User login
Age, C-reactive protein predict COVID-19 death in diabetes
The data, from the retrospective ACCREDIT cohort study, were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2021) by Daniel Kevin Llanera, MD.
The combination of older age and high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were linked to a tripled risk for death by day 7 after hospitalization for COVID-19 among people with diabetes. But, in contrast to other studies, recent A1c and body mass index did not predict COVID-19 outcomes.
“Both of these variables are easily available upon admission to hospital,” Dr. Llanera, who now works at Imperial College, London, said in an EASD press release.
“This means we can easily identify patients early on in their hospital stay who will likely require more aggressive interventions to try and improve survival.”
“It makes sense that CRP and age are important,” said Simon Heller, MB BChir, DM, of the University of Sheffield, England. “It may be that diabetes alone overwhelmed the additional effects of obesity and A1c.
“Certainly in other studies, age was the overwhelming bad prognostic sign among people with diabetes, and perhaps long-term diabetes has effects on the immune system which we haven’t yet identified.”
Kidney disease in younger patients also linked to poorer outcomes
The study, conducted when Dr. Llanera worked for the Countess of Chester NHS Foundation Trust, involved 1,004 patients with diabetes admitted with COVID-19 to seven hospitals in northwest England from Jan. 1 through June 30, 2020. The patients were a mean age of 74.1 years, 60.7% were male, and 45% were in the most deprived quintile based on the U.K. government deprivation index. Overall, 56.2% had macrovascular complications and 49.6% had microvascular complications.
They had a median BMI of 27.6 kg/m2, which is lower than that reported in previous studies and might explain the difference, Dr. Llanera noted.
The primary outcome, death within 7 days of admission, occurred in 24%. By day 30, 33% had died. These rates are higher than the rate found in previous studies, possibly because of greater socioeconomic deprivation and older age of the population, Dr. Llanera speculated.
A total of 7.5% of patients received intensive care by day 7 and 9.8% required intravenous insulin infusions.
On univariate analysis, insulin infusion was found to be protective, with those receiving it half as likely to die as those who didn’t need IV insulin (odds ratio [OR], 0.5).
In contrast, chronic kidney disease in people younger than 70 years increased the risk of death more than twofold (OR, 2.74), as did type 2 diabetes compared with other diabetes types (OR, 2.52).
As in previous studies, use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were not associated with COVID-19 outcomes, nor was the presence of diabetes-related complications.
In multivariate analysis, CRP and age emerged as the most significant predictors of the primary outcome, with those deemed high risk by a logistic regression model having an OR of 3.44 for death by day 7 compared with those at lower risk based on the two factors.
Data for glycemic control during the time of hospitalization weren’t available for this study, Dr. Llanera said in response to a question.
“We didn’t look into glycemic control during admission, just at entry, so I can’t answer whether strict glucose control is of benefit. I think it’s worth exploring further whether the use of IV insulin may be of benefit.”
Dr. Llanera also pointed out that people with diabetic kidney disease are in a chronic proinflammatory state and have immune dysregulation, thus potentially hindering their ability to “fight off” the virus.
“In addition, ACE2 receptors are upregulated in the kidneys of patients with diabetic kidney disease. These are molecules that facilitate entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. This may lead to direct attack of the kidneys by the virus, possibly leading to worse overall outcomes,” he said.
Dr. Llanera has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heller has reported serving as consultant or speaker for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Mannkind, Zealand, MSD, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data, from the retrospective ACCREDIT cohort study, were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2021) by Daniel Kevin Llanera, MD.
The combination of older age and high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were linked to a tripled risk for death by day 7 after hospitalization for COVID-19 among people with diabetes. But, in contrast to other studies, recent A1c and body mass index did not predict COVID-19 outcomes.
“Both of these variables are easily available upon admission to hospital,” Dr. Llanera, who now works at Imperial College, London, said in an EASD press release.
“This means we can easily identify patients early on in their hospital stay who will likely require more aggressive interventions to try and improve survival.”
“It makes sense that CRP and age are important,” said Simon Heller, MB BChir, DM, of the University of Sheffield, England. “It may be that diabetes alone overwhelmed the additional effects of obesity and A1c.
“Certainly in other studies, age was the overwhelming bad prognostic sign among people with diabetes, and perhaps long-term diabetes has effects on the immune system which we haven’t yet identified.”
Kidney disease in younger patients also linked to poorer outcomes
The study, conducted when Dr. Llanera worked for the Countess of Chester NHS Foundation Trust, involved 1,004 patients with diabetes admitted with COVID-19 to seven hospitals in northwest England from Jan. 1 through June 30, 2020. The patients were a mean age of 74.1 years, 60.7% were male, and 45% were in the most deprived quintile based on the U.K. government deprivation index. Overall, 56.2% had macrovascular complications and 49.6% had microvascular complications.
They had a median BMI of 27.6 kg/m2, which is lower than that reported in previous studies and might explain the difference, Dr. Llanera noted.
The primary outcome, death within 7 days of admission, occurred in 24%. By day 30, 33% had died. These rates are higher than the rate found in previous studies, possibly because of greater socioeconomic deprivation and older age of the population, Dr. Llanera speculated.
A total of 7.5% of patients received intensive care by day 7 and 9.8% required intravenous insulin infusions.
On univariate analysis, insulin infusion was found to be protective, with those receiving it half as likely to die as those who didn’t need IV insulin (odds ratio [OR], 0.5).
In contrast, chronic kidney disease in people younger than 70 years increased the risk of death more than twofold (OR, 2.74), as did type 2 diabetes compared with other diabetes types (OR, 2.52).
As in previous studies, use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were not associated with COVID-19 outcomes, nor was the presence of diabetes-related complications.
In multivariate analysis, CRP and age emerged as the most significant predictors of the primary outcome, with those deemed high risk by a logistic regression model having an OR of 3.44 for death by day 7 compared with those at lower risk based on the two factors.
Data for glycemic control during the time of hospitalization weren’t available for this study, Dr. Llanera said in response to a question.
“We didn’t look into glycemic control during admission, just at entry, so I can’t answer whether strict glucose control is of benefit. I think it’s worth exploring further whether the use of IV insulin may be of benefit.”
Dr. Llanera also pointed out that people with diabetic kidney disease are in a chronic proinflammatory state and have immune dysregulation, thus potentially hindering their ability to “fight off” the virus.
“In addition, ACE2 receptors are upregulated in the kidneys of patients with diabetic kidney disease. These are molecules that facilitate entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. This may lead to direct attack of the kidneys by the virus, possibly leading to worse overall outcomes,” he said.
Dr. Llanera has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heller has reported serving as consultant or speaker for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Mannkind, Zealand, MSD, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data, from the retrospective ACCREDIT cohort study, were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2021) by Daniel Kevin Llanera, MD.
The combination of older age and high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were linked to a tripled risk for death by day 7 after hospitalization for COVID-19 among people with diabetes. But, in contrast to other studies, recent A1c and body mass index did not predict COVID-19 outcomes.
“Both of these variables are easily available upon admission to hospital,” Dr. Llanera, who now works at Imperial College, London, said in an EASD press release.
“This means we can easily identify patients early on in their hospital stay who will likely require more aggressive interventions to try and improve survival.”
“It makes sense that CRP and age are important,” said Simon Heller, MB BChir, DM, of the University of Sheffield, England. “It may be that diabetes alone overwhelmed the additional effects of obesity and A1c.
“Certainly in other studies, age was the overwhelming bad prognostic sign among people with diabetes, and perhaps long-term diabetes has effects on the immune system which we haven’t yet identified.”
Kidney disease in younger patients also linked to poorer outcomes
The study, conducted when Dr. Llanera worked for the Countess of Chester NHS Foundation Trust, involved 1,004 patients with diabetes admitted with COVID-19 to seven hospitals in northwest England from Jan. 1 through June 30, 2020. The patients were a mean age of 74.1 years, 60.7% were male, and 45% were in the most deprived quintile based on the U.K. government deprivation index. Overall, 56.2% had macrovascular complications and 49.6% had microvascular complications.
They had a median BMI of 27.6 kg/m2, which is lower than that reported in previous studies and might explain the difference, Dr. Llanera noted.
The primary outcome, death within 7 days of admission, occurred in 24%. By day 30, 33% had died. These rates are higher than the rate found in previous studies, possibly because of greater socioeconomic deprivation and older age of the population, Dr. Llanera speculated.
A total of 7.5% of patients received intensive care by day 7 and 9.8% required intravenous insulin infusions.
On univariate analysis, insulin infusion was found to be protective, with those receiving it half as likely to die as those who didn’t need IV insulin (odds ratio [OR], 0.5).
In contrast, chronic kidney disease in people younger than 70 years increased the risk of death more than twofold (OR, 2.74), as did type 2 diabetes compared with other diabetes types (OR, 2.52).
As in previous studies, use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were not associated with COVID-19 outcomes, nor was the presence of diabetes-related complications.
In multivariate analysis, CRP and age emerged as the most significant predictors of the primary outcome, with those deemed high risk by a logistic regression model having an OR of 3.44 for death by day 7 compared with those at lower risk based on the two factors.
Data for glycemic control during the time of hospitalization weren’t available for this study, Dr. Llanera said in response to a question.
