User login
Clinical Endocrinology News is an independent news source that provides endocrinologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the endocrinologist's practice. Specialty topics include Diabetes, Lipid & Metabolic Disorders Menopause, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Pediatric Endocrinology, Pituitary, Thyroid & Adrenal Disorders, and Reproductive Endocrinology. Featured content includes Commentaries, Implementin Health Reform, Law & Medicine, and In the Loop, the blog of Clinical Endocrinology News. Clinical Endocrinology News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
addict
addicted
addicting
addiction
adult sites
alcohol
antibody
ass
attorney
audit
auditor
babies
babpa
baby
ban
banned
banning
best
bisexual
bitch
bleach
blog
blow job
bondage
boobs
booty
buy
cannabis
certificate
certification
certified
cheap
cheapest
class action
cocaine
cock
counterfeit drug
crack
crap
crime
criminal
cunt
curable
cure
dangerous
dangers
dead
deadly
death
defend
defended
depedent
dependence
dependent
detergent
dick
die
dildo
drug abuse
drug recall
dying
fag
fake
fatal
fatalities
fatality
free
fuck
gangs
gingivitis
guns
hardcore
herbal
herbs
heroin
herpes
home remedies
homo
horny
hypersensitivity
hypoglycemia treatment
illegal drug use
illegal use of prescription
incest
infant
infants
job
ketoacidosis
kill
killer
killing
kinky
law suit
lawsuit
lawyer
lesbian
marijuana
medicine for hypoglycemia
murder
naked
natural
newborn
nigger
noise
nude
nudity
orgy
over the counter
overdosage
overdose
overdosed
overdosing
penis
pimp
pistol
porn
porno
pornographic
pornography
prison
profanity
purchase
purchasing
pussy
queer
rape
rapist
recall
recreational drug
rob
robberies
sale
sales
sex
sexual
shit
shoot
slut
slutty
stole
stolen
store
sue
suicidal
suicide
supplements
supply company
theft
thief
thieves
tit
toddler
toddlers
toxic
toxin
tragedy
treating dka
treating hypoglycemia
treatment for hypoglycemia
vagina
violence
whore
withdrawal
without prescription
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
A Step-by-Step Guide for Diagnosing Cushing Syndrome
“Moon face” is a term that’s become popular on social media, used to describe people with unusually round faces who are purported to have high levels of cortisol. But the term “moon face” isn’t new. It was actually coined in the 1930s by neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing, MD, who identified patients with a constellation of clinical characteristics — a condition that came to bear his name — which included rapidly developing facial adiposity. And indeed, elevated cortisol is a hallmark feature of Cushing syndrome (CS), but there are other reasons for elevated cortisol and other manifestations of CS.
Today, the term “moon face” has been replaced with “round face,” which is considered more encompassing and culturally sensitive, said Maria Fleseriu, MD, professor of medicine and neurological surgery and director of the Pituitary Center at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, Oregon.
Facial roundness can lead clinicians to be suspicious that their patient is experiencing CS. But because a round face is associated with several other conditions, it’s important to be familiar with its particular presentation in CS, as well as how to diagnose and treat CS.
Pathophysiology of CS
Dr. Fleseriu defined CS as “prolonged nonphysiologic increase in cortisol, due either to exogenous use of steroids (oral, topical, or inhaled) or to excess endogenous cortisol production.” She added that it’s important “to always exclude exogenous causes before conducting a further workup to determine the type and cause of cortisol excess.”
Dr. Fleseriu said. Other causes of CS are ectopic (caused by neuroendocrine tumors) or adrenal. CS affects primarily females and typically has an onset between ages 20 and 50 years, depending on the CS type.
Diagnosis of CS is “substantially delayed for most patients, due to metabolic syndrome phenotypic overlap and lack of a single pathognomonic symptom,” according to Dr. Fleseriu.
An accurate diagnosis should be on the basis of signs and symptoms, biochemical screening, other laboratory testing, and diagnostic imaging.
Look for Clinical Signs and Symptoms of CS
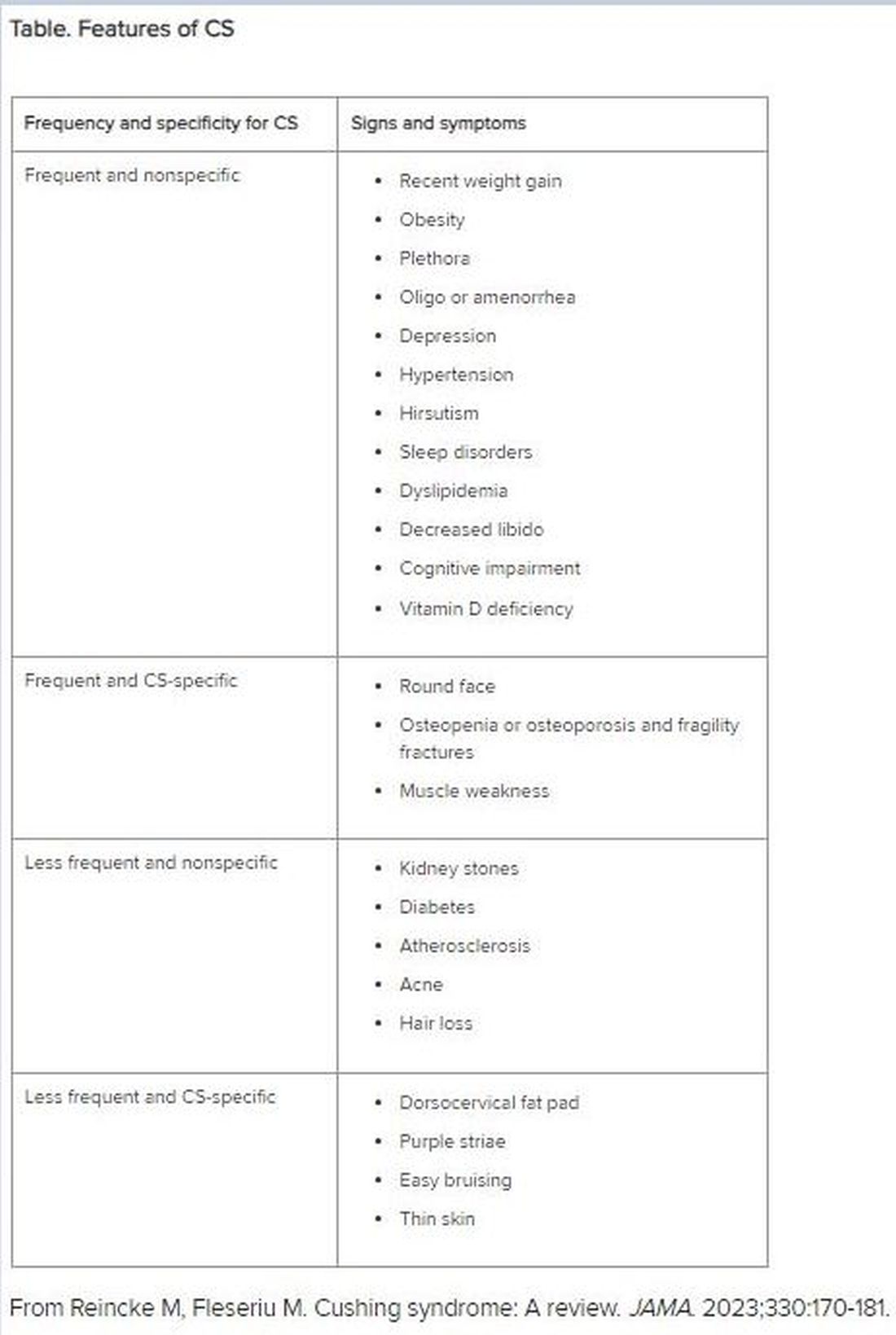
“CS mostly presents as a combination of two or more features,” Dr. Fleseriu stated. These include increased fat pads (in the face, neck, and trunk), skin changes, signs of protein catabolism, growth retardation and body weight increase in children, and metabolic dysregulations (Table).
“Biochemical screening should be performed in patients with a combination of symptoms, and therefore an increased pretest probability for CS,” Dr. Fleseriu advised.
A CS diagnosis requires not only biochemical confirmation of hypercortisolemia but also determination of the underlying cause of the excess endogenous cortisol production. This is a key step, as the management of CS is specific to its etiology.
Elevated plasma cortisol alone is insufficient for diagnosing CS, as several conditions can be associated with physiologic, nonneoplastic endogenous hypercortisolemia, according to the 2021 updated CS guidelines for which Dr. Fleseriu served as a coauthor. These include depression, alcohol dependence, glucocorticoid resistance, obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, prolonged physical exertion, malnutrition, and cortisol-binding globulin excess.
The diagnosis begins with the following screening tests:
- Late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC) to assess an abnormal circadian rhythm
According to the 2021 guideline, this is “based on the assumption that patients with CS lose the normal circadian nadir of cortisol secretion.”
- Overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test (DST) to assess impaired glucocorticoid feedback
The authors noted that in healthy individuals, a supraphysiologic dexamethasone dose inhibits vasopressin and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion, leading to decreased cortisol concentration. Cortisol concentrations of < 1-8 μg/dL in the morning (after administration of the dexamethasone between 11 p.m. and midnight) are considered “normal,” and a negative result “strongly predicts” the absence of CS. But false-positive and false-negative results can occur. Thus, “it is imperative that first-line testing is elected on the basis of physiologic conditions and drug intake — for example, use of CYP2A4/5 inhibitors or stimulators and oral estrogen — as well as laboratory quality control measure, and special attention to night shift workers,” Dr. Fleseriu emphasized.
- A 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) test to assess increased bioavailable cortisol
The guideline encourages conducting several 24-hour urine collections to account for intra-patient variability.
Dr. Fleseriu recommended utilizing at least two of the three screening tests, all of which have reasonable sensitivity and specificity.
“Two normal test results usually exclude the presence of CS, except in rare cyclic CS,” she added.
Conduct Additional Laboratory Testing
Additional laboratory abnormalities suggestive of CS include:
- Increased leukocytes with decreased lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils
- Elevated glucose and insulin levels
- Hypokalemia
- Increased triglycerides and total cholesterol levels
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Changes in activated thromboplastin time and plasma concentrations of pro- and anticoagulant factors
- Hypercalciuria, hypocalcemia (rare), hypophosphatemia, decreased phosphate maximum resorption, and increased alkaline phosphatase activity
Dr. Fleseriu noted that, in most cases, a final CS diagnosis can be reached after confirmation of biochemical hypercortisolism, which is done after an initial positive screening test.
She added that plasma ACTH levels are “instrumental” in distinguishing ACTH-depending forms of CS — such as Cushing disease and ectopic CS — from adrenal cases. Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling is necessary in ACTH-dependent CS.
Utilize Diagnostic Imaging
There are several diagnostic imaging techniques that localize the origin of the hypercortisolism, thus informing the course of treatment.
- Pituitary MRI to detect corticotropin-secreting corticotroph adenomas, which are typically small lesions (< 6 mm in diameter)
- CT evaluation of the neck, thoracic cavity, and abdomen to diagnose ectopic CS, including lung neuroendocrine tumors and bronchial neuroendocrine tumors
- Cervical and thyroid ultrasonography to identify primary or metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma, and PET scans, which have greater sensitivity in detecting tumors, compared with CT scans
- Contrast-enhanced CT scans to detect adrenal adenomas and adrenocortical carcinomas
Management of CS
“The primary aim of treatment is eucortisolemia, and in those with endogenous CS, complete surgical resection of the underlying tumor is the primary method,” Dr. Fleseriu said.
It’s critical to monitor for biochemical remission following surgery, utilizing 24-hour UFC, LNSC, and DST “because clinical manifestations may lag behind biochemical evidence.”
In Cushing disease, almost half of patients will have either persistent or recurrent hypercortisolemia after surgery. In those cases, individualized adjuvant treatments are recommended. These include repeat surgery, bilateral adrenalectomy, radiation, or medical treatments, including pituitary-directed drugs, adrenal steroidogenesis inhibitors, or glucocorticoid receptor-blocking agents. The last two groups are used for other types of CS.
Dr. Fleseriu pointed out that CS is “associated with increased metabolic, cardiovascular, psychiatric, infectious, and musculoskeletal morbidity, which are only partially reversible with successful [CS] treatment.” These comorbidities need to be addressed via individualized therapies. Moreover, long-term mortality is increased in all forms of CS. Thus, patients require lifelong follow-up to detect recurrence at an early stage and to treat comorbidities.
“It is likely that delayed diagnosis might explain the long-term consequences of CS, including increased morbidity and mortality despite remission,” she said.
Familiarity with the presenting signs and symptoms of CS and ordering recommended screening and confirmatory tests will enable appropriate management of the condition, leading to better outcomes.
Dr. Fleseriu reported receiving research grants from Sparrow Pharmaceuticals to Oregon Health and Science University as principal investigator and receiving occasional fees for scientific consulting/advisory boards from Sparrow Pharmaceuticals, Recordati Rare Diseases Inc., and Xeris Biopharma Holdings Inc.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Moon face” is a term that’s become popular on social media, used to describe people with unusually round faces who are purported to have high levels of cortisol. But the term “moon face” isn’t new. It was actually coined in the 1930s by neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing, MD, who identified patients with a constellation of clinical characteristics — a condition that came to bear his name — which included rapidly developing facial adiposity. And indeed, elevated cortisol is a hallmark feature of Cushing syndrome (CS), but there are other reasons for elevated cortisol and other manifestations of CS.
Today, the term “moon face” has been replaced with “round face,” which is considered more encompassing and culturally sensitive, said Maria Fleseriu, MD, professor of medicine and neurological surgery and director of the Pituitary Center at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, Oregon.
Facial roundness can lead clinicians to be suspicious that their patient is experiencing CS. But because a round face is associated with several other conditions, it’s important to be familiar with its particular presentation in CS, as well as how to diagnose and treat CS.
Pathophysiology of CS
Dr. Fleseriu defined CS as “prolonged nonphysiologic increase in cortisol, due either to exogenous use of steroids (oral, topical, or inhaled) or to excess endogenous cortisol production.” She added that it’s important “to always exclude exogenous causes before conducting a further workup to determine the type and cause of cortisol excess.”
Dr. Fleseriu said. Other causes of CS are ectopic (caused by neuroendocrine tumors) or adrenal. CS affects primarily females and typically has an onset between ages 20 and 50 years, depending on the CS type.
Diagnosis of CS is “substantially delayed for most patients, due to metabolic syndrome phenotypic overlap and lack of a single pathognomonic symptom,” according to Dr. Fleseriu.
An accurate diagnosis should be on the basis of signs and symptoms, biochemical screening, other laboratory testing, and diagnostic imaging.
Look for Clinical Signs and Symptoms of CS
“CS mostly presents as a combination of two or more features,” Dr. Fleseriu stated. These include increased fat pads (in the face, neck, and trunk), skin changes, signs of protein catabolism, growth retardation and body weight increase in children, and metabolic dysregulations (Table).
“Biochemical screening should be performed in patients with a combination of symptoms, and therefore an increased pretest probability for CS,” Dr. Fleseriu advised.
A CS diagnosis requires not only biochemical confirmation of hypercortisolemia but also determination of the underlying cause of the excess endogenous cortisol production. This is a key step, as the management of CS is specific to its etiology.
Elevated plasma cortisol alone is insufficient for diagnosing CS, as several conditions can be associated with physiologic, nonneoplastic endogenous hypercortisolemia, according to the 2021 updated CS guidelines for which Dr. Fleseriu served as a coauthor. These include depression, alcohol dependence, glucocorticoid resistance, obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, prolonged physical exertion, malnutrition, and cortisol-binding globulin excess.
The diagnosis begins with the following screening tests:
- Late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC) to assess an abnormal circadian rhythm
According to the 2021 guideline, this is “based on the assumption that patients with CS lose the normal circadian nadir of cortisol secretion.”
- Overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test (DST) to assess impaired glucocorticoid feedback
The authors noted that in healthy individuals, a supraphysiologic dexamethasone dose inhibits vasopressin and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion, leading to decreased cortisol concentration. Cortisol concentrations of < 1-8 μg/dL in the morning (after administration of the dexamethasone between 11 p.m. and midnight) are considered “normal,” and a negative result “strongly predicts” the absence of CS. But false-positive and false-negative results can occur. Thus, “it is imperative that first-line testing is elected on the basis of physiologic conditions and drug intake — for example, use of CYP2A4/5 inhibitors or stimulators and oral estrogen — as well as laboratory quality control measure, and special attention to night shift workers,” Dr. Fleseriu emphasized.
- A 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) test to assess increased bioavailable cortisol
The guideline encourages conducting several 24-hour urine collections to account for intra-patient variability.
Dr. Fleseriu recommended utilizing at least two of the three screening tests, all of which have reasonable sensitivity and specificity.
“Two normal test results usually exclude the presence of CS, except in rare cyclic CS,” she added.
Conduct Additional Laboratory Testing
Additional laboratory abnormalities suggestive of CS include:
- Increased leukocytes with decreased lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils
- Elevated glucose and insulin levels
- Hypokalemia
- Increased triglycerides and total cholesterol levels
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Changes in activated thromboplastin time and plasma concentrations of pro- and anticoagulant factors
- Hypercalciuria, hypocalcemia (rare), hypophosphatemia, decreased phosphate maximum resorption, and increased alkaline phosphatase activity
Dr. Fleseriu noted that, in most cases, a final CS diagnosis can be reached after confirmation of biochemical hypercortisolism, which is done after an initial positive screening test.
She added that plasma ACTH levels are “instrumental” in distinguishing ACTH-depending forms of CS — such as Cushing disease and ectopic CS — from adrenal cases. Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling is necessary in ACTH-dependent CS.
Utilize Diagnostic Imaging
There are several diagnostic imaging techniques that localize the origin of the hypercortisolism, thus informing the course of treatment.
- Pituitary MRI to detect corticotropin-secreting corticotroph adenomas, which are typically small lesions (< 6 mm in diameter)
- CT evaluation of the neck, thoracic cavity, and abdomen to diagnose ectopic CS, including lung neuroendocrine tumors and bronchial neuroendocrine tumors
- Cervical and thyroid ultrasonography to identify primary or metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma, and PET scans, which have greater sensitivity in detecting tumors, compared with CT scans
- Contrast-enhanced CT scans to detect adrenal adenomas and adrenocortical carcinomas
Management of CS
“The primary aim of treatment is eucortisolemia, and in those with endogenous CS, complete surgical resection of the underlying tumor is the primary method,” Dr. Fleseriu said.
It’s critical to monitor for biochemical remission following surgery, utilizing 24-hour UFC, LNSC, and DST “because clinical manifestations may lag behind biochemical evidence.”
In Cushing disease, almost half of patients will have either persistent or recurrent hypercortisolemia after surgery. In those cases, individualized adjuvant treatments are recommended. These include repeat surgery, bilateral adrenalectomy, radiation, or medical treatments, including pituitary-directed drugs, adrenal steroidogenesis inhibitors, or glucocorticoid receptor-blocking agents. The last two groups are used for other types of CS.
Dr. Fleseriu pointed out that CS is “associated with increased metabolic, cardiovascular, psychiatric, infectious, and musculoskeletal morbidity, which are only partially reversible with successful [CS] treatment.” These comorbidities need to be addressed via individualized therapies. Moreover, long-term mortality is increased in all forms of CS. Thus, patients require lifelong follow-up to detect recurrence at an early stage and to treat comorbidities.
“It is likely that delayed diagnosis might explain the long-term consequences of CS, including increased morbidity and mortality despite remission,” she said.
Familiarity with the presenting signs and symptoms of CS and ordering recommended screening and confirmatory tests will enable appropriate management of the condition, leading to better outcomes.
Dr. Fleseriu reported receiving research grants from Sparrow Pharmaceuticals to Oregon Health and Science University as principal investigator and receiving occasional fees for scientific consulting/advisory boards from Sparrow Pharmaceuticals, Recordati Rare Diseases Inc., and Xeris Biopharma Holdings Inc.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Moon face” is a term that’s become popular on social media, used to describe people with unusually round faces who are purported to have high levels of cortisol. But the term “moon face” isn’t new. It was actually coined in the 1930s by neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing, MD, who identified patients with a constellation of clinical characteristics — a condition that came to bear his name — which included rapidly developing facial adiposity. And indeed, elevated cortisol is a hallmark feature of Cushing syndrome (CS), but there are other reasons for elevated cortisol and other manifestations of CS.
Today, the term “moon face” has been replaced with “round face,” which is considered more encompassing and culturally sensitive, said Maria Fleseriu, MD, professor of medicine and neurological surgery and director of the Pituitary Center at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, Oregon.
Facial roundness can lead clinicians to be suspicious that their patient is experiencing CS. But because a round face is associated with several other conditions, it’s important to be familiar with its particular presentation in CS, as well as how to diagnose and treat CS.
Pathophysiology of CS
Dr. Fleseriu defined CS as “prolonged nonphysiologic increase in cortisol, due either to exogenous use of steroids (oral, topical, or inhaled) or to excess endogenous cortisol production.” She added that it’s important “to always exclude exogenous causes before conducting a further workup to determine the type and cause of cortisol excess.”
Dr. Fleseriu said. Other causes of CS are ectopic (caused by neuroendocrine tumors) or adrenal. CS affects primarily females and typically has an onset between ages 20 and 50 years, depending on the CS type.
Diagnosis of CS is “substantially delayed for most patients, due to metabolic syndrome phenotypic overlap and lack of a single pathognomonic symptom,” according to Dr. Fleseriu.
An accurate diagnosis should be on the basis of signs and symptoms, biochemical screening, other laboratory testing, and diagnostic imaging.
Look for Clinical Signs and Symptoms of CS
“CS mostly presents as a combination of two or more features,” Dr. Fleseriu stated. These include increased fat pads (in the face, neck, and trunk), skin changes, signs of protein catabolism, growth retardation and body weight increase in children, and metabolic dysregulations (Table).
“Biochemical screening should be performed in patients with a combination of symptoms, and therefore an increased pretest probability for CS,” Dr. Fleseriu advised.
A CS diagnosis requires not only biochemical confirmation of hypercortisolemia but also determination of the underlying cause of the excess endogenous cortisol production. This is a key step, as the management of CS is specific to its etiology.
Elevated plasma cortisol alone is insufficient for diagnosing CS, as several conditions can be associated with physiologic, nonneoplastic endogenous hypercortisolemia, according to the 2021 updated CS guidelines for which Dr. Fleseriu served as a coauthor. These include depression, alcohol dependence, glucocorticoid resistance, obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, prolonged physical exertion, malnutrition, and cortisol-binding globulin excess.
The diagnosis begins with the following screening tests:
- Late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC) to assess an abnormal circadian rhythm
According to the 2021 guideline, this is “based on the assumption that patients with CS lose the normal circadian nadir of cortisol secretion.”
- Overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test (DST) to assess impaired glucocorticoid feedback
The authors noted that in healthy individuals, a supraphysiologic dexamethasone dose inhibits vasopressin and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion, leading to decreased cortisol concentration. Cortisol concentrations of < 1-8 μg/dL in the morning (after administration of the dexamethasone between 11 p.m. and midnight) are considered “normal,” and a negative result “strongly predicts” the absence of CS. But false-positive and false-negative results can occur. Thus, “it is imperative that first-line testing is elected on the basis of physiologic conditions and drug intake — for example, use of CYP2A4/5 inhibitors or stimulators and oral estrogen — as well as laboratory quality control measure, and special attention to night shift workers,” Dr. Fleseriu emphasized.
- A 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) test to assess increased bioavailable cortisol
The guideline encourages conducting several 24-hour urine collections to account for intra-patient variability.
Dr. Fleseriu recommended utilizing at least two of the three screening tests, all of which have reasonable sensitivity and specificity.
“Two normal test results usually exclude the presence of CS, except in rare cyclic CS,” she added.
Conduct Additional Laboratory Testing
Additional laboratory abnormalities suggestive of CS include:
- Increased leukocytes with decreased lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils
- Elevated glucose and insulin levels
- Hypokalemia
- Increased triglycerides and total cholesterol levels
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Changes in activated thromboplastin time and plasma concentrations of pro- and anticoagulant factors
- Hypercalciuria, hypocalcemia (rare), hypophosphatemia, decreased phosphate maximum resorption, and increased alkaline phosphatase activity
Dr. Fleseriu noted that, in most cases, a final CS diagnosis can be reached after confirmation of biochemical hypercortisolism, which is done after an initial positive screening test.
She added that plasma ACTH levels are “instrumental” in distinguishing ACTH-depending forms of CS — such as Cushing disease and ectopic CS — from adrenal cases. Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling is necessary in ACTH-dependent CS.
Utilize Diagnostic Imaging
There are several diagnostic imaging techniques that localize the origin of the hypercortisolism, thus informing the course of treatment.
- Pituitary MRI to detect corticotropin-secreting corticotroph adenomas, which are typically small lesions (< 6 mm in diameter)
- CT evaluation of the neck, thoracic cavity, and abdomen to diagnose ectopic CS, including lung neuroendocrine tumors and bronchial neuroendocrine tumors
- Cervical and thyroid ultrasonography to identify primary or metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma, and PET scans, which have greater sensitivity in detecting tumors, compared with CT scans
- Contrast-enhanced CT scans to detect adrenal adenomas and adrenocortical carcinomas
Management of CS
“The primary aim of treatment is eucortisolemia, and in those with endogenous CS, complete surgical resection of the underlying tumor is the primary method,” Dr. Fleseriu said.
It’s critical to monitor for biochemical remission following surgery, utilizing 24-hour UFC, LNSC, and DST “because clinical manifestations may lag behind biochemical evidence.”
In Cushing disease, almost half of patients will have either persistent or recurrent hypercortisolemia after surgery. In those cases, individualized adjuvant treatments are recommended. These include repeat surgery, bilateral adrenalectomy, radiation, or medical treatments, including pituitary-directed drugs, adrenal steroidogenesis inhibitors, or glucocorticoid receptor-blocking agents. The last two groups are used for other types of CS.
Dr. Fleseriu pointed out that CS is “associated with increased metabolic, cardiovascular, psychiatric, infectious, and musculoskeletal morbidity, which are only partially reversible with successful [CS] treatment.” These comorbidities need to be addressed via individualized therapies. Moreover, long-term mortality is increased in all forms of CS. Thus, patients require lifelong follow-up to detect recurrence at an early stage and to treat comorbidities.
“It is likely that delayed diagnosis might explain the long-term consequences of CS, including increased morbidity and mortality despite remission,” she said.
Familiarity with the presenting signs and symptoms of CS and ordering recommended screening and confirmatory tests will enable appropriate management of the condition, leading to better outcomes.
Dr. Fleseriu reported receiving research grants from Sparrow Pharmaceuticals to Oregon Health and Science University as principal investigator and receiving occasional fees for scientific consulting/advisory boards from Sparrow Pharmaceuticals, Recordati Rare Diseases Inc., and Xeris Biopharma Holdings Inc.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians Lament Over Reliance on Relative Value Units: Survey
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases, Type 2 Diabetes Reap GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Benefits, Too
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Gift That Keeps Giving’: The Impact of GLP-1 in Asthma
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Welcome back to Medscape at ADA 2024, where Dr. James Kim, primary care physician from Calgary, Alberta, will be joining me in deciphering the key highlights at the ADA conference and bringing our own clinical twist into what the relevance would be for people like you and I to take back to our clinics.
Welcome back, Dr. Kim.
James Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you very much. It’s nice to be back.
Dr. Jain: This was a diabetes conference, so obviously we are very pancreas focused. At this conference, we went outside our general area of territory, going outside of the pancreas and delving into other organ states. What I found fascinating were some data regarding the effects of incretin therapy on the lung, and in particular, some of the restrictive lung disorders.
Dr. Kim, you attended these sessions as well. Can you tell us a little bit more about the results that were discussed?
Dr. Kim: This is an interesting field. The moderator of the session went up and said that there has been no time in any previous ADA sessions where the lung issue was actually discussed. This was the first time ever.
They had some of the world leaders in this field, so it was really awesome to see them. Just to paint a picture of these obese asthmatic patients, they are challenging cases because, as you know, the main therapy for any asthmatic patient is inhaled corticosteroid.
Patients who are obese have quite a bit of a steroid resistance. Therefore, they end up being on many medications that sometimes are off label, and many end up on biologics as well. Therefore, the respiratory world has been seeking therapies for these obese asthmatic patients who are likely to be steroid resistant because these people are also likely to end up on an oral steroid as well.
Dr. Jain, you know the effect of the steroids much better than I do, and it’s like a laundry list. We really don’t want our patients to be on oral steroids.
In the past few years, GLP-1 has been studied quite extensively in the lung, especially in the world of asthma, and also in COPD. What’s really fascinating is that the GLP-1 receptors have been found to be quite abundant in the airway. Some studies show that the highest concentration of GLP-1 lies in the airway, whereas some studies have said that it’s the third most common area to find the GLP-1.
It is not a surprise that GLP-1 is being studied in managing the airway, especially airway inflammation in asthma and COPD patients. The preliminary data have been quite encouraging. They also discussed that there are new medications coming out that seem to be incretin based, so we’ll wait to see what those studies show.
There are two current phase 3 trials being held at the moment. One is using semaglutide 2.4 mg subcutaneous and another one is using metformin to reduce the airway inflammation in these asthmatic patients and also in some COPD patients. We’ll look forward to these results.
Dr. Jain: That’s really important to note because we see that there is a high density of these receptors in the airways, and hitherto we had no idea about the overall effect. Now, we’re looking at, as you mentioned, individuals with obesity who have asthma, so there are both the restrictive and obstructive components in the lung coming into play here.
From an endocrinology perspective, I’m thinking that this could be multiple effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonists, where on one hand you’re managing the obesity and you’re working along that line, and on the other hand, it could have local anti-inflammatory effects in the lung. Hence, there could be potential improvement in the overall pulmonary function of these individuals.
Dr. Kim: We are seeing this in primary care. Ever since I found out this information, I have started numerous patients, who are obese, asthmatic patients who do not have diabetes, on GLP-1 therapies, and their pulmonary function tests have improved significantly.
As a matter of fact, one of my personal friends is a severe asthmatic patient. She ends up being on oral steroids about three times a year. There was even one day when I saw her in one of my classes and she was dyspneic. She was short of breath.
I introduced her to one of my colleagues who’s a respirologist and very much into the impact of the incretins and asthma, and she was started on a GLP-1 receptor agonist. She lost about 30 pounds of weight, but now she is labeled as a mild asthmatic. Her pulmonary function test is completely normal. She hasn’t touched an oral steroid for a couple of years now.
That is a huge success story and I’m seeing that even in my own clinic as well. It’s a huge win for the respiratory world.
Dr. Jain: I think from an endocrinology perspective as well, if we are initiating GLP-1 receptor agonists or medications in that class, where we use it for management of obesity, sooner or later we do hit a stage where people will plateau with their weight loss. They won’t have any additional weight loss.
We tell individuals at that time that the fact that they’re able to maintain the weight loss still means that the medication is working from the obesity perspective. For individuals who also have asthma, it would be a good point to tell them that it could still have potential effects on reducing inflammation ongoing. Hence, even though they may not be losing any additional weight, it would still be helpful to continue on these medications from a pulmonary perspective.
Dr. Kim: Right now these pleiotropic effects of GLP-1 agents are absolutely mind-blowing. I mentioned in one of my respiratory presentations to a bunch of respirologists that diabetes is taking over the world, including the respiratory world. Well, you can imagine what their faces were like. However, they were quite impressed at that, and they were very excited with what these two phase 3 trials will show.
