User login
You’ve been uneasy about the mother’s boyfriend: This may be why
The first patient of the afternoon is a 4-month-old in for his health maintenance visit. You’ve known his 20-year-old mother since she was a toddler. This infant has a 2-year-old sister. Also in the exam room is a young man you don’t recognize whom the mother introduces as Jason, her new boyfriend. He never makes eye contact and despite your best efforts you can’t get him to engage.
At the child’s next visit you are relieved to see the 6-month-old is alive and well and learn that your former patient and her two children have moved back in with her parents and Jason is no longer in the picture.
You don’t have to have been doing pediatrics very long to have learned that a “family” that includes an infant and a young adult male who is probably not the father is an environment in which the infant’s health and well-being is at significant risk. It is a situation in which child abuse even to the point of infanticide should be waving a red flag in your face.
Infanticide occurs in many animal species including our own. As abhorrent we may find the act, it occurs often enough to be, if not normal, at least not unexpected in certain circumstances. Theories abound as to what advantage the act of infanticide might convey to the success of a species. However, little if anything is known about any possible mechanisms that would allow it to occur.
Recently, a professor of molecular and cellular biology at Harvard University discovered a specific set of neurons in the mouse brain that controls aggressive behavior toward infants (Biological triggers for infant abuse, by Juan Siliezar, The Harvard Gazette, Sept 27, 2021). This same set of neurons also appears to trigger avoidance and neglect behaviors as well.
Research in other animal species has found that these antiparental behaviors occur in both virgins and sexually mature males who are strangers to the group. Interestingly, the behaviors switch off once individuals have their own offspring or have had the opportunity to familiarize themselves with infants. Not surprisingly, other studies have found that in some species environmental stress such as food shortage or threats of predation have triggered females to attack or ignore their offspring.
I think it is safe to assume a similar collection of neurons controlling aggressive behavior also exists in humans. One can imagine some well-read defense attorney dredging up this study and claiming that because his client had not yet fathered a child of his own that it was his nervous system’s normal response that made him toss his girlfriend’s baby against the wall.
The lead author of the study intends to study this collection of neurons in more depth to discover more about the process. It is conceivable that with more information her initial findings may help in the development of treatment and specific prevention strategies. Until that happens, we must rely on our intuition and keep our antennae tuned and alert for high-risk scenarios like the one I described at the opening of this letter.
We are left with leaning heavily on our community social work networks to keep close tabs on these high-risk families, offering both financial and emotional support. Parenting classes may be helpful, but some of this research leads me to suspect that immersing these young parents-to-be in hands-on child care situations might provide the best protection we can offer.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
The first patient of the afternoon is a 4-month-old in for his health maintenance visit. You’ve known his 20-year-old mother since she was a toddler. This infant has a 2-year-old sister. Also in the exam room is a young man you don’t recognize whom the mother introduces as Jason, her new boyfriend. He never makes eye contact and despite your best efforts you can’t get him to engage.
At the child’s next visit you are relieved to see the 6-month-old is alive and well and learn that your former patient and her two children have moved back in with her parents and Jason is no longer in the picture.
You don’t have to have been doing pediatrics very long to have learned that a “family” that includes an infant and a young adult male who is probably not the father is an environment in which the infant’s health and well-being is at significant risk. It is a situation in which child abuse even to the point of infanticide should be waving a red flag in your face.
Infanticide occurs in many animal species including our own. As abhorrent we may find the act, it occurs often enough to be, if not normal, at least not unexpected in certain circumstances. Theories abound as to what advantage the act of infanticide might convey to the success of a species. However, little if anything is known about any possible mechanisms that would allow it to occur.
Recently, a professor of molecular and cellular biology at Harvard University discovered a specific set of neurons in the mouse brain that controls aggressive behavior toward infants (Biological triggers for infant abuse, by Juan Siliezar, The Harvard Gazette, Sept 27, 2021). This same set of neurons also appears to trigger avoidance and neglect behaviors as well.
Research in other animal species has found that these antiparental behaviors occur in both virgins and sexually mature males who are strangers to the group. Interestingly, the behaviors switch off once individuals have their own offspring or have had the opportunity to familiarize themselves with infants. Not surprisingly, other studies have found that in some species environmental stress such as food shortage or threats of predation have triggered females to attack or ignore their offspring.
I think it is safe to assume a similar collection of neurons controlling aggressive behavior also exists in humans. One can imagine some well-read defense attorney dredging up this study and claiming that because his client had not yet fathered a child of his own that it was his nervous system’s normal response that made him toss his girlfriend’s baby against the wall.
The lead author of the study intends to study this collection of neurons in more depth to discover more about the process. It is conceivable that with more information her initial findings may help in the development of treatment and specific prevention strategies. Until that happens, we must rely on our intuition and keep our antennae tuned and alert for high-risk scenarios like the one I described at the opening of this letter.
We are left with leaning heavily on our community social work networks to keep close tabs on these high-risk families, offering both financial and emotional support. Parenting classes may be helpful, but some of this research leads me to suspect that immersing these young parents-to-be in hands-on child care situations might provide the best protection we can offer.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
The first patient of the afternoon is a 4-month-old in for his health maintenance visit. You’ve known his 20-year-old mother since she was a toddler. This infant has a 2-year-old sister. Also in the exam room is a young man you don’t recognize whom the mother introduces as Jason, her new boyfriend. He never makes eye contact and despite your best efforts you can’t get him to engage.
At the child’s next visit you are relieved to see the 6-month-old is alive and well and learn that your former patient and her two children have moved back in with her parents and Jason is no longer in the picture.
You don’t have to have been doing pediatrics very long to have learned that a “family” that includes an infant and a young adult male who is probably not the father is an environment in which the infant’s health and well-being is at significant risk. It is a situation in which child abuse even to the point of infanticide should be waving a red flag in your face.
Infanticide occurs in many animal species including our own. As abhorrent we may find the act, it occurs often enough to be, if not normal, at least not unexpected in certain circumstances. Theories abound as to what advantage the act of infanticide might convey to the success of a species. However, little if anything is known about any possible mechanisms that would allow it to occur.
Recently, a professor of molecular and cellular biology at Harvard University discovered a specific set of neurons in the mouse brain that controls aggressive behavior toward infants (Biological triggers for infant abuse, by Juan Siliezar, The Harvard Gazette, Sept 27, 2021). This same set of neurons also appears to trigger avoidance and neglect behaviors as well.
Research in other animal species has found that these antiparental behaviors occur in both virgins and sexually mature males who are strangers to the group. Interestingly, the behaviors switch off once individuals have their own offspring or have had the opportunity to familiarize themselves with infants. Not surprisingly, other studies have found that in some species environmental stress such as food shortage or threats of predation have triggered females to attack or ignore their offspring.
I think it is safe to assume a similar collection of neurons controlling aggressive behavior also exists in humans. One can imagine some well-read defense attorney dredging up this study and claiming that because his client had not yet fathered a child of his own that it was his nervous system’s normal response that made him toss his girlfriend’s baby against the wall.
The lead author of the study intends to study this collection of neurons in more depth to discover more about the process. It is conceivable that with more information her initial findings may help in the development of treatment and specific prevention strategies. Until that happens, we must rely on our intuition and keep our antennae tuned and alert for high-risk scenarios like the one I described at the opening of this letter.
We are left with leaning heavily on our community social work networks to keep close tabs on these high-risk families, offering both financial and emotional support. Parenting classes may be helpful, but some of this research leads me to suspect that immersing these young parents-to-be in hands-on child care situations might provide the best protection we can offer.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Maternal SSRI use linked to more encephalopathy in newborns, risk still small
, although the overall risk remains extremely low, a new study finds.
The findings were presented in a poster at the 50th annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society.
“Our work showed that neonates exposed to SSRI in utero had higher risks of neonatal encephalopathy even when adjusting for confounders such as maternal mental health disorders and age. SSRIs could cause side effects such as encephalopathy in neonates, and these risks need to be balanced carefully with the potential benefits of treatment to the mother,” study lead author Marie Cornet, MD, a neonatology fellow with Benioff Children’s Hospital at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
According to Dr. Cornet, “we know that SSRI exposure in utero is associated with increased risks of respiratory distress at birth, need for positive-pressure ventilation, and an abnormal neurologic exam.” The researchers launched the new study to determine if the estimated 4%-8% of pregnant women who take SSRIs may be putting their newborns at greater risk of NE.
The researchers retrospectively tracked 305,426 infants who were born in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California health system (≥35 weeks) from 2011 to 2019. The mothers had an average age of 31 years, and approximately 34.7% were White, 34.7% of unknown race, 23.3% Asian, and 6.2% Black.
The researchers defined NE as a “5-minute APGAR score <7 and abnormal level of consciousness, activity, tone, or reflexes.”
A total of 8,024 infants (2.6%) had mothers who used SSRIs in the third trimester, and 510 (0.17%) were determined to have had NE.
After adjustment for maternal depression or anxiety, maternal age, race, and hospital, exposed neonates had 2.7 times higher odds of NE (odds ratio, 2.7).
Each 25 mg per day increase in the dose of SSRIs, as equalized to doses of sertraline (Zoloft), was linked to a significant 31% increase in the odds of developing NE (OR, 1.31).
The study doesn’t examine the benefits of SSRI treatment in pregnancy. Those taking SSRIs were much more likely to have depression during pregnancy (76.5% vs. 13.5%) and anxiety (56.7% vs. 6.9%), compared with those who did not take the drug.
The possible connection between SSRIs and NE is unclear. “SSRIs may contribute to NE by a withdrawal mechanism or by a toxicity mechanism. It is also possible that SSRIs themselves are not responsible for encephalopathy, or that the severity of maternal mental health is itself responsible for increased neonatal encephalopathy,” Dr. Cornet said. “However, we believe we adjusted our results thoroughly for that. Furthermore, in this cohort, neonates born from mothers with untreated depression were not at higher risk of encephalopathy than neonates born to mothers without depression.”
She added: “When infants have acidosis or require prolonged resuscitation after birth, they get treated with therapeutic hypothermia. This invasive treatment was shown to decrease mortality and morbidity in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. However, therapeutic hypothermia may not be helpful in infants with encephalopathy due to other causes than acute hypoxia-ischemia, such as infection, inflammation, genetic conditions, or exposure to toxins. In the case of SSRIs, our results show that, while neonates often have encephalopathy, this encephalopathy is often mild and self-resolved. We did not see a statistically significant increase in acidosis or treatment with therapeutic hypothermia.”
In the future neurologists should consider SSRI use as a potential cause in cases of NE, Dr. Cornet said. “If there are no signs of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy – no evidence of acidosis, acute perinatal event – treatment with therapeutic hypothermia may not be indicated.”
Dr. Cornet said more research is in the works. “Studying the long-term side effect of SSRIs on neonatal brain development and injury is essential,” she said. “We plan to compare brain injury in neonates exposed and unexposed to SSRIs and examine long-term outcomes to assess if the effect of SSRI exposure is transient or has a lasting impact.”
This study was funded by the Thrasher Early Career Research Grant and by the Newborn Brain Research Innovation Award at UCSF. The authors have no relevant disclosures.
, although the overall risk remains extremely low, a new study finds.
The findings were presented in a poster at the 50th annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society.
“Our work showed that neonates exposed to SSRI in utero had higher risks of neonatal encephalopathy even when adjusting for confounders such as maternal mental health disorders and age. SSRIs could cause side effects such as encephalopathy in neonates, and these risks need to be balanced carefully with the potential benefits of treatment to the mother,” study lead author Marie Cornet, MD, a neonatology fellow with Benioff Children’s Hospital at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
According to Dr. Cornet, “we know that SSRI exposure in utero is associated with increased risks of respiratory distress at birth, need for positive-pressure ventilation, and an abnormal neurologic exam.” The researchers launched the new study to determine if the estimated 4%-8% of pregnant women who take SSRIs may be putting their newborns at greater risk of NE.
The researchers retrospectively tracked 305,426 infants who were born in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California health system (≥35 weeks) from 2011 to 2019. The mothers had an average age of 31 years, and approximately 34.7% were White, 34.7% of unknown race, 23.3% Asian, and 6.2% Black.
The researchers defined NE as a “5-minute APGAR score <7 and abnormal level of consciousness, activity, tone, or reflexes.”
A total of 8,024 infants (2.6%) had mothers who used SSRIs in the third trimester, and 510 (0.17%) were determined to have had NE.
After adjustment for maternal depression or anxiety, maternal age, race, and hospital, exposed neonates had 2.7 times higher odds of NE (odds ratio, 2.7).
Each 25 mg per day increase in the dose of SSRIs, as equalized to doses of sertraline (Zoloft), was linked to a significant 31% increase in the odds of developing NE (OR, 1.31).
The study doesn’t examine the benefits of SSRI treatment in pregnancy. Those taking SSRIs were much more likely to have depression during pregnancy (76.5% vs. 13.5%) and anxiety (56.7% vs. 6.9%), compared with those who did not take the drug.
The possible connection between SSRIs and NE is unclear. “SSRIs may contribute to NE by a withdrawal mechanism or by a toxicity mechanism. It is also possible that SSRIs themselves are not responsible for encephalopathy, or that the severity of maternal mental health is itself responsible for increased neonatal encephalopathy,” Dr. Cornet said. “However, we believe we adjusted our results thoroughly for that. Furthermore, in this cohort, neonates born from mothers with untreated depression were not at higher risk of encephalopathy than neonates born to mothers without depression.”
She added: “When infants have acidosis or require prolonged resuscitation after birth, they get treated with therapeutic hypothermia. This invasive treatment was shown to decrease mortality and morbidity in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. However, therapeutic hypothermia may not be helpful in infants with encephalopathy due to other causes than acute hypoxia-ischemia, such as infection, inflammation, genetic conditions, or exposure to toxins. In the case of SSRIs, our results show that, while neonates often have encephalopathy, this encephalopathy is often mild and self-resolved. We did not see a statistically significant increase in acidosis or treatment with therapeutic hypothermia.”
In the future neurologists should consider SSRI use as a potential cause in cases of NE, Dr. Cornet said. “If there are no signs of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy – no evidence of acidosis, acute perinatal event – treatment with therapeutic hypothermia may not be indicated.”
Dr. Cornet said more research is in the works. “Studying the long-term side effect of SSRIs on neonatal brain development and injury is essential,” she said. “We plan to compare brain injury in neonates exposed and unexposed to SSRIs and examine long-term outcomes to assess if the effect of SSRI exposure is transient or has a lasting impact.”
This study was funded by the Thrasher Early Career Research Grant and by the Newborn Brain Research Innovation Award at UCSF. The authors have no relevant disclosures.
, although the overall risk remains extremely low, a new study finds.
The findings were presented in a poster at the 50th annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society.
“Our work showed that neonates exposed to SSRI in utero had higher risks of neonatal encephalopathy even when adjusting for confounders such as maternal mental health disorders and age. SSRIs could cause side effects such as encephalopathy in neonates, and these risks need to be balanced carefully with the potential benefits of treatment to the mother,” study lead author Marie Cornet, MD, a neonatology fellow with Benioff Children’s Hospital at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
According to Dr. Cornet, “we know that SSRI exposure in utero is associated with increased risks of respiratory distress at birth, need for positive-pressure ventilation, and an abnormal neurologic exam.” The researchers launched the new study to determine if the estimated 4%-8% of pregnant women who take SSRIs may be putting their newborns at greater risk of NE.
The researchers retrospectively tracked 305,426 infants who were born in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California health system (≥35 weeks) from 2011 to 2019. The mothers had an average age of 31 years, and approximately 34.7% were White, 34.7% of unknown race, 23.3% Asian, and 6.2% Black.
The researchers defined NE as a “5-minute APGAR score <7 and abnormal level of consciousness, activity, tone, or reflexes.”
A total of 8,024 infants (2.6%) had mothers who used SSRIs in the third trimester, and 510 (0.17%) were determined to have had NE.
After adjustment for maternal depression or anxiety, maternal age, race, and hospital, exposed neonates had 2.7 times higher odds of NE (odds ratio, 2.7).
Each 25 mg per day increase in the dose of SSRIs, as equalized to doses of sertraline (Zoloft), was linked to a significant 31% increase in the odds of developing NE (OR, 1.31).
The study doesn’t examine the benefits of SSRI treatment in pregnancy. Those taking SSRIs were much more likely to have depression during pregnancy (76.5% vs. 13.5%) and anxiety (56.7% vs. 6.9%), compared with those who did not take the drug.
The possible connection between SSRIs and NE is unclear. “SSRIs may contribute to NE by a withdrawal mechanism or by a toxicity mechanism. It is also possible that SSRIs themselves are not responsible for encephalopathy, or that the severity of maternal mental health is itself responsible for increased neonatal encephalopathy,” Dr. Cornet said. “However, we believe we adjusted our results thoroughly for that. Furthermore, in this cohort, neonates born from mothers with untreated depression were not at higher risk of encephalopathy than neonates born to mothers without depression.”
She added: “When infants have acidosis or require prolonged resuscitation after birth, they get treated with therapeutic hypothermia. This invasive treatment was shown to decrease mortality and morbidity in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. However, therapeutic hypothermia may not be helpful in infants with encephalopathy due to other causes than acute hypoxia-ischemia, such as infection, inflammation, genetic conditions, or exposure to toxins. In the case of SSRIs, our results show that, while neonates often have encephalopathy, this encephalopathy is often mild and self-resolved. We did not see a statistically significant increase in acidosis or treatment with therapeutic hypothermia.”
In the future neurologists should consider SSRI use as a potential cause in cases of NE, Dr. Cornet said. “If there are no signs of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy – no evidence of acidosis, acute perinatal event – treatment with therapeutic hypothermia may not be indicated.”
Dr. Cornet said more research is in the works. “Studying the long-term side effect of SSRIs on neonatal brain development and injury is essential,” she said. “We plan to compare brain injury in neonates exposed and unexposed to SSRIs and examine long-term outcomes to assess if the effect of SSRI exposure is transient or has a lasting impact.”
This study was funded by the Thrasher Early Career Research Grant and by the Newborn Brain Research Innovation Award at UCSF. The authors have no relevant disclosures.
FROM CNS 2021
COVID-19 vaccines in pregnancy may protect baby, too
Women who receive COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy pass antibodies to their babies, which could protect newborns from the disease, research has shown.
.
Researchers with New York University Langone Health conducted a study that included pregnant women who had received at least one dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna) by June 4.
All neonates had antibodies to the spike protein at high titers, the researchers found.
Unlike similar prior studies, the researchers also looked for antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein, which would have indicated the presence of antibodies from natural COVID-19 infection. They did not detect antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein, and the lack of these antibodies suggests that the antibodies to the spike protein resulted from vaccination and not from prior infection, the researchers said.
The participants had a median time from completion of the vaccine series to delivery of 13 weeks. The study was published online in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM.
“The presence of these anti-spike antibodies in the cord blood should, at least in theory, offer these newborns some degree of protection,” said study investigator Ashley S. Roman, MD, director of the division of maternal-fetal medicine at NYU Langone Health. “While the primary rationale for vaccination during pregnancy is to keep moms healthy and keep moms out of the hospital, the outstanding question to us was whether there is any fetal or neonatal benefit conferred by receiving the vaccine during pregnancy.”
Questions remain about the degree and durability of protection for newborns from these antibodies. An ongoing study, MOMI-VAX, aims to systematically measure antibody levels in mothers who receive COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy and in their babies over time.
The present study contributes welcome preliminary evidence suggesting a benefit to infants, said Emily Adhikari, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, who was not involved in the study.
Still, “the main concern and our priority as obstetricians is to vaccinate pregnant women to protect them from severe or critical illness,” she said.
Although most individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 recover, a significant portion of pregnant women get seriously sick, Dr. Adhikari said. “With this recent Delta surge, we are seeing more pregnant patients who are sicker,” said Dr. Adhikari, who has published research from one hospital describing this trend.
When weighing whether patients should receive COVID-19 vaccines in pregnancy, the risks from infection have outweighed any risk from vaccination to such an extent that there is “not a comparison to make,” Dr. Adhikari said. “The risks of the infection are so much higher.
“For me, it is a matter of making sure that my patient understands that we have really good safety data on these vaccines and there is no reason to think that a pregnant person would be harmed by them. On the contrary, the benefit is to protect and maybe even save your life,” Dr. Adhikari said. “And now we have more evidence that the fetus may also benefit.”
The rationale for vaccinations during pregnancy can vary, Dr. Roman said. Flu shots in pregnancy mainly are intended to protect the mother, though they confer protection for newborns as well. With the whooping cough vaccine given in the third trimester, however, the primary aim is to protect the baby from whooping cough in the first months of life, Dr. Roman said.
“I think it is really important for pregnant women to understand that antibodies crossing the placenta is a good thing,” she added.
As patients who already have received COVID-19 vaccines become pregnant and may become eligible for a booster dose, Dr. Adhikari will offer it, she said, though she has confidence in the protection provided by the initial immune response.
Dr. Roman and Dr. Adhikari had no disclosures.
Women who receive COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy pass antibodies to their babies, which could protect newborns from the disease, research has shown.
.
Researchers with New York University Langone Health conducted a study that included pregnant women who had received at least one dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna) by June 4.
All neonates had antibodies to the spike protein at high titers, the researchers found.
Unlike similar prior studies, the researchers also looked for antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein, which would have indicated the presence of antibodies from natural COVID-19 infection. They did not detect antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein, and the lack of these antibodies suggests that the antibodies to the spike protein resulted from vaccination and not from prior infection, the researchers said.
The participants had a median time from completion of the vaccine series to delivery of 13 weeks. The study was published online in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM.
“The presence of these anti-spike antibodies in the cord blood should, at least in theory, offer these newborns some degree of protection,” said study investigator Ashley S. Roman, MD, director of the division of maternal-fetal medicine at NYU Langone Health. “While the primary rationale for vaccination during pregnancy is to keep moms healthy and keep moms out of the hospital, the outstanding question to us was whether there is any fetal or neonatal benefit conferred by receiving the vaccine during pregnancy.”
Questions remain about the degree and durability of protection for newborns from these antibodies. An ongoing study, MOMI-VAX, aims to systematically measure antibody levels in mothers who receive COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy and in their babies over time.
The present study contributes welcome preliminary evidence suggesting a benefit to infants, said Emily Adhikari, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, who was not involved in the study.
Still, “the main concern and our priority as obstetricians is to vaccinate pregnant women to protect them from severe or critical illness,” she said.
Although most individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 recover, a significant portion of pregnant women get seriously sick, Dr. Adhikari said. “With this recent Delta surge, we are seeing more pregnant patients who are sicker,” said Dr. Adhikari, who has published research from one hospital describing this trend.
When weighing whether patients should receive COVID-19 vaccines in pregnancy, the risks from infection have outweighed any risk from vaccination to such an extent that there is “not a comparison to make,” Dr. Adhikari said. “The risks of the infection are so much higher.
“For me, it is a matter of making sure that my patient understands that we have really good safety data on these vaccines and there is no reason to think that a pregnant person would be harmed by them. On the contrary, the benefit is to protect and maybe even save your life,” Dr. Adhikari said. “And now we have more evidence that the fetus may also benefit.”
The rationale for vaccinations during pregnancy can vary, Dr. Roman said. Flu shots in pregnancy mainly are intended to protect the mother, though they confer protection for newborns as well. With the whooping cough vaccine given in the third trimester, however, the primary aim is to protect the baby from whooping cough in the first months of life, Dr. Roman said.
“I think it is really important for pregnant women to understand that antibodies crossing the placenta is a good thing,” she added.
As patients who already have received COVID-19 vaccines become pregnant and may become eligible for a booster dose, Dr. Adhikari will offer it, she said, though she has confidence in the protection provided by the initial immune response.
Dr. Roman and Dr. Adhikari had no disclosures.
Women who receive COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy pass antibodies to their babies, which could protect newborns from the disease, research has shown.
.
Researchers with New York University Langone Health conducted a study that included pregnant women who had received at least one dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna) by June 4.
All neonates had antibodies to the spike protein at high titers, the researchers found.
Unlike similar prior studies, the researchers also looked for antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein, which would have indicated the presence of antibodies from natural COVID-19 infection. They did not detect antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein, and the lack of these antibodies suggests that the antibodies to the spike protein resulted from vaccination and not from prior infection, the researchers said.
The participants had a median time from completion of the vaccine series to delivery of 13 weeks. The study was published online in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM.
“The presence of these anti-spike antibodies in the cord blood should, at least in theory, offer these newborns some degree of protection,” said study investigator Ashley S. Roman, MD, director of the division of maternal-fetal medicine at NYU Langone Health. “While the primary rationale for vaccination during pregnancy is to keep moms healthy and keep moms out of the hospital, the outstanding question to us was whether there is any fetal or neonatal benefit conferred by receiving the vaccine during pregnancy.”
Questions remain about the degree and durability of protection for newborns from these antibodies. An ongoing study, MOMI-VAX, aims to systematically measure antibody levels in mothers who receive COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy and in their babies over time.
The present study contributes welcome preliminary evidence suggesting a benefit to infants, said Emily Adhikari, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, who was not involved in the study.
Still, “the main concern and our priority as obstetricians is to vaccinate pregnant women to protect them from severe or critical illness,” she said.
Although most individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 recover, a significant portion of pregnant women get seriously sick, Dr. Adhikari said. “With this recent Delta surge, we are seeing more pregnant patients who are sicker,” said Dr. Adhikari, who has published research from one hospital describing this trend.
When weighing whether patients should receive COVID-19 vaccines in pregnancy, the risks from infection have outweighed any risk from vaccination to such an extent that there is “not a comparison to make,” Dr. Adhikari said. “The risks of the infection are so much higher.
“For me, it is a matter of making sure that my patient understands that we have really good safety data on these vaccines and there is no reason to think that a pregnant person would be harmed by them. On the contrary, the benefit is to protect and maybe even save your life,” Dr. Adhikari said. “And now we have more evidence that the fetus may also benefit.”
The rationale for vaccinations during pregnancy can vary, Dr. Roman said. Flu shots in pregnancy mainly are intended to protect the mother, though they confer protection for newborns as well. With the whooping cough vaccine given in the third trimester, however, the primary aim is to protect the baby from whooping cough in the first months of life, Dr. Roman said.
“I think it is really important for pregnant women to understand that antibodies crossing the placenta is a good thing,” she added.
As patients who already have received COVID-19 vaccines become pregnant and may become eligible for a booster dose, Dr. Adhikari will offer it, she said, though she has confidence in the protection provided by the initial immune response.
Dr. Roman and Dr. Adhikari had no disclosures.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY MFM
COVID-19 linked to baby bust in high-income countries
In an assessment of the pandemic’s early effects, Arnstein Aassve, PhD, and colleagues found a significant COVID-19–related decline in crude birth rates (CBRs) in 7 of 22 high-income countries, particularly in Southwestern Europe.
Dr. Aassve, an economist at the Carlo F. Dondena Center for Research on Social Dynamics and Public Policy at the Università Commerciale Luigi Bocconi, Milan, and colleagues report the results in an article published online August 30 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Defining the start of the COVID-19 pandemic as February 2020, the study identifies strong declines in Italy (-9.1%), Hungary (-8.5%), Spain (-8.4%), and Portugal (-6.6%) beyond those predicted by past trends. In the United States, CBRs fell by 7.1% relative to 2019 for births occurring in Nov. and Dec. 2020 following conceptions in February and March of that year.
Significant declines in CBR also occurred in Belgium, Austria, and Singapore.
A year-to-year comparison of the mean for monthly CBRs per 1,000 population before and during the pandemic suggests a negative difference for all countries studied except for Denmark, Finland, Germany, and the Netherlands, Dr. Aassve and colleagues write. These findings may have policy implications for childcare, housing, and the labor market.
The Milan researchers compared monthly vital statistics data on live births from the international Human Fertility Database for the period of Jan. 2016 to March 2021. These figures reflect conceptions carried to term between April 2015 and June 2020. The 22 countries in the analysis represent 37% of the total reported COVID-19 cases and 34% of deaths worldwide.
The study findings align with surveys on “fertility intentions” collected early in the first COVID-19 wave in Germany, France, Spain, and the United Kingdom. These surveys indicated that 73% of people who were planning pregnancies in 2020 either decided to delay the pregnancy or they abandoned their plans.
“The popular media speculated that the lockdown would lead to a baby boom, as couples spent more time together,” Dr. Aassve told this news organization. “There’s very little evidence of this when you look to previous disasters and shocks, and the first data suggest more of an immediate collapse than a boom. But as you also see from the paper, the collapse is not seen everywhere.” Other current studies suggest the fertility drop is immediate but temporary, says Dr. Aassve, who is also a professor of demography.
Interestingly, Dr. Aassve and colleagues found that CBRs were relatively stable in Northern Europe. The authors point to supportive social and family policies in that region that might have reduced the effect of the pandemic on births. “These factors are likely to affect CBRs in the subsequent pandemic waves,” they write. They call for future studies to assess the full population implications of the pandemic, the moderating impact of policy interventions, and the nexus between short- and long-run effects in relation to the various waves of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Rebounds
Some regions have already reported a rebound from the COVID-19 fertility trough. Molly J. Stout, MD, director of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues used electronic medical records to predict a surge in births after the initial decline.
“The surge we’ve seen at the end of this summer is exceeding the usual annual birth rate, as predicted,” she said in an interview. “But I think there’ll be a return to normal after this transient escalation. I don’t think birth rates will stay elevated above the normal because the birth surge is a temporary response to an event, although there will likely be regional differences.”
Looking ahead, Dr. Stout, who was not involved in Dr. Aassve’s analysis, is not certain how a fourth pandemic wave might ultimately modify a couple’s overall family size. But the toll the health crisis has taken on working women who have been forced to withdraw from the economy because of a lack of childcare points to a societal need that should be addressed.
According to Philip N. Cohen, PhD, a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park, who’s been tracking fertility trends since the onset of the COVID-19 emergency, the pandemic has combined a health crisis with an economic crisis, along with “the additional factor of social distancing and isolation, which all contributed to the decline in birth rates. Some people changed their plans to hold off on having children, while others didn’t get pregnant because they weren’t socializing and meeting people as much.”
Dr. Cohen, who was not involved in the study by Dr. Aassve and associates, said his provisional data show that although in many places, birth rates have rebounded more or less to prepandemic levels after a nadir around Jan. 2021, some areas of the United States still show substantially lower rates, including California, Hawaii, and Oregon.
As to the duration of the pandemic effect, Dr. Aassve cautions that his group’s estimates refer to the first wave only. “We then have the second, third, and currently the fourth wave. We can’t be sure about the impact of these waves on fertility since the data are not there yet, but I’d be surprised if they didn’t continue to have an impact on fertility rates,” he said.
Dr. Cohen agreed: “Some people who delayed childbearing will make up the delay. However, whenever there’s a delay, there’s inevitably some portion of the decline that’s not recouped.”
As for the wider effect across the world, Dr. Aassve said his team’s figures derive from high-income countries where data are readily available. For middle- and low-income countries, fewer data exist, and the quality of those data is not as good.
The lessons from this and other upheavals teach us that unforeseen shocks almost always have a negative impact on fertility, says Dr. Aassve. “[B]ut these effects may be separate from existing declining trends. The issue here is that those overall declining trends may be driven by other factors. In contrast, the shock of the pandemic is short-lived, and we may return to normal rather quickly. But if the pandemic also impacts other societal structures, such as the occupational and industrial sectors, then the pandemic might exacerbate the negative trend.”
The study was supported by funding from the European Research Council for funding under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme. The study authors, Dr. Stout, and Dr. Cohen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an assessment of the pandemic’s early effects, Arnstein Aassve, PhD, and colleagues found a significant COVID-19–related decline in crude birth rates (CBRs) in 7 of 22 high-income countries, particularly in Southwestern Europe.
Dr. Aassve, an economist at the Carlo F. Dondena Center for Research on Social Dynamics and Public Policy at the Università Commerciale Luigi Bocconi, Milan, and colleagues report the results in an article published online August 30 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Defining the start of the COVID-19 pandemic as February 2020, the study identifies strong declines in Italy (-9.1%), Hungary (-8.5%), Spain (-8.4%), and Portugal (-6.6%) beyond those predicted by past trends. In the United States, CBRs fell by 7.1% relative to 2019 for births occurring in Nov. and Dec. 2020 following conceptions in February and March of that year.
Significant declines in CBR also occurred in Belgium, Austria, and Singapore.
A year-to-year comparison of the mean for monthly CBRs per 1,000 population before and during the pandemic suggests a negative difference for all countries studied except for Denmark, Finland, Germany, and the Netherlands, Dr. Aassve and colleagues write. These findings may have policy implications for childcare, housing, and the labor market.
The Milan researchers compared monthly vital statistics data on live births from the international Human Fertility Database for the period of Jan. 2016 to March 2021. These figures reflect conceptions carried to term between April 2015 and June 2020. The 22 countries in the analysis represent 37% of the total reported COVID-19 cases and 34% of deaths worldwide.
The study findings align with surveys on “fertility intentions” collected early in the first COVID-19 wave in Germany, France, Spain, and the United Kingdom. These surveys indicated that 73% of people who were planning pregnancies in 2020 either decided to delay the pregnancy or they abandoned their plans.
“The popular media speculated that the lockdown would lead to a baby boom, as couples spent more time together,” Dr. Aassve told this news organization. “There’s very little evidence of this when you look to previous disasters and shocks, and the first data suggest more of an immediate collapse than a boom. But as you also see from the paper, the collapse is not seen everywhere.” Other current studies suggest the fertility drop is immediate but temporary, says Dr. Aassve, who is also a professor of demography.
Interestingly, Dr. Aassve and colleagues found that CBRs were relatively stable in Northern Europe. The authors point to supportive social and family policies in that region that might have reduced the effect of the pandemic on births. “These factors are likely to affect CBRs in the subsequent pandemic waves,” they write. They call for future studies to assess the full population implications of the pandemic, the moderating impact of policy interventions, and the nexus between short- and long-run effects in relation to the various waves of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Rebounds
Some regions have already reported a rebound from the COVID-19 fertility trough. Molly J. Stout, MD, director of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues used electronic medical records to predict a surge in births after the initial decline.
“The surge we’ve seen at the end of this summer is exceeding the usual annual birth rate, as predicted,” she said in an interview. “But I think there’ll be a return to normal after this transient escalation. I don’t think birth rates will stay elevated above the normal because the birth surge is a temporary response to an event, although there will likely be regional differences.”
Looking ahead, Dr. Stout, who was not involved in Dr. Aassve’s analysis, is not certain how a fourth pandemic wave might ultimately modify a couple’s overall family size. But the toll the health crisis has taken on working women who have been forced to withdraw from the economy because of a lack of childcare points to a societal need that should be addressed.
According to Philip N. Cohen, PhD, a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park, who’s been tracking fertility trends since the onset of the COVID-19 emergency, the pandemic has combined a health crisis with an economic crisis, along with “the additional factor of social distancing and isolation, which all contributed to the decline in birth rates. Some people changed their plans to hold off on having children, while others didn’t get pregnant because they weren’t socializing and meeting people as much.”
Dr. Cohen, who was not involved in the study by Dr. Aassve and associates, said his provisional data show that although in many places, birth rates have rebounded more or less to prepandemic levels after a nadir around Jan. 2021, some areas of the United States still show substantially lower rates, including California, Hawaii, and Oregon.
As to the duration of the pandemic effect, Dr. Aassve cautions that his group’s estimates refer to the first wave only. “We then have the second, third, and currently the fourth wave. We can’t be sure about the impact of these waves on fertility since the data are not there yet, but I’d be surprised if they didn’t continue to have an impact on fertility rates,” he said.
Dr. Cohen agreed: “Some people who delayed childbearing will make up the delay. However, whenever there’s a delay, there’s inevitably some portion of the decline that’s not recouped.”
As for the wider effect across the world, Dr. Aassve said his team’s figures derive from high-income countries where data are readily available. For middle- and low-income countries, fewer data exist, and the quality of those data is not as good.
The lessons from this and other upheavals teach us that unforeseen shocks almost always have a negative impact on fertility, says Dr. Aassve. “[B]ut these effects may be separate from existing declining trends. The issue here is that those overall declining trends may be driven by other factors. In contrast, the shock of the pandemic is short-lived, and we may return to normal rather quickly. But if the pandemic also impacts other societal structures, such as the occupational and industrial sectors, then the pandemic might exacerbate the negative trend.”
The study was supported by funding from the European Research Council for funding under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme. The study authors, Dr. Stout, and Dr. Cohen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an assessment of the pandemic’s early effects, Arnstein Aassve, PhD, and colleagues found a significant COVID-19–related decline in crude birth rates (CBRs) in 7 of 22 high-income countries, particularly in Southwestern Europe.
Dr. Aassve, an economist at the Carlo F. Dondena Center for Research on Social Dynamics and Public Policy at the Università Commerciale Luigi Bocconi, Milan, and colleagues report the results in an article published online August 30 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Defining the start of the COVID-19 pandemic as February 2020, the study identifies strong declines in Italy (-9.1%), Hungary (-8.5%), Spain (-8.4%), and Portugal (-6.6%) beyond those predicted by past trends. In the United States, CBRs fell by 7.1% relative to 2019 for births occurring in Nov. and Dec. 2020 following conceptions in February and March of that year.
Significant declines in CBR also occurred in Belgium, Austria, and Singapore.
A year-to-year comparison of the mean for monthly CBRs per 1,000 population before and during the pandemic suggests a negative difference for all countries studied except for Denmark, Finland, Germany, and the Netherlands, Dr. Aassve and colleagues write. These findings may have policy implications for childcare, housing, and the labor market.
The Milan researchers compared monthly vital statistics data on live births from the international Human Fertility Database for the period of Jan. 2016 to March 2021. These figures reflect conceptions carried to term between April 2015 and June 2020. The 22 countries in the analysis represent 37% of the total reported COVID-19 cases and 34% of deaths worldwide.
The study findings align with surveys on “fertility intentions” collected early in the first COVID-19 wave in Germany, France, Spain, and the United Kingdom. These surveys indicated that 73% of people who were planning pregnancies in 2020 either decided to delay the pregnancy or they abandoned their plans.
“The popular media speculated that the lockdown would lead to a baby boom, as couples spent more time together,” Dr. Aassve told this news organization. “There’s very little evidence of this when you look to previous disasters and shocks, and the first data suggest more of an immediate collapse than a boom. But as you also see from the paper, the collapse is not seen everywhere.” Other current studies suggest the fertility drop is immediate but temporary, says Dr. Aassve, who is also a professor of demography.
Interestingly, Dr. Aassve and colleagues found that CBRs were relatively stable in Northern Europe. The authors point to supportive social and family policies in that region that might have reduced the effect of the pandemic on births. “These factors are likely to affect CBRs in the subsequent pandemic waves,” they write. They call for future studies to assess the full population implications of the pandemic, the moderating impact of policy interventions, and the nexus between short- and long-run effects in relation to the various waves of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Rebounds
Some regions have already reported a rebound from the COVID-19 fertility trough. Molly J. Stout, MD, director of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues used electronic medical records to predict a surge in births after the initial decline.
“The surge we’ve seen at the end of this summer is exceeding the usual annual birth rate, as predicted,” she said in an interview. “But I think there’ll be a return to normal after this transient escalation. I don’t think birth rates will stay elevated above the normal because the birth surge is a temporary response to an event, although there will likely be regional differences.”
Looking ahead, Dr. Stout, who was not involved in Dr. Aassve’s analysis, is not certain how a fourth pandemic wave might ultimately modify a couple’s overall family size. But the toll the health crisis has taken on working women who have been forced to withdraw from the economy because of a lack of childcare points to a societal need that should be addressed.
According to Philip N. Cohen, PhD, a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park, who’s been tracking fertility trends since the onset of the COVID-19 emergency, the pandemic has combined a health crisis with an economic crisis, along with “the additional factor of social distancing and isolation, which all contributed to the decline in birth rates. Some people changed their plans to hold off on having children, while others didn’t get pregnant because they weren’t socializing and meeting people as much.”
Dr. Cohen, who was not involved in the study by Dr. Aassve and associates, said his provisional data show that although in many places, birth rates have rebounded more or less to prepandemic levels after a nadir around Jan. 2021, some areas of the United States still show substantially lower rates, including California, Hawaii, and Oregon.
As to the duration of the pandemic effect, Dr. Aassve cautions that his group’s estimates refer to the first wave only. “We then have the second, third, and currently the fourth wave. We can’t be sure about the impact of these waves on fertility since the data are not there yet, but I’d be surprised if they didn’t continue to have an impact on fertility rates,” he said.
Dr. Cohen agreed: “Some people who delayed childbearing will make up the delay. However, whenever there’s a delay, there’s inevitably some portion of the decline that’s not recouped.”
As for the wider effect across the world, Dr. Aassve said his team’s figures derive from high-income countries where data are readily available. For middle- and low-income countries, fewer data exist, and the quality of those data is not as good.
The lessons from this and other upheavals teach us that unforeseen shocks almost always have a negative impact on fertility, says Dr. Aassve. “[B]ut these effects may be separate from existing declining trends. The issue here is that those overall declining trends may be driven by other factors. In contrast, the shock of the pandemic is short-lived, and we may return to normal rather quickly. But if the pandemic also impacts other societal structures, such as the occupational and industrial sectors, then the pandemic might exacerbate the negative trend.”
The study was supported by funding from the European Research Council for funding under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme. The study authors, Dr. Stout, and Dr. Cohen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Reassuring’ findings for second-generation antipsychotics during pregnancy
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) taken by pregnant women are linked to a low rate of adverse effects in their children, new research suggests.
Data from a large registry study of almost 2,000 women showed that 2.5% of the live births in a group that had been exposed to antipsychotics had confirmed major malformations compared with 2% of the live births in a non-exposed group. This translated into an estimated odds ratio of 1.5 for major malformations.
“The 2.5% absolute risk for major malformations is consistent with the estimates of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national baseline rate of major malformations in the general population,” lead author Adele Viguera, MD, MPH, director of research for women’s mental health, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, told this news organization.
“Our results are reassuring and suggest that second-generation antipsychotics, as a class, do not substantially increase the risk of major malformations,” Dr. Viguera said.
The findings were published online August 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Safety data scarce
Despite the increasing use of SGAs to treat a “spectrum of psychiatric disorders,” relatively little data are available on the reproductive safety of these agents, Dr. Viguera said.
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (NPRAA) was established in 2008 to determine risk for major malformation among infants exposed to these medications during the first trimester, relative to a comparison group of unexposed infants of mothers with histories of psychiatric morbidity.
The NPRAA follows pregnant women (aged 18 to 45 years) with psychiatric illness who are exposed or unexposed to SGAs during pregnancy. Participants are recruited through nationwide provider referral, self-referral, and advertisement through the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health website.
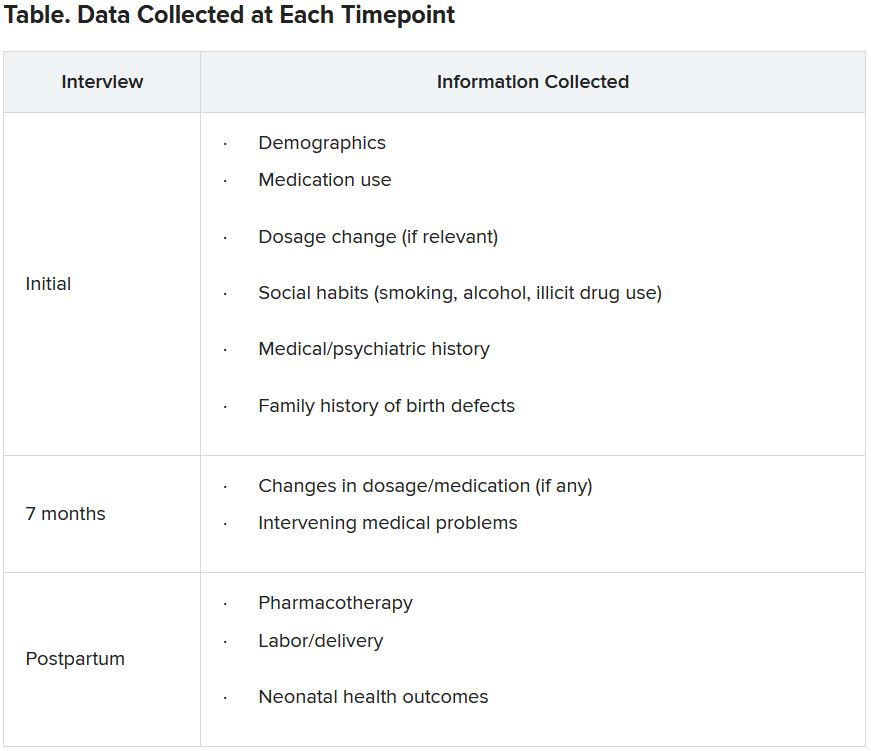
Specific data collected are shown in the following table.
Since publication of the first results in 2015, the sample size for the trial has increased – and the absolute and relative risk for major malformations observed in the study population are “more precise,” the investigators note. The current study presented updated previous findings.
Demographic differences
Of the 1,906 women who enrolled as of April 2020, 1,311 (mean age, 32.6 years; 81.3% White) completed the study and were eligible for inclusion in the analysis.
Although the groups had a virtually identical mean age, fewer women in the exposure group were married compared with those in the non-exposure group (77% vs. 90%, respectively) and fewer had a college education (71.2% vs. 87.8%). There was also a higher percentage of first-trimester cigarette smokers in the exposure group (18.4% vs. 5.1%).
On the other hand, more women in the non-exposure group used alcohol than in the exposure group (28.6% vs. 21.4%, respectively).
The most frequent psychiatric disorder in the exposure group was bipolar disorder (63.9%), followed by major depression (12.9%), anxiety (5.8%), and schizophrenia (4.5%). Only 11.4% of women in the non-exposure group were diagnosed with bipolar disorder, whereas 34.1% were diagnosed with major depression, 31.3% with anxiety, and none with schizophrenia.
Notably, a large percentage of women in both groups had a history of postpartum depression and/or psychosis (41.4% and 35.5%, respectively).
The most frequently used SGAs in the exposure group were quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda).
Participants in the exposure group had a higher age at initial onset of primary psychiatric diagnosis and a lower proportion of lifetime illness compared with those in the non-exposure group.
Major clinical implication?
Among 640 live births in the exposure group, which included 17 twin pregnancies and 1 triplet pregnancy, 2.5% reported major malformations. Among 704 live births in the control group, which included 14 twin pregnancies, 1.99% reported major malformations.
The estimated OR for major malformations comparing exposed and unexposed infants was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 0.625-3.517).
The authors note that their findings were consistent with one of the largest studies to date, which included a nationwide sample of more than 1 million women. Its results showed that, among infants exposed to SGAs versus those who were not exposed, the estimated risk ratio after adjusting for psychiatric conditions was 1.05 (95% CI, 0.96-1.16).
Additionally, “a hallmark of a teratogen is that it tends to cause a specific type or pattern of malformations, and we found no preponderance of one single type of major malformation or specific pattern of malformations among the exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Viguera said
“A major clinical implication of these findings is that for women with major mood and/or psychotic disorders, treatment with an atypical antipsychotic during pregnancy may be the most prudent clinical decision, much as continued treatment is recommended for pregnant women with other serious and chronic medical conditions, such as epilepsy,” she added.
The concept of ‘satisficing’
Commenting on the study, Vivien Burt, MD, PhD, founder and director/consultant of the Women’s Life Center at the Resnick University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Neuropsychiatric Hospital, called the findings “reassuring.”
The results “support the conclusion that in pregnant women with serious psychiatric illnesses, the use of SGAs is often a better option than avoiding these medications and exposing both the women and their offspring to the adverse consequences of maternal mental illness,” she said.
An accompanying editorial co-authored by Dr. Burt and colleague Sonya Rasminsky, MD, introduced the concept of “satisficing” – a term coined by Herbert Simon, a behavioral economist and Nobel Laureate. “Satisficing” is a “decision-making strategy that aims for a satisfactory (‘good enough’) outcome rather than a perfect one.”
The concept applies to decision-making beyond the field of economics “and is critical to how physicians help patients make decisions when they are faced with multiple treatment options,” said Dr. Burt, a professor emeritus of psychiatry at UCLA.
“The goal of ‘satisficing’ is to plan for the most satisfactory outcome, knowing that there are always unknowns, so in an uncertain world, clinicians should carefully help their patients make decisions that will allow them to achieve an outcome they can best live with,” she noted.
The investigators note that their findings may not be generalizable to the larger population of women taking SGAs, given that their participants were “overwhelmingly White, married, and well-educated women.”
They add that enrollment into the NPRAA registry is ongoing and larger sample sizes will “further narrow the confidence interval around the risk estimates and allow for adjustment of likely sources of confounding.”
The NPRAA is supported by Alkermes, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, SAGE Therapeutics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Aurobindo Pharma. Past sponsors of the NPRAA are listed in the original paper. Dr. Viguera receives research support from the NPRAA, Alkermes Biopharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and SAGE Therapeutics and receives adviser/consulting fees from Up-to-Date. Dr. Burt has been a consultant/speaker for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Rasminsky has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) taken by pregnant women are linked to a low rate of adverse effects in their children, new research suggests.
Data from a large registry study of almost 2,000 women showed that 2.5% of the live births in a group that had been exposed to antipsychotics had confirmed major malformations compared with 2% of the live births in a non-exposed group. This translated into an estimated odds ratio of 1.5 for major malformations.
“The 2.5% absolute risk for major malformations is consistent with the estimates of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national baseline rate of major malformations in the general population,” lead author Adele Viguera, MD, MPH, director of research for women’s mental health, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, told this news organization.
“Our results are reassuring and suggest that second-generation antipsychotics, as a class, do not substantially increase the risk of major malformations,” Dr. Viguera said.
The findings were published online August 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Safety data scarce
Despite the increasing use of SGAs to treat a “spectrum of psychiatric disorders,” relatively little data are available on the reproductive safety of these agents, Dr. Viguera said.
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (NPRAA) was established in 2008 to determine risk for major malformation among infants exposed to these medications during the first trimester, relative to a comparison group of unexposed infants of mothers with histories of psychiatric morbidity.
The NPRAA follows pregnant women (aged 18 to 45 years) with psychiatric illness who are exposed or unexposed to SGAs during pregnancy. Participants are recruited through nationwide provider referral, self-referral, and advertisement through the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health website.
Specific data collected are shown in the following table.
Since publication of the first results in 2015, the sample size for the trial has increased – and the absolute and relative risk for major malformations observed in the study population are “more precise,” the investigators note. The current study presented updated previous findings.
Demographic differences
Of the 1,906 women who enrolled as of April 2020, 1,311 (mean age, 32.6 years; 81.3% White) completed the study and were eligible for inclusion in the analysis.
Although the groups had a virtually identical mean age, fewer women in the exposure group were married compared with those in the non-exposure group (77% vs. 90%, respectively) and fewer had a college education (71.2% vs. 87.8%). There was also a higher percentage of first-trimester cigarette smokers in the exposure group (18.4% vs. 5.1%).
On the other hand, more women in the non-exposure group used alcohol than in the exposure group (28.6% vs. 21.4%, respectively).
The most frequent psychiatric disorder in the exposure group was bipolar disorder (63.9%), followed by major depression (12.9%), anxiety (5.8%), and schizophrenia (4.5%). Only 11.4% of women in the non-exposure group were diagnosed with bipolar disorder, whereas 34.1% were diagnosed with major depression, 31.3% with anxiety, and none with schizophrenia.
Notably, a large percentage of women in both groups had a history of postpartum depression and/or psychosis (41.4% and 35.5%, respectively).
The most frequently used SGAs in the exposure group were quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda).
Participants in the exposure group had a higher age at initial onset of primary psychiatric diagnosis and a lower proportion of lifetime illness compared with those in the non-exposure group.
Major clinical implication?
Among 640 live births in the exposure group, which included 17 twin pregnancies and 1 triplet pregnancy, 2.5% reported major malformations. Among 704 live births in the control group, which included 14 twin pregnancies, 1.99% reported major malformations.
The estimated OR for major malformations comparing exposed and unexposed infants was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 0.625-3.517).
The authors note that their findings were consistent with one of the largest studies to date, which included a nationwide sample of more than 1 million women. Its results showed that, among infants exposed to SGAs versus those who were not exposed, the estimated risk ratio after adjusting for psychiatric conditions was 1.05 (95% CI, 0.96-1.16).
Additionally, “a hallmark of a teratogen is that it tends to cause a specific type or pattern of malformations, and we found no preponderance of one single type of major malformation or specific pattern of malformations among the exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Viguera said
“A major clinical implication of these findings is that for women with major mood and/or psychotic disorders, treatment with an atypical antipsychotic during pregnancy may be the most prudent clinical decision, much as continued treatment is recommended for pregnant women with other serious and chronic medical conditions, such as epilepsy,” she added.
The concept of ‘satisficing’
Commenting on the study, Vivien Burt, MD, PhD, founder and director/consultant of the Women’s Life Center at the Resnick University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Neuropsychiatric Hospital, called the findings “reassuring.”
The results “support the conclusion that in pregnant women with serious psychiatric illnesses, the use of SGAs is often a better option than avoiding these medications and exposing both the women and their offspring to the adverse consequences of maternal mental illness,” she said.
An accompanying editorial co-authored by Dr. Burt and colleague Sonya Rasminsky, MD, introduced the concept of “satisficing” – a term coined by Herbert Simon, a behavioral economist and Nobel Laureate. “Satisficing” is a “decision-making strategy that aims for a satisfactory (‘good enough’) outcome rather than a perfect one.”
The concept applies to decision-making beyond the field of economics “and is critical to how physicians help patients make decisions when they are faced with multiple treatment options,” said Dr. Burt, a professor emeritus of psychiatry at UCLA.
“The goal of ‘satisficing’ is to plan for the most satisfactory outcome, knowing that there are always unknowns, so in an uncertain world, clinicians should carefully help their patients make decisions that will allow them to achieve an outcome they can best live with,” she noted.
The investigators note that their findings may not be generalizable to the larger population of women taking SGAs, given that their participants were “overwhelmingly White, married, and well-educated women.”
They add that enrollment into the NPRAA registry is ongoing and larger sample sizes will “further narrow the confidence interval around the risk estimates and allow for adjustment of likely sources of confounding.”
The NPRAA is supported by Alkermes, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, SAGE Therapeutics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Aurobindo Pharma. Past sponsors of the NPRAA are listed in the original paper. Dr. Viguera receives research support from the NPRAA, Alkermes Biopharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and SAGE Therapeutics and receives adviser/consulting fees from Up-to-Date. Dr. Burt has been a consultant/speaker for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Rasminsky has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) taken by pregnant women are linked to a low rate of adverse effects in their children, new research suggests.
Data from a large registry study of almost 2,000 women showed that 2.5% of the live births in a group that had been exposed to antipsychotics had confirmed major malformations compared with 2% of the live births in a non-exposed group. This translated into an estimated odds ratio of 1.5 for major malformations.
“The 2.5% absolute risk for major malformations is consistent with the estimates of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national baseline rate of major malformations in the general population,” lead author Adele Viguera, MD, MPH, director of research for women’s mental health, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, told this news organization.
“Our results are reassuring and suggest that second-generation antipsychotics, as a class, do not substantially increase the risk of major malformations,” Dr. Viguera said.
The findings were published online August 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Safety data scarce
Despite the increasing use of SGAs to treat a “spectrum of psychiatric disorders,” relatively little data are available on the reproductive safety of these agents, Dr. Viguera said.
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (NPRAA) was established in 2008 to determine risk for major malformation among infants exposed to these medications during the first trimester, relative to a comparison group of unexposed infants of mothers with histories of psychiatric morbidity.
The NPRAA follows pregnant women (aged 18 to 45 years) with psychiatric illness who are exposed or unexposed to SGAs during pregnancy. Participants are recruited through nationwide provider referral, self-referral, and advertisement through the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health website.
Specific data collected are shown in the following table.
Since publication of the first results in 2015, the sample size for the trial has increased – and the absolute and relative risk for major malformations observed in the study population are “more precise,” the investigators note. The current study presented updated previous findings.
Demographic differences
Of the 1,906 women who enrolled as of April 2020, 1,311 (mean age, 32.6 years; 81.3% White) completed the study and were eligible for inclusion in the analysis.
Although the groups had a virtually identical mean age, fewer women in the exposure group were married compared with those in the non-exposure group (77% vs. 90%, respectively) and fewer had a college education (71.2% vs. 87.8%). There was also a higher percentage of first-trimester cigarette smokers in the exposure group (18.4% vs. 5.1%).
On the other hand, more women in the non-exposure group used alcohol than in the exposure group (28.6% vs. 21.4%, respectively).
The most frequent psychiatric disorder in the exposure group was bipolar disorder (63.9%), followed by major depression (12.9%), anxiety (5.8%), and schizophrenia (4.5%). Only 11.4% of women in the non-exposure group were diagnosed with bipolar disorder, whereas 34.1% were diagnosed with major depression, 31.3% with anxiety, and none with schizophrenia.
Notably, a large percentage of women in both groups had a history of postpartum depression and/or psychosis (41.4% and 35.5%, respectively).
The most frequently used SGAs in the exposure group were quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda).
Participants in the exposure group had a higher age at initial onset of primary psychiatric diagnosis and a lower proportion of lifetime illness compared with those in the non-exposure group.
Major clinical implication?
Among 640 live births in the exposure group, which included 17 twin pregnancies and 1 triplet pregnancy, 2.5% reported major malformations. Among 704 live births in the control group, which included 14 twin pregnancies, 1.99% reported major malformations.
The estimated OR for major malformations comparing exposed and unexposed infants was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 0.625-3.517).
The authors note that their findings were consistent with one of the largest studies to date, which included a nationwide sample of more than 1 million women. Its results showed that, among infants exposed to SGAs versus those who were not exposed, the estimated risk ratio after adjusting for psychiatric conditions was 1.05 (95% CI, 0.96-1.16).
Additionally, “a hallmark of a teratogen is that it tends to cause a specific type or pattern of malformations, and we found no preponderance of one single type of major malformation or specific pattern of malformations among the exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Viguera said
“A major clinical implication of these findings is that for women with major mood and/or psychotic disorders, treatment with an atypical antipsychotic during pregnancy may be the most prudent clinical decision, much as continued treatment is recommended for pregnant women with other serious and chronic medical conditions, such as epilepsy,” she added.
The concept of ‘satisficing’
Commenting on the study, Vivien Burt, MD, PhD, founder and director/consultant of the Women’s Life Center at the Resnick University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Neuropsychiatric Hospital, called the findings “reassuring.”
The results “support the conclusion that in pregnant women with serious psychiatric illnesses, the use of SGAs is often a better option than avoiding these medications and exposing both the women and their offspring to the adverse consequences of maternal mental illness,” she said.
An accompanying editorial co-authored by Dr. Burt and colleague Sonya Rasminsky, MD, introduced the concept of “satisficing” – a term coined by Herbert Simon, a behavioral economist and Nobel Laureate. “Satisficing” is a “decision-making strategy that aims for a satisfactory (‘good enough’) outcome rather than a perfect one.”
The concept applies to decision-making beyond the field of economics “and is critical to how physicians help patients make decisions when they are faced with multiple treatment options,” said Dr. Burt, a professor emeritus of psychiatry at UCLA.
“The goal of ‘satisficing’ is to plan for the most satisfactory outcome, knowing that there are always unknowns, so in an uncertain world, clinicians should carefully help their patients make decisions that will allow them to achieve an outcome they can best live with,” she noted.
The investigators note that their findings may not be generalizable to the larger population of women taking SGAs, given that their participants were “overwhelmingly White, married, and well-educated women.”
They add that enrollment into the NPRAA registry is ongoing and larger sample sizes will “further narrow the confidence interval around the risk estimates and allow for adjustment of likely sources of confounding.”
The NPRAA is supported by Alkermes, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, SAGE Therapeutics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Aurobindo Pharma. Past sponsors of the NPRAA are listed in the original paper. Dr. Viguera receives research support from the NPRAA, Alkermes Biopharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and SAGE Therapeutics and receives adviser/consulting fees from Up-to-Date. Dr. Burt has been a consultant/speaker for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Rasminsky has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Febrile infant guideline allows wiggle room on hospital admission, testing
The long-anticipated American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines for the treatment of well-appearing febrile infants have arrived, and key points include updated guidance for cerebrospinal fluid testing and urine cultures, according to Robert Pantell, MD, and Kenneth Roberts, MD, who presented the guidelines at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine annual conference.
The AAP guideline was published in the August 2021 issue of Pediatrics. The guideline includes 21 key action statements and 40 total recommendations, and describes separate management algorithms for three age groups: infants aged 8-21 days, 22-28 days, and 29-60 days.
Dr. Roberts, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Dr. Pantell, of the University of California, San Francisco, emphasized that all pediatricians should read the full guideline, but they offered an overview of some of the notable points.
Some changes that drove the development of evidence-based guideline included changes in technology, such as the increased use of procalcitonin, the development of large research networks for studies of sufficient size, and a need to reduce the costs of unnecessary care and unnecessary trauma for infants, Dr. Roberts said. Use of data from large networks such as the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network provided enough evidence to support dividing the aged 8- to 60-day population into three groups.
The guideline applies to well-appearing term infants aged 8-60 days and at least 37 weeks’ gestation, with fever of 38° C (100.4° F) or higher in the past 24 hours in the home or clinical setting. The decision to exclude infants in the first week of life from the guideline was because at this age, infants “are sufficiently different in rates and types of illness, including early-onset bacterial infection,” according to the authors.
Dr. Roberts emphasized that the guidelines apply to “well-appearing infants,” which is not always obvious. “If a clinician is not confident an infant is well appearing, the clinical practice guideline should not be applied,” he said.
The guideline also includes a visual algorithm for each age group.
Dr. Pantell summarized the key action statements for the three age groups, and encouraged pediatricians to review the visual algorithms and footnotes available in the full text of the guideline.
The guideline includes seven key action statements for each of the three age groups. Four of these address evaluations, using urine, blood culture, inflammatory markers (IM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). One action statement focuses on initial treatment, and two on management: hospital admission versus monitoring at home, and treatment cessation.
Infants aged 8-21 days
The key action statements for well-appearing infants aged 8-21 days are similar to what clinicians likely would do for ill-appearing infants, the authors noted, based in part on the challenge of assessing an infant this age as “well appearing,” because they don’t yet have the ability to interact with the clinician.
For the 8- to 21-day group, the first two key actions are to obtain a urine specimen and blood culture, Dr. Pantell said. Also, clinicians “should” obtain a CSF for analysis and culture. “We recognize that the ability to get CSF quickly is a challenge,” he added. However, for the 8- to 21-day age group, a new feature is that these infants may be discharged if the CSF is negative. Evaluation in this youngest group states that clinicians “may assess inflammatory markers” including height of fever, absolute neutrophil count, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin.
Treatment of infants in the 8- to 21-day group “should” include parenteral antimicrobial therapy, according to the guideline, and these infants “should” be actively monitored in the hospital by nurses and staff experienced in neonatal care, Dr. Pantell said. The guideline also includes a key action statement to stop antimicrobials at 24-36 hours if cultures are negative, but to treat identified organisms.
Infants aged 22-28 days
In both the 22- to 28-day-old and 29- to 60-day-old groups, the guideline offers opportunities for less testing and treatment, such as avoiding a lumbar puncture, and fewer hospitalizations. The development of a separate guideline for the 22- to 28-day group is something new, said Dr. Pantell. The guideline states that clinicians should obtain urine specimens and blood culture, and should assess IM in this group. Further key action statements note that clinicians “should obtain a CSF if any IM is positive,” but “may” obtain CSF if the infant is hospitalized, if blood and urine cultures have been obtained, and if none of the IMs are abnormal.
As with younger patients, those with a negative CSF can go home, he said. As for treatment, clinicians “should” administer parenteral antimicrobial therapy to infants managed at home even if they have a negative CSF and urinalysis (UA), and no abnormal inflammatory markers Other points for management of infants in this age group at home include verbal teaching and written instructions for caregivers, plans for a re-evaluation at home in 24 hours, and a plan for communication and access to emergency care in case of a change in clinical status, Dr. Pantell explained. The guideline states that infants “should” be hospitalized if CSF is either not obtained or not interpretable, which leaves room for clinical judgment and individual circumstances. Antimicrobials “should” be discontinued in this group once all cultures are negative after 24-36 hours and no other infection requires treatment.
Infants aged 29-60 days
For the 29- to 60-day group, there are some differences, the main one is the recommendation of blood cultures in this group, said Dr. Pantell. “We are seeing a lot of UTIs [urinary tract infections], and we would like those treated.” However, clinicians need not obtain a CSF if other IMs are normal, but may do so if any IM is abnormal. Antimicrobial therapy may include ceftriaxone or cephalexin for UTIs, or vancomycin for bacteremia.
Although antimicrobial therapy is an option for UTIs and bacterial meningitis, clinicians “need not” use antimicrobials if CSF is normal, if UA is negative, and if no IMs are abnormal, Dr. Pantell added. Overall, further management of infants in this oldest age group should focus on discharge to home in the absence of abnormal findings, but hospitalization in the presence of abnormal CSF, IMs, or other concerns.
During a question-and-answer session, Dr. Roberts said that, while rectal temperature is preferable, any method is acceptable as a starting point for applying the guideline. Importantly, the guideline still leaves room for clinical judgment. “We hope this will change some thinking as far as whether one model fits all,” he noted. The authors tried to temper the word “should” with the word “may” when possible, so clinicians can say: “I’m going to individualize my decision to the infant in front of me.”
Ultimately, the guideline is meant as a guide, and not an absolute standard of care, the authors said. The language of the key action statements includes the words “should, may, need not” in place of “must, must not.” The guideline recommends factoring family values and preferences into any treatment decisions. “Variations, taking into account individual circumstances, may be appropriate.”
The guideline received no outside funding. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The long-anticipated American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines for the treatment of well-appearing febrile infants have arrived, and key points include updated guidance for cerebrospinal fluid testing and urine cultures, according to Robert Pantell, MD, and Kenneth Roberts, MD, who presented the guidelines at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine annual conference.
The AAP guideline was published in the August 2021 issue of Pediatrics. The guideline includes 21 key action statements and 40 total recommendations, and describes separate management algorithms for three age groups: infants aged 8-21 days, 22-28 days, and 29-60 days.
Dr. Roberts, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Dr. Pantell, of the University of California, San Francisco, emphasized that all pediatricians should read the full guideline, but they offered an overview of some of the notable points.
Some changes that drove the development of evidence-based guideline included changes in technology, such as the increased use of procalcitonin, the development of large research networks for studies of sufficient size, and a need to reduce the costs of unnecessary care and unnecessary trauma for infants, Dr. Roberts said. Use of data from large networks such as the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network provided enough evidence to support dividing the aged 8- to 60-day population into three groups.
The guideline applies to well-appearing term infants aged 8-60 days and at least 37 weeks’ gestation, with fever of 38° C (100.4° F) or higher in the past 24 hours in the home or clinical setting. The decision to exclude infants in the first week of life from the guideline was because at this age, infants “are sufficiently different in rates and types of illness, including early-onset bacterial infection,” according to the authors.
Dr. Roberts emphasized that the guidelines apply to “well-appearing infants,” which is not always obvious. “If a clinician is not confident an infant is well appearing, the clinical practice guideline should not be applied,” he said.
The guideline also includes a visual algorithm for each age group.
Dr. Pantell summarized the key action statements for the three age groups, and encouraged pediatricians to review the visual algorithms and footnotes available in the full text of the guideline.
The guideline includes seven key action statements for each of the three age groups. Four of these address evaluations, using urine, blood culture, inflammatory markers (IM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). One action statement focuses on initial treatment, and two on management: hospital admission versus monitoring at home, and treatment cessation.
Infants aged 8-21 days
The key action statements for well-appearing infants aged 8-21 days are similar to what clinicians likely would do for ill-appearing infants, the authors noted, based in part on the challenge of assessing an infant this age as “well appearing,” because they don’t yet have the ability to interact with the clinician.
For the 8- to 21-day group, the first two key actions are to obtain a urine specimen and blood culture, Dr. Pantell said. Also, clinicians “should” obtain a CSF for analysis and culture. “We recognize that the ability to get CSF quickly is a challenge,” he added. However, for the 8- to 21-day age group, a new feature is that these infants may be discharged if the CSF is negative. Evaluation in this youngest group states that clinicians “may assess inflammatory markers” including height of fever, absolute neutrophil count, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin.
Treatment of infants in the 8- to 21-day group “should” include parenteral antimicrobial therapy, according to the guideline, and these infants “should” be actively monitored in the hospital by nurses and staff experienced in neonatal care, Dr. Pantell said. The guideline also includes a key action statement to stop antimicrobials at 24-36 hours if cultures are negative, but to treat identified organisms.
Infants aged 22-28 days
In both the 22- to 28-day-old and 29- to 60-day-old groups, the guideline offers opportunities for less testing and treatment, such as avoiding a lumbar puncture, and fewer hospitalizations. The development of a separate guideline for the 22- to 28-day group is something new, said Dr. Pantell. The guideline states that clinicians should obtain urine specimens and blood culture, and should assess IM in this group. Further key action statements note that clinicians “should obtain a CSF if any IM is positive,” but “may” obtain CSF if the infant is hospitalized, if blood and urine cultures have been obtained, and if none of the IMs are abnormal.
As with younger patients, those with a negative CSF can go home, he said. As for treatment, clinicians “should” administer parenteral antimicrobial therapy to infants managed at home even if they have a negative CSF and urinalysis (UA), and no abnormal inflammatory markers Other points for management of infants in this age group at home include verbal teaching and written instructions for caregivers, plans for a re-evaluation at home in 24 hours, and a plan for communication and access to emergency care in case of a change in clinical status, Dr. Pantell explained. The guideline states that infants “should” be hospitalized if CSF is either not obtained or not interpretable, which leaves room for clinical judgment and individual circumstances. Antimicrobials “should” be discontinued in this group once all cultures are negative after 24-36 hours and no other infection requires treatment.
Infants aged 29-60 days
For the 29- to 60-day group, there are some differences, the main one is the recommendation of blood cultures in this group, said Dr. Pantell. “We are seeing a lot of UTIs [urinary tract infections], and we would like those treated.” However, clinicians need not obtain a CSF if other IMs are normal, but may do so if any IM is abnormal. Antimicrobial therapy may include ceftriaxone or cephalexin for UTIs, or vancomycin for bacteremia.
Although antimicrobial therapy is an option for UTIs and bacterial meningitis, clinicians “need not” use antimicrobials if CSF is normal, if UA is negative, and if no IMs are abnormal, Dr. Pantell added. Overall, further management of infants in this oldest age group should focus on discharge to home in the absence of abnormal findings, but hospitalization in the presence of abnormal CSF, IMs, or other concerns.
During a question-and-answer session, Dr. Roberts said that, while rectal temperature is preferable, any method is acceptable as a starting point for applying the guideline. Importantly, the guideline still leaves room for clinical judgment. “We hope this will change some thinking as far as whether one model fits all,” he noted. The authors tried to temper the word “should” with the word “may” when possible, so clinicians can say: “I’m going to individualize my decision to the infant in front of me.”
Ultimately, the guideline is meant as a guide, and not an absolute standard of care, the authors said. The language of the key action statements includes the words “should, may, need not” in place of “must, must not.” The guideline recommends factoring family values and preferences into any treatment decisions. “Variations, taking into account individual circumstances, may be appropriate.”
The guideline received no outside funding. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The long-anticipated American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines for the treatment of well-appearing febrile infants have arrived, and key points include updated guidance for cerebrospinal fluid testing and urine cultures, according to Robert Pantell, MD, and Kenneth Roberts, MD, who presented the guidelines at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine annual conference.
The AAP guideline was published in the August 2021 issue of Pediatrics. The guideline includes 21 key action statements and 40 total recommendations, and describes separate management algorithms for three age groups: infants aged 8-21 days, 22-28 days, and 29-60 days.
Dr. Roberts, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Dr. Pantell, of the University of California, San Francisco, emphasized that all pediatricians should read the full guideline, but they offered an overview of some of the notable points.
Some changes that drove the development of evidence-based guideline included changes in technology, such as the increased use of procalcitonin, the development of large research networks for studies of sufficient size, and a need to reduce the costs of unnecessary care and unnecessary trauma for infants, Dr. Roberts said. Use of data from large networks such as the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network provided enough evidence to support dividing the aged 8- to 60-day population into three groups.
The guideline applies to well-appearing term infants aged 8-60 days and at least 37 weeks’ gestation, with fever of 38° C (100.4° F) or higher in the past 24 hours in the home or clinical setting. The decision to exclude infants in the first week of life from the guideline was because at this age, infants “are sufficiently different in rates and types of illness, including early-onset bacterial infection,” according to the authors.
Dr. Roberts emphasized that the guidelines apply to “well-appearing infants,” which is not always obvious. “If a clinician is not confident an infant is well appearing, the clinical practice guideline should not be applied,” he said.
The guideline also includes a visual algorithm for each age group.
Dr. Pantell summarized the key action statements for the three age groups, and encouraged pediatricians to review the visual algorithms and footnotes available in the full text of the guideline.
The guideline includes seven key action statements for each of the three age groups. Four of these address evaluations, using urine, blood culture, inflammatory markers (IM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). One action statement focuses on initial treatment, and two on management: hospital admission versus monitoring at home, and treatment cessation.
Infants aged 8-21 days
The key action statements for well-appearing infants aged 8-21 days are similar to what clinicians likely would do for ill-appearing infants, the authors noted, based in part on the challenge of assessing an infant this age as “well appearing,” because they don’t yet have the ability to interact with the clinician.
For the 8- to 21-day group, the first two key actions are to obtain a urine specimen and blood culture, Dr. Pantell said. Also, clinicians “should” obtain a CSF for analysis and culture. “We recognize that the ability to get CSF quickly is a challenge,” he added. However, for the 8- to 21-day age group, a new feature is that these infants may be discharged if the CSF is negative. Evaluation in this youngest group states that clinicians “may assess inflammatory markers” including height of fever, absolute neutrophil count, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin.
Treatment of infants in the 8- to 21-day group “should” include parenteral antimicrobial therapy, according to the guideline, and these infants “should” be actively monitored in the hospital by nurses and staff experienced in neonatal care, Dr. Pantell said. The guideline also includes a key action statement to stop antimicrobials at 24-36 hours if cultures are negative, but to treat identified organisms.
Infants aged 22-28 days
In both the 22- to 28-day-old and 29- to 60-day-old groups, the guideline offers opportunities for less testing and treatment, such as avoiding a lumbar puncture, and fewer hospitalizations. The development of a separate guideline for the 22- to 28-day group is something new, said Dr. Pantell. The guideline states that clinicians should obtain urine specimens and blood culture, and should assess IM in this group. Further key action statements note that clinicians “should obtain a CSF if any IM is positive,” but “may” obtain CSF if the infant is hospitalized, if blood and urine cultures have been obtained, and if none of the IMs are abnormal.
As with younger patients, those with a negative CSF can go home, he said. As for treatment, clinicians “should” administer parenteral antimicrobial therapy to infants managed at home even if they have a negative CSF and urinalysis (UA), and no abnormal inflammatory markers Other points for management of infants in this age group at home include verbal teaching and written instructions for caregivers, plans for a re-evaluation at home in 24 hours, and a plan for communication and access to emergency care in case of a change in clinical status, Dr. Pantell explained. The guideline states that infants “should” be hospitalized if CSF is either not obtained or not interpretable, which leaves room for clinical judgment and individual circumstances. Antimicrobials “should” be discontinued in this group once all cultures are negative after 24-36 hours and no other infection requires treatment.
Infants aged 29-60 days
For the 29- to 60-day group, there are some differences, the main one is the recommendation of blood cultures in this group, said Dr. Pantell. “We are seeing a lot of UTIs [urinary tract infections], and we would like those treated.” However, clinicians need not obtain a CSF if other IMs are normal, but may do so if any IM is abnormal. Antimicrobial therapy may include ceftriaxone or cephalexin for UTIs, or vancomycin for bacteremia.
Although antimicrobial therapy is an option for UTIs and bacterial meningitis, clinicians “need not” use antimicrobials if CSF is normal, if UA is negative, and if no IMs are abnormal, Dr. Pantell added. Overall, further management of infants in this oldest age group should focus on discharge to home in the absence of abnormal findings, but hospitalization in the presence of abnormal CSF, IMs, or other concerns.
During a question-and-answer session, Dr. Roberts said that, while rectal temperature is preferable, any method is acceptable as a starting point for applying the guideline. Importantly, the guideline still leaves room for clinical judgment. “We hope this will change some thinking as far as whether one model fits all,” he noted. The authors tried to temper the word “should” with the word “may” when possible, so clinicians can say: “I’m going to individualize my decision to the infant in front of me.”
Ultimately, the guideline is meant as a guide, and not an absolute standard of care, the authors said. The language of the key action statements includes the words “should, may, need not” in place of “must, must not.” The guideline recommends factoring family values and preferences into any treatment decisions. “Variations, taking into account individual circumstances, may be appropriate.”
The guideline received no outside funding. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PHM 2021
Does early delivery for FGR affect school outcomes?
Iatrogenic delivery for suspected fetal growth restriction (FGR) may be associated with an increased likelihood of poorer school outcomes among infants born severely small for gestational age, a study of children in Australia suggests.
researchers reported in JAMA.
“It raises the question: in our efforts to improve outcomes in babies that are small, are we potentially doing more harm than good?” said Robert M. Silver, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who was not involved in the study. “I think that is a very important question to ask.”
However, “we can’t make that conclusion based on this one study,” he said in an interview. It could be that, in cases where severely small infants were delivered early, there may have been testing that indicated acute risks, and these infants may have tended to be sicker overall. “It may have been that if those babies weren’t delivered, they would have suffered a stillbirth or major brain injury,” Dr. Silver said. “It is really important that we acknowledge that we shouldn’t change our clinical practice” based on this one study.”
At the same time, the study underscores questions and challenges that surround the definition, identification, and management of suspected FGR, Dr. Silver said.
The study authors described their research as exploratory. In a related editorial Dr. Silver and Nathan R. Blue, MD said the findings should be considered hypothesis generating.
For the study, Roshan John Selvaratnam, BMedSc(Hons), a researcher affiliated with Monash University, Melbourne, and colleagues analyzed data from 181,902 children with developmental outcomes and 425,717 children with educational outcomes in Australia. They included children born at 32 weeks’ or more gestation between 2003 and 2013.
Severely small infants delivered early for suspected FGR had an average gestation of 37.9 weeks, whereas those not suspected of having FGR had an average gestation of 39.4 weeks.
Among infants who were severely small for gestational age, those delivered early for suspected FGR were more likely to be in the bottom 10th percentile on at least two developmental domains when they started school, compared with those not suspected of having FGR (16.2% vs. 12.7%; adjusted odds ratio, 1.36). They also were more likely to have low test scores in subsequent years. In grade 7, for example, the adjusted odds ratio for scoring below the national minimum standard on at least two educational domains was 1.33 (13.4% vs. 10.5%).
The researchers defined severely small for gestational age as birth weight below the third percentile. Among infants with normal growth, defined as birth weight at the 10th percentile or greater, school outcomes did not significantly differ between those with early delivery for suspected FGR and those not suspected of having FGR. Approximately 8% of the infants with normal growth had poor developmental outcomes.
The study authors described the dilemma that clinicians face with suspected FGR: “Either intervene early to prevent a small risk of stillbirth but potentially cause immediate and lifelong harm to the child or accept the increasing risk of stillbirth associated with prolonging the pregnancy to avoid more common neonatal and longer-term morbidities.”
It could be that severely small infants with suspected FGR in the study were “more compromised than those not suspected of having FGR,” which might explain the outcomes, Mr. Selvaratnam and coauthors wrote.
Another more plausible explanation is that “iatrogenic prematurity was harmful,” they said.
The researchers were unable to adjust for many factors that may influence academic success, including smoking and alcohol use during pregnancy, maternal body mass index, and breastfeeding, they noted. They also lacked information about the etiology for FGR and whether children had genetic abnormalities.
The study also does not take into account neonatal, infant, and childhood complications, Dr. Silver and Dr. Blue wrote in their editorial. “Nonetheless, these data are a welcome contribution given the knowledge gaps with regard to the optimal obstetric management of FGR.”
The establishment of a diagnostic standard for FGR is needed to properly investigate ways to improve risk stratification, diagnosis, and management, Dr. Silver and Dr. Blue added.
“What we have to do is get better at predicting which babies are at very high risk for continuing the pregnancy and which babies are at low risk for continuing the pregnancy so that we can better decide which babies would benefit from slightly early delivery,” Dr. Silver said.
Improved detection and management of FGR may be on the horizon. “Our ability to image the placental function has gotten a lot better, and I think that is really going to help us,” Dr. Silver said. Studies that aim to further improve the ability to assess whether babies are getting adequate blood flow during pregnancy are ongoing, which could further help doctors evaluate risks.
The study investigators and Dr. Silver had no conflict of interest disclosures. Dr. Blue disclosed grants from Samsung Medison and personal fees from Elsevier. The study was supported by a grant from the Australian government’s National Health and Medical Research Council Program, and Mr. Selvaratnam is supported by scholarships from an Australian government research training program and the National Centre of Research Excellence in Stillbirth.
Iatrogenic delivery for suspected fetal growth restriction (FGR) may be associated with an increased likelihood of poorer school outcomes among infants born severely small for gestational age, a study of children in Australia suggests.
researchers reported in JAMA.
“It raises the question: in our efforts to improve outcomes in babies that are small, are we potentially doing more harm than good?” said Robert M. Silver, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who was not involved in the study. “I think that is a very important question to ask.”
However, “we can’t make that conclusion based on this one study,” he said in an interview. It could be that, in cases where severely small infants were delivered early, there may have been testing that indicated acute risks, and these infants may have tended to be sicker overall. “It may have been that if those babies weren’t delivered, they would have suffered a stillbirth or major brain injury,” Dr. Silver said. “It is really important that we acknowledge that we shouldn’t change our clinical practice” based on this one study.”
At the same time, the study underscores questions and challenges that surround the definition, identification, and management of suspected FGR, Dr. Silver said.
The study authors described their research as exploratory. In a related editorial Dr. Silver and Nathan R. Blue, MD said the findings should be considered hypothesis generating.
For the study, Roshan John Selvaratnam, BMedSc(Hons), a researcher affiliated with Monash University, Melbourne, and colleagues analyzed data from 181,902 children with developmental outcomes and 425,717 children with educational outcomes in Australia. They included children born at 32 weeks’ or more gestation between 2003 and 2013.
Severely small infants delivered early for suspected FGR had an average gestation of 37.9 weeks, whereas those not suspected of having FGR had an average gestation of 39.4 weeks.
Among infants who were severely small for gestational age, those delivered early for suspected FGR were more likely to be in the bottom 10th percentile on at least two developmental domains when they started school, compared with those not suspected of having FGR (16.2% vs. 12.7%; adjusted odds ratio, 1.36). They also were more likely to have low test scores in subsequent years. In grade 7, for example, the adjusted odds ratio for scoring below the national minimum standard on at least two educational domains was 1.33 (13.4% vs. 10.5%).
The researchers defined severely small for gestational age as birth weight below the third percentile. Among infants with normal growth, defined as birth weight at the 10th percentile or greater, school outcomes did not significantly differ between those with early delivery for suspected FGR and those not suspected of having FGR. Approximately 8% of the infants with normal growth had poor developmental outcomes.
The study authors described the dilemma that clinicians face with suspected FGR: “Either intervene early to prevent a small risk of stillbirth but potentially cause immediate and lifelong harm to the child or accept the increasing risk of stillbirth associated with prolonging the pregnancy to avoid more common neonatal and longer-term morbidities.”
It could be that severely small infants with suspected FGR in the study were “more compromised than those not suspected of having FGR,” which might explain the outcomes, Mr. Selvaratnam and coauthors wrote.
Another more plausible explanation is that “iatrogenic prematurity was harmful,” they said.
The researchers were unable to adjust for many factors that may influence academic success, including smoking and alcohol use during pregnancy, maternal body mass index, and breastfeeding, they noted. They also lacked information about the etiology for FGR and whether children had genetic abnormalities.
The study also does not take into account neonatal, infant, and childhood complications, Dr. Silver and Dr. Blue wrote in their editorial. “Nonetheless, these data are a welcome contribution given the knowledge gaps with regard to the optimal obstetric management of FGR.”
The establishment of a diagnostic standard for FGR is needed to properly investigate ways to improve risk stratification, diagnosis, and management, Dr. Silver and Dr. Blue added.
“What we have to do is get better at predicting which babies are at very high risk for continuing the pregnancy and which babies are at low risk for continuing the pregnancy so that we can better decide which babies would benefit from slightly early delivery,” Dr. Silver said.
Improved detection and management of FGR may be on the horizon. “Our ability to image the placental function has gotten a lot better, and I think that is really going to help us,” Dr. Silver said. Studies that aim to further improve the ability to assess whether babies are getting adequate blood flow during pregnancy are ongoing, which could further help doctors evaluate risks.
The study investigators and Dr. Silver had no conflict of interest disclosures. Dr. Blue disclosed grants from Samsung Medison and personal fees from Elsevier. The study was supported by a grant from the Australian government’s National Health and Medical Research Council Program, and Mr. Selvaratnam is supported by scholarships from an Australian government research training program and the National Centre of Research Excellence in Stillbirth.
Iatrogenic delivery for suspected fetal growth restriction (FGR) may be associated with an increased likelihood of poorer school outcomes among infants born severely small for gestational age, a study of children in Australia suggests.
researchers reported in JAMA.
“It raises the question: in our efforts to improve outcomes in babies that are small, are we potentially doing more harm than good?” said Robert M. Silver, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who was not involved in the study. “I think that is a very important question to ask.”
However, “we can’t make that conclusion based on this one study,” he said in an interview. It could be that, in cases where severely small infants were delivered early, there may have been testing that indicated acute risks, and these infants may have tended to be sicker overall. “It may have been that if those babies weren’t delivered, they would have suffered a stillbirth or major brain injury,” Dr. Silver said. “It is really important that we acknowledge that we shouldn’t change our clinical practice” based on this one study.”
At the same time, the study underscores questions and challenges that surround the definition, identification, and management of suspected FGR, Dr. Silver said.
The study authors described their research as exploratory. In a related editorial Dr. Silver and Nathan R. Blue, MD said the findings should be considered hypothesis generating.
For the study, Roshan John Selvaratnam, BMedSc(Hons), a researcher affiliated with Monash University, Melbourne, and colleagues analyzed data from 181,902 children with developmental outcomes and 425,717 children with educational outcomes in Australia. They included children born at 32 weeks’ or more gestation between 2003 and 2013.
Severely small infants delivered early for suspected FGR had an average gestation of 37.9 weeks, whereas those not suspected of having FGR had an average gestation of 39.4 weeks.
Among infants who were severely small for gestational age, those delivered early for suspected FGR were more likely to be in the bottom 10th percentile on at least two developmental domains when they started school, compared with those not suspected of having FGR (16.2% vs. 12.7%; adjusted odds ratio, 1.36). They also were more likely to have low test scores in subsequent years. In grade 7, for example, the adjusted odds ratio for scoring below the national minimum standard on at least two educational domains was 1.33 (13.4% vs. 10.5%).
The researchers defined severely small for gestational age as birth weight below the third percentile. Among infants with normal growth, defined as birth weight at the 10th percentile or greater, school outcomes did not significantly differ between those with early delivery for suspected FGR and those not suspected of having FGR. Approximately 8% of the infants with normal growth had poor developmental outcomes.
The study authors described the dilemma that clinicians face with suspected FGR: “Either intervene early to prevent a small risk of stillbirth but potentially cause immediate and lifelong harm to the child or accept the increasing risk of stillbirth associated with prolonging the pregnancy to avoid more common neonatal and longer-term morbidities.”
It could be that severely small infants with suspected FGR in the study were “more compromised than those not suspected of having FGR,” which might explain the outcomes, Mr. Selvaratnam and coauthors wrote.
Another more plausible explanation is that “iatrogenic prematurity was harmful,” they said.
The researchers were unable to adjust for many factors that may influence academic success, including smoking and alcohol use during pregnancy, maternal body mass index, and breastfeeding, they noted. They also lacked information about the etiology for FGR and whether children had genetic abnormalities.
The study also does not take into account neonatal, infant, and childhood complications, Dr. Silver and Dr. Blue wrote in their editorial. “Nonetheless, these data are a welcome contribution given the knowledge gaps with regard to the optimal obstetric management of FGR.”
The establishment of a diagnostic standard for FGR is needed to properly investigate ways to improve risk stratification, diagnosis, and management, Dr. Silver and Dr. Blue added.
“What we have to do is get better at predicting which babies are at very high risk for continuing the pregnancy and which babies are at low risk for continuing the pregnancy so that we can better decide which babies would benefit from slightly early delivery,” Dr. Silver said.
Improved detection and management of FGR may be on the horizon. “Our ability to image the placental function has gotten a lot better, and I think that is really going to help us,” Dr. Silver said. Studies that aim to further improve the ability to assess whether babies are getting adequate blood flow during pregnancy are ongoing, which could further help doctors evaluate risks.
The study investigators and Dr. Silver had no conflict of interest disclosures. Dr. Blue disclosed grants from Samsung Medison and personal fees from Elsevier. The study was supported by a grant from the Australian government’s National Health and Medical Research Council Program, and Mr. Selvaratnam is supported by scholarships from an Australian government research training program and the National Centre of Research Excellence in Stillbirth.
FROM JAMA
Pregnant women no longer detained by ICE
Immigration and Customs Enforcement will no longer detain most migrant women who are pregnant, postpartum, or nursing for deportation. This reverses the policy previously put in place by the Trump administration.
Under the new directive, ICE officials generally will not detain or arrest women who are pregnant or nursing, or who have given birth within the previous year. In a July 1 memo signed by ICE Acting Director Tae Johnson, ICE officers are directed to house women in “an appropriate facility to manage their care.”
The memo goes on to state that “generally ICE should not detain, arrest, or take into custody for an administrative violation of the immigration laws individuals known to be pregnant, post partum, or nursing unless release is prohibited by law or exceptional circumstances exist.”
In addition, ICE is also required to evaluate those individuals who are already in custody “to determine if continued detention is appropriate.”
During the Obama administration, pregnant women were generally not detained except under extraordinary circumstances. However, these policies were reversed after Donald Trump took office, and there was an 80% increase in the number of times ICE detained pregnant women in the year that followed implementation of the new directive – from 1,160 in 2017 to 2,097 in 2018.
The new guidance now goes even further than the directive issued under President Obama as it also includes women who are nursing and the 1-year postpartum period.
This policy stems from the Biden-Harris administration’s plan to reform the immigration system, part of which was to create a more humane asylum system. In a statement released early in February 2021, the White House stated that the “Trump administration’s policies at the border have caused chaos, cruelty, and confusion,” and that they will now “begin to roll back the most damaging policies adopted by the prior administration, while taking effective action to manage migration across the region.” After migrant women are taken into custody, pregnancy tests are administered as part of regular health screenings. If women are found to be pregnant, the new ICE policy states that they “generally” should be released from detention.
However, there will still be circumstances when pregnant and postpartum women may be detained, such as when there is a high risk that the individual is violent or a national security concern. In these cases, a field office director must approve the arrest and detention as well as making sure that the women receive appropriate medical care.
“The harmful consequences of immigration detention have been documented for years,” said Rebekah Wolf, JD, staff attorney with the American Immigration Council. “Our 2017 joint complaint urging a thorough investigation into the increasing numbers of pregnant women facing harm in detention, illustrated the disturbing practice of detaining pregnant women and the lack of quality medical care provided to these women.”
She added that the “federal government should not be in the business of detaining pregnant or nursing individuals, and it’s good to see the Biden administration directing ICE to finally take meaningful steps to limit enforcement activities in this manner. We are hopeful that this announcement is an indication of a broader shift on detention policy.”
There are currently 13 pregnant women in ICE custody, and they are being considered for release under the new policy.
Immigration and Customs Enforcement will no longer detain most migrant women who are pregnant, postpartum, or nursing for deportation. This reverses the policy previously put in place by the Trump administration.
Under the new directive, ICE officials generally will not detain or arrest women who are pregnant or nursing, or who have given birth within the previous year. In a July 1 memo signed by ICE Acting Director Tae Johnson, ICE officers are directed to house women in “an appropriate facility to manage their care.”
The memo goes on to state that “generally ICE should not detain, arrest, or take into custody for an administrative violation of the immigration laws individuals known to be pregnant, post partum, or nursing unless release is prohibited by law or exceptional circumstances exist.”
In addition, ICE is also required to evaluate those individuals who are already in custody “to determine if continued detention is appropriate.”
During the Obama administration, pregnant women were generally not detained except under extraordinary circumstances. However, these policies were reversed after Donald Trump took office, and there was an 80% increase in the number of times ICE detained pregnant women in the year that followed implementation of the new directive – from 1,160 in 2017 to 2,097 in 2018.
The new guidance now goes even further than the directive issued under President Obama as it also includes women who are nursing and the 1-year postpartum period.
This policy stems from the Biden-Harris administration’s plan to reform the immigration system, part of which was to create a more humane asylum system. In a statement released early in February 2021, the White House stated that the “Trump administration’s policies at the border have caused chaos, cruelty, and confusion,” and that they will now “begin to roll back the most damaging policies adopted by the prior administration, while taking effective action to manage migration across the region.” After migrant women are taken into custody, pregnancy tests are administered as part of regular health screenings. If women are found to be pregnant, the new ICE policy states that they “generally” should be released from detention.
However, there will still be circumstances when pregnant and postpartum women may be detained, such as when there is a high risk that the individual is violent or a national security concern. In these cases, a field office director must approve the arrest and detention as well as making sure that the women receive appropriate medical care.
“The harmful consequences of immigration detention have been documented for years,” said Rebekah Wolf, JD, staff attorney with the American Immigration Council. “Our 2017 joint complaint urging a thorough investigation into the increasing numbers of pregnant women facing harm in detention, illustrated the disturbing practice of detaining pregnant women and the lack of quality medical care provided to these women.”
She added that the “federal government should not be in the business of detaining pregnant or nursing individuals, and it’s good to see the Biden administration directing ICE to finally take meaningful steps to limit enforcement activities in this manner. We are hopeful that this announcement is an indication of a broader shift on detention policy.”
There are currently 13 pregnant women in ICE custody, and they are being considered for release under the new policy.
Immigration and Customs Enforcement will no longer detain most migrant women who are pregnant, postpartum, or nursing for deportation. This reverses the policy previously put in place by the Trump administration.
Under the new directive, ICE officials generally will not detain or arrest women who are pregnant or nursing, or who have given birth within the previous year. In a July 1 memo signed by ICE Acting Director Tae Johnson, ICE officers are directed to house women in “an appropriate facility to manage their care.”
The memo goes on to state that “generally ICE should not detain, arrest, or take into custody for an administrative violation of the immigration laws individuals known to be pregnant, post partum, or nursing unless release is prohibited by law or exceptional circumstances exist.”
In addition, ICE is also required to evaluate those individuals who are already in custody “to determine if continued detention is appropriate.”
During the Obama administration, pregnant women were generally not detained except under extraordinary circumstances. However, these policies were reversed after Donald Trump took office, and there was an 80% increase in the number of times ICE detained pregnant women in the year that followed implementation of the new directive – from 1,160 in 2017 to 2,097 in 2018.
The new guidance now goes even further than the directive issued under President Obama as it also includes women who are nursing and the 1-year postpartum period.
This policy stems from the Biden-Harris administration’s plan to reform the immigration system, part of which was to create a more humane asylum system. In a statement released early in February 2021, the White House stated that the “Trump administration’s policies at the border have caused chaos, cruelty, and confusion,” and that they will now “begin to roll back the most damaging policies adopted by the prior administration, while taking effective action to manage migration across the region.” After migrant women are taken into custody, pregnancy tests are administered as part of regular health screenings. If women are found to be pregnant, the new ICE policy states that they “generally” should be released from detention.
However, there will still be circumstances when pregnant and postpartum women may be detained, such as when there is a high risk that the individual is violent or a national security concern. In these cases, a field office director must approve the arrest and detention as well as making sure that the women receive appropriate medical care.
“The harmful consequences of immigration detention have been documented for years,” said Rebekah Wolf, JD, staff attorney with the American Immigration Council. “Our 2017 joint complaint urging a thorough investigation into the increasing numbers of pregnant women facing harm in detention, illustrated the disturbing practice of detaining pregnant women and the lack of quality medical care provided to these women.”
She added that the “federal government should not be in the business of detaining pregnant or nursing individuals, and it’s good to see the Biden administration directing ICE to finally take meaningful steps to limit enforcement activities in this manner. We are hopeful that this announcement is an indication of a broader shift on detention policy.”
There are currently 13 pregnant women in ICE custody, and they are being considered for release under the new policy.
Postpartum depression affects dads, too
Michael W., a 38-year-old New Jersey–based attorney, and his wife had been excitedly planning for the birth of their baby and were overjoyed when she was born.
But after that, “I found that parenting a newborn was shockingly exhausting. I felt unprepared for the task, overwhelmed by the burden of the 24-hour-schedule and lack of sleep, and I struggled with feelings of inadequacy,” he said in an interview.
Michael never thought he had postpartum depression (PPD), perhaps because the condition is more commonly associated with women. But a study published in the American Journal of Men’s Health suggests that PPD also affects men.
A team of Danish investigators led by researcher Sarah Pedersen, of the department of public health, Aarhus University, extensively interviewed eight fathers with PPD and found their primary experiences involved feelings of being overwhelmed and powerless or inadequate, which sometimes turned into anger and frustration.
“I think one of the most important take-home messages is that practicing clinicians working with new parents should invite fathers to your consultations and engage the fathers as much as possible,” Ms. Pedersen said in an interview.
The findings also contained a message for parents, she says.
“I hope you will support each other and talk about your feelings and how you experience the transition to parenthood – know that it will take time to adjust to your new role,” she said.
Not enough attention
There’s been too little focus on fathers when it comes to PPD, according to Ms. Pedersen.
“During the last decade, several studies have examined the prevalence of PPD in men, and there is rising evidence that paternal PPD is associated with increased risk of long-term adverse behavioral and emotional outcomes in children,” she said.
Nevertheless, only three studies have been based on interviews with fathers who had personal experience with PPD.
“The purpose of our study was, first of all, to explore the lived experience of fathers who had PPD and, secondly, to gain deeper understanding of their help-seeking behavior – barriers to seeking help and facilitators of help-seeking,” Ms. Pedersen said.
The study was based on “semistructured” interviews with eight Danish fathers (ages 29-38 years) who had had PPD, none of whom had a previous history of depression.
All of them had received a formal diagnosis of PPD by a general practitioner or psychologist, and all had sought or received mental health care and considered themselves recovered from depression at the time of the interview.
The researchers used a technique called interpretative phenomenological analysis to analyze the interviews.
This method “aims to produce in-depth examinations of certain phenomena by examining how individuals make meaning of their own life experiences,” the authors wrote.
A ‘radical change’
Of the fathers, five described the period of pregnancy as a “time of happiness, full of positive expectations about fatherhood.”
But “the fathers’ great expectations were later replaced by a very different reality of fatherhood,” the authors wrote, noting that the transition to fatherhood was, in the words of one participant, a “radical change that you just can’t imagine.”
Most fathers expressed a feeling of being overwhelmed, and three felt unready for the task, which added to their depression.
“The participants wanted to be emotionally and physically present in their child’s life, but during the time of their depression, these kind-hearted intentions changed into feelings of guilt and inadequacy, as the participants did not feel they had enough energy and mental strength to become the kind of fathers they wanted to be,” the authors wrote.
The fathers mentioned stressors they believed contributed to their PPD, including complications during their partners’ pregnancies, unplanned cesarean birth (three fathers), the partners’ difficulties with breastfeeding (five fathers), and employment-related concerns. Five reported that their partners had postpartum emotional distress.
‘Masculine norms’
A second focus of the research was to examine fathers’ help-seeking behaviors, Ms. Pedersen said.
Ultimately, all the men sought formal help, either from their general practitioners or from a health visitor, with two seeking help right after birth.
Although the men were able to recognize changes in mood and behavior in retrospect, many did not regard them as signs of depression before their diagnosis.
Most had heard of PPD, but primarily as it affects women. Three sought information online about paternal PPD but couldn’t find any.
Four participants described experiencing PPD as “taboo,” based on a “combination of false beliefs, stigma, and masculine norms,” the authors stated, since men “are supposed to be big and strong and take care of everything, and suddenly you can’t.”
The authors reported that seven participants were screened for PPD or depression by a health care professional.
“The screening was an important part of the help-seeking process, as this was the first time two of the fathers were introduced to PPD,” the authors noted.
Although the screening “had the potential to spark conversation” about PPD, it was geared toward women, and some participants did not feel it was relevant to them.
“Future research should focus on identification of educational needs about paternal PPD among both parents, health care professionals, and other professionals taking care of new families,” Ms. Pedersen said.
Michael W. says it would have been helpful if someone had prepared him and his wife for what to expect, or if there had been some type of screening. Also, he advises expectant parents to “get some real-life experience by spending time around a newborn to see what’s involved.”
Different symptoms
“We often talk about mothers suffering from PPD, so it is more normalized for mothers to bring it up or for loved ones to ask mothers about how they are doing physically and psychologically after the birth,” Craig Garfield, MD, an attending physician and founder/director of Family and Child Health innovations at Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital, Chicago, said in an interview.
For fathers, “it is not discussed as commonly, so friends and families don’t often ask dads, and dads don’t know where to turn,” said Dr. Garfield, professor of pediatrics and medical social sciences at Northwestern University, Chicago. He was not involved with the study.
He noted that symptoms in fathers might differ from those of mothers.
“I have seen fathers who are anxious or more moody than they had been prior, or more angry, and I have seen fathers who throw themselves into work or begin drinking more – all related to changes in mood and depressive symptoms in the postnatal period,” he said.
Symptoms in men may last longer than in women. Dr. Garfield’s group published a study in which they surveyed 400 mothers and fathers of premature infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) about depressive symptoms around the time of NICU admission, at discharge home, and then after 30 days at home.
Roughly one-third of mothers screened positive for depressive symptoms around NICU admission, as did 17% of fathers. But the mothers’ depression scores improved by discharge and 30 days after being home, while the fathers’ remained “essentially unchanged,” he said.
“Further, we found that if doctors were to screen mothers and fathers during the NICU stay – at admission or even at discharge – that would greatly improve their ability to predict who would still have depressive symptoms 1 month after going home.”
Ms. Pedersen agrees that clinicians should incorporate screening for PPD into their practices and be proactive in encouraging fathers to get help.
“Keep pushing,” she advised, as “men rarely seek help, compared to women, in matters of mental health.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Michael W., a 38-year-old New Jersey–based attorney, and his wife had been excitedly planning for the birth of their baby and were overjoyed when she was born.
But after that, “I found that parenting a newborn was shockingly exhausting. I felt unprepared for the task, overwhelmed by the burden of the 24-hour-schedule and lack of sleep, and I struggled with feelings of inadequacy,” he said in an interview.
Michael never thought he had postpartum depression (PPD), perhaps because the condition is more commonly associated with women. But a study published in the American Journal of Men’s Health suggests that PPD also affects men.
A team of Danish investigators led by researcher Sarah Pedersen, of the department of public health, Aarhus University, extensively interviewed eight fathers with PPD and found their primary experiences involved feelings of being overwhelmed and powerless or inadequate, which sometimes turned into anger and frustration.
“I think one of the most important take-home messages is that practicing clinicians working with new parents should invite fathers to your consultations and engage the fathers as much as possible,” Ms. Pedersen said in an interview.
The findings also contained a message for parents, she says.
“I hope you will support each other and talk about your feelings and how you experience the transition to parenthood – know that it will take time to adjust to your new role,” she said.
Not enough attention
There’s been too little focus on fathers when it comes to PPD, according to Ms. Pedersen.
“During the last decade, several studies have examined the prevalence of PPD in men, and there is rising evidence that paternal PPD is associated with increased risk of long-term adverse behavioral and emotional outcomes in children,” she said.
Nevertheless, only three studies have been based on interviews with fathers who had personal experience with PPD.
“The purpose of our study was, first of all, to explore the lived experience of fathers who had PPD and, secondly, to gain deeper understanding of their help-seeking behavior – barriers to seeking help and facilitators of help-seeking,” Ms. Pedersen said.
The study was based on “semistructured” interviews with eight Danish fathers (ages 29-38 years) who had had PPD, none of whom had a previous history of depression.
All of them had received a formal diagnosis of PPD by a general practitioner or psychologist, and all had sought or received mental health care and considered themselves recovered from depression at the time of the interview.
The researchers used a technique called interpretative phenomenological analysis to analyze the interviews.
This method “aims to produce in-depth examinations of certain phenomena by examining how individuals make meaning of their own life experiences,” the authors wrote.
A ‘radical change’
Of the fathers, five described the period of pregnancy as a “time of happiness, full of positive expectations about fatherhood.”
But “the fathers’ great expectations were later replaced by a very different reality of fatherhood,” the authors wrote, noting that the transition to fatherhood was, in the words of one participant, a “radical change that you just can’t imagine.”
Most fathers expressed a feeling of being overwhelmed, and three felt unready for the task, which added to their depression.
“The participants wanted to be emotionally and physically present in their child’s life, but during the time of their depression, these kind-hearted intentions changed into feelings of guilt and inadequacy, as the participants did not feel they had enough energy and mental strength to become the kind of fathers they wanted to be,” the authors wrote.
The fathers mentioned stressors they believed contributed to their PPD, including complications during their partners’ pregnancies, unplanned cesarean birth (three fathers), the partners’ difficulties with breastfeeding (five fathers), and employment-related concerns. Five reported that their partners had postpartum emotional distress.
‘Masculine norms’
A second focus of the research was to examine fathers’ help-seeking behaviors, Ms. Pedersen said.
Ultimately, all the men sought formal help, either from their general practitioners or from a health visitor, with two seeking help right after birth.
Although the men were able to recognize changes in mood and behavior in retrospect, many did not regard them as signs of depression before their diagnosis.
Most had heard of PPD, but primarily as it affects women. Three sought information online about paternal PPD but couldn’t find any.
Four participants described experiencing PPD as “taboo,” based on a “combination of false beliefs, stigma, and masculine norms,” the authors stated, since men “are supposed to be big and strong and take care of everything, and suddenly you can’t.”
The authors reported that seven participants were screened for PPD or depression by a health care professional.
“The screening was an important part of the help-seeking process, as this was the first time two of the fathers were introduced to PPD,” the authors noted.
Although the screening “had the potential to spark conversation” about PPD, it was geared toward women, and some participants did not feel it was relevant to them.
“Future research should focus on identification of educational needs about paternal PPD among both parents, health care professionals, and other professionals taking care of new families,” Ms. Pedersen said.
Michael W. says it would have been helpful if someone had prepared him and his wife for what to expect, or if there had been some type of screening. Also, he advises expectant parents to “get some real-life experience by spending time around a newborn to see what’s involved.”
Different symptoms
“We often talk about mothers suffering from PPD, so it is more normalized for mothers to bring it up or for loved ones to ask mothers about how they are doing physically and psychologically after the birth,” Craig Garfield, MD, an attending physician and founder/director of Family and Child Health innovations at Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital, Chicago, said in an interview.
For fathers, “it is not discussed as commonly, so friends and families don’t often ask dads, and dads don’t know where to turn,” said Dr. Garfield, professor of pediatrics and medical social sciences at Northwestern University, Chicago. He was not involved with the study.
He noted that symptoms in fathers might differ from those of mothers.
“I have seen fathers who are anxious or more moody than they had been prior, or more angry, and I have seen fathers who throw themselves into work or begin drinking more – all related to changes in mood and depressive symptoms in the postnatal period,” he said.
Symptoms in men may last longer than in women. Dr. Garfield’s group published a study in which they surveyed 400 mothers and fathers of premature infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) about depressive symptoms around the time of NICU admission, at discharge home, and then after 30 days at home.
Roughly one-third of mothers screened positive for depressive symptoms around NICU admission, as did 17% of fathers. But the mothers’ depression scores improved by discharge and 30 days after being home, while the fathers’ remained “essentially unchanged,” he said.
“Further, we found that if doctors were to screen mothers and fathers during the NICU stay – at admission or even at discharge – that would greatly improve their ability to predict who would still have depressive symptoms 1 month after going home.”
Ms. Pedersen agrees that clinicians should incorporate screening for PPD into their practices and be proactive in encouraging fathers to get help.
“Keep pushing,” she advised, as “men rarely seek help, compared to women, in matters of mental health.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Michael W., a 38-year-old New Jersey–based attorney, and his wife had been excitedly planning for the birth of their baby and were overjoyed when she was born.
But after that, “I found that parenting a newborn was shockingly exhausting. I felt unprepared for the task, overwhelmed by the burden of the 24-hour-schedule and lack of sleep, and I struggled with feelings of inadequacy,” he said in an interview.
Michael never thought he had postpartum depression (PPD), perhaps because the condition is more commonly associated with women. But a study published in the American Journal of Men’s Health suggests that PPD also affects men.
A team of Danish investigators led by researcher Sarah Pedersen, of the department of public health, Aarhus University, extensively interviewed eight fathers with PPD and found their primary experiences involved feelings of being overwhelmed and powerless or inadequate, which sometimes turned into anger and frustration.
“I think one of the most important take-home messages is that practicing clinicians working with new parents should invite fathers to your consultations and engage the fathers as much as possible,” Ms. Pedersen said in an interview.
The findings also contained a message for parents, she says.
“I hope you will support each other and talk about your feelings and how you experience the transition to parenthood – know that it will take time to adjust to your new role,” she said.
Not enough attention
There’s been too little focus on fathers when it comes to PPD, according to Ms. Pedersen.
“During the last decade, several studies have examined the prevalence of PPD in men, and there is rising evidence that paternal PPD is associated with increased risk of long-term adverse behavioral and emotional outcomes in children,” she said.
Nevertheless, only three studies have been based on interviews with fathers who had personal experience with PPD.
“The purpose of our study was, first of all, to explore the lived experience of fathers who had PPD and, secondly, to gain deeper understanding of their help-seeking behavior – barriers to seeking help and facilitators of help-seeking,” Ms. Pedersen said.
The study was based on “semistructured” interviews with eight Danish fathers (ages 29-38 years) who had had PPD, none of whom had a previous history of depression.
All of them had received a formal diagnosis of PPD by a general practitioner or psychologist, and all had sought or received mental health care and considered themselves recovered from depression at the time of the interview.
The researchers used a technique called interpretative phenomenological analysis to analyze the interviews.
This method “aims to produce in-depth examinations of certain phenomena by examining how individuals make meaning of their own life experiences,” the authors wrote.
A ‘radical change’
Of the fathers, five described the period of pregnancy as a “time of happiness, full of positive expectations about fatherhood.”
But “the fathers’ great expectations were later replaced by a very different reality of fatherhood,” the authors wrote, noting that the transition to fatherhood was, in the words of one participant, a “radical change that you just can’t imagine.”
Most fathers expressed a feeling of being overwhelmed, and three felt unready for the task, which added to their depression.
“The participants wanted to be emotionally and physically present in their child’s life, but during the time of their depression, these kind-hearted intentions changed into feelings of guilt and inadequacy, as the participants did not feel they had enough energy and mental strength to become the kind of fathers they wanted to be,” the authors wrote.
The fathers mentioned stressors they believed contributed to their PPD, including complications during their partners’ pregnancies, unplanned cesarean birth (three fathers), the partners’ difficulties with breastfeeding (five fathers), and employment-related concerns. Five reported that their partners had postpartum emotional distress.
‘Masculine norms’
A second focus of the research was to examine fathers’ help-seeking behaviors, Ms. Pedersen said.
Ultimately, all the men sought formal help, either from their general practitioners or from a health visitor, with two seeking help right after birth.
Although the men were able to recognize changes in mood and behavior in retrospect, many did not regard them as signs of depression before their diagnosis.
Most had heard of PPD, but primarily as it affects women. Three sought information online about paternal PPD but couldn’t find any.
Four participants described experiencing PPD as “taboo,” based on a “combination of false beliefs, stigma, and masculine norms,” the authors stated, since men “are supposed to be big and strong and take care of everything, and suddenly you can’t.”
The authors reported that seven participants were screened for PPD or depression by a health care professional.
“The screening was an important part of the help-seeking process, as this was the first time two of the fathers were introduced to PPD,” the authors noted.
Although the screening “had the potential to spark conversation” about PPD, it was geared toward women, and some participants did not feel it was relevant to them.
“Future research should focus on identification of educational needs about paternal PPD among both parents, health care professionals, and other professionals taking care of new families,” Ms. Pedersen said.
Michael W. says it would have been helpful if someone had prepared him and his wife for what to expect, or if there had been some type of screening. Also, he advises expectant parents to “get some real-life experience by spending time around a newborn to see what’s involved.”
Different symptoms
“We often talk about mothers suffering from PPD, so it is more normalized for mothers to bring it up or for loved ones to ask mothers about how they are doing physically and psychologically after the birth,” Craig Garfield, MD, an attending physician and founder/director of Family and Child Health innovations at Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital, Chicago, said in an interview.
For fathers, “it is not discussed as commonly, so friends and families don’t often ask dads, and dads don’t know where to turn,” said Dr. Garfield, professor of pediatrics and medical social sciences at Northwestern University, Chicago. He was not involved with the study.
He noted that symptoms in fathers might differ from those of mothers.
“I have seen fathers who are anxious or more moody than they had been prior, or more angry, and I have seen fathers who throw themselves into work or begin drinking more – all related to changes in mood and depressive symptoms in the postnatal period,” he said.
Symptoms in men may last longer than in women. Dr. Garfield’s group published a study in which they surveyed 400 mothers and fathers of premature infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) about depressive symptoms around the time of NICU admission, at discharge home, and then after 30 days at home.
Roughly one-third of mothers screened positive for depressive symptoms around NICU admission, as did 17% of fathers. But the mothers’ depression scores improved by discharge and 30 days after being home, while the fathers’ remained “essentially unchanged,” he said.
“Further, we found that if doctors were to screen mothers and fathers during the NICU stay – at admission or even at discharge – that would greatly improve their ability to predict who would still have depressive symptoms 1 month after going home.”
Ms. Pedersen agrees that clinicians should incorporate screening for PPD into their practices and be proactive in encouraging fathers to get help.
“Keep pushing,” she advised, as “men rarely seek help, compared to women, in matters of mental health.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Bifidobacteria supplementation regulates newborn immune system
Supplementing breastfed infants with bifidobacteria promotes development of a well-regulated immune system, theoretically reducing risk of immune-mediated conditions like allergies and asthma, according to investigators.
These findings support the importance of early gut colonization with beneficial microbes, an event that may affect the immune system throughout life, reported lead author Bethany M. Henrick, PhD, director of immunology and diagnostics at Evolve Biosystems, Davis, Calif., and adjunct assistant professor at the University of Nebraska, Lincoln, and colleagues.
“Dysbiosis of the infant gut microbiome is common in modern societies and a likely contributing factor to the increased incidences of immune-mediated disorders,” the investigators wrote in Cell. “Therefore, there is great interest in identifying microbial factors that can support healthier immune system imprinting and hopefully prevent cases of allergy, autoimmunity, and possibly other conditions involving the immune system.”
Prevailing theory suggests that the rising incidence of neonatal intestinal dysbiosis – which is typical in developed countries – may be caused by a variety of factors, including cesarean sections; modern hygiene practices; antibiotics, antiseptics, and other medications; diets high in fat and sugar; and infant formula.
According to Dr. Henrick and colleagues, a healthy gut microbiome plays the greatest role in immunological development during the first 3 months post partum; specifically, a lack of bifidobacteria during this time has been linked with increased risks of autoimmunity and enteric inflammation, although underlying immune mechanisms remain unclear.
Bifidobacteria also exemplify the symbiotic relationship between mothers, babies, and beneficial microbes. The investigators pointed out that breast milk contains human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), which humans cannot digest, but are an excellent source of energy for bifidobacteria and other beneficial microbes, giving them a “selective nutritional advantage.”
Bifidobacteria should therefore be common residents within the infant gut, but this is often not now the case, leading Dr. Henrick and colleagues to zero in on the microbe, in hopes of determining the exactly how beneficial bacteria shape immune development.
It is only recently that the necessary knowledge and techniques to perform studies like this one have become available, the investigators wrote, noting a better understanding of cell-regulatory relationships, advances in immune profiling at the systems level, and new technology that allows for profiling small-volume samples from infants.
The present study involved a series of observational experiments and a small interventional trial.
First, the investigators conducted a wide array of blood- and fecal-based longitudinal analyses from 208 infants in Sweden to characterize immune cell expansion and microbiome colonization of the gut, with a focus on bifidobacteria.
Their results showed that infants lacking bifidobacteria, and HMO-utilization genes (which are expressed by bifidobacteria and other beneficial microbes), had higher levels of systemic inflammation, including increased T helper 2 (Th2) and Th17 responses.
“Infants not colonized by Bifidobacteriaceae or in cases where these microbes fail to expand during the first months of life there is evidence of systemic and intestinal inflammation, increased frequencies of activated immune cells, and reduced levels of regulatory cells indicative of systemic immune dysregulation,” the investigators wrote.
The interventional part of the study involved 60 breastfed infants in California. Twenty-nine of the newborns were given 1.8 x 1010 colony-forming units (CFUs) of B. longum subsp. infantis EVC001 daily from postnatal day 7 to day 28, while the remaining 31 infants were given no supplementation.
Fecal samples were collected on day 6 and day 60. At day 60, supplemented infants had high levels of HMO-utilization genes, plus significantly greater alpha diversity (P = .0001; Wilcoxon), compared with controls. Infants receiving EVC001 also had less inflammatory fecal cytokines, suggesting that microbes expressing HMO-utilization genes cause a shift away from proinflammatory Th2 and Th17 responses, and toward Th1.
“It is not the simple presence of bifidobacteria that is responsible for the immune effects but the metabolic partnership between the bacteria and HMOs,” the investigators noted.
According to principal investigator Petter Brodin, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric immunology at Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden, the findings deserve further investigation.
“Our data indicate that substitution with beneficial microbes efficiently metabolizing HMOs could open a way to prevent cases of immune-mediated diseases, but larger, randomized trials aimed at this will be required to determine this potential,” Dr. Brodin said in an interview.
Carolynn Dude, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, agreed that more work is needed.
“While this study provides some insight into the mechanisms that may set up a newborn for poor health outcomes later in life, the data is still very limited, and more long-term follow-up on these infants is needed before recommending any sort of bacterial supplementation to a newborn,” Dr. Dude said in an interview.
Dr. Brodin and colleagues are planning an array of related studies, including larger clinical trials; further investigations into mechanisms of action; comparisons between the present cohort and infants in Kenya, where immune-mediated diseases are rare; and evaluations of vaccine responses and infectious disease susceptibility.
The study was supported by the European Research Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Marianne & Marcus Wallenberg Foundation, and others. The investigators disclosed relationships with Cytodelics, Scailyte, Kancera, and others. Dr. Dude reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Supplementing breastfed infants with bifidobacteria promotes development of a well-regulated immune system, theoretically reducing risk of immune-mediated conditions like allergies and asthma, according to investigators.
These findings support the importance of early gut colonization with beneficial microbes, an event that may affect the immune system throughout life, reported lead author Bethany M. Henrick, PhD, director of immunology and diagnostics at Evolve Biosystems, Davis, Calif., and adjunct assistant professor at the University of Nebraska, Lincoln, and colleagues.
“Dysbiosis of the infant gut microbiome is common in modern societies and a likely contributing factor to the increased incidences of immune-mediated disorders,” the investigators wrote in Cell. “Therefore, there is great interest in identifying microbial factors that can support healthier immune system imprinting and hopefully prevent cases of allergy, autoimmunity, and possibly other conditions involving the immune system.”
Prevailing theory suggests that the rising incidence of neonatal intestinal dysbiosis – which is typical in developed countries – may be caused by a variety of factors, including cesarean sections; modern hygiene practices; antibiotics, antiseptics, and other medications; diets high in fat and sugar; and infant formula.
According to Dr. Henrick and colleagues, a healthy gut microbiome plays the greatest role in immunological development during the first 3 months post partum; specifically, a lack of bifidobacteria during this time has been linked with increased risks of autoimmunity and enteric inflammation, although underlying immune mechanisms remain unclear.
Bifidobacteria also exemplify the symbiotic relationship between mothers, babies, and beneficial microbes. The investigators pointed out that breast milk contains human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), which humans cannot digest, but are an excellent source of energy for bifidobacteria and other beneficial microbes, giving them a “selective nutritional advantage.”
Bifidobacteria should therefore be common residents within the infant gut, but this is often not now the case, leading Dr. Henrick and colleagues to zero in on the microbe, in hopes of determining the exactly how beneficial bacteria shape immune development.
It is only recently that the necessary knowledge and techniques to perform studies like this one have become available, the investigators wrote, noting a better understanding of cell-regulatory relationships, advances in immune profiling at the systems level, and new technology that allows for profiling small-volume samples from infants.
The present study involved a series of observational experiments and a small interventional trial.
First, the investigators conducted a wide array of blood- and fecal-based longitudinal analyses from 208 infants in Sweden to characterize immune cell expansion and microbiome colonization of the gut, with a focus on bifidobacteria.
Their results showed that infants lacking bifidobacteria, and HMO-utilization genes (which are expressed by bifidobacteria and other beneficial microbes), had higher levels of systemic inflammation, including increased T helper 2 (Th2) and Th17 responses.
“Infants not colonized by Bifidobacteriaceae or in cases where these microbes fail to expand during the first months of life there is evidence of systemic and intestinal inflammation, increased frequencies of activated immune cells, and reduced levels of regulatory cells indicative of systemic immune dysregulation,” the investigators wrote.
The interventional part of the study involved 60 breastfed infants in California. Twenty-nine of the newborns were given 1.8 x 1010 colony-forming units (CFUs) of B. longum subsp. infantis EVC001 daily from postnatal day 7 to day 28, while the remaining 31 infants were given no supplementation.
Fecal samples were collected on day 6 and day 60. At day 60, supplemented infants had high levels of HMO-utilization genes, plus significantly greater alpha diversity (P = .0001; Wilcoxon), compared with controls. Infants receiving EVC001 also had less inflammatory fecal cytokines, suggesting that microbes expressing HMO-utilization genes cause a shift away from proinflammatory Th2 and Th17 responses, and toward Th1.
“It is not the simple presence of bifidobacteria that is responsible for the immune effects but the metabolic partnership between the bacteria and HMOs,” the investigators noted.
According to principal investigator Petter Brodin, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric immunology at Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden, the findings deserve further investigation.
“Our data indicate that substitution with beneficial microbes efficiently metabolizing HMOs could open a way to prevent cases of immune-mediated diseases, but larger, randomized trials aimed at this will be required to determine this potential,” Dr. Brodin said in an interview.
Carolynn Dude, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, agreed that more work is needed.
“While this study provides some insight into the mechanisms that may set up a newborn for poor health outcomes later in life, the data is still very limited, and more long-term follow-up on these infants is needed before recommending any sort of bacterial supplementation to a newborn,” Dr. Dude said in an interview.
Dr. Brodin and colleagues are planning an array of related studies, including larger clinical trials; further investigations into mechanisms of action; comparisons between the present cohort and infants in Kenya, where immune-mediated diseases are rare; and evaluations of vaccine responses and infectious disease susceptibility.
The study was supported by the European Research Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Marianne & Marcus Wallenberg Foundation, and others. The investigators disclosed relationships with Cytodelics, Scailyte, Kancera, and others. Dr. Dude reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Supplementing breastfed infants with bifidobacteria promotes development of a well-regulated immune system, theoretically reducing risk of immune-mediated conditions like allergies and asthma, according to investigators.
These findings support the importance of early gut colonization with beneficial microbes, an event that may affect the immune system throughout life, reported lead author Bethany M. Henrick, PhD, director of immunology and diagnostics at Evolve Biosystems, Davis, Calif., and adjunct assistant professor at the University of Nebraska, Lincoln, and colleagues.
“Dysbiosis of the infant gut microbiome is common in modern societies and a likely contributing factor to the increased incidences of immune-mediated disorders,” the investigators wrote in Cell. “Therefore, there is great interest in identifying microbial factors that can support healthier immune system imprinting and hopefully prevent cases of allergy, autoimmunity, and possibly other conditions involving the immune system.”
Prevailing theory suggests that the rising incidence of neonatal intestinal dysbiosis – which is typical in developed countries – may be caused by a variety of factors, including cesarean sections; modern hygiene practices; antibiotics, antiseptics, and other medications; diets high in fat and sugar; and infant formula.
According to Dr. Henrick and colleagues, a healthy gut microbiome plays the greatest role in immunological development during the first 3 months post partum; specifically, a lack of bifidobacteria during this time has been linked with increased risks of autoimmunity and enteric inflammation, although underlying immune mechanisms remain unclear.
Bifidobacteria also exemplify the symbiotic relationship between mothers, babies, and beneficial microbes. The investigators pointed out that breast milk contains human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), which humans cannot digest, but are an excellent source of energy for bifidobacteria and other beneficial microbes, giving them a “selective nutritional advantage.”
Bifidobacteria should therefore be common residents within the infant gut, but this is often not now the case, leading Dr. Henrick and colleagues to zero in on the microbe, in hopes of determining the exactly how beneficial bacteria shape immune development.
It is only recently that the necessary knowledge and techniques to perform studies like this one have become available, the investigators wrote, noting a better understanding of cell-regulatory relationships, advances in immune profiling at the systems level, and new technology that allows for profiling small-volume samples from infants.
The present study involved a series of observational experiments and a small interventional trial.
First, the investigators conducted a wide array of blood- and fecal-based longitudinal analyses from 208 infants in Sweden to characterize immune cell expansion and microbiome colonization of the gut, with a focus on bifidobacteria.
Their results showed that infants lacking bifidobacteria, and HMO-utilization genes (which are expressed by bifidobacteria and other beneficial microbes), had higher levels of systemic inflammation, including increased T helper 2 (Th2) and Th17 responses.
“Infants not colonized by Bifidobacteriaceae or in cases where these microbes fail to expand during the first months of life there is evidence of systemic and intestinal inflammation, increased frequencies of activated immune cells, and reduced levels of regulatory cells indicative of systemic immune dysregulation,” the investigators wrote.
The interventional part of the study involved 60 breastfed infants in California. Twenty-nine of the newborns were given 1.8 x 1010 colony-forming units (CFUs) of B. longum subsp. infantis EVC001 daily from postnatal day 7 to day 28, while the remaining 31 infants were given no supplementation.
Fecal samples were collected on day 6 and day 60. At day 60, supplemented infants had high levels of HMO-utilization genes, plus significantly greater alpha diversity (P = .0001; Wilcoxon), compared with controls. Infants receiving EVC001 also had less inflammatory fecal cytokines, suggesting that microbes expressing HMO-utilization genes cause a shift away from proinflammatory Th2 and Th17 responses, and toward Th1.
“It is not the simple presence of bifidobacteria that is responsible for the immune effects but the metabolic partnership between the bacteria and HMOs,” the investigators noted.
According to principal investigator Petter Brodin, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric immunology at Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden, the findings deserve further investigation.
“Our data indicate that substitution with beneficial microbes efficiently metabolizing HMOs could open a way to prevent cases of immune-mediated diseases, but larger, randomized trials aimed at this will be required to determine this potential,” Dr. Brodin said in an interview.
Carolynn Dude, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, agreed that more work is needed.
“While this study provides some insight into the mechanisms that may set up a newborn for poor health outcomes later in life, the data is still very limited, and more long-term follow-up on these infants is needed before recommending any sort of bacterial supplementation to a newborn,” Dr. Dude said in an interview.
Dr. Brodin and colleagues are planning an array of related studies, including larger clinical trials; further investigations into mechanisms of action; comparisons between the present cohort and infants in Kenya, where immune-mediated diseases are rare; and evaluations of vaccine responses and infectious disease susceptibility.
The study was supported by the European Research Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Marianne & Marcus Wallenberg Foundation, and others. The investigators disclosed relationships with Cytodelics, Scailyte, Kancera, and others. Dr. Dude reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM CELL