User login
Merkel Cell: Immunotherapy Not Used for Many Patients With Metastatic Disease
PHOENIX — Immunotherapy has revolutionized outcomes for patients are better at high-volume centers.
The study has important implications, said study author Shayan Cheraghlou, MD, an incoming fellow in Mohs surgery at New York University, New York City. “We can see that in a real-world setting, these agents have an impact on survival,” he said. “We also found high-volume centers were significantly more likely to use the agents than low-volume centers.” He presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
MCC is a neuroendocrine skin cancer with a high rate of mortality, and even though it remains relatively rare, its incidence has been rising rapidly since the late 1990s and continues to increase. There were no approved treatments available until 2017, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the immunotherapy drug avelumab (Bavencio) to treat advanced MCC. Two years later, pembrolizumab (Keytruda) also received regulatory approval for MCC, and these two agents have revolutionized outcomes.
“In clinical trial settings, these agents led to significant and durable responses, and they are now the recommended treatments in guidelines for metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma,” said Dr. Cheraghlou. “However, we don’t have data as to how they are being used in the real-world setting and if survival outcomes are similar.”
Real World vs Clinical Trials
Real-world outcomes can differ from clinical trial data, and the adoption of novel therapeutics can be gradual. The goal of this study was to see if clinical trial data matched what was being observed in actual clinical use and if the agents were being used uniformly in centers across the United States.
The authors used data from the National Cancer Database that included patients diagnosed with cancer from 2004 to 2019 and identified 1017 adult cases of metastatic MCC. They then looked at the association of a variety of patient characteristics, tumors, and system factors with the likelihood of receiving systemic treatment for their disease.
“Our first finding was maybe the least surprising,” he said. “Patients who received these therapeutic agents had significantly improved survival compared to those who have not.”
Those who received immunotherapy had a 35% decrease in the risk for death per year compared with those who did not. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 47.2%, 21.8%, and 16.5%, respectively, for patients who did not receive immunotherapy compared with 62.7%, 34.4%, and 23.6%, respectively, for those who were treated with these agents.
Dr. Cheraghlou noted that they started to get some “surprising” findings when they looked at utilization data. “While it has been increasing over time, it is not as high as it should be,” he emphasized.
From 2017 to 2019, 54.2% of patients with metastatic MCC received immunotherapy. The data also showed an increase in use from 45.1% in 2017 to 63.0% in 2019. “This is an effective treatment for aggressive malignancy, so we have to ask why more patients aren’t getting them,” said Dr. Cheraghlou.
Their findings did suggest one possible reason, and that was that high-volume centers were significantly more likely to use the agents than low-volume centers. Centers that were in the top percentile for MCC case volume were three times as likely to use immunotherapy for MCC compared with other institutions. “So, if you have metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and go to a low volume center, you may be less likely to get potential lifesaving treatment,” he noted.
Implications Going Forward
Dr. Cheraghlou concluded his presentation by pointing out that this study has important implications. The data showed that in a real-world setting, these agents have an impact on survival, but all eligible patients do not have access. “In other countries, there are established referral patterns for all patients with aggressive rare malignancies and really all cancers,” he added. “But in the US, cancer care is more decentralized. Studies like this and others show that high-volume centers have much better outcomes for aggressive rare malignancies, and we should be looking at why this is the case and mitigating these disparities and outcomes.”
Commenting on the study results, Jeffrey M. Farma, MD, co-director of the Melanoma and Skin Cancer Program and professor of surgical oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, referred to the two immunotherapies that have been approved for MCC since 2017, which have demonstrated a survival benefit and improved outcomes in patients with metastatic MCC.
“In their study, immunotherapy was associated with improved outcomes,” said Dr. Farma. “This study highlights the continued lag of implementation of guidelines when new therapies are approved, and that for rare cancers like Merkel cell carcinoma, being treated at high-volume centers and the regionalization of care can lead to improved outcomes for patients.”
Dr. Cheraghlou and Dr. Farma had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX — Immunotherapy has revolutionized outcomes for patients are better at high-volume centers.
The study has important implications, said study author Shayan Cheraghlou, MD, an incoming fellow in Mohs surgery at New York University, New York City. “We can see that in a real-world setting, these agents have an impact on survival,” he said. “We also found high-volume centers were significantly more likely to use the agents than low-volume centers.” He presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
MCC is a neuroendocrine skin cancer with a high rate of mortality, and even though it remains relatively rare, its incidence has been rising rapidly since the late 1990s and continues to increase. There were no approved treatments available until 2017, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the immunotherapy drug avelumab (Bavencio) to treat advanced MCC. Two years later, pembrolizumab (Keytruda) also received regulatory approval for MCC, and these two agents have revolutionized outcomes.
“In clinical trial settings, these agents led to significant and durable responses, and they are now the recommended treatments in guidelines for metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma,” said Dr. Cheraghlou. “However, we don’t have data as to how they are being used in the real-world setting and if survival outcomes are similar.”
Real World vs Clinical Trials
Real-world outcomes can differ from clinical trial data, and the adoption of novel therapeutics can be gradual. The goal of this study was to see if clinical trial data matched what was being observed in actual clinical use and if the agents were being used uniformly in centers across the United States.
The authors used data from the National Cancer Database that included patients diagnosed with cancer from 2004 to 2019 and identified 1017 adult cases of metastatic MCC. They then looked at the association of a variety of patient characteristics, tumors, and system factors with the likelihood of receiving systemic treatment for their disease.
“Our first finding was maybe the least surprising,” he said. “Patients who received these therapeutic agents had significantly improved survival compared to those who have not.”
Those who received immunotherapy had a 35% decrease in the risk for death per year compared with those who did not. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 47.2%, 21.8%, and 16.5%, respectively, for patients who did not receive immunotherapy compared with 62.7%, 34.4%, and 23.6%, respectively, for those who were treated with these agents.
Dr. Cheraghlou noted that they started to get some “surprising” findings when they looked at utilization data. “While it has been increasing over time, it is not as high as it should be,” he emphasized.
From 2017 to 2019, 54.2% of patients with metastatic MCC received immunotherapy. The data also showed an increase in use from 45.1% in 2017 to 63.0% in 2019. “This is an effective treatment for aggressive malignancy, so we have to ask why more patients aren’t getting them,” said Dr. Cheraghlou.
Their findings did suggest one possible reason, and that was that high-volume centers were significantly more likely to use the agents than low-volume centers. Centers that were in the top percentile for MCC case volume were three times as likely to use immunotherapy for MCC compared with other institutions. “So, if you have metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and go to a low volume center, you may be less likely to get potential lifesaving treatment,” he noted.
Implications Going Forward
Dr. Cheraghlou concluded his presentation by pointing out that this study has important implications. The data showed that in a real-world setting, these agents have an impact on survival, but all eligible patients do not have access. “In other countries, there are established referral patterns for all patients with aggressive rare malignancies and really all cancers,” he added. “But in the US, cancer care is more decentralized. Studies like this and others show that high-volume centers have much better outcomes for aggressive rare malignancies, and we should be looking at why this is the case and mitigating these disparities and outcomes.”
Commenting on the study results, Jeffrey M. Farma, MD, co-director of the Melanoma and Skin Cancer Program and professor of surgical oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, referred to the two immunotherapies that have been approved for MCC since 2017, which have demonstrated a survival benefit and improved outcomes in patients with metastatic MCC.
“In their study, immunotherapy was associated with improved outcomes,” said Dr. Farma. “This study highlights the continued lag of implementation of guidelines when new therapies are approved, and that for rare cancers like Merkel cell carcinoma, being treated at high-volume centers and the regionalization of care can lead to improved outcomes for patients.”
Dr. Cheraghlou and Dr. Farma had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX — Immunotherapy has revolutionized outcomes for patients are better at high-volume centers.
The study has important implications, said study author Shayan Cheraghlou, MD, an incoming fellow in Mohs surgery at New York University, New York City. “We can see that in a real-world setting, these agents have an impact on survival,” he said. “We also found high-volume centers were significantly more likely to use the agents than low-volume centers.” He presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
MCC is a neuroendocrine skin cancer with a high rate of mortality, and even though it remains relatively rare, its incidence has been rising rapidly since the late 1990s and continues to increase. There were no approved treatments available until 2017, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the immunotherapy drug avelumab (Bavencio) to treat advanced MCC. Two years later, pembrolizumab (Keytruda) also received regulatory approval for MCC, and these two agents have revolutionized outcomes.
“In clinical trial settings, these agents led to significant and durable responses, and they are now the recommended treatments in guidelines for metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma,” said Dr. Cheraghlou. “However, we don’t have data as to how they are being used in the real-world setting and if survival outcomes are similar.”
Real World vs Clinical Trials
Real-world outcomes can differ from clinical trial data, and the adoption of novel therapeutics can be gradual. The goal of this study was to see if clinical trial data matched what was being observed in actual clinical use and if the agents were being used uniformly in centers across the United States.
The authors used data from the National Cancer Database that included patients diagnosed with cancer from 2004 to 2019 and identified 1017 adult cases of metastatic MCC. They then looked at the association of a variety of patient characteristics, tumors, and system factors with the likelihood of receiving systemic treatment for their disease.
“Our first finding was maybe the least surprising,” he said. “Patients who received these therapeutic agents had significantly improved survival compared to those who have not.”
Those who received immunotherapy had a 35% decrease in the risk for death per year compared with those who did not. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 47.2%, 21.8%, and 16.5%, respectively, for patients who did not receive immunotherapy compared with 62.7%, 34.4%, and 23.6%, respectively, for those who were treated with these agents.
Dr. Cheraghlou noted that they started to get some “surprising” findings when they looked at utilization data. “While it has been increasing over time, it is not as high as it should be,” he emphasized.
From 2017 to 2019, 54.2% of patients with metastatic MCC received immunotherapy. The data also showed an increase in use from 45.1% in 2017 to 63.0% in 2019. “This is an effective treatment for aggressive malignancy, so we have to ask why more patients aren’t getting them,” said Dr. Cheraghlou.
Their findings did suggest one possible reason, and that was that high-volume centers were significantly more likely to use the agents than low-volume centers. Centers that were in the top percentile for MCC case volume were three times as likely to use immunotherapy for MCC compared with other institutions. “So, if you have metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and go to a low volume center, you may be less likely to get potential lifesaving treatment,” he noted.
Implications Going Forward
Dr. Cheraghlou concluded his presentation by pointing out that this study has important implications. The data showed that in a real-world setting, these agents have an impact on survival, but all eligible patients do not have access. “In other countries, there are established referral patterns for all patients with aggressive rare malignancies and really all cancers,” he added. “But in the US, cancer care is more decentralized. Studies like this and others show that high-volume centers have much better outcomes for aggressive rare malignancies, and we should be looking at why this is the case and mitigating these disparities and outcomes.”
Commenting on the study results, Jeffrey M. Farma, MD, co-director of the Melanoma and Skin Cancer Program and professor of surgical oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, referred to the two immunotherapies that have been approved for MCC since 2017, which have demonstrated a survival benefit and improved outcomes in patients with metastatic MCC.
“In their study, immunotherapy was associated with improved outcomes,” said Dr. Farma. “This study highlights the continued lag of implementation of guidelines when new therapies are approved, and that for rare cancers like Merkel cell carcinoma, being treated at high-volume centers and the regionalization of care can lead to improved outcomes for patients.”
Dr. Cheraghlou and Dr. Farma had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACMS 2024
Post–Mohs Surgery Opioid Prescribing More Common in Some Patient Groups
PHOENIX — The study also found that patients who do receive opioids postoperatively are at an increased risk for chronic opioid use and complications.
This report represents the largest analysis to date of opioid prescribing after dermatologic surgery, said lead author Kyle C. Lauck, MD, a dermatology resident at Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, Texas. “Females, African Americans, and Latino patients may be at a higher risk of opioid prescription after dermatologic surgery. Surgeons should be aware of these populations and the risks they face when determining candidacy for postsurgical opioid analgesia.”
He presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
The opioid epidemic is a concern across all areas of medicine, and the majority of opioid prescriptions in dermatology are given following surgery. Dr. Lauck noted that even though guidelines delegate opioids as second line for pain control, the existing data on opioid prescribing in dermatologic surgery is mixed. For example, some reports have shown that up to 58% of patients receive opioids postoperatively. “No consensus exists when we should routinely give opioids to these patients,” he said.
Even though most surgeons prescribe short courses of opioids, even brief regimens are associated with increased risks for overuse and substance abuse. Population-level data are limited concerning opioid prescriptions in dermatologic surgery, and in particular, there is an absence of data on the risk for long-term complications associated with use.
Certain Populations at Risk
To evaluate opioid prescription rates in dermatologic surgery, focusing on disparities between demographic populations, as well as the risk for long-term complications of postoperative opioid prescriptions, Dr. Lauck and colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included 914,721 dermatologic surgery patients, with billing codes for Mohs micrographic surgery. Patient data were obtained from TriNetX, a federated health research network.
The mean age of patients in this cohort was 54 years, and 124,494 (13.6%) were prescribed postsurgical oral opioids. The most common was oxycodone, prescribed to 43% of patients. Dr. Lauck noted that, according to their data, certain groups appeared more likely to receive a prescription for opioids following surgery. These included Black or African American patients (23.75% vs 12.86% for White patients), females (13.73% vs 13.16% for males), and Latino or Hispanic patients (17.02% vs 13.61% non-Latino/Hispanic patients).
Patients with a history of prior oral opioid prescription, prior opioid abuse or dependence, and any type of substance abuse had a significant increase in absolute risk of being prescribed postsurgical opioids (P < .0001).
The type of surgery also was associated with prescribed postop opioids. For a malignant excision, 18.29% of patients were prescribed postop opioids compared with 14.9% for a benign excision. About a third of patients (34.9%) undergoing a graft repair received opioids.
There was an elevated rate of postop opioid prescribing that was specific to the site of surgery, with the highest rates observed with eyelids, scalp and neck, trunk, and genital sites. The highest overall rates of opioid prescriptions were for patients who underwent excisions in the genital area (54.5%).
Long-Term Consequences
The authors also looked at the longer-term consequences of postop opioid use. “Nearly one in three patients who were prescribed opioids needed subsequent prescriptions down the line,” said Dr. Lauck.
From 3 months to 5 years after surgery, patients who received postsurgical opioids were at significantly higher risk for not only subsequent oral opioid prescription but also opiate abuse, any substance abuse, overdose by opioid narcotics, constipation, and chronic pain. “An opioid prescription may confer further risks of longitudinal complications of chronic opioid use,” he concluded.
Commenting on the study, Jesse M. Lewin, MD, chief of Mohs micrographic and dermatologic surgery at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, noted an important finding of this study was the long-term sequelae of patients who did receive postop opioids.
“This is striking given that postsurgical opiate prescriptions are for short durations and limited number of pills,” he told this news organization. “This study highlights the potential danger of even short course of opiates and should serve as a reminder to dermatologic surgeons to be judicious about opiate prescribing.”
Dr. Lauck and Dr. Lewin had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX — The study also found that patients who do receive opioids postoperatively are at an increased risk for chronic opioid use and complications.
This report represents the largest analysis to date of opioid prescribing after dermatologic surgery, said lead author Kyle C. Lauck, MD, a dermatology resident at Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, Texas. “Females, African Americans, and Latino patients may be at a higher risk of opioid prescription after dermatologic surgery. Surgeons should be aware of these populations and the risks they face when determining candidacy for postsurgical opioid analgesia.”
He presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
The opioid epidemic is a concern across all areas of medicine, and the majority of opioid prescriptions in dermatology are given following surgery. Dr. Lauck noted that even though guidelines delegate opioids as second line for pain control, the existing data on opioid prescribing in dermatologic surgery is mixed. For example, some reports have shown that up to 58% of patients receive opioids postoperatively. “No consensus exists when we should routinely give opioids to these patients,” he said.
Even though most surgeons prescribe short courses of opioids, even brief regimens are associated with increased risks for overuse and substance abuse. Population-level data are limited concerning opioid prescriptions in dermatologic surgery, and in particular, there is an absence of data on the risk for long-term complications associated with use.
Certain Populations at Risk
To evaluate opioid prescription rates in dermatologic surgery, focusing on disparities between demographic populations, as well as the risk for long-term complications of postoperative opioid prescriptions, Dr. Lauck and colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included 914,721 dermatologic surgery patients, with billing codes for Mohs micrographic surgery. Patient data were obtained from TriNetX, a federated health research network.
The mean age of patients in this cohort was 54 years, and 124,494 (13.6%) were prescribed postsurgical oral opioids. The most common was oxycodone, prescribed to 43% of patients. Dr. Lauck noted that, according to their data, certain groups appeared more likely to receive a prescription for opioids following surgery. These included Black or African American patients (23.75% vs 12.86% for White patients), females (13.73% vs 13.16% for males), and Latino or Hispanic patients (17.02% vs 13.61% non-Latino/Hispanic patients).
Patients with a history of prior oral opioid prescription, prior opioid abuse or dependence, and any type of substance abuse had a significant increase in absolute risk of being prescribed postsurgical opioids (P < .0001).
The type of surgery also was associated with prescribed postop opioids. For a malignant excision, 18.29% of patients were prescribed postop opioids compared with 14.9% for a benign excision. About a third of patients (34.9%) undergoing a graft repair received opioids.
There was an elevated rate of postop opioid prescribing that was specific to the site of surgery, with the highest rates observed with eyelids, scalp and neck, trunk, and genital sites. The highest overall rates of opioid prescriptions were for patients who underwent excisions in the genital area (54.5%).
Long-Term Consequences
The authors also looked at the longer-term consequences of postop opioid use. “Nearly one in three patients who were prescribed opioids needed subsequent prescriptions down the line,” said Dr. Lauck.
From 3 months to 5 years after surgery, patients who received postsurgical opioids were at significantly higher risk for not only subsequent oral opioid prescription but also opiate abuse, any substance abuse, overdose by opioid narcotics, constipation, and chronic pain. “An opioid prescription may confer further risks of longitudinal complications of chronic opioid use,” he concluded.
Commenting on the study, Jesse M. Lewin, MD, chief of Mohs micrographic and dermatologic surgery at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, noted an important finding of this study was the long-term sequelae of patients who did receive postop opioids.
“This is striking given that postsurgical opiate prescriptions are for short durations and limited number of pills,” he told this news organization. “This study highlights the potential danger of even short course of opiates and should serve as a reminder to dermatologic surgeons to be judicious about opiate prescribing.”
Dr. Lauck and Dr. Lewin had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX — The study also found that patients who do receive opioids postoperatively are at an increased risk for chronic opioid use and complications.
This report represents the largest analysis to date of opioid prescribing after dermatologic surgery, said lead author Kyle C. Lauck, MD, a dermatology resident at Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, Texas. “Females, African Americans, and Latino patients may be at a higher risk of opioid prescription after dermatologic surgery. Surgeons should be aware of these populations and the risks they face when determining candidacy for postsurgical opioid analgesia.”
He presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
The opioid epidemic is a concern across all areas of medicine, and the majority of opioid prescriptions in dermatology are given following surgery. Dr. Lauck noted that even though guidelines delegate opioids as second line for pain control, the existing data on opioid prescribing in dermatologic surgery is mixed. For example, some reports have shown that up to 58% of patients receive opioids postoperatively. “No consensus exists when we should routinely give opioids to these patients,” he said.
Even though most surgeons prescribe short courses of opioids, even brief regimens are associated with increased risks for overuse and substance abuse. Population-level data are limited concerning opioid prescriptions in dermatologic surgery, and in particular, there is an absence of data on the risk for long-term complications associated with use.
Certain Populations at Risk
To evaluate opioid prescription rates in dermatologic surgery, focusing on disparities between demographic populations, as well as the risk for long-term complications of postoperative opioid prescriptions, Dr. Lauck and colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included 914,721 dermatologic surgery patients, with billing codes for Mohs micrographic surgery. Patient data were obtained from TriNetX, a federated health research network.
The mean age of patients in this cohort was 54 years, and 124,494 (13.6%) were prescribed postsurgical oral opioids. The most common was oxycodone, prescribed to 43% of patients. Dr. Lauck noted that, according to their data, certain groups appeared more likely to receive a prescription for opioids following surgery. These included Black or African American patients (23.75% vs 12.86% for White patients), females (13.73% vs 13.16% for males), and Latino or Hispanic patients (17.02% vs 13.61% non-Latino/Hispanic patients).
Patients with a history of prior oral opioid prescription, prior opioid abuse or dependence, and any type of substance abuse had a significant increase in absolute risk of being prescribed postsurgical opioids (P < .0001).
The type of surgery also was associated with prescribed postop opioids. For a malignant excision, 18.29% of patients were prescribed postop opioids compared with 14.9% for a benign excision. About a third of patients (34.9%) undergoing a graft repair received opioids.
There was an elevated rate of postop opioid prescribing that was specific to the site of surgery, with the highest rates observed with eyelids, scalp and neck, trunk, and genital sites. The highest overall rates of opioid prescriptions were for patients who underwent excisions in the genital area (54.5%).
Long-Term Consequences
The authors also looked at the longer-term consequences of postop opioid use. “Nearly one in three patients who were prescribed opioids needed subsequent prescriptions down the line,” said Dr. Lauck.
From 3 months to 5 years after surgery, patients who received postsurgical opioids were at significantly higher risk for not only subsequent oral opioid prescription but also opiate abuse, any substance abuse, overdose by opioid narcotics, constipation, and chronic pain. “An opioid prescription may confer further risks of longitudinal complications of chronic opioid use,” he concluded.
Commenting on the study, Jesse M. Lewin, MD, chief of Mohs micrographic and dermatologic surgery at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, noted an important finding of this study was the long-term sequelae of patients who did receive postop opioids.
“This is striking given that postsurgical opiate prescriptions are for short durations and limited number of pills,” he told this news organization. “This study highlights the potential danger of even short course of opiates and should serve as a reminder to dermatologic surgeons to be judicious about opiate prescribing.”
Dr. Lauck and Dr. Lewin had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACMS 2024
Subcutaneous Antifibrinolytic Reduces Bleeding After Mohs Surgery
“Though Mohs micrographic surgery is associated with low bleeding complication rates, around 1% of patients in the literature report postoperative bleeding,” corresponding author Abigail H. Waldman, MD, director of the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Intravenous tranexamic acid has been used across surgical specialties to reduce perioperative blood loss. Prior studies have shown topical TXA, an antifibrinolytic agent, following MMS may be effective in reducing postoperative bleeding complications, but there are no large cohort studies on injectable TXA utilization in all patients undergoing MMS.”
To improve the understanding of this intervention, the researchers examined the impact of off-label, locally injected TXA on postoperative bleeding outcomes following MMS conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. They evaluated two cohorts: 1843 patients who underwent MMS from January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2019 (the pre-TXA cohort), and 2101 patients who underwent MMS from July 1, 2022, to June 30, 2023 (the TXA cohort), and extracted data, including patient and tumor characteristics, MMS procedure details, antithrombotic medication use, systemic conditions that predispose to bleeding, encounters reporting postoperative bleeding, and interventions required for postoperative bleeding, from electronic medical records. Patients reconstructed by a non-MMS surgeon were excluded from the analysis.
Overall, 2509 cases among 1843 patients and 2818 cases among 2101 were included in the pre-TXA and TXA cohorts, respectively. The researchers found that local subcutaneous injection of TXA reduced the risk for postoperative phone calls or visits for bleeding by 25% (RR [risk ratio], 0.75; 0.57-0.99) and risk for bleeding necessitating a medical visit by 51% (RR, 0.49; 0.32-0.77).
The use of preoperative TXA in several subgroups of patients also was also associated with a reduction in visits for bleeding, including those using alcohol (52% reduction; RR, 0.47; 0.26-0.85), cigarettes (57% reduction; RR, 0.43; 0.23-0.82), oral anticoagulants (61% reduction; RR, 0.39; 0.20-0.77), or antiplatelets (60% reduction; RR, 0.40; 0.20-0.79). The use of TXA was also associated with reduced visits for bleeding in tumors of the head and neck (RR, 0.45; 0.26-0.77) and tumors with a preoperative diameter > 2 cm (RR, 0.37; 0.15-0.90).
Impact of Surgical Repair Type
In other findings, the type of surgical repair was a potential confounder, the authors reported. Grafts and flaps were associated with an increased risk for bleeding across both cohorts (RR, 2.36 [1.5-3.6] and 1.7 [1.1-2.6], respectively) and together comprised 15% of all procedures in the pre-TXA cohort compared with 11.1% in TXA cohort. Two patients in the TXA cohort (0.11%) developed deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 10- and 20-days postoperation, a rate that the authors said is comparable to that of the general population. The two patients had risk factors for hypercoagulability, including advanced cancer and recurrent DVT.
“Overall, local injection of TXA was an effective method for reducing the risk of clinically significant bleeding following MMS,” the researchers concluded. “Perioperative TXA may help to limit the risk of bleeding overall, as well as in populations predisposed to bleeding.” Adverse events with TXA use were rare “and delayed beyond the activity of TXA, indicating a low likelihood of being due to TXA,” they wrote.
“Dermatologists performing MMS may consider incorporating local TXA injection into their regular practice,” they noted, adding that “legal counsel on adverse effects in the setting of off-label pharmaceutical usage may be advised.”
In an interview, Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston Medical Center, who was asked to comment on the study, said that postoperative bleeding is one of the most commonly encountered Mohs surgery complications. “Because of increased clinic visits and phone calls, it can also often result in decreased patient satisfaction,” she said.
“This study is particularly notable in that we see that local subcutaneous TXA injection decreased visits for bleeding even in those using oral anticoagulants, antiplatelets, alcohol, and cigarettes. Dermatologic surgery has a very low complication rate, even in patients on anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, but this study shows that TXA is a fantastic option for Mohs surgeons and patients.”
Neither the study authors nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Though Mohs micrographic surgery is associated with low bleeding complication rates, around 1% of patients in the literature report postoperative bleeding,” corresponding author Abigail H. Waldman, MD, director of the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Intravenous tranexamic acid has been used across surgical specialties to reduce perioperative blood loss. Prior studies have shown topical TXA, an antifibrinolytic agent, following MMS may be effective in reducing postoperative bleeding complications, but there are no large cohort studies on injectable TXA utilization in all patients undergoing MMS.”
To improve the understanding of this intervention, the researchers examined the impact of off-label, locally injected TXA on postoperative bleeding outcomes following MMS conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. They evaluated two cohorts: 1843 patients who underwent MMS from January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2019 (the pre-TXA cohort), and 2101 patients who underwent MMS from July 1, 2022, to June 30, 2023 (the TXA cohort), and extracted data, including patient and tumor characteristics, MMS procedure details, antithrombotic medication use, systemic conditions that predispose to bleeding, encounters reporting postoperative bleeding, and interventions required for postoperative bleeding, from electronic medical records. Patients reconstructed by a non-MMS surgeon were excluded from the analysis.
Overall, 2509 cases among 1843 patients and 2818 cases among 2101 were included in the pre-TXA and TXA cohorts, respectively. The researchers found that local subcutaneous injection of TXA reduced the risk for postoperative phone calls or visits for bleeding by 25% (RR [risk ratio], 0.75; 0.57-0.99) and risk for bleeding necessitating a medical visit by 51% (RR, 0.49; 0.32-0.77).
The use of preoperative TXA in several subgroups of patients also was also associated with a reduction in visits for bleeding, including those using alcohol (52% reduction; RR, 0.47; 0.26-0.85), cigarettes (57% reduction; RR, 0.43; 0.23-0.82), oral anticoagulants (61% reduction; RR, 0.39; 0.20-0.77), or antiplatelets (60% reduction; RR, 0.40; 0.20-0.79). The use of TXA was also associated with reduced visits for bleeding in tumors of the head and neck (RR, 0.45; 0.26-0.77) and tumors with a preoperative diameter > 2 cm (RR, 0.37; 0.15-0.90).
Impact of Surgical Repair Type
In other findings, the type of surgical repair was a potential confounder, the authors reported. Grafts and flaps were associated with an increased risk for bleeding across both cohorts (RR, 2.36 [1.5-3.6] and 1.7 [1.1-2.6], respectively) and together comprised 15% of all procedures in the pre-TXA cohort compared with 11.1% in TXA cohort. Two patients in the TXA cohort (0.11%) developed deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 10- and 20-days postoperation, a rate that the authors said is comparable to that of the general population. The two patients had risk factors for hypercoagulability, including advanced cancer and recurrent DVT.
“Overall, local injection of TXA was an effective method for reducing the risk of clinically significant bleeding following MMS,” the researchers concluded. “Perioperative TXA may help to limit the risk of bleeding overall, as well as in populations predisposed to bleeding.” Adverse events with TXA use were rare “and delayed beyond the activity of TXA, indicating a low likelihood of being due to TXA,” they wrote.
“Dermatologists performing MMS may consider incorporating local TXA injection into their regular practice,” they noted, adding that “legal counsel on adverse effects in the setting of off-label pharmaceutical usage may be advised.”
In an interview, Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston Medical Center, who was asked to comment on the study, said that postoperative bleeding is one of the most commonly encountered Mohs surgery complications. “Because of increased clinic visits and phone calls, it can also often result in decreased patient satisfaction,” she said.
“This study is particularly notable in that we see that local subcutaneous TXA injection decreased visits for bleeding even in those using oral anticoagulants, antiplatelets, alcohol, and cigarettes. Dermatologic surgery has a very low complication rate, even in patients on anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, but this study shows that TXA is a fantastic option for Mohs surgeons and patients.”
Neither the study authors nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Though Mohs micrographic surgery is associated with low bleeding complication rates, around 1% of patients in the literature report postoperative bleeding,” corresponding author Abigail H. Waldman, MD, director of the Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Intravenous tranexamic acid has been used across surgical specialties to reduce perioperative blood loss. Prior studies have shown topical TXA, an antifibrinolytic agent, following MMS may be effective in reducing postoperative bleeding complications, but there are no large cohort studies on injectable TXA utilization in all patients undergoing MMS.”
To improve the understanding of this intervention, the researchers examined the impact of off-label, locally injected TXA on postoperative bleeding outcomes following MMS conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. They evaluated two cohorts: 1843 patients who underwent MMS from January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2019 (the pre-TXA cohort), and 2101 patients who underwent MMS from July 1, 2022, to June 30, 2023 (the TXA cohort), and extracted data, including patient and tumor characteristics, MMS procedure details, antithrombotic medication use, systemic conditions that predispose to bleeding, encounters reporting postoperative bleeding, and interventions required for postoperative bleeding, from electronic medical records. Patients reconstructed by a non-MMS surgeon were excluded from the analysis.
Overall, 2509 cases among 1843 patients and 2818 cases among 2101 were included in the pre-TXA and TXA cohorts, respectively. The researchers found that local subcutaneous injection of TXA reduced the risk for postoperative phone calls or visits for bleeding by 25% (RR [risk ratio], 0.75; 0.57-0.99) and risk for bleeding necessitating a medical visit by 51% (RR, 0.49; 0.32-0.77).
The use of preoperative TXA in several subgroups of patients also was also associated with a reduction in visits for bleeding, including those using alcohol (52% reduction; RR, 0.47; 0.26-0.85), cigarettes (57% reduction; RR, 0.43; 0.23-0.82), oral anticoagulants (61% reduction; RR, 0.39; 0.20-0.77), or antiplatelets (60% reduction; RR, 0.40; 0.20-0.79). The use of TXA was also associated with reduced visits for bleeding in tumors of the head and neck (RR, 0.45; 0.26-0.77) and tumors with a preoperative diameter > 2 cm (RR, 0.37; 0.15-0.90).
Impact of Surgical Repair Type
In other findings, the type of surgical repair was a potential confounder, the authors reported. Grafts and flaps were associated with an increased risk for bleeding across both cohorts (RR, 2.36 [1.5-3.6] and 1.7 [1.1-2.6], respectively) and together comprised 15% of all procedures in the pre-TXA cohort compared with 11.1% in TXA cohort. Two patients in the TXA cohort (0.11%) developed deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 10- and 20-days postoperation, a rate that the authors said is comparable to that of the general population. The two patients had risk factors for hypercoagulability, including advanced cancer and recurrent DVT.
“Overall, local injection of TXA was an effective method for reducing the risk of clinically significant bleeding following MMS,” the researchers concluded. “Perioperative TXA may help to limit the risk of bleeding overall, as well as in populations predisposed to bleeding.” Adverse events with TXA use were rare “and delayed beyond the activity of TXA, indicating a low likelihood of being due to TXA,” they wrote.
“Dermatologists performing MMS may consider incorporating local TXA injection into their regular practice,” they noted, adding that “legal counsel on adverse effects in the setting of off-label pharmaceutical usage may be advised.”
In an interview, Patricia M. Richey, MD, director of Mohs surgery at Boston Medical Center, who was asked to comment on the study, said that postoperative bleeding is one of the most commonly encountered Mohs surgery complications. “Because of increased clinic visits and phone calls, it can also often result in decreased patient satisfaction,” she said.
“This study is particularly notable in that we see that local subcutaneous TXA injection decreased visits for bleeding even in those using oral anticoagulants, antiplatelets, alcohol, and cigarettes. Dermatologic surgery has a very low complication rate, even in patients on anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, but this study shows that TXA is a fantastic option for Mohs surgeons and patients.”
Neither the study authors nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Urine Tests Could Be ‘Enormous Step’ in Diagnosing Cancer
Emerging science suggests that the body’s “liquid gold” could be particularly useful for liquid biopsies, offering a convenient, pain-free, and cost-effective way to spot otherwise hard-to-detect cancers.
“The search for cancer biomarkers that can be detected in urine could provide an enormous step forward to decrease cancer patient mortality,” said Kenneth R. Shroyer, MD, PhD, a pathologist at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, who studies cancer biomarkers.
Physicians have long known that urine can reveal a lot about our health — that’s why urinalysis has been part of medicine for 6000 years. Urine tests can detect diabetes, pregnancy, drug use, and urinary or kidney conditions.
But other conditions leave clues in urine, too, and cancer may be one of the most promising. “Urine testing could detect biomarkers of early-stage cancers, not only from local but also distant sites,” Dr. Shroyer said. It could also help flag recurrence in cancer survivors who have undergone treatment.
Granted, cancer biomarkers in urine are not nearly as widely studied as those in the blood, Dr. Shroyer noted. But a new wave of urine tests suggests research is gaining pace.
“The recent availability of high-throughput screening technologies has enabled researchers to investigate cancer from a top-down, comprehensive approach,” said Pak Kin Wong, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, and surgery at The Pennsylvania State University. “We are starting to understand the rich information that can be obtained from urine.”
Urine is mostly water (about 95%) and urea, a metabolic byproduct that imparts that signature yellow color (about 2%). The other 3% is a mix of waste products, minerals, and other compounds the kidneys removed from the blood. Even in trace amounts, these substances say a lot.
Among them are “exfoliated cancer cells, cell-free DNA, hormones, and the urine microbiota — the collection of microbes in our urinary tract system,” Dr. Wong said.
“It is highly promising to be one of the major biological fluids used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficiency in the era of precision medicine,” Dr. Wong said.
How Urine Testing Could Reveal Cancer
Still, as exciting as the prospect is, there’s a lot to consider in the hunt for cancer biomarkers in urine. These biomarkers must be able to pass through the renal nephrons (filtering units), remain stable in urine, and have high-level sensitivity, Dr. Shroyer said. They should also have high specificity for cancer vs benign conditions and be expressed at early stages, before the primary tumor has spread.
“At this stage, few circulating biomarkers have been found that are both sensitive and specific for early-stage disease,” said Dr. Shroyer.
But there are a few promising examples under investigation in humans:
Prostate cancer. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a urine test that detects high-grade prostate cancer more accurately than existing tests, including PHI, SelectMDx, 4Kscore, EPI, MPS, and IsoPSA.
The MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2) test, which looks for 18 genes associated with high-grade tumors, could reduce unnecessary biopsies in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels, according to a paper published in JAMA Oncology.
It makes sense. The prostate gland secretes fluid that becomes part of the semen, traces of which enter urine. After a digital rectal exam, even more prostate fluid enters the urine. If a patient has prostate cancer, genetic material from the cancer cells will infiltrate the urine.
In the MPS2 test, researchers used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in urine. “The technology used for COVID PCR is essentially the same as the PCR used to detect transcripts associated with high-grade prostate cancer in urine,” said study author Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “In the case of the MPS2 test, we are doing PCR on 18 genes simultaneously on urine samples.”
A statistical model uses levels of that genetic material to predict the risk for high-grade disease, helping doctors decide what to do next. At 95% sensitivity, the MPS2 model could eliminate 35%-45% of unnecessary biopsies, compared with 15%-30% for the other tests, and reduce repeat biopsies by 46%-51%, compared with 9%-21% for the other tests.
Head and neck cancer. In a paper published in JCI Insight, researchers described a test that finds ultra-short fragments of DNA in urine to enable early detection of head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
“Our data show that a relatively small volume of urine (30-60 mL) gives overall detection results comparable to a tube of blood,” said study author Muneesh Tewari, MD, PhD, professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Michigan .
A larger volume of urine could potentially “make cancer detection even more sensitive than blood,” Dr. Tewari said, “allowing cancers to be detected at the earliest stages when they are more curable.”
The team used a technique called droplet digital PCR to detect DNA fragments that are “ultra-short” (less than 50 base pairs long) and usually missed by conventional PCR testing. This transrenal cell-free tumor DNA, which travels from the tumor into the bloodstream, is broken down small enough to pass through the kidneys and into the urine. But the fragments are still long enough to carry information about the tumor’s genetic signature.
This test could spot cancer before a tumor grows big enough — about a centimeter wide and carrying a billion cells — to spot on a CT scan or other imaging test. “When we are instead detecting fragments of DNA released from a tumor,” said Dr. Tewari, “our testing methods are very sensitive and can detect DNA in urine that came from just 5-10 cells in a tumor that died and released their DNA into the blood, which then made its way into the urine.”
Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the deadliest cancers, largely because it is diagnosed so late. A urine panel now in clinical trials could help doctors diagnose the cancer before it has spread so more people can have the tumor surgically removed, improving prognosis.
Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, a common lab method that detects antibodies and other proteins, the team measured expression levels for three genes (LYVE1, REG1B, and TFF1) in urine samples collected from people up to 5 years before they were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. The researchers combined this result with patients’ urinary creatinine levels, a common component of existing urinalysis, and their age to develop a risk score.
This score performed similarly to an existing blood test, CA19-9, in predicting patients’ risk for pancreatic cancer up to 1 year before diagnosis. When combined with CA19-9, the urinary panel helped spot cancer up to 2 years before diagnosis.
According to a paper in the International Journal of Cancer, “the urine panel and affiliated PancRISK are currently being validated in a prospective clinical study (UroPanc).” If all goes well, they could be implemented in clinical practice in a few years as a “noninvasive stratification tool” to identify patients for further testing, speeding up diagnosis, and saving lives.
Limitations and Promises
Each cancer type is different, and more research is needed to map out which substances in urine predict which cancers and to develop tests for mass adoption. “There are medical and technological hurdles to the large-scale implementation of urine analysis for complex diseases such as cancer,” said Dr. Wong.
One possibility: Scientists and clinicians could collaborate and use artificial intelligence techniques to combine urine test results with other data.
“It is likely that future diagnostics may combine urine with other biological samples such as feces and saliva, among others,” said Dr. Wong. “This is especially true when novel data science and machine learning techniques can integrate comprehensive data from patients that span genetic, proteomic, metabolic, microbiomic, and even behavioral data to evaluate a patient’s condition.”
One thing that excites Dr. Tewari about urine-based cancer testing: “We think it could be especially impactful for patients living in rural areas or other areas with less access to healthcare services,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging science suggests that the body’s “liquid gold” could be particularly useful for liquid biopsies, offering a convenient, pain-free, and cost-effective way to spot otherwise hard-to-detect cancers.
“The search for cancer biomarkers that can be detected in urine could provide an enormous step forward to decrease cancer patient mortality,” said Kenneth R. Shroyer, MD, PhD, a pathologist at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, who studies cancer biomarkers.
Physicians have long known that urine can reveal a lot about our health — that’s why urinalysis has been part of medicine for 6000 years. Urine tests can detect diabetes, pregnancy, drug use, and urinary or kidney conditions.
But other conditions leave clues in urine, too, and cancer may be one of the most promising. “Urine testing could detect biomarkers of early-stage cancers, not only from local but also distant sites,” Dr. Shroyer said. It could also help flag recurrence in cancer survivors who have undergone treatment.
Granted, cancer biomarkers in urine are not nearly as widely studied as those in the blood, Dr. Shroyer noted. But a new wave of urine tests suggests research is gaining pace.
“The recent availability of high-throughput screening technologies has enabled researchers to investigate cancer from a top-down, comprehensive approach,” said Pak Kin Wong, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, and surgery at The Pennsylvania State University. “We are starting to understand the rich information that can be obtained from urine.”