“We didn’t look into glycemic control during admission, just at entry, so I can’t answer whether strict glucose control is of benefit. I think it’s worth exploring further whether the use of IV insulin may be of benefit.”
Dr. Llanera also pointed out that people with diabetic kidney disease are in a chronic proinflammatory state and have immune dysregulation, thus potentially hindering their ability to “fight off” the virus.
“In addition, ACE2 receptors are upregulated in the kidneys of patients with diabetic kidney disease. These are molecules that facilitate entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. This may lead to direct attack of the kidneys by the virus, possibly leading to worse overall outcomes,” he said.
Dr. Llanera has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heller has reported serving as consultant or speaker for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Mannkind, Zealand, MSD, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 hospitalization 80% more likely for smokers
Observational data was analyzed alongside hospital coronavirus test data and UK Biobank genetic information for the first time, and the findings are published in Thorax.
The data cover 421,469 people overall. Of these, 3.2% took a polymerase chain reaction swab test, 0.4% of these tested positive, 0.2% of them required hospitalization for COVID-19, and 0.1% of them died because of COVID-19.
When it came to smoking status, 59% had never smoked, 37% were ex-smokers, and 3% were current smokers.
Current smokers were 80% more likely to be admitted to hospital, and significantly more likely to die from COVID-19, than nonsmokers.
Time to quit
Heavy smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day were 6.11 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than people who had never smoked.
Analysis also showed those with a genetic predisposition to being smokers had a 45% higher infection risk, and 60% higher hospitalization risk.
The authors wrote: “Overall, the congruence of observational analyses indicating associations with recent smoking behaviors and [Mendelian randomization] analyses indicating associations with lifelong predisposition to smoking and smoking heaviness support a causal effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity.”
In a linked podcast, lead researcher Dr. Ashley Clift, said: “Our results strongly suggest that smoking is related to your risk of getting severe COVID, and just as smoking affects your risk of heart disease, different cancers, and all those other conditions we know smoking is linked to, it appears that it’s the same for COVID. So now might be as good a time as any to quit cigarettes and quit smoking.”
These results contrast with previous studies that have suggested a protective effect of smoking against COVID-19. In a linked editorial, Anthony Laverty, PhD, and Christopher Millet, PhD, Imperial College London, wrote: “The idea that tobacco smoking may protect against COVID-19 was always an improbable one.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Observational data was analyzed alongside hospital coronavirus test data and UK Biobank genetic information for the first time, and the findings are published in Thorax.
The data cover 421,469 people overall. Of these, 3.2% took a polymerase chain reaction swab test, 0.4% of these tested positive, 0.2% of them required hospitalization for COVID-19, and 0.1% of them died because of COVID-19.
When it came to smoking status, 59% had never smoked, 37% were ex-smokers, and 3% were current smokers.
Current smokers were 80% more likely to be admitted to hospital, and significantly more likely to die from COVID-19, than nonsmokers.
Time to quit
Heavy smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day were 6.11 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than people who had never smoked.
Analysis also showed those with a genetic predisposition to being smokers had a 45% higher infection risk, and 60% higher hospitalization risk.
The authors wrote: “Overall, the congruence of observational analyses indicating associations with recent smoking behaviors and [Mendelian randomization] analyses indicating associations with lifelong predisposition to smoking and smoking heaviness support a causal effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity.”
In a linked podcast, lead researcher Dr. Ashley Clift, said: “Our results strongly suggest that smoking is related to your risk of getting severe COVID, and just as smoking affects your risk of heart disease, different cancers, and all those other conditions we know smoking is linked to, it appears that it’s the same for COVID. So now might be as good a time as any to quit cigarettes and quit smoking.”
These results contrast with previous studies that have suggested a protective effect of smoking against COVID-19. In a linked editorial, Anthony Laverty, PhD, and Christopher Millet, PhD, Imperial College London, wrote: “The idea that tobacco smoking may protect against COVID-19 was always an improbable one.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Observational data was analyzed alongside hospital coronavirus test data and UK Biobank genetic information for the first time, and the findings are published in Thorax.
The data cover 421,469 people overall. Of these, 3.2% took a polymerase chain reaction swab test, 0.4% of these tested positive, 0.2% of them required hospitalization for COVID-19, and 0.1% of them died because of COVID-19.
When it came to smoking status, 59% had never smoked, 37% were ex-smokers, and 3% were current smokers.
Current smokers were 80% more likely to be admitted to hospital, and significantly more likely to die from COVID-19, than nonsmokers.
Time to quit
Heavy smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day were 6.11 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than people who had never smoked.
Analysis also showed those with a genetic predisposition to being smokers had a 45% higher infection risk, and 60% higher hospitalization risk.
The authors wrote: “Overall, the congruence of observational analyses indicating associations with recent smoking behaviors and [Mendelian randomization] analyses indicating associations with lifelong predisposition to smoking and smoking heaviness support a causal effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity.”
In a linked podcast, lead researcher Dr. Ashley Clift, said: “Our results strongly suggest that smoking is related to your risk of getting severe COVID, and just as smoking affects your risk of heart disease, different cancers, and all those other conditions we know smoking is linked to, it appears that it’s the same for COVID. So now might be as good a time as any to quit cigarettes and quit smoking.”
These results contrast with previous studies that have suggested a protective effect of smoking against COVID-19. In a linked editorial, Anthony Laverty, PhD, and Christopher Millet, PhD, Imperial College London, wrote: “The idea that tobacco smoking may protect against COVID-19 was always an improbable one.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth models of care for pediatric hospital medicine
PHM 2021 session
Let’s Go Virtual! Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Telehealth Models of Care for Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Presenters
Brooke Geyer, DO; Christina Olson, MD; and Amy Willis, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Geyer, Dr. Olson, and Dr. Willis of the University of Colorado presented and facilitated a workshop discussing the role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine. Participants were given a brief introduction to the basics of telehealth practices before breaking up into small groups to explore the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a telehealth model in a pediatric hospital. For each of these topics, the presenters led the breakout groups through a discussion of Colorado’s successful telehealth models, including virtual nocturnists, health system resource optimization, and virtual transitions of care, as well as addressed the participants’ questions unique to their telehealth experiences. The session emphasized the emerging role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine and that “telehealth is here to stay, and we have an opportunity to redesign health care forever.”
Key takeaways
- Telehealth is more than just synchronous virtual patient care, it encompasses asynchronous care, remote patient monitoring, education, policy, and more.
- Telehealth standards of care are the same as in-person care.
- Development and implementation of a telehealth model in pediatric hospital medicine is feasible with appropriate planning and conversations with key stakeholders.
- Evaluation and refinement of telehealth models is an iterative process that will take time, much like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles in quality improvement work.
Dr. Scott is a second-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at New York–Presbyterian Columbia/Cornell. Her academic interests are in curriculum development and evaluation in medical education with a focus on telemedicine.
PHM 2021 session
Let’s Go Virtual! Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Telehealth Models of Care for Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Presenters
Brooke Geyer, DO; Christina Olson, MD; and Amy Willis, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Geyer, Dr. Olson, and Dr. Willis of the University of Colorado presented and facilitated a workshop discussing the role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine. Participants were given a brief introduction to the basics of telehealth practices before breaking up into small groups to explore the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a telehealth model in a pediatric hospital. For each of these topics, the presenters led the breakout groups through a discussion of Colorado’s successful telehealth models, including virtual nocturnists, health system resource optimization, and virtual transitions of care, as well as addressed the participants’ questions unique to their telehealth experiences. The session emphasized the emerging role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine and that “telehealth is here to stay, and we have an opportunity to redesign health care forever.”
Key takeaways
- Telehealth is more than just synchronous virtual patient care, it encompasses asynchronous care, remote patient monitoring, education, policy, and more.
- Telehealth standards of care are the same as in-person care.
- Development and implementation of a telehealth model in pediatric hospital medicine is feasible with appropriate planning and conversations with key stakeholders.
- Evaluation and refinement of telehealth models is an iterative process that will take time, much like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles in quality improvement work.
Dr. Scott is a second-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at New York–Presbyterian Columbia/Cornell. Her academic interests are in curriculum development and evaluation in medical education with a focus on telemedicine.
PHM 2021 session
Let’s Go Virtual! Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Telehealth Models of Care for Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Presenters
Brooke Geyer, DO; Christina Olson, MD; and Amy Willis, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Geyer, Dr. Olson, and Dr. Willis of the University of Colorado presented and facilitated a workshop discussing the role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine. Participants were given a brief introduction to the basics of telehealth practices before breaking up into small groups to explore the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a telehealth model in a pediatric hospital. For each of these topics, the presenters led the breakout groups through a discussion of Colorado’s successful telehealth models, including virtual nocturnists, health system resource optimization, and virtual transitions of care, as well as addressed the participants’ questions unique to their telehealth experiences. The session emphasized the emerging role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine and that “telehealth is here to stay, and we have an opportunity to redesign health care forever.”
Key takeaways
- Telehealth is more than just synchronous virtual patient care, it encompasses asynchronous care, remote patient monitoring, education, policy, and more.
- Telehealth standards of care are the same as in-person care.
- Development and implementation of a telehealth model in pediatric hospital medicine is feasible with appropriate planning and conversations with key stakeholders.
- Evaluation and refinement of telehealth models is an iterative process that will take time, much like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles in quality improvement work.
