability exposure.
Mr. Fanelli, however, said that although he always reads over an agreement, he typically signs without negotiating. “I don’t usually worry about it because I’m just trying to talk at a particular seminar,” he said.
Prospective presenters “have to weigh that balance – do you want to talk at a seminar, or are you concerned about the legal issues?” said Mr. Fanelli.
If in doubt, talk with a lawyer.
“If you ever have a question on whether or not you should consult an attorney, the answer is always yes,” said Mr. Claussen. It would be “an ounce of prevention,” especially if it’s just a short agreement, he said.
Dr. Ohman, however, said that he believed “it would be fairly costly” and potentially unwieldy. “You can’t litigate everything in life,” he added.
As for Dr. Gardner, he said he would not be as likely to attend DDW in the future if he has to agree to cover any and all liability. “I can’t conceive of ever agreeing to personally indemnify DDW in order to make a presentation at the annual meeting,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Watchdog group demands removal of FDA leaders after aducanumab approval
In a letter to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra, Michael A. Carome, MD, director of Public Citizen’s Health Research Group, said: “The FDA’s decision to approve aducanumab for anyone with Alzheimer’s disease, regardless of severity, showed a stunning disregard for science, eviscerated the agency’s standards for approving new drugs, and ranks as one of the most irresponsible and egregious decisions in the history of the agency.”
Public Citizen urged Mr. Becerra to seek the resignations or the removal of the three FDA officials it said were most responsible for the approval – Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Director Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD; and CDER’s Office of Neuroscience Director Billy Dunn, MD.
“This decision is a disastrous blow to the agency’s credibility, public health, and the financial sustainability of the Medicare program,” writes Dr. Carome, noting that Biogen said it would charge $56,000 annually for the infusion.
Aaron Kesselheim, MD, one of three FDA Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs advisory committee members who resigned in the wake of the approval, agreed with Public Citizen that the agency’s credibility is suffering.
“The aducanumab decision is the worst example yet of the FDA’s movement away from its high standards,” Dr. Kesselheim, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Harvard colleague Jerry Avorn, MD, wrote in the New York Times on June 15.
“As physicians, we know well that Alzheimer’s disease is a terrible condition,” they wrote. However, they added, “approving a drug that has such poor evidence that it works and causes such worrisome side effects is not the solution.”
In his resignation letter, Dr. Kesselheim said he had also been dismayed by the agency’s 2016 approval of eteplirsen (Exondys 51, Sarepta Therapeutics) for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In both the eteplirsen and aducanumab approvals, the agency went against its advisers’ recommendations, Dr. Kesselheim said.
Advocates who backed approval decry cost
Aducanumab had a rocky road to approval but had unwavering backing from the Alzheimer’s Association and at least one other organization, UsAgainstAlzheimer’s.
The Alzheimer’s Association was particularly outspoken in its support and, in March, was accused of potential conflict of interest by Public Citizen and several neurologists because the association accepted at least $1.4 million from Biogen and its partner Eisai since fiscal year 2018.
The association applauded the FDA approval but, a few days later, expressed outrage over the $56,000-a-year price tag.
“This price is simply unacceptable,” the Alzheimer’s Association said in the statement. “For many, this price will pose an insurmountable barrier to access, it complicates and jeopardizes sustainable access to this treatment, and may further deepen issues of health equity,” the association said, adding, “We call on Biogen to change this price.”
UsAgainstAlzheimer’s also expressed concerns about access, even before it knew aducanumab’s price.
“Shockingly, Medicare does not reimburse patients for the expensive PET scans important to determine whether someone is appropriate for this drug,” noted George Vradenburg, chairman and cofounder of the group, in a June 7 statement. “We intend to work with Biogen and Medicare to make access to this drug affordable for every American who needs it,” Mr. Vradenburg said.
Dr. Carome said the advocates’ complaints were hard to fathom.
“This should not have come as a surprise to anyone,” Dr. Carome said, adding that “it’s essentially the ballpark figure the company threw out weeks ago.”
“Fifty-six-thousand-dollars is particularly egregiously overpriced for a drug that doesn’t work,” Dr. Carome said. “If the [Alzheimer’s Association] truly finds this objectionable, hopefully they’ll stop accepting money from Biogen and its partner Eisai,” he added.
“The Alzheimer’s Association is recognizing that the genie is out of the bottle and that they are going to have trouble reining in the inevitable run-away costs,” said Mike Greicius, MD, MPH, associate professor of neurology at Stanford University’s Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute, Stanford, California.