Dr. Jain: I think, based on the ADA 2024 conference, GLP-1 receptor agonists continue to be the gift that keeps giving. We have the effects on diabetes, obesity, kidney function, liver protection, lungs, and Alzheimer’s. We saw some sessions about potential use in people with alcohol misuse disorder or gambling problems. Clearly, there’s a large amount of research that›s being done with these agents.
Perhaps when you and I talk about ADA 2025, we might be able to talk about some more pleiotropic benefits outside the pancreas. Until then, please do check out our other videos from ADA 2024. Thanks for joining us again, Dr. Kim.
Dr. Kim: Thank you very much for having me.
Dr. Jain, clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, and endocrinologist, TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, has disclosed ties with Abbott, Acerus, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bausch Healthcare, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Care to Know, CCRN, Connected in Motion, CPD Network, Dexcom, Diabetes Canada, Eli Lilly, GSK, HLS Therapeutics, Janssen, Master Clinician Alliance, MDBriefcase, Merck, Medtronic, Moderna, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Partners in Progressive Medical Education, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Timed Right, WebMD, Gilead Sciences, Insulet, PocketPills, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Kim, clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary, Alberta, has disclosed ties with Abbott, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Embecta, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Linpharma, Novo Nordisk, Miravo, Otsuka, Pfizer, Teva, Takeda, and Sanofi, and Partners in Progressive Medical Education.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Welcome back to Medscape at ADA 2024, where Dr. James Kim, primary care physician from Calgary, Alberta, will be joining me in deciphering the key highlights at the ADA conference and bringing our own clinical twist into what the relevance would be for people like you and I to take back to our clinics.
Welcome back, Dr. Kim.
James Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you very much. It’s nice to be back.
Dr. Jain: This was a diabetes conference, so obviously we are very pancreas focused. At this conference, we went outside our general area of territory, going outside of the pancreas and delving into other organ states. What I found fascinating were some data regarding the effects of incretin therapy on the lung, and in particular, some of the restrictive lung disorders.
Dr. Kim, you attended these sessions as well. Can you tell us a little bit more about the results that were discussed?
Dr. Kim: This is an interesting field. The moderator of the session went up and said that there has been no time in any previous ADA sessions where the lung issue was actually discussed. This was the first time ever.
They had some of the world leaders in this field, so it was really awesome to see them. Just to paint a picture of these obese asthmatic patients, they are challenging cases because, as you know, the main therapy for any asthmatic patient is inhaled corticosteroid.
Patients who are obese have quite a bit of a steroid resistance. Therefore, they end up being on many medications that sometimes are off label, and many end up on biologics as well. Therefore, the respiratory world has been seeking therapies for these obese asthmatic patients who are likely to be steroid resistant because these people are also likely to end up on an oral steroid as well.
Dr. Jain, you know the effect of the steroids much better than I do, and it’s like a laundry list. We really don’t want our patients to be on oral steroids.
In the past few years, GLP-1 has been studied quite extensively in the lung, especially in the world of asthma, and also in COPD. What’s really fascinating is that the GLP-1 receptors have been found to be quite abundant in the airway. Some studies show that the highest concentration of GLP-1 lies in the airway, whereas some studies have said that it’s the third most common area to find the GLP-1.
It is not a surprise that GLP-1 is being studied in managing the airway, especially airway inflammation in asthma and COPD patients. The preliminary data have been quite encouraging. They also discussed that there are new medications coming out that seem to be incretin based, so we’ll wait to see what those studies show.
There are two current phase 3 trials being held at the moment. One is using semaglutide 2.4 mg subcutaneous and another one is using metformin to reduce the airway inflammation in these asthmatic patients and also in some COPD patients. We’ll look forward to these results.
Dr. Jain: That’s really important to note because we see that there is a high density of these receptors in the airways, and hitherto we had no idea about the overall effect. Now, we’re looking at, as you mentioned, individuals with obesity who have asthma, so there are both the restrictive and obstructive components in the lung coming into play here.
From an endocrinology perspective, I’m thinking that this could be multiple effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonists, where on one hand you’re managing the obesity and you’re working along that line, and on the other hand, it could have local anti-inflammatory effects in the lung. Hence, there could be potential improvement in the overall pulmonary function of these individuals.
Dr. Kim: We are seeing this in primary care. Ever since I found out this information, I have started numerous patients, who are obese, asthmatic patients who do not have diabetes, on GLP-1 therapies, and their pulmonary function tests have improved significantly.
As a matter of fact, one of my personal friends is a severe asthmatic patient. She ends up being on oral steroids about three times a year. There was even one day when I saw her in one of my classes and she was dyspneic. She was short of breath.
I introduced her to one of my colleagues who’s a respirologist and very much into the impact of the incretins and asthma, and she was started on a GLP-1 receptor agonist. She lost about 30 pounds of weight, but now she is labeled as a mild asthmatic. Her pulmonary function test is completely normal. She hasn’t touched an oral steroid for a couple of years now.
That is a huge success story and I’m seeing that even in my own clinic as well. It’s a huge win for the respiratory world.
Dr. Jain: I think from an endocrinology perspective as well, if we are initiating GLP-1 receptor agonists or medications in that class, where we use it for management of obesity, sooner or later we do hit a stage where people will plateau with their weight loss. They won’t have any additional weight loss.
We tell individuals at that time that the fact that they’re able to maintain the weight loss still means that the medication is working from the obesity perspective. For individuals who also have asthma, it would be a good point to tell them that it could still have potential effects on reducing inflammation ongoing. Hence, even though they may not be losing any additional weight, it would still be helpful to continue on these medications from a pulmonary perspective.
Dr. Kim: Right now these pleiotropic effects of GLP-1 agents are absolutely mind-blowing. I mentioned in one of my respiratory presentations to a bunch of respirologists that diabetes is taking over the world, including the respiratory world. Well, you can imagine what their faces were like. However, they were quite impressed at that, and they were very excited with what these two phase 3 trials will show.
Dr. Jain: I think, based on the ADA 2024 conference, GLP-1 receptor agonists continue to be the gift that keeps giving. We have the effects on diabetes, obesity, kidney function, liver protection, lungs, and Alzheimer’s. We saw some sessions about potential use in people with alcohol misuse disorder or gambling problems. Clearly, there’s a large amount of research that›s being done with these agents.
Perhaps when you and I talk about ADA 2025, we might be able to talk about some more pleiotropic benefits outside the pancreas. Until then, please do check out our other videos from ADA 2024. Thanks for joining us again, Dr. Kim.
Dr. Kim: Thank you very much for having me.
Dr. Jain, clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, and endocrinologist, TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, has disclosed ties with Abbott, Acerus, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bausch Healthcare, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Care to Know, CCRN, Connected in Motion, CPD Network, Dexcom, Diabetes Canada, Eli Lilly, GSK, HLS Therapeutics, Janssen, Master Clinician Alliance, MDBriefcase, Merck, Medtronic, Moderna, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Partners in Progressive Medical Education, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Timed Right, WebMD, Gilead Sciences, Insulet, PocketPills, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Kim, clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary, Alberta, has disclosed ties with Abbott, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Embecta, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Linpharma, Novo Nordisk, Miravo, Otsuka, Pfizer, Teva, Takeda, and Sanofi, and Partners in Progressive Medical Education.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Welcome back to Medscape at ADA 2024, where Dr. James Kim, primary care physician from Calgary, Alberta, will be joining me in deciphering the key highlights at the ADA conference and bringing our own clinical twist into what the relevance would be for people like you and I to take back to our clinics.
Welcome back, Dr. Kim.
James Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you very much. It’s nice to be back.
Dr. Jain: This was a diabetes conference, so obviously we are very pancreas focused. At this conference, we went outside our general area of territory, going outside of the pancreas and delving into other organ states. What I found fascinating were some data regarding the effects of incretin therapy on the lung, and in particular, some of the restrictive lung disorders.
Dr. Kim, you attended these sessions as well. Can you tell us a little bit more about the results that were discussed?
Dr. Kim: This is an interesting field. The moderator of the session went up and said that there has been no time in any previous ADA sessions where the lung issue was actually discussed. This was the first time ever.
They had some of the world leaders in this field, so it was really awesome to see them. Just to paint a picture of these obese asthmatic patients, they are challenging cases because, as you know, the main therapy for any asthmatic patient is inhaled corticosteroid.
Patients who are obese have quite a bit of a steroid resistance. Therefore, they end up being on many medications that sometimes are off label, and many end up on biologics as well. Therefore, the respiratory world has been seeking therapies for these obese asthmatic patients who are likely to be steroid resistant because these people are also likely to end up on an oral steroid as well.
Dr. Jain, you know the effect of the steroids much better than I do, and it’s like a laundry list. We really don’t want our patients to be on oral steroids.
In the past few years, GLP-1 has been studied quite extensively in the lung, especially in the world of asthma, and also in COPD. What’s really fascinating is that the GLP-1 receptors have been found to be quite abundant in the airway. Some studies show that the highest concentration of GLP-1 lies in the airway, whereas some studies have said that it’s the third most common area to find the GLP-1.
It is not a surprise that GLP-1 is being studied in managing the airway, especially airway inflammation in asthma and COPD patients. The preliminary data have been quite encouraging. They also discussed that there are new medications coming out that seem to be incretin based, so we’ll wait to see what those studies show.
There are two current phase 3 trials being held at the moment. One is using semaglutide 2.4 mg subcutaneous and another one is using metformin to reduce the airway inflammation in these asthmatic patients and also in some COPD patients. We’ll look forward to these results.
Dr. Jain: That’s really important to note because we see that there is a high density of these receptors in the airways, and hitherto we had no idea about the overall effect. Now, we’re looking at, as you mentioned, individuals with obesity who have asthma, so there are both the restrictive and obstructive components in the lung coming into play here.
From an endocrinology perspective, I’m thinking that this could be multiple effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonists, where on one hand you’re managing the obesity and you’re working along that line, and on the other hand, it could have local anti-inflammatory effects in the lung. Hence, there could be potential improvement in the overall pulmonary function of these individuals.
Dr. Kim: We are seeing this in primary care. Ever since I found out this information, I have started numerous patients, who are obese, asthmatic patients who do not have diabetes, on GLP-1 therapies, and their pulmonary function tests have improved significantly.
As a matter of fact, one of my personal friends is a severe asthmatic patient. She ends up being on oral steroids about three times a year. There was even one day when I saw her in one of my classes and she was dyspneic. She was short of breath.
I introduced her to one of my colleagues who’s a respirologist and very much into the impact of the incretins and asthma, and she was started on a GLP-1 receptor agonist. She lost about 30 pounds of weight, but now she is labeled as a mild asthmatic. Her pulmonary function test is completely normal. She hasn’t touched an oral steroid for a couple of years now.
That is a huge success story and I’m seeing that even in my own clinic as well. It’s a huge win for the respiratory world.
Dr. Jain: I think from an endocrinology perspective as well, if we are initiating GLP-1 receptor agonists or medications in that class, where we use it for management of obesity, sooner or later we do hit a stage where people will plateau with their weight loss. They won’t have any additional weight loss.
We tell individuals at that time that the fact that they’re able to maintain the weight loss still means that the medication is working from the obesity perspective. For individuals who also have asthma, it would be a good point to tell them that it could still have potential effects on reducing inflammation ongoing. Hence, even though they may not be losing any additional weight, it would still be helpful to continue on these medications from a pulmonary perspective.
Dr. Kim: Right now these pleiotropic effects of GLP-1 agents are absolutely mind-blowing. I mentioned in one of my respiratory presentations to a bunch of respirologists that diabetes is taking over the world, including the respiratory world. Well, you can imagine what their faces were like. However, they were quite impressed at that, and they were very excited with what these two phase 3 trials will show.
Dr. Jain: I think, based on the ADA 2024 conference, GLP-1 receptor agonists continue to be the gift that keeps giving. We have the effects on diabetes, obesity, kidney function, liver protection, lungs, and Alzheimer’s. We saw some sessions about potential use in people with alcohol misuse disorder or gambling problems. Clearly, there’s a large amount of research that›s being done with these agents.
Perhaps when you and I talk about ADA 2025, we might be able to talk about some more pleiotropic benefits outside the pancreas. Until then, please do check out our other videos from ADA 2024. Thanks for joining us again, Dr. Kim.
Dr. Kim: Thank you very much for having me.
Dr. Jain, clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, and endocrinologist, TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, has disclosed ties with Abbott, Acerus, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bausch Healthcare, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Care to Know, CCRN, Connected in Motion, CPD Network, Dexcom, Diabetes Canada, Eli Lilly, GSK, HLS Therapeutics, Janssen, Master Clinician Alliance, MDBriefcase, Merck, Medtronic, Moderna, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Partners in Progressive Medical Education, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Timed Right, WebMD, Gilead Sciences, Insulet, PocketPills, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Kim, clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary, Alberta, has disclosed ties with Abbott, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Embecta, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Linpharma, Novo Nordisk, Miravo, Otsuka, Pfizer, Teva, Takeda, and Sanofi, and Partners in Progressive Medical Education.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Childhood Cancer Survivors Face Sexual Challenges
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Will Compounding ‘Best Practices’ Guide Reassure Clinicians?
A new “best practices” guide released by the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) aims to educate compounding pharmacists and reassure prescribers about the ethical, legal, and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure quality standards and protect patients’ health.
Endocrinologists have expressed skepticism about the quality of compounded drugs, particularly the popular glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) semaglutide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued an alert linking hospitalizations to overdoses of compounded semaglutide.
“This document goes beyond today’s media-grabbing shortages,” APC Board Chair-Elect Gina Besteman, RPh, of Belmar Pharma Solutions told this news organization. “We developed these best practices to apply to all shortage drug compounding, and especially in this moment when so many are compounding GLP-1s. These serve as a reminder about what compliance and care look like.”
Prescribers determine whether a patient needs a compounded medication, not pharmacists, Ms. Besteman noted. “A patient-specific prescription order must be authorized for a compounded medication to be dispensed. Prescribers should ensure pharmacies they work with regularly check the FDA Drug Shortage List, as compounding of ‘essential copies’ of FDA-approved drugs is only allowed when a drug is listed as ‘currently in shortage.’ ”
Framework for Compounding
“With fake and illegal online stores popping up, it’s critical for legitimate, state-licensed compounding pharmacies to maintain the profession’s high standards,” the APC said in a media communication.
Highlights of its best practices, which are directed toward 503A state-licensed compounding pharmacies, include the following, among others:
- Pharmacies should check the FDA drug shortage list prior to preparing a copy of an FDA-approved drug and maintain documentation to demonstrate to regulators that the drug was in shortage at the time it was compounded.
- Pharmacies may only source active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from state-licensed wholesalers who purchase from FDA-registered manufacturers or order directly from FDA-registered manufacturers.
- Verify from the wholesaler that the manufacturer is registered with the FDA and the API meets all the requirements of section 503A, and that both hold the appropriate permits or licenses in their home state and the shipped to state.
- Adhere to USP Chapter <797> testing requirements for sterility, endotoxin, stability, particulate, antimicrobial effectiveness, and container closure integrity studies.
- Counseling must be offered to the patient or the patient’s agent/caregiver. Providing written information that assists in the understanding of how to properly use the compounded medication is advised.
- Instructions should be written in a way that a layperson can understand (especially directions including dosage titrations and conversions between milligrams and milliliters or units).
- Like all medications, compounded drugs can only be prescribed in the presence of a valid patient-practitioner relationship and can only be dispensed by a pharmacy after receipt of a valid patient-specific prescription order.
- When marketing, never make claims of safety or efficacy of the compounded product.
- Advertising that patients will/may save money using compounded medications, compared with manufactured products is not allowed.
