User login
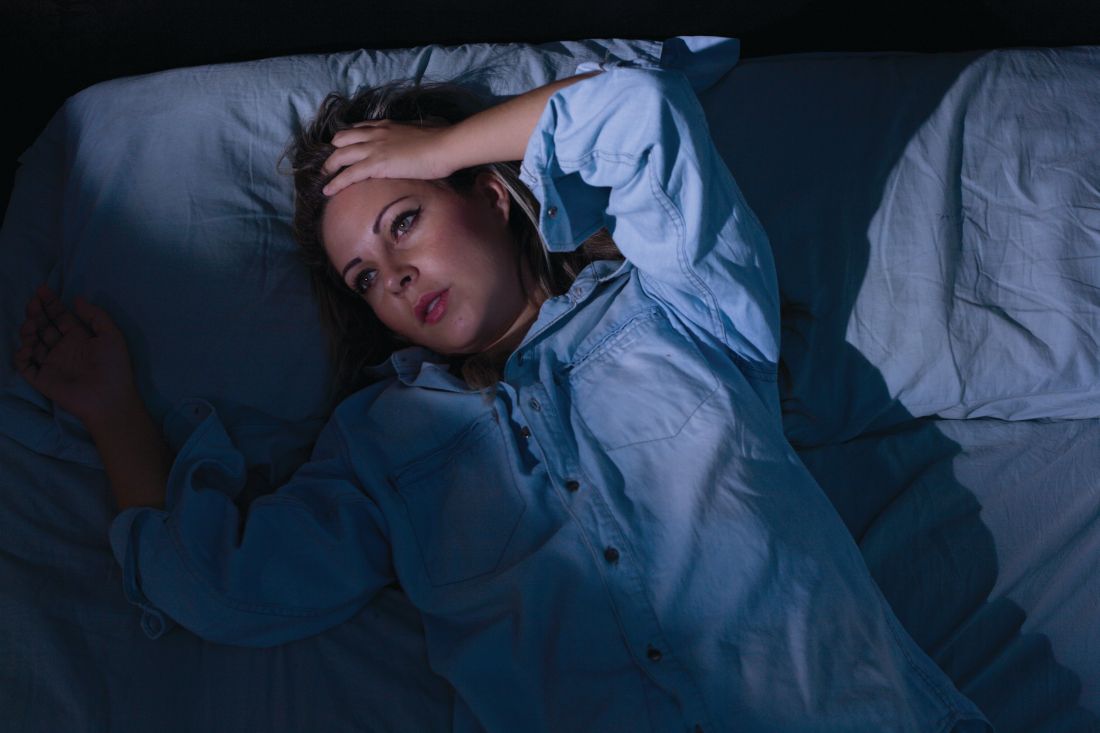
Sleepless in the pandemic
Sleep difficulties during the COVID-19 crisis may be exacerbated by media overexposure and other factors causing fear and stress, according to findings from a large survey of French individuals.
“Physicians usually recommend coping with sleep disorders by exercising, going outside, avoiding screen time, and having a regular schedule – all recommendations difficult to apply during lockdown. Being forced to stay home and the ensuing boredom and loneliness may have led to increased [media exposure], especially among disadvantaged people and overexposure to media COVID-19 content may have contributed to fright and emotional distress,” Damien Leger of the Centre du Sommeil et de la Vigilance, Hôtel Dieu APHP, Université de Paris, and his colleagues wrote in the journal Sleep.
The investigators analyzed data from survey respondents about their sleep problems since the COVID-19 lockdown and other topics such as employment, daily activities, and sleep medications. The survey was part of a large research project, COCONEL, that has been developed to study the French population on a variety of behaviors and comprises 750,000 permanent panelists who respond to surveys. The survey was sent to random sample of panelists with no topic label to avoid selection bias. Of the 25,800 surveys sent, 1,005 responses were recorded.
Respondents were classified as having severe sleep problems if they reported that their daytime activities were affected or if their sleeping medications had increased since the lockdown. While 73% of respondents reported poor sleep in the 8 previous days, 25% reported severe sleep problems, and 54% reported that their sleep problems had worsened during the COVID-19 lockdown.
A media exposure score was created with a Likert scale (strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree) about media exposures of different types. The investigators also queried respondents about the degree to which they found media coverage of the pandemic provoked a fear response. Overall, 68% of respondents agreed that media images and stories about COVD-19 were frightening.
The researchers found a strong association between severe sleeping problems and a high media exposure score (risk ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-2.01; P < .05).
In addition, trepidation and fear from media exposure to COVID-19 news were also associated with severe sleep problems (RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.92-1.75; P < .05). “Suffering from sleep problems may have increased media use at night, and thus increased stress and/or psychological distress and reinforced sleeping problems,” the investigators wrote.
Not surprisingly, respondents with financial difficulties due to the pandemic also reported severe sleeping difficulties (RR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.49-2.65; P < .05).
For individuals who have been treated for sleep problems, the COVID-19 pandemic may ratchet up their sleep challenges. The strongest association with severe sleep problems was found in those respondents who were already taking sleeping medications before the pandemic (RR, 2.72; 95% CI, 2.04-3.61; P < .05).
The COCONEL survey has been funded by the French and National Agency for Research, the Fondation de France, and the National Research Institute for Sustainable Development.
SOURCE: Leger D et al. Sleep. 2020, Jul 25. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaa125.
Sleep difficulties during the COVID-19 crisis may be exacerbated by media overexposure and other factors causing fear and stress, according to findings from a large survey of French individuals.
“Physicians usually recommend coping with sleep disorders by exercising, going outside, avoiding screen time, and having a regular schedule – all recommendations difficult to apply during lockdown. Being forced to stay home and the ensuing boredom and loneliness may have led to increased [media exposure], especially among disadvantaged people and overexposure to media COVID-19 content may have contributed to fright and emotional distress,” Damien Leger of the Centre du Sommeil et de la Vigilance, Hôtel Dieu APHP, Université de Paris, and his colleagues wrote in the journal Sleep.
The investigators analyzed data from survey respondents about their sleep problems since the COVID-19 lockdown and other topics such as employment, daily activities, and sleep medications. The survey was part of a large research project, COCONEL, that has been developed to study the French population on a variety of behaviors and comprises 750,000 permanent panelists who respond to surveys. The survey was sent to random sample of panelists with no topic label to avoid selection bias. Of the 25,800 surveys sent, 1,005 responses were recorded.
Respondents were classified as having severe sleep problems if they reported that their daytime activities were affected or if their sleeping medications had increased since the lockdown. While 73% of respondents reported poor sleep in the 8 previous days, 25% reported severe sleep problems, and 54% reported that their sleep problems had worsened during the COVID-19 lockdown.
A media exposure score was created with a Likert scale (strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree) about media exposures of different types. The investigators also queried respondents about the degree to which they found media coverage of the pandemic provoked a fear response. Overall, 68% of respondents agreed that media images and stories about COVD-19 were frightening.
The researchers found a strong association between severe sleeping problems and a high media exposure score (risk ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-2.01; P < .05).
In addition, trepidation and fear from media exposure to COVID-19 news were also associated with severe sleep problems (RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.92-1.75; P < .05). “Suffering from sleep problems may have increased media use at night, and thus increased stress and/or psychological distress and reinforced sleeping problems,” the investigators wrote.
Not surprisingly, respondents with financial difficulties due to the pandemic also reported severe sleeping difficulties (RR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.49-2.65; P < .05).
For individuals who have been treated for sleep problems, the COVID-19 pandemic may ratchet up their sleep challenges. The strongest association with severe sleep problems was found in those respondents who were already taking sleeping medications before the pandemic (RR, 2.72; 95% CI, 2.04-3.61; P < .05).
The COCONEL survey has been funded by the French and National Agency for Research, the Fondation de France, and the National Research Institute for Sustainable Development.
SOURCE: Leger D et al. Sleep. 2020, Jul 25. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaa125.
Sleep difficulties during the COVID-19 crisis may be exacerbated by media overexposure and other factors causing fear and stress, according to findings from a large survey of French individuals.
“Physicians usually recommend coping with sleep disorders by exercising, going outside, avoiding screen time, and having a regular schedule – all recommendations difficult to apply during lockdown. Being forced to stay home and the ensuing boredom and loneliness may have led to increased [media exposure], especially among disadvantaged people and overexposure to media COVID-19 content may have contributed to fright and emotional distress,” Damien Leger of the Centre du Sommeil et de la Vigilance, Hôtel Dieu APHP, Université de Paris, and his colleagues wrote in the journal Sleep.
The investigators analyzed data from survey respondents about their sleep problems since the COVID-19 lockdown and other topics such as employment, daily activities, and sleep medications. The survey was part of a large research project, COCONEL, that has been developed to study the French population on a variety of behaviors and comprises 750,000 permanent panelists who respond to surveys. The survey was sent to random sample of panelists with no topic label to avoid selection bias. Of the 25,800 surveys sent, 1,005 responses were recorded.
Respondents were classified as having severe sleep problems if they reported that their daytime activities were affected or if their sleeping medications had increased since the lockdown. While 73% of respondents reported poor sleep in the 8 previous days, 25% reported severe sleep problems, and 54% reported that their sleep problems had worsened during the COVID-19 lockdown.
A media exposure score was created with a Likert scale (strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree) about media exposures of different types. The investigators also queried respondents about the degree to which they found media coverage of the pandemic provoked a fear response. Overall, 68% of respondents agreed that media images and stories about COVD-19 were frightening.
The researchers found a strong association between severe sleeping problems and a high media exposure score (risk ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-2.01; P < .05).
In addition, trepidation and fear from media exposure to COVID-19 news were also associated with severe sleep problems (RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.92-1.75; P < .05). “Suffering from sleep problems may have increased media use at night, and thus increased stress and/or psychological distress and reinforced sleeping problems,” the investigators wrote.
Not surprisingly, respondents with financial difficulties due to the pandemic also reported severe sleeping difficulties (RR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.49-2.65; P < .05).
For individuals who have been treated for sleep problems, the COVID-19 pandemic may ratchet up their sleep challenges. The strongest association with severe sleep problems was found in those respondents who were already taking sleeping medications before the pandemic (RR, 2.72; 95% CI, 2.04-3.61; P < .05).
The COCONEL survey has been funded by the French and National Agency for Research, the Fondation de France, and the National Research Institute for Sustainable Development.
SOURCE: Leger D et al. Sleep. 2020, Jul 25. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaa125.
FROM SLEEP
In a first, proton therapy bests radiotherapy in an RCT
Less toxicity in esophageal cancer
The results, from 107 evaluable patients, were published online July 25 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Proton therapy significantly reduced the total toxicity burden (TTB), a coprimary endpoint, report the study authors, led by Steven Lin, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
However, the investigators of the single-center trial acknowledge that the better toxicity outcome is accompanied by a caveat: TTB, which combines 11 adverse effects, was not a previously validated endpoint.
Efficacy was similar. Proton therapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) had nearly identical 3-year rates of progression-free survival (50.8% vs 51.2%), the other coprimary endpoint, as well as overall survival (44.5% vs 44.5%). Median follow-up was 44.1 months.
Quality of life outcomes were also not significantly different in the phase 2B trial, which was underpowered due to protocol anomalies, including 22 patients who were randomized to proton therapy but then denied insurance coverage, and thus participation in the trial.
Lack of validation of TTB “dampens the enthusiasm of a positive primary endpoint,” writes Charles Simone, MD, of the New York Proton Center and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, in an accompanying editorial.
TTB encompasses seven postoperative complications measured up to 30 days after surgery (such as reintubation) and six toxicities measured up to 12 months from randomization (such as pleural effusion and radiation pneumonitis); two of the adverse events — atrial fibrillation and pneumonia — were included in both categories, depending on the timing of the event.
The posterior mean TTB, which is a synthesis of the cumulative severity of adverse events, was 2.3 times higher for IMRT (39.9) than for proton therapy (17.4), the investigators report.
Simone believes the TTB measure — and associated significant reduction in events with protons compared to IMRT in the current study — has value, especially in “high-stakes malignancies” such as esophageal and lung cancers.
“They are two of only a few cancers where there is an expected mortality rate from treatment,” he told Medscape Medical News. “For proton therapy to reduce those toxicities [measured by TTB in esophageal patients] may be a real benefit.”
Asked for independent comment, Mark Langer, MD, IU Health Simon Cancer Center, Indiana, Indianapolis, said “the novel TTB was well put together and is a credit to the investigators.”
He explained that the esophagus is typically the focus of complications, but that events like atrial fibrillation are important because the esophagus runs down to the stomach and passes by the lungs and heart. “The investigators call attention to morbidities that we may not have previously recognized,” said Langer, a radiation oncologist who does not use protons, as Indiana does not have a unit.
Reduced toxicity is the main claim for superiority for proton therapy over conventional radiotherapy, but to date there has been little clinical evidence.
For example, a randomized trial in inoperable lung cancer published 2 years ago showed that proton therapy was not superior in reducing serious lung toxicity compared with IMRT.
“That trial really disillusioned a lot of people,” Simone commented.
But he points out that protons have been found to be superior compared with photon radiation in terms of toxicity in a variety of observational studies, including multicenter retrospective comparative analyses.
Trial closed early
The RCT conducted by Lin and colleagues, which began in 2012, randomly assigned 145 patients with newly diagnosed locally advanced esophageal cancer to one of the two modalities (72 IMRT and 73 proton therapy). The investigators allowed a wide variety of patients, including those with ECOG performance status 2, differing tumor locations, squamous cell and adenocarcinoma histologies, and unresectable and potentially resectable cases. However, only 107 patients were evaluable (61 IMRT and 46 proton therapy), as the trial did not report on those afore-mentioned patients denied insurance coverage for proton therapy after randomization and those patients in the IMRT group who refused that treatment and wanted proton therapy.
Patients received 50.4 Gy (CGE) with concurrent chemotherapy and 51 patients underwent surgery, generally 8-10 weeks following chemoradiation.
The full list of adverse events for the TTB measure for toxicities was atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, pneumonia, and radiation pneumonitis. For post-op complications, the list was acute respiratory distress syndrome, anastomotic leak, atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, reintubation, stroke, and pneumonia.
The most common toxicity was pleural effusion (in 24 patients on IMRT and 13 on proton therapy). The most common post-op complication was atrial fibrillation (in seven patients on IMRT and two on proton therapy).
Simone points out that combining these adverse events in the TTB measure allowed a relatively small number of participants and events to show statistically significant results “without statistically apparent differences for [some] individual events.”
The investigators highlight the fact that 80% of patients in the proton group received passive scattering proton therapy, an older technology that increases normal tissue exposure relative to more modern intensity-modulated proton therapy.
The trial closed early because of the start of the phase 3 NRG-GI006 trial. The stoppage was just before the preplanned third and final interim analysis, which would have exceeded the trial’s stopping boundary (due to a positive result for TTB).
“The now-activated NRG-GI006 phase 3 randomized trial should prove to be the gold standard comparison of protons versus IMRT for esophageal cancer,” writes Simone in his editorial.
The trial was supported by National Cancer Institute. Multiple study authors have financial ties to industry, including radiation therapy manufacturers. Simone has reported financial ties to Varian Medical Systems. Langer has reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Less toxicity in esophageal cancer
Less toxicity in esophageal cancer
The results, from 107 evaluable patients, were published online July 25 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Proton therapy significantly reduced the total toxicity burden (TTB), a coprimary endpoint, report the study authors, led by Steven Lin, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
However, the investigators of the single-center trial acknowledge that the better toxicity outcome is accompanied by a caveat: TTB, which combines 11 adverse effects, was not a previously validated endpoint.
Efficacy was similar. Proton therapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) had nearly identical 3-year rates of progression-free survival (50.8% vs 51.2%), the other coprimary endpoint, as well as overall survival (44.5% vs 44.5%). Median follow-up was 44.1 months.
Quality of life outcomes were also not significantly different in the phase 2B trial, which was underpowered due to protocol anomalies, including 22 patients who were randomized to proton therapy but then denied insurance coverage, and thus participation in the trial.
Lack of validation of TTB “dampens the enthusiasm of a positive primary endpoint,” writes Charles Simone, MD, of the New York Proton Center and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, in an accompanying editorial.
TTB encompasses seven postoperative complications measured up to 30 days after surgery (such as reintubation) and six toxicities measured up to 12 months from randomization (such as pleural effusion and radiation pneumonitis); two of the adverse events — atrial fibrillation and pneumonia — were included in both categories, depending on the timing of the event.
The posterior mean TTB, which is a synthesis of the cumulative severity of adverse events, was 2.3 times higher for IMRT (39.9) than for proton therapy (17.4), the investigators report.
Simone believes the TTB measure — and associated significant reduction in events with protons compared to IMRT in the current study — has value, especially in “high-stakes malignancies” such as esophageal and lung cancers.
“They are two of only a few cancers where there is an expected mortality rate from treatment,” he told Medscape Medical News. “For proton therapy to reduce those toxicities [measured by TTB in esophageal patients] may be a real benefit.”
Asked for independent comment, Mark Langer, MD, IU Health Simon Cancer Center, Indiana, Indianapolis, said “the novel TTB was well put together and is a credit to the investigators.”
He explained that the esophagus is typically the focus of complications, but that events like atrial fibrillation are important because the esophagus runs down to the stomach and passes by the lungs and heart. “The investigators call attention to morbidities that we may not have previously recognized,” said Langer, a radiation oncologist who does not use protons, as Indiana does not have a unit.
Reduced toxicity is the main claim for superiority for proton therapy over conventional radiotherapy, but to date there has been little clinical evidence.
For example, a randomized trial in inoperable lung cancer published 2 years ago showed that proton therapy was not superior in reducing serious lung toxicity compared with IMRT.
“That trial really disillusioned a lot of people,” Simone commented.
But he points out that protons have been found to be superior compared with photon radiation in terms of toxicity in a variety of observational studies, including multicenter retrospective comparative analyses.
Trial closed early
The RCT conducted by Lin and colleagues, which began in 2012, randomly assigned 145 patients with newly diagnosed locally advanced esophageal cancer to one of the two modalities (72 IMRT and 73 proton therapy). The investigators allowed a wide variety of patients, including those with ECOG performance status 2, differing tumor locations, squamous cell and adenocarcinoma histologies, and unresectable and potentially resectable cases. However, only 107 patients were evaluable (61 IMRT and 46 proton therapy), as the trial did not report on those afore-mentioned patients denied insurance coverage for proton therapy after randomization and those patients in the IMRT group who refused that treatment and wanted proton therapy.
Patients received 50.4 Gy (CGE) with concurrent chemotherapy and 51 patients underwent surgery, generally 8-10 weeks following chemoradiation.
The full list of adverse events for the TTB measure for toxicities was atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, pneumonia, and radiation pneumonitis. For post-op complications, the list was acute respiratory distress syndrome, anastomotic leak, atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, reintubation, stroke, and pneumonia.
The most common toxicity was pleural effusion (in 24 patients on IMRT and 13 on proton therapy). The most common post-op complication was atrial fibrillation (in seven patients on IMRT and two on proton therapy).
Simone points out that combining these adverse events in the TTB measure allowed a relatively small number of participants and events to show statistically significant results “without statistically apparent differences for [some] individual events.”
The investigators highlight the fact that 80% of patients in the proton group received passive scattering proton therapy, an older technology that increases normal tissue exposure relative to more modern intensity-modulated proton therapy.
The trial closed early because of the start of the phase 3 NRG-GI006 trial. The stoppage was just before the preplanned third and final interim analysis, which would have exceeded the trial’s stopping boundary (due to a positive result for TTB).
“The now-activated NRG-GI006 phase 3 randomized trial should prove to be the gold standard comparison of protons versus IMRT for esophageal cancer,” writes Simone in his editorial.
The trial was supported by National Cancer Institute. Multiple study authors have financial ties to industry, including radiation therapy manufacturers. Simone has reported financial ties to Varian Medical Systems. Langer has reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results, from 107 evaluable patients, were published online July 25 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Proton therapy significantly reduced the total toxicity burden (TTB), a coprimary endpoint, report the study authors, led by Steven Lin, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
However, the investigators of the single-center trial acknowledge that the better toxicity outcome is accompanied by a caveat: TTB, which combines 11 adverse effects, was not a previously validated endpoint.
Efficacy was similar. Proton therapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) had nearly identical 3-year rates of progression-free survival (50.8% vs 51.2%), the other coprimary endpoint, as well as overall survival (44.5% vs 44.5%). Median follow-up was 44.1 months.
Quality of life outcomes were also not significantly different in the phase 2B trial, which was underpowered due to protocol anomalies, including 22 patients who were randomized to proton therapy but then denied insurance coverage, and thus participation in the trial.
Lack of validation of TTB “dampens the enthusiasm of a positive primary endpoint,” writes Charles Simone, MD, of the New York Proton Center and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, in an accompanying editorial.
TTB encompasses seven postoperative complications measured up to 30 days after surgery (such as reintubation) and six toxicities measured up to 12 months from randomization (such as pleural effusion and radiation pneumonitis); two of the adverse events — atrial fibrillation and pneumonia — were included in both categories, depending on the timing of the event.
The posterior mean TTB, which is a synthesis of the cumulative severity of adverse events, was 2.3 times higher for IMRT (39.9) than for proton therapy (17.4), the investigators report.
Simone believes the TTB measure — and associated significant reduction in events with protons compared to IMRT in the current study — has value, especially in “high-stakes malignancies” such as esophageal and lung cancers.
“They are two of only a few cancers where there is an expected mortality rate from treatment,” he told Medscape Medical News. “For proton therapy to reduce those toxicities [measured by TTB in esophageal patients] may be a real benefit.”
Asked for independent comment, Mark Langer, MD, IU Health Simon Cancer Center, Indiana, Indianapolis, said “the novel TTB was well put together and is a credit to the investigators.”
He explained that the esophagus is typically the focus of complications, but that events like atrial fibrillation are important because the esophagus runs down to the stomach and passes by the lungs and heart. “The investigators call attention to morbidities that we may not have previously recognized,” said Langer, a radiation oncologist who does not use protons, as Indiana does not have a unit.
Reduced toxicity is the main claim for superiority for proton therapy over conventional radiotherapy, but to date there has been little clinical evidence.
For example, a randomized trial in inoperable lung cancer published 2 years ago showed that proton therapy was not superior in reducing serious lung toxicity compared with IMRT.
“That trial really disillusioned a lot of people,” Simone commented.
But he points out that protons have been found to be superior compared with photon radiation in terms of toxicity in a variety of observational studies, including multicenter retrospective comparative analyses.
Trial closed early
The RCT conducted by Lin and colleagues, which began in 2012, randomly assigned 145 patients with newly diagnosed locally advanced esophageal cancer to one of the two modalities (72 IMRT and 73 proton therapy). The investigators allowed a wide variety of patients, including those with ECOG performance status 2, differing tumor locations, squamous cell and adenocarcinoma histologies, and unresectable and potentially resectable cases. However, only 107 patients were evaluable (61 IMRT and 46 proton therapy), as the trial did not report on those afore-mentioned patients denied insurance coverage for proton therapy after randomization and those patients in the IMRT group who refused that treatment and wanted proton therapy.
Patients received 50.4 Gy (CGE) with concurrent chemotherapy and 51 patients underwent surgery, generally 8-10 weeks following chemoradiation.
The full list of adverse events for the TTB measure for toxicities was atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, pneumonia, and radiation pneumonitis. For post-op complications, the list was acute respiratory distress syndrome, anastomotic leak, atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, reintubation, stroke, and pneumonia.
The most common toxicity was pleural effusion (in 24 patients on IMRT and 13 on proton therapy). The most common post-op complication was atrial fibrillation (in seven patients on IMRT and two on proton therapy).
Simone points out that combining these adverse events in the TTB measure allowed a relatively small number of participants and events to show statistically significant results “without statistically apparent differences for [some] individual events.”
The investigators highlight the fact that 80% of patients in the proton group received passive scattering proton therapy, an older technology that increases normal tissue exposure relative to more modern intensity-modulated proton therapy.
The trial closed early because of the start of the phase 3 NRG-GI006 trial. The stoppage was just before the preplanned third and final interim analysis, which would have exceeded the trial’s stopping boundary (due to a positive result for TTB).
“The now-activated NRG-GI006 phase 3 randomized trial should prove to be the gold standard comparison of protons versus IMRT for esophageal cancer,” writes Simone in his editorial.
The trial was supported by National Cancer Institute. Multiple study authors have financial ties to industry, including radiation therapy manufacturers. Simone has reported financial ties to Varian Medical Systems. Langer has reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnosing and Managing Tardive Dyskinesia

Click here to read the supplement and earn free CME/CE credits by learning about TD and evidence based treatments.
Educational Objectives
- Discuss the diagnosis, differential diagnosis and risk factors for TD
- Identify the prevalence of TD with antipsychotics
- Use the AIMS examination
- Review the evidence and non-evidence based treatments for TD
- Individualize treatment choices, giving consideration to efficacy, safety, long-term data, and unique patient characteristics
- Formulate appropriate treatment regimens considering
the emergence of new FDA approved treatments for TD
Click here to read the supplement.

Click here to read the supplement and earn free CME/CE credits by learning about TD and evidence based treatments.
Educational Objectives
- Discuss the diagnosis, differential diagnosis and risk factors for TD
- Identify the prevalence of TD with antipsychotics
- Use the AIMS examination
- Review the evidence and non-evidence based treatments for TD
- Individualize treatment choices, giving consideration to efficacy, safety, long-term data, and unique patient characteristics
- Formulate appropriate treatment regimens considering
the emergence of new FDA approved treatments for TD
Click here to read the supplement.

Click here to read the supplement and earn free CME/CE credits by learning about TD and evidence based treatments.
Educational Objectives
- Discuss the diagnosis, differential diagnosis and risk factors for TD
- Identify the prevalence of TD with antipsychotics
- Use the AIMS examination
- Review the evidence and non-evidence based treatments for TD
- Individualize treatment choices, giving consideration to efficacy, safety, long-term data, and unique patient characteristics
- Formulate appropriate treatment regimens considering
the emergence of new FDA approved treatments for TD
Click here to read the supplement.
Experimental blood test detects cancer years before symptoms
A blood test that may be able to detect cancer years before any symptoms appear is under development. The PanSeer assay, which detects methylation markers in blood, was used in healthy individuals and successfully detected five cancer types in 91% of samples from individuals who were diagnosed with cancer 1 to 4 years later.
“We can’t say for sure that the patients didn’t have any symptoms, but we detected the cancer years before they ever walked into the hospital,” said study author Kun Zhang, PhD, a professor of bioengineering at the University of California, San Diego. “We were also able to follow up with patients, so we actually knew that they had cancer.”
Zhang noted that they also followed the individuals whose tests indicated they were cancer free. “They were healthy at the time the samples were obtained, and they remained healthy,” he said. “Follow-up was key to validating these data.”
The PanSeer test is being developed by Singlera Genomics. Zhang is a cofounder and a paid consultant of the company.
The study was published online July 21 in Nature Communications.
Unique among tests
Several blood tests for the detection of cancer have been reported in recent years. A test developed by Grail was able to detect more than 50 types of cancer and also identified the tissues where the cancer originated. The CancerSEEK test identified eight common cancers by measuring circulating tumor DNA from 16 genes, as well as eight protein biomarkers.
Findings regarding the CellMax Life FirstSight blood test were released last month. The test detected all 11 cases of colorectal cancer in a cohort of 354 patients and detected 40 of 53 advanced adenomas.
The latest study with the PanSeer assay is unique, say the investigators, because they had access to blood samples from patients who may have been completely asymptomatic and had not yet been diagnosed with cancer. Other blood tests have typically involved the use of specimens from people with a known diagnosis.
The specimens were collected as part of a 10-year longitudinal study that began in 2007 in China. Zhang and his team were able to test blood samples before individuals had experienced any signs or symptoms of cancer, and they were able to conduct long-term follow-up of the cohort.
Study details
The PanSeer assay uses DNA methylation analysis and screens for a DNA signature called CpG methylation. The results of an early-stage proof-of-concept study were published 3 years ago (Nat Genet. 2017;49:635–642).
For the current study, data were drawn from the Taizhou Longitudinal Study, which included 123,115 individuals aged 25 to 90 years who provided blood samples for long-term storage from 2007 to 2014. Participants were monitored indefinitely for cancer occurrence using local cancer registries and health insurance databases.
The team identified 575 individuals who were initially asymptomatic and healthy but were subsequently diagnosed with one of five common cancer types (stomach, esophagus, colorectum, lung, or liver cancer) within 4 years of their initial blood sampling. The authors selected these five cancer types to study because the incidence rates of these cancers in this population are high and, taken together, account for the highest mortality.
The study design allowed the authors to evaluate specimens both from patients with cancer and from those who were healthy within the same cohort. Using 191 prediagnosis samples, 223 postdiagnosis samples, and 414 healthy samples, they created a training set and validation model.
A machine learning method was created to classify samples as being either from healthy individuals or from those with cancer, using blood samples from the training set. The final classifier achieved 88% sensitivity for postdiagnosis samples and 91% sensitivity for prediagnosis samples at a specificity of 95%.
Zhang feels that initially it would be more appropriate to use the test for high-risk patients and to then evaluate the clinical benefit. “For any test, it is always more prudent to begin with a high-risk population,” he said. “You want to see some benefit with the high-risk population first, and then it can slowly be extended to others at lower risk.”
He emphasized that more rigorous testing is needing before the PanSeer assay is ready for clinical use. The logistics of designing and conducting a clinical trial that would include more than one cancer type would be very complicated. “The option was to break it down to five different studies,” he said. “We decided to begin with colon cancer, and we are currently in the process of talking with the FDA and designing the study.”
High bar to reach
Approached for comment, Benjamin Weinberg, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Division of Hematology and Oncology, the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, noted that there is “quite a ways to go before this can be clinically actionable.
“A lot of us are looking at combining methylation with circulating tumor DNA and throw the kitchen sink at it, but as the paper nicely describes, there are pros and cons to all of these,” he said.
Many tests of this type are in development. Weinberg explained that a circulating tumor DNA test for colon cancer may hit the market soon, pending FDA approval, although that test will be used in a different setting. “This is something that’s used to assess for minimal residual disease in patients who have undergone surgery and appear to be ‘cured’ of the disease,” he said. “The test is looking to see if there is any circulating tumor DNA being shed from whatever tumor is left behind.”
The type of test that has piqued the most interest is one that is “tumor informed,” meaning that the company receives tumor tissue and develops a personalized test of that tumor on the basis of tumor genetics. “That is a very targeted way of surveillance,” said Weinberg, “But it would be very difficult to use a tumor-informed test on the population described in this study because you don’t know if there is going to be a tumor or not.”
The PanSeer test may also prove difficult to use in the clinic because it detects multiple cancers, Weinberg said. “If there is a positive finding, then which cancer do you look for?” he commented. “It has an issue in that regard, and that’s the problem with this type of test, as it is easier if there is one site of origin.”
Overall, the test was fairly sensitive and specific, with a very low false negative rate. Going forward, he noted, there is a very high bar for tests used as screening tools, although the authors do say that their focus is for use in a high-risk population.
“There would have to be a randomized trial, and the test will have to show a survival benefit,” Weinberg said. He noted that it can sometimes be challenging to do so.
“Colonoscopy has been shown to be beneficial, but early mammography has become controversial, and prostate cancer is a whole different animal,” he added. “And these are established tests, and they show how difficult this can be.”
The Taizhou Longitudinal Study study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Basic Research grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, the International S&T Cooperation Program of China, the Municipal Science and Technology Major Project program, the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China, and the 111 Project (B13016). Funding for the DNA methylation assays was provided by Singlera Genomics. Zhang is a cofounder, equity holder, and paid consultant of Singlera Genomics, a company that is developing early cancer detection tests, including the PanSeer test. Weinberg is a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Taiho Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, and Eli Lilly and Company; has received research grant from Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; and has received travel reimbursement from Caris Life Sciences.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A blood test that may be able to detect cancer years before any symptoms appear is under development. The PanSeer assay, which detects methylation markers in blood, was used in healthy individuals and successfully detected five cancer types in 91% of samples from individuals who were diagnosed with cancer 1 to 4 years later.
“We can’t say for sure that the patients didn’t have any symptoms, but we detected the cancer years before they ever walked into the hospital,” said study author Kun Zhang, PhD, a professor of bioengineering at the University of California, San Diego. “We were also able to follow up with patients, so we actually knew that they had cancer.”
Zhang noted that they also followed the individuals whose tests indicated they were cancer free. “They were healthy at the time the samples were obtained, and they remained healthy,” he said. “Follow-up was key to validating these data.”
The PanSeer test is being developed by Singlera Genomics. Zhang is a cofounder and a paid consultant of the company.
The study was published online July 21 in Nature Communications.
Unique among tests
Several blood tests for the detection of cancer have been reported in recent years. A test developed by Grail was able to detect more than 50 types of cancer and also identified the tissues where the cancer originated. The CancerSEEK test identified eight common cancers by measuring circulating tumor DNA from 16 genes, as well as eight protein biomarkers.
Findings regarding the CellMax Life FirstSight blood test were released last month. The test detected all 11 cases of colorectal cancer in a cohort of 354 patients and detected 40 of 53 advanced adenomas.
The latest study with the PanSeer assay is unique, say the investigators, because they had access to blood samples from patients who may have been completely asymptomatic and had not yet been diagnosed with cancer. Other blood tests have typically involved the use of specimens from people with a known diagnosis.
The specimens were collected as part of a 10-year longitudinal study that began in 2007 in China. Zhang and his team were able to test blood samples before individuals had experienced any signs or symptoms of cancer, and they were able to conduct long-term follow-up of the cohort.
Study details
The PanSeer assay uses DNA methylation analysis and screens for a DNA signature called CpG methylation. The results of an early-stage proof-of-concept study were published 3 years ago (Nat Genet. 2017;49:635–642).
For the current study, data were drawn from the Taizhou Longitudinal Study, which included 123,115 individuals aged 25 to 90 years who provided blood samples for long-term storage from 2007 to 2014. Participants were monitored indefinitely for cancer occurrence using local cancer registries and health insurance databases.
The team identified 575 individuals who were initially asymptomatic and healthy but were subsequently diagnosed with one of five common cancer types (stomach, esophagus, colorectum, lung, or liver cancer) within 4 years of their initial blood sampling. The authors selected these five cancer types to study because the incidence rates of these cancers in this population are high and, taken together, account for the highest mortality.
The study design allowed the authors to evaluate specimens both from patients with cancer and from those who were healthy within the same cohort. Using 191 prediagnosis samples, 223 postdiagnosis samples, and 414 healthy samples, they created a training set and validation model.
A machine learning method was created to classify samples as being either from healthy individuals or from those with cancer, using blood samples from the training set. The final classifier achieved 88% sensitivity for postdiagnosis samples and 91% sensitivity for prediagnosis samples at a specificity of 95%.
Zhang feels that initially it would be more appropriate to use the test for high-risk patients and to then evaluate the clinical benefit. “For any test, it is always more prudent to begin with a high-risk population,” he said. “You want to see some benefit with the high-risk population first, and then it can slowly be extended to others at lower risk.”
He emphasized that more rigorous testing is needing before the PanSeer assay is ready for clinical use. The logistics of designing and conducting a clinical trial that would include more than one cancer type would be very complicated. “The option was to break it down to five different studies,” he said. “We decided to begin with colon cancer, and we are currently in the process of talking with the FDA and designing the study.”
High bar to reach
Approached for comment, Benjamin Weinberg, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Division of Hematology and Oncology, the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, noted that there is “quite a ways to go before this can be clinically actionable.
“A lot of us are looking at combining methylation with circulating tumor DNA and throw the kitchen sink at it, but as the paper nicely describes, there are pros and cons to all of these,” he said.
Many tests of this type are in development. Weinberg explained that a circulating tumor DNA test for colon cancer may hit the market soon, pending FDA approval, although that test will be used in a different setting. “This is something that’s used to assess for minimal residual disease in patients who have undergone surgery and appear to be ‘cured’ of the disease,” he said. “The test is looking to see if there is any circulating tumor DNA being shed from whatever tumor is left behind.”
The type of test that has piqued the most interest is one that is “tumor informed,” meaning that the company receives tumor tissue and develops a personalized test of that tumor on the basis of tumor genetics. “That is a very targeted way of surveillance,” said Weinberg, “But it would be very difficult to use a tumor-informed test on the population described in this study because you don’t know if there is going to be a tumor or not.”
The PanSeer test may also prove difficult to use in the clinic because it detects multiple cancers, Weinberg said. “If there is a positive finding, then which cancer do you look for?” he commented. “It has an issue in that regard, and that’s the problem with this type of test, as it is easier if there is one site of origin.”
Overall, the test was fairly sensitive and specific, with a very low false negative rate. Going forward, he noted, there is a very high bar for tests used as screening tools, although the authors do say that their focus is for use in a high-risk population.
“There would have to be a randomized trial, and the test will have to show a survival benefit,” Weinberg said. He noted that it can sometimes be challenging to do so.
“Colonoscopy has been shown to be beneficial, but early mammography has become controversial, and prostate cancer is a whole different animal,” he added. “And these are established tests, and they show how difficult this can be.”
The Taizhou Longitudinal Study study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Basic Research grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, the International S&T Cooperation Program of China, the Municipal Science and Technology Major Project program, the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China, and the 111 Project (B13016). Funding for the DNA methylation assays was provided by Singlera Genomics. Zhang is a cofounder, equity holder, and paid consultant of Singlera Genomics, a company that is developing early cancer detection tests, including the PanSeer test. Weinberg is a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Taiho Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, and Eli Lilly and Company; has received research grant from Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; and has received travel reimbursement from Caris Life Sciences.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A blood test that may be able to detect cancer years before any symptoms appear is under development. The PanSeer assay, which detects methylation markers in blood, was used in healthy individuals and successfully detected five cancer types in 91% of samples from individuals who were diagnosed with cancer 1 to 4 years later.
“We can’t say for sure that the patients didn’t have any symptoms, but we detected the cancer years before they ever walked into the hospital,” said study author Kun Zhang, PhD, a professor of bioengineering at the University of California, San Diego. “We were also able to follow up with patients, so we actually knew that they had cancer.”
Zhang noted that they also followed the individuals whose tests indicated they were cancer free. “They were healthy at the time the samples were obtained, and they remained healthy,” he said. “Follow-up was key to validating these data.”
The PanSeer test is being developed by Singlera Genomics. Zhang is a cofounder and a paid consultant of the company.
The study was published online July 21 in Nature Communications.
Unique among tests
Several blood tests for the detection of cancer have been reported in recent years. A test developed by Grail was able to detect more than 50 types of cancer and also identified the tissues where the cancer originated. The CancerSEEK test identified eight common cancers by measuring circulating tumor DNA from 16 genes, as well as eight protein biomarkers.
Findings regarding the CellMax Life FirstSight blood test were released last month. The test detected all 11 cases of colorectal cancer in a cohort of 354 patients and detected 40 of 53 advanced adenomas.
The latest study with the PanSeer assay is unique, say the investigators, because they had access to blood samples from patients who may have been completely asymptomatic and had not yet been diagnosed with cancer. Other blood tests have typically involved the use of specimens from people with a known diagnosis.
The specimens were collected as part of a 10-year longitudinal study that began in 2007 in China. Zhang and his team were able to test blood samples before individuals had experienced any signs or symptoms of cancer, and they were able to conduct long-term follow-up of the cohort.
Study details
The PanSeer assay uses DNA methylation analysis and screens for a DNA signature called CpG methylation. The results of an early-stage proof-of-concept study were published 3 years ago (Nat Genet. 2017;49:635–642).
For the current study, data were drawn from the Taizhou Longitudinal Study, which included 123,115 individuals aged 25 to 90 years who provided blood samples for long-term storage from 2007 to 2014. Participants were monitored indefinitely for cancer occurrence using local cancer registries and health insurance databases.
The team identified 575 individuals who were initially asymptomatic and healthy but were subsequently diagnosed with one of five common cancer types (stomach, esophagus, colorectum, lung, or liver cancer) within 4 years of their initial blood sampling. The authors selected these five cancer types to study because the incidence rates of these cancers in this population are high and, taken together, account for the highest mortality.
The study design allowed the authors to evaluate specimens both from patients with cancer and from those who were healthy within the same cohort. Using 191 prediagnosis samples, 223 postdiagnosis samples, and 414 healthy samples, they created a training set and validation model.
A machine learning method was created to classify samples as being either from healthy individuals or from those with cancer, using blood samples from the training set. The final classifier achieved 88% sensitivity for postdiagnosis samples and 91% sensitivity for prediagnosis samples at a specificity of 95%.
Zhang feels that initially it would be more appropriate to use the test for high-risk patients and to then evaluate the clinical benefit. “For any test, it is always more prudent to begin with a high-risk population,” he said. “You want to see some benefit with the high-risk population first, and then it can slowly be extended to others at lower risk.”
He emphasized that more rigorous testing is needing before the PanSeer assay is ready for clinical use. The logistics of designing and conducting a clinical trial that would include more than one cancer type would be very complicated. “The option was to break it down to five different studies,” he said. “We decided to begin with colon cancer, and we are currently in the process of talking with the FDA and designing the study.”
High bar to reach
Approached for comment, Benjamin Weinberg, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Division of Hematology and Oncology, the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, noted that there is “quite a ways to go before this can be clinically actionable.
“A lot of us are looking at combining methylation with circulating tumor DNA and throw the kitchen sink at it, but as the paper nicely describes, there are pros and cons to all of these,” he said.
Many tests of this type are in development. Weinberg explained that a circulating tumor DNA test for colon cancer may hit the market soon, pending FDA approval, although that test will be used in a different setting. “This is something that’s used to assess for minimal residual disease in patients who have undergone surgery and appear to be ‘cured’ of the disease,” he said. “The test is looking to see if there is any circulating tumor DNA being shed from whatever tumor is left behind.”
The type of test that has piqued the most interest is one that is “tumor informed,” meaning that the company receives tumor tissue and develops a personalized test of that tumor on the basis of tumor genetics. “That is a very targeted way of surveillance,” said Weinberg, “But it would be very difficult to use a tumor-informed test on the population described in this study because you don’t know if there is going to be a tumor or not.”
The PanSeer test may also prove difficult to use in the clinic because it detects multiple cancers, Weinberg said. “If there is a positive finding, then which cancer do you look for?” he commented. “It has an issue in that regard, and that’s the problem with this type of test, as it is easier if there is one site of origin.”
Overall, the test was fairly sensitive and specific, with a very low false negative rate. Going forward, he noted, there is a very high bar for tests used as screening tools, although the authors do say that their focus is for use in a high-risk population.
“There would have to be a randomized trial, and the test will have to show a survival benefit,” Weinberg said. He noted that it can sometimes be challenging to do so.
“Colonoscopy has been shown to be beneficial, but early mammography has become controversial, and prostate cancer is a whole different animal,” he added. “And these are established tests, and they show how difficult this can be.”
The Taizhou Longitudinal Study study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Basic Research grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, the International S&T Cooperation Program of China, the Municipal Science and Technology Major Project program, the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China, and the 111 Project (B13016). Funding for the DNA methylation assays was provided by Singlera Genomics. Zhang is a cofounder, equity holder, and paid consultant of Singlera Genomics, a company that is developing early cancer detection tests, including the PanSeer test. Weinberg is a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Taiho Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, and Eli Lilly and Company; has received research grant from Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; and has received travel reimbursement from Caris Life Sciences.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
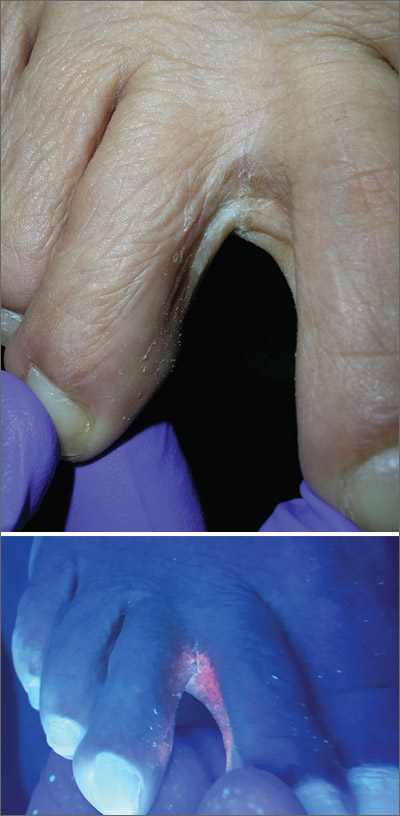
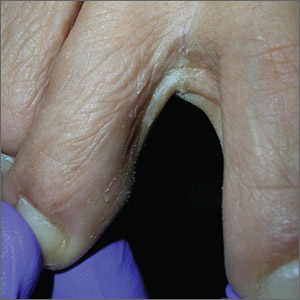
Scaly foot rash
The Wood’s lamp revealed a coral-red fluorescence in the interdigital spaces, which led to a diagnosis of erythrasma.
The coral-red fluorescence seen under the Wood’s lamp is due to porphyrins produced by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The organism invades the stratum corneum where it proliferates and causes erythrasma. Erythrasma typically appears as delineated, dry, red-brown patches in intertriginous areas, such as the axilla, groin, interdigital spaces, intergluteal cleft, perianal skin, and inframammary area.
Erythrasma affects 4% of the population; risk factors include poor hygiene, hyperhidrosis, obesity, warm climate, diabetes, and an immunocompromised state. The differential diagnosis for a pruritic rash between the toes includes tinea pedis and contact dermatitis.
First-line management of erythrasma includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic modalities. Good hygiene and, depending on the area affected, loose-fitting cotton undergarments can help treat and prevent erythrasma.
Topical 2% miconazole bid for 2 weeks has resulted in clearance rates as high as 88%. Its affordable price, over-the-counter availability, and lack of adverse effects make miconazole a reasonable choice. It is also a smart treatment choice when erythrasma is coexisting with tinea because it can treat both conditions.
Topical 1% clindamycin or 2% erythromycin solution or gel bid for 2 weeks also can be used to treat the condition. However, given that topical antibiotics are more expensive than single-dose oral treatment and are no better than the oral formulations of these antibiotics, clarithromycin 1 g taken once orally may be preferred. Our patient was treated with a single dose of clarithromycin 1 g. At follow-up, her erythrasma was clear.
This case was adapted from: Vo T, Usatine RP. Persistent rash on feet. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:107-109
The Wood’s lamp revealed a coral-red fluorescence in the interdigital spaces, which led to a diagnosis of erythrasma.
The coral-red fluorescence seen under the Wood’s lamp is due to porphyrins produced by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The organism invades the stratum corneum where it proliferates and causes erythrasma. Erythrasma typically appears as delineated, dry, red-brown patches in intertriginous areas, such as the axilla, groin, interdigital spaces, intergluteal cleft, perianal skin, and inframammary area.
Erythrasma affects 4% of the population; risk factors include poor hygiene, hyperhidrosis, obesity, warm climate, diabetes, and an immunocompromised state. The differential diagnosis for a pruritic rash between the toes includes tinea pedis and contact dermatitis.
First-line management of erythrasma includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic modalities. Good hygiene and, depending on the area affected, loose-fitting cotton undergarments can help treat and prevent erythrasma.
Topical 2% miconazole bid for 2 weeks has resulted in clearance rates as high as 88%. Its affordable price, over-the-counter availability, and lack of adverse effects make miconazole a reasonable choice. It is also a smart treatment choice when erythrasma is coexisting with tinea because it can treat both conditions.
Topical 1% clindamycin or 2% erythromycin solution or gel bid for 2 weeks also can be used to treat the condition. However, given that topical antibiotics are more expensive than single-dose oral treatment and are no better than the oral formulations of these antibiotics, clarithromycin 1 g taken once orally may be preferred. Our patient was treated with a single dose of clarithromycin 1 g. At follow-up, her erythrasma was clear.
This case was adapted from: Vo T, Usatine RP. Persistent rash on feet. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:107-109
The Wood’s lamp revealed a coral-red fluorescence in the interdigital spaces, which led to a diagnosis of erythrasma.
The coral-red fluorescence seen under the Wood’s lamp is due to porphyrins produced by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The organism invades the stratum corneum where it proliferates and causes erythrasma. Erythrasma typically appears as delineated, dry, red-brown patches in intertriginous areas, such as the axilla, groin, interdigital spaces, intergluteal cleft, perianal skin, and inframammary area.
Erythrasma affects 4% of the population; risk factors include poor hygiene, hyperhidrosis, obesity, warm climate, diabetes, and an immunocompromised state. The differential diagnosis for a pruritic rash between the toes includes tinea pedis and contact dermatitis.
First-line management of erythrasma includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic modalities. Good hygiene and, depending on the area affected, loose-fitting cotton undergarments can help treat and prevent erythrasma.
Topical 2% miconazole bid for 2 weeks has resulted in clearance rates as high as 88%. Its affordable price, over-the-counter availability, and lack of adverse effects make miconazole a reasonable choice. It is also a smart treatment choice when erythrasma is coexisting with tinea because it can treat both conditions.
Topical 1% clindamycin or 2% erythromycin solution or gel bid for 2 weeks also can be used to treat the condition. However, given that topical antibiotics are more expensive than single-dose oral treatment and are no better than the oral formulations of these antibiotics, clarithromycin 1 g taken once orally may be preferred. Our patient was treated with a single dose of clarithromycin 1 g. At follow-up, her erythrasma was clear.
This case was adapted from: Vo T, Usatine RP. Persistent rash on feet. J Fam Pract. 2018;67:107-109
Parental refusal of neonatal therapy a growing problem
according to an update at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine virtual. This finding indicates the value of preparing policies and strategies to guide parents to appropriate medical decisions in advance.
“Elimination of nonmedical exceptions to vaccinations and intramuscular vitamin K made it into two of the AAP [American Academy of Pediatrics] top 10 public health resolutions, most likely because refusal rates are going up,” reported Ha N. Nguyen, MD, of the division of pediatric hospital medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Importantly, state laws differ. For example, erythromycin ointment is mandated in neonates for prevention of gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum in many states, including New York, where it can be administered without consent, according to Dr. Nguyen. Conversely, California does not mandate this preventive therapy even though the law does not offer medico-legal protection to providers if it is not given.
“There is a glaring gap in the way the [California] law was written,” said Dr. Nguyen, who used this as an example of why protocols and strategies to reduce risk of parental refusal of neonatal therapies should be informed by, and consistent with, state laws.
Because of the low levels of vitamin K in infants, the rate of bleeding within the first few months of life is nearly 2%, according to figures cited by Dr. Nguyen. It falls to less than 0.001% with administration of intramuscular vitamin K.
Families who refuse intramuscular vitamin K often state that they understand the risks, but data from a survey Dr. Nguyen cited found this is not necessarily true. In this survey, about two-thirds knew that bleeding was the risk, but less than 20% understood bleeding risks included intracranial hemorrhage, and less than 10% were aware that there was potential for a fatal outcome.
“This is a huge piece of the puzzle for counseling,” Dr. Nguyen said. “The discussion with parents should explicitly involve the explanation that the risks include brain bleeds and death.”
Although most infant bleeds attributed to low vitamin K stores are mucocutaneous or gastrointestinal, intracranial hemorrhage does occur, and these outcomes can be devastating. Up to 25% of infants who experience an intracranial hemorrhage die, while 60% of those who survive have some degree of neurodevelopmental impairment, according to Dr. Nguyen.
Oral vitamin K, which requires multiple doses, is not an appropriate substitute for the recommended single injection of the intramuscular formulation. The one study that compared intramuscular and oral vitamin K did not prove equivalence, and no oral vitamin K products have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Nguyen reported.
“We do know confidently that oral vitamin K does often result in poor adherence,” she said,
In a recent review article of parental vitamin K refusal, one of the most significant predictors of refusal of any recommended neonatal preventive treatment was refusal of another. According to data in that article, summarized by Dr. Nguyen, 68% of the parents who declined intramuscular vitamin K also declined erythromycin ointment, and more than 90% declined hepatitis B vaccine.
“One reason that many parents refuse the hepatitis B vaccine is that they do not think their child is at risk,” explained Kimberly Horstman, MD, from Stanford University and John Muir Medical Center in Walnut Creek, Calif.
Yet hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which is asymptomatic, can be acquired from many sources, including nonfamily contacts, according to Dr. Horstman.
“The AAP supports universal hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for all infants over 2,000 g at birth,” Dr. Horstman said. In those weighing less, the vaccine is recommended within the first month of life.
The risk of parental refusal for recommended neonatal preventive medicines is higher among those with more education and higher income relative to those with less, Dr. Nguyen said. Other predictors include older maternal age, private insurance, and delivery by a midwife or at a birthing center.
Many parents who refuse preventive neonatal medications do not fully grasp what risks they are accepting by avoiding a recommended medication, according to both Dr. Nguyen and Dr. Horstman. In some cases, the goal is to protect their child from the pain of a needlestick, even when the health consequences might include far more invasive and painful therapies if the child develops the disease the medication would have prevented.
In the case of intramuscular vitamin K, “we encourage a presumptive approach,” Dr. Nguyen said. Concerns can then be addressed only if the parents refuse.
For another strategy, Dr. Nguyen recommended counseling parents about the need and value of preventive therapies during pregnancy. She cited data suggesting that it is more difficult to change the minds of parents after delivery.
Echoing this approach in regard to HBV vaccine, Dr. Horstman suggested encouraging colleagues, including obstetricians and community pediatricians, to raise and address this topic during prenatal counseling. By preparing parents for the recommended medications in the prenatal period, concerns can be addressed in advance.
The health risks posed by parents who refuse recommended medications is recognized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Both Dr. Horstman and Dr. Nguyen said there are handouts from the CDC and the AAP to inform parents of the purpose and benefit of recommended preventive therapies, as well as to equip caregivers with facts for effective counseling.
according to an update at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine virtual. This finding indicates the value of preparing policies and strategies to guide parents to appropriate medical decisions in advance.
“Elimination of nonmedical exceptions to vaccinations and intramuscular vitamin K made it into two of the AAP [American Academy of Pediatrics] top 10 public health resolutions, most likely because refusal rates are going up,” reported Ha N. Nguyen, MD, of the division of pediatric hospital medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Importantly, state laws differ. For example, erythromycin ointment is mandated in neonates for prevention of gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum in many states, including New York, where it can be administered without consent, according to Dr. Nguyen. Conversely, California does not mandate this preventive therapy even though the law does not offer medico-legal protection to providers if it is not given.
“There is a glaring gap in the way the [California] law was written,” said Dr. Nguyen, who used this as an example of why protocols and strategies to reduce risk of parental refusal of neonatal therapies should be informed by, and consistent with, state laws.
Because of the low levels of vitamin K in infants, the rate of bleeding within the first few months of life is nearly 2%, according to figures cited by Dr. Nguyen. It falls to less than 0.001% with administration of intramuscular vitamin K.
Families who refuse intramuscular vitamin K often state that they understand the risks, but data from a survey Dr. Nguyen cited found this is not necessarily true. In this survey, about two-thirds knew that bleeding was the risk, but less than 20% understood bleeding risks included intracranial hemorrhage, and less than 10% were aware that there was potential for a fatal outcome.
“This is a huge piece of the puzzle for counseling,” Dr. Nguyen said. “The discussion with parents should explicitly involve the explanation that the risks include brain bleeds and death.”
Although most infant bleeds attributed to low vitamin K stores are mucocutaneous or gastrointestinal, intracranial hemorrhage does occur, and these outcomes can be devastating. Up to 25% of infants who experience an intracranial hemorrhage die, while 60% of those who survive have some degree of neurodevelopmental impairment, according to Dr. Nguyen.
Oral vitamin K, which requires multiple doses, is not an appropriate substitute for the recommended single injection of the intramuscular formulation. The one study that compared intramuscular and oral vitamin K did not prove equivalence, and no oral vitamin K products have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Nguyen reported.
“We do know confidently that oral vitamin K does often result in poor adherence,” she said,
In a recent review article of parental vitamin K refusal, one of the most significant predictors of refusal of any recommended neonatal preventive treatment was refusal of another. According to data in that article, summarized by Dr. Nguyen, 68% of the parents who declined intramuscular vitamin K also declined erythromycin ointment, and more than 90% declined hepatitis B vaccine.
“One reason that many parents refuse the hepatitis B vaccine is that they do not think their child is at risk,” explained Kimberly Horstman, MD, from Stanford University and John Muir Medical Center in Walnut Creek, Calif.
Yet hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which is asymptomatic, can be acquired from many sources, including nonfamily contacts, according to Dr. Horstman.
“The AAP supports universal hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for all infants over 2,000 g at birth,” Dr. Horstman said. In those weighing less, the vaccine is recommended within the first month of life.
The risk of parental refusal for recommended neonatal preventive medicines is higher among those with more education and higher income relative to those with less, Dr. Nguyen said. Other predictors include older maternal age, private insurance, and delivery by a midwife or at a birthing center.
Many parents who refuse preventive neonatal medications do not fully grasp what risks they are accepting by avoiding a recommended medication, according to both Dr. Nguyen and Dr. Horstman. In some cases, the goal is to protect their child from the pain of a needlestick, even when the health consequences might include far more invasive and painful therapies if the child develops the disease the medication would have prevented.
In the case of intramuscular vitamin K, “we encourage a presumptive approach,” Dr. Nguyen said. Concerns can then be addressed only if the parents refuse.
For another strategy, Dr. Nguyen recommended counseling parents about the need and value of preventive therapies during pregnancy. She cited data suggesting that it is more difficult to change the minds of parents after delivery.
Echoing this approach in regard to HBV vaccine, Dr. Horstman suggested encouraging colleagues, including obstetricians and community pediatricians, to raise and address this topic during prenatal counseling. By preparing parents for the recommended medications in the prenatal period, concerns can be addressed in advance.
The health risks posed by parents who refuse recommended medications is recognized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Both Dr. Horstman and Dr. Nguyen said there are handouts from the CDC and the AAP to inform parents of the purpose and benefit of recommended preventive therapies, as well as to equip caregivers with facts for effective counseling.
according to an update at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine virtual. This finding indicates the value of preparing policies and strategies to guide parents to appropriate medical decisions in advance.
“Elimination of nonmedical exceptions to vaccinations and intramuscular vitamin K made it into two of the AAP [American Academy of Pediatrics] top 10 public health resolutions, most likely because refusal rates are going up,” reported Ha N. Nguyen, MD, of the division of pediatric hospital medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Importantly, state laws differ. For example, erythromycin ointment is mandated in neonates for prevention of gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum in many states, including New York, where it can be administered without consent, according to Dr. Nguyen. Conversely, California does not mandate this preventive therapy even though the law does not offer medico-legal protection to providers if it is not given.
“There is a glaring gap in the way the [California] law was written,” said Dr. Nguyen, who used this as an example of why protocols and strategies to reduce risk of parental refusal of neonatal therapies should be informed by, and consistent with, state laws.
Because of the low levels of vitamin K in infants, the rate of bleeding within the first few months of life is nearly 2%, according to figures cited by Dr. Nguyen. It falls to less than 0.001% with administration of intramuscular vitamin K.
Families who refuse intramuscular vitamin K often state that they understand the risks, but data from a survey Dr. Nguyen cited found this is not necessarily true. In this survey, about two-thirds knew that bleeding was the risk, but less than 20% understood bleeding risks included intracranial hemorrhage, and less than 10% were aware that there was potential for a fatal outcome.
“This is a huge piece of the puzzle for counseling,” Dr. Nguyen said. “The discussion with parents should explicitly involve the explanation that the risks include brain bleeds and death.”
Although most infant bleeds attributed to low vitamin K stores are mucocutaneous or gastrointestinal, intracranial hemorrhage does occur, and these outcomes can be devastating. Up to 25% of infants who experience an intracranial hemorrhage die, while 60% of those who survive have some degree of neurodevelopmental impairment, according to Dr. Nguyen.
Oral vitamin K, which requires multiple doses, is not an appropriate substitute for the recommended single injection of the intramuscular formulation. The one study that compared intramuscular and oral vitamin K did not prove equivalence, and no oral vitamin K products have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Nguyen reported.
“We do know confidently that oral vitamin K does often result in poor adherence,” she said,
In a recent review article of parental vitamin K refusal, one of the most significant predictors of refusal of any recommended neonatal preventive treatment was refusal of another. According to data in that article, summarized by Dr. Nguyen, 68% of the parents who declined intramuscular vitamin K also declined erythromycin ointment, and more than 90% declined hepatitis B vaccine.
“One reason that many parents refuse the hepatitis B vaccine is that they do not think their child is at risk,” explained Kimberly Horstman, MD, from Stanford University and John Muir Medical Center in Walnut Creek, Calif.
Yet hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which is asymptomatic, can be acquired from many sources, including nonfamily contacts, according to Dr. Horstman.
“The AAP supports universal hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for all infants over 2,000 g at birth,” Dr. Horstman said. In those weighing less, the vaccine is recommended within the first month of life.
The risk of parental refusal for recommended neonatal preventive medicines is higher among those with more education and higher income relative to those with less, Dr. Nguyen said. Other predictors include older maternal age, private insurance, and delivery by a midwife or at a birthing center.
Many parents who refuse preventive neonatal medications do not fully grasp what risks they are accepting by avoiding a recommended medication, according to both Dr. Nguyen and Dr. Horstman. In some cases, the goal is to protect their child from the pain of a needlestick, even when the health consequences might include far more invasive and painful therapies if the child develops the disease the medication would have prevented.
In the case of intramuscular vitamin K, “we encourage a presumptive approach,” Dr. Nguyen said. Concerns can then be addressed only if the parents refuse.
For another strategy, Dr. Nguyen recommended counseling parents about the need and value of preventive therapies during pregnancy. She cited data suggesting that it is more difficult to change the minds of parents after delivery.
Echoing this approach in regard to HBV vaccine, Dr. Horstman suggested encouraging colleagues, including obstetricians and community pediatricians, to raise and address this topic during prenatal counseling. By preparing parents for the recommended medications in the prenatal period, concerns can be addressed in advance.
The health risks posed by parents who refuse recommended medications is recognized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Both Dr. Horstman and Dr. Nguyen said there are handouts from the CDC and the AAP to inform parents of the purpose and benefit of recommended preventive therapies, as well as to equip caregivers with facts for effective counseling.
FROM PHM 2020
Large cohort study: Bevacizumab safe, effective for severe HHT bleeds
Systemic bevacizumab is safe and highly effective for the management of chronic bleeding and anemia in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), according to findings from an international observational study.
In 238 patients from 12 international centers who were treated with bevacizumab for a median of 12 months, mean hemoglobin levels increased by 3.2 g/dL (mean pre- and posttreatment levels, 8.6 vs. 11.8 g/dL), and epistaxis severity scores (ESS) decreased by a mean of 3.4 points (pre- and posttreatment scores, 6.8 vs. 3.4 points), Hanny Al-Samkari, MD, reported at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis virtual congress.
As established in prior studies, the minimal clinically important difference in the ESS, a well-validated 10-point bleeding score in HHT, is 0.71 points; the mean reduction seen in this study was 4.75 times that, noted Dr. Al-Samkari, a clinical investigator and hematologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Further, the median number of red blood cell units transfused during the first year of treatment decreased by 82%, compared with the 6 months prior to treatment (9.0 vs. 0 units), and median iron infusions decreased by 70% during the same period (8.0 vs. 2.0 infusions), he said, adding that these improvements occurred within the first 6 months of treatment and were maintained through 12 months.
Study subjects were adults with a mean age of 63 years who were treated with systemic bevacizumab, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGF) monoclonal antibody, between 2011 and 2019 for the primary indication of moderate to severe chronic HHT-related bleeding and anemia. Treatment involved four to eight induction infusions – typically at a dose of 5 mg/kg and given 4 weeks apart – followed by bevacizumab maintenance, either as continuous or scheduled maintenance at 4-, 8-, or 12-week intervals regardless of symptoms, or on an as-needed basis, with 2-6 infusions for signs or symptoms of rebleeding.
Patients received a median of 11 infusions, and 181 received maintenance treatment, including continuous or scheduled maintenance in 136 patients and as-needed maintenance in 45 patients, Dr. Al-Samkari said.
The treatment was generally well tolerated; the most common adverse events during 344 patient-years of treatment were hypertension, fatigue, and proteinuria. No fatal treatment-related adverse events occurred, and no increase in adverse events occurred with longer treatment, he noted
Venous thromboembolism occurred in five patients, including two patients who had “provoked events immediately following joint replacement surgery,” he said.
Thirteen patients (5%) discontinued treatment – 11 for inadequate effect and 2 for side effects, he noted.
Subgroup analyses showed that outcomes were similar regardless of underlying pathogenic mutation, but among those receiving bevacizumab maintenance, the continuous approach, compared with as-needed maintenance, was associated with greater improvement in hemoglobin (10.8 vs. 12.3 g/dL) and ESS (mean, 4.96 vs. 2.88) during months 7-12 of treatment, “which is the time most reflective of the effect of maintenance,” he said.
HHT, also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu disease, is a “rare, genetic, progressive, multisystem bleeding disorder resulting from disorder of angiogenesis,” Dr. Al-Samkari explained, adding that the condition is characterized by severe, recurrent epistaxis and chronic gastrointestinal bleeding.
“Bleeding frequently leads to iron deficiency anemia, which may be severe and dependent on regular iron infusions and/or blood transfusions,” he said.
Though rare, it is the second most common bleeding disorder worldwide, with a prevalence about twice that of hemophilia A and six times that of hemophilia B.
“Despite this, it has no FDA-approved therapies,” he said. “The current mainstay of care is surgical or procedural local hemostatic intervention – which is usually temporizing – and hematological support in the form of blood and iron.”
However, given that the underlying genetic defects that cause HHT result in elevations in VEGF, targeting VEGF with existing antiangiogenic agents is a promising approach.
In fact, several centers have been using bevacizumab for several years as an off-label treatment for bleeding in this setting, and while scattered case reports and small case series suggest efficacy, no “large or definitive studies” have been conducted, and safety hasn’t been carefully evaluated, he said.
To that end, the International Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Intravenous Bevacizumab Investigative Team (InHIBIT) was formed. The current report, “the largest study of antiangiogenic therapy to date in HHT,” represents the results of the InHIBIT-Bleed study, the first completed by the team. The next study will address bevacizumab for the treatment of high-output cardiac failure in HHT (the InHIBIT-HF study), Dr. Al-Samkari said.
Though limited by its retrospective nature and lack of a unified treatment protocol, the InHIBIT-Bleed study provides important information and is strengthened by the large cohort size, especially given that HHT is a rare disease, and by other factors, such as the substantial number of patient-years of treatment.
“Bevacizumab was effective in the management of severe HHT-related epistaxis and GI bleeds,” he said, noting the “significant and striking improvements” on a variety of measures.
Questioned about the durability of treatment effects after treatment discontinuation, Dr. Al-Samkari said outcomes are variable, “highly patient dependent,” and “something that we really need to investigate thoroughly.”
As for the potential for anti-VEGF therapy for bleeding in certain non-HHT settings, session moderator Michael Makris, MD, professor of haemostasis and thrombosis at the University of Sheffield, England, said the possibilities are intriguing.
“I work with lots of patients with von Willebrand disease and angiodysplasia,” he said, adding that angiodysplasia-related bleeding in type 2A von Willebrand disease is a major issue.
Dr. Al-Samkari agreed that the possibility is worth exploring.
“We have looked at this in a small number of patients, and the jury is still out,” he said. “But there is a publication in Gastroenterology – Albitar et al. – that evaluated bevacizumab in patients without HHT [who had] angiodysplasias from other causes – not specifically in type 2 von Willebrand syndrome ... and did find that it was effective at causing the angiodysplasias to regress, hemoglobin to improve.
“So the non-HHT use of this agent is certainly an important one [and] we do have retrospective evidence in a small group of patients who don’t have HHT, who do have angiodysplasias and bleeding, that it may be effective as well.”
Dr. Al-Samkari reported receiving research support and/or consulting fees from Agios, Amgen, and Dova.
SOURCE: Al-Samkari H et al. ISTH 2020, Abstract OC 09.2.
Systemic bevacizumab is safe and highly effective for the management of chronic bleeding and anemia in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), according to findings from an international observational study.
In 238 patients from 12 international centers who were treated with bevacizumab for a median of 12 months, mean hemoglobin levels increased by 3.2 g/dL (mean pre- and posttreatment levels, 8.6 vs. 11.8 g/dL), and epistaxis severity scores (ESS) decreased by a mean of 3.4 points (pre- and posttreatment scores, 6.8 vs. 3.4 points), Hanny Al-Samkari, MD, reported at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis virtual congress.
As established in prior studies, the minimal clinically important difference in the ESS, a well-validated 10-point bleeding score in HHT, is 0.71 points; the mean reduction seen in this study was 4.75 times that, noted Dr. Al-Samkari, a clinical investigator and hematologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Further, the median number of red blood cell units transfused during the first year of treatment decreased by 82%, compared with the 6 months prior to treatment (9.0 vs. 0 units), and median iron infusions decreased by 70% during the same period (8.0 vs. 2.0 infusions), he said, adding that these improvements occurred within the first 6 months of treatment and were maintained through 12 months.
Study subjects were adults with a mean age of 63 years who were treated with systemic bevacizumab, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGF) monoclonal antibody, between 2011 and 2019 for the primary indication of moderate to severe chronic HHT-related bleeding and anemia. Treatment involved four to eight induction infusions – typically at a dose of 5 mg/kg and given 4 weeks apart – followed by bevacizumab maintenance, either as continuous or scheduled maintenance at 4-, 8-, or 12-week intervals regardless of symptoms, or on an as-needed basis, with 2-6 infusions for signs or symptoms of rebleeding.
Patients received a median of 11 infusions, and 181 received maintenance treatment, including continuous or scheduled maintenance in 136 patients and as-needed maintenance in 45 patients, Dr. Al-Samkari said.
The treatment was generally well tolerated; the most common adverse events during 344 patient-years of treatment were hypertension, fatigue, and proteinuria. No fatal treatment-related adverse events occurred, and no increase in adverse events occurred with longer treatment, he noted
Venous thromboembolism occurred in five patients, including two patients who had “provoked events immediately following joint replacement surgery,” he said.
Thirteen patients (5%) discontinued treatment – 11 for inadequate effect and 2 for side effects, he noted.
Subgroup analyses showed that outcomes were similar regardless of underlying pathogenic mutation, but among those receiving bevacizumab maintenance, the continuous approach, compared with as-needed maintenance, was associated with greater improvement in hemoglobin (10.8 vs. 12.3 g/dL) and ESS (mean, 4.96 vs. 2.88) during months 7-12 of treatment, “which is the time most reflective of the effect of maintenance,” he said.
HHT, also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu disease, is a “rare, genetic, progressive, multisystem bleeding disorder resulting from disorder of angiogenesis,” Dr. Al-Samkari explained, adding that the condition is characterized by severe, recurrent epistaxis and chronic gastrointestinal bleeding.
“Bleeding frequently leads to iron deficiency anemia, which may be severe and dependent on regular iron infusions and/or blood transfusions,” he said.
Though rare, it is the second most common bleeding disorder worldwide, with a prevalence about twice that of hemophilia A and six times that of hemophilia B.
“Despite this, it has no FDA-approved therapies,” he said. “The current mainstay of care is surgical or procedural local hemostatic intervention – which is usually temporizing – and hematological support in the form of blood and iron.”
However, given that the underlying genetic defects that cause HHT result in elevations in VEGF, targeting VEGF with existing antiangiogenic agents is a promising approach.
In fact, several centers have been using bevacizumab for several years as an off-label treatment for bleeding in this setting, and while scattered case reports and small case series suggest efficacy, no “large or definitive studies” have been conducted, and safety hasn’t been carefully evaluated, he said.
To that end, the International Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Intravenous Bevacizumab Investigative Team (InHIBIT) was formed. The current report, “the largest study of antiangiogenic therapy to date in HHT,” represents the results of the InHIBIT-Bleed study, the first completed by the team. The next study will address bevacizumab for the treatment of high-output cardiac failure in HHT (the InHIBIT-HF study), Dr. Al-Samkari said.
Though limited by its retrospective nature and lack of a unified treatment protocol, the InHIBIT-Bleed study provides important information and is strengthened by the large cohort size, especially given that HHT is a rare disease, and by other factors, such as the substantial number of patient-years of treatment.
“Bevacizumab was effective in the management of severe HHT-related epistaxis and GI bleeds,” he said, noting the “significant and striking improvements” on a variety of measures.
Questioned about the durability of treatment effects after treatment discontinuation, Dr. Al-Samkari said outcomes are variable, “highly patient dependent,” and “something that we really need to investigate thoroughly.”
As for the potential for anti-VEGF therapy for bleeding in certain non-HHT settings, session moderator Michael Makris, MD, professor of haemostasis and thrombosis at the University of Sheffield, England, said the possibilities are intriguing.
“I work with lots of patients with von Willebrand disease and angiodysplasia,” he said, adding that angiodysplasia-related bleeding in type 2A von Willebrand disease is a major issue.
Dr. Al-Samkari agreed that the possibility is worth exploring.
“We have looked at this in a small number of patients, and the jury is still out,” he said. “But there is a publication in Gastroenterology – Albitar et al. – that evaluated bevacizumab in patients without HHT [who had] angiodysplasias from other causes – not specifically in type 2 von Willebrand syndrome ... and did find that it was effective at causing the angiodysplasias to regress, hemoglobin to improve.
“So the non-HHT use of this agent is certainly an important one [and] we do have retrospective evidence in a small group of patients who don’t have HHT, who do have angiodysplasias and bleeding, that it may be effective as well.”
Dr. Al-Samkari reported receiving research support and/or consulting fees from Agios, Amgen, and Dova.
SOURCE: Al-Samkari H et al. ISTH 2020, Abstract OC 09.2.
Systemic bevacizumab is safe and highly effective for the management of chronic bleeding and anemia in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), according to findings from an international observational study.
In 238 patients from 12 international centers who were treated with bevacizumab for a median of 12 months, mean hemoglobin levels increased by 3.2 g/dL (mean pre- and posttreatment levels, 8.6 vs. 11.8 g/dL), and epistaxis severity scores (ESS) decreased by a mean of 3.4 points (pre- and posttreatment scores, 6.8 vs. 3.4 points), Hanny Al-Samkari, MD, reported at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis virtual congress.
As established in prior studies, the minimal clinically important difference in the ESS, a well-validated 10-point bleeding score in HHT, is 0.71 points; the mean reduction seen in this study was 4.75 times that, noted Dr. Al-Samkari, a clinical investigator and hematologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Further, the median number of red blood cell units transfused during the first year of treatment decreased by 82%, compared with the 6 months prior to treatment (9.0 vs. 0 units), and median iron infusions decreased by 70% during the same period (8.0 vs. 2.0 infusions), he said, adding that these improvements occurred within the first 6 months of treatment and were maintained through 12 months.
Study subjects were adults with a mean age of 63 years who were treated with systemic bevacizumab, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGF) monoclonal antibody, between 2011 and 2019 for the primary indication of moderate to severe chronic HHT-related bleeding and anemia. Treatment involved four to eight induction infusions – typically at a dose of 5 mg/kg and given 4 weeks apart – followed by bevacizumab maintenance, either as continuous or scheduled maintenance at 4-, 8-, or 12-week intervals regardless of symptoms, or on an as-needed basis, with 2-6 infusions for signs or symptoms of rebleeding.
Patients received a median of 11 infusions, and 181 received maintenance treatment, including continuous or scheduled maintenance in 136 patients and as-needed maintenance in 45 patients, Dr. Al-Samkari said.
The treatment was generally well tolerated; the most common adverse events during 344 patient-years of treatment were hypertension, fatigue, and proteinuria. No fatal treatment-related adverse events occurred, and no increase in adverse events occurred with longer treatment, he noted
Venous thromboembolism occurred in five patients, including two patients who had “provoked events immediately following joint replacement surgery,” he said.
Thirteen patients (5%) discontinued treatment – 11 for inadequate effect and 2 for side effects, he noted.
Subgroup analyses showed that outcomes were similar regardless of underlying pathogenic mutation, but among those receiving bevacizumab maintenance, the continuous approach, compared with as-needed maintenance, was associated with greater improvement in hemoglobin (10.8 vs. 12.3 g/dL) and ESS (mean, 4.96 vs. 2.88) during months 7-12 of treatment, “which is the time most reflective of the effect of maintenance,” he said.
HHT, also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu disease, is a “rare, genetic, progressive, multisystem bleeding disorder resulting from disorder of angiogenesis,” Dr. Al-Samkari explained, adding that the condition is characterized by severe, recurrent epistaxis and chronic gastrointestinal bleeding.
“Bleeding frequently leads to iron deficiency anemia, which may be severe and dependent on regular iron infusions and/or blood transfusions,” he said.
Though rare, it is the second most common bleeding disorder worldwide, with a prevalence about twice that of hemophilia A and six times that of hemophilia B.
“Despite this, it has no FDA-approved therapies,” he said. “The current mainstay of care is surgical or procedural local hemostatic intervention – which is usually temporizing – and hematological support in the form of blood and iron.”
However, given that the underlying genetic defects that cause HHT result in elevations in VEGF, targeting VEGF with existing antiangiogenic agents is a promising approach.
In fact, several centers have been using bevacizumab for several years as an off-label treatment for bleeding in this setting, and while scattered case reports and small case series suggest efficacy, no “large or definitive studies” have been conducted, and safety hasn’t been carefully evaluated, he said.
To that end, the International Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Intravenous Bevacizumab Investigative Team (InHIBIT) was formed. The current report, “the largest study of antiangiogenic therapy to date in HHT,” represents the results of the InHIBIT-Bleed study, the first completed by the team. The next study will address bevacizumab for the treatment of high-output cardiac failure in HHT (the InHIBIT-HF study), Dr. Al-Samkari said.
Though limited by its retrospective nature and lack of a unified treatment protocol, the InHIBIT-Bleed study provides important information and is strengthened by the large cohort size, especially given that HHT is a rare disease, and by other factors, such as the substantial number of patient-years of treatment.
“Bevacizumab was effective in the management of severe HHT-related epistaxis and GI bleeds,” he said, noting the “significant and striking improvements” on a variety of measures.
Questioned about the durability of treatment effects after treatment discontinuation, Dr. Al-Samkari said outcomes are variable, “highly patient dependent,” and “something that we really need to investigate thoroughly.”
As for the potential for anti-VEGF therapy for bleeding in certain non-HHT settings, session moderator Michael Makris, MD, professor of haemostasis and thrombosis at the University of Sheffield, England, said the possibilities are intriguing.
“I work with lots of patients with von Willebrand disease and angiodysplasia,” he said, adding that angiodysplasia-related bleeding in type 2A von Willebrand disease is a major issue.
Dr. Al-Samkari agreed that the possibility is worth exploring.
“We have looked at this in a small number of patients, and the jury is still out,” he said. “But there is a publication in Gastroenterology – Albitar et al. – that evaluated bevacizumab in patients without HHT [who had] angiodysplasias from other causes – not specifically in type 2 von Willebrand syndrome ... and did find that it was effective at causing the angiodysplasias to regress, hemoglobin to improve.
“So the non-HHT use of this agent is certainly an important one [and] we do have retrospective evidence in a small group of patients who don’t have HHT, who do have angiodysplasias and bleeding, that it may be effective as well.”
Dr. Al-Samkari reported receiving research support and/or consulting fees from Agios, Amgen, and Dova.
SOURCE: Al-Samkari H et al. ISTH 2020, Abstract OC 09.2.
FROM THE 2020 ISTH CONGRESS
Microbiome research ‘opening doors’ to new Alzheimer’s disease treatments
Research into the microbiome is yielding some positive new potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease, according to George T. Grossberg, MD.
“I think the growing focus on the gut-brain axis is opening doors to new Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders, and I think the first of a possible future generation of compounds for prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease may indeed be emerging,” Dr. Grossberg said at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
Focus on the microbiome and microbiota is “a really hot, really new, really emerging area,” said Dr. Grossberg, professor in the department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience at Saint Louis University. But the microbiota, which is the microorganisms within a specific organ such as the colon, is sometimes confused with the microbiome – which is defined as all of the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms within a habitat as well as their genomes and the environment around them. “These are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same,” Dr. Grossberg said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education.
A person’s microbiome is unique to them, and nearly all of the microbiome is contained in the gut. A reduction in diversity of the microbiota in the digestive system has been linked to a wide variety of diseases, Dr. Grossberg explained. Conversely, a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis has been implicated in anxiety and/or depression, dementia, and certain cancers, he noted.
Bacteria that positively affect the microbiome come from two main genera: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Factors such as diet, medications, geography, stage of life, birthing process, infant feeding method, and stress can all affect a person’s microbiome. “We’re all beginning to understand that trying to manage or trying to diversify, trying to manipulate the microbiota may have a lot of remote effects – even effects on weight or diabetes, or other disorders,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or the process of administering a donor’s fecal matter into a recipient’s intestinal tract, has proved beneficial in improving the health of patients suffering from recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. A recent Harvard Health Letter, written by Jessica Allegretti, MD, MPH, observed that FMT is standard of care for patients with C. diff, and the procedure has a success rate of between 80% and 90%.
“It shows us very directly, in a very practical way, how addressing the dysbiosis – the imbalance of the gut microbiome – by infusing healthy bacteria may make a potential lifesaving difference,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Research is beginning to show that the link between gut microbiota and health extends to Alzheimer’s disease as well. Within the last few years, “we’ve started to understand that the microbial diversity in Alzheimer’s disease versus healthy age-matched controls is decreased,” Dr. Grossberg said.
In a study published by Nicholas M. Vogt and colleagues, there was decreased fecal microbial diversity among individuals with Alzheimer’s, compared with healthy individuals matched for age. Another study by Ping Liu, PhD, and colleagues found that patients with Alzheimer’s disease had decreased fecal microbial diversity, compared with individuals who had pre-onset amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal cognition.
Dr. Grossberg noted that, while these studies do not prove that less fecal microbial diversity is responsible for mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease, “it makes us think that, maybe, there’s a contributing factor.”
“What happens with the dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is increased permeability of the epithelial area of the gut, which can then lead to the gut-brain axis dysregulation and may in fact allow the selective entry of bacteria into the central nervous system because the blood-brain barrier comes to be dysfunctional,” he said.
Early evidence suggests that the gut-brain axis can affect cognition. In an animal model study, transferring the microbiota of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease to one that had been bred to be germ-free resulted in cognitive decline – but there was no cognitive decline for germ-free mice that received a microbiota transplant from a mouse in a healthy control group. Results from another animal study showed that transferring healthy microbiota from a mouse model into a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease reduces amyloid and tau pathology. “The conclusions of these studies seems to be that microbiota mediated intestinal and systemic immune changes or aberrations seem to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in these mouse models,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Consequently, restoring the gut microbial homeostasis may have beneficial effects on Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
Periodontal disease also might be linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. Several studies have shown gingipains secreted from Porphyromonas gingivalis, which contribute to inflammation in the brain, have been found in cadavers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5[1]:eaau3333). “There’s reason to think that the same changes may be occurring in the human brain with periodontal disease,” he said.
The relationship also might extend to the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. “There seems to be a direct communication, a direct relationship between normal gut physiology and healthy central nervous system functioning, and then, when you have abnormal gut function, it may result in a variety of abnormal central nervous system functions,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Studies that have examined a relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota have highlighted the potential of probiotics and prebiotics as a method of restoring the gut microbiota (Aging [Albany NY]. 2020 Mar 31; 12[6]:5539-50). Probiotics are popularly sold in health food aisles of grocery stores, and prebiotics are available in foods such as yogurts, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in drinks such as Kombucha tea. The effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics also are being examined in randomized, controlled trials in patients with mild cognitive decline and mild Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. One therapy, Sodium oligomannate, a marine algae–derived oral oligosaccharide, has shown effectiveness in remodeling gut microbiota and has been approved in China to treat patients with mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Currently, no approved gut microbiota therapies are approved in the United States to treat Alzheimer’s disease; however, encouraging use of a prebiotic, a probiotic, or a Mediterranean diet is something clinicians might want to consider for their patients.
“The fact that we’re studying these things has really led to the notion that it may not be a bad idea for people to consume these healthy bacteria in later life, either as a way to prevent or delay, or to treat Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Grossberg said. “There’s really no downside.”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Grossberg reported that he is a consultant for Acadia, Alkahest, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda; receives research support from the National Institute on Aging, Janssen, and Roche; performs safety monitoring for EryDel, Merck, and Newron; and serves on data monitoring committees for Avanex and ITI Therapeutics.
Research into the microbiome is yielding some positive new potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease, according to George T. Grossberg, MD.
“I think the growing focus on the gut-brain axis is opening doors to new Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders, and I think the first of a possible future generation of compounds for prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease may indeed be emerging,” Dr. Grossberg said at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
Focus on the microbiome and microbiota is “a really hot, really new, really emerging area,” said Dr. Grossberg, professor in the department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience at Saint Louis University. But the microbiota, which is the microorganisms within a specific organ such as the colon, is sometimes confused with the microbiome – which is defined as all of the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms within a habitat as well as their genomes and the environment around them. “These are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same,” Dr. Grossberg said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education.
A person’s microbiome is unique to them, and nearly all of the microbiome is contained in the gut. A reduction in diversity of the microbiota in the digestive system has been linked to a wide variety of diseases, Dr. Grossberg explained. Conversely, a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis has been implicated in anxiety and/or depression, dementia, and certain cancers, he noted.
Bacteria that positively affect the microbiome come from two main genera: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Factors such as diet, medications, geography, stage of life, birthing process, infant feeding method, and stress can all affect a person’s microbiome. “We’re all beginning to understand that trying to manage or trying to diversify, trying to manipulate the microbiota may have a lot of remote effects – even effects on weight or diabetes, or other disorders,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or the process of administering a donor’s fecal matter into a recipient’s intestinal tract, has proved beneficial in improving the health of patients suffering from recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. A recent Harvard Health Letter, written by Jessica Allegretti, MD, MPH, observed that FMT is standard of care for patients with C. diff, and the procedure has a success rate of between 80% and 90%.
“It shows us very directly, in a very practical way, how addressing the dysbiosis – the imbalance of the gut microbiome – by infusing healthy bacteria may make a potential lifesaving difference,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Research is beginning to show that the link between gut microbiota and health extends to Alzheimer’s disease as well. Within the last few years, “we’ve started to understand that the microbial diversity in Alzheimer’s disease versus healthy age-matched controls is decreased,” Dr. Grossberg said.
In a study published by Nicholas M. Vogt and colleagues, there was decreased fecal microbial diversity among individuals with Alzheimer’s, compared with healthy individuals matched for age. Another study by Ping Liu, PhD, and colleagues found that patients with Alzheimer’s disease had decreased fecal microbial diversity, compared with individuals who had pre-onset amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal cognition.
Dr. Grossberg noted that, while these studies do not prove that less fecal microbial diversity is responsible for mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease, “it makes us think that, maybe, there’s a contributing factor.”
“What happens with the dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is increased permeability of the epithelial area of the gut, which can then lead to the gut-brain axis dysregulation and may in fact allow the selective entry of bacteria into the central nervous system because the blood-brain barrier comes to be dysfunctional,” he said.
Early evidence suggests that the gut-brain axis can affect cognition. In an animal model study, transferring the microbiota of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease to one that had been bred to be germ-free resulted in cognitive decline – but there was no cognitive decline for germ-free mice that received a microbiota transplant from a mouse in a healthy control group. Results from another animal study showed that transferring healthy microbiota from a mouse model into a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease reduces amyloid and tau pathology. “The conclusions of these studies seems to be that microbiota mediated intestinal and systemic immune changes or aberrations seem to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in these mouse models,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Consequently, restoring the gut microbial homeostasis may have beneficial effects on Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
Periodontal disease also might be linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. Several studies have shown gingipains secreted from Porphyromonas gingivalis, which contribute to inflammation in the brain, have been found in cadavers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5[1]:eaau3333). “There’s reason to think that the same changes may be occurring in the human brain with periodontal disease,” he said.
The relationship also might extend to the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. “There seems to be a direct communication, a direct relationship between normal gut physiology and healthy central nervous system functioning, and then, when you have abnormal gut function, it may result in a variety of abnormal central nervous system functions,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Studies that have examined a relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota have highlighted the potential of probiotics and prebiotics as a method of restoring the gut microbiota (Aging [Albany NY]. 2020 Mar 31; 12[6]:5539-50). Probiotics are popularly sold in health food aisles of grocery stores, and prebiotics are available in foods such as yogurts, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in drinks such as Kombucha tea. The effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics also are being examined in randomized, controlled trials in patients with mild cognitive decline and mild Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. One therapy, Sodium oligomannate, a marine algae–derived oral oligosaccharide, has shown effectiveness in remodeling gut microbiota and has been approved in China to treat patients with mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Currently, no approved gut microbiota therapies are approved in the United States to treat Alzheimer’s disease; however, encouraging use of a prebiotic, a probiotic, or a Mediterranean diet is something clinicians might want to consider for their patients.
“The fact that we’re studying these things has really led to the notion that it may not be a bad idea for people to consume these healthy bacteria in later life, either as a way to prevent or delay, or to treat Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Grossberg said. “There’s really no downside.”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Grossberg reported that he is a consultant for Acadia, Alkahest, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda; receives research support from the National Institute on Aging, Janssen, and Roche; performs safety monitoring for EryDel, Merck, and Newron; and serves on data monitoring committees for Avanex and ITI Therapeutics.
Research into the microbiome is yielding some positive new potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease, according to George T. Grossberg, MD.
“I think the growing focus on the gut-brain axis is opening doors to new Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders, and I think the first of a possible future generation of compounds for prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease may indeed be emerging,” Dr. Grossberg said at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
Focus on the microbiome and microbiota is “a really hot, really new, really emerging area,” said Dr. Grossberg, professor in the department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience at Saint Louis University. But the microbiota, which is the microorganisms within a specific organ such as the colon, is sometimes confused with the microbiome – which is defined as all of the bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms within a habitat as well as their genomes and the environment around them. “These are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same,” Dr. Grossberg said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education.
A person’s microbiome is unique to them, and nearly all of the microbiome is contained in the gut. A reduction in diversity of the microbiota in the digestive system has been linked to a wide variety of diseases, Dr. Grossberg explained. Conversely, a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis has been implicated in anxiety and/or depression, dementia, and certain cancers, he noted.
Bacteria that positively affect the microbiome come from two main genera: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Factors such as diet, medications, geography, stage of life, birthing process, infant feeding method, and stress can all affect a person’s microbiome. “We’re all beginning to understand that trying to manage or trying to diversify, trying to manipulate the microbiota may have a lot of remote effects – even effects on weight or diabetes, or other disorders,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or the process of administering a donor’s fecal matter into a recipient’s intestinal tract, has proved beneficial in improving the health of patients suffering from recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. A recent Harvard Health Letter, written by Jessica Allegretti, MD, MPH, observed that FMT is standard of care for patients with C. diff, and the procedure has a success rate of between 80% and 90%.
“It shows us very directly, in a very practical way, how addressing the dysbiosis – the imbalance of the gut microbiome – by infusing healthy bacteria may make a potential lifesaving difference,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Research is beginning to show that the link between gut microbiota and health extends to Alzheimer’s disease as well. Within the last few years, “we’ve started to understand that the microbial diversity in Alzheimer’s disease versus healthy age-matched controls is decreased,” Dr. Grossberg said.
In a study published by Nicholas M. Vogt and colleagues, there was decreased fecal microbial diversity among individuals with Alzheimer’s, compared with healthy individuals matched for age. Another study by Ping Liu, PhD, and colleagues found that patients with Alzheimer’s disease had decreased fecal microbial diversity, compared with individuals who had pre-onset amnestic mild cognitive impairment and normal cognition.
Dr. Grossberg noted that, while these studies do not prove that less fecal microbial diversity is responsible for mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease, “it makes us think that, maybe, there’s a contributing factor.”
“What happens with the dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is increased permeability of the epithelial area of the gut, which can then lead to the gut-brain axis dysregulation and may in fact allow the selective entry of bacteria into the central nervous system because the blood-brain barrier comes to be dysfunctional,” he said.
Early evidence suggests that the gut-brain axis can affect cognition. In an animal model study, transferring the microbiota of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease to one that had been bred to be germ-free resulted in cognitive decline – but there was no cognitive decline for germ-free mice that received a microbiota transplant from a mouse in a healthy control group. Results from another animal study showed that transferring healthy microbiota from a mouse model into a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease reduces amyloid and tau pathology. “The conclusions of these studies seems to be that microbiota mediated intestinal and systemic immune changes or aberrations seem to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease in these mouse models,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Consequently, restoring the gut microbial homeostasis may have beneficial effects on Alzheimer’s disease treatment.”
Periodontal disease also might be linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. Several studies have shown gingipains secreted from Porphyromonas gingivalis, which contribute to inflammation in the brain, have been found in cadavers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5[1]:eaau3333). “There’s reason to think that the same changes may be occurring in the human brain with periodontal disease,” he said.
The relationship also might extend to the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. “There seems to be a direct communication, a direct relationship between normal gut physiology and healthy central nervous system functioning, and then, when you have abnormal gut function, it may result in a variety of abnormal central nervous system functions,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Studies that have examined a relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiota have highlighted the potential of probiotics and prebiotics as a method of restoring the gut microbiota (Aging [Albany NY]. 2020 Mar 31; 12[6]:5539-50). Probiotics are popularly sold in health food aisles of grocery stores, and prebiotics are available in foods such as yogurts, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in drinks such as Kombucha tea. The effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics also are being examined in randomized, controlled trials in patients with mild cognitive decline and mild Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Grossberg said. One therapy, Sodium oligomannate, a marine algae–derived oral oligosaccharide, has shown effectiveness in remodeling gut microbiota and has been approved in China to treat patients with mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Currently, no approved gut microbiota therapies are approved in the United States to treat Alzheimer’s disease; however, encouraging use of a prebiotic, a probiotic, or a Mediterranean diet is something clinicians might want to consider for their patients.
“The fact that we’re studying these things has really led to the notion that it may not be a bad idea for people to consume these healthy bacteria in later life, either as a way to prevent or delay, or to treat Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Grossberg said. “There’s really no downside.”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Grossberg reported that he is a consultant for Acadia, Alkahest, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda; receives research support from the National Institute on Aging, Janssen, and Roche; performs safety monitoring for EryDel, Merck, and Newron; and serves on data monitoring committees for Avanex and ITI Therapeutics.
FROM CP/AACP PSYCHIATRY UPDATE
A better tau blood test for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease?
.
In one new development, experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) compared phosphorylated-tau181 (P-tau181) to a related form of tau called P-tau217 to determine which can best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Results showed that the two biomarkers were similar overall, but P-tau 217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy. Importantly, both tau isoforms distinguished frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
“These new blood tests for P-tau are going to be really exciting because they will improve our ability to simply and inexpensively assess whether someone is at high risk for having Alzheimer’s disease,” said study author Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD, professor in UCSF’s department of neurology.
With the approval of the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease possibly around the corner, developing an accurate diagnostic blood test for this condition is even more urgent, added Dr. Boxer, who is also director of UCSF’s Neurosciences Clinical Research Unit and AD and FTD Clinical Trials Program.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Important implications
Currently, the only approved Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers are expensive positron emission tomography (PET) scans using agents that detect tau or amyloid, another hallmark Alzheimer’s disease protein, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid and tau, the measurement of which entails invasive lumbar puncture procedures. This limits the ability to easily confirm the underlying cause of dementia or cognitive impairment, which “obviously has important prognostic and therapeutic implications,” said Dr. Boxer.
Having a plasma biomarker, especially for tau, would be extremely useful. Patients with increased tau in the brain tend to exhibit Alzheimer’s disease symptoms while those with amyloid plaques do not always have clear signs, at least not immediately. “We think that P-tau is probably a better measure because it is much more closely related to symptoms of disease,” said Dr. Boxer.
Earlier this year, he and colleagues published a study in Nature Medicine showing that P-tau181 is more than three times as high in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared with healthy elderly people. It also differentiated Alzheimer’s disease from frontotemporal dementia (FTD). “We found that P-tau 181 was almost as good as a PET scan or lumbar puncture at identifying individuals with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain,” said Dr. Boxer.
They next wanted to assess how well P-tau 217 held up as a possible biomarker.
The new retrospective study was composed of 210 participants: 37 who acted as healthy controls, 99 who had FTLD, 39 who had Alzheimer’s disease, and 35 who had mild cognitive impairment.
More accurate test
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 was increased 5.7-fold in the participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls group, and increased fivefold compared with those who had FTLD (both comparisons, P < .001).
The increase in plasma P-tau181 was lower. It was increased only 4.5-times in participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls and 3.8-times relative to those with FTLD (both, P < .001). In addition, P-tau217 was potentially superior in predicting whether a person had a tau positive FTP-PET brain scan.
“This newer P-tau 217 test produces very similar results to the previous test we published [on P-tau181], but might be incrementally better or slightly more accurate, and even more closely related to the signal you get with a tau PET scan,” Dr. Boxer said.
The researchers are now examining these issues in a larger group of participants (N = 617). Results for those analyses are expected to be published soon. In addition to tau and amyloid markers, the researchers are examining another potential biomarker of neurodegeneration: the triple protein neurofilament light chain.
It’s too early to say which biomarker or biomarkers will prove to be the most useful in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Boxer noted. “It’s an open question whether it will be necessary to measure multiple P-taus plus beta amyloid plus neurofilament, or maybe just measuring one P-tau level will be sufficient,” he said.
Upcoming therapy?
Having a test that verifies Alzheimer’s disease is becoming all the more important now that a therapy might soon be available. Massachusetts-based biotech company Biogen has submitted aducanumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid-beta (Abeta), to the Food and Drug Administration for approval. Should that move forward, aducanumab would be the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
“If that’s the case, it will be even more important to have simple ways to screen people, to see if they might eventually be eligible for treatment,” said Dr. Boxer. Even if the drug isn’t approved, many patients simply want to know what is causing their cognitive problems, he added. Knowing they have Alzheimer’s disease might impact their life planning. If they have mild symptoms, interventions such as exercise and reducing cardiovascular risk could improve their overall health and quality of life, he said.
If individuals have another type of dementia, such as FTLD, that, too, might determine a different approach. Some forms of FTLD are caused by “completely different biological processes,” which are now being studied, Dr. Boxer said. So knowing that patients have this condition would allow them to participate in relevant clinical trials.
Exciting aspect
Having a tau blood test will also help those in underserviced and minority communities who can’t easily access memory specialists, Dr. Boxer noted. “It might allow them to access care, and get help much more easily, and that is a really exciting aspect of this new technology,” he said. It’s not clear when such blood tests will be on the market, although many companies are “scrambling” to make them available, said Dr. Boxer.
P-tau217 also holds promise as a marker for early Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to another study presented at AAIC 2020. A Swedish research team measured P-tau217 in more than 1,000 participants, including those who were unimpaired and those with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease dementia, or non-Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative diseases.
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 levels increase in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease when insoluble tau aggregates are not yet detectable with PET. They also predict subsequent increases in tau-PET, as well as conversion to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
‘Incredible breakthrough’
Commenting on the research, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, called the study amazing and “an incredible breakthrough.
“Researchers are able to detect disease up to 20 years before symptoms. The blood test has very good characteristics in terms of sensitivity and specificity. It correlates with the spinal fluid, it’s better than the PET imaging, it correlates with the amyloid test, and the results are being confirmed in many different cohorts,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved with the research.
A tau blood test, especially for P-tau 217, has the potential to be as important to determining dementia risk as cholesterol is to gauging heart disease risk, he added.
Having a tau blood test will “make our clinical trials much more precise and more efficient and reduce costs tremendously,” Dr. Fillit said, adding that he thinks tau blood tests might come to market as early as within a year.
Also commenting on the research, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said the new studies illustrate the rapid progress being made “in the blood biomarker space.”
Even 5 years ago, researchers would “never have thought” that blood biomarkers could be used as a tool to detect brain changes related to Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Edelmayer.
These new studies are “filling a gap in our understanding around tau” in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, she said. “Being able to distinguish between diseases is going to be very, very crucial for clinicians in the future,” she added.
Dr. Edelmayer foresees that in the future there will be a panel of blood biomarkers in addition to imaging tests to help clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Tau Research Consortium. Dr. Boxer disclosed that the blood p-tau test was done as part of a research collaboration between UCSF and Eli Lilly. Dr. Fillit and Dr. Edelmayer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
In one new development, experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) compared phosphorylated-tau181 (P-tau181) to a related form of tau called P-tau217 to determine which can best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Results showed that the two biomarkers were similar overall, but P-tau 217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy. Importantly, both tau isoforms distinguished frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
“These new blood tests for P-tau are going to be really exciting because they will improve our ability to simply and inexpensively assess whether someone is at high risk for having Alzheimer’s disease,” said study author Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD, professor in UCSF’s department of neurology.
With the approval of the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease possibly around the corner, developing an accurate diagnostic blood test for this condition is even more urgent, added Dr. Boxer, who is also director of UCSF’s Neurosciences Clinical Research Unit and AD and FTD Clinical Trials Program.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Important implications
Currently, the only approved Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers are expensive positron emission tomography (PET) scans using agents that detect tau or amyloid, another hallmark Alzheimer’s disease protein, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid and tau, the measurement of which entails invasive lumbar puncture procedures. This limits the ability to easily confirm the underlying cause of dementia or cognitive impairment, which “obviously has important prognostic and therapeutic implications,” said Dr. Boxer.
Having a plasma biomarker, especially for tau, would be extremely useful. Patients with increased tau in the brain tend to exhibit Alzheimer’s disease symptoms while those with amyloid plaques do not always have clear signs, at least not immediately. “We think that P-tau is probably a better measure because it is much more closely related to symptoms of disease,” said Dr. Boxer.
Earlier this year, he and colleagues published a study in Nature Medicine showing that P-tau181 is more than three times as high in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared with healthy elderly people. It also differentiated Alzheimer’s disease from frontotemporal dementia (FTD). “We found that P-tau 181 was almost as good as a PET scan or lumbar puncture at identifying individuals with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain,” said Dr. Boxer.
They next wanted to assess how well P-tau 217 held up as a possible biomarker.
The new retrospective study was composed of 210 participants: 37 who acted as healthy controls, 99 who had FTLD, 39 who had Alzheimer’s disease, and 35 who had mild cognitive impairment.
More accurate test
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 was increased 5.7-fold in the participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls group, and increased fivefold compared with those who had FTLD (both comparisons, P < .001).
The increase in plasma P-tau181 was lower. It was increased only 4.5-times in participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls and 3.8-times relative to those with FTLD (both, P < .001). In addition, P-tau217 was potentially superior in predicting whether a person had a tau positive FTP-PET brain scan.
“This newer P-tau 217 test produces very similar results to the previous test we published [on P-tau181], but might be incrementally better or slightly more accurate, and even more closely related to the signal you get with a tau PET scan,” Dr. Boxer said.
The researchers are now examining these issues in a larger group of participants (N = 617). Results for those analyses are expected to be published soon. In addition to tau and amyloid markers, the researchers are examining another potential biomarker of neurodegeneration: the triple protein neurofilament light chain.
It’s too early to say which biomarker or biomarkers will prove to be the most useful in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Boxer noted. “It’s an open question whether it will be necessary to measure multiple P-taus plus beta amyloid plus neurofilament, or maybe just measuring one P-tau level will be sufficient,” he said.
Upcoming therapy?
Having a test that verifies Alzheimer’s disease is becoming all the more important now that a therapy might soon be available. Massachusetts-based biotech company Biogen has submitted aducanumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid-beta (Abeta), to the Food and Drug Administration for approval. Should that move forward, aducanumab would be the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
“If that’s the case, it will be even more important to have simple ways to screen people, to see if they might eventually be eligible for treatment,” said Dr. Boxer. Even if the drug isn’t approved, many patients simply want to know what is causing their cognitive problems, he added. Knowing they have Alzheimer’s disease might impact their life planning. If they have mild symptoms, interventions such as exercise and reducing cardiovascular risk could improve their overall health and quality of life, he said.
If individuals have another type of dementia, such as FTLD, that, too, might determine a different approach. Some forms of FTLD are caused by “completely different biological processes,” which are now being studied, Dr. Boxer said. So knowing that patients have this condition would allow them to participate in relevant clinical trials.
Exciting aspect
Having a tau blood test will also help those in underserviced and minority communities who can’t easily access memory specialists, Dr. Boxer noted. “It might allow them to access care, and get help much more easily, and that is a really exciting aspect of this new technology,” he said. It’s not clear when such blood tests will be on the market, although many companies are “scrambling” to make them available, said Dr. Boxer.
P-tau217 also holds promise as a marker for early Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to another study presented at AAIC 2020. A Swedish research team measured P-tau217 in more than 1,000 participants, including those who were unimpaired and those with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease dementia, or non-Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative diseases.
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 levels increase in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease when insoluble tau aggregates are not yet detectable with PET. They also predict subsequent increases in tau-PET, as well as conversion to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
‘Incredible breakthrough’
Commenting on the research, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, called the study amazing and “an incredible breakthrough.
“Researchers are able to detect disease up to 20 years before symptoms. The blood test has very good characteristics in terms of sensitivity and specificity. It correlates with the spinal fluid, it’s better than the PET imaging, it correlates with the amyloid test, and the results are being confirmed in many different cohorts,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved with the research.
A tau blood test, especially for P-tau 217, has the potential to be as important to determining dementia risk as cholesterol is to gauging heart disease risk, he added.
Having a tau blood test will “make our clinical trials much more precise and more efficient and reduce costs tremendously,” Dr. Fillit said, adding that he thinks tau blood tests might come to market as early as within a year.
Also commenting on the research, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said the new studies illustrate the rapid progress being made “in the blood biomarker space.”
Even 5 years ago, researchers would “never have thought” that blood biomarkers could be used as a tool to detect brain changes related to Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Edelmayer.
These new studies are “filling a gap in our understanding around tau” in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, she said. “Being able to distinguish between diseases is going to be very, very crucial for clinicians in the future,” she added.
Dr. Edelmayer foresees that in the future there will be a panel of blood biomarkers in addition to imaging tests to help clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Tau Research Consortium. Dr. Boxer disclosed that the blood p-tau test was done as part of a research collaboration between UCSF and Eli Lilly. Dr. Fillit and Dr. Edelmayer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
In one new development, experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) compared phosphorylated-tau181 (P-tau181) to a related form of tau called P-tau217 to determine which can best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Results showed that the two biomarkers were similar overall, but P-tau 217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy. Importantly, both tau isoforms distinguished frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
“These new blood tests for P-tau are going to be really exciting because they will improve our ability to simply and inexpensively assess whether someone is at high risk for having Alzheimer’s disease,” said study author Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD, professor in UCSF’s department of neurology.
With the approval of the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease possibly around the corner, developing an accurate diagnostic blood test for this condition is even more urgent, added Dr. Boxer, who is also director of UCSF’s Neurosciences Clinical Research Unit and AD and FTD Clinical Trials Program.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Important implications
Currently, the only approved Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers are expensive positron emission tomography (PET) scans using agents that detect tau or amyloid, another hallmark Alzheimer’s disease protein, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid and tau, the measurement of which entails invasive lumbar puncture procedures. This limits the ability to easily confirm the underlying cause of dementia or cognitive impairment, which “obviously has important prognostic and therapeutic implications,” said Dr. Boxer.
Having a plasma biomarker, especially for tau, would be extremely useful. Patients with increased tau in the brain tend to exhibit Alzheimer’s disease symptoms while those with amyloid plaques do not always have clear signs, at least not immediately. “We think that P-tau is probably a better measure because it is much more closely related to symptoms of disease,” said Dr. Boxer.
Earlier this year, he and colleagues published a study in Nature Medicine showing that P-tau181 is more than three times as high in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease compared with healthy elderly people. It also differentiated Alzheimer’s disease from frontotemporal dementia (FTD). “We found that P-tau 181 was almost as good as a PET scan or lumbar puncture at identifying individuals with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain,” said Dr. Boxer.
They next wanted to assess how well P-tau 217 held up as a possible biomarker.
The new retrospective study was composed of 210 participants: 37 who acted as healthy controls, 99 who had FTLD, 39 who had Alzheimer’s disease, and 35 who had mild cognitive impairment.
More accurate test
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 was increased 5.7-fold in the participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls group, and increased fivefold compared with those who had FTLD (both comparisons, P < .001).
The increase in plasma P-tau181 was lower. It was increased only 4.5-times in participants with Alzheimer’s disease compared with the healthy controls and 3.8-times relative to those with FTLD (both, P < .001). In addition, P-tau217 was potentially superior in predicting whether a person had a tau positive FTP-PET brain scan.
“This newer P-tau 217 test produces very similar results to the previous test we published [on P-tau181], but might be incrementally better or slightly more accurate, and even more closely related to the signal you get with a tau PET scan,” Dr. Boxer said.
The researchers are now examining these issues in a larger group of participants (N = 617). Results for those analyses are expected to be published soon. In addition to tau and amyloid markers, the researchers are examining another potential biomarker of neurodegeneration: the triple protein neurofilament light chain.
It’s too early to say which biomarker or biomarkers will prove to be the most useful in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, Dr. Boxer noted. “It’s an open question whether it will be necessary to measure multiple P-taus plus beta amyloid plus neurofilament, or maybe just measuring one P-tau level will be sufficient,” he said.
Upcoming therapy?
Having a test that verifies Alzheimer’s disease is becoming all the more important now that a therapy might soon be available. Massachusetts-based biotech company Biogen has submitted aducanumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid-beta (Abeta), to the Food and Drug Administration for approval. Should that move forward, aducanumab would be the first disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
“If that’s the case, it will be even more important to have simple ways to screen people, to see if they might eventually be eligible for treatment,” said Dr. Boxer. Even if the drug isn’t approved, many patients simply want to know what is causing their cognitive problems, he added. Knowing they have Alzheimer’s disease might impact their life planning. If they have mild symptoms, interventions such as exercise and reducing cardiovascular risk could improve their overall health and quality of life, he said.
If individuals have another type of dementia, such as FTLD, that, too, might determine a different approach. Some forms of FTLD are caused by “completely different biological processes,” which are now being studied, Dr. Boxer said. So knowing that patients have this condition would allow them to participate in relevant clinical trials.
Exciting aspect
Having a tau blood test will also help those in underserviced and minority communities who can’t easily access memory specialists, Dr. Boxer noted. “It might allow them to access care, and get help much more easily, and that is a really exciting aspect of this new technology,” he said. It’s not clear when such blood tests will be on the market, although many companies are “scrambling” to make them available, said Dr. Boxer.
P-tau217 also holds promise as a marker for early Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to another study presented at AAIC 2020. A Swedish research team measured P-tau217 in more than 1,000 participants, including those who were unimpaired and those with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease dementia, or non-Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative diseases.
Results showed that plasma P-tau217 levels increase in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease when insoluble tau aggregates are not yet detectable with PET. They also predict subsequent increases in tau-PET, as well as conversion to Alzheimer’s disease dementia.
‘Incredible breakthrough’
Commenting on the research, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, called the study amazing and “an incredible breakthrough.
“Researchers are able to detect disease up to 20 years before symptoms. The blood test has very good characteristics in terms of sensitivity and specificity. It correlates with the spinal fluid, it’s better than the PET imaging, it correlates with the amyloid test, and the results are being confirmed in many different cohorts,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved with the research.
A tau blood test, especially for P-tau 217, has the potential to be as important to determining dementia risk as cholesterol is to gauging heart disease risk, he added.
Having a tau blood test will “make our clinical trials much more precise and more efficient and reduce costs tremendously,” Dr. Fillit said, adding that he thinks tau blood tests might come to market as early as within a year.
Also commenting on the research, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said the new studies illustrate the rapid progress being made “in the blood biomarker space.”
Even 5 years ago, researchers would “never have thought” that blood biomarkers could be used as a tool to detect brain changes related to Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Edelmayer.
These new studies are “filling a gap in our understanding around tau” in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, she said. “Being able to distinguish between diseases is going to be very, very crucial for clinicians in the future,” she added.
Dr. Edelmayer foresees that in the future there will be a panel of blood biomarkers in addition to imaging tests to help clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Tau Research Consortium. Dr. Boxer disclosed that the blood p-tau test was done as part of a research collaboration between UCSF and Eli Lilly. Dr. Fillit and Dr. Edelmayer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2020
Postmenopausal use of estrogen alone lowers breast cancer cases, deaths
A new follow-up study of menopausal hormone therapy found that prior use of conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) decreased both breast cancer incidence and mortality, while prior use of CEE plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) was associated with an increase in incidence.
“Prior use of CEE alone is, to our knowledge, the first pharmacologic intervention demonstrated to be associated with a statistically significantly reduction in deaths from breast cancer,” wrote Rowan T. Chlebowski, MD, PhD, of the Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation in Torrance, Calif., and his coauthors. The study was published July 28 in JAMA.
To further investigate the outcomes of the Women’s Health Initiative in regard to hormone therapy and breast cancer risk, the researchers analyzed the long-term follow-up of two randomized trials that included 27,347 postmenopausal women with no prior breast cancer and negative mammograms at baseline. Their mean (SD) age was 63.4 (7.2) years. Enrollment took place from 1993 to 1998; participants were contacted for follow-up every 6 months through 2005 and annually from then on. Mortality data were gathered from follow-up and the National Death Index.
The first trial included 16,608 women with a uterus. Among these women, 8,506 received 0.625 mg/day of CEE plus 2.5 mg/day of MPA, and 8,102 received placebo. The second trial included 10,739 women who’d gotten a hysterectomy, 5,310 of whom received 0.625 mg/day of CEE alone and 5,429 of whom received placebo. The first trial ended in 2002 after a median intervention period of 5.6 years, and the second trial ended in 2004 after a period of 7.2 years.
An analysis in 2015 found that CEE alone was associated with lower risk of breast cancer and CEE plus MPA was associated with increased risk.
The current analysis confirmed that, after a median of 20.3 years of follow-up, and with mortality data now available for more than 98% of participants, CEE alone was associated with fewer cases of breast cancer (238 cases, annualized rate 0.30%), compared with placebo (296 cases, annualized rate 0.37%; hazard ratio 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.65-0.93; P = .005).
Furthermore, CEE alone was also associated with lower mortality (30 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.031%), compared with placebo (46 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.046%; HR 0.60; 95% CI, 0.37-0.97; P = .04).
By comparison, CEE plus MPA was linked with more cases of breast cancer (584 cases, annualized rate 0.45%) than placebo (447 cases, annualized rate 0.36%; HR 1.28; 95% CI, 1.13-1.45; P < .001). In regard to mortality, there was no statistically significant difference between CEE plus MPA (71 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.045%) and placebo (53 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.035%; HR 1.35; 95% CI, 0.94-1.95; P = .11).
“The big thing to think about is estrogen alone reducing breast cancer mortality by 40%,” said Dr. Chlebowski in an interview. “None of the other interventions, including tamoxifen, had any change on mortality. This should change the way we look at breast cancer prevention, though we might have to be a little creative about it. I think you have to be a little away from menopause for it to reduce breast cancer. But we wanted to start that debate.
“On the other hand,” he said, “a woman takes estrogen plus progestin and when you look at that curve, it’s staying about 25% increased. You take it for 5.6 years and the increase continues through 20 years, so you’re maybe buying a lifetime of increase in breast cancer by taking estrogen plus progestin for 5 years.”
He also highlighted the comprehensiveness of the mortality data, noting that “when you hook up to the National Death Index, they find 98% of all deaths in the United States. That’s really remarkable; you retain the whole power of the randomization. It means our data, between the death index and our follow-up of participants, is essentially complete.”
Use of hormone therapy, and decoding the outcomes, remains ‘complex’
Decades after the data were gathered from the Women’s Health Initiative clinical trials, they continue to assist researchers and patients alike, wrote Christina A. Minami, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and Rachel A. Freedman, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
That said, in regard to the findings of this latest analysis, “many questions still remain on whether (and how) a hormone therapy intervention that occurred many years earlier may continue to affect breast cancer risk and mortality at 20 years,” they wrote. They noted that it’s “impossible” to isolate how exposure to certain therapies can impact long-term outcomes, and that a high percentage of patients who discontinued the drugs during each trial muddy the waters even further.
“Decisions to initiate these medications remain complex,” they added, emphasizing that breast cancer risk is just one of many factors that physicians must consider when considering hormone therapy for their patients.
Dr. Chlebowski and his coauthors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including the use of very specifically administered and formulated dosages making their findings “not necessarily generalizable to other preparations.” In addition, they noted the significant percentage of patients – 54% with CEE alone and 42% with CEE plus MPA – who discontinued drug usage during their respective trials.
The Women’s Health Initiative is supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving personal fees and grants from various government organizations, foundations, and pharmaceutical companies. The editorial’s authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chlebowski RT et al. JAMA. 2020 Jul 28. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9482.
A new follow-up study of menopausal hormone therapy found that prior use of conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) decreased both breast cancer incidence and mortality, while prior use of CEE plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) was associated with an increase in incidence.
“Prior use of CEE alone is, to our knowledge, the first pharmacologic intervention demonstrated to be associated with a statistically significantly reduction in deaths from breast cancer,” wrote Rowan T. Chlebowski, MD, PhD, of the Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation in Torrance, Calif., and his coauthors. The study was published July 28 in JAMA.
To further investigate the outcomes of the Women’s Health Initiative in regard to hormone therapy and breast cancer risk, the researchers analyzed the long-term follow-up of two randomized trials that included 27,347 postmenopausal women with no prior breast cancer and negative mammograms at baseline. Their mean (SD) age was 63.4 (7.2) years. Enrollment took place from 1993 to 1998; participants were contacted for follow-up every 6 months through 2005 and annually from then on. Mortality data were gathered from follow-up and the National Death Index.
The first trial included 16,608 women with a uterus. Among these women, 8,506 received 0.625 mg/day of CEE plus 2.5 mg/day of MPA, and 8,102 received placebo. The second trial included 10,739 women who’d gotten a hysterectomy, 5,310 of whom received 0.625 mg/day of CEE alone and 5,429 of whom received placebo. The first trial ended in 2002 after a median intervention period of 5.6 years, and the second trial ended in 2004 after a period of 7.2 years.
An analysis in 2015 found that CEE alone was associated with lower risk of breast cancer and CEE plus MPA was associated with increased risk.
The current analysis confirmed that, after a median of 20.3 years of follow-up, and with mortality data now available for more than 98% of participants, CEE alone was associated with fewer cases of breast cancer (238 cases, annualized rate 0.30%), compared with placebo (296 cases, annualized rate 0.37%; hazard ratio 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.65-0.93; P = .005).
Furthermore, CEE alone was also associated with lower mortality (30 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.031%), compared with placebo (46 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.046%; HR 0.60; 95% CI, 0.37-0.97; P = .04).
By comparison, CEE plus MPA was linked with more cases of breast cancer (584 cases, annualized rate 0.45%) than placebo (447 cases, annualized rate 0.36%; HR 1.28; 95% CI, 1.13-1.45; P < .001). In regard to mortality, there was no statistically significant difference between CEE plus MPA (71 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.045%) and placebo (53 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.035%; HR 1.35; 95% CI, 0.94-1.95; P = .11).
“The big thing to think about is estrogen alone reducing breast cancer mortality by 40%,” said Dr. Chlebowski in an interview. “None of the other interventions, including tamoxifen, had any change on mortality. This should change the way we look at breast cancer prevention, though we might have to be a little creative about it. I think you have to be a little away from menopause for it to reduce breast cancer. But we wanted to start that debate.
“On the other hand,” he said, “a woman takes estrogen plus progestin and when you look at that curve, it’s staying about 25% increased. You take it for 5.6 years and the increase continues through 20 years, so you’re maybe buying a lifetime of increase in breast cancer by taking estrogen plus progestin for 5 years.”
He also highlighted the comprehensiveness of the mortality data, noting that “when you hook up to the National Death Index, they find 98% of all deaths in the United States. That’s really remarkable; you retain the whole power of the randomization. It means our data, between the death index and our follow-up of participants, is essentially complete.”
Use of hormone therapy, and decoding the outcomes, remains ‘complex’
Decades after the data were gathered from the Women’s Health Initiative clinical trials, they continue to assist researchers and patients alike, wrote Christina A. Minami, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and Rachel A. Freedman, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
That said, in regard to the findings of this latest analysis, “many questions still remain on whether (and how) a hormone therapy intervention that occurred many years earlier may continue to affect breast cancer risk and mortality at 20 years,” they wrote. They noted that it’s “impossible” to isolate how exposure to certain therapies can impact long-term outcomes, and that a high percentage of patients who discontinued the drugs during each trial muddy the waters even further.
“Decisions to initiate these medications remain complex,” they added, emphasizing that breast cancer risk is just one of many factors that physicians must consider when considering hormone therapy for their patients.
Dr. Chlebowski and his coauthors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including the use of very specifically administered and formulated dosages making their findings “not necessarily generalizable to other preparations.” In addition, they noted the significant percentage of patients – 54% with CEE alone and 42% with CEE plus MPA – who discontinued drug usage during their respective trials.
The Women’s Health Initiative is supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving personal fees and grants from various government organizations, foundations, and pharmaceutical companies. The editorial’s authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chlebowski RT et al. JAMA. 2020 Jul 28. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9482.
A new follow-up study of menopausal hormone therapy found that prior use of conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) decreased both breast cancer incidence and mortality, while prior use of CEE plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) was associated with an increase in incidence.
“Prior use of CEE alone is, to our knowledge, the first pharmacologic intervention demonstrated to be associated with a statistically significantly reduction in deaths from breast cancer,” wrote Rowan T. Chlebowski, MD, PhD, of the Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation in Torrance, Calif., and his coauthors. The study was published July 28 in JAMA.
To further investigate the outcomes of the Women’s Health Initiative in regard to hormone therapy and breast cancer risk, the researchers analyzed the long-term follow-up of two randomized trials that included 27,347 postmenopausal women with no prior breast cancer and negative mammograms at baseline. Their mean (SD) age was 63.4 (7.2) years. Enrollment took place from 1993 to 1998; participants were contacted for follow-up every 6 months through 2005 and annually from then on. Mortality data were gathered from follow-up and the National Death Index.
The first trial included 16,608 women with a uterus. Among these women, 8,506 received 0.625 mg/day of CEE plus 2.5 mg/day of MPA, and 8,102 received placebo. The second trial included 10,739 women who’d gotten a hysterectomy, 5,310 of whom received 0.625 mg/day of CEE alone and 5,429 of whom received placebo. The first trial ended in 2002 after a median intervention period of 5.6 years, and the second trial ended in 2004 after a period of 7.2 years.
An analysis in 2015 found that CEE alone was associated with lower risk of breast cancer and CEE plus MPA was associated with increased risk.
The current analysis confirmed that, after a median of 20.3 years of follow-up, and with mortality data now available for more than 98% of participants, CEE alone was associated with fewer cases of breast cancer (238 cases, annualized rate 0.30%), compared with placebo (296 cases, annualized rate 0.37%; hazard ratio 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.65-0.93; P = .005).
Furthermore, CEE alone was also associated with lower mortality (30 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.031%), compared with placebo (46 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.046%; HR 0.60; 95% CI, 0.37-0.97; P = .04).
By comparison, CEE plus MPA was linked with more cases of breast cancer (584 cases, annualized rate 0.45%) than placebo (447 cases, annualized rate 0.36%; HR 1.28; 95% CI, 1.13-1.45; P < .001). In regard to mortality, there was no statistically significant difference between CEE plus MPA (71 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.045%) and placebo (53 deaths, annualized mortality rate 0.035%; HR 1.35; 95% CI, 0.94-1.95; P = .11).
“The big thing to think about is estrogen alone reducing breast cancer mortality by 40%,” said Dr. Chlebowski in an interview. “None of the other interventions, including tamoxifen, had any change on mortality. This should change the way we look at breast cancer prevention, though we might have to be a little creative about it. I think you have to be a little away from menopause for it to reduce breast cancer. But we wanted to start that debate.
“On the other hand,” he said, “a woman takes estrogen plus progestin and when you look at that curve, it’s staying about 25% increased. You take it for 5.6 years and the increase continues through 20 years, so you’re maybe buying a lifetime of increase in breast cancer by taking estrogen plus progestin for 5 years.”
He also highlighted the comprehensiveness of the mortality data, noting that “when you hook up to the National Death Index, they find 98% of all deaths in the United States. That’s really remarkable; you retain the whole power of the randomization. It means our data, between the death index and our follow-up of participants, is essentially complete.”
Use of hormone therapy, and decoding the outcomes, remains ‘complex’
Decades after the data were gathered from the Women’s Health Initiative clinical trials, they continue to assist researchers and patients alike, wrote Christina A. Minami, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and Rachel A. Freedman, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
That said, in regard to the findings of this latest analysis, “many questions still remain on whether (and how) a hormone therapy intervention that occurred many years earlier may continue to affect breast cancer risk and mortality at 20 years,” they wrote. They noted that it’s “impossible” to isolate how exposure to certain therapies can impact long-term outcomes, and that a high percentage of patients who discontinued the drugs during each trial muddy the waters even further.
“Decisions to initiate these medications remain complex,” they added, emphasizing that breast cancer risk is just one of many factors that physicians must consider when considering hormone therapy for their patients.
Dr. Chlebowski and his coauthors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including the use of very specifically administered and formulated dosages making their findings “not necessarily generalizable to other preparations.” In addition, they noted the significant percentage of patients – 54% with CEE alone and 42% with CEE plus MPA – who discontinued drug usage during their respective trials.
The Women’s Health Initiative is supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving personal fees and grants from various government organizations, foundations, and pharmaceutical companies. The editorial’s authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chlebowski RT et al. JAMA. 2020 Jul 28. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9482.
FROM JAMA