Dr. Scott is a second-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at New York–Presbyterian Columbia/Cornell. Her academic interests are in curriculum development and evaluation in medical education with a focus on telemedicine.
Children and COVID: New cases topped 200,000 after 3 weeks of declines
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
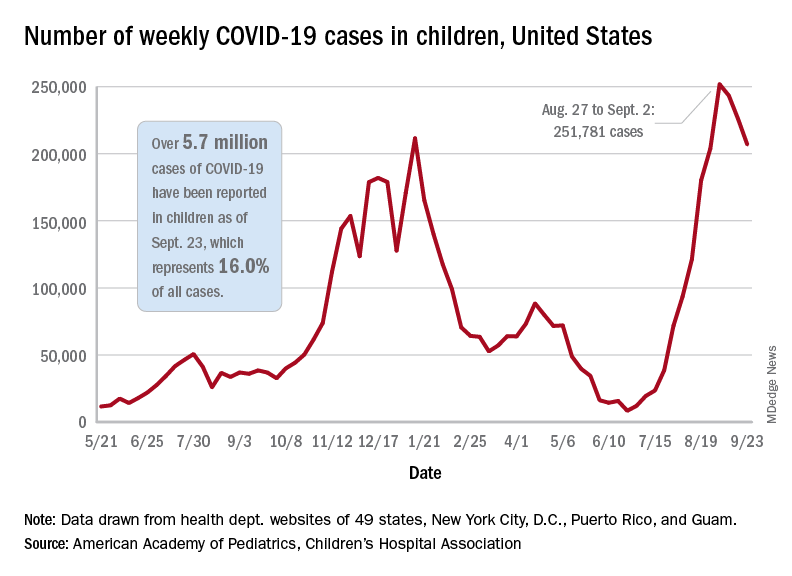
based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
POCUS in hospital pediatrics
PHM 2021 Session
Safe and (Ultra)sound: Why you should use POCUS in your Pediatric Practice
Presenter
Ria Dancel, MD, FAAP, FACP
Session summary
Dr. Ria Dancel and her colleagues from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill presented a broad overview of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) applications in the field of pediatric hospital medicine. They discussed its advantages and potential uses, ranging from common scenarios to critical care to procedural guidance. Using illustrative scenarios and interactive cases, she discussed the bedside applications to improve care of hospitalized children. The benefits and risks of radiography and POCUS were reviewed.
The session highlighted the use of POCUS in SSTI (skin and soft tissue infection) to help with differentiating cellulitis from abscesses. Use of POCUS for safer incision and drainages and making day-to-day changes in management was discussed. The ease and benefits of performing real-time lung ultrasound in different pathologies (like pneumonia, effusion, COVID-19) was presented. The speakers discussed the use of POCUS in emergency situations like hypotension and different types of shock. The use of ultrasound in common bedside procedures (bladder catheterization, lumbar ultrasound, peripheral IV placement) were also highlighted. Current literature and evidence were reviewed.
Key takeaways
- Pediatric POCUS is an extremely valuable bedside tool in pediatric hospital medicine.
- It can be used to guide clinical care for many conditions including SSTI, pneumonia, and shock.
- It can be used for procedural guidance for bladder catheterization, lumbar puncture, and intravenous access.
Dr. Patra is a pediatric hospitalist at West Virginia University Children’s Hospital, Morgantown, and associate professor at West Virginia University School of Medicine. He is interested in medical education, quality improvement and clinical research. He is a member of the Executive Council of the Pediatric Special Interest Group of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
PHM 2021 Session
Safe and (Ultra)sound: Why you should use POCUS in your Pediatric Practice
Presenter
Ria Dancel, MD, FAAP, FACP
Session summary
Dr. Ria Dancel and her colleagues from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill presented a broad overview of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) applications in the field of pediatric hospital medicine. They discussed its advantages and potential uses, ranging from common scenarios to critical care to procedural guidance. Using illustrative scenarios and interactive cases, she discussed the bedside applications to improve care of hospitalized children. The benefits and risks of radiography and POCUS were reviewed.
The session highlighted the use of POCUS in SSTI (skin and soft tissue infection) to help with differentiating cellulitis from abscesses. Use of POCUS for safer incision and drainages and making day-to-day changes in management was discussed. The ease and benefits of performing real-time lung ultrasound in different pathologies (like pneumonia, effusion, COVID-19) was presented. The speakers discussed the use of POCUS in emergency situations like hypotension and different types of shock. The use of ultrasound in common bedside procedures (bladder catheterization, lumbar ultrasound, peripheral IV placement) were also highlighted. Current literature and evidence were reviewed.
Key takeaways
- Pediatric POCUS is an extremely valuable bedside tool in pediatric hospital medicine.
- It can be used to guide clinical care for many conditions including SSTI, pneumonia, and shock.
- It can be used for procedural guidance for bladder catheterization, lumbar puncture, and intravenous access.
Dr. Patra is a pediatric hospitalist at West Virginia University Children’s Hospital, Morgantown, and associate professor at West Virginia University School of Medicine. He is interested in medical education, quality improvement and clinical research. He is a member of the Executive Council of the Pediatric Special Interest Group of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
PHM 2021 Session
Safe and (Ultra)sound: Why you should use POCUS in your Pediatric Practice
Presenter
Ria Dancel, MD, FAAP, FACP
Session summary
Dr. Ria Dancel and her colleagues from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill presented a broad overview of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) applications in the field of pediatric hospital medicine. They discussed its advantages and potential uses, ranging from common scenarios to critical care to procedural guidance. Using illustrative scenarios and interactive cases, she discussed the bedside applications to improve care of hospitalized children. The benefits and risks of radiography and POCUS were reviewed.
The session highlighted the use of POCUS in SSTI (skin and soft tissue infection) to help with differentiating cellulitis from abscesses. Use of POCUS for safer incision and drainages and making day-to-day changes in management was discussed. The ease and benefits of performing real-time lung ultrasound in different pathologies (like pneumonia, effusion, COVID-19) was presented. The speakers discussed the use of POCUS in emergency situations like hypotension and different types of shock. The use of ultrasound in common bedside procedures (bladder catheterization, lumbar ultrasound, peripheral IV placement) were also highlighted. Current literature and evidence were reviewed.
Key takeaways
- Pediatric POCUS is an extremely valuable bedside tool in pediatric hospital medicine.
- It can be used to guide clinical care for many conditions including SSTI, pneumonia, and shock.
- It can be used for procedural guidance for bladder catheterization, lumbar puncture, and intravenous access.
Dr. Patra is a pediatric hospitalist at West Virginia University Children’s Hospital, Morgantown, and associate professor at West Virginia University School of Medicine. He is interested in medical education, quality improvement and clinical research. He is a member of the Executive Council of the Pediatric Special Interest Group of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Heart failure hospitalization risk lower with SGLT2 inhibitors than GLP-1 RAs
Around a 30% reduction in the risk for being hospitalized for heart failure was achieved in people with type 2 diabetes who were treated with a SGLT2 inhibitor over a GLP-1 RA regardless of whether the patients had a preexisting heart condition.
The findings, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, also showed a 10% lower risk for myocardial infarction or stroke among those treated with a SGLT2 inhibitor who had preexisting cardiovascular disease (CVD), although there was no difference in risk between the two classes of drugs in those without preexisting CVD.
“These findings are important as they suggest that SGLT2 [inhibitors] and GLP-1 RA offer similar benefits in preventing myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with diabetes,” said study investigator Elisabetta Patorno, MD, DrPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, in an interview.
They also show “that SGLT2 [inhibitors] offer greater efficacy in preventing heart failure, which supports the existing guidelines,” she added.
Paul S. Jellinger, MD, MACE, of the Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Care in Hollywood, Fla., said these data were likely to be “additive to guidelines but not transformative.” The overall analysis results were “not surprising.” It was not unexpected that SGLT2 inhibitors provided a robust chronic heart failure (CHF) benefit, particularly in individuals with history of CVD, he said.
Dr. Jellinger, a clinical endocrinologist and professor of clinical medicine on the voluntary faculty at the University of Miami, observed, however, that “the similar CVD benefit in both drug classes in patients without known CVD adds to our knowledge in this somewhat controversial area and may be useful to the clinician in evaluating therapy in a diabetic individual without evidence of or at high risk for CHF.”
Furthermore, “the study also reminds us that, as demonstrated in published meta-analysis, there is also a modest CHF benefit associated with GLP-1 RA treatment particularly in patients with a history of CVD.”
Addressing the knowledge gap
Thanks to the results of many large-scale, prospective, cardiovascular outcomes studies, both SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 RA have been recommended as treatment for people with diabetes who have established CVD. But with no direct head-to-head trials having been conducted, there is a gap in knowledge and there is currently little guidance for physicians on which drug class to choose for an individual patient.
To try to clarify things, Dr. Patorno and associates looked at data from more than 370,000 people with type 2 diabetes who had been treated between April 2013 and December 2017 with either a SGLT2 inhibitor (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, or empagliflozin) or GLP-1 RA (albiglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, or liraglutide).
One-to-one propensity score matching was used to create the study groups: participants were first grouped according to their history of CVD, and then by the class of drug they had been prescribed. The primary outcomes were hospitalization for MI, stroke, or heart failure.
