User login
Patient Navigators for Serious Illnesses Can Now Bill Under New Medicare Codes
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

Special Report II: Tackling Burnout
Last month, we introduced the epidemic of burnout and the adverse consequences for both our vascular surgery patients and ourselves. Today we will outline a framework for addressing these issues. The foundation of this framework is informed by the social and neurosciences.
From the perspective of the social scientist: Christina Maslach, the originator of the widely used Maslach Burnout Inventory, theorized that burnout arises from a chronic mismatch between people and their work setting in some or all of the following domains: Workload (too much, wrong kind); control (lack of autonomy, or insufficient control over resources); reward (insufficient financial or social rewards commensurate with achievements); community (loss of positive connection with others); fairness (lack of perceived fairness, inequity of work, pay, or promotion); and values (conflict of personal and organizational values). The reality of practicing medicine in today’s business milieu – of achieving service efficiencies by meeting performance targets – brings many of these mismatches into sharp focus.
From the perspective of the neuroscientist: Recent advances, including functional MRI, have demonstrated that the human brain is hard wired for compassion. Compassion is the deep feeling that arises when confronted with another’s suffering, coupled with a strong desire to alleviate that suffering. There are at least two neural pathways: one activated during empathy, having us experience another’s pain; and the other activated during compassion, resulting in our sense of reward. Thus, burnout is thought to occur when you know what your patient needs but you are unable to deliver it. Compassionate medical care is purposeful work, which promotes a sense of reward and mitigates burnout.
Because burnout affects all caregivers (anyone who touches the patient), a successful program addressing workforce well-being must be comprehensive and organization wide, similar to successful patient safety, CPI [continuous process improvement] and LEAN [Six Sigma] initiatives.
There are no shortcuts. Creating a culture of compassionate, collaborative care requires an understanding of the interrelationships between the individual provider, the unit or team, and organizational leadership.
1) The individual provider: There is evidence to support the use of programs that build personal resilience. A recently published meta-analysis by West and colleagues concluded that while no specific physician burnout intervention has been shown to be better than other types of interventions, mindfulness, stress management, and small-group discussions can be effective approaches to reducing burnout scores. Strategies to build individual resilience, such as mindfulness and meditation, are easy to teach but place the burden for success on the individual. No amount of resilience can withstand an unsupportive or toxic workplace environment, so both individual and organizational strategies in combination are necessary.
2) The unit or team: Scheduling time for open and honest discussion of social and emotional issues that arise in caring for patients helps nourish caregiver to caregiver compassion. The Schwartz Center for Compassionate Healthcare is a national nonprofit leading the movement to bring compassion to every patient-caregiver interaction. More than 425 health care organization are Schwartz Center members and conduct Schwartz Rounds™ to bring doctors, nurses, and other caregivers together to discuss the human side of health care. (www.theschwartzcenter.org). Team member to team member support is essential for navigating the stressors of practice. With having lunch in front of your computer being the norm, and the disappearance of traditional spaces for colleagues to connect (for example, nurses’ lounge, physician dining rooms), the opportunity for caregivers to have a safe place to escape, a place to have their own humanity reaffirmed, a place to offer support to their peers, has been eliminated.
3) Organizational Leadership: Making compassion a core value, articulating it, and establishing metrics whereby it can be measured, is a good start. The barriers to a culture of compassion are related to our systems of care. There are burgeoning administrative and documentation tasks to be performed, and productivity expectations that turn our clinics and hospitals into assembly lines. No, we cannot expect the EMR [electronic medical records] to be eliminated, but workforce well-being cannot be sustainable in the context of inadequate resources. A culture of compassionate collaborative care requires programs and policies that are implemented by the organization itself. Examples of organization-wide initiatives that support workforce well-being and provider engagement include: screening for caregiver burnout, establishing policies for managing adverse events with an eye toward the second victim, and most importantly, supporting systems that preserve work control autonomy of physicians and nurses in clinical settings. The business sector has long recognized that workplace stress is a function of how demanding a person’s job is and how much control that person has over his or her responsibilities. The business community has also recognized that the experience of the worker (provider) drives the experience of the customer (patient). In a study of hospital compassionate practices and HCAHPS [the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems], McClelland and Vogus reported that how well a hospital compassionately supports it employees and rewards compassionate acts is significantly and positively is associated with that hospital’s ratings and likelihood of patients recommending it.
How does the Society of Vascular Surgery, or any professional medical/nursing society for that matter, fit into this model?
We propose that the SVS find ways to empower their members to be agents for culture change within their own health care organizations. How might this be done:
- Teach organizational leadership skills, starting with the SVS Board of Directors, the presidential line, and the chairs of committees. Offer leadership courses at the Annual Meeting.
- Develop a community of caregivers committed to creating a compassionate collaborative culture. The SVS is a founding member of the Schwartz Center Healthcare Society Leadership Council, and you, as members of the SVS benefit from reduced registration at the Annual Compassion in Action Healthcare Conference, June 24-27, 2017 in Boston. (http://compassioninactionconference.org) This conference is designed to be highly experiential, using a hands-on “how to do it” model.
- The SVS should make improving the overall wellness of its members a specific goal and find specific metrics to monitor our progress towards this goal. Members can be provided with the tools to identify, monitor, and measure burnout and compassion. Each committee and council of the SVS can reexamine their objectives through the lens of reducing burnout and improving the wellness of vascular surgeons.
- Provide members with evidence-based programs that build personal resilience. This will not be a successful initiative unless our surgeons recognize and acknowledge the symptoms of burnout, and are willing to admit vulnerability. Without doing so, it is difficult to reach out for help.
- Redesign postgraduate resident and fellowship education. Standardizing clinical care may reduce variation and promote efficiency. However, when processes such as time-limited appointment scheduling, EMR templates, and protocols that drive physician-patient interactions are embedded in Resident and Fellowship education, the result may well be inflexibility in practice, reduced face time with patients, and interactions that lack compassion; all leading to burnout. Graduate Medical Education leaders must develop programs that support the learner’s ability to connect with patients and families, cultivate and role-model skills and behaviors that strengthen compassionate interactions, and strive to develop clinical practice models that increase Resident and Fellow work control autonomy.
The SVS should work proactively to optimize workload, fairness, and reward on a larger scale for its members as it relates to the EMR, reimbursement, and systems coverage. While we may be relatively small in size, as leaders, we are perfectly poised to address these larger, global issues. Perhaps working within the current system (i.e., PAC and APM task force) and considering innovative solutions at a national leadership scale, the SVS can direct real change!
Changing culture is not easy, nor quick, nor does it have an easy-to-follow blueprint. The first step is recognizing the need. The second is taking a leadership role. The third is thinking deeply about implementation.
*The authors extend their thanks and appreciation for the guidance, resources and support of Michael Goldberg, MD, scholar in residence, Schwartz Center for Compassionate Care, Boston and clinical professor of orthopedics at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
REFERENCES
1. J Managerial Psychol. (2007) 22:309-28
2. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2012) 35:1-23
3. Medicine. (2016) 44:583-5
4. J Health Organization Manag. (2015) 29:973-87
5. De Zulueta P Developing compassionate leadership in health care: an integrative review. J Healthcare Leadership. (2016) 8:1-10
6. Dolan ED, Morh D, Lempa M et al. Using a single item to measure burnout in primary care staff: A psychometry evaluation. J Gen Intern Med. (2015) 30:582-7
7. Karasek RA Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job design. Administrative Sciences Quarterly (1979) 24: 285-308
8. Lee VS, Miller T, Daniels C, et al. Creating the exceptional patient experience in one academic health system. Acad Med. (2016) 91:338-44
9. Linzer M, Levine R, Meltzer D, et al. 10 bold steps to prevent burnout in general internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 29:18-20
10. Lown BA, Manning CF The Schwartz Center Rounds: Evaluation of an interdisciplinary approach to enhancing patient-centered communication, teamwork, and provider support. Acad Med. (2010) 85:1073-81
11. Lown BA, Muncer SJ, Chadwick R Can compassionate healthcare be measured? The Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale. Patient Education and Counseling (2015) 98:1005-10
12. Lown BA, McIntosh S, Gaines ME, et. al. Integrating compassionate collaborative care (“the Triple C”) into health professional education to advance the triple aim of health care. Acad Med (2016) 91:1-7
13. Lown BA A social neuroscience-informed model for teaching and practicing compassion in health care. Medical Education (2016) 50: 332-342
14. Maslach C, Schaufeli WG, Leiter MP Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol (2001) 52:397-422
15. McClelland LE, Vogus TJ Compassion practices and HCAHPS: Does rewarding and supporting workplace compassion influence patient perceptions? HSR: Health Serv Res. (2014) 49:1670-83
16. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH Executive leadership and physician well-being: Nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 6:1-18
17. Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye LN, West CP Addressing physician burnout: the way forward. JAMA (2017) 317:901-2
18. Singer T, Klimecki OM Empathy and compassion Curr Biol. (2014) 24: R875-8
19. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Satele DV et. al. Concurrent validity of single-item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization in burnout assessment. J Gen Intern Med. (2012) 27:1445-52
20. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, et al. Interventions to address and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272-81
21. Wuest TK, Goldberg MJ, Kelly JD Clinical faceoff: Physician burnout-Fact, fantasy, or the fourth component of the triple aim? Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) doi: 10.1007/5-11999-016-5193-5
Last month, we introduced the epidemic of burnout and the adverse consequences for both our vascular surgery patients and ourselves. Today we will outline a framework for addressing these issues. The foundation of this framework is informed by the social and neurosciences.
From the perspective of the social scientist: Christina Maslach, the originator of the widely used Maslach Burnout Inventory, theorized that burnout arises from a chronic mismatch between people and their work setting in some or all of the following domains: Workload (too much, wrong kind); control (lack of autonomy, or insufficient control over resources); reward (insufficient financial or social rewards commensurate with achievements); community (loss of positive connection with others); fairness (lack of perceived fairness, inequity of work, pay, or promotion); and values (conflict of personal and organizational values). The reality of practicing medicine in today’s business milieu – of achieving service efficiencies by meeting performance targets – brings many of these mismatches into sharp focus.
From the perspective of the neuroscientist: Recent advances, including functional MRI, have demonstrated that the human brain is hard wired for compassion. Compassion is the deep feeling that arises when confronted with another’s suffering, coupled with a strong desire to alleviate that suffering. There are at least two neural pathways: one activated during empathy, having us experience another’s pain; and the other activated during compassion, resulting in our sense of reward. Thus, burnout is thought to occur when you know what your patient needs but you are unable to deliver it. Compassionate medical care is purposeful work, which promotes a sense of reward and mitigates burnout.
Because burnout affects all caregivers (anyone who touches the patient), a successful program addressing workforce well-being must be comprehensive and organization wide, similar to successful patient safety, CPI [continuous process improvement] and LEAN [Six Sigma] initiatives.
There are no shortcuts. Creating a culture of compassionate, collaborative care requires an understanding of the interrelationships between the individual provider, the unit or team, and organizational leadership.
1) The individual provider: There is evidence to support the use of programs that build personal resilience. A recently published meta-analysis by West and colleagues concluded that while no specific physician burnout intervention has been shown to be better than other types of interventions, mindfulness, stress management, and small-group discussions can be effective approaches to reducing burnout scores. Strategies to build individual resilience, such as mindfulness and meditation, are easy to teach but place the burden for success on the individual. No amount of resilience can withstand an unsupportive or toxic workplace environment, so both individual and organizational strategies in combination are necessary.
2) The unit or team: Scheduling time for open and honest discussion of social and emotional issues that arise in caring for patients helps nourish caregiver to caregiver compassion. The Schwartz Center for Compassionate Healthcare is a national nonprofit leading the movement to bring compassion to every patient-caregiver interaction. More than 425 health care organization are Schwartz Center members and conduct Schwartz Rounds™ to bring doctors, nurses, and other caregivers together to discuss the human side of health care. (www.theschwartzcenter.org). Team member to team member support is essential for navigating the stressors of practice. With having lunch in front of your computer being the norm, and the disappearance of traditional spaces for colleagues to connect (for example, nurses’ lounge, physician dining rooms), the opportunity for caregivers to have a safe place to escape, a place to have their own humanity reaffirmed, a place to offer support to their peers, has been eliminated.
3) Organizational Leadership: Making compassion a core value, articulating it, and establishing metrics whereby it can be measured, is a good start. The barriers to a culture of compassion are related to our systems of care. There are burgeoning administrative and documentation tasks to be performed, and productivity expectations that turn our clinics and hospitals into assembly lines. No, we cannot expect the EMR [electronic medical records] to be eliminated, but workforce well-being cannot be sustainable in the context of inadequate resources. A culture of compassionate collaborative care requires programs and policies that are implemented by the organization itself. Examples of organization-wide initiatives that support workforce well-being and provider engagement include: screening for caregiver burnout, establishing policies for managing adverse events with an eye toward the second victim, and most importantly, supporting systems that preserve work control autonomy of physicians and nurses in clinical settings. The business sector has long recognized that workplace stress is a function of how demanding a person’s job is and how much control that person has over his or her responsibilities. The business community has also recognized that the experience of the worker (provider) drives the experience of the customer (patient). In a study of hospital compassionate practices and HCAHPS [the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems], McClelland and Vogus reported that how well a hospital compassionately supports it employees and rewards compassionate acts is significantly and positively is associated with that hospital’s ratings and likelihood of patients recommending it.
How does the Society of Vascular Surgery, or any professional medical/nursing society for that matter, fit into this model?
We propose that the SVS find ways to empower their members to be agents for culture change within their own health care organizations. How might this be done:
- Teach organizational leadership skills, starting with the SVS Board of Directors, the presidential line, and the chairs of committees. Offer leadership courses at the Annual Meeting.
- Develop a community of caregivers committed to creating a compassionate collaborative culture. The SVS is a founding member of the Schwartz Center Healthcare Society Leadership Council, and you, as members of the SVS benefit from reduced registration at the Annual Compassion in Action Healthcare Conference, June 24-27, 2017 in Boston. (http://compassioninactionconference.org) This conference is designed to be highly experiential, using a hands-on “how to do it” model.
- The SVS should make improving the overall wellness of its members a specific goal and find specific metrics to monitor our progress towards this goal. Members can be provided with the tools to identify, monitor, and measure burnout and compassion. Each committee and council of the SVS can reexamine their objectives through the lens of reducing burnout and improving the wellness of vascular surgeons.
- Provide members with evidence-based programs that build personal resilience. This will not be a successful initiative unless our surgeons recognize and acknowledge the symptoms of burnout, and are willing to admit vulnerability. Without doing so, it is difficult to reach out for help.
- Redesign postgraduate resident and fellowship education. Standardizing clinical care may reduce variation and promote efficiency. However, when processes such as time-limited appointment scheduling, EMR templates, and protocols that drive physician-patient interactions are embedded in Resident and Fellowship education, the result may well be inflexibility in practice, reduced face time with patients, and interactions that lack compassion; all leading to burnout. Graduate Medical Education leaders must develop programs that support the learner’s ability to connect with patients and families, cultivate and role-model skills and behaviors that strengthen compassionate interactions, and strive to develop clinical practice models that increase Resident and Fellow work control autonomy.
The SVS should work proactively to optimize workload, fairness, and reward on a larger scale for its members as it relates to the EMR, reimbursement, and systems coverage. While we may be relatively small in size, as leaders, we are perfectly poised to address these larger, global issues. Perhaps working within the current system (i.e., PAC and APM task force) and considering innovative solutions at a national leadership scale, the SVS can direct real change!
Changing culture is not easy, nor quick, nor does it have an easy-to-follow blueprint. The first step is recognizing the need. The second is taking a leadership role. The third is thinking deeply about implementation.
*The authors extend their thanks and appreciation for the guidance, resources and support of Michael Goldberg, MD, scholar in residence, Schwartz Center for Compassionate Care, Boston and clinical professor of orthopedics at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
REFERENCES
1. J Managerial Psychol. (2007) 22:309-28
2. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2012) 35:1-23
3. Medicine. (2016) 44:583-5
4. J Health Organization Manag. (2015) 29:973-87
5. De Zulueta P Developing compassionate leadership in health care: an integrative review. J Healthcare Leadership. (2016) 8:1-10
6. Dolan ED, Morh D, Lempa M et al. Using a single item to measure burnout in primary care staff: A psychometry evaluation. J Gen Intern Med. (2015) 30:582-7
7. Karasek RA Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job design. Administrative Sciences Quarterly (1979) 24: 285-308
8. Lee VS, Miller T, Daniels C, et al. Creating the exceptional patient experience in one academic health system. Acad Med. (2016) 91:338-44
9. Linzer M, Levine R, Meltzer D, et al. 10 bold steps to prevent burnout in general internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 29:18-20
10. Lown BA, Manning CF The Schwartz Center Rounds: Evaluation of an interdisciplinary approach to enhancing patient-centered communication, teamwork, and provider support. Acad Med. (2010) 85:1073-81
11. Lown BA, Muncer SJ, Chadwick R Can compassionate healthcare be measured? The Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale. Patient Education and Counseling (2015) 98:1005-10
12. Lown BA, McIntosh S, Gaines ME, et. al. Integrating compassionate collaborative care (“the Triple C”) into health professional education to advance the triple aim of health care. Acad Med (2016) 91:1-7
13. Lown BA A social neuroscience-informed model for teaching and practicing compassion in health care. Medical Education (2016) 50: 332-342
14. Maslach C, Schaufeli WG, Leiter MP Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol (2001) 52:397-422
15. McClelland LE, Vogus TJ Compassion practices and HCAHPS: Does rewarding and supporting workplace compassion influence patient perceptions? HSR: Health Serv Res. (2014) 49:1670-83
16. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH Executive leadership and physician well-being: Nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 6:1-18
17. Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye LN, West CP Addressing physician burnout: the way forward. JAMA (2017) 317:901-2
18. Singer T, Klimecki OM Empathy and compassion Curr Biol. (2014) 24: R875-8
19. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Satele DV et. al. Concurrent validity of single-item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization in burnout assessment. J Gen Intern Med. (2012) 27:1445-52
20. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, et al. Interventions to address and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272-81
21. Wuest TK, Goldberg MJ, Kelly JD Clinical faceoff: Physician burnout-Fact, fantasy, or the fourth component of the triple aim? Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) doi: 10.1007/5-11999-016-5193-5
Last month, we introduced the epidemic of burnout and the adverse consequences for both our vascular surgery patients and ourselves. Today we will outline a framework for addressing these issues. The foundation of this framework is informed by the social and neurosciences.
From the perspective of the social scientist: Christina Maslach, the originator of the widely used Maslach Burnout Inventory, theorized that burnout arises from a chronic mismatch between people and their work setting in some or all of the following domains: Workload (too much, wrong kind); control (lack of autonomy, or insufficient control over resources); reward (insufficient financial or social rewards commensurate with achievements); community (loss of positive connection with others); fairness (lack of perceived fairness, inequity of work, pay, or promotion); and values (conflict of personal and organizational values). The reality of practicing medicine in today’s business milieu – of achieving service efficiencies by meeting performance targets – brings many of these mismatches into sharp focus.
From the perspective of the neuroscientist: Recent advances, including functional MRI, have demonstrated that the human brain is hard wired for compassion. Compassion is the deep feeling that arises when confronted with another’s suffering, coupled with a strong desire to alleviate that suffering. There are at least two neural pathways: one activated during empathy, having us experience another’s pain; and the other activated during compassion, resulting in our sense of reward. Thus, burnout is thought to occur when you know what your patient needs but you are unable to deliver it. Compassionate medical care is purposeful work, which promotes a sense of reward and mitigates burnout.
Because burnout affects all caregivers (anyone who touches the patient), a successful program addressing workforce well-being must be comprehensive and organization wide, similar to successful patient safety, CPI [continuous process improvement] and LEAN [Six Sigma] initiatives.
There are no shortcuts. Creating a culture of compassionate, collaborative care requires an understanding of the interrelationships between the individual provider, the unit or team, and organizational leadership.
1) The individual provider: There is evidence to support the use of programs that build personal resilience. A recently published meta-analysis by West and colleagues concluded that while no specific physician burnout intervention has been shown to be better than other types of interventions, mindfulness, stress management, and small-group discussions can be effective approaches to reducing burnout scores. Strategies to build individual resilience, such as mindfulness and meditation, are easy to teach but place the burden for success on the individual. No amount of resilience can withstand an unsupportive or toxic workplace environment, so both individual and organizational strategies in combination are necessary.
2) The unit or team: Scheduling time for open and honest discussion of social and emotional issues that arise in caring for patients helps nourish caregiver to caregiver compassion. The Schwartz Center for Compassionate Healthcare is a national nonprofit leading the movement to bring compassion to every patient-caregiver interaction. More than 425 health care organization are Schwartz Center members and conduct Schwartz Rounds™ to bring doctors, nurses, and other caregivers together to discuss the human side of health care. (www.theschwartzcenter.org). Team member to team member support is essential for navigating the stressors of practice. With having lunch in front of your computer being the norm, and the disappearance of traditional spaces for colleagues to connect (for example, nurses’ lounge, physician dining rooms), the opportunity for caregivers to have a safe place to escape, a place to have their own humanity reaffirmed, a place to offer support to their peers, has been eliminated.
3) Organizational Leadership: Making compassion a core value, articulating it, and establishing metrics whereby it can be measured, is a good start. The barriers to a culture of compassion are related to our systems of care. There are burgeoning administrative and documentation tasks to be performed, and productivity expectations that turn our clinics and hospitals into assembly lines. No, we cannot expect the EMR [electronic medical records] to be eliminated, but workforce well-being cannot be sustainable in the context of inadequate resources. A culture of compassionate collaborative care requires programs and policies that are implemented by the organization itself. Examples of organization-wide initiatives that support workforce well-being and provider engagement include: screening for caregiver burnout, establishing policies for managing adverse events with an eye toward the second victim, and most importantly, supporting systems that preserve work control autonomy of physicians and nurses in clinical settings. The business sector has long recognized that workplace stress is a function of how demanding a person’s job is and how much control that person has over his or her responsibilities. The business community has also recognized that the experience of the worker (provider) drives the experience of the customer (patient). In a study of hospital compassionate practices and HCAHPS [the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems], McClelland and Vogus reported that how well a hospital compassionately supports it employees and rewards compassionate acts is significantly and positively is associated with that hospital’s ratings and likelihood of patients recommending it.
How does the Society of Vascular Surgery, or any professional medical/nursing society for that matter, fit into this model?
We propose that the SVS find ways to empower their members to be agents for culture change within their own health care organizations. How might this be done:
- Teach organizational leadership skills, starting with the SVS Board of Directors, the presidential line, and the chairs of committees. Offer leadership courses at the Annual Meeting.
- Develop a community of caregivers committed to creating a compassionate collaborative culture. The SVS is a founding member of the Schwartz Center Healthcare Society Leadership Council, and you, as members of the SVS benefit from reduced registration at the Annual Compassion in Action Healthcare Conference, June 24-27, 2017 in Boston. (http://compassioninactionconference.org) This conference is designed to be highly experiential, using a hands-on “how to do it” model.
- The SVS should make improving the overall wellness of its members a specific goal and find specific metrics to monitor our progress towards this goal. Members can be provided with the tools to identify, monitor, and measure burnout and compassion. Each committee and council of the SVS can reexamine their objectives through the lens of reducing burnout and improving the wellness of vascular surgeons.
- Provide members with evidence-based programs that build personal resilience. This will not be a successful initiative unless our surgeons recognize and acknowledge the symptoms of burnout, and are willing to admit vulnerability. Without doing so, it is difficult to reach out for help.
- Redesign postgraduate resident and fellowship education. Standardizing clinical care may reduce variation and promote efficiency. However, when processes such as time-limited appointment scheduling, EMR templates, and protocols that drive physician-patient interactions are embedded in Resident and Fellowship education, the result may well be inflexibility in practice, reduced face time with patients, and interactions that lack compassion; all leading to burnout. Graduate Medical Education leaders must develop programs that support the learner’s ability to connect with patients and families, cultivate and role-model skills and behaviors that strengthen compassionate interactions, and strive to develop clinical practice models that increase Resident and Fellow work control autonomy.
The SVS should work proactively to optimize workload, fairness, and reward on a larger scale for its members as it relates to the EMR, reimbursement, and systems coverage. While we may be relatively small in size, as leaders, we are perfectly poised to address these larger, global issues. Perhaps working within the current system (i.e., PAC and APM task force) and considering innovative solutions at a national leadership scale, the SVS can direct real change!
Changing culture is not easy, nor quick, nor does it have an easy-to-follow blueprint. The first step is recognizing the need. The second is taking a leadership role. The third is thinking deeply about implementation.
*The authors extend their thanks and appreciation for the guidance, resources and support of Michael Goldberg, MD, scholar in residence, Schwartz Center for Compassionate Care, Boston and clinical professor of orthopedics at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
REFERENCES
1. J Managerial Psychol. (2007) 22:309-28
2. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2012) 35:1-23
3. Medicine. (2016) 44:583-5
4. J Health Organization Manag. (2015) 29:973-87
5. De Zulueta P Developing compassionate leadership in health care: an integrative review. J Healthcare Leadership. (2016) 8:1-10
6. Dolan ED, Morh D, Lempa M et al. Using a single item to measure burnout in primary care staff: A psychometry evaluation. J Gen Intern Med. (2015) 30:582-7
7. Karasek RA Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job design. Administrative Sciences Quarterly (1979) 24: 285-308
8. Lee VS, Miller T, Daniels C, et al. Creating the exceptional patient experience in one academic health system. Acad Med. (2016) 91:338-44
9. Linzer M, Levine R, Meltzer D, et al. 10 bold steps to prevent burnout in general internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 29:18-20
10. Lown BA, Manning CF The Schwartz Center Rounds: Evaluation of an interdisciplinary approach to enhancing patient-centered communication, teamwork, and provider support. Acad Med. (2010) 85:1073-81
11. Lown BA, Muncer SJ, Chadwick R Can compassionate healthcare be measured? The Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale. Patient Education and Counseling (2015) 98:1005-10
12. Lown BA, McIntosh S, Gaines ME, et. al. Integrating compassionate collaborative care (“the Triple C”) into health professional education to advance the triple aim of health care. Acad Med (2016) 91:1-7
13. Lown BA A social neuroscience-informed model for teaching and practicing compassion in health care. Medical Education (2016) 50: 332-342
14. Maslach C, Schaufeli WG, Leiter MP Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol (2001) 52:397-422
15. McClelland LE, Vogus TJ Compassion practices and HCAHPS: Does rewarding and supporting workplace compassion influence patient perceptions? HSR: Health Serv Res. (2014) 49:1670-83
16. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH Executive leadership and physician well-being: Nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 6:1-18
17. Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye LN, West CP Addressing physician burnout: the way forward. JAMA (2017) 317:901-2
18. Singer T, Klimecki OM Empathy and compassion Curr Biol. (2014) 24: R875-8
19. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Satele DV et. al. Concurrent validity of single-item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization in burnout assessment. J Gen Intern Med. (2012) 27:1445-52
20. West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, et al. Interventions to address and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272-81
21. Wuest TK, Goldberg MJ, Kelly JD Clinical faceoff: Physician burnout-Fact, fantasy, or the fourth component of the triple aim? Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) doi: 10.1007/5-11999-016-5193-5
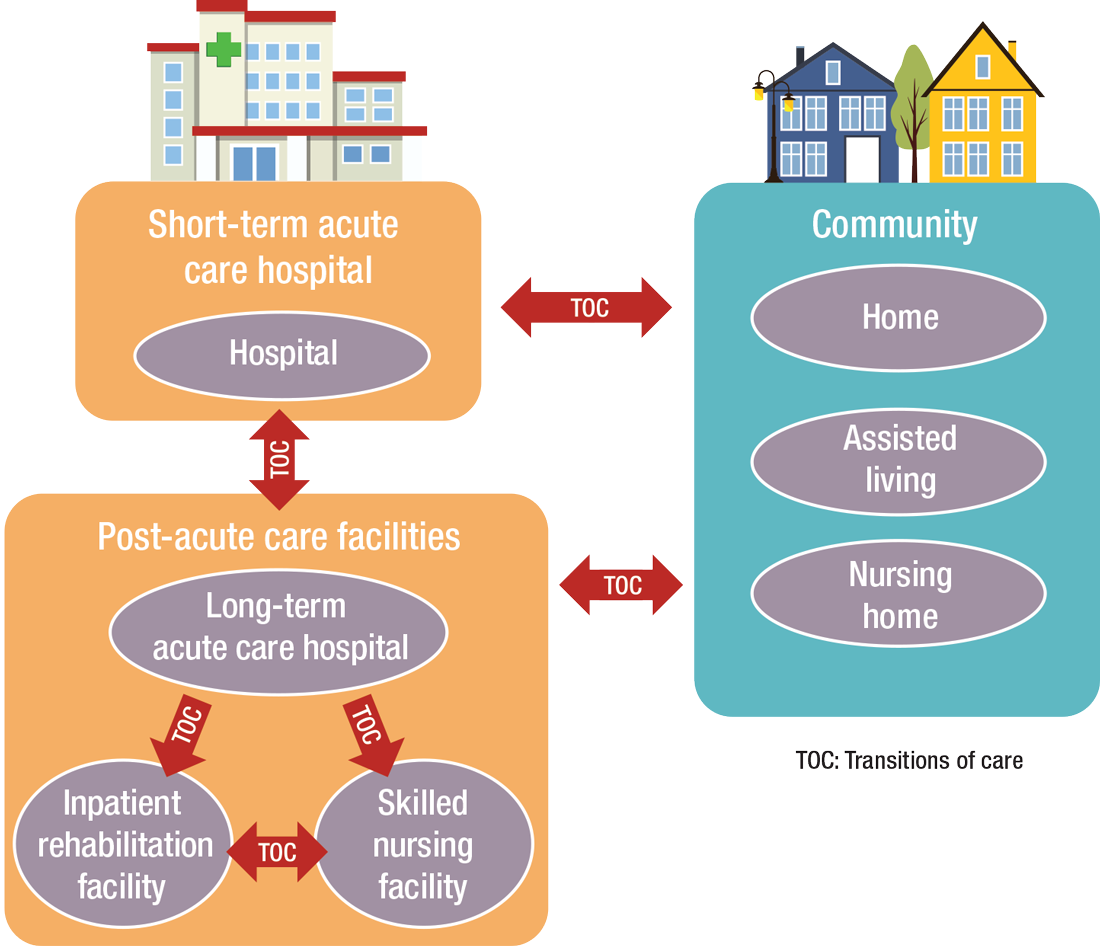
Ready for post-acute care?
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”
Hospitalists can fill a need

More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
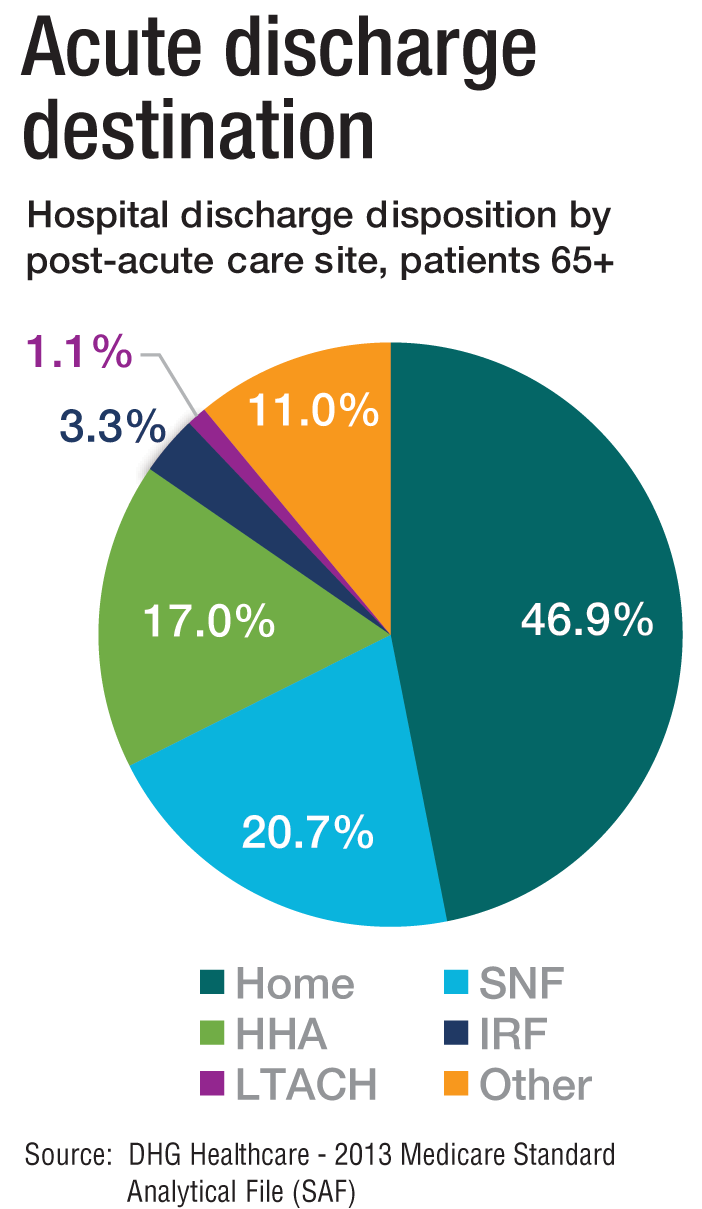
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
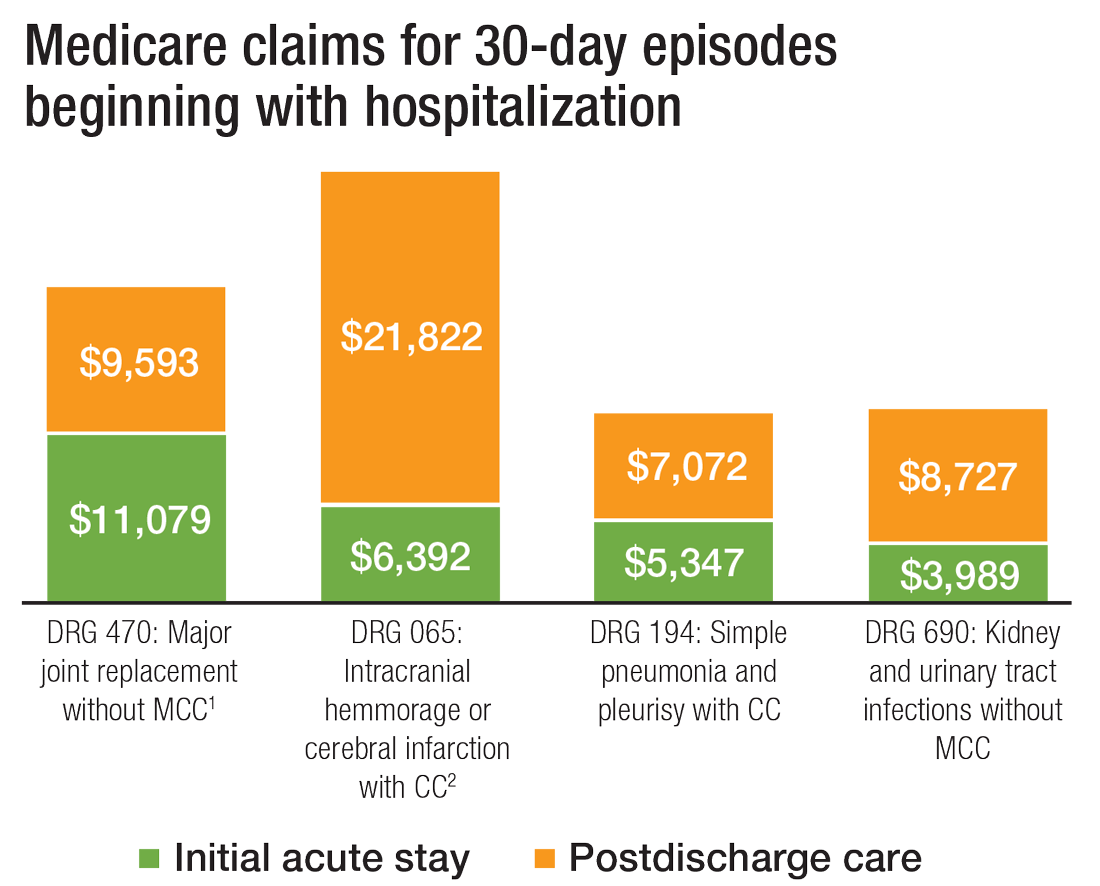
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”

Hospitalists can fill a need

More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”

Hospitalists can fill a need

More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
‘Cancer Doesn’t Wait’: How Prior Authorization Harms Care
Fantine Giap, MD, sat across from a 21-year-old with a rare sarcoma at the base of her skull.
Despite the large tumor, nestled in a sensitive area, the Boston-based radiation oncologist could envision a bright future for her patient.
She and the other members of the patient’s care team had an impressive cancer-fighting arsenal at her fingertips. The team had recommended surgery, followed by proton therapy — a sophisticated tool able to deliver concentrated, razor-focused radiation to the once apple-sized growth, while sparing the fragile brain stem, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Surgery went as planned. But as the days and weeks wore on and insurance prior authorization for the proton therapy never came, the tumor roared back, leading to more surgeries and more complications. Ultimately, the young woman needed a tracheostomy and a feeding tube.
By the time insurance said yes, more than 1 year from her initial visit, the future the team had envisioned seemed out of reach.
“Unfortunately for this patient, it went from a potentially curable situation to a likely not curable situation,” recalled Dr. Giap, a clinician at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I wanted to cry every day that she waited.’’
While a stark example, such insurance delays are not uncommon, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Other studies have found that number to be even higher, with more than 86% of prior authorization requests ultimately approved with few changes.
‘’It gives you the idea that this entire process might be a little futile — that it’s just wasting people’s time,’’ said Fumiko Chino, MD, coauthor on the JAMA study and now an assistant professor in radiation oncology at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. ‘’The problem is cancer doesn’t wait for bureaucracy.’’
Barriers at Every Step
As Dr. Chino and her study coauthors explained, advancements like intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery have allowed a new generation of specialists to treat previously untreatable cancers in ways that maximize tumor-killing power while minimizing collateral damage. But these tools require sophisticated planning, imaging, simulations and execution — all of which are subject to increased insurance scrutiny.
‘’We face barriers pretty much every step of the way for every patient,’’ said Dr. Chino.
To investigate how such barriers impact care, Dr. Chino and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — where she worked until July — looked at 206 cases in which payers denied prior authorization for radiation therapy from November 1, 2021 to December 8, 2022.
The team found that 62% were ultimately approved without any change to technique or dose, while 28% were authorized, but with lower doses or less sophisticated techniques. Four people, however, never got authorization at all — three abandoned treatment altogether, and one sought treatment at another institution.
Treatment delays ranged from 1 day to 49 days. Eighty-three patients died.
Would some of them have lived if it weren’t for prior authorization?
Dr. Chino cannot say for sure, but did note that certain cancers, like cervical cancer, can grow so quickly that every day of delayed treatment makes them harder to control.
Patients with metastatic or late-stage cancers are often denied more aggressive treatments by insurers who, in essence, “assume that they are going to die from their disease anyway,” Dr. Chino said.
She views this as tragically shortsighted.
‘’There’s actually a strong body of evidence to show that if you treat even metastatic stage IV diseases aggressively, you can prolong not just quality of life but also quantity,’’ she said.
In cases where the cancer is more localized and insurance mandates lower doses or cheaper techniques, the consequences can be equally heartbreaking.
‘’It’s like saying instead of taking an extra-strength Tylenol you can only have a baby aspirin,’’ she said. ‘’Their pain is less likely to be controlled, their disease is less likely to be controlled, and they are more likely to need retreatment.’’
Prior authorization delays can also significantly stress patients at the most vulnerable point of their lives.
In another recent study, Dr. Chino found that 69% of patients with cancer reported prior authorization-related delays in care, with one-third waiting a month or longer. One in five never got the care their doctors recommended, and 20% reported spending more than 11 hours on the phone haggling with their insurance companies.
Most patients rated the process as ‘’bad’’ or ‘’horrible,’’ and said it fueled anxiety.
Such delays can be hard on clinicians and the healthcare system too.
One 2022 study found that a typical academic radiation oncology practice spent about a half-million dollars per year seeking insurance preauthorization. Nationally, that number exceeds $40 million.
Then there is the burnout factor.
Dr. Giap, an early-career physician who specializes in rare, aggressive sarcomas, works at an institution that helped pioneer proton therapy. She says it pains her to tell a desperate patient, like the 21-year-old, who has traveled to her from out of state that they have to wait.
‘’Knowing that the majority of the cases are ultimately approved and that this wait is often unnecessary makes it even tougher,’’ she said.
Dr. Chino, a breast cancer specialist, has taken to warning patients before the alarming insurance letter arrives in the mail that their insurance may delay authorizing their care. But she tells patients that she will do everything she can to fight for them and develops a back-up plan to pivot to quickly, if needed.
‘’No one goes into medicine to spend their time talking to insurance companies,’’ said Dr. Chino.
The national trade group, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP), did not return repeated requests for an interview for this story. But their official position, as stated on their website, is that “prior authorization is one of many tools health insurance providers use to promote safe, timely, evidence-based, affordable, and efficient care.”
Both Dr. Giap and Dr. Chino believe that prior authorization was developed with good intentions: to save healthcare costs and rein in treatments that don’t necessarily benefit patients.
But, in their specialty, the burden has proliferated to a point that Dr. Chino characterizes as ‘’unconscionable.’’
She believes that policy changes like the proposed Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act — which would require real-time decisions for procedures that are routinely approved — could go a long way in improving patient care.
Meanwhile, Dr. Giap said, more research and professional guidelines are necessary to bolster insurance company confidence in newer technologies, particularly for rare cancers.
Her patient ultimately got her proton therapy and is ‘’doing relatively well, all things considered.’’
But not all the stories end like this.
Dr. Chino will never forget a patient with a cancer growing so rapidly she could see it protruding through her chest wall. She called for immediate surgery and a PET scan to see where else in the body cancer may be brewing. But due to prior authorization delays, that scan — which ultimately showed the cancer had spread — was delayed for weeks.
If the team had had those imaging results upfront, she said, they would have recommended a completely different course of treatment.
And her patient might be alive today.
‘’Unfortunately,” Dr. Chino said, “the people with the very worst prior authorization stories aren’t here anymore to tell you about them.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fantine Giap, MD, sat across from a 21-year-old with a rare sarcoma at the base of her skull.
Despite the large tumor, nestled in a sensitive area, the Boston-based radiation oncologist could envision a bright future for her patient.
She and the other members of the patient’s care team had an impressive cancer-fighting arsenal at her fingertips. The team had recommended surgery, followed by proton therapy — a sophisticated tool able to deliver concentrated, razor-focused radiation to the once apple-sized growth, while sparing the fragile brain stem, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Surgery went as planned. But as the days and weeks wore on and insurance prior authorization for the proton therapy never came, the tumor roared back, leading to more surgeries and more complications. Ultimately, the young woman needed a tracheostomy and a feeding tube.
By the time insurance said yes, more than 1 year from her initial visit, the future the team had envisioned seemed out of reach.
“Unfortunately for this patient, it went from a potentially curable situation to a likely not curable situation,” recalled Dr. Giap, a clinician at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I wanted to cry every day that she waited.’’
While a stark example, such insurance delays are not uncommon, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Other studies have found that number to be even higher, with more than 86% of prior authorization requests ultimately approved with few changes.
‘’It gives you the idea that this entire process might be a little futile — that it’s just wasting people’s time,’’ said Fumiko Chino, MD, coauthor on the JAMA study and now an assistant professor in radiation oncology at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. ‘’The problem is cancer doesn’t wait for bureaucracy.’’
Barriers at Every Step
As Dr. Chino and her study coauthors explained, advancements like intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery have allowed a new generation of specialists to treat previously untreatable cancers in ways that maximize tumor-killing power while minimizing collateral damage. But these tools require sophisticated planning, imaging, simulations and execution — all of which are subject to increased insurance scrutiny.
‘’We face barriers pretty much every step of the way for every patient,’’ said Dr. Chino.
To investigate how such barriers impact care, Dr. Chino and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — where she worked until July — looked at 206 cases in which payers denied prior authorization for radiation therapy from November 1, 2021 to December 8, 2022.
The team found that 62% were ultimately approved without any change to technique or dose, while 28% were authorized, but with lower doses or less sophisticated techniques. Four people, however, never got authorization at all — three abandoned treatment altogether, and one sought treatment at another institution.
Treatment delays ranged from 1 day to 49 days. Eighty-three patients died.
Would some of them have lived if it weren’t for prior authorization?
Dr. Chino cannot say for sure, but did note that certain cancers, like cervical cancer, can grow so quickly that every day of delayed treatment makes them harder to control.
Patients with metastatic or late-stage cancers are often denied more aggressive treatments by insurers who, in essence, “assume that they are going to die from their disease anyway,” Dr. Chino said.
She views this as tragically shortsighted.
‘’There’s actually a strong body of evidence to show that if you treat even metastatic stage IV diseases aggressively, you can prolong not just quality of life but also quantity,’’ she said.
In cases where the cancer is more localized and insurance mandates lower doses or cheaper techniques, the consequences can be equally heartbreaking.
‘’It’s like saying instead of taking an extra-strength Tylenol you can only have a baby aspirin,’’ she said. ‘’Their pain is less likely to be controlled, their disease is less likely to be controlled, and they are more likely to need retreatment.’’
Prior authorization delays can also significantly stress patients at the most vulnerable point of their lives.
In another recent study, Dr. Chino found that 69% of patients with cancer reported prior authorization-related delays in care, with one-third waiting a month or longer. One in five never got the care their doctors recommended, and 20% reported spending more than 11 hours on the phone haggling with their insurance companies.
Most patients rated the process as ‘’bad’’ or ‘’horrible,’’ and said it fueled anxiety.
Such delays can be hard on clinicians and the healthcare system too.
One 2022 study found that a typical academic radiation oncology practice spent about a half-million dollars per year seeking insurance preauthorization. Nationally, that number exceeds $40 million.
Then there is the burnout factor.
Dr. Giap, an early-career physician who specializes in rare, aggressive sarcomas, works at an institution that helped pioneer proton therapy. She says it pains her to tell a desperate patient, like the 21-year-old, who has traveled to her from out of state that they have to wait.
‘’Knowing that the majority of the cases are ultimately approved and that this wait is often unnecessary makes it even tougher,’’ she said.
Dr. Chino, a breast cancer specialist, has taken to warning patients before the alarming insurance letter arrives in the mail that their insurance may delay authorizing their care. But she tells patients that she will do everything she can to fight for them and develops a back-up plan to pivot to quickly, if needed.
‘’No one goes into medicine to spend their time talking to insurance companies,’’ said Dr. Chino.
The national trade group, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP), did not return repeated requests for an interview for this story. But their official position, as stated on their website, is that “prior authorization is one of many tools health insurance providers use to promote safe, timely, evidence-based, affordable, and efficient care.”
Both Dr. Giap and Dr. Chino believe that prior authorization was developed with good intentions: to save healthcare costs and rein in treatments that don’t necessarily benefit patients.
But, in their specialty, the burden has proliferated to a point that Dr. Chino characterizes as ‘’unconscionable.’’
She believes that policy changes like the proposed Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act — which would require real-time decisions for procedures that are routinely approved — could go a long way in improving patient care.
Meanwhile, Dr. Giap said, more research and professional guidelines are necessary to bolster insurance company confidence in newer technologies, particularly for rare cancers.
Her patient ultimately got her proton therapy and is ‘’doing relatively well, all things considered.’’
But not all the stories end like this.
Dr. Chino will never forget a patient with a cancer growing so rapidly she could see it protruding through her chest wall. She called for immediate surgery and a PET scan to see where else in the body cancer may be brewing. But due to prior authorization delays, that scan — which ultimately showed the cancer had spread — was delayed for weeks.
If the team had had those imaging results upfront, she said, they would have recommended a completely different course of treatment.
And her patient might be alive today.
‘’Unfortunately,” Dr. Chino said, “the people with the very worst prior authorization stories aren’t here anymore to tell you about them.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fantine Giap, MD, sat across from a 21-year-old with a rare sarcoma at the base of her skull.
Despite the large tumor, nestled in a sensitive area, the Boston-based radiation oncologist could envision a bright future for her patient.
She and the other members of the patient’s care team had an impressive cancer-fighting arsenal at her fingertips. The team had recommended surgery, followed by proton therapy — a sophisticated tool able to deliver concentrated, razor-focused radiation to the once apple-sized growth, while sparing the fragile brain stem, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Surgery went as planned. But as the days and weeks wore on and insurance prior authorization for the proton therapy never came, the tumor roared back, leading to more surgeries and more complications. Ultimately, the young woman needed a tracheostomy and a feeding tube.
By the time insurance said yes, more than 1 year from her initial visit, the future the team had envisioned seemed out of reach.
“Unfortunately for this patient, it went from a potentially curable situation to a likely not curable situation,” recalled Dr. Giap, a clinician at Massachusetts General Hospital and instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I wanted to cry every day that she waited.’’
While a stark example, such insurance delays are not uncommon, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Other studies have found that number to be even higher, with more than 86% of prior authorization requests ultimately approved with few changes.
‘’It gives you the idea that this entire process might be a little futile — that it’s just wasting people’s time,’’ said Fumiko Chino, MD, coauthor on the JAMA study and now an assistant professor in radiation oncology at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. ‘’The problem is cancer doesn’t wait for bureaucracy.’’
Barriers at Every Step
As Dr. Chino and her study coauthors explained, advancements like intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery have allowed a new generation of specialists to treat previously untreatable cancers in ways that maximize tumor-killing power while minimizing collateral damage. But these tools require sophisticated planning, imaging, simulations and execution — all of which are subject to increased insurance scrutiny.
‘’We face barriers pretty much every step of the way for every patient,’’ said Dr. Chino.
To investigate how such barriers impact care, Dr. Chino and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — where she worked until July — looked at 206 cases in which payers denied prior authorization for radiation therapy from November 1, 2021 to December 8, 2022.
The team found that 62% were ultimately approved without any change to technique or dose, while 28% were authorized, but with lower doses or less sophisticated techniques. Four people, however, never got authorization at all — three abandoned treatment altogether, and one sought treatment at another institution.
Treatment delays ranged from 1 day to 49 days. Eighty-three patients died.
Would some of them have lived if it weren’t for prior authorization?
Dr. Chino cannot say for sure, but did note that certain cancers, like cervical cancer, can grow so quickly that every day of delayed treatment makes them harder to control.
Patients with metastatic or late-stage cancers are often denied more aggressive treatments by insurers who, in essence, “assume that they are going to die from their disease anyway,” Dr. Chino said.
She views this as tragically shortsighted.
‘’There’s actually a strong body of evidence to show that if you treat even metastatic stage IV diseases aggressively, you can prolong not just quality of life but also quantity,’’ she said.
In cases where the cancer is more localized and insurance mandates lower doses or cheaper techniques, the consequences can be equally heartbreaking.
‘’It’s like saying instead of taking an extra-strength Tylenol you can only have a baby aspirin,’’ she said. ‘’Their pain is less likely to be controlled, their disease is less likely to be controlled, and they are more likely to need retreatment.’’
Prior authorization delays can also significantly stress patients at the most vulnerable point of their lives.
In another recent study, Dr. Chino found that 69% of patients with cancer reported prior authorization-related delays in care, with one-third waiting a month or longer. One in five never got the care their doctors recommended, and 20% reported spending more than 11 hours on the phone haggling with their insurance companies.
Most patients rated the process as ‘’bad’’ or ‘’horrible,’’ and said it fueled anxiety.
Such delays can be hard on clinicians and the healthcare system too.
One 2022 study found that a typical academic radiation oncology practice spent about a half-million dollars per year seeking insurance preauthorization. Nationally, that number exceeds $40 million.
Then there is the burnout factor.
Dr. Giap, an early-career physician who specializes in rare, aggressive sarcomas, works at an institution that helped pioneer proton therapy. She says it pains her to tell a desperate patient, like the 21-year-old, who has traveled to her from out of state that they have to wait.
‘’Knowing that the majority of the cases are ultimately approved and that this wait is often unnecessary makes it even tougher,’’ she said.
Dr. Chino, a breast cancer specialist, has taken to warning patients before the alarming insurance letter arrives in the mail that their insurance may delay authorizing their care. But she tells patients that she will do everything she can to fight for them and develops a back-up plan to pivot to quickly, if needed.
‘’No one goes into medicine to spend their time talking to insurance companies,’’ said Dr. Chino.
The national trade group, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP), did not return repeated requests for an interview for this story. But their official position, as stated on their website, is that “prior authorization is one of many tools health insurance providers use to promote safe, timely, evidence-based, affordable, and efficient care.”
Both Dr. Giap and Dr. Chino believe that prior authorization was developed with good intentions: to save healthcare costs and rein in treatments that don’t necessarily benefit patients.
But, in their specialty, the burden has proliferated to a point that Dr. Chino characterizes as ‘’unconscionable.’’
She believes that policy changes like the proposed Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act — which would require real-time decisions for procedures that are routinely approved — could go a long way in improving patient care.
Meanwhile, Dr. Giap said, more research and professional guidelines are necessary to bolster insurance company confidence in newer technologies, particularly for rare cancers.
Her patient ultimately got her proton therapy and is ‘’doing relatively well, all things considered.’’
But not all the stories end like this.
Dr. Chino will never forget a patient with a cancer growing so rapidly she could see it protruding through her chest wall. She called for immediate surgery and a PET scan to see where else in the body cancer may be brewing. But due to prior authorization delays, that scan — which ultimately showed the cancer had spread — was delayed for weeks.
If the team had had those imaging results upfront, she said, they would have recommended a completely different course of treatment.
And her patient might be alive today.
‘’Unfortunately,” Dr. Chino said, “the people with the very worst prior authorization stories aren’t here anymore to tell you about them.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
A Few Rural Towns Are Bucking the Trend and Building New Hospitals
There’s a new morning ritual in Pinedale, Wyoming, a town of about 2000, nestled against the Wind River Mountains.
Friends and neighbors in the oil- and gas-rich community “take their morning coffee and pull up” to watch workers building the county’s first hospital, said Kari DeWitt, the project’s public relations director.
“I think it’s just gratitude,” Ms. DeWitt said.
Sublette County is the only one in Wyoming — where counties span thousands of square miles — without a hospital. The 10-bed, 40,000-square-foot hospital, with a similarly sized attached long-term care facility, is slated to open by the summer of 2025.
Ms. DeWitt, who also is executive director of the Sublette County Health Foundation, has an office at the town’s health clinic with a window view of the construction.
Pinedale’s residents have good reason to be excited. New full-service hospitals with inpatient beds are rare in rural America, where declining population has spurred decades of downsizing and closures. Yet, a few communities in Wyoming and others in Kansas and Georgia are defying the trend.
“To be honest with you, it even seems strange to me,” said Wyoming Hospital Association President Eric Boley. Small rural “hospitals are really struggling all across the country,” he said.
There is no official tally of new hospitals being built in rural America, but industry experts such as Mr. Boley said they’re rare. Typically, health-related construction projects in rural areas are for smaller urgent care centers or stand-alone emergency facilities or are replacements for old hospitals.
About half of rural hospitals lost money in the prior year, according to Chartis, a health analytics and consulting firm. And nearly 150 rural hospitals have closed or converted to smaller operations since 2010, according to data collected by the University of North Carolina’s Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research.
To stem the tide of closures, Congress created a new rural emergency hospital designation that allowed struggling hospitals to close their inpatient units and provide only outpatient and emergency services. Since January 2023, when the program took effect, 32 of the more than 1700 eligible rural hospitals — from Georgia to New Mexico — have joined the program, according to data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Tony Breitlow is healthcare studio director for EUA, which has extensive experience working for rural health care systems. Mr. Breitlow said his national architecture and engineering firm’s work expands, replaces, or revamps older buildings, many of which were constructed during the middle of the last century.
The work, Mr. Breitlow said, is part of health care “systems figuring out how to remain robust and viable.”
Freeman Health System, based in Joplin, Missouri, announced plans last year to build a new 50-bed hospital across the state line in Kansas. Paula Baker, Freeman’s president and chief executive, said the system is building for patients in the southeastern corner of the state who travel 45 minutes or more to its bigger Joplin facilities for care.
Freeman’s new hospital, with construction on the building expected to begin in the spring, will be less than 10 miles away from an older, 64-bed hospital that has existed for decades. Kansas is one of more than a dozen states with no “certificate of need” law that would require health providers to obtain approval from the state before offering new services or building or expanding facilities.
Ms. Baker also said Freeman plans to operate emergency services and a small 10-bed outpost in Fort Scott, Kansas, opening early next year in a corner of a hospital that closed in late 2018. Residents there “cried, they cheered, they hugged me,” Ms. Baker said, adding that the “level of appreciation and gratitude that they felt and they displayed was overwhelming to me.”
Michael Topchik, executive director of the Chartis Center for Rural Health, said regional healthcare systems in the Upper Midwest have been particularly active in competing for patients by, among other things, building new hospitals.
And while private corporate money can drive construction, many rural hospital projects tap government programs, especially those supported by the US Department of Agriculture, Mr. Topchik said. That, he said, “surprises a lot of people.”
Since 2021, the USDA’s rural Community Facilities Programs have awarded $2.24 billion in loans and grants to 68 rural hospitals for work that was not related to an emergency or disaster, according to data analyzed by KFF Health News and confirmed by the agency. The federal program is funded through what is often known as the farm bill, which faces a September congressional renewal deadline.
Nearly all the projects are replacements or expansions and updates of older facilities.
The USDA confirmed that three new or planned Wyoming hospitals received federal funding. Hospital projects in Riverton and Saratoga received loans of $37.2 million and $18.3 million, respectively. Pinedale’s hospital received a $29.2 million loan from the agency.
Wyoming’s new construction is rare in a state where more than 80% of rural hospitals reported losses in the third quarter of 2023, according to Chartis. The state association’s Mr. Boley said he worries about several hospitals that have less than 10 days’ cash on hand “day and night.”
Pinedale’s project loan was approved after the community submitted a feasibility study to the USDA that included local clinics and a long-term care facility. “It’s pretty remote and right up in the mountains,” Mr. Boley said.
Pinedale’s Ms. DeWitt said the community was missing key services, such as blood transfusions, which are often necessary when there is a trauma like a car crash or if a pregnant woman faces severe complications. Local ambulances drove 94,000 miles last year, she said.
Ms. DeWitt began working to raise support for the new hospital after her own pregnancy-related trauma in 2014. She was bleeding heavily and arrived at the local health clinic believing it operated like a hospital.
“It was shocking to hear, ‘No, we’re not a hospital. We can’t do blood transfusions. We’re just going to have to pray you live for the next 45 minutes,’ ” Ms. DeWitt said.
Ms. DeWitt had to be airlifted to Idaho, where she delivered a few minutes after landing. When the hospital financing went on the ballot in 2020, Ms. DeWitt — fully recovered, with healthy grade-schoolers at home — began making five calls a night to rally support for a county tax increase to help fund the hospital.
“By improving health care, I think we improve everybody’s chances of survival. You know, it’s pretty basic,” Ms. DeWitt said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
There’s a new morning ritual in Pinedale, Wyoming, a town of about 2000, nestled against the Wind River Mountains.
Friends and neighbors in the oil- and gas-rich community “take their morning coffee and pull up” to watch workers building the county’s first hospital, said Kari DeWitt, the project’s public relations director.
“I think it’s just gratitude,” Ms. DeWitt said.
Sublette County is the only one in Wyoming — where counties span thousands of square miles — without a hospital. The 10-bed, 40,000-square-foot hospital, with a similarly sized attached long-term care facility, is slated to open by the summer of 2025.
Ms. DeWitt, who also is executive director of the Sublette County Health Foundation, has an office at the town’s health clinic with a window view of the construction.
Pinedale’s residents have good reason to be excited. New full-service hospitals with inpatient beds are rare in rural America, where declining population has spurred decades of downsizing and closures. Yet, a few communities in Wyoming and others in Kansas and Georgia are defying the trend.
“To be honest with you, it even seems strange to me,” said Wyoming Hospital Association President Eric Boley. Small rural “hospitals are really struggling all across the country,” he said.
There is no official tally of new hospitals being built in rural America, but industry experts such as Mr. Boley said they’re rare. Typically, health-related construction projects in rural areas are for smaller urgent care centers or stand-alone emergency facilities or are replacements for old hospitals.
About half of rural hospitals lost money in the prior year, according to Chartis, a health analytics and consulting firm. And nearly 150 rural hospitals have closed or converted to smaller operations since 2010, according to data collected by the University of North Carolina’s Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research.
To stem the tide of closures, Congress created a new rural emergency hospital designation that allowed struggling hospitals to close their inpatient units and provide only outpatient and emergency services. Since January 2023, when the program took effect, 32 of the more than 1700 eligible rural hospitals — from Georgia to New Mexico — have joined the program, according to data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Tony Breitlow is healthcare studio director for EUA, which has extensive experience working for rural health care systems. Mr. Breitlow said his national architecture and engineering firm’s work expands, replaces, or revamps older buildings, many of which were constructed during the middle of the last century.
The work, Mr. Breitlow said, is part of health care “systems figuring out how to remain robust and viable.”
Freeman Health System, based in Joplin, Missouri, announced plans last year to build a new 50-bed hospital across the state line in Kansas. Paula Baker, Freeman’s president and chief executive, said the system is building for patients in the southeastern corner of the state who travel 45 minutes or more to its bigger Joplin facilities for care.
Freeman’s new hospital, with construction on the building expected to begin in the spring, will be less than 10 miles away from an older, 64-bed hospital that has existed for decades. Kansas is one of more than a dozen states with no “certificate of need” law that would require health providers to obtain approval from the state before offering new services or building or expanding facilities.
Ms. Baker also said Freeman plans to operate emergency services and a small 10-bed outpost in Fort Scott, Kansas, opening early next year in a corner of a hospital that closed in late 2018. Residents there “cried, they cheered, they hugged me,” Ms. Baker said, adding that the “level of appreciation and gratitude that they felt and they displayed was overwhelming to me.”
Michael Topchik, executive director of the Chartis Center for Rural Health, said regional healthcare systems in the Upper Midwest have been particularly active in competing for patients by, among other things, building new hospitals.
And while private corporate money can drive construction, many rural hospital projects tap government programs, especially those supported by the US Department of Agriculture, Mr. Topchik said. That, he said, “surprises a lot of people.”
Since 2021, the USDA’s rural Community Facilities Programs have awarded $2.24 billion in loans and grants to 68 rural hospitals for work that was not related to an emergency or disaster, according to data analyzed by KFF Health News and confirmed by the agency. The federal program is funded through what is often known as the farm bill, which faces a September congressional renewal deadline.
Nearly all the projects are replacements or expansions and updates of older facilities.
The USDA confirmed that three new or planned Wyoming hospitals received federal funding. Hospital projects in Riverton and Saratoga received loans of $37.2 million and $18.3 million, respectively. Pinedale’s hospital received a $29.2 million loan from the agency.
Wyoming’s new construction is rare in a state where more than 80% of rural hospitals reported losses in the third quarter of 2023, according to Chartis. The state association’s Mr. Boley said he worries about several hospitals that have less than 10 days’ cash on hand “day and night.”
Pinedale’s project loan was approved after the community submitted a feasibility study to the USDA that included local clinics and a long-term care facility. “It’s pretty remote and right up in the mountains,” Mr. Boley said.
Pinedale’s Ms. DeWitt said the community was missing key services, such as blood transfusions, which are often necessary when there is a trauma like a car crash or if a pregnant woman faces severe complications. Local ambulances drove 94,000 miles last year, she said.
Ms. DeWitt began working to raise support for the new hospital after her own pregnancy-related trauma in 2014. She was bleeding heavily and arrived at the local health clinic believing it operated like a hospital.
“It was shocking to hear, ‘No, we’re not a hospital. We can’t do blood transfusions. We’re just going to have to pray you live for the next 45 minutes,’ ” Ms. DeWitt said.
Ms. DeWitt had to be airlifted to Idaho, where she delivered a few minutes after landing. When the hospital financing went on the ballot in 2020, Ms. DeWitt — fully recovered, with healthy grade-schoolers at home — began making five calls a night to rally support for a county tax increase to help fund the hospital.
“By improving health care, I think we improve everybody’s chances of survival. You know, it’s pretty basic,” Ms. DeWitt said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
There’s a new morning ritual in Pinedale, Wyoming, a town of about 2000, nestled against the Wind River Mountains.
Friends and neighbors in the oil- and gas-rich community “take their morning coffee and pull up” to watch workers building the county’s first hospital, said Kari DeWitt, the project’s public relations director.
“I think it’s just gratitude,” Ms. DeWitt said.
Sublette County is the only one in Wyoming — where counties span thousands of square miles — without a hospital. The 10-bed, 40,000-square-foot hospital, with a similarly sized attached long-term care facility, is slated to open by the summer of 2025.
Ms. DeWitt, who also is executive director of the Sublette County Health Foundation, has an office at the town’s health clinic with a window view of the construction.
Pinedale’s residents have good reason to be excited. New full-service hospitals with inpatient beds are rare in rural America, where declining population has spurred decades of downsizing and closures. Yet, a few communities in Wyoming and others in Kansas and Georgia are defying the trend.
“To be honest with you, it even seems strange to me,” said Wyoming Hospital Association President Eric Boley. Small rural “hospitals are really struggling all across the country,” he said.
There is no official tally of new hospitals being built in rural America, but industry experts such as Mr. Boley said they’re rare. Typically, health-related construction projects in rural areas are for smaller urgent care centers or stand-alone emergency facilities or are replacements for old hospitals.
About half of rural hospitals lost money in the prior year, according to Chartis, a health analytics and consulting firm. And nearly 150 rural hospitals have closed or converted to smaller operations since 2010, according to data collected by the University of North Carolina’s Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research.
To stem the tide of closures, Congress created a new rural emergency hospital designation that allowed struggling hospitals to close their inpatient units and provide only outpatient and emergency services. Since January 2023, when the program took effect, 32 of the more than 1700 eligible rural hospitals — from Georgia to New Mexico — have joined the program, according to data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Tony Breitlow is healthcare studio director for EUA, which has extensive experience working for rural health care systems. Mr. Breitlow said his national architecture and engineering firm’s work expands, replaces, or revamps older buildings, many of which were constructed during the middle of the last century.
The work, Mr. Breitlow said, is part of health care “systems figuring out how to remain robust and viable.”
Freeman Health System, based in Joplin, Missouri, announced plans last year to build a new 50-bed hospital across the state line in Kansas. Paula Baker, Freeman’s president and chief executive, said the system is building for patients in the southeastern corner of the state who travel 45 minutes or more to its bigger Joplin facilities for care.
Freeman’s new hospital, with construction on the building expected to begin in the spring, will be less than 10 miles away from an older, 64-bed hospital that has existed for decades. Kansas is one of more than a dozen states with no “certificate of need” law that would require health providers to obtain approval from the state before offering new services or building or expanding facilities.
Ms. Baker also said Freeman plans to operate emergency services and a small 10-bed outpost in Fort Scott, Kansas, opening early next year in a corner of a hospital that closed in late 2018. Residents there “cried, they cheered, they hugged me,” Ms. Baker said, adding that the “level of appreciation and gratitude that they felt and they displayed was overwhelming to me.”
Michael Topchik, executive director of the Chartis Center for Rural Health, said regional healthcare systems in the Upper Midwest have been particularly active in competing for patients by, among other things, building new hospitals.
And while private corporate money can drive construction, many rural hospital projects tap government programs, especially those supported by the US Department of Agriculture, Mr. Topchik said. That, he said, “surprises a lot of people.”
Since 2021, the USDA’s rural Community Facilities Programs have awarded $2.24 billion in loans and grants to 68 rural hospitals for work that was not related to an emergency or disaster, according to data analyzed by KFF Health News and confirmed by the agency. The federal program is funded through what is often known as the farm bill, which faces a September congressional renewal deadline.
Nearly all the projects are replacements or expansions and updates of older facilities.
The USDA confirmed that three new or planned Wyoming hospitals received federal funding. Hospital projects in Riverton and Saratoga received loans of $37.2 million and $18.3 million, respectively. Pinedale’s hospital received a $29.2 million loan from the agency.
Wyoming’s new construction is rare in a state where more than 80% of rural hospitals reported losses in the third quarter of 2023, according to Chartis. The state association’s Mr. Boley said he worries about several hospitals that have less than 10 days’ cash on hand “day and night.”
Pinedale’s project loan was approved after the community submitted a feasibility study to the USDA that included local clinics and a long-term care facility. “It’s pretty remote and right up in the mountains,” Mr. Boley said.
Pinedale’s Ms. DeWitt said the community was missing key services, such as blood transfusions, which are often necessary when there is a trauma like a car crash or if a pregnant woman faces severe complications. Local ambulances drove 94,000 miles last year, she said.
Ms. DeWitt began working to raise support for the new hospital after her own pregnancy-related trauma in 2014. She was bleeding heavily and arrived at the local health clinic believing it operated like a hospital.
“It was shocking to hear, ‘No, we’re not a hospital. We can’t do blood transfusions. We’re just going to have to pray you live for the next 45 minutes,’ ” Ms. DeWitt said.
Ms. DeWitt had to be airlifted to Idaho, where she delivered a few minutes after landing. When the hospital financing went on the ballot in 2020, Ms. DeWitt — fully recovered, with healthy grade-schoolers at home — began making five calls a night to rally support for a county tax increase to help fund the hospital.
“By improving health care, I think we improve everybody’s chances of survival. You know, it’s pretty basic,” Ms. DeWitt said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
FDA Panel Votes for Limits on Gastric, Esophageal Cancer Immunotherapy
During the meeting, the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) voted in favor of restricting the use of these immunotherapy agents to patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression of 1% or higher.
The agency usually follows the ODAC’s advice.
The FDA had originally approved the two immune checkpoint inhibitors for both indications in combination with chemotherapy, regardless of patients’ PD-L1 status. The FDA had also approved nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab for esophageal cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression. The approvals were based on overall benefit in intent-to-treat populations, not on specific PD-L1 expression subgroups.
Since then, additional studies — including the agency’s own pooled analyses of the approval trials — have found that overall survival benefits are limited to patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or higher.
These findings have raised concerns that patients with no or low PD-L1 expression face the risks associated with immunotherapy, which include death, but minimal to no benefits.
In response, the FDA has considered changing the labeling for these indications to require a PD-L1 cutoff point of 1% or higher. The move would mirror guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network that already recommend use with chemotherapy only at certain PD-L1 cutoffs.
Before the agency acts, however, the FDA wanted the advice of the ODAC. It asked the 14-member panel whether the risk-benefit assessment is “favorable for the use of PD-1 inhibitors in first line” for the two indications among patients with PD-L1 expression below 1%.
In two nearly unanimous decisions for each indication, the panel voted that risk-benefit assessment was not favorable. In other words, the risks do outweigh the benefits for this patient population with no or low PD-L1 expression.
The determination also applies to tislelizumab (Tevimbra), an immune checkpoint inhibitor under review by the FDA for the same indications.
Voting came after hours of testimony from FDA scientists and the three drug companies involved in the decisions.
Merck, maker of pembrolizumab, was against any labeling change. Nivolumab’s maker, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), also wanted to stick with the current PD-L1 agnostic indications but said that any indication change should be class-wide to avoid confusion. BeiGene USA, maker of tislelizumab, had no problem with a PD-L1 cutoff of 1% because its approval trial showed benefit only in patients at that level or higher.
In general, Merck and BMS said the drug benefits correspond with higher PD-L1 expression but noted that patients with low or no PD-L1 expression can sometimes benefit from treatment. The companies had several patients testify to the benefits of the agents and noted patients like this would likely lose access. But an ODAC panelist noted that patients who died from immunotherapy complications weren’t there to respond.
The companies also expressed concern about taking treatment decisions out of the hands of oncologists as well as the need for additional biopsies to determine if tumors cross the proposed PD-L1 threshold at some point during treatment. With this potential new restriction, the companies were worried that insurance companies would be even less likely to pay for their checkpoint inhibitors in low or no PD-L1 expressors.
ODAC wasn’t moved. With consistent findings across multiple trials, the strength of the FDA’s data carried the day.
In a pooled analysis of the three companies’ unresectable or metastatic HER2–negative, microsatellite-stable gastric/gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma approval trials across almost 4000 patients, those with PD-L1 levels below 1% did not demonstrate a significant overall survival benefit (hazard ratio [HR], 0.91; 95% CI, 0.75-1.09). The median overall survival with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy was only 1 month more — 13.4 months vs 12.4 months with chemotherapy alone.
FDA’s pooled analysis for unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma also showed no overall survival benefit (HR, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.76-1.58), with a trend suggesting harm. Median overall survival with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy was 14.6 months vs 9.8 months with chemotherapy alone.
Despite the vote on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, panelists had reservations about making decisions based on just over 160 patients with PD-L1 levels below 1% in the three esophageal squamous cell carcinoma trials.
Still, one panelist said, it’s likely “the best dataset we will get.”
The companies all used different methods to test PD-L1 levels, and attendees called for a single standardized PD-L1 test. Richard Pazdur, MD, head of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said the agency has been working with companies for years to get them to agree to such a test, with no luck.
If the FDA ultimately decides to restrict immunotherapy use in this patient population based on PD-L1 levels, insurance company coverage may become more limited. Pazdur asked the companies if they would be willing to expand their patient assistance programs to provide free coverage of immune checkpoint blockers to patients with low or no PD-L1 expression.
BeiGene and BMS seemed open to the idea. Merck said, “We’ll have to ... think about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During the meeting, the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) voted in favor of restricting the use of these immunotherapy agents to patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression of 1% or higher.
The agency usually follows the ODAC’s advice.
The FDA had originally approved the two immune checkpoint inhibitors for both indications in combination with chemotherapy, regardless of patients’ PD-L1 status. The FDA had also approved nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab for esophageal cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression. The approvals were based on overall benefit in intent-to-treat populations, not on specific PD-L1 expression subgroups.
Since then, additional studies — including the agency’s own pooled analyses of the approval trials — have found that overall survival benefits are limited to patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or higher.
These findings have raised concerns that patients with no or low PD-L1 expression face the risks associated with immunotherapy, which include death, but minimal to no benefits.
In response, the FDA has considered changing the labeling for these indications to require a PD-L1 cutoff point of 1% or higher. The move would mirror guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network that already recommend use with chemotherapy only at certain PD-L1 cutoffs.
Before the agency acts, however, the FDA wanted the advice of the ODAC. It asked the 14-member panel whether the risk-benefit assessment is “favorable for the use of PD-1 inhibitors in first line” for the two indications among patients with PD-L1 expression below 1%.
In two nearly unanimous decisions for each indication, the panel voted that risk-benefit assessment was not favorable. In other words, the risks do outweigh the benefits for this patient population with no or low PD-L1 expression.
The determination also applies to tislelizumab (Tevimbra), an immune checkpoint inhibitor under review by the FDA for the same indications.
Voting came after hours of testimony from FDA scientists and the three drug companies involved in the decisions.
Merck, maker of pembrolizumab, was against any labeling change. Nivolumab’s maker, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), also wanted to stick with the current PD-L1 agnostic indications but said that any indication change should be class-wide to avoid confusion. BeiGene USA, maker of tislelizumab, had no problem with a PD-L1 cutoff of 1% because its approval trial showed benefit only in patients at that level or higher.
In general, Merck and BMS said the drug benefits correspond with higher PD-L1 expression but noted that patients with low or no PD-L1 expression can sometimes benefit from treatment. The companies had several patients testify to the benefits of the agents and noted patients like this would likely lose access. But an ODAC panelist noted that patients who died from immunotherapy complications weren’t there to respond.
The companies also expressed concern about taking treatment decisions out of the hands of oncologists as well as the need for additional biopsies to determine if tumors cross the proposed PD-L1 threshold at some point during treatment. With this potential new restriction, the companies were worried that insurance companies would be even less likely to pay for their checkpoint inhibitors in low or no PD-L1 expressors.
ODAC wasn’t moved. With consistent findings across multiple trials, the strength of the FDA’s data carried the day.
In a pooled analysis of the three companies’ unresectable or metastatic HER2–negative, microsatellite-stable gastric/gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma approval trials across almost 4000 patients, those with PD-L1 levels below 1% did not demonstrate a significant overall survival benefit (hazard ratio [HR], 0.91; 95% CI, 0.75-1.09). The median overall survival with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy was only 1 month more — 13.4 months vs 12.4 months with chemotherapy alone.
FDA’s pooled analysis for unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma also showed no overall survival benefit (HR, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.76-1.58), with a trend suggesting harm. Median overall survival with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy was 14.6 months vs 9.8 months with chemotherapy alone.
Despite the vote on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, panelists had reservations about making decisions based on just over 160 patients with PD-L1 levels below 1% in the three esophageal squamous cell carcinoma trials.
Still, one panelist said, it’s likely “the best dataset we will get.”
The companies all used different methods to test PD-L1 levels, and attendees called for a single standardized PD-L1 test. Richard Pazdur, MD, head of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said the agency has been working with companies for years to get them to agree to such a test, with no luck.
If the FDA ultimately decides to restrict immunotherapy use in this patient population based on PD-L1 levels, insurance company coverage may become more limited. Pazdur asked the companies if they would be willing to expand their patient assistance programs to provide free coverage of immune checkpoint blockers to patients with low or no PD-L1 expression.
BeiGene and BMS seemed open to the idea. Merck said, “We’ll have to ... think about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During the meeting, the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) voted in favor of restricting the use of these immunotherapy agents to patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression of 1% or higher.
The agency usually follows the ODAC’s advice.
The FDA had originally approved the two immune checkpoint inhibitors for both indications in combination with chemotherapy, regardless of patients’ PD-L1 status. The FDA had also approved nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab for esophageal cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression. The approvals were based on overall benefit in intent-to-treat populations, not on specific PD-L1 expression subgroups.
Since then, additional studies — including the agency’s own pooled analyses of the approval trials — have found that overall survival benefits are limited to patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or higher.
These findings have raised concerns that patients with no or low PD-L1 expression face the risks associated with immunotherapy, which include death, but minimal to no benefits.
In response, the FDA has considered changing the labeling for these indications to require a PD-L1 cutoff point of 1% or higher. The move would mirror guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network that already recommend use with chemotherapy only at certain PD-L1 cutoffs.
Before the agency acts, however, the FDA wanted the advice of the ODAC. It asked the 14-member panel whether the risk-benefit assessment is “favorable for the use of PD-1 inhibitors in first line” for the two indications among patients with PD-L1 expression below 1%.
In two nearly unanimous decisions for each indication, the panel voted that risk-benefit assessment was not favorable. In other words, the risks do outweigh the benefits for this patient population with no or low PD-L1 expression.
The determination also applies to tislelizumab (Tevimbra), an immune checkpoint inhibitor under review by the FDA for the same indications.
Voting came after hours of testimony from FDA scientists and the three drug companies involved in the decisions.
Merck, maker of pembrolizumab, was against any labeling change. Nivolumab’s maker, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), also wanted to stick with the current PD-L1 agnostic indications but said that any indication change should be class-wide to avoid confusion. BeiGene USA, maker of tislelizumab, had no problem with a PD-L1 cutoff of 1% because its approval trial showed benefit only in patients at that level or higher.
In general, Merck and BMS said the drug benefits correspond with higher PD-L1 expression but noted that patients with low or no PD-L1 expression can sometimes benefit from treatment. The companies had several patients testify to the benefits of the agents and noted patients like this would likely lose access. But an ODAC panelist noted that patients who died from immunotherapy complications weren’t there to respond.
The companies also expressed concern about taking treatment decisions out of the hands of oncologists as well as the need for additional biopsies to determine if tumors cross the proposed PD-L1 threshold at some point during treatment. With this potential new restriction, the companies were worried that insurance companies would be even less likely to pay for their checkpoint inhibitors in low or no PD-L1 expressors.
ODAC wasn’t moved. With consistent findings across multiple trials, the strength of the FDA’s data carried the day.
In a pooled analysis of the three companies’ unresectable or metastatic HER2–negative, microsatellite-stable gastric/gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma approval trials across almost 4000 patients, those with PD-L1 levels below 1% did not demonstrate a significant overall survival benefit (hazard ratio [HR], 0.91; 95% CI, 0.75-1.09). The median overall survival with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy was only 1 month more — 13.4 months vs 12.4 months with chemotherapy alone.
FDA’s pooled analysis for unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma also showed no overall survival benefit (HR, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.76-1.58), with a trend suggesting harm. Median overall survival with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy was 14.6 months vs 9.8 months with chemotherapy alone.
Despite the vote on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, panelists had reservations about making decisions based on just over 160 patients with PD-L1 levels below 1% in the three esophageal squamous cell carcinoma trials.
Still, one panelist said, it’s likely “the best dataset we will get.”
The companies all used different methods to test PD-L1 levels, and attendees called for a single standardized PD-L1 test. Richard Pazdur, MD, head of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said the agency has been working with companies for years to get them to agree to such a test, with no luck.
If the FDA ultimately decides to restrict immunotherapy use in this patient population based on PD-L1 levels, insurance company coverage may become more limited. Pazdur asked the companies if they would be willing to expand their patient assistance programs to provide free coverage of immune checkpoint blockers to patients with low or no PD-L1 expression.
BeiGene and BMS seemed open to the idea. Merck said, “We’ll have to ... think about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First Hike of Medicare Funding for Residencies in 25 Years Aims to Help Shortages
Residency programs across the country may have a few more slots for incoming residents due to a recent bump in Medicare funding.
Case in point: The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB). The state has one of the top stroke rates in the country, and yet UAB has the only hospital in the state training future doctors to help stroke patients recover. “Our hospital cares for Alabama’s sickest patients, many who need rehabilitation services,” said Craig Hoesley, MD, senior associate dean for medical education, who oversees graduate medical education (GME) or residency programs.
After decades of stagnant support, a recent bump in Medicare funding will allow UAB to add two more physical medicine and rehabilitation residents to the four residencies already receiving such funding.
Medicare also awarded UAB more funding last year to add an addiction medicine fellowship, one of two such training programs in the state for the specialty that helps treat patients fighting addiction.
UAB is among healthcare systems and hospitals nationwide benefiting from a recent hike in Medicare funding for residency programs after some 25 years at the same level of federal support. Medicare is the largest funder of training positions. Otherwise, hospitals finance training through means such as state support.
The latest round of funding, which went into effect in July, adds 200 positions to the doctor pipeline, creating more openings for residents seeking positions after medical school.
In the next few months, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will notify teaching hospitals whether they’ll receive the next round of Medicare funding for more residency positions. At that time, CMS will have awarded nearly half of the 1200 residency training slots Congress approved in the past few years. In 2020 — for the first time since 1996 — Congress approved adding 1000 residency slots at teaching hospitals nationwide. CMS awards the money for 200 slots each year for 5 years.
More than half of the initial round of funding focused on training primary care specialists, with other slots designated for mental health specialists. Last year, Congress also approved a separate allocation of 200 more Medicare-funded residency positions, with at least half designated for psychiatry and related subspecialty residencies to help meet the growing need for more mental health specialists. On August 1, CMS announced it would distribute the funds next year, effective in 2026.
The additional Medicare funding attempts to address the shortage of healthcare providers and ensure future access to care, including in rural and underserved communities. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) estimates the nation will face a shortage of up to 86,000 physicians by 2036, including primary care doctors and specialists.
In addition, more than 100 million Americans, nearly a third of the nation, don’t have access to primary care due to the physician shortages in their communities, according to the National Association of Community Health Centers.
Major medical organizations, medical schools, and hospital groups have been pushing for years for increased Medicare funding to train new doctors to keep up with the demand for healthcare services and offset the physician shortage. As a cost-saving measure, Medicare set its cap in 1996 for how much it will reimburse each hospital offering GME training. However, according to the medical groups that continue to advocate to Congress for more funding, the funding hasn’t kept pace with the growing healthcare needs or rising medical school enrollment.
Adding Residency Spots
In April, Dr. Hoesley of UAB spoke at a Congressional briefing among health systems and hospitals that benefited from the additional funding. He told Congressional leaders how the increased number of GME positions affects UAB Medicine and its ability to care for rural areas.
“We have entire counties in Alabama that don’t have physicians. One way to address the physician shortage is to grow the GME programs. The funding we received will help us grow these programs and care for residents in our state.”
Still, the Medicare funding is only a drop in the bucket, Dr. Hoesley said. “We rely on Medicare funding alongside other funding partners to train residents and expand our care across the state.” He said many UAB residency programs are over their Medicare funding cap and would like to grow, but they can’t without more funding.
Mount Sinai Health System in New York City also will be able to expand its residency program after receiving Medicare support in the latest round of funding. The health system will use the federal funds to train an additional vascular surgeon. Mount Sinai currently receives CMS funding to train three residents in the specialty.
Over a 5-year program, that means CMS funding will help train 20 residents in the specialty that treats blood vessel blockages and diseases of the veins and arteries generally associated with aging.
“The funding is amazing,” said Peter L. Faries, MD, a surgery professor and system chief of vascular surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, who directs the residency program.
“We don’t have the capacity to provide an individual training program without the funding. It’s not economically feasible.”
The need for more vascular surgeons increases as the population continues to age, he said. Mount Sinai treats patients throughout New York, including underserved areas in Harlem, the Bronx, Washington Heights, Brooklyn, and Queens. “These individuals might not receive an appropriate level of vascular care if we don’t have clinicians to treat them.”
Of the recent funding, Dr. Faries said it’s taken the residency program 15 years of advocacy to increase by two slots. “It’s a long process to get funding.” Vascular training programs can remain very selective with Medicare funding, typically receiving two applicants for every position,” said Dr. Faries.
Pushing for More Funds
Nearly 98,000 students enrolled in medical school this year, according to the National Resident Matching Program. A total of 44,853 applicants vied for the 38,494 first-year residency positions and 3009 second-year slots, leaving 3350 medical school graduates without a match.
“There are not enough spots to meet the growing demand,” said Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, immediate past president of the American Medical Association. “Graduate medical education funding has not kept up.”
Despite the increase in medical school graduates over the past two decades, Medicare-supported training opportunities remained frozen at the 1996 level. A limited number of training positions meant residency programs couldn’t expand the physician pipeline to offset an aging workforce, contributing to the shortage. “The way to solve this is to expand GME,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “We continue to advocate to remove the cap.”
Dr. Ehrenfeld also told this news organization that he doesn’t mind that Congress recently designated GME funding to certain specialties, such as psychiatry, because he believes the need is great for residency spots across the board. “The good news is people recognize it’s challenging to get much through Congress.” He’s optimistic, though, about recent legislative efforts to increase funding.
AAMC, representing about a third of the nation’s 1100 teaching hospitals and health systems, feels the same. Congress “acknowledges and continues to recognize that the shortage is not getting better, and one way to address it is to increase Medicare-supported GME positions,” said Leonard Marquez, senior director of government relations and legislative advocacy.
Still, he said that the Medicare funding bump is only making a small dent in the need. AAMC estimates the average cost to train residents is $23 billion annually, and Medicare only funds 20% of that, or $5 billion. “Our members are at the point where they say: We already can’t add new training positions,” Mr. Marquez said. He added that without increasing residency slots, patient care will suffer. “We have to do anything possible we can to increase access to care.”
Mr. Marquez also believes Medicare funding should increase residency positions across the specialty spectrum, not just for psychiatry and primary care. He said that the targeted funding may prevent some teaching hospitals from applying for residency positions if they need other types of specialists based on their community’s needs.
Among the current proposals before Congress, the Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act of 2023 would add 14,000 Medicare-supported residency slots over 7 years. Mr. Marquez said it may be more realistic to expect fewer new slots. A decision on potential legislation is expected at the end of the year. He said that if the medical groups aren’t pleased with the decision, they’ll advocate again in 2025.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Residency programs across the country may have a few more slots for incoming residents due to a recent bump in Medicare funding.
Case in point: The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB). The state has one of the top stroke rates in the country, and yet UAB has the only hospital in the state training future doctors to help stroke patients recover. “Our hospital cares for Alabama’s sickest patients, many who need rehabilitation services,” said Craig Hoesley, MD, senior associate dean for medical education, who oversees graduate medical education (GME) or residency programs.
After decades of stagnant support, a recent bump in Medicare funding will allow UAB to add two more physical medicine and rehabilitation residents to the four residencies already receiving such funding.
Medicare also awarded UAB more funding last year to add an addiction medicine fellowship, one of two such training programs in the state for the specialty that helps treat patients fighting addiction.
UAB is among healthcare systems and hospitals nationwide benefiting from a recent hike in Medicare funding for residency programs after some 25 years at the same level of federal support. Medicare is the largest funder of training positions. Otherwise, hospitals finance training through means such as state support.
The latest round of funding, which went into effect in July, adds 200 positions to the doctor pipeline, creating more openings for residents seeking positions after medical school.
In the next few months, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will notify teaching hospitals whether they’ll receive the next round of Medicare funding for more residency positions. At that time, CMS will have awarded nearly half of the 1200 residency training slots Congress approved in the past few years. In 2020 — for the first time since 1996 — Congress approved adding 1000 residency slots at teaching hospitals nationwide. CMS awards the money for 200 slots each year for 5 years.
More than half of the initial round of funding focused on training primary care specialists, with other slots designated for mental health specialists. Last year, Congress also approved a separate allocation of 200 more Medicare-funded residency positions, with at least half designated for psychiatry and related subspecialty residencies to help meet the growing need for more mental health specialists. On August 1, CMS announced it would distribute the funds next year, effective in 2026.
The additional Medicare funding attempts to address the shortage of healthcare providers and ensure future access to care, including in rural and underserved communities. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) estimates the nation will face a shortage of up to 86,000 physicians by 2036, including primary care doctors and specialists.
In addition, more than 100 million Americans, nearly a third of the nation, don’t have access to primary care due to the physician shortages in their communities, according to the National Association of Community Health Centers.
Major medical organizations, medical schools, and hospital groups have been pushing for years for increased Medicare funding to train new doctors to keep up with the demand for healthcare services and offset the physician shortage. As a cost-saving measure, Medicare set its cap in 1996 for how much it will reimburse each hospital offering GME training. However, according to the medical groups that continue to advocate to Congress for more funding, the funding hasn’t kept pace with the growing healthcare needs or rising medical school enrollment.
Adding Residency Spots
In April, Dr. Hoesley of UAB spoke at a Congressional briefing among health systems and hospitals that benefited from the additional funding. He told Congressional leaders how the increased number of GME positions affects UAB Medicine and its ability to care for rural areas.
“We have entire counties in Alabama that don’t have physicians. One way to address the physician shortage is to grow the GME programs. The funding we received will help us grow these programs and care for residents in our state.”
Still, the Medicare funding is only a drop in the bucket, Dr. Hoesley said. “We rely on Medicare funding alongside other funding partners to train residents and expand our care across the state.” He said many UAB residency programs are over their Medicare funding cap and would like to grow, but they can’t without more funding.
Mount Sinai Health System in New York City also will be able to expand its residency program after receiving Medicare support in the latest round of funding. The health system will use the federal funds to train an additional vascular surgeon. Mount Sinai currently receives CMS funding to train three residents in the specialty.
Over a 5-year program, that means CMS funding will help train 20 residents in the specialty that treats blood vessel blockages and diseases of the veins and arteries generally associated with aging.
“The funding is amazing,” said Peter L. Faries, MD, a surgery professor and system chief of vascular surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, who directs the residency program.
“We don’t have the capacity to provide an individual training program without the funding. It’s not economically feasible.”
The need for more vascular surgeons increases as the population continues to age, he said. Mount Sinai treats patients throughout New York, including underserved areas in Harlem, the Bronx, Washington Heights, Brooklyn, and Queens. “These individuals might not receive an appropriate level of vascular care if we don’t have clinicians to treat them.”
Of the recent funding, Dr. Faries said it’s taken the residency program 15 years of advocacy to increase by two slots. “It’s a long process to get funding.” Vascular training programs can remain very selective with Medicare funding, typically receiving two applicants for every position,” said Dr. Faries.
Pushing for More Funds
Nearly 98,000 students enrolled in medical school this year, according to the National Resident Matching Program. A total of 44,853 applicants vied for the 38,494 first-year residency positions and 3009 second-year slots, leaving 3350 medical school graduates without a match.
“There are not enough spots to meet the growing demand,” said Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, immediate past president of the American Medical Association. “Graduate medical education funding has not kept up.”
Despite the increase in medical school graduates over the past two decades, Medicare-supported training opportunities remained frozen at the 1996 level. A limited number of training positions meant residency programs couldn’t expand the physician pipeline to offset an aging workforce, contributing to the shortage. “The way to solve this is to expand GME,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “We continue to advocate to remove the cap.”
Dr. Ehrenfeld also told this news organization that he doesn’t mind that Congress recently designated GME funding to certain specialties, such as psychiatry, because he believes the need is great for residency spots across the board. “The good news is people recognize it’s challenging to get much through Congress.” He’s optimistic, though, about recent legislative efforts to increase funding.
AAMC, representing about a third of the nation’s 1100 teaching hospitals and health systems, feels the same. Congress “acknowledges and continues to recognize that the shortage is not getting better, and one way to address it is to increase Medicare-supported GME positions,” said Leonard Marquez, senior director of government relations and legislative advocacy.
Still, he said that the Medicare funding bump is only making a small dent in the need. AAMC estimates the average cost to train residents is $23 billion annually, and Medicare only funds 20% of that, or $5 billion. “Our members are at the point where they say: We already can’t add new training positions,” Mr. Marquez said. He added that without increasing residency slots, patient care will suffer. “We have to do anything possible we can to increase access to care.”
Mr. Marquez also believes Medicare funding should increase residency positions across the specialty spectrum, not just for psychiatry and primary care. He said that the targeted funding may prevent some teaching hospitals from applying for residency positions if they need other types of specialists based on their community’s needs.
Among the current proposals before Congress, the Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act of 2023 would add 14,000 Medicare-supported residency slots over 7 years. Mr. Marquez said it may be more realistic to expect fewer new slots. A decision on potential legislation is expected at the end of the year. He said that if the medical groups aren’t pleased with the decision, they’ll advocate again in 2025.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Residency programs across the country may have a few more slots for incoming residents due to a recent bump in Medicare funding.
Case in point: The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB). The state has one of the top stroke rates in the country, and yet UAB has the only hospital in the state training future doctors to help stroke patients recover. “Our hospital cares for Alabama’s sickest patients, many who need rehabilitation services,” said Craig Hoesley, MD, senior associate dean for medical education, who oversees graduate medical education (GME) or residency programs.
After decades of stagnant support, a recent bump in Medicare funding will allow UAB to add two more physical medicine and rehabilitation residents to the four residencies already receiving such funding.
Medicare also awarded UAB more funding last year to add an addiction medicine fellowship, one of two such training programs in the state for the specialty that helps treat patients fighting addiction.
UAB is among healthcare systems and hospitals nationwide benefiting from a recent hike in Medicare funding for residency programs after some 25 years at the same level of federal support. Medicare is the largest funder of training positions. Otherwise, hospitals finance training through means such as state support.
The latest round of funding, which went into effect in July, adds 200 positions to the doctor pipeline, creating more openings for residents seeking positions after medical school.
In the next few months, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will notify teaching hospitals whether they’ll receive the next round of Medicare funding for more residency positions. At that time, CMS will have awarded nearly half of the 1200 residency training slots Congress approved in the past few years. In 2020 — for the first time since 1996 — Congress approved adding 1000 residency slots at teaching hospitals nationwide. CMS awards the money for 200 slots each year for 5 years.
More than half of the initial round of funding focused on training primary care specialists, with other slots designated for mental health specialists. Last year, Congress also approved a separate allocation of 200 more Medicare-funded residency positions, with at least half designated for psychiatry and related subspecialty residencies to help meet the growing need for more mental health specialists. On August 1, CMS announced it would distribute the funds next year, effective in 2026.
The additional Medicare funding attempts to address the shortage of healthcare providers and ensure future access to care, including in rural and underserved communities. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) estimates the nation will face a shortage of up to 86,000 physicians by 2036, including primary care doctors and specialists.
In addition, more than 100 million Americans, nearly a third of the nation, don’t have access to primary care due to the physician shortages in their communities, according to the National Association of Community Health Centers.
Major medical organizations, medical schools, and hospital groups have been pushing for years for increased Medicare funding to train new doctors to keep up with the demand for healthcare services and offset the physician shortage. As a cost-saving measure, Medicare set its cap in 1996 for how much it will reimburse each hospital offering GME training. However, according to the medical groups that continue to advocate to Congress for more funding, the funding hasn’t kept pace with the growing healthcare needs or rising medical school enrollment.
Adding Residency Spots
In April, Dr. Hoesley of UAB spoke at a Congressional briefing among health systems and hospitals that benefited from the additional funding. He told Congressional leaders how the increased number of GME positions affects UAB Medicine and its ability to care for rural areas.
“We have entire counties in Alabama that don’t have physicians. One way to address the physician shortage is to grow the GME programs. The funding we received will help us grow these programs and care for residents in our state.”
Still, the Medicare funding is only a drop in the bucket, Dr. Hoesley said. “We rely on Medicare funding alongside other funding partners to train residents and expand our care across the state.” He said many UAB residency programs are over their Medicare funding cap and would like to grow, but they can’t without more funding.
Mount Sinai Health System in New York City also will be able to expand its residency program after receiving Medicare support in the latest round of funding. The health system will use the federal funds to train an additional vascular surgeon. Mount Sinai currently receives CMS funding to train three residents in the specialty.
Over a 5-year program, that means CMS funding will help train 20 residents in the specialty that treats blood vessel blockages and diseases of the veins and arteries generally associated with aging.
“The funding is amazing,” said Peter L. Faries, MD, a surgery professor and system chief of vascular surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, who directs the residency program.
“We don’t have the capacity to provide an individual training program without the funding. It’s not economically feasible.”
The need for more vascular surgeons increases as the population continues to age, he said. Mount Sinai treats patients throughout New York, including underserved areas in Harlem, the Bronx, Washington Heights, Brooklyn, and Queens. “These individuals might not receive an appropriate level of vascular care if we don’t have clinicians to treat them.”
Of the recent funding, Dr. Faries said it’s taken the residency program 15 years of advocacy to increase by two slots. “It’s a long process to get funding.” Vascular training programs can remain very selective with Medicare funding, typically receiving two applicants for every position,” said Dr. Faries.
Pushing for More Funds
Nearly 98,000 students enrolled in medical school this year, according to the National Resident Matching Program. A total of 44,853 applicants vied for the 38,494 first-year residency positions and 3009 second-year slots, leaving 3350 medical school graduates without a match.
“There are not enough spots to meet the growing demand,” said Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, immediate past president of the American Medical Association. “Graduate medical education funding has not kept up.”
Despite the increase in medical school graduates over the past two decades, Medicare-supported training opportunities remained frozen at the 1996 level. A limited number of training positions meant residency programs couldn’t expand the physician pipeline to offset an aging workforce, contributing to the shortage. “The way to solve this is to expand GME,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “We continue to advocate to remove the cap.”
Dr. Ehrenfeld also told this news organization that he doesn’t mind that Congress recently designated GME funding to certain specialties, such as psychiatry, because he believes the need is great for residency spots across the board. “The good news is people recognize it’s challenging to get much through Congress.” He’s optimistic, though, about recent legislative efforts to increase funding.
AAMC, representing about a third of the nation’s 1100 teaching hospitals and health systems, feels the same. Congress “acknowledges and continues to recognize that the shortage is not getting better, and one way to address it is to increase Medicare-supported GME positions,” said Leonard Marquez, senior director of government relations and legislative advocacy.
Still, he said that the Medicare funding bump is only making a small dent in the need. AAMC estimates the average cost to train residents is $23 billion annually, and Medicare only funds 20% of that, or $5 billion. “Our members are at the point where they say: We already can’t add new training positions,” Mr. Marquez said. He added that without increasing residency slots, patient care will suffer. “We have to do anything possible we can to increase access to care.”
Mr. Marquez also believes Medicare funding should increase residency positions across the specialty spectrum, not just for psychiatry and primary care. He said that the targeted funding may prevent some teaching hospitals from applying for residency positions if they need other types of specialists based on their community’s needs.
Among the current proposals before Congress, the Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act of 2023 would add 14,000 Medicare-supported residency slots over 7 years. Mr. Marquez said it may be more realistic to expect fewer new slots. A decision on potential legislation is expected at the end of the year. He said that if the medical groups aren’t pleased with the decision, they’ll advocate again in 2025.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Okays Osimertinib After CRT in Locally Advanced, Unresectable NSCLC
Specifically, the third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) was approved for patients whose disease has not progressed during or after concurrent or sequential platinum-based chemoradiation therapy and whose tumors have EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutations. Such EGFR mutations can be detected by an FDA-approved test.
The FDA approved osimertinib in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with the same mutations in February. The EGFR-TKI also carries other indications, including as first-line monotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
Trial Findings Supporting Latest Approval
AstraZeneca announced in June that osimertinib had been granted Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy Designation for its newest indication.
The September 25 approval was based on findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled LAURA trial of 216 patients, which demonstrated improved median progression-free survival with osimertinib vs placebo (39.1 vs 5.6 months; hazard ratio, 0.16). Overall survival results were immature at the most recent analysis, but “no trend towards a detriment was observed,” with 36% of prespecified deaths for the final analysis reported, according to an FDA press release.
Adverse Events
Study participants were randomized 2:1 to receive the osimertinib recommended dose of 80 mg given orally once daily or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, were lymphopenia, leukopenia, interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, rash, diarrhea, nail toxicity, musculoskeletal pain, cough, and COVID-19 infection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) was approved for patients whose disease has not progressed during or after concurrent or sequential platinum-based chemoradiation therapy and whose tumors have EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutations. Such EGFR mutations can be detected by an FDA-approved test.
The FDA approved osimertinib in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with the same mutations in February. The EGFR-TKI also carries other indications, including as first-line monotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
Trial Findings Supporting Latest Approval
AstraZeneca announced in June that osimertinib had been granted Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy Designation for its newest indication.
The September 25 approval was based on findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled LAURA trial of 216 patients, which demonstrated improved median progression-free survival with osimertinib vs placebo (39.1 vs 5.6 months; hazard ratio, 0.16). Overall survival results were immature at the most recent analysis, but “no trend towards a detriment was observed,” with 36% of prespecified deaths for the final analysis reported, according to an FDA press release.
Adverse Events
Study participants were randomized 2:1 to receive the osimertinib recommended dose of 80 mg given orally once daily or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, were lymphopenia, leukopenia, interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, rash, diarrhea, nail toxicity, musculoskeletal pain, cough, and COVID-19 infection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) was approved for patients whose disease has not progressed during or after concurrent or sequential platinum-based chemoradiation therapy and whose tumors have EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutations. Such EGFR mutations can be detected by an FDA-approved test.
The FDA approved osimertinib in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with the same mutations in February. The EGFR-TKI also carries other indications, including as first-line monotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
Trial Findings Supporting Latest Approval
AstraZeneca announced in June that osimertinib had been granted Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy Designation for its newest indication.
The September 25 approval was based on findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled LAURA trial of 216 patients, which demonstrated improved median progression-free survival with osimertinib vs placebo (39.1 vs 5.6 months; hazard ratio, 0.16). Overall survival results were immature at the most recent analysis, but “no trend towards a detriment was observed,” with 36% of prespecified deaths for the final analysis reported, according to an FDA press release.
Adverse Events
Study participants were randomized 2:1 to receive the osimertinib recommended dose of 80 mg given orally once daily or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, were lymphopenia, leukopenia, interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, rash, diarrhea, nail toxicity, musculoskeletal pain, cough, and COVID-19 infection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Medicare Advantage Offer Higher-Value Chemotherapy?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Private Medicare Advantage plans enroll more than half of the Medicare population, but it is unknown if or how the cost restrictions they impose affect chemotherapy, which accounts for a large portion of cancer care costs.
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using national Medicare data from January 2015 to December 2019 to look at Medicare Advantage enrollment and treatment patterns for patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- The study included 96,501 Medicare Advantage enrollees and 206,274 traditional Medicare beneficiaries who initiated chemotherapy between January 2016 and December 2019 (mean age, ~73 years; ~56% women; Hispanic individuals, 15% and 8%; Black individuals, 15% and 8%; and White individuals, 75% and 86%, respectively).
- Resource use and care quality were measured during a 6-month period following chemotherapy initiation, and survival days were measured 18 months after beginning chemotherapy.
- Resource use measures included hospital inpatient services, outpatient care, prescription drugs, hospice services, and chemotherapy services. Quality measures included chemotherapy-related emergency visits and hospital admissions, as well as avoidable emergency visits and preventable hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Medicare Advantage plans had lower resource use than traditional Medicare per enrollee with cancer undergoing chemotherapy ($8718 lower; 95% CI, $8343-$9094).
- The lower resource use was largely caused by fewer chemotherapy visits and less expensive chemotherapy per visit in Medicare Advantage plans ($5032 lower; 95% CI, $4772-$5293).
- Medicare Advantage enrollees had 2.5 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related emergency department visits and 0.7 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related hospitalizations than traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
- There was no clinically meaningful difference in survival between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare beneficiaries during the 18 months following chemotherapy initiation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our new finding is that MA [Medicare Advantage] plans had lower resource use than TM [traditional Medicare] among enrollees with cancer undergoing chemotherapy — a serious condition managed by specialists and requiring expensive treatments. This suggests that MA’s cost advantages over TM are not limited to conditions for which low-cost primary care management can avoid costly services,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yamini Kalidindi, PhD, McDermott+ Consulting, Washington, DC. It was published online on September 20, 2024, in JAMA Network Open (doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34707), with a commentary.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings may be affected by unobserved patient characteristics despite the use of inverse-probability weighting. The exclusion of Medicare Advantage enrollees in contracts with incomplete encounter data limits the generalizability of the results. The study does not apply to beneficiaries without Part D drug coverage. Quality measures were limited to those available from claims and encounter data, lacking information on patients’ cancer stage. The 18-month measure of survival might not adequately capture survival differences associated with early-stage cancers. The study did not measure whether patient care followed recommended guidelines.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, The Commonwealth Fund, Arnold Ventures, the National Cancer Institute, the Department of Defense, and the National Institute of Health Care Management. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Private Medicare Advantage plans enroll more than half of the Medicare population, but it is unknown if or how the cost restrictions they impose affect chemotherapy, which accounts for a large portion of cancer care costs.
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using national Medicare data from January 2015 to December 2019 to look at Medicare Advantage enrollment and treatment patterns for patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- The study included 96,501 Medicare Advantage enrollees and 206,274 traditional Medicare beneficiaries who initiated chemotherapy between January 2016 and December 2019 (mean age, ~73 years; ~56% women; Hispanic individuals, 15% and 8%; Black individuals, 15% and 8%; and White individuals, 75% and 86%, respectively).
- Resource use and care quality were measured during a 6-month period following chemotherapy initiation, and survival days were measured 18 months after beginning chemotherapy.
- Resource use measures included hospital inpatient services, outpatient care, prescription drugs, hospice services, and chemotherapy services. Quality measures included chemotherapy-related emergency visits and hospital admissions, as well as avoidable emergency visits and preventable hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Medicare Advantage plans had lower resource use than traditional Medicare per enrollee with cancer undergoing chemotherapy ($8718 lower; 95% CI, $8343-$9094).
- The lower resource use was largely caused by fewer chemotherapy visits and less expensive chemotherapy per visit in Medicare Advantage plans ($5032 lower; 95% CI, $4772-$5293).
- Medicare Advantage enrollees had 2.5 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related emergency department visits and 0.7 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related hospitalizations than traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
- There was no clinically meaningful difference in survival between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare beneficiaries during the 18 months following chemotherapy initiation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our new finding is that MA [Medicare Advantage] plans had lower resource use than TM [traditional Medicare] among enrollees with cancer undergoing chemotherapy — a serious condition managed by specialists and requiring expensive treatments. This suggests that MA’s cost advantages over TM are not limited to conditions for which low-cost primary care management can avoid costly services,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yamini Kalidindi, PhD, McDermott+ Consulting, Washington, DC. It was published online on September 20, 2024, in JAMA Network Open (doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34707), with a commentary.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings may be affected by unobserved patient characteristics despite the use of inverse-probability weighting. The exclusion of Medicare Advantage enrollees in contracts with incomplete encounter data limits the generalizability of the results. The study does not apply to beneficiaries without Part D drug coverage. Quality measures were limited to those available from claims and encounter data, lacking information on patients’ cancer stage. The 18-month measure of survival might not adequately capture survival differences associated with early-stage cancers. The study did not measure whether patient care followed recommended guidelines.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, The Commonwealth Fund, Arnold Ventures, the National Cancer Institute, the Department of Defense, and the National Institute of Health Care Management. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Private Medicare Advantage plans enroll more than half of the Medicare population, but it is unknown if or how the cost restrictions they impose affect chemotherapy, which accounts for a large portion of cancer care costs.
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using national Medicare data from January 2015 to December 2019 to look at Medicare Advantage enrollment and treatment patterns for patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- The study included 96,501 Medicare Advantage enrollees and 206,274 traditional Medicare beneficiaries who initiated chemotherapy between January 2016 and December 2019 (mean age, ~73 years; ~56% women; Hispanic individuals, 15% and 8%; Black individuals, 15% and 8%; and White individuals, 75% and 86%, respectively).
- Resource use and care quality were measured during a 6-month period following chemotherapy initiation, and survival days were measured 18 months after beginning chemotherapy.
- Resource use measures included hospital inpatient services, outpatient care, prescription drugs, hospice services, and chemotherapy services. Quality measures included chemotherapy-related emergency visits and hospital admissions, as well as avoidable emergency visits and preventable hospitalizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- Medicare Advantage plans had lower resource use than traditional Medicare per enrollee with cancer undergoing chemotherapy ($8718 lower; 95% CI, $8343-$9094).
- The lower resource use was largely caused by fewer chemotherapy visits and less expensive chemotherapy per visit in Medicare Advantage plans ($5032 lower; 95% CI, $4772-$5293).
- Medicare Advantage enrollees had 2.5 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related emergency department visits and 0.7 percentage points fewer chemotherapy-related hospitalizations than traditional Medicare beneficiaries.
- There was no clinically meaningful difference in survival between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare beneficiaries during the 18 months following chemotherapy initiation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our new finding is that MA [Medicare Advantage] plans had lower resource use than TM [traditional Medicare] among enrollees with cancer undergoing chemotherapy — a serious condition managed by specialists and requiring expensive treatments. This suggests that MA’s cost advantages over TM are not limited to conditions for which low-cost primary care management can avoid costly services,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yamini Kalidindi, PhD, McDermott+ Consulting, Washington, DC. It was published online on September 20, 2024, in JAMA Network Open (doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34707), with a commentary.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings may be affected by unobserved patient characteristics despite the use of inverse-probability weighting. The exclusion of Medicare Advantage enrollees in contracts with incomplete encounter data limits the generalizability of the results. The study does not apply to beneficiaries without Part D drug coverage. Quality measures were limited to those available from claims and encounter data, lacking information on patients’ cancer stage. The 18-month measure of survival might not adequately capture survival differences associated with early-stage cancers. The study did not measure whether patient care followed recommended guidelines.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, The Commonwealth Fund, Arnold Ventures, the National Cancer Institute, the Department of Defense, and the National Institute of Health Care Management. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AACR Cancer Progress Report: Big Strides and Big Gaps
The AACR’s 216-page report — an annual endeavor now in its 14th year — focused on the “tremendous” strides made in cancer care, prevention, and early detection and highlighted areas where more research and attention are warranted.
One key area is funding. For the first time since 2016, federal funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) decreased in the past year. The cuts followed nearly a decade of funding increases that saw the NIH budget expand by nearly $15 billion, and that allowed for a “rapid pace and broad scope” of advances in cancer, AACR’s chief executive officer Margaret Foti, MD, PhD, said during a press briefing.
These recent cuts “threaten to curtail the medical progress seen in recent years and stymie future advancements,” said Dr. Foti, who called on Congress to commit to funding cancer research at significant and consistent levels to “maintain the momentum of progress against cancer.”
Inside the Report: Big Progress
Overall, advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment have helped catch more cancers earlier and save lives.
According to the AACR report, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the United States fell by 33% between 1991 and 2021, meaning about 4.1 million cancer deaths were averted. The overall cancer death rate for children and adolescents has declined by 24% in the past 2 decades. The 5-year relative survival rate for children diagnosed with cancer in the US has improved from 58% for those diagnosed in the mid-1970s to 85% for those diagnosed between 2013 and 2019.
The past fiscal year has seen many new approvals for cancer drugs, diagnostics, and screening tests. From July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 15 new anticancer therapeutics, as well as 15 new indications for previously approved agents, one new imaging agent, several artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve early cancer detection and diagnosis, and two minimally invasive tests for assessing inherited cancer risk or early cancer detection, according to the report.
“Cancer diagnostics are becoming more sophisticated,” AACR president Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD, said during the briefing. “New technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics, are helping us study tumors at a cellular level, and helping to unveil things that we did not initially even begin to understand or think of. AI-based approaches are beginning to transform cancer detection, diagnosis, clinical decision-making, and treatment response monitoring.”
The report also highlights the significant progress in many childhood and adolescent/young adult cancers, Dr. LoRusso noted. These include FDA approvals for two new molecularly targeted therapeutics: tovorafenib for children with certain types of brain tumor and repotrectinib for children with a wide array of cancer types that have a specific genetic alteration known as NTRK gene fusion. It also includes an expanded approval for eflornithine to reduce the risk for relapse in children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
“Decades — decades — of basic research discoveries, have led to these clinical breakthroughs,” she stressed. “These gains against cancer are because of the rapid progress in our ability to decode the cancer genome, which has opened new and innovative avenues for drug development.”
The Gaps
Even with progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, cancer remains a significant issue.
“In 2024, it is estimated that more than 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. More than 611,000 people will die from the disease,” according to the report.
The 2024 report shows that incidence rates for some cancers are increasing in the United States, including vaccine-preventable cancers such as human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers and, in young adults, cervical cancers. A recent analysis also found that overall cervical cancer incidence among women aged 30-34 years increased by 2.5% a year between 2012 and 2019.
Furthermore, despite clear evidence demonstrating that the HPV vaccine reduces cervical cancer incidence, uptake has remained poor, with only 38.6% of US children and adolescents aged 9-17 years receiving at least one dose of the vaccine in 2022.
Early-onset cancers are also increasing. Rates of breast, colorectal, and other cancers are on the rise in adults younger than 50 years, the report noted.
The report also pointed to data that 40% of all cancer cases in the United States can be attributed to preventable factors, such as smoking, excess body weight, and alcohol. However, our understanding of these risk factors has improved. Excessive levels of alcohol consumption have, for instance, been shown to increase the risk for six different types of cancer: certain types of head and neck cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast, colorectal, liver, and stomach cancers.
Financial toxicity remains prevalent as well.
The report explains that financial hardship following a cancer diagnosis is widespread, and the effects can last for years. In fact, more than 40% of patients can spend their entire life savings within the first 2 years of cancer treatment. Among adult survivors of childhood cancers, 20.7% had trouble paying their medical bills, 29.9% said they had been sent to debt collection for unpaid bills, 14.1% had forgone medical care, and 26.8% could not afford nutritious meals.
For young cancer survivors, the lifetime costs associated with a diagnosis of cancer are substantial, reaching an average of $259,324 per person.
On a global level, it is estimated that from 2020 to 2050, the cumulative economic burden of cancer will be $25.2 trillion.
The Path Forward
Despite these challenges, Dr. LoRusso said, “it is unquestionable that we are in a time of unparalleled opportunities in cancer research.
“I am excited about what the future holds for cancer research, and especially for patient care,” she said.
However, funding commitments are needed to avoid impeding this momentum and losing a “talented and creative young workforce” that has brought new ideas and new technologies to the table.
Continued robust funding will help “to markedly improve cancer care, increase cancer survivorship, spur economic growth, and maintain the United States’ position as the global leader in science and medical research,” she added.
The AACR report specifically calls on Congress to:
- Appropriate at least $51.3 billion in fiscal year 2025 for the base budget of the NIH and at least $7.934 billion for the NCI.
- Provide $3.6 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities through fiscal year 2026 in addition to other funding, consistent with the President’s fiscal year 2025 budget.
- Appropriate at least $472.4 million in fiscal year 2025 for the CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
- Allocate $55 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in fiscal year 2025 to provide regulators with the staff and tools necessary to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
By working together with Congress and other stakeholders, “we will be able to accelerate the pace of progress and make major strides toward the lifesaving goal of preventing and curing all cancers at the earliest possible time,” Dr. Foti said. “I believe if we do that ... one day we will win this war on cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The AACR’s 216-page report — an annual endeavor now in its 14th year — focused on the “tremendous” strides made in cancer care, prevention, and early detection and highlighted areas where more research and attention are warranted.
One key area is funding. For the first time since 2016, federal funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) decreased in the past year. The cuts followed nearly a decade of funding increases that saw the NIH budget expand by nearly $15 billion, and that allowed for a “rapid pace and broad scope” of advances in cancer, AACR’s chief executive officer Margaret Foti, MD, PhD, said during a press briefing.
These recent cuts “threaten to curtail the medical progress seen in recent years and stymie future advancements,” said Dr. Foti, who called on Congress to commit to funding cancer research at significant and consistent levels to “maintain the momentum of progress against cancer.”
Inside the Report: Big Progress
Overall, advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment have helped catch more cancers earlier and save lives.
According to the AACR report, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the United States fell by 33% between 1991 and 2021, meaning about 4.1 million cancer deaths were averted. The overall cancer death rate for children and adolescents has declined by 24% in the past 2 decades. The 5-year relative survival rate for children diagnosed with cancer in the US has improved from 58% for those diagnosed in the mid-1970s to 85% for those diagnosed between 2013 and 2019.
The past fiscal year has seen many new approvals for cancer drugs, diagnostics, and screening tests. From July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 15 new anticancer therapeutics, as well as 15 new indications for previously approved agents, one new imaging agent, several artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve early cancer detection and diagnosis, and two minimally invasive tests for assessing inherited cancer risk or early cancer detection, according to the report.
“Cancer diagnostics are becoming more sophisticated,” AACR president Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD, said during the briefing. “New technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics, are helping us study tumors at a cellular level, and helping to unveil things that we did not initially even begin to understand or think of. AI-based approaches are beginning to transform cancer detection, diagnosis, clinical decision-making, and treatment response monitoring.”
The report also highlights the significant progress in many childhood and adolescent/young adult cancers, Dr. LoRusso noted. These include FDA approvals for two new molecularly targeted therapeutics: tovorafenib for children with certain types of brain tumor and repotrectinib for children with a wide array of cancer types that have a specific genetic alteration known as NTRK gene fusion. It also includes an expanded approval for eflornithine to reduce the risk for relapse in children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
“Decades — decades — of basic research discoveries, have led to these clinical breakthroughs,” she stressed. “These gains against cancer are because of the rapid progress in our ability to decode the cancer genome, which has opened new and innovative avenues for drug development.”
The Gaps
Even with progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, cancer remains a significant issue.
“In 2024, it is estimated that more than 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. More than 611,000 people will die from the disease,” according to the report.
The 2024 report shows that incidence rates for some cancers are increasing in the United States, including vaccine-preventable cancers such as human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers and, in young adults, cervical cancers. A recent analysis also found that overall cervical cancer incidence among women aged 30-34 years increased by 2.5% a year between 2012 and 2019.
Furthermore, despite clear evidence demonstrating that the HPV vaccine reduces cervical cancer incidence, uptake has remained poor, with only 38.6% of US children and adolescents aged 9-17 years receiving at least one dose of the vaccine in 2022.
Early-onset cancers are also increasing. Rates of breast, colorectal, and other cancers are on the rise in adults younger than 50 years, the report noted.
The report also pointed to data that 40% of all cancer cases in the United States can be attributed to preventable factors, such as smoking, excess body weight, and alcohol. However, our understanding of these risk factors has improved. Excessive levels of alcohol consumption have, for instance, been shown to increase the risk for six different types of cancer: certain types of head and neck cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast, colorectal, liver, and stomach cancers.
Financial toxicity remains prevalent as well.
The report explains that financial hardship following a cancer diagnosis is widespread, and the effects can last for years. In fact, more than 40% of patients can spend their entire life savings within the first 2 years of cancer treatment. Among adult survivors of childhood cancers, 20.7% had trouble paying their medical bills, 29.9% said they had been sent to debt collection for unpaid bills, 14.1% had forgone medical care, and 26.8% could not afford nutritious meals.
For young cancer survivors, the lifetime costs associated with a diagnosis of cancer are substantial, reaching an average of $259,324 per person.
On a global level, it is estimated that from 2020 to 2050, the cumulative economic burden of cancer will be $25.2 trillion.
The Path Forward
Despite these challenges, Dr. LoRusso said, “it is unquestionable that we are in a time of unparalleled opportunities in cancer research.
“I am excited about what the future holds for cancer research, and especially for patient care,” she said.
However, funding commitments are needed to avoid impeding this momentum and losing a “talented and creative young workforce” that has brought new ideas and new technologies to the table.
Continued robust funding will help “to markedly improve cancer care, increase cancer survivorship, spur economic growth, and maintain the United States’ position as the global leader in science and medical research,” she added.
The AACR report specifically calls on Congress to:
- Appropriate at least $51.3 billion in fiscal year 2025 for the base budget of the NIH and at least $7.934 billion for the NCI.
- Provide $3.6 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities through fiscal year 2026 in addition to other funding, consistent with the President’s fiscal year 2025 budget.
- Appropriate at least $472.4 million in fiscal year 2025 for the CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
- Allocate $55 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in fiscal year 2025 to provide regulators with the staff and tools necessary to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
By working together with Congress and other stakeholders, “we will be able to accelerate the pace of progress and make major strides toward the lifesaving goal of preventing and curing all cancers at the earliest possible time,” Dr. Foti said. “I believe if we do that ... one day we will win this war on cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The AACR’s 216-page report — an annual endeavor now in its 14th year — focused on the “tremendous” strides made in cancer care, prevention, and early detection and highlighted areas where more research and attention are warranted.
One key area is funding. For the first time since 2016, federal funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) decreased in the past year. The cuts followed nearly a decade of funding increases that saw the NIH budget expand by nearly $15 billion, and that allowed for a “rapid pace and broad scope” of advances in cancer, AACR’s chief executive officer Margaret Foti, MD, PhD, said during a press briefing.
These recent cuts “threaten to curtail the medical progress seen in recent years and stymie future advancements,” said Dr. Foti, who called on Congress to commit to funding cancer research at significant and consistent levels to “maintain the momentum of progress against cancer.”
Inside the Report: Big Progress
Overall, advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment have helped catch more cancers earlier and save lives.
According to the AACR report, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the United States fell by 33% between 1991 and 2021, meaning about 4.1 million cancer deaths were averted. The overall cancer death rate for children and adolescents has declined by 24% in the past 2 decades. The 5-year relative survival rate for children diagnosed with cancer in the US has improved from 58% for those diagnosed in the mid-1970s to 85% for those diagnosed between 2013 and 2019.
The past fiscal year has seen many new approvals for cancer drugs, diagnostics, and screening tests. From July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 15 new anticancer therapeutics, as well as 15 new indications for previously approved agents, one new imaging agent, several artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve early cancer detection and diagnosis, and two minimally invasive tests for assessing inherited cancer risk or early cancer detection, according to the report.
“Cancer diagnostics are becoming more sophisticated,” AACR president Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD, said during the briefing. “New technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics, are helping us study tumors at a cellular level, and helping to unveil things that we did not initially even begin to understand or think of. AI-based approaches are beginning to transform cancer detection, diagnosis, clinical decision-making, and treatment response monitoring.”
The report also highlights the significant progress in many childhood and adolescent/young adult cancers, Dr. LoRusso noted. These include FDA approvals for two new molecularly targeted therapeutics: tovorafenib for children with certain types of brain tumor and repotrectinib for children with a wide array of cancer types that have a specific genetic alteration known as NTRK gene fusion. It also includes an expanded approval for eflornithine to reduce the risk for relapse in children with high-risk neuroblastoma.
“Decades — decades — of basic research discoveries, have led to these clinical breakthroughs,” she stressed. “These gains against cancer are because of the rapid progress in our ability to decode the cancer genome, which has opened new and innovative avenues for drug development.”
The Gaps
Even with progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, cancer remains a significant issue.
“In 2024, it is estimated that more than 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. More than 611,000 people will die from the disease,” according to the report.
The 2024 report shows that incidence rates for some cancers are increasing in the United States, including vaccine-preventable cancers such as human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated oral cancers and, in young adults, cervical cancers. A recent analysis also found that overall cervical cancer incidence among women aged 30-34 years increased by 2.5% a year between 2012 and 2019.
Furthermore, despite clear evidence demonstrating that the HPV vaccine reduces cervical cancer incidence, uptake has remained poor, with only 38.6% of US children and adolescents aged 9-17 years receiving at least one dose of the vaccine in 2022.
Early-onset cancers are also increasing. Rates of breast, colorectal, and other cancers are on the rise in adults younger than 50 years, the report noted.
The report also pointed to data that 40% of all cancer cases in the United States can be attributed to preventable factors, such as smoking, excess body weight, and alcohol. However, our understanding of these risk factors has improved. Excessive levels of alcohol consumption have, for instance, been shown to increase the risk for six different types of cancer: certain types of head and neck cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and breast, colorectal, liver, and stomach cancers.
Financial toxicity remains prevalent as well.
The report explains that financial hardship following a cancer diagnosis is widespread, and the effects can last for years. In fact, more than 40% of patients can spend their entire life savings within the first 2 years of cancer treatment. Among adult survivors of childhood cancers, 20.7% had trouble paying their medical bills, 29.9% said they had been sent to debt collection for unpaid bills, 14.1% had forgone medical care, and 26.8% could not afford nutritious meals.
For young cancer survivors, the lifetime costs associated with a diagnosis of cancer are substantial, reaching an average of $259,324 per person.
On a global level, it is estimated that from 2020 to 2050, the cumulative economic burden of cancer will be $25.2 trillion.
The Path Forward
Despite these challenges, Dr. LoRusso said, “it is unquestionable that we are in a time of unparalleled opportunities in cancer research.
“I am excited about what the future holds for cancer research, and especially for patient care,” she said.
However, funding commitments are needed to avoid impeding this momentum and losing a “talented and creative young workforce” that has brought new ideas and new technologies to the table.
Continued robust funding will help “to markedly improve cancer care, increase cancer survivorship, spur economic growth, and maintain the United States’ position as the global leader in science and medical research,” she added.
The AACR report specifically calls on Congress to:
- Appropriate at least $51.3 billion in fiscal year 2025 for the base budget of the NIH and at least $7.934 billion for the NCI.
- Provide $3.6 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities through fiscal year 2026 in addition to other funding, consistent with the President’s fiscal year 2025 budget.
- Appropriate at least $472.4 million in fiscal year 2025 for the CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
- Allocate $55 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in fiscal year 2025 to provide regulators with the staff and tools necessary to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
By working together with Congress and other stakeholders, “we will be able to accelerate the pace of progress and make major strides toward the lifesaving goal of preventing and curing all cancers at the earliest possible time,” Dr. Foti said. “I believe if we do that ... one day we will win this war on cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.