User login
Oral minoxidil improves anticancer treatment–induced alopecia in women with breast cancer
Topical minoxidil is widely used to treat hair loss, but new findings suggest that
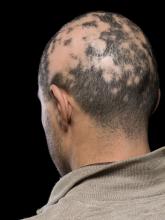
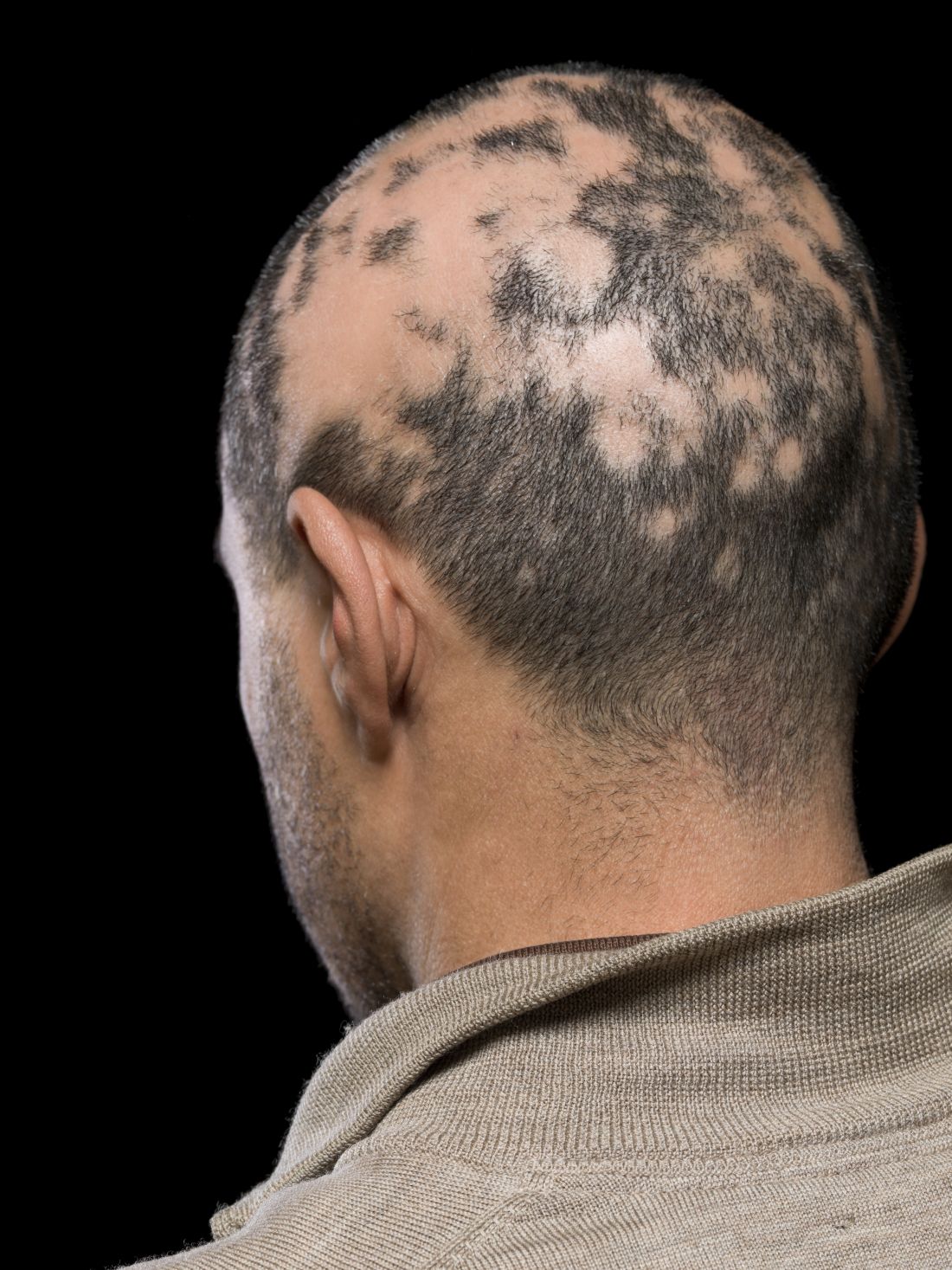
In a retrospective cohort study of women with breast cancer and anticancer therapy–induced alopecia, researchers found that combining low-dose oral minoxidil (LDOM) and topical minoxidil achieved better results than topical minoxidil alone and that the treatment was well tolerated. A total of 5 of the 37 patients (13.5%) in the combination therapy group achieved a complete response, defined as an improvement of alopecia severity from grade 2 to grade 1, compared with none of the 19 patients in the topical therapy–only group.
In contrast, none of the patients in the combination group experienced worsening of alopecia, compared with two (10.5%) in the topical monotherapy group.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Topical minoxidil is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat androgenetic alopecia. Oral minoxidil is not approved for treating hair loss but has been receiving increased attention as an adjunctive therapy for hair loss, particularly for women. Oral minoxidil is approved for treating hypertension but at much higher doses.
An increasing number of studies have been conducted on the use of oral minoxidil for the treatment of female pattern hair loss, dating back to a pilot study in 2017, with promising results. The findings suggest that LDOM might be more effective than topical therapy, well tolerated, and more convenient for individuals to take.
Hypothesis generating
In a comment, Kai Johnson, MD, a medical oncologist who specializes in treating patients with breast cancer at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute, Columbus, noted that the study, like most small-scale retrospective studies, is hypothesis generating. However, “I’d be hesitant to broadly recommend this practice of dual therapy – oral and topical minoxidil together – until we see a placebo-controlled prospective study performed demonstrating clinically meaningful benefits for patients.”
Another factor is the study endpoints. “While there was a statistically significant benefit documented with dual therapy in this study, it’s important to have study endpoints that are more patient oriented,” Dr. Johnson said. The most important endpoint for patients would be improvements “in the actual alopecia grade, which did occur in 5 of the 37 of dual-therapy patients, versus 0 topical minoxidil patients.”
George Cotsarelis, MD, chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, also weighed in. He questioned whether adding the topical therapy to oral minoxidil actually improved the results. “What was missing was a study arm that used the oral alone,” he said in an interview. “So we don’t know how effective the oral therapy would be by itself and if combining it with the topical is really adding anything.”
Oral minoxidil as a treatment for hair loss is gaining traction, and it’s clear that it is effective. However, the risk of side effects is higher, he said. “The risk isn’t that high with the low dose, but it can grow hair on places other than the scalp, and that can be disconcerting.” In this study, two women who took the oral drug reported edema, and one reported headache and dizziness. Hypertrichosis was reported by five patients who received the combination.
Study details
In the study, Jeewoo Kang, MD, and colleagues from the Seoul National University evaluated the efficacy of LDOM in 100 patients with breast cancer who had been diagnosed with persistent chemotherapy-induced alopecia (pCIA) and endocrine therapy–induced alopecia (EIA) at a dermatology clinic.
They conducted an analysis of medical records, standardized clinical photographs, and trichoscopic images to evaluate the alopecia pattern, severity, treatment response, and posttreatment changes in vertex hair density and thickness.
Compared with those with EIA alone, patients with pCIA were significantly more likely to have diffuse alopecia (P < .001), and they were more likely to have more severe alopecia, although this difference was not significant (P = .058). Outcomes were evaluated for 56 patients who were treated with minoxidil (19 with topical minoxidil alone and 37 with both LDOM and topical minoxidil) and for whom clinical and trichoscopic photos were available at baseline and at the last follow-up (all patients were scheduled for follow-up at 3-month intervals).
The results showed that those treated with 1.25-5.0 mg/d of oral minoxidil and 5% topical minoxidil solution once a day had better responses (P = .002) and a higher percentage increase in hair density from baseline (P = .003), compared with those who received topical minoxidil monotherapy.
However, changes in hair thickness after treatment were not significantly different between the two groups (P = .540).
In addition to the five (13.5%) cases of hypertrichosis, two cases of edema (5.4%), and one case of headache/dizziness (2.7%) among those who received the combination, there was also one report of palpitations (2.7%). Palpitations were reported in one patient (5%) who received topical monotherapy, the only adverse event reported in this group.
Dr. Johnson noted that, at his institution, a dermatologist is conducting a clinical trial with oncology patients post chemotherapy and endocrine therapy. “She is looking at a similar question, although she is comparing oral minoxidil to topical minoxidil directly rather than in combination.” There is also an active clinical trial at Northwestern University, Chicago, of LDOM alone for patients with chemotherapy-induced alopecia.
“So there is a lot of momentum surrounding this concept, and I feel we will continue to see it come up as a possible treatment option, but more data are needed at this time before it can become standard of care,” Dr. Johnson added.
No funding for the study was reported. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Topical minoxidil is widely used to treat hair loss, but new findings suggest that
In a retrospective cohort study of women with breast cancer and anticancer therapy–induced alopecia, researchers found that combining low-dose oral minoxidil (LDOM) and topical minoxidil achieved better results than topical minoxidil alone and that the treatment was well tolerated. A total of 5 of the 37 patients (13.5%) in the combination therapy group achieved a complete response, defined as an improvement of alopecia severity from grade 2 to grade 1, compared with none of the 19 patients in the topical therapy–only group.
In contrast, none of the patients in the combination group experienced worsening of alopecia, compared with two (10.5%) in the topical monotherapy group.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Topical minoxidil is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat androgenetic alopecia. Oral minoxidil is not approved for treating hair loss but has been receiving increased attention as an adjunctive therapy for hair loss, particularly for women. Oral minoxidil is approved for treating hypertension but at much higher doses.
An increasing number of studies have been conducted on the use of oral minoxidil for the treatment of female pattern hair loss, dating back to a pilot study in 2017, with promising results. The findings suggest that LDOM might be more effective than topical therapy, well tolerated, and more convenient for individuals to take.
Hypothesis generating
In a comment, Kai Johnson, MD, a medical oncologist who specializes in treating patients with breast cancer at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute, Columbus, noted that the study, like most small-scale retrospective studies, is hypothesis generating. However, “I’d be hesitant to broadly recommend this practice of dual therapy – oral and topical minoxidil together – until we see a placebo-controlled prospective study performed demonstrating clinically meaningful benefits for patients.”
Another factor is the study endpoints. “While there was a statistically significant benefit documented with dual therapy in this study, it’s important to have study endpoints that are more patient oriented,” Dr. Johnson said. The most important endpoint for patients would be improvements “in the actual alopecia grade, which did occur in 5 of the 37 of dual-therapy patients, versus 0 topical minoxidil patients.”
George Cotsarelis, MD, chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, also weighed in. He questioned whether adding the topical therapy to oral minoxidil actually improved the results. “What was missing was a study arm that used the oral alone,” he said in an interview. “So we don’t know how effective the oral therapy would be by itself and if combining it with the topical is really adding anything.”
Oral minoxidil as a treatment for hair loss is gaining traction, and it’s clear that it is effective. However, the risk of side effects is higher, he said. “The risk isn’t that high with the low dose, but it can grow hair on places other than the scalp, and that can be disconcerting.” In this study, two women who took the oral drug reported edema, and one reported headache and dizziness. Hypertrichosis was reported by five patients who received the combination.
Study details
In the study, Jeewoo Kang, MD, and colleagues from the Seoul National University evaluated the efficacy of LDOM in 100 patients with breast cancer who had been diagnosed with persistent chemotherapy-induced alopecia (pCIA) and endocrine therapy–induced alopecia (EIA) at a dermatology clinic.
They conducted an analysis of medical records, standardized clinical photographs, and trichoscopic images to evaluate the alopecia pattern, severity, treatment response, and posttreatment changes in vertex hair density and thickness.
Compared with those with EIA alone, patients with pCIA were significantly more likely to have diffuse alopecia (P < .001), and they were more likely to have more severe alopecia, although this difference was not significant (P = .058). Outcomes were evaluated for 56 patients who were treated with minoxidil (19 with topical minoxidil alone and 37 with both LDOM and topical minoxidil) and for whom clinical and trichoscopic photos were available at baseline and at the last follow-up (all patients were scheduled for follow-up at 3-month intervals).
The results showed that those treated with 1.25-5.0 mg/d of oral minoxidil and 5% topical minoxidil solution once a day had better responses (P = .002) and a higher percentage increase in hair density from baseline (P = .003), compared with those who received topical minoxidil monotherapy.
However, changes in hair thickness after treatment were not significantly different between the two groups (P = .540).
In addition to the five (13.5%) cases of hypertrichosis, two cases of edema (5.4%), and one case of headache/dizziness (2.7%) among those who received the combination, there was also one report of palpitations (2.7%). Palpitations were reported in one patient (5%) who received topical monotherapy, the only adverse event reported in this group.
Dr. Johnson noted that, at his institution, a dermatologist is conducting a clinical trial with oncology patients post chemotherapy and endocrine therapy. “She is looking at a similar question, although she is comparing oral minoxidil to topical minoxidil directly rather than in combination.” There is also an active clinical trial at Northwestern University, Chicago, of LDOM alone for patients with chemotherapy-induced alopecia.
“So there is a lot of momentum surrounding this concept, and I feel we will continue to see it come up as a possible treatment option, but more data are needed at this time before it can become standard of care,” Dr. Johnson added.
No funding for the study was reported. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Topical minoxidil is widely used to treat hair loss, but new findings suggest that
In a retrospective cohort study of women with breast cancer and anticancer therapy–induced alopecia, researchers found that combining low-dose oral minoxidil (LDOM) and topical minoxidil achieved better results than topical minoxidil alone and that the treatment was well tolerated. A total of 5 of the 37 patients (13.5%) in the combination therapy group achieved a complete response, defined as an improvement of alopecia severity from grade 2 to grade 1, compared with none of the 19 patients in the topical therapy–only group.
In contrast, none of the patients in the combination group experienced worsening of alopecia, compared with two (10.5%) in the topical monotherapy group.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Topical minoxidil is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat androgenetic alopecia. Oral minoxidil is not approved for treating hair loss but has been receiving increased attention as an adjunctive therapy for hair loss, particularly for women. Oral minoxidil is approved for treating hypertension but at much higher doses.
An increasing number of studies have been conducted on the use of oral minoxidil for the treatment of female pattern hair loss, dating back to a pilot study in 2017, with promising results. The findings suggest that LDOM might be more effective than topical therapy, well tolerated, and more convenient for individuals to take.
Hypothesis generating
In a comment, Kai Johnson, MD, a medical oncologist who specializes in treating patients with breast cancer at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute, Columbus, noted that the study, like most small-scale retrospective studies, is hypothesis generating. However, “I’d be hesitant to broadly recommend this practice of dual therapy – oral and topical minoxidil together – until we see a placebo-controlled prospective study performed demonstrating clinically meaningful benefits for patients.”
Another factor is the study endpoints. “While there was a statistically significant benefit documented with dual therapy in this study, it’s important to have study endpoints that are more patient oriented,” Dr. Johnson said. The most important endpoint for patients would be improvements “in the actual alopecia grade, which did occur in 5 of the 37 of dual-therapy patients, versus 0 topical minoxidil patients.”
George Cotsarelis, MD, chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, also weighed in. He questioned whether adding the topical therapy to oral minoxidil actually improved the results. “What was missing was a study arm that used the oral alone,” he said in an interview. “So we don’t know how effective the oral therapy would be by itself and if combining it with the topical is really adding anything.”
Oral minoxidil as a treatment for hair loss is gaining traction, and it’s clear that it is effective. However, the risk of side effects is higher, he said. “The risk isn’t that high with the low dose, but it can grow hair on places other than the scalp, and that can be disconcerting.” In this study, two women who took the oral drug reported edema, and one reported headache and dizziness. Hypertrichosis was reported by five patients who received the combination.
Study details
In the study, Jeewoo Kang, MD, and colleagues from the Seoul National University evaluated the efficacy of LDOM in 100 patients with breast cancer who had been diagnosed with persistent chemotherapy-induced alopecia (pCIA) and endocrine therapy–induced alopecia (EIA) at a dermatology clinic.
They conducted an analysis of medical records, standardized clinical photographs, and trichoscopic images to evaluate the alopecia pattern, severity, treatment response, and posttreatment changes in vertex hair density and thickness.
Compared with those with EIA alone, patients with pCIA were significantly more likely to have diffuse alopecia (P < .001), and they were more likely to have more severe alopecia, although this difference was not significant (P = .058). Outcomes were evaluated for 56 patients who were treated with minoxidil (19 with topical minoxidil alone and 37 with both LDOM and topical minoxidil) and for whom clinical and trichoscopic photos were available at baseline and at the last follow-up (all patients were scheduled for follow-up at 3-month intervals).
The results showed that those treated with 1.25-5.0 mg/d of oral minoxidil and 5% topical minoxidil solution once a day had better responses (P = .002) and a higher percentage increase in hair density from baseline (P = .003), compared with those who received topical minoxidil monotherapy.
However, changes in hair thickness after treatment were not significantly different between the two groups (P = .540).
In addition to the five (13.5%) cases of hypertrichosis, two cases of edema (5.4%), and one case of headache/dizziness (2.7%) among those who received the combination, there was also one report of palpitations (2.7%). Palpitations were reported in one patient (5%) who received topical monotherapy, the only adverse event reported in this group.
Dr. Johnson noted that, at his institution, a dermatologist is conducting a clinical trial with oncology patients post chemotherapy and endocrine therapy. “She is looking at a similar question, although she is comparing oral minoxidil to topical minoxidil directly rather than in combination.” There is also an active clinical trial at Northwestern University, Chicago, of LDOM alone for patients with chemotherapy-induced alopecia.
“So there is a lot of momentum surrounding this concept, and I feel we will continue to see it come up as a possible treatment option, but more data are needed at this time before it can become standard of care,” Dr. Johnson added.
No funding for the study was reported. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Study evaluates features of alopecia areata in Hispanic/Latinx patients
.
Those are among key findings from a retrospective analysis of Hispanic/Latinx patients at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) by Natasha Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, of UCI’s department of dermatology, and her coauthors. The findings were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A recent study examined the epidemiology of alopecia areata (AA) in Black patients, wrote Dr. Mesinkovska and coauthors Celine Phong, a UCI medical student, and Amy J. McMichael, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. “A similar unmet need exists to describe the characteristics of AA in Hispanic/Latinx (H/L) patients, the prevalent majority in California,” they added.
Drawing from chart reviews, ICD codes, and documented physical exams, they retrospectively identified 197 Hispanic/Latinx patients diagnosed with AA at UCI between 2015 and 2022, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
Nearly two-thirds of patients with alopecia were female (63%), and their mean age at diagnosis was 33 years. Most patients (79%) presented with patchy pattern AA, 13% had diffuse pattern AA, and only 12% had eyebrow, eyelash, or beard involvement. The most common comorbidity in patients overall was atopy (24%), including allergic rhinitis (12%), asthma (10%), and/or atopic dermatitis (7%).
The authors found that 18% of patients had one or more coexisting autoimmune conditions, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (9%) and thyroid disease (6%). No patients had celiac disease, myasthenia gravis, or inflammatory bowel disease, but 43% had another dermatologic condition.
In other findings, 22% of patients had vitamin D deficiency, 20% had hyperlipidemia, 18% had obesity, 16% had gastroesophageal reflux disease, and 12% had anemia. At the same time, depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders were identified in 14% of patients.
“Interestingly, the most common autoimmune comorbidity in H/L was rheumatoid arthritis, compared to thyroid disease in Black patients and overall AA patients,” the authors wrote. “This finding may be a reflection of a larger trend, as rheumatoid arthritis in the H/L population has been on the rise.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study including its small sample size and lack of a control group, and reported having no financial disclosures.
.
Those are among key findings from a retrospective analysis of Hispanic/Latinx patients at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) by Natasha Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, of UCI’s department of dermatology, and her coauthors. The findings were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A recent study examined the epidemiology of alopecia areata (AA) in Black patients, wrote Dr. Mesinkovska and coauthors Celine Phong, a UCI medical student, and Amy J. McMichael, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. “A similar unmet need exists to describe the characteristics of AA in Hispanic/Latinx (H/L) patients, the prevalent majority in California,” they added.
Drawing from chart reviews, ICD codes, and documented physical exams, they retrospectively identified 197 Hispanic/Latinx patients diagnosed with AA at UCI between 2015 and 2022, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
Nearly two-thirds of patients with alopecia were female (63%), and their mean age at diagnosis was 33 years. Most patients (79%) presented with patchy pattern AA, 13% had diffuse pattern AA, and only 12% had eyebrow, eyelash, or beard involvement. The most common comorbidity in patients overall was atopy (24%), including allergic rhinitis (12%), asthma (10%), and/or atopic dermatitis (7%).
The authors found that 18% of patients had one or more coexisting autoimmune conditions, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (9%) and thyroid disease (6%). No patients had celiac disease, myasthenia gravis, or inflammatory bowel disease, but 43% had another dermatologic condition.
In other findings, 22% of patients had vitamin D deficiency, 20% had hyperlipidemia, 18% had obesity, 16% had gastroesophageal reflux disease, and 12% had anemia. At the same time, depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders were identified in 14% of patients.
“Interestingly, the most common autoimmune comorbidity in H/L was rheumatoid arthritis, compared to thyroid disease in Black patients and overall AA patients,” the authors wrote. “This finding may be a reflection of a larger trend, as rheumatoid arthritis in the H/L population has been on the rise.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study including its small sample size and lack of a control group, and reported having no financial disclosures.
.
Those are among key findings from a retrospective analysis of Hispanic/Latinx patients at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) by Natasha Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, of UCI’s department of dermatology, and her coauthors. The findings were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A recent study examined the epidemiology of alopecia areata (AA) in Black patients, wrote Dr. Mesinkovska and coauthors Celine Phong, a UCI medical student, and Amy J. McMichael, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. “A similar unmet need exists to describe the characteristics of AA in Hispanic/Latinx (H/L) patients, the prevalent majority in California,” they added.
Drawing from chart reviews, ICD codes, and documented physical exams, they retrospectively identified 197 Hispanic/Latinx patients diagnosed with AA at UCI between 2015 and 2022, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
Nearly two-thirds of patients with alopecia were female (63%), and their mean age at diagnosis was 33 years. Most patients (79%) presented with patchy pattern AA, 13% had diffuse pattern AA, and only 12% had eyebrow, eyelash, or beard involvement. The most common comorbidity in patients overall was atopy (24%), including allergic rhinitis (12%), asthma (10%), and/or atopic dermatitis (7%).
The authors found that 18% of patients had one or more coexisting autoimmune conditions, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (9%) and thyroid disease (6%). No patients had celiac disease, myasthenia gravis, or inflammatory bowel disease, but 43% had another dermatologic condition.
In other findings, 22% of patients had vitamin D deficiency, 20% had hyperlipidemia, 18% had obesity, 16% had gastroesophageal reflux disease, and 12% had anemia. At the same time, depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders were identified in 14% of patients.
“Interestingly, the most common autoimmune comorbidity in H/L was rheumatoid arthritis, compared to thyroid disease in Black patients and overall AA patients,” the authors wrote. “This finding may be a reflection of a larger trend, as rheumatoid arthritis in the H/L population has been on the rise.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study including its small sample size and lack of a control group, and reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Hair supplements
in JAMA Dermatology in November 2022.
Drake and colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of nutritional supplements for treating hair loss. In a systematic database review from inception to Oct. 20, 2021, they evaluated and compiled the findings of all dietary and nutritional interventions for treatment of hair loss among individuals without a known baseline nutritional deficiency. Thirty articles were included, including 17 randomized clinical trials, 11 clinical trials, and 2 case series.
They found the highest-quality evidence showing the most potential benefit were for 12 of the 20 nutritional interventions in their review: Pumpkin seed oil capsules, omega-3 and -6 combined with antioxidants, tocotrienol, Pantogar, capsaicin and isoflavone, Viviscal (multiple formulations), Nourkrin, Nutrafol, apple nutraceutical, Lambdapil, total glucosides of paeony and compound glycyrrhizin tablets, and zinc. Vitamin D3, kimchi and cheonggukjang, and Forti5 had lower-quality evidence for disease course improvement. Adverse effects associated with the supplements were described as mild and rare.
In practice, for patients with nonscarring alopecia, I typically check screening labs for hair loss, in addition to the clinical exam, before starting treatment (including supplements), as addressing the underlying reason, if found, is always paramount. These labs are best performed when the patient is not taking biotin, as biotin has been shown numerous times to potentially be associated with endocrine lab abnormalities, most commonly thyroid-stimulating hormone, especially at higher doses, as well as troponin levels. Some over-the-counter hair supplements will contain much higher doses than the recommended 30 micrograms per day.
Separately, if ferritin levels are within normal range, but below 50 mcg/L, supplementation with Slow Fe or another slow-release iron supplement may also result in improved hair growth. Ferritin levels are typically rechecked 6 months after supplementation to see if levels of 50 mcg/L or above have been achieved.
Another point to consider before beginning supplementation is to educate patients about potential effects of supplementation, including increased hair growth in other areas besides the scalp. For some patients who are self-conscious about potential hirsutism, this could be an issue, whereas for others, this risk does not outweigh the benefit. Unwanted hair growth, should it occur, may also be addressed with hair removal methods including shaving, waxing, plucking, threading, depilatories, prescription eflornithine cream (Vaniqa), or laser hair removal if desired.
Our armamentarium for treating hair loss includes: addressing underlying systemic causes; topical treatments including topical minoxidil; oral supplements; platelet-rich plasma injections; prescription oral medications including finasteride in men or postmenopausal women or off-label oral minoxidil; and hair transplant surgery if warranted. Having this thorough review of the most common hair supplements currently available is extremely helpful and valuable in our specialty.
Dr. Wesley and Lily Talakoub, MD, are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to them at dermnews@mdedge.com. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. She had no relevant disclosures.
in JAMA Dermatology in November 2022.
Drake and colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of nutritional supplements for treating hair loss. In a systematic database review from inception to Oct. 20, 2021, they evaluated and compiled the findings of all dietary and nutritional interventions for treatment of hair loss among individuals without a known baseline nutritional deficiency. Thirty articles were included, including 17 randomized clinical trials, 11 clinical trials, and 2 case series.
They found the highest-quality evidence showing the most potential benefit were for 12 of the 20 nutritional interventions in their review: Pumpkin seed oil capsules, omega-3 and -6 combined with antioxidants, tocotrienol, Pantogar, capsaicin and isoflavone, Viviscal (multiple formulations), Nourkrin, Nutrafol, apple nutraceutical, Lambdapil, total glucosides of paeony and compound glycyrrhizin tablets, and zinc. Vitamin D3, kimchi and cheonggukjang, and Forti5 had lower-quality evidence for disease course improvement. Adverse effects associated with the supplements were described as mild and rare.
In practice, for patients with nonscarring alopecia, I typically check screening labs for hair loss, in addition to the clinical exam, before starting treatment (including supplements), as addressing the underlying reason, if found, is always paramount. These labs are best performed when the patient is not taking biotin, as biotin has been shown numerous times to potentially be associated with endocrine lab abnormalities, most commonly thyroid-stimulating hormone, especially at higher doses, as well as troponin levels. Some over-the-counter hair supplements will contain much higher doses than the recommended 30 micrograms per day.
Separately, if ferritin levels are within normal range, but below 50 mcg/L, supplementation with Slow Fe or another slow-release iron supplement may also result in improved hair growth. Ferritin levels are typically rechecked 6 months after supplementation to see if levels of 50 mcg/L or above have been achieved.
Another point to consider before beginning supplementation is to educate patients about potential effects of supplementation, including increased hair growth in other areas besides the scalp. For some patients who are self-conscious about potential hirsutism, this could be an issue, whereas for others, this risk does not outweigh the benefit. Unwanted hair growth, should it occur, may also be addressed with hair removal methods including shaving, waxing, plucking, threading, depilatories, prescription eflornithine cream (Vaniqa), or laser hair removal if desired.
Our armamentarium for treating hair loss includes: addressing underlying systemic causes; topical treatments including topical minoxidil; oral supplements; platelet-rich plasma injections; prescription oral medications including finasteride in men or postmenopausal women or off-label oral minoxidil; and hair transplant surgery if warranted. Having this thorough review of the most common hair supplements currently available is extremely helpful and valuable in our specialty.
Dr. Wesley and Lily Talakoub, MD, are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to them at dermnews@mdedge.com. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. She had no relevant disclosures.
in JAMA Dermatology in November 2022.
Drake and colleagues evaluated the safety and efficacy of nutritional supplements for treating hair loss. In a systematic database review from inception to Oct. 20, 2021, they evaluated and compiled the findings of all dietary and nutritional interventions for treatment of hair loss among individuals without a known baseline nutritional deficiency. Thirty articles were included, including 17 randomized clinical trials, 11 clinical trials, and 2 case series.
They found the highest-quality evidence showing the most potential benefit were for 12 of the 20 nutritional interventions in their review: Pumpkin seed oil capsules, omega-3 and -6 combined with antioxidants, tocotrienol, Pantogar, capsaicin and isoflavone, Viviscal (multiple formulations), Nourkrin, Nutrafol, apple nutraceutical, Lambdapil, total glucosides of paeony and compound glycyrrhizin tablets, and zinc. Vitamin D3, kimchi and cheonggukjang, and Forti5 had lower-quality evidence for disease course improvement. Adverse effects associated with the supplements were described as mild and rare.
In practice, for patients with nonscarring alopecia, I typically check screening labs for hair loss, in addition to the clinical exam, before starting treatment (including supplements), as addressing the underlying reason, if found, is always paramount. These labs are best performed when the patient is not taking biotin, as biotin has been shown numerous times to potentially be associated with endocrine lab abnormalities, most commonly thyroid-stimulating hormone, especially at higher doses, as well as troponin levels. Some over-the-counter hair supplements will contain much higher doses than the recommended 30 micrograms per day.
Separately, if ferritin levels are within normal range, but below 50 mcg/L, supplementation with Slow Fe or another slow-release iron supplement may also result in improved hair growth. Ferritin levels are typically rechecked 6 months after supplementation to see if levels of 50 mcg/L or above have been achieved.
Another point to consider before beginning supplementation is to educate patients about potential effects of supplementation, including increased hair growth in other areas besides the scalp. For some patients who are self-conscious about potential hirsutism, this could be an issue, whereas for others, this risk does not outweigh the benefit. Unwanted hair growth, should it occur, may also be addressed with hair removal methods including shaving, waxing, plucking, threading, depilatories, prescription eflornithine cream (Vaniqa), or laser hair removal if desired.
Our armamentarium for treating hair loss includes: addressing underlying systemic causes; topical treatments including topical minoxidil; oral supplements; platelet-rich plasma injections; prescription oral medications including finasteride in men or postmenopausal women or off-label oral minoxidil; and hair transplant surgery if warranted. Having this thorough review of the most common hair supplements currently available is extremely helpful and valuable in our specialty.
Dr. Wesley and Lily Talakoub, MD, are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to them at dermnews@mdedge.com. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. She had no relevant disclosures.
Current alopecia areata options include old and new therapies
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
“Some patients don’t have alopecia, but they have been managed for it,” he said. “Whenever there is an ounce of doubt, take a biopsy,” he advised.
Assessing disease severity in patients with alopecia areata (AA) is especially important as new therapies become available, said Dr. King, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score has been available since 2004, and remains a useful tool to estimate percent hair loss. The SALT Score divides the scalp into four sections: 18% each for the right and left sides, 40% for the top of the head, and 24% for the back of the head, said Dr. King. However, the SALT Score can be enhanced or modified based on a holistic approach to disease severity that categorizes alopecia as mild (scalp hair loss of 20% or less), moderate (scalp hair loss of 21 to 49%), or severe (scalp hair loss of 50% or more).
For example, if a patient’s hair loss based on SALT Score is mild or moderate, increase the severity by 1 level (from mild to moderate, or moderate to severe) if any of the following conditions apply: Noticeable eyebrow or eyelash involvement, inadequate treatment response after 6 months, diffuse positive hair pull test consistent with rapid progression of AA, or a negative impact on psychosocial functioning because of AA, he said.
Treatment advances
Understanding of the pathogenesis of AA has been slow to evolve, Dr. King noted. “We haven’t been able to shake this concept that people are causing the disease by being depressed,” as noted in the literature from the 1950s.
In 2014, breakthrough research changed the game by identifying the roles of interferon gamma and interleukin 15, Dr. King said. Since then, more research has been conducted on Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for AA. Dr. King was a coinvestigator on a 2014 case report in which a patient with psoriasis and alopecia universalis experienced regrowth of most of his body hair after 8 months of daily oral tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
However, despite the dramatic results in some patients, “tofacitinib doesn’t always work,” said Dr. King. In his experience, patients for whom tofacitinib didn’t work were those with complete or nearly complete scalp hair loss for more than 10 years.
Approval of baricitinib
Dr. King’s recent work supported the approval in June 2022 of oral baricitinib, a JAK inhibitor, for AA. He reviewed data from his late-breaker abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March 2022, where he reported that almost 40% of adults with AA treated with 4 mg of baricitinib daily had significant hair regrowth over 52 weeks.
Two other oral JAK inhibitors in the pipeline for AA are deuruxolitinib and ritlecitinib, which significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving SALT scores of 20 or less, compared with patients on placebo in early clinical trials. Data on both were presented at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
So far, topical JAK inhibitors have not shown success in hair regrowth for AA patients, said Dr. King. Phase 2 studies of both ruxolitinib 1.5% cream and delgocitinib ointment were ineffective for AA.
Emerging role for oral minoxidil
Oral minoxidil has had a recent resurgence as an adjunct therapy to the new JAK inhibitors. A study published in 1987 found that, with oral minoxidil monotherapy, a cosmetic response was seen in 18% of patients with AA, Dr. King said.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. King and colleagues noted that dose escalation is sometimes needed for effective treatment of AA with tofacitinib. They examined the effect of adding oral minoxidil to tofacitinib in patients with severe AA as a way to increase efficacy without increasing tofacitinib dosage. They reviewed data from 12 patients ages 18-51 years who were prescribed 5 mg of tofacitinib twice daily, plus 2.5 mg oral minoxidil daily for women and 2.5 mg of minoxidil twice daily for men; women received a lower dose to minimize the side effect of hypertrichosis.
After 6 months, 67% (eight patients) achieved at least 75% hair regrowth; of those eight patients, seven (58% of the total) had hair regrowth on a twice-daily dose of 5 mg tofacitinib with no need for dose escalation, Dr. King said.
More research is needed, but oral minoxidil may be a useful adjunct treatment for some patients with AA, he added.
During a question and answer session, Dr. King was asked to elaborate on the mechanism of minoxidil in combination with JAK inhibitors. “The truth is that I just don’t know” why the combination works for some patients. However, the majority of patients who succeed with this combination regrow hair by 4 months. “There is something special about that combination.”
Dr. King disclosed serving as a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, AltruBio, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bioniz, Bristol Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Horizon, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Twi Biotechnology, Viela Bio, and Visterra; serving as a speaker or as a member of the speakers bureau for Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme; and receiving research funding from Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
“Some patients don’t have alopecia, but they have been managed for it,” he said. “Whenever there is an ounce of doubt, take a biopsy,” he advised.
Assessing disease severity in patients with alopecia areata (AA) is especially important as new therapies become available, said Dr. King, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score has been available since 2004, and remains a useful tool to estimate percent hair loss. The SALT Score divides the scalp into four sections: 18% each for the right and left sides, 40% for the top of the head, and 24% for the back of the head, said Dr. King. However, the SALT Score can be enhanced or modified based on a holistic approach to disease severity that categorizes alopecia as mild (scalp hair loss of 20% or less), moderate (scalp hair loss of 21 to 49%), or severe (scalp hair loss of 50% or more).
For example, if a patient’s hair loss based on SALT Score is mild or moderate, increase the severity by 1 level (from mild to moderate, or moderate to severe) if any of the following conditions apply: Noticeable eyebrow or eyelash involvement, inadequate treatment response after 6 months, diffuse positive hair pull test consistent with rapid progression of AA, or a negative impact on psychosocial functioning because of AA, he said.
Treatment advances
Understanding of the pathogenesis of AA has been slow to evolve, Dr. King noted. “We haven’t been able to shake this concept that people are causing the disease by being depressed,” as noted in the literature from the 1950s.
In 2014, breakthrough research changed the game by identifying the roles of interferon gamma and interleukin 15, Dr. King said. Since then, more research has been conducted on Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for AA. Dr. King was a coinvestigator on a 2014 case report in which a patient with psoriasis and alopecia universalis experienced regrowth of most of his body hair after 8 months of daily oral tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
However, despite the dramatic results in some patients, “tofacitinib doesn’t always work,” said Dr. King. In his experience, patients for whom tofacitinib didn’t work were those with complete or nearly complete scalp hair loss for more than 10 years.
Approval of baricitinib
Dr. King’s recent work supported the approval in June 2022 of oral baricitinib, a JAK inhibitor, for AA. He reviewed data from his late-breaker abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March 2022, where he reported that almost 40% of adults with AA treated with 4 mg of baricitinib daily had significant hair regrowth over 52 weeks.
Two other oral JAK inhibitors in the pipeline for AA are deuruxolitinib and ritlecitinib, which significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving SALT scores of 20 or less, compared with patients on placebo in early clinical trials. Data on both were presented at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
So far, topical JAK inhibitors have not shown success in hair regrowth for AA patients, said Dr. King. Phase 2 studies of both ruxolitinib 1.5% cream and delgocitinib ointment were ineffective for AA.
Emerging role for oral minoxidil
Oral minoxidil has had a recent resurgence as an adjunct therapy to the new JAK inhibitors. A study published in 1987 found that, with oral minoxidil monotherapy, a cosmetic response was seen in 18% of patients with AA, Dr. King said.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. King and colleagues noted that dose escalation is sometimes needed for effective treatment of AA with tofacitinib. They examined the effect of adding oral minoxidil to tofacitinib in patients with severe AA as a way to increase efficacy without increasing tofacitinib dosage. They reviewed data from 12 patients ages 18-51 years who were prescribed 5 mg of tofacitinib twice daily, plus 2.5 mg oral minoxidil daily for women and 2.5 mg of minoxidil twice daily for men; women received a lower dose to minimize the side effect of hypertrichosis.
After 6 months, 67% (eight patients) achieved at least 75% hair regrowth; of those eight patients, seven (58% of the total) had hair regrowth on a twice-daily dose of 5 mg tofacitinib with no need for dose escalation, Dr. King said.
More research is needed, but oral minoxidil may be a useful adjunct treatment for some patients with AA, he added.
During a question and answer session, Dr. King was asked to elaborate on the mechanism of minoxidil in combination with JAK inhibitors. “The truth is that I just don’t know” why the combination works for some patients. However, the majority of patients who succeed with this combination regrow hair by 4 months. “There is something special about that combination.”
Dr. King disclosed serving as a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, AltruBio, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bioniz, Bristol Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Horizon, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Twi Biotechnology, Viela Bio, and Visterra; serving as a speaker or as a member of the speakers bureau for Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme; and receiving research funding from Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
“Some patients don’t have alopecia, but they have been managed for it,” he said. “Whenever there is an ounce of doubt, take a biopsy,” he advised.
Assessing disease severity in patients with alopecia areata (AA) is especially important as new therapies become available, said Dr. King, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score has been available since 2004, and remains a useful tool to estimate percent hair loss. The SALT Score divides the scalp into four sections: 18% each for the right and left sides, 40% for the top of the head, and 24% for the back of the head, said Dr. King. However, the SALT Score can be enhanced or modified based on a holistic approach to disease severity that categorizes alopecia as mild (scalp hair loss of 20% or less), moderate (scalp hair loss of 21 to 49%), or severe (scalp hair loss of 50% or more).
For example, if a patient’s hair loss based on SALT Score is mild or moderate, increase the severity by 1 level (from mild to moderate, or moderate to severe) if any of the following conditions apply: Noticeable eyebrow or eyelash involvement, inadequate treatment response after 6 months, diffuse positive hair pull test consistent with rapid progression of AA, or a negative impact on psychosocial functioning because of AA, he said.
Treatment advances
Understanding of the pathogenesis of AA has been slow to evolve, Dr. King noted. “We haven’t been able to shake this concept that people are causing the disease by being depressed,” as noted in the literature from the 1950s.
In 2014, breakthrough research changed the game by identifying the roles of interferon gamma and interleukin 15, Dr. King said. Since then, more research has been conducted on Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for AA. Dr. King was a coinvestigator on a 2014 case report in which a patient with psoriasis and alopecia universalis experienced regrowth of most of his body hair after 8 months of daily oral tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
However, despite the dramatic results in some patients, “tofacitinib doesn’t always work,” said Dr. King. In his experience, patients for whom tofacitinib didn’t work were those with complete or nearly complete scalp hair loss for more than 10 years.
Approval of baricitinib
Dr. King’s recent work supported the approval in June 2022 of oral baricitinib, a JAK inhibitor, for AA. He reviewed data from his late-breaker abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March 2022, where he reported that almost 40% of adults with AA treated with 4 mg of baricitinib daily had significant hair regrowth over 52 weeks.
Two other oral JAK inhibitors in the pipeline for AA are deuruxolitinib and ritlecitinib, which significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving SALT scores of 20 or less, compared with patients on placebo in early clinical trials. Data on both were presented at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
So far, topical JAK inhibitors have not shown success in hair regrowth for AA patients, said Dr. King. Phase 2 studies of both ruxolitinib 1.5% cream and delgocitinib ointment were ineffective for AA.
Emerging role for oral minoxidil
Oral minoxidil has had a recent resurgence as an adjunct therapy to the new JAK inhibitors. A study published in 1987 found that, with oral minoxidil monotherapy, a cosmetic response was seen in 18% of patients with AA, Dr. King said.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. King and colleagues noted that dose escalation is sometimes needed for effective treatment of AA with tofacitinib. They examined the effect of adding oral minoxidil to tofacitinib in patients with severe AA as a way to increase efficacy without increasing tofacitinib dosage. They reviewed data from 12 patients ages 18-51 years who were prescribed 5 mg of tofacitinib twice daily, plus 2.5 mg oral minoxidil daily for women and 2.5 mg of minoxidil twice daily for men; women received a lower dose to minimize the side effect of hypertrichosis.
After 6 months, 67% (eight patients) achieved at least 75% hair regrowth; of those eight patients, seven (58% of the total) had hair regrowth on a twice-daily dose of 5 mg tofacitinib with no need for dose escalation, Dr. King said.
More research is needed, but oral minoxidil may be a useful adjunct treatment for some patients with AA, he added.
During a question and answer session, Dr. King was asked to elaborate on the mechanism of minoxidil in combination with JAK inhibitors. “The truth is that I just don’t know” why the combination works for some patients. However, the majority of patients who succeed with this combination regrow hair by 4 months. “There is something special about that combination.”
Dr. King disclosed serving as a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, AltruBio, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bioniz, Bristol Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Horizon, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Twi Biotechnology, Viela Bio, and Visterra; serving as a speaker or as a member of the speakers bureau for Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme; and receiving research funding from Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Review gives weight to supplements for hair loss
because of small sample sizes, heterogeneity of hair loss types in study subjects, or other limitations.
The review, published online in JAMA Dermatology, notes that “Twelve of the 20 nutritional interventions had high-quality studies suggesting objectively evaluated effectiveness.”
It is “ground breaking,” in part because of its breadth and depth, said Eva Simmons-O’Brien, MD, a dermatologist in Towson, Md., who often recommends supplements for her patients with hair loss. “It basically kind of vindicates what some of us have been doing for a number of years in terms of treating hair loss,” she told this news organization. “It should hopefully make it more commonplace for dermatologists to consider using nutritional supplements as an adjuvant to treating hair loss,” added Dr. Simmons-O’Brien.
The review “is very helpful,” agreed Lynne J. Goldberg, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology and laboratory medicine at Boston University. Dr. Goldberg noted that many patients are already taking supplements and want to know whether they are safe and effective. The review “points out what the problems are; it talks about what the individual ingredients are and what they do, what the problems are; and it concluded that some people may find these helpful. Which is exactly what I tell my patients,” said Dr. Goldberg, who is also director of the Hair Clinic at Boston Medical Center.
“For patients who are highly motivated and eager to try this, we’re hoping that this systematic review serves as a foundation to have a conversation,” study coauthor Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, of the department of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, told this news organization. “When there’s medical uncertainty and the question is how much risk is one willing to take, the most important thing to do is to present the data and engage in shared decision-making with the patient,” noted Dr. Mostaghimi, who is also director of the inpatient dermatology consult service at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Surprising effectiveness
Going into the study, “we felt it would be likely that majority of nutritional supplements would either not be effective or not studied,” he said.
Dr. Mostaghimi and his coauthors conducted the study because so many patients take nutritional supplements to address hair loss, he said. An initial literature survey yielded more than 6,300 citations, but after screening and reviews, the authors included 30 articles for evaluation.
The review begins with a look at studies of saw palmetto (Serenoa repens), a botanical compound thought to inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase (5AR), which converts testosterone to dihydroxytestosterone (DHT). DHT is a mediator of androgenic alopecia (AGA). The studies suggest that the compound might stabilize hair loss, “although its effect is likely less than that of finasteride,” write the authors. They also note that side effects associated with finasteride, such as sexual dysfunction, were also observed with saw palmetto “but to a lesser extent.”
For AGA, pumpkin seed oil may also be effective and a “potential alternative” to finasteride for AGA, and Forti5, a nutritional supplement that includes botanical 5AR inhibitors and other ingredients, had favorable effects in one study, the authors write. But neither has been compared to finasteride, and the Forti5 study lacked a control group.
The review also examines the micronutrients vitamin D, zinc, B vitamins, and antioxidants. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with alopecia areata (AA), AGA, and telogen effluvium (TE) in some studies, and zinc deficiencies have been associated with TE, hair breakage, and thinning, according to the review. A single-arm vitamin D study showed improved results at 6 months for women with TE, but there was no control group and TE is self-resolving, the authors add. Studies in patients with normal zinc levels at baseline who had AA or hair loss showed significant hair regrowth and increased hair thickness and density, but the trials were a mishmash of controls and no controls and relied on self-perceived hair-loss data.
Larger more rigorous studies should be done to evaluate zinc’s effectiveness with AA, the authors comment.
Many patients take vitamin B7 (biotin) for hair loss. It has not been studied on its own but was an ingredient in some supplements in the review. Dr. Simmons-O’Brien said that biotin won’t result in new hair growth but that it can help strengthen the new hairs that grow as a result of other therapies. Both she and the study authors note that the Food and Drug Administration has warned against biotin supplementation because it can interfere with troponin and other test results.
The review also finds that immunomodulators –such as Chinese herbal extracts from paeony and glycyrrhizin – were effective in severe AA. Growth hormone modulators targeting deficiencies in insulin growth factor 1 or growth hormone are also promising. Studies of the modulators capsaicin and isoflavones – used topically – spurred hair growth, the authors write.
Products containing marine protein supplements, including Viviscal and Nourkrin, appeared effective in increasing hair counts in men and women, but the studies were funded by the manufacturer and were not well controlled. Side effects with Viviscal included bloating, according to the review.
The multi-ingredient supplements Nutrafol, Omni-Three, Apple Nutraceutical, and Lambdapil were also included in the review. Only Omni-Three showed no effectiveness, but studies of the other supplements had various limitations, including lack of controls and small sample sizes.
Complicated problem, multiple solutions
Given the many reasons for hair loss, multiple solutions are needed, the dermatologists note.
Dr. Mostaghimi said that he’s still a bit skeptical that supplements work as consistently as described or as well as described, given that he and his coauthors were unable to find any negative studies. In talking with patients who are taking supplements, he said that his first aim is to make sure they are safe. At least the supplements in the review have been studied for safety, he added.
He will encourage replacement of vitamin D or zinc or other vitamins or minerals if patients are deficient but said that he does not “actively encourage supplementation.”
Dr. Simmons-O’Brien said that, when evaluating patients with hair loss, she orders lab tests to determine whether the patient has anemia or a thyroid issue or deficiencies in vitamins or minerals or other nutritional deficiencies, asks about diet and styling practices, and takes a scalp biopsy. It is not uncommon to recommend supplementation on the basis of those findings, she added.
“As a hair-loss specialist, my job is to treat the patient at their level, in their framework, in their comfort zone,” said Dr. Goldberg. Some patients don’t want to take medications for hair loss, so she might recommend supplements in those cases but tells patients that they aren’t well studied.
She added that it can be hard to tell whether a supplement is working, particularly if it has multiple ingredients.
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from Pfizer, Concert, Lilly, Hims and Hers, Equillium, AbbVie, Digital Diagnostics, and Bioniz and grants from Pfizer, all outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. Mostaghimi disclosed that he is an associate editor of JAMA Dermatology but was not involved in any of the decisions regarding the review of the manuscript or its acceptance. No other disclosures were reported by the other study authors. Dr. Goldberg reported no disclosures. Dr. Simmons-O›Brien is a medical consultant for Isdin, but not for hair products.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
because of small sample sizes, heterogeneity of hair loss types in study subjects, or other limitations.
The review, published online in JAMA Dermatology, notes that “Twelve of the 20 nutritional interventions had high-quality studies suggesting objectively evaluated effectiveness.”
It is “ground breaking,” in part because of its breadth and depth, said Eva Simmons-O’Brien, MD, a dermatologist in Towson, Md., who often recommends supplements for her patients with hair loss. “It basically kind of vindicates what some of us have been doing for a number of years in terms of treating hair loss,” she told this news organization. “It should hopefully make it more commonplace for dermatologists to consider using nutritional supplements as an adjuvant to treating hair loss,” added Dr. Simmons-O’Brien.
The review “is very helpful,” agreed Lynne J. Goldberg, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology and laboratory medicine at Boston University. Dr. Goldberg noted that many patients are already taking supplements and want to know whether they are safe and effective. The review “points out what the problems are; it talks about what the individual ingredients are and what they do, what the problems are; and it concluded that some people may find these helpful. Which is exactly what I tell my patients,” said Dr. Goldberg, who is also director of the Hair Clinic at Boston Medical Center.
“For patients who are highly motivated and eager to try this, we’re hoping that this systematic review serves as a foundation to have a conversation,” study coauthor Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, of the department of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, told this news organization. “When there’s medical uncertainty and the question is how much risk is one willing to take, the most important thing to do is to present the data and engage in shared decision-making with the patient,” noted Dr. Mostaghimi, who is also director of the inpatient dermatology consult service at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Surprising effectiveness
Going into the study, “we felt it would be likely that majority of nutritional supplements would either not be effective or not studied,” he said.
Dr. Mostaghimi and his coauthors conducted the study because so many patients take nutritional supplements to address hair loss, he said. An initial literature survey yielded more than 6,300 citations, but after screening and reviews, the authors included 30 articles for evaluation.
The review begins with a look at studies of saw palmetto (Serenoa repens), a botanical compound thought to inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase (5AR), which converts testosterone to dihydroxytestosterone (DHT). DHT is a mediator of androgenic alopecia (AGA). The studies suggest that the compound might stabilize hair loss, “although its effect is likely less than that of finasteride,” write the authors. They also note that side effects associated with finasteride, such as sexual dysfunction, were also observed with saw palmetto “but to a lesser extent.”
