User login
Rash with fever and shortness of breath
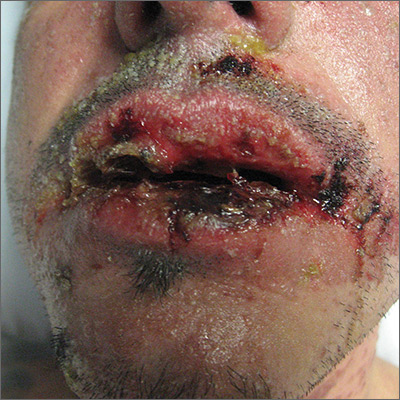
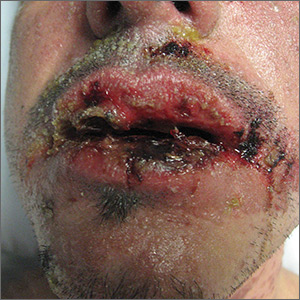
The skin biopsy confirmed toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), possibly secondary to one of the antibiotics he’d been given upon hospital admission. The health care team suspected that the patient had Stevens-Johns Syndrome when he sought care and that it had evolved into TEN. Both diseases are life-threatening and require intensive in-hospital care.
TEN is part of a spectrum of disorders that includes erythema multiforme (< 10% of the body surface is involved); SJS/TEN (10%-30% involvement with erythematous or pruritic macules, widespread blisters on the trunk and face, and erosions of ≥ 1 mucous membranes); and TEN (> 30% involvement).
Drugs most commonly known to cause SJS and TEN include sulfonamide antibiotics, allopurinol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, amine antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin and carbamazepine), and lamotrigine. Fifty percent of SJS/TEN cases have no identifiable cause. Not all SJS is secondary to drug exposure, but it is the job of the clinician to investigate this cause and stop any suspicious medications.
In this case, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole was discontinued immediately and the patient was transferred to a burn unit and given intravenous gamma-globulin 1 g/kg for 3 days. Fortunately, the patient survived with intensive supportive care in the burn unit. The exfoliation of > 30% of the skin is like a large secondary burn, and a burn unit is the optimal location for lifesaving measures.
Photo courtesy of Robert T. Gilson, MD, and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Milana C, Smith M. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1161-1168.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com
The skin biopsy confirmed toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), possibly secondary to one of the antibiotics he’d been given upon hospital admission. The health care team suspected that the patient had Stevens-Johns Syndrome when he sought care and that it had evolved into TEN. Both diseases are life-threatening and require intensive in-hospital care.
TEN is part of a spectrum of disorders that includes erythema multiforme (< 10% of the body surface is involved); SJS/TEN (10%-30% involvement with erythematous or pruritic macules, widespread blisters on the trunk and face, and erosions of ≥ 1 mucous membranes); and TEN (> 30% involvement).
Drugs most commonly known to cause SJS and TEN include sulfonamide antibiotics, allopurinol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, amine antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin and carbamazepine), and lamotrigine. Fifty percent of SJS/TEN cases have no identifiable cause. Not all SJS is secondary to drug exposure, but it is the job of the clinician to investigate this cause and stop any suspicious medications.
In this case, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole was discontinued immediately and the patient was transferred to a burn unit and given intravenous gamma-globulin 1 g/kg for 3 days. Fortunately, the patient survived with intensive supportive care in the burn unit. The exfoliation of > 30% of the skin is like a large secondary burn, and a burn unit is the optimal location for lifesaving measures.
Photo courtesy of Robert T. Gilson, MD, and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Milana C, Smith M. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1161-1168.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com
The skin biopsy confirmed toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), possibly secondary to one of the antibiotics he’d been given upon hospital admission. The health care team suspected that the patient had Stevens-Johns Syndrome when he sought care and that it had evolved into TEN. Both diseases are life-threatening and require intensive in-hospital care.
TEN is part of a spectrum of disorders that includes erythema multiforme (< 10% of the body surface is involved); SJS/TEN (10%-30% involvement with erythematous or pruritic macules, widespread blisters on the trunk and face, and erosions of ≥ 1 mucous membranes); and TEN (> 30% involvement).
Drugs most commonly known to cause SJS and TEN include sulfonamide antibiotics, allopurinol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, amine antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin and carbamazepine), and lamotrigine. Fifty percent of SJS/TEN cases have no identifiable cause. Not all SJS is secondary to drug exposure, but it is the job of the clinician to investigate this cause and stop any suspicious medications.
In this case, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole was discontinued immediately and the patient was transferred to a burn unit and given intravenous gamma-globulin 1 g/kg for 3 days. Fortunately, the patient survived with intensive supportive care in the burn unit. The exfoliation of > 30% of the skin is like a large secondary burn, and a burn unit is the optimal location for lifesaving measures.
Photo courtesy of Robert T. Gilson, MD, and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Milana C, Smith M. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1161-1168.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com
Two-drug integrase inhibitor–based regimen noninferior to standard in HIV-infected adults
New studies of a two-drug, integrase inhibitor–based regimen, presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, provide additional data to challenge the three-drug HIV treatment paradigm.
In the results of one study, known as TANGO (NCT03446573), switching to the fixed-dose combination of dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) from a tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)–based three- or four-drug regimen maintained virologic suppression at 48 weeks in HIV-1 infected adults, an investigator said, and was noninferior to continuing TAF-based therapy.
In another presentation, updating results of the GEMINI-1 (NCT02831673) and GEMINI-2 studies (NCT02831764), a researcher said the DTG+3TC combination remained noninferior to DTG plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) at week 96 in antiretroviral (ART) treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, with no treatment-emergent resistance and no increase in risk of virologic failure.
,” according to IAS Past President Pedro Cahn, MD, PhD, of Fundación Huésped, Buenos Aires, who presented the updated GEMINI study results.
“We don’t mean to say now everything should be dual therapy, and we are going to wipe out all other options, but I think we have another strong option for initiating therapy, and probably also for switch therapy,” Dr. Cahn said in a press conference.
Dr. Cahn presented an updated analysis of GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2, two identically designed phase 3 randomized clinical trials including a total of 1,400 patients.
The 48-week results from those trials, presented in 2018, showed for the first time that a dual-therapy combination of an integrase inhibitor with 3TC was noninferior to the triple-drug regimen of DTG+TDF/FTC, Dr. Cahn said.
In the updated analysis, including 96 weeks of data, the two-drug regimen remained noninferior to the three-drug regimen, according to the investigator.
A total of 11 patients on DTG+3TC and 7 on DTG+TDF/FTC met virologic withdrawal criteria through week 96, with no treatment-emergent resistance mutations seen in either arm, according to results reported in the study abstract.
The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA below 50 c/mL at week 96 was 86% for the two-drug regimen and 90% for the three-drug regimen (adjusted difference, –3.4; 95% confidence interval, –6.7 to 0.0), the reported data showed.
Drug-related adverse events were numerically more common in the three-drug arm, though rates of adverse event–related withdrawal were low in both arms, according to investigators.
The strategy of switching to DTG+3TC was evaluated in the randomized, phase 3 TANGO trial, which included 741 subjects who were already virally suppressed on a TAF-based three- or four-drug regimen. After 48 weeks of therapy, the two-drug regimen was noninferior to remaining on TAF-based therapy in terms of achieving and maintaining viral suppression, according to investigator Jean van Wyk, MB, ChB, Global Medical Lead for dolutegravir at ViiV Healthcare.
Safety outcomes were similar between the arms, though the absolute number of treatment-related adverse events was higher in the DTG+3TC arm “as expected in a switch study,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The percentage of subjects withdrawing from the study because of adverse events was 4% in the DTG+3TC arm and less than 1% in the TAF-based treatment arm, according to reported data.
And with regard to safety there were similar outcomes between the two arms, with regard to overall adverse events, “but as expected in a switch study, we did see more treatment-related adverse events in the dolutegravir plus lamivudine arm, and that’s because the majority of patients were on two new agents in the form of dolutegravir plus lamivudine, so it’s completely expected,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The study met its primary endpoint for noninferiority at week 48, based on the Food and Drug Administration snapshot algorithm. Results showed that switching to DTG+3TC was noninferior to continuing the TAF-containing regimen at week 48, with virologic failure per snapshot criteria seen in less than 1% of subjects in either arm, according to reported data. The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 c/mL was 93.2% and 93.0% for the DTG+3TC and TAF-based treatment arms, respectively.
Longer-term follow-up will be important to confirm the noninferiority of the two-drug approach, Dr. van Wyk and Dr. Cahn said in the press conference. The TANGO study of the switch strategy will continue through 148 weeks, while an additional year of follow-up is ongoing for the GEMINI studies of the initial therapy approach.
TANGO and both GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 were sponsored by ViiV Healthcare. Dr. van Wyk is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Cahn has received research support grants, and fees as consultant and speaker from ViiV Healthcare.
SOURCE: Cahn P et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0404LB; van Wyk J et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0403LB.
New studies of a two-drug, integrase inhibitor–based regimen, presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, provide additional data to challenge the three-drug HIV treatment paradigm.
In the results of one study, known as TANGO (NCT03446573), switching to the fixed-dose combination of dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) from a tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)–based three- or four-drug regimen maintained virologic suppression at 48 weeks in HIV-1 infected adults, an investigator said, and was noninferior to continuing TAF-based therapy.
In another presentation, updating results of the GEMINI-1 (NCT02831673) and GEMINI-2 studies (NCT02831764), a researcher said the DTG+3TC combination remained noninferior to DTG plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) at week 96 in antiretroviral (ART) treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, with no treatment-emergent resistance and no increase in risk of virologic failure.
,” according to IAS Past President Pedro Cahn, MD, PhD, of Fundación Huésped, Buenos Aires, who presented the updated GEMINI study results.
“We don’t mean to say now everything should be dual therapy, and we are going to wipe out all other options, but I think we have another strong option for initiating therapy, and probably also for switch therapy,” Dr. Cahn said in a press conference.
Dr. Cahn presented an updated analysis of GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2, two identically designed phase 3 randomized clinical trials including a total of 1,400 patients.
The 48-week results from those trials, presented in 2018, showed for the first time that a dual-therapy combination of an integrase inhibitor with 3TC was noninferior to the triple-drug regimen of DTG+TDF/FTC, Dr. Cahn said.
In the updated analysis, including 96 weeks of data, the two-drug regimen remained noninferior to the three-drug regimen, according to the investigator.
A total of 11 patients on DTG+3TC and 7 on DTG+TDF/FTC met virologic withdrawal criteria through week 96, with no treatment-emergent resistance mutations seen in either arm, according to results reported in the study abstract.
The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA below 50 c/mL at week 96 was 86% for the two-drug regimen and 90% for the three-drug regimen (adjusted difference, –3.4; 95% confidence interval, –6.7 to 0.0), the reported data showed.
Drug-related adverse events were numerically more common in the three-drug arm, though rates of adverse event–related withdrawal were low in both arms, according to investigators.
The strategy of switching to DTG+3TC was evaluated in the randomized, phase 3 TANGO trial, which included 741 subjects who were already virally suppressed on a TAF-based three- or four-drug regimen. After 48 weeks of therapy, the two-drug regimen was noninferior to remaining on TAF-based therapy in terms of achieving and maintaining viral suppression, according to investigator Jean van Wyk, MB, ChB, Global Medical Lead for dolutegravir at ViiV Healthcare.
Safety outcomes were similar between the arms, though the absolute number of treatment-related adverse events was higher in the DTG+3TC arm “as expected in a switch study,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The percentage of subjects withdrawing from the study because of adverse events was 4% in the DTG+3TC arm and less than 1% in the TAF-based treatment arm, according to reported data.
And with regard to safety there were similar outcomes between the two arms, with regard to overall adverse events, “but as expected in a switch study, we did see more treatment-related adverse events in the dolutegravir plus lamivudine arm, and that’s because the majority of patients were on two new agents in the form of dolutegravir plus lamivudine, so it’s completely expected,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The study met its primary endpoint for noninferiority at week 48, based on the Food and Drug Administration snapshot algorithm. Results showed that switching to DTG+3TC was noninferior to continuing the TAF-containing regimen at week 48, with virologic failure per snapshot criteria seen in less than 1% of subjects in either arm, according to reported data. The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 c/mL was 93.2% and 93.0% for the DTG+3TC and TAF-based treatment arms, respectively.
Longer-term follow-up will be important to confirm the noninferiority of the two-drug approach, Dr. van Wyk and Dr. Cahn said in the press conference. The TANGO study of the switch strategy will continue through 148 weeks, while an additional year of follow-up is ongoing for the GEMINI studies of the initial therapy approach.