“Compounding FDA-approved drugs during shortages is nothing new — pharmacies have been doing it well before GLP-1s came on the scene, and they’ll continue long after this current shortage ends,” Ms. Besteman said. “Prescribers should be aware of APC’s guidelines because they provide a framework for ethically and legally compounding medications during drug shortages.
“To paraphrase The Police,” she concluded, “every move you make, every step you take, they’ll be watching you. Make sure they see those best practices in action.”
‘Reduces the Risks’
Commenting on the best practices guidance, Ivania Rizo, MD, director of Obesity Medicine and Diabetes and clinical colead at Boston Medical Center’s Health Equity Accelerator in Massachusetts, said: “These best practices will hopefully make a difference in the quality of compounded drugs.”
“The emphasis on rigorous testing of APIs and adherence to USP standards is particularly important for maintaining drug quality,” she noted. “This structured approach reduces the risk of variability and ensures that compounded drugs meet high-quality standards, thus enhancing their reliability.”
“Knowing that compounding pharmacies are adhering to rigorous standards for sourcing, testing, and compounding can at least reassure clinicians that specific steps are being taken for the safety and efficacy of these medications,” she said. “The transparency in documenting compliance with FDA guidelines and maintaining high-quality control measures can enhance trust among healthcare providers.”
Although clinicians are likely to have more confidence in compounded drugs when these best practices are followed, she said, “overall, we all hope that the shortages of medications such as tirzepatide are resolved promptly, allowing patients to access FDA-approved drugs without the need for compounding.”
“While the implementation of best practices for compounding during shortages is a positive and necessary step, our ultimate goal remains to address and resolve these shortages in the near future,” she concluded.
Dr. Rizo declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new “best practices” guide released by the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) aims to educate compounding pharmacists and reassure prescribers about the ethical, legal, and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure quality standards and protect patients’ health.
Endocrinologists have expressed skepticism about the quality of compounded drugs, particularly the popular glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) semaglutide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued an alert linking hospitalizations to overdoses of compounded semaglutide.
“This document goes beyond today’s media-grabbing shortages,” APC Board Chair-Elect Gina Besteman, RPh, of Belmar Pharma Solutions told this news organization. “We developed these best practices to apply to all shortage drug compounding, and especially in this moment when so many are compounding GLP-1s. These serve as a reminder about what compliance and care look like.”
Prescribers determine whether a patient needs a compounded medication, not pharmacists, Ms. Besteman noted. “A patient-specific prescription order must be authorized for a compounded medication to be dispensed. Prescribers should ensure pharmacies they work with regularly check the FDA Drug Shortage List, as compounding of ‘essential copies’ of FDA-approved drugs is only allowed when a drug is listed as ‘currently in shortage.’ ”
Framework for Compounding
“With fake and illegal online stores popping up, it’s critical for legitimate, state-licensed compounding pharmacies to maintain the profession’s high standards,” the APC said in a media communication.
Highlights of its best practices, which are directed toward 503A state-licensed compounding pharmacies, include the following, among others:
- Pharmacies should check the FDA drug shortage list prior to preparing a copy of an FDA-approved drug and maintain documentation to demonstrate to regulators that the drug was in shortage at the time it was compounded.
- Pharmacies may only source active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from state-licensed wholesalers who purchase from FDA-registered manufacturers or order directly from FDA-registered manufacturers.
- Verify from the wholesaler that the manufacturer is registered with the FDA and the API meets all the requirements of section 503A, and that both hold the appropriate permits or licenses in their home state and the shipped to state.
- Adhere to USP Chapter <797> testing requirements for sterility, endotoxin, stability, particulate, antimicrobial effectiveness, and container closure integrity studies.
- Counseling must be offered to the patient or the patient’s agent/caregiver. Providing written information that assists in the understanding of how to properly use the compounded medication is advised.
- Instructions should be written in a way that a layperson can understand (especially directions including dosage titrations and conversions between milligrams and milliliters or units).
- Like all medications, compounded drugs can only be prescribed in the presence of a valid patient-practitioner relationship and can only be dispensed by a pharmacy after receipt of a valid patient-specific prescription order.
- When marketing, never make claims of safety or efficacy of the compounded product.
- Advertising that patients will/may save money using compounded medications, compared with manufactured products is not allowed.
“Compounding FDA-approved drugs during shortages is nothing new — pharmacies have been doing it well before GLP-1s came on the scene, and they’ll continue long after this current shortage ends,” Ms. Besteman said. “Prescribers should be aware of APC’s guidelines because they provide a framework for ethically and legally compounding medications during drug shortages.
“To paraphrase The Police,” she concluded, “every move you make, every step you take, they’ll be watching you. Make sure they see those best practices in action.”
‘Reduces the Risks’
Commenting on the best practices guidance, Ivania Rizo, MD, director of Obesity Medicine and Diabetes and clinical colead at Boston Medical Center’s Health Equity Accelerator in Massachusetts, said: “These best practices will hopefully make a difference in the quality of compounded drugs.”
“The emphasis on rigorous testing of APIs and adherence to USP standards is particularly important for maintaining drug quality,” she noted. “This structured approach reduces the risk of variability and ensures that compounded drugs meet high-quality standards, thus enhancing their reliability.”
“Knowing that compounding pharmacies are adhering to rigorous standards for sourcing, testing, and compounding can at least reassure clinicians that specific steps are being taken for the safety and efficacy of these medications,” she said. “The transparency in documenting compliance with FDA guidelines and maintaining high-quality control measures can enhance trust among healthcare providers.”
Although clinicians are likely to have more confidence in compounded drugs when these best practices are followed, she said, “overall, we all hope that the shortages of medications such as tirzepatide are resolved promptly, allowing patients to access FDA-approved drugs without the need for compounding.”
“While the implementation of best practices for compounding during shortages is a positive and necessary step, our ultimate goal remains to address and resolve these shortages in the near future,” she concluded.
Dr. Rizo declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new “best practices” guide released by the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) aims to educate compounding pharmacists and reassure prescribers about the ethical, legal, and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure quality standards and protect patients’ health.
Endocrinologists have expressed skepticism about the quality of compounded drugs, particularly the popular glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) semaglutide. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued an alert linking hospitalizations to overdoses of compounded semaglutide.
“This document goes beyond today’s media-grabbing shortages,” APC Board Chair-Elect Gina Besteman, RPh, of Belmar Pharma Solutions told this news organization. “We developed these best practices to apply to all shortage drug compounding, and especially in this moment when so many are compounding GLP-1s. These serve as a reminder about what compliance and care look like.”
Prescribers determine whether a patient needs a compounded medication, not pharmacists, Ms. Besteman noted. “A patient-specific prescription order must be authorized for a compounded medication to be dispensed. Prescribers should ensure pharmacies they work with regularly check the FDA Drug Shortage List, as compounding of ‘essential copies’ of FDA-approved drugs is only allowed when a drug is listed as ‘currently in shortage.’ ”
Framework for Compounding
“With fake and illegal online stores popping up, it’s critical for legitimate, state-licensed compounding pharmacies to maintain the profession’s high standards,” the APC said in a media communication.
Highlights of its best practices, which are directed toward 503A state-licensed compounding pharmacies, include the following, among others:
- Pharmacies should check the FDA drug shortage list prior to preparing a copy of an FDA-approved drug and maintain documentation to demonstrate to regulators that the drug was in shortage at the time it was compounded.
- Pharmacies may only source active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from state-licensed wholesalers who purchase from FDA-registered manufacturers or order directly from FDA-registered manufacturers.
- Verify from the wholesaler that the manufacturer is registered with the FDA and the API meets all the requirements of section 503A, and that both hold the appropriate permits or licenses in their home state and the shipped to state.
- Adhere to USP Chapter <797> testing requirements for sterility, endotoxin, stability, particulate, antimicrobial effectiveness, and container closure integrity studies.
- Counseling must be offered to the patient or the patient’s agent/caregiver. Providing written information that assists in the understanding of how to properly use the compounded medication is advised.
- Instructions should be written in a way that a layperson can understand (especially directions including dosage titrations and conversions between milligrams and milliliters or units).
- Like all medications, compounded drugs can only be prescribed in the presence of a valid patient-practitioner relationship and can only be dispensed by a pharmacy after receipt of a valid patient-specific prescription order.
- When marketing, never make claims of safety or efficacy of the compounded product.
- Advertising that patients will/may save money using compounded medications, compared with manufactured products is not allowed.
“Compounding FDA-approved drugs during shortages is nothing new — pharmacies have been doing it well before GLP-1s came on the scene, and they’ll continue long after this current shortage ends,” Ms. Besteman said. “Prescribers should be aware of APC’s guidelines because they provide a framework for ethically and legally compounding medications during drug shortages.
“To paraphrase The Police,” she concluded, “every move you make, every step you take, they’ll be watching you. Make sure they see those best practices in action.”
‘Reduces the Risks’
Commenting on the best practices guidance, Ivania Rizo, MD, director of Obesity Medicine and Diabetes and clinical colead at Boston Medical Center’s Health Equity Accelerator in Massachusetts, said: “These best practices will hopefully make a difference in the quality of compounded drugs.”
“The emphasis on rigorous testing of APIs and adherence to USP standards is particularly important for maintaining drug quality,” she noted. “This structured approach reduces the risk of variability and ensures that compounded drugs meet high-quality standards, thus enhancing their reliability.”
“Knowing that compounding pharmacies are adhering to rigorous standards for sourcing, testing, and compounding can at least reassure clinicians that specific steps are being taken for the safety and efficacy of these medications,” she said. “The transparency in documenting compliance with FDA guidelines and maintaining high-quality control measures can enhance trust among healthcare providers.”
Although clinicians are likely to have more confidence in compounded drugs when these best practices are followed, she said, “overall, we all hope that the shortages of medications such as tirzepatide are resolved promptly, allowing patients to access FDA-approved drugs without the need for compounding.”
“While the implementation of best practices for compounding during shortages is a positive and necessary step, our ultimate goal remains to address and resolve these shortages in the near future,” she concluded.
Dr. Rizo declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Which Medications Can Cause Edema?
Edema in the feet and legs is a common complaint in our practices. It can cause pain, weakness, heaviness, discomfort, limited movement, and a negative body image. Medications can contribute to edema, either alone or in combination with other health issues.
Therefore, it is important to know how to treat or prevent medication-induced edema.
There are four main causes of edema, and all can facilitate medication-induced edema.
- Increased capillary pressure. Conditions such as heart failure, renal dysfunction, venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis, and cirrhosis can increase capillary pressure, leading to edema.
- Decreased oncotic pressure. Hypoalbuminemia, a primary cause of reduced colloid oncotic pressure, can result from nephrotic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy, lupus nephropathy, amyloidosis, nephropathies, cirrhosis, chronic liver disease, and malabsorption or malnutrition.
- Increased capillary permeability. Vascular injury, often associated with diabetes, can increase capillary permeability and contribute to edema.
- Impaired lymphatic drainage. Lymphatic obstruction is common in patients with lymphedema, tumors, inflammation, fibrosis, certain infections, surgery, and congenital anomalies. Conditions such as thyroid disorders can also cause an increase in interstitial albumin and other proteins without a corresponding increase in lymphatic flow, leading to lymphedema.
Medications That Can Cause Edema
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs). Drugs such as nifedipine and amlodipine can increase hydrostatic pressure by causing selective vasodilation of precapillary vessels, leading to increased intracapillary pressures. Newer lipophilic CCBs (eg, levamlodipine) exhibit lower rates of edema. Reducing the dose is often effective. Diuretics are not very effective for vasodilation-induced edema. Combining CCBs with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), which induce postcapillary dilation and normalize intracapillary pressure, may reduce fluid leakage into the interstitial space. This combination may be more beneficial than high-dose CCB monotherapy.
- Thiazolidinedione (eg, pioglitazone). These increase vascular permeability and hydrostatic pressure. They work by stimulating the peroxisome proliferator–activated gamma receptor, increasing vascular endothelial permeability, vascular endothelial growth factor secretion, and renal retention of sodium and fluids. Because of other adverse effects, their use is now limited.
- Agents for neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin). These drugs can induce selective vasodilation of arterioles through a mechanism similar to that of CCBs, causing increased intracapillary pressures. Edema usually begins within the first month of treatment or dose increase and often regresses after dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
- Antiparkinsonian dopamine agonists. These increase hydrostatic pressure by reducing sympathetic tone and dilating arterioles through alpha-2 adrenergic receptor activity.
- New antipsychotics. Drugs like clozapine, iloperidone, lurasidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone can increase hydrostatic pressure through antagonistic effects on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing vasodilation.
- Nitrates. These drugs increase hydrostatic pressure by causing preferential venous dilation, leading to increased venous pooling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs can increase hydrostatic pressure by inhibiting vasodilation of afferent renal arterioles, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate, and stimulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which leads to sodium and water retention. These adverse effects warrant cautious use of these agents.
- ACE inhibitors. Drugs such as enalapril and ramipril can increase vascular permeability. They reduce the metabolism and accumulation of bradykinin, which increases vascular permeability and fluid leakage. These effects are rare and are usually related to allergic responses.
- Insulin. Insulin decreases capillary oncotic pressure and increases vascular permeability. Rapid correction of hyperglycemia can cause a loss of oncotic pressure, while chronic hyperglycemia can damage vascular membranes, increasing permeability. These effects are generally benign and can be managed with careful dose titration, sodium restriction, or diuretics.
- Steroids. Steroids with mineralocorticoid activity can increase renal sodium and water retention, leading to increased blood volume. Fludrocortisone has the highest mineralocorticoid activity, while dexamethasone and methylprednisolone have negligible activity.
Implications
Understanding how these medications cause edema is important for effective management. For example, in the case of those causing edema due to reduced oncotic pressure, like insulin, slow dose titrations can help adapt to osmolarity changes. For drugs causing edema due to increased hydrostatic pressure, diuretics are more effective in acute management.
The key takeaways from this review are:
- Awareness of drug-induced edema. Many drugs besides CCBs can cause edema.
- Combination therapy. Combining ACE inhibitors or ARBs with CCBs can prevent or reduce CCB-induced edema.
- Edema management strategies. Strategies to manage or prevent edema should include dose reductions or replacement of the problematic medication, especially in severe or refractory cases.
Dr. Wajngarten, professor of cardiology, University of São Paulo, Brazil, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Edema in the feet and legs is a common complaint in our practices. It can cause pain, weakness, heaviness, discomfort, limited movement, and a negative body image. Medications can contribute to edema, either alone or in combination with other health issues.
Therefore, it is important to know how to treat or prevent medication-induced edema.
There are four main causes of edema, and all can facilitate medication-induced edema.
- Increased capillary pressure. Conditions such as heart failure, renal dysfunction, venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis, and cirrhosis can increase capillary pressure, leading to edema.
- Decreased oncotic pressure. Hypoalbuminemia, a primary cause of reduced colloid oncotic pressure, can result from nephrotic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy, lupus nephropathy, amyloidosis, nephropathies, cirrhosis, chronic liver disease, and malabsorption or malnutrition.
- Increased capillary permeability. Vascular injury, often associated with diabetes, can increase capillary permeability and contribute to edema.
- Impaired lymphatic drainage. Lymphatic obstruction is common in patients with lymphedema, tumors, inflammation, fibrosis, certain infections, surgery, and congenital anomalies. Conditions such as thyroid disorders can also cause an increase in interstitial albumin and other proteins without a corresponding increase in lymphatic flow, leading to lymphedema.
Medications That Can Cause Edema
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs). Drugs such as nifedipine and amlodipine can increase hydrostatic pressure by causing selective vasodilation of precapillary vessels, leading to increased intracapillary pressures. Newer lipophilic CCBs (eg, levamlodipine) exhibit lower rates of edema. Reducing the dose is often effective. Diuretics are not very effective for vasodilation-induced edema. Combining CCBs with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), which induce postcapillary dilation and normalize intracapillary pressure, may reduce fluid leakage into the interstitial space. This combination may be more beneficial than high-dose CCB monotherapy.