Urine is mostly water (about 95%) and urea, a metabolic byproduct that imparts that signature yellow color (about 2%). The other 3% is a mix of waste products, minerals, and other compounds the kidneys removed from the blood. Even in trace amounts, these substances say a lot.
Among them are “exfoliated cancer cells, cell-free DNA, hormones, and the urine microbiota — the collection of microbes in our urinary tract system,” Dr. Wong said.
“It is highly promising to be one of the major biological fluids used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficiency in the era of precision medicine,” Dr. Wong said.
How Urine Testing Could Reveal Cancer
Still, as exciting as the prospect is, there’s a lot to consider in the hunt for cancer biomarkers in urine. These biomarkers must be able to pass through the renal nephrons (filtering units), remain stable in urine, and have high-level sensitivity, Dr. Shroyer said. They should also have high specificity for cancer vs benign conditions and be expressed at early stages, before the primary tumor has spread.
“At this stage, few circulating biomarkers have been found that are both sensitive and specific for early-stage disease,” said Dr. Shroyer.
But there are a few promising examples under investigation in humans:
Prostate cancer. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a urine test that detects high-grade prostate cancer more accurately than existing tests, including PHI, SelectMDx, 4Kscore, EPI, MPS, and IsoPSA.
The MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2) test, which looks for 18 genes associated with high-grade tumors, could reduce unnecessary biopsies in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels, according to a paper published in JAMA Oncology.
It makes sense. The prostate gland secretes fluid that becomes part of the semen, traces of which enter urine. After a digital rectal exam, even more prostate fluid enters the urine. If a patient has prostate cancer, genetic material from the cancer cells will infiltrate the urine.
In the MPS2 test, researchers used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in urine. “The technology used for COVID PCR is essentially the same as the PCR used to detect transcripts associated with high-grade prostate cancer in urine,” said study author Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “In the case of the MPS2 test, we are doing PCR on 18 genes simultaneously on urine samples.”
A statistical model uses levels of that genetic material to predict the risk for high-grade disease, helping doctors decide what to do next. At 95% sensitivity, the MPS2 model could eliminate 35%-45% of unnecessary biopsies, compared with 15%-30% for the other tests, and reduce repeat biopsies by 46%-51%, compared with 9%-21% for the other tests.
Head and neck cancer. In a paper published in JCI Insight, researchers described a test that finds ultra-short fragments of DNA in urine to enable early detection of head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
“Our data show that a relatively small volume of urine (30-60 mL) gives overall detection results comparable to a tube of blood,” said study author Muneesh Tewari, MD, PhD, professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Michigan .
A larger volume of urine could potentially “make cancer detection even more sensitive than blood,” Dr. Tewari said, “allowing cancers to be detected at the earliest stages when they are more curable.”
The team used a technique called droplet digital PCR to detect DNA fragments that are “ultra-short” (less than 50 base pairs long) and usually missed by conventional PCR testing. This transrenal cell-free tumor DNA, which travels from the tumor into the bloodstream, is broken down small enough to pass through the kidneys and into the urine. But the fragments are still long enough to carry information about the tumor’s genetic signature.
This test could spot cancer before a tumor grows big enough — about a centimeter wide and carrying a billion cells — to spot on a CT scan or other imaging test. “When we are instead detecting fragments of DNA released from a tumor,” said Dr. Tewari, “our testing methods are very sensitive and can detect DNA in urine that came from just 5-10 cells in a tumor that died and released their DNA into the blood, which then made its way into the urine.”
Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the deadliest cancers, largely because it is diagnosed so late. A urine panel now in clinical trials could help doctors diagnose the cancer before it has spread so more people can have the tumor surgically removed, improving prognosis.
Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, a common lab method that detects antibodies and other proteins, the team measured expression levels for three genes (LYVE1, REG1B, and TFF1) in urine samples collected from people up to 5 years before they were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. The researchers combined this result with patients’ urinary creatinine levels, a common component of existing urinalysis, and their age to develop a risk score.
This score performed similarly to an existing blood test, CA19-9, in predicting patients’ risk for pancreatic cancer up to 1 year before diagnosis. When combined with CA19-9, the urinary panel helped spot cancer up to 2 years before diagnosis.
According to a paper in the International Journal of Cancer, “the urine panel and affiliated PancRISK are currently being validated in a prospective clinical study (UroPanc).” If all goes well, they could be implemented in clinical practice in a few years as a “noninvasive stratification tool” to identify patients for further testing, speeding up diagnosis, and saving lives.
Limitations and Promises
Each cancer type is different, and more research is needed to map out which substances in urine predict which cancers and to develop tests for mass adoption. “There are medical and technological hurdles to the large-scale implementation of urine analysis for complex diseases such as cancer,” said Dr. Wong.
One possibility: Scientists and clinicians could collaborate and use artificial intelligence techniques to combine urine test results with other data.
“It is likely that future diagnostics may combine urine with other biological samples such as feces and saliva, among others,” said Dr. Wong. “This is especially true when novel data science and machine learning techniques can integrate comprehensive data from patients that span genetic, proteomic, metabolic, microbiomic, and even behavioral data to evaluate a patient’s condition.”
One thing that excites Dr. Tewari about urine-based cancer testing: “We think it could be especially impactful for patients living in rural areas or other areas with less access to healthcare services,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging science suggests that the body’s “liquid gold” could be particularly useful for liquid biopsies, offering a convenient, pain-free, and cost-effective way to spot otherwise hard-to-detect cancers.
“The search for cancer biomarkers that can be detected in urine could provide an enormous step forward to decrease cancer patient mortality,” said Kenneth R. Shroyer, MD, PhD, a pathologist at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, who studies cancer biomarkers.
Physicians have long known that urine can reveal a lot about our health — that’s why urinalysis has been part of medicine for 6000 years. Urine tests can detect diabetes, pregnancy, drug use, and urinary or kidney conditions.
But other conditions leave clues in urine, too, and cancer may be one of the most promising. “Urine testing could detect biomarkers of early-stage cancers, not only from local but also distant sites,” Dr. Shroyer said. It could also help flag recurrence in cancer survivors who have undergone treatment.
Granted, cancer biomarkers in urine are not nearly as widely studied as those in the blood, Dr. Shroyer noted. But a new wave of urine tests suggests research is gaining pace.
“The recent availability of high-throughput screening technologies has enabled researchers to investigate cancer from a top-down, comprehensive approach,” said Pak Kin Wong, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, and surgery at The Pennsylvania State University. “We are starting to understand the rich information that can be obtained from urine.”
Urine is mostly water (about 95%) and urea, a metabolic byproduct that imparts that signature yellow color (about 2%). The other 3% is a mix of waste products, minerals, and other compounds the kidneys removed from the blood. Even in trace amounts, these substances say a lot.
Among them are “exfoliated cancer cells, cell-free DNA, hormones, and the urine microbiota — the collection of microbes in our urinary tract system,” Dr. Wong said.
“It is highly promising to be one of the major biological fluids used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficiency in the era of precision medicine,” Dr. Wong said.
How Urine Testing Could Reveal Cancer
Still, as exciting as the prospect is, there’s a lot to consider in the hunt for cancer biomarkers in urine. These biomarkers must be able to pass through the renal nephrons (filtering units), remain stable in urine, and have high-level sensitivity, Dr. Shroyer said. They should also have high specificity for cancer vs benign conditions and be expressed at early stages, before the primary tumor has spread.
“At this stage, few circulating biomarkers have been found that are both sensitive and specific for early-stage disease,” said Dr. Shroyer.
But there are a few promising examples under investigation in humans:
Prostate cancer. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a urine test that detects high-grade prostate cancer more accurately than existing tests, including PHI, SelectMDx, 4Kscore, EPI, MPS, and IsoPSA.
The MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2) test, which looks for 18 genes associated with high-grade tumors, could reduce unnecessary biopsies in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels, according to a paper published in JAMA Oncology.
It makes sense. The prostate gland secretes fluid that becomes part of the semen, traces of which enter urine. After a digital rectal exam, even more prostate fluid enters the urine. If a patient has prostate cancer, genetic material from the cancer cells will infiltrate the urine.
In the MPS2 test, researchers used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in urine. “The technology used for COVID PCR is essentially the same as the PCR used to detect transcripts associated with high-grade prostate cancer in urine,” said study author Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “In the case of the MPS2 test, we are doing PCR on 18 genes simultaneously on urine samples.”
A statistical model uses levels of that genetic material to predict the risk for high-grade disease, helping doctors decide what to do next. At 95% sensitivity, the MPS2 model could eliminate 35%-45% of unnecessary biopsies, compared with 15%-30% for the other tests, and reduce repeat biopsies by 46%-51%, compared with 9%-21% for the other tests.
Head and neck cancer. In a paper published in JCI Insight, researchers described a test that finds ultra-short fragments of DNA in urine to enable early detection of head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
“Our data show that a relatively small volume of urine (30-60 mL) gives overall detection results comparable to a tube of blood,” said study author Muneesh Tewari, MD, PhD, professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Michigan .
A larger volume of urine could potentially “make cancer detection even more sensitive than blood,” Dr. Tewari said, “allowing cancers to be detected at the earliest stages when they are more curable.”
The team used a technique called droplet digital PCR to detect DNA fragments that are “ultra-short” (less than 50 base pairs long) and usually missed by conventional PCR testing. This transrenal cell-free tumor DNA, which travels from the tumor into the bloodstream, is broken down small enough to pass through the kidneys and into the urine. But the fragments are still long enough to carry information about the tumor’s genetic signature.
This test could spot cancer before a tumor grows big enough — about a centimeter wide and carrying a billion cells — to spot on a CT scan or other imaging test. “When we are instead detecting fragments of DNA released from a tumor,” said Dr. Tewari, “our testing methods are very sensitive and can detect DNA in urine that came from just 5-10 cells in a tumor that died and released their DNA into the blood, which then made its way into the urine.”
Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the deadliest cancers, largely because it is diagnosed so late. A urine panel now in clinical trials could help doctors diagnose the cancer before it has spread so more people can have the tumor surgically removed, improving prognosis.
Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, a common lab method that detects antibodies and other proteins, the team measured expression levels for three genes (LYVE1, REG1B, and TFF1) in urine samples collected from people up to 5 years before they were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. The researchers combined this result with patients’ urinary creatinine levels, a common component of existing urinalysis, and their age to develop a risk score.
This score performed similarly to an existing blood test, CA19-9, in predicting patients’ risk for pancreatic cancer up to 1 year before diagnosis. When combined with CA19-9, the urinary panel helped spot cancer up to 2 years before diagnosis.
According to a paper in the International Journal of Cancer, “the urine panel and affiliated PancRISK are currently being validated in a prospective clinical study (UroPanc).” If all goes well, they could be implemented in clinical practice in a few years as a “noninvasive stratification tool” to identify patients for further testing, speeding up diagnosis, and saving lives.
Limitations and Promises
Each cancer type is different, and more research is needed to map out which substances in urine predict which cancers and to develop tests for mass adoption. “There are medical and technological hurdles to the large-scale implementation of urine analysis for complex diseases such as cancer,” said Dr. Wong.
One possibility: Scientists and clinicians could collaborate and use artificial intelligence techniques to combine urine test results with other data.
“It is likely that future diagnostics may combine urine with other biological samples such as feces and saliva, among others,” said Dr. Wong. “This is especially true when novel data science and machine learning techniques can integrate comprehensive data from patients that span genetic, proteomic, metabolic, microbiomic, and even behavioral data to evaluate a patient’s condition.”
One thing that excites Dr. Tewari about urine-based cancer testing: “We think it could be especially impactful for patients living in rural areas or other areas with less access to healthcare services,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Exploring Skin Pigmentation Adaptation: A Systematic Review on the Vitamin D Adaptation Hypothesis
The risk for developing skin cancer can be somewhat attributed to variations in skin pigmentation. Historically, lighter skin pigmentation has been observed in populations living in higher latitudes and darker pigmentation in populations near the equator. Although skin pigmentation is a conglomeration of genetic and environmental factors, anthropologic studies have demonstrated an association of human skin lightening with historic human migratory patterns.1 It is postulated that migration to latitudes with less UVB light penetration has resulted in a compensatory natural selection of lighter skin types. Furthermore, the driving force behind this migration-associated skin lightening has remained unclear.1
The need for folate metabolism, vitamin D synthesis, and barrier protection, as well as cultural practices, has been postulated as driving factors for skin pigmentation variation. Synthesis of vitamin D is a UV radiation (UVR)–dependent process and has remained a prominent theoretical driver for the basis of evolutionary skin lightening. Vitamin D can be acquired both exogenously or endogenously via dietary supplementation or sunlight; however, historically it has been obtained through UVB exposure primarily. Once UVB is absorbed by the skin, it catalyzes conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which is converted to vitamin D in the kidneys.2,3 It is suggested that lighter skin tones have an advantage over darker skin tones in synthesizing vitamin D at higher latitudes where there is less UVB, thus leading to the adaptation process.1 In this systematic review, we analyzed the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis and assessed the validity of evidence supporting this theory in the literature.
Methods
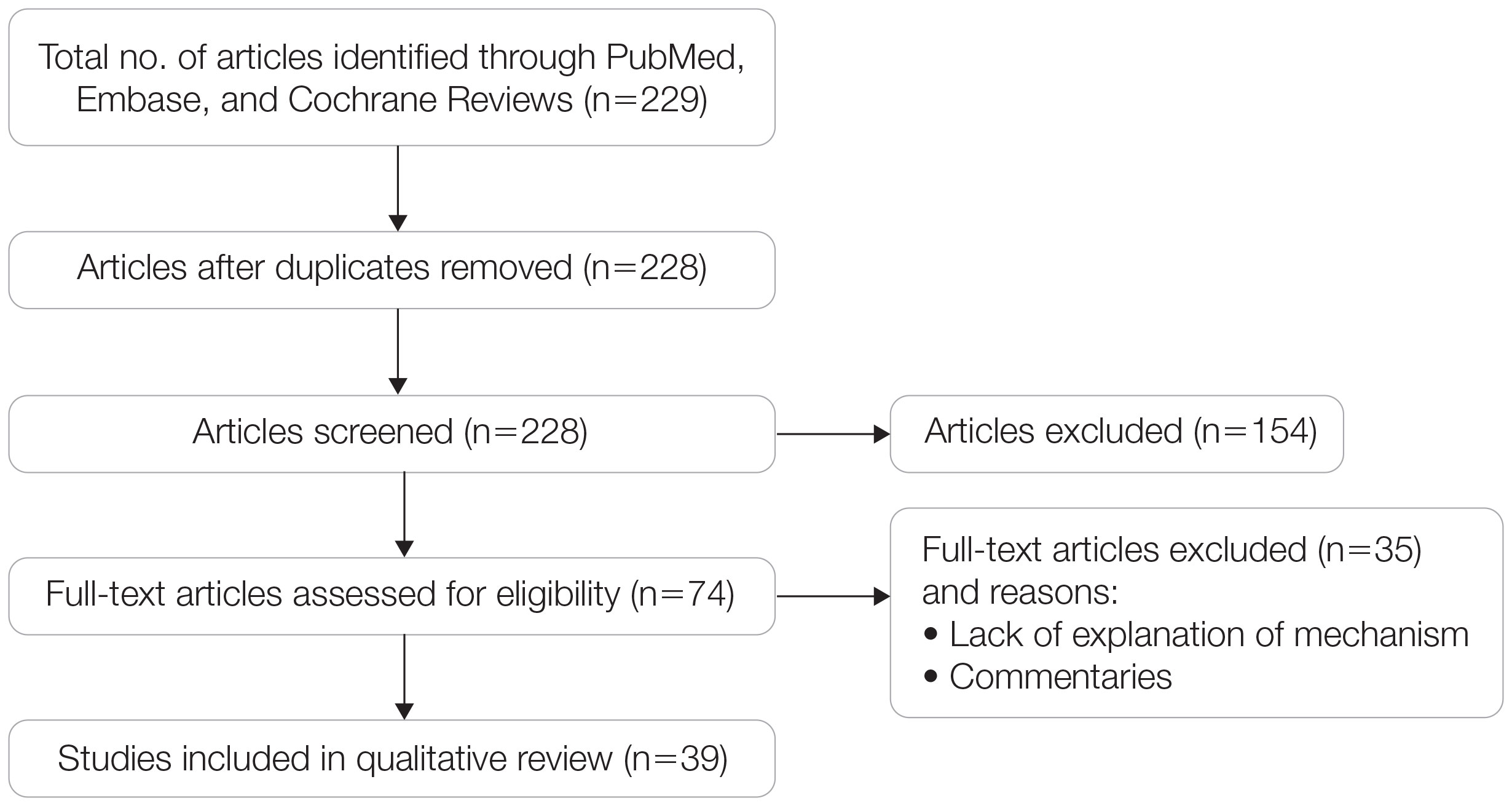
A search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Reviews database was conducted using the terms evolution, vitamin D, and skin to generate articles published from 2010 to 2022 that evaluated the influence of UVR-dependent production of vitamin D on skin pigmentation through historical migration patterns (Figure). Studies were excluded during an initial screening of abstracts followed by full-text assessment if they only had abstracts and if articles were inaccessible for review or in the form of case reports and commentaries.
The following data were extracted from each included study: reference citation, affiliated institutions of authors, author specialties, journal name, year of publication, study period, type of article, type of study, mechanism of adaptation, data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver, and data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver. Data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver were recorded from statistically significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotations. Data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver also were recorded from significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotes. The mechanism of adaptation was based on vitamin D synthesis modulation, melanin upregulation, genetic selections, genetic drift, mating patterns, increased vitamin D sensitivity, interbreeding, and diet.
Studies included in the analysis were placed into 1 of 3 categories: supporting, neutral, and against. Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) criteria were used to classify the level of evidence of each article.4 Each article’s level of evidence was then graded (Table 1). The SORT grading levels were based on quality and evidence type: level 1 signified good-quality, patient-oriented evidence; level 2 signified limited-quality, patient-oriented evidence; and level 3 signified other evidence.4
Results
Article Selection—A total of 229 articles were identified for screening, and 39 studies met inclusion criteria.1-3,5-40 Systematic and retrospective reviews were the most common types of studies. Genomic analysis/sequencing/genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were the most common methods of analysis. Of these 39 articles, 26 were classified as supporting the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis, 10 were classified as neutral, and 3 were classified as against (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as supporting the vitamin D hypothesis, 13 articles were level 1 evidence, 9 were level 2, and 4 were level 3. Key findings supporting the vitamin D hypothesis included genetic natural selection favoring vitamin D synthesis genes at higher latitudes with lower UVR and the skin lightening that occurred to protect against vitamin D deficiency (Table 1). Specific genes supporting these findings included 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), vitamin D receptor (VDR), tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), oculocutaneous albinism type 2 melanosomal transmembrane protein (OCA2), solute carrier family 45 member 2 (SLC45A2), solute carrier family 4 member 5 (SLC24A5), Kit ligand (KITLG), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), and HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (HERC2)(Table 2).
Of the articles classified as being against the vitamin D hypothesis, 1 article was level 1 evidence, 1 was level 2, and 1 was level 3. Key findings refuting the vitamin D hypothesis included similar amounts of vitamin D synthesis in contemporary dark- and light-pigmented individuals, vitamin D–rich diets in the late Paleolithic period and in early agriculturalists, and metabolic conservation being the primary driver (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as neutral to the hypothesis, 7 articles were level 1 evidence and 3 were level 2. Key findings of these articles included genetic selection favoring vitamin D synthesis only for populations at extremely northern latitudes, skin lightening that was sustained in northern latitudes from the neighboring human ancestor the chimpanzee, and evidence for long-term evolutionary pressures and short-term plastic adaptations in vitamin D genes (Table 1).
Comment
The importance of appropriate vitamin D levels is hypothesized as a potent driver in skin lightening because the vitamin is essential for many biochemical processes within the human body. Proper calcification of bones requires activated vitamin D to prevent rickets in childhood. Pelvic deformation in women with rickets can obstruct childbirth in primitive medical environments.15 This direct reproductive impairment suggests a strong selective pressure for skin lightening in populations that migrated northward to enhance vitamin D synthesis.
Of the 39 articles that we reviewed, the majority (n=26 [66.7%]) supported the hypothesis that vitamin D synthesis was the main driver behind skin lightening, whereas 3 (7.7%) did not support the hypothesis and 10 (25.6%) were neutral. Other leading theories explaining skin lightening included the idea that enhanced melanogenesis protected against folate degradation; genetic selection for light-skin alleles due to genetic drift; skin lightening being the result of sexual selection; and a combination of factors, including dietary choices, clothing preferences, and skin permeability barriers.