TANGO and both GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 were sponsored by ViiV Healthcare. Dr. van Wyk is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Cahn has received research support grants, and fees as consultant and speaker from ViiV Healthcare.
SOURCE: Cahn P et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0404LB; van Wyk J et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0403LB.
New studies of a two-drug, integrase inhibitor–based regimen, presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, provide additional data to challenge the three-drug HIV treatment paradigm.
In the results of one study, known as TANGO (NCT03446573), switching to the fixed-dose combination of dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) from a tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)–based three- or four-drug regimen maintained virologic suppression at 48 weeks in HIV-1 infected adults, an investigator said, and was noninferior to continuing TAF-based therapy.
In another presentation, updating results of the GEMINI-1 (NCT02831673) and GEMINI-2 studies (NCT02831764), a researcher said the DTG+3TC combination remained noninferior to DTG plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) at week 96 in antiretroviral (ART) treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, with no treatment-emergent resistance and no increase in risk of virologic failure.
,” according to IAS Past President Pedro Cahn, MD, PhD, of Fundación Huésped, Buenos Aires, who presented the updated GEMINI study results.
“We don’t mean to say now everything should be dual therapy, and we are going to wipe out all other options, but I think we have another strong option for initiating therapy, and probably also for switch therapy,” Dr. Cahn said in a press conference.
Dr. Cahn presented an updated analysis of GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2, two identically designed phase 3 randomized clinical trials including a total of 1,400 patients.
The 48-week results from those trials, presented in 2018, showed for the first time that a dual-therapy combination of an integrase inhibitor with 3TC was noninferior to the triple-drug regimen of DTG+TDF/FTC, Dr. Cahn said.
In the updated analysis, including 96 weeks of data, the two-drug regimen remained noninferior to the three-drug regimen, according to the investigator.
A total of 11 patients on DTG+3TC and 7 on DTG+TDF/FTC met virologic withdrawal criteria through week 96, with no treatment-emergent resistance mutations seen in either arm, according to results reported in the study abstract.
The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA below 50 c/mL at week 96 was 86% for the two-drug regimen and 90% for the three-drug regimen (adjusted difference, –3.4; 95% confidence interval, –6.7 to 0.0), the reported data showed.
Drug-related adverse events were numerically more common in the three-drug arm, though rates of adverse event–related withdrawal were low in both arms, according to investigators.
The strategy of switching to DTG+3TC was evaluated in the randomized, phase 3 TANGO trial, which included 741 subjects who were already virally suppressed on a TAF-based three- or four-drug regimen. After 48 weeks of therapy, the two-drug regimen was noninferior to remaining on TAF-based therapy in terms of achieving and maintaining viral suppression, according to investigator Jean van Wyk, MB, ChB, Global Medical Lead for dolutegravir at ViiV Healthcare.
Safety outcomes were similar between the arms, though the absolute number of treatment-related adverse events was higher in the DTG+3TC arm “as expected in a switch study,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The percentage of subjects withdrawing from the study because of adverse events was 4% in the DTG+3TC arm and less than 1% in the TAF-based treatment arm, according to reported data.
And with regard to safety there were similar outcomes between the two arms, with regard to overall adverse events, “but as expected in a switch study, we did see more treatment-related adverse events in the dolutegravir plus lamivudine arm, and that’s because the majority of patients were on two new agents in the form of dolutegravir plus lamivudine, so it’s completely expected,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The study met its primary endpoint for noninferiority at week 48, based on the Food and Drug Administration snapshot algorithm. Results showed that switching to DTG+3TC was noninferior to continuing the TAF-containing regimen at week 48, with virologic failure per snapshot criteria seen in less than 1% of subjects in either arm, according to reported data. The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 c/mL was 93.2% and 93.0% for the DTG+3TC and TAF-based treatment arms, respectively.
Longer-term follow-up will be important to confirm the noninferiority of the two-drug approach, Dr. van Wyk and Dr. Cahn said in the press conference. The TANGO study of the switch strategy will continue through 148 weeks, while an additional year of follow-up is ongoing for the GEMINI studies of the initial therapy approach.
TANGO and both GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 were sponsored by ViiV Healthcare. Dr. van Wyk is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Cahn has received research support grants, and fees as consultant and speaker from ViiV Healthcare.
SOURCE: Cahn P et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0404LB; van Wyk J et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0403LB.
REPORTING FROM IAS 2019
Increased cardiovascular risk seen early on with testosterone replacement therapy
Testosterone replacement therapy is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in older men, particularly during the first 2 years of use, a study in the American Journal of Medicine has found.
Simone Y. Loo of the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research at the Jewish General Hospital in Montreal and colleagues looked at a cohort of 15,401 men aged 45 years or older with low testosterone levels, of whom 4,485 (29.1%) were prescribed testosterone replacement therapy on at least one occasion during a mean follow-up of 4.7 years. They saw that individuals who were currently using testosterone replacement therapy had a 21% increase in the risk of the composite outcome of ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, or myocardial infarction, compared with those who had not had hormone therapy.
In the first 6 months to 2 years after initiation of continuous treatment, the risk was even higher – at 35% – and was particularly high in individuals aged 45-59 years (at 44%).
However, the study also noted a significant 36% reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality in individuals currently using testosterone replacement therapy and a significant 28% higher risk of all-cause mortality in past users, compared with nonusers.
Concerns about the safety of testosterone replacement therapy had previously been kindled by the outcomes of the Testosterone in Older Men trial, which was stopped early because of the higher number of cardiovascular events in the treatment group. However, other randomized controlled trials have not seen that effect, the authors said.
They noted that the protective effect of current hormone replacement use on mortality was surprising, but suggested it could be the result of reverse causality, “in which physicians may discontinue TRT based on perceived deterioration of health or imminent death, because TRT is not a vital medication.”
“Moreover, TRT may be less frequently initiated among men with a higher baseline risk of mortality, particularly in the elderly, and those who received TRT may have been healthier overall, compared with their untreated counterparts,” the authors wrote.
Despite this, they suggested that larger observational studies were still needed to investigate the potential harms of testosterone replacement therapy. In the meantime, they advised that potential harms should be weighed against perceived benefits and caution be applied to prescribing.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Loo S et al. Am J Med 2019 Apr 3. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.03.022.
Testosterone replacement therapy is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in older men, particularly during the first 2 years of use, a study in the American Journal of Medicine has found.
Simone Y. Loo of the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research at the Jewish General Hospital in Montreal and colleagues looked at a cohort of 15,401 men aged 45 years or older with low testosterone levels, of whom 4,485 (29.1%) were prescribed testosterone replacement therapy on at least one occasion during a mean follow-up of 4.7 years. They saw that individuals who were currently using testosterone replacement therapy had a 21% increase in the risk of the composite outcome of ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, or myocardial infarction, compared with those who had not had hormone therapy.
In the first 6 months to 2 years after initiation of continuous treatment, the risk was even higher – at 35% – and was particularly high in individuals aged 45-59 years (at 44%).
However, the study also noted a significant 36% reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality in individuals currently using testosterone replacement therapy and a significant 28% higher risk of all-cause mortality in past users, compared with nonusers.
Concerns about the safety of testosterone replacement therapy had previously been kindled by the outcomes of the Testosterone in Older Men trial, which was stopped early because of the higher number of cardiovascular events in the treatment group. However, other randomized controlled trials have not seen that effect, the authors said.
They noted that the protective effect of current hormone replacement use on mortality was surprising, but suggested it could be the result of reverse causality, “in which physicians may discontinue TRT based on perceived deterioration of health or imminent death, because TRT is not a vital medication.”
“Moreover, TRT may be less frequently initiated among men with a higher baseline risk of mortality, particularly in the elderly, and those who received TRT may have been healthier overall, compared with their untreated counterparts,” the authors wrote.
Despite this, they suggested that larger observational studies were still needed to investigate the potential harms of testosterone replacement therapy. In the meantime, they advised that potential harms should be weighed against perceived benefits and caution be applied to prescribing.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Loo S et al. Am J Med 2019 Apr 3. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.03.022.
Testosterone replacement therapy is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in older men, particularly during the first 2 years of use, a study in the American Journal of Medicine has found.
Simone Y. Loo of the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research at the Jewish General Hospital in Montreal and colleagues looked at a cohort of 15,401 men aged 45 years or older with low testosterone levels, of whom 4,485 (29.1%) were prescribed testosterone replacement therapy on at least one occasion during a mean follow-up of 4.7 years. They saw that individuals who were currently using testosterone replacement therapy had a 21% increase in the risk of the composite outcome of ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, or myocardial infarction, compared with those who had not had hormone therapy.
In the first 6 months to 2 years after initiation of continuous treatment, the risk was even higher – at 35% – and was particularly high in individuals aged 45-59 years (at 44%).
However, the study also noted a significant 36% reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality in individuals currently using testosterone replacement therapy and a significant 28% higher risk of all-cause mortality in past users, compared with nonusers.
Concerns about the safety of testosterone replacement therapy had previously been kindled by the outcomes of the Testosterone in Older Men trial, which was stopped early because of the higher number of cardiovascular events in the treatment group. However, other randomized controlled trials have not seen that effect, the authors said.
They noted that the protective effect of current hormone replacement use on mortality was surprising, but suggested it could be the result of reverse causality, “in which physicians may discontinue TRT based on perceived deterioration of health or imminent death, because TRT is not a vital medication.”
“Moreover, TRT may be less frequently initiated among men with a higher baseline risk of mortality, particularly in the elderly, and those who received TRT may have been healthier overall, compared with their untreated counterparts,” the authors wrote.
Despite this, they suggested that larger observational studies were still needed to investigate the potential harms of testosterone replacement therapy. In the meantime, they advised that potential harms should be weighed against perceived benefits and caution be applied to prescribing.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Loo S et al. Am J Med 2019 Apr 3. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.03.022.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
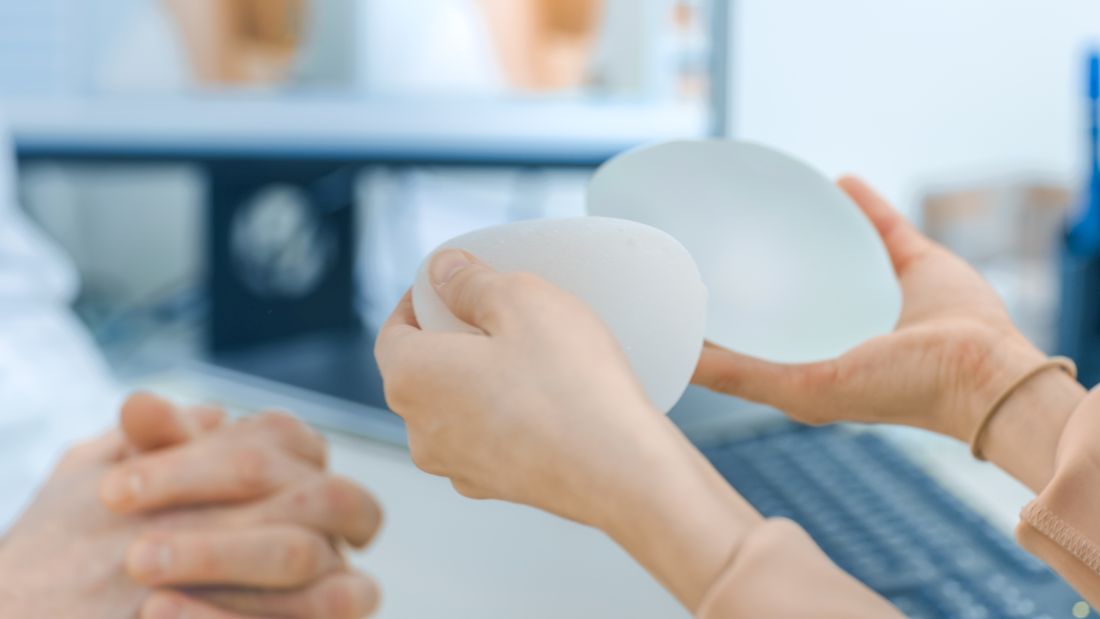
Lymphoma risk prompts FDA recall of Allergan’s textured breast implants
The Food and Drug Administration requested on July 24 that Allergan pull six brands of textured breast implants and breast expanders from the U.S. market, an action the agency took because of new data that substantially increased the number of women who developed a rare cancer – anaplastic large-cell lymphoma – in association with receiving these textured breast devices.