“In addition to the eye-popping annual cost that Biogen has invented, I hope the Alzheimer’s Association is also concerned about the dangerously loose and broad FDA labeling which does not require screening for amyloid-positivity and does not restrict use to the milder forms of disease studied in the Phase 3 trials,” Dr. Greicius said.
Another advocacy group, Patients For Affordable Drugs, commended the Alzheimer’s Association. Its statement “was nothing short of courageous, especially in light of the Alzheimer’s Association’s reliance on funding from drug corporations, including Biogen,” said David Mitchell, a cancer patient and founder of Patients For Affordable Drugs, in a statement.
Mr. Mitchell said his members “stand with the Alzheimer’s Association in its denunciation of the price set by Biogen” and called for a new law that would allow Medicare to negotiate drug prices.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a letter to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra, Michael A. Carome, MD, director of Public Citizen’s Health Research Group, said: “The FDA’s decision to approve aducanumab for anyone with Alzheimer’s disease, regardless of severity, showed a stunning disregard for science, eviscerated the agency’s standards for approving new drugs, and ranks as one of the most irresponsible and egregious decisions in the history of the agency.”
Public Citizen urged Mr. Becerra to seek the resignations or the removal of the three FDA officials it said were most responsible for the approval – Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Director Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD; and CDER’s Office of Neuroscience Director Billy Dunn, MD.
“This decision is a disastrous blow to the agency’s credibility, public health, and the financial sustainability of the Medicare program,” writes Dr. Carome, noting that Biogen said it would charge $56,000 annually for the infusion.
Aaron Kesselheim, MD, one of three FDA Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs advisory committee members who resigned in the wake of the approval, agreed with Public Citizen that the agency’s credibility is suffering.
“The aducanumab decision is the worst example yet of the FDA’s movement away from its high standards,” Dr. Kesselheim, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Harvard colleague Jerry Avorn, MD, wrote in the New York Times on June 15.
“As physicians, we know well that Alzheimer’s disease is a terrible condition,” they wrote. However, they added, “approving a drug that has such poor evidence that it works and causes such worrisome side effects is not the solution.”
In his resignation letter, Dr. Kesselheim said he had also been dismayed by the agency’s 2016 approval of eteplirsen (Exondys 51, Sarepta Therapeutics) for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In both the eteplirsen and aducanumab approvals, the agency went against its advisers’ recommendations, Dr. Kesselheim said.
Advocates who backed approval decry cost
Aducanumab had a rocky road to approval but had unwavering backing from the Alzheimer’s Association and at least one other organization, UsAgainstAlzheimer’s.
The Alzheimer’s Association was particularly outspoken in its support and, in March, was accused of potential conflict of interest by Public Citizen and several neurologists because the association accepted at least $1.4 million from Biogen and its partner Eisai since fiscal year 2018.
The association applauded the FDA approval but, a few days later, expressed outrage over the $56,000-a-year price tag.
“This price is simply unacceptable,” the Alzheimer’s Association said in the statement. “For many, this price will pose an insurmountable barrier to access, it complicates and jeopardizes sustainable access to this treatment, and may further deepen issues of health equity,” the association said, adding, “We call on Biogen to change this price.”
UsAgainstAlzheimer’s also expressed concerns about access, even before it knew aducanumab’s price.
“Shockingly, Medicare does not reimburse patients for the expensive PET scans important to determine whether someone is appropriate for this drug,” noted George Vradenburg, chairman and cofounder of the group, in a June 7 statement. “We intend to work with Biogen and Medicare to make access to this drug affordable for every American who needs it,” Mr. Vradenburg said.
Dr. Carome said the advocates’ complaints were hard to fathom.
“This should not have come as a surprise to anyone,” Dr. Carome said, adding that “it’s essentially the ballpark figure the company threw out weeks ago.”
“Fifty-six-thousand-dollars is particularly egregiously overpriced for a drug that doesn’t work,” Dr. Carome said. “If the [Alzheimer’s Association] truly finds this objectionable, hopefully they’ll stop accepting money from Biogen and its partner Eisai,” he added.
“The Alzheimer’s Association is recognizing that the genie is out of the bottle and that they are going to have trouble reining in the inevitable run-away costs,” said Mike Greicius, MD, MPH, associate professor of neurology at Stanford University’s Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute, Stanford, California.
“In addition to the eye-popping annual cost that Biogen has invented, I hope the Alzheimer’s Association is also concerned about the dangerously loose and broad FDA labeling which does not require screening for amyloid-positivity and does not restrict use to the milder forms of disease studied in the Phase 3 trials,” Dr. Greicius said.
Another advocacy group, Patients For Affordable Drugs, commended the Alzheimer’s Association. Its statement “was nothing short of courageous, especially in light of the Alzheimer’s Association’s reliance on funding from drug corporations, including Biogen,” said David Mitchell, a cancer patient and founder of Patients For Affordable Drugs, in a statement.
