User login
Mental health risks higher among young people with IBD
, a new U.K. study suggests.
The retrospective, observational study of young people with IBD versus those without assessed the incidence of a wide range of mental health conditions in people aged 5-25 years.
“Anxiety and depression will not be a surprise to most of us. But we also saw changes for eating disorders, PTSD, and sleep changes,” said Richard K. Russell, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist at the Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh.
Dr. Russell presented the research at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, held in Copenhagen and virtually.
The findings indicate an unmet need for mental health care for young patients with IBD, he said. “All of us at ECCO need to address this gap.”
Key findings
Dr. Russell and colleagues identified 3,898 young people diagnosed with IBD in the 10-year period Jan. 1, 2010, through Jan. 1, 2020, using the Optimum Patient Care Research Database, which includes de-identified data from more than 1,000 general practices across the United Kingdom. They used propensity score matching to create a control group of 15,571 people without IBD, controlling for age, sex, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and health conditions other than IBD.
Median follow-up was about 3 years.
The cumulative lifetime risk for developing any mental health condition by age 25 was 31.1% in the IBD group versus 25.1% in controls, a statistically significant difference.
Compared with the control group, the people with incident IBD were significantly more likely to develop the following:
- PTSD.
- Eating disorders.
- Self-harm.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Depression.
- Anxiety disorder.
- ‘Any mental health condition.’
Those most are risk included males overall, and specifically boys aged 12-17 years. Those with Crohn’s disease versus other types of IBD were also most at risk.
In a subgroup analysis, presented as a poster at the meeting, Dr. Russell and colleagues also found that mental health comorbidity in children and young adults with IBD is associated with increased IBD symptoms and health care utilization, as well as time off work.
Children and young adults with both IBD and mental health conditions should be monitored and receive appropriate mental health support as part of their multidisciplinary care, Dr. Russell said.
Dr. Russell added that the study period ended a few months before the COVID-19 pandemic began, so the research does not reflect its impact on mental health in the study population.
“The number of children and young adults we’re seeing in our clinic with mental health issues has rocketed through the roof because of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Russell suggested that the organization create a psychology subgroup called Proactive Psychologists of ECCO, or Prosecco for short.
Clinical implications
The study is important for highlighting the increased burden of mental health problems in young people with IBD, said session comoderator Nick Kennedy, MD, a consultant gastroenterologist and chief research information officer with the Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust in England.
Dr. Kennedy, who was not affiliated with the research, is also supportive of the idea of a psychological subgroup within ECCO.
The peak age for developing mental health disorders found by the study (12-17 years) “is a unique and very sensitive time,” said Sara Mesilhy, MBBS, a gastroenterologist with the Royal College of Physicians in London.
“These results highlight the need for development of early screening psychiatric programs starting from time of diagnosis and continuing on periodic intervals to offer the best management plan for IBD patients, especially those with childhood-onset IBD,” said Dr. Mesilhy, who was not affiliated with the research.
Such programs would “improve the patient’s quality of life, protecting them from a lot of suffering and preventing the bad sequelae for these disorders,” said Dr. Mesilhy. “Moreover, we still need further studies to identify the most efficient monitoring and treatment protocols.”
Dr. Kennedy applauded the researchers for conducting a population-based study because it ensured an adequate cohort size and maximized identification of mental health disorders.
“It was interesting to see that there were a range of conditions where risk was increased, and that males with IBD were at particularly increased risk,” he added.
Researchers’ use of coded primary care data was a study limitation, but it was “appropriately acknowledged by the presenter,” Dr. Kennedy said.
The study was supported by Pfizer. Dr. Russell disclosed he is a consultant and member of a speakers’ bureau for Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Kennedy and Dr. Mesilhy report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new U.K. study suggests.
The retrospective, observational study of young people with IBD versus those without assessed the incidence of a wide range of mental health conditions in people aged 5-25 years.
“Anxiety and depression will not be a surprise to most of us. But we also saw changes for eating disorders, PTSD, and sleep changes,” said Richard K. Russell, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist at the Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh.
Dr. Russell presented the research at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, held in Copenhagen and virtually.
The findings indicate an unmet need for mental health care for young patients with IBD, he said. “All of us at ECCO need to address this gap.”
Key findings
Dr. Russell and colleagues identified 3,898 young people diagnosed with IBD in the 10-year period Jan. 1, 2010, through Jan. 1, 2020, using the Optimum Patient Care Research Database, which includes de-identified data from more than 1,000 general practices across the United Kingdom. They used propensity score matching to create a control group of 15,571 people without IBD, controlling for age, sex, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and health conditions other than IBD.
Median follow-up was about 3 years.
The cumulative lifetime risk for developing any mental health condition by age 25 was 31.1% in the IBD group versus 25.1% in controls, a statistically significant difference.
Compared with the control group, the people with incident IBD were significantly more likely to develop the following:
- PTSD.
- Eating disorders.
- Self-harm.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Depression.
- Anxiety disorder.
- ‘Any mental health condition.’
Those most are risk included males overall, and specifically boys aged 12-17 years. Those with Crohn’s disease versus other types of IBD were also most at risk.
In a subgroup analysis, presented as a poster at the meeting, Dr. Russell and colleagues also found that mental health comorbidity in children and young adults with IBD is associated with increased IBD symptoms and health care utilization, as well as time off work.
Children and young adults with both IBD and mental health conditions should be monitored and receive appropriate mental health support as part of their multidisciplinary care, Dr. Russell said.
Dr. Russell added that the study period ended a few months before the COVID-19 pandemic began, so the research does not reflect its impact on mental health in the study population.
“The number of children and young adults we’re seeing in our clinic with mental health issues has rocketed through the roof because of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Russell suggested that the organization create a psychology subgroup called Proactive Psychologists of ECCO, or Prosecco for short.
Clinical implications
The study is important for highlighting the increased burden of mental health problems in young people with IBD, said session comoderator Nick Kennedy, MD, a consultant gastroenterologist and chief research information officer with the Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust in England.
Dr. Kennedy, who was not affiliated with the research, is also supportive of the idea of a psychological subgroup within ECCO.
The peak age for developing mental health disorders found by the study (12-17 years) “is a unique and very sensitive time,” said Sara Mesilhy, MBBS, a gastroenterologist with the Royal College of Physicians in London.
“These results highlight the need for development of early screening psychiatric programs starting from time of diagnosis and continuing on periodic intervals to offer the best management plan for IBD patients, especially those with childhood-onset IBD,” said Dr. Mesilhy, who was not affiliated with the research.
Such programs would “improve the patient’s quality of life, protecting them from a lot of suffering and preventing the bad sequelae for these disorders,” said Dr. Mesilhy. “Moreover, we still need further studies to identify the most efficient monitoring and treatment protocols.”
Dr. Kennedy applauded the researchers for conducting a population-based study because it ensured an adequate cohort size and maximized identification of mental health disorders.
“It was interesting to see that there were a range of conditions where risk was increased, and that males with IBD were at particularly increased risk,” he added.
Researchers’ use of coded primary care data was a study limitation, but it was “appropriately acknowledged by the presenter,” Dr. Kennedy said.
The study was supported by Pfizer. Dr. Russell disclosed he is a consultant and member of a speakers’ bureau for Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Kennedy and Dr. Mesilhy report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new U.K. study suggests.
The retrospective, observational study of young people with IBD versus those without assessed the incidence of a wide range of mental health conditions in people aged 5-25 years.
“Anxiety and depression will not be a surprise to most of us. But we also saw changes for eating disorders, PTSD, and sleep changes,” said Richard K. Russell, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist at the Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh.
Dr. Russell presented the research at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, held in Copenhagen and virtually.
The findings indicate an unmet need for mental health care for young patients with IBD, he said. “All of us at ECCO need to address this gap.”
Key findings
Dr. Russell and colleagues identified 3,898 young people diagnosed with IBD in the 10-year period Jan. 1, 2010, through Jan. 1, 2020, using the Optimum Patient Care Research Database, which includes de-identified data from more than 1,000 general practices across the United Kingdom. They used propensity score matching to create a control group of 15,571 people without IBD, controlling for age, sex, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and health conditions other than IBD.
Median follow-up was about 3 years.
The cumulative lifetime risk for developing any mental health condition by age 25 was 31.1% in the IBD group versus 25.1% in controls, a statistically significant difference.
Compared with the control group, the people with incident IBD were significantly more likely to develop the following:
- PTSD.
- Eating disorders.
- Self-harm.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Depression.
- Anxiety disorder.
- ‘Any mental health condition.’
Those most are risk included males overall, and specifically boys aged 12-17 years. Those with Crohn’s disease versus other types of IBD were also most at risk.
In a subgroup analysis, presented as a poster at the meeting, Dr. Russell and colleagues also found that mental health comorbidity in children and young adults with IBD is associated with increased IBD symptoms and health care utilization, as well as time off work.
Children and young adults with both IBD and mental health conditions should be monitored and receive appropriate mental health support as part of their multidisciplinary care, Dr. Russell said.
Dr. Russell added that the study period ended a few months before the COVID-19 pandemic began, so the research does not reflect its impact on mental health in the study population.
“The number of children and young adults we’re seeing in our clinic with mental health issues has rocketed through the roof because of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Russell suggested that the organization create a psychology subgroup called Proactive Psychologists of ECCO, or Prosecco for short.
Clinical implications
The study is important for highlighting the increased burden of mental health problems in young people with IBD, said session comoderator Nick Kennedy, MD, a consultant gastroenterologist and chief research information officer with the Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust in England.
Dr. Kennedy, who was not affiliated with the research, is also supportive of the idea of a psychological subgroup within ECCO.
The peak age for developing mental health disorders found by the study (12-17 years) “is a unique and very sensitive time,” said Sara Mesilhy, MBBS, a gastroenterologist with the Royal College of Physicians in London.
“These results highlight the need for development of early screening psychiatric programs starting from time of diagnosis and continuing on periodic intervals to offer the best management plan for IBD patients, especially those with childhood-onset IBD,” said Dr. Mesilhy, who was not affiliated with the research.
Such programs would “improve the patient’s quality of life, protecting them from a lot of suffering and preventing the bad sequelae for these disorders,” said Dr. Mesilhy. “Moreover, we still need further studies to identify the most efficient monitoring and treatment protocols.”
Dr. Kennedy applauded the researchers for conducting a population-based study because it ensured an adequate cohort size and maximized identification of mental health disorders.
“It was interesting to see that there were a range of conditions where risk was increased, and that males with IBD were at particularly increased risk,” he added.
Researchers’ use of coded primary care data was a study limitation, but it was “appropriately acknowledged by the presenter,” Dr. Kennedy said.
The study was supported by Pfizer. Dr. Russell disclosed he is a consultant and member of a speakers’ bureau for Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Kennedy and Dr. Mesilhy report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECCO 2023
Ketamine plus psychotherapy ‘highly effective’ for PTSD
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of four studies investigating combined use of psychotherapy and ketamine for PTSD, results showed that all the studies showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptom scores.
Overall, the treatment was “highly effective, as seen by the significant improvements in symptoms on multiple measures,” Aaron E. Philipp-Muller, BScH, Centre for Neuroscience Studies, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues write.
Furthermore, the study “demonstrates the potential feasibility of this treatment model and corroborates previous work,” the investigators write.
However, a limitation they note was that only 34 participants were included in the analysis.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Emerging treatment
Ketamine is an “emerging treatment for a number of psychopathologies, such as major depressive disorder and PTSD, with a higher response than other pharmacologic agents,” the researchers write.
It is hypothesized that ketamine rapidly facilitates long-term potentiation, “thereby allowing a patient to disengage from an established pattern of thought more readily,” they write.
However, ketamine has several drawbacks, including the fact that it brings only 1 week of relief for PTSD. Also, because it must be administered intravenously, it is “impractical for long-term weekly administration,” they note.
Pharmacologically enhanced psychotherapy is a potential way to prolong ketamine’s effects. Several prior studies have investigated this model using other psychedelic medications, with encouraging results.
The current investigators decided to review all literature to date on the subject of ketamine plus psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD.
To be included, the study had to include patients diagnosed with PTSD, an intervention involving ketamine alongside any form of psychotherapy, and assessment of all patients before and after treatment using the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) or the PTSD Checklist (PCL).
Four studies met inclusion criteria. Of these, two were of “moderate” quality and two were of “low” quality, based on the GRADE assessment. The studies encompassed a total of 34 patients with “diverse traumatic experiences” and included several types of ketamine administration protocols, including one used previously for treating depression and another used previously for chronic pain.
The psychotherapy modalities also differed between the studies. In two studies, patients received 12 sessions of trauma interventions using mindfulness-based extinction and reconsolidation therapy; in a third study, patients received 10 weekly sessions of prolonged exposure therapy; and in the fourth study, patients received five daily sessions of exposure therapy.
Across the studies, the psychotherapies were paired differently with ketamine administration, such as the number of ketamine administrations in conjunction with therapy.
Despite the differences in protocols, all the studies of ketamine plus psychotherapy showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, with a pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of –7.26 (95% CI, –12.28 to –2.25; P = .005) for the CAPS and a pooled SMD of –5.17 (95% CI, –7.99 to –2.35; P < .001) for the PCL.
The researchers acknowledge that the sample size was very small “due to the novelty of this research area.” This prompted the inclusion of nonrandomized studies that “lowered the quality of the evidence,” they note.
Nevertheless, “these preliminary findings indicate the potential of ketamine-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD,” the investigators write.
A promising avenue?
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, called the combination of ketamine and psychotherapy in PTSD “a very promising treatment avenue.”
Dr. Iosifescu, who was not involved with the research, noted that “several PTSD-focused psychotherapies are ultimately very effective but very hard to tolerate for participants.” For example, prolonged exposure therapy has dropout rates as high as 50%.
In addition, ketamine has rapid but not sustained effects in PTSD, he said.
“So in theory, a course of ketamine could help PTSD patients improve rapidly and tolerate the psychotherapy, which could provide sustained benefits,” he added.
However, Dr. Iosifescu cautioned that the data supporting this “is very sparse for now.”
He also noted that the meta-analysis included only “four tiny studies” and had only 34 total participants. In addition, several of the studies had no comparison group and the study designs were all different – “both with respect to the administration of ketamine and to the paired PTSD psychotherapy.”
For this reason, “any conclusions are only a very preliminary suggestion that this may be a fruitful avenue,” he said.
Dr. Iosifescu added that additional studies on this topic are ongoing. The largest one at the Veterans Administration will hopefully include 100 participants and “will provide more reliable evidence for this important topic,” he said.
The study was indirectly supported by the Internal Faculty Grant from the department of psychiatry, Queen’s University. Dr. Iosifescu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of four studies investigating combined use of psychotherapy and ketamine for PTSD, results showed that all the studies showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptom scores.
Overall, the treatment was “highly effective, as seen by the significant improvements in symptoms on multiple measures,” Aaron E. Philipp-Muller, BScH, Centre for Neuroscience Studies, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues write.
Furthermore, the study “demonstrates the potential feasibility of this treatment model and corroborates previous work,” the investigators write.
However, a limitation they note was that only 34 participants were included in the analysis.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Emerging treatment
Ketamine is an “emerging treatment for a number of psychopathologies, such as major depressive disorder and PTSD, with a higher response than other pharmacologic agents,” the researchers write.
It is hypothesized that ketamine rapidly facilitates long-term potentiation, “thereby allowing a patient to disengage from an established pattern of thought more readily,” they write.
However, ketamine has several drawbacks, including the fact that it brings only 1 week of relief for PTSD. Also, because it must be administered intravenously, it is “impractical for long-term weekly administration,” they note.
Pharmacologically enhanced psychotherapy is a potential way to prolong ketamine’s effects. Several prior studies have investigated this model using other psychedelic medications, with encouraging results.
The current investigators decided to review all literature to date on the subject of ketamine plus psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD.
To be included, the study had to include patients diagnosed with PTSD, an intervention involving ketamine alongside any form of psychotherapy, and assessment of all patients before and after treatment using the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) or the PTSD Checklist (PCL).
Four studies met inclusion criteria. Of these, two were of “moderate” quality and two were of “low” quality, based on the GRADE assessment. The studies encompassed a total of 34 patients with “diverse traumatic experiences” and included several types of ketamine administration protocols, including one used previously for treating depression and another used previously for chronic pain.
The psychotherapy modalities also differed between the studies. In two studies, patients received 12 sessions of trauma interventions using mindfulness-based extinction and reconsolidation therapy; in a third study, patients received 10 weekly sessions of prolonged exposure therapy; and in the fourth study, patients received five daily sessions of exposure therapy.
Across the studies, the psychotherapies were paired differently with ketamine administration, such as the number of ketamine administrations in conjunction with therapy.
Despite the differences in protocols, all the studies of ketamine plus psychotherapy showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, with a pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of –7.26 (95% CI, –12.28 to –2.25; P = .005) for the CAPS and a pooled SMD of –5.17 (95% CI, –7.99 to –2.35; P < .001) for the PCL.
The researchers acknowledge that the sample size was very small “due to the novelty of this research area.” This prompted the inclusion of nonrandomized studies that “lowered the quality of the evidence,” they note.
Nevertheless, “these preliminary findings indicate the potential of ketamine-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD,” the investigators write.
A promising avenue?
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, called the combination of ketamine and psychotherapy in PTSD “a very promising treatment avenue.”
Dr. Iosifescu, who was not involved with the research, noted that “several PTSD-focused psychotherapies are ultimately very effective but very hard to tolerate for participants.” For example, prolonged exposure therapy has dropout rates as high as 50%.
In addition, ketamine has rapid but not sustained effects in PTSD, he said.
“So in theory, a course of ketamine could help PTSD patients improve rapidly and tolerate the psychotherapy, which could provide sustained benefits,” he added.
However, Dr. Iosifescu cautioned that the data supporting this “is very sparse for now.”
He also noted that the meta-analysis included only “four tiny studies” and had only 34 total participants. In addition, several of the studies had no comparison group and the study designs were all different – “both with respect to the administration of ketamine and to the paired PTSD psychotherapy.”
For this reason, “any conclusions are only a very preliminary suggestion that this may be a fruitful avenue,” he said.
Dr. Iosifescu added that additional studies on this topic are ongoing. The largest one at the Veterans Administration will hopefully include 100 participants and “will provide more reliable evidence for this important topic,” he said.
The study was indirectly supported by the Internal Faculty Grant from the department of psychiatry, Queen’s University. Dr. Iosifescu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of four studies investigating combined use of psychotherapy and ketamine for PTSD, results showed that all the studies showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptom scores.
Overall, the treatment was “highly effective, as seen by the significant improvements in symptoms on multiple measures,” Aaron E. Philipp-Muller, BScH, Centre for Neuroscience Studies, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues write.
Furthermore, the study “demonstrates the potential feasibility of this treatment model and corroborates previous work,” the investigators write.
However, a limitation they note was that only 34 participants were included in the analysis.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Emerging treatment
Ketamine is an “emerging treatment for a number of psychopathologies, such as major depressive disorder and PTSD, with a higher response than other pharmacologic agents,” the researchers write.
It is hypothesized that ketamine rapidly facilitates long-term potentiation, “thereby allowing a patient to disengage from an established pattern of thought more readily,” they write.
However, ketamine has several drawbacks, including the fact that it brings only 1 week of relief for PTSD. Also, because it must be administered intravenously, it is “impractical for long-term weekly administration,” they note.
Pharmacologically enhanced psychotherapy is a potential way to prolong ketamine’s effects. Several prior studies have investigated this model using other psychedelic medications, with encouraging results.
The current investigators decided to review all literature to date on the subject of ketamine plus psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD.
To be included, the study had to include patients diagnosed with PTSD, an intervention involving ketamine alongside any form of psychotherapy, and assessment of all patients before and after treatment using the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) or the PTSD Checklist (PCL).
Four studies met inclusion criteria. Of these, two were of “moderate” quality and two were of “low” quality, based on the GRADE assessment. The studies encompassed a total of 34 patients with “diverse traumatic experiences” and included several types of ketamine administration protocols, including one used previously for treating depression and another used previously for chronic pain.
The psychotherapy modalities also differed between the studies. In two studies, patients received 12 sessions of trauma interventions using mindfulness-based extinction and reconsolidation therapy; in a third study, patients received 10 weekly sessions of prolonged exposure therapy; and in the fourth study, patients received five daily sessions of exposure therapy.
Across the studies, the psychotherapies were paired differently with ketamine administration, such as the number of ketamine administrations in conjunction with therapy.
Despite the differences in protocols, all the studies of ketamine plus psychotherapy showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, with a pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of –7.26 (95% CI, –12.28 to –2.25; P = .005) for the CAPS and a pooled SMD of –5.17 (95% CI, –7.99 to –2.35; P < .001) for the PCL.
The researchers acknowledge that the sample size was very small “due to the novelty of this research area.” This prompted the inclusion of nonrandomized studies that “lowered the quality of the evidence,” they note.
Nevertheless, “these preliminary findings indicate the potential of ketamine-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD,” the investigators write.
A promising avenue?
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, called the combination of ketamine and psychotherapy in PTSD “a very promising treatment avenue.”
Dr. Iosifescu, who was not involved with the research, noted that “several PTSD-focused psychotherapies are ultimately very effective but very hard to tolerate for participants.” For example, prolonged exposure therapy has dropout rates as high as 50%.
In addition, ketamine has rapid but not sustained effects in PTSD, he said.
“So in theory, a course of ketamine could help PTSD patients improve rapidly and tolerate the psychotherapy, which could provide sustained benefits,” he added.
However, Dr. Iosifescu cautioned that the data supporting this “is very sparse for now.”
He also noted that the meta-analysis included only “four tiny studies” and had only 34 total participants. In addition, several of the studies had no comparison group and the study designs were all different – “both with respect to the administration of ketamine and to the paired PTSD psychotherapy.”
For this reason, “any conclusions are only a very preliminary suggestion that this may be a fruitful avenue,” he said.
Dr. Iosifescu added that additional studies on this topic are ongoing. The largest one at the Veterans Administration will hopefully include 100 participants and “will provide more reliable evidence for this important topic,” he said.