This is the first product recall the FDA has made to address the issue of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), a complication that first came to national attention with a 2011 FDA report that had tallied 60 identified BIA-ALCL cases worldwide. By the end of September 2018, the number of reported worldwide BIA-ALCL cases had jumped to 457 cases reported to the agency via medical device reporting. In July 2019, the FDA cited a total of 573 unique, global case reports for BIA-ALCL sent to the agency through July 6, including 33 episodes that led to death.
It was inclusion of these additional 116 cases since September 2018 and 24 additional deaths that led FDA researchers to conclude that “the risk of BIA-ALCL with Allergan BIOCELL textured implants is approximately six-times the risk of BIA-ALCL with textured implants from other manufacturers marketing in the U.S.,” according to a statement from the agency.
The FDA is not recommending that patients who received one of the six products covered by the recall have the material removed if symptoms have not appeared because of the potential risk from explantation.
The agency also stressed that its investigation of the risk posed by placement of other brands of textured breast implants is ongoing and that overall less than 5% of all breast implants performed in current U.S. practice involve the macrotextured implants of the type specified in the Allergan recall.
This U.S. recall follows similar actions taken in France (and the rest of the European Union), Canada, and Australia, and it contrasts with the agency’s prior decision in May 2019 not to start a recall or ban of textured implants following a advisory committee meeting that discussed BIA-ALCL.
The six products that Allergan agreed to recall from marketing at the FDA’s request are four textured breast implants (Natrelle Saline-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Inspira Silicone-Filled breast Implants, and Natrelle 410 Highly Cohesive Anatomically Shaped Silicone-Filled Breast Implants) and two tissue expanders used prior to a breast implant (Natrelle 133 Plus Tissue Expander and the Natrelle 133 Tissue Expander with Suture Tabs).
FDA officials said they are considering recommendations for changes to the labeling of breast implant products, including a possible boxed warning and beefed up patient information.
“The recall of these textured implants is a big deal in protecting women from the potential risks of developing, and dying from, this rare type of aggressive lymphoma,” Joshua Brody, MD, a medical oncologist and director of the lymphoma immunotherapy program at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York said in a statement. “While case reports have suggested a potential link between some types of breast implants and this disease – anaplastic lymphoma – for over 20 years, it has taken time to gain sufficient evidence to suggest, and understand, the causality. Some types of implants induce inflammation, which can both increase the chance of developing cancer, and also help to ‘hide’ developing cancers from the immune system. By preventing further use of these implants, the FDA is helping women to protect themselves from the medically serious and emotionally exhausting effects of these risks.”
Dr. Brody reported having no relevant disclosures.
The Food and Drug Administration requested on July 24 that Allergan pull six brands of textured breast implants and breast expanders from the U.S. market, an action the agency took because of new data that substantially increased the number of women who developed a rare cancer – anaplastic large-cell lymphoma – in association with receiving these textured breast devices.
This is the first product recall the FDA has made to address the issue of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), a complication that first came to national attention with a 2011 FDA report that had tallied 60 identified BIA-ALCL cases worldwide. By the end of September 2018, the number of reported worldwide BIA-ALCL cases had jumped to 457 cases reported to the agency via medical device reporting. In July 2019, the FDA cited a total of 573 unique, global case reports for BIA-ALCL sent to the agency through July 6, including 33 episodes that led to death.
It was inclusion of these additional 116 cases since September 2018 and 24 additional deaths that led FDA researchers to conclude that “the risk of BIA-ALCL with Allergan BIOCELL textured implants is approximately six-times the risk of BIA-ALCL with textured implants from other manufacturers marketing in the U.S.,” according to a statement from the agency.
The FDA is not recommending that patients who received one of the six products covered by the recall have the material removed if symptoms have not appeared because of the potential risk from explantation.
The agency also stressed that its investigation of the risk posed by placement of other brands of textured breast implants is ongoing and that overall less than 5% of all breast implants performed in current U.S. practice involve the macrotextured implants of the type specified in the Allergan recall.
This U.S. recall follows similar actions taken in France (and the rest of the European Union), Canada, and Australia, and it contrasts with the agency’s prior decision in May 2019 not to start a recall or ban of textured implants following a advisory committee meeting that discussed BIA-ALCL.
The six products that Allergan agreed to recall from marketing at the FDA’s request are four textured breast implants (Natrelle Saline-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Inspira Silicone-Filled breast Implants, and Natrelle 410 Highly Cohesive Anatomically Shaped Silicone-Filled Breast Implants) and two tissue expanders used prior to a breast implant (Natrelle 133 Plus Tissue Expander and the Natrelle 133 Tissue Expander with Suture Tabs).
FDA officials said they are considering recommendations for changes to the labeling of breast implant products, including a possible boxed warning and beefed up patient information.
“The recall of these textured implants is a big deal in protecting women from the potential risks of developing, and dying from, this rare type of aggressive lymphoma,” Joshua Brody, MD, a medical oncologist and director of the lymphoma immunotherapy program at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York said in a statement. “While case reports have suggested a potential link between some types of breast implants and this disease – anaplastic lymphoma – for over 20 years, it has taken time to gain sufficient evidence to suggest, and understand, the causality. Some types of implants induce inflammation, which can both increase the chance of developing cancer, and also help to ‘hide’ developing cancers from the immune system. By preventing further use of these implants, the FDA is helping women to protect themselves from the medically serious and emotionally exhausting effects of these risks.”
Dr. Brody reported having no relevant disclosures.
The Food and Drug Administration requested on July 24 that Allergan pull six brands of textured breast implants and breast expanders from the U.S. market, an action the agency took because of new data that substantially increased the number of women who developed a rare cancer – anaplastic large-cell lymphoma – in association with receiving these textured breast devices.
This is the first product recall the FDA has made to address the issue of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), a complication that first came to national attention with a 2011 FDA report that had tallied 60 identified BIA-ALCL cases worldwide. By the end of September 2018, the number of reported worldwide BIA-ALCL cases had jumped to 457 cases reported to the agency via medical device reporting. In July 2019, the FDA cited a total of 573 unique, global case reports for BIA-ALCL sent to the agency through July 6, including 33 episodes that led to death.
It was inclusion of these additional 116 cases since September 2018 and 24 additional deaths that led FDA researchers to conclude that “the risk of BIA-ALCL with Allergan BIOCELL textured implants is approximately six-times the risk of BIA-ALCL with textured implants from other manufacturers marketing in the U.S.,” according to a statement from the agency.
The FDA is not recommending that patients who received one of the six products covered by the recall have the material removed if symptoms have not appeared because of the potential risk from explantation.
The agency also stressed that its investigation of the risk posed by placement of other brands of textured breast implants is ongoing and that overall less than 5% of all breast implants performed in current U.S. practice involve the macrotextured implants of the type specified in the Allergan recall.
This U.S. recall follows similar actions taken in France (and the rest of the European Union), Canada, and Australia, and it contrasts with the agency’s prior decision in May 2019 not to start a recall or ban of textured implants following a advisory committee meeting that discussed BIA-ALCL.
The six products that Allergan agreed to recall from marketing at the FDA’s request are four textured breast implants (Natrelle Saline-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Inspira Silicone-Filled breast Implants, and Natrelle 410 Highly Cohesive Anatomically Shaped Silicone-Filled Breast Implants) and two tissue expanders used prior to a breast implant (Natrelle 133 Plus Tissue Expander and the Natrelle 133 Tissue Expander with Suture Tabs).
FDA officials said they are considering recommendations for changes to the labeling of breast implant products, including a possible boxed warning and beefed up patient information.
“The recall of these textured implants is a big deal in protecting women from the potential risks of developing, and dying from, this rare type of aggressive lymphoma,” Joshua Brody, MD, a medical oncologist and director of the lymphoma immunotherapy program at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York said in a statement. “While case reports have suggested a potential link between some types of breast implants and this disease – anaplastic lymphoma – for over 20 years, it has taken time to gain sufficient evidence to suggest, and understand, the causality. Some types of implants induce inflammation, which can both increase the chance of developing cancer, and also help to ‘hide’ developing cancers from the immune system. By preventing further use of these implants, the FDA is helping women to protect themselves from the medically serious and emotionally exhausting effects of these risks.”
Dr. Brody reported having no relevant disclosures.
Moderately high dietary riboflavin linked to fewer migraines
PHILADELPHIA – People with moderately high levels of riboflavin consumption from food – two to three times the recommended dietary allowance – had a significantly lower prevalence of a recent severe or migraine headache in a study of more than 3,600 younger U.S. adults.
Adults 20-50 years old who consumed 2.07-2.87 mg riboflavin (vitamin B2) in food a day based on a 24-hour recall questionnaire had an adjusted, statistically significant 27% reduced prevalence of a recent severe or migraine headache, compared with people in the lowest quartile of dietary riboflavin intake, 1.45 mg/day or less, Margaret Slavin, Ph.D., said at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Foods particularly high in riboflavin include eggs, milk, and meat.
Dietary riboflavin intakes greater than 2.87 mg/day were not linked to a difference in the prevalence of a recent history of severe or migraine headache, compared with lowest-quartile consumption. Additionally, riboflavin intake from supplements alone at any level of consumption also showed no statistically significant link with the prevalence of a recent, severe headache, said Dr. Slavin, a nutrition and food studies researcher at George Mason University in Fairfax, Va.
The “vast majority” of people in the study had a riboflavin intake that at least matched the U.S. recommended dietary allowance (RDA),1.3 mg/ day for men and 1.1 mg/day for women), “but it’s possible that people with migraine headaches need more riboflavin,” Dr. Slavin suggested. Professional societies in the United States (Neurology. 2012 Apr;78[17]: 1346-53) and Canada (Can J Neurol Sci. 2012 Mar;39[Suppl 2]S8-S28) have gone on record with some level of recommendation for a daily riboflavin supplement of 400 mg to prevent migraine headaches, she said.
A U.S. guideline that included riboflavin has been “retired” because of an issue unrelated to riboflavin, according to the Neurology website.
The new study ran data collected in the biennial National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), specifically the surveys from 2001-2002 and 2003-2004. The combined data included 5,528 adults 20-50 years old, and 3,634 with complete data and without an excluding condition such as pregnancy, diabetes, or menopause. Among the study participants 884 reported having “severe headaches or migraines,” during the 3 months preceding the survey and the remaining 2,750 people served as controls. People who reported recent severe headache or migraine overall had a significantly lower average amount of vitamin B2 in their diet than did the controls, but the two subgroups showed no significant differences in their levels of riboflavin intake from supplements, or from both diet and supplements combined.
The researchers calculated odds ratios for people having severe headaches or migraines relative to their riboflavin-intake quartile, and they adjusted the findings for age, sex, body mass index, and alcohol intake.
Further analysis that looked at total riboflavin intake, from both food and supplements, showed that the two middle quartiles for this metric, with a combined riboflavin intake of 1.6-3.8 mg/day, had a significantly reduced prevalence of recent severe or migraine headaches, compared with the lowest-intake quartile, with an odds ratio that roughly matched the dietary riboflavin analysis.
Dr. Slavin has received research funding from the Egg Nutrition Center, the Maryland Soybean Board, the McCormick Science Institute, and PepsiCo.
SOURCE: Slavin M. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, Abstract LBOR04.
PHILADELPHIA – People with moderately high levels of riboflavin consumption from food – two to three times the recommended dietary allowance – had a significantly lower prevalence of a recent severe or migraine headache in a study of more than 3,600 younger U.S. adults.
Adults 20-50 years old who consumed 2.07-2.87 mg riboflavin (vitamin B2) in food a day based on a 24-hour recall questionnaire had an adjusted, statistically significant 27% reduced prevalence of a recent severe or migraine headache, compared with people in the lowest quartile of dietary riboflavin intake, 1.45 mg/day or less, Margaret Slavin, Ph.D., said at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Foods particularly high in riboflavin include eggs, milk, and meat.
Dietary riboflavin intakes greater than 2.87 mg/day were not linked to a difference in the prevalence of a recent history of severe or migraine headache, compared with lowest-quartile consumption. Additionally, riboflavin intake from supplements alone at any level of consumption also showed no statistically significant link with the prevalence of a recent, severe headache, said Dr. Slavin, a nutrition and food studies researcher at George Mason University in Fairfax, Va.
The “vast majority” of people in the study had a riboflavin intake that at least matched the U.S. recommended dietary allowance (RDA),1.3 mg/ day for men and 1.1 mg/day for women), “but it’s possible that people with migraine headaches need more riboflavin,” Dr. Slavin suggested. Professional societies in the United States (Neurology. 2012 Apr;78[17]: 1346-53) and Canada (Can J Neurol Sci. 2012 Mar;39[Suppl 2]S8-S28) have gone on record with some level of recommendation for a daily riboflavin supplement of 400 mg to prevent migraine headaches, she said.
A U.S. guideline that included riboflavin has been “retired” because of an issue unrelated to riboflavin, according to the Neurology website.
The new study ran data collected in the biennial National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), specifically the surveys from 2001-2002 and 2003-2004. The combined data included 5,528 adults 20-50 years old, and 3,634 with complete data and without an excluding condition such as pregnancy, diabetes, or menopause. Among the study participants 884 reported having “severe headaches or migraines,” during the 3 months preceding the survey and the remaining 2,750 people served as controls. People who reported recent severe headache or migraine overall had a significantly lower average amount of vitamin B2 in their diet than did the controls, but the two subgroups showed no significant differences in their levels of riboflavin intake from supplements, or from both diet and supplements combined.
The researchers calculated odds ratios for people having severe headaches or migraines relative to their riboflavin-intake quartile, and they adjusted the findings for age, sex, body mass index, and alcohol intake.
Further analysis that looked at total riboflavin intake, from both food and supplements, showed that the two middle quartiles for this metric, with a combined riboflavin intake of 1.6-3.8 mg/day, had a significantly reduced prevalence of recent severe or migraine headaches, compared with the lowest-intake quartile, with an odds ratio that roughly matched the dietary riboflavin analysis.
Dr. Slavin has received research funding from the Egg Nutrition Center, the Maryland Soybean Board, the McCormick Science Institute, and PepsiCo.
SOURCE: Slavin M. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, Abstract LBOR04.
PHILADELPHIA – People with moderately high levels of riboflavin consumption from food – two to three times the recommended dietary allowance – had a significantly lower prevalence of a recent severe or migraine headache in a study of more than 3,600 younger U.S. adults.
Adults 20-50 years old who consumed 2.07-2.87 mg riboflavin (vitamin B2) in food a day based on a 24-hour recall questionnaire had an adjusted, statistically significant 27% reduced prevalence of a recent severe or migraine headache, compared with people in the lowest quartile of dietary riboflavin intake, 1.45 mg/day or less, Margaret Slavin, Ph.D., said at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Foods particularly high in riboflavin include eggs, milk, and meat.
Dietary riboflavin intakes greater than 2.87 mg/day were not linked to a difference in the prevalence of a recent history of severe or migraine headache, compared with lowest-quartile consumption. Additionally, riboflavin intake from supplements alone at any level of consumption also showed no statistically significant link with the prevalence of a recent, severe headache, said Dr. Slavin, a nutrition and food studies researcher at George Mason University in Fairfax, Va.
The “vast majority” of people in the study had a riboflavin intake that at least matched the U.S. recommended dietary allowance (RDA),1.3 mg/ day for men and 1.1 mg/day for women), “but it’s possible that people with migraine headaches need more riboflavin,” Dr. Slavin suggested. Professional societies in the United States (Neurology. 2012 Apr;78[17]: 1346-53) and Canada (Can J Neurol Sci. 2012 Mar;39[Suppl 2]S8-S28) have gone on record with some level of recommendation for a daily riboflavin supplement of 400 mg to prevent migraine headaches, she said.
A U.S. guideline that included riboflavin has been “retired” because of an issue unrelated to riboflavin, according to the Neurology website.
The new study ran data collected in the biennial National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), specifically the surveys from 2001-2002 and 2003-2004. The combined data included 5,528 adults 20-50 years old, and 3,634 with complete data and without an excluding condition such as pregnancy, diabetes, or menopause. Among the study participants 884 reported having “severe headaches or migraines,” during the 3 months preceding the survey and the remaining 2,750 people served as controls. People who reported recent severe headache or migraine overall had a significantly lower average amount of vitamin B2 in their diet than did the controls, but the two subgroups showed no significant differences in their levels of riboflavin intake from supplements, or from both diet and supplements combined.
The researchers calculated odds ratios for people having severe headaches or migraines relative to their riboflavin-intake quartile, and they adjusted the findings for age, sex, body mass index, and alcohol intake.
Further analysis that looked at total riboflavin intake, from both food and supplements, showed that the two middle quartiles for this metric, with a combined riboflavin intake of 1.6-3.8 mg/day, had a significantly reduced prevalence of recent severe or migraine headaches, compared with the lowest-intake quartile, with an odds ratio that roughly matched the dietary riboflavin analysis.
Dr. Slavin has received research funding from the Egg Nutrition Center, the Maryland Soybean Board, the McCormick Science Institute, and PepsiCo.
SOURCE: Slavin M. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, Abstract LBOR04.
REPORTING FROM AHS 2019
Key clinical point: Higher dietary riboflavin intake may reduce the risk for severe or migraine headaches.
Major finding: People with dietary riboflavin levels 2-3 times the RDA had a 27% lower prevalence of severe or migraine headaches compared with the lowest riboflavin quartile.
Study details: Review of NHANES data from 2001-2004 for 3,634 adults 20-50 years old.
Disclosures: Dr. Slavin has received research funding from the Egg Nutrition Center, the Maryland Soybean Board, the McCormick Science Institute, and PepsiCo.
Source: Slavin M. Headache. 2019 June;59[S1]:1-208, Abstract LBOR04.
Erdafitinib is efficacious in FGFR-altered urothelial carcinoma
Erdafitinib, an oral pan–fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is efficacious when used to treat urothelial cancer harboring FGFR genetic alterations, although dose adjustments are commonly needed, suggests a multicenter phase 2 trial.
“Mutations and fusions in FGFR2/3 are common in patients with urothelial carcinoma, particularly in the luminal I subtype, and can cause constitutive FGFR signaling that may contribute to carcinogenesis,” write Yohann Loriot, MD, of Gustave Roussy, Université Paris-Sud and Université Paris-Saclay, in Villejuif, France, and coinvestigators. Up to 20% of patients with advanced disease and fully 37% of those with upper-tract tumors have alterations in these genes. “ Thus, FGFR inhibition may be particularly appropriate in patients with luminal I subtype disease, in which immunotherapeutic approaches may be less effective,” they noted.
In the trial, 99 patients with pretreated locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma having FGFR alterations were given single-agent, open-label erdafitinib (Balversa) for a median of five cycles. The drug was recently granted accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for this indication.
The rate of confirmed response according to investigator assessment was 40% (3% of patients had a complete response and 37% had a partial response), based on trial results reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. The response rate was 59% among the subset who had previously received immunotherapy.
With a median follow-up of 11.0 months, the median duration of progression-free survival was 5.5 months, and the median duration of overall survival was 13.8 months.
Fully 46% of patients experienced a grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse event, most commonly hyponatremia (11%), stomatitis (10%), and asthenia (7%). Nearly 56% of the trial population as a whole required a dose reduction. However, only 13% of patients stopped treatment because of an adverse event, and there were no treatment-related deaths.
“This study met its primary objective,” Dr. Loriot and coinvestigators concluded. “These findings showed that among patients with locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with certain FGFR alterations, erdafitinib had promising antitumor activity.”
“The response to erdafitinib was rapid and independent of the number of previous courses and types of therapy, the presence of visceral metastasis, or tumor location,” they wrote. In addition, the efficacy appears to be better than that achieved previously with chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and antibody-drug conjugates.
The trial was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Loriot reports grants and personal fees from Janssen, during the conduct of the study.
SOURCE: Loriot Y et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:338-348. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1817323.
Erdafitinib, an oral pan–fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is efficacious when used to treat urothelial cancer harboring FGFR genetic alterations, although dose adjustments are commonly needed, suggests a multicenter phase 2 trial.
“Mutations and fusions in FGFR2/3 are common in patients with urothelial carcinoma, particularly in the luminal I subtype, and can cause constitutive FGFR signaling that may contribute to carcinogenesis,” write Yohann Loriot, MD, of Gustave Roussy, Université Paris-Sud and Université Paris-Saclay, in Villejuif, France, and coinvestigators. Up to 20% of patients with advanced disease and fully 37% of those with upper-tract tumors have alterations in these genes. “ Thus, FGFR inhibition may be particularly appropriate in patients with luminal I subtype disease, in which immunotherapeutic approaches may be less effective,” they noted.
In the trial, 99 patients with pretreated locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma having FGFR alterations were given single-agent, open-label erdafitinib (Balversa) for a median of five cycles. The drug was recently granted accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for this indication.
The rate of confirmed response according to investigator assessment was 40% (3% of patients had a complete response and 37% had a partial response), based on trial results reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. The response rate was 59% among the subset who had previously received immunotherapy.
With a median follow-up of 11.0 months, the median duration of progression-free survival was 5.5 months, and the median duration of overall survival was 13.8 months.
Fully 46% of patients experienced a grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse event, most commonly hyponatremia (11%), stomatitis (10%), and asthenia (7%). Nearly 56% of the trial population as a whole required a dose reduction. However, only 13% of patients stopped treatment because of an adverse event, and there were no treatment-related deaths.
“This study met its primary objective,” Dr. Loriot and coinvestigators concluded. “These findings showed that among patients with locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with certain FGFR alterations, erdafitinib had promising antitumor activity.”
“The response to erdafitinib was rapid and independent of the number of previous courses and types of therapy, the presence of visceral metastasis, or tumor location,” they wrote. In addition, the efficacy appears to be better than that achieved previously with chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and antibody-drug conjugates.
The trial was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Loriot reports grants and personal fees from Janssen, during the conduct of the study.
SOURCE: Loriot Y et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:338-348. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1817323.
Erdafitinib, an oral pan–fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is efficacious when used to treat urothelial cancer harboring FGFR genetic alterations, although dose adjustments are commonly needed, suggests a multicenter phase 2 trial.
“Mutations and fusions in FGFR2/3 are common in patients with urothelial carcinoma, particularly in the luminal I subtype, and can cause constitutive FGFR signaling that may contribute to carcinogenesis,” write Yohann Loriot, MD, of Gustave Roussy, Université Paris-Sud and Université Paris-Saclay, in Villejuif, France, and coinvestigators. Up to 20% of patients with advanced disease and fully 37% of those with upper-tract tumors have alterations in these genes. “ Thus, FGFR inhibition may be particularly appropriate in patients with luminal I subtype disease, in which immunotherapeutic approaches may be less effective,” they noted.
In the trial, 99 patients with pretreated locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma having FGFR alterations were given single-agent, open-label erdafitinib (Balversa) for a median of five cycles. The drug was recently granted accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for this indication.
The rate of confirmed response according to investigator assessment was 40% (3% of patients had a complete response and 37% had a partial response), based on trial results reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. The response rate was 59% among the subset who had previously received immunotherapy.
With a median follow-up of 11.0 months, the median duration of progression-free survival was 5.5 months, and the median duration of overall survival was 13.8 months.
Fully 46% of patients experienced a grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse event, most commonly hyponatremia (11%), stomatitis (10%), and asthenia (7%). Nearly 56% of the trial population as a whole required a dose reduction. However, only 13% of patients stopped treatment because of an adverse event, and there were no treatment-related deaths.
“This study met its primary objective,” Dr. Loriot and coinvestigators concluded. “These findings showed that among patients with locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with certain FGFR alterations, erdafitinib had promising antitumor activity.”
“The response to erdafitinib was rapid and independent of the number of previous courses and types of therapy, the presence of visceral metastasis, or tumor location,” they wrote. In addition, the efficacy appears to be better than that achieved previously with chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and antibody-drug conjugates.
The trial was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Loriot reports grants and personal fees from Janssen, during the conduct of the study.
SOURCE: Loriot Y et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:338-348. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1817323.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Erdafitinib has good efficacy when used to treat advanced urothelial carcinoma harboring FGFR alterations.
Major finding: The confirmed response rate was 40% (3% of patients had a complete response, 37% of patients had a partial response). With a median follow-up of 11.0 months, the median duration of progression-free survival was 5.5 months, and the median duration of overall survival was 13.8 months.
Study details: A multicenter, open-label, single-arm phase 2 trial among 99 patients with pretreated locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma having FGFR alterations.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Loriot reports grants and personal fees from Janssen, during the conduct of the study.
Source: Loriot Y et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:338-48. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1817323.
Standard chemotherapy remains superior in early breast cancer
Standard adjuvant chemotherapy remained superior to capecitabine in older patients with early breast cancer, according to long-term follow-up results from a randomized study.
“We previously reported the primary analysis after a median follow-up of 2.4 years,” wrote Hyman B. Muss, MD, of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, and his colleagues in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“We now assess the risks and benefits of treatment after a median follow-up time of 11.4 years,” they said.
The Cancer and Leukemia Group B 49907 trial included 633 women aged 65 years and over with early breast cancer. Study patients were randomly assigned to receive either standard adjuvant chemotherapy (either cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, methotrexate and fluorouracil, or cyclophosphamide) or capecitabine.
The study was designed to evaluate noninferiority of capecitabine versus standard chemotherapy. The primary outcome measured was recurrence-free survival (RFS); overall survival (OS) was included as a secondary endpoint.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the 10-year RFS rates were 56% with standard chemotherapy versus 50% with capecitabine (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .03).
In addition, the breast cancer–specific survival rates were 88% and 82% in patients treated with standard chemotherapy, compared with capecitabine, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.62; P = .03). OS rates were 62% and 56% in the same groups (HR, 0.84; P = .16).
“With longer follow-up, RFS remains superior for standard adjuvant chemotherapy versus capecitabine, especially in patients with hormone receptor–negative disease,” Dr. Muss and his colleagues wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that the presence of comorbidities in this older population may diminish overall survival benefits.
“Optimally, we must increase the number of older patients in cancer clinical trials to have accurate data on outcomes, especially toxicity, for newer agents,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported financial affiliations with Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Genentech, Novartis, Puma Biotechnology, Pfizer, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, and several others.
SOURCE: Muss HB et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00647.
Standard adjuvant chemotherapy remained superior to capecitabine in older patients with early breast cancer, according to long-term follow-up results from a randomized study.
“We previously reported the primary analysis after a median follow-up of 2.4 years,” wrote Hyman B. Muss, MD, of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, and his colleagues in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“We now assess the risks and benefits of treatment after a median follow-up time of 11.4 years,” they said.
The Cancer and Leukemia Group B 49907 trial included 633 women aged 65 years and over with early breast cancer. Study patients were randomly assigned to receive either standard adjuvant chemotherapy (either cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, methotrexate and fluorouracil, or cyclophosphamide) or capecitabine.
The study was designed to evaluate noninferiority of capecitabine versus standard chemotherapy. The primary outcome measured was recurrence-free survival (RFS); overall survival (OS) was included as a secondary endpoint.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the 10-year RFS rates were 56% with standard chemotherapy versus 50% with capecitabine (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .03).
In addition, the breast cancer–specific survival rates were 88% and 82% in patients treated with standard chemotherapy, compared with capecitabine, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.62; P = .03). OS rates were 62% and 56% in the same groups (HR, 0.84; P = .16).
“With longer follow-up, RFS remains superior for standard adjuvant chemotherapy versus capecitabine, especially in patients with hormone receptor–negative disease,” Dr. Muss and his colleagues wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that the presence of comorbidities in this older population may diminish overall survival benefits.
“Optimally, we must increase the number of older patients in cancer clinical trials to have accurate data on outcomes, especially toxicity, for newer agents,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported financial affiliations with Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Genentech, Novartis, Puma Biotechnology, Pfizer, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, and several others.
SOURCE: Muss HB et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00647.
Standard adjuvant chemotherapy remained superior to capecitabine in older patients with early breast cancer, according to long-term follow-up results from a randomized study.
“We previously reported the primary analysis after a median follow-up of 2.4 years,” wrote Hyman B. Muss, MD, of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, and his colleagues in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“We now assess the risks and benefits of treatment after a median follow-up time of 11.4 years,” they said.
The Cancer and Leukemia Group B 49907 trial included 633 women aged 65 years and over with early breast cancer. Study patients were randomly assigned to receive either standard adjuvant chemotherapy (either cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, methotrexate and fluorouracil, or cyclophosphamide) or capecitabine.
The study was designed to evaluate noninferiority of capecitabine versus standard chemotherapy. The primary outcome measured was recurrence-free survival (RFS); overall survival (OS) was included as a secondary endpoint.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the 10-year RFS rates were 56% with standard chemotherapy versus 50% with capecitabine (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .03).
In addition, the breast cancer–specific survival rates were 88% and 82% in patients treated with standard chemotherapy, compared with capecitabine, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.62; P = .03). OS rates were 62% and 56% in the same groups (HR, 0.84; P = .16).
“With longer follow-up, RFS remains superior for standard adjuvant chemotherapy versus capecitabine, especially in patients with hormone receptor–negative disease,” Dr. Muss and his colleagues wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that the presence of comorbidities in this older population may diminish overall survival benefits.
“Optimally, we must increase the number of older patients in cancer clinical trials to have accurate data on outcomes, especially toxicity, for newer agents,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported financial affiliations with Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Genentech, Novartis, Puma Biotechnology, Pfizer, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, and several others.
SOURCE: Muss HB et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00647.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of ovarian remnant syndrome
Ovarian remnant syndrome (ORS) is an uncommon problem, but one that seems to be increasing in incidence and one that is important to diagnose and treat properly, as well as prevent. Retrospective cohort studies published in the past 15 years or so have improved our understanding of its presentation and the outcomes of surgical management – and recent literature has demonstrated that a minimally invasive surgical approach with either conventional laparoscopy or robot-assisted laparoscopy yields improved outcomes in a skilled surgeon’s hands.
Diagnosis is based on clinical history and should be further supported with imaging and laboratory evaluation. A definitive diagnosis of the disease comes through surgical intervention and pathological findings.
Surgery therefore is technically challenging, usually requiring complete ureterolysis, careful adhesiolysis (often enterolysis), and excision of much of the pelvic sidewall peritoneum with extirpation of the remnant and endometriosis. High ligation of the ovarian vasculature also often is required.
This complexity and the consequent risk of intraoperative injury to the bowel, bladder, and ureters requires careful preoperative preparation. When an ovarian remnant is suspected, it may be important to have other surgeons – such as gynecologic oncologists, urologists, colorectal surgeons, or general surgeons – either present or on standby during the surgical intervention. In expert hands, surgical intervention has been shown to resolve or improve pain in the majority of patients, with no recurrence of the syndrome.
Diagnosis of ORS

Courtesy Dr. Charles E. Miller and Dr. Kirsten J. Sasaki
Patients with ORS have had previous oophorectomies with incomplete removal of ovarian tissue. Pelvic pain, either cyclical or most commonly chronic, is a common symptom. Other symptoms can include dyspareunia, dysuria and other urinary symptoms, and bowel symptoms. Ovarian remnants may have an expanding cystic structure – oftentimes secondary to endometriosis – that causes mass-like effects leading to pain and inflammation and to symptoms such as low back pain, constipation, and even urinary retention.
It also is important to discuss the patient’s history of menopausal symptoms, because the absence of these symptoms after oophorectomy may be a sign that ovarian tissue has been left behind. Menopausal symptoms do not exclude the diagnosis, however. Endometriosis, extensive surgical history, and other diseases that lead to significant adhesion formation – and a higher risk of incomplete removal of ovarian tissue, theoretically – also should be explored during history-taking.
Laboratory assessment of serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol can be helpful. Values that are indicative of ovarian function – FSH less than 30 mIU/mL and estradiol greater than 35 pg/mL – point towards ORS, but the absence of such premenopausal values should not rule out the possibility of an ovarian remnant.
The literature shows that FSH and estradiol levels are variable in women with ORS. A retrospective review published in 2005 by Paul M. Magtibay, MD, and colleagues at the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., and Rochester, Minn., involved 186 patients treated surgically from 1985 to 2003 with a mean follow-up, via questionnaire, of 1.2 years. This is the largest series published thus far of patients with pathologically confirmed ORS. It reported premenopausal levels of FSH and estradiol in 69% and 63% of patients, respectively, who had preoperative hormonal evaluations.1
In another retrospective cohort study published in 2011 of 30 women – also with pathologically confirmed ovarian remnants – Deborah Arden, MD, and Ted Lee, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center reported premenopausal levels of FSH and estradiol in 59% and 71%, respectively, of women whose concentrations were measured.2
ORS often involves a pelvic mass, and preoperative imaging is important in this regard. In Dr. Magtibay’s series, a pelvic mass was identified in 93%, 92%, and 78% of those who were imaged presurgically with ultrasonography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, respectively.1 As with laboratory testing, however, a negative result does not rule out the presence of an ovarian remnant.
Some authors have advocated the use of clomiphene citrate stimulation before preoperative imaging – or before repeat imaging – to identify remnant ovarian tissue. Typically, clomiphene citrate 100 mg is administered for 10 days prior to imaging to potentially induce ovulation in patients with suspected ORS. Alternatively, at the Advanced Gynecologic Surgery Institute in Naperville and Park Ridge, Ill., ovarian stimulation is performed using FSH 300 IUs for 5 days. A finding of cystic structures consistent with ovarian follicles will help narrow the diagnosis.
Use of gonadotropins is superior in that an intact pituitary-ovarian axis is not required. Moreover, monitoring can be in real time; increasing estradiol levels and increasing mass size on ultrasound can be monitored as gonadotropin treatment is rendered. Again, however, negative findings should not necessarily rule out ORS. Unfortunately, there have been no clinical studies looking at the use of controlled ovarian stimulation as a definitive test.
The differential diagnosis includes supernumerary ovary (a rare gynecologic congenital anomaly) and residual ovary syndrome (a condition in which an ovary is intentionally or unintentionally left in place during a hysterectomy, as well as often an intended bilateral oophorectomy, and later causes pain). The latter occurs when surgical anatomy is poor and the surgery is consequently very difficult.
Surgical principles and approach
Previously, laparotomy was believed to be the best approach for minimizing intraoperative complications and achieving the extensive dissections necessary for effective treatment of ORS. In recent years, conventional laparoscopy and robot-assisted laparoscopy have been shown in retrospective reviews such as that by Arden et al.2 and a 2007 review by Rosanne M. Kho, MD,3 to be just as safe and effective provided that the same surgical principles – extensive retroperitoneal dissections and ureterolysis – are applied.
Good outcomes can be achieved with less blood loss, shorter operating room time, and less time in the hospital. The better visualization with greater magnification afforded by a minimally invasive approach offers a distinct advantage for such complex dissections.
A remnant of ovarian tissue can be located anywhere along the pelvic sidewall, which makes the surgical protocol largely individualized and based on the suspected location of the remnant.
Still, there are certain standard components of any surgical approach to ORS: The retroperitoneum should be entered at the level of the pelvic brim and the ureter must be clearly identified; usually, a partial or complete ureterolysis is necessary. Then, a window into the broad ligament inferior to the infundibulopelvic (IP) ligament is created, or the peritoneum of the broad ligament is removed, in order to completely isolate both the IP ligament and the ureter.
Once the ovarian remnant is isolated, a wide excision at least 2 cm from all ovarian tissue is performed. This wide surgical clearance is critical to prevent recurrence.
These standard components form the crux of the most basic and straightforward surgery for ORS. In some cases, more extensive dissections such as a cystectomy or even a bowel resection might be necessary. Ligation of the IP ligament as high because its connection to the aortic bifurcation also may be necessary – depending, again, on the location of the ovarian remnant.
The risk of intraoperative injury to the bowel, bladder, and ureters is not insignificant, but with careful planning and the involvement of other surgeons in the most complex cases, these risks can be minimized.
For patients who have a significant surgical history and do not want more surgery, pharmacologic therapy, such as leuprolide (Lupron) or danazol, is an option for ORS. It’s important to note, however, that no studies have been done to demonstrate that medical therapy is a curative option. In addition, one must consider the small risk that remnants may harbor or develop malignancy.
Malignancy has been reported in ovarian remnant tissue. While the risk is believed to be very small, 2 of the 20 patients in Dr. Kho’s cohort had malignancy in remnant tissue,3 and it is generally recommended that surgeons send frozen sections of suspected ovarian tissue to pathology. Frozen-section diagnosis of ovarian tissue is about 95% accurate.
Preventing ovarian remnants
Oophorectomy is a common procedure performed by gynecologic surgeons. While routine, it is imperative that it be performed correctly to prevent ovarian remnants from occurring. When performing a laparoscopic or robot-assisted laparoscopic oophorectomy, it is important to optimize visualization of the ovary and the IP ligament, and to account for the significant magnification provided by laparoscopic cameras.
Surgeons must make sure all adhesions are completely cleared in order to optimally transect the IP ligament. Furthermore, wide excision around ovarian tissue is critical. Accessory ovarian tissue has been found up to 1.4 cm away from the ovary itself, which is why we recommend that surgeons excise at least 2-3 cm away from the IP in order to safely ensure complete removal of ovarian tissue.
Dr. Kooperman completed the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL) Fellowship Program in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill., and will be starting practice at the Highland Park (Ill.) North Shore Hospital System in August 2019. He reported no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193(6):2062-6.
2. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18(2):194-9.
3. Fertil Steril. 2007;87(5):1005-9.
Ovarian remnant syndrome (ORS) is an uncommon problem, but one that seems to be increasing in incidence and one that is important to diagnose and treat properly, as well as prevent. Retrospective cohort studies published in the past 15 years or so have improved our understanding of its presentation and the outcomes of surgical management – and recent literature has demonstrated that a minimally invasive surgical approach with either conventional laparoscopy or robot-assisted laparoscopy yields improved outcomes in a skilled surgeon’s hands.
Diagnosis is based on clinical history and should be further supported with imaging and laboratory evaluation. A definitive diagnosis of the disease comes through surgical intervention and pathological findings.
Surgery therefore is technically challenging, usually requiring complete ureterolysis, careful adhesiolysis (often enterolysis), and excision of much of the pelvic sidewall peritoneum with extirpation of the remnant and endometriosis. High ligation of the ovarian vasculature also often is required.
This complexity and the consequent risk of intraoperative injury to the bowel, bladder, and ureters requires careful preoperative preparation. When an ovarian remnant is suspected, it may be important to have other surgeons – such as gynecologic oncologists, urologists, colorectal surgeons, or general surgeons – either present or on standby during the surgical intervention. In expert hands, surgical intervention has been shown to resolve or improve pain in the majority of patients, with no recurrence of the syndrome.
Diagnosis of ORS

Courtesy Dr. Charles E. Miller and Dr. Kirsten J. Sasaki
Patients with ORS have had previous oophorectomies with incomplete removal of ovarian tissue. Pelvic pain, either cyclical or most commonly chronic, is a common symptom. Other symptoms can include dyspareunia, dysuria and other urinary symptoms, and bowel symptoms. Ovarian remnants may have an expanding cystic structure – oftentimes secondary to endometriosis – that causes mass-like effects leading to pain and inflammation and to symptoms such as low back pain, constipation, and even urinary retention.
It also is important to discuss the patient’s history of menopausal symptoms, because the absence of these symptoms after oophorectomy may be a sign that ovarian tissue has been left behind. Menopausal symptoms do not exclude the diagnosis, however. Endometriosis, extensive surgical history, and other diseases that lead to significant adhesion formation – and a higher risk of incomplete removal of ovarian tissue, theoretically – also should be explored during history-taking.
Laboratory assessment of serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol can be helpful. Values that are indicative of ovarian function – FSH less than 30 mIU/mL and estradiol greater than 35 pg/mL – point towards ORS, but the absence of such premenopausal values should not rule out the possibility of an ovarian remnant.
The literature shows that FSH and estradiol levels are variable in women with ORS. A retrospective review published in 2005 by Paul M. Magtibay, MD, and colleagues at the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., and Rochester, Minn., involved 186 patients treated surgically from 1985 to 2003 with a mean follow-up, via questionnaire, of 1.2 years. This is the largest series published thus far of patients with pathologically confirmed ORS. It reported premenopausal levels of FSH and estradiol in 69% and 63% of patients, respectively, who had preoperative hormonal evaluations.1
In another retrospective cohort study published in 2011 of 30 women – also with pathologically confirmed ovarian remnants – Deborah Arden, MD, and Ted Lee, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center reported premenopausal levels of FSH and estradiol in 59% and 71%, respectively, of women whose concentrations were measured.2
ORS often involves a pelvic mass, and preoperative imaging is important in this regard. In Dr. Magtibay’s series, a pelvic mass was identified in 93%, 92%, and 78% of those who were imaged presurgically with ultrasonography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, respectively.1 As with laboratory testing, however, a negative result does not rule out the presence of an ovarian remnant.
Some authors have advocated the use of clomiphene citrate stimulation before preoperative imaging – or before repeat imaging – to identify remnant ovarian tissue. Typically, clomiphene citrate 100 mg is administered for 10 days prior to imaging to potentially induce ovulation in patients with suspected ORS. Alternatively, at the Advanced Gynecologic Surgery Institute in Naperville and Park Ridge, Ill., ovarian stimulation is performed using FSH 300 IUs for 5 days. A finding of cystic structures consistent with ovarian follicles will help narrow the diagnosis.
Use of gonadotropins is superior in that an intact pituitary-ovarian axis is not required. Moreover, monitoring can be in real time; increasing estradiol levels and increasing mass size on ultrasound can be monitored as gonadotropin treatment is rendered. Again, however, negative findings should not necessarily rule out ORS. Unfortunately, there have been no clinical studies looking at the use of controlled ovarian stimulation as a definitive test.
The differential diagnosis includes supernumerary ovary (a rare gynecologic congenital anomaly) and residual ovary syndrome (a condition in which an ovary is intentionally or unintentionally left in place during a hysterectomy, as well as often an intended bilateral oophorectomy, and later causes pain). The latter occurs when surgical anatomy is poor and the surgery is consequently very difficult.
Surgical principles and approach
Previously, laparotomy was believed to be the best approach for minimizing intraoperative complications and achieving the extensive dissections necessary for effective treatment of ORS. In recent years, conventional laparoscopy and robot-assisted laparoscopy have been shown in retrospective reviews such as that by Arden et al.2 and a 2007 review by Rosanne M. Kho, MD,3 to be just as safe and effective provided that the same surgical principles – extensive retroperitoneal dissections and ureterolysis – are applied.
Good outcomes can be achieved with less blood loss, shorter operating room time, and less time in the hospital. The better visualization with greater magnification afforded by a minimally invasive approach offers a distinct advantage for such complex dissections.
A remnant of ovarian tissue can be located anywhere along the pelvic sidewall, which makes the surgical protocol largely individualized and based on the suspected location of the remnant.
Still, there are certain standard components of any surgical approach to ORS: The retroperitoneum should be entered at the level of the pelvic brim and the ureter must be clearly identified; usually, a partial or complete ureterolysis is necessary. Then, a window into the broad ligament inferior to the infundibulopelvic (IP) ligament is created, or the peritoneum of the broad ligament is removed, in order to completely isolate both the IP ligament and the ureter.
Once the ovarian remnant is isolated, a wide excision at least 2 cm from all ovarian tissue is performed. This wide surgical clearance is critical to prevent recurrence.
These standard components form the crux of the most basic and straightforward surgery for ORS. In some cases, more extensive dissections such as a cystectomy or even a bowel resection might be necessary. Ligation of the IP ligament as high because its connection to the aortic bifurcation also may be necessary – depending, again, on the location of the ovarian remnant.
The risk of intraoperative injury to the bowel, bladder, and ureters is not insignificant, but with careful planning and the involvement of other surgeons in the most complex cases, these risks can be minimized.
For patients who have a significant surgical history and do not want more surgery, pharmacologic therapy, such as leuprolide (Lupron) or danazol, is an option for ORS. It’s important to note, however, that no studies have been done to demonstrate that medical therapy is a curative option. In addition, one must consider the small risk that remnants may harbor or develop malignancy.
Malignancy has been reported in ovarian remnant tissue. While the risk is believed to be very small, 2 of the 20 patients in Dr. Kho’s cohort had malignancy in remnant tissue,3 and it is generally recommended that surgeons send frozen sections of suspected ovarian tissue to pathology. Frozen-section diagnosis of ovarian tissue is about 95% accurate.
Preventing ovarian remnants
Oophorectomy is a common procedure performed by gynecologic surgeons. While routine, it is imperative that it be performed correctly to prevent ovarian remnants from occurring. When performing a laparoscopic or robot-assisted laparoscopic oophorectomy, it is important to optimize visualization of the ovary and the IP ligament, and to account for the significant magnification provided by laparoscopic cameras.
Surgeons must make sure all adhesions are completely cleared in order to optimally transect the IP ligament. Furthermore, wide excision around ovarian tissue is critical. Accessory ovarian tissue has been found up to 1.4 cm away from the ovary itself, which is why we recommend that surgeons excise at least 2-3 cm away from the IP in order to safely ensure complete removal of ovarian tissue.
Dr. Kooperman completed the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL) Fellowship Program in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill., and will be starting practice at the Highland Park (Ill.) North Shore Hospital System in August 2019. He reported no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193(6):2062-6.
2. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18(2):194-9.
3. Fertil Steril. 2007;87(5):1005-9.
Ovarian remnant syndrome (ORS) is an uncommon problem, but one that seems to be increasing in incidence and one that is important to diagnose and treat properly, as well as prevent. Retrospective cohort studies published in the past 15 years or so have improved our understanding of its presentation and the outcomes of surgical management – and recent literature has demonstrated that a minimally invasive surgical approach with either conventional laparoscopy or robot-assisted laparoscopy yields improved outcomes in a skilled surgeon’s hands.
Diagnosis is based on clinical history and should be further supported with imaging and laboratory evaluation. A definitive diagnosis of the disease comes through surgical intervention and pathological findings.
Surgery therefore is technically challenging, usually requiring complete ureterolysis, careful adhesiolysis (often enterolysis), and excision of much of the pelvic sidewall peritoneum with extirpation of the remnant and endometriosis. High ligation of the ovarian vasculature also often is required.
This complexity and the consequent risk of intraoperative injury to the bowel, bladder, and ureters requires careful preoperative preparation. When an ovarian remnant is suspected, it may be important to have other surgeons – such as gynecologic oncologists, urologists, colorectal surgeons, or general surgeons – either present or on standby during the surgical intervention. In expert hands, surgical intervention has been shown to resolve or improve pain in the majority of patients, with no recurrence of the syndrome.
Diagnosis of ORS

Courtesy Dr. Charles E. Miller and Dr. Kirsten J. Sasaki
Patients with ORS have had previous oophorectomies with incomplete removal of ovarian tissue. Pelvic pain, either cyclical or most commonly chronic, is a common symptom. Other symptoms can include dyspareunia, dysuria and other urinary symptoms, and bowel symptoms. Ovarian remnants may have an expanding cystic structure – oftentimes secondary to endometriosis – that causes mass-like effects leading to pain and inflammation and to symptoms such as low back pain, constipation, and even urinary retention.
It also is important to discuss the patient’s history of menopausal symptoms, because the absence of these symptoms after oophorectomy may be a sign that ovarian tissue has been left behind. Menopausal symptoms do not exclude the diagnosis, however. Endometriosis, extensive surgical history, and other diseases that lead to significant adhesion formation – and a higher risk of incomplete removal of ovarian tissue, theoretically – also should be explored during history-taking.
Laboratory assessment of serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol can be helpful. Values that are indicative of ovarian function – FSH less than 30 mIU/mL and estradiol greater than 35 pg/mL – point towards ORS, but the absence of such premenopausal values should not rule out the possibility of an ovarian remnant.
The literature shows that FSH and estradiol levels are variable in women with ORS. A retrospective review published in 2005 by Paul M. Magtibay, MD, and colleagues at the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., and Rochester, Minn., involved 186 patients treated surgically from 1985 to 2003 with a mean follow-up, via questionnaire, of 1.2 years. This is the largest series published thus far of patients with pathologically confirmed ORS. It reported premenopausal levels of FSH and estradiol in 69% and 63% of patients, respectively, who had preoperative hormonal evaluations.1
In another retrospective cohort study published in 2011 of 30 women – also with pathologically confirmed ovarian remnants – Deborah Arden, MD, and Ted Lee, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center reported premenopausal levels of FSH and estradiol in 59% and 71%, respectively, of women whose concentrations were measured.2
ORS often involves a pelvic mass, and preoperative imaging is important in this regard. In Dr. Magtibay’s series, a pelvic mass was identified in 93%, 92%, and 78% of those who were imaged presurgically with ultrasonography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, respectively.1 As with laboratory testing, however, a negative result does not rule out the presence of an ovarian remnant.
Some authors have advocated the use of clomiphene citrate stimulation before preoperative imaging – or before repeat imaging – to identify remnant ovarian tissue. Typically, clomiphene citrate 100 mg is administered for 10 days prior to imaging to potentially induce ovulation in patients with suspected ORS. Alternatively, at the Advanced Gynecologic Surgery Institute in Naperville and Park Ridge, Ill., ovarian stimulation is performed using FSH 300 IUs for 5 days. A finding of cystic structures consistent with ovarian follicles will help narrow the diagnosis.
Use of gonadotropins is superior in that an intact pituitary-ovarian axis is not required. Moreover, monitoring can be in real time; increasing estradiol levels and increasing mass size on ultrasound can be monitored as gonadotropin treatment is rendered. Again, however, negative findings should not necessarily rule out ORS. Unfortunately, there have been no clinical studies looking at the use of controlled ovarian stimulation as a definitive test.
The differential diagnosis includes supernumerary ovary (a rare gynecologic congenital anomaly) and residual ovary syndrome (a condition in which an ovary is intentionally or unintentionally left in place during a hysterectomy, as well as often an intended bilateral oophorectomy, and later causes pain). The latter occurs when surgical anatomy is poor and the surgery is consequently very difficult.
Surgical principles and approach
Previously, laparotomy was believed to be the best approach for minimizing intraoperative complications and achieving the extensive dissections necessary for effective treatment of ORS. In recent years, conventional laparoscopy and robot-assisted laparoscopy have been shown in retrospective reviews such as that by Arden et al.2 and a 2007 review by Rosanne M. Kho, MD,3 to be just as safe and effective provided that the same surgical principles – extensive retroperitoneal dissections and ureterolysis – are applied.
Good outcomes can be achieved with less blood loss, shorter operating room time, and less time in the hospital. The better visualization with greater magnification afforded by a minimally invasive approach offers a distinct advantage for such complex dissections.
A remnant of ovarian tissue can be located anywhere along the pelvic sidewall, which makes the surgical protocol largely individualized and based on the suspected location of the remnant.
Still, there are certain standard components of any surgical approach to ORS: The retroperitoneum should be entered at the level of the pelvic brim and the ureter must be clearly identified; usually, a partial or complete ureterolysis is necessary. Then, a window into the broad ligament inferior to the infundibulopelvic (IP) ligament is created, or the peritoneum of the broad ligament is removed, in order to completely isolate both the IP ligament and the ureter.
Once the ovarian remnant is isolated, a wide excision at least 2 cm from all ovarian tissue is performed. This wide surgical clearance is critical to prevent recurrence.
These standard components form the crux of the most basic and straightforward surgery for ORS. In some cases, more extensive dissections such as a cystectomy or even a bowel resection might be necessary. Ligation of the IP ligament as high because its connection to the aortic bifurcation also may be necessary – depending, again, on the location of the ovarian remnant.
The risk of intraoperative injury to the bowel, bladder, and ureters is not insignificant, but with careful planning and the involvement of other surgeons in the most complex cases, these risks can be minimized.
For patients who have a significant surgical history and do not want more surgery, pharmacologic therapy, such as leuprolide (Lupron) or danazol, is an option for ORS. It’s important to note, however, that no studies have been done to demonstrate that medical therapy is a curative option. In addition, one must consider the small risk that remnants may harbor or develop malignancy.
Malignancy has been reported in ovarian remnant tissue. While the risk is believed to be very small, 2 of the 20 patients in Dr. Kho’s cohort had malignancy in remnant tissue,3 and it is generally recommended that surgeons send frozen sections of suspected ovarian tissue to pathology. Frozen-section diagnosis of ovarian tissue is about 95% accurate.
Preventing ovarian remnants
Oophorectomy is a common procedure performed by gynecologic surgeons. While routine, it is imperative that it be performed correctly to prevent ovarian remnants from occurring. When performing a laparoscopic or robot-assisted laparoscopic oophorectomy, it is important to optimize visualization of the ovary and the IP ligament, and to account for the significant magnification provided by laparoscopic cameras.
Surgeons must make sure all adhesions are completely cleared in order to optimally transect the IP ligament. Furthermore, wide excision around ovarian tissue is critical. Accessory ovarian tissue has been found up to 1.4 cm away from the ovary itself, which is why we recommend that surgeons excise at least 2-3 cm away from the IP in order to safely ensure complete removal of ovarian tissue.
Dr. Kooperman completed the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL) Fellowship Program in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill., and will be starting practice at the Highland Park (Ill.) North Shore Hospital System in August 2019. He reported no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193(6):2062-6.
2. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18(2):194-9.
3. Fertil Steril. 2007;87(5):1005-9.
BTK mutations linked to CLL progression on ibrutinib
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
FROM BLOOD
Psychiatrists face challenges in creating Spravato practices
At Actify Neurotherapies, a longtime provider of ketamine infusion therapy, Steven P. Levine, MD, and staff are busy making preparations for a new offering: intranasal esketamine.
The nasal spray, called Spravato and developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2019 for treatment-resistant depression in adults who have failed at least two oral antidepressants of different classes.
“We’ve been anticipating this for years,” said Dr. Levine, founder and chief medical officer for Actify Neurotherapies, formerly Ketamine Treatment Centers.“Being used to giving IV ketamine every day, this really fits right into our daily practice. For us, [it means] adding a few staff members here and there to make sure we have adequate monitoring, [and] setting up recovery spaces so that patients have a nice place to spend time.”
Dr. Levine is far from alone. After the recent intranasal esketamine approval, many psychiatrists are considering how they might integrate the medication into their practice. The FDA is managing the drug under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires prescriber training on esketamine risks and patient monitoring. Facilities must be licensed to dispense esketamine and are required to monitor patients in person for at least 2 hours after administration.
The rigid requirements are important for safety, but they mean that a limited number of psychiatrists will likely have the capacity to deliver the medication, said Gerard Sanacora, MD, PhD, director of the Yale Depression Research Program in New Haven, Conn., and a principal investigator for several clinical trials associated with the esketamine nasal spray. Psychiatrists interested in providing the medication have much to consider in the way of logistics, structure, and staffing.
“The requirements do [present] hurdles,” Dr. Sanacora said. “This is a medication that requires a fair amount of infrastructure. This is not going to be a treatment that is going to be given by every corner psychiatrist.”
In addition to delivery obstacles, questions remain about the ideal Spravato regimen, particularly the optimal dose frequency during maintenance and the best way to track long-term outcomes. Some have also raised concerns about the potential for esketamine/ketamine abuse following the FDA approval.
Despite the questions, one thing most psychiatrists agree on is the need for intranasal esketamine and its promising impact.
“There’s no secret that at this point: We really haven’t put a dent in the rates of depression and the rates of suicide over the past several decades,” Dr. Levine said. “We’ve needed something that’s truly new, something that’s innovative. It makes the FDA approval of intranasal esketamine a really big deal. It’s a new mechanism, a new approach to depression, and provides hope to patients and the field of psychiatry.”
Addressing delivery challenges
After the FDA approval, Jacqueline Posada, MD, was tasked with helping a small psychiatry practice develop the framework to incorporate intranasal esketamine. Dr. Posada, a consultation-liaison psychiatry fellow at the Inova Fairfax Hospital-George Washington University program in Falls Church, Va., started by creating a comprehensive screening form for esketamine candidates, developing an informed-consent protocol, and researching storage guidelines for an outpatient practice.
Before the practice could move forward, however, Dr. Posada learned that building regulations for the office prohibited “medical procedures” from occurring in the space. While the 10-doctor practice is associated with George Washington University, Washington, it is located several blocks away in an office setting.
“It was pretty disappointing,” Dr. Posada said. “Our organization is looking for another spot that allows psychiatry to administer a medical procedure. There’s a lot of people who are in private practice who are in a type of office building that may restrict medical procedures. Depending on the type of space they are renting, they need to know what is allowed in their office building.”
Patient privacy is also a primary consideration when delivering the medication. Dr. Posada said she and her staff had contemplated conducting the 2-hour patient monitoring in a group setting, but that idea was quickly thwarted.
“Our plan was in 15- to 20-minute appointments, administer the esketamine, and have maybe 5-10 people monitored in a room with barriers between each chair,” she said. “We were advised by our privacy officer that that could hinder patient confidentiality and was not a viable option for administering the medication in our practice.”
Practices should also determine a long-term treatment plan for each patient receiving esketamine, Dr. Sanacora said, particularly in light of data suggesting that a substantial number of patients will relapse if treatment is stopped. A long-term treatment plan should be considered prior to, or at the same time that esketamine treatment is initiated.
Comanagement of patients by clinicians is another essential part of esketamine treatment, Dr. Sanacora added.
“It is going to be important for the community clinicians not directly offering the treatment to develop close and ongoing relationships with the clinicians and sites that are offering this treatment to optimize the care of their patients,” he said. “Conversely, it is going to be imperative that the esketamine providers develop effective and efficient methods of maintaining close communications with the referring clinicians.”
Reimbursement comes with upfront cost
As far as payment, Dr. Levine expects that the nasal spray will be widely reimbursed. Clinics must first purchase the medication and insurers will reimburse them later for the drug, a method commonly referred to as “buy and bill.” The upfront cost could be too expensive for some physicians.
“That’s not something psychiatrists are used to, storing a controlled substance on site, having the financial outlay of keeping inventory of an expensive drug, and waiting for reimbursement,” Dr. Levine said.
Practices can also bill an evaluation and management code for the treatment as well as for observation time. At this point, it appears insurers will not cover psychotherapy delivered at the same time, which is disappointing, he said.
Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, a psychiatry professor and vice chair for research at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said because many psychiatrists who specialize in psychopharmacology and who see treatment-resistant depression patients do not accept private insurance or Medicare/Medicaid, patient access to the drug may be limited.
“Given the REMS and the need for 2-hour monitoring following the treatment, I believe that primarily, specialized clinics and centers for ‘interventional psychiatry’ will be the early adopters,” he said. “The typical office-based psychiatrist who does not accept insurance, and does not have means to store and dispense a controlled substance or monitor patients, may not readily adopt this new approach.”
Experts say abuse potential low
Meanwhile, the potential for abuse with intranasal esketamine is low, considering the REMS requirements, said Mark S. Gold, MD, an addiction medicine specialist. If practices follow the guidelines, which restrict patients from taking the medication home, misuse is not likely.
However, the drug’s counterpart, ketamine, which has been abused globally for decades, may see an uptick in illicit use after the recent FDA approval of esketamine, Dr. Gold said. Ketamine is currently produced in clandestine labs for use on the club scene and for date rape purposes, Dr. Gold said. Most recently, ketamine has been mixed with cocaine and referred to as “Calvin Klein” for street use.
“You do have the unintended consequence when a medication is approved, [that] the general public may not be sophisticated enough to understand dose, duration, and supervised administration, and think that street ketamine is equally a medication,” Dr. Gold said. “You have the capacity for black market ketamine to undercut the price and be distributed in a form that can be extremely dangerous and life threatening. Just calling it ketamine provides confusion and the opportunity for black market sales distribution and increases in use.”
Dr. Mathew hopes the REMS designation will not only aid in risk mitigation for esketamine, but also result in valuable postapproval information with respect to longer term safety and efficacy. Questions that still need to be addressed include the best antidepressant regimens in conjunction with intranasal esketamine, the ideal long-term monitoring method, and the potential impact of benzodiazepines on response to Spravato.
“These answers will come with more research – phase 4 postmarketing studies – and also clinical experience in the community, as clinicians begin to prescribe esketamine,” Dr. Mathew said. “Input from organizations, such as the American Society of Ketamine Physicians, will be important as well.”
Dr. Levine, Dr. Posada, and Dr. Gold reported no disclosures. Dr. Sanacora served as principal investigator for several clinical trials associated with intranasal esketamine. Dr. Mathew served as a consultant to several pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen.
At Actify Neurotherapies, a longtime provider of ketamine infusion therapy, Steven P. Levine, MD, and staff are busy making preparations for a new offering: intranasal esketamine.
The nasal spray, called Spravato and developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2019 for treatment-resistant depression in adults who have failed at least two oral antidepressants of different classes.
“We’ve been anticipating this for years,” said Dr. Levine, founder and chief medical officer for Actify Neurotherapies, formerly Ketamine Treatment Centers.“Being used to giving IV ketamine every day, this really fits right into our daily practice. For us, [it means] adding a few staff members here and there to make sure we have adequate monitoring, [and] setting up recovery spaces so that patients have a nice place to spend time.”
Dr. Levine is far from alone. After the recent intranasal esketamine approval, many psychiatrists are considering how they might integrate the medication into their practice. The FDA is managing the drug under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires prescriber training on esketamine risks and patient monitoring. Facilities must be licensed to dispense esketamine and are required to monitor patients in person for at least 2 hours after administration.
The rigid requirements are important for safety, but they mean that a limited number of psychiatrists will likely have the capacity to deliver the medication, said Gerard Sanacora, MD, PhD, director of the Yale Depression Research Program in New Haven, Conn., and a principal investigator for several clinical trials associated with the esketamine nasal spray. Psychiatrists interested in providing the medication have much to consider in the way of logistics, structure, and staffing.
“The requirements do [present] hurdles,” Dr. Sanacora said. “This is a medication that requires a fair amount of infrastructure. This is not going to be a treatment that is going to be given by every corner psychiatrist.”
In addition to delivery obstacles, questions remain about the ideal Spravato regimen, particularly the optimal dose frequency during maintenance and the best way to track long-term outcomes. Some have also raised concerns about the potential for esketamine/ketamine abuse following the FDA approval.
Despite the questions, one thing most psychiatrists agree on is the need for intranasal esketamine and its promising impact.
“There’s no secret that at this point: We really haven’t put a dent in the rates of depression and the rates of suicide over the past several decades,” Dr. Levine said. “We’ve needed something that’s truly new, something that’s innovative. It makes the FDA approval of intranasal esketamine a really big deal. It’s a new mechanism, a new approach to depression, and provides hope to patients and the field of psychiatry.”
Addressing delivery challenges
After the FDA approval, Jacqueline Posada, MD, was tasked with helping a small psychiatry practice develop the framework to incorporate intranasal esketamine. Dr. Posada, a consultation-liaison psychiatry fellow at the Inova Fairfax Hospital-George Washington University program in Falls Church, Va., started by creating a comprehensive screening form for esketamine candidates, developing an informed-consent protocol, and researching storage guidelines for an outpatient practice.
Before the practice could move forward, however, Dr. Posada learned that building regulations for the office prohibited “medical procedures” from occurring in the space. While the 10-doctor practice is associated with George Washington University, Washington, it is located several blocks away in an office setting.
“It was pretty disappointing,” Dr. Posada said. “Our organization is looking for another spot that allows psychiatry to administer a medical procedure. There’s a lot of people who are in private practice who are in a type of office building that may restrict medical procedures. Depending on the type of space they are renting, they need to know what is allowed in their office building.”
Patient privacy is also a primary consideration when delivering the medication. Dr. Posada said she and her staff had contemplated conducting the 2-hour patient monitoring in a group setting, but that idea was quickly thwarted.
“Our plan was in 15- to 20-minute appointments, administer the esketamine, and have maybe 5-10 people monitored in a room with barriers between each chair,” she said. “We were advised by our privacy officer that that could hinder patient confidentiality and was not a viable option for administering the medication in our practice.”
Practices should also determine a long-term treatment plan for each patient receiving esketamine, Dr. Sanacora said, particularly in light of data suggesting that a substantial number of patients will relapse if treatment is stopped. A long-term treatment plan should be considered prior to, or at the same time that esketamine treatment is initiated.
Comanagement of patients by clinicians is another essential part of esketamine treatment, Dr. Sanacora added.
“It is going to be important for the community clinicians not directly offering the treatment to develop close and ongoing relationships with the clinicians and sites that are offering this treatment to optimize the care of their patients,” he said. “Conversely, it is going to be imperative that the esketamine providers develop effective and efficient methods of maintaining close communications with the referring clinicians.”
Reimbursement comes with upfront cost
As far as payment, Dr. Levine expects that the nasal spray will be widely reimbursed. Clinics must first purchase the medication and insurers will reimburse them later for the drug, a method commonly referred to as “buy and bill.” The upfront cost could be too expensive for some physicians.
“That’s not something psychiatrists are used to, storing a controlled substance on site, having the financial outlay of keeping inventory of an expensive drug, and waiting for reimbursement,” Dr. Levine said.
Practices can also bill an evaluation and management code for the treatment as well as for observation time. At this point, it appears insurers will not cover psychotherapy delivered at the same time, which is disappointing, he said.
Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, a psychiatry professor and vice chair for research at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said because many psychiatrists who specialize in psychopharmacology and who see treatment-resistant depression patients do not accept private insurance or Medicare/Medicaid, patient access to the drug may be limited.
“Given the REMS and the need for 2-hour monitoring following the treatment, I believe that primarily, specialized clinics and centers for ‘interventional psychiatry’ will be the early adopters,” he said. “The typical office-based psychiatrist who does not accept insurance, and does not have means to store and dispense a controlled substance or monitor patients, may not readily adopt this new approach.”
Experts say abuse potential low
Meanwhile, the potential for abuse with intranasal esketamine is low, considering the REMS requirements, said Mark S. Gold, MD, an addiction medicine specialist. If practices follow the guidelines, which restrict patients from taking the medication home, misuse is not likely.
However, the drug’s counterpart, ketamine, which has been abused globally for decades, may see an uptick in illicit use after the recent FDA approval of esketamine, Dr. Gold said. Ketamine is currently produced in clandestine labs for use on the club scene and for date rape purposes, Dr. Gold said. Most recently, ketamine has been mixed with cocaine and referred to as “Calvin Klein” for street use.
“You do have the unintended consequence when a medication is approved, [that] the general public may not be sophisticated enough to understand dose, duration, and supervised administration, and think that street ketamine is equally a medication,” Dr. Gold said. “You have the capacity for black market ketamine to undercut the price and be distributed in a form that can be extremely dangerous and life threatening. Just calling it ketamine provides confusion and the opportunity for black market sales distribution and increases in use.”
Dr. Mathew hopes the REMS designation will not only aid in risk mitigation for esketamine, but also result in valuable postapproval information with respect to longer term safety and efficacy. Questions that still need to be addressed include the best antidepressant regimens in conjunction with intranasal esketamine, the ideal long-term monitoring method, and the potential impact of benzodiazepines on response to Spravato.
“These answers will come with more research – phase 4 postmarketing studies – and also clinical experience in the community, as clinicians begin to prescribe esketamine,” Dr. Mathew said. “Input from organizations, such as the American Society of Ketamine Physicians, will be important as well.”
Dr. Levine, Dr. Posada, and Dr. Gold reported no disclosures. Dr. Sanacora served as principal investigator for several clinical trials associated with intranasal esketamine. Dr. Mathew served as a consultant to several pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen.
At Actify Neurotherapies, a longtime provider of ketamine infusion therapy, Steven P. Levine, MD, and staff are busy making preparations for a new offering: intranasal esketamine.
The nasal spray, called Spravato and developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2019 for treatment-resistant depression in adults who have failed at least two oral antidepressants of different classes.
“We’ve been anticipating this for years,” said Dr. Levine, founder and chief medical officer for Actify Neurotherapies, formerly Ketamine Treatment Centers.“Being used to giving IV ketamine every day, this really fits right into our daily practice. For us, [it means] adding a few staff members here and there to make sure we have adequate monitoring, [and] setting up recovery spaces so that patients have a nice place to spend time.”
Dr. Levine is far from alone. After the recent intranasal esketamine approval, many psychiatrists are considering how they might integrate the medication into their practice. The FDA is managing the drug under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires prescriber training on esketamine risks and patient monitoring. Facilities must be licensed to dispense esketamine and are required to monitor patients in person for at least 2 hours after administration.
The rigid requirements are important for safety, but they mean that a limited number of psychiatrists will likely have the capacity to deliver the medication, said Gerard Sanacora, MD, PhD, director of the Yale Depression Research Program in New Haven, Conn., and a principal investigator for several clinical trials associated with the esketamine nasal spray. Psychiatrists interested in providing the medication have much to consider in the way of logistics, structure, and staffing.
“The requirements do [present] hurdles,” Dr. Sanacora said. “This is a medication that requires a fair amount of infrastructure. This is not going to be a treatment that is going to be given by every corner psychiatrist.”
In addition to delivery obstacles, questions remain about the ideal Spravato regimen, particularly the optimal dose frequency during maintenance and the best way to track long-term outcomes. Some have also raised concerns about the potential for esketamine/ketamine abuse following the FDA approval.
Despite the questions, one thing most psychiatrists agree on is the need for intranasal esketamine and its promising impact.
“There’s no secret that at this point: We really haven’t put a dent in the rates of depression and the rates of suicide over the past several decades,” Dr. Levine said. “We’ve needed something that’s truly new, something that’s innovative. It makes the FDA approval of intranasal esketamine a really big deal. It’s a new mechanism, a new approach to depression, and provides hope to patients and the field of psychiatry.”
Addressing delivery challenges
After the FDA approval, Jacqueline Posada, MD, was tasked with helping a small psychiatry practice develop the framework to incorporate intranasal esketamine. Dr. Posada, a consultation-liaison psychiatry fellow at the Inova Fairfax Hospital-George Washington University program in Falls Church, Va., started by creating a comprehensive screening form for esketamine candidates, developing an informed-consent protocol, and researching storage guidelines for an outpatient practice.
Before the practice could move forward, however, Dr. Posada learned that building regulations for the office prohibited “medical procedures” from occurring in the space. While the 10-doctor practice is associated with George Washington University, Washington, it is located several blocks away in an office setting.
“It was pretty disappointing,” Dr. Posada said. “Our organization is looking for another spot that allows psychiatry to administer a medical procedure. There’s a lot of people who are in private practice who are in a type of office building that may restrict medical procedures. Depending on the type of space they are renting, they need to know what is allowed in their office building.”
Patient privacy is also a primary consideration when delivering the medication. Dr. Posada said she and her staff had contemplated conducting the 2-hour patient monitoring in a group setting, but that idea was quickly thwarted.
“Our plan was in 15- to 20-minute appointments, administer the esketamine, and have maybe 5-10 people monitored in a room with barriers between each chair,” she said. “We were advised by our privacy officer that that could hinder patient confidentiality and was not a viable option for administering the medication in our practice.”
Practices should also determine a long-term treatment plan for each patient receiving esketamine, Dr. Sanacora said, particularly in light of data suggesting that a substantial number of patients will relapse if treatment is stopped. A long-term treatment plan should be considered prior to, or at the same time that esketamine treatment is initiated.
Comanagement of patients by clinicians is another essential part of esketamine treatment, Dr. Sanacora added.
“It is going to be important for the community clinicians not directly offering the treatment to develop close and ongoing relationships with the clinicians and sites that are offering this treatment to optimize the care of their patients,” he said. “Conversely, it is going to be imperative that the esketamine providers develop effective and efficient methods of maintaining close communications with the referring clinicians.”
Reimbursement comes with upfront cost
As far as payment, Dr. Levine expects that the nasal spray will be widely reimbursed. Clinics must first purchase the medication and insurers will reimburse them later for the drug, a method commonly referred to as “buy and bill.” The upfront cost could be too expensive for some physicians.
“That’s not something psychiatrists are used to, storing a controlled substance on site, having the financial outlay of keeping inventory of an expensive drug, and waiting for reimbursement,” Dr. Levine said.
Practices can also bill an evaluation and management code for the treatment as well as for observation time. At this point, it appears insurers will not cover psychotherapy delivered at the same time, which is disappointing, he said.
Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, a psychiatry professor and vice chair for research at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said because many psychiatrists who specialize in psychopharmacology and who see treatment-resistant depression patients do not accept private insurance or Medicare/Medicaid, patient access to the drug may be limited.
“Given the REMS and the need for 2-hour monitoring following the treatment, I believe that primarily, specialized clinics and centers for ‘interventional psychiatry’ will be the early adopters,” he said. “The typical office-based psychiatrist who does not accept insurance, and does not have means to store and dispense a controlled substance or monitor patients, may not readily adopt this new approach.”
Experts say abuse potential low
Meanwhile, the potential for abuse with intranasal esketamine is low, considering the REMS requirements, said Mark S. Gold, MD, an addiction medicine specialist. If practices follow the guidelines, which restrict patients from taking the medication home, misuse is not likely.
However, the drug’s counterpart, ketamine, which has been abused globally for decades, may see an uptick in illicit use after the recent FDA approval of esketamine, Dr. Gold said. Ketamine is currently produced in clandestine labs for use on the club scene and for date rape purposes, Dr. Gold said. Most recently, ketamine has been mixed with cocaine and referred to as “Calvin Klein” for street use.
“You do have the unintended consequence when a medication is approved, [that] the general public may not be sophisticated enough to understand dose, duration, and supervised administration, and think that street ketamine is equally a medication,” Dr. Gold said. “You have the capacity for black market ketamine to undercut the price and be distributed in a form that can be extremely dangerous and life threatening. Just calling it ketamine provides confusion and the opportunity for black market sales distribution and increases in use.”
Dr. Mathew hopes the REMS designation will not only aid in risk mitigation for esketamine, but also result in valuable postapproval information with respect to longer term safety and efficacy. Questions that still need to be addressed include the best antidepressant regimens in conjunction with intranasal esketamine, the ideal long-term monitoring method, and the potential impact of benzodiazepines on response to Spravato.
“These answers will come with more research – phase 4 postmarketing studies – and also clinical experience in the community, as clinicians begin to prescribe esketamine,” Dr. Mathew said. “Input from organizations, such as the American Society of Ketamine Physicians, will be important as well.”
Dr. Levine, Dr. Posada, and Dr. Gold reported no disclosures. Dr. Sanacora served as principal investigator for several clinical trials associated with intranasal esketamine. Dr. Mathew served as a consultant to several pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen.