User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
On Second Thought: The Truth About Beta-Blockers
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Giving patients a beta-blocker after a myocardial infarction is standard of care. It’s in the guidelines. It’s one of the performance measures used by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA). If you aren’t putting your post–acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients on a beta-blocker, the ACC and the AHA both think you suck.
They are very disappointed in you, just like your mother was when you told her you didn’t want to become a surgeon because you don’t like waking up early, your hands shake when you get nervous, it’s not your fault, there’s nothing you can do about it, so just leave me alone!
The data on beta-blockers are decades old. In the time before stents, statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and dual antiplatelet therapy, when patients either died or got better on their own, beta-blockers showed major benefits. Studies like the Norwegian Multicenter Study Group, the BHAT trial, and the ISIS-1 trial proved the benefits of beta blockade. These studies date back to the 1980s, when you could call a study ISIS without controversy.
It was a simpler time, when all you had to worry about was the Cold War, apartheid, and the global AIDS pandemic. It was a time when doctors smoked in their offices, and patients had bigger infarcts that caused large scars and systolic dysfunction. That world is no longer our world, except for the war, the global pandemic, and the out-of-control gas prices.
The reality is that, before troponins, we probably missed most small heart attacks. Now, most infarcts are small, and most patients walk away from their heart attacks with essentially normal hearts. Do beta-blockers still matter? If you’re a fan of Cochrane reviews, the answer is yes.
In 2021, Cochrane published a review of beta-blockers in patients without heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI). The authors of that analysis concluded, after the usual caveats about heterogeneity, potential bias, and the whims of a random universe, that, yes, beta-blockers do reduce mortality. The risk ratio for max all-cause mortality was 0.81.
What does that mean practically? The absolute risk was reduced from 10.9% to 8.7%, a 2.2–percentage point absolute decrease and about a 20% relative drop. A little math gives us a third number: 46. That’s the number needed to treat. If you think about how many patients you admit during a typical week of critical care unit with an MI, a number needed to treat of 46 is a pretty good trade-off for a fairly inexpensive medication with fairly minimal side effects.
Of course, these are the same people who claim that masks don’t stop the spread of COVID-19. Sure, were they the only people who thought that handwashing was the best way to stop a respiratory virus? No. We all believed that fantasy for far longer than we should have. Not everybody can bat a thousand, if by batting a thousand, you mean reflecting on how your words will impact on a broader population primed to believe misinformation because of the increasingly toxic social media environment and worsening politicization and radicalization of our politics.
By the way, if any of you want to come to Canada, you can stay with me. Things are incrementally better here. In this day and age, incrementally better is the best we can hope for.
Here’s the wrinkle with the Cochrane beta-blocker review: Many of the studies took place before early revascularization became the norm and before our current armamentarium of drugs became standard of care.
Back in the day, bed rest and the power of positive thinking were the mainstays of cardiac treatment. Also, many of these studies mixed together ST-segment MI (STEMI) and non-STEMI patients, so you’re obviously going to see more benefits in STEMI patients who are at higher risk. Some of them used intravenous (IV) beta-blockers right away, whereas some were looking only at oral beta-blockers started days after the infarct.
We don’t use IV beta-blockers that much anymore because of the risk for shock.
Also, some studies had short-term follow-up where the benefits were less pronounced, and some studies used doses and types of beta-blockers rarely used today. Some of the studies had a mix of coronary and heart failure patients, which muddies the water because the heart failure patients would clearly benefit from being on a beta-blocker.
Basically, the data are not definitive because they are old and don’t reflect our current standard of care. The data contain a heterogeneous mix of patients that aren’t really relevant to the question that we’re asking. The question we’re asking is, should you put all your post-MI patients on a beta-blocker routinely, even if they don’t have heart failure?
The REDUCE-AMI trial is the first of a few trials testing, or to be more accurate, retesting, whether beta-blockers are useful after an MI. BETAMI, REBOOT, DANBLOCK— you’ll be hearing these names in the next few years, either because the studies get published or because they’re the Twitter handles of people harassing you online. Either/or. (By the way, I’ll be cold in my grave before I call it X.)
For now, REDUCE-AMI is the first across the finish line, and at least in cardiology, finishing first is a good thing. This study enrolled patients with ACS, both STEMI and non-STEMI, with a post-MI ejection fraction ≥ 50%, and the result was nothing. The risk ratio for all-cause mortality was 0.94 and was not statistically significant.
In absolute terms, that’s a reduction from 4.1% to 3.9%, or a 0.2–percentage point decrease; this translates into a number needed to treat of 500, which is 10 times higher than what the Cochrane review found. That’s if you assume that there is, in fact, a small benefit amidst all the statistical noise, which there probably isn’t.
Now, studies like this can never rule out small effects, either positive or negative, so maybe there is a small benefit from using beta-blockers. If it’s there, it’s really small. Do beta-blockers work? Well, yes, obviously, for heart failure and atrial fibrillation — which, let’s face it, are not exactly rare and often coexist in patients with heart disease. They probably aren’t that great as blood pressure pills, but that’s a story for another day and another video.
Yes, beta-blockers are useful pills, and they are standard of care, just maybe not for post-MI patients with normal ejection fractions because they probably don’t really need them. They worked in the pre-stent, pre-aspirin, pre-anything era.
That’s not our world anymore. Things change. It’s not the 1980s. That’s why I don’t have a mullet, and that’s why you need to update your kitchen.
Dr. Labos, a cardiologist at Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Giving patients a beta-blocker after a myocardial infarction is standard of care. It’s in the guidelines. It’s one of the performance measures used by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA). If you aren’t putting your post–acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients on a beta-blocker, the ACC and the AHA both think you suck.
They are very disappointed in you, just like your mother was when you told her you didn’t want to become a surgeon because you don’t like waking up early, your hands shake when you get nervous, it’s not your fault, there’s nothing you can do about it, so just leave me alone!
The data on beta-blockers are decades old. In the time before stents, statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and dual antiplatelet therapy, when patients either died or got better on their own, beta-blockers showed major benefits. Studies like the Norwegian Multicenter Study Group, the BHAT trial, and the ISIS-1 trial proved the benefits of beta blockade. These studies date back to the 1980s, when you could call a study ISIS without controversy.
It was a simpler time, when all you had to worry about was the Cold War, apartheid, and the global AIDS pandemic. It was a time when doctors smoked in their offices, and patients had bigger infarcts that caused large scars and systolic dysfunction. That world is no longer our world, except for the war, the global pandemic, and the out-of-control gas prices.
The reality is that, before troponins, we probably missed most small heart attacks. Now, most infarcts are small, and most patients walk away from their heart attacks with essentially normal hearts. Do beta-blockers still matter? If you’re a fan of Cochrane reviews, the answer is yes.
In 2021, Cochrane published a review of beta-blockers in patients without heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI). The authors of that analysis concluded, after the usual caveats about heterogeneity, potential bias, and the whims of a random universe, that, yes, beta-blockers do reduce mortality. The risk ratio for max all-cause mortality was 0.81.
What does that mean practically? The absolute risk was reduced from 10.9% to 8.7%, a 2.2–percentage point absolute decrease and about a 20% relative drop. A little math gives us a third number: 46. That’s the number needed to treat. If you think about how many patients you admit during a typical week of critical care unit with an MI, a number needed to treat of 46 is a pretty good trade-off for a fairly inexpensive medication with fairly minimal side effects.
Of course, these are the same people who claim that masks don’t stop the spread of COVID-19. Sure, were they the only people who thought that handwashing was the best way to stop a respiratory virus? No. We all believed that fantasy for far longer than we should have. Not everybody can bat a thousand, if by batting a thousand, you mean reflecting on how your words will impact on a broader population primed to believe misinformation because of the increasingly toxic social media environment and worsening politicization and radicalization of our politics.
By the way, if any of you want to come to Canada, you can stay with me. Things are incrementally better here. In this day and age, incrementally better is the best we can hope for.
Here’s the wrinkle with the Cochrane beta-blocker review: Many of the studies took place before early revascularization became the norm and before our current armamentarium of drugs became standard of care.
Back in the day, bed rest and the power of positive thinking were the mainstays of cardiac treatment. Also, many of these studies mixed together ST-segment MI (STEMI) and non-STEMI patients, so you’re obviously going to see more benefits in STEMI patients who are at higher risk. Some of them used intravenous (IV) beta-blockers right away, whereas some were looking only at oral beta-blockers started days after the infarct.
We don’t use IV beta-blockers that much anymore because of the risk for shock.
Also, some studies had short-term follow-up where the benefits were less pronounced, and some studies used doses and types of beta-blockers rarely used today. Some of the studies had a mix of coronary and heart failure patients, which muddies the water because the heart failure patients would clearly benefit from being on a beta-blocker.
Basically, the data are not definitive because they are old and don’t reflect our current standard of care. The data contain a heterogeneous mix of patients that aren’t really relevant to the question that we’re asking. The question we’re asking is, should you put all your post-MI patients on a beta-blocker routinely, even if they don’t have heart failure?
The REDUCE-AMI trial is the first of a few trials testing, or to be more accurate, retesting, whether beta-blockers are useful after an MI. BETAMI, REBOOT, DANBLOCK— you’ll be hearing these names in the next few years, either because the studies get published or because they’re the Twitter handles of people harassing you online. Either/or. (By the way, I’ll be cold in my grave before I call it X.)
For now, REDUCE-AMI is the first across the finish line, and at least in cardiology, finishing first is a good thing. This study enrolled patients with ACS, both STEMI and non-STEMI, with a post-MI ejection fraction ≥ 50%, and the result was nothing. The risk ratio for all-cause mortality was 0.94 and was not statistically significant.
In absolute terms, that’s a reduction from 4.1% to 3.9%, or a 0.2–percentage point decrease; this translates into a number needed to treat of 500, which is 10 times higher than what the Cochrane review found. That’s if you assume that there is, in fact, a small benefit amidst all the statistical noise, which there probably isn’t.
Now, studies like this can never rule out small effects, either positive or negative, so maybe there is a small benefit from using beta-blockers. If it’s there, it’s really small. Do beta-blockers work? Well, yes, obviously, for heart failure and atrial fibrillation — which, let’s face it, are not exactly rare and often coexist in patients with heart disease. They probably aren’t that great as blood pressure pills, but that’s a story for another day and another video.
Yes, beta-blockers are useful pills, and they are standard of care, just maybe not for post-MI patients with normal ejection fractions because they probably don’t really need them. They worked in the pre-stent, pre-aspirin, pre-anything era.
That’s not our world anymore. Things change. It’s not the 1980s. That’s why I don’t have a mullet, and that’s why you need to update your kitchen.
Dr. Labos, a cardiologist at Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Giving patients a beta-blocker after a myocardial infarction is standard of care. It’s in the guidelines. It’s one of the performance measures used by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA). If you aren’t putting your post–acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients on a beta-blocker, the ACC and the AHA both think you suck.
They are very disappointed in you, just like your mother was when you told her you didn’t want to become a surgeon because you don’t like waking up early, your hands shake when you get nervous, it’s not your fault, there’s nothing you can do about it, so just leave me alone!
The data on beta-blockers are decades old. In the time before stents, statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and dual antiplatelet therapy, when patients either died or got better on their own, beta-blockers showed major benefits. Studies like the Norwegian Multicenter Study Group, the BHAT trial, and the ISIS-1 trial proved the benefits of beta blockade. These studies date back to the 1980s, when you could call a study ISIS without controversy.
It was a simpler time, when all you had to worry about was the Cold War, apartheid, and the global AIDS pandemic. It was a time when doctors smoked in their offices, and patients had bigger infarcts that caused large scars and systolic dysfunction. That world is no longer our world, except for the war, the global pandemic, and the out-of-control gas prices.
The reality is that, before troponins, we probably missed most small heart attacks. Now, most infarcts are small, and most patients walk away from their heart attacks with essentially normal hearts. Do beta-blockers still matter? If you’re a fan of Cochrane reviews, the answer is yes.
In 2021, Cochrane published a review of beta-blockers in patients without heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI). The authors of that analysis concluded, after the usual caveats about heterogeneity, potential bias, and the whims of a random universe, that, yes, beta-blockers do reduce mortality. The risk ratio for max all-cause mortality was 0.81.
What does that mean practically? The absolute risk was reduced from 10.9% to 8.7%, a 2.2–percentage point absolute decrease and about a 20% relative drop. A little math gives us a third number: 46. That’s the number needed to treat. If you think about how many patients you admit during a typical week of critical care unit with an MI, a number needed to treat of 46 is a pretty good trade-off for a fairly inexpensive medication with fairly minimal side effects.
Of course, these are the same people who claim that masks don’t stop the spread of COVID-19. Sure, were they the only people who thought that handwashing was the best way to stop a respiratory virus? No. We all believed that fantasy for far longer than we should have. Not everybody can bat a thousand, if by batting a thousand, you mean reflecting on how your words will impact on a broader population primed to believe misinformation because of the increasingly toxic social media environment and worsening politicization and radicalization of our politics.
By the way, if any of you want to come to Canada, you can stay with me. Things are incrementally better here. In this day and age, incrementally better is the best we can hope for.
Here’s the wrinkle with the Cochrane beta-blocker review: Many of the studies took place before early revascularization became the norm and before our current armamentarium of drugs became standard of care.
Back in the day, bed rest and the power of positive thinking were the mainstays of cardiac treatment. Also, many of these studies mixed together ST-segment MI (STEMI) and non-STEMI patients, so you’re obviously going to see more benefits in STEMI patients who are at higher risk. Some of them used intravenous (IV) beta-blockers right away, whereas some were looking only at oral beta-blockers started days after the infarct.
We don’t use IV beta-blockers that much anymore because of the risk for shock.
Also, some studies had short-term follow-up where the benefits were less pronounced, and some studies used doses and types of beta-blockers rarely used today. Some of the studies had a mix of coronary and heart failure patients, which muddies the water because the heart failure patients would clearly benefit from being on a beta-blocker.
Basically, the data are not definitive because they are old and don’t reflect our current standard of care. The data contain a heterogeneous mix of patients that aren’t really relevant to the question that we’re asking. The question we’re asking is, should you put all your post-MI patients on a beta-blocker routinely, even if they don’t have heart failure?
The REDUCE-AMI trial is the first of a few trials testing, or to be more accurate, retesting, whether beta-blockers are useful after an MI. BETAMI, REBOOT, DANBLOCK— you’ll be hearing these names in the next few years, either because the studies get published or because they’re the Twitter handles of people harassing you online. Either/or. (By the way, I’ll be cold in my grave before I call it X.)
For now, REDUCE-AMI is the first across the finish line, and at least in cardiology, finishing first is a good thing. This study enrolled patients with ACS, both STEMI and non-STEMI, with a post-MI ejection fraction ≥ 50%, and the result was nothing. The risk ratio for all-cause mortality was 0.94 and was not statistically significant.
In absolute terms, that’s a reduction from 4.1% to 3.9%, or a 0.2–percentage point decrease; this translates into a number needed to treat of 500, which is 10 times higher than what the Cochrane review found. That’s if you assume that there is, in fact, a small benefit amidst all the statistical noise, which there probably isn’t.
Now, studies like this can never rule out small effects, either positive or negative, so maybe there is a small benefit from using beta-blockers. If it’s there, it’s really small. Do beta-blockers work? Well, yes, obviously, for heart failure and atrial fibrillation — which, let’s face it, are not exactly rare and often coexist in patients with heart disease. They probably aren’t that great as blood pressure pills, but that’s a story for another day and another video.
Yes, beta-blockers are useful pills, and they are standard of care, just maybe not for post-MI patients with normal ejection fractions because they probably don’t really need them. They worked in the pre-stent, pre-aspirin, pre-anything era.
That’s not our world anymore. Things change. It’s not the 1980s. That’s why I don’t have a mullet, and that’s why you need to update your kitchen.
Dr. Labos, a cardiologist at Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Guidance on Genetic Testing for Kidney Disease
A new consensus statement recommended genetic testing for all categories of kidney diseases whenever a genetic cause is suspected and offered guidance on who to test, which tests are the most useful, and how to talk to patients about results.
The statement, published online in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases, is the work of four dozen authors — including patients, nephrologists, experts in clinical and laboratory genetics, kidney pathology, genetic counseling, and ethics. The experts were brought together by the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) with the goal of broadening use and understanding of the tests.
About 10% or more of kidney diseases in adults and 70% of selected chronic kidney diseases (CKDs) in children have genetic causes. But nephrologists have reported a lack of education about genetic testing, and other barriers to wider use, including limited access to testing, cost, insurance coverage, and a small number of genetic counselors who are versed in kidney genetics.
Genetic testing “in the kidney field is a little less developed than in other fields,” said co–lead author Nora Franceschini, MD, MPH, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, Chapel Hill, and a nephrologist who studies the genetic epidemiology of hypertension and kidney and cardiovascular diseases.
There are already many known variants that play a role in various kidney diseases and more are on the horizon, Dr. Franceschini told this news organization. More genetic tests will be available in the near future. “The workforce needs to be prepared,” she said.
The statement is an initial step that gets clinicians thinking about testing in a more systematic way, said Dr. Franceschini. “Genetic testing is just another test that physicians can use to complete the story when evaluating patients.
“I think clinicians are ready to implement” testing, said Dr. Franceschini. “We just need to have better guidance.”
Who, When, What to Test
The NKF statement is not the first to try to address gaps in use and knowledge. A European Renal Association Working Group published guidelines in 2022.
The NKF Working Group came up with 56 recommendations and separate algorithms to guide testing for adult and pediatric individuals who are considered at-risk (and currently asymptomatic) and for those who already have clinical disease.
Testing can help determine a cause if there’s an atypical clinical presentation, and it can help avoid biopsies, said the group. Tests can also guide choice of therapy.
For at-risk individuals, there are two broad situations in which testing might be considered: In family members of a patient who already has kidney disease and in potential kidney donors. But testing at-risk children younger than 18 years should only be done if there is an intervention available that could prevent, treat, or slow progression of disease, said the authors.
For patients with an established genetic diagnosis, at-risk family members should be tested with the known single-gene variant diagnostic instead of a broad panel, said the group.
Single-gene variant testing is most appropriate in situations when clinical disease is already evident or when there is known genetic disease in the family, according to the NKF panel. A large diagnostic panel that covers the many common genetic causes of kidney disease is recommended for the majority of patients.
The group recommended that apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) testing should be included in gene panels for CKD, and it should be offered to any patient “with clinical findings suggestive of APOL1-association nephropathy, regardless of race and ethnicity.”
High-risk APOL1 genotypes confer a 5- to 10-fold increased risk for CKD and are found in one out of seven individuals of African ancestry, which means the focus has largely been on testing those with that ancestry.
However, with many unknowns about APOL1, the NKF panel did not want to “profile” individuals and suggest that testing should not be based on skin color or race/ethnicity, said Dr. Franceschini.
In addition, only about 10% of those with the variant develop disease, so testing is not currently warranted for those who do not already have kidney disease, said the group.
They also recommended against the use of polygenic risk scores, saying that there are not enough data from diverse populations in genome-wide association studies for kidney disease or on their clinical utility.
More Education Needed; Many Barriers
The authors acknowledged that nephrologists generally receive little education in genetics and lack support for interpreting and discussing results.
“Nephrologists should be provided with training and best practice resources to interpret genetic testing and discuss the results with individuals and their families,” they wrote, adding that there’s a need for genomic medicine boards at academic centers that would be available to help nephrologists interpret results and plot clinical management.
The group did not, however, cite some of the other barriers to adoption of testing, including a limited number of sites offering testing, cost, and lack of insurance coverage for the diagnostics.
Medicare may cover genetic testing for kidney disease when an individual has symptoms and there is a Food and Drug Administration–approved test. Joseph Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer for the NKF, said private insurance may cover the testing if the nephrologist deems it medically necessary, but that he usually confirms coverage before initiating testing. The often-used Renasight panel, which tests for 385 genes related to kidney diseases, costs $300-$400 out of pocket, Dr. Vassalotti told this news organization.
In a survey of 149 nephrologists conducted in 2021, both users (46%) and nonusers of the tests (69%) said that high cost was the most significant perceived barrier to implementing widespread testing. A third of users and almost two thirds of nonusers said that poor availability or lack of ease of testing was the second most significant barrier.
Clinics that test for kidney genes “are largely confined to large academic centers and some specialty clinics,” said Dominic Raj, MD, the Bert B. Brooks chair, and Divya Shankaranarayanan, MD, director of the Kidney Precision Medicine Clinic, both at George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Washington, DC, in an email.
Testing is also limited by cultural barriers, lack of genetic literacy, and patients’ concerns that a positive result could lead to a loss of health insurance coverage, said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan.
Paper Will Help Expand Use
A lack of consensus has also held back expansion. The new statement “may lead to increased and possibly judicious utilization of genetic testing in nephrology practices,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan. “Most importantly, the panel has given specific guidance as to what type of genetic test platform is likely to yield the best and most cost-effective yield.”
The most effective use is “in monogenic kidney diseases and to a lesser extent in oligogenic kidney disease,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan, adding that testing is of less-certain utility in polygenic kidney diseases, “where complex genetic and epigenetic factors determine the phenotype.”
Genetic testing might be especially useful “in atypical clinical presentations” and can help clinicians avoid unnecessary expensive and extensive investigations when multiple organ systems are involved, they said.
“Most importantly, [testing] might prevent unnecessary and potentially harmful treatment and enable targeted specific treatment, when available,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan.
Dr. Franceschini and Dr. Shankaranarayanan reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Raj disclosed that he received consulting fees and honoraria from Novo Nordisk and is a national leader for the company’s Zeus trial, studying whether ziltivekimab reduces the risk for cardiovascular events in cardiovascular disease, CKD, and inflammation. He also participated in a study of Natera’s Renasight, a 385-gene panel for kidney disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new consensus statement recommended genetic testing for all categories of kidney diseases whenever a genetic cause is suspected and offered guidance on who to test, which tests are the most useful, and how to talk to patients about results.
The statement, published online in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases, is the work of four dozen authors — including patients, nephrologists, experts in clinical and laboratory genetics, kidney pathology, genetic counseling, and ethics. The experts were brought together by the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) with the goal of broadening use and understanding of the tests.
About 10% or more of kidney diseases in adults and 70% of selected chronic kidney diseases (CKDs) in children have genetic causes. But nephrologists have reported a lack of education about genetic testing, and other barriers to wider use, including limited access to testing, cost, insurance coverage, and a small number of genetic counselors who are versed in kidney genetics.
Genetic testing “in the kidney field is a little less developed than in other fields,” said co–lead author Nora Franceschini, MD, MPH, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, Chapel Hill, and a nephrologist who studies the genetic epidemiology of hypertension and kidney and cardiovascular diseases.
There are already many known variants that play a role in various kidney diseases and more are on the horizon, Dr. Franceschini told this news organization. More genetic tests will be available in the near future. “The workforce needs to be prepared,” she said.
The statement is an initial step that gets clinicians thinking about testing in a more systematic way, said Dr. Franceschini. “Genetic testing is just another test that physicians can use to complete the story when evaluating patients.
“I think clinicians are ready to implement” testing, said Dr. Franceschini. “We just need to have better guidance.”
Who, When, What to Test
The NKF statement is not the first to try to address gaps in use and knowledge. A European Renal Association Working Group published guidelines in 2022.
The NKF Working Group came up with 56 recommendations and separate algorithms to guide testing for adult and pediatric individuals who are considered at-risk (and currently asymptomatic) and for those who already have clinical disease.
Testing can help determine a cause if there’s an atypical clinical presentation, and it can help avoid biopsies, said the group. Tests can also guide choice of therapy.
For at-risk individuals, there are two broad situations in which testing might be considered: In family members of a patient who already has kidney disease and in potential kidney donors. But testing at-risk children younger than 18 years should only be done if there is an intervention available that could prevent, treat, or slow progression of disease, said the authors.
For patients with an established genetic diagnosis, at-risk family members should be tested with the known single-gene variant diagnostic instead of a broad panel, said the group.
Single-gene variant testing is most appropriate in situations when clinical disease is already evident or when there is known genetic disease in the family, according to the NKF panel. A large diagnostic panel that covers the many common genetic causes of kidney disease is recommended for the majority of patients.
The group recommended that apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) testing should be included in gene panels for CKD, and it should be offered to any patient “with clinical findings suggestive of APOL1-association nephropathy, regardless of race and ethnicity.”
High-risk APOL1 genotypes confer a 5- to 10-fold increased risk for CKD and are found in one out of seven individuals of African ancestry, which means the focus has largely been on testing those with that ancestry.
However, with many unknowns about APOL1, the NKF panel did not want to “profile” individuals and suggest that testing should not be based on skin color or race/ethnicity, said Dr. Franceschini.
In addition, only about 10% of those with the variant develop disease, so testing is not currently warranted for those who do not already have kidney disease, said the group.
They also recommended against the use of polygenic risk scores, saying that there are not enough data from diverse populations in genome-wide association studies for kidney disease or on their clinical utility.
More Education Needed; Many Barriers
The authors acknowledged that nephrologists generally receive little education in genetics and lack support for interpreting and discussing results.
“Nephrologists should be provided with training and best practice resources to interpret genetic testing and discuss the results with individuals and their families,” they wrote, adding that there’s a need for genomic medicine boards at academic centers that would be available to help nephrologists interpret results and plot clinical management.
The group did not, however, cite some of the other barriers to adoption of testing, including a limited number of sites offering testing, cost, and lack of insurance coverage for the diagnostics.
Medicare may cover genetic testing for kidney disease when an individual has symptoms and there is a Food and Drug Administration–approved test. Joseph Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer for the NKF, said private insurance may cover the testing if the nephrologist deems it medically necessary, but that he usually confirms coverage before initiating testing. The often-used Renasight panel, which tests for 385 genes related to kidney diseases, costs $300-$400 out of pocket, Dr. Vassalotti told this news organization.
In a survey of 149 nephrologists conducted in 2021, both users (46%) and nonusers of the tests (69%) said that high cost was the most significant perceived barrier to implementing widespread testing. A third of users and almost two thirds of nonusers said that poor availability or lack of ease of testing was the second most significant barrier.
Clinics that test for kidney genes “are largely confined to large academic centers and some specialty clinics,” said Dominic Raj, MD, the Bert B. Brooks chair, and Divya Shankaranarayanan, MD, director of the Kidney Precision Medicine Clinic, both at George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Washington, DC, in an email.
Testing is also limited by cultural barriers, lack of genetic literacy, and patients’ concerns that a positive result could lead to a loss of health insurance coverage, said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan.
Paper Will Help Expand Use
A lack of consensus has also held back expansion. The new statement “may lead to increased and possibly judicious utilization of genetic testing in nephrology practices,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan. “Most importantly, the panel has given specific guidance as to what type of genetic test platform is likely to yield the best and most cost-effective yield.”
The most effective use is “in monogenic kidney diseases and to a lesser extent in oligogenic kidney disease,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan, adding that testing is of less-certain utility in polygenic kidney diseases, “where complex genetic and epigenetic factors determine the phenotype.”
Genetic testing might be especially useful “in atypical clinical presentations” and can help clinicians avoid unnecessary expensive and extensive investigations when multiple organ systems are involved, they said.
“Most importantly, [testing] might prevent unnecessary and potentially harmful treatment and enable targeted specific treatment, when available,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan.
Dr. Franceschini and Dr. Shankaranarayanan reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Raj disclosed that he received consulting fees and honoraria from Novo Nordisk and is a national leader for the company’s Zeus trial, studying whether ziltivekimab reduces the risk for cardiovascular events in cardiovascular disease, CKD, and inflammation. He also participated in a study of Natera’s Renasight, a 385-gene panel for kidney disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new consensus statement recommended genetic testing for all categories of kidney diseases whenever a genetic cause is suspected and offered guidance on who to test, which tests are the most useful, and how to talk to patients about results.
The statement, published online in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases, is the work of four dozen authors — including patients, nephrologists, experts in clinical and laboratory genetics, kidney pathology, genetic counseling, and ethics. The experts were brought together by the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) with the goal of broadening use and understanding of the tests.
About 10% or more of kidney diseases in adults and 70% of selected chronic kidney diseases (CKDs) in children have genetic causes. But nephrologists have reported a lack of education about genetic testing, and other barriers to wider use, including limited access to testing, cost, insurance coverage, and a small number of genetic counselors who are versed in kidney genetics.
Genetic testing “in the kidney field is a little less developed than in other fields,” said co–lead author Nora Franceschini, MD, MPH, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, Chapel Hill, and a nephrologist who studies the genetic epidemiology of hypertension and kidney and cardiovascular diseases.
There are already many known variants that play a role in various kidney diseases and more are on the horizon, Dr. Franceschini told this news organization. More genetic tests will be available in the near future. “The workforce needs to be prepared,” she said.
The statement is an initial step that gets clinicians thinking about testing in a more systematic way, said Dr. Franceschini. “Genetic testing is just another test that physicians can use to complete the story when evaluating patients.
“I think clinicians are ready to implement” testing, said Dr. Franceschini. “We just need to have better guidance.”
Who, When, What to Test
The NKF statement is not the first to try to address gaps in use and knowledge. A European Renal Association Working Group published guidelines in 2022.
The NKF Working Group came up with 56 recommendations and separate algorithms to guide testing for adult and pediatric individuals who are considered at-risk (and currently asymptomatic) and for those who already have clinical disease.
Testing can help determine a cause if there’s an atypical clinical presentation, and it can help avoid biopsies, said the group. Tests can also guide choice of therapy.
For at-risk individuals, there are two broad situations in which testing might be considered: In family members of a patient who already has kidney disease and in potential kidney donors. But testing at-risk children younger than 18 years should only be done if there is an intervention available that could prevent, treat, or slow progression of disease, said the authors.
For patients with an established genetic diagnosis, at-risk family members should be tested with the known single-gene variant diagnostic instead of a broad panel, said the group.
Single-gene variant testing is most appropriate in situations when clinical disease is already evident or when there is known genetic disease in the family, according to the NKF panel. A large diagnostic panel that covers the many common genetic causes of kidney disease is recommended for the majority of patients.
The group recommended that apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) testing should be included in gene panels for CKD, and it should be offered to any patient “with clinical findings suggestive of APOL1-association nephropathy, regardless of race and ethnicity.”
High-risk APOL1 genotypes confer a 5- to 10-fold increased risk for CKD and are found in one out of seven individuals of African ancestry, which means the focus has largely been on testing those with that ancestry.