For AGA, pumpkin seed oil may also be effective and a “potential alternative” to finasteride for AGA, and Forti5, a nutritional supplement that includes botanical 5AR inhibitors and other ingredients, had favorable effects in one study, the authors write. But neither has been compared to finasteride, and the Forti5 study lacked a control group.
The review also examines the micronutrients vitamin D, zinc, B vitamins, and antioxidants. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with alopecia areata (AA), AGA, and telogen effluvium (TE) in some studies, and zinc deficiencies have been associated with TE, hair breakage, and thinning, according to the review. A single-arm vitamin D study showed improved results at 6 months for women with TE, but there was no control group and TE is self-resolving, the authors add. Studies in patients with normal zinc levels at baseline who had AA or hair loss showed significant hair regrowth and increased hair thickness and density, but the trials were a mishmash of controls and no controls and relied on self-perceived hair-loss data.
Larger more rigorous studies should be done to evaluate zinc’s effectiveness with AA, the authors comment.
Many patients take vitamin B7 (biotin) for hair loss. It has not been studied on its own but was an ingredient in some supplements in the review. Dr. Simmons-O’Brien said that biotin won’t result in new hair growth but that it can help strengthen the new hairs that grow as a result of other therapies. Both she and the study authors note that the Food and Drug Administration has warned against biotin supplementation because it can interfere with troponin and other test results.
The review also finds that immunomodulators –such as Chinese herbal extracts from paeony and glycyrrhizin – were effective in severe AA. Growth hormone modulators targeting deficiencies in insulin growth factor 1 or growth hormone are also promising. Studies of the modulators capsaicin and isoflavones – used topically – spurred hair growth, the authors write.
Products containing marine protein supplements, including Viviscal and Nourkrin, appeared effective in increasing hair counts in men and women, but the studies were funded by the manufacturer and were not well controlled. Side effects with Viviscal included bloating, according to the review.
The multi-ingredient supplements Nutrafol, Omni-Three, Apple Nutraceutical, and Lambdapil were also included in the review. Only Omni-Three showed no effectiveness, but studies of the other supplements had various limitations, including lack of controls and small sample sizes.
Complicated problem, multiple solutions
Given the many reasons for hair loss, multiple solutions are needed, the dermatologists note.
Dr. Mostaghimi said that he’s still a bit skeptical that supplements work as consistently as described or as well as described, given that he and his coauthors were unable to find any negative studies. In talking with patients who are taking supplements, he said that his first aim is to make sure they are safe. At least the supplements in the review have been studied for safety, he added.
He will encourage replacement of vitamin D or zinc or other vitamins or minerals if patients are deficient but said that he does not “actively encourage supplementation.”
Dr. Simmons-O’Brien said that, when evaluating patients with hair loss, she orders lab tests to determine whether the patient has anemia or a thyroid issue or deficiencies in vitamins or minerals or other nutritional deficiencies, asks about diet and styling practices, and takes a scalp biopsy. It is not uncommon to recommend supplementation on the basis of those findings, she added.
“As a hair-loss specialist, my job is to treat the patient at their level, in their framework, in their comfort zone,” said Dr. Goldberg. Some patients don’t want to take medications for hair loss, so she might recommend supplements in those cases but tells patients that they aren’t well studied.
She added that it can be hard to tell whether a supplement is working, particularly if it has multiple ingredients.
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from Pfizer, Concert, Lilly, Hims and Hers, Equillium, AbbVie, Digital Diagnostics, and Bioniz and grants from Pfizer, all outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. Mostaghimi disclosed that he is an associate editor of JAMA Dermatology but was not involved in any of the decisions regarding the review of the manuscript or its acceptance. No other disclosures were reported by the other study authors. Dr. Goldberg reported no disclosures. Dr. Simmons-O›Brien is a medical consultant for Isdin, but not for hair products.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
because of small sample sizes, heterogeneity of hair loss types in study subjects, or other limitations.
The review, published online in JAMA Dermatology, notes that “Twelve of the 20 nutritional interventions had high-quality studies suggesting objectively evaluated effectiveness.”
It is “ground breaking,” in part because of its breadth and depth, said Eva Simmons-O’Brien, MD, a dermatologist in Towson, Md., who often recommends supplements for her patients with hair loss. “It basically kind of vindicates what some of us have been doing for a number of years in terms of treating hair loss,” she told this news organization. “It should hopefully make it more commonplace for dermatologists to consider using nutritional supplements as an adjuvant to treating hair loss,” added Dr. Simmons-O’Brien.
The review “is very helpful,” agreed Lynne J. Goldberg, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology and laboratory medicine at Boston University. Dr. Goldberg noted that many patients are already taking supplements and want to know whether they are safe and effective. The review “points out what the problems are; it talks about what the individual ingredients are and what they do, what the problems are; and it concluded that some people may find these helpful. Which is exactly what I tell my patients,” said Dr. Goldberg, who is also director of the Hair Clinic at Boston Medical Center.
“For patients who are highly motivated and eager to try this, we’re hoping that this systematic review serves as a foundation to have a conversation,” study coauthor Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, of the department of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, told this news organization. “When there’s medical uncertainty and the question is how much risk is one willing to take, the most important thing to do is to present the data and engage in shared decision-making with the patient,” noted Dr. Mostaghimi, who is also director of the inpatient dermatology consult service at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Surprising effectiveness
Going into the study, “we felt it would be likely that majority of nutritional supplements would either not be effective or not studied,” he said.
Dr. Mostaghimi and his coauthors conducted the study because so many patients take nutritional supplements to address hair loss, he said. An initial literature survey yielded more than 6,300 citations, but after screening and reviews, the authors included 30 articles for evaluation.
The review begins with a look at studies of saw palmetto (Serenoa repens), a botanical compound thought to inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase (5AR), which converts testosterone to dihydroxytestosterone (DHT). DHT is a mediator of androgenic alopecia (AGA). The studies suggest that the compound might stabilize hair loss, “although its effect is likely less than that of finasteride,” write the authors. They also note that side effects associated with finasteride, such as sexual dysfunction, were also observed with saw palmetto “but to a lesser extent.”
For AGA, pumpkin seed oil may also be effective and a “potential alternative” to finasteride for AGA, and Forti5, a nutritional supplement that includes botanical 5AR inhibitors and other ingredients, had favorable effects in one study, the authors write. But neither has been compared to finasteride, and the Forti5 study lacked a control group.
The review also examines the micronutrients vitamin D, zinc, B vitamins, and antioxidants. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with alopecia areata (AA), AGA, and telogen effluvium (TE) in some studies, and zinc deficiencies have been associated with TE, hair breakage, and thinning, according to the review. A single-arm vitamin D study showed improved results at 6 months for women with TE, but there was no control group and TE is self-resolving, the authors add. Studies in patients with normal zinc levels at baseline who had AA or hair loss showed significant hair regrowth and increased hair thickness and density, but the trials were a mishmash of controls and no controls and relied on self-perceived hair-loss data.
Larger more rigorous studies should be done to evaluate zinc’s effectiveness with AA, the authors comment.
Many patients take vitamin B7 (biotin) for hair loss. It has not been studied on its own but was an ingredient in some supplements in the review. Dr. Simmons-O’Brien said that biotin won’t result in new hair growth but that it can help strengthen the new hairs that grow as a result of other therapies. Both she and the study authors note that the Food and Drug Administration has warned against biotin supplementation because it can interfere with troponin and other test results.
The review also finds that immunomodulators –such as Chinese herbal extracts from paeony and glycyrrhizin – were effective in severe AA. Growth hormone modulators targeting deficiencies in insulin growth factor 1 or growth hormone are also promising. Studies of the modulators capsaicin and isoflavones – used topically – spurred hair growth, the authors write.
Products containing marine protein supplements, including Viviscal and Nourkrin, appeared effective in increasing hair counts in men and women, but the studies were funded by the manufacturer and were not well controlled. Side effects with Viviscal included bloating, according to the review.
The multi-ingredient supplements Nutrafol, Omni-Three, Apple Nutraceutical, and Lambdapil were also included in the review. Only Omni-Three showed no effectiveness, but studies of the other supplements had various limitations, including lack of controls and small sample sizes.
Complicated problem, multiple solutions
Given the many reasons for hair loss, multiple solutions are needed, the dermatologists note.
Dr. Mostaghimi said that he’s still a bit skeptical that supplements work as consistently as described or as well as described, given that he and his coauthors were unable to find any negative studies. In talking with patients who are taking supplements, he said that his first aim is to make sure they are safe. At least the supplements in the review have been studied for safety, he added.
He will encourage replacement of vitamin D or zinc or other vitamins or minerals if patients are deficient but said that he does not “actively encourage supplementation.”
Dr. Simmons-O’Brien said that, when evaluating patients with hair loss, she orders lab tests to determine whether the patient has anemia or a thyroid issue or deficiencies in vitamins or minerals or other nutritional deficiencies, asks about diet and styling practices, and takes a scalp biopsy. It is not uncommon to recommend supplementation on the basis of those findings, she added.
“As a hair-loss specialist, my job is to treat the patient at their level, in their framework, in their comfort zone,” said Dr. Goldberg. Some patients don’t want to take medications for hair loss, so she might recommend supplements in those cases but tells patients that they aren’t well studied.
She added that it can be hard to tell whether a supplement is working, particularly if it has multiple ingredients.
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from Pfizer, Concert, Lilly, Hims and Hers, Equillium, AbbVie, Digital Diagnostics, and Bioniz and grants from Pfizer, all outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. Mostaghimi disclosed that he is an associate editor of JAMA Dermatology but was not involved in any of the decisions regarding the review of the manuscript or its acceptance. No other disclosures were reported by the other study authors. Dr. Goldberg reported no disclosures. Dr. Simmons-O›Brien is a medical consultant for Isdin, but not for hair products.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
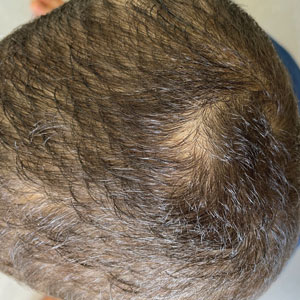
New Razor Technology Improves Appearance and Quality of Life in Men With Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB)(also known as razor bumps or shaving bumps)1 is a skin condition that consists of papules resulting from ingrown hairs.2 In more severe cases, papules become pustules, then abscesses, which can cause scarring.1,2 The condition can be distressing for patients, with considerable negative impact on their daily lives.3 The condition also is associated with shaving-related stinging, burning, pruritus, and cuts on the skin.4
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most common in men of African descent due to the curved nature of the hair follicle,2,5,6 with an estimated prevalence in this population of 45% to 83%,1,6 but it can affect men of other ethnicities.7 A genetic polymorphism in a gene encoding a keratin specific to the hair follicle also has been found to predispose some individuals to PFB.5 When hair from a curved or destabilized hair follicle is cut to form a sharp tip, it is susceptible to extrafollicular and/or transfollicular penetration,5,6,8 as illustrated in Figure 1.
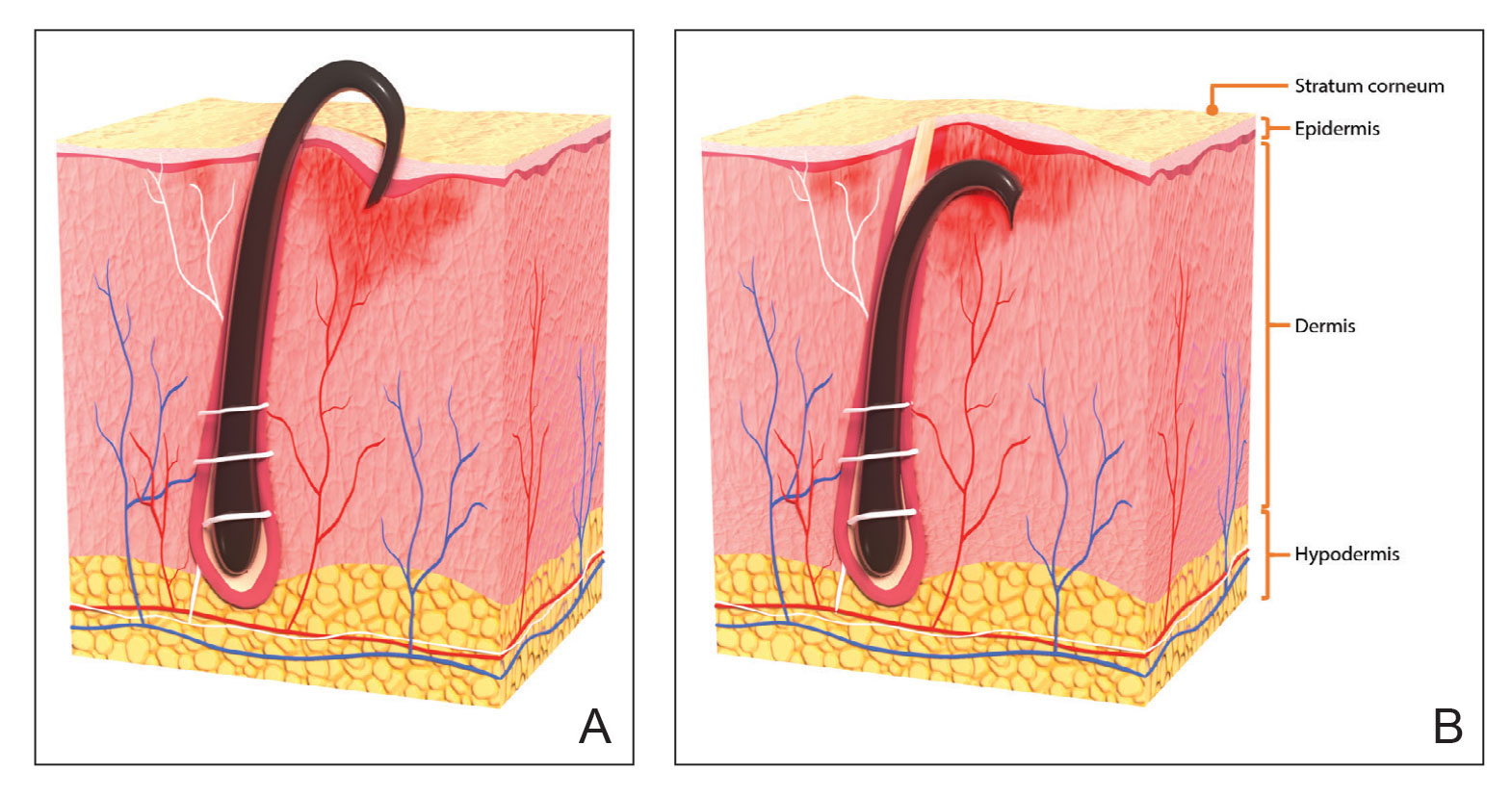
With extrafollicular or transfollicular penetration, the hair shaft re-enters or retracts into the dermis, triggering an inflammatory response that may be exacerbated by subsequent shaving.2 Few studies have been published that aim to identify potential shaving solutions for individuals with PFB who elect to or need to continue shaving.
A new razor technology comprising 2 blades separated by a bridge feature has been designed specifically for men with razor bumps (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]). The SkinGuard razor redistributes shaving pressure so that there is less force from the blades on the skin and inflamed lesions than without the bridge, as seen in Figure 2. The razor has been designed to protect the skin from the blades, thereby minimizing the occurrence of new lesions and allowing existing lesions to heal.
![Test razor bridge feature (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]) minimizes the force of the razor blades on the skin. Copyright 2022 The Procter & Gamble Company. Test razor bridge feature (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]) minimizes the force of the razor blades on the skin. Copyright 2022 The Procter & Gamble Company.](https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/Moran_2.jpg)
The primary purpose of this study was to assess the appearance of males with razor bumps and shaving irritation when using the new razor technology in a regular shaving routine. The secondary objective was to measure satisfaction of the shaving experience when using the new razor by means of assessing itching, burning, and stinging using the participant global severity assessment (PGSA) and the impact on quality of life (QOL) measures.
Methods
Participants—Eligible participants were male, aged 20 to 60 years, and had clinically diagnosed PFB as well as symptoms of skin irritation from shaving. Participants were recruited from a dermatology clinic and via institutional review board–approved advertising.
Those eligible for inclusion in the study had a shaving routine that comprised shaving at least 3 times a week using a wet-shave, blade-razor technique accompanied by only a shave gel or foam. In addition, eligible participants had mild to moderate symptoms of skin irritation (a minimum of 10 razor bumps) from shaving based on investigator global severity assessment (IGSA) rating scales and were willing to shave at least 5 times a week during the study period. Participants could continue certain topical and systemic interventions for their skin.
Participants were excluded from the study if they had an underlying inflammatory disease that could manifest with a skin rash or were using any of these medications: topical benzoyl peroxide, topical clindamycin, topical retinoids, or oral antibiotics.
Study Design—A prospective, open-label study was conducted over a period of 12 weeks at a single site in the United States. Investigators instructed participants to shave 5 or more times per week with the test razor and to keep a daily shaving journal to track the number of shaves and compliance.
Participants were evaluated at the baseline screening visit, then at 4, 8, and 12 weeks. Evaluations included an investigator lesion count, the IGSA, and the PGSA. The PGSA was used to evaluate subjective clinical measurements (ie, indicate how much postshave burning/itching/stinging the participant was experiencing). The impact of shaving on daily life was evaluated at the baseline screening visit and at 12 weeks with the Participant Quality of Life Questionnaire comprised of 22 QOL statements. eTable 1 summarizes the investigator assessments used in the study, and eTable 2 summarizes the participant self-assessments. Both tables include the scale details and results interpretation for each assessment.
The study was approved by the local institutional review board, and all participants provided written informed consent in accordance with Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 50.
Study Visits—At the baseline screening visit, participants provided written informed consent and completed a prestudy shave questionnaire concerning shaving preparations, techniques, and opinions. Participants also provided a medical history, including prior and concomitant medications, and were evaluated using the inclusion/exclusion criteria. Investigators explained adverse event reporting to the participants. Participants were provided with an adequate supply of test razors for the 12-week period.
Data Analysis—Means and SDs were calculated for the study measures assessed at each visit. Analyses were performed evaluating change from baseline in repeated-measures analysis of variance models. These models were adjusted for baseline levels of the outcome measure and visit number. The magnitude of change from baseline was evaluated against a null hypothesis of 0% change. This longitudinal model adjusted for any potential differing baseline levels among participants. Statistical significance was defined as P<.05. SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used for all analyses.
Results
In total, 21 individuals were enrolled, and 20 completed the study. Participants who completed the study were non-Hispanic Black (n=10); non-Hispanic White (n=8); Asian (n=1); or White, American Indian (n=1). All participants adhered to the protocol and reported shaving at least 5 times a week for 12 weeks using the test razor. One participant was removed after he was found to have a history of sarcoidosis, making him ineligible for the study. No study-related adverse events were reported.
Papules and Pustules—Over the course of the 12-week study, the papule count decreased significantly from baseline. Results from the investigator lesion count (see eTable 1 for key) indicated that by week 12—adjusted for number of papules at baseline—the mean percentage reduction was estimated to be 59.6% (P<.0001). A significant decrease in papule count also was observed between the baseline visit and week 8 (57.2%; P<.0001). A nonsignificant decrease was observed at week 4 (18.9%; P=.17). Only 3 participants presented with pustules at baseline, and the pustule count remained low over the course of the study. No significant change was noted at week 12 vs baseline (P=.98). Notably, there was no increase in pustule count at the end of the study compared with baseline (Table 1).
Skin Appearance—An improvement in the skin’s appearance over the course of the study from baseline was consistent with an improvement in the IGSA. The IGSA score significantly improved from a mean (SD) measurement of 2.5 (0.6) (indicating mild to moderate inflammation) at baseline to 1.4 (0.8) at week 8 (P<.0001) and 1.2 (1.1) (indicating mild inflammation to almost clear) at week 12 (P<.0001). The observed decrease in severity of skin condition and skin inflammation is shown in Figure 3.
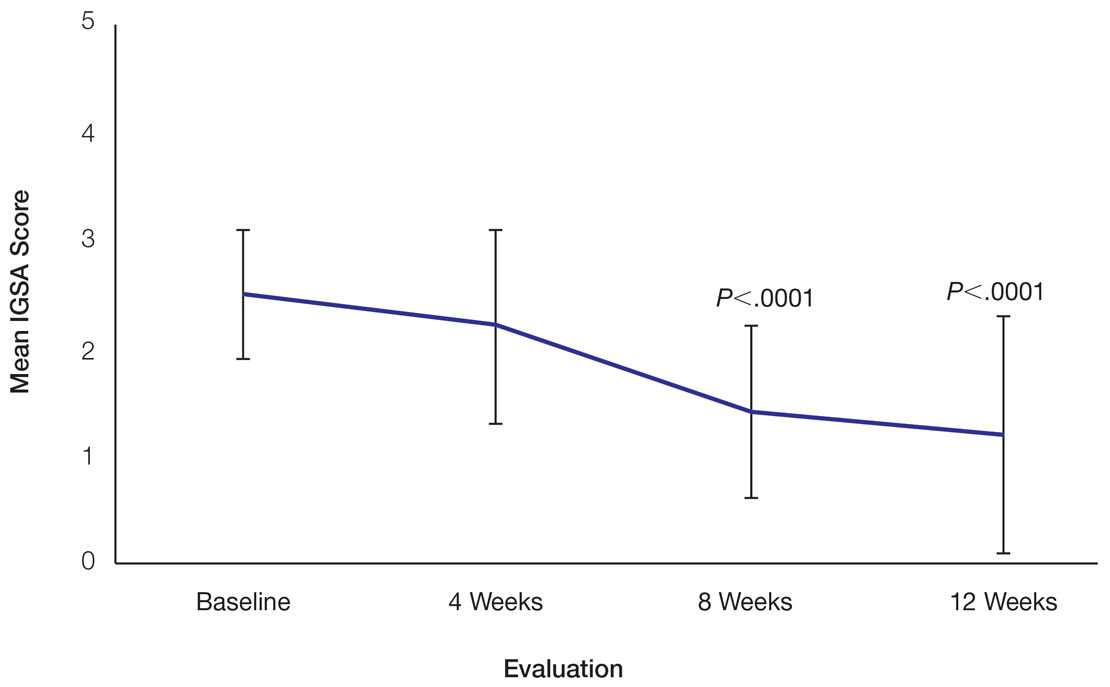
Significant improvements were observed in every category of the PGSA at week 12 vs baseline (P≤.0007)(Table 2). At week 12, there was a significant (P≤.05) increase from baseline in participant agreement for all 22 QOL metrics describing positive shave experience, achieving results, skin feel, self-confidence, and social interactions (Figure 4), which supports the positive impact of adopting a shaving regimen with the test razor. Notably, after using the test razor for 12 weeks, men reported that they were more likely to agree with the statements “my skin felt smooth,” “my skin felt good to touch,” and “I was able to achieve a consistently good shave.” Other meaningful increases occurred in “shaving was something I looked forward to doing,” “others thought I looked clean cut,” “I looked my best for my family/others/work,” and “I felt comfortable/confident getting closer to others.” All QOL statements are shown in Figure 4.
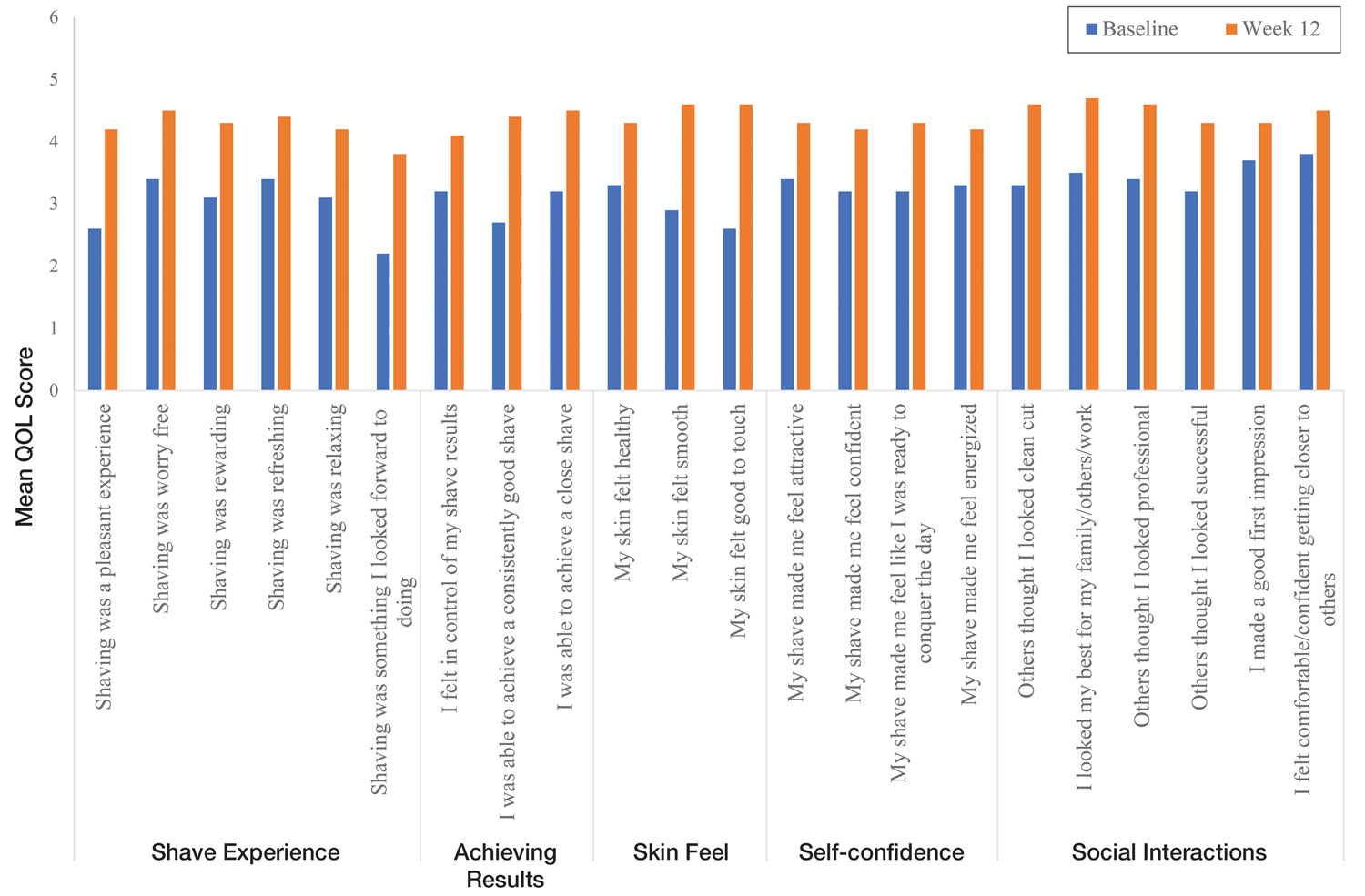
Comment
Improvement With Novel Razor Technology—For the first time, frequent use of a novel razor technology designed specifically for men with PFB was found to significantly improve skin appearance, shave satisfaction, and QOL after 12 weeks vs baseline in participants clinically diagnosed with PFB. In men with shave-related skin irritation and razor bumps who typically wet-shaved with a razor at least 3 times a week, use of the test razor with their regular shaving preparation product 5 or more times per week for 12 weeks was associated with significant improvements from baseline in investigator lesion count, IGSA, PGSA, and Participant Quality of Life Questionnaire measurements.