The study was indirectly supported by the Internal Faculty Grant from the department of psychiatry, Queen’s University. Dr. Iosifescu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
More on psilocybin
I would like to remark on “Psychedelics for treating psychiatric disorders: Are they safe?” (
The Oregon Psilocybin Services that will begin in 2023 are not specific to therapeutic use; this is a common misconception. These are specifically referred to as “psilocybin services” in the Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR), and psilocybin facilitators are required to limit their scope such that they are not practicing psychotherapy or other interventions, even if they do have a medical or psychotherapy background. The intention of the Oregon Psilocybin Services rollout was that these services would not be of the medical model. In the spirit of this, services do not require a medical diagnosis or referral, and services are not a medical or clinical treatment (OAR 333-333-5040). Additionally, services cannot be provided in a health care facility (OAR 441). Facilitators receive robust training as defined by Oregon law, and licensed facilitators provide this information during preparation for services. When discussing this model on a large public scale, I have noticed substantial misconceptions; it is imperative that we refer to these services as they are defined so that individuals with mental health conditions who seek them are aware that such services are different from psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy. Instead, Oregon Psilocybin Services might be better categorized as supported psilocybin use.
I would like to remark on “Psychedelics for treating psychiatric disorders: Are they safe?” (
The Oregon Psilocybin Services that will begin in 2023 are not specific to therapeutic use; this is a common misconception. These are specifically referred to as “psilocybin services” in the Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR), and psilocybin facilitators are required to limit their scope such that they are not practicing psychotherapy or other interventions, even if they do have a medical or psychotherapy background. The intention of the Oregon Psilocybin Services rollout was that these services would not be of the medical model. In the spirit of this, services do not require a medical diagnosis or referral, and services are not a medical or clinical treatment (OAR 333-333-5040). Additionally, services cannot be provided in a health care facility (OAR 441). Facilitators receive robust training as defined by Oregon law, and licensed facilitators provide this information during preparation for services. When discussing this model on a large public scale, I have noticed substantial misconceptions; it is imperative that we refer to these services as they are defined so that individuals with mental health conditions who seek them are aware that such services are different from psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy. Instead, Oregon Psilocybin Services might be better categorized as supported psilocybin use.
I would like to remark on “Psychedelics for treating psychiatric disorders: Are they safe?” (
The Oregon Psilocybin Services that will begin in 2023 are not specific to therapeutic use; this is a common misconception. These are specifically referred to as “psilocybin services” in the Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR), and psilocybin facilitators are required to limit their scope such that they are not practicing psychotherapy or other interventions, even if they do have a medical or psychotherapy background. The intention of the Oregon Psilocybin Services rollout was that these services would not be of the medical model. In the spirit of this, services do not require a medical diagnosis or referral, and services are not a medical or clinical treatment (OAR 333-333-5040). Additionally, services cannot be provided in a health care facility (OAR 441). Facilitators receive robust training as defined by Oregon law, and licensed facilitators provide this information during preparation for services. When discussing this model on a large public scale, I have noticed substantial misconceptions; it is imperative that we refer to these services as they are defined so that individuals with mental health conditions who seek them are aware that such services are different from psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy. Instead, Oregon Psilocybin Services might be better categorized as supported psilocybin use.
Two short-term exposure therapies linked to PTSD reductions
Two forms of short-term exposure therapy may help reduce symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.
In addition, remission rates of around 50% were sustained in both groups up to the 6-month mark.
“With about two-thirds of study participants reporting clinically meaningful symptom improvement and more than half losing their PTSD diagnosis, this study provides important new evidence that combat-related PTSD can be effectively treated – in as little as 3 weeks,” lead investigator Alan Peterson, PhD, told this news organization.
Dr. Peterson, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, and director of the Consortium to Alleviate PTSD, noted that while condensed treatments may not be feasible for everyone, “results show that compressed formats adapted to the military context resulted in significant, meaningful, and lasting improvements in PTSD, disability, and functional impairments for most participants.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Breathing, direct exposure, education
The investigators randomly recruited 234 military personnel and veterans from two military treatment facilities and two Veterans Affairs facilities in south and central Texas.
Participants (78% men; mean age, 39 years) were active-duty service members or veterans who had deployed post Sept. 11 and met diagnostic criteria for PTSD. They could receive psychotropic medications at stable doses and were excluded if they had mania, substance abuse, psychosis, or suicidality.
The sample included 44% White participants, 26% Black participants, and 25% Hispanic participants.
The researchers randomly assigned the participants to receive either massed-PE (n = 117) or IOP-PE (n = 117).
PE, the foundation of both protocols, includes psychoeducation about trauma, diaphragmatic breathing, direct and imaginal exposure, and processing of the trauma.
The massed-PE protocol was delivered in 15 daily 90-minute sessions over 3 consecutive weeks, as was the IOP-PE. However, the IOP-PE also included eight additional multiple daily feedback sessions, homework, social support from friends or family, and three booster sessions post treatment.
The investigators conducted baseline assessments and follow-up assessments at 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. At the 6-month follow-up, there were 57 participants left to analyze in the massed-PE group and 57 in the IOP-PE group.
Significantly decreased symptoms
As measured by the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5), PTSD symptoms decreased significantly from baseline to the 1-month follow-up in both groups (massed-PE mean change, –14.13; P < .001; IOP-PE mean change, –13.85; P < .001).
Both groups also failed to meet PTSD diagnostic criteria at 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-ups.
At the 1-month follow-up, 62% of participants who received massed-PE and 48% of those who received IOP-PE no longer met diagnostic criteria on the CAPS-5. Diagnostic remission was maintained in more than half of the massed-PE group (52%) and the IOP-PE group (53%) at the 6-month follow-up.
Disability scores as measured by the Sheehan Disability Scale also decreased significantly in both groups (P < .001) from baseline to the 1-month follow-up mark; as did psychosocial functioning scores, as reflected by the Brief Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning (P < .001).
Dr. Peterson noted that the condensed treatment format could be an essential option to consider even in other countries, such as Ukraine, where there are concerns about PTSD in military personnel.
Study limitations included the lack of a placebo or inactive comparison group, and the lack of generalizability of the results to the entire population of U.S. service members and veterans outside of Texas.
Dr. Peterson said he plans to continue his research and that the compressed treatment formats studied “are well-suited for the evaluation of alternative modes of therapy combining cognitive-behavioral treatments with medications and medical devices.”
Generalizability limited?
Commenting on the research, Joshua Morganstein, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s committee on the psychiatric dimensions of disaster, said he was reassured to see participants achieve and keep improvements throughout the study.
“One of the biggest challenges we have, particularly with trauma and stress disorders, is keeping people in therapy” because of the difficult nature of the exposure therapy, said Dr. Morganstein, who was not involved with the research.
“The number of people assigned to each group and who ultimately completed the last follow-up gives a good idea of the utility of the intervention,” he added.
However, Dr. Morganstein noted that some of the exclusion criteria, particularly suicidality and substance abuse, affected the study’s relevance to real-world populations.
“The people in the study become less representative of those who are actually in clinical care,” he said, noting that these two conditions are often comorbid with PTSD.
The study was funded by the Department of Defense, the Defense Health Program, the Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury Research Program, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Office of Research and Development, and the Clinical Science Research & Development Service. The investigators and Dr. Morganstein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two forms of short-term exposure therapy may help reduce symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.
In addition, remission rates of around 50% were sustained in both groups up to the 6-month mark.
“With about two-thirds of study participants reporting clinically meaningful symptom improvement and more than half losing their PTSD diagnosis, this study provides important new evidence that combat-related PTSD can be effectively treated – in as little as 3 weeks,” lead investigator Alan Peterson, PhD, told this news organization.
Dr. Peterson, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, and director of the Consortium to Alleviate PTSD, noted that while condensed treatments may not be feasible for everyone, “results show that compressed formats adapted to the military context resulted in significant, meaningful, and lasting improvements in PTSD, disability, and functional impairments for most participants.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Breathing, direct exposure, education
The investigators randomly recruited 234 military personnel and veterans from two military treatment facilities and two Veterans Affairs facilities in south and central Texas.
Participants (78% men; mean age, 39 years) were active-duty service members or veterans who had deployed post Sept. 11 and met diagnostic criteria for PTSD. They could receive psychotropic medications at stable doses and were excluded if they had mania, substance abuse, psychosis, or suicidality.
The sample included 44% White participants, 26% Black participants, and 25% Hispanic participants.
The researchers randomly assigned the participants to receive either massed-PE (n = 117) or IOP-PE (n = 117).
PE, the foundation of both protocols, includes psychoeducation about trauma, diaphragmatic breathing, direct and imaginal exposure, and processing of the trauma.
The massed-PE protocol was delivered in 15 daily 90-minute sessions over 3 consecutive weeks, as was the IOP-PE. However, the IOP-PE also included eight additional multiple daily feedback sessions, homework, social support from friends or family, and three booster sessions post treatment.
The investigators conducted baseline assessments and follow-up assessments at 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. At the 6-month follow-up, there were 57 participants left to analyze in the massed-PE group and 57 in the IOP-PE group.
Significantly decreased symptoms
As measured by the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5), PTSD symptoms decreased significantly from baseline to the 1-month follow-up in both groups (massed-PE mean change, –14.13; P < .001; IOP-PE mean change, –13.85; P < .001).
Both groups also failed to meet PTSD diagnostic criteria at 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-ups.
At the 1-month follow-up, 62% of participants who received massed-PE and 48% of those who received IOP-PE no longer met diagnostic criteria on the CAPS-5. Diagnostic remission was maintained in more than half of the massed-PE group (52%) and the IOP-PE group (53%) at the 6-month follow-up.
Disability scores as measured by the Sheehan Disability Scale also decreased significantly in both groups (P < .001) from baseline to the 1-month follow-up mark; as did psychosocial functioning scores, as reflected by the Brief Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning (P < .001).
Dr. Peterson noted that the condensed treatment format could be an essential option to consider even in other countries, such as Ukraine, where there are concerns about PTSD in military personnel.
Study limitations included the lack of a placebo or inactive comparison group, and the lack of generalizability of the results to the entire population of U.S. service members and veterans outside of Texas.
Dr. Peterson said he plans to continue his research and that the compressed treatment formats studied “are well-suited for the evaluation of alternative modes of therapy combining cognitive-behavioral treatments with medications and medical devices.”
Generalizability limited?
Commenting on the research, Joshua Morganstein, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s committee on the psychiatric dimensions of disaster, said he was reassured to see participants achieve and keep improvements throughout the study.
“One of the biggest challenges we have, particularly with trauma and stress disorders, is keeping people in therapy” because of the difficult nature of the exposure therapy, said Dr. Morganstein, who was not involved with the research.
“The number of people assigned to each group and who ultimately completed the last follow-up gives a good idea of the utility of the intervention,” he added.
However, Dr. Morganstein noted that some of the exclusion criteria, particularly suicidality and substance abuse, affected the study’s relevance to real-world populations.
“The people in the study become less representative of those who are actually in clinical care,” he said, noting that these two conditions are often comorbid with PTSD.
The study was funded by the Department of Defense, the Defense Health Program, the Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury Research Program, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Office of Research and Development, and the Clinical Science Research & Development Service. The investigators and Dr. Morganstein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two forms of short-term exposure therapy may help reduce symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.
In addition, remission rates of around 50% were sustained in both groups up to the 6-month mark.
“With about two-thirds of study participants reporting clinically meaningful symptom improvement and more than half losing their PTSD diagnosis, this study provides important new evidence that combat-related PTSD can be effectively treated – in as little as 3 weeks,” lead investigator Alan Peterson, PhD, told this news organization.
Dr. Peterson, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, and director of the Consortium to Alleviate PTSD, noted that while condensed treatments may not be feasible for everyone, “results show that compressed formats adapted to the military context resulted in significant, meaningful, and lasting improvements in PTSD, disability, and functional impairments for most participants.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Breathing, direct exposure, education
The investigators randomly recruited 234 military personnel and veterans from two military treatment facilities and two Veterans Affairs facilities in south and central Texas.
Participants (78% men; mean age, 39 years) were active-duty service members or veterans who had deployed post Sept. 11 and met diagnostic criteria for PTSD. They could receive psychotropic medications at stable doses and were excluded if they had mania, substance abuse, psychosis, or suicidality.
The sample included 44% White participants, 26% Black participants, and 25% Hispanic participants.
The researchers randomly assigned the participants to receive either massed-PE (n = 117) or IOP-PE (n = 117).
PE, the foundation of both protocols, includes psychoeducation about trauma, diaphragmatic breathing, direct and imaginal exposure, and processing of the trauma.
The massed-PE protocol was delivered in 15 daily 90-minute sessions over 3 consecutive weeks, as was the IOP-PE. However, the IOP-PE also included eight additional multiple daily feedback sessions, homework, social support from friends or family, and three booster sessions post treatment.
The investigators conducted baseline assessments and follow-up assessments at 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. At the 6-month follow-up, there were 57 participants left to analyze in the massed-PE group and 57 in the IOP-PE group.
Significantly decreased symptoms
As measured by the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5), PTSD symptoms decreased significantly from baseline to the 1-month follow-up in both groups (massed-PE mean change, –14.13; P < .001; IOP-PE mean change, –13.85; P < .001).
Both groups also failed to meet PTSD diagnostic criteria at 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-ups.
At the 1-month follow-up, 62% of participants who received massed-PE and 48% of those who received IOP-PE no longer met diagnostic criteria on the CAPS-5. Diagnostic remission was maintained in more than half of the massed-PE group (52%) and the IOP-PE group (53%) at the 6-month follow-up.
Disability scores as measured by the Sheehan Disability Scale also decreased significantly in both groups (P < .001) from baseline to the 1-month follow-up mark; as did psychosocial functioning scores, as reflected by the Brief Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning (P < .001).
Dr. Peterson noted that the condensed treatment format could be an essential option to consider even in other countries, such as Ukraine, where there are concerns about PTSD in military personnel.
Study limitations included the lack of a placebo or inactive comparison group, and the lack of generalizability of the results to the entire population of U.S. service members and veterans outside of Texas.
Dr. Peterson said he plans to continue his research and that the compressed treatment formats studied “are well-suited for the evaluation of alternative modes of therapy combining cognitive-behavioral treatments with medications and medical devices.”
Generalizability limited?
Commenting on the research, Joshua Morganstein, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s committee on the psychiatric dimensions of disaster, said he was reassured to see participants achieve and keep improvements throughout the study.
“One of the biggest challenges we have, particularly with trauma and stress disorders, is keeping people in therapy” because of the difficult nature of the exposure therapy, said Dr. Morganstein, who was not involved with the research.
“The number of people assigned to each group and who ultimately completed the last follow-up gives a good idea of the utility of the intervention,” he added.
However, Dr. Morganstein noted that some of the exclusion criteria, particularly suicidality and substance abuse, affected the study’s relevance to real-world populations.
“The people in the study become less representative of those who are actually in clinical care,” he said, noting that these two conditions are often comorbid with PTSD.
The study was funded by the Department of Defense, the Defense Health Program, the Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury Research Program, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Office of Research and Development, and the Clinical Science Research & Development Service. The investigators and Dr. Morganstein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Anxiety sensitivity fuels depression in dissociative identity disorder
Anxiety sensitivity refers to fear of the signs and symptoms of anxiety based on the individual’s belief that the signs of anxiety will have harmful consequences, wrote Xi Pan, LICSW, MPA, of McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., and colleagues.
Anxiety sensitivity can include cognitive, physical, and social elements: for example, fear that the inability to focus signals mental illness, fear that a racing heart might cause a heart attack, or fear that exhibiting anxiety signs in public (e.g., sweaty palms) will cause embarrassment, the researchers said.
Previous studies have found associations between anxiety sensitivity and panic attacks, and anxiety sensitivity has been shown to contribute to worsening symptoms in patients with anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and trauma-related disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder. However, “anxiety sensitivity has not been studied in individuals with complex dissociative disorders such as dissociative identity disorder (DID)” – who often have co-occurring PTSD and depression, the researchers said.
In a study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research, the authors analyzed data from 21 treatment-seeking adult women with histories of childhood trauma, current PTSD, and dissociative identity disorder. Participants completed the Anxiety Sensitivity Index (ASI), Beck Depression Inventory-II, Childhood Trauma Questionnaire, Multidimensional Inventory of Dissociation, and PTSD Checklist for DSM-5.
Anxiety sensitivity in cognitive, physical, and social domains was assessed using ASI subscales.
Pearson correlations showed that symptoms of depression were significantly associated with anxiety sensitivity total scores and across all anxiety subscales. However, no direct associations appeared between anxiety sensitivity and PTSD or severe dissociative symptoms.
In a multiple regression analysis, the ASI cognitive subscale was a positive predictor of depressive symptoms, although physical and social subscale scores were not.
The researchers also tested for an indirect relationship between anxiety sensitivity and dissociative symptoms through depression. “Specifically, more severe ASI cognitive concerns were associated with more depressive symptoms, and more depressive symptoms predicted more severe pathological dissociation symptoms,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by the inability to show a direct causal relationship between anxiety sensitivity and depression, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the small sample size, use of self-reports, and the population of mainly White women, which may not generalize to other populations, they said.
However, the results represent the first empirical investigation of the relationship between anxiety sensitivity and DID symptoms, and support the value of assessment for anxiety sensitivity in DID patients in clinical practice, they said.
“If high levels of anxiety sensitivity are identified, the individual may benefit from targeted interventions, which in turn may alleviate some symptoms of depression and dissociation in DID,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the Julia Kasparian Fund for Neuroscience Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Anxiety sensitivity refers to fear of the signs and symptoms of anxiety based on the individual’s belief that the signs of anxiety will have harmful consequences, wrote Xi Pan, LICSW, MPA, of McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., and colleagues.
Anxiety sensitivity can include cognitive, physical, and social elements: for example, fear that the inability to focus signals mental illness, fear that a racing heart might cause a heart attack, or fear that exhibiting anxiety signs in public (e.g., sweaty palms) will cause embarrassment, the researchers said.
Previous studies have found associations between anxiety sensitivity and panic attacks, and anxiety sensitivity has been shown to contribute to worsening symptoms in patients with anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and trauma-related disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder. However, “anxiety sensitivity has not been studied in individuals with complex dissociative disorders such as dissociative identity disorder (DID)” – who often have co-occurring PTSD and depression, the researchers said.
In a study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research, the authors analyzed data from 21 treatment-seeking adult women with histories of childhood trauma, current PTSD, and dissociative identity disorder. Participants completed the Anxiety Sensitivity Index (ASI), Beck Depression Inventory-II, Childhood Trauma Questionnaire, Multidimensional Inventory of Dissociation, and PTSD Checklist for DSM-5.
Anxiety sensitivity in cognitive, physical, and social domains was assessed using ASI subscales.
Pearson correlations showed that symptoms of depression were significantly associated with anxiety sensitivity total scores and across all anxiety subscales. However, no direct associations appeared between anxiety sensitivity and PTSD or severe dissociative symptoms.
In a multiple regression analysis, the ASI cognitive subscale was a positive predictor of depressive symptoms, although physical and social subscale scores were not.
The researchers also tested for an indirect relationship between anxiety sensitivity and dissociative symptoms through depression. “Specifically, more severe ASI cognitive concerns were associated with more depressive symptoms, and more depressive symptoms predicted more severe pathological dissociation symptoms,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by the inability to show a direct causal relationship between anxiety sensitivity and depression, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the small sample size, use of self-reports, and the population of mainly White women, which may not generalize to other populations, they said.
However, the results represent the first empirical investigation of the relationship between anxiety sensitivity and DID symptoms, and support the value of assessment for anxiety sensitivity in DID patients in clinical practice, they said.
“If high levels of anxiety sensitivity are identified, the individual may benefit from targeted interventions, which in turn may alleviate some symptoms of depression and dissociation in DID,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the Julia Kasparian Fund for Neuroscience Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Anxiety sensitivity refers to fear of the signs and symptoms of anxiety based on the individual’s belief that the signs of anxiety will have harmful consequences, wrote Xi Pan, LICSW, MPA, of McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., and colleagues.
Anxiety sensitivity can include cognitive, physical, and social elements: for example, fear that the inability to focus signals mental illness, fear that a racing heart might cause a heart attack, or fear that exhibiting anxiety signs in public (e.g., sweaty palms) will cause embarrassment, the researchers said.
Previous studies have found associations between anxiety sensitivity and panic attacks, and anxiety sensitivity has been shown to contribute to worsening symptoms in patients with anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and trauma-related disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder. However, “anxiety sensitivity has not been studied in individuals with complex dissociative disorders such as dissociative identity disorder (DID)” – who often have co-occurring PTSD and depression, the researchers said.
In a study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research, the authors analyzed data from 21 treatment-seeking adult women with histories of childhood trauma, current PTSD, and dissociative identity disorder. Participants completed the Anxiety Sensitivity Index (ASI), Beck Depression Inventory-II, Childhood Trauma Questionnaire, Multidimensional Inventory of Dissociation, and PTSD Checklist for DSM-5.
Anxiety sensitivity in cognitive, physical, and social domains was assessed using ASI subscales.
Pearson correlations showed that symptoms of depression were significantly associated with anxiety sensitivity total scores and across all anxiety subscales. However, no direct associations appeared between anxiety sensitivity and PTSD or severe dissociative symptoms.
In a multiple regression analysis, the ASI cognitive subscale was a positive predictor of depressive symptoms, although physical and social subscale scores were not.
The researchers also tested for an indirect relationship between anxiety sensitivity and dissociative symptoms through depression. “Specifically, more severe ASI cognitive concerns were associated with more depressive symptoms, and more depressive symptoms predicted more severe pathological dissociation symptoms,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by the inability to show a direct causal relationship between anxiety sensitivity and depression, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the small sample size, use of self-reports, and the population of mainly White women, which may not generalize to other populations, they said.
However, the results represent the first empirical investigation of the relationship between anxiety sensitivity and DID symptoms, and support the value of assessment for anxiety sensitivity in DID patients in clinical practice, they said.
“If high levels of anxiety sensitivity are identified, the individual may benefit from targeted interventions, which in turn may alleviate some symptoms of depression and dissociation in DID,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the Julia Kasparian Fund for Neuroscience Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH
More support for MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD
The MAPP2 study is the second randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD.