Mr. Mitchell said his members “stand with the Alzheimer’s Association in its denunciation of the price set by Biogen” and called for a new law that would allow Medicare to negotiate drug prices.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a letter to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra, Michael A. Carome, MD, director of Public Citizen’s Health Research Group, said: “The FDA’s decision to approve aducanumab for anyone with Alzheimer’s disease, regardless of severity, showed a stunning disregard for science, eviscerated the agency’s standards for approving new drugs, and ranks as one of the most irresponsible and egregious decisions in the history of the agency.”
Public Citizen urged Mr. Becerra to seek the resignations or the removal of the three FDA officials it said were most responsible for the approval – Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Director Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD; and CDER’s Office of Neuroscience Director Billy Dunn, MD.
“This decision is a disastrous blow to the agency’s credibility, public health, and the financial sustainability of the Medicare program,” writes Dr. Carome, noting that Biogen said it would charge $56,000 annually for the infusion.
Aaron Kesselheim, MD, one of three FDA Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs advisory committee members who resigned in the wake of the approval, agreed with Public Citizen that the agency’s credibility is suffering.
“The aducanumab decision is the worst example yet of the FDA’s movement away from its high standards,” Dr. Kesselheim, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Harvard colleague Jerry Avorn, MD, wrote in the New York Times on June 15.
“As physicians, we know well that Alzheimer’s disease is a terrible condition,” they wrote. However, they added, “approving a drug that has such poor evidence that it works and causes such worrisome side effects is not the solution.”
In his resignation letter, Dr. Kesselheim said he had also been dismayed by the agency’s 2016 approval of eteplirsen (Exondys 51, Sarepta Therapeutics) for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In both the eteplirsen and aducanumab approvals, the agency went against its advisers’ recommendations, Dr. Kesselheim said.
Advocates who backed approval decry cost
Aducanumab had a rocky road to approval but had unwavering backing from the Alzheimer’s Association and at least one other organization, UsAgainstAlzheimer’s.
The Alzheimer’s Association was particularly outspoken in its support and, in March, was accused of potential conflict of interest by Public Citizen and several neurologists because the association accepted at least $1.4 million from Biogen and its partner Eisai since fiscal year 2018.
The association applauded the FDA approval but, a few days later, expressed outrage over the $56,000-a-year price tag.
“This price is simply unacceptable,” the Alzheimer’s Association said in the statement. “For many, this price will pose an insurmountable barrier to access, it complicates and jeopardizes sustainable access to this treatment, and may further deepen issues of health equity,” the association said, adding, “We call on Biogen to change this price.”
UsAgainstAlzheimer’s also expressed concerns about access, even before it knew aducanumab’s price.
“Shockingly, Medicare does not reimburse patients for the expensive PET scans important to determine whether someone is appropriate for this drug,” noted George Vradenburg, chairman and cofounder of the group, in a June 7 statement. “We intend to work with Biogen and Medicare to make access to this drug affordable for every American who needs it,” Mr. Vradenburg said.
Dr. Carome said the advocates’ complaints were hard to fathom.
“This should not have come as a surprise to anyone,” Dr. Carome said, adding that “it’s essentially the ballpark figure the company threw out weeks ago.”
“Fifty-six-thousand-dollars is particularly egregiously overpriced for a drug that doesn’t work,” Dr. Carome said. “If the [Alzheimer’s Association] truly finds this objectionable, hopefully they’ll stop accepting money from Biogen and its partner Eisai,” he added.
“The Alzheimer’s Association is recognizing that the genie is out of the bottle and that they are going to have trouble reining in the inevitable run-away costs,” said Mike Greicius, MD, MPH, associate professor of neurology at Stanford University’s Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute, Stanford, California.
“In addition to the eye-popping annual cost that Biogen has invented, I hope the Alzheimer’s Association is also concerned about the dangerously loose and broad FDA labeling which does not require screening for amyloid-positivity and does not restrict use to the milder forms of disease studied in the Phase 3 trials,” Dr. Greicius said.
Another advocacy group, Patients For Affordable Drugs, commended the Alzheimer’s Association. Its statement “was nothing short of courageous, especially in light of the Alzheimer’s Association’s reliance on funding from drug corporations, including Biogen,” said David Mitchell, a cancer patient and founder of Patients For Affordable Drugs, in a statement.
Mr. Mitchell said his members “stand with the Alzheimer’s Association in its denunciation of the price set by Biogen” and called for a new law that would allow Medicare to negotiate drug prices.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.