Study strengths included the quantification of the change in the number of lesions and the degree of severity by a trained investigator in a prospective clinical study along with an assessment of the impact on participant QOL. A lack of a control arm could be considered a limitation of the study; however, study end points were evaluated compared with baseline, with each participant serving as their own control. Spontaneous resolution of the condition with their standard routine was considered highly unlikely in these participants; therefore, in the absence of any other changes, improvements were attributed to regular use of the test product over the course of the study. The results presented here provide strong support for the effectiveness of the new razor technology in improving the appearance of men with razor bumps and shaving irritation.
Hair Removal Tools for the Management of PFB—Although various tools and techniques have been proposed in the past for men with PFB, the current test razor technology provided unique benefits, including improvements in appearance and severity of the condition as well as a positive impact on QOL. In 1979, Conte and Lawrence9 evaluated the effect of using an electric hair clipper and twice-daily use of a skin-cleansing pad on the occurrence of PFB. Participants (n=96) allowed their beards to grow out for 1 month, after which they started shaving with an electric clipper with a triple O head. The authors reported a favorable response in 95% (91/96) of cases. However, the electric clippers left 1 mm of beard at the skin level,9 which may not be acceptable for those who prefer a clean-shaven appearance.6
A prospective survey of 22 men of African descent with PFB found use of a safety razor was preferred over an electric razor.10 The single-arm study evaluated use of a foil-guarded shaver (single-razor blade) in the management of PFB based on investigator lesion counts and a participant questionnaire. Participants were asked to shave at least every other day and use a specially designed preshave brush. A mean reduction in lesion counts was observed at 2 weeks (29.6%), 4 weeks (38.1%), and 6 weeks (47.1%); statistical significance was not reported. At 6 weeks, 77.3% (17/22) of participants judged the foil-guarded shaver to be superior to other shaving devices in controlling their razor bumps, and 90.9% (20/22) indicated they would recommend the shaver to others with PFB. The authors hypothesized that the guard buffered the skin from the blade, which might otherwise facilitate the penetration of ingrowing hairs and cause trauma to existing lesions.
The mean reduction in lesion count from baseline observed at week 4 was greater in the study with the foil-guarded shaver and preshave brush (38% reduction)10 than in our study (19% reduction in papule count). Different methodologies, use of a preshave brush in the earlier study, and a difference in lesion severity at baseline may have contributed to this difference. The study with the foil-guarded shaver concluded after 6 weeks, and there was a 47.1% reduction in lesion counts vs baseline.10 In contrast, the current study continued for 12 weeks, and a 59.6% reduction in lesion counts was reported. Participants from both studies reported an improved shaving experience compared with their usual practice,10 though only the current study explored the positive impact of the new razor technology on participant QOL.
Preventing Hairs From Being Cut Too Close—The closeness of the shave is believed to be a contributory factor in the development and persistence of PFB6,8,11 based on a tendency for the distal portion of tightly curled hair shafts to re-enter the skin after shaving via transfollicular penetration.12 Inclusion of a buffer in the razor between the sharp blades and the skin has been proposed to prevent hairs from being cut too close and causing transfollicular penetration.12
In the test razor used in the current study, the bridge technology acted as the buffer to prevent hairs from being cut too close to the skin and to reduce blade contact with the skin (Figure 2). Having only 2 blades also reduced the closeness of the shave compared with 5-bladed technologies,13 as each hair can only be pulled and cut up to a maximum of 2 times per shaving stroke. Notably, this did not impact the participants’ QOL scores related to achieving a close shave or skin feeling smooth; both attributes were significantly improved at 12 weeks vs baseline (Figure 4).
By reducing blade contact with the skin, the bridge technology in the test razor was designed to prevent excessive force from being applied to the skin through the blades. Reduced blade loading minimizes contact with and impact on sensitive skin.14 Additional design features of the test razor to minimize the impact of shaving on the skin include treatment of the 2 blades with low-friction coatings, which allows the blades to cut through the beard hair with minimal force, helping to reduce the tug-and-pull effect that may otherwise result in irritation and inflammation.13,15 Lubrication strips before and after the blades in the test razor reduce friction between the blades and the skin to further protect the skin from the blades.15
Shaving With Multiblade Razors Does Not Exacerbate PFB—In a 1-week, split-faced, randomized study of 45 Black men, shaving with a manual 3-bladed razor was compared with use of 3 different chemical depilatory formulations.16 Shaving every other day for 1 week with the manual razor resulted in more papule formation but less irritation than use of the depilatories. The authors concluded that a study with longer duration was needed to explore the impact of shaving on papule formation in participants with a history of PFB.16
In 2013, an investigator-blinded study of 90 African American men with PFB compared the impact of different shaving regimens on the signs and symptoms of PFB over a 12-week period.4 Participants were randomized to 1 of 3 arms: (1) shaving 2 to 3 times per week with a triple-blade razor and standard products (control group); (2) shaving daily with a 5-bladed razor and standard products; and (3) shaving daily with a 5-bladed razor and “advanced” specific pre- and postshave products. The researchers found that the mean papule measurement significantly decreased from baseline in the advanced (P=.01) and control (P=.016) groups. Between-group comparison revealed no significant differences for papule or pustule count among each arm. For the investigator-graded severity, the change from baseline was significant for all 3 groups (P≤.04); however, the differences among groups were not significant. Importantly, these data demonstrated that PFB was not exacerbated by multiblade razors used as part of a daily shaving regimen.4
The findings of the current study were consistent with those of Daniel et al4 in that there was no exacerbation of the signs and symptoms of PFB associated with daily shaving. However, rather than requiring participants to change their entire shaving regimen, the present study only required a change of razor type. Moreover, the use of the new razor technology significantly decreased papule counts at week 12 vs the baseline measurement (P<.0001) and was associated with an improvement in subjective skin severity measurements. The participants in the present study reported significantly less burning, stinging, and itching after using the test product for 12 weeks (P<.0001).
Impact of Treatment on QOL—The current study further expanded on prior findings by combining these clinical end points with the QOL results to assess the test razor’s impact on participants’ lives. Results showed that over the course of 12 weeks, the new razor technology significantly improved the participants’ QOL in all questions related to shaving experience, achieving results, skin feel, self-confidence, and social interactions. The significant improvement in QOL included statements such as “shaving was a pleasant experience,” “I was able to achieve a consistently good shave,” and “my skin felt smooth.” Participants also reported improvements in meaningful categories such as “my shave made me feel attractive” and “I felt comfortable/confident getting closer to others.” As the current study showed, a shave regimen has the potential to change participants’ overall assessment of their QOL, a variable that must not be overlooked.
Conclusion
In men with clinically diagnosed PFB, regular shaving with a razor designed to protect the skin was found to significantly decrease lesion counts, increase shave satisfaction, and improve QOL after 12 weeks compared with their usual shaving practice (baseline measures). This razor technology provides another option to help manage PFB for men who wish to or need to continue shaving.
Acknowledgments—The clinical study was funded by the Procter & Gamble Company. Editorial writing assistance, supported financially by the Procter & Gamble Company, was provided by Gill McFeat, PhD, of McFeat Science Ltd (Devon, United Kingdom).
- Alexander AM, Delph WI. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military. a medical, administrative and social problem. J Natl Med Assoc. 1974;66:459-464, 479.
- Kligman AM, Strauss JS. Pseudofolliculitis of the beard. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74:533-542.
- Banta J, Bowen C, Wong E, et al. Perceptions of shaving profiles and their potential impacts on career progression in the United States Air Force. Mil Med. 2021;186:187-189.
- Daniel A, Gustafson CJ, Zupkosky PJ, et al. Shave frequency and regimen variation effects on the management of pseudofolliculitis barbae. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:410-418.
- Winter H, Schissel D, Parry DA, et al. An unusual Ala12Thr polymorphism in the 1A alpha-helical segment of the companion layer-specific keratin K6hf: evidence for a risk factor in the etiology of the common hair disorder pseudofolliculitis barbae. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;122:652-657.
- Perry PK, Cook-Bolden FE, Rahman Z, et al. Defining pseudofolliculitis barbae in 2001: a review of the literature and current trends. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S113-S119.
- McMichael AJ. Hair and scalp disorders in ethnic populations. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:629-644.
- Ribera M, Fernández-Chico N, Casals M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:749-757.
- Conte MS, Lawrence JE. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. no ‘pseudoproblem.’ JAMA. 1979;241:53-54.
- Alexander AM. Evaluation of a foil-guarded shaver in the management of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 1981;27:534-537, 540-542.
- Weiss AN, Arballo OM, Miletta NR, et al. Military grooming standards and their impact on skin diseases of the head and neck. Cutis. 2018;102:328;331-333.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K, Ertel K, et al. Blade shaving. In: Draelos ZD, ed. Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and Procedures. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons; 2015:166-173.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K. Insights into shaving and its impact on skin. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166(suppl 1):6-12.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K. The biomechanics of blade shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):17-23.
- Kindred C, Oresajo CO, Yatskayer M, et al. Comparative evaluation of men’s depilatory composition versus razor in black men. Cutis. 2011;88:98-103.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB)(also known as razor bumps or shaving bumps)1 is a skin condition that consists of papules resulting from ingrown hairs.2 In more severe cases, papules become pustules, then abscesses, which can cause scarring.1,2 The condition can be distressing for patients, with considerable negative impact on their daily lives.3 The condition also is associated with shaving-related stinging, burning, pruritus, and cuts on the skin.4
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most common in men of African descent due to the curved nature of the hair follicle,2,5,6 with an estimated prevalence in this population of 45% to 83%,1,6 but it can affect men of other ethnicities.7 A genetic polymorphism in a gene encoding a keratin specific to the hair follicle also has been found to predispose some individuals to PFB.5 When hair from a curved or destabilized hair follicle is cut to form a sharp tip, it is susceptible to extrafollicular and/or transfollicular penetration,5,6,8 as illustrated in Figure 1.

With extrafollicular or transfollicular penetration, the hair shaft re-enters or retracts into the dermis, triggering an inflammatory response that may be exacerbated by subsequent shaving.2 Few studies have been published that aim to identify potential shaving solutions for individuals with PFB who elect to or need to continue shaving.
A new razor technology comprising 2 blades separated by a bridge feature has been designed specifically for men with razor bumps (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]). The SkinGuard razor redistributes shaving pressure so that there is less force from the blades on the skin and inflamed lesions than without the bridge, as seen in Figure 2. The razor has been designed to protect the skin from the blades, thereby minimizing the occurrence of new lesions and allowing existing lesions to heal.
![Test razor bridge feature (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]) minimizes the force of the razor blades on the skin. Copyright 2022 The Procter & Gamble Company. Test razor bridge feature (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]) minimizes the force of the razor blades on the skin. Copyright 2022 The Procter & Gamble Company.](https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/Moran_2.jpg)
The primary purpose of this study was to assess the appearance of males with razor bumps and shaving irritation when using the new razor technology in a regular shaving routine. The secondary objective was to measure satisfaction of the shaving experience when using the new razor by means of assessing itching, burning, and stinging using the participant global severity assessment (PGSA) and the impact on quality of life (QOL) measures.
Methods
Participants—Eligible participants were male, aged 20 to 60 years, and had clinically diagnosed PFB as well as symptoms of skin irritation from shaving. Participants were recruited from a dermatology clinic and via institutional review board–approved advertising.
Those eligible for inclusion in the study had a shaving routine that comprised shaving at least 3 times a week using a wet-shave, blade-razor technique accompanied by only a shave gel or foam. In addition, eligible participants had mild to moderate symptoms of skin irritation (a minimum of 10 razor bumps) from shaving based on investigator global severity assessment (IGSA) rating scales and were willing to shave at least 5 times a week during the study period. Participants could continue certain topical and systemic interventions for their skin.
Participants were excluded from the study if they had an underlying inflammatory disease that could manifest with a skin rash or were using any of these medications: topical benzoyl peroxide, topical clindamycin, topical retinoids, or oral antibiotics.
Study Design—A prospective, open-label study was conducted over a period of 12 weeks at a single site in the United States. Investigators instructed participants to shave 5 or more times per week with the test razor and to keep a daily shaving journal to track the number of shaves and compliance.
Participants were evaluated at the baseline screening visit, then at 4, 8, and 12 weeks. Evaluations included an investigator lesion count, the IGSA, and the PGSA. The PGSA was used to evaluate subjective clinical measurements (ie, indicate how much postshave burning/itching/stinging the participant was experiencing). The impact of shaving on daily life was evaluated at the baseline screening visit and at 12 weeks with the Participant Quality of Life Questionnaire comprised of 22 QOL statements. eTable 1 summarizes the investigator assessments used in the study, and eTable 2 summarizes the participant self-assessments. Both tables include the scale details and results interpretation for each assessment.

The study was approved by the local institutional review board, and all participants provided written informed consent in accordance with Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 50.

Study Visits—At the baseline screening visit, participants provided written informed consent and completed a prestudy shave questionnaire concerning shaving preparations, techniques, and opinions. Participants also provided a medical history, including prior and concomitant medications, and were evaluated using the inclusion/exclusion criteria. Investigators explained adverse event reporting to the participants. Participants were provided with an adequate supply of test razors for the 12-week period.
Data Analysis—Means and SDs were calculated for the study measures assessed at each visit. Analyses were performed evaluating change from baseline in repeated-measures analysis of variance models. These models were adjusted for baseline levels of the outcome measure and visit number. The magnitude of change from baseline was evaluated against a null hypothesis of 0% change. This longitudinal model adjusted for any potential differing baseline levels among participants. Statistical significance was defined as P<.05. SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used for all analyses.
Results
In total, 21 individuals were enrolled, and 20 completed the study. Participants who completed the study were non-Hispanic Black (n=10); non-Hispanic White (n=8); Asian (n=1); or White, American Indian (n=1). All participants adhered to the protocol and reported shaving at least 5 times a week for 12 weeks using the test razor. One participant was removed after he was found to have a history of sarcoidosis, making him ineligible for the study. No study-related adverse events were reported.
Papules and Pustules—Over the course of the 12-week study, the papule count decreased significantly from baseline. Results from the investigator lesion count (see eTable 1 for key) indicated that by week 12—adjusted for number of papules at baseline—the mean percentage reduction was estimated to be 59.6% (P<.0001). A significant decrease in papule count also was observed between the baseline visit and week 8 (57.2%; P<.0001). A nonsignificant decrease was observed at week 4 (18.9%; P=.17). Only 3 participants presented with pustules at baseline, and the pustule count remained low over the course of the study. No significant change was noted at week 12 vs baseline (P=.98). Notably, there was no increase in pustule count at the end of the study compared with baseline (Table 1).
Skin Appearance—An improvement in the skin’s appearance over the course of the study from baseline was consistent with an improvement in the IGSA. The IGSA score significantly improved from a mean (SD) measurement of 2.5 (0.6) (indicating mild to moderate inflammation) at baseline to 1.4 (0.8) at week 8 (P<.0001) and 1.2 (1.1) (indicating mild inflammation to almost clear) at week 12 (P<.0001). The observed decrease in severity of skin condition and skin inflammation is shown in Figure 3.

Significant improvements were observed in every category of the PGSA at week 12 vs baseline (P≤.0007)(Table 2). At week 12, there was a significant (P≤.05) increase from baseline in participant agreement for all 22 QOL metrics describing positive shave experience, achieving results, skin feel, self-confidence, and social interactions (Figure 4), which supports the positive impact of adopting a shaving regimen with the test razor. Notably, after using the test razor for 12 weeks, men reported that they were more likely to agree with the statements “my skin felt smooth,” “my skin felt good to touch,” and “I was able to achieve a consistently good shave.” Other meaningful increases occurred in “shaving was something I looked forward to doing,” “others thought I looked clean cut,” “I looked my best for my family/others/work,” and “I felt comfortable/confident getting closer to others.” All QOL statements are shown in Figure 4.

Comment
Improvement With Novel Razor Technology—For the first time, frequent use of a novel razor technology designed specifically for men with PFB was found to significantly improve skin appearance, shave satisfaction, and QOL after 12 weeks vs baseline in participants clinically diagnosed with PFB. In men with shave-related skin irritation and razor bumps who typically wet-shaved with a razor at least 3 times a week, use of the test razor with their regular shaving preparation product 5 or more times per week for 12 weeks was associated with significant improvements from baseline in investigator lesion count, IGSA, PGSA, and Participant Quality of Life Questionnaire measurements.
Study strengths included the quantification of the change in the number of lesions and the degree of severity by a trained investigator in a prospective clinical study along with an assessment of the impact on participant QOL. A lack of a control arm could be considered a limitation of the study; however, study end points were evaluated compared with baseline, with each participant serving as their own control. Spontaneous resolution of the condition with their standard routine was considered highly unlikely in these participants; therefore, in the absence of any other changes, improvements were attributed to regular use of the test product over the course of the study. The results presented here provide strong support for the effectiveness of the new razor technology in improving the appearance of men with razor bumps and shaving irritation.
Hair Removal Tools for the Management of PFB—Although various tools and techniques have been proposed in the past for men with PFB, the current test razor technology provided unique benefits, including improvements in appearance and severity of the condition as well as a positive impact on QOL. In 1979, Conte and Lawrence9 evaluated the effect of using an electric hair clipper and twice-daily use of a skin-cleansing pad on the occurrence of PFB. Participants (n=96) allowed their beards to grow out for 1 month, after which they started shaving with an electric clipper with a triple O head. The authors reported a favorable response in 95% (91/96) of cases. However, the electric clippers left 1 mm of beard at the skin level,9 which may not be acceptable for those who prefer a clean-shaven appearance.6
A prospective survey of 22 men of African descent with PFB found use of a safety razor was preferred over an electric razor.10 The single-arm study evaluated use of a foil-guarded shaver (single-razor blade) in the management of PFB based on investigator lesion counts and a participant questionnaire. Participants were asked to shave at least every other day and use a specially designed preshave brush. A mean reduction in lesion counts was observed at 2 weeks (29.6%), 4 weeks (38.1%), and 6 weeks (47.1%); statistical significance was not reported. At 6 weeks, 77.3% (17/22) of participants judged the foil-guarded shaver to be superior to other shaving devices in controlling their razor bumps, and 90.9% (20/22) indicated they would recommend the shaver to others with PFB. The authors hypothesized that the guard buffered the skin from the blade, which might otherwise facilitate the penetration of ingrowing hairs and cause trauma to existing lesions.
The mean reduction in lesion count from baseline observed at week 4 was greater in the study with the foil-guarded shaver and preshave brush (38% reduction)10 than in our study (19% reduction in papule count). Different methodologies, use of a preshave brush in the earlier study, and a difference in lesion severity at baseline may have contributed to this difference. The study with the foil-guarded shaver concluded after 6 weeks, and there was a 47.1% reduction in lesion counts vs baseline.10 In contrast, the current study continued for 12 weeks, and a 59.6% reduction in lesion counts was reported. Participants from both studies reported an improved shaving experience compared with their usual practice,10 though only the current study explored the positive impact of the new razor technology on participant QOL.
Preventing Hairs From Being Cut Too Close—The closeness of the shave is believed to be a contributory factor in the development and persistence of PFB6,8,11 based on a tendency for the distal portion of tightly curled hair shafts to re-enter the skin after shaving via transfollicular penetration.12 Inclusion of a buffer in the razor between the sharp blades and the skin has been proposed to prevent hairs from being cut too close and causing transfollicular penetration.12
In the test razor used in the current study, the bridge technology acted as the buffer to prevent hairs from being cut too close to the skin and to reduce blade contact with the skin (Figure 2). Having only 2 blades also reduced the closeness of the shave compared with 5-bladed technologies,13 as each hair can only be pulled and cut up to a maximum of 2 times per shaving stroke. Notably, this did not impact the participants’ QOL scores related to achieving a close shave or skin feeling smooth; both attributes were significantly improved at 12 weeks vs baseline (Figure 4).
By reducing blade contact with the skin, the bridge technology in the test razor was designed to prevent excessive force from being applied to the skin through the blades. Reduced blade loading minimizes contact with and impact on sensitive skin.14 Additional design features of the test razor to minimize the impact of shaving on the skin include treatment of the 2 blades with low-friction coatings, which allows the blades to cut through the beard hair with minimal force, helping to reduce the tug-and-pull effect that may otherwise result in irritation and inflammation.13,15 Lubrication strips before and after the blades in the test razor reduce friction between the blades and the skin to further protect the skin from the blades.15
Shaving With Multiblade Razors Does Not Exacerbate PFB—In a 1-week, split-faced, randomized study of 45 Black men, shaving with a manual 3-bladed razor was compared with use of 3 different chemical depilatory formulations.16 Shaving every other day for 1 week with the manual razor resulted in more papule formation but less irritation than use of the depilatories. The authors concluded that a study with longer duration was needed to explore the impact of shaving on papule formation in participants with a history of PFB.16
In 2013, an investigator-blinded study of 90 African American men with PFB compared the impact of different shaving regimens on the signs and symptoms of PFB over a 12-week period.4 Participants were randomized to 1 of 3 arms: (1) shaving 2 to 3 times per week with a triple-blade razor and standard products (control group); (2) shaving daily with a 5-bladed razor and standard products; and (3) shaving daily with a 5-bladed razor and “advanced” specific pre- and postshave products. The researchers found that the mean papule measurement significantly decreased from baseline in the advanced (P=.01) and control (P=.016) groups. Between-group comparison revealed no significant differences for papule or pustule count among each arm. For the investigator-graded severity, the change from baseline was significant for all 3 groups (P≤.04); however, the differences among groups were not significant. Importantly, these data demonstrated that PFB was not exacerbated by multiblade razors used as part of a daily shaving regimen.4
The findings of the current study were consistent with those of Daniel et al4 in that there was no exacerbation of the signs and symptoms of PFB associated with daily shaving. However, rather than requiring participants to change their entire shaving regimen, the present study only required a change of razor type. Moreover, the use of the new razor technology significantly decreased papule counts at week 12 vs the baseline measurement (P<.0001) and was associated with an improvement in subjective skin severity measurements. The participants in the present study reported significantly less burning, stinging, and itching after using the test product for 12 weeks (P<.0001).
Impact of Treatment on QOL—The current study further expanded on prior findings by combining these clinical end points with the QOL results to assess the test razor’s impact on participants’ lives. Results showed that over the course of 12 weeks, the new razor technology significantly improved the participants’ QOL in all questions related to shaving experience, achieving results, skin feel, self-confidence, and social interactions. The significant improvement in QOL included statements such as “shaving was a pleasant experience,” “I was able to achieve a consistently good shave,” and “my skin felt smooth.” Participants also reported improvements in meaningful categories such as “my shave made me feel attractive” and “I felt comfortable/confident getting closer to others.” As the current study showed, a shave regimen has the potential to change participants’ overall assessment of their QOL, a variable that must not be overlooked.
Conclusion
In men with clinically diagnosed PFB, regular shaving with a razor designed to protect the skin was found to significantly decrease lesion counts, increase shave satisfaction, and improve QOL after 12 weeks compared with their usual shaving practice (baseline measures). This razor technology provides another option to help manage PFB for men who wish to or need to continue shaving.
Acknowledgments—The clinical study was funded by the Procter & Gamble Company. Editorial writing assistance, supported financially by the Procter & Gamble Company, was provided by Gill McFeat, PhD, of McFeat Science Ltd (Devon, United Kingdom).
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB)(also known as razor bumps or shaving bumps)1 is a skin condition that consists of papules resulting from ingrown hairs.2 In more severe cases, papules become pustules, then abscesses, which can cause scarring.1,2 The condition can be distressing for patients, with considerable negative impact on their daily lives.3 The condition also is associated with shaving-related stinging, burning, pruritus, and cuts on the skin.4
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most common in men of African descent due to the curved nature of the hair follicle,2,5,6 with an estimated prevalence in this population of 45% to 83%,1,6 but it can affect men of other ethnicities.7 A genetic polymorphism in a gene encoding a keratin specific to the hair follicle also has been found to predispose some individuals to PFB.5 When hair from a curved or destabilized hair follicle is cut to form a sharp tip, it is susceptible to extrafollicular and/or transfollicular penetration,5,6,8 as illustrated in Figure 1.

With extrafollicular or transfollicular penetration, the hair shaft re-enters or retracts into the dermis, triggering an inflammatory response that may be exacerbated by subsequent shaving.2 Few studies have been published that aim to identify potential shaving solutions for individuals with PFB who elect to or need to continue shaving.
A new razor technology comprising 2 blades separated by a bridge feature has been designed specifically for men with razor bumps (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]). The SkinGuard razor redistributes shaving pressure so that there is less force from the blades on the skin and inflamed lesions than without the bridge, as seen in Figure 2. The razor has been designed to protect the skin from the blades, thereby minimizing the occurrence of new lesions and allowing existing lesions to heal.
![Test razor bridge feature (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]) minimizes the force of the razor blades on the skin. Copyright 2022 The Procter & Gamble Company. Test razor bridge feature (SkinGuard [Procter & Gamble]) minimizes the force of the razor blades on the skin. Copyright 2022 The Procter & Gamble Company.](https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/Moran_2.jpg)
The primary purpose of this study was to assess the appearance of males with razor bumps and shaving irritation when using the new razor technology in a regular shaving routine. The secondary objective was to measure satisfaction of the shaving experience when using the new razor by means of assessing itching, burning, and stinging using the participant global severity assessment (PGSA) and the impact on quality of life (QOL) measures.
Methods
Participants—Eligible participants were male, aged 20 to 60 years, and had clinically diagnosed PFB as well as symptoms of skin irritation from shaving. Participants were recruited from a dermatology clinic and via institutional review board–approved advertising.
Those eligible for inclusion in the study had a shaving routine that comprised shaving at least 3 times a week using a wet-shave, blade-razor technique accompanied by only a shave gel or foam. In addition, eligible participants had mild to moderate symptoms of skin irritation (a minimum of 10 razor bumps) from shaving based on investigator global severity assessment (IGSA) rating scales and were willing to shave at least 5 times a week during the study period. Participants could continue certain topical and systemic interventions for their skin.
Participants were excluded from the study if they had an underlying inflammatory disease that could manifest with a skin rash or were using any of these medications: topical benzoyl peroxide, topical clindamycin, topical retinoids, or oral antibiotics.
Study Design—A prospective, open-label study was conducted over a period of 12 weeks at a single site in the United States. Investigators instructed participants to shave 5 or more times per week with the test razor and to keep a daily shaving journal to track the number of shaves and compliance.
Participants were evaluated at the baseline screening visit, then at 4, 8, and 12 weeks. Evaluations included an investigator lesion count, the IGSA, and the PGSA. The PGSA was used to evaluate subjective clinical measurements (ie, indicate how much postshave burning/itching/stinging the participant was experiencing). The impact of shaving on daily life was evaluated at the baseline screening visit and at 12 weeks with the Participant Quality of Life Questionnaire comprised of 22 QOL statements. eTable 1 summarizes the investigator assessments used in the study, and eTable 2 summarizes the participant self-assessments. Both tables include the scale details and results interpretation for each assessment.

The study was approved by the local institutional review board, and all participants provided written informed consent in accordance with Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 50.

Study Visits—At the baseline screening visit, participants provided written informed consent and completed a prestudy shave questionnaire concerning shaving preparations, techniques, and opinions. Participants also provided a medical history, including prior and concomitant medications, and were evaluated using the inclusion/exclusion criteria. Investigators explained adverse event reporting to the participants. Participants were provided with an adequate supply of test razors for the 12-week period.
Data Analysis—Means and SDs were calculated for the study measures assessed at each visit. Analyses were performed evaluating change from baseline in repeated-measures analysis of variance models. These models were adjusted for baseline levels of the outcome measure and visit number. The magnitude of change from baseline was evaluated against a null hypothesis of 0% change. This longitudinal model adjusted for any potential differing baseline levels among participants. Statistical significance was defined as P<.05. SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used for all analyses.
Results
In total, 21 individuals were enrolled, and 20 completed the study. Participants who completed the study were non-Hispanic Black (n=10); non-Hispanic White (n=8); Asian (n=1); or White, American Indian (n=1). All participants adhered to the protocol and reported shaving at least 5 times a week for 12 weeks using the test razor. One participant was removed after he was found to have a history of sarcoidosis, making him ineligible for the study. No study-related adverse events were reported.
Papules and Pustules—Over the course of the 12-week study, the papule count decreased significantly from baseline. Results from the investigator lesion count (see eTable 1 for key) indicated that by week 12—adjusted for number of papules at baseline—the mean percentage reduction was estimated to be 59.6% (P<.0001). A significant decrease in papule count also was observed between the baseline visit and week 8 (57.2%; P<.0001). A nonsignificant decrease was observed at week 4 (18.9%; P=.17). Only 3 participants presented with pustules at baseline, and the pustule count remained low over the course of the study. No significant change was noted at week 12 vs baseline (P=.98). Notably, there was no increase in pustule count at the end of the study compared with baseline (Table 1).
Skin Appearance—An improvement in the skin’s appearance over the course of the study from baseline was consistent with an improvement in the IGSA. The IGSA score significantly improved from a mean (SD) measurement of 2.5 (0.6) (indicating mild to moderate inflammation) at baseline to 1.4 (0.8) at week 8 (P<.0001) and 1.2 (1.1) (indicating mild inflammation to almost clear) at week 12 (P<.0001). The observed decrease in severity of skin condition and skin inflammation is shown in Figure 3.

Significant improvements were observed in every category of the PGSA at week 12 vs baseline (P≤.0007)(Table 2). At week 12, there was a significant (P≤.05) increase from baseline in participant agreement for all 22 QOL metrics describing positive shave experience, achieving results, skin feel, self-confidence, and social interactions (Figure 4), which supports the positive impact of adopting a shaving regimen with the test razor. Notably, after using the test razor for 12 weeks, men reported that they were more likely to agree with the statements “my skin felt smooth,” “my skin felt good to touch,” and “I was able to achieve a consistently good shave.” Other meaningful increases occurred in “shaving was something I looked forward to doing,” “others thought I looked clean cut,” “I looked my best for my family/others/work,” and “I felt comfortable/confident getting closer to others.” All QOL statements are shown in Figure 4.

Comment
Improvement With Novel Razor Technology—For the first time, frequent use of a novel razor technology designed specifically for men with PFB was found to significantly improve skin appearance, shave satisfaction, and QOL after 12 weeks vs baseline in participants clinically diagnosed with PFB. In men with shave-related skin irritation and razor bumps who typically wet-shaved with a razor at least 3 times a week, use of the test razor with their regular shaving preparation product 5 or more times per week for 12 weeks was associated with significant improvements from baseline in investigator lesion count, IGSA, PGSA, and Participant Quality of Life Questionnaire measurements.
Study strengths included the quantification of the change in the number of lesions and the degree of severity by a trained investigator in a prospective clinical study along with an assessment of the impact on participant QOL. A lack of a control arm could be considered a limitation of the study; however, study end points were evaluated compared with baseline, with each participant serving as their own control. Spontaneous resolution of the condition with their standard routine was considered highly unlikely in these participants; therefore, in the absence of any other changes, improvements were attributed to regular use of the test product over the course of the study. The results presented here provide strong support for the effectiveness of the new razor technology in improving the appearance of men with razor bumps and shaving irritation.
Hair Removal Tools for the Management of PFB—Although various tools and techniques have been proposed in the past for men with PFB, the current test razor technology provided unique benefits, including improvements in appearance and severity of the condition as well as a positive impact on QOL. In 1979, Conte and Lawrence9 evaluated the effect of using an electric hair clipper and twice-daily use of a skin-cleansing pad on the occurrence of PFB. Participants (n=96) allowed their beards to grow out for 1 month, after which they started shaving with an electric clipper with a triple O head. The authors reported a favorable response in 95% (91/96) of cases. However, the electric clippers left 1 mm of beard at the skin level,9 which may not be acceptable for those who prefer a clean-shaven appearance.6
A prospective survey of 22 men of African descent with PFB found use of a safety razor was preferred over an electric razor.10 The single-arm study evaluated use of a foil-guarded shaver (single-razor blade) in the management of PFB based on investigator lesion counts and a participant questionnaire. Participants were asked to shave at least every other day and use a specially designed preshave brush. A mean reduction in lesion counts was observed at 2 weeks (29.6%), 4 weeks (38.1%), and 6 weeks (47.1%); statistical significance was not reported. At 6 weeks, 77.3% (17/22) of participants judged the foil-guarded shaver to be superior to other shaving devices in controlling their razor bumps, and 90.9% (20/22) indicated they would recommend the shaver to others with PFB. The authors hypothesized that the guard buffered the skin from the blade, which might otherwise facilitate the penetration of ingrowing hairs and cause trauma to existing lesions.
The mean reduction in lesion count from baseline observed at week 4 was greater in the study with the foil-guarded shaver and preshave brush (38% reduction)10 than in our study (19% reduction in papule count). Different methodologies, use of a preshave brush in the earlier study, and a difference in lesion severity at baseline may have contributed to this difference. The study with the foil-guarded shaver concluded after 6 weeks, and there was a 47.1% reduction in lesion counts vs baseline.10 In contrast, the current study continued for 12 weeks, and a 59.6% reduction in lesion counts was reported. Participants from both studies reported an improved shaving experience compared with their usual practice,10 though only the current study explored the positive impact of the new razor technology on participant QOL.
Preventing Hairs From Being Cut Too Close—The closeness of the shave is believed to be a contributory factor in the development and persistence of PFB6,8,11 based on a tendency for the distal portion of tightly curled hair shafts to re-enter the skin after shaving via transfollicular penetration.12 Inclusion of a buffer in the razor between the sharp blades and the skin has been proposed to prevent hairs from being cut too close and causing transfollicular penetration.12
In the test razor used in the current study, the bridge technology acted as the buffer to prevent hairs from being cut too close to the skin and to reduce blade contact with the skin (Figure 2). Having only 2 blades also reduced the closeness of the shave compared with 5-bladed technologies,13 as each hair can only be pulled and cut up to a maximum of 2 times per shaving stroke. Notably, this did not impact the participants’ QOL scores related to achieving a close shave or skin feeling smooth; both attributes were significantly improved at 12 weeks vs baseline (Figure 4).
By reducing blade contact with the skin, the bridge technology in the test razor was designed to prevent excessive force from being applied to the skin through the blades. Reduced blade loading minimizes contact with and impact on sensitive skin.14 Additional design features of the test razor to minimize the impact of shaving on the skin include treatment of the 2 blades with low-friction coatings, which allows the blades to cut through the beard hair with minimal force, helping to reduce the tug-and-pull effect that may otherwise result in irritation and inflammation.13,15 Lubrication strips before and after the blades in the test razor reduce friction between the blades and the skin to further protect the skin from the blades.15
Shaving With Multiblade Razors Does Not Exacerbate PFB—In a 1-week, split-faced, randomized study of 45 Black men, shaving with a manual 3-bladed razor was compared with use of 3 different chemical depilatory formulations.16 Shaving every other day for 1 week with the manual razor resulted in more papule formation but less irritation than use of the depilatories. The authors concluded that a study with longer duration was needed to explore the impact of shaving on papule formation in participants with a history of PFB.16
In 2013, an investigator-blinded study of 90 African American men with PFB compared the impact of different shaving regimens on the signs and symptoms of PFB over a 12-week period.4 Participants were randomized to 1 of 3 arms: (1) shaving 2 to 3 times per week with a triple-blade razor and standard products (control group); (2) shaving daily with a 5-bladed razor and standard products; and (3) shaving daily with a 5-bladed razor and “advanced” specific pre- and postshave products. The researchers found that the mean papule measurement significantly decreased from baseline in the advanced (P=.01) and control (P=.016) groups. Between-group comparison revealed no significant differences for papule or pustule count among each arm. For the investigator-graded severity, the change from baseline was significant for all 3 groups (P≤.04); however, the differences among groups were not significant. Importantly, these data demonstrated that PFB was not exacerbated by multiblade razors used as part of a daily shaving regimen.4
The findings of the current study were consistent with those of Daniel et al4 in that there was no exacerbation of the signs and symptoms of PFB associated with daily shaving. However, rather than requiring participants to change their entire shaving regimen, the present study only required a change of razor type. Moreover, the use of the new razor technology significantly decreased papule counts at week 12 vs the baseline measurement (P<.0001) and was associated with an improvement in subjective skin severity measurements. The participants in the present study reported significantly less burning, stinging, and itching after using the test product for 12 weeks (P<.0001).
Impact of Treatment on QOL—The current study further expanded on prior findings by combining these clinical end points with the QOL results to assess the test razor’s impact on participants’ lives. Results showed that over the course of 12 weeks, the new razor technology significantly improved the participants’ QOL in all questions related to shaving experience, achieving results, skin feel, self-confidence, and social interactions. The significant improvement in QOL included statements such as “shaving was a pleasant experience,” “I was able to achieve a consistently good shave,” and “my skin felt smooth.” Participants also reported improvements in meaningful categories such as “my shave made me feel attractive” and “I felt comfortable/confident getting closer to others.” As the current study showed, a shave regimen has the potential to change participants’ overall assessment of their QOL, a variable that must not be overlooked.
Conclusion
In men with clinically diagnosed PFB, regular shaving with a razor designed to protect the skin was found to significantly decrease lesion counts, increase shave satisfaction, and improve QOL after 12 weeks compared with their usual shaving practice (baseline measures). This razor technology provides another option to help manage PFB for men who wish to or need to continue shaving.
Acknowledgments—The clinical study was funded by the Procter & Gamble Company. Editorial writing assistance, supported financially by the Procter & Gamble Company, was provided by Gill McFeat, PhD, of McFeat Science Ltd (Devon, United Kingdom).
- Alexander AM, Delph WI. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military. a medical, administrative and social problem. J Natl Med Assoc. 1974;66:459-464, 479.
- Kligman AM, Strauss JS. Pseudofolliculitis of the beard. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74:533-542.
- Banta J, Bowen C, Wong E, et al. Perceptions of shaving profiles and their potential impacts on career progression in the United States Air Force. Mil Med. 2021;186:187-189.
- Daniel A, Gustafson CJ, Zupkosky PJ, et al. Shave frequency and regimen variation effects on the management of pseudofolliculitis barbae. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:410-418.
- Winter H, Schissel D, Parry DA, et al. An unusual Ala12Thr polymorphism in the 1A alpha-helical segment of the companion layer-specific keratin K6hf: evidence for a risk factor in the etiology of the common hair disorder pseudofolliculitis barbae. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;122:652-657.
- Perry PK, Cook-Bolden FE, Rahman Z, et al. Defining pseudofolliculitis barbae in 2001: a review of the literature and current trends. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S113-S119.
- McMichael AJ. Hair and scalp disorders in ethnic populations. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:629-644.
- Ribera M, Fernández-Chico N, Casals M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:749-757.
- Conte MS, Lawrence JE. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. no ‘pseudoproblem.’ JAMA. 1979;241:53-54.
- Alexander AM. Evaluation of a foil-guarded shaver in the management of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 1981;27:534-537, 540-542.
- Weiss AN, Arballo OM, Miletta NR, et al. Military grooming standards and their impact on skin diseases of the head and neck. Cutis. 2018;102:328;331-333.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K, Ertel K, et al. Blade shaving. In: Draelos ZD, ed. Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and Procedures. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons; 2015:166-173.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K. Insights into shaving and its impact on skin. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166(suppl 1):6-12.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K. The biomechanics of blade shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):17-23.
- Kindred C, Oresajo CO, Yatskayer M, et al. Comparative evaluation of men’s depilatory composition versus razor in black men. Cutis. 2011;88:98-103.
- Alexander AM, Delph WI. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military. a medical, administrative and social problem. J Natl Med Assoc. 1974;66:459-464, 479.
- Kligman AM, Strauss JS. Pseudofolliculitis of the beard. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74:533-542.
- Banta J, Bowen C, Wong E, et al. Perceptions of shaving profiles and their potential impacts on career progression in the United States Air Force. Mil Med. 2021;186:187-189.
- Daniel A, Gustafson CJ, Zupkosky PJ, et al. Shave frequency and regimen variation effects on the management of pseudofolliculitis barbae. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:410-418.
- Winter H, Schissel D, Parry DA, et al. An unusual Ala12Thr polymorphism in the 1A alpha-helical segment of the companion layer-specific keratin K6hf: evidence for a risk factor in the etiology of the common hair disorder pseudofolliculitis barbae. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;122:652-657.
- Perry PK, Cook-Bolden FE, Rahman Z, et al. Defining pseudofolliculitis barbae in 2001: a review of the literature and current trends. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S113-S119.
- McMichael AJ. Hair and scalp disorders in ethnic populations. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:629-644.
- Ribera M, Fernández-Chico N, Casals M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:749-757.
- Conte MS, Lawrence JE. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. no ‘pseudoproblem.’ JAMA. 1979;241:53-54.
- Alexander AM. Evaluation of a foil-guarded shaver in the management of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 1981;27:534-537, 540-542.
- Weiss AN, Arballo OM, Miletta NR, et al. Military grooming standards and their impact on skin diseases of the head and neck. Cutis. 2018;102:328;331-333.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K, Ertel K, et al. Blade shaving. In: Draelos ZD, ed. Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and Procedures. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons; 2015:166-173.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K. Insights into shaving and its impact on skin. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166(suppl 1):6-12.
- Cowley K, Vanoosthuyze K. The biomechanics of blade shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):17-23.
- Kindred C, Oresajo CO, Yatskayer M, et al. Comparative evaluation of men’s depilatory composition versus razor in black men. Cutis. 2011;88:98-103.
Practice Points
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is a common follicular inflammatory disorder associated with shaving, most commonly seen in men of African ancestry. It can be distressing and cause a substantial impact on quality of life (QOL).
- Frequent use of a novel razor technology designed specifically for men with PFB was found to improve skin appearance and QOL after 12 weeks vs baseline.
- This razor technology provides an alternative approach to help manage PFB for men who wish to or need to continue shaving.
Dupilumab as a Therapeutic Approach in Alopecia Universalis
To the Editor:
Atopic diseases, specifically atopic dermatitis (AD) and alopecia areata (AA), are at the forefront of a new era in dermatology involving molecular-directed therapy. Dupilumab is one specific example, having received US Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2017 for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD.1 It currently is being investigated for use in pediatric AD. The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of dupilumab include headaches, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, nasopharyngitis, and injection-site reactions.2 We discuss a case of hair regrowth in a patient who was previously diagnosed with AA after treatment with dupilumab for refractory AD.
A 65-year-old White man presented with a history of AD since childhood. Additional medical history included hyperlipidemia; herpes simplex virus infection; asthma; and a diagnosis of AA 6 years prior, which eventually progressed to alopecia universalis. Physical examination demonstrated scattered erythematous lichenified plaques with excoriations involving the arms, legs, and trunk. The patient’s face and scalp were spared of lesions. Complete loss of body hair including the eyelashes and eyebrows also was noted, which was consistent with alopecia universalis.
The patient was started on dupilumab for refractory AD after multiple courses of topical and systemic steroids failed. Prior treatment for AD did not include immunosuppressive or light therapy. The standard dosage of dupilumab was administered, which consisted of a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. There was no concurrent topical corticosteroid or topical calcineurin inhibitor prescribed. After 1 month of treatment with dupilumab, near-complete resolution of the patient’s AD was noted, and after 10 months of treatment, the patient experienced regrowth of the eyelashes, terminal hairs of the beard area (Figure), and vellus hairs of the eyebrows. This hair regrowth persists today with continued dupilumab treatment, and the patient has experienced no additional side effects.
Multiple retrospective and meta-analysis studies have demonstrated a high occurrence of AD comorbid with AA, which strongly suggests a common pathogenesis.3,4 Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 of the helper T-cell type 2 (TH2) pathway.1 Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4Rα, which also is found in IL-13 receptors. Dupilumab prevents TH2 pathway-related downstream signaling effects of both cytokines. Although this effect was originally utilized to suppress the TH2-mediated signaling in AD, our patient and others have demonstrated successful hair regrowth with dupilumab, which likely stems from a similar TH2-related antagonism in AA.5,6
The cause of AA is unknown, but IL-4 and IL-13 of the TH2 pathway have been implicated, which renders support for the therapeutic effect of dupilumab in the treatment of AA. Scalp samples of patients with AA have demonstrated upregulation of TH2, helper T-cell type 1 (TH1), and IL-23 cytokines, suggesting efficacy with the use of anti-TH2, anti-TH1, and anti–IL-23 therapies.7 Polymerase chain reaction testing performed on serum samples in patients with AA displayed marked elevation of TH2 cytokines, notably IL-13, which were reduced following intralesional corticosteroid treatment.8 It also has been demonstrated that multiple TH2-related genes contribute to the genetic susceptibility of developing AA, specifically IL-4 and IL-13.9,10
Prior case reports have shown contradicting effects (dupilumab-induced AA), which are speculated to be caused by a stronger TH1 response from TH2 suppression.11,12 In one report, dupilumab was initiated for AD refractory to multiple topical and oral interventions. New-onset hair loss to the scalp was noted after 18 weeks of therapy. Twenty-six weeks into therapy with dupilumab, full hair regrowth was then reported.11 Despite this report, our patient’s hair regrowth after the use of dupilumab for refractory AD further strengthens support for the use of dupilumab as a potential therapy for alopecia universalis and other lymphocyte-mediated hair loss conditions. However, a large disparity in response time and an overall slower progression of hair regrowth reported in our case separate it from other reports of rapid voluminous hair regrowth.5,6 Our findings support the potential use of dupilumab in the treatment of patients with AA.
- Shirly M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77:1115-1121.
- Ou Z, Chen C, Chen A, et al. Adverse events of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;54:303-310.
- Andersen YMF, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, et al. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:274-280.e1.
- Mohan GC, Silverberg JI. Association of vitiligo and alopecia areata with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;15:522-528.
- Penzi LR, Yasuda M, Manatis-Lornell A, et al. Hair regrowth in a patient with long-standing alopecia totalis and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1358-1360.
- Alniemi DT, McGevna L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:111-112.
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, Noda S, et al. Alopecia areata profiling shows TH1, TH2, and IL-23 cytokine activation without parallel TH17/TH22 skewing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1277-1287.
- Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulati N, Bonifacio KM, et al. Biomarkers of alopecia areata disease activity and response to corticosteroid treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:282-286.
- Jagielska D, Redler S, Brockschmidt FF, et al. Follow-up study of the first genome-wide association scan in alopecia areata: IL13 and KIAA0350 as susceptibility loci supported with genome-wide significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2192-2197.
- Kalkan G, Karakus N, Bas¸ Y, et al. The association between interleukin (IL)-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism and alopecia areata (AA) in Turkish population. Gene. 2013;527:565-569.
- Flanagan K, Sperling L, Lin J. Drug-induced alopecia after dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:54-56.
- Mitchell K, Levitt J. Alopecia areata after dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:143-144.
To the Editor:
Atopic diseases, specifically atopic dermatitis (AD) and alopecia areata (AA), are at the forefront of a new era in dermatology involving molecular-directed therapy. Dupilumab is one specific example, having received US Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2017 for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD.1 It currently is being investigated for use in pediatric AD. The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of dupilumab include headaches, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, nasopharyngitis, and injection-site reactions.2 We discuss a case of hair regrowth in a patient who was previously diagnosed with AA after treatment with dupilumab for refractory AD.
A 65-year-old White man presented with a history of AD since childhood. Additional medical history included hyperlipidemia; herpes simplex virus infection; asthma; and a diagnosis of AA 6 years prior, which eventually progressed to alopecia universalis. Physical examination demonstrated scattered erythematous lichenified plaques with excoriations involving the arms, legs, and trunk. The patient’s face and scalp were spared of lesions. Complete loss of body hair including the eyelashes and eyebrows also was noted, which was consistent with alopecia universalis.
The patient was started on dupilumab for refractory AD after multiple courses of topical and systemic steroids failed. Prior treatment for AD did not include immunosuppressive or light therapy. The standard dosage of dupilumab was administered, which consisted of a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. There was no concurrent topical corticosteroid or topical calcineurin inhibitor prescribed. After 1 month of treatment with dupilumab, near-complete resolution of the patient’s AD was noted, and after 10 months of treatment, the patient experienced regrowth of the eyelashes, terminal hairs of the beard area (Figure), and vellus hairs of the eyebrows. This hair regrowth persists today with continued dupilumab treatment, and the patient has experienced no additional side effects.

Multiple retrospective and meta-analysis studies have demonstrated a high occurrence of AD comorbid with AA, which strongly suggests a common pathogenesis.3,4 Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 of the helper T-cell type 2 (TH2) pathway.1 Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4Rα, which also is found in IL-13 receptors. Dupilumab prevents TH2 pathway-related downstream signaling effects of both cytokines. Although this effect was originally utilized to suppress the TH2-mediated signaling in AD, our patient and others have demonstrated successful hair regrowth with dupilumab, which likely stems from a similar TH2-related antagonism in AA.5,6
The cause of AA is unknown, but IL-4 and IL-13 of the TH2 pathway have been implicated, which renders support for the therapeutic effect of dupilumab in the treatment of AA. Scalp samples of patients with AA have demonstrated upregulation of TH2, helper T-cell type 1 (TH1), and IL-23 cytokines, suggesting efficacy with the use of anti-TH2, anti-TH1, and anti–IL-23 therapies.7 Polymerase chain reaction testing performed on serum samples in patients with AA displayed marked elevation of TH2 cytokines, notably IL-13, which were reduced following intralesional corticosteroid treatment.8 It also has been demonstrated that multiple TH2-related genes contribute to the genetic susceptibility of developing AA, specifically IL-4 and IL-13.9,10
Prior case reports have shown contradicting effects (dupilumab-induced AA), which are speculated to be caused by a stronger TH1 response from TH2 suppression.11,12 In one report, dupilumab was initiated for AD refractory to multiple topical and oral interventions. New-onset hair loss to the scalp was noted after 18 weeks of therapy. Twenty-six weeks into therapy with dupilumab, full hair regrowth was then reported.11 Despite this report, our patient’s hair regrowth after the use of dupilumab for refractory AD further strengthens support for the use of dupilumab as a potential therapy for alopecia universalis and other lymphocyte-mediated hair loss conditions. However, a large disparity in response time and an overall slower progression of hair regrowth reported in our case separate it from other reports of rapid voluminous hair regrowth.5,6 Our findings support the potential use of dupilumab in the treatment of patients with AA.
To the Editor:
Atopic diseases, specifically atopic dermatitis (AD) and alopecia areata (AA), are at the forefront of a new era in dermatology involving molecular-directed therapy. Dupilumab is one specific example, having received US Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2017 for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD.1 It currently is being investigated for use in pediatric AD. The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of dupilumab include headaches, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, nasopharyngitis, and injection-site reactions.2 We discuss a case of hair regrowth in a patient who was previously diagnosed with AA after treatment with dupilumab for refractory AD.
A 65-year-old White man presented with a history of AD since childhood. Additional medical history included hyperlipidemia; herpes simplex virus infection; asthma; and a diagnosis of AA 6 years prior, which eventually progressed to alopecia universalis. Physical examination demonstrated scattered erythematous lichenified plaques with excoriations involving the arms, legs, and trunk. The patient’s face and scalp were spared of lesions. Complete loss of body hair including the eyelashes and eyebrows also was noted, which was consistent with alopecia universalis.
The patient was started on dupilumab for refractory AD after multiple courses of topical and systemic steroids failed. Prior treatment for AD did not include immunosuppressive or light therapy. The standard dosage of dupilumab was administered, which consisted of a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. There was no concurrent topical corticosteroid or topical calcineurin inhibitor prescribed. After 1 month of treatment with dupilumab, near-complete resolution of the patient’s AD was noted, and after 10 months of treatment, the patient experienced regrowth of the eyelashes, terminal hairs of the beard area (Figure), and vellus hairs of the eyebrows. This hair regrowth persists today with continued dupilumab treatment, and the patient has experienced no additional side effects.

Multiple retrospective and meta-analysis studies have demonstrated a high occurrence of AD comorbid with AA, which strongly suggests a common pathogenesis.3,4 Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 of the helper T-cell type 2 (TH2) pathway.1 Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4Rα, which also is found in IL-13 receptors. Dupilumab prevents TH2 pathway-related downstream signaling effects of both cytokines. Although this effect was originally utilized to suppress the TH2-mediated signaling in AD, our patient and others have demonstrated successful hair regrowth with dupilumab, which likely stems from a similar TH2-related antagonism in AA.5,6
The cause of AA is unknown, but IL-4 and IL-13 of the TH2 pathway have been implicated, which renders support for the therapeutic effect of dupilumab in the treatment of AA. Scalp samples of patients with AA have demonstrated upregulation of TH2, helper T-cell type 1 (TH1), and IL-23 cytokines, suggesting efficacy with the use of anti-TH2, anti-TH1, and anti–IL-23 therapies.7 Polymerase chain reaction testing performed on serum samples in patients with AA displayed marked elevation of TH2 cytokines, notably IL-13, which were reduced following intralesional corticosteroid treatment.8 It also has been demonstrated that multiple TH2-related genes contribute to the genetic susceptibility of developing AA, specifically IL-4 and IL-13.9,10
Prior case reports have shown contradicting effects (dupilumab-induced AA), which are speculated to be caused by a stronger TH1 response from TH2 suppression.11,12 In one report, dupilumab was initiated for AD refractory to multiple topical and oral interventions. New-onset hair loss to the scalp was noted after 18 weeks of therapy. Twenty-six weeks into therapy with dupilumab, full hair regrowth was then reported.11 Despite this report, our patient’s hair regrowth after the use of dupilumab for refractory AD further strengthens support for the use of dupilumab as a potential therapy for alopecia universalis and other lymphocyte-mediated hair loss conditions. However, a large disparity in response time and an overall slower progression of hair regrowth reported in our case separate it from other reports of rapid voluminous hair regrowth.5,6 Our findings support the potential use of dupilumab in the treatment of patients with AA.
- Shirly M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77:1115-1121.
- Ou Z, Chen C, Chen A, et al. Adverse events of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;54:303-310.
- Andersen YMF, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, et al. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:274-280.e1.
- Mohan GC, Silverberg JI. Association of vitiligo and alopecia areata with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;15:522-528.
- Penzi LR, Yasuda M, Manatis-Lornell A, et al. Hair regrowth in a patient with long-standing alopecia totalis and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1358-1360.
- Alniemi DT, McGevna L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:111-112.
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, Noda S, et al. Alopecia areata profiling shows TH1, TH2, and IL-23 cytokine activation without parallel TH17/TH22 skewing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1277-1287.
- Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulati N, Bonifacio KM, et al. Biomarkers of alopecia areata disease activity and response to corticosteroid treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:282-286.
- Jagielska D, Redler S, Brockschmidt FF, et al. Follow-up study of the first genome-wide association scan in alopecia areata: IL13 and KIAA0350 as susceptibility loci supported with genome-wide significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2192-2197.
- Kalkan G, Karakus N, Bas¸ Y, et al. The association between interleukin (IL)-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism and alopecia areata (AA) in Turkish population. Gene. 2013;527:565-569.
- Flanagan K, Sperling L, Lin J. Drug-induced alopecia after dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:54-56.
- Mitchell K, Levitt J. Alopecia areata after dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:143-144.
- Shirly M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77:1115-1121.
- Ou Z, Chen C, Chen A, et al. Adverse events of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;54:303-310.
- Andersen YMF, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, et al. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:274-280.e1.
- Mohan GC, Silverberg JI. Association of vitiligo and alopecia areata with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;15:522-528.
- Penzi LR, Yasuda M, Manatis-Lornell A, et al. Hair regrowth in a patient with long-standing alopecia totalis and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1358-1360.
- Alniemi DT, McGevna L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:111-112.
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, Noda S, et al. Alopecia areata profiling shows TH1, TH2, and IL-23 cytokine activation without parallel TH17/TH22 skewing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1277-1287.
- Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulati N, Bonifacio KM, et al. Biomarkers of alopecia areata disease activity and response to corticosteroid treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:282-286.
- Jagielska D, Redler S, Brockschmidt FF, et al. Follow-up study of the first genome-wide association scan in alopecia areata: IL13 and KIAA0350 as susceptibility loci supported with genome-wide significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2192-2197.
- Kalkan G, Karakus N, Bas¸ Y, et al. The association between interleukin (IL)-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism and alopecia areata (AA) in Turkish population. Gene. 2013;527:565-569.
- Flanagan K, Sperling L, Lin J. Drug-induced alopecia after dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:54-56.
- Mitchell K, Levitt J. Alopecia areata after dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:143-144.
Practice Points
- Practicing dermatologists should be aware of the shared pathophysiology of alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis and the relief patients with these conditions can experience when treated with dupilumab.
- As molecular-directed biologic therapies emerge in the marketplace, their potential for targeting one atopic disease may offer notable benefits for use in the treatment of other atopic diseases.
Update on Tinea Capitis Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea capitis (TC) most often is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. The peak incidence is between 3 and 7 years of age. Noninflammatory TC typically presents as fine scaling with single or multiple scaly patches of circular alopecia (grey patches); diffuse or patchy, fine, white, adherent scaling of the scalp resembling generalized dandruff with subtle hair loss; or single or multiple patches of well-demarcated areas of alopecia with fine scale studded with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface, resulting in a black dot appearance. Inflammatory variants of TC include kerion and favus.1 Herein, updates on diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of TC are provided, as well as a discussion of changes in the fungal microbiome associated with TC. Lastly, insights to some queries that practitioners may encounter when treating children with TC are provided.
Genetic Susceptibility
Molecular techniques have identified a number of macrophage regulator, leukocyte activation and migration, and cutaneous permeability genes associated with susceptibility to TC. These findings indicate that genetically determined deficiency in adaptive immune responses may affect the predisposition to dermatophyte infections.2
Clinical Varieties of Infection
Dermatophytes causing ringworm are capable of invading the hair shafts and can simultaneously invade smooth or glabrous skin (eg, T tonsurans, Trichophyton schoenleinii, Trichophyton violaceum). Some causative dermatophytes can even penetrate the nails (eg, Trichophyton soudanense). The clinical presentation is dependent on 3 main patterns of hair invasion3:
• Ectothrix: A mid-follicular pattern of invasion with hyphae growing down to the hair bulb that commonly is caused by Microsporum species. It clinically presents with scaling and inflammation with hair shafts breaking 2 to 3 mm above the scalp level.
• Endothrix: This pattern is nonfluorescent on Wood lamp examination, and hairs often break at the scalp level (black dot type). Trichophyton tonsurans, T soudanense, Trichophyton rubrum, and T violaceum are common causes.
• Favus: In this pattern, T schoenleinii is a common cause, and hairs grow to considerable lengths above the scalp with less damage than the other patterns. The hair shafts present with characteristic air spaces, and hyphae form clusters at the level of the epidermis.
Diagnosis
Optimal treatment of TC relies on proper identification of the causative agent. Fungal culture remains the gold standard of mycologic diagnosis regardless of its delayed results, which may take up to 4 weeks for proper identification of the fungal colonies and require ample expertise to interpret the morphologic features of the grown colonies.4
Other tests such as the potassium hydroxide preparation are nonspecific and do not identify the dermatophyte species. Although this method has been reported to have 5% to 15% false-negative results in routine practice depending on the skill of the observer and the quality of sampling, microscopic examination is essential, as it may allow the clinician to start treatment sooner pending culture results. The use of a Wood lamp is not suitable for definitive species identification, as this technique primarily is useful for observing fluorescence in ectothrix infection caused by Microsporum species, with the exception of T schoenleinii; otherwise, Trichophyton species, which cause endothrix infections, do not fluoresce.5Polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive technique that can help identify both the genus and species of common dermatophytes. Common target sequences include the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and translation elongation factor 1α. The use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry also has become popular for dermatophyte identification.6Trichoscopic diagnosis of TC, which is simple and noninvasive, is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as short, broken, black dot, comma, corkscrew, and/or zigzag hairs, as well as perifollicular scaling, are helpful for diagnosing TC (Figure). Moreover, trichoscopy can be useful for differentiating other common causes of hair loss, such as trichotillomania and alopecia areata. It had been reported that the trichoscopic features of TC can be seen as early as 2 weeks after starting treatment and therefore this can be a reliable period in which to follow-up with the patient to evaluate progress. The disappearance of black dots and comma hairs can be appreciated from 2 weeks onwards by trichoscopic evaluation.4
Treatment
The common recommendation for first-line treatment of TC is the use of systemic antifungals with the use of a topical agent as an adjuvant to prevent the spread of fungal spores. For almost 6 decades, griseofulvin had been the gold-standard fungistatic used for treating TC in patients older than 2 years until the 2007 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of terbinafine fungicidal oral granules for treatment of TC in patients older than 4 years.7
Meta-analyses have demonstrated comparable efficacy for a 4-week course of terbinafine compared to 6 weeks of griseofulvin for TC based on the infectious organism. Terbinafine demonstrated superiority in treating T tonsurans and a similar efficacy in treating T violaceum, while griseofulvin was superior in treating M canis and other Microsporum species.8,9
The off-label use of fluconazole and itraconazole to treat TC is gaining popularity, with limited trials showing increased evidence of their effectiveness. There is not much clinical evidence to support the use of other oral antifungals, including the newer azoles such as voriconazole or posaconazole.9
Newer limited evidence has shown the off-label use of photodynamic therapy to be a promising alternative to systemic antifungal therapy in treating TC, pending validation by larger sample trials.10In my practice, I have found that severe cases of TC demonstrating inflammation or possible widespread id reactions are better treated with oral steroids. Ketoconazole shampoo or selenium sulfide used 2 to 3 times weekly to prevent spread in the early phases of therapy is a good adjunct to systemic treatment. Cases with kerions should be assessed for the possibility of a coexisting bacterial infection under the crusts, and if confirmed, antibiotics should be started.9The commonly used systemic antifungals generally are safe with a low side-effect profile, but there is a risk for hepatotoxicity. The FDA recommends that baseline alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase levels should be obtained prior to beginning a terbinafine-based treatment regimen.11 The American Academy of Pediatrics has specifically stated that laboratory testing of serum hepatic enzymes is not a requirement if a griseofulvin-based regimen does not exceed 8 weeks; however, transaminase levels (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) should be considered in patients using terbinafine at baseline or if treatment is prolonged beyond 4 to 6 weeks.12 In agreement with the FDA guidelines, the Canadian Pediatric Society has suggested that liver enzymes should be periodically monitored in patients being treated with terbinafine beyond 4 to 6 weeks.13
Changes in the Fungal Microbiome
Research has shown that changes in the fungal microbiome were associated with an altered bacterial community in patients with TC. During fungal infection, the relative abundances of Cutibacterium and Corynebacterium increased, and the relative abundance of Streptococcus decreased. In addition, some uncommon bacterial genera such as Herbaspirillum and Methylorubrum were detected on the scalp in TC.14
Carrier State
Carrier state is determined for those siblings and contacts of cases with a clinically normal scalp that are positive on culture. Those individuals could represent a potential reservoir responsible for contamination (or recontamination) of the patient as well as treatment failure. Opinions remain divided as to whether to use oral antifungal therapy in these carriers or maintain therapy on antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or povidone-iodine. Due to the paucity of available data, my experience has shown that it is sufficient to use antifungal shampoos for such carriers. In zoophilic infections, it is important to identify and treat the animal source.6-9
Final Thoughts
Successful treatment of TC requires accurate identification of the pathogen, which commonly is achieved via fungal culture. Despite its practical value, the conventional identification of dermatophytes based on morphologic features can be highly challenging due to the low positive rate and delayed results. Trichoscopy is a quick, handy, and noninvasive tool that can better indicate the diagnosis and also is helpful for follow-up on treatment progress. Due to better understanding of the immunology and genetic susceptibility associated with TC spread, the current treatment pipeline holds more insight into better control of this condition. Increased surveillance, prompt diagnosis, and early onset of systemic treatment are the key to proper prevention of spread of TC.
- Leung AKC, Hon KL, Leong KF, et al. Tinea capitis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:58-68.
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Preuett BL. Genetic predictors of susceptibility to cutaneous fungal infections: a pilot genome wide association study to refine a candidate gene search. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;67:147-152.
- Hay RJ. Tinea capitis: current status. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:87-93.
- Wahbah HR, Atallah RB, Eldahshan RM, et al. A prospective clinical and trichoscopic study of tinea capitis in children during treatment [published online May 23, 2022]. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15582. doi:10.1111/dth.15582
- Salehi Z, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility of major pathogenic dermatophytes isolated from human dermatophytosis. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:643509.
- Lamisil. Package insert. Novartis; 2011. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020539s021lbl.pdf
- Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Tey HL, Tan AS, Chan YC. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing griseofulvin and terbinafine in the treatment of tinea capitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:663-670.
- Gupta AK, Friedlander SF, Simkovich AJ. Tinea capitis: an update. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:167-172.
- Aspiroz C, Melcon B, Cerro PA, et al. Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum canis treated with methyl-aminolevulinate daylight photodynamic therapy and ketoconazole shampooing. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:567-568.
- Aleohin N, Bar J, Bar-Ilan E, et al. Laboratory monitoring during antifungal treatment of paediatric tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2021;64:157-161.
- Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, et al, eds. Tinea capitis. In: Red Book 2018-2021: Report of the Committee of Infectious Diseases. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:798-801.
- Bortolussi R, Martin S, Audcent T, et al. Antifungal agents for common outpatient paediatric infections. Canadian Paediatric Society website. Published June 20, 2019. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/antifungal-agents-common-infections
- Tao R, Zhu P, Zhou Y, et al. Altered skin fungal and bacterial community compositions in tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2022;65:834-840.
Tinea capitis (TC) most often is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. The peak incidence is between 3 and 7 years of age. Noninflammatory TC typically presents as fine scaling with single or multiple scaly patches of circular alopecia (grey patches); diffuse or patchy, fine, white, adherent scaling of the scalp resembling generalized dandruff with subtle hair loss; or single or multiple patches of well-demarcated areas of alopecia with fine scale studded with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface, resulting in a black dot appearance. Inflammatory variants of TC include kerion and favus.1 Herein, updates on diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of TC are provided, as well as a discussion of changes in the fungal microbiome associated with TC. Lastly, insights to some queries that practitioners may encounter when treating children with TC are provided.
Genetic Susceptibility
Molecular techniques have identified a number of macrophage regulator, leukocyte activation and migration, and cutaneous permeability genes associated with susceptibility to TC. These findings indicate that genetically determined deficiency in adaptive immune responses may affect the predisposition to dermatophyte infections.2
Clinical Varieties of Infection
Dermatophytes causing ringworm are capable of invading the hair shafts and can simultaneously invade smooth or glabrous skin (eg, T tonsurans, Trichophyton schoenleinii, Trichophyton violaceum). Some causative dermatophytes can even penetrate the nails (eg, Trichophyton soudanense). The clinical presentation is dependent on 3 main patterns of hair invasion3:
• Ectothrix: A mid-follicular pattern of invasion with hyphae growing down to the hair bulb that commonly is caused by Microsporum species. It clinically presents with scaling and inflammation with hair shafts breaking 2 to 3 mm above the scalp level.
• Endothrix: This pattern is nonfluorescent on Wood lamp examination, and hairs often break at the scalp level (black dot type). Trichophyton tonsurans, T soudanense, Trichophyton rubrum, and T violaceum are common causes.
• Favus: In this pattern, T schoenleinii is a common cause, and hairs grow to considerable lengths above the scalp with less damage than the other patterns. The hair shafts present with characteristic air spaces, and hyphae form clusters at the level of the epidermis.
Diagnosis
Optimal treatment of TC relies on proper identification of the causative agent. Fungal culture remains the gold standard of mycologic diagnosis regardless of its delayed results, which may take up to 4 weeks for proper identification of the fungal colonies and require ample expertise to interpret the morphologic features of the grown colonies.4
Other tests such as the potassium hydroxide preparation are nonspecific and do not identify the dermatophyte species. Although this method has been reported to have 5% to 15% false-negative results in routine practice depending on the skill of the observer and the quality of sampling, microscopic examination is essential, as it may allow the clinician to start treatment sooner pending culture results. The use of a Wood lamp is not suitable for definitive species identification, as this technique primarily is useful for observing fluorescence in ectothrix infection caused by Microsporum species, with the exception of T schoenleinii; otherwise, Trichophyton species, which cause endothrix infections, do not fluoresce.5Polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive technique that can help identify both the genus and species of common dermatophytes. Common target sequences include the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and translation elongation factor 1α. The use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry also has become popular for dermatophyte identification.6Trichoscopic diagnosis of TC, which is simple and noninvasive, is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as short, broken, black dot, comma, corkscrew, and/or zigzag hairs, as well as perifollicular scaling, are helpful for diagnosing TC (Figure). Moreover, trichoscopy can be useful for differentiating other common causes of hair loss, such as trichotillomania and alopecia areata. It had been reported that the trichoscopic features of TC can be seen as early as 2 weeks after starting treatment and therefore this can be a reliable period in which to follow-up with the patient to evaluate progress. The disappearance of black dots and comma hairs can be appreciated from 2 weeks onwards by trichoscopic evaluation.4

Treatment
The common recommendation for first-line treatment of TC is the use of systemic antifungals with the use of a topical agent as an adjuvant to prevent the spread of fungal spores. For almost 6 decades, griseofulvin had been the gold-standard fungistatic used for treating TC in patients older than 2 years until the 2007 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of terbinafine fungicidal oral granules for treatment of TC in patients older than 4 years.7
Meta-analyses have demonstrated comparable efficacy for a 4-week course of terbinafine compared to 6 weeks of griseofulvin for TC based on the infectious organism. Terbinafine demonstrated superiority in treating T tonsurans and a similar efficacy in treating T violaceum, while griseofulvin was superior in treating M canis and other Microsporum species.8,9
The off-label use of fluconazole and itraconazole to treat TC is gaining popularity, with limited trials showing increased evidence of their effectiveness. There is not much clinical evidence to support the use of other oral antifungals, including the newer azoles such as voriconazole or posaconazole.9
Newer limited evidence has shown the off-label use of photodynamic therapy to be a promising alternative to systemic antifungal therapy in treating TC, pending validation by larger sample trials.10In my practice, I have found that severe cases of TC demonstrating inflammation or possible widespread id reactions are better treated with oral steroids. Ketoconazole shampoo or selenium sulfide used 2 to 3 times weekly to prevent spread in the early phases of therapy is a good adjunct to systemic treatment. Cases with kerions should be assessed for the possibility of a coexisting bacterial infection under the crusts, and if confirmed, antibiotics should be started.9The commonly used systemic antifungals generally are safe with a low side-effect profile, but there is a risk for hepatotoxicity. The FDA recommends that baseline alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase levels should be obtained prior to beginning a terbinafine-based treatment regimen.11 The American Academy of Pediatrics has specifically stated that laboratory testing of serum hepatic enzymes is not a requirement if a griseofulvin-based regimen does not exceed 8 weeks; however, transaminase levels (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) should be considered in patients using terbinafine at baseline or if treatment is prolonged beyond 4 to 6 weeks.12 In agreement with the FDA guidelines, the Canadian Pediatric Society has suggested that liver enzymes should be periodically monitored in patients being treated with terbinafine beyond 4 to 6 weeks.13
Changes in the Fungal Microbiome
Research has shown that changes in the fungal microbiome were associated with an altered bacterial community in patients with TC. During fungal infection, the relative abundances of Cutibacterium and Corynebacterium increased, and the relative abundance of Streptococcus decreased. In addition, some uncommon bacterial genera such as Herbaspirillum and Methylorubrum were detected on the scalp in TC.14
Carrier State
Carrier state is determined for those siblings and contacts of cases with a clinically normal scalp that are positive on culture. Those individuals could represent a potential reservoir responsible for contamination (or recontamination) of the patient as well as treatment failure. Opinions remain divided as to whether to use oral antifungal therapy in these carriers or maintain therapy on antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or povidone-iodine. Due to the paucity of available data, my experience has shown that it is sufficient to use antifungal shampoos for such carriers. In zoophilic infections, it is important to identify and treat the animal source.6-9
Final Thoughts
Successful treatment of TC requires accurate identification of the pathogen, which commonly is achieved via fungal culture. Despite its practical value, the conventional identification of dermatophytes based on morphologic features can be highly challenging due to the low positive rate and delayed results. Trichoscopy is a quick, handy, and noninvasive tool that can better indicate the diagnosis and also is helpful for follow-up on treatment progress. Due to better understanding of the immunology and genetic susceptibility associated with TC spread, the current treatment pipeline holds more insight into better control of this condition. Increased surveillance, prompt diagnosis, and early onset of systemic treatment are the key to proper prevention of spread of TC.
Tinea capitis (TC) most often is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. The peak incidence is between 3 and 7 years of age. Noninflammatory TC typically presents as fine scaling with single or multiple scaly patches of circular alopecia (grey patches); diffuse or patchy, fine, white, adherent scaling of the scalp resembling generalized dandruff with subtle hair loss; or single or multiple patches of well-demarcated areas of alopecia with fine scale studded with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface, resulting in a black dot appearance. Inflammatory variants of TC include kerion and favus.1 Herein, updates on diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of TC are provided, as well as a discussion of changes in the fungal microbiome associated with TC. Lastly, insights to some queries that practitioners may encounter when treating children with TC are provided.
Genetic Susceptibility
Molecular techniques have identified a number of macrophage regulator, leukocyte activation and migration, and cutaneous permeability genes associated with susceptibility to TC. These findings indicate that genetically determined deficiency in adaptive immune responses may affect the predisposition to dermatophyte infections.2
Clinical Varieties of Infection
Dermatophytes causing ringworm are capable of invading the hair shafts and can simultaneously invade smooth or glabrous skin (eg, T tonsurans, Trichophyton schoenleinii, Trichophyton violaceum). Some causative dermatophytes can even penetrate the nails (eg, Trichophyton soudanense). The clinical presentation is dependent on 3 main patterns of hair invasion3:
• Ectothrix: A mid-follicular pattern of invasion with hyphae growing down to the hair bulb that commonly is caused by Microsporum species. It clinically presents with scaling and inflammation with hair shafts breaking 2 to 3 mm above the scalp level.
• Endothrix: This pattern is nonfluorescent on Wood lamp examination, and hairs often break at the scalp level (black dot type). Trichophyton tonsurans, T soudanense, Trichophyton rubrum, and T violaceum are common causes.
• Favus: In this pattern, T schoenleinii is a common cause, and hairs grow to considerable lengths above the scalp with less damage than the other patterns. The hair shafts present with characteristic air spaces, and hyphae form clusters at the level of the epidermis.
Diagnosis
Optimal treatment of TC relies on proper identification of the causative agent. Fungal culture remains the gold standard of mycologic diagnosis regardless of its delayed results, which may take up to 4 weeks for proper identification of the fungal colonies and require ample expertise to interpret the morphologic features of the grown colonies.4
Other tests such as the potassium hydroxide preparation are nonspecific and do not identify the dermatophyte species. Although this method has been reported to have 5% to 15% false-negative results in routine practice depending on the skill of the observer and the quality of sampling, microscopic examination is essential, as it may allow the clinician to start treatment sooner pending culture results. The use of a Wood lamp is not suitable for definitive species identification, as this technique primarily is useful for observing fluorescence in ectothrix infection caused by Microsporum species, with the exception of T schoenleinii; otherwise, Trichophyton species, which cause endothrix infections, do not fluoresce.5Polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive technique that can help identify both the genus and species of common dermatophytes. Common target sequences include the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and translation elongation factor 1α. The use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry also has become popular for dermatophyte identification.6Trichoscopic diagnosis of TC, which is simple and noninvasive, is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as short, broken, black dot, comma, corkscrew, and/or zigzag hairs, as well as perifollicular scaling, are helpful for diagnosing TC (Figure). Moreover, trichoscopy can be useful for differentiating other common causes of hair loss, such as trichotillomania and alopecia areata. It had been reported that the trichoscopic features of TC can be seen as early as 2 weeks after starting treatment and therefore this can be a reliable period in which to follow-up with the patient to evaluate progress. The disappearance of black dots and comma hairs can be appreciated from 2 weeks onwards by trichoscopic evaluation.4

Treatment
The common recommendation for first-line treatment of TC is the use of systemic antifungals with the use of a topical agent as an adjuvant to prevent the spread of fungal spores. For almost 6 decades, griseofulvin had been the gold-standard fungistatic used for treating TC in patients older than 2 years until the 2007 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of terbinafine fungicidal oral granules for treatment of TC in patients older than 4 years.7
Meta-analyses have demonstrated comparable efficacy for a 4-week course of terbinafine compared to 6 weeks of griseofulvin for TC based on the infectious organism. Terbinafine demonstrated superiority in treating T tonsurans and a similar efficacy in treating T violaceum, while griseofulvin was superior in treating M canis and other Microsporum species.8,9
The off-label use of fluconazole and itraconazole to treat TC is gaining popularity, with limited trials showing increased evidence of their effectiveness. There is not much clinical evidence to support the use of other oral antifungals, including the newer azoles such as voriconazole or posaconazole.9
Newer limited evidence has shown the off-label use of photodynamic therapy to be a promising alternative to systemic antifungal therapy in treating TC, pending validation by larger sample trials.10In my practice, I have found that severe cases of TC demonstrating inflammation or possible widespread id reactions are better treated with oral steroids. Ketoconazole shampoo or selenium sulfide used 2 to 3 times weekly to prevent spread in the early phases of therapy is a good adjunct to systemic treatment. Cases with kerions should be assessed for the possibility of a coexisting bacterial infection under the crusts, and if confirmed, antibiotics should be started.9The commonly used systemic antifungals generally are safe with a low side-effect profile, but there is a risk for hepatotoxicity. The FDA recommends that baseline alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase levels should be obtained prior to beginning a terbinafine-based treatment regimen.11 The American Academy of Pediatrics has specifically stated that laboratory testing of serum hepatic enzymes is not a requirement if a griseofulvin-based regimen does not exceed 8 weeks; however, transaminase levels (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) should be considered in patients using terbinafine at baseline or if treatment is prolonged beyond 4 to 6 weeks.12 In agreement with the FDA guidelines, the Canadian Pediatric Society has suggested that liver enzymes should be periodically monitored in patients being treated with terbinafine beyond 4 to 6 weeks.13
Changes in the Fungal Microbiome
Research has shown that changes in the fungal microbiome were associated with an altered bacterial community in patients with TC. During fungal infection, the relative abundances of Cutibacterium and Corynebacterium increased, and the relative abundance of Streptococcus decreased. In addition, some uncommon bacterial genera such as Herbaspirillum and Methylorubrum were detected on the scalp in TC.14
Carrier State
Carrier state is determined for those siblings and contacts of cases with a clinically normal scalp that are positive on culture. Those individuals could represent a potential reservoir responsible for contamination (or recontamination) of the patient as well as treatment failure. Opinions remain divided as to whether to use oral antifungal therapy in these carriers or maintain therapy on antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or povidone-iodine. Due to the paucity of available data, my experience has shown that it is sufficient to use antifungal shampoos for such carriers. In zoophilic infections, it is important to identify and treat the animal source.6-9
Final Thoughts
Successful treatment of TC requires accurate identification of the pathogen, which commonly is achieved via fungal culture. Despite its practical value, the conventional identification of dermatophytes based on morphologic features can be highly challenging due to the low positive rate and delayed results. Trichoscopy is a quick, handy, and noninvasive tool that can better indicate the diagnosis and also is helpful for follow-up on treatment progress. Due to better understanding of the immunology and genetic susceptibility associated with TC spread, the current treatment pipeline holds more insight into better control of this condition. Increased surveillance, prompt diagnosis, and early onset of systemic treatment are the key to proper prevention of spread of TC.
- Leung AKC, Hon KL, Leong KF, et al. Tinea capitis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:58-68.
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Preuett BL. Genetic predictors of susceptibility to cutaneous fungal infections: a pilot genome wide association study to refine a candidate gene search. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;67:147-152.
- Hay RJ. Tinea capitis: current status. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:87-93.
- Wahbah HR, Atallah RB, Eldahshan RM, et al. A prospective clinical and trichoscopic study of tinea capitis in children during treatment [published online May 23, 2022]. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15582. doi:10.1111/dth.15582
- Salehi Z, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility of major pathogenic dermatophytes isolated from human dermatophytosis. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:643509.
- Lamisil. Package insert. Novartis; 2011. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020539s021lbl.pdf
- Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Tey HL, Tan AS, Chan YC. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing griseofulvin and terbinafine in the treatment of tinea capitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:663-670.
- Gupta AK, Friedlander SF, Simkovich AJ. Tinea capitis: an update. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:167-172.
- Aspiroz C, Melcon B, Cerro PA, et al. Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum canis treated with methyl-aminolevulinate daylight photodynamic therapy and ketoconazole shampooing. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:567-568.
- Aleohin N, Bar J, Bar-Ilan E, et al. Laboratory monitoring during antifungal treatment of paediatric tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2021;64:157-161.
- Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, et al, eds. Tinea capitis. In: Red Book 2018-2021: Report of the Committee of Infectious Diseases. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:798-801.
- Bortolussi R, Martin S, Audcent T, et al. Antifungal agents for common outpatient paediatric infections. Canadian Paediatric Society website. Published June 20, 2019. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/antifungal-agents-common-infections
- Tao R, Zhu P, Zhou Y, et al. Altered skin fungal and bacterial community compositions in tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2022;65:834-840.
- Leung AKC, Hon KL, Leong KF, et al. Tinea capitis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:58-68.
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Preuett BL. Genetic predictors of susceptibility to cutaneous fungal infections: a pilot genome wide association study to refine a candidate gene search. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;67:147-152.
- Hay RJ. Tinea capitis: current status. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:87-93.
- Wahbah HR, Atallah RB, Eldahshan RM, et al. A prospective clinical and trichoscopic study of tinea capitis in children during treatment [published online May 23, 2022]. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15582. doi:10.1111/dth.15582
- Salehi Z, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility of major pathogenic dermatophytes isolated from human dermatophytosis. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:643509.
- Lamisil. Package insert. Novartis; 2011. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020539s021lbl.pdf
- Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Tey HL, Tan AS, Chan YC. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing griseofulvin and terbinafine in the treatment of tinea capitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:663-670.
- Gupta AK, Friedlander SF, Simkovich AJ. Tinea capitis: an update. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:167-172.
- Aspiroz C, Melcon B, Cerro PA, et al. Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum canis treated with methyl-aminolevulinate daylight photodynamic therapy and ketoconazole shampooing. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:567-568.
- Aleohin N, Bar J, Bar-Ilan E, et al. Laboratory monitoring during antifungal treatment of paediatric tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2021;64:157-161.
- Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, et al, eds. Tinea capitis. In: Red Book 2018-2021: Report of the Committee of Infectious Diseases. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:798-801.
- Bortolussi R, Martin S, Audcent T, et al. Antifungal agents for common outpatient paediatric infections. Canadian Paediatric Society website. Published June 20, 2019. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/antifungal-agents-common-infections
- Tao R, Zhu P, Zhou Y, et al. Altered skin fungal and bacterial community compositions in tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2022;65:834-840.
Iron Screening in Alopecia Areata Patients May Catch Hereditary Hemochromatosis Early
The role of micronutrients in the hair follicle cycle is not fully understood; thus deficiency and/or excess of certain micronutrients may be a modifiable risk factor associated with the development and/or treatment of some types of hair loss and therefore may be included in the workup during an alopecia consultation.
Hereditary hemochromatosis (HHC) is the most common genetic disorder identified in White individuals, with a worldwide prevalence of 1 in 220 to 1 in 250 individuals for a homozygous mutation. It most commonly affects individuals of Northern European descent.1 Men usually present in the fourth to sixth decades of life, while women usually develop symptoms after menopause, as pregnancy and menstruation delay the onset of the disease.2 Early symptoms of HHC include fatigue, joint pain, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Men are more likely to develop complications; in fact, 1 in 10 men with HHC will develop severe liver disease.3 As the disease progresses, affected individuals can present with cardiomyopathy (restrictive and dilated), cirrhosis, hypogonadism (usually hypogonadotrophic), arthropathy, diabetes mellitus, hepatomegaly, hepatic cirrhosis, and primary liver cancer (eg, hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma).2 Approximately 90% of patients with HHC present with hyperpigmentation at the time of diagnosis.4 Thinning or loss of hair is another finding in HHC, primarily reported in the axillae and pubic regions, and is ascribed to hepatotesticular insufficiency.5
Alopecia areata (AA) is the most common cause of autoimmune, inflammation-induced hair loss, with a calculated lifetime risk of 2%.6 This disease manifests as loss of hair in well-circumscribed patches of skin, most commonly on the scalp; AA also may affect other hair-bearing sites on the body. It is associated with an increased risk for other autoimmune disorders, such as psoriasis, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and vitiligo.7
Alopecia areata is induced by an inflammatory infiltrate of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes around hair follicles in the anagen stage, the active growth phase.8 Although the diagnosis is clinical, some clinicians order laboratory thyroid studies to investigate conditions that may be associated with AA. Common treatments include topical, intralesional, and/or systemic corticosteroids; contact immunotherapy; topical and more recently oral minoxidil; phototherapy; and topical and systemic JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib.4,9
We reviewed the medical records of 533 patients who were seen in The University of Texas Southwestern (Dallas, Texas) dermatology clinic from January 2015 through January 2020 and were diagnosed with AA. We examined their demographic data and medical history. We sought to determine any relationship between various types of alopecia and certain micronutrient levels through laboratory test results. Ferritin and iron saturation studies were evaluated. We report 4 cases of HHC concurrent with AA, of which 2 HHC diagnoses were uncovered through iron studies as part of the alopecia evaluation.
Case Reports
Patient 1—A 55-year-old White woman presented to the clinic for an alopecia consultation. She had a medical history of hypothyroidism and AA that was treated unsuccessfully with triamcinolone acetonide steroid injections; topical minoxidil; topical steroids; and systemic steroids, specifically oral prednisone. Following evaluation, she successfully transitioned to treatment with oral tofacitinib and continued to do well on tofacitinib.
The patient’s alopecia workup revealed a ferritin level of 245 ng/mL (reference range, 13–150 ng/mL) and iron saturation of 60% (reference range, 20%–50%). She was referred to the hematology department for further evaluation and was diagnosed with HHC. Genetic testing revealed a heterozygous H63D mutation; therapeutic phlebotomy was recommended. Her sister also was recently diagnosed with HHC.
Patient 2—A 55-year-old White man was referred for evaluation and treatment of alopecia universalis. He had a medical history of skin cancer and vitiligo. He attempted contact immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone scalp treatment but stopped due to intolerable inflammation. Intervention with a topical steroid and topical minoxidil was unsuccessful, but use of triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection on the scalp and topical bimatoprost 0.03% on the eyebrows produced satisfactory results.
The patient’s alopecia workup revealed a ferritin level of 422 ng/mL (reference range, 30–400 ng/mL), which prompted a hematology consultation for further evaluation. Notably, the patient ate red meat several times a week, used iron skillets, and denied receiving blood transfusions. His social habits included 3 alcoholic beverages a night, 5 days a week. Ultrasonography of the liver was recommended to assess potential damage from iron overload and alcohol consumption; the results suggested chronic liver disease, not definitive for cirrhosis, and no evidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genetic analysis later revealed the heterozygous H63D variant; therapeutic phlebotomy was recommended.
Patient 3—A 22-year-old White man presented with AA involving his facial beard. He had a medical history of vitiligo and psoriasis and a family history of AA as well as other autoimmune diseases including Hashimoto thyroiditis, psoriasis, eczema, and autoimmune hepatitis. Diphenylcyclopropenone treatment was not successful.
Laboratory studies revealed mildly elevated transaminase and ferritin levels. The patient also presented to the gastroenterologist for evaluation of abdominal pain. Subsequent hematology evaluation confirmed the presence of compound heterozygous C282Y and H63D mutations in the HFE gene, and the patient’s mother was later determined to be homozygous for the C282Y mutation with no elevated ferritin level. The patient’s ferritin level at diagnosis was approximately 500 ng/mL (reference range, 22–322 ng/mL); he required a modest number of therapeutic phlebotomies to normalize his ferritin level.
Patient 4—A 62-year-old White woman presented for evaluation and treatment of patchy hair loss on the scalp of 7 months’ duration. She was subsequently diagnosed with AA. After unsuccessful treatment with a triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection, topical immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone was recommended. The patient achieved full hair regrowth after 35 treatments administered at 3-week intervals.
The patient had a medical history of HHC, including homozygosity for the C282Y mutation, and a family history of HHC in 1 sister. Treatment was therapeutic phlebotomy.
Comment
HHC in the Setting of AA—We presented 4 White patients with both HHC and AA. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms HHC and AA yielded only 1 other reported case of newly identified HHC in a 56-year-old man who presented with pigmented purpuric dermatitis and AA that affected the beard.10 Because HHC is the most common genetic disorder identified in White individuals and has a varied clinical presentation, the documentation of AA may be an important cutaneous clue to help clinicians diagnose HHC early.
Iron Overload in Patients With HHC—The genetic association between HHC and AA, if any, is unknown. What is known is that iron overload can catalyze reactive oxygen species, which can overwhelm cellular antioxidant capacities at particular levels and cause injury to its constituents.11 Data show that the levels of oxidative stress are elevated in the scalp of patients with AA compared to controls and increased 2-fold during the early phase of disease vs late-phase disease.12 Thus, it is possible that increased iron levels in HHC may contribute to AA in genetically susceptible individuals by direct toxicity that ultimately results in the AA hair disorder that is CD8+ T-cell mediated.
Data show that 78% (31/40) of men and 36% (14/39) of women identified with homozygous C282Y mutations determined from family genetic analyses exhibited iron overload.13 In general, a normal life expectancy is possible for patients promptly treated with appropriate therapeutic phlebotomies.14 Thus, early diagnosis and appropriate therapy can prevent consequences of iron overload, which include cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, and cardiomyopathy.13Iron Screening in the Alopecia Workup—Our cases illustrate how iron screening tests as part of the alopecia workup identified a cohort of White patients with iron overload and subsequently led to an early diagnosis of HHC. The calculated 2% lifetime risk for developing AA highlights the importance of evaluating iron status as part of the AA workup, particularly for White men, and the potential health benefit from early diagnosis of HHC. Limitations of this case series included its retrospective nature and small patient number.
- Bacon BR, Adams PC, Kowdley KV, et al. Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis: 2011 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2011;54:328-343.
- Barton JC, Edwards CQ. HFE hemochromatosis. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Accessed September 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/disease/hemochromatosis.htm
- Ibrahim O, Bayart CB, Hogan S, et al. Treatment of alopecia areata with tofacitinib. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:600-602.
- Tweed MJ, Roland JM. Haemochromatosis as an endocrine cause of subfertility. BMJ. 1998;316:915-916. doi:10.1136/bmj.316.7135.915
- Gilhar A, Etzioni A, Paus R. Alopecia areata. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1515-1525.
- Barahmani N, Schabath MB, Duvic M, et al. History of atopy or autoimmunity increases risk of alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:581-591.
- McElwee KJ, Freyschmidt-Paul P, Hoffmann R, et al. Transfer of CD8(+) cells induces localized hair loss whereas CD4(+)/CD25(−) cells promote systemic alopecia areata and CD4(+)/CD25(+) cells blockade disease onset in the C3H/HeJ mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:947-957.
- MacDonald Hull SP, Wood ML, Hutchinson PE, et al. Guidelines for the management of alopecia areata. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:692-699.
- Sredoja Tišma V, Bulimbašic´ S, Jaganjac M, et al. Progressive pigmented purpuric dermatitis and alopecia areata as unusual skin manifestations in recognizing hereditary hemochromatosis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2012;20:181-186.
- Cabantchik ZI. Labile iron in cells and body fluids: physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:45.
- Akar A, Arca E, Erbil H, et al. Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in the scalp of patients with alopecia areata. J Dermatol Sci. 2002;29:85-90.
- Ryan E, Byrnes V, Coughlan B, et al. Underdiagnosis of hereditary haemochromatosis: lack of presentation or penetration? Gut. 2002;51:108-112.
- Niederau C, Strohmeyer G. Strategies for early diagnosis of haemochromatosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14:217-221.
The role of micronutrients in the hair follicle cycle is not fully understood; thus deficiency and/or excess of certain micronutrients may be a modifiable risk factor associated with the development and/or treatment of some types of hair loss and therefore may be included in the workup during an alopecia consultation.
Hereditary hemochromatosis (HHC) is the most common genetic disorder identified in White individuals, with a worldwide prevalence of 1 in 220 to 1 in 250 individuals for a homozygous mutation. It most commonly affects individuals of Northern European descent.1 Men usually present in the fourth to sixth decades of life, while women usually develop symptoms after menopause, as pregnancy and menstruation delay the onset of the disease.2 Early symptoms of HHC include fatigue, joint pain, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Men are more likely to develop complications; in fact, 1 in 10 men with HHC will develop severe liver disease.3 As the disease progresses, affected individuals can present with cardiomyopathy (restrictive and dilated), cirrhosis, hypogonadism (usually hypogonadotrophic), arthropathy, diabetes mellitus, hepatomegaly, hepatic cirrhosis, and primary liver cancer (eg, hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma).2 Approximately 90% of patients with HHC present with hyperpigmentation at the time of diagnosis.4 Thinning or loss of hair is another finding in HHC, primarily reported in the axillae and pubic regions, and is ascribed to hepatotesticular insufficiency.5
Alopecia areata (AA) is the most common cause of autoimmune, inflammation-induced hair loss, with a calculated lifetime risk of 2%.6 This disease manifests as loss of hair in well-circumscribed patches of skin, most commonly on the scalp; AA also may affect other hair-bearing sites on the body. It is associated with an increased risk for other autoimmune disorders, such as psoriasis, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and vitiligo.7
Alopecia areata is induced by an inflammatory infiltrate of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes around hair follicles in the anagen stage, the active growth phase.8 Although the diagnosis is clinical, some clinicians order laboratory thyroid studies to investigate conditions that may be associated with AA. Common treatments include topical, intralesional, and/or systemic corticosteroids; contact immunotherapy; topical and more recently oral minoxidil; phototherapy; and topical and systemic JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib.4,9
We reviewed the medical records of 533 patients who were seen in The University of Texas Southwestern (Dallas, Texas) dermatology clinic from January 2015 through January 2020 and were diagnosed with AA. We examined their demographic data and medical history. We sought to determine any relationship between various types of alopecia and certain micronutrient levels through laboratory test results. Ferritin and iron saturation studies were evaluated. We report 4 cases of HHC concurrent with AA, of which 2 HHC diagnoses were uncovered through iron studies as part of the alopecia evaluation.
Case Reports
Patient 1—A 55-year-old White woman presented to the clinic for an alopecia consultation. She had a medical history of hypothyroidism and AA that was treated unsuccessfully with triamcinolone acetonide steroid injections; topical minoxidil; topical steroids; and systemic steroids, specifically oral prednisone. Following evaluation, she successfully transitioned to treatment with oral tofacitinib and continued to do well on tofacitinib.
The patient’s alopecia workup revealed a ferritin level of 245 ng/mL (reference range, 13–150 ng/mL) and iron saturation of 60% (reference range, 20%–50%). She was referred to the hematology department for further evaluation and was diagnosed with HHC. Genetic testing revealed a heterozygous H63D mutation; therapeutic phlebotomy was recommended. Her sister also was recently diagnosed with HHC.
Patient 2—A 55-year-old White man was referred for evaluation and treatment of alopecia universalis. He had a medical history of skin cancer and vitiligo. He attempted contact immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone scalp treatment but stopped due to intolerable inflammation. Intervention with a topical steroid and topical minoxidil was unsuccessful, but use of triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection on the scalp and topical bimatoprost 0.03% on the eyebrows produced satisfactory results.
The patient’s alopecia workup revealed a ferritin level of 422 ng/mL (reference range, 30–400 ng/mL), which prompted a hematology consultation for further evaluation. Notably, the patient ate red meat several times a week, used iron skillets, and denied receiving blood transfusions. His social habits included 3 alcoholic beverages a night, 5 days a week. Ultrasonography of the liver was recommended to assess potential damage from iron overload and alcohol consumption; the results suggested chronic liver disease, not definitive for cirrhosis, and no evidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genetic analysis later revealed the heterozygous H63D variant; therapeutic phlebotomy was recommended.
Patient 3—A 22-year-old White man presented with AA involving his facial beard. He had a medical history of vitiligo and psoriasis and a family history of AA as well as other autoimmune diseases including Hashimoto thyroiditis, psoriasis, eczema, and autoimmune hepatitis. Diphenylcyclopropenone treatment was not successful.
Laboratory studies revealed mildly elevated transaminase and ferritin levels. The patient also presented to the gastroenterologist for evaluation of abdominal pain. Subsequent hematology evaluation confirmed the presence of compound heterozygous C282Y and H63D mutations in the HFE gene, and the patient’s mother was later determined to be homozygous for the C282Y mutation with no elevated ferritin level. The patient’s ferritin level at diagnosis was approximately 500 ng/mL (reference range, 22–322 ng/mL); he required a modest number of therapeutic phlebotomies to normalize his ferritin level.
Patient 4—A 62-year-old White woman presented for evaluation and treatment of patchy hair loss on the scalp of 7 months’ duration. She was subsequently diagnosed with AA. After unsuccessful treatment with a triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection, topical immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone was recommended. The patient achieved full hair regrowth after 35 treatments administered at 3-week intervals.
The patient had a medical history of HHC, including homozygosity for the C282Y mutation, and a family history of HHC in 1 sister. Treatment was therapeutic phlebotomy.
Comment
HHC in the Setting of AA—We presented 4 White patients with both HHC and AA. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms HHC and AA yielded only 1 other reported case of newly identified HHC in a 56-year-old man who presented with pigmented purpuric dermatitis and AA that affected the beard.10 Because HHC is the most common genetic disorder identified in White individuals and has a varied clinical presentation, the documentation of AA may be an important cutaneous clue to help clinicians diagnose HHC early.
Iron Overload in Patients With HHC—The genetic association between HHC and AA, if any, is unknown. What is known is that iron overload can catalyze reactive oxygen species, which can overwhelm cellular antioxidant capacities at particular levels and cause injury to its constituents.11 Data show that the levels of oxidative stress are elevated in the scalp of patients with AA compared to controls and increased 2-fold during the early phase of disease vs late-phase disease.12 Thus, it is possible that increased iron levels in HHC may contribute to AA in genetically susceptible individuals by direct toxicity that ultimately results in the AA hair disorder that is CD8+ T-cell mediated.
Data show that 78% (31/40) of men and 36% (14/39) of women identified with homozygous C282Y mutations determined from family genetic analyses exhibited iron overload.13 In general, a normal life expectancy is possible for patients promptly treated with appropriate therapeutic phlebotomies.14 Thus, early diagnosis and appropriate therapy can prevent consequences of iron overload, which include cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, and cardiomyopathy.13Iron Screening in the Alopecia Workup—Our cases illustrate how iron screening tests as part of the alopecia workup identified a cohort of White patients with iron overload and subsequently led to an early diagnosis of HHC. The calculated 2% lifetime risk for developing AA highlights the importance of evaluating iron status as part of the AA workup, particularly for White men, and the potential health benefit from early diagnosis of HHC. Limitations of this case series included its retrospective nature and small patient number.
The role of micronutrients in the hair follicle cycle is not fully understood; thus deficiency and/or excess of certain micronutrients may be a modifiable risk factor associated with the development and/or treatment of some types of hair loss and therefore may be included in the workup during an alopecia consultation.
Hereditary hemochromatosis (HHC) is the most common genetic disorder identified in White individuals, with a worldwide prevalence of 1 in 220 to 1 in 250 individuals for a homozygous mutation. It most commonly affects individuals of Northern European descent.1 Men usually present in the fourth to sixth decades of life, while women usually develop symptoms after menopause, as pregnancy and menstruation delay the onset of the disease.2 Early symptoms of HHC include fatigue, joint pain, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Men are more likely to develop complications; in fact, 1 in 10 men with HHC will develop severe liver disease.3 As the disease progresses, affected individuals can present with cardiomyopathy (restrictive and dilated), cirrhosis, hypogonadism (usually hypogonadotrophic), arthropathy, diabetes mellitus, hepatomegaly, hepatic cirrhosis, and primary liver cancer (eg, hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma).2 Approximately 90% of patients with HHC present with hyperpigmentation at the time of diagnosis.4 Thinning or loss of hair is another finding in HHC, primarily reported in the axillae and pubic regions, and is ascribed to hepatotesticular insufficiency.5
Alopecia areata (AA) is the most common cause of autoimmune, inflammation-induced hair loss, with a calculated lifetime risk of 2%.6 This disease manifests as loss of hair in well-circumscribed patches of skin, most commonly on the scalp; AA also may affect other hair-bearing sites on the body. It is associated with an increased risk for other autoimmune disorders, such as psoriasis, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and vitiligo.7
Alopecia areata is induced by an inflammatory infiltrate of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes around hair follicles in the anagen stage, the active growth phase.8 Although the diagnosis is clinical, some clinicians order laboratory thyroid studies to investigate conditions that may be associated with AA. Common treatments include topical, intralesional, and/or systemic corticosteroids; contact immunotherapy; topical and more recently oral minoxidil; phototherapy; and topical and systemic JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib.4,9
We reviewed the medical records of 533 patients who were seen in The University of Texas Southwestern (Dallas, Texas) dermatology clinic from January 2015 through January 2020 and were diagnosed with AA. We examined their demographic data and medical history. We sought to determine any relationship between various types of alopecia and certain micronutrient levels through laboratory test results. Ferritin and iron saturation studies were evaluated. We report 4 cases of HHC concurrent with AA, of which 2 HHC diagnoses were uncovered through iron studies as part of the alopecia evaluation.
Case Reports
Patient 1—A 55-year-old White woman presented to the clinic for an alopecia consultation. She had a medical history of hypothyroidism and AA that was treated unsuccessfully with triamcinolone acetonide steroid injections; topical minoxidil; topical steroids; and systemic steroids, specifically oral prednisone. Following evaluation, she successfully transitioned to treatment with oral tofacitinib and continued to do well on tofacitinib.
The patient’s alopecia workup revealed a ferritin level of 245 ng/mL (reference range, 13–150 ng/mL) and iron saturation of 60% (reference range, 20%–50%). She was referred to the hematology department for further evaluation and was diagnosed with HHC. Genetic testing revealed a heterozygous H63D mutation; therapeutic phlebotomy was recommended. Her sister also was recently diagnosed with HHC.
Patient 2—A 55-year-old White man was referred for evaluation and treatment of alopecia universalis. He had a medical history of skin cancer and vitiligo. He attempted contact immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone scalp treatment but stopped due to intolerable inflammation. Intervention with a topical steroid and topical minoxidil was unsuccessful, but use of triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection on the scalp and topical bimatoprost 0.03% on the eyebrows produced satisfactory results.
The patient’s alopecia workup revealed a ferritin level of 422 ng/mL (reference range, 30–400 ng/mL), which prompted a hematology consultation for further evaluation. Notably, the patient ate red meat several times a week, used iron skillets, and denied receiving blood transfusions. His social habits included 3 alcoholic beverages a night, 5 days a week. Ultrasonography of the liver was recommended to assess potential damage from iron overload and alcohol consumption; the results suggested chronic liver disease, not definitive for cirrhosis, and no evidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genetic analysis later revealed the heterozygous H63D variant; therapeutic phlebotomy was recommended.
Patient 3—A 22-year-old White man presented with AA involving his facial beard. He had a medical history of vitiligo and psoriasis and a family history of AA as well as other autoimmune diseases including Hashimoto thyroiditis, psoriasis, eczema, and autoimmune hepatitis. Diphenylcyclopropenone treatment was not successful.
Laboratory studies revealed mildly elevated transaminase and ferritin levels. The patient also presented to the gastroenterologist for evaluation of abdominal pain. Subsequent hematology evaluation confirmed the presence of compound heterozygous C282Y and H63D mutations in the HFE gene, and the patient’s mother was later determined to be homozygous for the C282Y mutation with no elevated ferritin level. The patient’s ferritin level at diagnosis was approximately 500 ng/mL (reference range, 22–322 ng/mL); he required a modest number of therapeutic phlebotomies to normalize his ferritin level.
Patient 4—A 62-year-old White woman presented for evaluation and treatment of patchy hair loss on the scalp of 7 months’ duration. She was subsequently diagnosed with AA. After unsuccessful treatment with a triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection, topical immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone was recommended. The patient achieved full hair regrowth after 35 treatments administered at 3-week intervals.
The patient had a medical history of HHC, including homozygosity for the C282Y mutation, and a family history of HHC in 1 sister. Treatment was therapeutic phlebotomy.
Comment
HHC in the Setting of AA—We presented 4 White patients with both HHC and AA. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms HHC and AA yielded only 1 other reported case of newly identified HHC in a 56-year-old man who presented with pigmented purpuric dermatitis and AA that affected the beard.10 Because HHC is the most common genetic disorder identified in White individuals and has a varied clinical presentation, the documentation of AA may be an important cutaneous clue to help clinicians diagnose HHC early.
Iron Overload in Patients With HHC—The genetic association between HHC and AA, if any, is unknown. What is known is that iron overload can catalyze reactive oxygen species, which can overwhelm cellular antioxidant capacities at particular levels and cause injury to its constituents.11 Data show that the levels of oxidative stress are elevated in the scalp of patients with AA compared to controls and increased 2-fold during the early phase of disease vs late-phase disease.12 Thus, it is possible that increased iron levels in HHC may contribute to AA in genetically susceptible individuals by direct toxicity that ultimately results in the AA hair disorder that is CD8+ T-cell mediated.
Data show that 78% (31/40) of men and 36% (14/39) of women identified with homozygous C282Y mutations determined from family genetic analyses exhibited iron overload.13 In general, a normal life expectancy is possible for patients promptly treated with appropriate therapeutic phlebotomies.14 Thus, early diagnosis and appropriate therapy can prevent consequences of iron overload, which include cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, and cardiomyopathy.13Iron Screening in the Alopecia Workup—Our cases illustrate how iron screening tests as part of the alopecia workup identified a cohort of White patients with iron overload and subsequently led to an early diagnosis of HHC. The calculated 2% lifetime risk for developing AA highlights the importance of evaluating iron status as part of the AA workup, particularly for White men, and the potential health benefit from early diagnosis of HHC. Limitations of this case series included its retrospective nature and small patient number.
- Bacon BR, Adams PC, Kowdley KV, et al. Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis: 2011 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2011;54:328-343.
- Barton JC, Edwards CQ. HFE hemochromatosis. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Accessed September 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/disease/hemochromatosis.htm
- Ibrahim O, Bayart CB, Hogan S, et al. Treatment of alopecia areata with tofacitinib. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:600-602.
- Tweed MJ, Roland JM. Haemochromatosis as an endocrine cause of subfertility. BMJ. 1998;316:915-916. doi:10.1136/bmj.316.7135.915
- Gilhar A, Etzioni A, Paus R. Alopecia areata. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1515-1525.
- Barahmani N, Schabath MB, Duvic M, et al. History of atopy or autoimmunity increases risk of alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:581-591.
- McElwee KJ, Freyschmidt-Paul P, Hoffmann R, et al. Transfer of CD8(+) cells induces localized hair loss whereas CD4(+)/CD25(−) cells promote systemic alopecia areata and CD4(+)/CD25(+) cells blockade disease onset in the C3H/HeJ mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:947-957.
- MacDonald Hull SP, Wood ML, Hutchinson PE, et al. Guidelines for the management of alopecia areata. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:692-699.
- Sredoja Tišma V, Bulimbašic´ S, Jaganjac M, et al. Progressive pigmented purpuric dermatitis and alopecia areata as unusual skin manifestations in recognizing hereditary hemochromatosis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2012;20:181-186.
- Cabantchik ZI. Labile iron in cells and body fluids: physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:45.
- Akar A, Arca E, Erbil H, et al. Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in the scalp of patients with alopecia areata. J Dermatol Sci. 2002;29:85-90.
- Ryan E, Byrnes V, Coughlan B, et al. Underdiagnosis of hereditary haemochromatosis: lack of presentation or penetration? Gut. 2002;51:108-112.
- Niederau C, Strohmeyer G. Strategies for early diagnosis of haemochromatosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14:217-221.
- Bacon BR, Adams PC, Kowdley KV, et al. Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis: 2011 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2011;54:328-343.
- Barton JC, Edwards CQ. HFE hemochromatosis. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Accessed September 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/disease/hemochromatosis.htm
- Ibrahim O, Bayart CB, Hogan S, et al. Treatment of alopecia areata with tofacitinib. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:600-602.
- Tweed MJ, Roland JM. Haemochromatosis as an endocrine cause of subfertility. BMJ. 1998;316:915-916. doi:10.1136/bmj.316.7135.915
- Gilhar A, Etzioni A, Paus R. Alopecia areata. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1515-1525.
- Barahmani N, Schabath MB, Duvic M, et al. History of atopy or autoimmunity increases risk of alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:581-591.
- McElwee KJ, Freyschmidt-Paul P, Hoffmann R, et al. Transfer of CD8(+) cells induces localized hair loss whereas CD4(+)/CD25(−) cells promote systemic alopecia areata and CD4(+)/CD25(+) cells blockade disease onset in the C3H/HeJ mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:947-957.
- MacDonald Hull SP, Wood ML, Hutchinson PE, et al. Guidelines for the management of alopecia areata. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:692-699.
- Sredoja Tišma V, Bulimbašic´ S, Jaganjac M, et al. Progressive pigmented purpuric dermatitis and alopecia areata as unusual skin manifestations in recognizing hereditary hemochromatosis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2012;20:181-186.
- Cabantchik ZI. Labile iron in cells and body fluids: physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:45.
- Akar A, Arca E, Erbil H, et al. Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in the scalp of patients with alopecia areata. J Dermatol Sci. 2002;29:85-90.
- Ryan E, Byrnes V, Coughlan B, et al. Underdiagnosis of hereditary haemochromatosis: lack of presentation or penetration? Gut. 2002;51:108-112.
- Niederau C, Strohmeyer G. Strategies for early diagnosis of haemochromatosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14:217-221.
Practice Points
- Hereditary hemochromatosis (HHC) is a disorder of iron overload that presents with clinical phenotypic heterogeneity. Complications can be mitigated with early intervention.
- Alopecia areata (AA) may be a rare early cutaneous manifestation of HHC in individuals with a predisposition for autoimmunity; therefore, it is important to evaluate iron status as part of the AA workup.
JAK inhibitors show no excess cardiovascular safety signal in French nationwide cohort
Janus kinase inhibitors tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and baricitinib (Olumiant) may pose no greater risk than does adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) on the basis of a nationwide cohort study.
The French data, which included almost 16,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, revealed similar safety across subgroups, including older patients with at least one preexisting cardiovascular risk factor, reported lead author Léa Hoisnard, MD, of Henri Mondor Hospital, Paris, and colleagues.
These findings arrive 1 year after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration imposed class-wide boxed warnings on three Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, citing increased risks for both cancer and serious cardiac events detected by the open-label, randomized ORAL Surveillance postmarketing trial, which compared tofacitinib against adalimumab and etanercept.
More recently, the observational STAR-RA study, relying upon private insurance and Medicare claims in the United States, found no significant increase in cardiovascular events among patients taking tofacitinib, adding some uncertainty to the conversation.
“In this context, observational studies of unselected populations outside of North America are still needed to assess other JAK inhibitor agents,” Dr. Hoisnard and colleagues write in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Their retrospective study included 8,481 patients who received baricitinib or tofacitinib, and 7,354 patients who received adalimumab. Almost all patients in the tofacitinib group received 5 mg twice daily instead of 10 mg twice daily (99.4% vs. 0.6%), so cardiovascular safety was assessed only for the 5-mg dose. Baricitinib was prescribed at 4-mg and 2-mg doses (79.5% vs. 20.5%), allowing inclusion of both dose levels. The investigators accounted for a range of covariates, including concurrent therapy, comorbidities, and other patient characteristics.
Median follow-up durations were 440 days in the JAK inhibitor group and 344 days in the adalimumab group. The JAK inhibitor group had numerically more MACEs than did the adalimumab group, but the difference in risk was not statistically significant (54 vs. 35 MACEs; weighted hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.7-1.5; P = .99). Similarly, more patients taking JAK inhibitors had VTEs, but relative risk was, again, not significant (75 vs. 32 VTEs; HRw, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.7-1.6; P = .63).
These findings were consistent for all subgroups, including patients aged 50 years or older and patients aged 65 years or older, although the investigators noted that statistical power was lacking for subgroup analyses.
Findings from Echo ORAL Surveillance
“I think the baricitinib data are important,” Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “There’s no difference between 2 mg and 4 mg [dose levels] in this analysis. And there doesn’t really seem to be a difference between baricitinib and tofacitinib. Most of the results are pretty consistent with ORAL Surveillance, which was a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Winthrop, who has been active in JAK inhibitor clinical trials, recently coauthored an article in Nature Reviews Rheumatology encouraging clinicians to remember that the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are relative to adalimumab, and safety should be framed within the context of risk-to-benefit ratios.
He and his coauthor also called into question the FDA’s “better to be safe than sorry” approach, which resulted in boxed warnings across all JAK inhibitors, despite differences in target specificity.
“There are pros and cons of taking that approach,” Dr. Winthrop said in an interview. “The FDA might ultimately be right. Certainly, these drugs appear similar for some types of events, like herpes zoster, for example. But whether they’re similar with regard to malignancy or cardiovascular events, I don’t think we know.”
Dr. Winthrop noted that deucravacitinib was recently approved for psoriasis sans boxed warning, suggesting inconsistency in the FDA’s approach. The agent headlines as a “TYK2 inhibitor,” but TYK2 is a member of the JAK family.
“I don’t know why the FDA decided to treat them differently,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Boxed warnings encourage caution, lock treatment sequence
Michael Thakor, MD, of Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinic of Northern Colorado, Fort Collins, supports the boxed warnings because they encourage caution and transparency.
“It forces you to have that discussion with your patient, which may take some time, but it’s actually a very good thing,” Dr. Thakor said in an interview. “Some patients will say, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t want to take that drug.’ But most patients, considering the level of risk that you’re talking about, are actually okay going ahead with the medication.”
If these risks aren’t discussed, he noted, patient trust may falter.
“They’re going to go online, and they’re going to be reading about it,” Dr. Thakor said. “And then they tend to get more spooked. They also may question your advice from then on, if you’re not telling them the possible risk.”
Reflecting on the present study, Dr. Thakor said that the findings initially appeared reassuring, but he became concerned about the lack of power and how adverse events trended higher in the JAK inhibitor group, particularly for VTEs, most of which occurred with baricitinib. This latter finding is challenging to interpret, however, because the 4-mg dose is not used in the United States, he added.
Dr. Thakor described how JAK inhibitors once seemed poised to assume a frontline role in RA until the boxed warnings came out. These safety concerns don’t take JAK inhibitors off the table, he said, but they do keep the class further down the treatment sequence, and the present data don’t alter this picture in daily practice.
“If I had a patient who was over the age of 50 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, I might have a little bit of concern, but if they need their RA treated, I would definitely discuss the possibility of using a JAK inhibitor,” Dr. Thakor said. “If the patient is comfortable with it, then I would feel comfortable going ahead.”
The investigators disclosed no outside funding or conflicts of interest. Dr. Winthrop disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and others. Dr. Thakor disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Janus kinase inhibitors tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and baricitinib (Olumiant) may pose no greater risk than does adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) on the basis of a nationwide cohort study.
The French data, which included almost 16,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, revealed similar safety across subgroups, including older patients with at least one preexisting cardiovascular risk factor, reported lead author Léa Hoisnard, MD, of Henri Mondor Hospital, Paris, and colleagues.
These findings arrive 1 year after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration imposed class-wide boxed warnings on three Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, citing increased risks for both cancer and serious cardiac events detected by the open-label, randomized ORAL Surveillance postmarketing trial, which compared tofacitinib against adalimumab and etanercept.
More recently, the observational STAR-RA study, relying upon private insurance and Medicare claims in the United States, found no significant increase in cardiovascular events among patients taking tofacitinib, adding some uncertainty to the conversation.
“In this context, observational studies of unselected populations outside of North America are still needed to assess other JAK inhibitor agents,” Dr. Hoisnard and colleagues write in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Their retrospective study included 8,481 patients who received baricitinib or tofacitinib, and 7,354 patients who received adalimumab. Almost all patients in the tofacitinib group received 5 mg twice daily instead of 10 mg twice daily (99.4% vs. 0.6%), so cardiovascular safety was assessed only for the 5-mg dose. Baricitinib was prescribed at 4-mg and 2-mg doses (79.5% vs. 20.5%), allowing inclusion of both dose levels. The investigators accounted for a range of covariates, including concurrent therapy, comorbidities, and other patient characteristics.
Median follow-up durations were 440 days in the JAK inhibitor group and 344 days in the adalimumab group. The JAK inhibitor group had numerically more MACEs than did the adalimumab group, but the difference in risk was not statistically significant (54 vs. 35 MACEs; weighted hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.7-1.5; P = .99). Similarly, more patients taking JAK inhibitors had VTEs, but relative risk was, again, not significant (75 vs. 32 VTEs; HRw, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.7-1.6; P = .63).
These findings were consistent for all subgroups, including patients aged 50 years or older and patients aged 65 years or older, although the investigators noted that statistical power was lacking for subgroup analyses.
Findings from Echo ORAL Surveillance
“I think the baricitinib data are important,” Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “There’s no difference between 2 mg and 4 mg [dose levels] in this analysis. And there doesn’t really seem to be a difference between baricitinib and tofacitinib. Most of the results are pretty consistent with ORAL Surveillance, which was a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Winthrop, who has been active in JAK inhibitor clinical trials, recently coauthored an article in Nature Reviews Rheumatology encouraging clinicians to remember that the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are relative to adalimumab, and safety should be framed within the context of risk-to-benefit ratios.
He and his coauthor also called into question the FDA’s “better to be safe than sorry” approach, which resulted in boxed warnings across all JAK inhibitors, despite differences in target specificity.
“There are pros and cons of taking that approach,” Dr. Winthrop said in an interview. “The FDA might ultimately be right. Certainly, these drugs appear similar for some types of events, like herpes zoster, for example. But whether they’re similar with regard to malignancy or cardiovascular events, I don’t think we know.”
Dr. Winthrop noted that deucravacitinib was recently approved for psoriasis sans boxed warning, suggesting inconsistency in the FDA’s approach. The agent headlines as a “TYK2 inhibitor,” but TYK2 is a member of the JAK family.
“I don’t know why the FDA decided to treat them differently,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Boxed warnings encourage caution, lock treatment sequence
Michael Thakor, MD, of Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinic of Northern Colorado, Fort Collins, supports the boxed warnings because they encourage caution and transparency.
“It forces you to have that discussion with your patient, which may take some time, but it’s actually a very good thing,” Dr. Thakor said in an interview. “Some patients will say, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t want to take that drug.’ But most patients, considering the level of risk that you’re talking about, are actually okay going ahead with the medication.”
If these risks aren’t discussed, he noted, patient trust may falter.
“They’re going to go online, and they’re going to be reading about it,” Dr. Thakor said. “And then they tend to get more spooked. They also may question your advice from then on, if you’re not telling them the possible risk.”
Reflecting on the present study, Dr. Thakor said that the findings initially appeared reassuring, but he became concerned about the lack of power and how adverse events trended higher in the JAK inhibitor group, particularly for VTEs, most of which occurred with baricitinib. This latter finding is challenging to interpret, however, because the 4-mg dose is not used in the United States, he added.
Dr. Thakor described how JAK inhibitors once seemed poised to assume a frontline role in RA until the boxed warnings came out. These safety concerns don’t take JAK inhibitors off the table, he said, but they do keep the class further down the treatment sequence, and the present data don’t alter this picture in daily practice.
“If I had a patient who was over the age of 50 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, I might have a little bit of concern, but if they need their RA treated, I would definitely discuss the possibility of using a JAK inhibitor,” Dr. Thakor said. “If the patient is comfortable with it, then I would feel comfortable going ahead.”
The investigators disclosed no outside funding or conflicts of interest. Dr. Winthrop disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and others. Dr. Thakor disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Janus kinase inhibitors tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and baricitinib (Olumiant) may pose no greater risk than does adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) on the basis of a nationwide cohort study.
The French data, which included almost 16,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, revealed similar safety across subgroups, including older patients with at least one preexisting cardiovascular risk factor, reported lead author Léa Hoisnard, MD, of Henri Mondor Hospital, Paris, and colleagues.
These findings arrive 1 year after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration imposed class-wide boxed warnings on three Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, citing increased risks for both cancer and serious cardiac events detected by the open-label, randomized ORAL Surveillance postmarketing trial, which compared tofacitinib against adalimumab and etanercept.
More recently, the observational STAR-RA study, relying upon private insurance and Medicare claims in the United States, found no significant increase in cardiovascular events among patients taking tofacitinib, adding some uncertainty to the conversation.
“In this context, observational studies of unselected populations outside of North America are still needed to assess other JAK inhibitor agents,” Dr. Hoisnard and colleagues write in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Their retrospective study included 8,481 patients who received baricitinib or tofacitinib, and 7,354 patients who received adalimumab. Almost all patients in the tofacitinib group received 5 mg twice daily instead of 10 mg twice daily (99.4% vs. 0.6%), so cardiovascular safety was assessed only for the 5-mg dose. Baricitinib was prescribed at 4-mg and 2-mg doses (79.5% vs. 20.5%), allowing inclusion of both dose levels. The investigators accounted for a range of covariates, including concurrent therapy, comorbidities, and other patient characteristics.
Median follow-up durations were 440 days in the JAK inhibitor group and 344 days in the adalimumab group. The JAK inhibitor group had numerically more MACEs than did the adalimumab group, but the difference in risk was not statistically significant (54 vs. 35 MACEs; weighted hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.7-1.5; P = .99). Similarly, more patients taking JAK inhibitors had VTEs, but relative risk was, again, not significant (75 vs. 32 VTEs; HRw, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.7-1.6; P = .63).
These findings were consistent for all subgroups, including patients aged 50 years or older and patients aged 65 years or older, although the investigators noted that statistical power was lacking for subgroup analyses.
Findings from Echo ORAL Surveillance
“I think the baricitinib data are important,” Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “There’s no difference between 2 mg and 4 mg [dose levels] in this analysis. And there doesn’t really seem to be a difference between baricitinib and tofacitinib. Most of the results are pretty consistent with ORAL Surveillance, which was a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Winthrop, who has been active in JAK inhibitor clinical trials, recently coauthored an article in Nature Reviews Rheumatology encouraging clinicians to remember that the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are relative to adalimumab, and safety should be framed within the context of risk-to-benefit ratios.
He and his coauthor also called into question the FDA’s “better to be safe than sorry” approach, which resulted in boxed warnings across all JAK inhibitors, despite differences in target specificity.
“There are pros and cons of taking that approach,” Dr. Winthrop said in an interview. “The FDA might ultimately be right. Certainly, these drugs appear similar for some types of events, like herpes zoster, for example. But whether they’re similar with regard to malignancy or cardiovascular events, I don’t think we know.”
Dr. Winthrop noted that deucravacitinib was recently approved for psoriasis sans boxed warning, suggesting inconsistency in the FDA’s approach. The agent headlines as a “TYK2 inhibitor,” but TYK2 is a member of the JAK family.
“I don’t know why the FDA decided to treat them differently,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Boxed warnings encourage caution, lock treatment sequence
Michael Thakor, MD, of Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinic of Northern Colorado, Fort Collins, supports the boxed warnings because they encourage caution and transparency.
“It forces you to have that discussion with your patient, which may take some time, but it’s actually a very good thing,” Dr. Thakor said in an interview. “Some patients will say, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t want to take that drug.’ But most patients, considering the level of risk that you’re talking about, are actually okay going ahead with the medication.”
If these risks aren’t discussed, he noted, patient trust may falter.
“They’re going to go online, and they’re going to be reading about it,” Dr. Thakor said. “And then they tend to get more spooked. They also may question your advice from then on, if you’re not telling them the possible risk.”
Reflecting on the present study, Dr. Thakor said that the findings initially appeared reassuring, but he became concerned about the lack of power and how adverse events trended higher in the JAK inhibitor group, particularly for VTEs, most of which occurred with baricitinib. This latter finding is challenging to interpret, however, because the 4-mg dose is not used in the United States, he added.
Dr. Thakor described how JAK inhibitors once seemed poised to assume a frontline role in RA until the boxed warnings came out. These safety concerns don’t take JAK inhibitors off the table, he said, but they do keep the class further down the treatment sequence, and the present data don’t alter this picture in daily practice.
“If I had a patient who was over the age of 50 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, I might have a little bit of concern, but if they need their RA treated, I would definitely discuss the possibility of using a JAK inhibitor,” Dr. Thakor said. “If the patient is comfortable with it, then I would feel comfortable going ahead.”
The investigators disclosed no outside funding or conflicts of interest. Dr. Winthrop disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and others. Dr. Thakor disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES