User login
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.) 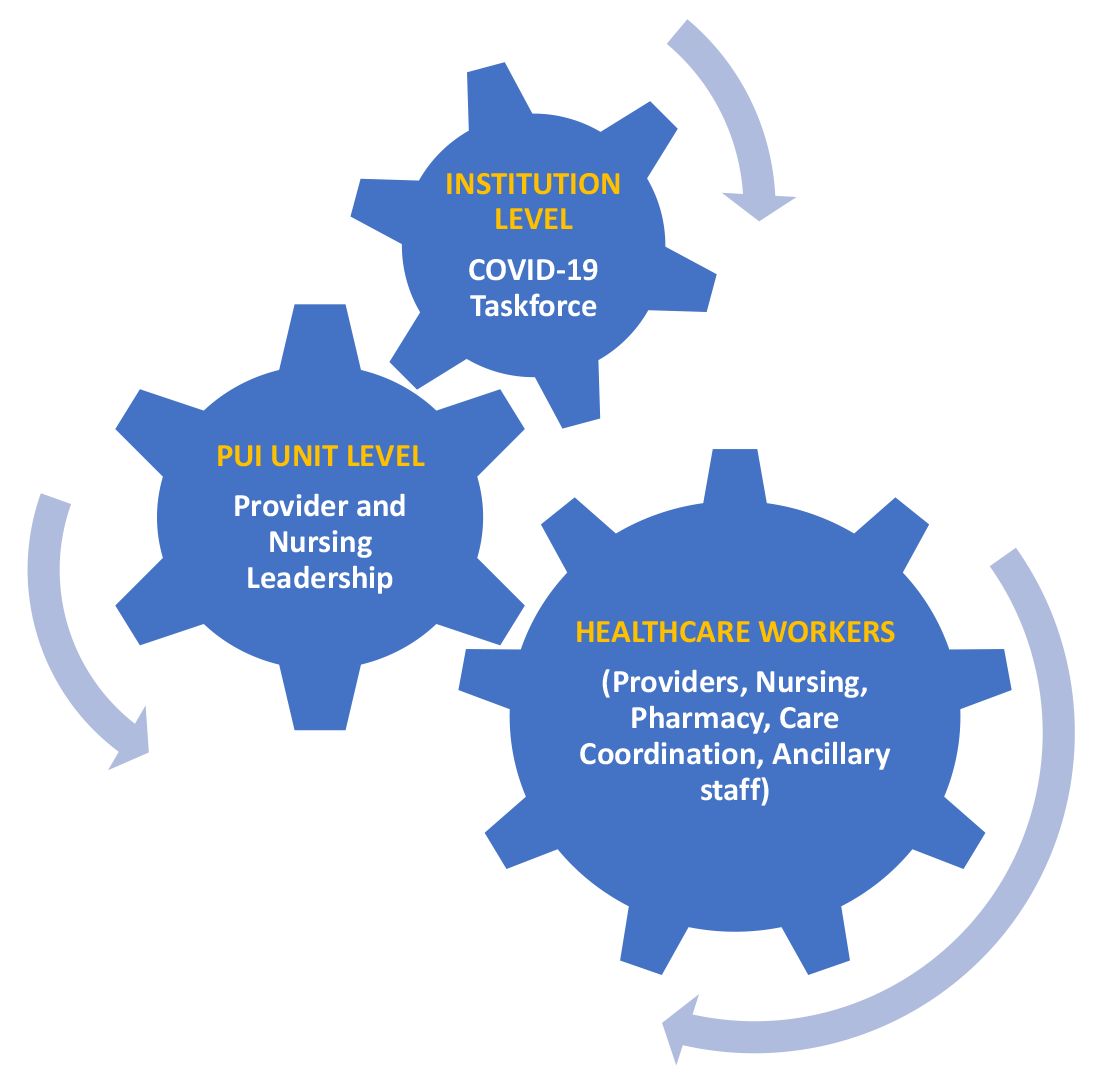
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara (psunkara@wakehealth.edu) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert (wlippert@wakehealth.edu) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris (chrmorri@wakehealth.edu) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang (chuang@wakehealth.edu) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.) 
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara (psunkara@wakehealth.edu) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert (wlippert@wakehealth.edu) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris (chrmorri@wakehealth.edu) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang (chuang@wakehealth.edu) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.) 
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara (psunkara@wakehealth.edu) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert (wlippert@wakehealth.edu) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris (chrmorri@wakehealth.edu) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang (chuang@wakehealth.edu) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.