Articles With Supporting Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—As Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa, migration patterns demonstrated the correlation between distance from the equator and skin pigmentation from natural selection. Individuals with darker skin pigment required higher levels of UVR to synthesize vitamin D. According to Beleza et al,1 as humans migrated to areas of higher latitudes with lower levels of UVR, natural selection favored the development of lighter skin to maximize vitamin D production. Vitamin D is linked to calcium metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to bone malformations and poor immune function.35 Several genes affecting melanogenesis and skin pigment have been found to have geospatial patterns that map to different geographic locations of various populations, indicating how human migration patterns out of Africa created this natural selection for skin lightening. The gene KITLG—associated with lighter skin pigmentation—has been found in high frequencies in both European and East Asian populations and is proposed to have increased in frequency after the migration out of Africa. However, the genes TYRP1, SLC24A5, and SLC45A2 were found at high frequencies only in European populations, and this selection occurred 11,000 to 19,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum (15,000–20,000 years ago), demonstrating the selection for European over East Asian characteristics. During this period, seasonal changes increased the risk for vitamin D deficiency and provided an urgency for selection to a lighter skin pigment.1
The migration of H sapiens to northern latitudes prompted the selection of alleles that would increasevitamin D synthesis to counteract the reduced UV exposure. Genetic analysis studies have found key associations between genes encoding for the metabolism of vitamin D and pigmentation. Among this complex network are the essential downstream enzymes in the melanocortin receptor 1 pathway, including TYR and TYRP1. Forty-six of 960 single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in 29 different genes involved in skin pigmentation that were analyzed in a cohort of 2970 individuals were significantly associated with serum vitamin D levels (P<.05). The exocyst complex component 2 (EXOC2), TYR, and TYRP1 gene variants were shown to have the greatest influence on vitamin D status.9 These data reveal how pigment genotypes are predictive of vitamin D levels and the epistatic potential among many genes in this complex network.
Gene variation plays an important role in vitamin D status when comparing genetic polymorphisms in populations in northern latitudes to African populations. Vitamin D3 precursor availability is decreased by 7-DHCR catalyzing the precursors substrate to cholesterol. In a study using GWAS, it was found that “variations in DHCR7 may aid vitamin D production by conserving cutaneous 7-DHC levels. A high prevalence of DHCR7 variants were found in European and Northeast Asian populations but not in African populations, suggesting that selection occurred for these DHCR7 mutations in populations who migrated to more northern latitudes.5 Multilocus networks have been established between the VDR promotor and skin color genes (Table 2) that exhibit a strong in-Africa vs out-of-Africa frequency pattern. It also has been shown that genetic variation (suggesting a long-term evolutionary inclination) and epigenetic modification (indicative of short-term exposure) of VDR lends support to the vitamin D hypothesis. As latitude decreases, prevalence of VDR FokI (F allele), BsmI (B allele), ApaI (A allele), and TaqI (T allele) also decreases in a linear manner, linking latitude to VDR polymorphisms. Plasma vitamin D levels and photoperiod of conception—UV exposure during the periconceptional period—also were extrapolative of VDR methylation in a study involving 80 participants, where these 2 factors accounted for 17% of variance in methylation.6
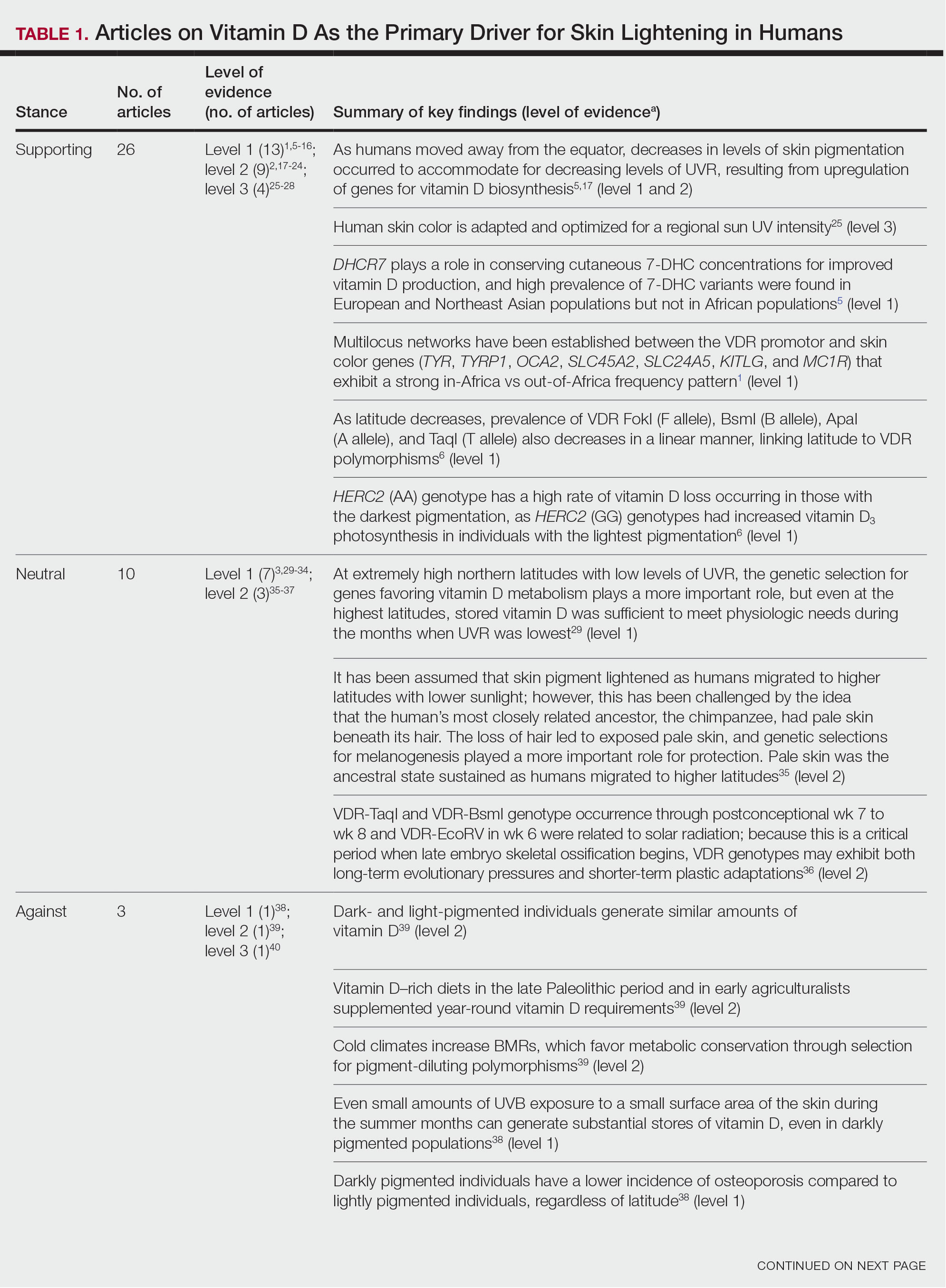
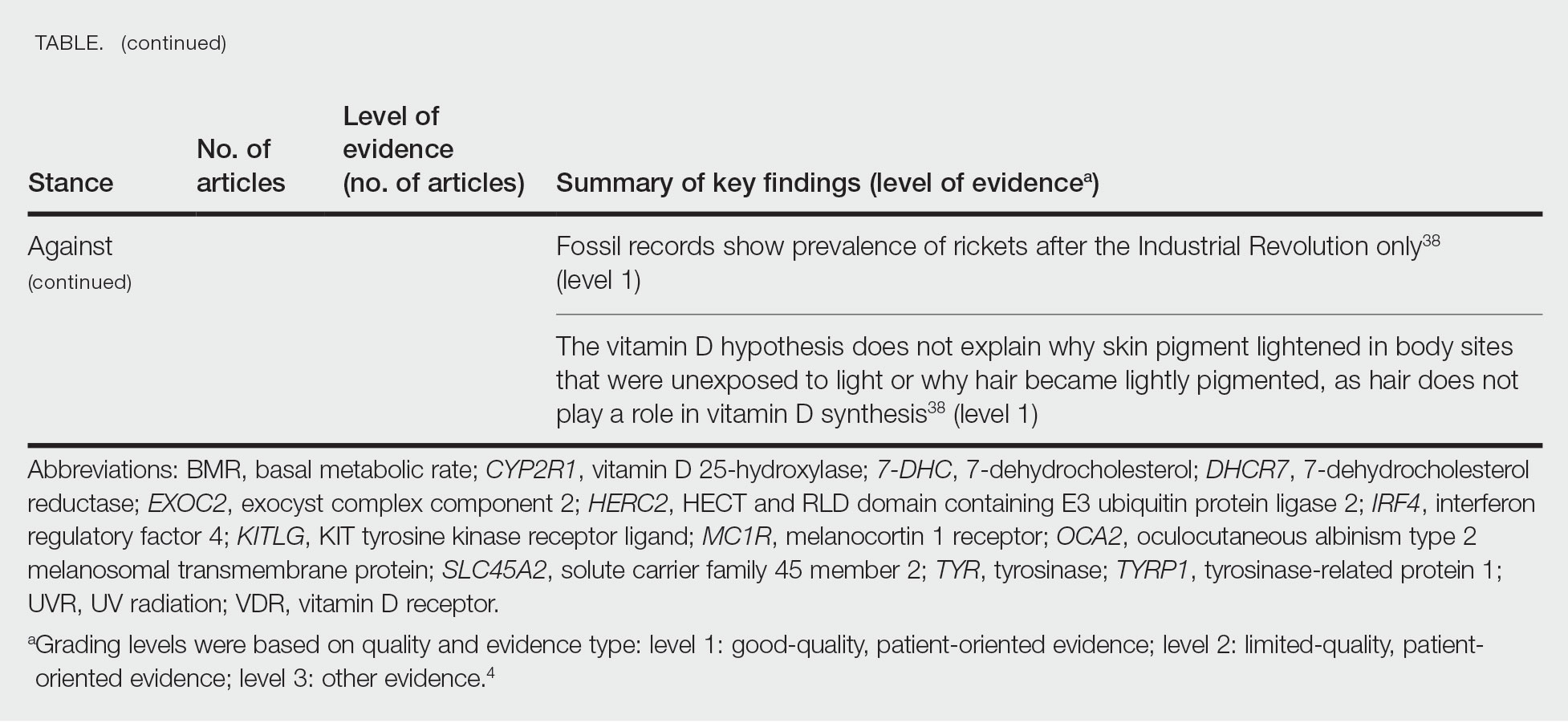
Other noteworthy genes included HERC2, which has implications in the expression of OCA2 (melanocyte-specific transporter protein), and IRF4, which encodes for an important enzyme in folate-dependent melanin production. In an Australian cross-sectional study that analyzed vitamin D and pigmentation gene polymorphisms in conjunction with plasma vitamin D levels, the most notable rate of vitamin D loss occurred in individuals with the darkest pigmentation HERC2 (AA) genotype.31 In contrast, the lightest pigmentation HERC2 (GG) genotypes had increased vitamin D3 photosynthesis. Interestingly, the lightest interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) TT genotype and the darkest HERC2 AA genotype, rendering the greatest folate loss and largest synthesis of vitamin D3, were not seen in combination in any of the participants.30 In addition to HERC2, derived alleles from pigment-associated genes SLC24A5*A and SLC45A2*G demonstrated greater frequencies in Europeans (>90%) compared to Africans and East Asians, where the allelic frequencies were either rare or absent.1 This evidence delineates not only the complexity but also the strong relationship between skin pigmentation, latitude, and vitamin D status. The GWAS also have supported this concept. In comparing European populations to African populations, there was a 4-fold increase in the frequencies of “derived alleles of the vitamin D transport protein (GC, rs3755967), the 25(OH)D3 synthesizing enzyme (CYP2R1, rs10741657), VDR (rs2228570 (commonly known as FokI polymorphism), rs1544410 (Bsm1), and rs731236 (Taq1) and the VDR target genes CYP24A1 (rs17216707), CD14 (rs2569190), and CARD9 (rs4077515).”32
Articles With Evidence Against the Vitamin D Theory—This review analyzed the level of support for the theory that vitamin D was the main driver for skin lightening. Although most articles supported this theory, there were articles that listed other plausible counterarguments. Jablonski and Chaplin3 suggested that humans living in higher latitudes compensated for increased demand of vitamin D by placing cultural importance on a diet of vitamin D–rich foods and thus would not have experienced decreased vitamin D levels, which we hypothesize were the driver for skin lightening. Elias et al39 argued that initial pigment dilution may have instead served to improve metabolic conservation, as the authors found no evidence of rickets—the sequelae of vitamin D deficiency—in pre–industrial age human fossils. Elias and Williams38 proposed that differences in skin pigment are due to a more intact skin permeability barrier as “a requirement for life in a desiccating terrestrial environment,” which is seen in darker skin tones compared to lighter skin tones and thus can survive better in warmer climates with less risk of infections or dehydration.
Articles With Neutral Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—Greaves41 argued against the idea that skin evolved to become lighter to protect against vitamin D deficiency. They proposed that the chimpanzee, which is the human’s most closely related species, had light skin covered by hair, and the loss of this hair led to exposed pale skin that created a need for increased melanin production for protection from UVR. Greaves41 stated that the MC1R gene (associated with darker pigmentation) was selected for in African populations, and those with pale skin retained their original pigment as they migrated to higher latitudes. Further research has demonstrated that the genetic natural selection for skin pigment is a complex process that involves multiple gene variants found throughout cultures across the globe.
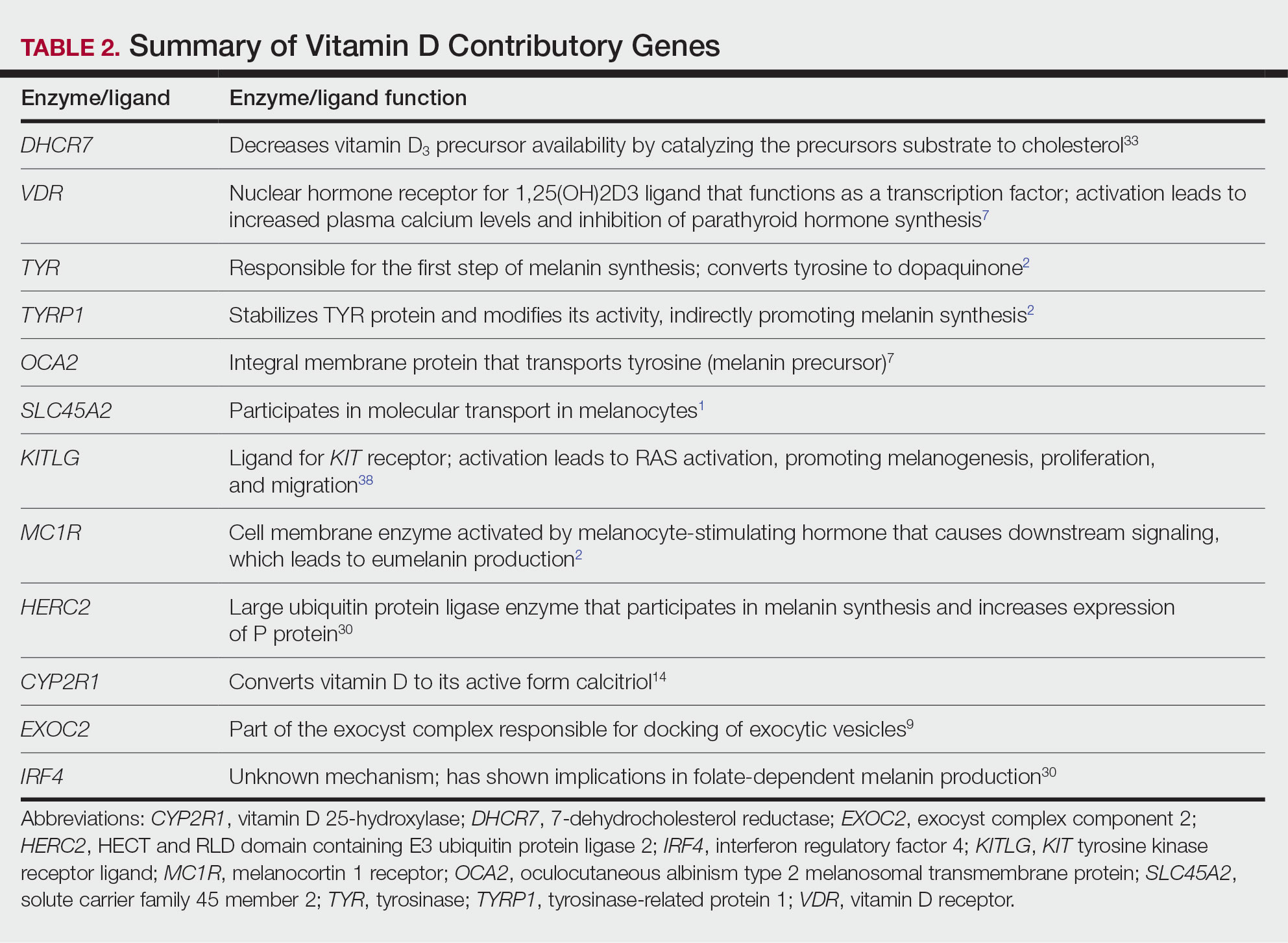
Conclusion
Skin pigmentation has continuously evolved alongside humans. Genetic selection for lighter skin coincides with a favorable selection for genes involved in vitamin D synthesis as humans migrated to northern latitudes, which enabled humans to produce adequate levels of exogenous vitamin D in low-UVR areas and in turn promoted survival. Early humans without access to supplementation or foods rich in vitamin D acquired vitamin D primarily through sunlight. In comparison to modern society, where vitamin D supplementation is accessible and human lifespans are prolonged, lighter skin tone is now a risk factor for malignant cancers of the skin rather than being a protective adaptation. Current sun behavior recommendations conclude that the body’s need for vitamin D is satisfied by UV exposure to the arms, legs, hands, and/or face for only 5 to 30 minutes between 10
The hypothesis that skin lightening primarily was driven by the need for vitamin D can only be partially supported by our review. Studies have shown that there is a corresponding complex network of genes that determines skin pigmentation as well as vitamin D synthesis and conservation. However, there is sufficient evidence that skin lightening is multifactorial in nature, and vitamin D alone may not be the sole driver. The information in this review can be used by health care providers to educate patients on sun protection, given the lesser threat of severe vitamin D deficiency in developed communities today that have access to adequate nutrition and supplementation.
Skin lightening and its coinciding evolutionary drivers are a rather neglected area of research. Due to heterogeneous cohorts and conservative data analysis, GWAS studies run the risk of type II error, yielding a limitation in our data analysis.9 Furthermore, the data regarding specific time frames in evolutionary skin lightening as well as the intensity of gene polymorphisms are limited.1 Further studies are needed to determine the interconnectedness of the current skin-lightening theories to identify other important factors that may play a role in the process. Determining the key event can help us better understand skin-adaptation mechanisms and create a framework for understanding the vital process involved in adaptation, survival, and disease manifestation in different patient populations.
- Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, et al. The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:24-35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207
- Carlberg C. Nutrigenomics of vitamin D. Nutrients. 2019;11:676. doi:10.3390/nu11030676
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The roles of vitamin D and cutaneous vitamin D production in human evolution and health. Int J Paleopathol. 2018;23:54-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijpp.2018.01.005
- Weiss BD. SORT: strength of recommendation taxonomy. Fam Med. 2004;36:141-143.
- Wolf ST, Kenney WL. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis in human vascular health. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiology. 2019;317:R491-R501. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2019
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Photobiology of vitamins. Nutr Rev. 2018;76:512-525. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy013
- Hochberg Z, Hochberg I. Evolutionary perspective in rickets and vitamin D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:306. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306
- Rossberg W, Saternus R, Wagenpfeil S, et al. Human pigmentation, cutaneous vitamin D synthesis and evolution: variants of genes (SNPs) involved in skin pigmentation are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1429-1437.