Comparing the initiation of a SGLT2 inhibitor with GLP-1 RA therapy, the hazard ratios (HRs) for MI or stroke in patients with and without a history of CVD were a respective 0.90 (95% CI, 0.82 to 0.98) and 1.07 (0.97 to 1.18).
The corresponding hazard ratios for heart failure hospitalizations were 0.71 (0.64 to 0.79) and 0.69 (0.56 to 0.85).
Real-world studies are of ‘increasing value’
“As in other not-randomized studies based on real-world data, residual confounding cannot be completely ruled out,” Dr. Patorno acknowledged. She added, however that “state-of-the-art methodological strategies were implemented to minimize this possibility.”
Limitations notwithstanding, “real world studies are demonstrating increasing value,” observed Dr. Jellinger. Further large-scale cardiovascular outcomes trials that directly compare these two drug classes “are unlikely given the depth of information available now,” Dr. Jellinger suggested.
“This head-to-head retrospective study may be as close as we get and does represent the first effort at a comparison of these two classes.”
Dr. Patorno said of the potential clinical implications: “Because the two classes are equally effective for stroke and myocardial infarction, but the SGLT2 inhibitors are superior for heart failure, when considered in aggregate, SGLT2 inhibitors are likely to prevent more of these adverse cardiovascular events than GLP-1 RA.”
The study received no commercial funding and was supported by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics.
Dr. Patorno reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jellinger is on the speaker’s bureau for Astra Zeneca, Amgen, and Esperion, and has served on advisory boards for Corcept and Regeneron.
Around a 30% reduction in the risk for being hospitalized for heart failure was achieved in people with type 2 diabetes who were treated with a SGLT2 inhibitor over a GLP-1 RA regardless of whether the patients had a preexisting heart condition.
The findings, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, also showed a 10% lower risk for myocardial infarction or stroke among those treated with a SGLT2 inhibitor who had preexisting cardiovascular disease (CVD), although there was no difference in risk between the two classes of drugs in those without preexisting CVD.
“These findings are important as they suggest that SGLT2 [inhibitors] and GLP-1 RA offer similar benefits in preventing myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with diabetes,” said study investigator Elisabetta Patorno, MD, DrPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, in an interview.
They also show “that SGLT2 [inhibitors] offer greater efficacy in preventing heart failure, which supports the existing guidelines,” she added.
Paul S. Jellinger, MD, MACE, of the Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Care in Hollywood, Fla., said these data were likely to be “additive to guidelines but not transformative.” The overall analysis results were “not surprising.” It was not unexpected that SGLT2 inhibitors provided a robust chronic heart failure (CHF) benefit, particularly in individuals with history of CVD, he said.
Dr. Jellinger, a clinical endocrinologist and professor of clinical medicine on the voluntary faculty at the University of Miami, observed, however, that “the similar CVD benefit in both drug classes in patients without known CVD adds to our knowledge in this somewhat controversial area and may be useful to the clinician in evaluating therapy in a diabetic individual without evidence of or at high risk for CHF.”
Furthermore, “the study also reminds us that, as demonstrated in published meta-analysis, there is also a modest CHF benefit associated with GLP-1 RA treatment particularly in patients with a history of CVD.”
Addressing the knowledge gap
Thanks to the results of many large-scale, prospective, cardiovascular outcomes studies, both SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 RA have been recommended as treatment for people with diabetes who have established CVD. But with no direct head-to-head trials having been conducted, there is a gap in knowledge and there is currently little guidance for physicians on which drug class to choose for an individual patient.
To try to clarify things, Dr. Patorno and associates looked at data from more than 370,000 people with type 2 diabetes who had been treated between April 2013 and December 2017 with either a SGLT2 inhibitor (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, or empagliflozin) or GLP-1 RA (albiglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, or liraglutide).
One-to-one propensity score matching was used to create the study groups: participants were first grouped according to their history of CVD, and then by the class of drug they had been prescribed. The primary outcomes were hospitalization for MI, stroke, or heart failure.
Comparing the initiation of a SGLT2 inhibitor with GLP-1 RA therapy, the hazard ratios (HRs) for MI or stroke in patients with and without a history of CVD were a respective 0.90 (95% CI, 0.82 to 0.98) and 1.07 (0.97 to 1.18).
The corresponding hazard ratios for heart failure hospitalizations were 0.71 (0.64 to 0.79) and 0.69 (0.56 to 0.85).
Real-world studies are of ‘increasing value’
“As in other not-randomized studies based on real-world data, residual confounding cannot be completely ruled out,” Dr. Patorno acknowledged. She added, however that “state-of-the-art methodological strategies were implemented to minimize this possibility.”
Limitations notwithstanding, “real world studies are demonstrating increasing value,” observed Dr. Jellinger. Further large-scale cardiovascular outcomes trials that directly compare these two drug classes “are unlikely given the depth of information available now,” Dr. Jellinger suggested.
“This head-to-head retrospective study may be as close as we get and does represent the first effort at a comparison of these two classes.”
Dr. Patorno said of the potential clinical implications: “Because the two classes are equally effective for stroke and myocardial infarction, but the SGLT2 inhibitors are superior for heart failure, when considered in aggregate, SGLT2 inhibitors are likely to prevent more of these adverse cardiovascular events than GLP-1 RA.”
The study received no commercial funding and was supported by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics.
Dr. Patorno reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jellinger is on the speaker’s bureau for Astra Zeneca, Amgen, and Esperion, and has served on advisory boards for Corcept and Regeneron.
Around a 30% reduction in the risk for being hospitalized for heart failure was achieved in people with type 2 diabetes who were treated with a SGLT2 inhibitor over a GLP-1 RA regardless of whether the patients had a preexisting heart condition.
The findings, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, also showed a 10% lower risk for myocardial infarction or stroke among those treated with a SGLT2 inhibitor who had preexisting cardiovascular disease (CVD), although there was no difference in risk between the two classes of drugs in those without preexisting CVD.
“These findings are important as they suggest that SGLT2 [inhibitors] and GLP-1 RA offer similar benefits in preventing myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with diabetes,” said study investigator Elisabetta Patorno, MD, DrPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, in an interview.
They also show “that SGLT2 [inhibitors] offer greater efficacy in preventing heart failure, which supports the existing guidelines,” she added.
Paul S. Jellinger, MD, MACE, of the Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Care in Hollywood, Fla., said these data were likely to be “additive to guidelines but not transformative.” The overall analysis results were “not surprising.” It was not unexpected that SGLT2 inhibitors provided a robust chronic heart failure (CHF) benefit, particularly in individuals with history of CVD, he said.
Dr. Jellinger, a clinical endocrinologist and professor of clinical medicine on the voluntary faculty at the University of Miami, observed, however, that “the similar CVD benefit in both drug classes in patients without known CVD adds to our knowledge in this somewhat controversial area and may be useful to the clinician in evaluating therapy in a diabetic individual without evidence of or at high risk for CHF.”
Furthermore, “the study also reminds us that, as demonstrated in published meta-analysis, there is also a modest CHF benefit associated with GLP-1 RA treatment particularly in patients with a history of CVD.”
Addressing the knowledge gap
Thanks to the results of many large-scale, prospective, cardiovascular outcomes studies, both SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 RA have been recommended as treatment for people with diabetes who have established CVD. But with no direct head-to-head trials having been conducted, there is a gap in knowledge and there is currently little guidance for physicians on which drug class to choose for an individual patient.
To try to clarify things, Dr. Patorno and associates looked at data from more than 370,000 people with type 2 diabetes who had been treated between April 2013 and December 2017 with either a SGLT2 inhibitor (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, or empagliflozin) or GLP-1 RA (albiglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, or liraglutide).
One-to-one propensity score matching was used to create the study groups: participants were first grouped according to their history of CVD, and then by the class of drug they had been prescribed. The primary outcomes were hospitalization for MI, stroke, or heart failure.
Comparing the initiation of a SGLT2 inhibitor with GLP-1 RA therapy, the hazard ratios (HRs) for MI or stroke in patients with and without a history of CVD were a respective 0.90 (95% CI, 0.82 to 0.98) and 1.07 (0.97 to 1.18).
The corresponding hazard ratios for heart failure hospitalizations were 0.71 (0.64 to 0.79) and 0.69 (0.56 to 0.85).
Real-world studies are of ‘increasing value’
“As in other not-randomized studies based on real-world data, residual confounding cannot be completely ruled out,” Dr. Patorno acknowledged. She added, however that “state-of-the-art methodological strategies were implemented to minimize this possibility.”
Limitations notwithstanding, “real world studies are demonstrating increasing value,” observed Dr. Jellinger. Further large-scale cardiovascular outcomes trials that directly compare these two drug classes “are unlikely given the depth of information available now,” Dr. Jellinger suggested.
“This head-to-head retrospective study may be as close as we get and does represent the first effort at a comparison of these two classes.”
Dr. Patorno said of the potential clinical implications: “Because the two classes are equally effective for stroke and myocardial infarction, but the SGLT2 inhibitors are superior for heart failure, when considered in aggregate, SGLT2 inhibitors are likely to prevent more of these adverse cardiovascular events than GLP-1 RA.”
The study received no commercial funding and was supported by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics.
Dr. Patorno reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jellinger is on the speaker’s bureau for Astra Zeneca, Amgen, and Esperion, and has served on advisory boards for Corcept and Regeneron.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
New virus causing ‘Alaskapox’ detected in two more cases
Both people were diagnosed after receiving urgent care in a Fairbanks-area clinic. One was a child with a sore on the left elbow, along with fever and swollen lymph nodes. And the other was an unrelated middle-aged woman with a pox mark on her leg, swollen lymph nodes, and joint pain. In both cases, symptoms improved within 3 weeks.
This isn’t the first time the so-called Alaskapox virus has been detected in the region. In 2015, a woman living near Fairbanks turned up at her doctor’s office with a single reddened pox-like mark on her upper arm and a feeling of fatigue.
Sampling of the pox mark showed that it was caused by a previously unidentified virus of the same family as smallpox and cowpox.
Five years later, another woman showed up with similar signs and symptoms, and her pox also proved to be the result of what public health experts started calling the Alaskapox virus.
In both cases, the women recovered completely.
Smallpox-like illness
Public health sleuths figured out that in three of the four cases, the patients lived in a home with a cat or cats, and one of these cats was known to hunt small animals.
Experts already knew that cats mingling in cow pastures and sickened by cattle virus had helped cowpox make the leap from bovines to humans. And just as in the case of cowpox, they suspected that cats might again be spreading this new virus to people, too.
All four of the infected people lived in sparsely populated areas amid forests. Officials laid animal traps where some of the affected people lived and identified the virus in several species of small wild animals.
The animals that turned up most often with Alaskapox were small mouse-like voles. The rodents with rounded muzzles are known for burrowing in the region. And scientists suspect the Alaskapox virus makes its way from these wild animals to humans through their pet cats or possibly by direct exposure outdoors.
None of the four people identified so far with Alaskapox knew each other or interacted, so officials also suspect that there are more cases going unrecognized, possibly because the symptoms are mild or nonexistent.
There are no documented cases of person-to-person transmission of Alaskapox, according to public health officials monitoring the small number of cases. But other pox viruses can spread by direct contact with skin lesions, so clinicians are recommending that people cover wounds with bandages. Three of the people with Alaskapox mistook their lesions at first for a bite from a spider or insect.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Both people were diagnosed after receiving urgent care in a Fairbanks-area clinic. One was a child with a sore on the left elbow, along with fever and swollen lymph nodes. And the other was an unrelated middle-aged woman with a pox mark on her leg, swollen lymph nodes, and joint pain. In both cases, symptoms improved within 3 weeks.
This isn’t the first time the so-called Alaskapox virus has been detected in the region. In 2015, a woman living near Fairbanks turned up at her doctor’s office with a single reddened pox-like mark on her upper arm and a feeling of fatigue.
Sampling of the pox mark showed that it was caused by a previously unidentified virus of the same family as smallpox and cowpox.
Five years later, another woman showed up with similar signs and symptoms, and her pox also proved to be the result of what public health experts started calling the Alaskapox virus.
In both cases, the women recovered completely.
Smallpox-like illness
Public health sleuths figured out that in three of the four cases, the patients lived in a home with a cat or cats, and one of these cats was known to hunt small animals.
Experts already knew that cats mingling in cow pastures and sickened by cattle virus had helped cowpox make the leap from bovines to humans. And just as in the case of cowpox, they suspected that cats might again be spreading this new virus to people, too.
All four of the infected people lived in sparsely populated areas amid forests. Officials laid animal traps where some of the affected people lived and identified the virus in several species of small wild animals.
The animals that turned up most often with Alaskapox were small mouse-like voles. The rodents with rounded muzzles are known for burrowing in the region. And scientists suspect the Alaskapox virus makes its way from these wild animals to humans through their pet cats or possibly by direct exposure outdoors.
None of the four people identified so far with Alaskapox knew each other or interacted, so officials also suspect that there are more cases going unrecognized, possibly because the symptoms are mild or nonexistent.
There are no documented cases of person-to-person transmission of Alaskapox, according to public health officials monitoring the small number of cases. But other pox viruses can spread by direct contact with skin lesions, so clinicians are recommending that people cover wounds with bandages. Three of the people with Alaskapox mistook their lesions at first for a bite from a spider or insect.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Both people were diagnosed after receiving urgent care in a Fairbanks-area clinic. One was a child with a sore on the left elbow, along with fever and swollen lymph nodes. And the other was an unrelated middle-aged woman with a pox mark on her leg, swollen lymph nodes, and joint pain. In both cases, symptoms improved within 3 weeks.
This isn’t the first time the so-called Alaskapox virus has been detected in the region. In 2015, a woman living near Fairbanks turned up at her doctor’s office with a single reddened pox-like mark on her upper arm and a feeling of fatigue.
Sampling of the pox mark showed that it was caused by a previously unidentified virus of the same family as smallpox and cowpox.
Five years later, another woman showed up with similar signs and symptoms, and her pox also proved to be the result of what public health experts started calling the Alaskapox virus.
In both cases, the women recovered completely.
Smallpox-like illness
Public health sleuths figured out that in three of the four cases, the patients lived in a home with a cat or cats, and one of these cats was known to hunt small animals.
Experts already knew that cats mingling in cow pastures and sickened by cattle virus had helped cowpox make the leap from bovines to humans. And just as in the case of cowpox, they suspected that cats might again be spreading this new virus to people, too.
All four of the infected people lived in sparsely populated areas amid forests. Officials laid animal traps where some of the affected people lived and identified the virus in several species of small wild animals.
The animals that turned up most often with Alaskapox were small mouse-like voles. The rodents with rounded muzzles are known for burrowing in the region. And scientists suspect the Alaskapox virus makes its way from these wild animals to humans through their pet cats or possibly by direct exposure outdoors.
None of the four people identified so far with Alaskapox knew each other or interacted, so officials also suspect that there are more cases going unrecognized, possibly because the symptoms are mild or nonexistent.
There are no documented cases of person-to-person transmission of Alaskapox, according to public health officials monitoring the small number of cases. But other pox viruses can spread by direct contact with skin lesions, so clinicians are recommending that people cover wounds with bandages. Three of the people with Alaskapox mistook their lesions at first for a bite from a spider or insect.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 a rare trigger for Guillain-Barré syndrome
Although Guillain-Barré syndrome may rarely follow a recent infection with SARS-CoV-2, a strong relationship of GBS with the novel coronavirus is unlikely, say researchers with the International GBS Outcome Study (IGOS) consortium.
“Our study shows that COVID-19 may precede Guillain-Barré syndrome in rare cases, but the existence of a true association or causal relation still needs to be established,” Bart Jacobs, MD, PhD, department of neurology and immunology, Erasmus Medical Center and University Medical Center, both in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in a statement.
The study was published online in the journal Brain.
No uptick in pandemic cases
Since the beginning of the pandemic, there are reports of more than 90 GBS diagnoses following a possible COVID-19 infection. However, it remains unclear whether COVID-19 is another potential infectious trigger or whether the reported cases are coincidental.
To investigate further, Dr. Jacobs and the IGOS consortium reviewed 49 patients (median age, 56 years) with GBS who were added to their ongoing prospective observational cohort study between Jan. 30 and May 30, 2020.
The patients came from China, Denmark, France, Greece, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.
Of the 49 GBS patients, 8 (16%) had a confirmed and 3 (6%) had a probable SARS-CoV-2 infection; 15 had possible SARS-CoV-2 infection, 21 had no suspicion of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and 2 were “unclassifiable.”
Of the 11 patients with confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection, 9 had no serological evidence of any other recent preceding infection known to be associated with GBS.
The other two had serological evidence of a recent Campylobacter jejuni infection, which could have played a role in GBS onset, the researchers noted.
Most patients with a confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection had a sensorimotor GBS variant (73%), although Miller Fisher syndrome–GBS overlap (18%) and an ataxic variant (9%) were also found.
All patients with a confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection had a severe form of GBS. Common early neurologic features were facial weakness (64%), sensory deficits (82%), and autonomic dysfunction (64%), although not significantly different, compared with the other patients.
All eight patients who underwent nerve conduction study had a demyelinating subtype, which was more frequent than in the other GBS patients (47%; P = .012) as well as historical region and age-matched controls included in the IGOS cohort before the pandemic (52%, P = .016).
The median time from the onset of SARS-CoV-2 infection to neurologic symptoms was 16 days and ranged from 12 to 22 days.
More research needed
The researchers noted that the 22% frequency of a preceding SARS-CoV-2 infection in this study population was “higher than estimates of the contemporaneous background prevalence of SARS-CoV-2, which may be a result of recruitment bias during the pandemic, but could also indicate that GBS may rarely follow a recent SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Importantly, however, they did not find more patients diagnosed with GBS during the first 4 months of the pandemic, compared with previous years, “suggesting that a strong association between SARS-CoV-2 and GBS is unlikely.”
“Should SARS-CoV-2 indeed be able to trigger GBS, our data are consistent with a postinfectious disease mechanism rather than direct viral invasion,” they noted, adding that the study was not designed to quantify a causative link between GBS and SARS-CoV-2.
“An unbiased multicenter, international, case-control study is needed to determine whether there is an association or not,” they wrote.
The IGOS is financially supported by the GBS-CIDP Foundation International, Gain, Erasmus MC University Medical Center Rotterdam, Glasgow University, CSL Behring, Grifols, Annexon and Hansa Biopharma. Dr. Jacobs received grants from Grifols, CSL-Behring, Annexon, Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, Hansa Biopharma, and GBS-CIDP Foundation International and is on the global medical advisory board of the GBS CIDP Foundation International.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although Guillain-Barré syndrome may rarely follow a recent infection with SARS-CoV-2, a strong relationship of GBS with the novel coronavirus is unlikely, say researchers with the International GBS Outcome Study (IGOS) consortium.
“Our study shows that COVID-19 may precede Guillain-Barré syndrome in rare cases, but the existence of a true association or causal relation still needs to be established,” Bart Jacobs, MD, PhD, department of neurology and immunology, Erasmus Medical Center and University Medical Center, both in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in a statement.
The study was published online in the journal Brain.
No uptick in pandemic cases
Since the beginning of the pandemic, there are reports of more than 90 GBS diagnoses following a possible COVID-19 infection. However, it remains unclear whether COVID-19 is another potential infectious trigger or whether the reported cases are coincidental.
To investigate further, Dr. Jacobs and the IGOS consortium reviewed 49 patients (median age, 56 years) with GBS who were added to their ongoing prospective observational cohort study between Jan. 30 and May 30, 2020.
The patients came from China, Denmark, France, Greece, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.
Of the 49 GBS patients, 8 (16%) had a confirmed and 3 (6%) had a probable SARS-CoV-2 infection; 15 had possible SARS-CoV-2 infection, 21 had no suspicion of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and 2 were “unclassifiable.”
Of the 11 patients with confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection, 9 had no serological evidence of any other recent preceding infection known to be associated with GBS.
The other two had serological evidence of a recent Campylobacter jejuni infection, which could have played a role in GBS onset, the researchers noted.
Most patients with a confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection had a sensorimotor GBS variant (73%), although Miller Fisher syndrome–GBS overlap (18%) and an ataxic variant (9%) were also found.
All patients with a confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection had a severe form of GBS. Common early neurologic features were facial weakness (64%), sensory deficits (82%), and autonomic dysfunction (64%), although not significantly different, compared with the other patients.
All eight patients who underwent nerve conduction study had a demyelinating subtype, which was more frequent than in the other GBS patients (47%; P = .012) as well as historical region and age-matched controls included in the IGOS cohort before the pandemic (52%, P = .016).
The median time from the onset of SARS-CoV-2 infection to neurologic symptoms was 16 days and ranged from 12 to 22 days.
More research needed
The researchers noted that the 22% frequency of a preceding SARS-CoV-2 infection in this study population was “higher than estimates of the contemporaneous background prevalence of SARS-CoV-2, which may be a result of recruitment bias during the pandemic, but could also indicate that GBS may rarely follow a recent SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Importantly, however, they did not find more patients diagnosed with GBS during the first 4 months of the pandemic, compared with previous years, “suggesting that a strong association between SARS-CoV-2 and GBS is unlikely.”
“Should SARS-CoV-2 indeed be able to trigger GBS, our data are consistent with a postinfectious disease mechanism rather than direct viral invasion,” they noted, adding that the study was not designed to quantify a causative link between GBS and SARS-CoV-2.
“An unbiased multicenter, international, case-control study is needed to determine whether there is an association or not,” they wrote.
The IGOS is financially supported by the GBS-CIDP Foundation International, Gain, Erasmus MC University Medical Center Rotterdam, Glasgow University, CSL Behring, Grifols, Annexon and Hansa Biopharma. Dr. Jacobs received grants from Grifols, CSL-Behring, Annexon, Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, Hansa Biopharma, and GBS-CIDP Foundation International and is on the global medical advisory board of the GBS CIDP Foundation International.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although Guillain-Barré syndrome may rarely follow a recent infection with SARS-CoV-2, a strong relationship of GBS with the novel coronavirus is unlikely, say researchers with the International GBS Outcome Study (IGOS) consortium.
“Our study shows that COVID-19 may precede Guillain-Barré syndrome in rare cases, but the existence of a true association or causal relation still needs to be established,” Bart Jacobs, MD, PhD, department of neurology and immunology, Erasmus Medical Center and University Medical Center, both in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in a statement.
The study was published online in the journal Brain.
No uptick in pandemic cases
Since the beginning of the pandemic, there are reports of more than 90 GBS diagnoses following a possible COVID-19 infection. However, it remains unclear whether COVID-19 is another potential infectious trigger or whether the reported cases are coincidental.
To investigate further, Dr. Jacobs and the IGOS consortium reviewed 49 patients (median age, 56 years) with GBS who were added to their ongoing prospective observational cohort study between Jan. 30 and May 30, 2020.
The patients came from China, Denmark, France, Greece, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.
Of the 49 GBS patients, 8 (16%) had a confirmed and 3 (6%) had a probable SARS-CoV-2 infection; 15 had possible SARS-CoV-2 infection, 21 had no suspicion of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and 2 were “unclassifiable.”
Of the 11 patients with confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection, 9 had no serological evidence of any other recent preceding infection known to be associated with GBS.
The other two had serological evidence of a recent Campylobacter jejuni infection, which could have played a role in GBS onset, the researchers noted.
Most patients with a confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection had a sensorimotor GBS variant (73%), although Miller Fisher syndrome–GBS overlap (18%) and an ataxic variant (9%) were also found.
All patients with a confirmed/probable SARS-CoV-2 infection had a severe form of GBS. Common early neurologic features were facial weakness (64%), sensory deficits (82%), and autonomic dysfunction (64%), although not significantly different, compared with the other patients.
All eight patients who underwent nerve conduction study had a demyelinating subtype, which was more frequent than in the other GBS patients (47%; P = .012) as well as historical region and age-matched controls included in the IGOS cohort before the pandemic (52%, P = .016).
The median time from the onset of SARS-CoV-2 infection to neurologic symptoms was 16 days and ranged from 12 to 22 days.
More research needed
The researchers noted that the 22% frequency of a preceding SARS-CoV-2 infection in this study population was “higher than estimates of the contemporaneous background prevalence of SARS-CoV-2, which may be a result of recruitment bias during the pandemic, but could also indicate that GBS may rarely follow a recent SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Importantly, however, they did not find more patients diagnosed with GBS during the first 4 months of the pandemic, compared with previous years, “suggesting that a strong association between SARS-CoV-2 and GBS is unlikely.”
“Should SARS-CoV-2 indeed be able to trigger GBS, our data are consistent with a postinfectious disease mechanism rather than direct viral invasion,” they noted, adding that the study was not designed to quantify a causative link between GBS and SARS-CoV-2.
“An unbiased multicenter, international, case-control study is needed to determine whether there is an association or not,” they wrote.
The IGOS is financially supported by the GBS-CIDP Foundation International, Gain, Erasmus MC University Medical Center Rotterdam, Glasgow University, CSL Behring, Grifols, Annexon and Hansa Biopharma. Dr. Jacobs received grants from Grifols, CSL-Behring, Annexon, Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, Hansa Biopharma, and GBS-CIDP Foundation International and is on the global medical advisory board of the GBS CIDP Foundation International.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC chief overrules panel, OKs boosters for health care workers
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices earlier Thursday voted to allow several groups of Americans to get a booster shot, but voted not to recommend it for adults age 18 to 64 who live or work in a place where the risk of COVID-19 is high. That would have included health care workers and other frontline employees.
But CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, decided to reverse that recommendation and include the 18-to-64-year-olds in her final decision.
“As CDC Director, it is my job to recognize where our actions can have the greatest impact,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement late Thursday night, according to published reports. “At CDC, we are tasked with analyzing complex, often imperfect data to make concrete recommendations that optimize health. In a pandemic, even with uncertainty, we must take actions that we anticipate will do the greatest good.”
Dr. Walensky agreed with the rest of the advisory committee's decisions, which included recommendations that the following groups also be eligible for a booster shot:
- Adults ages 65 and up and residents of long-term care facilities
- Adults ages 50 to 64 who have an underlying medical condition that may increase their risk from a COVID infection
- Adults ages 18 to 49 who may be at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection because of an underlying medical condition, if a person feels like they need one based on a consideration of their individual benefit and risks.
About 26 million Americans are at least 6 months past the last dose of the Pfizer vaccines, making them eligible to receive a third dose. About 13.6 million of them are over the age of 65. Another 5.3 million are ages 50 to 64.
In making the recommendations, the committee left out healthcare workers. This was a departure from the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization which included boosters for those 65 and over, and for people 18 through 64 years of age who are at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers – such as those in healthcare -- whose jobs increase their risk for infection.
This is the group Dr. Walensky added to the eligible list on her own.
Committee members “did not buy the need in occupational or institutional settings,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. Dr. Schaffner sits on the ACIP workgroup that considered the evidence behind boosters. He said that he would have voted yes to offer boosters to healthcare and other essential workers.
“There was a real split in the committee,” he said.
The vote on boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers was rejected 9 to 6.
“I think that there is ample evidence that people such as healthcare workers do not have repeated exposure in the workplace,” said Beth Bell, MD, a clinical professor at the University of Washington. “They’re using PPE as they should and they’re following the other policies within the healthcare setting. There’s lots of evidence that suggest that health care workers who become infected become infected because of exposures in the community.”
She was not alone in feeling cautious.
“I think this is an extremely slippery slope,” said Sarah Long, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Drexel University in Philadelphia, before her vote to reject boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers.
“We might as well just say, ‘Give it to everybody 18 and over.’ We have an extremely effective vaccine. It’s like saying it’s not working, and it is working.”
The committee saw data showing that all of the vaccines remain highly protective against hospitalization and death for all age groups, though protection against getting sick with COVID has waned slightly over time and with the dominance of the more contagious Delta variant. Those at highest risk for a severe breakthrough infection — those that cause hospitalization or death — are older adults.
How much will the U.S. benefit from boosters?
Some felt squeamish about broadly recommending boosters at all.
“We have too much hope on the line with these boosters,” said James Loehr, MD, who is a family physician in Ithaca, N.Y. Dr. Loehr said he felt the goal of giving boosters in the United States should be to decrease hospitalizations, and he felt they would, but that the impact would likely be smaller than appreciated.
Based on his calculations of the benefits of boosters for each age group, Dr. Loehr said if boosters were given to all 13 million seniors previously vaccinated with the Pfizer vaccine, we might prevent 200 hospitalizations a day, “which would be a lot,” he noted. But, he said, “considering that we have 10,000 hospitalizations a day now, it’s probably not that much.”
Others agreed.
“I really think this is a solution looking for a problem,” said Jason Goldman, MD, an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University who was representing the American College of Physicians. “You know, I don’t think it’s going to address the issue of the pandemic. I really think it’s just going to create more confusion on the provider from the position of implementation, and I really think it’s going really far afield of the data.”
ACIP Chair Grace Lee, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford, said she had cared for children who had died of COVID.
“I can tell you that their family members really wished they had extra protection for their kids, because they weren’t symptomatic. Nobody else was sick at home,” she said.
Dr. Lee said for her, access was paramount, and she was in favor of expanding access to boosters for as many people as possible.
Next steps
People who were initially vaccinated with either Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccines are excluded from booster recommendations, something many on the committee were uncomfortable with.
The FDA is still considering Moderna’s application to market booster doses. Johnson & Johnson hasn’t yet applied to the FDA for permission to offer second doses in the United States.
While the ACIP’s recommendations are important, in this case, they may not have a huge practical effect, said Schaffner. The CDC has already approved third shots for people who are immunocompromised, and no proof of a medical condition is required to get one.
More than 2 million people have already gotten a third dose, he noted, and not all of them are immunocompromised.
“They have heard the president say that, you know, everybody should get a booster, and they’ve taken that at face value,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices earlier Thursday voted to allow several groups of Americans to get a booster shot, but voted not to recommend it for adults age 18 to 64 who live or work in a place where the risk of COVID-19 is high. That would have included health care workers and other frontline employees.
But CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, decided to reverse that recommendation and include the 18-to-64-year-olds in her final decision.
“As CDC Director, it is my job to recognize where our actions can have the greatest impact,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement late Thursday night, according to published reports. “At CDC, we are tasked with analyzing complex, often imperfect data to make concrete recommendations that optimize health. In a pandemic, even with uncertainty, we must take actions that we anticipate will do the greatest good.”
Dr. Walensky agreed with the rest of the advisory committee's decisions, which included recommendations that the following groups also be eligible for a booster shot:
- Adults ages 65 and up and residents of long-term care facilities
- Adults ages 50 to 64 who have an underlying medical condition that may increase their risk from a COVID infection
- Adults ages 18 to 49 who may be at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection because of an underlying medical condition, if a person feels like they need one based on a consideration of their individual benefit and risks.
About 26 million Americans are at least 6 months past the last dose of the Pfizer vaccines, making them eligible to receive a third dose. About 13.6 million of them are over the age of 65. Another 5.3 million are ages 50 to 64.
In making the recommendations, the committee left out healthcare workers. This was a departure from the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization which included boosters for those 65 and over, and for people 18 through 64 years of age who are at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers – such as those in healthcare -- whose jobs increase their risk for infection.
This is the group Dr. Walensky added to the eligible list on her own.
Committee members “did not buy the need in occupational or institutional settings,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. Dr. Schaffner sits on the ACIP workgroup that considered the evidence behind boosters. He said that he would have voted yes to offer boosters to healthcare and other essential workers.
“There was a real split in the committee,” he said.
The vote on boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers was rejected 9 to 6.
“I think that there is ample evidence that people such as healthcare workers do not have repeated exposure in the workplace,” said Beth Bell, MD, a clinical professor at the University of Washington. “They’re using PPE as they should and they’re following the other policies within the healthcare setting. There’s lots of evidence that suggest that health care workers who become infected become infected because of exposures in the community.”
She was not alone in feeling cautious.
“I think this is an extremely slippery slope,” said Sarah Long, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Drexel University in Philadelphia, before her vote to reject boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers.
“We might as well just say, ‘Give it to everybody 18 and over.’ We have an extremely effective vaccine. It’s like saying it’s not working, and it is working.”
The committee saw data showing that all of the vaccines remain highly protective against hospitalization and death for all age groups, though protection against getting sick with COVID has waned slightly over time and with the dominance of the more contagious Delta variant. Those at highest risk for a severe breakthrough infection — those that cause hospitalization or death — are older adults.
How much will the U.S. benefit from boosters?
Some felt squeamish about broadly recommending boosters at all.
“We have too much hope on the line with these boosters,” said James Loehr, MD, who is a family physician in Ithaca, N.Y. Dr. Loehr said he felt the goal of giving boosters in the United States should be to decrease hospitalizations, and he felt they would, but that the impact would likely be smaller than appreciated.
Based on his calculations of the benefits of boosters for each age group, Dr. Loehr said if boosters were given to all 13 million seniors previously vaccinated with the Pfizer vaccine, we might prevent 200 hospitalizations a day, “which would be a lot,” he noted. But, he said, “considering that we have 10,000 hospitalizations a day now, it’s probably not that much.”
Others agreed.
“I really think this is a solution looking for a problem,” said Jason Goldman, MD, an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University who was representing the American College of Physicians. “You know, I don’t think it’s going to address the issue of the pandemic. I really think it’s just going to create more confusion on the provider from the position of implementation, and I really think it’s going really far afield of the data.”
ACIP Chair Grace Lee, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford, said she had cared for children who had died of COVID.
“I can tell you that their family members really wished they had extra protection for their kids, because they weren’t symptomatic. Nobody else was sick at home,” she said.
Dr. Lee said for her, access was paramount, and she was in favor of expanding access to boosters for as many people as possible.
Next steps
People who were initially vaccinated with either Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccines are excluded from booster recommendations, something many on the committee were uncomfortable with.
The FDA is still considering Moderna’s application to market booster doses. Johnson & Johnson hasn’t yet applied to the FDA for permission to offer second doses in the United States.
While the ACIP’s recommendations are important, in this case, they may not have a huge practical effect, said Schaffner. The CDC has already approved third shots for people who are immunocompromised, and no proof of a medical condition is required to get one.
More than 2 million people have already gotten a third dose, he noted, and not all of them are immunocompromised.
“They have heard the president say that, you know, everybody should get a booster, and they’ve taken that at face value,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices earlier Thursday voted to allow several groups of Americans to get a booster shot, but voted not to recommend it for adults age 18 to 64 who live or work in a place where the risk of COVID-19 is high. That would have included health care workers and other frontline employees.
But CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, decided to reverse that recommendation and include the 18-to-64-year-olds in her final decision.
“As CDC Director, it is my job to recognize where our actions can have the greatest impact,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement late Thursday night, according to published reports. “At CDC, we are tasked with analyzing complex, often imperfect data to make concrete recommendations that optimize health. In a pandemic, even with uncertainty, we must take actions that we anticipate will do the greatest good.”
Dr. Walensky agreed with the rest of the advisory committee's decisions, which included recommendations that the following groups also be eligible for a booster shot:
- Adults ages 65 and up and residents of long-term care facilities
- Adults ages 50 to 64 who have an underlying medical condition that may increase their risk from a COVID infection
- Adults ages 18 to 49 who may be at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection because of an underlying medical condition, if a person feels like they need one based on a consideration of their individual benefit and risks.
About 26 million Americans are at least 6 months past the last dose of the Pfizer vaccines, making them eligible to receive a third dose. About 13.6 million of them are over the age of 65. Another 5.3 million are ages 50 to 64.
In making the recommendations, the committee left out healthcare workers. This was a departure from the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization which included boosters for those 65 and over, and for people 18 through 64 years of age who are at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers – such as those in healthcare -- whose jobs increase their risk for infection.
This is the group Dr. Walensky added to the eligible list on her own.
Committee members “did not buy the need in occupational or institutional settings,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. Dr. Schaffner sits on the ACIP workgroup that considered the evidence behind boosters. He said that he would have voted yes to offer boosters to healthcare and other essential workers.
“There was a real split in the committee,” he said.
The vote on boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers was rejected 9 to 6.
“I think that there is ample evidence that people such as healthcare workers do not have repeated exposure in the workplace,” said Beth Bell, MD, a clinical professor at the University of Washington. “They’re using PPE as they should and they’re following the other policies within the healthcare setting. There’s lots of evidence that suggest that health care workers who become infected become infected because of exposures in the community.”
She was not alone in feeling cautious.
“I think this is an extremely slippery slope,” said Sarah Long, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Drexel University in Philadelphia, before her vote to reject boosters for healthcare and other high-risk workers.
“We might as well just say, ‘Give it to everybody 18 and over.’ We have an extremely effective vaccine. It’s like saying it’s not working, and it is working.”
The committee saw data showing that all of the vaccines remain highly protective against hospitalization and death for all age groups, though protection against getting sick with COVID has waned slightly over time and with the dominance of the more contagious Delta variant. Those at highest risk for a severe breakthrough infection — those that cause hospitalization or death — are older adults.
How much will the U.S. benefit from boosters?
Some felt squeamish about broadly recommending boosters at all.
“We have too much hope on the line with these boosters,” said James Loehr, MD, who is a family physician in Ithaca, N.Y. Dr. Loehr said he felt the goal of giving boosters in the United States should be to decrease hospitalizations, and he felt they would, but that the impact would likely be smaller than appreciated.
Based on his calculations of the benefits of boosters for each age group, Dr. Loehr said if boosters were given to all 13 million seniors previously vaccinated with the Pfizer vaccine, we might prevent 200 hospitalizations a day, “which would be a lot,” he noted. But, he said, “considering that we have 10,000 hospitalizations a day now, it’s probably not that much.”
Others agreed.
“I really think this is a solution looking for a problem,” said Jason Goldman, MD, an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University who was representing the American College of Physicians. “You know, I don’t think it’s going to address the issue of the pandemic. I really think it’s just going to create more confusion on the provider from the position of implementation, and I really think it’s going really far afield of the data.”
ACIP Chair Grace Lee, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford, said she had cared for children who had died of COVID.
“I can tell you that their family members really wished they had extra protection for their kids, because they weren’t symptomatic. Nobody else was sick at home,” she said.
Dr. Lee said for her, access was paramount, and she was in favor of expanding access to boosters for as many people as possible.
Next steps
People who were initially vaccinated with either Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccines are excluded from booster recommendations, something many on the committee were uncomfortable with.
The FDA is still considering Moderna’s application to market booster doses. Johnson & Johnson hasn’t yet applied to the FDA for permission to offer second doses in the United States.
While the ACIP’s recommendations are important, in this case, they may not have a huge practical effect, said Schaffner. The CDC has already approved third shots for people who are immunocompromised, and no proof of a medical condition is required to get one.
More than 2 million people have already gotten a third dose, he noted, and not all of them are immunocompromised.
“They have heard the president say that, you know, everybody should get a booster, and they’ve taken that at face value,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Remdesivir sharply cuts COVID hospitalization risk, Gilead says
Remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) was found to reduce some COVID-19 patients’ risk of hospitalization by 87% in a phase 3 trial, the drug’s manufacturer announced Sept. 22 in a press release.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of a 3-day course of intravenous remdesivir in an analysis of 562 nonhospitalized patients at high risk for disease progression.
Remdesivir demonstrated a statistically significant 87% reduction in risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 28 (0.7% [2/279]) compared with placebo (5.3% [15/283]) P = .008. Participants were assigned 1:1 to remdesivir or the placebo group.
Researchers also found an 81% reduction in risk for the composite secondary endpoint – medical visits due to COVID-19 or all-cause death by Day 28. Only 1.6% had COVID-19 medical visits ([4/246]) compared with those in the placebo group (8.3% [21/252]) P = .002. No deaths were observed in either arm by Day 28.
“These latest data show remdesivir’s potential to help high-risk patients recover before they get sicker and stay out of the hospital altogether,” coauthor Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, from Baylor University Medical Center, Houston, said in the press release.
Remdesivir is the only drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for hospitalized COVID-19 patients at least 12 years old. Its treatment of nonhospitalized patients with 3 days of dosing is investigational, and the safety and efficacy for this use and dosing duration have not been established or approved by any regulatory agency, the Gilead press release notes.
The patients in this study were considered high-risk for disease progression based on comorbidities – commonly obesity, hypertension, and diabetes – and age, but had not recently been hospitalized due to COVID-19.
A third of the participants were at least 60 years old. Participants in the study must have received a positive diagnosis within 4 days of starting treatment and experienced symptoms for 7 days or less.
Use of remdesivir controversial
Results from the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT-1) showed remdesivir was superior to placebo in shortening time to recovery in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 with evidence of lower respiratory tract infection.
However, a large trial of more than 11,000 people in 30 countries, sponsored by the World Health Organization, did not show any benefit for the drug in reducing COVID deaths.
The WHO has conditionally recommended against using remdesivir in hospitalized patients, regardless of disease severity, “as there is currently no evidence that remdesivir improves survival and other outcomes in these patients.”
The drug also is given intravenously, and this study tested three infusions over 3 days, a difficult treatment for nonhospitalized patients.
The study results were released ahead of IDWeek, where the late-breaking abstract will be presented at the virtual conference in full at the end of next week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) was found to reduce some COVID-19 patients’ risk of hospitalization by 87% in a phase 3 trial, the drug’s manufacturer announced Sept. 22 in a press release.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of a 3-day course of intravenous remdesivir in an analysis of 562 nonhospitalized patients at high risk for disease progression.
Remdesivir demonstrated a statistically significant 87% reduction in risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 28 (0.7% [2/279]) compared with placebo (5.3% [15/283]) P = .008. Participants were assigned 1:1 to remdesivir or the placebo group.
Researchers also found an 81% reduction in risk for the composite secondary endpoint – medical visits due to COVID-19 or all-cause death by Day 28. Only 1.6% had COVID-19 medical visits ([4/246]) compared with those in the placebo group (8.3% [21/252]) P = .002. No deaths were observed in either arm by Day 28.
“These latest data show remdesivir’s potential to help high-risk patients recover before they get sicker and stay out of the hospital altogether,” coauthor Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, from Baylor University Medical Center, Houston, said in the press release.
Remdesivir is the only drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for hospitalized COVID-19 patients at least 12 years old. Its treatment of nonhospitalized patients with 3 days of dosing is investigational, and the safety and efficacy for this use and dosing duration have not been established or approved by any regulatory agency, the Gilead press release notes.
The patients in this study were considered high-risk for disease progression based on comorbidities – commonly obesity, hypertension, and diabetes – and age, but had not recently been hospitalized due to COVID-19.
A third of the participants were at least 60 years old. Participants in the study must have received a positive diagnosis within 4 days of starting treatment and experienced symptoms for 7 days or less.
Use of remdesivir controversial
Results from the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT-1) showed remdesivir was superior to placebo in shortening time to recovery in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 with evidence of lower respiratory tract infection.
However, a large trial of more than 11,000 people in 30 countries, sponsored by the World Health Organization, did not show any benefit for the drug in reducing COVID deaths.
The WHO has conditionally recommended against using remdesivir in hospitalized patients, regardless of disease severity, “as there is currently no evidence that remdesivir improves survival and other outcomes in these patients.”
The drug also is given intravenously, and this study tested three infusions over 3 days, a difficult treatment for nonhospitalized patients.
The study results were released ahead of IDWeek, where the late-breaking abstract will be presented at the virtual conference in full at the end of next week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) was found to reduce some COVID-19 patients’ risk of hospitalization by 87% in a phase 3 trial, the drug’s manufacturer announced Sept. 22 in a press release.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of a 3-day course of intravenous remdesivir in an analysis of 562 nonhospitalized patients at high risk for disease progression.
Remdesivir demonstrated a statistically significant 87% reduction in risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization or all-cause death by Day 28 (0.7% [2/279]) compared with placebo (5.3% [15/283]) P = .008. Participants were assigned 1:1 to remdesivir or the placebo group.
Researchers also found an 81% reduction in risk for the composite secondary endpoint – medical visits due to COVID-19 or all-cause death by Day 28. Only 1.6% had COVID-19 medical visits ([4/246]) compared with those in the placebo group (8.3% [21/252]) P = .002. No deaths were observed in either arm by Day 28.
“These latest data show remdesivir’s potential to help high-risk patients recover before they get sicker and stay out of the hospital altogether,” coauthor Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, from Baylor University Medical Center, Houston, said in the press release.
Remdesivir is the only drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for hospitalized COVID-19 patients at least 12 years old. Its treatment of nonhospitalized patients with 3 days of dosing is investigational, and the safety and efficacy for this use and dosing duration have not been established or approved by any regulatory agency, the Gilead press release notes.
The patients in this study were considered high-risk for disease progression based on comorbidities – commonly obesity, hypertension, and diabetes – and age, but had not recently been hospitalized due to COVID-19.
A third of the participants were at least 60 years old. Participants in the study must have received a positive diagnosis within 4 days of starting treatment and experienced symptoms for 7 days or less.
Use of remdesivir controversial
Results from the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT-1) showed remdesivir was superior to placebo in shortening time to recovery in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 with evidence of lower respiratory tract infection.
However, a large trial of more than 11,000 people in 30 countries, sponsored by the World Health Organization, did not show any benefit for the drug in reducing COVID deaths.
The WHO has conditionally recommended against using remdesivir in hospitalized patients, regardless of disease severity, “as there is currently no evidence that remdesivir improves survival and other outcomes in these patients.”
The drug also is given intravenously, and this study tested three infusions over 3 days, a difficult treatment for nonhospitalized patients.
The study results were released ahead of IDWeek, where the late-breaking abstract will be presented at the virtual conference in full at the end of next week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.