However, with many unknowns about APOL1, the NKF panel did not want to “profile” individuals and suggest that testing should not be based on skin color or race/ethnicity, said Dr. Franceschini.
In addition, only about 10% of those with the variant develop disease, so testing is not currently warranted for those who do not already have kidney disease, said the group.
They also recommended against the use of polygenic risk scores, saying that there are not enough data from diverse populations in genome-wide association studies for kidney disease or on their clinical utility.
More Education Needed; Many Barriers
The authors acknowledged that nephrologists generally receive little education in genetics and lack support for interpreting and discussing results.
“Nephrologists should be provided with training and best practice resources to interpret genetic testing and discuss the results with individuals and their families,” they wrote, adding that there’s a need for genomic medicine boards at academic centers that would be available to help nephrologists interpret results and plot clinical management.
The group did not, however, cite some of the other barriers to adoption of testing, including a limited number of sites offering testing, cost, and lack of insurance coverage for the diagnostics.
Medicare may cover genetic testing for kidney disease when an individual has symptoms and there is a Food and Drug Administration–approved test. Joseph Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer for the NKF, said private insurance may cover the testing if the nephrologist deems it medically necessary, but that he usually confirms coverage before initiating testing. The often-used Renasight panel, which tests for 385 genes related to kidney diseases, costs $300-$400 out of pocket, Dr. Vassalotti told this news organization.
In a survey of 149 nephrologists conducted in 2021, both users (46%) and nonusers of the tests (69%) said that high cost was the most significant perceived barrier to implementing widespread testing. A third of users and almost two thirds of nonusers said that poor availability or lack of ease of testing was the second most significant barrier.
Clinics that test for kidney genes “are largely confined to large academic centers and some specialty clinics,” said Dominic Raj, MD, the Bert B. Brooks chair, and Divya Shankaranarayanan, MD, director of the Kidney Precision Medicine Clinic, both at George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Washington, DC, in an email.
Testing is also limited by cultural barriers, lack of genetic literacy, and patients’ concerns that a positive result could lead to a loss of health insurance coverage, said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan.
Paper Will Help Expand Use
A lack of consensus has also held back expansion. The new statement “may lead to increased and possibly judicious utilization of genetic testing in nephrology practices,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan. “Most importantly, the panel has given specific guidance as to what type of genetic test platform is likely to yield the best and most cost-effective yield.”
The most effective use is “in monogenic kidney diseases and to a lesser extent in oligogenic kidney disease,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan, adding that testing is of less-certain utility in polygenic kidney diseases, “where complex genetic and epigenetic factors determine the phenotype.”
Genetic testing might be especially useful “in atypical clinical presentations” and can help clinicians avoid unnecessary expensive and extensive investigations when multiple organ systems are involved, they said.
“Most importantly, [testing] might prevent unnecessary and potentially harmful treatment and enable targeted specific treatment, when available,” said Dr. Raj and Dr. Shankaranarayanan.
Dr. Franceschini and Dr. Shankaranarayanan reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Raj disclosed that he received consulting fees and honoraria from Novo Nordisk and is a national leader for the company’s Zeus trial, studying whether ziltivekimab reduces the risk for cardiovascular events in cardiovascular disease, CKD, and inflammation. He also participated in a study of Natera’s Renasight, a 385-gene panel for kidney disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF KIDNEY DISEASES
Weight Loss in Obesity May Create ‘Positive’ Hormone Changes
TOPLINE:
In middle-aged patients with severe obesity, changes in endogenous sex hormones may be proportional to the amount of weight loss after bariatric surgery and dietary intervention, leading to an improved hormonal balance, with more pronounced androgen changes in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Obesity-related hormonal imbalances are common among those seeking weight loss treatment.
- This prospective observational study evaluated the incremental effect of weight loss by three bariatric procedures and a dietary intervention on endogenous sex hormones in men and women over 3 years.
- The study included 61 adults (median age, 50.9 years; baseline mean body mass index, 40.2; 72% women) from obesity clinics and private bariatric services in Sydney, Australia, between 2009 and 2012, who underwent bariatric surgery or received dietary interventions based on their probability of diabetes remission.
- The researchers evaluated weight loss and hormone levels at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
- Changes in hormones were also compared among patients who received dietary intervention and those who underwent bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic gastric banding.
TAKEAWAY:
- In women, testosterone levels decreased and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels increased at 6 months; these changes were maintained at 24 and 36 months and remained statistically significant when controlled for age and menopausal status.
- In men, testosterone levels were significantly higher at 12, 24, and 36 months, and SHBG levels increased at 12 and 24 months. There were no differences in the estradiol levels among men and women.
- Women who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery experienced the greatest weight loss and the largest reduction (54%) in testosterone levels (P = .004), and sleeve gastrectomy led to an increase of 51% in SHBG levels (P = .0001), all compared with dietary interventions. In men, there were no differences in testosterone and SHBG levels between the diet and surgical groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and metabolic parameters is crucial for patients undergoing bariatric procedures to ensure long-term optimal health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, MD, PhD, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, and was published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitations were a small sample size, lack of randomization, and absence of data on clinical outcomes related to hormone changes. Additionally, the researchers did not evaluate women for polycystic ovary syndrome or menstrual irregularities, and the clinical significance of testosterone reductions within the normal range remains unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council. Some authors have received honoraria and consulting and research support from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In middle-aged patients with severe obesity, changes in endogenous sex hormones may be proportional to the amount of weight loss after bariatric surgery and dietary intervention, leading to an improved hormonal balance, with more pronounced androgen changes in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Obesity-related hormonal imbalances are common among those seeking weight loss treatment.
- This prospective observational study evaluated the incremental effect of weight loss by three bariatric procedures and a dietary intervention on endogenous sex hormones in men and women over 3 years.
- The study included 61 adults (median age, 50.9 years; baseline mean body mass index, 40.2; 72% women) from obesity clinics and private bariatric services in Sydney, Australia, between 2009 and 2012, who underwent bariatric surgery or received dietary interventions based on their probability of diabetes remission.
- The researchers evaluated weight loss and hormone levels at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
- Changes in hormones were also compared among patients who received dietary intervention and those who underwent bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic gastric banding.
TAKEAWAY:
- In women, testosterone levels decreased and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels increased at 6 months; these changes were maintained at 24 and 36 months and remained statistically significant when controlled for age and menopausal status.
- In men, testosterone levels were significantly higher at 12, 24, and 36 months, and SHBG levels increased at 12 and 24 months. There were no differences in the estradiol levels among men and women.
- Women who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery experienced the greatest weight loss and the largest reduction (54%) in testosterone levels (P = .004), and sleeve gastrectomy led to an increase of 51% in SHBG levels (P = .0001), all compared with dietary interventions. In men, there were no differences in testosterone and SHBG levels between the diet and surgical groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and metabolic parameters is crucial for patients undergoing bariatric procedures to ensure long-term optimal health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, MD, PhD, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, and was published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitations were a small sample size, lack of randomization, and absence of data on clinical outcomes related to hormone changes. Additionally, the researchers did not evaluate women for polycystic ovary syndrome or menstrual irregularities, and the clinical significance of testosterone reductions within the normal range remains unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council. Some authors have received honoraria and consulting and research support from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In middle-aged patients with severe obesity, changes in endogenous sex hormones may be proportional to the amount of weight loss after bariatric surgery and dietary intervention, leading to an improved hormonal balance, with more pronounced androgen changes in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Obesity-related hormonal imbalances are common among those seeking weight loss treatment.
- This prospective observational study evaluated the incremental effect of weight loss by three bariatric procedures and a dietary intervention on endogenous sex hormones in men and women over 3 years.
- The study included 61 adults (median age, 50.9 years; baseline mean body mass index, 40.2; 72% women) from obesity clinics and private bariatric services in Sydney, Australia, between 2009 and 2012, who underwent bariatric surgery or received dietary interventions based on their probability of diabetes remission.
- The researchers evaluated weight loss and hormone levels at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
- Changes in hormones were also compared among patients who received dietary intervention and those who underwent bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic gastric banding.
TAKEAWAY:
- In women, testosterone levels decreased and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels increased at 6 months; these changes were maintained at 24 and 36 months and remained statistically significant when controlled for age and menopausal status.
- In men, testosterone levels were significantly higher at 12, 24, and 36 months, and SHBG levels increased at 12 and 24 months. There were no differences in the estradiol levels among men and women.
- Women who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery experienced the greatest weight loss and the largest reduction (54%) in testosterone levels (P = .004), and sleeve gastrectomy led to an increase of 51% in SHBG levels (P = .0001), all compared with dietary interventions. In men, there were no differences in testosterone and SHBG levels between the diet and surgical groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and metabolic parameters is crucial for patients undergoing bariatric procedures to ensure long-term optimal health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, MD, PhD, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, and was published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitations were a small sample size, lack of randomization, and absence of data on clinical outcomes related to hormone changes. Additionally, the researchers did not evaluate women for polycystic ovary syndrome or menstrual irregularities, and the clinical significance of testosterone reductions within the normal range remains unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council. Some authors have received honoraria and consulting and research support from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Links Melasma With Comorbidities, Races, Ethnicities
TOPLINE:
A study found significant associations between melasma and several comorbidities, including hypertension and hormonal contraception use, which were the most common.
METHODOLOGY:
- Melasma predominantly affects young women of color and often worsens in hyperestrogen states; understanding the association with comorbidities can improve surveillance and treatment strategies.
- Researchers evaluated 41,283 patients with melasma (mean age, 48.8 years; 93% women) from the TriNetX database and an equal number of matched control individuals.
- The main outcome was comorbidities including allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, anticonvulsants, diabetes, hormonal contraceptives, hypothyroidism, hypertension, lupus, rosacea, skin cancer, and malignancy.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among those with melasma, 25% had hypertension and 24% used hormonal contraception, the two most commonly associated risk factors identified.
- Rosacea (odds ratio [OR], 5.1), atopic dermatitis (OR, 3.3), lupus (OR, 2.5), history of skin cancer (OR, 2.5), and history of internal malignancy (OR, 2.1) were associated with the highest risk of developing melasma (P < .01 for all).
- Asian (OR, 2.0; P < .01) and “other/unknown” races (OR, 1.7; P < .01) and Hispanic ethnicity (OR, 1.3; P < .01) were also significantly associated with melasma, while the odds were slightly lower among White, Black/African American, and “not Hispanic” groups (ORs, 0.8; P < .01 for all groups).
IN PRACTICE:
the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ajay N. Sharma, MD, MBA, of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, Irvine, was published online in Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations included the retrospective design, potential misclassification of diagnoses, and the inability to establish causality.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any funding sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A study found significant associations between melasma and several comorbidities, including hypertension and hormonal contraception use, which were the most common.
METHODOLOGY:
- Melasma predominantly affects young women of color and often worsens in hyperestrogen states; understanding the association with comorbidities can improve surveillance and treatment strategies.
- Researchers evaluated 41,283 patients with melasma (mean age, 48.8 years; 93% women) from the TriNetX database and an equal number of matched control individuals.
- The main outcome was comorbidities including allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, anticonvulsants, diabetes, hormonal contraceptives, hypothyroidism, hypertension, lupus, rosacea, skin cancer, and malignancy.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among those with melasma, 25% had hypertension and 24% used hormonal contraception, the two most commonly associated risk factors identified.
- Rosacea (odds ratio [OR], 5.1), atopic dermatitis (OR, 3.3), lupus (OR, 2.5), history of skin cancer (OR, 2.5), and history of internal malignancy (OR, 2.1) were associated with the highest risk of developing melasma (P < .01 for all).
- Asian (OR, 2.0; P < .01) and “other/unknown” races (OR, 1.7; P < .01) and Hispanic ethnicity (OR, 1.3; P < .01) were also significantly associated with melasma, while the odds were slightly lower among White, Black/African American, and “not Hispanic” groups (ORs, 0.8; P < .01 for all groups).
IN PRACTICE:
the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ajay N. Sharma, MD, MBA, of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, Irvine, was published online in Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations included the retrospective design, potential misclassification of diagnoses, and the inability to establish causality.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any funding sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A study found significant associations between melasma and several comorbidities, including hypertension and hormonal contraception use, which were the most common.
METHODOLOGY:
- Melasma predominantly affects young women of color and often worsens in hyperestrogen states; understanding the association with comorbidities can improve surveillance and treatment strategies.
- Researchers evaluated 41,283 patients with melasma (mean age, 48.8 years; 93% women) from the TriNetX database and an equal number of matched control individuals.
- The main outcome was comorbidities including allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, anticonvulsants, diabetes, hormonal contraceptives, hypothyroidism, hypertension, lupus, rosacea, skin cancer, and malignancy.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among those with melasma, 25% had hypertension and 24% used hormonal contraception, the two most commonly associated risk factors identified.
- Rosacea (odds ratio [OR], 5.1), atopic dermatitis (OR, 3.3), lupus (OR, 2.5), history of skin cancer (OR, 2.5), and history of internal malignancy (OR, 2.1) were associated with the highest risk of developing melasma (P < .01 for all).
- Asian (OR, 2.0; P < .01) and “other/unknown” races (OR, 1.7; P < .01) and Hispanic ethnicity (OR, 1.3; P < .01) were also significantly associated with melasma, while the odds were slightly lower among White, Black/African American, and “not Hispanic” groups (ORs, 0.8; P < .01 for all groups).
IN PRACTICE:
the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ajay N. Sharma, MD, MBA, of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, Irvine, was published online in Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations included the retrospective design, potential misclassification of diagnoses, and the inability to establish causality.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any funding sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Government Accuses Health System of Paying Docs Outrageous Salaries for Patient Referrals
Strapped for cash and searching for new profits, Tennessee-based Erlanger Health System illegally paid excessive salaries to physicians in exchange for patient referrals, the US government alleged in a federal lawsuit.
Erlanger changed its compensation model to entice revenue-generating doctors, paying some two to three times the median salary for their specialty, according to the complaint.
The physicians in turn referred numerous patients to Erlanger, and the health system submitted claims to Medicare for the referred services in violation of the Stark Law, according to the suit, filed in US District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.
The government’s complaint “serves as a warning” to healthcare providers who try to boost profits through improper financial arrangements with referring physicians, said Tamala E. Miles, Special Agent in Charge for the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG).
In a statement provided to this news organization, Erlanger denied the allegations and said it would “vigorously” defend the lawsuit.
“Erlanger paid physicians based on amounts that outside experts advised was fair market value,” Erlanger officials said in the statement. “Erlanger did not pay for referrals. A complete picture of the facts will demonstrate that the allegations lack merit and tell a very different story than what the government now claims.”
The Erlanger case is a reminder to physicians to consult their own knowledgeable advisors when considering financial arrangements with hospitals, said William Sarraille, JD, adjunct professor for the University of Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law in Baltimore and a regulatory consultant.
“There is a tendency by physicians when contracting ... to rely on [hospitals’] perceived compliance and legal expertise,” Mr. Sarraille told this news organization. “This case illustrates the risks in doing so. Sometimes bigger doesn’t translate into more sophisticated or more effective from a compliance perspective.”
Stark Law Prohibits Kickbacks
The Stark Law prohibits hospitals from billing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for services referred by a physician with whom the hospital has an improper financial relationship.
CMS paid Erlanger about $27.8 million for claims stemming from the improper financial arrangements, the government contends.
“HHS-OIG will continue to investigate such deals to prevent financial arrangements that could compromise impartial medical judgment, increase healthcare costs, and erode public trust in the healthcare system,” Ms. Miles said in a statement.
Suit: Health System’s Money Woes Led to Illegal Arrangements
Erlanger’s financial troubles allegedly started after a previous run-in with the US government over false claims.
In 2005, Erlanger Health System agreed to pay the government $40 million to resolve allegations that it knowingly submitted false claims to Medicare, according to the government’s complaint. At the time, Erlanger entered into a Corporate Integrity Agreement (CIA) with the OIG that required Erlanger to put controls in place to ensure its financial relationships did not violate the Stark Law.
Erlanger’s agreement with OIG ended in 2010. Over the next 3 years, the health system lost nearly $32 million and in fiscal year 2013, had only 65 days of cash on hand, according to the government’s lawsuit.
Beginning in 2013, Erlanger allegedly implemented a strategy to increase profits by employing more physicians, particularly specialists from competing hospitals whose patients would need costly hospital stays, according to the complaint.
Once hired, Erlanger’s physicians were expected to treat patients at Erlanger’s hospitals and refer them to other providers within the health system, the suit claims. Erlanger also relaxed or eliminated the oversight and controls on physician compensation put in place under the CIA. For example, Erlanger’s CEO signed some compensation contracts before its chief compliance officer could review them and no longer allowed the compliance officer to vote on whether to approve compensation arrangements, according to the complaint.
Erlanger also changed its compensation model to include large salaries for medical director and academic positions and allegedly paid such salaries to physicians without ensuring the required work was performed. As a result, Erlanger physicians with profitable referrals were among the highest paid in the nation for their specialties, the government claims. For example, according to the complaint:
- Erlanger paid an electrophysiologist an annual clinical salary of $816,701, a medical director salary of $101,080, an academic salary of $59,322, and a productivity incentive based on work relative value units (wRVUs). The medical director and academic salaries paid were near the 90th percentile of comparable salaries in the specialty.
- The health system paid a neurosurgeon a base salary of $654,735, a productivity incentive based on wRVUs, and payments for excess call coverage ranging from $400 to $1000 per 24-hour shift. In 2016, the neurosurgeon made $500,000 in excess call payments.
- Erlanger paid a cardiothoracic surgeon a base clinical salary of $1,070,000, a sign-on bonus of $150,000, a retention bonus of $100,000 (payable in the 4th year of the contract), and a program incentive of up to $150,000 per year.
In addition, Erlanger ignored patient safety concerns about some of its high revenue-generating physicians, the government claims.
For instance, Erlanger received multiple complaints that a cardiothoracic surgeon was misusing an expensive form of life support in which pumps and oxygenators take over heart and lung function. Overuse of the equipment prolonged patients’ hospital stays and increased the hospital fees generated by the surgeon, according to the complaint. Staff also raised concerns about the cardiothoracic surgeon’s patient outcomes.
But Erlanger disregarded the concerns and in 2018, increased the cardiothoracic surgeon’s retention bonus from $100,000 to $250,000, the suit alleges. A year later, the health system increased his base salary from $1,070,000 to $1,195,000.
Health care compensation and billing consultants alerted Erlanger that it was overpaying salaries and handing out bonuses based on measures that overstated the work physicians were performing, but Erlanger ignored the warnings, according to the complaint.
Administrators allegedly resisted efforts by the chief compliance officer to hire an outside consultant to review its compensation models. Erlanger fired the compliance officer in 2019.
The former chief compliance officer and another administrator filed a whistleblower lawsuit against Erlanger in 2021. The two administrators are relators in the government’s July 2024 lawsuit.
How to Protect Yourself From Illegal Hospital Deals
The Erlanger case is the latest in a series of recent complaints by the federal government involving financial arrangements between hospitals and physicians.
In December 2023, Indianapolis-based Community Health Network Inc. agreed to pay the government $345 million to resolve claims that it paid physicians above fair market value and awarded bonuses tied to referrals in violation of the Stark Law.
Also in 2023, Saginaw, Michigan–based Covenant HealthCare and two physicians paid the government $69 million to settle allegations that administrators engaged in improper financial arrangements with referring physicians and a physician-owned investment group. In another 2023 case, Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston agreed to pay $5.7 million to resolve claims that some of its physician compensation plans violated the Stark Law.
Before you enter into a financial arrangement with a hospital, it’s also important to examine what percentile the aggregate compensation would reflect, law professor Mr. Sarraille said. The Erlanger case highlights federal officials’ suspicion of compensation, in aggregate, that exceeds the 90th percentile and increased attention to compensation that exceeds the 75th percentile, he said.
To research compensation levels, doctors can review the Medical Group Management Association’s annual compensation report or search its compensation data.
Before signing any contracts, Mr. Sarraille suggests, physicians should also consider whether the hospital shares the same values. Ask physicians at the hospital what they have to say about the hospital’s culture, vision, and values. Have physicians left the hospital after their practices were acquired? Consider speaking with them to learn why.
Keep in mind that a doctor’s reputation could be impacted by a compliance complaint, regardless of whether it’s directed at the hospital and not the employed physician, Mr. Sarraille said.
“The [Erlanger] complaint focuses on the compensation of specific, named physicians saying they were wildly overcompensated,” he said. “The implication is that they sold their referral power in exchange for a pay day. It’s a bad look, no matter how the case evolves from here.”
Physicians could also face their own liability risk under the Stark Law and False Claims Act, depending on the circumstances. In the event of related quality-of-care issues, medical liability could come into play, Mr. Sarraille noted. In such cases, plaintiffs’ attorneys may see an opportunity to boost their claims with allegations that the patient harm was a function of “chasing compensation dollars,” Mr. Sarraille said.
“Where that happens, plaintiff lawyers see the potential for crippling punitive damages, which might not be covered by an insurer,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Strapped for cash and searching for new profits, Tennessee-based Erlanger Health System illegally paid excessive salaries to physicians in exchange for patient referrals, the US government alleged in a federal lawsuit.
Erlanger changed its compensation model to entice revenue-generating doctors, paying some two to three times the median salary for their specialty, according to the complaint.
The physicians in turn referred numerous patients to Erlanger, and the health system submitted claims to Medicare for the referred services in violation of the Stark Law, according to the suit, filed in US District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.
The government’s complaint “serves as a warning” to healthcare providers who try to boost profits through improper financial arrangements with referring physicians, said Tamala E. Miles, Special Agent in Charge for the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG).
In a statement provided to this news organization, Erlanger denied the allegations and said it would “vigorously” defend the lawsuit.
“Erlanger paid physicians based on amounts that outside experts advised was fair market value,” Erlanger officials said in the statement. “Erlanger did not pay for referrals. A complete picture of the facts will demonstrate that the allegations lack merit and tell a very different story than what the government now claims.”
The Erlanger case is a reminder to physicians to consult their own knowledgeable advisors when considering financial arrangements with hospitals, said William Sarraille, JD, adjunct professor for the University of Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law in Baltimore and a regulatory consultant.
“There is a tendency by physicians when contracting ... to rely on [hospitals’] perceived compliance and legal expertise,” Mr. Sarraille told this news organization. “This case illustrates the risks in doing so. Sometimes bigger doesn’t translate into more sophisticated or more effective from a compliance perspective.”
Stark Law Prohibits Kickbacks
The Stark Law prohibits hospitals from billing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for services referred by a physician with whom the hospital has an improper financial relationship.
CMS paid Erlanger about $27.8 million for claims stemming from the improper financial arrangements, the government contends.
“HHS-OIG will continue to investigate such deals to prevent financial arrangements that could compromise impartial medical judgment, increase healthcare costs, and erode public trust in the healthcare system,” Ms. Miles said in a statement.
Suit: Health System’s Money Woes Led to Illegal Arrangements
Erlanger’s financial troubles allegedly started after a previous run-in with the US government over false claims.
In 2005, Erlanger Health System agreed to pay the government $40 million to resolve allegations that it knowingly submitted false claims to Medicare, according to the government’s complaint. At the time, Erlanger entered into a Corporate Integrity Agreement (CIA) with the OIG that required Erlanger to put controls in place to ensure its financial relationships did not violate the Stark Law.
Erlanger’s agreement with OIG ended in 2010. Over the next 3 years, the health system lost nearly $32 million and in fiscal year 2013, had only 65 days of cash on hand, according to the government’s lawsuit.
Beginning in 2013, Erlanger allegedly implemented a strategy to increase profits by employing more physicians, particularly specialists from competing hospitals whose patients would need costly hospital stays, according to the complaint.
Once hired, Erlanger’s physicians were expected to treat patients at Erlanger’s hospitals and refer them to other providers within the health system, the suit claims. Erlanger also relaxed or eliminated the oversight and controls on physician compensation put in place under the CIA. For example, Erlanger’s CEO signed some compensation contracts before its chief compliance officer could review them and no longer allowed the compliance officer to vote on whether to approve compensation arrangements, according to the complaint.
Erlanger also changed its compensation model to include large salaries for medical director and academic positions and allegedly paid such salaries to physicians without ensuring the required work was performed. As a result, Erlanger physicians with profitable referrals were among the highest paid in the nation for their specialties, the government claims. For example, according to the complaint:
- Erlanger paid an electrophysiologist an annual clinical salary of $816,701, a medical director salary of $101,080, an academic salary of $59,322, and a productivity incentive based on work relative value units (wRVUs). The medical director and academic salaries paid were near the 90th percentile of comparable salaries in the specialty.
- The health system paid a neurosurgeon a base salary of $654,735, a productivity incentive based on wRVUs, and payments for excess call coverage ranging from $400 to $1000 per 24-hour shift. In 2016, the neurosurgeon made $500,000 in excess call payments.
- Erlanger paid a cardiothoracic surgeon a base clinical salary of $1,070,000, a sign-on bonus of $150,000, a retention bonus of $100,000 (payable in the 4th year of the contract), and a program incentive of up to $150,000 per year.
In addition, Erlanger ignored patient safety concerns about some of its high revenue-generating physicians, the government claims.
For instance, Erlanger received multiple complaints that a cardiothoracic surgeon was misusing an expensive form of life support in which pumps and oxygenators take over heart and lung function. Overuse of the equipment prolonged patients’ hospital stays and increased the hospital fees generated by the surgeon, according to the complaint. Staff also raised concerns about the cardiothoracic surgeon’s patient outcomes.
But Erlanger disregarded the concerns and in 2018, increased the cardiothoracic surgeon’s retention bonus from $100,000 to $250,000, the suit alleges. A year later, the health system increased his base salary from $1,070,000 to $1,195,000.
Health care compensation and billing consultants alerted Erlanger that it was overpaying salaries and handing out bonuses based on measures that overstated the work physicians were performing, but Erlanger ignored the warnings, according to the complaint.
Administrators allegedly resisted efforts by the chief compliance officer to hire an outside consultant to review its compensation models. Erlanger fired the compliance officer in 2019.
The former chief compliance officer and another administrator filed a whistleblower lawsuit against Erlanger in 2021. The two administrators are relators in the government’s July 2024 lawsuit.
How to Protect Yourself From Illegal Hospital Deals
The Erlanger case is the latest in a series of recent complaints by the federal government involving financial arrangements between hospitals and physicians.
In December 2023, Indianapolis-based Community Health Network Inc. agreed to pay the government $345 million to resolve claims that it paid physicians above fair market value and awarded bonuses tied to referrals in violation of the Stark Law.
Also in 2023, Saginaw, Michigan–based Covenant HealthCare and two physicians paid the government $69 million to settle allegations that administrators engaged in improper financial arrangements with referring physicians and a physician-owned investment group. In another 2023 case, Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston agreed to pay $5.7 million to resolve claims that some of its physician compensation plans violated the Stark Law.
Before you enter into a financial arrangement with a hospital, it’s also important to examine what percentile the aggregate compensation would reflect, law professor Mr. Sarraille said. The Erlanger case highlights federal officials’ suspicion of compensation, in aggregate, that exceeds the 90th percentile and increased attention to compensation that exceeds the 75th percentile, he said.
To research compensation levels, doctors can review the Medical Group Management Association’s annual compensation report or search its compensation data.
Before signing any contracts, Mr. Sarraille suggests, physicians should also consider whether the hospital shares the same values. Ask physicians at the hospital what they have to say about the hospital’s culture, vision, and values. Have physicians left the hospital after their practices were acquired? Consider speaking with them to learn why.
Keep in mind that a doctor’s reputation could be impacted by a compliance complaint, regardless of whether it’s directed at the hospital and not the employed physician, Mr. Sarraille said.
“The [Erlanger] complaint focuses on the compensation of specific, named physicians saying they were wildly overcompensated,” he said. “The implication is that they sold their referral power in exchange for a pay day. It’s a bad look, no matter how the case evolves from here.”
Physicians could also face their own liability risk under the Stark Law and False Claims Act, depending on the circumstances. In the event of related quality-of-care issues, medical liability could come into play, Mr. Sarraille noted. In such cases, plaintiffs’ attorneys may see an opportunity to boost their claims with allegations that the patient harm was a function of “chasing compensation dollars,” Mr. Sarraille said.
“Where that happens, plaintiff lawyers see the potential for crippling punitive damages, which might not be covered by an insurer,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Strapped for cash and searching for new profits, Tennessee-based Erlanger Health System illegally paid excessive salaries to physicians in exchange for patient referrals, the US government alleged in a federal lawsuit.
Erlanger changed its compensation model to entice revenue-generating doctors, paying some two to three times the median salary for their specialty, according to the complaint.
The physicians in turn referred numerous patients to Erlanger, and the health system submitted claims to Medicare for the referred services in violation of the Stark Law, according to the suit, filed in US District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.
The government’s complaint “serves as a warning” to healthcare providers who try to boost profits through improper financial arrangements with referring physicians, said Tamala E. Miles, Special Agent in Charge for the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG).
In a statement provided to this news organization, Erlanger denied the allegations and said it would “vigorously” defend the lawsuit.
“Erlanger paid physicians based on amounts that outside experts advised was fair market value,” Erlanger officials said in the statement. “Erlanger did not pay for referrals. A complete picture of the facts will demonstrate that the allegations lack merit and tell a very different story than what the government now claims.”
The Erlanger case is a reminder to physicians to consult their own knowledgeable advisors when considering financial arrangements with hospitals, said William Sarraille, JD, adjunct professor for the University of Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law in Baltimore and a regulatory consultant.
“There is a tendency by physicians when contracting ... to rely on [hospitals’] perceived compliance and legal expertise,” Mr. Sarraille told this news organization. “This case illustrates the risks in doing so. Sometimes bigger doesn’t translate into more sophisticated or more effective from a compliance perspective.”
Stark Law Prohibits Kickbacks
The Stark Law prohibits hospitals from billing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for services referred by a physician with whom the hospital has an improper financial relationship.
CMS paid Erlanger about $27.8 million for claims stemming from the improper financial arrangements, the government contends.
“HHS-OIG will continue to investigate such deals to prevent financial arrangements that could compromise impartial medical judgment, increase healthcare costs, and erode public trust in the healthcare system,” Ms. Miles said in a statement.
Suit: Health System’s Money Woes Led to Illegal Arrangements
Erlanger’s financial troubles allegedly started after a previous run-in with the US government over false claims.
In 2005, Erlanger Health System agreed to pay the government $40 million to resolve allegations that it knowingly submitted false claims to Medicare, according to the government’s complaint. At the time, Erlanger entered into a Corporate Integrity Agreement (CIA) with the OIG that required Erlanger to put controls in place to ensure its financial relationships did not violate the Stark Law.
Erlanger’s agreement with OIG ended in 2010. Over the next 3 years, the health system lost nearly $32 million and in fiscal year 2013, had only 65 days of cash on hand, according to the government’s lawsuit.
Beginning in 2013, Erlanger allegedly implemented a strategy to increase profits by employing more physicians, particularly specialists from competing hospitals whose patients would need costly hospital stays, according to the complaint.
Once hired, Erlanger’s physicians were expected to treat patients at Erlanger’s hospitals and refer them to other providers within the health system, the suit claims. Erlanger also relaxed or eliminated the oversight and controls on physician compensation put in place under the CIA. For example, Erlanger’s CEO signed some compensation contracts before its chief compliance officer could review them and no longer allowed the compliance officer to vote on whether to approve compensation arrangements, according to the complaint.
Erlanger also changed its compensation model to include large salaries for medical director and academic positions and allegedly paid such salaries to physicians without ensuring the required work was performed. As a result, Erlanger physicians with profitable referrals were among the highest paid in the nation for their specialties, the government claims. For example, according to the complaint:
- Erlanger paid an electrophysiologist an annual clinical salary of $816,701, a medical director salary of $101,080, an academic salary of $59,322, and a productivity incentive based on work relative value units (wRVUs). The medical director and academic salaries paid were near the 90th percentile of comparable salaries in the specialty.
- The health system paid a neurosurgeon a base salary of $654,735, a productivity incentive based on wRVUs, and payments for excess call coverage ranging from $400 to $1000 per 24-hour shift. In 2016, the neurosurgeon made $500,000 in excess call payments.
- Erlanger paid a cardiothoracic surgeon a base clinical salary of $1,070,000, a sign-on bonus of $150,000, a retention bonus of $100,000 (payable in the 4th year of the contract), and a program incentive of up to $150,000 per year.
In addition, Erlanger ignored patient safety concerns about some of its high revenue-generating physicians, the government claims.
For instance, Erlanger received multiple complaints that a cardiothoracic surgeon was misusing an expensive form of life support in which pumps and oxygenators take over heart and lung function. Overuse of the equipment prolonged patients’ hospital stays and increased the hospital fees generated by the surgeon, according to the complaint. Staff also raised concerns about the cardiothoracic surgeon’s patient outcomes.
But Erlanger disregarded the concerns and in 2018, increased the cardiothoracic surgeon’s retention bonus from $100,000 to $250,000, the suit alleges. A year later, the health system increased his base salary from $1,070,000 to $1,195,000.
Health care compensation and billing consultants alerted Erlanger that it was overpaying salaries and handing out bonuses based on measures that overstated the work physicians were performing, but Erlanger ignored the warnings, according to the complaint.
Administrators allegedly resisted efforts by the chief compliance officer to hire an outside consultant to review its compensation models. Erlanger fired the compliance officer in 2019.
The former chief compliance officer and another administrator filed a whistleblower lawsuit against Erlanger in 2021. The two administrators are relators in the government’s July 2024 lawsuit.
How to Protect Yourself From Illegal Hospital Deals
The Erlanger case is the latest in a series of recent complaints by the federal government involving financial arrangements between hospitals and physicians.
In December 2023, Indianapolis-based Community Health Network Inc. agreed to pay the government $345 million to resolve claims that it paid physicians above fair market value and awarded bonuses tied to referrals in violation of the Stark Law.
Also in 2023, Saginaw, Michigan–based Covenant HealthCare and two physicians paid the government $69 million to settle allegations that administrators engaged in improper financial arrangements with referring physicians and a physician-owned investment group. In another 2023 case, Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston agreed to pay $5.7 million to resolve claims that some of its physician compensation plans violated the Stark Law.
Before you enter into a financial arrangement with a hospital, it’s also important to examine what percentile the aggregate compensation would reflect, law professor Mr. Sarraille said. The Erlanger case highlights federal officials’ suspicion of compensation, in aggregate, that exceeds the 90th percentile and increased attention to compensation that exceeds the 75th percentile, he said.
To research compensation levels, doctors can review the Medical Group Management Association’s annual compensation report or search its compensation data.
Before signing any contracts, Mr. Sarraille suggests, physicians should also consider whether the hospital shares the same values. Ask physicians at the hospital what they have to say about the hospital’s culture, vision, and values. Have physicians left the hospital after their practices were acquired? Consider speaking with them to learn why.
Keep in mind that a doctor’s reputation could be impacted by a compliance complaint, regardless of whether it’s directed at the hospital and not the employed physician, Mr. Sarraille said.
“The [Erlanger] complaint focuses on the compensation of specific, named physicians saying they were wildly overcompensated,” he said. “The implication is that they sold their referral power in exchange for a pay day. It’s a bad look, no matter how the case evolves from here.”
Physicians could also face their own liability risk under the Stark Law and False Claims Act, depending on the circumstances. In the event of related quality-of-care issues, medical liability could come into play, Mr. Sarraille noted. In such cases, plaintiffs’ attorneys may see an opportunity to boost their claims with allegations that the patient harm was a function of “chasing compensation dollars,” Mr. Sarraille said.
“Where that happens, plaintiff lawyers see the potential for crippling punitive damages, which might not be covered by an insurer,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Non-Prescription Semaglutide Purchased Online Poses Risks
Semaglutide products sold online without a prescription may pose multiple risks to consumers, new research found.
Of six test purchases of semaglutide products offered online without a prescription, only three were actually received. The other three vendors demanded additional payment. Of the three delivered, one was potentially contaminated, and all three contained higher concentrations of semaglutide than indicated on the label, potentially resulting in an overdose.
“Semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products,” wrote Amir Reza Ashraf, PharmD, of the University of Pécs, Hungary, and colleagues in their paper, published online on August 2, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted in July 2023, but its publication comes a week after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an alert about dosing errors in compounded semaglutide, which typically does require a prescription.
Study coauthor Tim K. Mackey, PhD, told this news organization, “Compounding pharmacies are another element of this risk that has become more prominent now but arguably have more controls if prescribed appropriately, while the traditional ‘no-prescription’ online market still exists and will continue to evolve.”
Overall, said Dr. Mackey, professor of global health at the University of California San Diego and director of the Global Health Policy and Data Institute,
He advises clinicians to actively discuss with their patients the risks associated with semaglutide and, specifically, the dangers of buying it online. “Clinicians can act as a primary information source for patient safety information by letting their patients know about these risks ... and also asking where patients get their medications in case they are concerned about reports of adverse events or other patient safety issues.”
Buyer Beware: Online Semaglutide Purchases Not as They Seem
The investigators began by searching online for websites advertising semaglutide without a prescription. They ordered products from six online vendors that showed up prominently in the searches. Of those, three offered prefilled 0.25 mg/dose semaglutide injection pens, while the other three sold vials of lyophilized semaglutide powder to be reconstituted to solution for injection. Prices for the smallest dose and quantity ranged from $113 to $360.
Only three of the ordered products — all vials — actually showed up. The advertised prefilled pens were all nondelivery scams, with requests for an extra payment of $650-$1200 purportedly to clear customs. This was confirmed as fraudulent by customs agencies, the authors noted.
The three vial products were received and assessed physically, of both the packaging and the actual product, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine purity and peptide concentration, and microbiologically, to examine sterility.
Using a checklist from the International Pharmaceutical Federation, Dr. Ashraf and colleagues found “clear discrepancies in regulatory registration information, accurate labeling, and evidence products were likely unregistered or unlicensed.”
Quality testing showed that one sample had an elevated presence of endotoxin suggesting possible contamination. While all three actually did contain semaglutide, the measured content exceeded the labeled amount by 29%-39%, posing a risk that users could receive up to 39% more than intended per injection, “particularly concerning if a consumer has to reconstitute and self-inject,” Dr. Mackey noted.
At least one of these sites in this study, “semaspace.com,” was subsequently sent a warning letter by the FDA for unauthorized semaglutide sale, Mackey noted.
Unfortunately, he told this news organization, these dangers are likely to persist. “There is a strong market opportunity to introduce counterfeit and unauthorized versions of semaglutide. Counterfeiters will continue to innovate with where they sell products, what products they offer, and how they mislead consumers about the safety and legality of what they are offering online. We are likely just at the beginning of counterfeiting of semaglutide, and it is likely that these false products will become endemic in our supply chain.”
The research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. The authors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide products sold online without a prescription may pose multiple risks to consumers, new research found.
Of six test purchases of semaglutide products offered online without a prescription, only three were actually received. The other three vendors demanded additional payment. Of the three delivered, one was potentially contaminated, and all three contained higher concentrations of semaglutide than indicated on the label, potentially resulting in an overdose.
“Semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products,” wrote Amir Reza Ashraf, PharmD, of the University of Pécs, Hungary, and colleagues in their paper, published online on August 2, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted in July 2023, but its publication comes a week after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an alert about dosing errors in compounded semaglutide, which typically does require a prescription.
Study coauthor Tim K. Mackey, PhD, told this news organization, “Compounding pharmacies are another element of this risk that has become more prominent now but arguably have more controls if prescribed appropriately, while the traditional ‘no-prescription’ online market still exists and will continue to evolve.”
Overall, said Dr. Mackey, professor of global health at the University of California San Diego and director of the Global Health Policy and Data Institute,
He advises clinicians to actively discuss with their patients the risks associated with semaglutide and, specifically, the dangers of buying it online. “Clinicians can act as a primary information source for patient safety information by letting their patients know about these risks ... and also asking where patients get their medications in case they are concerned about reports of adverse events or other patient safety issues.”
Buyer Beware: Online Semaglutide Purchases Not as They Seem
The investigators began by searching online for websites advertising semaglutide without a prescription. They ordered products from six online vendors that showed up prominently in the searches. Of those, three offered prefilled 0.25 mg/dose semaglutide injection pens, while the other three sold vials of lyophilized semaglutide powder to be reconstituted to solution for injection. Prices for the smallest dose and quantity ranged from $113 to $360.
Only three of the ordered products — all vials — actually showed up. The advertised prefilled pens were all nondelivery scams, with requests for an extra payment of $650-$1200 purportedly to clear customs. This was confirmed as fraudulent by customs agencies, the authors noted.
The three vial products were received and assessed physically, of both the packaging and the actual product, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine purity and peptide concentration, and microbiologically, to examine sterility.
Using a checklist from the International Pharmaceutical Federation, Dr. Ashraf and colleagues found “clear discrepancies in regulatory registration information, accurate labeling, and evidence products were likely unregistered or unlicensed.”
Quality testing showed that one sample had an elevated presence of endotoxin suggesting possible contamination. While all three actually did contain semaglutide, the measured content exceeded the labeled amount by 29%-39%, posing a risk that users could receive up to 39% more than intended per injection, “particularly concerning if a consumer has to reconstitute and self-inject,” Dr. Mackey noted.
At least one of these sites in this study, “semaspace.com,” was subsequently sent a warning letter by the FDA for unauthorized semaglutide sale, Mackey noted.
Unfortunately, he told this news organization, these dangers are likely to persist. “There is a strong market opportunity to introduce counterfeit and unauthorized versions of semaglutide. Counterfeiters will continue to innovate with where they sell products, what products they offer, and how they mislead consumers about the safety and legality of what they are offering online. We are likely just at the beginning of counterfeiting of semaglutide, and it is likely that these false products will become endemic in our supply chain.”
The research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. The authors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide products sold online without a prescription may pose multiple risks to consumers, new research found.
Of six test purchases of semaglutide products offered online without a prescription, only three were actually received. The other three vendors demanded additional payment. Of the three delivered, one was potentially contaminated, and all three contained higher concentrations of semaglutide than indicated on the label, potentially resulting in an overdose.
“Semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products,” wrote Amir Reza Ashraf, PharmD, of the University of Pécs, Hungary, and colleagues in their paper, published online on August 2, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted in July 2023, but its publication comes a week after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an alert about dosing errors in compounded semaglutide, which typically does require a prescription.
Study coauthor Tim K. Mackey, PhD, told this news organization, “Compounding pharmacies are another element of this risk that has become more prominent now but arguably have more controls if prescribed appropriately, while the traditional ‘no-prescription’ online market still exists and will continue to evolve.”
Overall, said Dr. Mackey, professor of global health at the University of California San Diego and director of the Global Health Policy and Data Institute,
He advises clinicians to actively discuss with their patients the risks associated with semaglutide and, specifically, the dangers of buying it online. “Clinicians can act as a primary information source for patient safety information by letting their patients know about these risks ... and also asking where patients get their medications in case they are concerned about reports of adverse events or other patient safety issues.”
Buyer Beware: Online Semaglutide Purchases Not as They Seem
The investigators began by searching online for websites advertising semaglutide without a prescription. They ordered products from six online vendors that showed up prominently in the searches. Of those, three offered prefilled 0.25 mg/dose semaglutide injection pens, while the other three sold vials of lyophilized semaglutide powder to be reconstituted to solution for injection. Prices for the smallest dose and quantity ranged from $113 to $360.
Only three of the ordered products — all vials — actually showed up. The advertised prefilled pens were all nondelivery scams, with requests for an extra payment of $650-$1200 purportedly to clear customs. This was confirmed as fraudulent by customs agencies, the authors noted.
The three vial products were received and assessed physically, of both the packaging and the actual product, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine purity and peptide concentration, and microbiologically, to examine sterility.
Using a checklist from the International Pharmaceutical Federation, Dr. Ashraf and colleagues found “clear discrepancies in regulatory registration information, accurate labeling, and evidence products were likely unregistered or unlicensed.”
Quality testing showed that one sample had an elevated presence of endotoxin suggesting possible contamination. While all three actually did contain semaglutide, the measured content exceeded the labeled amount by 29%-39%, posing a risk that users could receive up to 39% more than intended per injection, “particularly concerning if a consumer has to reconstitute and self-inject,” Dr. Mackey noted.
At least one of these sites in this study, “semaspace.com,” was subsequently sent a warning letter by the FDA for unauthorized semaglutide sale, Mackey noted.
Unfortunately, he told this news organization, these dangers are likely to persist. “There is a strong market opportunity to introduce counterfeit and unauthorized versions of semaglutide. Counterfeiters will continue to innovate with where they sell products, what products they offer, and how they mislead consumers about the safety and legality of what they are offering online. We are likely just at the beginning of counterfeiting of semaglutide, and it is likely that these false products will become endemic in our supply chain.”
The research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. The authors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine Doc Charged With $1.5M Fraud
In a case that spotlights the importance of comprehensive financial controls in medical offices,
Michael Lucchesi, MD, who had served as chairman of Emergency Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City, was arraigned on July 9 and pleaded not guilty. Dr. Lucchesi’s attorney, Earl Ward, did not respond to messages from this news organization, but he told the New York Post that “the funds he used were not stolen funds.”
Dr. Lucchesi, who’s in his late 60s, faces nine counts of first- and second-degree grand larceny, first-degree falsifying business records, and third-degree criminal tax fraud. According to a press statement from the district attorney of Kings County, which encompasses the borough of Brooklyn, Dr. Lucchesi is accused of using his clinical practice’s business card for cash advances (about $115,000), high-end pet care ($176,000), personal travel ($348,000), gym membership and personal training ($109,000), catering ($52,000), tuition payments for his children ($46,000), and other expenses such as online shopping, flowers, liquor, and electronics.
Most of the alleged pet care spending — $120,000 — went to the Green Leaf Pet Resort, which has two locations in New Jersey, including one with “56 acres of nature and lots of tail wagging.” Some of the alleged spending on gym membership was at the New York Sports Clubs chain, where monthly membership tops out at $139.99.
The alleged spending occurred between 2016 and 2023 and was discovered by SUNY Downstate during an audit. Dr. Lucchesi reportedly left his position at the hospital, where he made $399,712 in 2022 as a professor, according to public records.
“As a high-ranking doctor at this vital healthcare institution, this defendant was entrusted with access to significant funds, which he allegedly exploited, stealing more than 1 million dollars to pay for a lavish lifestyle,” District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said in a statement.
SUNY Downstate is in a fight for its life amid efforts by New York Governor Kathy Hochul to shut it down. According to The New York Times, it is the only state-run hospital in New York City.
Dr. Lucchesi, who had previously served as the hospital’s chief medical officer and acting head, was released without bail. His next court date is September 25, 2024.
Size of Alleged Theft Is ‘Very Unusual’
David P. Weber, JD, DBA, a professor and fraud specialist at Salisbury University, Salisbury, Maryland, told this news organization that the fraudulent use of a business or purchase credit card is a form of embezzlement and “one of the most frequently seen types of frauds against organizations.”
William J. Kresse, JD, MSA, CPA/CFF, who studies fraud at Governors State University in University Park, Illinois, noted in an interview with this news organization that the high amount of alleged fraud in this case is “very unusual,” as is the period it is said to have occurred (over 6 years).
Mr. Kresse highlighted a 2024 report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, which found that the median fraud loss in healthcare, on the basis of 117 cases, is $100,000. The most common form of fraud in the industry is corruption (47%), followed by billing (38%), noncash theft such as inventory (22%), and expense reimbursement (21%).
The details of the current case suggest that “SUNY Downstate had weak or insufficient internal controls to prevent this type of fraud,” Salisbury University’s Mr. Weber said. “However, research also makes clear that the tenure and position of the perpetrator play a significant role in the size of the fraud. Internal controls are supposed to apply to all employees, but the higher in the organization the perpetrator is, the easier it can be to engage in fraud.”
Even Small Medical Offices Can Act to Prevent Fraud
What can be done to prevent this kind of fraud? “Each employee should be required to submit actual receipts or scanned copies, and the reimbursement requests should be reviewed and inputted by a separate department or office of the organization to ensure that the expenses are legitimate,” Mr. Weber said. “In addition, all credit card statements should be available for review by the organization either simultaneously with the bill going to the employee or available for audit or review at any time without notification to the employee. Expenses that are in certain categories should be prohibited automatically and coded to the card so such a charge is rejected by the credit card bank.”
Smaller businesses — like many medical practices — may not have the manpower to handle these roles. In that case, Mr. Weber said, “The key is segregation or separation of duties. The bookkeeper cannot be the person receiving the bank statements, the payments from patients, and the invoices from vendors. There needs to be at least one other person in the loop to have some level of control.”
One strategy, he said, “is that the practice should institute a policy that only the doctor or owner of the practice can receive the mail, not the bookkeeper. Even if the practice leader does not actually review the bank statements, simply opening them before handing them off to the bookkeeper can provide a level of deterrence [since] the employee may get caught if someone else is reviewing the bank statements.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a case that spotlights the importance of comprehensive financial controls in medical offices,
Michael Lucchesi, MD, who had served as chairman of Emergency Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City, was arraigned on July 9 and pleaded not guilty. Dr. Lucchesi’s attorney, Earl Ward, did not respond to messages from this news organization, but he told the New York Post that “the funds he used were not stolen funds.”
Dr. Lucchesi, who’s in his late 60s, faces nine counts of first- and second-degree grand larceny, first-degree falsifying business records, and third-degree criminal tax fraud. According to a press statement from the district attorney of Kings County, which encompasses the borough of Brooklyn, Dr. Lucchesi is accused of using his clinical practice’s business card for cash advances (about $115,000), high-end pet care ($176,000), personal travel ($348,000), gym membership and personal training ($109,000), catering ($52,000), tuition payments for his children ($46,000), and other expenses such as online shopping, flowers, liquor, and electronics.
Most of the alleged pet care spending — $120,000 — went to the Green Leaf Pet Resort, which has two locations in New Jersey, including one with “56 acres of nature and lots of tail wagging.” Some of the alleged spending on gym membership was at the New York Sports Clubs chain, where monthly membership tops out at $139.99.
The alleged spending occurred between 2016 and 2023 and was discovered by SUNY Downstate during an audit. Dr. Lucchesi reportedly left his position at the hospital, where he made $399,712 in 2022 as a professor, according to public records.
“As a high-ranking doctor at this vital healthcare institution, this defendant was entrusted with access to significant funds, which he allegedly exploited, stealing more than 1 million dollars to pay for a lavish lifestyle,” District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said in a statement.
SUNY Downstate is in a fight for its life amid efforts by New York Governor Kathy Hochul to shut it down. According to The New York Times, it is the only state-run hospital in New York City.
Dr. Lucchesi, who had previously served as the hospital’s chief medical officer and acting head, was released without bail. His next court date is September 25, 2024.
Size of Alleged Theft Is ‘Very Unusual’
David P. Weber, JD, DBA, a professor and fraud specialist at Salisbury University, Salisbury, Maryland, told this news organization that the fraudulent use of a business or purchase credit card is a form of embezzlement and “one of the most frequently seen types of frauds against organizations.”
William J. Kresse, JD, MSA, CPA/CFF, who studies fraud at Governors State University in University Park, Illinois, noted in an interview with this news organization that the high amount of alleged fraud in this case is “very unusual,” as is the period it is said to have occurred (over 6 years).
Mr. Kresse highlighted a 2024 report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, which found that the median fraud loss in healthcare, on the basis of 117 cases, is $100,000. The most common form of fraud in the industry is corruption (47%), followed by billing (38%), noncash theft such as inventory (22%), and expense reimbursement (21%).
The details of the current case suggest that “SUNY Downstate had weak or insufficient internal controls to prevent this type of fraud,” Salisbury University’s Mr. Weber said. “However, research also makes clear that the tenure and position of the perpetrator play a significant role in the size of the fraud. Internal controls are supposed to apply to all employees, but the higher in the organization the perpetrator is, the easier it can be to engage in fraud.”
Even Small Medical Offices Can Act to Prevent Fraud
What can be done to prevent this kind of fraud? “Each employee should be required to submit actual receipts or scanned copies, and the reimbursement requests should be reviewed and inputted by a separate department or office of the organization to ensure that the expenses are legitimate,” Mr. Weber said. “In addition, all credit card statements should be available for review by the organization either simultaneously with the bill going to the employee or available for audit or review at any time without notification to the employee. Expenses that are in certain categories should be prohibited automatically and coded to the card so such a charge is rejected by the credit card bank.”
Smaller businesses — like many medical practices — may not have the manpower to handle these roles. In that case, Mr. Weber said, “The key is segregation or separation of duties. The bookkeeper cannot be the person receiving the bank statements, the payments from patients, and the invoices from vendors. There needs to be at least one other person in the loop to have some level of control.”
One strategy, he said, “is that the practice should institute a policy that only the doctor or owner of the practice can receive the mail, not the bookkeeper. Even if the practice leader does not actually review the bank statements, simply opening them before handing them off to the bookkeeper can provide a level of deterrence [since] the employee may get caught if someone else is reviewing the bank statements.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a case that spotlights the importance of comprehensive financial controls in medical offices,
Michael Lucchesi, MD, who had served as chairman of Emergency Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City, was arraigned on July 9 and pleaded not guilty. Dr. Lucchesi’s attorney, Earl Ward, did not respond to messages from this news organization, but he told the New York Post that “the funds he used were not stolen funds.”
Dr. Lucchesi, who’s in his late 60s, faces nine counts of first- and second-degree grand larceny, first-degree falsifying business records, and third-degree criminal tax fraud. According to a press statement from the district attorney of Kings County, which encompasses the borough of Brooklyn, Dr. Lucchesi is accused of using his clinical practice’s business card for cash advances (about $115,000), high-end pet care ($176,000), personal travel ($348,000), gym membership and personal training ($109,000), catering ($52,000), tuition payments for his children ($46,000), and other expenses such as online shopping, flowers, liquor, and electronics.
Most of the alleged pet care spending — $120,000 — went to the Green Leaf Pet Resort, which has two locations in New Jersey, including one with “56 acres of nature and lots of tail wagging.” Some of the alleged spending on gym membership was at the New York Sports Clubs chain, where monthly membership tops out at $139.99.
The alleged spending occurred between 2016 and 2023 and was discovered by SUNY Downstate during an audit. Dr. Lucchesi reportedly left his position at the hospital, where he made $399,712 in 2022 as a professor, according to public records.
“As a high-ranking doctor at this vital healthcare institution, this defendant was entrusted with access to significant funds, which he allegedly exploited, stealing more than 1 million dollars to pay for a lavish lifestyle,” District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said in a statement.
SUNY Downstate is in a fight for its life amid efforts by New York Governor Kathy Hochul to shut it down. According to The New York Times, it is the only state-run hospital in New York City.
Dr. Lucchesi, who had previously served as the hospital’s chief medical officer and acting head, was released without bail. His next court date is September 25, 2024.
Size of Alleged Theft Is ‘Very Unusual’
David P. Weber, JD, DBA, a professor and fraud specialist at Salisbury University, Salisbury, Maryland, told this news organization that the fraudulent use of a business or purchase credit card is a form of embezzlement and “one of the most frequently seen types of frauds against organizations.”
William J. Kresse, JD, MSA, CPA/CFF, who studies fraud at Governors State University in University Park, Illinois, noted in an interview with this news organization that the high amount of alleged fraud in this case is “very unusual,” as is the period it is said to have occurred (over 6 years).
Mr. Kresse highlighted a 2024 report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, which found that the median fraud loss in healthcare, on the basis of 117 cases, is $100,000. The most common form of fraud in the industry is corruption (47%), followed by billing (38%), noncash theft such as inventory (22%), and expense reimbursement (21%).
The details of the current case suggest that “SUNY Downstate had weak or insufficient internal controls to prevent this type of fraud,” Salisbury University’s Mr. Weber said. “However, research also makes clear that the tenure and position of the perpetrator play a significant role in the size of the fraud. Internal controls are supposed to apply to all employees, but the higher in the organization the perpetrator is, the easier it can be to engage in fraud.”
Even Small Medical Offices Can Act to Prevent Fraud
What can be done to prevent this kind of fraud? “Each employee should be required to submit actual receipts or scanned copies, and the reimbursement requests should be reviewed and inputted by a separate department or office of the organization to ensure that the expenses are legitimate,” Mr. Weber said. “In addition, all credit card statements should be available for review by the organization either simultaneously with the bill going to the employee or available for audit or review at any time without notification to the employee. Expenses that are in certain categories should be prohibited automatically and coded to the card so such a charge is rejected by the credit card bank.”
Smaller businesses — like many medical practices — may not have the manpower to handle these roles. In that case, Mr. Weber said, “The key is segregation or separation of duties. The bookkeeper cannot be the person receiving the bank statements, the payments from patients, and the invoices from vendors. There needs to be at least one other person in the loop to have some level of control.”
One strategy, he said, “is that the practice should institute a policy that only the doctor or owner of the practice can receive the mail, not the bookkeeper. Even if the practice leader does not actually review the bank statements, simply opening them before handing them off to the bookkeeper can provide a level of deterrence [since] the employee may get caught if someone else is reviewing the bank statements.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fruits and Vegetables May Promote Kidney and Cardiovascular Health in Hypertensive Patients
Progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiovascular disease risk in hypertensive adults was significantly slower among those who consumed more fruits and vegetables or oral sodium bicarbonate, compared with controls who received usual care.
A primary focus on pharmacologic strategies has failed to reduced hypertension-related CKD and cardiovascular disease mortality, Nimrit Goraya, MD, of Texas A&M Health Sciences Center College of Medicine, Temple, and colleagues wrote. High-acid diets (those with greater amounts of animal-sourced foods) have been associated with increased incidence and progression of CKD and with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Diets high in fruits and vegetables are associated with reduced CKD and cardiovascular disease but are not routinely used as part of hypertension treatment. The researchers hypothesized that dietary acid reduction could slow kidney disease progression and reduce cardiovascular disease risk.
In a study published in The American Journal of Medicine, the researchers randomized 153 adults aged 18-70 years with hypertension and CKD to fruits and vegetables, oral sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), or usual care; 51 to each group. The fruit and vegetable group received 2-4 cups daily of base-producing food items including apples, apricots, oranges, peaches, pears, raisins, strawberries, carrots, cauliflower, eggplant, lettuce, potatoes, spinach, tomatoes, and zucchini. Participants were not instructed how to incorporate these foods into their diets. The sodium bicarbonate group received an average of four to five NaHCO3 tablets daily (650 mg), divided into two doses.
The mean age of the participants was 48.8 years, 51% were female, and 47% were African American. The primary outcome was CKD progression and cardiovascular disease risk over 5 years. All participants met criteria at baseline for macroalbuminuria (a urine albumin to creatinine ratio of at least 200 mg/g) and were considered at increased risk for CKD progression.
Over the 5-year follow-up, CKD progression was significantly slower in the groups receiving fruits and vegetables and oral sodium bicarbonate, compared with usual care, based on trajectories showing a lower decline of estimated glomerular filtration rates (mean declines of 1.08 and 1.17 for fruits/vegetables and NaHCO3, respectively, vs 19.4 for usual care, P < .001 for both).
However, systolic blood pressure and subsequent cardiovascular disease risk indicators were lower only in the fruit and vegetable group, compared with both the NaHCO3 or usual-care groups over the long term. “Specifically, with fruits and vegetables, systolic blood pressure, plasma LDL and Lp(a) cholesterol, and body mass index decreased from baseline, consistent with better cardiovascular disease protection,” the researchers wrote. The protection against cardiovascular disease in the fruits and vegetables group occurred with lower doses of antihypertensive and statin medications and was not affected by baseline differences in medication doses.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data on compliance with the NaHCO3 supplements, although urine net acid excretion in this group suggested increased alkali intake similar to that provided by fruits and vegetables, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the focus only on individuals with very high albuminuria.
More basic science studies are needed to explore how the potential vascular injury suggested by albuminuria affects CKD progression and cardiovascular disease, and clinical studies are needed to assess the impact of dietary acid reduction on patients with lower levels of albuminuria that the current study, the researchers said.
However, the results suggest that consuming fruits and vegetables, rather than NaHCO3, is the preferred strategy for dietary acid reduction for patients with primary hypertension and CKD, they concluded. The findings also support routine measurement of urine albumin-to-creatinine ratios in hypertensive patients to identify CKD and assess risk for progression and subsequent cardiovascular disease.
The study was supported by the Larry and Jane Woirhaye Memorial Endowment in Renal Research at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, the University Medical Center (both in Lubbock, Texas), the Endowment, Academic Operations Division of Baylor Scott & White Health, and the Episcopal Health Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiovascular disease risk in hypertensive adults was significantly slower among those who consumed more fruits and vegetables or oral sodium bicarbonate, compared with controls who received usual care.
A primary focus on pharmacologic strategies has failed to reduced hypertension-related CKD and cardiovascular disease mortality, Nimrit Goraya, MD, of Texas A&M Health Sciences Center College of Medicine, Temple, and colleagues wrote. High-acid diets (those with greater amounts of animal-sourced foods) have been associated with increased incidence and progression of CKD and with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Diets high in fruits and vegetables are associated with reduced CKD and cardiovascular disease but are not routinely used as part of hypertension treatment. The researchers hypothesized that dietary acid reduction could slow kidney disease progression and reduce cardiovascular disease risk.
In a study published in The American Journal of Medicine, the researchers randomized 153 adults aged 18-70 years with hypertension and CKD to fruits and vegetables, oral sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), or usual care; 51 to each group. The fruit and vegetable group received 2-4 cups daily of base-producing food items including apples, apricots, oranges, peaches, pears, raisins, strawberries, carrots, cauliflower, eggplant, lettuce, potatoes, spinach, tomatoes, and zucchini. Participants were not instructed how to incorporate these foods into their diets. The sodium bicarbonate group received an average of four to five NaHCO3 tablets daily (650 mg), divided into two doses.
The mean age of the participants was 48.8 years, 51% were female, and 47% were African American. The primary outcome was CKD progression and cardiovascular disease risk over 5 years. All participants met criteria at baseline for macroalbuminuria (a urine albumin to creatinine ratio of at least 200 mg/g) and were considered at increased risk for CKD progression.
Over the 5-year follow-up, CKD progression was significantly slower in the groups receiving fruits and vegetables and oral sodium bicarbonate, compared with usual care, based on trajectories showing a lower decline of estimated glomerular filtration rates (mean declines of 1.08 and 1.17 for fruits/vegetables and NaHCO3, respectively, vs 19.4 for usual care, P < .001 for both).
However, systolic blood pressure and subsequent cardiovascular disease risk indicators were lower only in the fruit and vegetable group, compared with both the NaHCO3 or usual-care groups over the long term. “Specifically, with fruits and vegetables, systolic blood pressure, plasma LDL and Lp(a) cholesterol, and body mass index decreased from baseline, consistent with better cardiovascular disease protection,” the researchers wrote. The protection against cardiovascular disease in the fruits and vegetables group occurred with lower doses of antihypertensive and statin medications and was not affected by baseline differences in medication doses.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data on compliance with the NaHCO3 supplements, although urine net acid excretion in this group suggested increased alkali intake similar to that provided by fruits and vegetables, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the focus only on individuals with very high albuminuria.
More basic science studies are needed to explore how the potential vascular injury suggested by albuminuria affects CKD progression and cardiovascular disease, and clinical studies are needed to assess the impact of dietary acid reduction on patients with lower levels of albuminuria that the current study, the researchers said.
However, the results suggest that consuming fruits and vegetables, rather than NaHCO3, is the preferred strategy for dietary acid reduction for patients with primary hypertension and CKD, they concluded. The findings also support routine measurement of urine albumin-to-creatinine ratios in hypertensive patients to identify CKD and assess risk for progression and subsequent cardiovascular disease.
The study was supported by the Larry and Jane Woirhaye Memorial Endowment in Renal Research at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, the University Medical Center (both in Lubbock, Texas), the Endowment, Academic Operations Division of Baylor Scott & White Health, and the Episcopal Health Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiovascular disease risk in hypertensive adults was significantly slower among those who consumed more fruits and vegetables or oral sodium bicarbonate, compared with controls who received usual care.
A primary focus on pharmacologic strategies has failed to reduced hypertension-related CKD and cardiovascular disease mortality, Nimrit Goraya, MD, of Texas A&M Health Sciences Center College of Medicine, Temple, and colleagues wrote. High-acid diets (those with greater amounts of animal-sourced foods) have been associated with increased incidence and progression of CKD and with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Diets high in fruits and vegetables are associated with reduced CKD and cardiovascular disease but are not routinely used as part of hypertension treatment. The researchers hypothesized that dietary acid reduction could slow kidney disease progression and reduce cardiovascular disease risk.
In a study published in The American Journal of Medicine, the researchers randomized 153 adults aged 18-70 years with hypertension and CKD to fruits and vegetables, oral sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), or usual care; 51 to each group. The fruit and vegetable group received 2-4 cups daily of base-producing food items including apples, apricots, oranges, peaches, pears, raisins, strawberries, carrots, cauliflower, eggplant, lettuce, potatoes, spinach, tomatoes, and zucchini. Participants were not instructed how to incorporate these foods into their diets. The sodium bicarbonate group received an average of four to five NaHCO3 tablets daily (650 mg), divided into two doses.
The mean age of the participants was 48.8 years, 51% were female, and 47% were African American. The primary outcome was CKD progression and cardiovascular disease risk over 5 years. All participants met criteria at baseline for macroalbuminuria (a urine albumin to creatinine ratio of at least 200 mg/g) and were considered at increased risk for CKD progression.
Over the 5-year follow-up, CKD progression was significantly slower in the groups receiving fruits and vegetables and oral sodium bicarbonate, compared with usual care, based on trajectories showing a lower decline of estimated glomerular filtration rates (mean declines of 1.08 and 1.17 for fruits/vegetables and NaHCO3, respectively, vs 19.4 for usual care, P < .001 for both).
However, systolic blood pressure and subsequent cardiovascular disease risk indicators were lower only in the fruit and vegetable group, compared with both the NaHCO3 or usual-care groups over the long term. “Specifically, with fruits and vegetables, systolic blood pressure, plasma LDL and Lp(a) cholesterol, and body mass index decreased from baseline, consistent with better cardiovascular disease protection,” the researchers wrote. The protection against cardiovascular disease in the fruits and vegetables group occurred with lower doses of antihypertensive and statin medications and was not affected by baseline differences in medication doses.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data on compliance with the NaHCO3 supplements, although urine net acid excretion in this group suggested increased alkali intake similar to that provided by fruits and vegetables, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the focus only on individuals with very high albuminuria.
More basic science studies are needed to explore how the potential vascular injury suggested by albuminuria affects CKD progression and cardiovascular disease, and clinical studies are needed to assess the impact of dietary acid reduction on patients with lower levels of albuminuria that the current study, the researchers said.
However, the results suggest that consuming fruits and vegetables, rather than NaHCO3, is the preferred strategy for dietary acid reduction for patients with primary hypertension and CKD, they concluded. The findings also support routine measurement of urine albumin-to-creatinine ratios in hypertensive patients to identify CKD and assess risk for progression and subsequent cardiovascular disease.
The study was supported by the Larry and Jane Woirhaye Memorial Endowment in Renal Research at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, the University Medical Center (both in Lubbock, Texas), the Endowment, Academic Operations Division of Baylor Scott & White Health, and the Episcopal Health Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Wearables May Confirm Sleep Disruption Impact on Chronic Disease
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, deep sleep, and sleep irregularity were significantly associated with increased risk for a range of chronic diseases, based on a new study of > 6000 individuals.
“Most of what we think we know about sleep patterns in adults comes from either self-report surveys, which are widely used but have all sorts of problems with over- and under-estimating sleep duration and quality, or single-night sleep studies,” corresponding author Evan L. Brittain, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, said in an interview.
The single-night study yields the highest quality data but is limited by extrapolating a single night’s sleep to represent habitual sleep patterns, which is often not the case, he said. In the current study, published in Nature Medicine, “we had a unique opportunity to understand sleep using a large cohort of individuals using wearable devices that measure sleep duration, quality, and variability. The All of Us Research Program is the first to link wearables data to the electronic health record at scale and allowed us to study long-term, real-world sleep behavior,” Dr. Brittain said.
The timing of the study is important because the American Heart Association now recognizes sleep as a key component of heart health, and public awareness of the value of sleep is increasing, he added.
The researchers reviewed objectively measured, longitudinal sleep data from 6785 adults who used commercial wearable devices (Fitbit) linked to electronic health record data in the All of Us Research Program. The median age of the participants was 50.2 years, 71% were women, and 84% self-identified as White individuals. The median period of sleep monitoring was 4.5 years.
REM sleep and deep sleep were inversely associated with the odds of incident heart rhythm and heart rate abnormalities. A higher percentage of deep sleep was associated with reduced odds of atrial fibrillation (OR, 0.87), major depressive disorder (OR, 0.93), and anxiety disorder (OR, 0.94).
Increased irregular sleep was significantly associated with increased odds of incident obesity (OR, 1.49), hyperlipidemia (OR, 1.39), and hypertension (OR, 1.56), as well as major depressive disorder (OR, 1.75), anxiety disorder (OR, 1.55), and bipolar disorder (OR, 2.27).
The researchers also identified J-shaped associations between average daily sleep duration and hypertension (P for nonlinearity = .003), as well as major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder (both P < .001).
The study was limited by several factors including the relatively young, White, and female study population. However, the results illustrate how sleep stages, duration, and regularity are associated with chronic disease development, and may inform evidence-based recommendations on healthy sleeping habits, the researchers wrote.
Findings Support Need for Sleep Consistency
“The biggest surprise for me was the impact of sleep variability of health,” Dr. Brittain told this news organization. “The more your sleep duration varies, the higher your risk of numerous chronic diseases across the entire spectrum of organ systems. Sleep duration and quality were also important but that was less surprising,” he said.
The clinical implications of the findings are that sleep duration, quality, and variability are all important, said Dr. Brittain. “To me, the easiest finding to translate into the clinic is the importance of reducing the variability of sleep duration as much as possible,” he said. For patients, that means explaining that they need to go to sleep and wake up at roughly the same time night to night, he said.
“Commercial wearable devices are not perfect compared with research grade devices, but our study showed that they nonetheless collect clinically relevant information,” Dr. Brittain added. “For patients who own a device, I have adopted the practice of reviewing my patients’ sleep and activity data which gives objective insight into behavior that is not always accurate through routine questioning,” he said.
As for other limitations, “Our cohort was limited to individuals who already owned a Fitbit; not surprisingly, these individuals differ from a random sample of the community in important ways, both demographic and behavioral, and our findings need to be validated in a more diverse population,” said Dr. Brittain.
Looking ahead, “we are interested in using commercial devices as a tool for sleep interventions to test the impact of improving sleep hygiene on chronic disease incidence, severity, and progression,” he said.
Device Data Will Evolve to Inform Patient Care
“With the increasing use of commercial wearable devices, it is crucial to identify and understand the data they can collect,” said Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, a pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in an interview. “This study specifically analyzed sleep data from Fitbit devices among participants in the All of Us Research Program to assess sleep patterns and their association with chronic disease risk,” said Dr. Baldomero, who was not involved in the study.
The significant relationships between sleep patterns and risk for chronic diseases were not surprising, said Dr. Baldomero. The findings of an association between shorter sleep duration and greater sleep irregularity with obesity and sleep apnea validated previous studies in large-scale population surveys, she said. Findings from the current study also reflect data from the literature on sleep duration associated with hypertension, major depressive disorder, and generalized anxiety findings, she added.
“This study reinforces the importance of adequate sleep, typically around 7 hours per night, and suggests that insufficient or poor-quality sleep may be associated with chronic diseases,” Dr. Baldomero told this news organization. “Pulmonologists should remain vigilant about sleep-related issues, and consider further investigation and referrals to sleep specialty clinics for patients suspected of having sleep disturbances,” she said.
“What remains unclear is whether abnormal sleep patterns are a cause or an effect of chronic diseases,” Dr. Baldomero noted. “Additionally, it is essential to ensure that these devices accurately capture sleep patterns and continue to validate their data against gold standard measures of sleep disturbances,” she said.
The study was based on work that was partially funded by an unrestricted gift from Google, and the study itself was supported by National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brittain disclosed received research funds unrelated to this work from United Therapeutics. Dr. Baldomero had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, deep sleep, and sleep irregularity were significantly associated with increased risk for a range of chronic diseases, based on a new study of > 6000 individuals.
“Most of what we think we know about sleep patterns in adults comes from either self-report surveys, which are widely used but have all sorts of problems with over- and under-estimating sleep duration and quality, or single-night sleep studies,” corresponding author Evan L. Brittain, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, said in an interview.
The single-night study yields the highest quality data but is limited by extrapolating a single night’s sleep to represent habitual sleep patterns, which is often not the case, he said. In the current study, published in Nature Medicine, “we had a unique opportunity to understand sleep using a large cohort of individuals using wearable devices that measure sleep duration, quality, and variability. The All of Us Research Program is the first to link wearables data to the electronic health record at scale and allowed us to study long-term, real-world sleep behavior,” Dr. Brittain said.
The timing of the study is important because the American Heart Association now recognizes sleep as a key component of heart health, and public awareness of the value of sleep is increasing, he added.
The researchers reviewed objectively measured, longitudinal sleep data from 6785 adults who used commercial wearable devices (Fitbit) linked to electronic health record data in the All of Us Research Program. The median age of the participants was 50.2 years, 71% were women, and 84% self-identified as White individuals. The median period of sleep monitoring was 4.5 years.
REM sleep and deep sleep were inversely associated with the odds of incident heart rhythm and heart rate abnormalities. A higher percentage of deep sleep was associated with reduced odds of atrial fibrillation (OR, 0.87), major depressive disorder (OR, 0.93), and anxiety disorder (OR, 0.94).
Increased irregular sleep was significantly associated with increased odds of incident obesity (OR, 1.49), hyperlipidemia (OR, 1.39), and hypertension (OR, 1.56), as well as major depressive disorder (OR, 1.75), anxiety disorder (OR, 1.55), and bipolar disorder (OR, 2.27).
The researchers also identified J-shaped associations between average daily sleep duration and hypertension (P for nonlinearity = .003), as well as major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder (both P < .001).
The study was limited by several factors including the relatively young, White, and female study population. However, the results illustrate how sleep stages, duration, and regularity are associated with chronic disease development, and may inform evidence-based recommendations on healthy sleeping habits, the researchers wrote.
Findings Support Need for Sleep Consistency
“The biggest surprise for me was the impact of sleep variability of health,” Dr. Brittain told this news organization. “The more your sleep duration varies, the higher your risk of numerous chronic diseases across the entire spectrum of organ systems. Sleep duration and quality were also important but that was less surprising,” he said.
The clinical implications of the findings are that sleep duration, quality, and variability are all important, said Dr. Brittain. “To me, the easiest finding to translate into the clinic is the importance of reducing the variability of sleep duration as much as possible,” he said. For patients, that means explaining that they need to go to sleep and wake up at roughly the same time night to night, he said.
“Commercial wearable devices are not perfect compared with research grade devices, but our study showed that they nonetheless collect clinically relevant information,” Dr. Brittain added. “For patients who own a device, I have adopted the practice of reviewing my patients’ sleep and activity data which gives objective insight into behavior that is not always accurate through routine questioning,” he said.
As for other limitations, “Our cohort was limited to individuals who already owned a Fitbit; not surprisingly, these individuals differ from a random sample of the community in important ways, both demographic and behavioral, and our findings need to be validated in a more diverse population,” said Dr. Brittain.
Looking ahead, “we are interested in using commercial devices as a tool for sleep interventions to test the impact of improving sleep hygiene on chronic disease incidence, severity, and progression,” he said.
Device Data Will Evolve to Inform Patient Care
“With the increasing use of commercial wearable devices, it is crucial to identify and understand the data they can collect,” said Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, a pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in an interview. “This study specifically analyzed sleep data from Fitbit devices among participants in the All of Us Research Program to assess sleep patterns and their association with chronic disease risk,” said Dr. Baldomero, who was not involved in the study.
The significant relationships between sleep patterns and risk for chronic diseases were not surprising, said Dr. Baldomero. The findings of an association between shorter sleep duration and greater sleep irregularity with obesity and sleep apnea validated previous studies in large-scale population surveys, she said. Findings from the current study also reflect data from the literature on sleep duration associated with hypertension, major depressive disorder, and generalized anxiety findings, she added.
“This study reinforces the importance of adequate sleep, typically around 7 hours per night, and suggests that insufficient or poor-quality sleep may be associated with chronic diseases,” Dr. Baldomero told this news organization. “Pulmonologists should remain vigilant about sleep-related issues, and consider further investigation and referrals to sleep specialty clinics for patients suspected of having sleep disturbances,” she said.
“What remains unclear is whether abnormal sleep patterns are a cause or an effect of chronic diseases,” Dr. Baldomero noted. “Additionally, it is essential to ensure that these devices accurately capture sleep patterns and continue to validate their data against gold standard measures of sleep disturbances,” she said.
The study was based on work that was partially funded by an unrestricted gift from Google, and the study itself was supported by National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brittain disclosed received research funds unrelated to this work from United Therapeutics. Dr. Baldomero had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, deep sleep, and sleep irregularity were significantly associated with increased risk for a range of chronic diseases, based on a new study of > 6000 individuals.
“Most of what we think we know about sleep patterns in adults comes from either self-report surveys, which are widely used but have all sorts of problems with over- and under-estimating sleep duration and quality, or single-night sleep studies,” corresponding author Evan L. Brittain, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, said in an interview.
The single-night study yields the highest quality data but is limited by extrapolating a single night’s sleep to represent habitual sleep patterns, which is often not the case, he said. In the current study, published in Nature Medicine, “we had a unique opportunity to understand sleep using a large cohort of individuals using wearable devices that measure sleep duration, quality, and variability. The All of Us Research Program is the first to link wearables data to the electronic health record at scale and allowed us to study long-term, real-world sleep behavior,” Dr. Brittain said.
The timing of the study is important because the American Heart Association now recognizes sleep as a key component of heart health, and public awareness of the value of sleep is increasing, he added.
The researchers reviewed objectively measured, longitudinal sleep data from 6785 adults who used commercial wearable devices (Fitbit) linked to electronic health record data in the All of Us Research Program. The median age of the participants was 50.2 years, 71% were women, and 84% self-identified as White individuals. The median period of sleep monitoring was 4.5 years.
REM sleep and deep sleep were inversely associated with the odds of incident heart rhythm and heart rate abnormalities. A higher percentage of deep sleep was associated with reduced odds of atrial fibrillation (OR, 0.87), major depressive disorder (OR, 0.93), and anxiety disorder (OR, 0.94).
Increased irregular sleep was significantly associated with increased odds of incident obesity (OR, 1.49), hyperlipidemia (OR, 1.39), and hypertension (OR, 1.56), as well as major depressive disorder (OR, 1.75), anxiety disorder (OR, 1.55), and bipolar disorder (OR, 2.27).
The researchers also identified J-shaped associations between average daily sleep duration and hypertension (P for nonlinearity = .003), as well as major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder (both P < .001).
The study was limited by several factors including the relatively young, White, and female study population. However, the results illustrate how sleep stages, duration, and regularity are associated with chronic disease development, and may inform evidence-based recommendations on healthy sleeping habits, the researchers wrote.
Findings Support Need for Sleep Consistency
“The biggest surprise for me was the impact of sleep variability of health,” Dr. Brittain told this news organization. “The more your sleep duration varies, the higher your risk of numerous chronic diseases across the entire spectrum of organ systems. Sleep duration and quality were also important but that was less surprising,” he said.
The clinical implications of the findings are that sleep duration, quality, and variability are all important, said Dr. Brittain. “To me, the easiest finding to translate into the clinic is the importance of reducing the variability of sleep duration as much as possible,” he said. For patients, that means explaining that they need to go to sleep and wake up at roughly the same time night to night, he said.
“Commercial wearable devices are not perfect compared with research grade devices, but our study showed that they nonetheless collect clinically relevant information,” Dr. Brittain added. “For patients who own a device, I have adopted the practice of reviewing my patients’ sleep and activity data which gives objective insight into behavior that is not always accurate through routine questioning,” he said.
As for other limitations, “Our cohort was limited to individuals who already owned a Fitbit; not surprisingly, these individuals differ from a random sample of the community in important ways, both demographic and behavioral, and our findings need to be validated in a more diverse population,” said Dr. Brittain.
Looking ahead, “we are interested in using commercial devices as a tool for sleep interventions to test the impact of improving sleep hygiene on chronic disease incidence, severity, and progression,” he said.
Device Data Will Evolve to Inform Patient Care
“With the increasing use of commercial wearable devices, it is crucial to identify and understand the data they can collect,” said Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, a pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in an interview. “This study specifically analyzed sleep data from Fitbit devices among participants in the All of Us Research Program to assess sleep patterns and their association with chronic disease risk,” said Dr. Baldomero, who was not involved in the study.
The significant relationships between sleep patterns and risk for chronic diseases were not surprising, said Dr. Baldomero. The findings of an association between shorter sleep duration and greater sleep irregularity with obesity and sleep apnea validated previous studies in large-scale population surveys, she said. Findings from the current study also reflect data from the literature on sleep duration associated with hypertension, major depressive disorder, and generalized anxiety findings, she added.
“This study reinforces the importance of adequate sleep, typically around 7 hours per night, and suggests that insufficient or poor-quality sleep may be associated with chronic diseases,” Dr. Baldomero told this news organization. “Pulmonologists should remain vigilant about sleep-related issues, and consider further investigation and referrals to sleep specialty clinics for patients suspected of having sleep disturbances,” she said.
“What remains unclear is whether abnormal sleep patterns are a cause or an effect of chronic diseases,” Dr. Baldomero noted. “Additionally, it is essential to ensure that these devices accurately capture sleep patterns and continue to validate their data against gold standard measures of sleep disturbances,” she said.
The study was based on work that was partially funded by an unrestricted gift from Google, and the study itself was supported by National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brittain disclosed received research funds unrelated to this work from United Therapeutics. Dr. Baldomero had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ozempic Curbs Hunger – And Not Just for Food
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 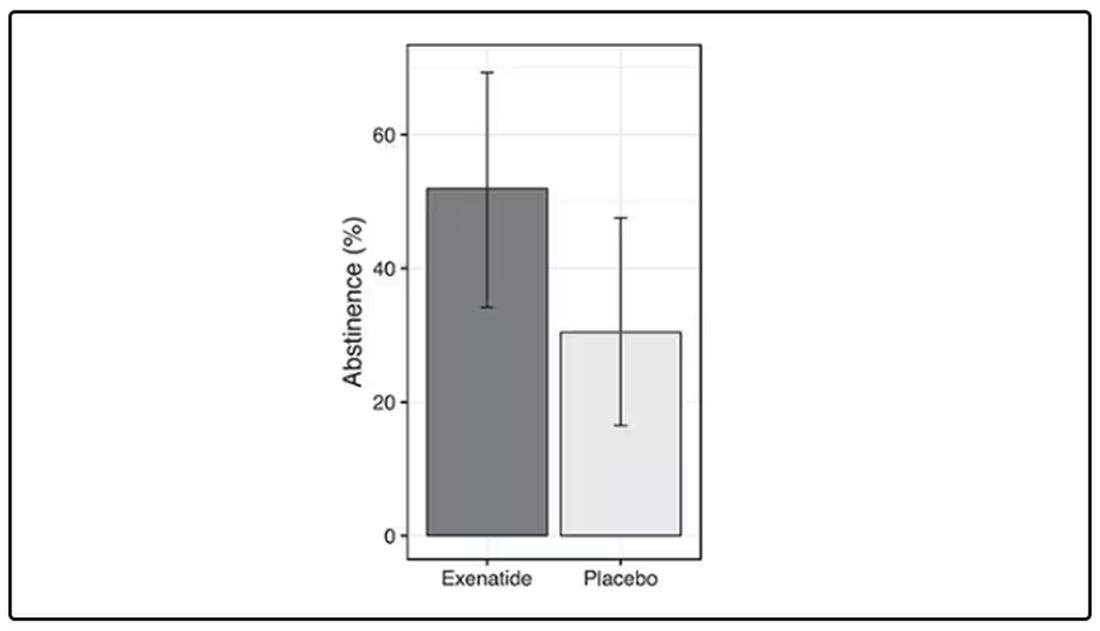
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.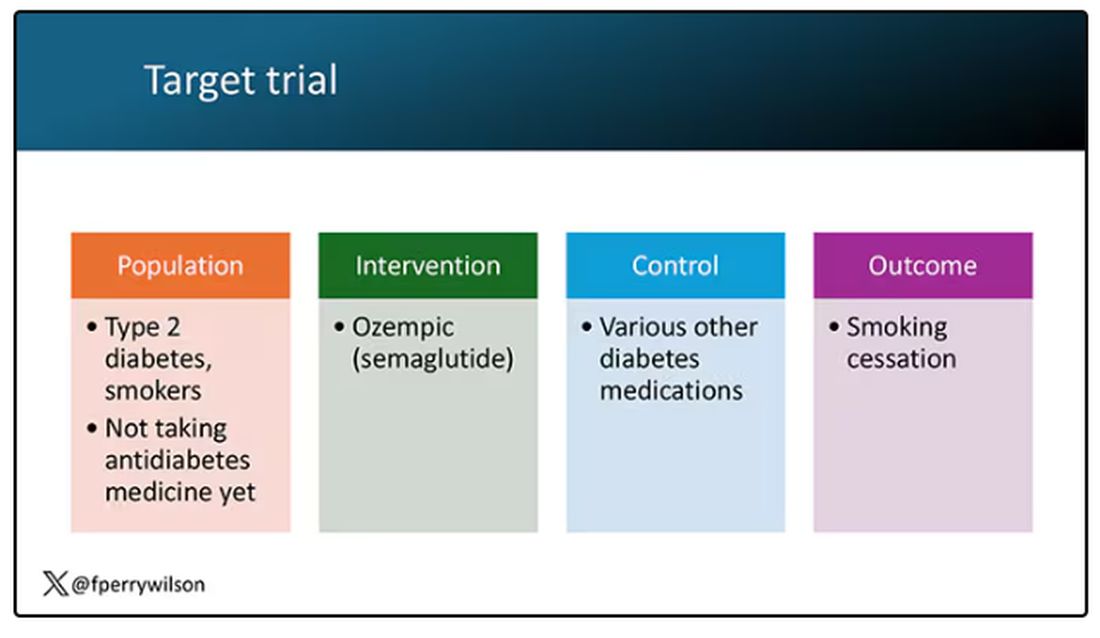
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.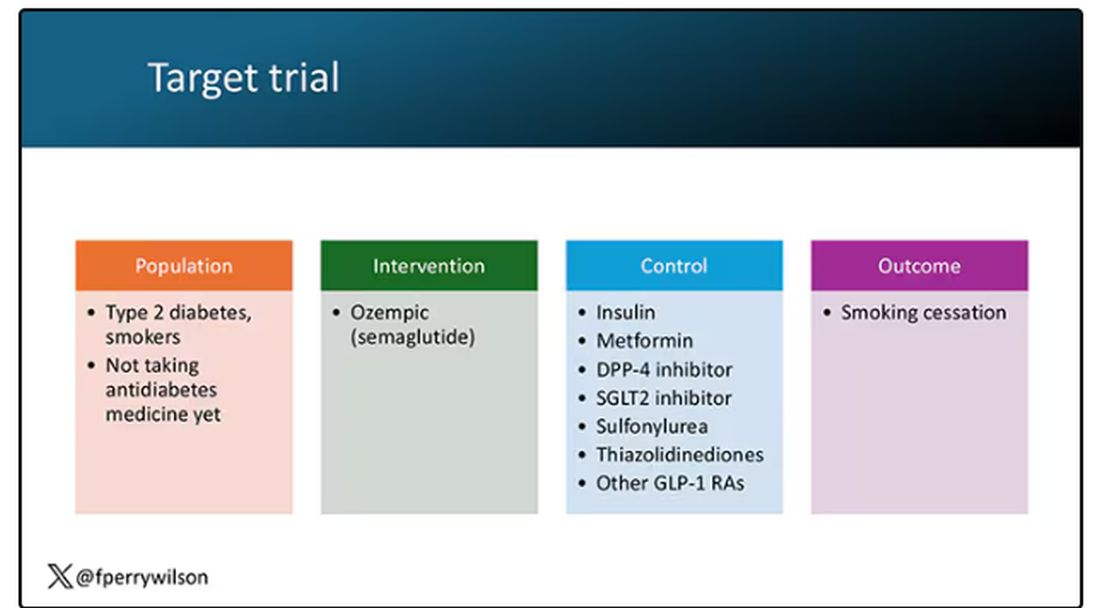
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 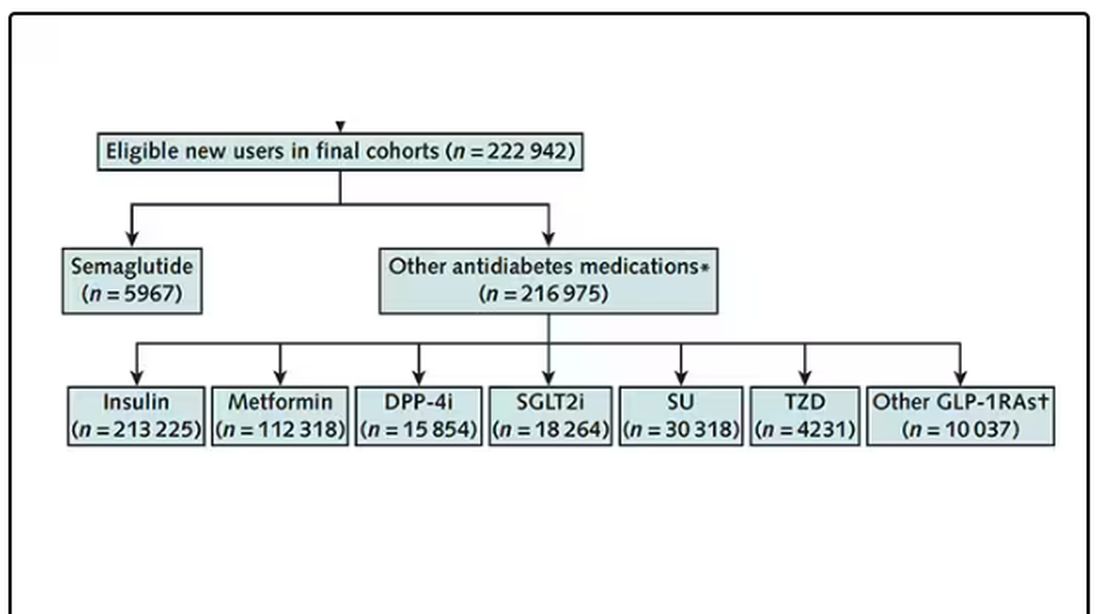
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.