- Saternus R, Pilz S, Gräber S, et al. A closer look at evolution: variants (SNPs) of genes involved in skin pigmentation, including EXOC2, TYR, TYRP1, and DCT, are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Endocrinology. 2015;156:39-47. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1238
- López S, García Ó, Yurrebaso I, et al. The interplay between natural selection and susceptibility to melanoma on allele 374F of SLC45A2 gene in a south European population. PloS One. 2014;9:E104367. doi:1371/journal.pone.0104367
- Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and potential early lifecycle environmental origin of significant adult phenotypes. Evol Med Public Health. 2014;2014:69-91. doi:10.1093/emph/eou013
- Hudjashov G, Villems R, Kivisild T. Global patterns of diversity and selection in human tyrosinase gene. PloS One. 2013;8:E74307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074307
- Khan R, Khan BSR. Diet, disease and pigment variation in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75:363-367. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.033
- Kuan V, Martineau AR, Griffiths CJ, et al. DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to northern latitudes. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:144. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
- Omenn GS. Evolution and public health. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 1):1702-1709. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906198106
- Yuen AWC, Jablonski NG. Vitamin D: in the evolution of human skin colour. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:39-44. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.08.007
- Vieth R. Weaker bones and white skin as adaptions to improve anthropological “fitness” for northern environments. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31:617-624. doi:10.1007/s00198-019-05167-4
- Carlberg C. Vitamin D: a micronutrient regulating genes. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25:1740-1746. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190705193227
- Haddadeen C, Lai C, Cho SY, et al. Variants of the melanocortin‐1 receptor: do they matter clinically? Exp Dermatol. 2015;1:5-9. doi:10.1111/exd.12540
- Yao S, Ambrosone CB. Associations between vitamin D deficiency and risk of aggressive breast cancer in African-American women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;136:337-341. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.010
- Jablonski N. The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. J Royal Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:58-63. doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2012.114
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Hochberg Z, Templeton AR. Evolutionary perspective in skin color, vitamin D and its receptor. Hormones. 2010;9:307-311. doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1281
- Jones P, Lucock M, Veysey M, et al. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis as an evolutionary model for skin pigmentation: an update and integration of current ideas. Nutrients. 2018;10:554. doi:10.3390/nu10050554
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, et al. Women with fair phenotypes seem to confer a survival advantage in a low UV milieu. a nested matched case control study. PloS One. 2020;15:E0228582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228582
- Holick MF. Shedding new light on the role of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: the lncRNA–skin cancer connection. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:391-392. doi:10.1111/exd.12386
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Epidermal pigmentation in the human lineage is an adaptation to ultraviolet radiation. J Hum Evol. 2013;65:671-675. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.06.004
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of skin pigmentation and hair texture in people of African ancestry. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:113-121. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.11.003
- Jablonski NG. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:707-7 doi:10.1111/pcmr.12976
- Lucock MD, Jones PR, Veysey M, et al. Biophysical evidence to support and extend the vitamin D‐folate hypothesis as a paradigm for the evolution of human skin pigmentation. Am J Hum Biol. 2022;34:E23667. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23667
- Missaggia BO, Reales G, Cybis GB, et al. Adaptation and co‐adaptation of skin pigmentation and vitamin D genes in native Americans. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020;184:1060-1077. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31873
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Skin colour and vitamin D: an update. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:864-875. doi:10.1111/exd.14142
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Vitamin D and evolution: pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;173:113595. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.024
- Flegr J, Sýkorová K, Fiala V, et al. Increased 25(OH)D3 level in redheaded people: could redheadedness be an adaptation to temperate climate? Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:598-609. doi:10.1111/exd.14119
- James WPT, Johnson RJ, Speakman JR, et al. Nutrition and its role in human evolution. J Intern Med. 2019;285:533-549. doi:10.1111/joim.12878
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D: beyond metabolism. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:310-322. doi:10.1177/2156587215580491
- Jarrett P, Scragg R. Evolution, prehistory and vitamin D. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:646. doi:10.3390/ijerph17020646
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Re-appraisal of current theories for thedevelopment and loss of epidermal pigmentation in hominins and modern humans. J Hum Evol. 2013;64:687-692. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.003
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Basis for the gain and subsequent dilution of epidermal pigmentation during human evolution: the barrier and metabolic conservation hypotheses revisited. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016;161:189-207. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23030
- Williams JD, Jacobson EL, Kim H, et al. Water soluble vitamins, clinical research and future application. Subcell Biochem. 2011;56:181-197. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_10
- Greaves M. Was skin cancer a selective force for black pigmentation in early hominin evolution [published online February 26, 2014]? Proc Biol Sci. 2014;281:20132955. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2955
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281. doi:10.1056/nejmra070553
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:466-479. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.31
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2014. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/call-to-action-prevent-skin-cancer.pdf
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al, eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/
The risk for developing skin cancer can be somewhat attributed to variations in skin pigmentation. Historically, lighter skin pigmentation has been observed in populations living in higher latitudes and darker pigmentation in populations near the equator. Although skin pigmentation is a conglomeration of genetic and environmental factors, anthropologic studies have demonstrated an association of human skin lightening with historic human migratory patterns.1 It is postulated that migration to latitudes with less UVB light penetration has resulted in a compensatory natural selection of lighter skin types. Furthermore, the driving force behind this migration-associated skin lightening has remained unclear.1
The need for folate metabolism, vitamin D synthesis, and barrier protection, as well as cultural practices, has been postulated as driving factors for skin pigmentation variation. Synthesis of vitamin D is a UV radiation (UVR)–dependent process and has remained a prominent theoretical driver for the basis of evolutionary skin lightening. Vitamin D can be acquired both exogenously or endogenously via dietary supplementation or sunlight; however, historically it has been obtained through UVB exposure primarily. Once UVB is absorbed by the skin, it catalyzes conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which is converted to vitamin D in the kidneys.2,3 It is suggested that lighter skin tones have an advantage over darker skin tones in synthesizing vitamin D at higher latitudes where there is less UVB, thus leading to the adaptation process.1 In this systematic review, we analyzed the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis and assessed the validity of evidence supporting this theory in the literature.
Methods
A search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Reviews database was conducted using the terms evolution, vitamin D, and skin to generate articles published from 2010 to 2022 that evaluated the influence of UVR-dependent production of vitamin D on skin pigmentation through historical migration patterns (Figure). Studies were excluded during an initial screening of abstracts followed by full-text assessment if they only had abstracts and if articles were inaccessible for review or in the form of case reports and commentaries.
The following data were extracted from each included study: reference citation, affiliated institutions of authors, author specialties, journal name, year of publication, study period, type of article, type of study, mechanism of adaptation, data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver, and data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver. Data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver were recorded from statistically significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotations. Data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver also were recorded from significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotes. The mechanism of adaptation was based on vitamin D synthesis modulation, melanin upregulation, genetic selections, genetic drift, mating patterns, increased vitamin D sensitivity, interbreeding, and diet.
Studies included in the analysis were placed into 1 of 3 categories: supporting, neutral, and against. Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) criteria were used to classify the level of evidence of each article.4 Each article’s level of evidence was then graded (Table 1). The SORT grading levels were based on quality and evidence type: level 1 signified good-quality, patient-oriented evidence; level 2 signified limited-quality, patient-oriented evidence; and level 3 signified other evidence.4
Results
Article Selection—A total of 229 articles were identified for screening, and 39 studies met inclusion criteria.1-3,5-40 Systematic and retrospective reviews were the most common types of studies. Genomic analysis/sequencing/genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were the most common methods of analysis. Of these 39 articles, 26 were classified as supporting the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis, 10 were classified as neutral, and 3 were classified as against (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as supporting the vitamin D hypothesis, 13 articles were level 1 evidence, 9 were level 2, and 4 were level 3. Key findings supporting the vitamin D hypothesis included genetic natural selection favoring vitamin D synthesis genes at higher latitudes with lower UVR and the skin lightening that occurred to protect against vitamin D deficiency (Table 1). Specific genes supporting these findings included 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), vitamin D receptor (VDR), tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), oculocutaneous albinism type 2 melanosomal transmembrane protein (OCA2), solute carrier family 45 member 2 (SLC45A2), solute carrier family 4 member 5 (SLC24A5), Kit ligand (KITLG), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), and HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (HERC2)(Table 2).

Of the articles classified as being against the vitamin D hypothesis, 1 article was level 1 evidence, 1 was level 2, and 1 was level 3. Key findings refuting the vitamin D hypothesis included similar amounts of vitamin D synthesis in contemporary dark- and light-pigmented individuals, vitamin D–rich diets in the late Paleolithic period and in early agriculturalists, and metabolic conservation being the primary driver (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as neutral to the hypothesis, 7 articles were level 1 evidence and 3 were level 2. Key findings of these articles included genetic selection favoring vitamin D synthesis only for populations at extremely northern latitudes, skin lightening that was sustained in northern latitudes from the neighboring human ancestor the chimpanzee, and evidence for long-term evolutionary pressures and short-term plastic adaptations in vitamin D genes (Table 1).
Comment
The importance of appropriate vitamin D levels is hypothesized as a potent driver in skin lightening because the vitamin is essential for many biochemical processes within the human body. Proper calcification of bones requires activated vitamin D to prevent rickets in childhood. Pelvic deformation in women with rickets can obstruct childbirth in primitive medical environments.15 This direct reproductive impairment suggests a strong selective pressure for skin lightening in populations that migrated northward to enhance vitamin D synthesis.
Of the 39 articles that we reviewed, the majority (n=26 [66.7%]) supported the hypothesis that vitamin D synthesis was the main driver behind skin lightening, whereas 3 (7.7%) did not support the hypothesis and 10 (25.6%) were neutral. Other leading theories explaining skin lightening included the idea that enhanced melanogenesis protected against folate degradation; genetic selection for light-skin alleles due to genetic drift; skin lightening being the result of sexual selection; and a combination of factors, including dietary choices, clothing preferences, and skin permeability barriers.
Articles With Supporting Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—As Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa, migration patterns demonstrated the correlation between distance from the equator and skin pigmentation from natural selection. Individuals with darker skin pigment required higher levels of UVR to synthesize vitamin D. According to Beleza et al,1 as humans migrated to areas of higher latitudes with lower levels of UVR, natural selection favored the development of lighter skin to maximize vitamin D production. Vitamin D is linked to calcium metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to bone malformations and poor immune function.35 Several genes affecting melanogenesis and skin pigment have been found to have geospatial patterns that map to different geographic locations of various populations, indicating how human migration patterns out of Africa created this natural selection for skin lightening. The gene KITLG—associated with lighter skin pigmentation—has been found in high frequencies in both European and East Asian populations and is proposed to have increased in frequency after the migration out of Africa. However, the genes TYRP1, SLC24A5, and SLC45A2 were found at high frequencies only in European populations, and this selection occurred 11,000 to 19,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum (15,000–20,000 years ago), demonstrating the selection for European over East Asian characteristics. During this period, seasonal changes increased the risk for vitamin D deficiency and provided an urgency for selection to a lighter skin pigment.1
The migration of H sapiens to northern latitudes prompted the selection of alleles that would increasevitamin D synthesis to counteract the reduced UV exposure. Genetic analysis studies have found key associations between genes encoding for the metabolism of vitamin D and pigmentation. Among this complex network are the essential downstream enzymes in the melanocortin receptor 1 pathway, including TYR and TYRP1. Forty-six of 960 single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in 29 different genes involved in skin pigmentation that were analyzed in a cohort of 2970 individuals were significantly associated with serum vitamin D levels (P<.05). The exocyst complex component 2 (EXOC2), TYR, and TYRP1 gene variants were shown to have the greatest influence on vitamin D status.9 These data reveal how pigment genotypes are predictive of vitamin D levels and the epistatic potential among many genes in this complex network.
Gene variation plays an important role in vitamin D status when comparing genetic polymorphisms in populations in northern latitudes to African populations. Vitamin D3 precursor availability is decreased by 7-DHCR catalyzing the precursors substrate to cholesterol. In a study using GWAS, it was found that “variations in DHCR7 may aid vitamin D production by conserving cutaneous 7-DHC levels. A high prevalence of DHCR7 variants were found in European and Northeast Asian populations but not in African populations, suggesting that selection occurred for these DHCR7 mutations in populations who migrated to more northern latitudes.5 Multilocus networks have been established between the VDR promotor and skin color genes (Table 2) that exhibit a strong in-Africa vs out-of-Africa frequency pattern. It also has been shown that genetic variation (suggesting a long-term evolutionary inclination) and epigenetic modification (indicative of short-term exposure) of VDR lends support to the vitamin D hypothesis. As latitude decreases, prevalence of VDR FokI (F allele), BsmI (B allele), ApaI (A allele), and TaqI (T allele) also decreases in a linear manner, linking latitude to VDR polymorphisms. Plasma vitamin D levels and photoperiod of conception—UV exposure during the periconceptional period—also were extrapolative of VDR methylation in a study involving 80 participants, where these 2 factors accounted for 17% of variance in methylation.6


Other noteworthy genes included HERC2, which has implications in the expression of OCA2 (melanocyte-specific transporter protein), and IRF4, which encodes for an important enzyme in folate-dependent melanin production. In an Australian cross-sectional study that analyzed vitamin D and pigmentation gene polymorphisms in conjunction with plasma vitamin D levels, the most notable rate of vitamin D loss occurred in individuals with the darkest pigmentation HERC2 (AA) genotype.31 In contrast, the lightest pigmentation HERC2 (GG) genotypes had increased vitamin D3 photosynthesis. Interestingly, the lightest interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) TT genotype and the darkest HERC2 AA genotype, rendering the greatest folate loss and largest synthesis of vitamin D3, were not seen in combination in any of the participants.30 In addition to HERC2, derived alleles from pigment-associated genes SLC24A5*A and SLC45A2*G demonstrated greater frequencies in Europeans (>90%) compared to Africans and East Asians, where the allelic frequencies were either rare or absent.1 This evidence delineates not only the complexity but also the strong relationship between skin pigmentation, latitude, and vitamin D status. The GWAS also have supported this concept. In comparing European populations to African populations, there was a 4-fold increase in the frequencies of “derived alleles of the vitamin D transport protein (GC, rs3755967), the 25(OH)D3 synthesizing enzyme (CYP2R1, rs10741657), VDR (rs2228570 (commonly known as FokI polymorphism), rs1544410 (Bsm1), and rs731236 (Taq1) and the VDR target genes CYP24A1 (rs17216707), CD14 (rs2569190), and CARD9 (rs4077515).”32
Articles With Evidence Against the Vitamin D Theory—This review analyzed the level of support for the theory that vitamin D was the main driver for skin lightening. Although most articles supported this theory, there were articles that listed other plausible counterarguments. Jablonski and Chaplin3 suggested that humans living in higher latitudes compensated for increased demand of vitamin D by placing cultural importance on a diet of vitamin D–rich foods and thus would not have experienced decreased vitamin D levels, which we hypothesize were the driver for skin lightening. Elias et al39 argued that initial pigment dilution may have instead served to improve metabolic conservation, as the authors found no evidence of rickets—the sequelae of vitamin D deficiency—in pre–industrial age human fossils. Elias and Williams38 proposed that differences in skin pigment are due to a more intact skin permeability barrier as “a requirement for life in a desiccating terrestrial environment,” which is seen in darker skin tones compared to lighter skin tones and thus can survive better in warmer climates with less risk of infections or dehydration.
Articles With Neutral Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—Greaves41 argued against the idea that skin evolved to become lighter to protect against vitamin D deficiency. They proposed that the chimpanzee, which is the human’s most closely related species, had light skin covered by hair, and the loss of this hair led to exposed pale skin that created a need for increased melanin production for protection from UVR. Greaves41 stated that the MC1R gene (associated with darker pigmentation) was selected for in African populations, and those with pale skin retained their original pigment as they migrated to higher latitudes. Further research has demonstrated that the genetic natural selection for skin pigment is a complex process that involves multiple gene variants found throughout cultures across the globe.

Conclusion
Skin pigmentation has continuously evolved alongside humans. Genetic selection for lighter skin coincides with a favorable selection for genes involved in vitamin D synthesis as humans migrated to northern latitudes, which enabled humans to produce adequate levels of exogenous vitamin D in low-UVR areas and in turn promoted survival. Early humans without access to supplementation or foods rich in vitamin D acquired vitamin D primarily through sunlight. In comparison to modern society, where vitamin D supplementation is accessible and human lifespans are prolonged, lighter skin tone is now a risk factor for malignant cancers of the skin rather than being a protective adaptation. Current sun behavior recommendations conclude that the body’s need for vitamin D is satisfied by UV exposure to the arms, legs, hands, and/or face for only 5 to 30 minutes between 10
The hypothesis that skin lightening primarily was driven by the need for vitamin D can only be partially supported by our review. Studies have shown that there is a corresponding complex network of genes that determines skin pigmentation as well as vitamin D synthesis and conservation. However, there is sufficient evidence that skin lightening is multifactorial in nature, and vitamin D alone may not be the sole driver. The information in this review can be used by health care providers to educate patients on sun protection, given the lesser threat of severe vitamin D deficiency in developed communities today that have access to adequate nutrition and supplementation.
Skin lightening and its coinciding evolutionary drivers are a rather neglected area of research. Due to heterogeneous cohorts and conservative data analysis, GWAS studies run the risk of type II error, yielding a limitation in our data analysis.9 Furthermore, the data regarding specific time frames in evolutionary skin lightening as well as the intensity of gene polymorphisms are limited.1 Further studies are needed to determine the interconnectedness of the current skin-lightening theories to identify other important factors that may play a role in the process. Determining the key event can help us better understand skin-adaptation mechanisms and create a framework for understanding the vital process involved in adaptation, survival, and disease manifestation in different patient populations.
The risk for developing skin cancer can be somewhat attributed to variations in skin pigmentation. Historically, lighter skin pigmentation has been observed in populations living in higher latitudes and darker pigmentation in populations near the equator. Although skin pigmentation is a conglomeration of genetic and environmental factors, anthropologic studies have demonstrated an association of human skin lightening with historic human migratory patterns.1 It is postulated that migration to latitudes with less UVB light penetration has resulted in a compensatory natural selection of lighter skin types. Furthermore, the driving force behind this migration-associated skin lightening has remained unclear.1
The need for folate metabolism, vitamin D synthesis, and barrier protection, as well as cultural practices, has been postulated as driving factors for skin pigmentation variation. Synthesis of vitamin D is a UV radiation (UVR)–dependent process and has remained a prominent theoretical driver for the basis of evolutionary skin lightening. Vitamin D can be acquired both exogenously or endogenously via dietary supplementation or sunlight; however, historically it has been obtained through UVB exposure primarily. Once UVB is absorbed by the skin, it catalyzes conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which is converted to vitamin D in the kidneys.2,3 It is suggested that lighter skin tones have an advantage over darker skin tones in synthesizing vitamin D at higher latitudes where there is less UVB, thus leading to the adaptation process.1 In this systematic review, we analyzed the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis and assessed the validity of evidence supporting this theory in the literature.
Methods
A search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Reviews database was conducted using the terms evolution, vitamin D, and skin to generate articles published from 2010 to 2022 that evaluated the influence of UVR-dependent production of vitamin D on skin pigmentation through historical migration patterns (Figure). Studies were excluded during an initial screening of abstracts followed by full-text assessment if they only had abstracts and if articles were inaccessible for review or in the form of case reports and commentaries.
The following data were extracted from each included study: reference citation, affiliated institutions of authors, author specialties, journal name, year of publication, study period, type of article, type of study, mechanism of adaptation, data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver, and data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver. Data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver were recorded from statistically significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotations. Data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver also were recorded from significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotes. The mechanism of adaptation was based on vitamin D synthesis modulation, melanin upregulation, genetic selections, genetic drift, mating patterns, increased vitamin D sensitivity, interbreeding, and diet.
Studies included in the analysis were placed into 1 of 3 categories: supporting, neutral, and against. Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) criteria were used to classify the level of evidence of each article.4 Each article’s level of evidence was then graded (Table 1). The SORT grading levels were based on quality and evidence type: level 1 signified good-quality, patient-oriented evidence; level 2 signified limited-quality, patient-oriented evidence; and level 3 signified other evidence.4
Results
Article Selection—A total of 229 articles were identified for screening, and 39 studies met inclusion criteria.1-3,5-40 Systematic and retrospective reviews were the most common types of studies. Genomic analysis/sequencing/genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were the most common methods of analysis. Of these 39 articles, 26 were classified as supporting the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis, 10 were classified as neutral, and 3 were classified as against (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as supporting the vitamin D hypothesis, 13 articles were level 1 evidence, 9 were level 2, and 4 were level 3. Key findings supporting the vitamin D hypothesis included genetic natural selection favoring vitamin D synthesis genes at higher latitudes with lower UVR and the skin lightening that occurred to protect against vitamin D deficiency (Table 1). Specific genes supporting these findings included 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), vitamin D receptor (VDR), tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), oculocutaneous albinism type 2 melanosomal transmembrane protein (OCA2), solute carrier family 45 member 2 (SLC45A2), solute carrier family 4 member 5 (SLC24A5), Kit ligand (KITLG), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), and HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (HERC2)(Table 2).

Of the articles classified as being against the vitamin D hypothesis, 1 article was level 1 evidence, 1 was level 2, and 1 was level 3. Key findings refuting the vitamin D hypothesis included similar amounts of vitamin D synthesis in contemporary dark- and light-pigmented individuals, vitamin D–rich diets in the late Paleolithic period and in early agriculturalists, and metabolic conservation being the primary driver (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as neutral to the hypothesis, 7 articles were level 1 evidence and 3 were level 2. Key findings of these articles included genetic selection favoring vitamin D synthesis only for populations at extremely northern latitudes, skin lightening that was sustained in northern latitudes from the neighboring human ancestor the chimpanzee, and evidence for long-term evolutionary pressures and short-term plastic adaptations in vitamin D genes (Table 1).
Comment
The importance of appropriate vitamin D levels is hypothesized as a potent driver in skin lightening because the vitamin is essential for many biochemical processes within the human body. Proper calcification of bones requires activated vitamin D to prevent rickets in childhood. Pelvic deformation in women with rickets can obstruct childbirth in primitive medical environments.15 This direct reproductive impairment suggests a strong selective pressure for skin lightening in populations that migrated northward to enhance vitamin D synthesis.
Of the 39 articles that we reviewed, the majority (n=26 [66.7%]) supported the hypothesis that vitamin D synthesis was the main driver behind skin lightening, whereas 3 (7.7%) did not support the hypothesis and 10 (25.6%) were neutral. Other leading theories explaining skin lightening included the idea that enhanced melanogenesis protected against folate degradation; genetic selection for light-skin alleles due to genetic drift; skin lightening being the result of sexual selection; and a combination of factors, including dietary choices, clothing preferences, and skin permeability barriers.
Articles With Supporting Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—As Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa, migration patterns demonstrated the correlation between distance from the equator and skin pigmentation from natural selection. Individuals with darker skin pigment required higher levels of UVR to synthesize vitamin D. According to Beleza et al,1 as humans migrated to areas of higher latitudes with lower levels of UVR, natural selection favored the development of lighter skin to maximize vitamin D production. Vitamin D is linked to calcium metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to bone malformations and poor immune function.35 Several genes affecting melanogenesis and skin pigment have been found to have geospatial patterns that map to different geographic locations of various populations, indicating how human migration patterns out of Africa created this natural selection for skin lightening. The gene KITLG—associated with lighter skin pigmentation—has been found in high frequencies in both European and East Asian populations and is proposed to have increased in frequency after the migration out of Africa. However, the genes TYRP1, SLC24A5, and SLC45A2 were found at high frequencies only in European populations, and this selection occurred 11,000 to 19,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum (15,000–20,000 years ago), demonstrating the selection for European over East Asian characteristics. During this period, seasonal changes increased the risk for vitamin D deficiency and provided an urgency for selection to a lighter skin pigment.1
The migration of H sapiens to northern latitudes prompted the selection of alleles that would increasevitamin D synthesis to counteract the reduced UV exposure. Genetic analysis studies have found key associations between genes encoding for the metabolism of vitamin D and pigmentation. Among this complex network are the essential downstream enzymes in the melanocortin receptor 1 pathway, including TYR and TYRP1. Forty-six of 960 single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in 29 different genes involved in skin pigmentation that were analyzed in a cohort of 2970 individuals were significantly associated with serum vitamin D levels (P<.05). The exocyst complex component 2 (EXOC2), TYR, and TYRP1 gene variants were shown to have the greatest influence on vitamin D status.9 These data reveal how pigment genotypes are predictive of vitamin D levels and the epistatic potential among many genes in this complex network.
Gene variation plays an important role in vitamin D status when comparing genetic polymorphisms in populations in northern latitudes to African populations. Vitamin D3 precursor availability is decreased by 7-DHCR catalyzing the precursors substrate to cholesterol. In a study using GWAS, it was found that “variations in DHCR7 may aid vitamin D production by conserving cutaneous 7-DHC levels. A high prevalence of DHCR7 variants were found in European and Northeast Asian populations but not in African populations, suggesting that selection occurred for these DHCR7 mutations in populations who migrated to more northern latitudes.5 Multilocus networks have been established between the VDR promotor and skin color genes (Table 2) that exhibit a strong in-Africa vs out-of-Africa frequency pattern. It also has been shown that genetic variation (suggesting a long-term evolutionary inclination) and epigenetic modification (indicative of short-term exposure) of VDR lends support to the vitamin D hypothesis. As latitude decreases, prevalence of VDR FokI (F allele), BsmI (B allele), ApaI (A allele), and TaqI (T allele) also decreases in a linear manner, linking latitude to VDR polymorphisms. Plasma vitamin D levels and photoperiod of conception—UV exposure during the periconceptional period—also were extrapolative of VDR methylation in a study involving 80 participants, where these 2 factors accounted for 17% of variance in methylation.6


Other noteworthy genes included HERC2, which has implications in the expression of OCA2 (melanocyte-specific transporter protein), and IRF4, which encodes for an important enzyme in folate-dependent melanin production. In an Australian cross-sectional study that analyzed vitamin D and pigmentation gene polymorphisms in conjunction with plasma vitamin D levels, the most notable rate of vitamin D loss occurred in individuals with the darkest pigmentation HERC2 (AA) genotype.31 In contrast, the lightest pigmentation HERC2 (GG) genotypes had increased vitamin D3 photosynthesis. Interestingly, the lightest interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) TT genotype and the darkest HERC2 AA genotype, rendering the greatest folate loss and largest synthesis of vitamin D3, were not seen in combination in any of the participants.30 In addition to HERC2, derived alleles from pigment-associated genes SLC24A5*A and SLC45A2*G demonstrated greater frequencies in Europeans (>90%) compared to Africans and East Asians, where the allelic frequencies were either rare or absent.1 This evidence delineates not only the complexity but also the strong relationship between skin pigmentation, latitude, and vitamin D status. The GWAS also have supported this concept. In comparing European populations to African populations, there was a 4-fold increase in the frequencies of “derived alleles of the vitamin D transport protein (GC, rs3755967), the 25(OH)D3 synthesizing enzyme (CYP2R1, rs10741657), VDR (rs2228570 (commonly known as FokI polymorphism), rs1544410 (Bsm1), and rs731236 (Taq1) and the VDR target genes CYP24A1 (rs17216707), CD14 (rs2569190), and CARD9 (rs4077515).”32
Articles With Evidence Against the Vitamin D Theory—This review analyzed the level of support for the theory that vitamin D was the main driver for skin lightening. Although most articles supported this theory, there were articles that listed other plausible counterarguments. Jablonski and Chaplin3 suggested that humans living in higher latitudes compensated for increased demand of vitamin D by placing cultural importance on a diet of vitamin D–rich foods and thus would not have experienced decreased vitamin D levels, which we hypothesize were the driver for skin lightening. Elias et al39 argued that initial pigment dilution may have instead served to improve metabolic conservation, as the authors found no evidence of rickets—the sequelae of vitamin D deficiency—in pre–industrial age human fossils. Elias and Williams38 proposed that differences in skin pigment are due to a more intact skin permeability barrier as “a requirement for life in a desiccating terrestrial environment,” which is seen in darker skin tones compared to lighter skin tones and thus can survive better in warmer climates with less risk of infections or dehydration.
Articles With Neutral Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—Greaves41 argued against the idea that skin evolved to become lighter to protect against vitamin D deficiency. They proposed that the chimpanzee, which is the human’s most closely related species, had light skin covered by hair, and the loss of this hair led to exposed pale skin that created a need for increased melanin production for protection from UVR. Greaves41 stated that the MC1R gene (associated with darker pigmentation) was selected for in African populations, and those with pale skin retained their original pigment as they migrated to higher latitudes. Further research has demonstrated that the genetic natural selection for skin pigment is a complex process that involves multiple gene variants found throughout cultures across the globe.

Conclusion
Skin pigmentation has continuously evolved alongside humans. Genetic selection for lighter skin coincides with a favorable selection for genes involved in vitamin D synthesis as humans migrated to northern latitudes, which enabled humans to produce adequate levels of exogenous vitamin D in low-UVR areas and in turn promoted survival. Early humans without access to supplementation or foods rich in vitamin D acquired vitamin D primarily through sunlight. In comparison to modern society, where vitamin D supplementation is accessible and human lifespans are prolonged, lighter skin tone is now a risk factor for malignant cancers of the skin rather than being a protective adaptation. Current sun behavior recommendations conclude that the body’s need for vitamin D is satisfied by UV exposure to the arms, legs, hands, and/or face for only 5 to 30 minutes between 10
The hypothesis that skin lightening primarily was driven by the need for vitamin D can only be partially supported by our review. Studies have shown that there is a corresponding complex network of genes that determines skin pigmentation as well as vitamin D synthesis and conservation. However, there is sufficient evidence that skin lightening is multifactorial in nature, and vitamin D alone may not be the sole driver. The information in this review can be used by health care providers to educate patients on sun protection, given the lesser threat of severe vitamin D deficiency in developed communities today that have access to adequate nutrition and supplementation.
Skin lightening and its coinciding evolutionary drivers are a rather neglected area of research. Due to heterogeneous cohorts and conservative data analysis, GWAS studies run the risk of type II error, yielding a limitation in our data analysis.9 Furthermore, the data regarding specific time frames in evolutionary skin lightening as well as the intensity of gene polymorphisms are limited.1 Further studies are needed to determine the interconnectedness of the current skin-lightening theories to identify other important factors that may play a role in the process. Determining the key event can help us better understand skin-adaptation mechanisms and create a framework for understanding the vital process involved in adaptation, survival, and disease manifestation in different patient populations.
- Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, et al. The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:24-35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207
- Carlberg C. Nutrigenomics of vitamin D. Nutrients. 2019;11:676. doi:10.3390/nu11030676
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The roles of vitamin D and cutaneous vitamin D production in human evolution and health. Int J Paleopathol. 2018;23:54-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijpp.2018.01.005
- Weiss BD. SORT: strength of recommendation taxonomy. Fam Med. 2004;36:141-143.
- Wolf ST, Kenney WL. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis in human vascular health. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiology. 2019;317:R491-R501. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2019
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Photobiology of vitamins. Nutr Rev. 2018;76:512-525. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy013
- Hochberg Z, Hochberg I. Evolutionary perspective in rickets and vitamin D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:306. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306
- Rossberg W, Saternus R, Wagenpfeil S, et al. Human pigmentation, cutaneous vitamin D synthesis and evolution: variants of genes (SNPs) involved in skin pigmentation are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1429-1437.
- Saternus R, Pilz S, Gräber S, et al. A closer look at evolution: variants (SNPs) of genes involved in skin pigmentation, including EXOC2, TYR, TYRP1, and DCT, are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Endocrinology. 2015;156:39-47. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1238
- López S, García Ó, Yurrebaso I, et al. The interplay between natural selection and susceptibility to melanoma on allele 374F of SLC45A2 gene in a south European population. PloS One. 2014;9:E104367. doi:1371/journal.pone.0104367
- Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and potential early lifecycle environmental origin of significant adult phenotypes. Evol Med Public Health. 2014;2014:69-91. doi:10.1093/emph/eou013
- Hudjashov G, Villems R, Kivisild T. Global patterns of diversity and selection in human tyrosinase gene. PloS One. 2013;8:E74307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074307
- Khan R, Khan BSR. Diet, disease and pigment variation in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75:363-367. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.033
- Kuan V, Martineau AR, Griffiths CJ, et al. DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to northern latitudes. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:144. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
- Omenn GS. Evolution and public health. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 1):1702-1709. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906198106
- Yuen AWC, Jablonski NG. Vitamin D: in the evolution of human skin colour. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:39-44. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.08.007
- Vieth R. Weaker bones and white skin as adaptions to improve anthropological “fitness” for northern environments. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31:617-624. doi:10.1007/s00198-019-05167-4
- Carlberg C. Vitamin D: a micronutrient regulating genes. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25:1740-1746. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190705193227
- Haddadeen C, Lai C, Cho SY, et al. Variants of the melanocortin‐1 receptor: do they matter clinically? Exp Dermatol. 2015;1:5-9. doi:10.1111/exd.12540
- Yao S, Ambrosone CB. Associations between vitamin D deficiency and risk of aggressive breast cancer in African-American women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;136:337-341. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.010
- Jablonski N. The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. J Royal Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:58-63. doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2012.114
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Hochberg Z, Templeton AR. Evolutionary perspective in skin color, vitamin D and its receptor. Hormones. 2010;9:307-311. doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1281
- Jones P, Lucock M, Veysey M, et al. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis as an evolutionary model for skin pigmentation: an update and integration of current ideas. Nutrients. 2018;10:554. doi:10.3390/nu10050554
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, et al. Women with fair phenotypes seem to confer a survival advantage in a low UV milieu. a nested matched case control study. PloS One. 2020;15:E0228582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228582
- Holick MF. Shedding new light on the role of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: the lncRNA–skin cancer connection. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:391-392. doi:10.1111/exd.12386
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Epidermal pigmentation in the human lineage is an adaptation to ultraviolet radiation. J Hum Evol. 2013;65:671-675. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.06.004
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of skin pigmentation and hair texture in people of African ancestry. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:113-121. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.11.003
- Jablonski NG. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:707-7 doi:10.1111/pcmr.12976
- Lucock MD, Jones PR, Veysey M, et al. Biophysical evidence to support and extend the vitamin D‐folate hypothesis as a paradigm for the evolution of human skin pigmentation. Am J Hum Biol. 2022;34:E23667. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23667
- Missaggia BO, Reales G, Cybis GB, et al. Adaptation and co‐adaptation of skin pigmentation and vitamin D genes in native Americans. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020;184:1060-1077. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31873
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Skin colour and vitamin D: an update. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:864-875. doi:10.1111/exd.14142
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Vitamin D and evolution: pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;173:113595. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.024
- Flegr J, Sýkorová K, Fiala V, et al. Increased 25(OH)D3 level in redheaded people: could redheadedness be an adaptation to temperate climate? Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:598-609. doi:10.1111/exd.14119
- James WPT, Johnson RJ, Speakman JR, et al. Nutrition and its role in human evolution. J Intern Med. 2019;285:533-549. doi:10.1111/joim.12878
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D: beyond metabolism. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:310-322. doi:10.1177/2156587215580491
- Jarrett P, Scragg R. Evolution, prehistory and vitamin D. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:646. doi:10.3390/ijerph17020646
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Re-appraisal of current theories for thedevelopment and loss of epidermal pigmentation in hominins and modern humans. J Hum Evol. 2013;64:687-692. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.003
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Basis for the gain and subsequent dilution of epidermal pigmentation during human evolution: the barrier and metabolic conservation hypotheses revisited. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016;161:189-207. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23030
- Williams JD, Jacobson EL, Kim H, et al. Water soluble vitamins, clinical research and future application. Subcell Biochem. 2011;56:181-197. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_10
- Greaves M. Was skin cancer a selective force for black pigmentation in early hominin evolution [published online February 26, 2014]? Proc Biol Sci. 2014;281:20132955. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2955
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281. doi:10.1056/nejmra070553
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:466-479. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.31
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2014. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/call-to-action-prevent-skin-cancer.pdf
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al, eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/
- Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, et al. The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:24-35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207
- Carlberg C. Nutrigenomics of vitamin D. Nutrients. 2019;11:676. doi:10.3390/nu11030676
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The roles of vitamin D and cutaneous vitamin D production in human evolution and health. Int J Paleopathol. 2018;23:54-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijpp.2018.01.005
- Weiss BD. SORT: strength of recommendation taxonomy. Fam Med. 2004;36:141-143.
- Wolf ST, Kenney WL. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis in human vascular health. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiology. 2019;317:R491-R501. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2019
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Photobiology of vitamins. Nutr Rev. 2018;76:512-525. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy013
- Hochberg Z, Hochberg I. Evolutionary perspective in rickets and vitamin D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:306. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306
- Rossberg W, Saternus R, Wagenpfeil S, et al. Human pigmentation, cutaneous vitamin D synthesis and evolution: variants of genes (SNPs) involved in skin pigmentation are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1429-1437.
- Saternus R, Pilz S, Gräber S, et al. A closer look at evolution: variants (SNPs) of genes involved in skin pigmentation, including EXOC2, TYR, TYRP1, and DCT, are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Endocrinology. 2015;156:39-47. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1238
- López S, García Ó, Yurrebaso I, et al. The interplay between natural selection and susceptibility to melanoma on allele 374F of SLC45A2 gene in a south European population. PloS One. 2014;9:E104367. doi:1371/journal.pone.0104367
- Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and potential early lifecycle environmental origin of significant adult phenotypes. Evol Med Public Health. 2014;2014:69-91. doi:10.1093/emph/eou013
- Hudjashov G, Villems R, Kivisild T. Global patterns of diversity and selection in human tyrosinase gene. PloS One. 2013;8:E74307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074307
- Khan R, Khan BSR. Diet, disease and pigment variation in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75:363-367. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.033
- Kuan V, Martineau AR, Griffiths CJ, et al. DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to northern latitudes. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:144. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
- Omenn GS. Evolution and public health. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 1):1702-1709. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906198106
- Yuen AWC, Jablonski NG. Vitamin D: in the evolution of human skin colour. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:39-44. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.08.007
- Vieth R. Weaker bones and white skin as adaptions to improve anthropological “fitness” for northern environments. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31:617-624. doi:10.1007/s00198-019-05167-4
- Carlberg C. Vitamin D: a micronutrient regulating genes. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25:1740-1746. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190705193227
- Haddadeen C, Lai C, Cho SY, et al. Variants of the melanocortin‐1 receptor: do they matter clinically? Exp Dermatol. 2015;1:5-9. doi:10.1111/exd.12540
- Yao S, Ambrosone CB. Associations between vitamin D deficiency and risk of aggressive breast cancer in African-American women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;136:337-341. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.010
- Jablonski N. The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. J Royal Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:58-63. doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2012.114
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Hochberg Z, Templeton AR. Evolutionary perspective in skin color, vitamin D and its receptor. Hormones. 2010;9:307-311. doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1281
- Jones P, Lucock M, Veysey M, et al. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis as an evolutionary model for skin pigmentation: an update and integration of current ideas. Nutrients. 2018;10:554. doi:10.3390/nu10050554
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, et al. Women with fair phenotypes seem to confer a survival advantage in a low UV milieu. a nested matched case control study. PloS One. 2020;15:E0228582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228582
- Holick MF. Shedding new light on the role of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: the lncRNA–skin cancer connection. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:391-392. doi:10.1111/exd.12386
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Epidermal pigmentation in the human lineage is an adaptation to ultraviolet radiation. J Hum Evol. 2013;65:671-675. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.06.004
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of skin pigmentation and hair texture in people of African ancestry. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:113-121. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.11.003
- Jablonski NG. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:707-7 doi:10.1111/pcmr.12976
- Lucock MD, Jones PR, Veysey M, et al. Biophysical evidence to support and extend the vitamin D‐folate hypothesis as a paradigm for the evolution of human skin pigmentation. Am J Hum Biol. 2022;34:E23667. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23667
- Missaggia BO, Reales G, Cybis GB, et al. Adaptation and co‐adaptation of skin pigmentation and vitamin D genes in native Americans. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020;184:1060-1077. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31873
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Skin colour and vitamin D: an update. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:864-875. doi:10.1111/exd.14142
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Vitamin D and evolution: pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;173:113595. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.024
- Flegr J, Sýkorová K, Fiala V, et al. Increased 25(OH)D3 level in redheaded people: could redheadedness be an adaptation to temperate climate? Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:598-609. doi:10.1111/exd.14119
- James WPT, Johnson RJ, Speakman JR, et al. Nutrition and its role in human evolution. J Intern Med. 2019;285:533-549. doi:10.1111/joim.12878
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D: beyond metabolism. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:310-322. doi:10.1177/2156587215580491
- Jarrett P, Scragg R. Evolution, prehistory and vitamin D. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:646. doi:10.3390/ijerph17020646
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Re-appraisal of current theories for thedevelopment and loss of epidermal pigmentation in hominins and modern humans. J Hum Evol. 2013;64:687-692. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.003
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Basis for the gain and subsequent dilution of epidermal pigmentation during human evolution: the barrier and metabolic conservation hypotheses revisited. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016;161:189-207. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23030
- Williams JD, Jacobson EL, Kim H, et al. Water soluble vitamins, clinical research and future application. Subcell Biochem. 2011;56:181-197. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_10
- Greaves M. Was skin cancer a selective force for black pigmentation in early hominin evolution [published online February 26, 2014]? Proc Biol Sci. 2014;281:20132955. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2955
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281. doi:10.1056/nejmra070553
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:466-479. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.31
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2014. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/call-to-action-prevent-skin-cancer.pdf
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al, eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/
Practice Points
- Sufficient UV radiation exposure is required to synthesize vitamin D, but excess exposure increases skin cancer risk.