The investigators confirm results of the MAPP1 study, which were published in Nature Medicine. Patients who received MDMA-assisted psychotherapy in MAPP1 demonstrated greater improvement in PTSD symptoms, mood, and empathy, compared with participants who received psychotherapy with placebo.
The design of the MAPP2 study was similar to that of MAPP1, and its results were similar, the nonprofit Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS), which sponsored MAPP1 and MAPP2, said in a news release.
No specific results from MAPP2 were provided at this time. The full data from MAPP2 are expected to be published in a peer-reviewed journal later this year, and a new drug application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration will follow.
The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to MDMA as an adjunct to psychotherapy for adults with PTSD in 2017.
MAPS was founded in 1986 to fund and facilitate research into the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies; to educate the public about psychedelics for medical, social, and spiritual use; and to advocate for drug policy reform.
“When I first articulated a plan to legitimize a psychedelic-assisted therapy through FDA approval, many people said it was impossible,” Rick Doblin, PhD, founder and executive director of MAPS, said in the news release.
“Thirty-seven years later, we are on the precipice of bringing a novel therapy to the millions of Americans living with PTSD who haven’t found relief through current treatments,” said Dr. Doblin.
“The impossible became possible through the bravery of clinical trial participants, the compassion of mental health practitioners, and the generosity of thousands of donors. Today, we can imagine that MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD may soon be available and accessible to all who could benefit,” Dr. Doblin added.
According to MAPS, phase 2 trials are being planned or conducted regarding the efficacy of MDMA-assisted therapies for substance use disorder and eating disorders, as well as couples therapy and group therapy among veterans.
Currently, no psychedelic-assisted therapy has been approved by the FDA or other regulatory authorities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The MAPP2 study is the second randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD.
The investigators confirm results of the MAPP1 study, which were published in Nature Medicine. Patients who received MDMA-assisted psychotherapy in MAPP1 demonstrated greater improvement in PTSD symptoms, mood, and empathy, compared with participants who received psychotherapy with placebo.
The design of the MAPP2 study was similar to that of MAPP1, and its results were similar, the nonprofit Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS), which sponsored MAPP1 and MAPP2, said in a news release.
No specific results from MAPP2 were provided at this time. The full data from MAPP2 are expected to be published in a peer-reviewed journal later this year, and a new drug application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration will follow.
The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to MDMA as an adjunct to psychotherapy for adults with PTSD in 2017.
MAPS was founded in 1986 to fund and facilitate research into the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies; to educate the public about psychedelics for medical, social, and spiritual use; and to advocate for drug policy reform.
“When I first articulated a plan to legitimize a psychedelic-assisted therapy through FDA approval, many people said it was impossible,” Rick Doblin, PhD, founder and executive director of MAPS, said in the news release.
“Thirty-seven years later, we are on the precipice of bringing a novel therapy to the millions of Americans living with PTSD who haven’t found relief through current treatments,” said Dr. Doblin.
“The impossible became possible through the bravery of clinical trial participants, the compassion of mental health practitioners, and the generosity of thousands of donors. Today, we can imagine that MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD may soon be available and accessible to all who could benefit,” Dr. Doblin added.
According to MAPS, phase 2 trials are being planned or conducted regarding the efficacy of MDMA-assisted therapies for substance use disorder and eating disorders, as well as couples therapy and group therapy among veterans.
Currently, no psychedelic-assisted therapy has been approved by the FDA or other regulatory authorities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The MAPP2 study is the second randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD.
The investigators confirm results of the MAPP1 study, which were published in Nature Medicine. Patients who received MDMA-assisted psychotherapy in MAPP1 demonstrated greater improvement in PTSD symptoms, mood, and empathy, compared with participants who received psychotherapy with placebo.
The design of the MAPP2 study was similar to that of MAPP1, and its results were similar, the nonprofit Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS), which sponsored MAPP1 and MAPP2, said in a news release.
No specific results from MAPP2 were provided at this time. The full data from MAPP2 are expected to be published in a peer-reviewed journal later this year, and a new drug application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration will follow.
The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to MDMA as an adjunct to psychotherapy for adults with PTSD in 2017.
MAPS was founded in 1986 to fund and facilitate research into the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies; to educate the public about psychedelics for medical, social, and spiritual use; and to advocate for drug policy reform.
“When I first articulated a plan to legitimize a psychedelic-assisted therapy through FDA approval, many people said it was impossible,” Rick Doblin, PhD, founder and executive director of MAPS, said in the news release.
“Thirty-seven years later, we are on the precipice of bringing a novel therapy to the millions of Americans living with PTSD who haven’t found relief through current treatments,” said Dr. Doblin.
“The impossible became possible through the bravery of clinical trial participants, the compassion of mental health practitioners, and the generosity of thousands of donors. Today, we can imagine that MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD may soon be available and accessible to all who could benefit,” Dr. Doblin added.
According to MAPS, phase 2 trials are being planned or conducted regarding the efficacy of MDMA-assisted therapies for substance use disorder and eating disorders, as well as couples therapy and group therapy among veterans.
Currently, no psychedelic-assisted therapy has been approved by the FDA or other regulatory authorities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More evidence suicidal thoughts, behaviors are genetically based
“It’s really important for us to continue to study the genetic risk factors for suicidal behaviors so we can really understand the biology and develop better treatments,” study investigator Allison E. Ashley-Koch, PhD, professor in the department of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry).
SITB heritability
Suicide is a leading cause of death, particularly among individuals aged 15-29 years. Whereas the global rate of suicide has decreased by 36% in the past 20 years, the rate in the United States has increased by 35%, with the greatest rise in military veterans.
Twin studies suggest heritability for SITB is between 30% and 55%, but the molecular genetic basis of SITB remains elusive.
To address this research gap, investigators conducted a study of 633,778 U.S. military veterans from the Million Veteran Program (MVP) cohort. Of these, 71% had European ancestry, 19% had African ancestry, 8% were Hispanic, and 1% were Asian. Just under 10% of the sample was female.
Study participants donated a blood sample and agreed to have their genetic information linked with their electronic health record data.
From diagnostic codes and other sources, researchers identified 121,211 individuals with SITB. They classified participants with no documented lifetime history of suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, or suicide death as controls.
Rates of SITB differed significantly by ancestry – 25% in those with African or Hispanic ancestry, 21% in those with Asian ancestry, and 16.8% in those with European ancestry. Rates also differed by age and sex; those with SITB were younger and more likely to be female.
In addition to age and sex, covariates included “genetic principal components,” which Dr. Ashley-Koch said accounts for combining data of individuals with different ethnic/racial backgrounds.
Through meta-analysis, the investigators identified seven genome-wide, significant cross-ancestry risk loci.
To evaluate whether the findings could be replicated, researchers used the International Suicide Genetics Consortium (ISGC), a primarily civilian international consortium of roughly 550,000 individuals of mostly European ancestry.
The analysis showed the top replicated cross-ancestry risk locus was rs6557168, an intronic single-nucleotide variant (SNV) in the ESR1 gene that encodes an estrogen receptor. Previous work identified ESR1 as a causal genetic driver gene for development of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression, both of which are risk factors for SITB among veterans.
The second-strongest replicated cross-ancestry locus was rs12808482, an intronic variant in the DRD2 gene, which encodes the D2 dopamine-receptor subtype. The authors noted DRD2 is highly expressed in brain tissue and has been associated with numerous psychiatric phenotypes.
Research suggests DRD2 is associated with other risk factors for SITB, such as schizophrenia, mood disorders, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, but DRD2 could also contribute to suicide risk directly. The authors noted it is highly expressed in the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, and hippocampus.
Outstanding candidate gene
The study revealed a cross-ancestry GWS association for rs10671545, a variant in DCC, which is “also an outstanding candidate gene,” the investigators write.
They note it is expressed in brain tissue, is involved in synaptic plasticity, axon guidance, and circadian entrainment, and has been associated with multiple psychiatric phenotypes.
Researchers also found what they called “intriguing” cross-ancestry GWS associations for the TRAF3 gene, which regulates type-1 interferon production. Many patients receiving interferon therapy develop major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation.
TRAF3 is also associated with antisocial behavior, substance use, and ADHD. Lithium – a standard treatment for bipolar disorder that reduces suicide risk – modulates the expression of TRAF3.
Dr. Ashley-Koch noted the replication of these loci (ESR1, DRD2, TRAF3, and DCC) was in a population of mostly White civilians. “This suggests to us that at least some of the risk for suicidal thoughts and behaviors does cross ancestry and also crosses military and civilian populations.”
It was “exciting” that all four genes the study focused on had previously been implicated in other psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Ashley-Koch. “What gave us a little more confidence, above and beyond the replication, was that these genes are somehow important for psychiatric disorders, and not any psychiatric disorders, but the ones that are also associated with a high risk of suicide behavior, such as depression, PTSD, schizophrenia, and ADHD.”
The findings will not have an immediate impact on clinical practice, said Dr. Ashley-Koch.
“We need to take the next step, which is to try to understand how these genetic factors may impact risk and what else is happening biologically to increase that risk. Then once we do that, hopefully we can develop some new treatments,” she added.
‘Valuable and noble’ research
Commenting on the study, Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, said this kind of genetic research is “valuable and noble.”
Researchers have long been interested in risk factors for suicide among military personnel and veterans, said Dr. Ritchie. Evidence to date suggests being a young male is a risk factor as is feeling excluded or not fitting into the unit, and drug or alcohol addiction.
Dr. Ritchie noted other psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, depression, and bipolar disorder, are at least partially inherited.
She noted the study’s findings should not be used to discriminate against those who might have the identified genetic loci without clearer evidence of their impact.
“If we were able to identify these genes, would we start screening everybody who joins the military to see if they have these genes, and how would that impact the ability to recruit or retain personnel?”
She agreed additional work is needed to determine if and how carrying these genes might impact clinical care.
In addition, she pointed out that behavior is influenced not only by genetic load but also by environment. “This study may show the impact of the genetic load a little bit more clearly; right now, we tend to look at environmental factors.”
The study was supported by an award from the Clinical Science Research and Development (CSR&D) service of the Veterans Health Administration’s Office of Research and Development. The work was also supported in part by the joint U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and U.S. Department of Energy MVP CHAMPION program.
Dr. Ashley-Koch reported grants from Veterans Administration during the conduct of the study. Several other coauthors report relationships with industry, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies. The full list can be found with the original article. Dr. Ritchie reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“It’s really important for us to continue to study the genetic risk factors for suicidal behaviors so we can really understand the biology and develop better treatments,” study investigator Allison E. Ashley-Koch, PhD, professor in the department of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry).
SITB heritability
Suicide is a leading cause of death, particularly among individuals aged 15-29 years. Whereas the global rate of suicide has decreased by 36% in the past 20 years, the rate in the United States has increased by 35%, with the greatest rise in military veterans.
Twin studies suggest heritability for SITB is between 30% and 55%, but the molecular genetic basis of SITB remains elusive.
To address this research gap, investigators conducted a study of 633,778 U.S. military veterans from the Million Veteran Program (MVP) cohort. Of these, 71% had European ancestry, 19% had African ancestry, 8% were Hispanic, and 1% were Asian. Just under 10% of the sample was female.
Study participants donated a blood sample and agreed to have their genetic information linked with their electronic health record data.
From diagnostic codes and other sources, researchers identified 121,211 individuals with SITB. They classified participants with no documented lifetime history of suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, or suicide death as controls.
Rates of SITB differed significantly by ancestry – 25% in those with African or Hispanic ancestry, 21% in those with Asian ancestry, and 16.8% in those with European ancestry. Rates also differed by age and sex; those with SITB were younger and more likely to be female.
In addition to age and sex, covariates included “genetic principal components,” which Dr. Ashley-Koch said accounts for combining data of individuals with different ethnic/racial backgrounds.
Through meta-analysis, the investigators identified seven genome-wide, significant cross-ancestry risk loci.
To evaluate whether the findings could be replicated, researchers used the International Suicide Genetics Consortium (ISGC), a primarily civilian international consortium of roughly 550,000 individuals of mostly European ancestry.
The analysis showed the top replicated cross-ancestry risk locus was rs6557168, an intronic single-nucleotide variant (SNV) in the ESR1 gene that encodes an estrogen receptor. Previous work identified ESR1 as a causal genetic driver gene for development of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression, both of which are risk factors for SITB among veterans.
The second-strongest replicated cross-ancestry locus was rs12808482, an intronic variant in the DRD2 gene, which encodes the D2 dopamine-receptor subtype. The authors noted DRD2 is highly expressed in brain tissue and has been associated with numerous psychiatric phenotypes.
Research suggests DRD2 is associated with other risk factors for SITB, such as schizophrenia, mood disorders, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, but DRD2 could also contribute to suicide risk directly. The authors noted it is highly expressed in the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, and hippocampus.
Outstanding candidate gene
The study revealed a cross-ancestry GWS association for rs10671545, a variant in DCC, which is “also an outstanding candidate gene,” the investigators write.
They note it is expressed in brain tissue, is involved in synaptic plasticity, axon guidance, and circadian entrainment, and has been associated with multiple psychiatric phenotypes.
Researchers also found what they called “intriguing” cross-ancestry GWS associations for the TRAF3 gene, which regulates type-1 interferon production. Many patients receiving interferon therapy develop major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation.
TRAF3 is also associated with antisocial behavior, substance use, and ADHD. Lithium – a standard treatment for bipolar disorder that reduces suicide risk – modulates the expression of TRAF3.
Dr. Ashley-Koch noted the replication of these loci (ESR1, DRD2, TRAF3, and DCC) was in a population of mostly White civilians. “This suggests to us that at least some of the risk for suicidal thoughts and behaviors does cross ancestry and also crosses military and civilian populations.”
It was “exciting” that all four genes the study focused on had previously been implicated in other psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Ashley-Koch. “What gave us a little more confidence, above and beyond the replication, was that these genes are somehow important for psychiatric disorders, and not any psychiatric disorders, but the ones that are also associated with a high risk of suicide behavior, such as depression, PTSD, schizophrenia, and ADHD.”
The findings will not have an immediate impact on clinical practice, said Dr. Ashley-Koch.
“We need to take the next step, which is to try to understand how these genetic factors may impact risk and what else is happening biologically to increase that risk. Then once we do that, hopefully we can develop some new treatments,” she added.
‘Valuable and noble’ research
Commenting on the study, Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, said this kind of genetic research is “valuable and noble.”
Researchers have long been interested in risk factors for suicide among military personnel and veterans, said Dr. Ritchie. Evidence to date suggests being a young male is a risk factor as is feeling excluded or not fitting into the unit, and drug or alcohol addiction.
Dr. Ritchie noted other psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, depression, and bipolar disorder, are at least partially inherited.
She noted the study’s findings should not be used to discriminate against those who might have the identified genetic loci without clearer evidence of their impact.
“If we were able to identify these genes, would we start screening everybody who joins the military to see if they have these genes, and how would that impact the ability to recruit or retain personnel?”
She agreed additional work is needed to determine if and how carrying these genes might impact clinical care.
In addition, she pointed out that behavior is influenced not only by genetic load but also by environment. “This study may show the impact of the genetic load a little bit more clearly; right now, we tend to look at environmental factors.”
The study was supported by an award from the Clinical Science Research and Development (CSR&D) service of the Veterans Health Administration’s Office of Research and Development. The work was also supported in part by the joint U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and U.S. Department of Energy MVP CHAMPION program.
Dr. Ashley-Koch reported grants from Veterans Administration during the conduct of the study. Several other coauthors report relationships with industry, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies. The full list can be found with the original article. Dr. Ritchie reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“It’s really important for us to continue to study the genetic risk factors for suicidal behaviors so we can really understand the biology and develop better treatments,” study investigator Allison E. Ashley-Koch, PhD, professor in the department of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry).
SITB heritability
Suicide is a leading cause of death, particularly among individuals aged 15-29 years. Whereas the global rate of suicide has decreased by 36% in the past 20 years, the rate in the United States has increased by 35%, with the greatest rise in military veterans.
Twin studies suggest heritability for SITB is between 30% and 55%, but the molecular genetic basis of SITB remains elusive.
To address this research gap, investigators conducted a study of 633,778 U.S. military veterans from the Million Veteran Program (MVP) cohort. Of these, 71% had European ancestry, 19% had African ancestry, 8% were Hispanic, and 1% were Asian. Just under 10% of the sample was female.
Study participants donated a blood sample and agreed to have their genetic information linked with their electronic health record data.
From diagnostic codes and other sources, researchers identified 121,211 individuals with SITB. They classified participants with no documented lifetime history of suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, or suicide death as controls.
Rates of SITB differed significantly by ancestry – 25% in those with African or Hispanic ancestry, 21% in those with Asian ancestry, and 16.8% in those with European ancestry. Rates also differed by age and sex; those with SITB were younger and more likely to be female.
In addition to age and sex, covariates included “genetic principal components,” which Dr. Ashley-Koch said accounts for combining data of individuals with different ethnic/racial backgrounds.
Through meta-analysis, the investigators identified seven genome-wide, significant cross-ancestry risk loci.
To evaluate whether the findings could be replicated, researchers used the International Suicide Genetics Consortium (ISGC), a primarily civilian international consortium of roughly 550,000 individuals of mostly European ancestry.
The analysis showed the top replicated cross-ancestry risk locus was rs6557168, an intronic single-nucleotide variant (SNV) in the ESR1 gene that encodes an estrogen receptor. Previous work identified ESR1 as a causal genetic driver gene for development of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression, both of which are risk factors for SITB among veterans.
The second-strongest replicated cross-ancestry locus was rs12808482, an intronic variant in the DRD2 gene, which encodes the D2 dopamine-receptor subtype. The authors noted DRD2 is highly expressed in brain tissue and has been associated with numerous psychiatric phenotypes.
Research suggests DRD2 is associated with other risk factors for SITB, such as schizophrenia, mood disorders, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, but DRD2 could also contribute to suicide risk directly. The authors noted it is highly expressed in the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, and hippocampus.
Outstanding candidate gene
The study revealed a cross-ancestry GWS association for rs10671545, a variant in DCC, which is “also an outstanding candidate gene,” the investigators write.
They note it is expressed in brain tissue, is involved in synaptic plasticity, axon guidance, and circadian entrainment, and has been associated with multiple psychiatric phenotypes.
Researchers also found what they called “intriguing” cross-ancestry GWS associations for the TRAF3 gene, which regulates type-1 interferon production. Many patients receiving interferon therapy develop major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation.
TRAF3 is also associated with antisocial behavior, substance use, and ADHD. Lithium – a standard treatment for bipolar disorder that reduces suicide risk – modulates the expression of TRAF3.
Dr. Ashley-Koch noted the replication of these loci (ESR1, DRD2, TRAF3, and DCC) was in a population of mostly White civilians. “This suggests to us that at least some of the risk for suicidal thoughts and behaviors does cross ancestry and also crosses military and civilian populations.”
It was “exciting” that all four genes the study focused on had previously been implicated in other psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Ashley-Koch. “What gave us a little more confidence, above and beyond the replication, was that these genes are somehow important for psychiatric disorders, and not any psychiatric disorders, but the ones that are also associated with a high risk of suicide behavior, such as depression, PTSD, schizophrenia, and ADHD.”
The findings will not have an immediate impact on clinical practice, said Dr. Ashley-Koch.
“We need to take the next step, which is to try to understand how these genetic factors may impact risk and what else is happening biologically to increase that risk. Then once we do that, hopefully we can develop some new treatments,” she added.
‘Valuable and noble’ research
Commenting on the study, Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, said this kind of genetic research is “valuable and noble.”
Researchers have long been interested in risk factors for suicide among military personnel and veterans, said Dr. Ritchie. Evidence to date suggests being a young male is a risk factor as is feeling excluded or not fitting into the unit, and drug or alcohol addiction.
Dr. Ritchie noted other psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, depression, and bipolar disorder, are at least partially inherited.
She noted the study’s findings should not be used to discriminate against those who might have the identified genetic loci without clearer evidence of their impact.
“If we were able to identify these genes, would we start screening everybody who joins the military to see if they have these genes, and how would that impact the ability to recruit or retain personnel?”
She agreed additional work is needed to determine if and how carrying these genes might impact clinical care.
In addition, she pointed out that behavior is influenced not only by genetic load but also by environment. “This study may show the impact of the genetic load a little bit more clearly; right now, we tend to look at environmental factors.”
The study was supported by an award from the Clinical Science Research and Development (CSR&D) service of the Veterans Health Administration’s Office of Research and Development. The work was also supported in part by the joint U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and U.S. Department of Energy MVP CHAMPION program.
Dr. Ashley-Koch reported grants from Veterans Administration during the conduct of the study. Several other coauthors report relationships with industry, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies. The full list can be found with the original article. Dr. Ritchie reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Treating PTSD: A review of 8 studies
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder. The lifetime prevalence among American adults is 6.8%.1 Management of PTSD includes treating distressing symptoms, reducing avoidant behaviors, treating comorbid conditions (eg, depression, substance use disorders, or mood dysregulation), and improving adaptive functioning, which includes restoring a psychological sense of safety and trust. PTSD can be treated using evidence-based psychotherapies, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of both modalities. For adults, evidence-based treatment guidelines recommend the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, cognitive therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy.2 These guidelines also recommend (with some reservations) the use of brief eclectic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, and narrative exposure therapy.2 Although the evidence base for the use of medications is not as strong as that for the psychotherapies listed above, the guidelines recommend the use of fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine.2
Currently available treatments for PTSD have significant limitations. For example, trauma-focused psychotherapies can have significant rates of nonresponse, partial response, or treatment dropout.3,4 Additionally, such therapies are not widely accessible. As for pharmacotherapy, very few available options are supported by evidence, and the efficacy of these options is limited, as shown by the reports that only 60% of patients with PTSD show a response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and only 20% to 30% achieve complete remission.5 Additionally, it may take months for patients to achieve an acceptable level of improvement with medications. As a result, a substantial proportion of patients who seek treatment continue to remain symptomatic, with impaired levels of functioning. This lack of progress in PTSD treatment has been labeled as a national crisis, calling for an urgent need to find effective pharmacologic treatments for PTSD.6
In this article, we review 8 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of treatments for PTSD published within the last 5 years (Table7-14).
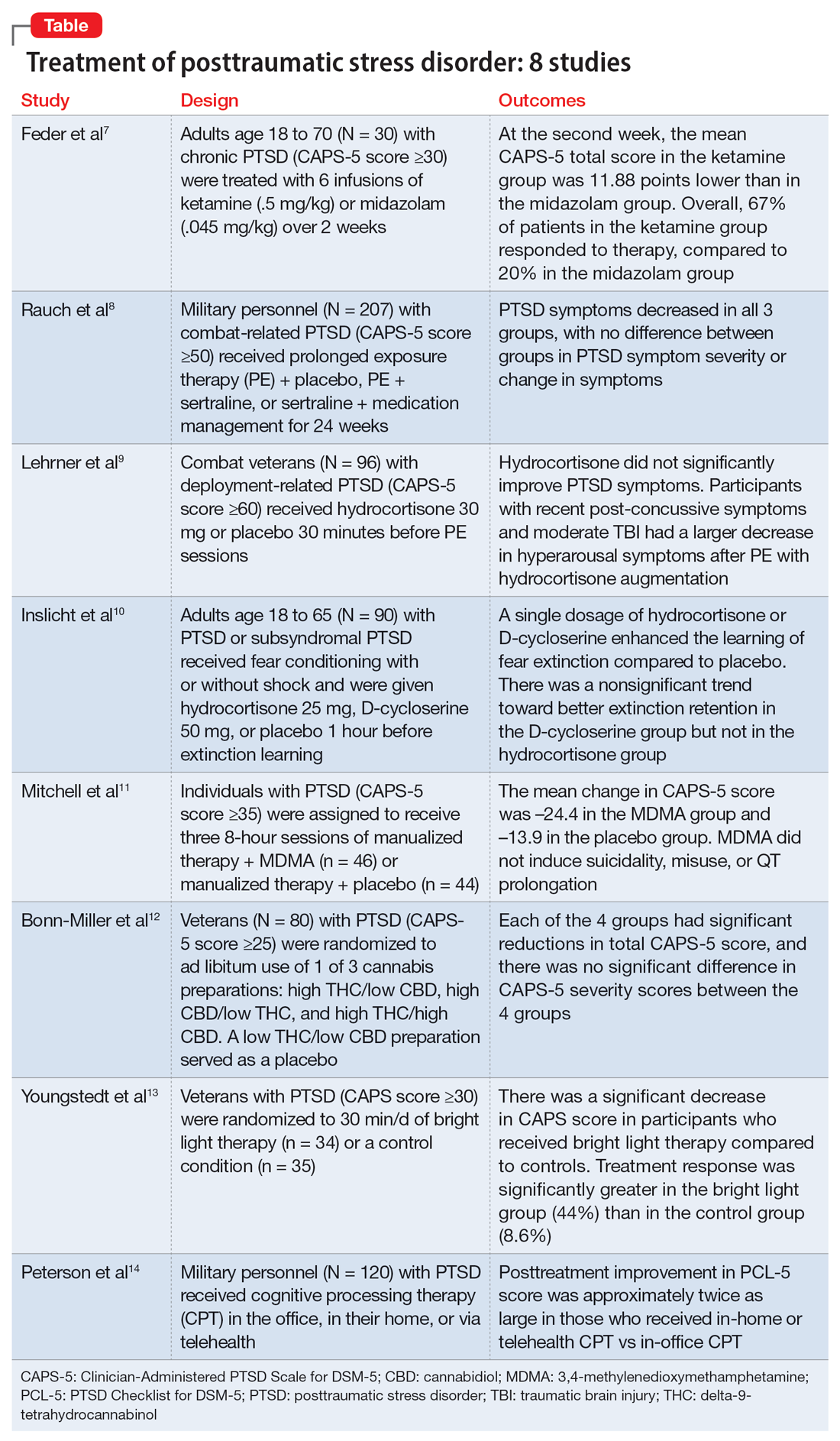
1. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202
Feder et al had previously found a significant and quick decrease in PTSD symptoms after a single dose of IV ketamine had. This is the first RCT to examine the effectiveness and safety of repeated IV ketamine infusions for the treatment of persistent PTSD.7
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, parallel-arm controlled trial treated 30 individuals with chronic PTSD with 6 infusions of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) over 2 consecutive weeks.
- Participants were individuals age 18 to 70 with a primary diagnosis of chronic PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria and determined by The Structure Clinical Interview for DSM-5, with a score ≥30 on the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5).
- Any severe or unstable medical condition, active suicidal or homicidal ideation, lifetime history of psychotic or bipolar disorder, current anorexia nervosa or bulimia, alcohol or substance use disorder within 3 months of screening, history of recreational ketamine or phencyclidine use on more than 1 occasion or any use in the previous 2 years, and ongoing treatment with a long-acting benzodiazepine or opioid medication were all considered exclusion criteria. Individuals who took short-acting benzodiazepines had their morning doses held on infusion days. Marijuana or cannabis derivatives were allowed.
- The primary outcome measure was a change in PTSD symptom severity as measured with CAPS-5. This was administered before the first infusion and weekly thereafter. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised, the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and adverse effect measurements were used as secondary outcome measures.
- Treatment response was defined as ≥30% symptom improvement 2 weeks after the first infusion as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Individuals who responded to treatment were followed naturalistically weekly for up to 4 weeks and then monthly until loss of responder status, or up to 6 months if there was no loss of response.
Outcomes
- At the second week, the mean CAPS-5 total score in the ketamine group was 11.88 points (SE = 3.96) lower than in the midazolam group (d = 1.13; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.91).
- In the ketamine group, 67% of patients responded to therapy, compared to 20% in the midazolam group.
- Following the 2-week course of infusions, the median period until loss of response among ketamine responders was 27.5 days.
- Ketamine infusions showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated ketamine infusions are effective in reducing symptom severity in individuals with chronic PTSD.
- Limitations to this study include the exclusion of individuals with comorbid bipolar disorder, current alcohol or substance use disorder, or suicidal ideations, the small sample size, and a higher rate of transient dissociative symptoms in the ketamine group.
- Future studies could evaluate the efficacy of repeated ketamine infusions in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Also, further studies are required to assess the efficacy of novel interventions to prevent relapse and evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of periodic IV ketamine use as maintenance.
- Additional research might determine whether pairing psychotherapy with ketamine administration can lessen the risk of recurrence for PTSD patients after stopping ketamine infusions.
2. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126
Clinical practice recommendations for PTSD have identified trauma-focused psychotherapies and SSRIs as very effective treatments. The few studies that have compared trauma-focused psychotherapy to SSRIs or to a combination of treatments are not generalizable, have significant limitations, or are primarily concerned with refractory disorders or augmentation techniques. This study evaluated the efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy (PE) plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management in the treatment of PTSD.8
Study design
- This randomized, 4-site, 24-week clinical trial divided participants into 3 subgroups: PE plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management.
- Participants were veterans or service members of the Iraq and/or Afghanistan wars with combat-related PTSD and significant impairment as indicated by a CAPS score ≥50 for at least 3 months. The DSM-IV-TR version of CAPS was used because the DSM-5 version was not available at the time of the study.
- Individuals who had a current, imminent risk of suicide; active psychosis; alcohol or substance dependence in the past 8 weeks; inability to attend weekly appointments for the treatment period; prior intolerance to or failure of an adequate trial of PE or sertraline; medical illness likely to result in hospitalization or contraindication to study treatment; serious cognitive impairment; mild traumatic brain injury; or concurrent use of antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, prazosin, or sleep agents were excluded.
- Participants completed up to thirteen 90-minute sessions of PE.
- The sertraline dosage was titrated during a 10-week period and continued until Week 24. Dosages were adjusted between 50 and 200 mg/d, with the last dose increase at Week 10.
- The primary outcome measure was symptom severity of PTSD in the past month as determined by CAPS score at Week 24.
- The secondary outcome was self-reported symptoms of PTSD (PTSD checklist [PCL] Specific Stressor Version), clinically meaningful change (reduction of ≥20 points or score ≤35 on CAPS), response (reduction of ≥50% in CAPS score), and remission (CAPS score ≤35).
Outcomes
- At Week 24, 149 participants completed the study; 207 were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- PTSD symptoms significantly decreased over 24 weeks, according to a modified intent-to-treat analysis utilizing a mixed model of repeated measurements; nevertheless, slopes were similar across therapy groups.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Although the severity of PTSD symptoms decreased in all 3 subgroups, there was no difference in PTSD symptom severity or change in symptoms at Week 24 among all 3 subgroups.
- The main limitation of this study was the inclusion of only combat veterans.
- Further research should focus on enhancing treatment retention and should include administering sustained exposure therapy at brief intervals.
3. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924
First-line therapy for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapies such as PE. However, because many people still have major adverse effects after receiving medication, improving treatment efficacy is a concern. Glucocorticoids promote extinction learning, and alterations in glucocorticoid signaling pathways have been associated with PTSD. Lehrner et al previously showed that adding hydrocortisone (HCORT) to PE therapy increased patients’ glucocorticoid sensitivity at baseline, improved treatment retention, and resulted in greater treatment improvements. This study evaluated HCORT in conjunction with PE for combat veterans with PTSD following deployment to Iraq and Afghanistan.9
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial administered HCORT 30 mg oral or placebo to 96 combat veterans 30 minutes before PE sessions.
- Participants were veterans previously deployed to Afghanistan or Iraq with deployment-related PTSD >6 months with a minimum CAPS score of 60. They were unmedicated or on a stable psychotropic regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of a primary psychotic disorder (bipolar I disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder), medical or mental health condition other than PTSD that required immediate clinical attention, moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), substance abuse or dependence within the past 3 months, medical illness that contraindicated ingestion of hydrocortisone, acute suicide risk, and pregnancy or intent to become pregnant.
- The primary outcome measures included PTSD severity as assessed with CAPS.
- Secondary outcome measures included self-reported PTSD symptoms as assessed with the Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale (PDS) and depression as assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI). These scales were administered pretreatment, posttreatment, and at 3-months follow-up.
Outcomes
- Out of 96 veterans enrolled, 60 were randomized and 52 completed the treatment.
- Five participants were considered recovered early and completed <12 sessions.
- Of those who completed treatment, 50 completed the 1-week posttreatment evaluations and 49 completed the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
- There was no difference in the proportion of dropouts (13.33%) across the conditions.
- HCORT failed to significantly improve either secondary outcomes or PTSD symptoms, according to an intent-to-treat analysis.
- However, exploratory analyses revealed that veterans with recent post-concussive symptoms and moderate TBI exposure saw a larger decrease in hyperarousal symptoms after PE therapy with HCORT augmentation.
- The reduction in avoidance symptoms with HCORT augmentation was also larger in veterans with higher baseline glucocorticoid sensitivity.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- HCORT does not improve PTSD symptoms as assessed with the CAPS and PDS, or depression as assessed with the BDI.
- The main limitation of this study is generalizability.
- Further studies are needed to determine whether PE with HCORT could benefit veterans with indicators of enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity, mild TBI, or postconcussive syndrome.
4. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952
PE, one of the most well-researched therapies for PTSD, is based on fear extinction. Exploring pharmacotherapies that improve fear extinction learning and their potential as supplements to PE is gaining increased attention. Such pharmacotherapies aim to improve the clinical impact of PE on the extent and persistence of symptom reduction. This study evaluated the effects of HCORT and D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, on the learning and consolidation of fear extinction in patients with PTSD.10
Study design
- This double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-group experimental design evaluated 90 individuals with PTSD who underwent fear conditioning with stimuli that was paired (CS+) or unpaired (CS−) with shock.
- Participants were veterans and civilians age 18 to 65 recruited from VA outpatient and community clinics and internet advertisements who met the criteria for PTSD or subsyndromal PTSD (according to DSM-IV criteria) for at least 3 months.
- Exclusion criteria included schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, substance abuse or dependence, alcohol dependence, previous moderate or severe head injury, seizure or neurological disorder, current infectious illness, systemic illness affecting CNS function, or other conditions known to affect psychophysiological responses. Excluded medications were antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, alpha- and beta-adrenergics, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, and steroids.
- Extinction learning took place 72 hours after extinction, and extinction retention was evaluated 1 week later. Placebo, HCORT 25 mg, or DCS 50 mg was given 1 hour before extinction learning.
- Clinical measures included PTSD diagnosis and symptom levels as determined by interview using CAPS and skin conduction response.
Outcomes
- The mean shock level, mean pre-stimulus skin conductance level (SCL) during habituation, and mean SC orienting response during the habituation phase did not differ between groups and were not associated with differential fear conditioning. Therefore, variations in shock level preference, resting SCL, or SC orienting response magnitude are unlikely to account for differences between groups during extinction learning and retention.
- During extinction learning, the DCS and HCORT groups showed a reduced differential CS+/CS− skin conductance response (SCR) compared to placebo.
- One week later, during the retention testing, there was a nonsignificant trend toward a smaller differential CS+/CS− SCR in the DCS group compared to placebo. HCORT and DCS administered as a single dosage facilitated fear extinction learning in individuals with PTSD symptoms.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- In traumatized people with PTSD symptoms, a single dosage of HCORT or DCS enhanced the learning of fear extinction compared to placebo. A nonsignificant trend toward better extinction retention in the DCS group but not the HCORT group was also visible.
- These results imply that glucocorticoids and NMDA agonists have the potential to promote extinction learning in PTSD.
- Limitations include a lack of measures of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
- Further studies could evaluate these findings with the addition of blood biomarker measures such as glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
5. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
Poor PTSD treatment results are associated with numerous comorbid conditions, such as dissociation, depression, alcohol and substance use disorders, childhood trauma, and suicidal ideation, which frequently leads to treatment resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to find a treatment that works for individuals with PTSD who also have comorbid conditions. In animal models, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), an empathogen/entactogen with stimulant properties, has been shown to enhance fear memory extinction and modulate fear memory reconsolidation. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy for treating patients with severe PTSD, including those with common comorbidities.11
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-site, phase 3 clinical trial evaluated individuals randomized to receive manualized therapy with MDMA or with placebo, combined with 3 preparatory and 9 integrative therapy sessions.
- Participants were 90 individuals (46 randomized to MDMA and 44 to placebo) with PTSD with a symptom duration ≥6 months and CAPS-5 total severity score ≥35 at baseline.
- Exclusion criteria included primary psychotic disorder, bipolar I disorder, eating disorders with active purging, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, dissociative identity disorder, personality disorders, current alcohol and substance use disorders, lactation or pregnancy, and any condition that could make receiving a sympathomimetic medication dangerous due to hypertension or tachycardia, including uncontrolled hypertension, history of arrhythmia, or marked baseline prolongation of QT and/or QTc interval.
- Three 8-hour experimental sessions of either therapy with MDMA assistance or therapy with a placebo control were given during the treatment period, and they were spaced approximately 4 weeks apart.
- In each session, participants received placebo or a single divided dose of MDMA 80 to 180 mg.
- At baseline and 2 months after the last experimental sessions, PTSD symptoms were measured with CAPS-5, and functional impairment was measured with Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS).
- The primary outcome measure was CAPS-5 total severity score at 18 weeks compared to baseline for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
- The secondary outcome measure was clinician-rated functional impairment using the mean difference in SDS total scores from baseline to 18 weeks for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
Outcomes
- MDMA was found to induce significant and robust attenuation in CAPS-5 score compared to placebo.
- The mean change in CAPS-5 score in completers was –24.4 in the MDMA group and –13.9 in the placebo group.
- MDMA significantly decreased the SDS total score.
- MDMA did not induce suicidality, misuse, or QT prolongation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- MDMA-assisted therapy is significantly more effective than manualized therapy with placebo in treating patients with severe PTSD, and it is also safe and well-tolerated, even in individuals with comorbidities.
- No major safety issues were associated with MDMA-assisted treatment.
- MDMA-assisted therapy should be promptly assessed for clinical usage because it has the potential to significantly transform the way PTSD is treated.
- Limitations of this study include a smaller sample size (due to the COVID-19 pandemic); lack of ethnic and racial diversity; short duration; safety data were collected by site therapist, which limited the blinding; and the blinding of participants was difficult due to the subjective effects of MDMA, which could have resulted in expectation effects.
6. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990
Sertraline and paroxetine are the only FDA-approved medications for treating PTSD. Some evidence suggests cannabis may provide a therapeutic benefit for PTSD.15 This study examined the effects of 3 different preparations of cannabis for treating PTSD symptoms.12
Study design
- This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial used 3 active treatment groups of cannabis: high delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/low cannabidiol (CBD), high CBD/low THC, and high THC/high CBD (THC+CBD). A low THC/low CBD preparation was used as a placebo. “High” content contained 9% to 15% concentration by weight of the respective cannabinoid, and “low” content contained <2% concentration by weight.
- Inclusion criteria included being a US military veteran, meeting DSM-5 PTSD criteria for ≥6 months, having moderate symptom severity (CAPS-5 score ≥25), abstaining from cannabis 2 weeks prior to study and agreeing not to use any non-study cannabis during the trial, and being stable on medications/therapy prior to the study.
- Exclusion criteria included women who were pregnant/nursing/child-bearing age and not taking an effective means of birth control; current/past serious mental illness, including psychotic and personality disorders; having a first-degree relative with a psychotic or bipolar disorder; having a high suicide risk based on Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale; meeting DSM-5 criteria for moderate-severe cannabis use disorder; screening positive for illicit substances; or having significant medical disease.
- Participants in Stage 1 (n = 80) were randomized to 1 of the 3 active treatments or placebo for 3 weeks. After a 2-week washout, participants in Stage 2 (n = 74) were randomized to receive for 3 weeks 1 of the 3 active treatments they had not previously received.
- During each stage, participants had ad libitum use for a maximum of 1.8 g/d.
- The primary outcome was change in PTSD symptom severity by the end of Stage 1 as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Secondary outcomes included the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the general depression subscale and anxiety subscale from the self-report Inventory of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms (IDAS), the Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning, and the Insomnia Severity Index.
Outcomes
- Six participants did not continue to Stage 2. Three participants did not finish Stage 2 due to adverse effects, and 7 did not complete outcome measurements. The overall attrition rate was 16.3%.
- There was no significant difference in total grams of smoked cannabis or placebo between the 4 treatment groups in Stage 1 at the end of 3 weeks. In Stage 2, there was a significant difference, with the THC+CBD group using more cannabis compared to the other 2 groups.
- Each of the 4 groups had significant reductions in total CAPS-5 scores at the end of Stage 1, and there was no significant difference in CAPS-5 severity scores between the 4 groups.
- In Stage 1, PCL-5 scores were not significantly different between treatment groups from baseline to the end of stage. There was a significant difference in Stage 2 between the high CBD and THC+CBD groups, with the combined group reporting greater improvement of symptoms.
- In Stage 2, the THC+CBD group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores and IDAS general depression scores, and the high THC group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores.
- In Stage 1, 37 of 60 participants in the active groups reported at least 1 adverse event, and 45 of the 74 Stage 2 participants reported at least 1 adverse event. The most common adverse events were cough, throat irritation, and anxiety. Participants in the Stage 1 high THC group had a significant increase in reported withdrawal symptoms after 1 week of stopping use.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- This first randomized, placebo-control trial of cannabis in US veterans did not show a significant difference among treatment groups, including placebo, on the primary outcome of CAPS-5 score. All 4 groups had significant reductions in symptom severity on CAPS-5 and showed good tolerability.
- Prior beliefs about the effects of cannabis may have played a role in the reduction of PTSD symptoms in the placebo group.
- Many participants (n =34) were positive for THC during the screening process, so previous cannabis use/chronicity of cannabis use may have contributed.
- One limitation was that participants assigned to the Stage 1 high THC group had Cannabis Use Disorders Identification Test scores (which assesses cannabis use disorder risk) about 2 times greater than participants in other conditions.
- Another limitation was that total cannabis use was lower than expected, as participants in Stage 1 used 8.2 g to 14.6 g over 3 weeks, though they had access to up to 37.8 g.
- There was no placebo in Stage 2.
- Future studies should look at longer treatment periods with more participants.
7. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444
Bright light therapy is an inexpensive treatment approach that may affect serotonergic pathways.16 This study examined bright light therapy for reducing PTSD symptoms and examined if improvement of PTSD is related to a shift in circadian rhythm.13
Study design
- Veterans with combat-related PTSD had to have been stable on treatment for at least 8 weeks or to have not received any other PTSD treatments prior to the study.
- Participants were randomized to active treatment of 30 minutes daily 10,000 lux ultraviolet-filtered white light while sitting within 18 inches (n = 34) or a control condition of 30 minutes daily inactivated negative ion generator (n = 35) for 4 weeks.
- Inclusion criteria included a CAPS score ≥30.
- Exclusion criteria included high suicidality, high probability of alcohol/substance abuse in the past 3 months, bipolar disorder/mania/schizophrenia/psychosis, ophthalmologic deformities, shift work in past 2 months or travel across time zones in past 2 weeks, head trauma, high outdoor light exposure, history of winter depression, history of seizures, or myocardial infarction/stroke/cancer within 3 years.
- Primary outcomes were improvement on CAPS and Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-IM) score at Week 4.
- Wrist actigraphy recordings measured sleep.
- Other measurements included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton atypical symptoms (HAM-AS), PCL-Military (PCL-M), Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), BDI, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI Form Y-2), Beck Suicide Scale, and Systematic Assessment for Treatment Emergent Effects questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There was a significant decrease in CAPS score in participants who received bright light therapy compared to controls. Treatment response (defined as ≥33% reduction in score) was significantly greater in the bright light (44%) vs control (8.6%) group. No participants achieved remission.
- There was a significant improvement in CGI-IM scores in the bright light group, but no significant difference in participants who were judged to improve “much” or “very much.”
- PCL-M scores did not change significantly between groups, although a significantly greater proportion of participants had treatment response in the bright light group (33%) vs control (6%).
- There were no significant changes in HAM-D, HAM-AS, STAI, BDI, actigraphic estimates of sleep, or PSQI scores.
- Bright light therapy resulted in phase advancement while control treatment had phase delay.
- There were no significant differences in adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Bright light therapy may be a treatment option or adjunct for combat-related PTSD as seen by improvement on CAPS and CGI scores, as well as a greater treatment response seen on CAPS and PCL-5 scores in the bright light group.
- There was no significant difference for other measures, including depression, anxiety, and sleep.
- Limitations include excluding patients with a wide variety of medical or psychiatric comorbidities, as well as limited long-term follow up data.
- Other limitations include not knowing the precise amount of time participants stayed in front of the light device and loss of some actigraphic data (data from only 49 of 69 participants).
8. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41 doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT), a type of trauma-focused psychotherapy, is an effective treatment for PTSD in the military population.17,18 However, patients may not be able to or want to participate in such therapy due to barriers such as difficulty arranging transportation, being homebound due to injury, concerns about COVID-19, stigma, familial obligations, and job constraints. This study looked at if CPT delivered face-to-face at the patient’s home or via telehealth in home would be effective and increase accessibility.14
Study design
- Participants (n = 120) were active-duty military and veterans who met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD. They were randomized to receive CPT in the office, in their home, or via telehealth. Participants could choose not to partake in 1 modality but were then randomized to 1 of the other 2.
- Exclusion criteria included suicide/homicide risk needing intervention, items/situations pertaining to danger (ie, aggressive pet or unsafe neighborhood), significant alcohol/substance use, active psychosis, and impaired cognitive functioning.
- The primary outcome measurement was change in PCL-5 and CAPS-5 score over 6 months. The BDI-II was used to assess depressive symptoms.
- Secondary outcomes included the Reliable Change Index (defined as “an improvement of 10 or more points that was sustained at all subsequent assessments”) on the PCL-5 and remission on the CAPS-5.
- CPT was delivered in 60-minute sessions twice a week for 6 weeks. Participants who did not have electronic resources were loaned a telehealth apparatus.
Outcomes
- Overall, 57% of participants opted out of 1 modality, which resulted in fewer participants being placed into the in-home arm (n = 32). Most participants chose not to do in-home treatments (54%), followed by in-office (29%), and telehealth (17%).
- There was a significant posttreatment improvement in PCL-5 scores in all treatment arms, with improvement greater with in-home (d = 2.1) and telehealth (d = 2.0) vs in-office (d=1.3). The in-home and telehealth scores were significantly improved compared to in-office, and the difference between in-home and telehealth PCL-5 scores was minimal.
- At 6 months posttreatment, the differences between the 3 treatment groups on PCL-5 score were negligible.
- CAPS-5 scores were significantly improved in all treatment arms, with improvement largest with in-home treatment; however, the differences between the groups were not significant.
- BDI-II scores improved in all modalities but were larger in the in-home (d = 1.2) and telehealth (d = 1.1) arms than the in-office arm (d = 0.52).
- Therapist time commitment was greater for the in-home and in-office arms (2 hours/session) than the telehealth arm (1 hour/session). This difference was due to commuting time for the patient or therapist.
- The dropout rate was not statistically significant between the groups.
- Adverse events did not significantly differ per group. The most commonly reported ones included nightmares, sleep difficulty, depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients undergoing CPT had significant improvement in PTSD symptoms, with posttreatment PCL-5 improvement approximately twice as large in those who received the in-home and telehealth modalities vs in-office treatment.
- The group differences were not seen on CAPS-5 scores at posttreatment, or PCL-5 or CAPS-5 scores at 6 months posttreatment.
- In-home CPT was declined the most, which suggests that in-home distractions or the stigma of a mental health clinician being in their home played a role in patients’ decision-making. However, in-home CPT produced the greatest amount of improvement in PTSD symptoms. The authors concluded that in-home therapy should be reserved for those who are homebound or have travel limitations.
- This study shows evidence that telehealth may be a good modality for CPT, as seen by improvement in PTSD symptoms and good acceptability and retention.
- Limitations include more patients opting out of in-home CPT, and reimbursement for travel may not be available in the real-world setting.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Delmer O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Guideline Development Panel for the Treatment of PTSD in Adults, American Psychological Association. Summary of the clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. Am Psychol. 2019;74(5):596-607. doi: 10.1037/amp0000473
3. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Hoge CW, et al. Psychotherapy for military-related PTSD: a review of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2015;314(5):489-500.
4. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Marmar CR. First-line psychotherapies for military-related PTSD. JAMA. 2020;323(7):656-657.
5. Berger W, Mendlowicz MV, Marques-Portella C, et al. Pharmacologic alternatives to antidepressants in posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33(3):169-180.
6. Krystal JH, Davis LL, Neylan TC, et al. It is time to address the crisis in the pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a consensus statement of the PTSD Psychopharmacology Working Group. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(7):e51-e59.
7. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20050596
8. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3412
9. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2021.103924
10. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01222-z
11. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
12. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246990
13. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab014
14. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
15. Loflin MJ, Babson KA, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabinoids as therapeutic for PTSD. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;14:78-83. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.12.001
16. Neumeister A, Praschak-Rieder N, Besselmann B, et al. Effects of tryptophan depletion on drug-free patients with seasonal affective disorder during a stable response to bright light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(2):133-138. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140043008
17. Kaysen D, Schumm J, Pedersen ER, et al. Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorders. Addict Behav. 2014;39(2):420-427. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.08.016
18. Resick PA, Wachen JS, Mintz J, et al. A randomized clinical trial of group cognitive processing therapy compared with group present-centered therapy for PTSD among active duty military personnel. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(6):1058-1068. doi:10.1037/ccp0000016
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder. The lifetime prevalence among American adults is 6.8%.1 Management of PTSD includes treating distressing symptoms, reducing avoidant behaviors, treating comorbid conditions (eg, depression, substance use disorders, or mood dysregulation), and improving adaptive functioning, which includes restoring a psychological sense of safety and trust. PTSD can be treated using evidence-based psychotherapies, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of both modalities. For adults, evidence-based treatment guidelines recommend the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, cognitive therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy.2 These guidelines also recommend (with some reservations) the use of brief eclectic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, and narrative exposure therapy.2 Although the evidence base for the use of medications is not as strong as that for the psychotherapies listed above, the guidelines recommend the use of fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine.2
Currently available treatments for PTSD have significant limitations. For example, trauma-focused psychotherapies can have significant rates of nonresponse, partial response, or treatment dropout.3,4 Additionally, such therapies are not widely accessible. As for pharmacotherapy, very few available options are supported by evidence, and the efficacy of these options is limited, as shown by the reports that only 60% of patients with PTSD show a response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and only 20% to 30% achieve complete remission.5 Additionally, it may take months for patients to achieve an acceptable level of improvement with medications. As a result, a substantial proportion of patients who seek treatment continue to remain symptomatic, with impaired levels of functioning. This lack of progress in PTSD treatment has been labeled as a national crisis, calling for an urgent need to find effective pharmacologic treatments for PTSD.6
In this article, we review 8 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of treatments for PTSD published within the last 5 years (Table7-14).

1. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202
Feder et al had previously found a significant and quick decrease in PTSD symptoms after a single dose of IV ketamine had. This is the first RCT to examine the effectiveness and safety of repeated IV ketamine infusions for the treatment of persistent PTSD.7
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, parallel-arm controlled trial treated 30 individuals with chronic PTSD with 6 infusions of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) over 2 consecutive weeks.
- Participants were individuals age 18 to 70 with a primary diagnosis of chronic PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria and determined by The Structure Clinical Interview for DSM-5, with a score ≥30 on the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5).
- Any severe or unstable medical condition, active suicidal or homicidal ideation, lifetime history of psychotic or bipolar disorder, current anorexia nervosa or bulimia, alcohol or substance use disorder within 3 months of screening, history of recreational ketamine or phencyclidine use on more than 1 occasion or any use in the previous 2 years, and ongoing treatment with a long-acting benzodiazepine or opioid medication were all considered exclusion criteria. Individuals who took short-acting benzodiazepines had their morning doses held on infusion days. Marijuana or cannabis derivatives were allowed.
- The primary outcome measure was a change in PTSD symptom severity as measured with CAPS-5. This was administered before the first infusion and weekly thereafter. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised, the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and adverse effect measurements were used as secondary outcome measures.
- Treatment response was defined as ≥30% symptom improvement 2 weeks after the first infusion as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Individuals who responded to treatment were followed naturalistically weekly for up to 4 weeks and then monthly until loss of responder status, or up to 6 months if there was no loss of response.
Outcomes
- At the second week, the mean CAPS-5 total score in the ketamine group was 11.88 points (SE = 3.96) lower than in the midazolam group (d = 1.13; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.91).
- In the ketamine group, 67% of patients responded to therapy, compared to 20% in the midazolam group.
- Following the 2-week course of infusions, the median period until loss of response among ketamine responders was 27.5 days.
- Ketamine infusions showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated ketamine infusions are effective in reducing symptom severity in individuals with chronic PTSD.
- Limitations to this study include the exclusion of individuals with comorbid bipolar disorder, current alcohol or substance use disorder, or suicidal ideations, the small sample size, and a higher rate of transient dissociative symptoms in the ketamine group.
- Future studies could evaluate the efficacy of repeated ketamine infusions in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Also, further studies are required to assess the efficacy of novel interventions to prevent relapse and evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of periodic IV ketamine use as maintenance.
- Additional research might determine whether pairing psychotherapy with ketamine administration can lessen the risk of recurrence for PTSD patients after stopping ketamine infusions.
2. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126
Clinical practice recommendations for PTSD have identified trauma-focused psychotherapies and SSRIs as very effective treatments. The few studies that have compared trauma-focused psychotherapy to SSRIs or to a combination of treatments are not generalizable, have significant limitations, or are primarily concerned with refractory disorders or augmentation techniques. This study evaluated the efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy (PE) plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management in the treatment of PTSD.8
Study design
- This randomized, 4-site, 24-week clinical trial divided participants into 3 subgroups: PE plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management.
- Participants were veterans or service members of the Iraq and/or Afghanistan wars with combat-related PTSD and significant impairment as indicated by a CAPS score ≥50 for at least 3 months. The DSM-IV-TR version of CAPS was used because the DSM-5 version was not available at the time of the study.
- Individuals who had a current, imminent risk of suicide; active psychosis; alcohol or substance dependence in the past 8 weeks; inability to attend weekly appointments for the treatment period; prior intolerance to or failure of an adequate trial of PE or sertraline; medical illness likely to result in hospitalization or contraindication to study treatment; serious cognitive impairment; mild traumatic brain injury; or concurrent use of antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, prazosin, or sleep agents were excluded.
- Participants completed up to thirteen 90-minute sessions of PE.
- The sertraline dosage was titrated during a 10-week period and continued until Week 24. Dosages were adjusted between 50 and 200 mg/d, with the last dose increase at Week 10.
- The primary outcome measure was symptom severity of PTSD in the past month as determined by CAPS score at Week 24.
- The secondary outcome was self-reported symptoms of PTSD (PTSD checklist [PCL] Specific Stressor Version), clinically meaningful change (reduction of ≥20 points or score ≤35 on CAPS), response (reduction of ≥50% in CAPS score), and remission (CAPS score ≤35).
Outcomes
- At Week 24, 149 participants completed the study; 207 were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- PTSD symptoms significantly decreased over 24 weeks, according to a modified intent-to-treat analysis utilizing a mixed model of repeated measurements; nevertheless, slopes were similar across therapy groups.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Although the severity of PTSD symptoms decreased in all 3 subgroups, there was no difference in PTSD symptom severity or change in symptoms at Week 24 among all 3 subgroups.
- The main limitation of this study was the inclusion of only combat veterans.
- Further research should focus on enhancing treatment retention and should include administering sustained exposure therapy at brief intervals.
3. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924
First-line therapy for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapies such as PE. However, because many people still have major adverse effects after receiving medication, improving treatment efficacy is a concern. Glucocorticoids promote extinction learning, and alterations in glucocorticoid signaling pathways have been associated with PTSD. Lehrner et al previously showed that adding hydrocortisone (HCORT) to PE therapy increased patients’ glucocorticoid sensitivity at baseline, improved treatment retention, and resulted in greater treatment improvements. This study evaluated HCORT in conjunction with PE for combat veterans with PTSD following deployment to Iraq and Afghanistan.9
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial administered HCORT 30 mg oral or placebo to 96 combat veterans 30 minutes before PE sessions.
- Participants were veterans previously deployed to Afghanistan or Iraq with deployment-related PTSD >6 months with a minimum CAPS score of 60. They were unmedicated or on a stable psychotropic regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of a primary psychotic disorder (bipolar I disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder), medical or mental health condition other than PTSD that required immediate clinical attention, moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), substance abuse or dependence within the past 3 months, medical illness that contraindicated ingestion of hydrocortisone, acute suicide risk, and pregnancy or intent to become pregnant.
- The primary outcome measures included PTSD severity as assessed with CAPS.
- Secondary outcome measures included self-reported PTSD symptoms as assessed with the Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale (PDS) and depression as assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI). These scales were administered pretreatment, posttreatment, and at 3-months follow-up.
Outcomes
- Out of 96 veterans enrolled, 60 were randomized and 52 completed the treatment.
- Five participants were considered recovered early and completed <12 sessions.
- Of those who completed treatment, 50 completed the 1-week posttreatment evaluations and 49 completed the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
- There was no difference in the proportion of dropouts (13.33%) across the conditions.
- HCORT failed to significantly improve either secondary outcomes or PTSD symptoms, according to an intent-to-treat analysis.
- However, exploratory analyses revealed that veterans with recent post-concussive symptoms and moderate TBI exposure saw a larger decrease in hyperarousal symptoms after PE therapy with HCORT augmentation.
- The reduction in avoidance symptoms with HCORT augmentation was also larger in veterans with higher baseline glucocorticoid sensitivity.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- HCORT does not improve PTSD symptoms as assessed with the CAPS and PDS, or depression as assessed with the BDI.
- The main limitation of this study is generalizability.
- Further studies are needed to determine whether PE with HCORT could benefit veterans with indicators of enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity, mild TBI, or postconcussive syndrome.
4. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952
PE, one of the most well-researched therapies for PTSD, is based on fear extinction. Exploring pharmacotherapies that improve fear extinction learning and their potential as supplements to PE is gaining increased attention. Such pharmacotherapies aim to improve the clinical impact of PE on the extent and persistence of symptom reduction. This study evaluated the effects of HCORT and D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, on the learning and consolidation of fear extinction in patients with PTSD.10
Study design
- This double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-group experimental design evaluated 90 individuals with PTSD who underwent fear conditioning with stimuli that was paired (CS+) or unpaired (CS−) with shock.
- Participants were veterans and civilians age 18 to 65 recruited from VA outpatient and community clinics and internet advertisements who met the criteria for PTSD or subsyndromal PTSD (according to DSM-IV criteria) for at least 3 months.
- Exclusion criteria included schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, substance abuse or dependence, alcohol dependence, previous moderate or severe head injury, seizure or neurological disorder, current infectious illness, systemic illness affecting CNS function, or other conditions known to affect psychophysiological responses. Excluded medications were antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, alpha- and beta-adrenergics, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, and steroids.
- Extinction learning took place 72 hours after extinction, and extinction retention was evaluated 1 week later. Placebo, HCORT 25 mg, or DCS 50 mg was given 1 hour before extinction learning.
- Clinical measures included PTSD diagnosis and symptom levels as determined by interview using CAPS and skin conduction response.
Outcomes
- The mean shock level, mean pre-stimulus skin conductance level (SCL) during habituation, and mean SC orienting response during the habituation phase did not differ between groups and were not associated with differential fear conditioning. Therefore, variations in shock level preference, resting SCL, or SC orienting response magnitude are unlikely to account for differences between groups during extinction learning and retention.
- During extinction learning, the DCS and HCORT groups showed a reduced differential CS+/CS− skin conductance response (SCR) compared to placebo.
- One week later, during the retention testing, there was a nonsignificant trend toward a smaller differential CS+/CS− SCR in the DCS group compared to placebo. HCORT and DCS administered as a single dosage facilitated fear extinction learning in individuals with PTSD symptoms.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- In traumatized people with PTSD symptoms, a single dosage of HCORT or DCS enhanced the learning of fear extinction compared to placebo. A nonsignificant trend toward better extinction retention in the DCS group but not the HCORT group was also visible.
- These results imply that glucocorticoids and NMDA agonists have the potential to promote extinction learning in PTSD.
- Limitations include a lack of measures of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
- Further studies could evaluate these findings with the addition of blood biomarker measures such as glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
5. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
Poor PTSD treatment results are associated with numerous comorbid conditions, such as dissociation, depression, alcohol and substance use disorders, childhood trauma, and suicidal ideation, which frequently leads to treatment resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to find a treatment that works for individuals with PTSD who also have comorbid conditions. In animal models, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), an empathogen/entactogen with stimulant properties, has been shown to enhance fear memory extinction and modulate fear memory reconsolidation. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy for treating patients with severe PTSD, including those with common comorbidities.11
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-site, phase 3 clinical trial evaluated individuals randomized to receive manualized therapy with MDMA or with placebo, combined with 3 preparatory and 9 integrative therapy sessions.
- Participants were 90 individuals (46 randomized to MDMA and 44 to placebo) with PTSD with a symptom duration ≥6 months and CAPS-5 total severity score ≥35 at baseline.
- Exclusion criteria included primary psychotic disorder, bipolar I disorder, eating disorders with active purging, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, dissociative identity disorder, personality disorders, current alcohol and substance use disorders, lactation or pregnancy, and any condition that could make receiving a sympathomimetic medication dangerous due to hypertension or tachycardia, including uncontrolled hypertension, history of arrhythmia, or marked baseline prolongation of QT and/or QTc interval.
- Three 8-hour experimental sessions of either therapy with MDMA assistance or therapy with a placebo control were given during the treatment period, and they were spaced approximately 4 weeks apart.
- In each session, participants received placebo or a single divided dose of MDMA 80 to 180 mg.
- At baseline and 2 months after the last experimental sessions, PTSD symptoms were measured with CAPS-5, and functional impairment was measured with Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS).
- The primary outcome measure was CAPS-5 total severity score at 18 weeks compared to baseline for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
- The secondary outcome measure was clinician-rated functional impairment using the mean difference in SDS total scores from baseline to 18 weeks for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
Outcomes
- MDMA was found to induce significant and robust attenuation in CAPS-5 score compared to placebo.
- The mean change in CAPS-5 score in completers was –24.4 in the MDMA group and –13.9 in the placebo group.
- MDMA significantly decreased the SDS total score.
- MDMA did not induce suicidality, misuse, or QT prolongation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- MDMA-assisted therapy is significantly more effective than manualized therapy with placebo in treating patients with severe PTSD, and it is also safe and well-tolerated, even in individuals with comorbidities.
- No major safety issues were associated with MDMA-assisted treatment.
- MDMA-assisted therapy should be promptly assessed for clinical usage because it has the potential to significantly transform the way PTSD is treated.
- Limitations of this study include a smaller sample size (due to the COVID-19 pandemic); lack of ethnic and racial diversity; short duration; safety data were collected by site therapist, which limited the blinding; and the blinding of participants was difficult due to the subjective effects of MDMA, which could have resulted in expectation effects.
6. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990
Sertraline and paroxetine are the only FDA-approved medications for treating PTSD. Some evidence suggests cannabis may provide a therapeutic benefit for PTSD.15 This study examined the effects of 3 different preparations of cannabis for treating PTSD symptoms.12
Study design
- This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial used 3 active treatment groups of cannabis: high delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/low cannabidiol (CBD), high CBD/low THC, and high THC/high CBD (THC+CBD). A low THC/low CBD preparation was used as a placebo. “High” content contained 9% to 15% concentration by weight of the respective cannabinoid, and “low” content contained <2% concentration by weight.
- Inclusion criteria included being a US military veteran, meeting DSM-5 PTSD criteria for ≥6 months, having moderate symptom severity (CAPS-5 score ≥25), abstaining from cannabis 2 weeks prior to study and agreeing not to use any non-study cannabis during the trial, and being stable on medications/therapy prior to the study.
- Exclusion criteria included women who were pregnant/nursing/child-bearing age and not taking an effective means of birth control; current/past serious mental illness, including psychotic and personality disorders; having a first-degree relative with a psychotic or bipolar disorder; having a high suicide risk based on Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale; meeting DSM-5 criteria for moderate-severe cannabis use disorder; screening positive for illicit substances; or having significant medical disease.
- Participants in Stage 1 (n = 80) were randomized to 1 of the 3 active treatments or placebo for 3 weeks. After a 2-week washout, participants in Stage 2 (n = 74) were randomized to receive for 3 weeks 1 of the 3 active treatments they had not previously received.
- During each stage, participants had ad libitum use for a maximum of 1.8 g/d.
- The primary outcome was change in PTSD symptom severity by the end of Stage 1 as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Secondary outcomes included the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the general depression subscale and anxiety subscale from the self-report Inventory of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms (IDAS), the Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning, and the Insomnia Severity Index.
Outcomes
- Six participants did not continue to Stage 2. Three participants did not finish Stage 2 due to adverse effects, and 7 did not complete outcome measurements. The overall attrition rate was 16.3%.
- There was no significant difference in total grams of smoked cannabis or placebo between the 4 treatment groups in Stage 1 at the end of 3 weeks. In Stage 2, there was a significant difference, with the THC+CBD group using more cannabis compared to the other 2 groups.
- Each of the 4 groups had significant reductions in total CAPS-5 scores at the end of Stage 1, and there was no significant difference in CAPS-5 severity scores between the 4 groups.
- In Stage 1, PCL-5 scores were not significantly different between treatment groups from baseline to the end of stage. There was a significant difference in Stage 2 between the high CBD and THC+CBD groups, with the combined group reporting greater improvement of symptoms.
- In Stage 2, the THC+CBD group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores and IDAS general depression scores, and the high THC group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores.
- In Stage 1, 37 of 60 participants in the active groups reported at least 1 adverse event, and 45 of the 74 Stage 2 participants reported at least 1 adverse event. The most common adverse events were cough, throat irritation, and anxiety. Participants in the Stage 1 high THC group had a significant increase in reported withdrawal symptoms after 1 week of stopping use.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- This first randomized, placebo-control trial of cannabis in US veterans did not show a significant difference among treatment groups, including placebo, on the primary outcome of CAPS-5 score. All 4 groups had significant reductions in symptom severity on CAPS-5 and showed good tolerability.
- Prior beliefs about the effects of cannabis may have played a role in the reduction of PTSD symptoms in the placebo group.
- Many participants (n =34) were positive for THC during the screening process, so previous cannabis use/chronicity of cannabis use may have contributed.
- One limitation was that participants assigned to the Stage 1 high THC group had Cannabis Use Disorders Identification Test scores (which assesses cannabis use disorder risk) about 2 times greater than participants in other conditions.
- Another limitation was that total cannabis use was lower than expected, as participants in Stage 1 used 8.2 g to 14.6 g over 3 weeks, though they had access to up to 37.8 g.
- There was no placebo in Stage 2.
- Future studies should look at longer treatment periods with more participants.
7. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444
Bright light therapy is an inexpensive treatment approach that may affect serotonergic pathways.16 This study examined bright light therapy for reducing PTSD symptoms and examined if improvement of PTSD is related to a shift in circadian rhythm.13
Study design
- Veterans with combat-related PTSD had to have been stable on treatment for at least 8 weeks or to have not received any other PTSD treatments prior to the study.
- Participants were randomized to active treatment of 30 minutes daily 10,000 lux ultraviolet-filtered white light while sitting within 18 inches (n = 34) or a control condition of 30 minutes daily inactivated negative ion generator (n = 35) for 4 weeks.
- Inclusion criteria included a CAPS score ≥30.
- Exclusion criteria included high suicidality, high probability of alcohol/substance abuse in the past 3 months, bipolar disorder/mania/schizophrenia/psychosis, ophthalmologic deformities, shift work in past 2 months or travel across time zones in past 2 weeks, head trauma, high outdoor light exposure, history of winter depression, history of seizures, or myocardial infarction/stroke/cancer within 3 years.
- Primary outcomes were improvement on CAPS and Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-IM) score at Week 4.
- Wrist actigraphy recordings measured sleep.
- Other measurements included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton atypical symptoms (HAM-AS), PCL-Military (PCL-M), Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), BDI, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI Form Y-2), Beck Suicide Scale, and Systematic Assessment for Treatment Emergent Effects questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There was a significant decrease in CAPS score in participants who received bright light therapy compared to controls. Treatment response (defined as ≥33% reduction in score) was significantly greater in the bright light (44%) vs control (8.6%) group. No participants achieved remission.
- There was a significant improvement in CGI-IM scores in the bright light group, but no significant difference in participants who were judged to improve “much” or “very much.”
- PCL-M scores did not change significantly between groups, although a significantly greater proportion of participants had treatment response in the bright light group (33%) vs control (6%).
- There were no significant changes in HAM-D, HAM-AS, STAI, BDI, actigraphic estimates of sleep, or PSQI scores.
- Bright light therapy resulted in phase advancement while control treatment had phase delay.
- There were no significant differences in adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Bright light therapy may be a treatment option or adjunct for combat-related PTSD as seen by improvement on CAPS and CGI scores, as well as a greater treatment response seen on CAPS and PCL-5 scores in the bright light group.
- There was no significant difference for other measures, including depression, anxiety, and sleep.
- Limitations include excluding patients with a wide variety of medical or psychiatric comorbidities, as well as limited long-term follow up data.
- Other limitations include not knowing the precise amount of time participants stayed in front of the light device and loss of some actigraphic data (data from only 49 of 69 participants).
8. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41 doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT), a type of trauma-focused psychotherapy, is an effective treatment for PTSD in the military population.17,18 However, patients may not be able to or want to participate in such therapy due to barriers such as difficulty arranging transportation, being homebound due to injury, concerns about COVID-19, stigma, familial obligations, and job constraints. This study looked at if CPT delivered face-to-face at the patient’s home or via telehealth in home would be effective and increase accessibility.14
Study design
- Participants (n = 120) were active-duty military and veterans who met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD. They were randomized to receive CPT in the office, in their home, or via telehealth. Participants could choose not to partake in 1 modality but were then randomized to 1 of the other 2.
- Exclusion criteria included suicide/homicide risk needing intervention, items/situations pertaining to danger (ie, aggressive pet or unsafe neighborhood), significant alcohol/substance use, active psychosis, and impaired cognitive functioning.
- The primary outcome measurement was change in PCL-5 and CAPS-5 score over 6 months. The BDI-II was used to assess depressive symptoms.
- Secondary outcomes included the Reliable Change Index (defined as “an improvement of 10 or more points that was sustained at all subsequent assessments”) on the PCL-5 and remission on the CAPS-5.
- CPT was delivered in 60-minute sessions twice a week for 6 weeks. Participants who did not have electronic resources were loaned a telehealth apparatus.
Outcomes
- Overall, 57% of participants opted out of 1 modality, which resulted in fewer participants being placed into the in-home arm (n = 32). Most participants chose not to do in-home treatments (54%), followed by in-office (29%), and telehealth (17%).
- There was a significant posttreatment improvement in PCL-5 scores in all treatment arms, with improvement greater with in-home (d = 2.1) and telehealth (d = 2.0) vs in-office (d=1.3). The in-home and telehealth scores were significantly improved compared to in-office, and the difference between in-home and telehealth PCL-5 scores was minimal.
- At 6 months posttreatment, the differences between the 3 treatment groups on PCL-5 score were negligible.
- CAPS-5 scores were significantly improved in all treatment arms, with improvement largest with in-home treatment; however, the differences between the groups were not significant.
- BDI-II scores improved in all modalities but were larger in the in-home (d = 1.2) and telehealth (d = 1.1) arms than the in-office arm (d = 0.52).
- Therapist time commitment was greater for the in-home and in-office arms (2 hours/session) than the telehealth arm (1 hour/session). This difference was due to commuting time for the patient or therapist.
- The dropout rate was not statistically significant between the groups.
- Adverse events did not significantly differ per group. The most commonly reported ones included nightmares, sleep difficulty, depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients undergoing CPT had significant improvement in PTSD symptoms, with posttreatment PCL-5 improvement approximately twice as large in those who received the in-home and telehealth modalities vs in-office treatment.
- The group differences were not seen on CAPS-5 scores at posttreatment, or PCL-5 or CAPS-5 scores at 6 months posttreatment.
- In-home CPT was declined the most, which suggests that in-home distractions or the stigma of a mental health clinician being in their home played a role in patients’ decision-making. However, in-home CPT produced the greatest amount of improvement in PTSD symptoms. The authors concluded that in-home therapy should be reserved for those who are homebound or have travel limitations.
- This study shows evidence that telehealth may be a good modality for CPT, as seen by improvement in PTSD symptoms and good acceptability and retention.
- Limitations include more patients opting out of in-home CPT, and reimbursement for travel may not be available in the real-world setting.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder. The lifetime prevalence among American adults is 6.8%.1 Management of PTSD includes treating distressing symptoms, reducing avoidant behaviors, treating comorbid conditions (eg, depression, substance use disorders, or mood dysregulation), and improving adaptive functioning, which includes restoring a psychological sense of safety and trust. PTSD can be treated using evidence-based psychotherapies, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of both modalities. For adults, evidence-based treatment guidelines recommend the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, cognitive therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy.2 These guidelines also recommend (with some reservations) the use of brief eclectic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, and narrative exposure therapy.2 Although the evidence base for the use of medications is not as strong as that for the psychotherapies listed above, the guidelines recommend the use of fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine.2
Currently available treatments for PTSD have significant limitations. For example, trauma-focused psychotherapies can have significant rates of nonresponse, partial response, or treatment dropout.3,4 Additionally, such therapies are not widely accessible. As for pharmacotherapy, very few available options are supported by evidence, and the efficacy of these options is limited, as shown by the reports that only 60% of patients with PTSD show a response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and only 20% to 30% achieve complete remission.5 Additionally, it may take months for patients to achieve an acceptable level of improvement with medications. As a result, a substantial proportion of patients who seek treatment continue to remain symptomatic, with impaired levels of functioning. This lack of progress in PTSD treatment has been labeled as a national crisis, calling for an urgent need to find effective pharmacologic treatments for PTSD.6
In this article, we review 8 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of treatments for PTSD published within the last 5 years (Table7-14).

1. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202
Feder et al had previously found a significant and quick decrease in PTSD symptoms after a single dose of IV ketamine had. This is the first RCT to examine the effectiveness and safety of repeated IV ketamine infusions for the treatment of persistent PTSD.7
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, parallel-arm controlled trial treated 30 individuals with chronic PTSD with 6 infusions of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) over 2 consecutive weeks.
- Participants were individuals age 18 to 70 with a primary diagnosis of chronic PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria and determined by The Structure Clinical Interview for DSM-5, with a score ≥30 on the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5).
- Any severe or unstable medical condition, active suicidal or homicidal ideation, lifetime history of psychotic or bipolar disorder, current anorexia nervosa or bulimia, alcohol or substance use disorder within 3 months of screening, history of recreational ketamine or phencyclidine use on more than 1 occasion or any use in the previous 2 years, and ongoing treatment with a long-acting benzodiazepine or opioid medication were all considered exclusion criteria. Individuals who took short-acting benzodiazepines had their morning doses held on infusion days. Marijuana or cannabis derivatives were allowed.
- The primary outcome measure was a change in PTSD symptom severity as measured with CAPS-5. This was administered before the first infusion and weekly thereafter. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised, the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and adverse effect measurements were used as secondary outcome measures.
- Treatment response was defined as ≥30% symptom improvement 2 weeks after the first infusion as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Individuals who responded to treatment were followed naturalistically weekly for up to 4 weeks and then monthly until loss of responder status, or up to 6 months if there was no loss of response.
Outcomes
- At the second week, the mean CAPS-5 total score in the ketamine group was 11.88 points (SE = 3.96) lower than in the midazolam group (d = 1.13; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.91).
- In the ketamine group, 67% of patients responded to therapy, compared to 20% in the midazolam group.
- Following the 2-week course of infusions, the median period until loss of response among ketamine responders was 27.5 days.
- Ketamine infusions showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated ketamine infusions are effective in reducing symptom severity in individuals with chronic PTSD.
- Limitations to this study include the exclusion of individuals with comorbid bipolar disorder, current alcohol or substance use disorder, or suicidal ideations, the small sample size, and a higher rate of transient dissociative symptoms in the ketamine group.
- Future studies could evaluate the efficacy of repeated ketamine infusions in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Also, further studies are required to assess the efficacy of novel interventions to prevent relapse and evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of periodic IV ketamine use as maintenance.
- Additional research might determine whether pairing psychotherapy with ketamine administration can lessen the risk of recurrence for PTSD patients after stopping ketamine infusions.
2. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126
Clinical practice recommendations for PTSD have identified trauma-focused psychotherapies and SSRIs as very effective treatments. The few studies that have compared trauma-focused psychotherapy to SSRIs or to a combination of treatments are not generalizable, have significant limitations, or are primarily concerned with refractory disorders or augmentation techniques. This study evaluated the efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy (PE) plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management in the treatment of PTSD.8
Study design
- This randomized, 4-site, 24-week clinical trial divided participants into 3 subgroups: PE plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management.
- Participants were veterans or service members of the Iraq and/or Afghanistan wars with combat-related PTSD and significant impairment as indicated by a CAPS score ≥50 for at least 3 months. The DSM-IV-TR version of CAPS was used because the DSM-5 version was not available at the time of the study.
- Individuals who had a current, imminent risk of suicide; active psychosis; alcohol or substance dependence in the past 8 weeks; inability to attend weekly appointments for the treatment period; prior intolerance to or failure of an adequate trial of PE or sertraline; medical illness likely to result in hospitalization or contraindication to study treatment; serious cognitive impairment; mild traumatic brain injury; or concurrent use of antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, prazosin, or sleep agents were excluded.
- Participants completed up to thirteen 90-minute sessions of PE.
- The sertraline dosage was titrated during a 10-week period and continued until Week 24. Dosages were adjusted between 50 and 200 mg/d, with the last dose increase at Week 10.
- The primary outcome measure was symptom severity of PTSD in the past month as determined by CAPS score at Week 24.
- The secondary outcome was self-reported symptoms of PTSD (PTSD checklist [PCL] Specific Stressor Version), clinically meaningful change (reduction of ≥20 points or score ≤35 on CAPS), response (reduction of ≥50% in CAPS score), and remission (CAPS score ≤35).
Outcomes
- At Week 24, 149 participants completed the study; 207 were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- PTSD symptoms significantly decreased over 24 weeks, according to a modified intent-to-treat analysis utilizing a mixed model of repeated measurements; nevertheless, slopes were similar across therapy groups.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Although the severity of PTSD symptoms decreased in all 3 subgroups, there was no difference in PTSD symptom severity or change in symptoms at Week 24 among all 3 subgroups.
- The main limitation of this study was the inclusion of only combat veterans.
- Further research should focus on enhancing treatment retention and should include administering sustained exposure therapy at brief intervals.
3. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924
First-line therapy for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapies such as PE. However, because many people still have major adverse effects after receiving medication, improving treatment efficacy is a concern. Glucocorticoids promote extinction learning, and alterations in glucocorticoid signaling pathways have been associated with PTSD. Lehrner et al previously showed that adding hydrocortisone (HCORT) to PE therapy increased patients’ glucocorticoid sensitivity at baseline, improved treatment retention, and resulted in greater treatment improvements. This study evaluated HCORT in conjunction with PE for combat veterans with PTSD following deployment to Iraq and Afghanistan.9
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial administered HCORT 30 mg oral or placebo to 96 combat veterans 30 minutes before PE sessions.
- Participants were veterans previously deployed to Afghanistan or Iraq with deployment-related PTSD >6 months with a minimum CAPS score of 60. They were unmedicated or on a stable psychotropic regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of a primary psychotic disorder (bipolar I disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder), medical or mental health condition other than PTSD that required immediate clinical attention, moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), substance abuse or dependence within the past 3 months, medical illness that contraindicated ingestion of hydrocortisone, acute suicide risk, and pregnancy or intent to become pregnant.
- The primary outcome measures included PTSD severity as assessed with CAPS.
- Secondary outcome measures included self-reported PTSD symptoms as assessed with the Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale (PDS) and depression as assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI). These scales were administered pretreatment, posttreatment, and at 3-months follow-up.
Outcomes
- Out of 96 veterans enrolled, 60 were randomized and 52 completed the treatment.
- Five participants were considered recovered early and completed <12 sessions.
- Of those who completed treatment, 50 completed the 1-week posttreatment evaluations and 49 completed the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
- There was no difference in the proportion of dropouts (13.33%) across the conditions.
- HCORT failed to significantly improve either secondary outcomes or PTSD symptoms, according to an intent-to-treat analysis.
- However, exploratory analyses revealed that veterans with recent post-concussive symptoms and moderate TBI exposure saw a larger decrease in hyperarousal symptoms after PE therapy with HCORT augmentation.
- The reduction in avoidance symptoms with HCORT augmentation was also larger in veterans with higher baseline glucocorticoid sensitivity.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- HCORT does not improve PTSD symptoms as assessed with the CAPS and PDS, or depression as assessed with the BDI.
- The main limitation of this study is generalizability.
- Further studies are needed to determine whether PE with HCORT could benefit veterans with indicators of enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity, mild TBI, or postconcussive syndrome.
4. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952
PE, one of the most well-researched therapies for PTSD, is based on fear extinction. Exploring pharmacotherapies that improve fear extinction learning and their potential as supplements to PE is gaining increased attention. Such pharmacotherapies aim to improve the clinical impact of PE on the extent and persistence of symptom reduction. This study evaluated the effects of HCORT and D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, on the learning and consolidation of fear extinction in patients with PTSD.10
Study design
- This double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-group experimental design evaluated 90 individuals with PTSD who underwent fear conditioning with stimuli that was paired (CS+) or unpaired (CS−) with shock.
- Participants were veterans and civilians age 18 to 65 recruited from VA outpatient and community clinics and internet advertisements who met the criteria for PTSD or subsyndromal PTSD (according to DSM-IV criteria) for at least 3 months.
- Exclusion criteria included schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, substance abuse or dependence, alcohol dependence, previous moderate or severe head injury, seizure or neurological disorder, current infectious illness, systemic illness affecting CNS function, or other conditions known to affect psychophysiological responses. Excluded medications were antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, alpha- and beta-adrenergics, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, and steroids.
- Extinction learning took place 72 hours after extinction, and extinction retention was evaluated 1 week later. Placebo, HCORT 25 mg, or DCS 50 mg was given 1 hour before extinction learning.
- Clinical measures included PTSD diagnosis and symptom levels as determined by interview using CAPS and skin conduction response.
Outcomes
- The mean shock level, mean pre-stimulus skin conductance level (SCL) during habituation, and mean SC orienting response during the habituation phase did not differ between groups and were not associated with differential fear conditioning. Therefore, variations in shock level preference, resting SCL, or SC orienting response magnitude are unlikely to account for differences between groups during extinction learning and retention.
- During extinction learning, the DCS and HCORT groups showed a reduced differential CS+/CS− skin conductance response (SCR) compared to placebo.
- One week later, during the retention testing, there was a nonsignificant trend toward a smaller differential CS+/CS− SCR in the DCS group compared to placebo. HCORT and DCS administered as a single dosage facilitated fear extinction learning in individuals with PTSD symptoms.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- In traumatized people with PTSD symptoms, a single dosage of HCORT or DCS enhanced the learning of fear extinction compared to placebo. A nonsignificant trend toward better extinction retention in the DCS group but not the HCORT group was also visible.
- These results imply that glucocorticoids and NMDA agonists have the potential to promote extinction learning in PTSD.
- Limitations include a lack of measures of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
- Further studies could evaluate these findings with the addition of blood biomarker measures such as glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
5. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
Poor PTSD treatment results are associated with numerous comorbid conditions, such as dissociation, depression, alcohol and substance use disorders, childhood trauma, and suicidal ideation, which frequently leads to treatment resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to find a treatment that works for individuals with PTSD who also have comorbid conditions. In animal models, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), an empathogen/entactogen with stimulant properties, has been shown to enhance fear memory extinction and modulate fear memory reconsolidation. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy for treating patients with severe PTSD, including those with common comorbidities.11
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-site, phase 3 clinical trial evaluated individuals randomized to receive manualized therapy with MDMA or with placebo, combined with 3 preparatory and 9 integrative therapy sessions.
- Participants were 90 individuals (46 randomized to MDMA and 44 to placebo) with PTSD with a symptom duration ≥6 months and CAPS-5 total severity score ≥35 at baseline.
- Exclusion criteria included primary psychotic disorder, bipolar I disorder, eating disorders with active purging, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, dissociative identity disorder, personality disorders, current alcohol and substance use disorders, lactation or pregnancy, and any condition that could make receiving a sympathomimetic medication dangerous due to hypertension or tachycardia, including uncontrolled hypertension, history of arrhythmia, or marked baseline prolongation of QT and/or QTc interval.
- Three 8-hour experimental sessions of either therapy with MDMA assistance or therapy with a placebo control were given during the treatment period, and they were spaced approximately 4 weeks apart.
- In each session, participants received placebo or a single divided dose of MDMA 80 to 180 mg.
- At baseline and 2 months after the last experimental sessions, PTSD symptoms were measured with CAPS-5, and functional impairment was measured with Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS).
- The primary outcome measure was CAPS-5 total severity score at 18 weeks compared to baseline for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
- The secondary outcome measure was clinician-rated functional impairment using the mean difference in SDS total scores from baseline to 18 weeks for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
Outcomes
- MDMA was found to induce significant and robust attenuation in CAPS-5 score compared to placebo.
- The mean change in CAPS-5 score in completers was –24.4 in the MDMA group and –13.9 in the placebo group.
- MDMA significantly decreased the SDS total score.
- MDMA did not induce suicidality, misuse, or QT prolongation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- MDMA-assisted therapy is significantly more effective than manualized therapy with placebo in treating patients with severe PTSD, and it is also safe and well-tolerated, even in individuals with comorbidities.
- No major safety issues were associated with MDMA-assisted treatment.
- MDMA-assisted therapy should be promptly assessed for clinical usage because it has the potential to significantly transform the way PTSD is treated.
- Limitations of this study include a smaller sample size (due to the COVID-19 pandemic); lack of ethnic and racial diversity; short duration; safety data were collected by site therapist, which limited the blinding; and the blinding of participants was difficult due to the subjective effects of MDMA, which could have resulted in expectation effects.
6. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990
Sertraline and paroxetine are the only FDA-approved medications for treating PTSD. Some evidence suggests cannabis may provide a therapeutic benefit for PTSD.15 This study examined the effects of 3 different preparations of cannabis for treating PTSD symptoms.12
Study design
- This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial used 3 active treatment groups of cannabis: high delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/low cannabidiol (CBD), high CBD/low THC, and high THC/high CBD (THC+CBD). A low THC/low CBD preparation was used as a placebo. “High” content contained 9% to 15% concentration by weight of the respective cannabinoid, and “low” content contained <2% concentration by weight.
- Inclusion criteria included being a US military veteran, meeting DSM-5 PTSD criteria for ≥6 months, having moderate symptom severity (CAPS-5 score ≥25), abstaining from cannabis 2 weeks prior to study and agreeing not to use any non-study cannabis during the trial, and being stable on medications/therapy prior to the study.
- Exclusion criteria included women who were pregnant/nursing/child-bearing age and not taking an effective means of birth control; current/past serious mental illness, including psychotic and personality disorders; having a first-degree relative with a psychotic or bipolar disorder; having a high suicide risk based on Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale; meeting DSM-5 criteria for moderate-severe cannabis use disorder; screening positive for illicit substances; or having significant medical disease.
- Participants in Stage 1 (n = 80) were randomized to 1 of the 3 active treatments or placebo for 3 weeks. After a 2-week washout, participants in Stage 2 (n = 74) were randomized to receive for 3 weeks 1 of the 3 active treatments they had not previously received.
- During each stage, participants had ad libitum use for a maximum of 1.8 g/d.
- The primary outcome was change in PTSD symptom severity by the end of Stage 1 as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Secondary outcomes included the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the general depression subscale and anxiety subscale from the self-report Inventory of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms (IDAS), the Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning, and the Insomnia Severity Index.
Outcomes
- Six participants did not continue to Stage 2. Three participants did not finish Stage 2 due to adverse effects, and 7 did not complete outcome measurements. The overall attrition rate was 16.3%.
- There was no significant difference in total grams of smoked cannabis or placebo between the 4 treatment groups in Stage 1 at the end of 3 weeks. In Stage 2, there was a significant difference, with the THC+CBD group using more cannabis compared to the other 2 groups.
- Each of the 4 groups had significant reductions in total CAPS-5 scores at the end of Stage 1, and there was no significant difference in CAPS-5 severity scores between the 4 groups.
- In Stage 1, PCL-5 scores were not significantly different between treatment groups from baseline to the end of stage. There was a significant difference in Stage 2 between the high CBD and THC+CBD groups, with the combined group reporting greater improvement of symptoms.
- In Stage 2, the THC+CBD group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores and IDAS general depression scores, and the high THC group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores.
- In Stage 1, 37 of 60 participants in the active groups reported at least 1 adverse event, and 45 of the 74 Stage 2 participants reported at least 1 adverse event. The most common adverse events were cough, throat irritation, and anxiety. Participants in the Stage 1 high THC group had a significant increase in reported withdrawal symptoms after 1 week of stopping use.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- This first randomized, placebo-control trial of cannabis in US veterans did not show a significant difference among treatment groups, including placebo, on the primary outcome of CAPS-5 score. All 4 groups had significant reductions in symptom severity on CAPS-5 and showed good tolerability.
- Prior beliefs about the effects of cannabis may have played a role in the reduction of PTSD symptoms in the placebo group.
- Many participants (n =34) were positive for THC during the screening process, so previous cannabis use/chronicity of cannabis use may have contributed.
- One limitation was that participants assigned to the Stage 1 high THC group had Cannabis Use Disorders Identification Test scores (which assesses cannabis use disorder risk) about 2 times greater than participants in other conditions.
- Another limitation was that total cannabis use was lower than expected, as participants in Stage 1 used 8.2 g to 14.6 g over 3 weeks, though they had access to up to 37.8 g.
- There was no placebo in Stage 2.
- Future studies should look at longer treatment periods with more participants.
7. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444
Bright light therapy is an inexpensive treatment approach that may affect serotonergic pathways.16 This study examined bright light therapy for reducing PTSD symptoms and examined if improvement of PTSD is related to a shift in circadian rhythm.13
Study design
- Veterans with combat-related PTSD had to have been stable on treatment for at least 8 weeks or to have not received any other PTSD treatments prior to the study.
- Participants were randomized to active treatment of 30 minutes daily 10,000 lux ultraviolet-filtered white light while sitting within 18 inches (n = 34) or a control condition of 30 minutes daily inactivated negative ion generator (n = 35) for 4 weeks.
- Inclusion criteria included a CAPS score ≥30.
- Exclusion criteria included high suicidality, high probability of alcohol/substance abuse in the past 3 months, bipolar disorder/mania/schizophrenia/psychosis, ophthalmologic deformities, shift work in past 2 months or travel across time zones in past 2 weeks, head trauma, high outdoor light exposure, history of winter depression, history of seizures, or myocardial infarction/stroke/cancer within 3 years.
- Primary outcomes were improvement on CAPS and Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-IM) score at Week 4.
- Wrist actigraphy recordings measured sleep.
- Other measurements included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton atypical symptoms (HAM-AS), PCL-Military (PCL-M), Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), BDI, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI Form Y-2), Beck Suicide Scale, and Systematic Assessment for Treatment Emergent Effects questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There was a significant decrease in CAPS score in participants who received bright light therapy compared to controls. Treatment response (defined as ≥33% reduction in score) was significantly greater in the bright light (44%) vs control (8.6%) group. No participants achieved remission.
- There was a significant improvement in CGI-IM scores in the bright light group, but no significant difference in participants who were judged to improve “much” or “very much.”
- PCL-M scores did not change significantly between groups, although a significantly greater proportion of participants had treatment response in the bright light group (33%) vs control (6%).
- There were no significant changes in HAM-D, HAM-AS, STAI, BDI, actigraphic estimates of sleep, or PSQI scores.
- Bright light therapy resulted in phase advancement while control treatment had phase delay.
- There were no significant differences in adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Bright light therapy may be a treatment option or adjunct for combat-related PTSD as seen by improvement on CAPS and CGI scores, as well as a greater treatment response seen on CAPS and PCL-5 scores in the bright light group.
- There was no significant difference for other measures, including depression, anxiety, and sleep.
- Limitations include excluding patients with a wide variety of medical or psychiatric comorbidities, as well as limited long-term follow up data.
- Other limitations include not knowing the precise amount of time participants stayed in front of the light device and loss of some actigraphic data (data from only 49 of 69 participants).
8. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41 doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT), a type of trauma-focused psychotherapy, is an effective treatment for PTSD in the military population.17,18 However, patients may not be able to or want to participate in such therapy due to barriers such as difficulty arranging transportation, being homebound due to injury, concerns about COVID-19, stigma, familial obligations, and job constraints. This study looked at if CPT delivered face-to-face at the patient’s home or via telehealth in home would be effective and increase accessibility.14
Study design
- Participants (n = 120) were active-duty military and veterans who met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD. They were randomized to receive CPT in the office, in their home, or via telehealth. Participants could choose not to partake in 1 modality but were then randomized to 1 of the other 2.
- Exclusion criteria included suicide/homicide risk needing intervention, items/situations pertaining to danger (ie, aggressive pet or unsafe neighborhood), significant alcohol/substance use, active psychosis, and impaired cognitive functioning.
- The primary outcome measurement was change in PCL-5 and CAPS-5 score over 6 months. The BDI-II was used to assess depressive symptoms.
- Secondary outcomes included the Reliable Change Index (defined as “an improvement of 10 or more points that was sustained at all subsequent assessments”) on the PCL-5 and remission on the CAPS-5.
- CPT was delivered in 60-minute sessions twice a week for 6 weeks. Participants who did not have electronic resources were loaned a telehealth apparatus.
Outcomes
- Overall, 57% of participants opted out of 1 modality, which resulted in fewer participants being placed into the in-home arm (n = 32). Most participants chose not to do in-home treatments (54%), followed by in-office (29%), and telehealth (17%).
- There was a significant posttreatment improvement in PCL-5 scores in all treatment arms, with improvement greater with in-home (d = 2.1) and telehealth (d = 2.0) vs in-office (d=1.3). The in-home and telehealth scores were significantly improved compared to in-office, and the difference between in-home and telehealth PCL-5 scores was minimal.
- At 6 months posttreatment, the differences between the 3 treatment groups on PCL-5 score were negligible.
- CAPS-5 scores were significantly improved in all treatment arms, with improvement largest with in-home treatment; however, the differences between the groups were not significant.
- BDI-II scores improved in all modalities but were larger in the in-home (d = 1.2) and telehealth (d = 1.1) arms than the in-office arm (d = 0.52).
- Therapist time commitment was greater for the in-home and in-office arms (2 hours/session) than the telehealth arm (1 hour/session). This difference was due to commuting time for the patient or therapist.
- The dropout rate was not statistically significant between the groups.
- Adverse events did not significantly differ per group. The most commonly reported ones included nightmares, sleep difficulty, depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients undergoing CPT had significant improvement in PTSD symptoms, with posttreatment PCL-5 improvement approximately twice as large in those who received the in-home and telehealth modalities vs in-office treatment.
- The group differences were not seen on CAPS-5 scores at posttreatment, or PCL-5 or CAPS-5 scores at 6 months posttreatment.
- In-home CPT was declined the most, which suggests that in-home distractions or the stigma of a mental health clinician being in their home played a role in patients’ decision-making. However, in-home CPT produced the greatest amount of improvement in PTSD symptoms. The authors concluded that in-home therapy should be reserved for those who are homebound or have travel limitations.
- This study shows evidence that telehealth may be a good modality for CPT, as seen by improvement in PTSD symptoms and good acceptability and retention.
- Limitations include more patients opting out of in-home CPT, and reimbursement for travel may not be available in the real-world setting.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Delmer O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Guideline Development Panel for the Treatment of PTSD in Adults, American Psychological Association. Summary of the clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. Am Psychol. 2019;74(5):596-607. doi: 10.1037/amp0000473
3. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Hoge CW, et al. Psychotherapy for military-related PTSD: a review of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2015;314(5):489-500.
4. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Marmar CR. First-line psychotherapies for military-related PTSD. JAMA. 2020;323(7):656-657.
5. Berger W, Mendlowicz MV, Marques-Portella C, et al. Pharmacologic alternatives to antidepressants in posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33(3):169-180.
6. Krystal JH, Davis LL, Neylan TC, et al. It is time to address the crisis in the pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a consensus statement of the PTSD Psychopharmacology Working Group. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(7):e51-e59.
7. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20050596
8. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3412
9. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2021.103924
10. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01222-z
11. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
12. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246990
13. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab014
14. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
15. Loflin MJ, Babson KA, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabinoids as therapeutic for PTSD. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;14:78-83. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.12.001
16. Neumeister A, Praschak-Rieder N, Besselmann B, et al. Effects of tryptophan depletion on drug-free patients with seasonal affective disorder during a stable response to bright light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(2):133-138. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140043008
17. Kaysen D, Schumm J, Pedersen ER, et al. Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorders. Addict Behav. 2014;39(2):420-427. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.08.016
18. Resick PA, Wachen JS, Mintz J, et al. A randomized clinical trial of group cognitive processing therapy compared with group present-centered therapy for PTSD among active duty military personnel. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(6):1058-1068. doi:10.1037/ccp0000016
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Delmer O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Guideline Development Panel for the Treatment of PTSD in Adults, American Psychological Association. Summary of the clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. Am Psychol. 2019;74(5):596-607. doi: 10.1037/amp0000473
3. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Hoge CW, et al. Psychotherapy for military-related PTSD: a review of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2015;314(5):489-500.
4. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Marmar CR. First-line psychotherapies for military-related PTSD. JAMA. 2020;323(7):656-657.
5. Berger W, Mendlowicz MV, Marques-Portella C, et al. Pharmacologic alternatives to antidepressants in posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33(3):169-180.
6. Krystal JH, Davis LL, Neylan TC, et al. It is time to address the crisis in the pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a consensus statement of the PTSD Psychopharmacology Working Group. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(7):e51-e59.
7. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20050596
8. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3412
9. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2021.103924
10. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01222-z
11. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
12. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246990
13. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab014
14. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
15. Loflin MJ, Babson KA, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabinoids as therapeutic for PTSD. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;14:78-83. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.12.001
16. Neumeister A, Praschak-Rieder N, Besselmann B, et al. Effects of tryptophan depletion on drug-free patients with seasonal affective disorder during a stable response to bright light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(2):133-138. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140043008
17. Kaysen D, Schumm J, Pedersen ER, et al. Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorders. Addict Behav. 2014;39(2):420-427. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.08.016
18. Resick PA, Wachen JS, Mintz J, et al. A randomized clinical trial of group cognitive processing therapy compared with group present-centered therapy for PTSD among active duty military personnel. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(6):1058-1068. doi:10.1037/ccp0000016
Aerobic exercise augments PTSD therapy
Investigators randomly assigned individuals with PTSD to receive either exposure therapy with aerobic exercise or exposure therapy with passive stretching for 9 weeks. At 6 months post intervention, participants in the aerobic exercise group showed greater reductions in PTSD severity, compared with those in the stretching group.
“There is a critical need to improve outcomes for treating people with PTSD, and this finding points to one potentially cheap and ready-to-use strategy that all clinicians could employ with most patients,” lead author Richard Bryant, MPsych, PhD, DSc, director of the Traumatic Stress Clinic and Scientia Professor of Psychology at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, told this news organization.
The study was published online in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Promoting BDNF
“Trauma-focused psychotherapy is the recommended treatment for PTSD, but up to half of patients do not respond to this treatment,” Dr. Bryant said.
“We know that brain-derived neurotrophic factors [BDNF] are critical for synaptic plasticity, which underpins the learning that occurs in therapy so that reminders of trauma are no longer fear-provoking,” he continued. “Preclinical animal and human research inform us that brief aerobic exercise can promote BDNF and new learning that inhibits fear responses.”
The researchers “hypothesized that brief exercise after exposure therapy to trauma memories – which is the key ingredient of trauma-focused psychotherapy – would lead to greater reductions in PTSD, relative to standard trauma-focused therapy,” he said.
To investigate the question, the researchers randomly assigned 130 adults with PTSD (mean age, 39 years; 61% female; 76% White) to receive nine 90-minute sessions of exposure therapy with either aerobic exercise or passive stretching (n = 65 in each group).
There were no differences at baseline in sociodemographic characteristics or psychopathology measures, although the mean age of the stretching group was slightly older than that of the aerobic group (40 years vs. 37 years, respectively), and there was a slightly higher proportion of women in the stretching group (68% vs. 54%).
Participants did not differ on weekly exercise either at baseline, immediately post treatment, or at 6-week follow-up.
PTSD severity (the primary outcome) was measured using the clinician-administered PTSD scale CAPS-2, with assessments conducted at baseline, 1 week post treatment, and 6 months post treatment.
The aerobic exercise regimen was tailored to each participant, based on an assessment of his/her aerobic target zone.
The exposure therapy sessions were identical for both groups. Following the exposure sessions, participants engaged in their respective exercises: Those in the passive stretching group engaged in 20 minutes of exercise, while those in the aerobic group participated in a total of 20 minutes of exercise, with 10 conducted at their personal aerobic target heart rate.
“This level of exercise was chosen because BDNF concentration in the serum is increased by two 3-minute bouts of aerobic exercise, and 10 minutes of aerobic exercise can facilitate extinction learning,” the authors explained.
The aerobic activity consisted of running on a stepper exercise platform while having cardiac activity recorded. A small portion (10%) of the therapy sessions were recorded and rated for treatment fidelity.
Change in PTSD was the primary outcome, with secondary outcomes consisting of changes in depression, anxiety, alcohol use disorder, and posttraumatic cognitions.
Few barriers
The researchers found no significant differences in PTSD severity, as measured by CAPS-2 score, between treatment groups at 10 weeks – that is, immediately post treatment (mean difference, 7.0; 95% confidence interval, –2.3 to 16.4; P = .14).
However, significantly greater reductions in PTSD severity were found in the aerobic versus the stretching group at 6-month follow-up (mean difference, 12.1;95% CI, 2.4-21.8; P = .023), pointing to a “moderate effect size” (d = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.1-1.1]).
Although there were no differences found at 6-month assessment between rates of PTSD diagnosis (25% of the aerobic vs 27% of the stretching group), more participants in the aerobic group reached a “minimal clinically important difference,” compared to those in the stretching group (96% vs. 84%, respectively, x2 = 4.4; P = .036).
There were also superior benefits found in the aerobic versus the stretching group on depression severity at 6 months (a secondary outcome), with a mean difference in Beck Depression Inventory-2 score of 5.7 (95% CI, 0.5-10.9; P = .022), yielding a “moderate effect size” (d = 0.5; 95% CI, 0.1-1.0]).
There were no adverse events associated with the intervention, and almost all the sessions (88%) complied with the treatment protocol.
The researchers noted several limitations. For example, they did not obtain plasma to measure BDNF concentrations, so they could not “infer whether the mechanism of change involved BDNF.”
In addition, they did not perform sex-specific analyses. “Future studies could increase the sample size to investigate sex differences because females display less BDNF change following exercise than do males,” they wrote.
Nevertheless, the study “provides initial evidence of a simple and accessible strategy that clinicians could readily apply in combination with exposure therapy,” they stated. “Whereas many pharmacologic interventions pose barriers, including cost, requirement for prescriptions, and patient resistance to drugs, exercise offers clinicians a strategy that can be implemented with few barriers.”
Dr. Bryant emphasized that one study “does not represent a body of evidence, and so it is essential that this finding be replicated in other trials before it can be recommended for clinical use.” He noted that other trials are “currently underway.”
Easy augmentation
In a comment, Barbara Rothbaum, PhD, professor in psychiatry and director of the Trauma and Anxiety Recovery Program at Emory University, Atlanta, called it a “well-controlled trial augmenting exposure therapy for PTSD with brief aerobic exercise and finding some benefits of the augmented condition at 6 months posttreatment but not immediately posttreatment.”
The study’s methodology – that is, using independent standard assessment of PTSD and rating audio recordings of therapy sessions for treatment fidelity and quality – can lead us to “be confident in their [the researchers’] conclusions,” she said.
Dr. Rothbaum, who was not associated with this study, described research into methods to augment exposure therapy for PTSD as “timely and clinically relevant.”
Exercise “would be an easy augmentation for many clinicians if it is helpful,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. The authors and Dr. Rothbaum reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators randomly assigned individuals with PTSD to receive either exposure therapy with aerobic exercise or exposure therapy with passive stretching for 9 weeks. At 6 months post intervention, participants in the aerobic exercise group showed greater reductions in PTSD severity, compared with those in the stretching group.
“There is a critical need to improve outcomes for treating people with PTSD, and this finding points to one potentially cheap and ready-to-use strategy that all clinicians could employ with most patients,” lead author Richard Bryant, MPsych, PhD, DSc, director of the Traumatic Stress Clinic and Scientia Professor of Psychology at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, told this news organization.
The study was published online in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Promoting BDNF
“Trauma-focused psychotherapy is the recommended treatment for PTSD, but up to half of patients do not respond to this treatment,” Dr. Bryant said.
“We know that brain-derived neurotrophic factors [BDNF] are critical for synaptic plasticity, which underpins the learning that occurs in therapy so that reminders of trauma are no longer fear-provoking,” he continued. “Preclinical animal and human research inform us that brief aerobic exercise can promote BDNF and new learning that inhibits fear responses.”
The researchers “hypothesized that brief exercise after exposure therapy to trauma memories – which is the key ingredient of trauma-focused psychotherapy – would lead to greater reductions in PTSD, relative to standard trauma-focused therapy,” he said.
To investigate the question, the researchers randomly assigned 130 adults with PTSD (mean age, 39 years; 61% female; 76% White) to receive nine 90-minute sessions of exposure therapy with either aerobic exercise or passive stretching (n = 65 in each group).
There were no differences at baseline in sociodemographic characteristics or psychopathology measures, although the mean age of the stretching group was slightly older than that of the aerobic group (40 years vs. 37 years, respectively), and there was a slightly higher proportion of women in the stretching group (68% vs. 54%).
Participants did not differ on weekly exercise either at baseline, immediately post treatment, or at 6-week follow-up.
PTSD severity (the primary outcome) was measured using the clinician-administered PTSD scale CAPS-2, with assessments conducted at baseline, 1 week post treatment, and 6 months post treatment.
The aerobic exercise regimen was tailored to each participant, based on an assessment of his/her aerobic target zone.
The exposure therapy sessions were identical for both groups. Following the exposure sessions, participants engaged in their respective exercises: Those in the passive stretching group engaged in 20 minutes of exercise, while those in the aerobic group participated in a total of 20 minutes of exercise, with 10 conducted at their personal aerobic target heart rate.
“This level of exercise was chosen because BDNF concentration in the serum is increased by two 3-minute bouts of aerobic exercise, and 10 minutes of aerobic exercise can facilitate extinction learning,” the authors explained.
The aerobic activity consisted of running on a stepper exercise platform while having cardiac activity recorded. A small portion (10%) of the therapy sessions were recorded and rated for treatment fidelity.
Change in PTSD was the primary outcome, with secondary outcomes consisting of changes in depression, anxiety, alcohol use disorder, and posttraumatic cognitions.
Few barriers
The researchers found no significant differences in PTSD severity, as measured by CAPS-2 score, between treatment groups at 10 weeks – that is, immediately post treatment (mean difference, 7.0; 95% confidence interval, –2.3 to 16.4; P = .14).
However, significantly greater reductions in PTSD severity were found in the aerobic versus the stretching group at 6-month follow-up (mean difference, 12.1;95% CI, 2.4-21.8; P = .023), pointing to a “moderate effect size” (d = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.1-1.1]).
Although there were no differences found at 6-month assessment between rates of PTSD diagnosis (25% of the aerobic vs 27% of the stretching group), more participants in the aerobic group reached a “minimal clinically important difference,” compared to those in the stretching group (96% vs. 84%, respectively, x2 = 4.4; P = .036).
There were also superior benefits found in the aerobic versus the stretching group on depression severity at 6 months (a secondary outcome), with a mean difference in Beck Depression Inventory-2 score of 5.7 (95% CI, 0.5-10.9; P = .022), yielding a “moderate effect size” (d = 0.5; 95% CI, 0.1-1.0]).
There were no adverse events associated with the intervention, and almost all the sessions (88%) complied with the treatment protocol.
The researchers noted several limitations. For example, they did not obtain plasma to measure BDNF concentrations, so they could not “infer whether the mechanism of change involved BDNF.”
In addition, they did not perform sex-specific analyses. “Future studies could increase the sample size to investigate sex differences because females display less BDNF change following exercise than do males,” they wrote.
Nevertheless, the study “provides initial evidence of a simple and accessible strategy that clinicians could readily apply in combination with exposure therapy,” they stated. “Whereas many pharmacologic interventions pose barriers, including cost, requirement for prescriptions, and patient resistance to drugs, exercise offers clinicians a strategy that can be implemented with few barriers.”
Dr. Bryant emphasized that one study “does not represent a body of evidence, and so it is essential that this finding be replicated in other trials before it can be recommended for clinical use.” He noted that other trials are “currently underway.”
Easy augmentation
In a comment, Barbara Rothbaum, PhD, professor in psychiatry and director of the Trauma and Anxiety Recovery Program at Emory University, Atlanta, called it a “well-controlled trial augmenting exposure therapy for PTSD with brief aerobic exercise and finding some benefits of the augmented condition at 6 months posttreatment but not immediately posttreatment.”
The study’s methodology – that is, using independent standard assessment of PTSD and rating audio recordings of therapy sessions for treatment fidelity and quality – can lead us to “be confident in their [the researchers’] conclusions,” she said.
Dr. Rothbaum, who was not associated with this study, described research into methods to augment exposure therapy for PTSD as “timely and clinically relevant.”
Exercise “would be an easy augmentation for many clinicians if it is helpful,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. The authors and Dr. Rothbaum reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators randomly assigned individuals with PTSD to receive either exposure therapy with aerobic exercise or exposure therapy with passive stretching for 9 weeks. At 6 months post intervention, participants in the aerobic exercise group showed greater reductions in PTSD severity, compared with those in the stretching group.
“There is a critical need to improve outcomes for treating people with PTSD, and this finding points to one potentially cheap and ready-to-use strategy that all clinicians could employ with most patients,” lead author Richard Bryant, MPsych, PhD, DSc, director of the Traumatic Stress Clinic and Scientia Professor of Psychology at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, told this news organization.
The study was published online in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Promoting BDNF
“Trauma-focused psychotherapy is the recommended treatment for PTSD, but up to half of patients do not respond to this treatment,” Dr. Bryant said.
“We know that brain-derived neurotrophic factors [BDNF] are critical for synaptic plasticity, which underpins the learning that occurs in therapy so that reminders of trauma are no longer fear-provoking,” he continued. “Preclinical animal and human research inform us that brief aerobic exercise can promote BDNF and new learning that inhibits fear responses.”
The researchers “hypothesized that brief exercise after exposure therapy to trauma memories – which is the key ingredient of trauma-focused psychotherapy – would lead to greater reductions in PTSD, relative to standard trauma-focused therapy,” he said.
To investigate the question, the researchers randomly assigned 130 adults with PTSD (mean age, 39 years; 61% female; 76% White) to receive nine 90-minute sessions of exposure therapy with either aerobic exercise or passive stretching (n = 65 in each group).
There were no differences at baseline in sociodemographic characteristics or psychopathology measures, although the mean age of the stretching group was slightly older than that of the aerobic group (40 years vs. 37 years, respectively), and there was a slightly higher proportion of women in the stretching group (68% vs. 54%).
Participants did not differ on weekly exercise either at baseline, immediately post treatment, or at 6-week follow-up.
PTSD severity (the primary outcome) was measured using the clinician-administered PTSD scale CAPS-2, with assessments conducted at baseline, 1 week post treatment, and 6 months post treatment.
The aerobic exercise regimen was tailored to each participant, based on an assessment of his/her aerobic target zone.
The exposure therapy sessions were identical for both groups. Following the exposure sessions, participants engaged in their respective exercises: Those in the passive stretching group engaged in 20 minutes of exercise, while those in the aerobic group participated in a total of 20 minutes of exercise, with 10 conducted at their personal aerobic target heart rate.
“This level of exercise was chosen because BDNF concentration in the serum is increased by two 3-minute bouts of aerobic exercise, and 10 minutes of aerobic exercise can facilitate extinction learning,” the authors explained.
The aerobic activity consisted of running on a stepper exercise platform while having cardiac activity recorded. A small portion (10%) of the therapy sessions were recorded and rated for treatment fidelity.
Change in PTSD was the primary outcome, with secondary outcomes consisting of changes in depression, anxiety, alcohol use disorder, and posttraumatic cognitions.
Few barriers
The researchers found no significant differences in PTSD severity, as measured by CAPS-2 score, between treatment groups at 10 weeks – that is, immediately post treatment (mean difference, 7.0; 95% confidence interval, –2.3 to 16.4; P = .14).
However, significantly greater reductions in PTSD severity were found in the aerobic versus the stretching group at 6-month follow-up (mean difference, 12.1;95% CI, 2.4-21.8; P = .023), pointing to a “moderate effect size” (d = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.1-1.1]).
Although there were no differences found at 6-month assessment between rates of PTSD diagnosis (25% of the aerobic vs 27% of the stretching group), more participants in the aerobic group reached a “minimal clinically important difference,” compared to those in the stretching group (96% vs. 84%, respectively, x2 = 4.4; P = .036).
There were also superior benefits found in the aerobic versus the stretching group on depression severity at 6 months (a secondary outcome), with a mean difference in Beck Depression Inventory-2 score of 5.7 (95% CI, 0.5-10.9; P = .022), yielding a “moderate effect size” (d = 0.5; 95% CI, 0.1-1.0]).
There were no adverse events associated with the intervention, and almost all the sessions (88%) complied with the treatment protocol.
The researchers noted several limitations. For example, they did not obtain plasma to measure BDNF concentrations, so they could not “infer whether the mechanism of change involved BDNF.”
In addition, they did not perform sex-specific analyses. “Future studies could increase the sample size to investigate sex differences because females display less BDNF change following exercise than do males,” they wrote.
Nevertheless, the study “provides initial evidence of a simple and accessible strategy that clinicians could readily apply in combination with exposure therapy,” they stated. “Whereas many pharmacologic interventions pose barriers, including cost, requirement for prescriptions, and patient resistance to drugs, exercise offers clinicians a strategy that can be implemented with few barriers.”
Dr. Bryant emphasized that one study “does not represent a body of evidence, and so it is essential that this finding be replicated in other trials before it can be recommended for clinical use.” He noted that other trials are “currently underway.”
Easy augmentation
In a comment, Barbara Rothbaum, PhD, professor in psychiatry and director of the Trauma and Anxiety Recovery Program at Emory University, Atlanta, called it a “well-controlled trial augmenting exposure therapy for PTSD with brief aerobic exercise and finding some benefits of the augmented condition at 6 months posttreatment but not immediately posttreatment.”
The study’s methodology – that is, using independent standard assessment of PTSD and rating audio recordings of therapy sessions for treatment fidelity and quality – can lead us to “be confident in their [the researchers’] conclusions,” she said.
Dr. Rothbaum, who was not associated with this study, described research into methods to augment exposure therapy for PTSD as “timely and clinically relevant.”
Exercise “would be an easy augmentation for many clinicians if it is helpful,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. The authors and Dr. Rothbaum reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET PSYCHIATRY
The kids may not be alright, but psychiatry can help
When I was growing up, I can remember experiencing “duck and cover” drills at school. If a flash appeared in our peripheral vision, we were told we should not look at it but crawl under our desks. My classmates and I were being taught how to protect ourselves in case of a nuclear attack.
Clearly, had there been such an attack, ducking under our desks would not have saved us. Thankfully, such a conflict never occurred – and hopefully never will. Still, the warning did penetrate our psyches. In those days, families and children in schools were worried, and some were scared.
The situation is quite different today. Our children and grandchildren are being taught to protect themselves not from actions overseas – that never happened – but from what someone living in their community might do that has been occurring in real time. According to my daughter-in-law, her young children are taught during “lockdowns” to hide in their classrooms’ closets. During these drills, some children are directed to line up against a wall that would be out of sight of a shooter, and to stay as still as possible.
Since 2017, the number of intentional shootings in U.S. kindergarten through grade 12 schools increased precipitously (Prev Med. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.107280). Imagine the psychological impact that the vigilance required to deal with such impending threats must be having on our children, as they learn to fear injury and possible death every day they go to school. I’ve talked with numerous parents about this, including my own adult children, and this is clearly a new dimension of life that is on everyone’s minds. Schools, once bastions of safety, are no longer that safe.
For many years, I’ve written about the need to destigmatize mental illness so that it is treated on a par with physical illness. As we look at the challenges faced by young people, reframing mental illness is more important now than ever. This means finding ways to increase the funding of studies that help us understand young people with mental health issues. It also means encouraging patients to pursue treatment from psychiatrists, psychologists, or mental health counselors who specialize in short-term therapy.
The emphasis here on short-term therapy is not to discourage longer-term care when needed, but clearly short-term care strategies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapies, not only work for problem resolution, they also help in the destigmatization of mental health care – as the circumscribed treatment with a clear beginning, middle, and end is consistent with CBT and consistent with much of medical care for physical disorders.
Furthermore, as we aim to destigmatize mental health care, it’s important to equate it with physical care. For example, taking a day or two from school or work for a sprained ankle, seeing a dentist, or an eye exam, plus a myriad of physical issues is quite acceptable. Why is it not also acceptable for a mental health issue and evaluation, such as for anxiety or PTSD, plus being able to talk about it without stigma? Seeing the “shrink” needs to be removed as a negative but viewed as a very positive move toward care for oneself.
In addition, children and adolescents are battling countless other health challenges that could have implications for mental health professionals, for example:
- During the height of the coronavirus pandemic, pediatric endocrinologists reportedly saw a surge of referrals for girls experiencing early puberty. Puberty should never be medicalized, but early maturation has been linked to numerous psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and eating disorders (J Pediatr Adolec Gynecol. 2022 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2022.05.005).
- A global epidemiologic study of children estimates that nearly 8 million youth lost a parent or caregiver because of a pandemic-related cause between Jan. 1, 2020, and May 1, 2022. An additional 2.5 million children were affected by the loss of secondary caregivers such as grandparents (JAMA Pediatr. 2022 Sept. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.3157).
- The inpatient and outpatient volume of adolescents and young adults receiving care for eating disorders skyrocketed before and after the pandemic, according to the results of case study series (JAMA Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 7. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.4346).
- Children and adolescents who developed COVID-19 suffered tremendously during the height of the pandemic. A nationwide analysis shows that COVID-19 nearly tripled children’s risks of developing new mental health illnesses, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anxiety, trauma, or stress disorder (Psychiatric Services. 2022 Jun 2. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.202100646).
In addition to those challenges, young children are facing an increase in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. We were told the “flu” would be quite bad this year and to beware of monkeypox. However, very little mention is made of the equally distressing “epidemic” of mental health issues, PTSD, anxiety, and depression as we are still in the midst of the COVID pandemic in the United States with almost 400 deaths a day – a very unacceptable number.
Interestingly, we seem to have abandoned the use of masks as protection against COVID and other respiratory diseases, despite their effectiveness. A study in Boston that looked at children in two school districts that did not lift mask mandates demonstrated that mask wearing does indeed lead to significant reductions in the number of pediatric COVID cases. In addition to societal violence and school shootings – which certainly exacerbate anxiety – the fear of dying or the death of a loved one, tied to COVID, may lead to epidemic proportions of PTSD in children. As an article in WebMD noted, “pediatricians are imploring the federal government to declare a national emergency as cases of pediatric respiratory illnesses continue to soar.”
In light of the acknowledged mental health crisis in children, which appears epidemic, I would hope the psychiatric and psychological associations would publicly sound an alarm so that resources could be brought to bear to address this critical issue. I believe doing so would also aid in destigmatizing mental disorders, and increase education and treatment.
Layered on top of those issues are natural disasters, such as the fallout from Tropical Storm Nicole when it recently caused devastation across western Florida. The mental health trauma caused by recent tropical storms seems all but forgotten – except for those who are still suffering. All of this adds up to a society-wide mental health crisis, which seems far more expansive than monkeypox, for example. Yet monkeypox, which did lead to thousands of cases and approximately 29 deaths in the United States, was declared a national public health emergency.
Additionally, RSV killed 100-500 U.S. children under age 5 each year before the pandemic, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and currently it appears even worse. Yet despite the seriousness of RSV, it nowhere matches the emotional toll COVID has taken on children globally.
Let’s make it standard practice for children – and of course, adults – to be taught that anxiety is a normal response at times. We should teach that, in some cases, feeling “down” or in despair and even experiencing symptoms of PTSD based on what’s going on personally and within our environment (i.e., COVID, school shootings, etc.) are triggers and responses that can be addressed and often quickly treated by talking with a mental health professional.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist and has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in and writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
When I was growing up, I can remember experiencing “duck and cover” drills at school. If a flash appeared in our peripheral vision, we were told we should not look at it but crawl under our desks. My classmates and I were being taught how to protect ourselves in case of a nuclear attack.
Clearly, had there been such an attack, ducking under our desks would not have saved us. Thankfully, such a conflict never occurred – and hopefully never will. Still, the warning did penetrate our psyches. In those days, families and children in schools were worried, and some were scared.
The situation is quite different today. Our children and grandchildren are being taught to protect themselves not from actions overseas – that never happened – but from what someone living in their community might do that has been occurring in real time. According to my daughter-in-law, her young children are taught during “lockdowns” to hide in their classrooms’ closets. During these drills, some children are directed to line up against a wall that would be out of sight of a shooter, and to stay as still as possible.
Since 2017, the number of intentional shootings in U.S. kindergarten through grade 12 schools increased precipitously (Prev Med. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.107280). Imagine the psychological impact that the vigilance required to deal with such impending threats must be having on our children, as they learn to fear injury and possible death every day they go to school. I’ve talked with numerous parents about this, including my own adult children, and this is clearly a new dimension of life that is on everyone’s minds. Schools, once bastions of safety, are no longer that safe.
For many years, I’ve written about the need to destigmatize mental illness so that it is treated on a par with physical illness. As we look at the challenges faced by young people, reframing mental illness is more important now than ever. This means finding ways to increase the funding of studies that help us understand young people with mental health issues. It also means encouraging patients to pursue treatment from psychiatrists, psychologists, or mental health counselors who specialize in short-term therapy.
The emphasis here on short-term therapy is not to discourage longer-term care when needed, but clearly short-term care strategies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapies, not only work for problem resolution, they also help in the destigmatization of mental health care – as the circumscribed treatment with a clear beginning, middle, and end is consistent with CBT and consistent with much of medical care for physical disorders.
Furthermore, as we aim to destigmatize mental health care, it’s important to equate it with physical care. For example, taking a day or two from school or work for a sprained ankle, seeing a dentist, or an eye exam, plus a myriad of physical issues is quite acceptable. Why is it not also acceptable for a mental health issue and evaluation, such as for anxiety or PTSD, plus being able to talk about it without stigma? Seeing the “shrink” needs to be removed as a negative but viewed as a very positive move toward care for oneself.
In addition, children and adolescents are battling countless other health challenges that could have implications for mental health professionals, for example:
- During the height of the coronavirus pandemic, pediatric endocrinologists reportedly saw a surge of referrals for girls experiencing early puberty. Puberty should never be medicalized, but early maturation has been linked to numerous psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and eating disorders (J Pediatr Adolec Gynecol. 2022 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2022.05.005).
- A global epidemiologic study of children estimates that nearly 8 million youth lost a parent or caregiver because of a pandemic-related cause between Jan. 1, 2020, and May 1, 2022. An additional 2.5 million children were affected by the loss of secondary caregivers such as grandparents (JAMA Pediatr. 2022 Sept. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.3157).
- The inpatient and outpatient volume of adolescents and young adults receiving care for eating disorders skyrocketed before and after the pandemic, according to the results of case study series (JAMA Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 7. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.4346).
- Children and adolescents who developed COVID-19 suffered tremendously during the height of the pandemic. A nationwide analysis shows that COVID-19 nearly tripled children’s risks of developing new mental health illnesses, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anxiety, trauma, or stress disorder (Psychiatric Services. 2022 Jun 2. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.202100646).
In addition to those challenges, young children are facing an increase in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. We were told the “flu” would be quite bad this year and to beware of monkeypox. However, very little mention is made of the equally distressing “epidemic” of mental health issues, PTSD, anxiety, and depression as we are still in the midst of the COVID pandemic in the United States with almost 400 deaths a day – a very unacceptable number.
Interestingly, we seem to have abandoned the use of masks as protection against COVID and other respiratory diseases, despite their effectiveness. A study in Boston that looked at children in two school districts that did not lift mask mandates demonstrated that mask wearing does indeed lead to significant reductions in the number of pediatric COVID cases. In addition to societal violence and school shootings – which certainly exacerbate anxiety – the fear of dying or the death of a loved one, tied to COVID, may lead to epidemic proportions of PTSD in children. As an article in WebMD noted, “pediatricians are imploring the federal government to declare a national emergency as cases of pediatric respiratory illnesses continue to soar.”
In light of the acknowledged mental health crisis in children, which appears epidemic, I would hope the psychiatric and psychological associations would publicly sound an alarm so that resources could be brought to bear to address this critical issue. I believe doing so would also aid in destigmatizing mental disorders, and increase education and treatment.
Layered on top of those issues are natural disasters, such as the fallout from Tropical Storm Nicole when it recently caused devastation across western Florida. The mental health trauma caused by recent tropical storms seems all but forgotten – except for those who are still suffering. All of this adds up to a society-wide mental health crisis, which seems far more expansive than monkeypox, for example. Yet monkeypox, which did lead to thousands of cases and approximately 29 deaths in the United States, was declared a national public health emergency.
Additionally, RSV killed 100-500 U.S. children under age 5 each year before the pandemic, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and currently it appears even worse. Yet despite the seriousness of RSV, it nowhere matches the emotional toll COVID has taken on children globally.
Let’s make it standard practice for children – and of course, adults – to be taught that anxiety is a normal response at times. We should teach that, in some cases, feeling “down” or in despair and even experiencing symptoms of PTSD based on what’s going on personally and within our environment (i.e., COVID, school shootings, etc.) are triggers and responses that can be addressed and often quickly treated by talking with a mental health professional.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist and has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in and writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
When I was growing up, I can remember experiencing “duck and cover” drills at school. If a flash appeared in our peripheral vision, we were told we should not look at it but crawl under our desks. My classmates and I were being taught how to protect ourselves in case of a nuclear attack.
Clearly, had there been such an attack, ducking under our desks would not have saved us. Thankfully, such a conflict never occurred – and hopefully never will. Still, the warning did penetrate our psyches. In those days, families and children in schools were worried, and some were scared.
The situation is quite different today. Our children and grandchildren are being taught to protect themselves not from actions overseas – that never happened – but from what someone living in their community might do that has been occurring in real time. According to my daughter-in-law, her young children are taught during “lockdowns” to hide in their classrooms’ closets. During these drills, some children are directed to line up against a wall that would be out of sight of a shooter, and to stay as still as possible.
Since 2017, the number of intentional shootings in U.S. kindergarten through grade 12 schools increased precipitously (Prev Med. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.107280). Imagine the psychological impact that the vigilance required to deal with such impending threats must be having on our children, as they learn to fear injury and possible death every day they go to school. I’ve talked with numerous parents about this, including my own adult children, and this is clearly a new dimension of life that is on everyone’s minds. Schools, once bastions of safety, are no longer that safe.
For many years, I’ve written about the need to destigmatize mental illness so that it is treated on a par with physical illness. As we look at the challenges faced by young people, reframing mental illness is more important now than ever. This means finding ways to increase the funding of studies that help us understand young people with mental health issues. It also means encouraging patients to pursue treatment from psychiatrists, psychologists, or mental health counselors who specialize in short-term therapy.
The emphasis here on short-term therapy is not to discourage longer-term care when needed, but clearly short-term care strategies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapies, not only work for problem resolution, they also help in the destigmatization of mental health care – as the circumscribed treatment with a clear beginning, middle, and end is consistent with CBT and consistent with much of medical care for physical disorders.
Furthermore, as we aim to destigmatize mental health care, it’s important to equate it with physical care. For example, taking a day or two from school or work for a sprained ankle, seeing a dentist, or an eye exam, plus a myriad of physical issues is quite acceptable. Why is it not also acceptable for a mental health issue and evaluation, such as for anxiety or PTSD, plus being able to talk about it without stigma? Seeing the “shrink” needs to be removed as a negative but viewed as a very positive move toward care for oneself.
In addition, children and adolescents are battling countless other health challenges that could have implications for mental health professionals, for example:
- During the height of the coronavirus pandemic, pediatric endocrinologists reportedly saw a surge of referrals for girls experiencing early puberty. Puberty should never be medicalized, but early maturation has been linked to numerous psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and eating disorders (J Pediatr Adolec Gynecol. 2022 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2022.05.005).
- A global epidemiologic study of children estimates that nearly 8 million youth lost a parent or caregiver because of a pandemic-related cause between Jan. 1, 2020, and May 1, 2022. An additional 2.5 million children were affected by the loss of secondary caregivers such as grandparents (JAMA Pediatr. 2022 Sept. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.3157).
- The inpatient and outpatient volume of adolescents and young adults receiving care for eating disorders skyrocketed before and after the pandemic, according to the results of case study series (JAMA Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 7. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.4346).
- Children and adolescents who developed COVID-19 suffered tremendously during the height of the pandemic. A nationwide analysis shows that COVID-19 nearly tripled children’s risks of developing new mental health illnesses, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anxiety, trauma, or stress disorder (Psychiatric Services. 2022 Jun 2. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.202100646).
In addition to those challenges, young children are facing an increase in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. We were told the “flu” would be quite bad this year and to beware of monkeypox. However, very little mention is made of the equally distressing “epidemic” of mental health issues, PTSD, anxiety, and depression as we are still in the midst of the COVID pandemic in the United States with almost 400 deaths a day – a very unacceptable number.
Interestingly, we seem to have abandoned the use of masks as protection against COVID and other respiratory diseases, despite their effectiveness. A study in Boston that looked at children in two school districts that did not lift mask mandates demonstrated that mask wearing does indeed lead to significant reductions in the number of pediatric COVID cases. In addition to societal violence and school shootings – which certainly exacerbate anxiety – the fear of dying or the death of a loved one, tied to COVID, may lead to epidemic proportions of PTSD in children. As an article in WebMD noted, “pediatricians are imploring the federal government to declare a national emergency as cases of pediatric respiratory illnesses continue to soar.”
In light of the acknowledged mental health crisis in children, which appears epidemic, I would hope the psychiatric and psychological associations would publicly sound an alarm so that resources could be brought to bear to address this critical issue. I believe doing so would also aid in destigmatizing mental disorders, and increase education and treatment.
Layered on top of those issues are natural disasters, such as the fallout from Tropical Storm Nicole when it recently caused devastation across western Florida. The mental health trauma caused by recent tropical storms seems all but forgotten – except for those who are still suffering. All of this adds up to a society-wide mental health crisis, which seems far more expansive than monkeypox, for example. Yet monkeypox, which did lead to thousands of cases and approximately 29 deaths in the United States, was declared a national public health emergency.
Additionally, RSV killed 100-500 U.S. children under age 5 each year before the pandemic, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and currently it appears even worse. Yet despite the seriousness of RSV, it nowhere matches the emotional toll COVID has taken on children globally.
Let’s make it standard practice for children – and of course, adults – to be taught that anxiety is a normal response at times. We should teach that, in some cases, feeling “down” or in despair and even experiencing symptoms of PTSD based on what’s going on personally and within our environment (i.e., COVID, school shootings, etc.) are triggers and responses that can be addressed and often quickly treated by talking with a mental health professional.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist and has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in and writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.