- Thiazolidinedione (eg, pioglitazone). These increase vascular permeability and hydrostatic pressure. They work by stimulating the peroxisome proliferator–activated gamma receptor, increasing vascular endothelial permeability, vascular endothelial growth factor secretion, and renal retention of sodium and fluids. Because of other adverse effects, their use is now limited.
- Agents for neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin). These drugs can induce selective vasodilation of arterioles through a mechanism similar to that of CCBs, causing increased intracapillary pressures. Edema usually begins within the first month of treatment or dose increase and often regresses after dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
- Antiparkinsonian dopamine agonists. These increase hydrostatic pressure by reducing sympathetic tone and dilating arterioles through alpha-2 adrenergic receptor activity.
- New antipsychotics. Drugs like clozapine, iloperidone, lurasidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone can increase hydrostatic pressure through antagonistic effects on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing vasodilation.
- Nitrates. These drugs increase hydrostatic pressure by causing preferential venous dilation, leading to increased venous pooling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs can increase hydrostatic pressure by inhibiting vasodilation of afferent renal arterioles, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate, and stimulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which leads to sodium and water retention. These adverse effects warrant cautious use of these agents.
- ACE inhibitors. Drugs such as enalapril and ramipril can increase vascular permeability. They reduce the metabolism and accumulation of bradykinin, which increases vascular permeability and fluid leakage. These effects are rare and are usually related to allergic responses.
- Insulin. Insulin decreases capillary oncotic pressure and increases vascular permeability. Rapid correction of hyperglycemia can cause a loss of oncotic pressure, while chronic hyperglycemia can damage vascular membranes, increasing permeability. These effects are generally benign and can be managed with careful dose titration, sodium restriction, or diuretics.
- Steroids. Steroids with mineralocorticoid activity can increase renal sodium and water retention, leading to increased blood volume. Fludrocortisone has the highest mineralocorticoid activity, while dexamethasone and methylprednisolone have negligible activity.
Implications
Understanding how these medications cause edema is important for effective management. For example, in the case of those causing edema due to reduced oncotic pressure, like insulin, slow dose titrations can help adapt to osmolarity changes. For drugs causing edema due to increased hydrostatic pressure, diuretics are more effective in acute management.
The key takeaways from this review are:
- Awareness of drug-induced edema. Many drugs besides CCBs can cause edema.
- Combination therapy. Combining ACE inhibitors or ARBs with CCBs can prevent or reduce CCB-induced edema.
- Edema management strategies. Strategies to manage or prevent edema should include dose reductions or replacement of the problematic medication, especially in severe or refractory cases.
Dr. Wajngarten, professor of cardiology, University of São Paulo, Brazil, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Edema in the feet and legs is a common complaint in our practices. It can cause pain, weakness, heaviness, discomfort, limited movement, and a negative body image. Medications can contribute to edema, either alone or in combination with other health issues.
Therefore, it is important to know how to treat or prevent medication-induced edema.
There are four main causes of edema, and all can facilitate medication-induced edema.
- Increased capillary pressure. Conditions such as heart failure, renal dysfunction, venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis, and cirrhosis can increase capillary pressure, leading to edema.
- Decreased oncotic pressure. Hypoalbuminemia, a primary cause of reduced colloid oncotic pressure, can result from nephrotic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy, lupus nephropathy, amyloidosis, nephropathies, cirrhosis, chronic liver disease, and malabsorption or malnutrition.
- Increased capillary permeability. Vascular injury, often associated with diabetes, can increase capillary permeability and contribute to edema.
- Impaired lymphatic drainage. Lymphatic obstruction is common in patients with lymphedema, tumors, inflammation, fibrosis, certain infections, surgery, and congenital anomalies. Conditions such as thyroid disorders can also cause an increase in interstitial albumin and other proteins without a corresponding increase in lymphatic flow, leading to lymphedema.
Medications That Can Cause Edema
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs). Drugs such as nifedipine and amlodipine can increase hydrostatic pressure by causing selective vasodilation of precapillary vessels, leading to increased intracapillary pressures. Newer lipophilic CCBs (eg, levamlodipine) exhibit lower rates of edema. Reducing the dose is often effective. Diuretics are not very effective for vasodilation-induced edema. Combining CCBs with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), which induce postcapillary dilation and normalize intracapillary pressure, may reduce fluid leakage into the interstitial space. This combination may be more beneficial than high-dose CCB monotherapy.
- Thiazolidinedione (eg, pioglitazone). These increase vascular permeability and hydrostatic pressure. They work by stimulating the peroxisome proliferator–activated gamma receptor, increasing vascular endothelial permeability, vascular endothelial growth factor secretion, and renal retention of sodium and fluids. Because of other adverse effects, their use is now limited.
- Agents for neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin). These drugs can induce selective vasodilation of arterioles through a mechanism similar to that of CCBs, causing increased intracapillary pressures. Edema usually begins within the first month of treatment or dose increase and often regresses after dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
- Antiparkinsonian dopamine agonists. These increase hydrostatic pressure by reducing sympathetic tone and dilating arterioles through alpha-2 adrenergic receptor activity.
- New antipsychotics. Drugs like clozapine, iloperidone, lurasidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone can increase hydrostatic pressure through antagonistic effects on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing vasodilation.
- Nitrates. These drugs increase hydrostatic pressure by causing preferential venous dilation, leading to increased venous pooling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs can increase hydrostatic pressure by inhibiting vasodilation of afferent renal arterioles, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate, and stimulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which leads to sodium and water retention. These adverse effects warrant cautious use of these agents.
- ACE inhibitors. Drugs such as enalapril and ramipril can increase vascular permeability. They reduce the metabolism and accumulation of bradykinin, which increases vascular permeability and fluid leakage. These effects are rare and are usually related to allergic responses.
- Insulin. Insulin decreases capillary oncotic pressure and increases vascular permeability. Rapid correction of hyperglycemia can cause a loss of oncotic pressure, while chronic hyperglycemia can damage vascular membranes, increasing permeability. These effects are generally benign and can be managed with careful dose titration, sodium restriction, or diuretics.
- Steroids. Steroids with mineralocorticoid activity can increase renal sodium and water retention, leading to increased blood volume. Fludrocortisone has the highest mineralocorticoid activity, while dexamethasone and methylprednisolone have negligible activity.
Implications
Understanding how these medications cause edema is important for effective management. For example, in the case of those causing edema due to reduced oncotic pressure, like insulin, slow dose titrations can help adapt to osmolarity changes. For drugs causing edema due to increased hydrostatic pressure, diuretics are more effective in acute management.
The key takeaways from this review are:
- Awareness of drug-induced edema. Many drugs besides CCBs can cause edema.
- Combination therapy. Combining ACE inhibitors or ARBs with CCBs can prevent or reduce CCB-induced edema.
- Edema management strategies. Strategies to manage or prevent edema should include dose reductions or replacement of the problematic medication, especially in severe or refractory cases.
Dr. Wajngarten, professor of cardiology, University of São Paulo, Brazil, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Research Promises Better Diabetic Retinopathy Management
STOCKHOLM — At the American Society of Retina Specialists (ASRS) 2024 Annual Meeting, researchers discussed how insights into potential risk factors and new treatments could improve outcomes for patients with diabetic retinopathy.
Jennifer Lim, MD, an ophthalmologist and director of the Retina Service at the University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System in Chicago, told this news organization that emerging approaches to treating diabetic retinopathy offer hope because they address the root causes of the disease beyond just targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). She said innovative methods and add-on treatments could lead to more durable and effective drugs.
Exploration of risk factors and treatment options for diabetic retinopathy could lead to more effective management strategies for the condition, agreed David Boyer, MD, an ophthalmologist at Retina Vitreous Associates Medical Group in Los Angeles, speaking with this news organization.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have gained popularity because of their benefits beyond glycemic control, including weight loss, and cardiovascular and kidney protection. However, the impact of these medications on vision-threatening retinal complications is not fully understood. “There has always been a question about whether these newer diabetes medications might exacerbate diabetic eye disease,” said Dr. Boyer.
In a retrospective observational study, researchers included adults with type 2 diabetes and moderate cardiovascular disease risk who had no history of advanced diabetic retinal complications. These patients initiated treatment with GLP-1 RA, SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, or sulfonylureas. The study used inverse probability of treatment weighting to mimic randomization and compared the time to the first treatment for diabetic macular edema or proliferative diabetic retinopathy across the treatment groups.
Results, presented by Andrew J. Barkmeier, MD, an associate professor of ophthalmology at the Mayo Clinic, showed that among 371,698 patients, those who initiated therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors had a lower risk of requiring treatment for sight-threatening retinopathy compared with those using other medication classes. GLP-1 RA did not increase retinopathy risk relative to dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and sulfonylurea medications.
“[This study] told us that we do have to keep an eye on patients’ retinopathy when they start on these new inhibitors. But the progression is minimal and, overall, I think most people today favor keeping blood sugar levels as good as possible,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study.
Another factor that might increase diabetic retinopathy progression is obstructive sleep apnea. This underdiagnosed condition is linked to several health issues, including dementia, stroke, and myocardial infarctions. Although not easily treated, obstructive sleep apnea is manageable, Dr. Boyer explained.
Researchers utilized the TriNetX electronic health records research network to identify patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, both with and without obstructive sleep apnea.
The results, presented by Ehsan Rahimy, MD, a retinal specialist at Palo Alto Medical Foundation and a professor at Stanford University, showed that patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a significantly higher risk of progressing to proliferative diabetic retinopathy and developing new-onset diabetic macular edema. These patients were more likely to require ocular interventions, such as intravitreal injections and laser photocoagulation. They also had greater risks for stroke, myocardial infarction, and death compared with those who did not have obstructive sleep apnea.
“It was good to bring this to everybody’s attention,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study. “It’s an easy question to ask someone if they snore.”
New Treatments on the Horizon
In another presentation, Nathan C. Steinle, MD, of California Retina Consultants, presented a study that assessed the durability of response to sozinibercept in patients with retinal vascular diseases. This novel therapeutic agent is designed to inhibit VEGF-C and VEGF-D in conditions where VEGF-A suppression alone is insufficient.
Sozinibercept was combined with standard anti–VEGF-A therapies such as ranibizumab or aflibercept. It involved a prospective, post hoc analysis of two phase 1b, open-label, dose-escalation studies, including 40 patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD; 31 patients) or diabetic macular edema (nine patients). These patients, either treatment-naive or previously treated, received three intravitreal injections of ranibizumab or aflibercept in combination with sozinibercept at various doses.
Results indicated that sozinibercept combination therapy was well tolerated, with no dose-limiting toxicities. In treatment-naive nAMD patients, the mean best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improved significantly from baseline at months 3 and 6. Previously treated nAMD patients also showed BCVA improvements, although to a lesser extent. For patients with persistent diabetic macular edema, switching to sozinibercept plus aflibercept resulted in notable BCVA gains. The mean time to requiring retreatment was longer in treatment-naive patients than in those previously treated, indicating a durable response.
“Combination therapy with sozinibercept is going to be really important,” said Dr. Lim, who was not involved in the study, “because it attacks with a dual mechanism of action.”
Oral agents promise a potentially easier alternative for patients compared with frequent injections. CU06-1004 is a novel orally administered endothelial dysfunction blocker that has shown promise in stabilizing damaged capillaries, reducing abnormal angiogenesis, and inhibiting inflammatory activation in preclinical studies. “CU06 is very interesting to me because by preventing endothelial loss, it gets to the pathophysiology of why the blood vessels break down,” Dr. Lim said.
In a proof-of-concept phase 2a, multicenter, open-label, parallel-group trial, investigators randomly assigned 67 patients with diabetic macular edema to receive 100 mg, 200 mg, or 300 mg of CU06-1004 once daily for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week follow-up.
Results presented by Victor Gonzalez, MD, of Valley Retina Institute in Texas, indicated that the oral agent improved BCVA, stabilized central subfield thickness, and showed positive anatomical changes in optical coherence tomography images. CU06-1004 was well tolerated, with no drug-related serious adverse events.
“The number [of patients] was very small, and we will need a much longer, larger trial to see if [CU06-1004] has benefits long term,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study. “But I think we’re all very excited if we can find an oral agent for treating diabetic retinopathy. It would be easier for the patient to take a pill than having to come in for injections.”
The sustained-release axitinib implant, OTX-TKI, is also generating significant interest, particularly for nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Axitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), targets signaling pathways crucial in cellular processes, providing a novel approach to managing diseases where traditional therapies might fall short. Unlike traditional anti-VEGF treatments that focus solely on cytokine levels, TKIs block the activation of signaling pathways, preventing downstream signaling regardless of cytokine levels. This mechanism is particularly important because it effectively inhibits disease progression even if levels of VEGF are high, Dr. Lim explained.
In the phase 1 HELIOS trial, OTX-TKI was assessed in patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. This multicenter, double-masked, parallel-group clinical study included 21 patients who had not received anti-VEGF treatment, dexamethasone intravitreal implants in the previous 12 months, or intraocular steroid injections in the prior 4 months. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either OTX-TKI or sham treatment.
Results presented by Dilsher S. Dhoot, MD, of California Retina Consultants, indicated that OTX-TKI was generally well tolerated, with no serious ocular adverse events. At 48 weeks, 46.2% of eyes treated with OTX-TKI showed a 1- or 2-step improvement on the Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale (DRSS) compared with none in the sham arm. Additionally, no eyes treated with OTX-TKI experienced a worsening on the DRSS, whereas 25% of eyes in the sham arm did. Vision-threatening complications, such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy or diabetic macular edema, developed in 37.5% of the sham group but in none of the OTX-TKI treated eyes. A single injection of OTX-TKI provided durable DRSS improvement for up to 48 weeks, with no patients in either arm requiring rescue therapy.
“This is a really exciting add-on treatment,” Dr. Lim said, who was not involved in the study. She explained that it is initially necessary to control the disease with standard treatments, because TKIs may take longer to exhibit their effects. Once the disease is stabilized, TKIs can be used alongside other therapies, potentially reducing the reliance on frequent anti-VEGF injections. “These are preliminary results, but that’s the hope going forward.”
Dr. Lim and Dr. Boyer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM — At the American Society of Retina Specialists (ASRS) 2024 Annual Meeting, researchers discussed how insights into potential risk factors and new treatments could improve outcomes for patients with diabetic retinopathy.
Jennifer Lim, MD, an ophthalmologist and director of the Retina Service at the University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System in Chicago, told this news organization that emerging approaches to treating diabetic retinopathy offer hope because they address the root causes of the disease beyond just targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). She said innovative methods and add-on treatments could lead to more durable and effective drugs.
Exploration of risk factors and treatment options for diabetic retinopathy could lead to more effective management strategies for the condition, agreed David Boyer, MD, an ophthalmologist at Retina Vitreous Associates Medical Group in Los Angeles, speaking with this news organization.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have gained popularity because of their benefits beyond glycemic control, including weight loss, and cardiovascular and kidney protection. However, the impact of these medications on vision-threatening retinal complications is not fully understood. “There has always been a question about whether these newer diabetes medications might exacerbate diabetic eye disease,” said Dr. Boyer.
In a retrospective observational study, researchers included adults with type 2 diabetes and moderate cardiovascular disease risk who had no history of advanced diabetic retinal complications. These patients initiated treatment with GLP-1 RA, SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, or sulfonylureas. The study used inverse probability of treatment weighting to mimic randomization and compared the time to the first treatment for diabetic macular edema or proliferative diabetic retinopathy across the treatment groups.
Results, presented by Andrew J. Barkmeier, MD, an associate professor of ophthalmology at the Mayo Clinic, showed that among 371,698 patients, those who initiated therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors had a lower risk of requiring treatment for sight-threatening retinopathy compared with those using other medication classes. GLP-1 RA did not increase retinopathy risk relative to dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and sulfonylurea medications.
“[This study] told us that we do have to keep an eye on patients’ retinopathy when they start on these new inhibitors. But the progression is minimal and, overall, I think most people today favor keeping blood sugar levels as good as possible,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study.
Another factor that might increase diabetic retinopathy progression is obstructive sleep apnea. This underdiagnosed condition is linked to several health issues, including dementia, stroke, and myocardial infarctions. Although not easily treated, obstructive sleep apnea is manageable, Dr. Boyer explained.
Researchers utilized the TriNetX electronic health records research network to identify patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, both with and without obstructive sleep apnea.
The results, presented by Ehsan Rahimy, MD, a retinal specialist at Palo Alto Medical Foundation and a professor at Stanford University, showed that patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a significantly higher risk of progressing to proliferative diabetic retinopathy and developing new-onset diabetic macular edema. These patients were more likely to require ocular interventions, such as intravitreal injections and laser photocoagulation. They also had greater risks for stroke, myocardial infarction, and death compared with those who did not have obstructive sleep apnea.
“It was good to bring this to everybody’s attention,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study. “It’s an easy question to ask someone if they snore.”
New Treatments on the Horizon
In another presentation, Nathan C. Steinle, MD, of California Retina Consultants, presented a study that assessed the durability of response to sozinibercept in patients with retinal vascular diseases. This novel therapeutic agent is designed to inhibit VEGF-C and VEGF-D in conditions where VEGF-A suppression alone is insufficient.
Sozinibercept was combined with standard anti–VEGF-A therapies such as ranibizumab or aflibercept. It involved a prospective, post hoc analysis of two phase 1b, open-label, dose-escalation studies, including 40 patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD; 31 patients) or diabetic macular edema (nine patients). These patients, either treatment-naive or previously treated, received three intravitreal injections of ranibizumab or aflibercept in combination with sozinibercept at various doses.
Results indicated that sozinibercept combination therapy was well tolerated, with no dose-limiting toxicities. In treatment-naive nAMD patients, the mean best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improved significantly from baseline at months 3 and 6. Previously treated nAMD patients also showed BCVA improvements, although to a lesser extent. For patients with persistent diabetic macular edema, switching to sozinibercept plus aflibercept resulted in notable BCVA gains. The mean time to requiring retreatment was longer in treatment-naive patients than in those previously treated, indicating a durable response.
“Combination therapy with sozinibercept is going to be really important,” said Dr. Lim, who was not involved in the study, “because it attacks with a dual mechanism of action.”
Oral agents promise a potentially easier alternative for patients compared with frequent injections. CU06-1004 is a novel orally administered endothelial dysfunction blocker that has shown promise in stabilizing damaged capillaries, reducing abnormal angiogenesis, and inhibiting inflammatory activation in preclinical studies. “CU06 is very interesting to me because by preventing endothelial loss, it gets to the pathophysiology of why the blood vessels break down,” Dr. Lim said.
In a proof-of-concept phase 2a, multicenter, open-label, parallel-group trial, investigators randomly assigned 67 patients with diabetic macular edema to receive 100 mg, 200 mg, or 300 mg of CU06-1004 once daily for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week follow-up.
Results presented by Victor Gonzalez, MD, of Valley Retina Institute in Texas, indicated that the oral agent improved BCVA, stabilized central subfield thickness, and showed positive anatomical changes in optical coherence tomography images. CU06-1004 was well tolerated, with no drug-related serious adverse events.
“The number [of patients] was very small, and we will need a much longer, larger trial to see if [CU06-1004] has benefits long term,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study. “But I think we’re all very excited if we can find an oral agent for treating diabetic retinopathy. It would be easier for the patient to take a pill than having to come in for injections.”
The sustained-release axitinib implant, OTX-TKI, is also generating significant interest, particularly for nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Axitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), targets signaling pathways crucial in cellular processes, providing a novel approach to managing diseases where traditional therapies might fall short. Unlike traditional anti-VEGF treatments that focus solely on cytokine levels, TKIs block the activation of signaling pathways, preventing downstream signaling regardless of cytokine levels. This mechanism is particularly important because it effectively inhibits disease progression even if levels of VEGF are high, Dr. Lim explained.
In the phase 1 HELIOS trial, OTX-TKI was assessed in patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. This multicenter, double-masked, parallel-group clinical study included 21 patients who had not received anti-VEGF treatment, dexamethasone intravitreal implants in the previous 12 months, or intraocular steroid injections in the prior 4 months. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either OTX-TKI or sham treatment.
Results presented by Dilsher S. Dhoot, MD, of California Retina Consultants, indicated that OTX-TKI was generally well tolerated, with no serious ocular adverse events. At 48 weeks, 46.2% of eyes treated with OTX-TKI showed a 1- or 2-step improvement on the Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale (DRSS) compared with none in the sham arm. Additionally, no eyes treated with OTX-TKI experienced a worsening on the DRSS, whereas 25% of eyes in the sham arm did. Vision-threatening complications, such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy or diabetic macular edema, developed in 37.5% of the sham group but in none of the OTX-TKI treated eyes. A single injection of OTX-TKI provided durable DRSS improvement for up to 48 weeks, with no patients in either arm requiring rescue therapy.
“This is a really exciting add-on treatment,” Dr. Lim said, who was not involved in the study. She explained that it is initially necessary to control the disease with standard treatments, because TKIs may take longer to exhibit their effects. Once the disease is stabilized, TKIs can be used alongside other therapies, potentially reducing the reliance on frequent anti-VEGF injections. “These are preliminary results, but that’s the hope going forward.”
Dr. Lim and Dr. Boyer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM — At the American Society of Retina Specialists (ASRS) 2024 Annual Meeting, researchers discussed how insights into potential risk factors and new treatments could improve outcomes for patients with diabetic retinopathy.
Jennifer Lim, MD, an ophthalmologist and director of the Retina Service at the University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System in Chicago, told this news organization that emerging approaches to treating diabetic retinopathy offer hope because they address the root causes of the disease beyond just targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). She said innovative methods and add-on treatments could lead to more durable and effective drugs.
Exploration of risk factors and treatment options for diabetic retinopathy could lead to more effective management strategies for the condition, agreed David Boyer, MD, an ophthalmologist at Retina Vitreous Associates Medical Group in Los Angeles, speaking with this news organization.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have gained popularity because of their benefits beyond glycemic control, including weight loss, and cardiovascular and kidney protection. However, the impact of these medications on vision-threatening retinal complications is not fully understood. “There has always been a question about whether these newer diabetes medications might exacerbate diabetic eye disease,” said Dr. Boyer.
In a retrospective observational study, researchers included adults with type 2 diabetes and moderate cardiovascular disease risk who had no history of advanced diabetic retinal complications. These patients initiated treatment with GLP-1 RA, SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, or sulfonylureas. The study used inverse probability of treatment weighting to mimic randomization and compared the time to the first treatment for diabetic macular edema or proliferative diabetic retinopathy across the treatment groups.
Results, presented by Andrew J. Barkmeier, MD, an associate professor of ophthalmology at the Mayo Clinic, showed that among 371,698 patients, those who initiated therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors had a lower risk of requiring treatment for sight-threatening retinopathy compared with those using other medication classes. GLP-1 RA did not increase retinopathy risk relative to dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and sulfonylurea medications.
“[This study] told us that we do have to keep an eye on patients’ retinopathy when they start on these new inhibitors. But the progression is minimal and, overall, I think most people today favor keeping blood sugar levels as good as possible,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study.
Another factor that might increase diabetic retinopathy progression is obstructive sleep apnea. This underdiagnosed condition is linked to several health issues, including dementia, stroke, and myocardial infarctions. Although not easily treated, obstructive sleep apnea is manageable, Dr. Boyer explained.
Researchers utilized the TriNetX electronic health records research network to identify patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, both with and without obstructive sleep apnea.
The results, presented by Ehsan Rahimy, MD, a retinal specialist at Palo Alto Medical Foundation and a professor at Stanford University, showed that patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a significantly higher risk of progressing to proliferative diabetic retinopathy and developing new-onset diabetic macular edema. These patients were more likely to require ocular interventions, such as intravitreal injections and laser photocoagulation. They also had greater risks for stroke, myocardial infarction, and death compared with those who did not have obstructive sleep apnea.
“It was good to bring this to everybody’s attention,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study. “It’s an easy question to ask someone if they snore.”
New Treatments on the Horizon
In another presentation, Nathan C. Steinle, MD, of California Retina Consultants, presented a study that assessed the durability of response to sozinibercept in patients with retinal vascular diseases. This novel therapeutic agent is designed to inhibit VEGF-C and VEGF-D in conditions where VEGF-A suppression alone is insufficient.
Sozinibercept was combined with standard anti–VEGF-A therapies such as ranibizumab or aflibercept. It involved a prospective, post hoc analysis of two phase 1b, open-label, dose-escalation studies, including 40 patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD; 31 patients) or diabetic macular edema (nine patients). These patients, either treatment-naive or previously treated, received three intravitreal injections of ranibizumab or aflibercept in combination with sozinibercept at various doses.
Results indicated that sozinibercept combination therapy was well tolerated, with no dose-limiting toxicities. In treatment-naive nAMD patients, the mean best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improved significantly from baseline at months 3 and 6. Previously treated nAMD patients also showed BCVA improvements, although to a lesser extent. For patients with persistent diabetic macular edema, switching to sozinibercept plus aflibercept resulted in notable BCVA gains. The mean time to requiring retreatment was longer in treatment-naive patients than in those previously treated, indicating a durable response.
“Combination therapy with sozinibercept is going to be really important,” said Dr. Lim, who was not involved in the study, “because it attacks with a dual mechanism of action.”
Oral agents promise a potentially easier alternative for patients compared with frequent injections. CU06-1004 is a novel orally administered endothelial dysfunction blocker that has shown promise in stabilizing damaged capillaries, reducing abnormal angiogenesis, and inhibiting inflammatory activation in preclinical studies. “CU06 is very interesting to me because by preventing endothelial loss, it gets to the pathophysiology of why the blood vessels break down,” Dr. Lim said.
In a proof-of-concept phase 2a, multicenter, open-label, parallel-group trial, investigators randomly assigned 67 patients with diabetic macular edema to receive 100 mg, 200 mg, or 300 mg of CU06-1004 once daily for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week follow-up.
Results presented by Victor Gonzalez, MD, of Valley Retina Institute in Texas, indicated that the oral agent improved BCVA, stabilized central subfield thickness, and showed positive anatomical changes in optical coherence tomography images. CU06-1004 was well tolerated, with no drug-related serious adverse events.
“The number [of patients] was very small, and we will need a much longer, larger trial to see if [CU06-1004] has benefits long term,” said Dr. Boyer, who was not involved in the study. “But I think we’re all very excited if we can find an oral agent for treating diabetic retinopathy. It would be easier for the patient to take a pill than having to come in for injections.”
The sustained-release axitinib implant, OTX-TKI, is also generating significant interest, particularly for nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Axitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), targets signaling pathways crucial in cellular processes, providing a novel approach to managing diseases where traditional therapies might fall short. Unlike traditional anti-VEGF treatments that focus solely on cytokine levels, TKIs block the activation of signaling pathways, preventing downstream signaling regardless of cytokine levels. This mechanism is particularly important because it effectively inhibits disease progression even if levels of VEGF are high, Dr. Lim explained.
In the phase 1 HELIOS trial, OTX-TKI was assessed in patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. This multicenter, double-masked, parallel-group clinical study included 21 patients who had not received anti-VEGF treatment, dexamethasone intravitreal implants in the previous 12 months, or intraocular steroid injections in the prior 4 months. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either OTX-TKI or sham treatment.
Results presented by Dilsher S. Dhoot, MD, of California Retina Consultants, indicated that OTX-TKI was generally well tolerated, with no serious ocular adverse events. At 48 weeks, 46.2% of eyes treated with OTX-TKI showed a 1- or 2-step improvement on the Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale (DRSS) compared with none in the sham arm. Additionally, no eyes treated with OTX-TKI experienced a worsening on the DRSS, whereas 25% of eyes in the sham arm did. Vision-threatening complications, such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy or diabetic macular edema, developed in 37.5% of the sham group but in none of the OTX-TKI treated eyes. A single injection of OTX-TKI provided durable DRSS improvement for up to 48 weeks, with no patients in either arm requiring rescue therapy.
“This is a really exciting add-on treatment,” Dr. Lim said, who was not involved in the study. She explained that it is initially necessary to control the disease with standard treatments, because TKIs may take longer to exhibit their effects. Once the disease is stabilized, TKIs can be used alongside other therapies, potentially reducing the reliance on frequent anti-VEGF injections. “These are preliminary results, but that’s the hope going forward.”
Dr. Lim and Dr. Boyer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASRS 2024
Could Adipose Tissue Be a Better Measure for Obesity Than BMI?
Take a look at any of the evidence-based US obesity treatment guidelines. The key criteria for diagnosing overweight and obesity is based on the body mass index (BMI).
The guidelines also use BMI to stratify care options to decrease cardiovascular risk. For example, persons with BMI ≥30 are classified as having obesity, and antiobesity medications are recommended. Those with BMI ≥ 40 are classified as having severe obesity, and metabolic bariatric surgery may be appropriate.
But where did these cutoff points for more and less aggressive treatments come from? These BMI cutoffs are based primarily on mortality data collected from large non-Hispanic White populations, without data on potential differences by gender and ethnicity.
For example, it is certainly true that those with BMI ≥ 30 have more cardiovascular risk factors than those with BMI < 30. But Asian American individuals have more risk factors at lower BMIs than do White or African American individuals likely because of more visceral fat accumulation at lower BMIs.
Besides the variation in gender and ethnicity, BMI does not take the type and location of body fat into consideration. Adipose tissue in visceral or ectopic areas have much higher risks for disease than subcutaneous adipose tissue because of the associated inflammation. Measures such as waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and skinfold measurements aim to capture this aspect but often fall short because of variation in techniques.
BMI does not account for muscle mass either, so fit athletes and bodybuilders can be classified as having obesity by BMI alone. More accurate body fat percent measures, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry or MRI specifically for ectopic fat, are labor intensive, expensive, and not feasible to perform in a busy primary care or endocrinology clinic.
Assessing Risks From Obesity Beyond BMI
Clearly, better risk measures than BMI are needed, but until they are available, supplemental clinical tools can aid diagnosis and treatment decisions at obesity medicine specialty centers, endocrinology and diabetes centers, and those centers that focus on the treatment of obesity.
For example, a seca scale can measure percent body fat by bioelectric impedance analysis. This technique also has its limitations, but for persons who are well hydrated, it can be used as a baseline to determine efficacy of behavioral interventions, such as resistance-exercise training and a high-protein diet to protect muscle mass as the patient loses weight.
A lot also can be gleaned from diet and exercise history, social history, family history, and physical exam as well as laboratory analyses. For example, an Asian American patient with a BMI of 26 who has been gaining weight mostly in the abdominal region after age 35 years is likely to have cardiometabolic risk, and a family history can solidify that. An exam can show signs of acanthosis nigricans or an enlarged liver and generous abdominal adipose tissue. This would be the patient in whom you would want to obtain a hemoglobin A1c measurement in the chance that it is elevated at > 5.7 mg/dL, suggesting high risk for type 2 diabetes.
A Fibrosis-4 score can assess the risk for liver disease from aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase and platelet count and age, providing clues to cardiometabolic disease risk.
In the next 10, years there may be a better measure for cardiometabolic risk that is more accurate than BMI is. It could be the sagittal abdominal diameter, which has been purported to more accurately measure visceral abdominal fat. But this has not made it to be one of the vital signs in a busy primary care clinic, however.
Will New Body Fat Tools Change Practice?
In the next 10 years, there may be an affordable gadget to scan the body to determine visceral vs subcutaneous deposition of fat — like radiography for tissue. Now, three-dimensional (3D) total-body scanners can obtain body composition, but they are extremely expensive. The more important clinical question is: How will the use of these imaging modalities change your practice protocol for a particular patient?
Think about the FibroScan, a type of ultrasound used to determine fatty liver disease and fibrosis. We order the test for those patients in whom we already have a strong suspicion for liver disease and, in obesity practices, for fatty liver and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease or metabolic associated steatohepatitis.
The test results do much to educate the patient and help the patient understand the need for aggressive treatment for their obesity. But it doesn’t necessarily change the clinician’s practice protocols and decisions. We would still recommend weight management and medications or surgery to patients regardless of the findings.
A FibroScan is an expense, and not all primary care or endocrine practitioners may feel it necessary to purchase one for the added benefit of patient education. And I would argue that a 3D body scanner is a great tool but more for educational purposes than to really determine practice decision-making or outcomes.
In the meantime, an old-fashioned physical examination, along with a thorough medical, social, and family history should give even the busiest primary care provider enough information to decide whether their patient is a candidate for preventive measures to reduce body fat with diet, exercise, and medication as well as whether the patient is a candidate for metabolic bariatric surgery. Higher suspicion of cardiovascular risk at lower BMI ranges for various ethnicities can help primary care providers pick up on the patients with low BMI but who are at higher risk for type 2 diabetes or prediabetes and cardiovascular disease.
So the answer to whether we need a better measure than the BMI: Yes, we do. We need a physical examination on all patients.
Dr. Apovian, professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School, and codirector, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts, disclosed ties with Altimmune, CinFina Pharma, Cowen and Company, EPG Communication Holdings, Form Health, Gelesis, L-Nutra, NeuroBo Pharm, Novo, OptumRx, Pain Script, Palatin, Pursuit by You, Roman Health, Xeno, and Riverview School.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Take a look at any of the evidence-based US obesity treatment guidelines. The key criteria for diagnosing overweight and obesity is based on the body mass index (BMI).
The guidelines also use BMI to stratify care options to decrease cardiovascular risk. For example, persons with BMI ≥30 are classified as having obesity, and antiobesity medications are recommended. Those with BMI ≥ 40 are classified as having severe obesity, and metabolic bariatric surgery may be appropriate.
But where did these cutoff points for more and less aggressive treatments come from? These BMI cutoffs are based primarily on mortality data collected from large non-Hispanic White populations, without data on potential differences by gender and ethnicity.
For example, it is certainly true that those with BMI ≥ 30 have more cardiovascular risk factors than those with BMI < 30. But Asian American individuals have more risk factors at lower BMIs than do White or African American individuals likely because of more visceral fat accumulation at lower BMIs.
Besides the variation in gender and ethnicity, BMI does not take the type and location of body fat into consideration. Adipose tissue in visceral or ectopic areas have much higher risks for disease than subcutaneous adipose tissue because of the associated inflammation. Measures such as waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and skinfold measurements aim to capture this aspect but often fall short because of variation in techniques.
BMI does not account for muscle mass either, so fit athletes and bodybuilders can be classified as having obesity by BMI alone. More accurate body fat percent measures, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry or MRI specifically for ectopic fat, are labor intensive, expensive, and not feasible to perform in a busy primary care or endocrinology clinic.
Assessing Risks From Obesity Beyond BMI
Clearly, better risk measures than BMI are needed, but until they are available, supplemental clinical tools can aid diagnosis and treatment decisions at obesity medicine specialty centers, endocrinology and diabetes centers, and those centers that focus on the treatment of obesity.
For example, a seca scale can measure percent body fat by bioelectric impedance analysis. This technique also has its limitations, but for persons who are well hydrated, it can be used as a baseline to determine efficacy of behavioral interventions, such as resistance-exercise training and a high-protein diet to protect muscle mass as the patient loses weight.
A lot also can be gleaned from diet and exercise history, social history, family history, and physical exam as well as laboratory analyses. For example, an Asian American patient with a BMI of 26 who has been gaining weight mostly in the abdominal region after age 35 years is likely to have cardiometabolic risk, and a family history can solidify that. An exam can show signs of acanthosis nigricans or an enlarged liver and generous abdominal adipose tissue. This would be the patient in whom you would want to obtain a hemoglobin A1c measurement in the chance that it is elevated at > 5.7 mg/dL, suggesting high risk for type 2 diabetes.
A Fibrosis-4 score can assess the risk for liver disease from aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase and platelet count and age, providing clues to cardiometabolic disease risk.
In the next 10, years there may be a better measure for cardiometabolic risk that is more accurate than BMI is. It could be the sagittal abdominal diameter, which has been purported to more accurately measure visceral abdominal fat. But this has not made it to be one of the vital signs in a busy primary care clinic, however.
Will New Body Fat Tools Change Practice?
In the next 10 years, there may be an affordable gadget to scan the body to determine visceral vs subcutaneous deposition of fat — like radiography for tissue. Now, three-dimensional (3D) total-body scanners can obtain body composition, but they are extremely expensive. The more important clinical question is: How will the use of these imaging modalities change your practice protocol for a particular patient?
Think about the FibroScan, a type of ultrasound used to determine fatty liver disease and fibrosis. We order the test for those patients in whom we already have a strong suspicion for liver disease and, in obesity practices, for fatty liver and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease or metabolic associated steatohepatitis.
The test results do much to educate the patient and help the patient understand the need for aggressive treatment for their obesity. But it doesn’t necessarily change the clinician’s practice protocols and decisions. We would still recommend weight management and medications or surgery to patients regardless of the findings.
A FibroScan is an expense, and not all primary care or endocrine practitioners may feel it necessary to purchase one for the added benefit of patient education. And I would argue that a 3D body scanner is a great tool but more for educational purposes than to really determine practice decision-making or outcomes.
In the meantime, an old-fashioned physical examination, along with a thorough medical, social, and family history should give even the busiest primary care provider enough information to decide whether their patient is a candidate for preventive measures to reduce body fat with diet, exercise, and medication as well as whether the patient is a candidate for metabolic bariatric surgery. Higher suspicion of cardiovascular risk at lower BMI ranges for various ethnicities can help primary care providers pick up on the patients with low BMI but who are at higher risk for type 2 diabetes or prediabetes and cardiovascular disease.
So the answer to whether we need a better measure than the BMI: Yes, we do. We need a physical examination on all patients.
Dr. Apovian, professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School, and codirector, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts, disclosed ties with Altimmune, CinFina Pharma, Cowen and Company, EPG Communication Holdings, Form Health, Gelesis, L-Nutra, NeuroBo Pharm, Novo, OptumRx, Pain Script, Palatin, Pursuit by You, Roman Health, Xeno, and Riverview School.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Take a look at any of the evidence-based US obesity treatment guidelines. The key criteria for diagnosing overweight and obesity is based on the body mass index (BMI).
The guidelines also use BMI to stratify care options to decrease cardiovascular risk. For example, persons with BMI ≥30 are classified as having obesity, and antiobesity medications are recommended. Those with BMI ≥ 40 are classified as having severe obesity, and metabolic bariatric surgery may be appropriate.
But where did these cutoff points for more and less aggressive treatments come from? These BMI cutoffs are based primarily on mortality data collected from large non-Hispanic White populations, without data on potential differences by gender and ethnicity.
For example, it is certainly true that those with BMI ≥ 30 have more cardiovascular risk factors than those with BMI < 30. But Asian American individuals have more risk factors at lower BMIs than do White or African American individuals likely because of more visceral fat accumulation at lower BMIs.
Besides the variation in gender and ethnicity, BMI does not take the type and location of body fat into consideration. Adipose tissue in visceral or ectopic areas have much higher risks for disease than subcutaneous adipose tissue because of the associated inflammation. Measures such as waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and skinfold measurements aim to capture this aspect but often fall short because of variation in techniques.
BMI does not account for muscle mass either, so fit athletes and bodybuilders can be classified as having obesity by BMI alone. More accurate body fat percent measures, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry or MRI specifically for ectopic fat, are labor intensive, expensive, and not feasible to perform in a busy primary care or endocrinology clinic.
Assessing Risks From Obesity Beyond BMI
Clearly, better risk measures than BMI are needed, but until they are available, supplemental clinical tools can aid diagnosis and treatment decisions at obesity medicine specialty centers, endocrinology and diabetes centers, and those centers that focus on the treatment of obesity.
For example, a seca scale can measure percent body fat by bioelectric impedance analysis. This technique also has its limitations, but for persons who are well hydrated, it can be used as a baseline to determine efficacy of behavioral interventions, such as resistance-exercise training and a high-protein diet to protect muscle mass as the patient loses weight.
A lot also can be gleaned from diet and exercise history, social history, family history, and physical exam as well as laboratory analyses. For example, an Asian American patient with a BMI of 26 who has been gaining weight mostly in the abdominal region after age 35 years is likely to have cardiometabolic risk, and a family history can solidify that. An exam can show signs of acanthosis nigricans or an enlarged liver and generous abdominal adipose tissue. This would be the patient in whom you would want to obtain a hemoglobin A1c measurement in the chance that it is elevated at > 5.7 mg/dL, suggesting high risk for type 2 diabetes.
A Fibrosis-4 score can assess the risk for liver disease from aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase and platelet count and age, providing clues to cardiometabolic disease risk.
In the next 10, years there may be a better measure for cardiometabolic risk that is more accurate than BMI is. It could be the sagittal abdominal diameter, which has been purported to more accurately measure visceral abdominal fat. But this has not made it to be one of the vital signs in a busy primary care clinic, however.
Will New Body Fat Tools Change Practice?
In the next 10 years, there may be an affordable gadget to scan the body to determine visceral vs subcutaneous deposition of fat — like radiography for tissue. Now, three-dimensional (3D) total-body scanners can obtain body composition, but they are extremely expensive. The more important clinical question is: How will the use of these imaging modalities change your practice protocol for a particular patient?
Think about the FibroScan, a type of ultrasound used to determine fatty liver disease and fibrosis. We order the test for those patients in whom we already have a strong suspicion for liver disease and, in obesity practices, for fatty liver and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease or metabolic associated steatohepatitis.
The test results do much to educate the patient and help the patient understand the need for aggressive treatment for their obesity. But it doesn’t necessarily change the clinician’s practice protocols and decisions. We would still recommend weight management and medications or surgery to patients regardless of the findings.
A FibroScan is an expense, and not all primary care or endocrine practitioners may feel it necessary to purchase one for the added benefit of patient education. And I would argue that a 3D body scanner is a great tool but more for educational purposes than to really determine practice decision-making or outcomes.
In the meantime, an old-fashioned physical examination, along with a thorough medical, social, and family history should give even the busiest primary care provider enough information to decide whether their patient is a candidate for preventive measures to reduce body fat with diet, exercise, and medication as well as whether the patient is a candidate for metabolic bariatric surgery. Higher suspicion of cardiovascular risk at lower BMI ranges for various ethnicities can help primary care providers pick up on the patients with low BMI but who are at higher risk for type 2 diabetes or prediabetes and cardiovascular disease.
So the answer to whether we need a better measure than the BMI: Yes, we do. We need a physical examination on all patients.
Dr. Apovian, professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School, and codirector, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts, disclosed ties with Altimmune, CinFina Pharma, Cowen and Company, EPG Communication Holdings, Form Health, Gelesis, L-Nutra, NeuroBo Pharm, Novo, OptumRx, Pain Script, Palatin, Pursuit by You, Roman Health, Xeno, and Riverview School.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Gender and Sports: Can Science Enable Fair Competition?
The allegations against Algerian boxer Imane Khelif at the Paris Olympics raised the questions of intersexuality and its implications in competitive sports. This news organization has decided to delve into the topic to assist doctors who suspect a similar condition in their patients. No certain clinical data about Ms. Khelif have been made public, so this article does not concern the boxer but rather takes inspiration from the media controversy.
What Is Intersexuality?
Intersexuality encompasses a spectrum of variations in sexual development that lead to the simultaneous presence of typical male and female characteristics. As reiterated by the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, the medical definition does not affect the patient’s self-identification of gender or sexual orientation.
“The percentage of people who fall within the intersexuality spectrum is less than 0.5 per thousand of the general population, but there are no precise statistics, given the difficulty of definition,” said Roberto Lala, MD, pediatric endocrinologist and president of the Federation of Rare Childhood Diseases.
Indeed, there is not only a strict definition of intersexuality that involves a significant presence of these mixed physical characteristics in a way that conditions the self-image of the subject but also a broad definition, said Dr. Lala. “For example, clitoral hypertrophy in a female otherwise conforming to the female gender, which does not raise doubts about identity,” he said.
Chromosomes, Genes, and Hormones
“The human body is, so to speak, programmed to take on female appearances in development and shifts toward male ones only if exposed to testosterone and other factors. For this to happen, testosterone must be produced during embryonic development, and it must function properly,” said Paolo Moghetti, full professor of endocrinology at the University of Verona, Italy.
The protein encoded by SRY, which is located on the Y chromosome, determines the development of the testicles from undifferentiated tissue of the embryonic gonads. The testicles of the embryo then produce testosterone. The absence of the Y chromosome is a common characteristic of most female individuals. However, there are individuals with a female phenotype who have X and Y chromosomes but lack SRY or have a variant of it that is not entirely functional.
Numerous other chromosomal or genetic variations can lead to alterations in sexual differentiation. “In phenotypically male adult subjects (with a chromosomal makeup of 46XY) with complete androgen insensitivity (so-called Morris syndrome), testosterone levels in the blood are elevated, above normal even for a male, but the hormone is totally ineffective, and the phenotype is totally female at birth, with completely female development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty,” said Dr. Moghetti.
This means that affected individuals have well-developed breasts and a complete lack or extremely reduced presence of hair, including underarm and pubic hair. Menstruation is also completely absent because there is no uterus, and there are testes, not visible because they are considered in the abdomen.
“There are syndromes that are currently considered congenital but not genetic, of which a genetic origin will probably be identified in the future,” said Dr. Lala.
Some variations in sexual development can be diagnosed prenatally, such as an alteration of the number of sex chromosomes or a discordance between the morphologic characteristics highlighted by ultrasound and the genotype detected by amniocentesis. Some variations are evident at birth because of atypical anatomical characteristics. Others are diagnosed during puberty or later in adulthood, in the presence of infertility. The Italian National Institute of Health details these variations on its website, describing the characteristics that determine diagnosis and treatment.
Pathologies or Variations?
Some anomalies in sexual development negatively affect the patient’s physical health. One example is congenital adrenal hyperplasia. “It results from an inherited defect of the adrenal glands, which reduces cortisol production while increasing testosterone production,” said Dr. Lala. “In addition to the appearance of male characteristics in females, in more severe forms, it carries the risk of collapse and shock and requires pharmacological treatment.” It is undoubtedly a pathology.
Other variations in sexual characteristics do not affect the patient’s physical health negatively. They may, however, have a psychologic effect, sometimes a significant one, because of the lack of social acceptance of a person who cannot be classified within the binary classification of sexes.
“Conditions in which mixed male and female aspects are clearly evident have been and are still pathologized by the family, the treating physician, and society,” said Dr. Lala. “In the late 1970s, when a child was born with intersexual anatomical characteristics, it was common practice to surgically intervene, making them female, because it was technically easier.”
Over the years, patients who, as they grew up, were dissatisfied with the solution adopted at birth began to make their voices heard, Dr. Lala added. Scientific societies and international organizations have spoken out against subjecting intersexual newborns to surgical interventions that are not medically necessary. “Nowadays, decisions are made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the families’ wishes. Interventions are justified with medical reasons, which are often very nuanced,” Dr. Lala concluded.
Implications for Sports
Traditionally, athletes participating in competitions in certain sports have been divided into male and female categories to ensure a certain equity and uniformity in performance. Over the years, the emergence of new information about sexual development has made it necessary to update the criteria used in this division.
The main factor responsible for the performance diversity between males and females is the action of testosterone on the male and female organism. “Testosterone has important effects on muscle mass and enhances training results,” said Dr. Moghetti. “As a demonstration of this fact, before puberty, the best performances in athletics or swimming by males and females are similar, then males gain a significant advantage of around 10%-20%.”
A few years ago, the World Athletics Federation conducted widespread screening of athletes participating in its world championships. “It identified a small group of individuals with potentially abnormal testosterone levels for the female sex,” said Dr. Moghetti. “Some were found to be doping, others had genetic defects, and for some, an interpretation was not even possible.”
Some of the individuals had a male genotype but a defect in 5-alpha-reductase, an enzyme essential for the formation of male genitals and hair growth. An athlete with these characteristics, assigned female sex at birth, has a male level of testosterone that stimulates the accumulation of muscle mass, Dr. Moghetti explained. Therefore, the individual has a considerable advantage in performances influenced by this hormone.
“In the end, the Federation decided to set limits on the testosterone levels of athletes participating in certain types of races, especially those in middle distance, that appeared to be more sensitive to differences in hormone levels,” said Dr. Moghetti. “The limitation does not apply to athletes with Morris syndrome, ie, with a male genotype and complete resistance to testosterone, for whom the high level of this hormone does not provide any advantage.” Given the complexity of the problem, he hopes for a case-by-case policy that considers the needs of patients with genetic alterations and those of athletes who have to compete with them.
Not the First Time
A recent incident underscored the difficulty of regulating such complex issues. The World Athletics Federation excluded South African middle-distance runner Caster Semenya from competitions years ago because of excessively high testosterone levels.
“The Federation’s regulations recommend that athletes in these cases reduce hormone levels to values below the threshold of 5 nmol/L of blood for a period of at least 6 months before the race by using hormonal contraceptives. The use of such drugs does not pose a health risk, as they are substances normally taken by women for contraception purposes,” said Amelia Filippelli, a pharmacologist at the University of Salerno in Italy. The South African middle-distance runner refused the drug and appealed to the Court of Arbitration for Sport and later to the Swiss Federal Court. Both rejected her appeal. Finally, Ms. Semenya appealed to the European Court of Human Rights, which in 2023 recognized a violation of her rights but does not have the authority to order a change in the Federation’s regulations.
Beyond the ideologic positions of nonexperts, therefore, the issue is still the subject of debate in the scientific community, which is evaluating not only its medical aspects but also its ethical implications.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The allegations against Algerian boxer Imane Khelif at the Paris Olympics raised the questions of intersexuality and its implications in competitive sports. This news organization has decided to delve into the topic to assist doctors who suspect a similar condition in their patients. No certain clinical data about Ms. Khelif have been made public, so this article does not concern the boxer but rather takes inspiration from the media controversy.
What Is Intersexuality?
Intersexuality encompasses a spectrum of variations in sexual development that lead to the simultaneous presence of typical male and female characteristics. As reiterated by the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, the medical definition does not affect the patient’s self-identification of gender or sexual orientation.
“The percentage of people who fall within the intersexuality spectrum is less than 0.5 per thousand of the general population, but there are no precise statistics, given the difficulty of definition,” said Roberto Lala, MD, pediatric endocrinologist and president of the Federation of Rare Childhood Diseases.
Indeed, there is not only a strict definition of intersexuality that involves a significant presence of these mixed physical characteristics in a way that conditions the self-image of the subject but also a broad definition, said Dr. Lala. “For example, clitoral hypertrophy in a female otherwise conforming to the female gender, which does not raise doubts about identity,” he said.
Chromosomes, Genes, and Hormones
“The human body is, so to speak, programmed to take on female appearances in development and shifts toward male ones only if exposed to testosterone and other factors. For this to happen, testosterone must be produced during embryonic development, and it must function properly,” said Paolo Moghetti, full professor of endocrinology at the University of Verona, Italy.
The protein encoded by SRY, which is located on the Y chromosome, determines the development of the testicles from undifferentiated tissue of the embryonic gonads. The testicles of the embryo then produce testosterone. The absence of the Y chromosome is a common characteristic of most female individuals. However, there are individuals with a female phenotype who have X and Y chromosomes but lack SRY or have a variant of it that is not entirely functional.
Numerous other chromosomal or genetic variations can lead to alterations in sexual differentiation. “In phenotypically male adult subjects (with a chromosomal makeup of 46XY) with complete androgen insensitivity (so-called Morris syndrome), testosterone levels in the blood are elevated, above normal even for a male, but the hormone is totally ineffective, and the phenotype is totally female at birth, with completely female development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty,” said Dr. Moghetti.
This means that affected individuals have well-developed breasts and a complete lack or extremely reduced presence of hair, including underarm and pubic hair. Menstruation is also completely absent because there is no uterus, and there are testes, not visible because they are considered in the abdomen.
“There are syndromes that are currently considered congenital but not genetic, of which a genetic origin will probably be identified in the future,” said Dr. Lala.
Some variations in sexual development can be diagnosed prenatally, such as an alteration of the number of sex chromosomes or a discordance between the morphologic characteristics highlighted by ultrasound and the genotype detected by amniocentesis. Some variations are evident at birth because of atypical anatomical characteristics. Others are diagnosed during puberty or later in adulthood, in the presence of infertility. The Italian National Institute of Health details these variations on its website, describing the characteristics that determine diagnosis and treatment.
Pathologies or Variations?
Some anomalies in sexual development negatively affect the patient’s physical health. One example is congenital adrenal hyperplasia. “It results from an inherited defect of the adrenal glands, which reduces cortisol production while increasing testosterone production,” said Dr. Lala. “In addition to the appearance of male characteristics in females, in more severe forms, it carries the risk of collapse and shock and requires pharmacological treatment.” It is undoubtedly a pathology.
Other variations in sexual characteristics do not affect the patient’s physical health negatively. They may, however, have a psychologic effect, sometimes a significant one, because of the lack of social acceptance of a person who cannot be classified within the binary classification of sexes.
“Conditions in which mixed male and female aspects are clearly evident have been and are still pathologized by the family, the treating physician, and society,” said Dr. Lala. “In the late 1970s, when a child was born with intersexual anatomical characteristics, it was common practice to surgically intervene, making them female, because it was technically easier.”
Over the years, patients who, as they grew up, were dissatisfied with the solution adopted at birth began to make their voices heard, Dr. Lala added. Scientific societies and international organizations have spoken out against subjecting intersexual newborns to surgical interventions that are not medically necessary. “Nowadays, decisions are made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the families’ wishes. Interventions are justified with medical reasons, which are often very nuanced,” Dr. Lala concluded.
Implications for Sports
Traditionally, athletes participating in competitions in certain sports have been divided into male and female categories to ensure a certain equity and uniformity in performance. Over the years, the emergence of new information about sexual development has made it necessary to update the criteria used in this division.
The main factor responsible for the performance diversity between males and females is the action of testosterone on the male and female organism. “Testosterone has important effects on muscle mass and enhances training results,” said Dr. Moghetti. “As a demonstration of this fact, before puberty, the best performances in athletics or swimming by males and females are similar, then males gain a significant advantage of around 10%-20%.”
A few years ago, the World Athletics Federation conducted widespread screening of athletes participating in its world championships. “It identified a small group of individuals with potentially abnormal testosterone levels for the female sex,” said Dr. Moghetti. “Some were found to be doping, others had genetic defects, and for some, an interpretation was not even possible.”
Some of the individuals had a male genotype but a defect in 5-alpha-reductase, an enzyme essential for the formation of male genitals and hair growth. An athlete with these characteristics, assigned female sex at birth, has a male level of testosterone that stimulates the accumulation of muscle mass, Dr. Moghetti explained. Therefore, the individual has a considerable advantage in performances influenced by this hormone.
“In the end, the Federation decided to set limits on the testosterone levels of athletes participating in certain types of races, especially those in middle distance, that appeared to be more sensitive to differences in hormone levels,” said Dr. Moghetti. “The limitation does not apply to athletes with Morris syndrome, ie, with a male genotype and complete resistance to testosterone, for whom the high level of this hormone does not provide any advantage.” Given the complexity of the problem, he hopes for a case-by-case policy that considers the needs of patients with genetic alterations and those of athletes who have to compete with them.
Not the First Time
A recent incident underscored the difficulty of regulating such complex issues. The World Athletics Federation excluded South African middle-distance runner Caster Semenya from competitions years ago because of excessively high testosterone levels.
“The Federation’s regulations recommend that athletes in these cases reduce hormone levels to values below the threshold of 5 nmol/L of blood for a period of at least 6 months before the race by using hormonal contraceptives. The use of such drugs does not pose a health risk, as they are substances normally taken by women for contraception purposes,” said Amelia Filippelli, a pharmacologist at the University of Salerno in Italy. The South African middle-distance runner refused the drug and appealed to the Court of Arbitration for Sport and later to the Swiss Federal Court. Both rejected her appeal. Finally, Ms. Semenya appealed to the European Court of Human Rights, which in 2023 recognized a violation of her rights but does not have the authority to order a change in the Federation’s regulations.
Beyond the ideologic positions of nonexperts, therefore, the issue is still the subject of debate in the scientific community, which is evaluating not only its medical aspects but also its ethical implications.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The allegations against Algerian boxer Imane Khelif at the Paris Olympics raised the questions of intersexuality and its implications in competitive sports. This news organization has decided to delve into the topic to assist doctors who suspect a similar condition in their patients. No certain clinical data about Ms. Khelif have been made public, so this article does not concern the boxer but rather takes inspiration from the media controversy.
What Is Intersexuality?
Intersexuality encompasses a spectrum of variations in sexual development that lead to the simultaneous presence of typical male and female characteristics. As reiterated by the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, the medical definition does not affect the patient’s self-identification of gender or sexual orientation.
“The percentage of people who fall within the intersexuality spectrum is less than 0.5 per thousand of the general population, but there are no precise statistics, given the difficulty of definition,” said Roberto Lala, MD, pediatric endocrinologist and president of the Federation of Rare Childhood Diseases.
Indeed, there is not only a strict definition of intersexuality that involves a significant presence of these mixed physical characteristics in a way that conditions the self-image of the subject but also a broad definition, said Dr. Lala. “For example, clitoral hypertrophy in a female otherwise conforming to the female gender, which does not raise doubts about identity,” he said.
Chromosomes, Genes, and Hormones
“The human body is, so to speak, programmed to take on female appearances in development and shifts toward male ones only if exposed to testosterone and other factors. For this to happen, testosterone must be produced during embryonic development, and it must function properly,” said Paolo Moghetti, full professor of endocrinology at the University of Verona, Italy.
The protein encoded by SRY, which is located on the Y chromosome, determines the development of the testicles from undifferentiated tissue of the embryonic gonads. The testicles of the embryo then produce testosterone. The absence of the Y chromosome is a common characteristic of most female individuals. However, there are individuals with a female phenotype who have X and Y chromosomes but lack SRY or have a variant of it that is not entirely functional.
Numerous other chromosomal or genetic variations can lead to alterations in sexual differentiation. “In phenotypically male adult subjects (with a chromosomal makeup of 46XY) with complete androgen insensitivity (so-called Morris syndrome), testosterone levels in the blood are elevated, above normal even for a male, but the hormone is totally ineffective, and the phenotype is totally female at birth, with completely female development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty,” said Dr. Moghetti.
This means that affected individuals have well-developed breasts and a complete lack or extremely reduced presence of hair, including underarm and pubic hair. Menstruation is also completely absent because there is no uterus, and there are testes, not visible because they are considered in the abdomen.
“There are syndromes that are currently considered congenital but not genetic, of which a genetic origin will probably be identified in the future,” said Dr. Lala.
Some variations in sexual development can be diagnosed prenatally, such as an alteration of the number of sex chromosomes or a discordance between the morphologic characteristics highlighted by ultrasound and the genotype detected by amniocentesis. Some variations are evident at birth because of atypical anatomical characteristics. Others are diagnosed during puberty or later in adulthood, in the presence of infertility. The Italian National Institute of Health details these variations on its website, describing the characteristics that determine diagnosis and treatment.
Pathologies or Variations?
Some anomalies in sexual development negatively affect the patient’s physical health. One example is congenital adrenal hyperplasia. “It results from an inherited defect of the adrenal glands, which reduces cortisol production while increasing testosterone production,” said Dr. Lala. “In addition to the appearance of male characteristics in females, in more severe forms, it carries the risk of collapse and shock and requires pharmacological treatment.” It is undoubtedly a pathology.
Other variations in sexual characteristics do not affect the patient’s physical health negatively. They may, however, have a psychologic effect, sometimes a significant one, because of the lack of social acceptance of a person who cannot be classified within the binary classification of sexes.
“Conditions in which mixed male and female aspects are clearly evident have been and are still pathologized by the family, the treating physician, and society,” said Dr. Lala. “In the late 1970s, when a child was born with intersexual anatomical characteristics, it was common practice to surgically intervene, making them female, because it was technically easier.”
Over the years, patients who, as they grew up, were dissatisfied with the solution adopted at birth began to make their voices heard, Dr. Lala added. Scientific societies and international organizations have spoken out against subjecting intersexual newborns to surgical interventions that are not medically necessary. “Nowadays, decisions are made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the families’ wishes. Interventions are justified with medical reasons, which are often very nuanced,” Dr. Lala concluded.
Implications for Sports
Traditionally, athletes participating in competitions in certain sports have been divided into male and female categories to ensure a certain equity and uniformity in performance. Over the years, the emergence of new information about sexual development has made it necessary to update the criteria used in this division.
The main factor responsible for the performance diversity between males and females is the action of testosterone on the male and female organism. “Testosterone has important effects on muscle mass and enhances training results,” said Dr. Moghetti. “As a demonstration of this fact, before puberty, the best performances in athletics or swimming by males and females are similar, then males gain a significant advantage of around 10%-20%.”
A few years ago, the World Athletics Federation conducted widespread screening of athletes participating in its world championships. “It identified a small group of individuals with potentially abnormal testosterone levels for the female sex,” said Dr. Moghetti. “Some were found to be doping, others had genetic defects, and for some, an interpretation was not even possible.”
Some of the individuals had a male genotype but a defect in 5-alpha-reductase, an enzyme essential for the formation of male genitals and hair growth. An athlete with these characteristics, assigned female sex at birth, has a male level of testosterone that stimulates the accumulation of muscle mass, Dr. Moghetti explained. Therefore, the individual has a considerable advantage in performances influenced by this hormone.
“In the end, the Federation decided to set limits on the testosterone levels of athletes participating in certain types of races, especially those in middle distance, that appeared to be more sensitive to differences in hormone levels,” said Dr. Moghetti. “The limitation does not apply to athletes with Morris syndrome, ie, with a male genotype and complete resistance to testosterone, for whom the high level of this hormone does not provide any advantage.” Given the complexity of the problem, he hopes for a case-by-case policy that considers the needs of patients with genetic alterations and those of athletes who have to compete with them.
Not the First Time
A recent incident underscored the difficulty of regulating such complex issues. The World Athletics Federation excluded South African middle-distance runner Caster Semenya from competitions years ago because of excessively high testosterone levels.
“The Federation’s regulations recommend that athletes in these cases reduce hormone levels to values below the threshold of 5 nmol/L of blood for a period of at least 6 months before the race by using hormonal contraceptives. The use of such drugs does not pose a health risk, as they are substances normally taken by women for contraception purposes,” said Amelia Filippelli, a pharmacologist at the University of Salerno in Italy. The South African middle-distance runner refused the drug and appealed to the Court of Arbitration for Sport and later to the Swiss Federal Court. Both rejected her appeal. Finally, Ms. Semenya appealed to the European Court of Human Rights, which in 2023 recognized a violation of her rights but does not have the authority to order a change in the Federation’s regulations.
Beyond the ideologic positions of nonexperts, therefore, the issue is still the subject of debate in the scientific community, which is evaluating not only its medical aspects but also its ethical implications.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.