- Genes associated with vitamin D production and melanin synthesis form an interconnected network that explains skin tone polymorphisms and their influence on healthy sun behaviors.
- Adaptations in genetics of skin pigmentation and vitamin D metabolism due to anthropologic patterns of migration to northern latitudes may help explain predisposition to dermatologic diseases such as skin cancer.
Chatbots Seem More Empathetic Than Docs in Cancer Discussions
Large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT have shown mixed results in the quality of their responses to consumer questions about cancer.
One recent study found AI chatbots to churn out incomplete, inaccurate, or even nonsensical cancer treatment recommendations, while another found them to generate largely accurate — if technical — responses to the most common cancer questions.
While researchers have seen success with purpose-built chatbots created to address patient concerns about specific cancers, the consensus to date has been that the generalized models like ChatGPT remain works in progress and that physicians should avoid pointing patients to them, for now.
Yet new findings suggest that these chatbots may do better than individual physicians, at least on some measures, when it comes to answering queries about cancer. For research published May 16 in JAMA Oncology (doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0836), David Chen, a medical student at the University of Toronto, and his colleagues, isolated a random sample of 200 questions related to cancer care addressed to doctors on the public online forum Reddit. They then compared responses from oncologists with responses generated by three different AI chatbots. The blinded responses were rated for quality, readability, and empathy by six physicians, including oncologists and palliative and supportive care specialists.
Mr. Chen and colleagues’ research was modeled after a 2023 study that measured the quality of physician responses compared with chatbots for general medicine questions addressed to doctors on Reddit. That study found that the chatbots produced more empathetic-sounding answers, something Mr. Chen’s study also found. : quality, empathy, and readability.
Q&A With Author of New Research
Mr. Chen discussed his new study’s implications during an interview with this news organization.
Question: What is novel about this study?
Mr. Chen: We’ve seen many evaluations of chatbots that test for medical accuracy, but this study occurs in the domain of oncology care, where there are unique psychosocial and emotional considerations that are not precisely reflected in a general medicine setting. In effect, this study is putting these chatbots through a harder challenge.
Question: Why would chatbot responses seem more empathetic than those of physicians?
Mr. Chen: With the physician responses that we observed in our sample data set, we saw that there was very high variation of amount of apparent effort [in the physician responses]. Some physicians would put in a lot of time and effort, thinking through their response, and others wouldn’t do so as much. These chatbots don’t face fatigue the way humans do, or burnout. So they’re able to consistently provide responses with less variation in empathy.
Question: Do chatbots just seem empathetic because they are chattier?
Mr. Chen: We did think of verbosity as a potential confounder in this study. So we set a word count limit for the chatbot responses to keep it in the range of the physician responses. That way, verbosity was no longer a significant factor.
Question: How were quality and empathy measured by the reviewers?
Mr. Chen: For our study we used two teams of readers, each team composed of three physicians. In terms of the actual metrics we used, they were pilot metrics. There are no well-defined measurement scales or checklists that we could use to measure empathy. This is an emerging field of research. So we came up by consensus with our own set of ratings, and we feel that this is an area for the research to define a standardized set of guidelines.
Another novel aspect of this study is that we separated out different dimensions of quality and empathy. A quality response didn’t just mean it was medically accurate — quality also had to do with the focus and completeness of the response.
With empathy there are cognitive and emotional dimensions. Cognitive empathy uses critical thinking to understand the person’s emotions and thoughts and then adjusting a response to fit that. A patient may not want the best medically indicated treatment for their condition, because they want to preserve their quality of life. The chatbot may be able to adjust its recommendation with consideration of some of those humanistic elements that the patient is presenting with.
Emotional empathy is more about being supportive of the patient’s emotions by using expressions like ‘I understand where you’re coming from.’ or, ‘I can see how that makes you feel.’
Question: Why would physicians, not patients, be the best evaluators of empathy?
Mr. Chen: We’re actually very interested in evaluating patient ratings of empathy. We are conducting a follow-up study that evaluates patient ratings of empathy to the same set of chatbot and physician responses,to see if there are differences.
Question: Should cancer patients go ahead and consult chatbots?
Mr. Chen: Although we did observe increases in all of the metrics compared with physicians, this is a very specialized evaluation scenario where we’re using these Reddit questions and responses.
Naturally, we would need to do a trial, a head to head randomized comparison of physicians versus chatbots.
This pilot study does highlight the promising potential of these chatbots to suggest responses. But we can’t fully recommend that they should be used as standalone clinical tools without physicians.
This Q&A was edited for clarity.
Large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT have shown mixed results in the quality of their responses to consumer questions about cancer.
One recent study found AI chatbots to churn out incomplete, inaccurate, or even nonsensical cancer treatment recommendations, while another found them to generate largely accurate — if technical — responses to the most common cancer questions.
While researchers have seen success with purpose-built chatbots created to address patient concerns about specific cancers, the consensus to date has been that the generalized models like ChatGPT remain works in progress and that physicians should avoid pointing patients to them, for now.
Yet new findings suggest that these chatbots may do better than individual physicians, at least on some measures, when it comes to answering queries about cancer. For research published May 16 in JAMA Oncology (doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0836), David Chen, a medical student at the University of Toronto, and his colleagues, isolated a random sample of 200 questions related to cancer care addressed to doctors on the public online forum Reddit. They then compared responses from oncologists with responses generated by three different AI chatbots. The blinded responses were rated for quality, readability, and empathy by six physicians, including oncologists and palliative and supportive care specialists.
Mr. Chen and colleagues’ research was modeled after a 2023 study that measured the quality of physician responses compared with chatbots for general medicine questions addressed to doctors on Reddit. That study found that the chatbots produced more empathetic-sounding answers, something Mr. Chen’s study also found. : quality, empathy, and readability.
Q&A With Author of New Research
Mr. Chen discussed his new study’s implications during an interview with this news organization.
Question: What is novel about this study?
Mr. Chen: We’ve seen many evaluations of chatbots that test for medical accuracy, but this study occurs in the domain of oncology care, where there are unique psychosocial and emotional considerations that are not precisely reflected in a general medicine setting. In effect, this study is putting these chatbots through a harder challenge.
Question: Why would chatbot responses seem more empathetic than those of physicians?
Mr. Chen: With the physician responses that we observed in our sample data set, we saw that there was very high variation of amount of apparent effort [in the physician responses]. Some physicians would put in a lot of time and effort, thinking through their response, and others wouldn’t do so as much. These chatbots don’t face fatigue the way humans do, or burnout. So they’re able to consistently provide responses with less variation in empathy.
Question: Do chatbots just seem empathetic because they are chattier?
Mr. Chen: We did think of verbosity as a potential confounder in this study. So we set a word count limit for the chatbot responses to keep it in the range of the physician responses. That way, verbosity was no longer a significant factor.
Question: How were quality and empathy measured by the reviewers?
Mr. Chen: For our study we used two teams of readers, each team composed of three physicians. In terms of the actual metrics we used, they were pilot metrics. There are no well-defined measurement scales or checklists that we could use to measure empathy. This is an emerging field of research. So we came up by consensus with our own set of ratings, and we feel that this is an area for the research to define a standardized set of guidelines.
Another novel aspect of this study is that we separated out different dimensions of quality and empathy. A quality response didn’t just mean it was medically accurate — quality also had to do with the focus and completeness of the response.
With empathy there are cognitive and emotional dimensions. Cognitive empathy uses critical thinking to understand the person’s emotions and thoughts and then adjusting a response to fit that. A patient may not want the best medically indicated treatment for their condition, because they want to preserve their quality of life. The chatbot may be able to adjust its recommendation with consideration of some of those humanistic elements that the patient is presenting with.
Emotional empathy is more about being supportive of the patient’s emotions by using expressions like ‘I understand where you’re coming from.’ or, ‘I can see how that makes you feel.’
Question: Why would physicians, not patients, be the best evaluators of empathy?
Mr. Chen: We’re actually very interested in evaluating patient ratings of empathy. We are conducting a follow-up study that evaluates patient ratings of empathy to the same set of chatbot and physician responses,to see if there are differences.
Question: Should cancer patients go ahead and consult chatbots?
Mr. Chen: Although we did observe increases in all of the metrics compared with physicians, this is a very specialized evaluation scenario where we’re using these Reddit questions and responses.
Naturally, we would need to do a trial, a head to head randomized comparison of physicians versus chatbots.
This pilot study does highlight the promising potential of these chatbots to suggest responses. But we can’t fully recommend that they should be used as standalone clinical tools without physicians.
This Q&A was edited for clarity.
Large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT have shown mixed results in the quality of their responses to consumer questions about cancer.
One recent study found AI chatbots to churn out incomplete, inaccurate, or even nonsensical cancer treatment recommendations, while another found them to generate largely accurate — if technical — responses to the most common cancer questions.
While researchers have seen success with purpose-built chatbots created to address patient concerns about specific cancers, the consensus to date has been that the generalized models like ChatGPT remain works in progress and that physicians should avoid pointing patients to them, for now.
Yet new findings suggest that these chatbots may do better than individual physicians, at least on some measures, when it comes to answering queries about cancer. For research published May 16 in JAMA Oncology (doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0836), David Chen, a medical student at the University of Toronto, and his colleagues, isolated a random sample of 200 questions related to cancer care addressed to doctors on the public online forum Reddit. They then compared responses from oncologists with responses generated by three different AI chatbots. The blinded responses were rated for quality, readability, and empathy by six physicians, including oncologists and palliative and supportive care specialists.
Mr. Chen and colleagues’ research was modeled after a 2023 study that measured the quality of physician responses compared with chatbots for general medicine questions addressed to doctors on Reddit. That study found that the chatbots produced more empathetic-sounding answers, something Mr. Chen’s study also found. : quality, empathy, and readability.
Q&A With Author of New Research
Mr. Chen discussed his new study’s implications during an interview with this news organization.
Question: What is novel about this study?
Mr. Chen: We’ve seen many evaluations of chatbots that test for medical accuracy, but this study occurs in the domain of oncology care, where there are unique psychosocial and emotional considerations that are not precisely reflected in a general medicine setting. In effect, this study is putting these chatbots through a harder challenge.
Question: Why would chatbot responses seem more empathetic than those of physicians?
Mr. Chen: With the physician responses that we observed in our sample data set, we saw that there was very high variation of amount of apparent effort [in the physician responses]. Some physicians would put in a lot of time and effort, thinking through their response, and others wouldn’t do so as much. These chatbots don’t face fatigue the way humans do, or burnout. So they’re able to consistently provide responses with less variation in empathy.
Question: Do chatbots just seem empathetic because they are chattier?
Mr. Chen: We did think of verbosity as a potential confounder in this study. So we set a word count limit for the chatbot responses to keep it in the range of the physician responses. That way, verbosity was no longer a significant factor.
Question: How were quality and empathy measured by the reviewers?
Mr. Chen: For our study we used two teams of readers, each team composed of three physicians. In terms of the actual metrics we used, they were pilot metrics. There are no well-defined measurement scales or checklists that we could use to measure empathy. This is an emerging field of research. So we came up by consensus with our own set of ratings, and we feel that this is an area for the research to define a standardized set of guidelines.
Another novel aspect of this study is that we separated out different dimensions of quality and empathy. A quality response didn’t just mean it was medically accurate — quality also had to do with the focus and completeness of the response.
With empathy there are cognitive and emotional dimensions. Cognitive empathy uses critical thinking to understand the person’s emotions and thoughts and then adjusting a response to fit that. A patient may not want the best medically indicated treatment for their condition, because they want to preserve their quality of life. The chatbot may be able to adjust its recommendation with consideration of some of those humanistic elements that the patient is presenting with.
Emotional empathy is more about being supportive of the patient’s emotions by using expressions like ‘I understand where you’re coming from.’ or, ‘I can see how that makes you feel.’
Question: Why would physicians, not patients, be the best evaluators of empathy?
Mr. Chen: We’re actually very interested in evaluating patient ratings of empathy. We are conducting a follow-up study that evaluates patient ratings of empathy to the same set of chatbot and physician responses,to see if there are differences.
Question: Should cancer patients go ahead and consult chatbots?
Mr. Chen: Although we did observe increases in all of the metrics compared with physicians, this is a very specialized evaluation scenario where we’re using these Reddit questions and responses.
Naturally, we would need to do a trial, a head to head randomized comparison of physicians versus chatbots.
This pilot study does highlight the promising potential of these chatbots to suggest responses. But we can’t fully recommend that they should be used as standalone clinical tools without physicians.
This Q&A was edited for clarity.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Survey Spotlights Identification of Dermatologic Adverse Events From Cancer Therapies
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Darker Skin Tones Underrepresented on Skin Cancer Education Websites
“Given the known disparities patients with darker skin tones face in terms of increased skin cancer morbidity and mortality, this lack of representation further disadvantages those patients by not providing them with an adequate representation of how skin cancers manifest on their skin tones,” the study’s first author, Alana Sadur, who recently completed her third year at the George Washington School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, said in an interview. “By not having images to refer to, patients are less likely to self-identify and seek treatment for concerning skin lesions.”
For the study, which was published in Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, Ms. Sadur and coauthors evaluated the inclusivity and representation of skin tones in photos of skin cancer on the following patient-facing websites: CDC.gov, NIH.gov, skincancer.org, americancancerfund.org, mayoclinic.org, and cancer.org. The researchers counted each individual person or image showing skin as a separate representation, and three independent reviewers used the 5-color Pantone swatch as described in a dermatology atlas to categorize representations as “lighter-toned skin” (Pantones A-B or lighter) or “darker-toned skin” (Pantones C-E or darker).
Of the 372 total representations identified on the websites, only 49 (13.2%) showed darker skin tones. Of these, 44.9% depicted Pantone C, 34.7% depicted Pantone D, and 20.4% depicted Pantone E. The researchers also found that only 11% of nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSC) and 5.8% of melanoma skin cancers (MSC) were shown on darker skin tones, while no cartoon portrayals of NMSC or MSC included darker skin tones.
In findings related to nondisease representations on the websites, darker skin tones were depicted in just 22.7% of stock photos and 26.1% of website front pages.
The study’s senior author, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, emphasized the need for trusted sources like national organizations and federally funded agencies to be purposeful with their selection of images to “ensure all visitors to the site are represented,” he told this news organization.
“This is very important when dealing with skin cancer as a lack of representation could easily be misinterpreted as epidemiological data, meaning this gap could suggest certain individuals do not get skin cancer because photos in those skin tones are not present,” he added. “This doesn’t even begin to touch upon the diversity of individuals in the stock photos or lack thereof, which can perpetuate the lack of diversity in our specialty. We need to do better.”
The authors reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Given the known disparities patients with darker skin tones face in terms of increased skin cancer morbidity and mortality, this lack of representation further disadvantages those patients by not providing them with an adequate representation of how skin cancers manifest on their skin tones,” the study’s first author, Alana Sadur, who recently completed her third year at the George Washington School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, said in an interview. “By not having images to refer to, patients are less likely to self-identify and seek treatment for concerning skin lesions.”
For the study, which was published in Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, Ms. Sadur and coauthors evaluated the inclusivity and representation of skin tones in photos of skin cancer on the following patient-facing websites: CDC.gov, NIH.gov, skincancer.org, americancancerfund.org, mayoclinic.org, and cancer.org. The researchers counted each individual person or image showing skin as a separate representation, and three independent reviewers used the 5-color Pantone swatch as described in a dermatology atlas to categorize representations as “lighter-toned skin” (Pantones A-B or lighter) or “darker-toned skin” (Pantones C-E or darker).
Of the 372 total representations identified on the websites, only 49 (13.2%) showed darker skin tones. Of these, 44.9% depicted Pantone C, 34.7% depicted Pantone D, and 20.4% depicted Pantone E. The researchers also found that only 11% of nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSC) and 5.8% of melanoma skin cancers (MSC) were shown on darker skin tones, while no cartoon portrayals of NMSC or MSC included darker skin tones.
In findings related to nondisease representations on the websites, darker skin tones were depicted in just 22.7% of stock photos and 26.1% of website front pages.
The study’s senior author, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, emphasized the need for trusted sources like national organizations and federally funded agencies to be purposeful with their selection of images to “ensure all visitors to the site are represented,” he told this news organization.
“This is very important when dealing with skin cancer as a lack of representation could easily be misinterpreted as epidemiological data, meaning this gap could suggest certain individuals do not get skin cancer because photos in those skin tones are not present,” he added. “This doesn’t even begin to touch upon the diversity of individuals in the stock photos or lack thereof, which can perpetuate the lack of diversity in our specialty. We need to do better.”
The authors reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Given the known disparities patients with darker skin tones face in terms of increased skin cancer morbidity and mortality, this lack of representation further disadvantages those patients by not providing them with an adequate representation of how skin cancers manifest on their skin tones,” the study’s first author, Alana Sadur, who recently completed her third year at the George Washington School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, said in an interview. “By not having images to refer to, patients are less likely to self-identify and seek treatment for concerning skin lesions.”
For the study, which was published in Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, Ms. Sadur and coauthors evaluated the inclusivity and representation of skin tones in photos of skin cancer on the following patient-facing websites: CDC.gov, NIH.gov, skincancer.org, americancancerfund.org, mayoclinic.org, and cancer.org. The researchers counted each individual person or image showing skin as a separate representation, and three independent reviewers used the 5-color Pantone swatch as described in a dermatology atlas to categorize representations as “lighter-toned skin” (Pantones A-B or lighter) or “darker-toned skin” (Pantones C-E or darker).
Of the 372 total representations identified on the websites, only 49 (13.2%) showed darker skin tones. Of these, 44.9% depicted Pantone C, 34.7% depicted Pantone D, and 20.4% depicted Pantone E. The researchers also found that only 11% of nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSC) and 5.8% of melanoma skin cancers (MSC) were shown on darker skin tones, while no cartoon portrayals of NMSC or MSC included darker skin tones.
In findings related to nondisease representations on the websites, darker skin tones were depicted in just 22.7% of stock photos and 26.1% of website front pages.
The study’s senior author, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, emphasized the need for trusted sources like national organizations and federally funded agencies to be purposeful with their selection of images to “ensure all visitors to the site are represented,” he told this news organization.
“This is very important when dealing with skin cancer as a lack of representation could easily be misinterpreted as epidemiological data, meaning this gap could suggest certain individuals do not get skin cancer because photos in those skin tones are not present,” he added. “This doesn’t even begin to touch upon the diversity of individuals in the stock photos or lack thereof, which can perpetuate the lack of diversity in our specialty. We need to do better.”
The authors reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF DRUGS IN DERMATOLOGY
New mRNA Vaccines in Development for Cancer and Infections
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can a Risk Score Predict Kidney Injury After Cisplatin?
Cisplatin is a preferred treatment for a wide range of cancers, including breast, head and neck, lung, ovary, and more. However, its side effects — particularly nephrotoxicity — can be severe. Kidney injury on cisplatin is associated with higher mortality and can jeopardize a patient’s eligibility for other therapies.
Now, in a large study using data from six US cancer centers, researchers have developed a risk algorithm to predict acute kidney injury (AKI) after cisplatin administration.
A risk prediction calculator based on the algorithm is available online for patients and providers to determine an individual patient›s risk for kidney injury from cisplatin using readily available clinical data.
Other risk scores and risk prediction models have been developed to help clinicians assess in advance whether a patient might develop AKI after receiving cisplatin, so that more careful monitoring, dose adjustments, or an alternative treatment, if available, might be considered.
However, previous models were limited by factors such as small sample sizes, lack of external validation, older data, and liberal definitions of AKI, said Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, director of onco-nephrology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, director of clinical and translational research in AKI, Division of Renal Medicine, BWH, Boston.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf believe their risk score for predicting severe AKI after intravenous (IV) cisplatin, published online in The BMJ, is “more accurate and generalizable than prior models for several reasons,” they told this news organization in a joint email.
“First, we externally validated our findings across cancer centers other than the one where it was developed,” they said. “Second, we focused on moderate to severe kidney injury, the most clinically relevant form of kidney damage, whereas prior models examined more mild forms of kidney injury. Third, we collected data on nearly 25,000 patients receiving their first dose of IV cisplatin, which is larger than all previous studies combined.”
‘Herculean Effort’
“We conceived of this study back in 2018, contacted collaborators at each participating cancer center, and had numerous meetings to try to gather granular data on patients treated with their first dose of intravenous (IV) cisplatin,” Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf explained. They also incorporated patient feedback from focus groups and surveys.
“This was truly a Herculean effort that involved physicians, programmers, research coordinators, and patients,” they said.
The multicenter study included 24,717 patients — 11,766 in the derivation cohort and 12,951 in the validation cohort. Overall, the median age was about 60 years, about 58% were men, and about 78% were White.
The primary outcome was cisplatin-induced AKI (CP-AKI), defined as a twofold or greater increase in serum creatinine or kidney replacement therapy within 14 days of a first dose of IV cisplatin.
Their simple risk score consisting of nine covariates — age, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin level, white blood cell count, platelet count, serum albumin level, serum magnesium level, and cisplatin dose — predicted a higher risk for CP-AKI in both cohorts.
Notably, adding serum creatinine to the model did not change the area under the curve, and therefore, serum creatinine, though also an independent risk factor for CP-AKI, was not included in the score.
Patients in the highest risk category had 24-fold higher odds of CP-AKI in the derivation cohort and close to 18-fold higher odds in the validation cohort than those in the lowest risk category.
The primary model had a C statistic of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.73-0.76) and showed better discrimination for CP-AKI than previously published models, for which the C statistics ranged from 0.60 to 0.68. The first author of a paper on an earlier model, Shveta Motwani, MD, MMSc, of BWH and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is also a coauthor of the new study.
Greater severity of CP-AKI was associated with shorter 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.63; 95% CI, 3.56-6.02) for stage III CP-AKI vs no CP-AKI.
‘Definitive Work’
Joel M. Topf, MD, a nephrologist with expertise in chronic kidney disease in Detroit, who wasn’t involved in the development of the risk score, called the study “a definitive work on an important concept in oncology and nephrology.”
“While this is not the first attempt to devise a risk score, it is by far the biggest,” he told this news organization. Furthermore, the authors “used a diverse population, recruiting patients with a variety of cancers (previous attempts had often used a homogenous diagnosis, putting into question how generalizable the results were) from six different cancer centers.”
In addition, he said, “The authors did not restrict patients with chronic kidney disease or other significant comorbidities and used the geographic diversity to produce a cohort that has an age, gender, racial, and ethnic distribution, which is more representative of the US than previous, single-center attempts to risk score patients.”
An earlier model used the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus definition of AKI of an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL, he noted. “While a sensitive definition of AKI, it captures mild, hemodynamic increases in creatinine of questionable significance,” he said.
By contrast, the new score uses KDIGO stage II and above to define AKI. “This is a better choice, as we do not want to dissuade patients and doctors from choosing chemotherapy due to a fear of insignificant kidney damage,” he said.
All that said, Dr. Topf noted that neither the current score nor the earlier model included serum creatinine. “This is curious to me and may represent the small number of patients with representative elevated creatinine in the derivation cohort (only 1.3% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 45).”
“Since the cohort is made up of people who received cis-platinum, the low prevalence of eGFRs < 45 may be due to physicians steering away from cis-platinum in this group,” he suggested. “It would be unfortunate if this risk score gave an unintentional ‘green light’ to these patients, exposing them to predictable harm.”
‘Certainly Useful’
Anushree Shirali, MD, an associate professor in the Section of Nephrology and consulting physician, Yale Onco-Nephrology, Yale School of Medicine, in New Haven, Connecticut, said that having a prediction score for which patients are more likely to develop AKI after a single dose of cisplatin would be helpful for oncologists, as well as nephrologists.
As a nephrologist, Dr. Shirali mostly sees patients who already have AKI, she told this news organization. But there are circumstances in which the tool could still be helpful.
“Let’s say someone has abnormal kidney function at baseline — ie, creatinine is higher than the normal range — and they were on dialysis 5 years ago for something else, and now, they have cancer and may be given cisplatin. They worry about their chances of getting AKI and needing dialysis again,” she said. “That’s just one scenario in which I might be asked to answer that question and the tool would certainly be useful.”
Other scenarios could include someone who has just one kidney because they donated a kidney for transplant years ago, and now, they have a malignancy and wonder what their actual risk is of getting kidney issues on cisplatin.
Oncologists could use the tool to determine whether a patient should be treated with cisplatin, or if they’re at high risk, whether an alternative that’s not nephrotoxic might be used. By contrast, “if somebody’s low risk and an oncologist thinks cisplatin is the best agent they have, then they might want to go ahead and use it,” Dr. Shirali said.
Future research could take into consideration that CP-AKI is dose dependent, she suggested, because a prediction score that included the number of cisplatin doses could be even more helpful to determine risk. And, even though the derivation and validation cohorts for the new tool are representative of the US population, additional research should also include more racial/ethnic diversity, she said.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf hope their tool “will be utilized immediately by patients and providers to help predict an individual’s risk of cisplatin-associated kidney damage. It is easy to use, available for free online, and incorporates readily available clinical variables.”
If a patient is at high risk, the clinical team can consider preventive measures such as administering more IV fluids before receiving cisplatin or monitoring kidney function more closely afterward, they suggested.
Dr. Gupta reported research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. She also reported research funding from BTG International, GE HealthCare, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. She is a member of GlaxoSmithKline’s Global Anemia Council, a consultant for Secretome and Proletariat Therapeutics, and founder and president emeritus of the American Society of Onconephrology (unpaid). Dr. Leaf is supported by NIH grants, reported research support from BioPorto, BTG International, and Metro International Biotech, and has served as a consultant. Dr. Topf reported an ownership stake in a few DaVita-run dialysis clinics. He also runs a vascular access center and has participated in advisory boards with Cara Therapeutics, Vifor, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Renibus Therapeutics, Travere Therapeutics, and GlaxoSmithKline. He is president of NephJC, a nonprofit educational organization with no industry support. Dr. Shirali declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cisplatin is a preferred treatment for a wide range of cancers, including breast, head and neck, lung, ovary, and more. However, its side effects — particularly nephrotoxicity — can be severe. Kidney injury on cisplatin is associated with higher mortality and can jeopardize a patient’s eligibility for other therapies.
Now, in a large study using data from six US cancer centers, researchers have developed a risk algorithm to predict acute kidney injury (AKI) after cisplatin administration.
A risk prediction calculator based on the algorithm is available online for patients and providers to determine an individual patient›s risk for kidney injury from cisplatin using readily available clinical data.
Other risk scores and risk prediction models have been developed to help clinicians assess in advance whether a patient might develop AKI after receiving cisplatin, so that more careful monitoring, dose adjustments, or an alternative treatment, if available, might be considered.
However, previous models were limited by factors such as small sample sizes, lack of external validation, older data, and liberal definitions of AKI, said Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, director of onco-nephrology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, director of clinical and translational research in AKI, Division of Renal Medicine, BWH, Boston.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf believe their risk score for predicting severe AKI after intravenous (IV) cisplatin, published online in The BMJ, is “more accurate and generalizable than prior models for several reasons,” they told this news organization in a joint email.
“First, we externally validated our findings across cancer centers other than the one where it was developed,” they said. “Second, we focused on moderate to severe kidney injury, the most clinically relevant form of kidney damage, whereas prior models examined more mild forms of kidney injury. Third, we collected data on nearly 25,000 patients receiving their first dose of IV cisplatin, which is larger than all previous studies combined.”
‘Herculean Effort’
“We conceived of this study back in 2018, contacted collaborators at each participating cancer center, and had numerous meetings to try to gather granular data on patients treated with their first dose of intravenous (IV) cisplatin,” Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf explained. They also incorporated patient feedback from focus groups and surveys.
“This was truly a Herculean effort that involved physicians, programmers, research coordinators, and patients,” they said.
The multicenter study included 24,717 patients — 11,766 in the derivation cohort and 12,951 in the validation cohort. Overall, the median age was about 60 years, about 58% were men, and about 78% were White.
The primary outcome was cisplatin-induced AKI (CP-AKI), defined as a twofold or greater increase in serum creatinine or kidney replacement therapy within 14 days of a first dose of IV cisplatin.
Their simple risk score consisting of nine covariates — age, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin level, white blood cell count, platelet count, serum albumin level, serum magnesium level, and cisplatin dose — predicted a higher risk for CP-AKI in both cohorts.
Notably, adding serum creatinine to the model did not change the area under the curve, and therefore, serum creatinine, though also an independent risk factor for CP-AKI, was not included in the score.
Patients in the highest risk category had 24-fold higher odds of CP-AKI in the derivation cohort and close to 18-fold higher odds in the validation cohort than those in the lowest risk category.
The primary model had a C statistic of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.73-0.76) and showed better discrimination for CP-AKI than previously published models, for which the C statistics ranged from 0.60 to 0.68. The first author of a paper on an earlier model, Shveta Motwani, MD, MMSc, of BWH and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is also a coauthor of the new study.
Greater severity of CP-AKI was associated with shorter 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.63; 95% CI, 3.56-6.02) for stage III CP-AKI vs no CP-AKI.
‘Definitive Work’
Joel M. Topf, MD, a nephrologist with expertise in chronic kidney disease in Detroit, who wasn’t involved in the development of the risk score, called the study “a definitive work on an important concept in oncology and nephrology.”
“While this is not the first attempt to devise a risk score, it is by far the biggest,” he told this news organization. Furthermore, the authors “used a diverse population, recruiting patients with a variety of cancers (previous attempts had often used a homogenous diagnosis, putting into question how generalizable the results were) from six different cancer centers.”
In addition, he said, “The authors did not restrict patients with chronic kidney disease or other significant comorbidities and used the geographic diversity to produce a cohort that has an age, gender, racial, and ethnic distribution, which is more representative of the US than previous, single-center attempts to risk score patients.”
An earlier model used the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus definition of AKI of an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL, he noted. “While a sensitive definition of AKI, it captures mild, hemodynamic increases in creatinine of questionable significance,” he said.
By contrast, the new score uses KDIGO stage II and above to define AKI. “This is a better choice, as we do not want to dissuade patients and doctors from choosing chemotherapy due to a fear of insignificant kidney damage,” he said.
All that said, Dr. Topf noted that neither the current score nor the earlier model included serum creatinine. “This is curious to me and may represent the small number of patients with representative elevated creatinine in the derivation cohort (only 1.3% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 45).”
“Since the cohort is made up of people who received cis-platinum, the low prevalence of eGFRs < 45 may be due to physicians steering away from cis-platinum in this group,” he suggested. “It would be unfortunate if this risk score gave an unintentional ‘green light’ to these patients, exposing them to predictable harm.”
‘Certainly Useful’
Anushree Shirali, MD, an associate professor in the Section of Nephrology and consulting physician, Yale Onco-Nephrology, Yale School of Medicine, in New Haven, Connecticut, said that having a prediction score for which patients are more likely to develop AKI after a single dose of cisplatin would be helpful for oncologists, as well as nephrologists.
As a nephrologist, Dr. Shirali mostly sees patients who already have AKI, she told this news organization. But there are circumstances in which the tool could still be helpful.
“Let’s say someone has abnormal kidney function at baseline — ie, creatinine is higher than the normal range — and they were on dialysis 5 years ago for something else, and now, they have cancer and may be given cisplatin. They worry about their chances of getting AKI and needing dialysis again,” she said. “That’s just one scenario in which I might be asked to answer that question and the tool would certainly be useful.”
Other scenarios could include someone who has just one kidney because they donated a kidney for transplant years ago, and now, they have a malignancy and wonder what their actual risk is of getting kidney issues on cisplatin.
Oncologists could use the tool to determine whether a patient should be treated with cisplatin, or if they’re at high risk, whether an alternative that’s not nephrotoxic might be used. By contrast, “if somebody’s low risk and an oncologist thinks cisplatin is the best agent they have, then they might want to go ahead and use it,” Dr. Shirali said.
Future research could take into consideration that CP-AKI is dose dependent, she suggested, because a prediction score that included the number of cisplatin doses could be even more helpful to determine risk. And, even though the derivation and validation cohorts for the new tool are representative of the US population, additional research should also include more racial/ethnic diversity, she said.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf hope their tool “will be utilized immediately by patients and providers to help predict an individual’s risk of cisplatin-associated kidney damage. It is easy to use, available for free online, and incorporates readily available clinical variables.”
If a patient is at high risk, the clinical team can consider preventive measures such as administering more IV fluids before receiving cisplatin or monitoring kidney function more closely afterward, they suggested.
Dr. Gupta reported research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. She also reported research funding from BTG International, GE HealthCare, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. She is a member of GlaxoSmithKline’s Global Anemia Council, a consultant for Secretome and Proletariat Therapeutics, and founder and president emeritus of the American Society of Onconephrology (unpaid). Dr. Leaf is supported by NIH grants, reported research support from BioPorto, BTG International, and Metro International Biotech, and has served as a consultant. Dr. Topf reported an ownership stake in a few DaVita-run dialysis clinics. He also runs a vascular access center and has participated in advisory boards with Cara Therapeutics, Vifor, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Renibus Therapeutics, Travere Therapeutics, and GlaxoSmithKline. He is president of NephJC, a nonprofit educational organization with no industry support. Dr. Shirali declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cisplatin is a preferred treatment for a wide range of cancers, including breast, head and neck, lung, ovary, and more. However, its side effects — particularly nephrotoxicity — can be severe. Kidney injury on cisplatin is associated with higher mortality and can jeopardize a patient’s eligibility for other therapies.
Now, in a large study using data from six US cancer centers, researchers have developed a risk algorithm to predict acute kidney injury (AKI) after cisplatin administration.
A risk prediction calculator based on the algorithm is available online for patients and providers to determine an individual patient›s risk for kidney injury from cisplatin using readily available clinical data.
Other risk scores and risk prediction models have been developed to help clinicians assess in advance whether a patient might develop AKI after receiving cisplatin, so that more careful monitoring, dose adjustments, or an alternative treatment, if available, might be considered.
However, previous models were limited by factors such as small sample sizes, lack of external validation, older data, and liberal definitions of AKI, said Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, director of onco-nephrology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, director of clinical and translational research in AKI, Division of Renal Medicine, BWH, Boston.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf believe their risk score for predicting severe AKI after intravenous (IV) cisplatin, published online in The BMJ, is “more accurate and generalizable than prior models for several reasons,” they told this news organization in a joint email.
“First, we externally validated our findings across cancer centers other than the one where it was developed,” they said. “Second, we focused on moderate to severe kidney injury, the most clinically relevant form of kidney damage, whereas prior models examined more mild forms of kidney injury. Third, we collected data on nearly 25,000 patients receiving their first dose of IV cisplatin, which is larger than all previous studies combined.”
‘Herculean Effort’
“We conceived of this study back in 2018, contacted collaborators at each participating cancer center, and had numerous meetings to try to gather granular data on patients treated with their first dose of intravenous (IV) cisplatin,” Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf explained. They also incorporated patient feedback from focus groups and surveys.
“This was truly a Herculean effort that involved physicians, programmers, research coordinators, and patients,” they said.
The multicenter study included 24,717 patients — 11,766 in the derivation cohort and 12,951 in the validation cohort. Overall, the median age was about 60 years, about 58% were men, and about 78% were White.
The primary outcome was cisplatin-induced AKI (CP-AKI), defined as a twofold or greater increase in serum creatinine or kidney replacement therapy within 14 days of a first dose of IV cisplatin.
Their simple risk score consisting of nine covariates — age, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin level, white blood cell count, platelet count, serum albumin level, serum magnesium level, and cisplatin dose — predicted a higher risk for CP-AKI in both cohorts.
Notably, adding serum creatinine to the model did not change the area under the curve, and therefore, serum creatinine, though also an independent risk factor for CP-AKI, was not included in the score.
Patients in the highest risk category had 24-fold higher odds of CP-AKI in the derivation cohort and close to 18-fold higher odds in the validation cohort than those in the lowest risk category.
The primary model had a C statistic of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.73-0.76) and showed better discrimination for CP-AKI than previously published models, for which the C statistics ranged from 0.60 to 0.68. The first author of a paper on an earlier model, Shveta Motwani, MD, MMSc, of BWH and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is also a coauthor of the new study.
Greater severity of CP-AKI was associated with shorter 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.63; 95% CI, 3.56-6.02) for stage III CP-AKI vs no CP-AKI.
‘Definitive Work’
Joel M. Topf, MD, a nephrologist with expertise in chronic kidney disease in Detroit, who wasn’t involved in the development of the risk score, called the study “a definitive work on an important concept in oncology and nephrology.”
“While this is not the first attempt to devise a risk score, it is by far the biggest,” he told this news organization. Furthermore, the authors “used a diverse population, recruiting patients with a variety of cancers (previous attempts had often used a homogenous diagnosis, putting into question how generalizable the results were) from six different cancer centers.”
In addition, he said, “The authors did not restrict patients with chronic kidney disease or other significant comorbidities and used the geographic diversity to produce a cohort that has an age, gender, racial, and ethnic distribution, which is more representative of the US than previous, single-center attempts to risk score patients.”
An earlier model used the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus definition of AKI of an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL, he noted. “While a sensitive definition of AKI, it captures mild, hemodynamic increases in creatinine of questionable significance,” he said.
By contrast, the new score uses KDIGO stage II and above to define AKI. “This is a better choice, as we do not want to dissuade patients and doctors from choosing chemotherapy due to a fear of insignificant kidney damage,” he said.
All that said, Dr. Topf noted that neither the current score nor the earlier model included serum creatinine. “This is curious to me and may represent the small number of patients with representative elevated creatinine in the derivation cohort (only 1.3% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 45).”
“Since the cohort is made up of people who received cis-platinum, the low prevalence of eGFRs < 45 may be due to physicians steering away from cis-platinum in this group,” he suggested. “It would be unfortunate if this risk score gave an unintentional ‘green light’ to these patients, exposing them to predictable harm.”
‘Certainly Useful’
Anushree Shirali, MD, an associate professor in the Section of Nephrology and consulting physician, Yale Onco-Nephrology, Yale School of Medicine, in New Haven, Connecticut, said that having a prediction score for which patients are more likely to develop AKI after a single dose of cisplatin would be helpful for oncologists, as well as nephrologists.
As a nephrologist, Dr. Shirali mostly sees patients who already have AKI, she told this news organization. But there are circumstances in which the tool could still be helpful.
“Let’s say someone has abnormal kidney function at baseline — ie, creatinine is higher than the normal range — and they were on dialysis 5 years ago for something else, and now, they have cancer and may be given cisplatin. They worry about their chances of getting AKI and needing dialysis again,” she said. “That’s just one scenario in which I might be asked to answer that question and the tool would certainly be useful.”
Other scenarios could include someone who has just one kidney because they donated a kidney for transplant years ago, and now, they have a malignancy and wonder what their actual risk is of getting kidney issues on cisplatin.
Oncologists could use the tool to determine whether a patient should be treated with cisplatin, or if they’re at high risk, whether an alternative that’s not nephrotoxic might be used. By contrast, “if somebody’s low risk and an oncologist thinks cisplatin is the best agent they have, then they might want to go ahead and use it,” Dr. Shirali said.
Future research could take into consideration that CP-AKI is dose dependent, she suggested, because a prediction score that included the number of cisplatin doses could be even more helpful to determine risk. And, even though the derivation and validation cohorts for the new tool are representative of the US population, additional research should also include more racial/ethnic diversity, she said.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf hope their tool “will be utilized immediately by patients and providers to help predict an individual’s risk of cisplatin-associated kidney damage. It is easy to use, available for free online, and incorporates readily available clinical variables.”
If a patient is at high risk, the clinical team can consider preventive measures such as administering more IV fluids before receiving cisplatin or monitoring kidney function more closely afterward, they suggested.
Dr. Gupta reported research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. She also reported research funding from BTG International, GE HealthCare, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. She is a member of GlaxoSmithKline’s Global Anemia Council, a consultant for Secretome and Proletariat Therapeutics, and founder and president emeritus of the American Society of Onconephrology (unpaid). Dr. Leaf is supported by NIH grants, reported research support from BioPorto, BTG International, and Metro International Biotech, and has served as a consultant. Dr. Topf reported an ownership stake in a few DaVita-run dialysis clinics. He also runs a vascular access center and has participated in advisory boards with Cara Therapeutics, Vifor, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Renibus Therapeutics, Travere Therapeutics, and GlaxoSmithKline. He is president of NephJC, a nonprofit educational organization with no industry support. Dr. Shirali declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BMJ

