User login
Preparing patients with serious mental illness for extreme HEAT
Climate change is causing intense heat waves that threaten human health across the globe.
A confluence of factors increases risk
Thermoregulatory dysfunction is thought to be intrinsic to patients with schizophrenia partly due to dysregulated dopaminergic neurotransmission.2 This is compounded by these patients’ higher burden of chronic medical comorbidities such as cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses, which together with psychotropic (ie, antipsychotics, antidepressants, lithium, benzodiazepines) and medical medications (ie, certain antihypertensives, diuretics, treatment for urinary incontinence) further disrupt the body’s cooling strategies and increase vulnerability to heat-related illnesses.1,3 Antipsychotics commonly prescribed to patients with SMI increase hyperthermia risk largely by 2 mechanisms: central and peripheral thermal dysregulation, and anticholinergic properties (ie, olanzapine, clozapine, chlorpromazine).2,3 Other anticholinergic medications prescribed to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (ie, diphenhydramine, benztropine, trihexyphenidyl), anxiety, depression, and insomnia (ie, paroxetine, trazodone, doxepin) further add insult to injury because they impair sweating, which decreases the body’s ability to eliminate heat through evaporation.2,3 Additionally, high temperature exacerbates psychiatric symptoms in patients with SMI, resulting in increased hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
How to keep patients safe
The acronym HEAT provides a framework that psychiatrists can use to highlight the importance of planning for heat waves in their institution and guiding discussions with individual patients about heat-related illnesses (Table 1).

Help the health care system where you work plan and prepare for heat waves. In-service training in mental health settings such as outpatient clinics, shelters, group homes, and residential programs can help staff identify patients at particular risk and reinforce key prevention messages.
Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies for preventing heat-related illness. Informational materials can be distributed in clinics, residential settings, and day programs. A 1-page downloadable pamphlet available at https://smiadviser.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SMI-Heat-Stroke-ver1.0-FINAL.pdf summarizes key prevention messages of staying hydrated, staying cool, and staying safe.
Assess personalized heat-related risks. Inquire about patients’ daily activities, access to air conditioning, and water intake. Minimize the use of anticholinergic medications. Identify who patients can turn to for assistance, especially for those who struggle with cognitive impairment and social isolation.
Teach patients, caregivers, and staff the signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke and how to respond in such situations.
HEAT focuses psychiatric clinicians on preparing and protecting patients with SMI against dangerous heat waves. Clinicians can take a proactive leadership role in disseminating basic principles of heat-related illness prevention and heat-wave toolkits by using resources available from organizations such as the Climate Psychiatry Alliance (Table 2). They can also initiate advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the elevated risks of heat-related illnesses in this vulnerable population.

1. Schmeltz MT, Gamble JL. Risk characterization of hospitalizations for mental illness and/or behavioral disorders with concurrent heat-related illness. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186509
2. Lee CP, Chen PJ, Chang CM. Heat stroke during treatment with olanzapine, trihexyphenidyl, and trazodone in a patient with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2015;27(6):380-385.
3. Bongers KS, Salahudeen MS, Peterson GM. Drug-associated non-pyrogenic hyperthermia: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(1):9-16.
Climate change is causing intense heat waves that threaten human health across the globe.
A confluence of factors increases risk
Thermoregulatory dysfunction is thought to be intrinsic to patients with schizophrenia partly due to dysregulated dopaminergic neurotransmission.2 This is compounded by these patients’ higher burden of chronic medical comorbidities such as cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses, which together with psychotropic (ie, antipsychotics, antidepressants, lithium, benzodiazepines) and medical medications (ie, certain antihypertensives, diuretics, treatment for urinary incontinence) further disrupt the body’s cooling strategies and increase vulnerability to heat-related illnesses.1,3 Antipsychotics commonly prescribed to patients with SMI increase hyperthermia risk largely by 2 mechanisms: central and peripheral thermal dysregulation, and anticholinergic properties (ie, olanzapine, clozapine, chlorpromazine).2,3 Other anticholinergic medications prescribed to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (ie, diphenhydramine, benztropine, trihexyphenidyl), anxiety, depression, and insomnia (ie, paroxetine, trazodone, doxepin) further add insult to injury because they impair sweating, which decreases the body’s ability to eliminate heat through evaporation.2,3 Additionally, high temperature exacerbates psychiatric symptoms in patients with SMI, resulting in increased hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
How to keep patients safe
The acronym HEAT provides a framework that psychiatrists can use to highlight the importance of planning for heat waves in their institution and guiding discussions with individual patients about heat-related illnesses (Table 1).

Help the health care system where you work plan and prepare for heat waves. In-service training in mental health settings such as outpatient clinics, shelters, group homes, and residential programs can help staff identify patients at particular risk and reinforce key prevention messages.
Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies for preventing heat-related illness. Informational materials can be distributed in clinics, residential settings, and day programs. A 1-page downloadable pamphlet available at https://smiadviser.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SMI-Heat-Stroke-ver1.0-FINAL.pdf summarizes key prevention messages of staying hydrated, staying cool, and staying safe.
Assess personalized heat-related risks. Inquire about patients’ daily activities, access to air conditioning, and water intake. Minimize the use of anticholinergic medications. Identify who patients can turn to for assistance, especially for those who struggle with cognitive impairment and social isolation.
Teach patients, caregivers, and staff the signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke and how to respond in such situations.
HEAT focuses psychiatric clinicians on preparing and protecting patients with SMI against dangerous heat waves. Clinicians can take a proactive leadership role in disseminating basic principles of heat-related illness prevention and heat-wave toolkits by using resources available from organizations such as the Climate Psychiatry Alliance (Table 2). They can also initiate advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the elevated risks of heat-related illnesses in this vulnerable population.

Climate change is causing intense heat waves that threaten human health across the globe.
A confluence of factors increases risk
Thermoregulatory dysfunction is thought to be intrinsic to patients with schizophrenia partly due to dysregulated dopaminergic neurotransmission.2 This is compounded by these patients’ higher burden of chronic medical comorbidities such as cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses, which together with psychotropic (ie, antipsychotics, antidepressants, lithium, benzodiazepines) and medical medications (ie, certain antihypertensives, diuretics, treatment for urinary incontinence) further disrupt the body’s cooling strategies and increase vulnerability to heat-related illnesses.1,3 Antipsychotics commonly prescribed to patients with SMI increase hyperthermia risk largely by 2 mechanisms: central and peripheral thermal dysregulation, and anticholinergic properties (ie, olanzapine, clozapine, chlorpromazine).2,3 Other anticholinergic medications prescribed to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (ie, diphenhydramine, benztropine, trihexyphenidyl), anxiety, depression, and insomnia (ie, paroxetine, trazodone, doxepin) further add insult to injury because they impair sweating, which decreases the body’s ability to eliminate heat through evaporation.2,3 Additionally, high temperature exacerbates psychiatric symptoms in patients with SMI, resulting in increased hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
How to keep patients safe
The acronym HEAT provides a framework that psychiatrists can use to highlight the importance of planning for heat waves in their institution and guiding discussions with individual patients about heat-related illnesses (Table 1).

Help the health care system where you work plan and prepare for heat waves. In-service training in mental health settings such as outpatient clinics, shelters, group homes, and residential programs can help staff identify patients at particular risk and reinforce key prevention messages.
Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies for preventing heat-related illness. Informational materials can be distributed in clinics, residential settings, and day programs. A 1-page downloadable pamphlet available at https://smiadviser.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SMI-Heat-Stroke-ver1.0-FINAL.pdf summarizes key prevention messages of staying hydrated, staying cool, and staying safe.
Assess personalized heat-related risks. Inquire about patients’ daily activities, access to air conditioning, and water intake. Minimize the use of anticholinergic medications. Identify who patients can turn to for assistance, especially for those who struggle with cognitive impairment and social isolation.
Teach patients, caregivers, and staff the signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke and how to respond in such situations.
HEAT focuses psychiatric clinicians on preparing and protecting patients with SMI against dangerous heat waves. Clinicians can take a proactive leadership role in disseminating basic principles of heat-related illness prevention and heat-wave toolkits by using resources available from organizations such as the Climate Psychiatry Alliance (Table 2). They can also initiate advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the elevated risks of heat-related illnesses in this vulnerable population.

1. Schmeltz MT, Gamble JL. Risk characterization of hospitalizations for mental illness and/or behavioral disorders with concurrent heat-related illness. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186509
2. Lee CP, Chen PJ, Chang CM. Heat stroke during treatment with olanzapine, trihexyphenidyl, and trazodone in a patient with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2015;27(6):380-385.
3. Bongers KS, Salahudeen MS, Peterson GM. Drug-associated non-pyrogenic hyperthermia: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(1):9-16.
1. Schmeltz MT, Gamble JL. Risk characterization of hospitalizations for mental illness and/or behavioral disorders with concurrent heat-related illness. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186509
2. Lee CP, Chen PJ, Chang CM. Heat stroke during treatment with olanzapine, trihexyphenidyl, and trazodone in a patient with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2015;27(6):380-385.
3. Bongers KS, Salahudeen MS, Peterson GM. Drug-associated non-pyrogenic hyperthermia: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(1):9-16.
Lithium for bipolar disorder: Which patients will respond?
Though Cade discovered it 70 years ago, lithium is still considered the gold standard treatment for preventing manic and depressive phases of bipolar disorder (BD). In addition to its primary indication as a mood stabilizer, lithium has demonstrated efficacy as an augmenting medication for unipolar major depressive disorder.1 While lithium is a first-line agent for BD, it does not improve symptoms in every patient. In a 2004 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials of patients with BD, Geddes et al2 found lithium was more effective than placebo in preventing the recurrence of mania, with 60% in the lithium group remaining stable compared to 40% in the placebo group. Being able to predict which patients will respond to lithium is crucial to prevent unnecessary exposure to lithium, which can produce significant adverse effects, including somnolence, nausea, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism.2
Several studies have investigated various clinical factors that might predict which patients with BD will respond to lithium. In a review, Kleindienst et al3 highlighted 3 factors that predicted a positive response to lithium:
- fewer hospitalizations prior to treatment
- an episodic course characterized sequentially by mania, depression, and then euthymia
- a later age (>50) at onset of BD.
Recent studies and reviews have isolated additional positive predictors, including having a family history of BD and a shorter duration of illness before receiving lithium, as well as negative predictors, such as rapid cycling, a large number of previous hospitalizations, a depression/mania/euthymia pattern, mood-incongruent psychotic features, and the presence of residual symptoms between mood episodes.3,4
The Table provides a list of probable and possible positive and negative predictors for therapeutic response to lithium in patients with BD.3-6 While relevant, the factors listed as possible predictors may not carry as much influence on lithium responsivity as those categorized as probable predictors.
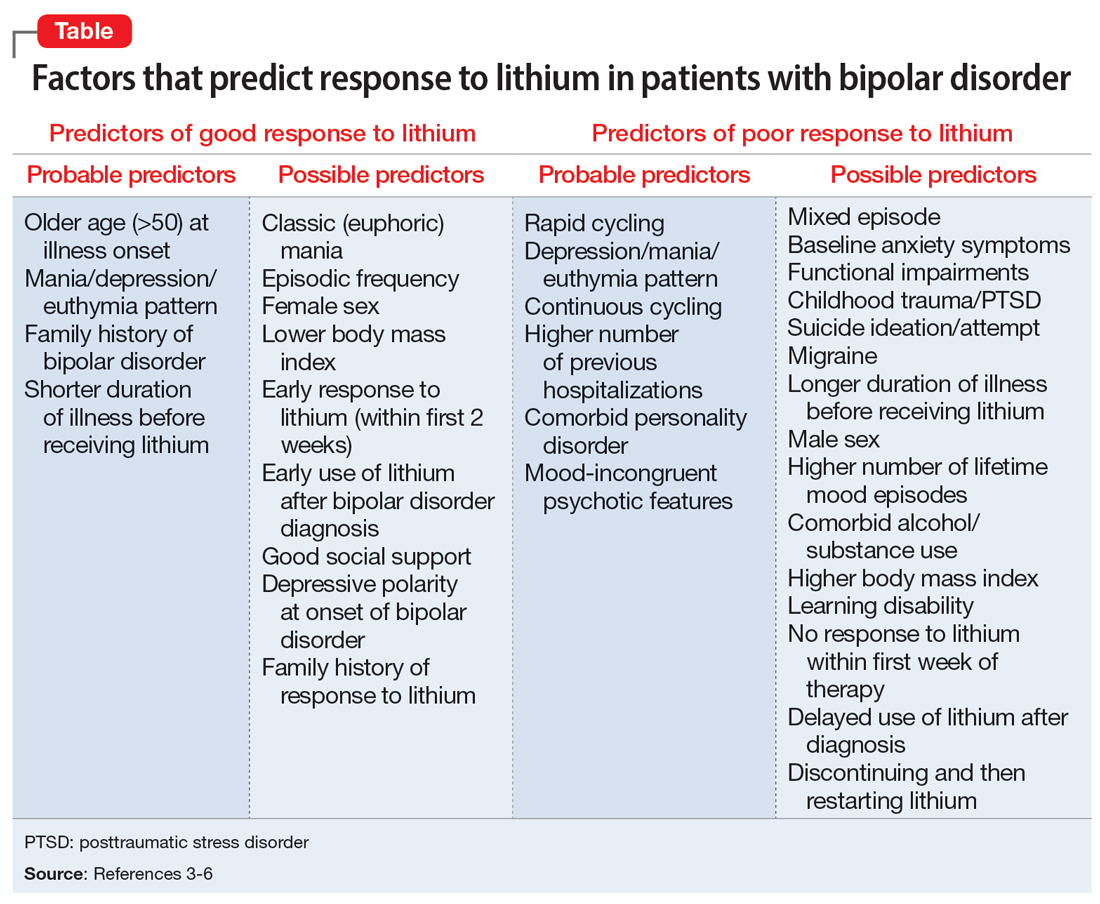
Because of heterogeneity among studies, clinicians should consider their patient’s presentation as a whole, rather than basing medication choice on independent factors. Ultimately, more studies are required to fully determine the most relevant clinical parameters for lithium response. Overall, however, it appears these clinical factors could be extremely useful to guide psychiatrists in the optimal use of lithium while caring for patients with BD.
1. Crossley NA, Bauer M. Acceleration and augmentation of antidepressants with lithium for depressive disorders: two meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(6):935-940.
2. Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, et al. Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;1m61(2):217-222.
3. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Which clinical factors predict response to prophylactic lithium? A systematic review for bipolar disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(5):404-417.
4. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Psychosocial and demographic factors associated with response to prophylactic lithium: a systematic review for bipolar disorders. Psychol Med. 2005;35(12):1685-1694.
5. Hui TP, Kandola A, Shen L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical predictors of lithium response in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;140(2):94-115.
6. Grillault Laroche D, Etain B, Severus E, et al. Socio-demographic and clinical predictors of outcome to long-term treatment with lithium in bipolar disorders: a systematic review of the contemporary literature and recommendations from the ISBD/IGSLI Task Force on treatment with lithium. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2020;8(1):40.
Though Cade discovered it 70 years ago, lithium is still considered the gold standard treatment for preventing manic and depressive phases of bipolar disorder (BD). In addition to its primary indication as a mood stabilizer, lithium has demonstrated efficacy as an augmenting medication for unipolar major depressive disorder.1 While lithium is a first-line agent for BD, it does not improve symptoms in every patient. In a 2004 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials of patients with BD, Geddes et al2 found lithium was more effective than placebo in preventing the recurrence of mania, with 60% in the lithium group remaining stable compared to 40% in the placebo group. Being able to predict which patients will respond to lithium is crucial to prevent unnecessary exposure to lithium, which can produce significant adverse effects, including somnolence, nausea, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism.2
Several studies have investigated various clinical factors that might predict which patients with BD will respond to lithium. In a review, Kleindienst et al3 highlighted 3 factors that predicted a positive response to lithium:
- fewer hospitalizations prior to treatment
- an episodic course characterized sequentially by mania, depression, and then euthymia
- a later age (>50) at onset of BD.
Recent studies and reviews have isolated additional positive predictors, including having a family history of BD and a shorter duration of illness before receiving lithium, as well as negative predictors, such as rapid cycling, a large number of previous hospitalizations, a depression/mania/euthymia pattern, mood-incongruent psychotic features, and the presence of residual symptoms between mood episodes.3,4
The Table provides a list of probable and possible positive and negative predictors for therapeutic response to lithium in patients with BD.3-6 While relevant, the factors listed as possible predictors may not carry as much influence on lithium responsivity as those categorized as probable predictors.

Because of heterogeneity among studies, clinicians should consider their patient’s presentation as a whole, rather than basing medication choice on independent factors. Ultimately, more studies are required to fully determine the most relevant clinical parameters for lithium response. Overall, however, it appears these clinical factors could be extremely useful to guide psychiatrists in the optimal use of lithium while caring for patients with BD.
Though Cade discovered it 70 years ago, lithium is still considered the gold standard treatment for preventing manic and depressive phases of bipolar disorder (BD). In addition to its primary indication as a mood stabilizer, lithium has demonstrated efficacy as an augmenting medication for unipolar major depressive disorder.1 While lithium is a first-line agent for BD, it does not improve symptoms in every patient. In a 2004 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials of patients with BD, Geddes et al2 found lithium was more effective than placebo in preventing the recurrence of mania, with 60% in the lithium group remaining stable compared to 40% in the placebo group. Being able to predict which patients will respond to lithium is crucial to prevent unnecessary exposure to lithium, which can produce significant adverse effects, including somnolence, nausea, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism.2
Several studies have investigated various clinical factors that might predict which patients with BD will respond to lithium. In a review, Kleindienst et al3 highlighted 3 factors that predicted a positive response to lithium:
- fewer hospitalizations prior to treatment
- an episodic course characterized sequentially by mania, depression, and then euthymia
- a later age (>50) at onset of BD.
Recent studies and reviews have isolated additional positive predictors, including having a family history of BD and a shorter duration of illness before receiving lithium, as well as negative predictors, such as rapid cycling, a large number of previous hospitalizations, a depression/mania/euthymia pattern, mood-incongruent psychotic features, and the presence of residual symptoms between mood episodes.3,4
The Table provides a list of probable and possible positive and negative predictors for therapeutic response to lithium in patients with BD.3-6 While relevant, the factors listed as possible predictors may not carry as much influence on lithium responsivity as those categorized as probable predictors.

Because of heterogeneity among studies, clinicians should consider their patient’s presentation as a whole, rather than basing medication choice on independent factors. Ultimately, more studies are required to fully determine the most relevant clinical parameters for lithium response. Overall, however, it appears these clinical factors could be extremely useful to guide psychiatrists in the optimal use of lithium while caring for patients with BD.
1. Crossley NA, Bauer M. Acceleration and augmentation of antidepressants with lithium for depressive disorders: two meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(6):935-940.
2. Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, et al. Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;1m61(2):217-222.
3. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Which clinical factors predict response to prophylactic lithium? A systematic review for bipolar disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(5):404-417.
4. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Psychosocial and demographic factors associated with response to prophylactic lithium: a systematic review for bipolar disorders. Psychol Med. 2005;35(12):1685-1694.
5. Hui TP, Kandola A, Shen L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical predictors of lithium response in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;140(2):94-115.
6. Grillault Laroche D, Etain B, Severus E, et al. Socio-demographic and clinical predictors of outcome to long-term treatment with lithium in bipolar disorders: a systematic review of the contemporary literature and recommendations from the ISBD/IGSLI Task Force on treatment with lithium. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2020;8(1):40.
1. Crossley NA, Bauer M. Acceleration and augmentation of antidepressants with lithium for depressive disorders: two meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(6):935-940.
2. Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, et al. Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;1m61(2):217-222.
3. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Which clinical factors predict response to prophylactic lithium? A systematic review for bipolar disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(5):404-417.
4. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Psychosocial and demographic factors associated with response to prophylactic lithium: a systematic review for bipolar disorders. Psychol Med. 2005;35(12):1685-1694.
5. Hui TP, Kandola A, Shen L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical predictors of lithium response in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;140(2):94-115.
6. Grillault Laroche D, Etain B, Severus E, et al. Socio-demographic and clinical predictors of outcome to long-term treatment with lithium in bipolar disorders: a systematic review of the contemporary literature and recommendations from the ISBD/IGSLI Task Force on treatment with lithium. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2020;8(1):40.
Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale succeeds as transdiagnostic measure
“Current DSM and ICD diagnoses do not depict psychopathology accurately, therefore their validity in research and utility in clinical practice is questioned,” wrote Andreas B. Hofmann, PhD, of the University of Zürich and colleagues.
The BPRS was developed to assess changes in psychopathology across a range of severe psychiatric disorders, but its potential to assess symptoms in nonpsychotic disorders has not been explored, the researchers said.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the investigators analyzed data from 600 adult psychiatric inpatients divided equally into six diagnostic categories: alcohol use disorder, major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and personality disorders. The mean age of the patients was 41.5 years and 45.5% were women. The demographic characteristics were similar across most groups, although patients with a personality disorder were significantly more likely than other patients to be younger and female.
Patients were assessed using the BPRS based on their main diagnosis. The mini-ICF-APP, another validated measure for assessing psychiatric disorders, served as a comparator, and both were compared to the Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGI).
Overall, the BPRS and mini-ICF-APP showed moderate correlation and good agreement, the researchers said. The Pearson correlation coefficient for the BPRS and mini-ICF-APP scales was 0.53 and the concordance correlation coefficient was 0.52. The mean sum scores for the BPRS, the mini-ICF-APP, and the CGI were 45.4 (standard deviation, 14.4), 19.93 (SD, 8.21), and 5.55 (SD, 0.84), respectively, which indicated “markedly ill” to “severely ill” patients, the researchers said.
The researchers were able to detect three clusters of symptoms corresponding to externalizing, internalizing, and thought disturbance domains using the BPRS, and four clusters using the mini-ICF-APP.
The symptoms using BPRS and the functionality domains using the mini-ICF-APP “showed a close interplay,” the researchers noted.
“The symptoms and functional domains we found to be central within the network structure are among the first targets of any psychiatric or psychotherapeutic intervention, namely the building of a common language and understanding as well as the establishment of confidence in relationships and a trustworthy therapeutic alliance,” they wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the collection of data from routine practice rather than clinical trials, the focus on only the main diagnosis without comorbidities, and the inclusion only of patients requiring hospitalization, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and demonstrate the validity of the BPRS as a measurement tool across a range of psychiatric diagnoses, they said.
“Since the BPRS is a widely known and readily available psychometric scale, our results support its use as a transdiagnostic measurement instrument of psychopathology,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Current DSM and ICD diagnoses do not depict psychopathology accurately, therefore their validity in research and utility in clinical practice is questioned,” wrote Andreas B. Hofmann, PhD, of the University of Zürich and colleagues.
The BPRS was developed to assess changes in psychopathology across a range of severe psychiatric disorders, but its potential to assess symptoms in nonpsychotic disorders has not been explored, the researchers said.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the investigators analyzed data from 600 adult psychiatric inpatients divided equally into six diagnostic categories: alcohol use disorder, major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and personality disorders. The mean age of the patients was 41.5 years and 45.5% were women. The demographic characteristics were similar across most groups, although patients with a personality disorder were significantly more likely than other patients to be younger and female.
Patients were assessed using the BPRS based on their main diagnosis. The mini-ICF-APP, another validated measure for assessing psychiatric disorders, served as a comparator, and both were compared to the Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGI).
Overall, the BPRS and mini-ICF-APP showed moderate correlation and good agreement, the researchers said. The Pearson correlation coefficient for the BPRS and mini-ICF-APP scales was 0.53 and the concordance correlation coefficient was 0.52. The mean sum scores for the BPRS, the mini-ICF-APP, and the CGI were 45.4 (standard deviation, 14.4), 19.93 (SD, 8.21), and 5.55 (SD, 0.84), respectively, which indicated “markedly ill” to “severely ill” patients, the researchers said.
The researchers were able to detect three clusters of symptoms corresponding to externalizing, internalizing, and thought disturbance domains using the BPRS, and four clusters using the mini-ICF-APP.
The symptoms using BPRS and the functionality domains using the mini-ICF-APP “showed a close interplay,” the researchers noted.
“The symptoms and functional domains we found to be central within the network structure are among the first targets of any psychiatric or psychotherapeutic intervention, namely the building of a common language and understanding as well as the establishment of confidence in relationships and a trustworthy therapeutic alliance,” they wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the collection of data from routine practice rather than clinical trials, the focus on only the main diagnosis without comorbidities, and the inclusion only of patients requiring hospitalization, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and demonstrate the validity of the BPRS as a measurement tool across a range of psychiatric diagnoses, they said.
“Since the BPRS is a widely known and readily available psychometric scale, our results support its use as a transdiagnostic measurement instrument of psychopathology,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Current DSM and ICD diagnoses do not depict psychopathology accurately, therefore their validity in research and utility in clinical practice is questioned,” wrote Andreas B. Hofmann, PhD, of the University of Zürich and colleagues.
The BPRS was developed to assess changes in psychopathology across a range of severe psychiatric disorders, but its potential to assess symptoms in nonpsychotic disorders has not been explored, the researchers said.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the investigators analyzed data from 600 adult psychiatric inpatients divided equally into six diagnostic categories: alcohol use disorder, major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and personality disorders. The mean age of the patients was 41.5 years and 45.5% were women. The demographic characteristics were similar across most groups, although patients with a personality disorder were significantly more likely than other patients to be younger and female.
Patients were assessed using the BPRS based on their main diagnosis. The mini-ICF-APP, another validated measure for assessing psychiatric disorders, served as a comparator, and both were compared to the Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGI).
Overall, the BPRS and mini-ICF-APP showed moderate correlation and good agreement, the researchers said. The Pearson correlation coefficient for the BPRS and mini-ICF-APP scales was 0.53 and the concordance correlation coefficient was 0.52. The mean sum scores for the BPRS, the mini-ICF-APP, and the CGI were 45.4 (standard deviation, 14.4), 19.93 (SD, 8.21), and 5.55 (SD, 0.84), respectively, which indicated “markedly ill” to “severely ill” patients, the researchers said.
The researchers were able to detect three clusters of symptoms corresponding to externalizing, internalizing, and thought disturbance domains using the BPRS, and four clusters using the mini-ICF-APP.
The symptoms using BPRS and the functionality domains using the mini-ICF-APP “showed a close interplay,” the researchers noted.
“The symptoms and functional domains we found to be central within the network structure are among the first targets of any psychiatric or psychotherapeutic intervention, namely the building of a common language and understanding as well as the establishment of confidence in relationships and a trustworthy therapeutic alliance,” they wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the collection of data from routine practice rather than clinical trials, the focus on only the main diagnosis without comorbidities, and the inclusion only of patients requiring hospitalization, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and demonstrate the validity of the BPRS as a measurement tool across a range of psychiatric diagnoses, they said.
“Since the BPRS is a widely known and readily available psychometric scale, our results support its use as a transdiagnostic measurement instrument of psychopathology,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PSYCHIATRY RESEARCH
Telemental health linked with improvements in key outcomes
, new research suggests.
In a nationwide study, researchers drew on Medicare data from nearly 3,000 counties covering the period from 2000 to 2018. Results show that counties in which there was greater use of telemental health services reported higher increases of clinical visits and better follow-up after hospitalization among patients with bipolar 1 disorder and schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders.
In the study, “clinical visits” referred to both in-person and telemental health visits.
“These findings really support the idea that telemental health can be safe and effective and beneficial for in-person care for people with severe mental illness,” coinvestigator Haiden Huskamp, PhD, professor of health care policy at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Continuing trend?
Past studies have pointed to a sharp increase in the use of telepsychiatry services for patients with SMI. As reported by this news organization, this is a trend some clinicians say is likely to continue after the pandemic.
Use of telemedicine during the pandemic received a boost by the temporary suspension of certain Medicare rules that restrict telehealth use. Debate continues at the federal and state levels on whether to make that suspension permanent. Dr. Huskamp said more information is needed about the efficacy and accessibility of telemental health.
To investigate, researchers used Medicare fee-for-service data from 118,170 patients in 2,916 counties. More than two-thirds of the patients were aged 65 years or younger.
During the study period, telemental health service increased from 0.03 visits per patient with SMI in 2010 to 0.19 visits per patient in 2018. This increase was broad, with the number of counties reporting high use of telemental health increasing from 2% in 2010 to 17% in 2018.
Compared with counties in which there was no telemental health services, those with high use were less densely populated and had fewer health care professionals and hospital beds.
The number of overall visits with a mental health professional increased slightly in high-use counties compared to no-use counties, from 4.65 visits in 2010 to 4.79 visits in 2018. The number of in-person visits during that period declined from 4.55 visits in 2010 to 3.73 visits in 2018, which suggests that the overall increase was due to higher use of telemental health.
In the high-use group, the number of patients who had at least four mental health care visits increased 8%, and the number of patients who had a follow-up visit within 30 days of a hospitalization increased 20.4%.
A ‘helpful option’
“Telemedicine doesn’t address the national shortage of providers, but it definitely helps in underserved areas [and] rural areas,” Dr. Huskamp said.
“We need more mental health providers and need to develop new models of care that can leverage the providers we have in the best way possible. This is at least a helpful option, especially when you’re thinking about the maldistribution of providers across the country,” she added.
The study results showed that there was no difference in medication adherence between low- and high-use counties.
There was greater contact with mental health care providers in counties with high use of telemental health, and patients in the high-use group were 7.6% more likely to be hospitalized within a year compared with their peers in counties that had no telemental health use.
“We did see modest increases in inpatient use in counties that shifted the most to telemental health services, but that’s not typically viewed as a measure of quality because it can mean so many different things,” Dr. Huskamp said.
For example, it could mean that counties with greater telemental health use did a better job of identifying and responding to patients’ need for acute care, she noted. It could also be a reflection of the loss of psychiatric inpatient care in low-use communities.
Another tool
Commenting on the findings, Robert Caudill, MD, director of Telemedicine and Information Technology Programs at the University of Louisville (Ky.), called the increase in hospitalization in high-use counties “surprising.” However, he noted it might be a reflection of the need to fine-tune telemental health for patients with SMI.
“I think that more time and experience with telehealth will further normalize the practice and help to narrow, if not close, the gap,” said Dr. Caudill, who was not involved with the research.
“There are so many side benefits to doing things via telehealth,” he added. “It is a simple matter of continuing to learn how to do those things better.”
A multidisciplinary approach that includes psychiatric care and case management is generally considered to be the gold standard in treating patients with the types of mental illness included in this study, Dr. Caudill said.
While some of that care can be delivered effectively via telemedicine, it is possible other aspects, such as case management, are better handled in person, he added.
“I don’t think it is the role of telehealth to make in-person care obsolete. It is simply a tool to be used when appropriate,” said Dr. Caudill, past chair of the American Telemedicine Association’s Telemental Health Special Interest Group.
“Surgeons did not abandon scalpels when laser surgery became possible,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Mental Health. Dr. Huskamp and Dr. Caudill report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a nationwide study, researchers drew on Medicare data from nearly 3,000 counties covering the period from 2000 to 2018. Results show that counties in which there was greater use of telemental health services reported higher increases of clinical visits and better follow-up after hospitalization among patients with bipolar 1 disorder and schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders.
In the study, “clinical visits” referred to both in-person and telemental health visits.
“These findings really support the idea that telemental health can be safe and effective and beneficial for in-person care for people with severe mental illness,” coinvestigator Haiden Huskamp, PhD, professor of health care policy at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Continuing trend?
Past studies have pointed to a sharp increase in the use of telepsychiatry services for patients with SMI. As reported by this news organization, this is a trend some clinicians say is likely to continue after the pandemic.
Use of telemedicine during the pandemic received a boost by the temporary suspension of certain Medicare rules that restrict telehealth use. Debate continues at the federal and state levels on whether to make that suspension permanent. Dr. Huskamp said more information is needed about the efficacy and accessibility of telemental health.
To investigate, researchers used Medicare fee-for-service data from 118,170 patients in 2,916 counties. More than two-thirds of the patients were aged 65 years or younger.
During the study period, telemental health service increased from 0.03 visits per patient with SMI in 2010 to 0.19 visits per patient in 2018. This increase was broad, with the number of counties reporting high use of telemental health increasing from 2% in 2010 to 17% in 2018.
Compared with counties in which there was no telemental health services, those with high use were less densely populated and had fewer health care professionals and hospital beds.
The number of overall visits with a mental health professional increased slightly in high-use counties compared to no-use counties, from 4.65 visits in 2010 to 4.79 visits in 2018. The number of in-person visits during that period declined from 4.55 visits in 2010 to 3.73 visits in 2018, which suggests that the overall increase was due to higher use of telemental health.
In the high-use group, the number of patients who had at least four mental health care visits increased 8%, and the number of patients who had a follow-up visit within 30 days of a hospitalization increased 20.4%.
A ‘helpful option’
“Telemedicine doesn’t address the national shortage of providers, but it definitely helps in underserved areas [and] rural areas,” Dr. Huskamp said.
“We need more mental health providers and need to develop new models of care that can leverage the providers we have in the best way possible. This is at least a helpful option, especially when you’re thinking about the maldistribution of providers across the country,” she added.
The study results showed that there was no difference in medication adherence between low- and high-use counties.
There was greater contact with mental health care providers in counties with high use of telemental health, and patients in the high-use group were 7.6% more likely to be hospitalized within a year compared with their peers in counties that had no telemental health use.
“We did see modest increases in inpatient use in counties that shifted the most to telemental health services, but that’s not typically viewed as a measure of quality because it can mean so many different things,” Dr. Huskamp said.
For example, it could mean that counties with greater telemental health use did a better job of identifying and responding to patients’ need for acute care, she noted. It could also be a reflection of the loss of psychiatric inpatient care in low-use communities.
Another tool
Commenting on the findings, Robert Caudill, MD, director of Telemedicine and Information Technology Programs at the University of Louisville (Ky.), called the increase in hospitalization in high-use counties “surprising.” However, he noted it might be a reflection of the need to fine-tune telemental health for patients with SMI.
“I think that more time and experience with telehealth will further normalize the practice and help to narrow, if not close, the gap,” said Dr. Caudill, who was not involved with the research.
“There are so many side benefits to doing things via telehealth,” he added. “It is a simple matter of continuing to learn how to do those things better.”
A multidisciplinary approach that includes psychiatric care and case management is generally considered to be the gold standard in treating patients with the types of mental illness included in this study, Dr. Caudill said.
While some of that care can be delivered effectively via telemedicine, it is possible other aspects, such as case management, are better handled in person, he added.
“I don’t think it is the role of telehealth to make in-person care obsolete. It is simply a tool to be used when appropriate,” said Dr. Caudill, past chair of the American Telemedicine Association’s Telemental Health Special Interest Group.
“Surgeons did not abandon scalpels when laser surgery became possible,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Mental Health. Dr. Huskamp and Dr. Caudill report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a nationwide study, researchers drew on Medicare data from nearly 3,000 counties covering the period from 2000 to 2018. Results show that counties in which there was greater use of telemental health services reported higher increases of clinical visits and better follow-up after hospitalization among patients with bipolar 1 disorder and schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders.
In the study, “clinical visits” referred to both in-person and telemental health visits.
“These findings really support the idea that telemental health can be safe and effective and beneficial for in-person care for people with severe mental illness,” coinvestigator Haiden Huskamp, PhD, professor of health care policy at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Continuing trend?
Past studies have pointed to a sharp increase in the use of telepsychiatry services for patients with SMI. As reported by this news organization, this is a trend some clinicians say is likely to continue after the pandemic.
Use of telemedicine during the pandemic received a boost by the temporary suspension of certain Medicare rules that restrict telehealth use. Debate continues at the federal and state levels on whether to make that suspension permanent. Dr. Huskamp said more information is needed about the efficacy and accessibility of telemental health.
To investigate, researchers used Medicare fee-for-service data from 118,170 patients in 2,916 counties. More than two-thirds of the patients were aged 65 years or younger.
During the study period, telemental health service increased from 0.03 visits per patient with SMI in 2010 to 0.19 visits per patient in 2018. This increase was broad, with the number of counties reporting high use of telemental health increasing from 2% in 2010 to 17% in 2018.
Compared with counties in which there was no telemental health services, those with high use were less densely populated and had fewer health care professionals and hospital beds.
The number of overall visits with a mental health professional increased slightly in high-use counties compared to no-use counties, from 4.65 visits in 2010 to 4.79 visits in 2018. The number of in-person visits during that period declined from 4.55 visits in 2010 to 3.73 visits in 2018, which suggests that the overall increase was due to higher use of telemental health.
In the high-use group, the number of patients who had at least four mental health care visits increased 8%, and the number of patients who had a follow-up visit within 30 days of a hospitalization increased 20.4%.
A ‘helpful option’
“Telemedicine doesn’t address the national shortage of providers, but it definitely helps in underserved areas [and] rural areas,” Dr. Huskamp said.
“We need more mental health providers and need to develop new models of care that can leverage the providers we have in the best way possible. This is at least a helpful option, especially when you’re thinking about the maldistribution of providers across the country,” she added.
The study results showed that there was no difference in medication adherence between low- and high-use counties.
There was greater contact with mental health care providers in counties with high use of telemental health, and patients in the high-use group were 7.6% more likely to be hospitalized within a year compared with their peers in counties that had no telemental health use.
“We did see modest increases in inpatient use in counties that shifted the most to telemental health services, but that’s not typically viewed as a measure of quality because it can mean so many different things,” Dr. Huskamp said.
For example, it could mean that counties with greater telemental health use did a better job of identifying and responding to patients’ need for acute care, she noted. It could also be a reflection of the loss of psychiatric inpatient care in low-use communities.
Another tool
Commenting on the findings, Robert Caudill, MD, director of Telemedicine and Information Technology Programs at the University of Louisville (Ky.), called the increase in hospitalization in high-use counties “surprising.” However, he noted it might be a reflection of the need to fine-tune telemental health for patients with SMI.
“I think that more time and experience with telehealth will further normalize the practice and help to narrow, if not close, the gap,” said Dr. Caudill, who was not involved with the research.
“There are so many side benefits to doing things via telehealth,” he added. “It is a simple matter of continuing to learn how to do those things better.”
A multidisciplinary approach that includes psychiatric care and case management is generally considered to be the gold standard in treating patients with the types of mental illness included in this study, Dr. Caudill said.
While some of that care can be delivered effectively via telemedicine, it is possible other aspects, such as case management, are better handled in person, he added.
“I don’t think it is the role of telehealth to make in-person care obsolete. It is simply a tool to be used when appropriate,” said Dr. Caudill, past chair of the American Telemedicine Association’s Telemental Health Special Interest Group.
“Surgeons did not abandon scalpels when laser surgery became possible,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Mental Health. Dr. Huskamp and Dr. Caudill report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advance directives for psychiatric care reduce compulsory admissions
, new research shows.
Results of a randomized trial showed the peer worker PAD group had a 42% reduction in compulsory admission over the following 12 months. This study group also had lower symptom scores, greater rates of recovery, and increased empowerment, compared with patients assigned to usual care.
In addition to proving that PADs are effective in reducing compulsory admission, the results show that facilitation by peer workers is relevant, study investigator Aurélie Tinland, MD, PhD, Faculté de Médecine Timone, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, told delegates attending the virtual European Psychiatric Association (EPA) 2022 Congress. The study was simultaneously published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
However, Dr. Tinland noted that more research that includes “harder to reach” populations is needed. In addition, greater use of PADs is also key to reducing compulsory admissions.
‘Most coercive’ country
The researchers note that respect for patient autonomy is a strong pillar of health care, such that “involuntary treatment should be unusual.” However, they point out that “compulsory psychiatric admissions are far too common in countries of all income levels.”
In France, said Dr. Tinland, 24% of psychiatric hospitalizations are compulsory. The country is ranked the sixth “most coercive” country in the world, and there are concerns about human rights in French psychiatric facilities.
She added that advance care statements are the most efficient tool for reducing coercion, with one study suggesting they could cut rates by 25%, compared with usual care.
However, she noted there is an “asymmetry” between medical professionals and patients and a risk of “undue influence” when clinicians facilitate the completion of care statements.
To examine the impact on clinical outcomes of peer-worker facilitated PADs, the researchers studied adults with a diagnosis of schizophrenia, bipolar I disorder, or schizoaffective disorder who were admitted to a psychiatric hospital within the previous 12 months. Peer workers are individuals who have lived experience with mental illness and help inform and guide current patients about care options in the event of a mental health crisis.
Study participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to an intervention group or a usual care control group. The intervention group received a PAD document and were assigned a peer worker while the usual care group received comprehensive information about the PAD concept at study entry and were free to complete it, but they were not connected with a peer worker.
The PAD document included information about future treatment and support preferences, early signs of relapse, and coping strategies. Participants could meet the peer worker in a place of their choice and be supported in drafting the document and in sharing it with health care professionals.
In all, 394 individuals completed the study. The majority (61%) of participants were male and 66% had completed post-secondary education. Schizophrenia was diagnosed in 45%, bipolar I disorder in 36%, and schizoaffective disorder in 19%.
Participants in the intervention group were significantly younger than those in the control group, with a mean of 37.4 years versus 41 years (P = .003) and were less likely to have one or more somatic comorbidities, at 61.2% versus 69.2%.
A PAD was completed by 54.6% of individuals in the intervention group versus 7.1% of controls (P < .001). The PAD was written with peer worker support by 41.3% of those in the intervention and by 2% of controls. Of those who completed a PAD, 75.7% met care facilitators, and 27.1% used it during a crisis over the following 12 months.
Results showed that the rate of compulsory admissions was significantly lower in the peer worker PAD group, at 27% versus 39.9% in control participants, at an odds ratio of 0.58 (P = .007).
Participants in the intervention group had lower symptoms on the modified Colorado Symptom Score than usual care patients with an effect size of -0.20 (P = .03) and higher scores on the Empowerment Scale (effect size 0.30, P = .003).
Scores on the Recovery Assessment Scale were also significantly higher in the peer worker PAD group versus controls with an effect size of 0.44 (P < .001). There were no significant differences, however, in overall admission rates, the quality of the therapeutic alliance, or quality of life.
Putting patients in the driver’s seat
Commenting on the findings, Robert Dabney Jr., MA, MDiv, peer apprentice program manager at the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance, Chicago, said the study “tells us there are many benefits to completing a psychiatric advance directive, but perhaps the most powerful one is putting the person receiving mental health care in the driver’s seat of their own recovery.”
However, he noted that “many people living with mental health conditions don’t know the option exists to decide on their treatment plan in advance of a crisis.”
“This is where peer support specialists can come in. Having a peer who has been through similar experiences and can guide you through the process is as comforting as it is empowering. I have witnessed and experienced firsthand the power of peer support,” he said.
“It’s my personal hope and the goal of the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance to empower more people to either become peer support specialists or seek out peer support services, because we know it improves and even saves lives,” Mr. Dabney added.
Virginia A. Brown, PhD, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences, University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, noted there are huge differences between the health care systems in France and the United States.
She explained that two of the greatest barriers to PADs in the United States is that until 2016, filling one out was not billable and that “practitioners don’t know anything about advanced care plans.”
Dr. Brown said her own work shows that individuals who support patients during a crisis believe it would be “really helpful if we had some kind of document that we could share with the health care system that says: ‘Hey, look, I’m the designated person to speak for this patient, they’ve identified me through a document.’ So, people were actually describing a need for this document but didn’t know that it existed.”
Another problem is that in the United States, hospitals operate in a “closed system” and cannot talk to an unrelated hospital or to the police department “to get information to those first responders during an emergency about who to talk to about their wishes and preferences.”
“There are a lot of hurdles that we’ve got to get over to make a more robust system that protects the autonomy of people who live with serious mental illness,” Dr. Brown said, as “losing capacity during a crisis is time-limited, and it requires us to respond to it as a medical emergency.”
The study was supported by an institutional grant from the French 2017 National Program of Health Services Research. The Clinical Research Direction of Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Marseille sponsored the trial. Dr. Tinland declares grants from the French Ministry of Health Directorate General of Health Care Services during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Results of a randomized trial showed the peer worker PAD group had a 42% reduction in compulsory admission over the following 12 months. This study group also had lower symptom scores, greater rates of recovery, and increased empowerment, compared with patients assigned to usual care.
In addition to proving that PADs are effective in reducing compulsory admission, the results show that facilitation by peer workers is relevant, study investigator Aurélie Tinland, MD, PhD, Faculté de Médecine Timone, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, told delegates attending the virtual European Psychiatric Association (EPA) 2022 Congress. The study was simultaneously published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
However, Dr. Tinland noted that more research that includes “harder to reach” populations is needed. In addition, greater use of PADs is also key to reducing compulsory admissions.
‘Most coercive’ country
The researchers note that respect for patient autonomy is a strong pillar of health care, such that “involuntary treatment should be unusual.” However, they point out that “compulsory psychiatric admissions are far too common in countries of all income levels.”
In France, said Dr. Tinland, 24% of psychiatric hospitalizations are compulsory. The country is ranked the sixth “most coercive” country in the world, and there are concerns about human rights in French psychiatric facilities.
She added that advance care statements are the most efficient tool for reducing coercion, with one study suggesting they could cut rates by 25%, compared with usual care.
However, she noted there is an “asymmetry” between medical professionals and patients and a risk of “undue influence” when clinicians facilitate the completion of care statements.
To examine the impact on clinical outcomes of peer-worker facilitated PADs, the researchers studied adults with a diagnosis of schizophrenia, bipolar I disorder, or schizoaffective disorder who were admitted to a psychiatric hospital within the previous 12 months. Peer workers are individuals who have lived experience with mental illness and help inform and guide current patients about care options in the event of a mental health crisis.
Study participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to an intervention group or a usual care control group. The intervention group received a PAD document and were assigned a peer worker while the usual care group received comprehensive information about the PAD concept at study entry and were free to complete it, but they were not connected with a peer worker.
The PAD document included information about future treatment and support preferences, early signs of relapse, and coping strategies. Participants could meet the peer worker in a place of their choice and be supported in drafting the document and in sharing it with health care professionals.
In all, 394 individuals completed the study. The majority (61%) of participants were male and 66% had completed post-secondary education. Schizophrenia was diagnosed in 45%, bipolar I disorder in 36%, and schizoaffective disorder in 19%.
Participants in the intervention group were significantly younger than those in the control group, with a mean of 37.4 years versus 41 years (P = .003) and were less likely to have one or more somatic comorbidities, at 61.2% versus 69.2%.
A PAD was completed by 54.6% of individuals in the intervention group versus 7.1% of controls (P < .001). The PAD was written with peer worker support by 41.3% of those in the intervention and by 2% of controls. Of those who completed a PAD, 75.7% met care facilitators, and 27.1% used it during a crisis over the following 12 months.
Results showed that the rate of compulsory admissions was significantly lower in the peer worker PAD group, at 27% versus 39.9% in control participants, at an odds ratio of 0.58 (P = .007).
Participants in the intervention group had lower symptoms on the modified Colorado Symptom Score than usual care patients with an effect size of -0.20 (P = .03) and higher scores on the Empowerment Scale (effect size 0.30, P = .003).
Scores on the Recovery Assessment Scale were also significantly higher in the peer worker PAD group versus controls with an effect size of 0.44 (P < .001). There were no significant differences, however, in overall admission rates, the quality of the therapeutic alliance, or quality of life.
Putting patients in the driver’s seat
Commenting on the findings, Robert Dabney Jr., MA, MDiv, peer apprentice program manager at the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance, Chicago, said the study “tells us there are many benefits to completing a psychiatric advance directive, but perhaps the most powerful one is putting the person receiving mental health care in the driver’s seat of their own recovery.”
However, he noted that “many people living with mental health conditions don’t know the option exists to decide on their treatment plan in advance of a crisis.”
“This is where peer support specialists can come in. Having a peer who has been through similar experiences and can guide you through the process is as comforting as it is empowering. I have witnessed and experienced firsthand the power of peer support,” he said.
“It’s my personal hope and the goal of the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance to empower more people to either become peer support specialists or seek out peer support services, because we know it improves and even saves lives,” Mr. Dabney added.
Virginia A. Brown, PhD, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences, University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, noted there are huge differences between the health care systems in France and the United States.
She explained that two of the greatest barriers to PADs in the United States is that until 2016, filling one out was not billable and that “practitioners don’t know anything about advanced care plans.”
Dr. Brown said her own work shows that individuals who support patients during a crisis believe it would be “really helpful if we had some kind of document that we could share with the health care system that says: ‘Hey, look, I’m the designated person to speak for this patient, they’ve identified me through a document.’ So, people were actually describing a need for this document but didn’t know that it existed.”
Another problem is that in the United States, hospitals operate in a “closed system” and cannot talk to an unrelated hospital or to the police department “to get information to those first responders during an emergency about who to talk to about their wishes and preferences.”
“There are a lot of hurdles that we’ve got to get over to make a more robust system that protects the autonomy of people who live with serious mental illness,” Dr. Brown said, as “losing capacity during a crisis is time-limited, and it requires us to respond to it as a medical emergency.”
The study was supported by an institutional grant from the French 2017 National Program of Health Services Research. The Clinical Research Direction of Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Marseille sponsored the trial. Dr. Tinland declares grants from the French Ministry of Health Directorate General of Health Care Services during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Results of a randomized trial showed the peer worker PAD group had a 42% reduction in compulsory admission over the following 12 months. This study group also had lower symptom scores, greater rates of recovery, and increased empowerment, compared with patients assigned to usual care.
In addition to proving that PADs are effective in reducing compulsory admission, the results show that facilitation by peer workers is relevant, study investigator Aurélie Tinland, MD, PhD, Faculté de Médecine Timone, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, told delegates attending the virtual European Psychiatric Association (EPA) 2022 Congress. The study was simultaneously published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
However, Dr. Tinland noted that more research that includes “harder to reach” populations is needed. In addition, greater use of PADs is also key to reducing compulsory admissions.
‘Most coercive’ country
The researchers note that respect for patient autonomy is a strong pillar of health care, such that “involuntary treatment should be unusual.” However, they point out that “compulsory psychiatric admissions are far too common in countries of all income levels.”
In France, said Dr. Tinland, 24% of psychiatric hospitalizations are compulsory. The country is ranked the sixth “most coercive” country in the world, and there are concerns about human rights in French psychiatric facilities.
She added that advance care statements are the most efficient tool for reducing coercion, with one study suggesting they could cut rates by 25%, compared with usual care.
However, she noted there is an “asymmetry” between medical professionals and patients and a risk of “undue influence” when clinicians facilitate the completion of care statements.
To examine the impact on clinical outcomes of peer-worker facilitated PADs, the researchers studied adults with a diagnosis of schizophrenia, bipolar I disorder, or schizoaffective disorder who were admitted to a psychiatric hospital within the previous 12 months. Peer workers are individuals who have lived experience with mental illness and help inform and guide current patients about care options in the event of a mental health crisis.
Study participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to an intervention group or a usual care control group. The intervention group received a PAD document and were assigned a peer worker while the usual care group received comprehensive information about the PAD concept at study entry and were free to complete it, but they were not connected with a peer worker.
The PAD document included information about future treatment and support preferences, early signs of relapse, and coping strategies. Participants could meet the peer worker in a place of their choice and be supported in drafting the document and in sharing it with health care professionals.
In all, 394 individuals completed the study. The majority (61%) of participants were male and 66% had completed post-secondary education. Schizophrenia was diagnosed in 45%, bipolar I disorder in 36%, and schizoaffective disorder in 19%.
Participants in the intervention group were significantly younger than those in the control group, with a mean of 37.4 years versus 41 years (P = .003) and were less likely to have one or more somatic comorbidities, at 61.2% versus 69.2%.
A PAD was completed by 54.6% of individuals in the intervention group versus 7.1% of controls (P < .001). The PAD was written with peer worker support by 41.3% of those in the intervention and by 2% of controls. Of those who completed a PAD, 75.7% met care facilitators, and 27.1% used it during a crisis over the following 12 months.
Results showed that the rate of compulsory admissions was significantly lower in the peer worker PAD group, at 27% versus 39.9% in control participants, at an odds ratio of 0.58 (P = .007).
Participants in the intervention group had lower symptoms on the modified Colorado Symptom Score than usual care patients with an effect size of -0.20 (P = .03) and higher scores on the Empowerment Scale (effect size 0.30, P = .003).
Scores on the Recovery Assessment Scale were also significantly higher in the peer worker PAD group versus controls with an effect size of 0.44 (P < .001). There were no significant differences, however, in overall admission rates, the quality of the therapeutic alliance, or quality of life.
Putting patients in the driver’s seat
Commenting on the findings, Robert Dabney Jr., MA, MDiv, peer apprentice program manager at the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance, Chicago, said the study “tells us there are many benefits to completing a psychiatric advance directive, but perhaps the most powerful one is putting the person receiving mental health care in the driver’s seat of their own recovery.”
However, he noted that “many people living with mental health conditions don’t know the option exists to decide on their treatment plan in advance of a crisis.”
“This is where peer support specialists can come in. Having a peer who has been through similar experiences and can guide you through the process is as comforting as it is empowering. I have witnessed and experienced firsthand the power of peer support,” he said.
“It’s my personal hope and the goal of the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance to empower more people to either become peer support specialists or seek out peer support services, because we know it improves and even saves lives,” Mr. Dabney added.
Virginia A. Brown, PhD, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences, University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, noted there are huge differences between the health care systems in France and the United States.
She explained that two of the greatest barriers to PADs in the United States is that until 2016, filling one out was not billable and that “practitioners don’t know anything about advanced care plans.”
Dr. Brown said her own work shows that individuals who support patients during a crisis believe it would be “really helpful if we had some kind of document that we could share with the health care system that says: ‘Hey, look, I’m the designated person to speak for this patient, they’ve identified me through a document.’ So, people were actually describing a need for this document but didn’t know that it existed.”
Another problem is that in the United States, hospitals operate in a “closed system” and cannot talk to an unrelated hospital or to the police department “to get information to those first responders during an emergency about who to talk to about their wishes and preferences.”
“There are a lot of hurdles that we’ve got to get over to make a more robust system that protects the autonomy of people who live with serious mental illness,” Dr. Brown said, as “losing capacity during a crisis is time-limited, and it requires us to respond to it as a medical emergency.”
The study was supported by an institutional grant from the French 2017 National Program of Health Services Research. The Clinical Research Direction of Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Marseille sponsored the trial. Dr. Tinland declares grants from the French Ministry of Health Directorate General of Health Care Services during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EPA 2022
A prescription for de-diagnosing
In 2016, Gupta and Cahill challenged the field of psychiatry to reexamine prescribing patterns.1 They warned against the use of polypharmacy when not attached to improved patient functioning. They were concerned with the limited evidence for polypharmacy as well as DSM diagnostic criteria. In their inspiring article, they described a process of deprescribing.
In an effort to study and practice their recommendations, we have noticed a lack of literature examining the elimination of diagnostic labels. While there have been some studies looking at comorbidity, especially with substance use disorders,2 there is a paucity of scientific evidence on patients with numerous diagnoses. Yet our practices are filled with patients who have been labeled with multiple conflicting or redundant diagnoses throughout their lives depending on the setting or the orientation of the practitioner.
The DSM-5 warns against diagnosing disorders when “the occurrence … is not better explained by” another disorder.3 A mix of diagnoses creates confusion for patients as well as clinicians trying to sort through their reported psychiatric histories.
A routine example would include a patient presenting for an initial evaluation and stating “I’ve been diagnosed as manic-depressive, high anxiety, split personality, posttraumatic stress, insomnia, ADD, and depression.” A review of the medical record will reveal a list of diagnoses, including bipolar II, generalized anxiety disorder, borderline personality disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, unspecified insomnia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and major depressive disorder. The medication list includes lamotrigine, valproic acid, citalopram, bupropion, buspirone, prazosin, methylphenidate, clonazepam, hydroxyzine, and low-dose quetiapine at night as needed.
This is an example of polypharmacy treating multiple, and at times conflicting, diagnoses. While an extreme case, in our experience, cases like this are not uncommon. It was actually in our efforts to examine deprescribing that we noticed this quandary. When inquiring about patients on many psychotropic medications, we often receive this retort: the patient is only prescribed one medication per disorder. Some providers have the belief that multiple disorders justify multiple medications, and that this tautological thinking legitimizes polypharmacy.
A patient who has varying moods, some fears, a fluctuating temperament, past traumas, occasional difficulty sleeping, intermittent inattention, and some sadness may be given all the diagnoses listed above and the resulting medication list. The multiplication of diagnoses, “polydiagnosing,” is a convenient justification for future polypharmacy. A lack of careful assessment and thinking in the application of new diagnoses permits the use of increasing numbers of pharmacological agents. A constellation of symptoms of anxiety, concentration deficits, affective dysregulation, and psychosis may justify the combination of benzodiazepines, stimulants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics, while a patient with “just” schizophrenia who is sometimes sad, scared, or distracted is more likely to be kept on just one medication, likely an antipsychotic.
Contrary to most medical disorders (for example, tuberculosis) but similar to others (for example, chronic pain), psychiatric disorders are based on the opinion of a “modest number of ‘expert’ classifications.”4 While the broad categories of disorders are justifiable, individual diagnoses are burdened with high rates of comorbidity; lack of treatment specificity; and evidence that distinct syndromes share a genetic basis. Those concerns were exemplified in the study examining the inter-rater reliability of DSM-5 diagnoses, where many disorders were found to have questionable validity.5
A psychiatric diagnosis should be based on biological, psychological, and social factors, which align with our understanding of the natural course of an illness. A patient presenting with transient symptoms of sadness in the context of significant social factors like homelessness and/or significant biological factors associated with schizophrenia should not reflexively receive an additional diagnosis of a depressive disorder. A patient reporting poor concentration in the context of a manic episode should not receive an additional diagnosis of attention-deficit disorder. An older patient with depression on multiple antipsychotics for adjunctive treatment should not necessarily receive a diagnosis of cognitive disorder at the first sign of memory problems.
The cavalier and inconsistent use of diagnoses renders the patients with no clear narrative of who they are. They end up integrating the varying providers’ opinions as a cacophony of labels of unclear significance. Many patients have contradictory diagnoses like major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Those inaccurate diagnoses could not only lead to treatment mistakes, but also psychological harm.6
A clearer diagnostic picture is not only more scientifically sound but also more coherent to the patient. This in turn can lead to an improved treatment alliance and buy-in from the patient.
How should a provider practice de-diagnosing? Based on the work of Reeve, et al.,7 on the principles crucial to deprescribing, and subsequent research by Gupta and Cahill,8 we compiled a list of considerations for practitioners wishing to engage in this type of work with their patients.
Choose the right time. While insurance companies require diagnostic findings from the first visit, abrupt de-diagnosing for the sake of simplifying the record from that first visit could be detrimental. Patients can become attached to and find meaning in their diagnostic labels. This was exemplified with the removal of Asperger’s syndrome from the DSM-5.9 Acute symptomatology may be an opportune time to revisit the core pathology of a patient, or a poor time for a patient to have this discussion.
Compile a list of all the patient’s diagnoses. Our initial visits are often illuminated when patients enumerate the vast number of diagnoses they have been given by different providers. Patients will often list half a dozen diagnoses. The patterns often follow life courses with ADHD, conduct disorder, and learning disability in childhood; with anxiety, depression, and/or bipolar disorder in early adulthood; to complicated grief, depression with pseudodementia, and neurocognitive disorders in older adults. Yet patients rarely appreciate the temporary or episodic nature of mental disorders and instead accumulate diagnoses at each change of provider.
Initiate discussion with the patient. It is meaningful to see if patients resonate with the question, “Do you ever feel like every psychiatrist you have seen has given you a different diagnosis?” In our experience, patients’ reactions to this question usually exemplify the problematic nature of the vast array of diagnoses our patients are given. The majority of them are unable to confidently explain the meaning of those diagnoses, the context in which they were given, or their significance. This simple exercise has a powerful effect on raising awareness to patients of the problematic nature of polydiagnosing.
Introduce de-diagnosing. The engagement of patients in the diagnostic process has a significant effect. Reviewing not only diagnostic criteria but also nosology and debates in our understanding of diagnoses can provide patients with further engagement in their care. A simple review of the debate of the bereavement exclusion may permit a patient to not only understand the complexity, but also the changing nature of diagnoses. Suddenly, they are no longer bystanders, but informed participants in their care.
Identify diagnoses most appropriate for removal. Contradictory diagnoses are common in the clinical settings we work in. We routinely see patients carrying multiple mood diagnoses, despite our diagnostic systems not permitting one to have both unipolar and bipolar depression. Superfluous diagnoses are also frequent, with patients receiving depressive, or anxious labels when in an acute state of psychosis or mania. This is exemplified by patients suffering from thought blocking and receiving cognitive or attention-related diagnoses. Concurrent yet different diagnoses are also common in patients with a different list of diagnoses by their primary care provider, their therapist, and their psychiatrist. This is particularly problematic as it forces the patient to alternate their thinking or choose between their providers.
Create a new narrative for the patient. Once diagnoses are explained, clarified, and understood, patients with the help of their providers can reexamine their life story under a new and simplified construct. This process often leads to a less confusing sense of self, an increased dedication to the treatment process, whether behavioral, social, psychological, or pharmacologic.
Consider deprescribing. With a more straightforward and more grounded list of diagnoses (or simply one diagnosis), we find the process of deprescribing to be simpler and more engaging for patients. For example, patients can clearly understand the lack of necessity of an antipsychotic prescription for a resolved substance-induced psychosis. Patients are more engaged in their care, leading to improved medication compliance and less attachment to discontinued medications.
Monitor and adapt. One should of course reevaluate diagnoses as the course of illness provides us with additional information. However, we suggest waiting for a manic episode to emerge prior to diagnosing bipolar rather than suggesting the diagnosis because a patient was wearing red shoes, spoke multiple languages, had multiple degrees and was creative.10 The contextual basis and progression of the symptoms should lead to continual reassessment of diagnoses.
Physicians are aware of the balance between Occam’s razor, which promotes the simplest single explanation for a problem, versus Hickam’s dictum that reminds us that patients can have as many diseases as they please. However, similarly to polypharmacy, “polydiagnosing” has negative effects. While the field of psychiatry’s advancing knowledge may encourage providers to diagnose their patients with the growing number of diagnoses, patients still need and benefit from a coherent and clear medical narrative. Psychiatry would be wise to recognize this concerning trend, in its attempt at rectifying polypharmacy.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lehman is a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is codirector of all acute and intensive psychiatric treatment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego, where he practices clinical psychiatry. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Gupta S & Cahill JD. A prescription for “deprescribing” in psychiatry. Psychiatr Serv. 2016 Aug 1;67(8):904-7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201500359.
2. Schuckit MA. Comorbidity between substance use disorders and psychiatric conditions. Addiction. 2006 Sep;101 Suppl 1:76-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01592.x.
3. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). American Psychiatric Association, 2022. https://psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm.
4. Kendler KS. An historical framework for psychiatric nosology. Psychol Med. 2009 Dec;39(12):1935-41. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709005753.
5. Regier DA et al. DSM-5 field trials in the United States and Canada. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;170(1):59-70. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12070999.
6. Bhattacharya R et al. When good news is bad news: psychological impact of false-positive diagnosis of HIV. AIDS Care. 2008 May;20(5):560-4. doi: 10.1080/09540120701867206.
7. Reeve E et al. Review of deprescribing processes and development of an evidence‐based, patient‐centred deprescribing process. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;78(4):738-47. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12386.
8. Gupta S and Cahill JD. A prescription for “deprescribing” in psychiatry.
9. Solomon M. “On the appearance and disappearance of Asperger’s syndrome” in Kendler and Parnas (eds.) Philosophical Issues in Psychiatry IV: Classification of Psychiatric Illness. Oxford University Press, 2017. doi: 10.1093/med/9780198796022.003.0023.
10. Akiskal HS. Searching for behavioral indicators of bipolar II in patients presenting with major depressive episodes: The “red sign,” the “rule of three,” and other biographic signs of temperamental extravagance, activation, and hypomania. J Affect Disord. 2005 Feb;84(2-3):279-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2004.06.002.
In 2016, Gupta and Cahill challenged the field of psychiatry to reexamine prescribing patterns.1 They warned against the use of polypharmacy when not attached to improved patient functioning. They were concerned with the limited evidence for polypharmacy as well as DSM diagnostic criteria. In their inspiring article, they described a process of deprescribing.
In an effort to study and practice their recommendations, we have noticed a lack of literature examining the elimination of diagnostic labels. While there have been some studies looking at comorbidity, especially with substance use disorders,2 there is a paucity of scientific evidence on patients with numerous diagnoses. Yet our practices are filled with patients who have been labeled with multiple conflicting or redundant diagnoses throughout their lives depending on the setting or the orientation of the practitioner.
The DSM-5 warns against diagnosing disorders when “the occurrence … is not better explained by” another disorder.3 A mix of diagnoses creates confusion for patients as well as clinicians trying to sort through their reported psychiatric histories.
A routine example would include a patient presenting for an initial evaluation and stating “I’ve been diagnosed as manic-depressive, high anxiety, split personality, posttraumatic stress, insomnia, ADD, and depression.” A review of the medical record will reveal a list of diagnoses, including bipolar II, generalized anxiety disorder, borderline personality disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, unspecified insomnia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and major depressive disorder. The medication list includes lamotrigine, valproic acid, citalopram, bupropion, buspirone, prazosin, methylphenidate, clonazepam, hydroxyzine, and low-dose quetiapine at night as needed.
This is an example of polypharmacy treating multiple, and at times conflicting, diagnoses. While an extreme case, in our experience, cases like this are not uncommon. It was actually in our efforts to examine deprescribing that we noticed this quandary. When inquiring about patients on many psychotropic medications, we often receive this retort: the patient is only prescribed one medication per disorder. Some providers have the belief that multiple disorders justify multiple medications, and that this tautological thinking legitimizes polypharmacy.
A patient who has varying moods, some fears, a fluctuating temperament, past traumas, occasional difficulty sleeping, intermittent inattention, and some sadness may be given all the diagnoses listed above and the resulting medication list. The multiplication of diagnoses, “polydiagnosing,” is a convenient justification for future polypharmacy. A lack of careful assessment and thinking in the application of new diagnoses permits the use of increasing numbers of pharmacological agents. A constellation of symptoms of anxiety, concentration deficits, affective dysregulation, and psychosis may justify the combination of benzodiazepines, stimulants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics, while a patient with “just” schizophrenia who is sometimes sad, scared, or distracted is more likely to be kept on just one medication, likely an antipsychotic.
Contrary to most medical disorders (for example, tuberculosis) but similar to others (for example, chronic pain), psychiatric disorders are based on the opinion of a “modest number of ‘expert’ classifications.”4 While the broad categories of disorders are justifiable, individual diagnoses are burdened with high rates of comorbidity; lack of treatment specificity; and evidence that distinct syndromes share a genetic basis. Those concerns were exemplified in the study examining the inter-rater reliability of DSM-5 diagnoses, where many disorders were found to have questionable validity.5
A psychiatric diagnosis should be based on biological, psychological, and social factors, which align with our understanding of the natural course of an illness. A patient presenting with transient symptoms of sadness in the context of significant social factors like homelessness and/or significant biological factors associated with schizophrenia should not reflexively receive an additional diagnosis of a depressive disorder. A patient reporting poor concentration in the context of a manic episode should not receive an additional diagnosis of attention-deficit disorder. An older patient with depression on multiple antipsychotics for adjunctive treatment should not necessarily receive a diagnosis of cognitive disorder at the first sign of memory problems.
The cavalier and inconsistent use of diagnoses renders the patients with no clear narrative of who they are. They end up integrating the varying providers’ opinions as a cacophony of labels of unclear significance. Many patients have contradictory diagnoses like major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Those inaccurate diagnoses could not only lead to treatment mistakes, but also psychological harm.6
A clearer diagnostic picture is not only more scientifically sound but also more coherent to the patient. This in turn can lead to an improved treatment alliance and buy-in from the patient.
How should a provider practice de-diagnosing? Based on the work of Reeve, et al.,7 on the principles crucial to deprescribing, and subsequent research by Gupta and Cahill,8 we compiled a list of considerations for practitioners wishing to engage in this type of work with their patients.
Choose the right time. While insurance companies require diagnostic findings from the first visit, abrupt de-diagnosing for the sake of simplifying the record from that first visit could be detrimental. Patients can become attached to and find meaning in their diagnostic labels. This was exemplified with the removal of Asperger’s syndrome from the DSM-5.9 Acute symptomatology may be an opportune time to revisit the core pathology of a patient, or a poor time for a patient to have this discussion.
Compile a list of all the patient’s diagnoses. Our initial visits are often illuminated when patients enumerate the vast number of diagnoses they have been given by different providers. Patients will often list half a dozen diagnoses. The patterns often follow life courses with ADHD, conduct disorder, and learning disability in childhood; with anxiety, depression, and/or bipolar disorder in early adulthood; to complicated grief, depression with pseudodementia, and neurocognitive disorders in older adults. Yet patients rarely appreciate the temporary or episodic nature of mental disorders and instead accumulate diagnoses at each change of provider.
Initiate discussion with the patient. It is meaningful to see if patients resonate with the question, “Do you ever feel like every psychiatrist you have seen has given you a different diagnosis?” In our experience, patients’ reactions to this question usually exemplify the problematic nature of the vast array of diagnoses our patients are given. The majority of them are unable to confidently explain the meaning of those diagnoses, the context in which they were given, or their significance. This simple exercise has a powerful effect on raising awareness to patients of the problematic nature of polydiagnosing.
Introduce de-diagnosing. The engagement of patients in the diagnostic process has a significant effect. Reviewing not only diagnostic criteria but also nosology and debates in our understanding of diagnoses can provide patients with further engagement in their care. A simple review of the debate of the bereavement exclusion may permit a patient to not only understand the complexity, but also the changing nature of diagnoses. Suddenly, they are no longer bystanders, but informed participants in their care.
Identify diagnoses most appropriate for removal. Contradictory diagnoses are common in the clinical settings we work in. We routinely see patients carrying multiple mood diagnoses, despite our diagnostic systems not permitting one to have both unipolar and bipolar depression. Superfluous diagnoses are also frequent, with patients receiving depressive, or anxious labels when in an acute state of psychosis or mania. This is exemplified by patients suffering from thought blocking and receiving cognitive or attention-related diagnoses. Concurrent yet different diagnoses are also common in patients with a different list of diagnoses by their primary care provider, their therapist, and their psychiatrist. This is particularly problematic as it forces the patient to alternate their thinking or choose between their providers.
Create a new narrative for the patient. Once diagnoses are explained, clarified, and understood, patients with the help of their providers can reexamine their life story under a new and simplified construct. This process often leads to a less confusing sense of self, an increased dedication to the treatment process, whether behavioral, social, psychological, or pharmacologic.
Consider deprescribing. With a more straightforward and more grounded list of diagnoses (or simply one diagnosis), we find the process of deprescribing to be simpler and more engaging for patients. For example, patients can clearly understand the lack of necessity of an antipsychotic prescription for a resolved substance-induced psychosis. Patients are more engaged in their care, leading to improved medication compliance and less attachment to discontinued medications.
Monitor and adapt. One should of course reevaluate diagnoses as the course of illness provides us with additional information. However, we suggest waiting for a manic episode to emerge prior to diagnosing bipolar rather than suggesting the diagnosis because a patient was wearing red shoes, spoke multiple languages, had multiple degrees and was creative.10 The contextual basis and progression of the symptoms should lead to continual reassessment of diagnoses.
Physicians are aware of the balance between Occam’s razor, which promotes the simplest single explanation for a problem, versus Hickam’s dictum that reminds us that patients can have as many diseases as they please. However, similarly to polypharmacy, “polydiagnosing” has negative effects. While the field of psychiatry’s advancing knowledge may encourage providers to diagnose their patients with the growing number of diagnoses, patients still need and benefit from a coherent and clear medical narrative. Psychiatry would be wise to recognize this concerning trend, in its attempt at rectifying polypharmacy.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lehman is a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is codirector of all acute and intensive psychiatric treatment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego, where he practices clinical psychiatry. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Gupta S & Cahill JD. A prescription for “deprescribing” in psychiatry. Psychiatr Serv. 2016 Aug 1;67(8):904-7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201500359.
2. Schuckit MA. Comorbidity between substance use disorders and psychiatric conditions. Addiction. 2006 Sep;101 Suppl 1:76-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01592.x.
3. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). American Psychiatric Association, 2022. https://psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm.
4. Kendler KS. An historical framework for psychiatric nosology. Psychol Med. 2009 Dec;39(12):1935-41. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709005753.
5. Regier DA et al. DSM-5 field trials in the United States and Canada. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;170(1):59-70. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12070999.
6. Bhattacharya R et al. When good news is bad news: psychological impact of false-positive diagnosis of HIV. AIDS Care. 2008 May;20(5):560-4. doi: 10.1080/09540120701867206.
7. Reeve E et al. Review of deprescribing processes and development of an evidence‐based, patient‐centred deprescribing process. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;78(4):738-47. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12386.
8. Gupta S and Cahill JD. A prescription for “deprescribing” in psychiatry.
9. Solomon M. “On the appearance and disappearance of Asperger’s syndrome” in Kendler and Parnas (eds.) Philosophical Issues in Psychiatry IV: Classification of Psychiatric Illness. Oxford University Press, 2017. doi: 10.1093/med/9780198796022.003.0023.
10. Akiskal HS. Searching for behavioral indicators of bipolar II in patients presenting with major depressive episodes: The “red sign,” the “rule of three,” and other biographic signs of temperamental extravagance, activation, and hypomania. J Affect Disord. 2005 Feb;84(2-3):279-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2004.06.002.
In 2016, Gupta and Cahill challenged the field of psychiatry to reexamine prescribing patterns.1 They warned against the use of polypharmacy when not attached to improved patient functioning. They were concerned with the limited evidence for polypharmacy as well as DSM diagnostic criteria. In their inspiring article, they described a process of deprescribing.
In an effort to study and practice their recommendations, we have noticed a lack of literature examining the elimination of diagnostic labels. While there have been some studies looking at comorbidity, especially with substance use disorders,2 there is a paucity of scientific evidence on patients with numerous diagnoses. Yet our practices are filled with patients who have been labeled with multiple conflicting or redundant diagnoses throughout their lives depending on the setting or the orientation of the practitioner.
The DSM-5 warns against diagnosing disorders when “the occurrence … is not better explained by” another disorder.3 A mix of diagnoses creates confusion for patients as well as clinicians trying to sort through their reported psychiatric histories.
A routine example would include a patient presenting for an initial evaluation and stating “I’ve been diagnosed as manic-depressive, high anxiety, split personality, posttraumatic stress, insomnia, ADD, and depression.” A review of the medical record will reveal a list of diagnoses, including bipolar II, generalized anxiety disorder, borderline personality disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, unspecified insomnia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and major depressive disorder. The medication list includes lamotrigine, valproic acid, citalopram, bupropion, buspirone, prazosin, methylphenidate, clonazepam, hydroxyzine, and low-dose quetiapine at night as needed.
This is an example of polypharmacy treating multiple, and at times conflicting, diagnoses. While an extreme case, in our experience, cases like this are not uncommon. It was actually in our efforts to examine deprescribing that we noticed this quandary. When inquiring about patients on many psychotropic medications, we often receive this retort: the patient is only prescribed one medication per disorder. Some providers have the belief that multiple disorders justify multiple medications, and that this tautological thinking legitimizes polypharmacy.
A patient who has varying moods, some fears, a fluctuating temperament, past traumas, occasional difficulty sleeping, intermittent inattention, and some sadness may be given all the diagnoses listed above and the resulting medication list. The multiplication of diagnoses, “polydiagnosing,” is a convenient justification for future polypharmacy. A lack of careful assessment and thinking in the application of new diagnoses permits the use of increasing numbers of pharmacological agents. A constellation of symptoms of anxiety, concentration deficits, affective dysregulation, and psychosis may justify the combination of benzodiazepines, stimulants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics, while a patient with “just” schizophrenia who is sometimes sad, scared, or distracted is more likely to be kept on just one medication, likely an antipsychotic.
Contrary to most medical disorders (for example, tuberculosis) but similar to others (for example, chronic pain), psychiatric disorders are based on the opinion of a “modest number of ‘expert’ classifications.”4 While the broad categories of disorders are justifiable, individual diagnoses are burdened with high rates of comorbidity; lack of treatment specificity; and evidence that distinct syndromes share a genetic basis. Those concerns were exemplified in the study examining the inter-rater reliability of DSM-5 diagnoses, where many disorders were found to have questionable validity.5
A psychiatric diagnosis should be based on biological, psychological, and social factors, which align with our understanding of the natural course of an illness. A patient presenting with transient symptoms of sadness in the context of significant social factors like homelessness and/or significant biological factors associated with schizophrenia should not reflexively receive an additional diagnosis of a depressive disorder. A patient reporting poor concentration in the context of a manic episode should not receive an additional diagnosis of attention-deficit disorder. An older patient with depression on multiple antipsychotics for adjunctive treatment should not necessarily receive a diagnosis of cognitive disorder at the first sign of memory problems.
The cavalier and inconsistent use of diagnoses renders the patients with no clear narrative of who they are. They end up integrating the varying providers’ opinions as a cacophony of labels of unclear significance. Many patients have contradictory diagnoses like major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Those inaccurate diagnoses could not only lead to treatment mistakes, but also psychological harm.6
A clearer diagnostic picture is not only more scientifically sound but also more coherent to the patient. This in turn can lead to an improved treatment alliance and buy-in from the patient.
How should a provider practice de-diagnosing? Based on the work of Reeve, et al.,7 on the principles crucial to deprescribing, and subsequent research by Gupta and Cahill,8 we compiled a list of considerations for practitioners wishing to engage in this type of work with their patients.
Choose the right time. While insurance companies require diagnostic findings from the first visit, abrupt de-diagnosing for the sake of simplifying the record from that first visit could be detrimental. Patients can become attached to and find meaning in their diagnostic labels. This was exemplified with the removal of Asperger’s syndrome from the DSM-5.9 Acute symptomatology may be an opportune time to revisit the core pathology of a patient, or a poor time for a patient to have this discussion.
Compile a list of all the patient’s diagnoses. Our initial visits are often illuminated when patients enumerate the vast number of diagnoses they have been given by different providers. Patients will often list half a dozen diagnoses. The patterns often follow life courses with ADHD, conduct disorder, and learning disability in childhood; with anxiety, depression, and/or bipolar disorder in early adulthood; to complicated grief, depression with pseudodementia, and neurocognitive disorders in older adults. Yet patients rarely appreciate the temporary or episodic nature of mental disorders and instead accumulate diagnoses at each change of provider.
Initiate discussion with the patient. It is meaningful to see if patients resonate with the question, “Do you ever feel like every psychiatrist you have seen has given you a different diagnosis?” In our experience, patients’ reactions to this question usually exemplify the problematic nature of the vast array of diagnoses our patients are given. The majority of them are unable to confidently explain the meaning of those diagnoses, the context in which they were given, or their significance. This simple exercise has a powerful effect on raising awareness to patients of the problematic nature of polydiagnosing.
Introduce de-diagnosing. The engagement of patients in the diagnostic process has a significant effect. Reviewing not only diagnostic criteria but also nosology and debates in our understanding of diagnoses can provide patients with further engagement in their care. A simple review of the debate of the bereavement exclusion may permit a patient to not only understand the complexity, but also the changing nature of diagnoses. Suddenly, they are no longer bystanders, but informed participants in their care.
Identify diagnoses most appropriate for removal. Contradictory diagnoses are common in the clinical settings we work in. We routinely see patients carrying multiple mood diagnoses, despite our diagnostic systems not permitting one to have both unipolar and bipolar depression. Superfluous diagnoses are also frequent, with patients receiving depressive, or anxious labels when in an acute state of psychosis or mania. This is exemplified by patients suffering from thought blocking and receiving cognitive or attention-related diagnoses. Concurrent yet different diagnoses are also common in patients with a different list of diagnoses by their primary care provider, their therapist, and their psychiatrist. This is particularly problematic as it forces the patient to alternate their thinking or choose between their providers.
Create a new narrative for the patient. Once diagnoses are explained, clarified, and understood, patients with the help of their providers can reexamine their life story under a new and simplified construct. This process often leads to a less confusing sense of self, an increased dedication to the treatment process, whether behavioral, social, psychological, or pharmacologic.
Consider deprescribing. With a more straightforward and more grounded list of diagnoses (or simply one diagnosis), we find the process of deprescribing to be simpler and more engaging for patients. For example, patients can clearly understand the lack of necessity of an antipsychotic prescription for a resolved substance-induced psychosis. Patients are more engaged in their care, leading to improved medication compliance and less attachment to discontinued medications.
Monitor and adapt. One should of course reevaluate diagnoses as the course of illness provides us with additional information. However, we suggest waiting for a manic episode to emerge prior to diagnosing bipolar rather than suggesting the diagnosis because a patient was wearing red shoes, spoke multiple languages, had multiple degrees and was creative.10 The contextual basis and progression of the symptoms should lead to continual reassessment of diagnoses.
Physicians are aware of the balance between Occam’s razor, which promotes the simplest single explanation for a problem, versus Hickam’s dictum that reminds us that patients can have as many diseases as they please. However, similarly to polypharmacy, “polydiagnosing” has negative effects. While the field of psychiatry’s advancing knowledge may encourage providers to diagnose their patients with the growing number of diagnoses, patients still need and benefit from a coherent and clear medical narrative. Psychiatry would be wise to recognize this concerning trend, in its attempt at rectifying polypharmacy.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lehman is a professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is codirector of all acute and intensive psychiatric treatment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego, where he practices clinical psychiatry. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Gupta S & Cahill JD. A prescription for “deprescribing” in psychiatry. Psychiatr Serv. 2016 Aug 1;67(8):904-7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201500359.
2. Schuckit MA. Comorbidity between substance use disorders and psychiatric conditions. Addiction. 2006 Sep;101 Suppl 1:76-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01592.x.
3. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). American Psychiatric Association, 2022. https://psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm.
4. Kendler KS. An historical framework for psychiatric nosology. Psychol Med. 2009 Dec;39(12):1935-41. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709005753.
5. Regier DA et al. DSM-5 field trials in the United States and Canada. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;170(1):59-70. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12070999.
6. Bhattacharya R et al. When good news is bad news: psychological impact of false-positive diagnosis of HIV. AIDS Care. 2008 May;20(5):560-4. doi: 10.1080/09540120701867206.
7. Reeve E et al. Review of deprescribing processes and development of an evidence‐based, patient‐centred deprescribing process. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;78(4):738-47. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12386.
8. Gupta S and Cahill JD. A prescription for “deprescribing” in psychiatry.
9. Solomon M. “On the appearance and disappearance of Asperger’s syndrome” in Kendler and Parnas (eds.) Philosophical Issues in Psychiatry IV: Classification of Psychiatric Illness. Oxford University Press, 2017. doi: 10.1093/med/9780198796022.003.0023.
10. Akiskal HS. Searching for behavioral indicators of bipolar II in patients presenting with major depressive episodes: The “red sign,” the “rule of three,” and other biographic signs of temperamental extravagance, activation, and hypomania. J Affect Disord. 2005 Feb;84(2-3):279-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2004.06.002.
Youth with bipolar disorder at high risk of eating disorders
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.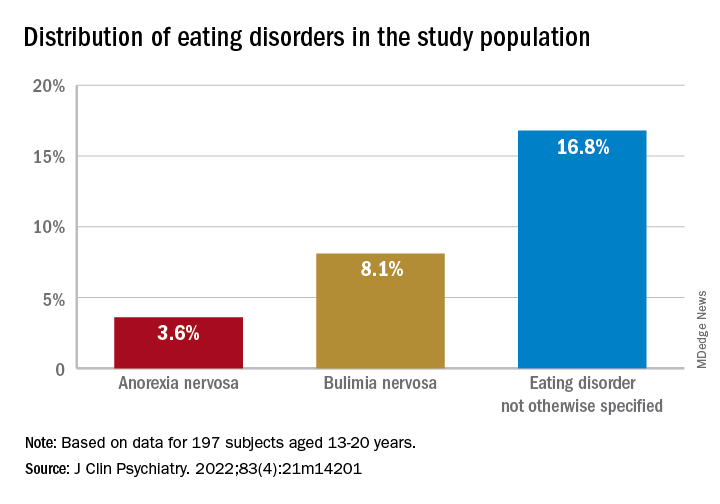
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.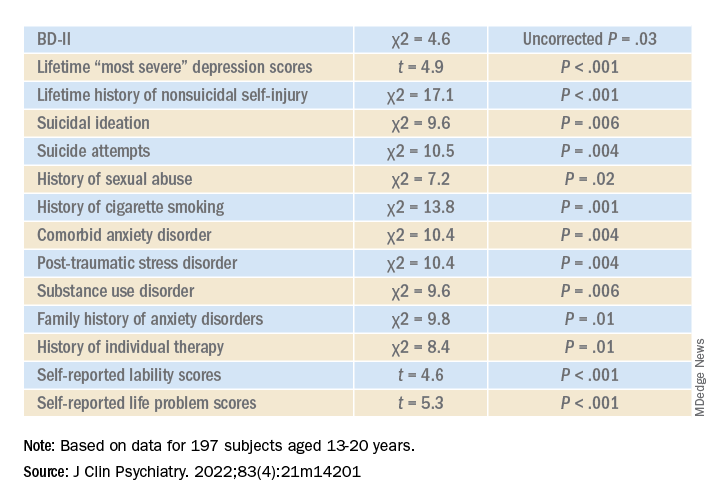
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”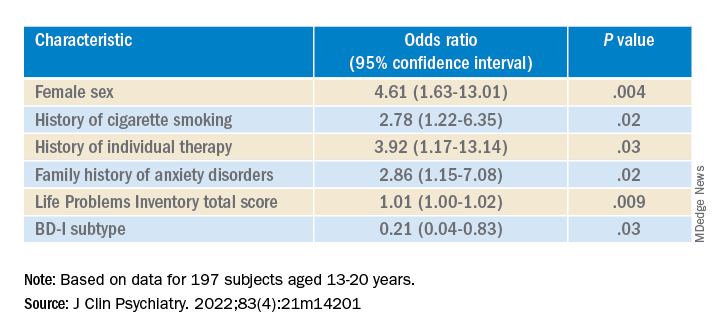
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Social activities may offset psychosis risk in poor communities
, new research suggests.
A study of more than 170 young participants showed reduced hippocampal volume in those living in poor neighborhoods who had low social engagement versus their peers with greater community engagement.
“These findings demonstrate the importance of considering broader environmental influences and indices of social engagement when conceptualizing adversity and potential interventions for individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis,” co-investigator Benson Ku, MD, a postdoctoral fellow and psychiatry resident at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, told this news organization.
The results were presented at the virtual American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology annual meeting.
A personal connection
It’s well known that growing up in low-income housing is associated with lower hippocampal volume and an increased risk for schizophrenia, said Dr. Ku.
“The inverse relationship between poverty and hippocampal gray matter volume has [also] been shown to be mediated by social stress, which can include things like lack of parental caregiving and stressful life events,” he added.
Dr. Ku himself grew up in a socioeconomically disadvantaged family in Queens, New York, and he said he had initially performed poorly in school. His early experiences have helped inform his clinical and research interests in the social determinants of mental health.
“I found community support in the Boys’ Club of New York and a local Magic Shop near where I lived, which helped me thrive and become the successful man I am today. I have also heard from my patients how their living conditions and neighborhood have significantly impacted their mental health,” Dr. Ku said.
“A more in-depth understanding of the social determinants of mental health has helped build rapport and empathy with my patients,” he added.
To explore the association between neighborhood poverty, social engagement, and hippocampal volume in youth at high risk for psychosis, the researchers analyzed data from the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study Phase 2, a multisite consortium.
The researchers recruited and followed up with help-seeking adolescents and young adults from diverse neighborhoods. The analysis included 174 youth, ages 12-33 years, at high clinical risk for psychosis.
Hippocampal volume was assessed using structural MRI. Neighborhood poverty was defined as the percentage of residents with an annual income below the poverty level in the past year.
Social engagement was derived from the desirable events subscale items of the Life Events Scale. These activities included involvement in a church or synagogue; participation in a club, neighborhood, or other organization; taking a vacation; engaging in a hobby, sport, craft, or recreational activity; acquiring a pet; or making new friends.
Lower hippocampal volume
Results showed neighborhood poverty was associated with reduced hippocampal volume, even after controlling for several confounders, including race/ethnicity, family history of mental illnesses, household poverty, educational level, and stressful life events.
Among the 77 participants with lower social engagement, which was defined as three or fewer social activities, neighborhood poverty was associated with reduced hippocampal volume.
However, in the 97 participants who reported greater social engagement, which was defined as four or more social activities, neighborhood poverty was not significantly associated with hippocampal volume.
“It is possible that social engagement may mitigate the deleterious effects of neighborhood poverty on brain morphology, which may inform interventions offered to individuals from disadvantaged neighborhoods,” Dr. Ku said.
“If replication of the relationships between neighborhood poverty, hippocampal volume, and social engagement is established in other populations in longitudinal studies, then targeted interventions at the community level and increased social engagement may potentially play a major role in disease prevention among at-risk youth,” he said.
Dr. Ku noted social engagement might look different in urban versus rural settings.
“In urban areas, it might mean friends, clubs, neighborhood organizations, etc. In rural areas, it might mean family, pets, crafts, etc. The level of social engagement may also depend on neighborhood characteristics, and more research would be needed to better understand how geographic area characteristics – remote, rural, urban – affects social engagement,” he said.
Interesting, innovative
Nagy Youssef, MD, PhD, director of clinical research and professor of psychiatry, Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus, said the study suggests “social engagement may reduce the negative effect of poverty in this population, and if replicated in a larger study, could assist and be a part of the early intervention and prevention in psychosis.”
Overall, “this is an interesting and innovative study that has important medical and social implications and is a good step toward helping us understand these relationships and mitigate and prevent negative consequences, as best as possible, in this population,” said Dr. Youssef, who was not part of the research.
The analysis was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health to the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study. Dr. Ku and Dr. Youssef report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
A study of more than 170 young participants showed reduced hippocampal volume in those living in poor neighborhoods who had low social engagement versus their peers with greater community engagement.
“These findings demonstrate the importance of considering broader environmental influences and indices of social engagement when conceptualizing adversity and potential interventions for individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis,” co-investigator Benson Ku, MD, a postdoctoral fellow and psychiatry resident at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, told this news organization.
The results were presented at the virtual American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology annual meeting.
A personal connection
It’s well known that growing up in low-income housing is associated with lower hippocampal volume and an increased risk for schizophrenia, said Dr. Ku.
“The inverse relationship between poverty and hippocampal gray matter volume has [also] been shown to be mediated by social stress, which can include things like lack of parental caregiving and stressful life events,” he added.
Dr. Ku himself grew up in a socioeconomically disadvantaged family in Queens, New York, and he said he had initially performed poorly in school. His early experiences have helped inform his clinical and research interests in the social determinants of mental health.
“I found community support in the Boys’ Club of New York and a local Magic Shop near where I lived, which helped me thrive and become the successful man I am today. I have also heard from my patients how their living conditions and neighborhood have significantly impacted their mental health,” Dr. Ku said.
“A more in-depth understanding of the social determinants of mental health has helped build rapport and empathy with my patients,” he added.
To explore the association between neighborhood poverty, social engagement, and hippocampal volume in youth at high risk for psychosis, the researchers analyzed data from the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study Phase 2, a multisite consortium.
The researchers recruited and followed up with help-seeking adolescents and young adults from diverse neighborhoods. The analysis included 174 youth, ages 12-33 years, at high clinical risk for psychosis.
Hippocampal volume was assessed using structural MRI. Neighborhood poverty was defined as the percentage of residents with an annual income below the poverty level in the past year.
Social engagement was derived from the desirable events subscale items of the Life Events Scale. These activities included involvement in a church or synagogue; participation in a club, neighborhood, or other organization; taking a vacation; engaging in a hobby, sport, craft, or recreational activity; acquiring a pet; or making new friends.
Lower hippocampal volume
Results showed neighborhood poverty was associated with reduced hippocampal volume, even after controlling for several confounders, including race/ethnicity, family history of mental illnesses, household poverty, educational level, and stressful life events.
Among the 77 participants with lower social engagement, which was defined as three or fewer social activities, neighborhood poverty was associated with reduced hippocampal volume.
However, in the 97 participants who reported greater social engagement, which was defined as four or more social activities, neighborhood poverty was not significantly associated with hippocampal volume.
“It is possible that social engagement may mitigate the deleterious effects of neighborhood poverty on brain morphology, which may inform interventions offered to individuals from disadvantaged neighborhoods,” Dr. Ku said.
“If replication of the relationships between neighborhood poverty, hippocampal volume, and social engagement is established in other populations in longitudinal studies, then targeted interventions at the community level and increased social engagement may potentially play a major role in disease prevention among at-risk youth,” he said.
Dr. Ku noted social engagement might look different in urban versus rural settings.
“In urban areas, it might mean friends, clubs, neighborhood organizations, etc. In rural areas, it might mean family, pets, crafts, etc. The level of social engagement may also depend on neighborhood characteristics, and more research would be needed to better understand how geographic area characteristics – remote, rural, urban – affects social engagement,” he said.
Interesting, innovative
Nagy Youssef, MD, PhD, director of clinical research and professor of psychiatry, Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus, said the study suggests “social engagement may reduce the negative effect of poverty in this population, and if replicated in a larger study, could assist and be a part of the early intervention and prevention in psychosis.”
Overall, “this is an interesting and innovative study that has important medical and social implications and is a good step toward helping us understand these relationships and mitigate and prevent negative consequences, as best as possible, in this population,” said Dr. Youssef, who was not part of the research.
The analysis was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health to the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study. Dr. Ku and Dr. Youssef report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
A study of more than 170 young participants showed reduced hippocampal volume in those living in poor neighborhoods who had low social engagement versus their peers with greater community engagement.
“These findings demonstrate the importance of considering broader environmental influences and indices of social engagement when conceptualizing adversity and potential interventions for individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis,” co-investigator Benson Ku, MD, a postdoctoral fellow and psychiatry resident at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, told this news organization.
The results were presented at the virtual American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology annual meeting.
A personal connection
It’s well known that growing up in low-income housing is associated with lower hippocampal volume and an increased risk for schizophrenia, said Dr. Ku.
“The inverse relationship between poverty and hippocampal gray matter volume has [also] been shown to be mediated by social stress, which can include things like lack of parental caregiving and stressful life events,” he added.
Dr. Ku himself grew up in a socioeconomically disadvantaged family in Queens, New York, and he said he had initially performed poorly in school. His early experiences have helped inform his clinical and research interests in the social determinants of mental health.
“I found community support in the Boys’ Club of New York and a local Magic Shop near where I lived, which helped me thrive and become the successful man I am today. I have also heard from my patients how their living conditions and neighborhood have significantly impacted their mental health,” Dr. Ku said.
“A more in-depth understanding of the social determinants of mental health has helped build rapport and empathy with my patients,” he added.
To explore the association between neighborhood poverty, social engagement, and hippocampal volume in youth at high risk for psychosis, the researchers analyzed data from the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study Phase 2, a multisite consortium.
The researchers recruited and followed up with help-seeking adolescents and young adults from diverse neighborhoods. The analysis included 174 youth, ages 12-33 years, at high clinical risk for psychosis.
Hippocampal volume was assessed using structural MRI. Neighborhood poverty was defined as the percentage of residents with an annual income below the poverty level in the past year.
Social engagement was derived from the desirable events subscale items of the Life Events Scale. These activities included involvement in a church or synagogue; participation in a club, neighborhood, or other organization; taking a vacation; engaging in a hobby, sport, craft, or recreational activity; acquiring a pet; or making new friends.
Lower hippocampal volume
Results showed neighborhood poverty was associated with reduced hippocampal volume, even after controlling for several confounders, including race/ethnicity, family history of mental illnesses, household poverty, educational level, and stressful life events.
Among the 77 participants with lower social engagement, which was defined as three or fewer social activities, neighborhood poverty was associated with reduced hippocampal volume.
However, in the 97 participants who reported greater social engagement, which was defined as four or more social activities, neighborhood poverty was not significantly associated with hippocampal volume.
“It is possible that social engagement may mitigate the deleterious effects of neighborhood poverty on brain morphology, which may inform interventions offered to individuals from disadvantaged neighborhoods,” Dr. Ku said.
“If replication of the relationships between neighborhood poverty, hippocampal volume, and social engagement is established in other populations in longitudinal studies, then targeted interventions at the community level and increased social engagement may potentially play a major role in disease prevention among at-risk youth,” he said.
Dr. Ku noted social engagement might look different in urban versus rural settings.
“In urban areas, it might mean friends, clubs, neighborhood organizations, etc. In rural areas, it might mean family, pets, crafts, etc. The level of social engagement may also depend on neighborhood characteristics, and more research would be needed to better understand how geographic area characteristics – remote, rural, urban – affects social engagement,” he said.
Interesting, innovative
Nagy Youssef, MD, PhD, director of clinical research and professor of psychiatry, Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus, said the study suggests “social engagement may reduce the negative effect of poverty in this population, and if replicated in a larger study, could assist and be a part of the early intervention and prevention in psychosis.”
Overall, “this is an interesting and innovative study that has important medical and social implications and is a good step toward helping us understand these relationships and mitigate and prevent negative consequences, as best as possible, in this population,” said Dr. Youssef, who was not part of the research.
The analysis was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health to the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study. Dr. Ku and Dr. Youssef report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCP 2022
Antipsychotic tied to dose-related weight gain, higher cholesterol
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.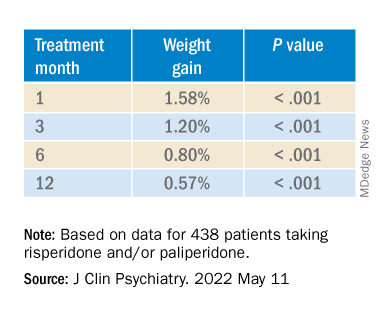
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.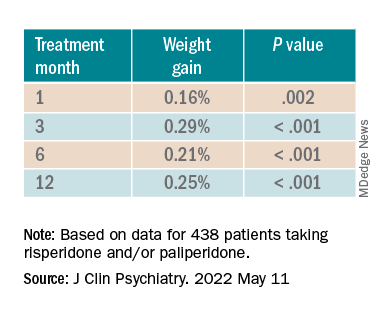
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.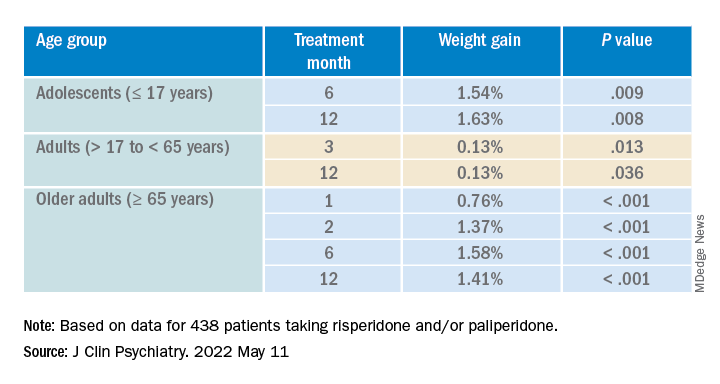
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Early metformin minimizes antipsychotic-induced weight gain
MAR DEL PLATA, ARGENTINA – , according to a new evidence-based Irish guideline for the management of this common complication in adults with psychoses who are taking medications.
The document was discussed during one of the sessions of the XXXV Argentine Congress of Psychiatry of the Association of Argentine Psychiatrists. The document also was presented by one of its authors at the European Congress on Obesity 2022.
The guideline encourages psychiatrists not to underestimate the adverse metabolic effects of their treatments and encourages them to contemplate and carry out this prevention and management strategy, commented María Delia Michat, PhD, professor of clinical psychiatry and psychopharmacology at the APSA Postgraduate Training Institute, Buenos Aires.
“Although it is always good to work as a team, it is usually we psychiatrists who coordinate the pharmacological treatment of our patients, and we have to know how to manage drugs that can prevent cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Michat said in an interview.
“The new guideline is helpful because it protocolizes the use of metformin, which is the cheapest drug and has the most evidence for antipsychotic-induced weight gain,” she added.
Avoiding metabolic syndrome
In patients with schizophrenia, obesity rates are 40% higher than in the general population, and 80% of patients develop weight gain after their first treatment, noted Dr. Michat. “Right away, weight gain is seen in the first month. And it is a serious problem, because patients with schizophrenia, major depression, or bipolar disorder already have an increased risk of premature mortality, especially from cardiovascular diseases, and they have an increased risk of metabolic syndrome. And we sometimes give drugs that further increase that risk,” she said.
Being overweight is a major criterion for defining metabolic syndrome. Dr. Michat noted that, among the antipsychotic drugs that increase weight the most are clozapine, olanzapine, chlorpromazine, quetiapine, and risperidone, in addition to other psychoactive drugs, such as valproic acid, lithium, mirtazapine, and tricyclic antidepressants.
Several clinical trials, such as a pioneering Chinese study from 2008, have shown the potential of metformin to mitigate the weight gain induced by this type of drug.
However, Dr. Michat noted that so far the major guidelines (for example, the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments [CANMAT]/International Society for Bipolar Disorders [ISBD] for bipolar disorder and the American Psychiatric Association [APA] for schizophrenia) “say very little” on how to address this complication. They propose what she defined as a “problematic” order of action in which the initial emphasis is on promoting lifestyle changes, which are difficult for these patients to carry out, as well as general proposals for changing medication (which is not simple to implement when the patient’s condition is stabilized) and eventual consultation with a clinician to start therapy with metformin or other drugs, such as liraglutide, semaglutide, and topiramate.
The new clinical practice guideline, which was published in Evidence-Based Mental Health (of the BMJ journal group), was written by a multidisciplinary team of pharmacists, psychiatrists, and mental health nurses from Ireland. It aims to fill that gap. The investigators reviewed 1,270 scientific articles and analyzed 26 of them in depth, including seven randomized clinical trials and a 2016 systematic review and meta-analysis. The authors made a “strong” recommendation, for which there was moderate-quality evidence, that for patients for whom a lifestyle intervention is unacceptable or inappropriate the use of metformin is an “alternative first-line intervention” for antipsychotic drug–induced weight gain.
Likewise, as a strong recommendation with moderate-quality evidence, the guidance encourages the use of metformin when nonpharmacologic intervention does not seem to be effective.
The guideline also says it is preferable to start metformin early for patients who gain more than 7% of their baseline weight within the first month of antipsychotic treatment. It also endorses metformin when weight gain is established.
Other recommendations include evaluating baseline kidney function before starting metformin treatment and suggest a dose adjustment when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The guidance says the use of metformin is contraindicated for patients in whom eGFR is <30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The proposed starting dosage is 500 mg twice per day with meals, with increments of 500 mg every 1-2 weeks until reaching a target dose of 2,000 mg/day. The guidance recommends that consideration always be given to individual tolerability and efficacy.
Treatment goals should be personalized and agreed upon with patients. In the case of early intervention, the guideline proposes initially stabilizing the weight gained or, if possible, reverse excess weight. When weight gain is established, the goal would be to lose at least 5% of the weight within the next 6 months.
The authors also recommend monitoring kidney function annually, as well as vitamin B12 levels and individual tolerability and compliance. Gastrointestinal adverse effects can be managed by dose reduction or slower dose titration. The risk of lactic acidosis, which affects 4.3 per 100,000 person-years among those taking metformin, can be attenuated by adjusting the dose according to kidney function or avoiding prescribing it to patients who have a history of alcohol abuse or who are receiving treatment that may interact with the drug.
Validating pharmacologic management
The lead author of the new guideline, Ita Fitzgerald, a teacher in clinical pharmacy and senior pharmacist at St. Patrick’s Mental Health Services in Dublin, pointed out that there is a bias toward not using drugs for weight management and shifting the responsibility onto the patients themselves, something that is very often out of their control.
“The purpose of the guideline was to decide on a range of criteria to maximize the use of metformin, to recognize that for many people, pharmacological management is a valid and important option that could and should be more widely used and to provide precise and practical guidance to physicians to facilitate a more widespread use,” Ms. Fitzgerald said in an interview.
According to Fitzgerald, who is pursuing her doctorate at University College Cork (Ireland), one of the most outstanding results of the work is that it highlights that the main benefit of metformin is to flatten rather than reverse antipsychotic-induced weight gain and that indicating it late can nullify that effect.
“In all the recommendations, we try very hard to shift the focus from metformin’s role as a weight reversal agent to one as a weight management agent that should be used early in treatment, which is when most weight gain occurs. If metformin succeeds in flattening that increase, that’s a huge potential benefit for an inexpensive and easily accessible drug. When people have already established weight gain, metformin may not be enough and alternative treatments should be used,” she said.
In addition to its effects on weight, metformin has many other potential health benefits. Of particular importance is that it reduces hyperphagia-mediated antipsychotic-induced weight gain, Ms. Fitzgerald pointed out.
“This is subjectively very important for patients and provides a more positive experience when taking antipsychotics. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain is one of the main reasons for premature discontinuation or incomplete adherence to these drugs and therefore needs to be addressed proactively,” she concluded.
Ms. Fitzgerald and Dr. Michat have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition.
MAR DEL PLATA, ARGENTINA – , according to a new evidence-based Irish guideline for the management of this common complication in adults with psychoses who are taking medications.
The document was discussed during one of the sessions of the XXXV Argentine Congress of Psychiatry of the Association of Argentine Psychiatrists. The document also was presented by one of its authors at the European Congress on Obesity 2022.
The guideline encourages psychiatrists not to underestimate the adverse metabolic effects of their treatments and encourages them to contemplate and carry out this prevention and management strategy, commented María Delia Michat, PhD, professor of clinical psychiatry and psychopharmacology at the APSA Postgraduate Training Institute, Buenos Aires.
“Although it is always good to work as a team, it is usually we psychiatrists who coordinate the pharmacological treatment of our patients, and we have to know how to manage drugs that can prevent cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Michat said in an interview.
“The new guideline is helpful because it protocolizes the use of metformin, which is the cheapest drug and has the most evidence for antipsychotic-induced weight gain,” she added.
Avoiding metabolic syndrome
In patients with schizophrenia, obesity rates are 40% higher than in the general population, and 80% of patients develop weight gain after their first treatment, noted Dr. Michat. “Right away, weight gain is seen in the first month. And it is a serious problem, because patients with schizophrenia, major depression, or bipolar disorder already have an increased risk of premature mortality, especially from cardiovascular diseases, and they have an increased risk of metabolic syndrome. And we sometimes give drugs that further increase that risk,” she said.
Being overweight is a major criterion for defining metabolic syndrome. Dr. Michat noted that, among the antipsychotic drugs that increase weight the most are clozapine, olanzapine, chlorpromazine, quetiapine, and risperidone, in addition to other psychoactive drugs, such as valproic acid, lithium, mirtazapine, and tricyclic antidepressants.
Several clinical trials, such as a pioneering Chinese study from 2008, have shown the potential of metformin to mitigate the weight gain induced by this type of drug.
However, Dr. Michat noted that so far the major guidelines (for example, the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments [CANMAT]/International Society for Bipolar Disorders [ISBD] for bipolar disorder and the American Psychiatric Association [APA] for schizophrenia) “say very little” on how to address this complication. They propose what she defined as a “problematic” order of action in which the initial emphasis is on promoting lifestyle changes, which are difficult for these patients to carry out, as well as general proposals for changing medication (which is not simple to implement when the patient’s condition is stabilized) and eventual consultation with a clinician to start therapy with metformin or other drugs, such as liraglutide, semaglutide, and topiramate.
The new clinical practice guideline, which was published in Evidence-Based Mental Health (of the BMJ journal group), was written by a multidisciplinary team of pharmacists, psychiatrists, and mental health nurses from Ireland. It aims to fill that gap. The investigators reviewed 1,270 scientific articles and analyzed 26 of them in depth, including seven randomized clinical trials and a 2016 systematic review and meta-analysis. The authors made a “strong” recommendation, for which there was moderate-quality evidence, that for patients for whom a lifestyle intervention is unacceptable or inappropriate the use of metformin is an “alternative first-line intervention” for antipsychotic drug–induced weight gain.
Likewise, as a strong recommendation with moderate-quality evidence, the guidance encourages the use of metformin when nonpharmacologic intervention does not seem to be effective.
The guideline also says it is preferable to start metformin early for patients who gain more than 7% of their baseline weight within the first month of antipsychotic treatment. It also endorses metformin when weight gain is established.
Other recommendations include evaluating baseline kidney function before starting metformin treatment and suggest a dose adjustment when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The guidance says the use of metformin is contraindicated for patients in whom eGFR is <30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The proposed starting dosage is 500 mg twice per day with meals, with increments of 500 mg every 1-2 weeks until reaching a target dose of 2,000 mg/day. The guidance recommends that consideration always be given to individual tolerability and efficacy.
Treatment goals should be personalized and agreed upon with patients. In the case of early intervention, the guideline proposes initially stabilizing the weight gained or, if possible, reverse excess weight. When weight gain is established, the goal would be to lose at least 5% of the weight within the next 6 months.
The authors also recommend monitoring kidney function annually, as well as vitamin B12 levels and individual tolerability and compliance. Gastrointestinal adverse effects can be managed by dose reduction or slower dose titration. The risk of lactic acidosis, which affects 4.3 per 100,000 person-years among those taking metformin, can be attenuated by adjusting the dose according to kidney function or avoiding prescribing it to patients who have a history of alcohol abuse or who are receiving treatment that may interact with the drug.
Validating pharmacologic management
The lead author of the new guideline, Ita Fitzgerald, a teacher in clinical pharmacy and senior pharmacist at St. Patrick’s Mental Health Services in Dublin, pointed out that there is a bias toward not using drugs for weight management and shifting the responsibility onto the patients themselves, something that is very often out of their control.
“The purpose of the guideline was to decide on a range of criteria to maximize the use of metformin, to recognize that for many people, pharmacological management is a valid and important option that could and should be more widely used and to provide precise and practical guidance to physicians to facilitate a more widespread use,” Ms. Fitzgerald said in an interview.
According to Fitzgerald, who is pursuing her doctorate at University College Cork (Ireland), one of the most outstanding results of the work is that it highlights that the main benefit of metformin is to flatten rather than reverse antipsychotic-induced weight gain and that indicating it late can nullify that effect.
“In all the recommendations, we try very hard to shift the focus from metformin’s role as a weight reversal agent to one as a weight management agent that should be used early in treatment, which is when most weight gain occurs. If metformin succeeds in flattening that increase, that’s a huge potential benefit for an inexpensive and easily accessible drug. When people have already established weight gain, metformin may not be enough and alternative treatments should be used,” she said.
In addition to its effects on weight, metformin has many other potential health benefits. Of particular importance is that it reduces hyperphagia-mediated antipsychotic-induced weight gain, Ms. Fitzgerald pointed out.
“This is subjectively very important for patients and provides a more positive experience when taking antipsychotics. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain is one of the main reasons for premature discontinuation or incomplete adherence to these drugs and therefore needs to be addressed proactively,” she concluded.
Ms. Fitzgerald and Dr. Michat have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition.
MAR DEL PLATA, ARGENTINA – , according to a new evidence-based Irish guideline for the management of this common complication in adults with psychoses who are taking medications.
The document was discussed during one of the sessions of the XXXV Argentine Congress of Psychiatry of the Association of Argentine Psychiatrists. The document also was presented by one of its authors at the European Congress on Obesity 2022.
The guideline encourages psychiatrists not to underestimate the adverse metabolic effects of their treatments and encourages them to contemplate and carry out this prevention and management strategy, commented María Delia Michat, PhD, professor of clinical psychiatry and psychopharmacology at the APSA Postgraduate Training Institute, Buenos Aires.
“Although it is always good to work as a team, it is usually we psychiatrists who coordinate the pharmacological treatment of our patients, and we have to know how to manage drugs that can prevent cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Michat said in an interview.
“The new guideline is helpful because it protocolizes the use of metformin, which is the cheapest drug and has the most evidence for antipsychotic-induced weight gain,” she added.
Avoiding metabolic syndrome
In patients with schizophrenia, obesity rates are 40% higher than in the general population, and 80% of patients develop weight gain after their first treatment, noted Dr. Michat. “Right away, weight gain is seen in the first month. And it is a serious problem, because patients with schizophrenia, major depression, or bipolar disorder already have an increased risk of premature mortality, especially from cardiovascular diseases, and they have an increased risk of metabolic syndrome. And we sometimes give drugs that further increase that risk,” she said.
Being overweight is a major criterion for defining metabolic syndrome. Dr. Michat noted that, among the antipsychotic drugs that increase weight the most are clozapine, olanzapine, chlorpromazine, quetiapine, and risperidone, in addition to other psychoactive drugs, such as valproic acid, lithium, mirtazapine, and tricyclic antidepressants.
Several clinical trials, such as a pioneering Chinese study from 2008, have shown the potential of metformin to mitigate the weight gain induced by this type of drug.
However, Dr. Michat noted that so far the major guidelines (for example, the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments [CANMAT]/International Society for Bipolar Disorders [ISBD] for bipolar disorder and the American Psychiatric Association [APA] for schizophrenia) “say very little” on how to address this complication. They propose what she defined as a “problematic” order of action in which the initial emphasis is on promoting lifestyle changes, which are difficult for these patients to carry out, as well as general proposals for changing medication (which is not simple to implement when the patient’s condition is stabilized) and eventual consultation with a clinician to start therapy with metformin or other drugs, such as liraglutide, semaglutide, and topiramate.
The new clinical practice guideline, which was published in Evidence-Based Mental Health (of the BMJ journal group), was written by a multidisciplinary team of pharmacists, psychiatrists, and mental health nurses from Ireland. It aims to fill that gap. The investigators reviewed 1,270 scientific articles and analyzed 26 of them in depth, including seven randomized clinical trials and a 2016 systematic review and meta-analysis. The authors made a “strong” recommendation, for which there was moderate-quality evidence, that for patients for whom a lifestyle intervention is unacceptable or inappropriate the use of metformin is an “alternative first-line intervention” for antipsychotic drug–induced weight gain.
Likewise, as a strong recommendation with moderate-quality evidence, the guidance encourages the use of metformin when nonpharmacologic intervention does not seem to be effective.
The guideline also says it is preferable to start metformin early for patients who gain more than 7% of their baseline weight within the first month of antipsychotic treatment. It also endorses metformin when weight gain is established.
Other recommendations include evaluating baseline kidney function before starting metformin treatment and suggest a dose adjustment when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The guidance says the use of metformin is contraindicated for patients in whom eGFR is <30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The proposed starting dosage is 500 mg twice per day with meals, with increments of 500 mg every 1-2 weeks until reaching a target dose of 2,000 mg/day. The guidance recommends that consideration always be given to individual tolerability and efficacy.
Treatment goals should be personalized and agreed upon with patients. In the case of early intervention, the guideline proposes initially stabilizing the weight gained or, if possible, reverse excess weight. When weight gain is established, the goal would be to lose at least 5% of the weight within the next 6 months.
The authors also recommend monitoring kidney function annually, as well as vitamin B12 levels and individual tolerability and compliance. Gastrointestinal adverse effects can be managed by dose reduction or slower dose titration. The risk of lactic acidosis, which affects 4.3 per 100,000 person-years among those taking metformin, can be attenuated by adjusting the dose according to kidney function or avoiding prescribing it to patients who have a history of alcohol abuse or who are receiving treatment that may interact with the drug.
Validating pharmacologic management
The lead author of the new guideline, Ita Fitzgerald, a teacher in clinical pharmacy and senior pharmacist at St. Patrick’s Mental Health Services in Dublin, pointed out that there is a bias toward not using drugs for weight management and shifting the responsibility onto the patients themselves, something that is very often out of their control.
“The purpose of the guideline was to decide on a range of criteria to maximize the use of metformin, to recognize that for many people, pharmacological management is a valid and important option that could and should be more widely used and to provide precise and practical guidance to physicians to facilitate a more widespread use,” Ms. Fitzgerald said in an interview.
According to Fitzgerald, who is pursuing her doctorate at University College Cork (Ireland), one of the most outstanding results of the work is that it highlights that the main benefit of metformin is to flatten rather than reverse antipsychotic-induced weight gain and that indicating it late can nullify that effect.
“In all the recommendations, we try very hard to shift the focus from metformin’s role as a weight reversal agent to one as a weight management agent that should be used early in treatment, which is when most weight gain occurs. If metformin succeeds in flattening that increase, that’s a huge potential benefit for an inexpensive and easily accessible drug. When people have already established weight gain, metformin may not be enough and alternative treatments should be used,” she said.
In addition to its effects on weight, metformin has many other potential health benefits. Of particular importance is that it reduces hyperphagia-mediated antipsychotic-induced weight gain, Ms. Fitzgerald pointed out.
“This is subjectively very important for patients and provides a more positive experience when taking antipsychotics. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain is one of the main reasons for premature discontinuation or incomplete adherence to these drugs and therefore needs to be addressed proactively,” she concluded.
Ms. Fitzgerald and Dr. Michat have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition.










