User login
Infliximab vs Adalimumab: Which Is Best for Behçet Syndrome?
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
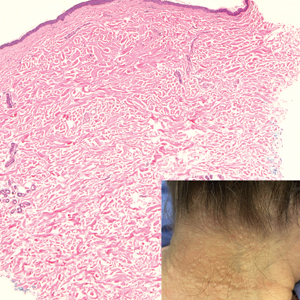
Asymptomatic Papules on the Neck
THE DIAGNOSIS: White Fibrous Papulosis
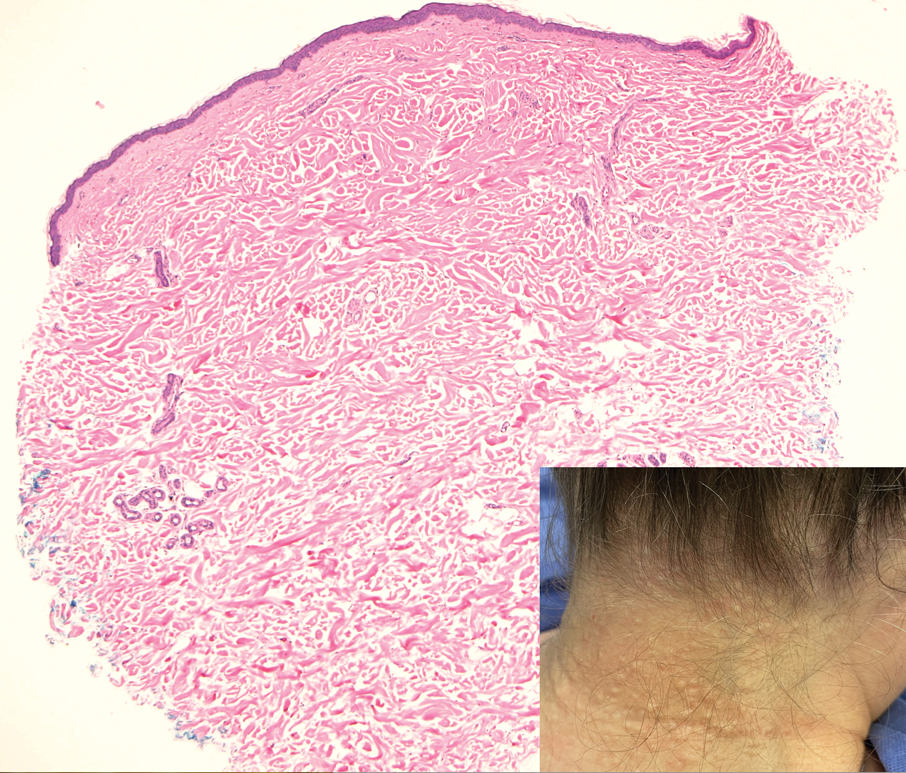
Given the histopathology findings, location on a sun-exposed site, lack of any additional systemic signs or symptoms, and no family history of similar lesions to suggest an underlying genetic condition, a diagnosis of white fibrous papulosis (WFP) was made. White fibrous papulosis is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder that was first reported by Shimizu et al1 in 1985. It is characterized by numerous grouped, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules that in most cases are confined to the neck in middle-aged to elderly individuals; however, cases involving the upper trunk and axillae also have been reported.1-3 The etiology of this condition is unclear but is thought to be related to aging and chronic exposure to UV light. Although treatment is not required, various modalities including tretinoin, excision, and laser therapy have been trialed with varying success.2,4 Our patient elected not to proceed with treatment.
Histologically, WFP may manifest similarly to connective tissue nevi; the overall architecture is nonspecific with focally thickened collagen and often elastic fibers that may be normal to reduced and/or fragmented, as well as an overall decrease in superficial dermal elastic tissue.3,5 Therefore, the differential diagnosis may include connective tissue nevi and require clinical correlation to make a correct diagnosis.
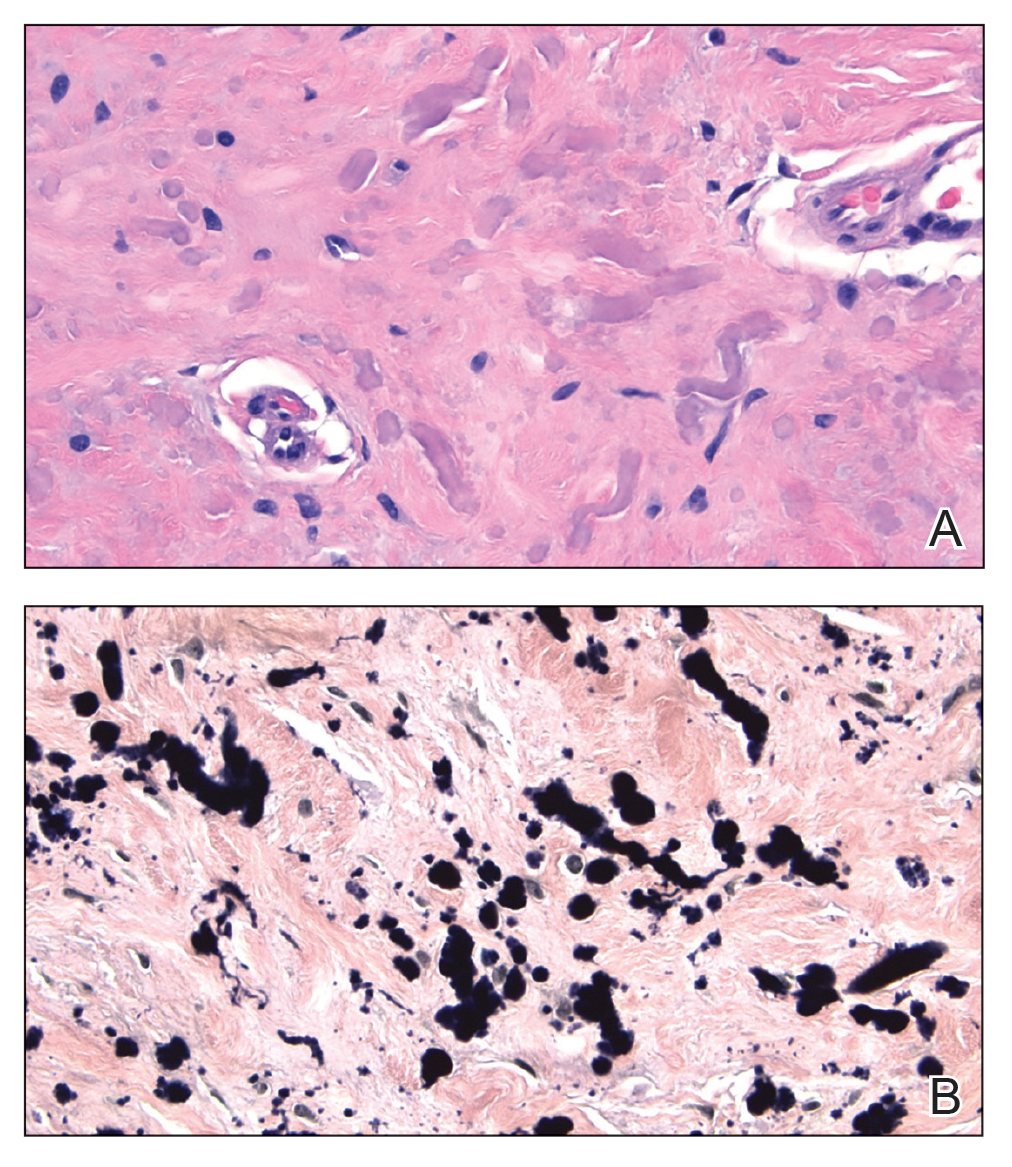
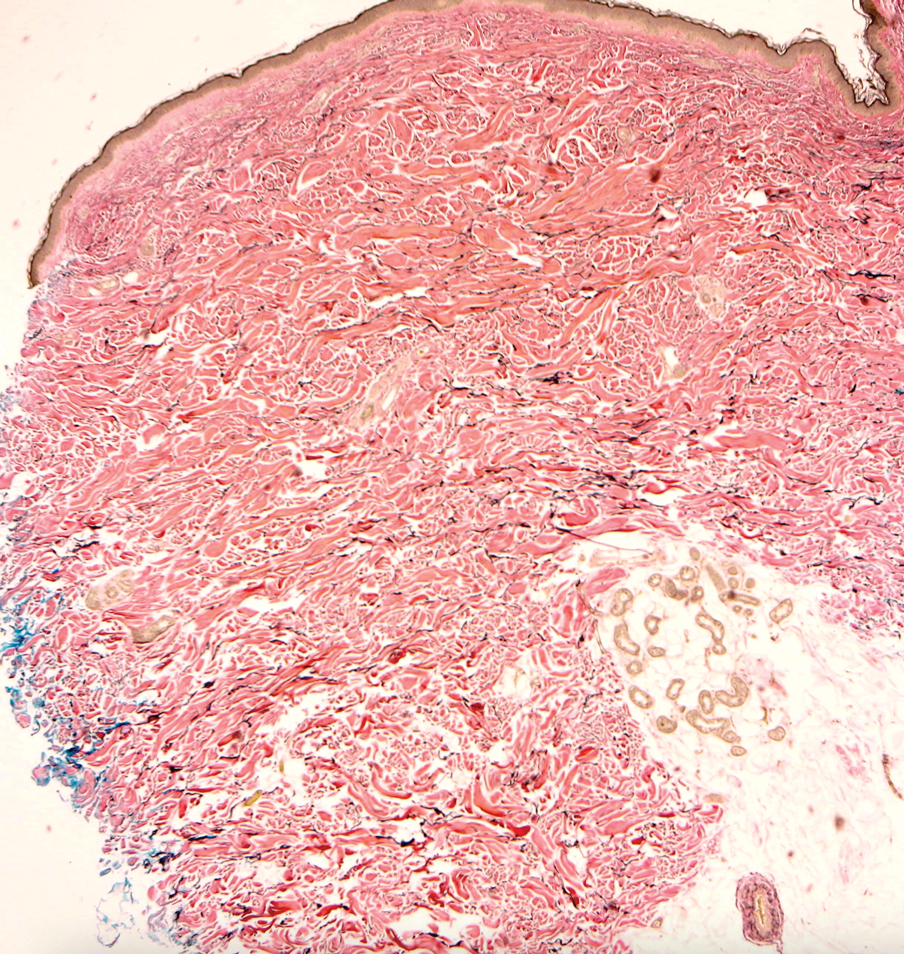
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is an autosomalrecessive disorder most commonly related to mutations in the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) gene that tends to manifest clinically on the neck and flexural extremities.6 This disease affects elastic fibers, which may become calcified over time. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is associated with ocular complications relating to the Bruch membrane of the retina and angioid streaks; choroidal neovascularization involving the damaged Bruch membrane and episodes of acute retinopathy may result in vision loss in later stages of the disease.7 Involvement of the elastic laminae of arteries can be associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as stroke, coronary artery disease, claudication, and aneurysms. Involvement of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts also may occur and most commonly manifests with bleeding. Pathologic alterations in the elastic fibers of the lungs also have been reported in patients with PXE.8 Histologically, PXE exhibits increased abnormally clumped and fragmented elastic fibers in the superficial dermis, often with calcification (Figure 1). Pseudo-PXE related to D-penicillamine use often lacks calcification and has a bramble bush appearance.9

Fibrofolliculomas may manifest alone or in association with an underlying condition such as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, in which lesions are most frequently seen scattered on the scalp, face, ears, neck, or upper trunk.10 This condition is related to a folliculin (FLCN) gene germline mutation. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome also may be associated with acrochordons, trichodiscomas, renal cancer, and lung cysts with or without spontaneous pneumothorax. Less frequently noted findings include oral papules, epidermal cysts, angiofibromas, lipomas/angiolipomas, parotid gland tumors, and thyroid neoplasms. Connective tissue nevi/collagenomas can appear clinically similar to fibrofolliculomas; true connective tissue nevi are reported less commonly in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.11 Histologically, a fibrofolliculoma manifests with epidermal strands originating from a hair follicle associated with prominent surrounding connective tissue (Figure 2).
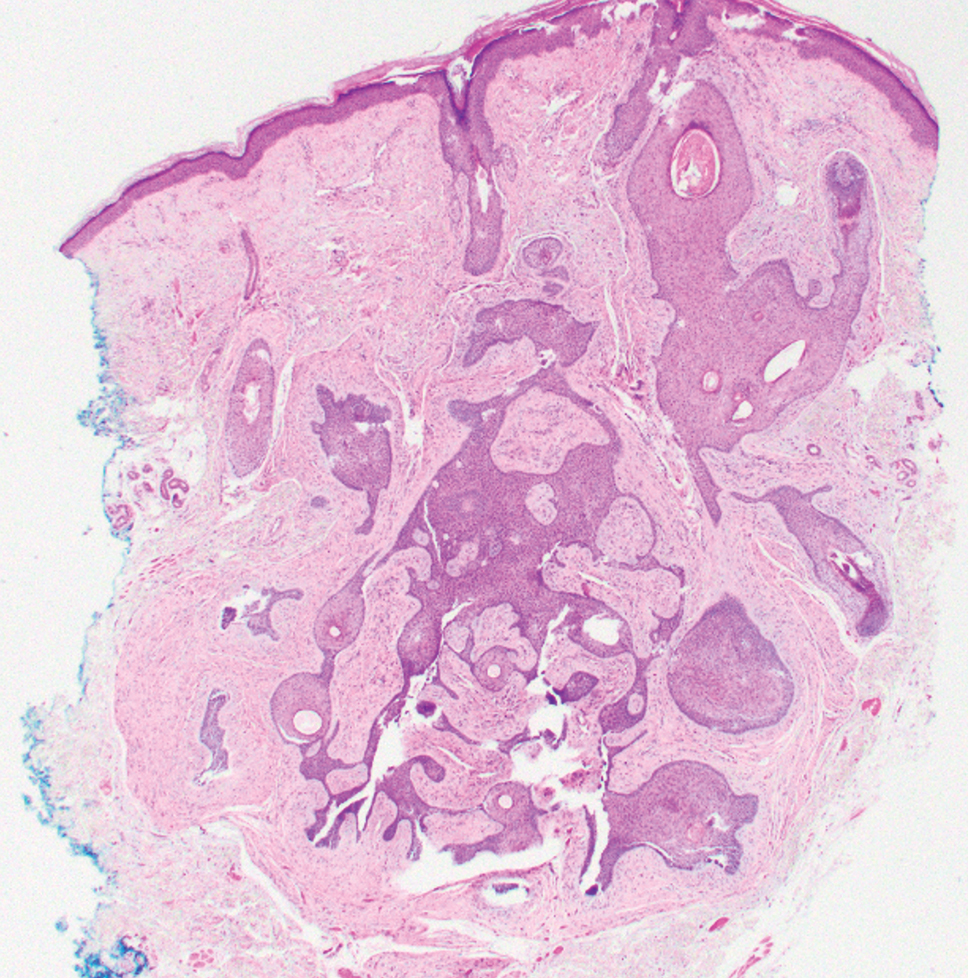
Elastofibroma dorsi is a benign tumor of connective tissue that most commonly manifests clinically as a solitary subcutaneous mass on the back near the inferior angle of the scapula; it typically develops below the rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi muscles.12 The pathogenesis is uncertain, but some patients have reported a family history of the condition or a history of repetitive shoulder movement/trauma prior to onset; the mass may be asymptomatic or associated with pain and/or swelling. Those affected tend to be older than 50 years.13 Histologically, thickened and rounded to beaded elastic fibers are seen admixed with collagen (Figure 3).
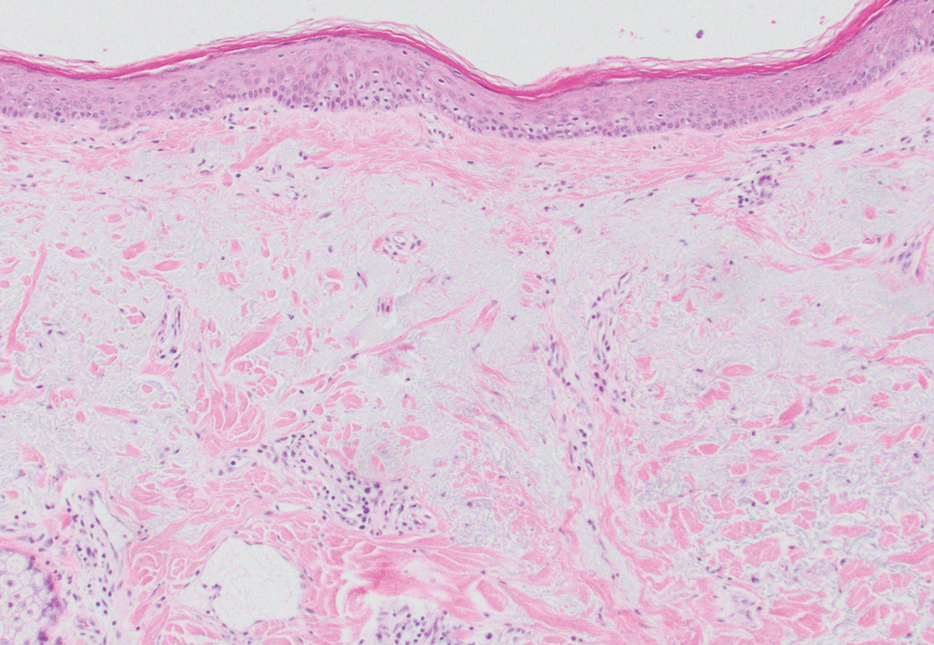
Actinic (solar) elastosis frequently is encountered in many skin biopsies and is caused by chronic photodamage. More hypertrophic variants, such as papular or nodular solar elastosis, may clinically manifest similarly to WFP.14 Histologically, actinic elastosis manifests as a considerable increase in elastic tissue in the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 4).
- Shimizu H, Nishikawa T, Kimura S. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: review of our 16 cases. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;95:1077-1084.
- Teo W, Pang S. White fibrous papulosis of the chest and back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB33.
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635.
- Lueangarun S, Panchaprateep R. White fibrous papulosis of the neck treated with fractionated 1550-nm erbium glass laser: a case report. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016;7:256-258.
- Rios-Gomez M, Ramos-Garibay JA, Perez-Santana ME, et al. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25661.
- Váradi A, Szabó Z, Pomozi V, et al. ABCC6 as a target in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:671-682.
- Gliem M, Birtel J, Müller PL, et al. Acute retinopathy in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1165-1173.
- Germain DP. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:85. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0639-8
- Chisti MA, Binamer Y, Alfadley A, et al. D-penicillamine-induced pseudo-pseudoxanthoma elasticum and extensive elastosis perforans serpiginosa with excellent response to acitretin. Ann Saudi Med. 2019;39:56-60.
- Criscito MC, Mu EW, Meehan SA, et al. Dermoscopic features of a solitary fibrofolliculoma on the left cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(2 suppl 1):S8-S9.
- Sattler EC, Steinlein OK. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Updated January 30, 2020. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1522
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Settipalli S, et al. Elastofibroma: an uncommon tumor revisited. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9:34-37. doi:10.4103/0974- 2077.178543
- Chandrasekar CR, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: an uncommon benign pseudotumour. Sarcoma. 2008;2008:756565. doi:10.1155/2008/756565
- Kwittken J. Papular elastosis. Cutis. 2000;66:81-83.
THE DIAGNOSIS: White Fibrous Papulosis
Given the histopathology findings, location on a sun-exposed site, lack of any additional systemic signs or symptoms, and no family history of similar lesions to suggest an underlying genetic condition, a diagnosis of white fibrous papulosis (WFP) was made. White fibrous papulosis is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder that was first reported by Shimizu et al1 in 1985. It is characterized by numerous grouped, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules that in most cases are confined to the neck in middle-aged to elderly individuals; however, cases involving the upper trunk and axillae also have been reported.1-3 The etiology of this condition is unclear but is thought to be related to aging and chronic exposure to UV light. Although treatment is not required, various modalities including tretinoin, excision, and laser therapy have been trialed with varying success.2,4 Our patient elected not to proceed with treatment.
Histologically, WFP may manifest similarly to connective tissue nevi; the overall architecture is nonspecific with focally thickened collagen and often elastic fibers that may be normal to reduced and/or fragmented, as well as an overall decrease in superficial dermal elastic tissue.3,5 Therefore, the differential diagnosis may include connective tissue nevi and require clinical correlation to make a correct diagnosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is an autosomalrecessive disorder most commonly related to mutations in the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) gene that tends to manifest clinically on the neck and flexural extremities.6 This disease affects elastic fibers, which may become calcified over time. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is associated with ocular complications relating to the Bruch membrane of the retina and angioid streaks; choroidal neovascularization involving the damaged Bruch membrane and episodes of acute retinopathy may result in vision loss in later stages of the disease.7 Involvement of the elastic laminae of arteries can be associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as stroke, coronary artery disease, claudication, and aneurysms. Involvement of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts also may occur and most commonly manifests with bleeding. Pathologic alterations in the elastic fibers of the lungs also have been reported in patients with PXE.8 Histologically, PXE exhibits increased abnormally clumped and fragmented elastic fibers in the superficial dermis, often with calcification (Figure 1). Pseudo-PXE related to D-penicillamine use often lacks calcification and has a bramble bush appearance.9

Fibrofolliculomas may manifest alone or in association with an underlying condition such as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, in which lesions are most frequently seen scattered on the scalp, face, ears, neck, or upper trunk.10 This condition is related to a folliculin (FLCN) gene germline mutation. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome also may be associated with acrochordons, trichodiscomas, renal cancer, and lung cysts with or without spontaneous pneumothorax. Less frequently noted findings include oral papules, epidermal cysts, angiofibromas, lipomas/angiolipomas, parotid gland tumors, and thyroid neoplasms. Connective tissue nevi/collagenomas can appear clinically similar to fibrofolliculomas; true connective tissue nevi are reported less commonly in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.11 Histologically, a fibrofolliculoma manifests with epidermal strands originating from a hair follicle associated with prominent surrounding connective tissue (Figure 2).

Elastofibroma dorsi is a benign tumor of connective tissue that most commonly manifests clinically as a solitary subcutaneous mass on the back near the inferior angle of the scapula; it typically develops below the rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi muscles.12 The pathogenesis is uncertain, but some patients have reported a family history of the condition or a history of repetitive shoulder movement/trauma prior to onset; the mass may be asymptomatic or associated with pain and/or swelling. Those affected tend to be older than 50 years.13 Histologically, thickened and rounded to beaded elastic fibers are seen admixed with collagen (Figure 3).

Actinic (solar) elastosis frequently is encountered in many skin biopsies and is caused by chronic photodamage. More hypertrophic variants, such as papular or nodular solar elastosis, may clinically manifest similarly to WFP.14 Histologically, actinic elastosis manifests as a considerable increase in elastic tissue in the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 4).

THE DIAGNOSIS: White Fibrous Papulosis
Given the histopathology findings, location on a sun-exposed site, lack of any additional systemic signs or symptoms, and no family history of similar lesions to suggest an underlying genetic condition, a diagnosis of white fibrous papulosis (WFP) was made. White fibrous papulosis is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder that was first reported by Shimizu et al1 in 1985. It is characterized by numerous grouped, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules that in most cases are confined to the neck in middle-aged to elderly individuals; however, cases involving the upper trunk and axillae also have been reported.1-3 The etiology of this condition is unclear but is thought to be related to aging and chronic exposure to UV light. Although treatment is not required, various modalities including tretinoin, excision, and laser therapy have been trialed with varying success.2,4 Our patient elected not to proceed with treatment.
Histologically, WFP may manifest similarly to connective tissue nevi; the overall architecture is nonspecific with focally thickened collagen and often elastic fibers that may be normal to reduced and/or fragmented, as well as an overall decrease in superficial dermal elastic tissue.3,5 Therefore, the differential diagnosis may include connective tissue nevi and require clinical correlation to make a correct diagnosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is an autosomalrecessive disorder most commonly related to mutations in the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) gene that tends to manifest clinically on the neck and flexural extremities.6 This disease affects elastic fibers, which may become calcified over time. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is associated with ocular complications relating to the Bruch membrane of the retina and angioid streaks; choroidal neovascularization involving the damaged Bruch membrane and episodes of acute retinopathy may result in vision loss in later stages of the disease.7 Involvement of the elastic laminae of arteries can be associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as stroke, coronary artery disease, claudication, and aneurysms. Involvement of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts also may occur and most commonly manifests with bleeding. Pathologic alterations in the elastic fibers of the lungs also have been reported in patients with PXE.8 Histologically, PXE exhibits increased abnormally clumped and fragmented elastic fibers in the superficial dermis, often with calcification (Figure 1). Pseudo-PXE related to D-penicillamine use often lacks calcification and has a bramble bush appearance.9

Fibrofolliculomas may manifest alone or in association with an underlying condition such as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, in which lesions are most frequently seen scattered on the scalp, face, ears, neck, or upper trunk.10 This condition is related to a folliculin (FLCN) gene germline mutation. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome also may be associated with acrochordons, trichodiscomas, renal cancer, and lung cysts with or without spontaneous pneumothorax. Less frequently noted findings include oral papules, epidermal cysts, angiofibromas, lipomas/angiolipomas, parotid gland tumors, and thyroid neoplasms. Connective tissue nevi/collagenomas can appear clinically similar to fibrofolliculomas; true connective tissue nevi are reported less commonly in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.11 Histologically, a fibrofolliculoma manifests with epidermal strands originating from a hair follicle associated with prominent surrounding connective tissue (Figure 2).

Elastofibroma dorsi is a benign tumor of connective tissue that most commonly manifests clinically as a solitary subcutaneous mass on the back near the inferior angle of the scapula; it typically develops below the rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi muscles.12 The pathogenesis is uncertain, but some patients have reported a family history of the condition or a history of repetitive shoulder movement/trauma prior to onset; the mass may be asymptomatic or associated with pain and/or swelling. Those affected tend to be older than 50 years.13 Histologically, thickened and rounded to beaded elastic fibers are seen admixed with collagen (Figure 3).

Actinic (solar) elastosis frequently is encountered in many skin biopsies and is caused by chronic photodamage. More hypertrophic variants, such as papular or nodular solar elastosis, may clinically manifest similarly to WFP.14 Histologically, actinic elastosis manifests as a considerable increase in elastic tissue in the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 4).

- Shimizu H, Nishikawa T, Kimura S. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: review of our 16 cases. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;95:1077-1084.
- Teo W, Pang S. White fibrous papulosis of the chest and back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB33.
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635.
- Lueangarun S, Panchaprateep R. White fibrous papulosis of the neck treated with fractionated 1550-nm erbium glass laser: a case report. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016;7:256-258.
- Rios-Gomez M, Ramos-Garibay JA, Perez-Santana ME, et al. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25661.
- Váradi A, Szabó Z, Pomozi V, et al. ABCC6 as a target in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:671-682.
- Gliem M, Birtel J, Müller PL, et al. Acute retinopathy in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1165-1173.
- Germain DP. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:85. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0639-8
- Chisti MA, Binamer Y, Alfadley A, et al. D-penicillamine-induced pseudo-pseudoxanthoma elasticum and extensive elastosis perforans serpiginosa with excellent response to acitretin. Ann Saudi Med. 2019;39:56-60.
- Criscito MC, Mu EW, Meehan SA, et al. Dermoscopic features of a solitary fibrofolliculoma on the left cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(2 suppl 1):S8-S9.
- Sattler EC, Steinlein OK. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Updated January 30, 2020. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1522
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Settipalli S, et al. Elastofibroma: an uncommon tumor revisited. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9:34-37. doi:10.4103/0974- 2077.178543
- Chandrasekar CR, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: an uncommon benign pseudotumour. Sarcoma. 2008;2008:756565. doi:10.1155/2008/756565
- Kwittken J. Papular elastosis. Cutis. 2000;66:81-83.
- Shimizu H, Nishikawa T, Kimura S. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: review of our 16 cases. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;95:1077-1084.
- Teo W, Pang S. White fibrous papulosis of the chest and back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB33.
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635.
- Lueangarun S, Panchaprateep R. White fibrous papulosis of the neck treated with fractionated 1550-nm erbium glass laser: a case report. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016;7:256-258.
- Rios-Gomez M, Ramos-Garibay JA, Perez-Santana ME, et al. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25661.
- Váradi A, Szabó Z, Pomozi V, et al. ABCC6 as a target in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:671-682.
- Gliem M, Birtel J, Müller PL, et al. Acute retinopathy in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1165-1173.
- Germain DP. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:85. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0639-8
- Chisti MA, Binamer Y, Alfadley A, et al. D-penicillamine-induced pseudo-pseudoxanthoma elasticum and extensive elastosis perforans serpiginosa with excellent response to acitretin. Ann Saudi Med. 2019;39:56-60.
- Criscito MC, Mu EW, Meehan SA, et al. Dermoscopic features of a solitary fibrofolliculoma on the left cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(2 suppl 1):S8-S9.
- Sattler EC, Steinlein OK. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Updated January 30, 2020. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1522
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Settipalli S, et al. Elastofibroma: an uncommon tumor revisited. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9:34-37. doi:10.4103/0974- 2077.178543
- Chandrasekar CR, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: an uncommon benign pseudotumour. Sarcoma. 2008;2008:756565. doi:10.1155/2008/756565
- Kwittken J. Papular elastosis. Cutis. 2000;66:81-83.
A 70-year-old woman with a history of osteoporosis and breast cancer presented for evaluation of asymptomatic, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules concentrated on the inferior occipital scalp and posterior neck (inset) for at least several months. She had no additional systemic signs or symptoms, and there was no family history of similar skin findings. A punch biopsy was performed.
Eating Disorder Risk Factors and the Impact of Obesity in Patients With Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic multisystemic inflammatory skin disease with a worldwide prevalence of 2% to 3%.1 Psoriasis can be accompanied by other conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and anxiety/depression. It is important to manage comorbidities of psoriasis in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of the disease.1
Obesity is a major public health concern worldwide. Numerous observational and epidemiologic studies have reported a high prevalence of obesity among patients with psoriasis.2 Current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate or worsen psoriasis; furthermore, it is important to note that obesity may negatively impact the effectiveness of psoriasis-specific treatments or increase the incidence of adverse effects. Therefore, managing obesity is crucial in the treatment of psoriasis.3 Numerous studies have investigated the association between psoriasis and obesity, and they commonly conclude that both conditions share the same genetic metabolic pathways.2-4 However, it is important to consider environmental factors such as dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle—all of which are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to the development of obesity.5 Because of the effects of obesity in psoriasis patients, factors that impact the development of obesity have become a popular research topic.
Eating disorders (EDs) are a crucial risk factor for both developing and maintaining obesity. In particular, two EDs that are associated with obesity include binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa.6 According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition,7 binge eating disorder can be diagnosed when a patient has at least 1 episode of binge eating per week over a 3-month period. Bulimia nervosa can be diagnosed when a patient is excessively concerned with their body weight and shape and engages in behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives).7 Psychiatrists who specialize in EDs make diagnoses based on these criteria. In daily practice, there are several quick and simple questionnaires available to screen for EDs that can be used by nonpsychiatrist physicians, including the commonly used 26-item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).8 The EAT-26 has been used to screen for EDs in patients with inflammatory disorders.9
The aim of this study was to screen for EDs in patients with psoriasis to identify potential risk factors for development of obesity.
Materials and Methods
This study included patients with psoriasis who were screened for EDs at a tertiary dermatology clinic in Turkey between January 2021 and December 2023. This study was approved by the local ethics committee and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (decision number E-93471371-514.99-225000079).
Study Design and Patient Inclusion Criteria—This quantitative cross-sectional study utilized EAT-26, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition (ASHN), and Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scores. All the questionnaire scales used in the study were adapted and validated in Turkey.8,10-12 The inclusion criteria consisted of being older than 18 years of age, being literate, having psoriasis for at least 1 year that was not treated topically or systemically, and having no psychiatric diseases outside an ED. The questionnaires were presented in written format following the clinical examination. Literacy was an inclusion criterion in this study due to the absence of auxiliary health personnel.
Study Variables—The study variables included age, sex, marital status (single/divorced or married), education status (primary/secondary school or high school/university), employment status (employed or unemployed/retired), body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol-consumption status, Psoriasis Area Severity Index score, presence of nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, duration of psoriasis, family history of psoriasis, EAT-26 score, ASHN score, DLQI score, and DASS-21 score. Body mass index was calculated by taking a participant’s weight in kilograms and dividing it by their height in meters squared. The BMI values were classified into 3 categories: normal (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).13
Questionnaires—The EAT-26 questionnaire includes 26 questions that are used to detect EDs. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “always,” “usually,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never.”) Patients with scores of 20 points or higher (range, 0–78) are classified as high risk for EDs.8 In our study, EAT-26 scores were grouped into 2 categories: patients scoring less than 20 points and those scoring 20 points or higher.
The DLQI questionnaire includes 10 questions to measure dermatologic symptoms and qualiy of life. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “not at all,” “a little,” “a lot,” or “very much.”) On the DLQI scale, the higher the score, the lower the quality of life (score range, 0–30).10
The ASHN questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure attitudes toward healthy nutrition with 5 possible answer options (“strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “undecided,” “agree,” and “strongly agree”). On this scale, higher scores indicate the participant is more knowledgeable about healthy nutrition (score range, 0–78).11
The DASS-21 questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure the severity of a range of symptoms common to depression, anxiety, and stress. Responses include Likert-type answer options (eg, “never,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “almost always.”) On this scale, a higher score (range of 0–21 for each) indicates higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress.12
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were analyzed using SPSS software version 22.0 (IBM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to determine whether the data were normally distributed. For categorical variables, frequency differences among groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test. A t test was used to compare the means of 2 independent groups with a normal distribution. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey Honest Significant Difference post hoc analysis were used to test whether there was a statistically significant difference among the normally distributed means of independent groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine whether there was a linear relationship between 2 numeric measurements and, if so, to determine the direction and severity of this relationship. P<.05 indicated statistical significance in this study.
Results
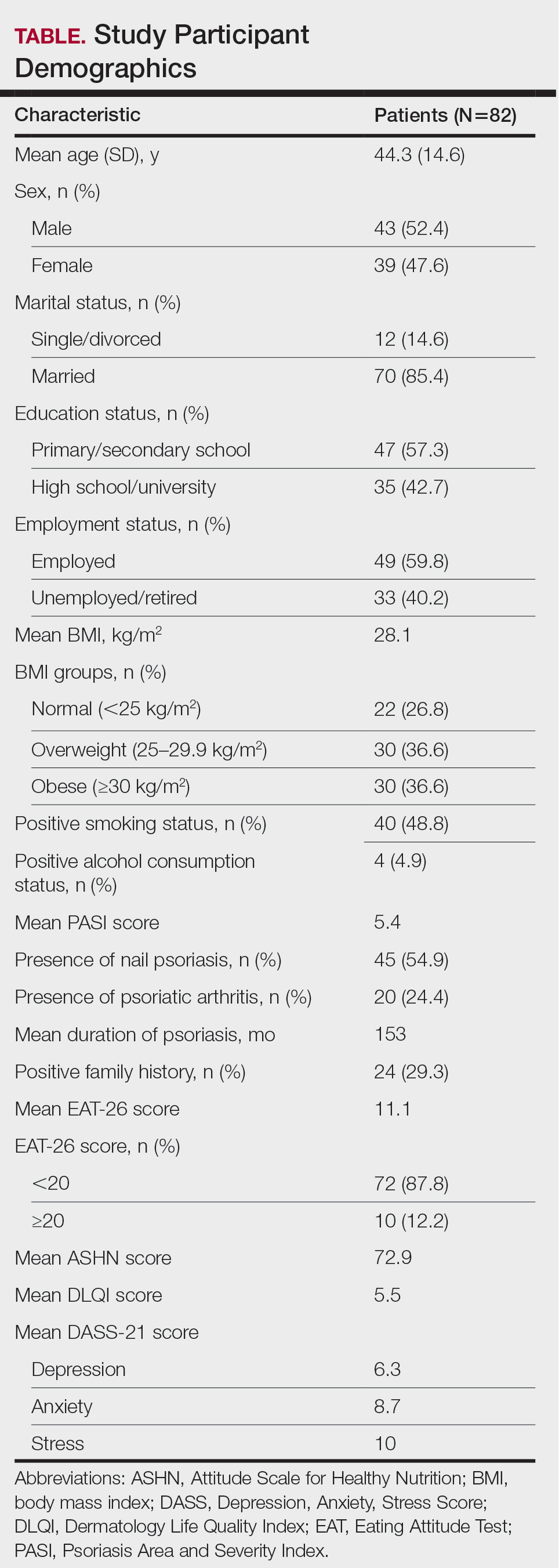
Study Participant Demographics—This study included 82 participants with a mean age of 44.3 years; 52.4% (43/82) were female, and 85.4% (70/82) were married. The questionnaire took an average of 4.2 minutes for participants to complete. A total of 57.3% (47/82) of patients had completed primary/secondary education and 59.8% (49/82) were employed. The mean BMI was 28.1 kg/m2. According to the BMI classification, 26.8% (22/82) participants had a normal weight, 36.6% (30/82) were overweight, and 43.9% (36/82) were obese. A total of 48.8% (40/82) of participants smoked, and 4.9% (4/82) consumed alcohol. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was 5.4. A total of 54.9% (45/82) of participants had nail psoriasis, and 24.4% (20/82) had psoriatic arthritis. The mean duration of psoriasis was 153 months. A total of 29.3% (24/82) of participants had a positive family history of psoriasis. The mean EAT-26 score was 11.1. A total of 12.2% (10/82) of participants had an EAT-26 score of 20 points or higher and were considered at high risk for an ED. The mean ASHN score was 72.9; the mean DLQI score was 5.5; and on the DASS-21 scale, mean scores for depression, anxiety, and stress were 6.3, 8.7, and 10.0, respectively (Table).
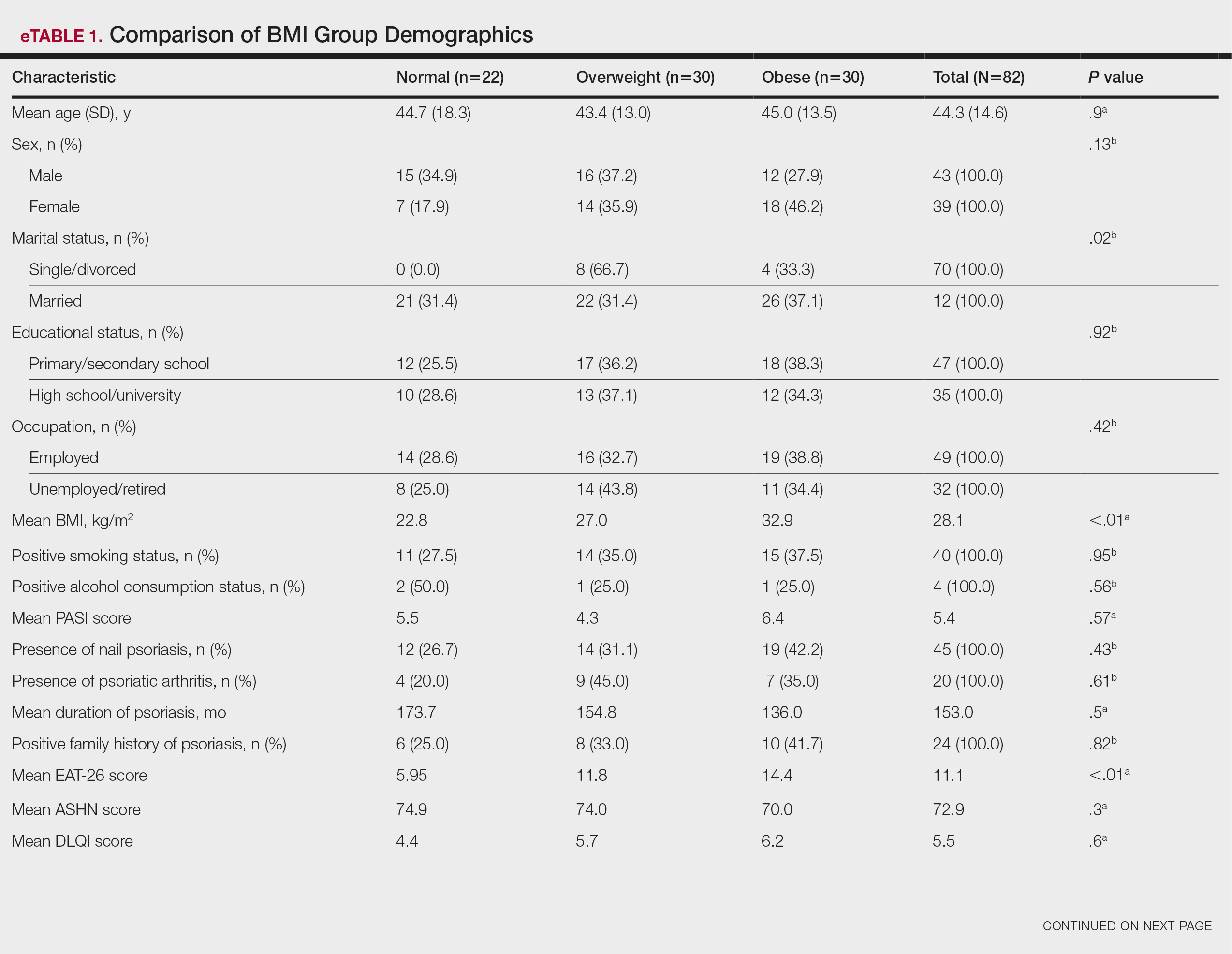
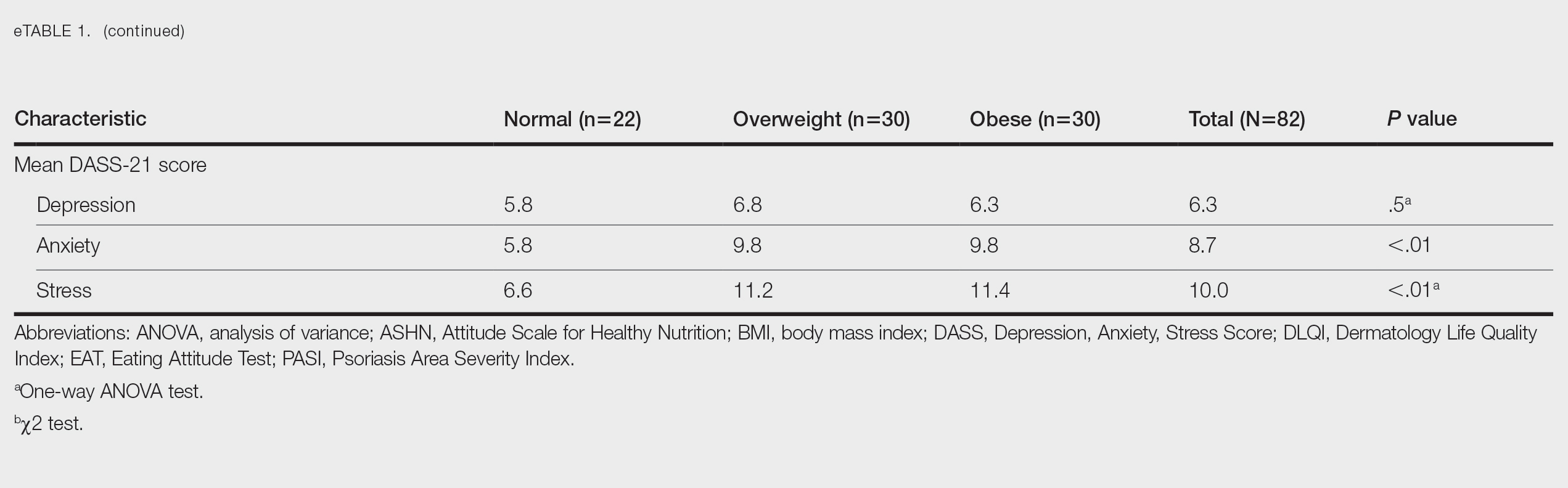
Comparative Evaluation of the BMI Groups—The only statistically significant differences among the 3 BMI groups were related to marital status, EAT-26 score, and anxiety and stress scores (P=.02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively)(eTable 1). The number of single/divorced participants in the overweight group was significantly (P=.02) greater than in the normal weight group. The mean EAT-26 score for the normal weight group was significantly (P<.01) lower than for the overweight and obese groups; there was no significant difference in mean EAT-26 scores between the overweight and obese groups. The mean anxiety score was significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group compared with the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean depression score. The mean stress and anxiety scores were significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group than in the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean anxiety score.
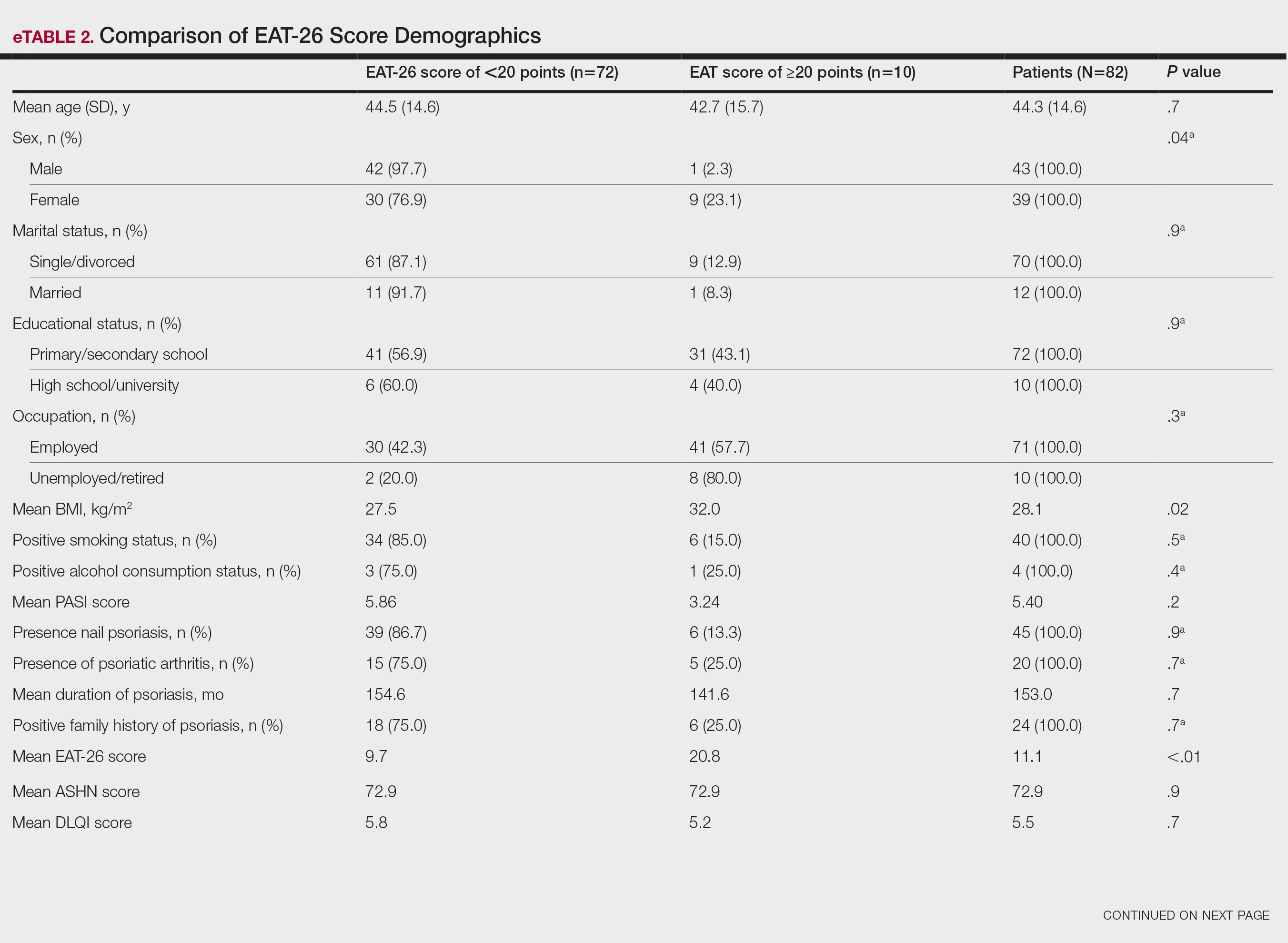
Comparative Evaluation of the EAT-26 Scores—There were statistically significant differences among the EAT-26 scores related to sex; BMI; and depression, anxiety, and stress scores (P=.04, .02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively). The number of females in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.04) less than that in the group scoring less than 20 points. The mean BMI in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.02) greater than in group scoring less than 20 points. The mean depression, anxiety, and stress scores of the group scoring 20 points or higher were significantly (P<.01 for all) greater than in the group scoring less than 20 points (eTable 2).
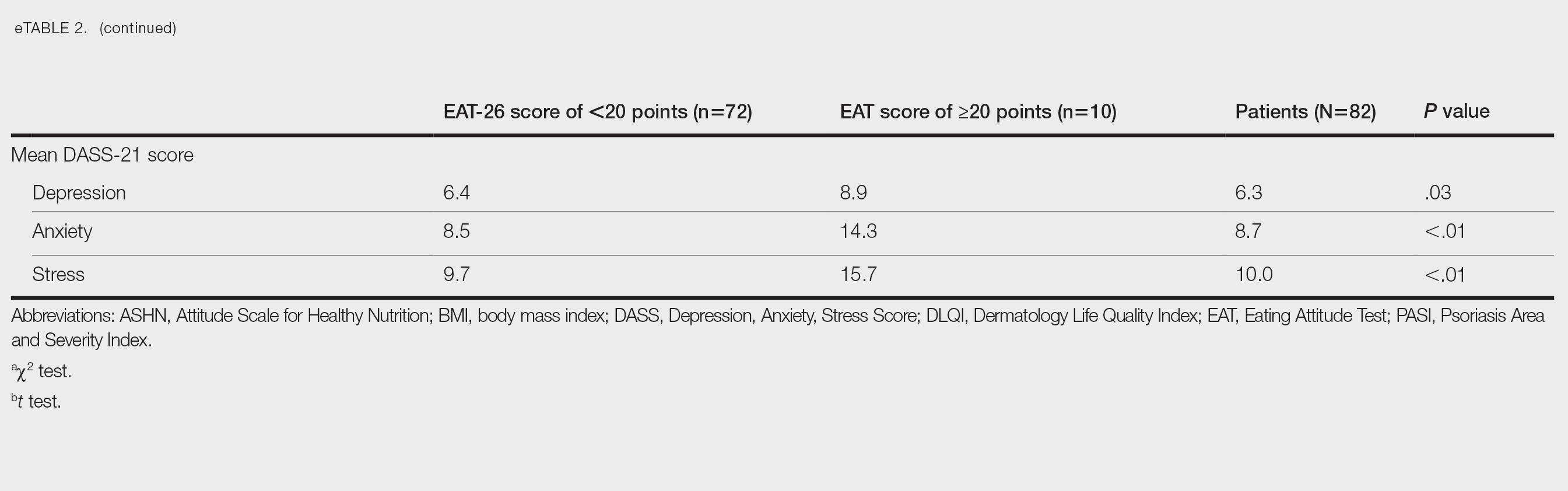
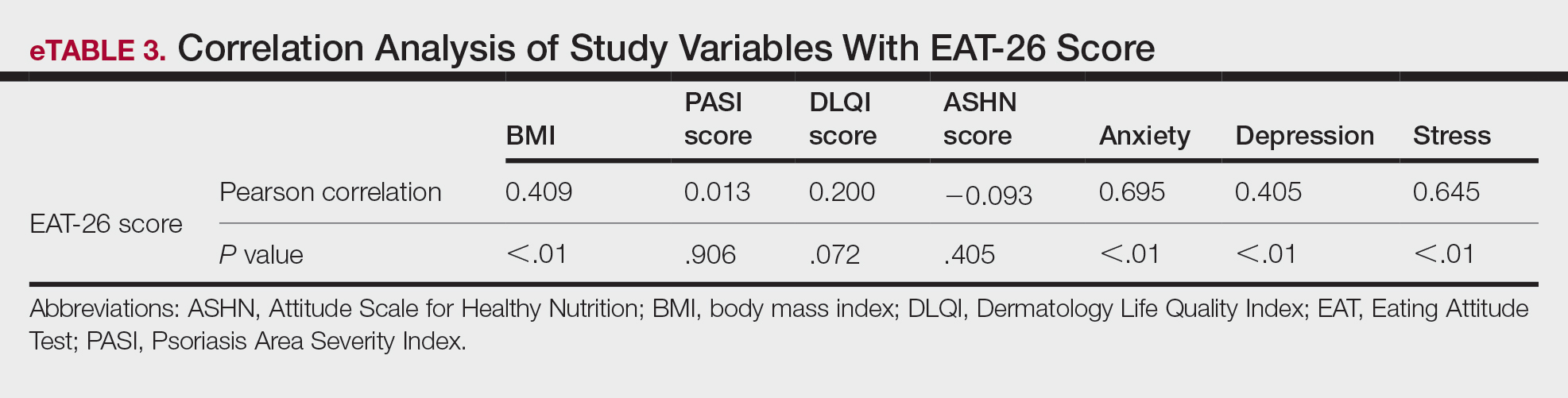
Correlation Analysis of the Study Variables—The EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress (P<.01 for all)(eTable 3).
Comment
Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach. Nonpsychiatric medical departments may be involved due to the severe consequences (eg, various skin changes14) of these disorders. Psoriasis is not known to be directly affected by the presence of an ED; however, it is possible that EDs could indirectly affect patients with psoriasis by influencing obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between ED risk factors and obesity in this population.
The relationship between psoriasis and obesity has been a popular research topic in dermatology since the 1990s.15 Epidemiologic and observational studies have reported that patients with psoriasis are more likely to be overweight or have obesity, which is an independent risk factor for psoriasis.3,16 However, the causal relationship between psoriasis and obesity remains unclear. In a comprehensive review, Barros et al17 emphasized the causal relationship between obesity and psoriasis under several headings. Firstly, a higher BMI increases the risk for psoriasis by promoting cytokine release and immune system dysregulation. Secondly, a Western diet (eg, processed foods and fast food) triggers obesity and psoriasis by increasing adipose tissue. Thirdly, the alteration of the skin and gut microbiota triggers chronic inflammation as a result of bacterial translocation in patients with obesity. Fourthly, a high-fat diet and palmitic acid disrupt the intestinal integrity of the gut and increase the risk for psoriasis and obesity by triggering chronic inflammation of bacterial fragments that pass into the blood. Finally, the decrease in the amount of adiponectin and the increase in the amount of leptin in patients with obesity may cause psoriasis by increasing proinflammatory cytokines, which are similar to those involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.17 Additionally, psoriatic inflammation can cause insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, leading to obesity.18 The relationship between psoriasis and obesity cannot be solely explained by metabolic pathways. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle all are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to obesity.5 Our study revealed no significant difference in smoking or alcohol consumption between the normal weight and overweight/obesity groups. Based on our data, we determined that smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect obesity in our patients with psoriasis.
Observational and epidemiologic studies have shown that patients with psoriasis experience increased rates of depression, anxiety, and stress.19 In studies of pathogenesis, a connection between depression and psoriatic inflammation has been established.20 It is known that inflammatory cytokines similar to those in psoriasis are involved in the development of obesity.18 In addition, depression and anxiety can lead to binge eating, unhealthy food choices, and a more sedentary lifestyle.5 All of these variables may contribute to the associations between depression and anxiety with psoriasis and obesity. Zafiriou et al21 conducted a study to investigate the relationship between psoriasis, obesity, and depression through inflammatory pathways with a focus on the importance of IL-17. Data showing that IL-17–producing Th17-cell subgroups play a considerable role in the development of obesity and depression prompted the authors to suggest that psoriasis, obesity, and anxiety/depression may be interconnected manifestations of immune dysregulation, potentially linked to IL-17 and its associated cells.21 Mrowietz et al22 also suggested that metabolic inflammation may contribute to obesity and depression in patients with psoriasis and highlighted the importance of several cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-23. Our study revealed no significant differences in depression scores between BMI groups. Another meta-analysis reported conflicting findings on the incidence of depression in obese patients with psoriasis.23 Some of the studies had a small number of participants. Compared to depression, anxiety has received less attention in studies of patients with obesity with psoriasis. However, these studies have shown a positive correlation between anxiety scores and BMI in patients with psoriasis.24,25 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, overweight patients and those with obesitywho have psoriasis had significantly (P<.01) greater anxiety and stress scores than did normal weight patients with psoriasis.
Obesity should be assessed in patients with psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that takes into account genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.26 Eating disorders are considered to be one of the factors contributing to obesity. Numerous studies in the literature have demonstrated a greater incidence of EDs in patients with obesity vs those without obesity.5,6,27 Obesity and EDs have a bidirectional relationship: individuals with obesity are at risk for EDs due to body dissatisfaction, dieting habits, and depressive states. Conversely, poor eating behaviors in individuals with a normal weight can lead to obesity.28
There are few studies in the literature exploring the relationship between psoriasis and EDs. Crosta et al29 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis had impaired results on ED screening tests and that these scores deteriorated further as BMI increased. Moreover, Altunay et al30 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome had higher scores on the ED screening test. In this study, patients with higher scores also exhibited high levels of anxiety.30 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity had significantly (P<.01) greater EAT-26 scores than those in the normal weight group. Patients with high EAT-26 scores also exhibited elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress scores. Our study as well as other studies in the literature indicate that additional research is needed to determine the associations between EDs and obesity in psoriasis.
Conclusion
Managing obesity is crucial for patients with psoriasis. This study showed that EAT-26 scores were higher in patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity than in those who were normal weight. Participants with high EAT-26 scores (≥20 points) were more likely to be female and have higher anxiety and stress scores. In addition, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI as well as depression, anxiety, and stress scores. Eating disorders may contribute to the development of obesity in patients with psoriasis. Although our study was limited by a small sample size, the results suggest that there is a need for large-scale multicenter studies to investigate the relationship between psoriasis and EDs.
- Kalkan G. Comorbidities in psoriasis: the recognition of psoriasis as a systemic disease and current management. Turkderm-Turk Arch Dermatol Venereol. 2017;51:71-77.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Mirghani H, Altemani AT, Altemani ST, et al. The cross talk between psoriasis, obesity, and dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2023;15:e49253.
- Roehring M, Mashep MR, White MA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and behavioral correlates in obese patients with binge disorders. Obesity. 2009;17:481-486.
- da Luz FQ, Hay P, Touyz S, et al. Obesity with comorbid eating disorders: associated health risks and treatment approaches. Nutrients. 2018;10:829.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Ergüney Okumus¸ FE, Sertel Berk HÖ. The psychometric properties of the Eating Attitudes Test short form (EAT-26) in a college sample. Stud Psychol. 2020;40:57-78.
- Stoleru G, Leopold A, Auerbach A, et al. Female gender, dissatisfaction with weight, and number of IBD related surgeries as independent risk factors for eating disorders among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:438.
- Öztürkcan S, Ermertcan AT, Eser E, et al. Cross validation of the Turkish version of dermatology life quality index. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1300-1307.
- Demir GT, Ciciog˘lu HI˙. Attitude scale for healthy nutrition (ASHN): validity and reliability study. Gaziantep Univ J Sport Sci. 2019;4:256-274.
- Yılmaz O, Boz H, Arslan A. The validity and reliability of depression stress and anxiety scale (DASS 21) Turkish short form. Res Financial Econ Soc Stud. 2017;2:78-91.
- Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50:117-128.
- Strumia R, Manzata E, Gualandi M. Is there a role for dermatologists in eating disorders? Expert Rev Dermatol. 2017; 2:109-112.
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Disease concomitance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:982-986.
- Naldi L, Addis A, Chimenti S, et al. Impact of body mass index and obesity on clinical response to systemic treatment for psoriasis. evidence from the Psocare project. Dermatology. 2008;217:365-373.
- Barros G, Duran P, Vera I, et al. Exploring the links between obesity and psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7499.
- Hao Y, Zhu YJ, Zou S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: mechanisms and future directions. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711060.
- Jing D, Xiao H, Shen M, et al. Association of psoriasis with anxiety and depression: a case–control study in Chinese patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:771645.
- Sahi FM, Masood A, Danawar NA, et al. Association between psoriasis and depression: a traditional review. Cureus. 2020;12:E9708.
- Zafiriou E, Daponte AI, Siokas V, et al. Depression and obesity in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: is IL-17–mediated immune dysregulation the connecting link? Front Immunol. 2021;12:699848.
- Mrowietz U, Sümbül M, Gerdes S. Depression, a major comorbidity of psoriatic disease, is caused by metabolic inflammation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1731-1738.
- Pavlova NT, Kioskli K, Smith C, et al. Psychosocial aspects of obesity in adults with psoriasis: a systematic review. Skin Health Dis. 2021;1:E33.
- Innamorati M, Quinto RM, Imperatori C, et al. Health-related quality of life and its association with alexithymia and difficulties in emotion regulation in patients with psoriasis. Compr Psychiatry. 2016;70:200-208.
- Tabolli S, Naldi L, Pagliarello C, et al. Evaluation of the impact of writing exercises interventions on quality of life in patients with psoriasis undergoing systemic treatments. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1254‐1264.
- Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, et al. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull. 2017;123:159‐173.
- Balantekin KN, Grammer AC, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, et al. Overweight and obesity are associated with increased eating disorder correlates and general psychopathology in university women with eating disorders. Eat Behav. 2021;41:101482.
- Jebeile H, Lister NB, Baur LA, et al. Eating disorder risk in adolescents with obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22:E13173.
- Crosta ML, Caldarola G, Fraietta S, et al. Psychopathology and eating disorders in patients with psoriasis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014;149:355-361.
- Altunay I, Demirci GT, Ates B, et al. Do eating disorders accompany metabolic syndrome in psoriasis patients? results of a preliminary study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2011;4:139-143.
Psoriasis is a chronic multisystemic inflammatory skin disease with a worldwide prevalence of 2% to 3%.1 Psoriasis can be accompanied by other conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and anxiety/depression. It is important to manage comorbidities of psoriasis in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of the disease.1
Obesity is a major public health concern worldwide. Numerous observational and epidemiologic studies have reported a high prevalence of obesity among patients with psoriasis.2 Current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate or worsen psoriasis; furthermore, it is important to note that obesity may negatively impact the effectiveness of psoriasis-specific treatments or increase the incidence of adverse effects. Therefore, managing obesity is crucial in the treatment of psoriasis.3 Numerous studies have investigated the association between psoriasis and obesity, and they commonly conclude that both conditions share the same genetic metabolic pathways.2-4 However, it is important to consider environmental factors such as dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle—all of which are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to the development of obesity.5 Because of the effects of obesity in psoriasis patients, factors that impact the development of obesity have become a popular research topic.
Eating disorders (EDs) are a crucial risk factor for both developing and maintaining obesity. In particular, two EDs that are associated with obesity include binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa.6 According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition,7 binge eating disorder can be diagnosed when a patient has at least 1 episode of binge eating per week over a 3-month period. Bulimia nervosa can be diagnosed when a patient is excessively concerned with their body weight and shape and engages in behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives).7 Psychiatrists who specialize in EDs make diagnoses based on these criteria. In daily practice, there are several quick and simple questionnaires available to screen for EDs that can be used by nonpsychiatrist physicians, including the commonly used 26-item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).8 The EAT-26 has been used to screen for EDs in patients with inflammatory disorders.9
The aim of this study was to screen for EDs in patients with psoriasis to identify potential risk factors for development of obesity.
Materials and Methods
This study included patients with psoriasis who were screened for EDs at a tertiary dermatology clinic in Turkey between January 2021 and December 2023. This study was approved by the local ethics committee and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (decision number E-93471371-514.99-225000079).
Study Design and Patient Inclusion Criteria—This quantitative cross-sectional study utilized EAT-26, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition (ASHN), and Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scores. All the questionnaire scales used in the study were adapted and validated in Turkey.8,10-12 The inclusion criteria consisted of being older than 18 years of age, being literate, having psoriasis for at least 1 year that was not treated topically or systemically, and having no psychiatric diseases outside an ED. The questionnaires were presented in written format following the clinical examination. Literacy was an inclusion criterion in this study due to the absence of auxiliary health personnel.
Study Variables—The study variables included age, sex, marital status (single/divorced or married), education status (primary/secondary school or high school/university), employment status (employed or unemployed/retired), body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol-consumption status, Psoriasis Area Severity Index score, presence of nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, duration of psoriasis, family history of psoriasis, EAT-26 score, ASHN score, DLQI score, and DASS-21 score. Body mass index was calculated by taking a participant’s weight in kilograms and dividing it by their height in meters squared. The BMI values were classified into 3 categories: normal (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).13
Questionnaires—The EAT-26 questionnaire includes 26 questions that are used to detect EDs. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “always,” “usually,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never.”) Patients with scores of 20 points or higher (range, 0–78) are classified as high risk for EDs.8 In our study, EAT-26 scores were grouped into 2 categories: patients scoring less than 20 points and those scoring 20 points or higher.
The DLQI questionnaire includes 10 questions to measure dermatologic symptoms and qualiy of life. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “not at all,” “a little,” “a lot,” or “very much.”) On the DLQI scale, the higher the score, the lower the quality of life (score range, 0–30).10
The ASHN questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure attitudes toward healthy nutrition with 5 possible answer options (“strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “undecided,” “agree,” and “strongly agree”). On this scale, higher scores indicate the participant is more knowledgeable about healthy nutrition (score range, 0–78).11
The DASS-21 questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure the severity of a range of symptoms common to depression, anxiety, and stress. Responses include Likert-type answer options (eg, “never,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “almost always.”) On this scale, a higher score (range of 0–21 for each) indicates higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress.12
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were analyzed using SPSS software version 22.0 (IBM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to determine whether the data were normally distributed. For categorical variables, frequency differences among groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test. A t test was used to compare the means of 2 independent groups with a normal distribution. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey Honest Significant Difference post hoc analysis were used to test whether there was a statistically significant difference among the normally distributed means of independent groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine whether there was a linear relationship between 2 numeric measurements and, if so, to determine the direction and severity of this relationship. P<.05 indicated statistical significance in this study.
Results
Study Participant Demographics—This study included 82 participants with a mean age of 44.3 years; 52.4% (43/82) were female, and 85.4% (70/82) were married. The questionnaire took an average of 4.2 minutes for participants to complete. A total of 57.3% (47/82) of patients had completed primary/secondary education and 59.8% (49/82) were employed. The mean BMI was 28.1 kg/m2. According to the BMI classification, 26.8% (22/82) participants had a normal weight, 36.6% (30/82) were overweight, and 43.9% (36/82) were obese. A total of 48.8% (40/82) of participants smoked, and 4.9% (4/82) consumed alcohol. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was 5.4. A total of 54.9% (45/82) of participants had nail psoriasis, and 24.4% (20/82) had psoriatic arthritis. The mean duration of psoriasis was 153 months. A total of 29.3% (24/82) of participants had a positive family history of psoriasis. The mean EAT-26 score was 11.1. A total of 12.2% (10/82) of participants had an EAT-26 score of 20 points or higher and were considered at high risk for an ED. The mean ASHN score was 72.9; the mean DLQI score was 5.5; and on the DASS-21 scale, mean scores for depression, anxiety, and stress were 6.3, 8.7, and 10.0, respectively (Table).

Comparative Evaluation of the BMI Groups—The only statistically significant differences among the 3 BMI groups were related to marital status, EAT-26 score, and anxiety and stress scores (P=.02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively)(eTable 1). The number of single/divorced participants in the overweight group was significantly (P=.02) greater than in the normal weight group. The mean EAT-26 score for the normal weight group was significantly (P<.01) lower than for the overweight and obese groups; there was no significant difference in mean EAT-26 scores between the overweight and obese groups. The mean anxiety score was significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group compared with the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean depression score. The mean stress and anxiety scores were significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group than in the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean anxiety score.


Comparative Evaluation of the EAT-26 Scores—There were statistically significant differences among the EAT-26 scores related to sex; BMI; and depression, anxiety, and stress scores (P=.04, .02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively). The number of females in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.04) less than that in the group scoring less than 20 points. The mean BMI in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.02) greater than in group scoring less than 20 points. The mean depression, anxiety, and stress scores of the group scoring 20 points or higher were significantly (P<.01 for all) greater than in the group scoring less than 20 points (eTable 2).


Correlation Analysis of the Study Variables—The EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress (P<.01 for all)(eTable 3).

Comment
Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach. Nonpsychiatric medical departments may be involved due to the severe consequences (eg, various skin changes14) of these disorders. Psoriasis is not known to be directly affected by the presence of an ED; however, it is possible that EDs could indirectly affect patients with psoriasis by influencing obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between ED risk factors and obesity in this population.
The relationship between psoriasis and obesity has been a popular research topic in dermatology since the 1990s.15 Epidemiologic and observational studies have reported that patients with psoriasis are more likely to be overweight or have obesity, which is an independent risk factor for psoriasis.3,16 However, the causal relationship between psoriasis and obesity remains unclear. In a comprehensive review, Barros et al17 emphasized the causal relationship between obesity and psoriasis under several headings. Firstly, a higher BMI increases the risk for psoriasis by promoting cytokine release and immune system dysregulation. Secondly, a Western diet (eg, processed foods and fast food) triggers obesity and psoriasis by increasing adipose tissue. Thirdly, the alteration of the skin and gut microbiota triggers chronic inflammation as a result of bacterial translocation in patients with obesity. Fourthly, a high-fat diet and palmitic acid disrupt the intestinal integrity of the gut and increase the risk for psoriasis and obesity by triggering chronic inflammation of bacterial fragments that pass into the blood. Finally, the decrease in the amount of adiponectin and the increase in the amount of leptin in patients with obesity may cause psoriasis by increasing proinflammatory cytokines, which are similar to those involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.17 Additionally, psoriatic inflammation can cause insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, leading to obesity.18 The relationship between psoriasis and obesity cannot be solely explained by metabolic pathways. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle all are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to obesity.5 Our study revealed no significant difference in smoking or alcohol consumption between the normal weight and overweight/obesity groups. Based on our data, we determined that smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect obesity in our patients with psoriasis.
Observational and epidemiologic studies have shown that patients with psoriasis experience increased rates of depression, anxiety, and stress.19 In studies of pathogenesis, a connection between depression and psoriatic inflammation has been established.20 It is known that inflammatory cytokines similar to those in psoriasis are involved in the development of obesity.18 In addition, depression and anxiety can lead to binge eating, unhealthy food choices, and a more sedentary lifestyle.5 All of these variables may contribute to the associations between depression and anxiety with psoriasis and obesity. Zafiriou et al21 conducted a study to investigate the relationship between psoriasis, obesity, and depression through inflammatory pathways with a focus on the importance of IL-17. Data showing that IL-17–producing Th17-cell subgroups play a considerable role in the development of obesity and depression prompted the authors to suggest that psoriasis, obesity, and anxiety/depression may be interconnected manifestations of immune dysregulation, potentially linked to IL-17 and its associated cells.21 Mrowietz et al22 also suggested that metabolic inflammation may contribute to obesity and depression in patients with psoriasis and highlighted the importance of several cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-23. Our study revealed no significant differences in depression scores between BMI groups. Another meta-analysis reported conflicting findings on the incidence of depression in obese patients with psoriasis.23 Some of the studies had a small number of participants. Compared to depression, anxiety has received less attention in studies of patients with obesity with psoriasis. However, these studies have shown a positive correlation between anxiety scores and BMI in patients with psoriasis.24,25 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, overweight patients and those with obesitywho have psoriasis had significantly (P<.01) greater anxiety and stress scores than did normal weight patients with psoriasis.
Obesity should be assessed in patients with psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that takes into account genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.26 Eating disorders are considered to be one of the factors contributing to obesity. Numerous studies in the literature have demonstrated a greater incidence of EDs in patients with obesity vs those without obesity.5,6,27 Obesity and EDs have a bidirectional relationship: individuals with obesity are at risk for EDs due to body dissatisfaction, dieting habits, and depressive states. Conversely, poor eating behaviors in individuals with a normal weight can lead to obesity.28
There are few studies in the literature exploring the relationship between psoriasis and EDs. Crosta et al29 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis had impaired results on ED screening tests and that these scores deteriorated further as BMI increased. Moreover, Altunay et al30 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome had higher scores on the ED screening test. In this study, patients with higher scores also exhibited high levels of anxiety.30 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity had significantly (P<.01) greater EAT-26 scores than those in the normal weight group. Patients with high EAT-26 scores also exhibited elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress scores. Our study as well as other studies in the literature indicate that additional research is needed to determine the associations between EDs and obesity in psoriasis.
Conclusion
Managing obesity is crucial for patients with psoriasis. This study showed that EAT-26 scores were higher in patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity than in those who were normal weight. Participants with high EAT-26 scores (≥20 points) were more likely to be female and have higher anxiety and stress scores. In addition, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI as well as depression, anxiety, and stress scores. Eating disorders may contribute to the development of obesity in patients with psoriasis. Although our study was limited by a small sample size, the results suggest that there is a need for large-scale multicenter studies to investigate the relationship between psoriasis and EDs.
Psoriasis is a chronic multisystemic inflammatory skin disease with a worldwide prevalence of 2% to 3%.1 Psoriasis can be accompanied by other conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and anxiety/depression. It is important to manage comorbidities of psoriasis in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of the disease.1
Obesity is a major public health concern worldwide. Numerous observational and epidemiologic studies have reported a high prevalence of obesity among patients with psoriasis.2 Current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate or worsen psoriasis; furthermore, it is important to note that obesity may negatively impact the effectiveness of psoriasis-specific treatments or increase the incidence of adverse effects. Therefore, managing obesity is crucial in the treatment of psoriasis.3 Numerous studies have investigated the association between psoriasis and obesity, and they commonly conclude that both conditions share the same genetic metabolic pathways.2-4 However, it is important to consider environmental factors such as dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle—all of which are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to the development of obesity.5 Because of the effects of obesity in psoriasis patients, factors that impact the development of obesity have become a popular research topic.
Eating disorders (EDs) are a crucial risk factor for both developing and maintaining obesity. In particular, two EDs that are associated with obesity include binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa.6 According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition,7 binge eating disorder can be diagnosed when a patient has at least 1 episode of binge eating per week over a 3-month period. Bulimia nervosa can be diagnosed when a patient is excessively concerned with their body weight and shape and engages in behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives).7 Psychiatrists who specialize in EDs make diagnoses based on these criteria. In daily practice, there are several quick and simple questionnaires available to screen for EDs that can be used by nonpsychiatrist physicians, including the commonly used 26-item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).8 The EAT-26 has been used to screen for EDs in patients with inflammatory disorders.9
The aim of this study was to screen for EDs in patients with psoriasis to identify potential risk factors for development of obesity.
Materials and Methods
This study included patients with psoriasis who were screened for EDs at a tertiary dermatology clinic in Turkey between January 2021 and December 2023. This study was approved by the local ethics committee and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (decision number E-93471371-514.99-225000079).
Study Design and Patient Inclusion Criteria—This quantitative cross-sectional study utilized EAT-26, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition (ASHN), and Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scores. All the questionnaire scales used in the study were adapted and validated in Turkey.8,10-12 The inclusion criteria consisted of being older than 18 years of age, being literate, having psoriasis for at least 1 year that was not treated topically or systemically, and having no psychiatric diseases outside an ED. The questionnaires were presented in written format following the clinical examination. Literacy was an inclusion criterion in this study due to the absence of auxiliary health personnel.
Study Variables—The study variables included age, sex, marital status (single/divorced or married), education status (primary/secondary school or high school/university), employment status (employed or unemployed/retired), body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol-consumption status, Psoriasis Area Severity Index score, presence of nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, duration of psoriasis, family history of psoriasis, EAT-26 score, ASHN score, DLQI score, and DASS-21 score. Body mass index was calculated by taking a participant’s weight in kilograms and dividing it by their height in meters squared. The BMI values were classified into 3 categories: normal (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).13
Questionnaires—The EAT-26 questionnaire includes 26 questions that are used to detect EDs. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “always,” “usually,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never.”) Patients with scores of 20 points or higher (range, 0–78) are classified as high risk for EDs.8 In our study, EAT-26 scores were grouped into 2 categories: patients scoring less than 20 points and those scoring 20 points or higher.
The DLQI questionnaire includes 10 questions to measure dermatologic symptoms and qualiy of life. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “not at all,” “a little,” “a lot,” or “very much.”) On the DLQI scale, the higher the score, the lower the quality of life (score range, 0–30).10
The ASHN questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure attitudes toward healthy nutrition with 5 possible answer options (“strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “undecided,” “agree,” and “strongly agree”). On this scale, higher scores indicate the participant is more knowledgeable about healthy nutrition (score range, 0–78).11
The DASS-21 questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure the severity of a range of symptoms common to depression, anxiety, and stress. Responses include Likert-type answer options (eg, “never,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “almost always.”) On this scale, a higher score (range of 0–21 for each) indicates higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress.12
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were analyzed using SPSS software version 22.0 (IBM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to determine whether the data were normally distributed. For categorical variables, frequency differences among groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test. A t test was used to compare the means of 2 independent groups with a normal distribution. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey Honest Significant Difference post hoc analysis were used to test whether there was a statistically significant difference among the normally distributed means of independent groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine whether there was a linear relationship between 2 numeric measurements and, if so, to determine the direction and severity of this relationship. P<.05 indicated statistical significance in this study.
Results
Study Participant Demographics—This study included 82 participants with a mean age of 44.3 years; 52.4% (43/82) were female, and 85.4% (70/82) were married. The questionnaire took an average of 4.2 minutes for participants to complete. A total of 57.3% (47/82) of patients had completed primary/secondary education and 59.8% (49/82) were employed. The mean BMI was 28.1 kg/m2. According to the BMI classification, 26.8% (22/82) participants had a normal weight, 36.6% (30/82) were overweight, and 43.9% (36/82) were obese. A total of 48.8% (40/82) of participants smoked, and 4.9% (4/82) consumed alcohol. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was 5.4. A total of 54.9% (45/82) of participants had nail psoriasis, and 24.4% (20/82) had psoriatic arthritis. The mean duration of psoriasis was 153 months. A total of 29.3% (24/82) of participants had a positive family history of psoriasis. The mean EAT-26 score was 11.1. A total of 12.2% (10/82) of participants had an EAT-26 score of 20 points or higher and were considered at high risk for an ED. The mean ASHN score was 72.9; the mean DLQI score was 5.5; and on the DASS-21 scale, mean scores for depression, anxiety, and stress were 6.3, 8.7, and 10.0, respectively (Table).

Comparative Evaluation of the BMI Groups—The only statistically significant differences among the 3 BMI groups were related to marital status, EAT-26 score, and anxiety and stress scores (P=.02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively)(eTable 1). The number of single/divorced participants in the overweight group was significantly (P=.02) greater than in the normal weight group. The mean EAT-26 score for the normal weight group was significantly (P<.01) lower than for the overweight and obese groups; there was no significant difference in mean EAT-26 scores between the overweight and obese groups. The mean anxiety score was significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group compared with the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean depression score. The mean stress and anxiety scores were significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group than in the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean anxiety score.


Comparative Evaluation of the EAT-26 Scores—There were statistically significant differences among the EAT-26 scores related to sex; BMI; and depression, anxiety, and stress scores (P=.04, .02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively). The number of females in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.04) less than that in the group scoring less than 20 points. The mean BMI in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.02) greater than in group scoring less than 20 points. The mean depression, anxiety, and stress scores of the group scoring 20 points or higher were significantly (P<.01 for all) greater than in the group scoring less than 20 points (eTable 2).


Correlation Analysis of the Study Variables—The EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress (P<.01 for all)(eTable 3).

Comment
Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach. Nonpsychiatric medical departments may be involved due to the severe consequences (eg, various skin changes14) of these disorders. Psoriasis is not known to be directly affected by the presence of an ED; however, it is possible that EDs could indirectly affect patients with psoriasis by influencing obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between ED risk factors and obesity in this population.
The relationship between psoriasis and obesity has been a popular research topic in dermatology since the 1990s.15 Epidemiologic and observational studies have reported that patients with psoriasis are more likely to be overweight or have obesity, which is an independent risk factor for psoriasis.3,16 However, the causal relationship between psoriasis and obesity remains unclear. In a comprehensive review, Barros et al17 emphasized the causal relationship between obesity and psoriasis under several headings. Firstly, a higher BMI increases the risk for psoriasis by promoting cytokine release and immune system dysregulation. Secondly, a Western diet (eg, processed foods and fast food) triggers obesity and psoriasis by increasing adipose tissue. Thirdly, the alteration of the skin and gut microbiota triggers chronic inflammation as a result of bacterial translocation in patients with obesity. Fourthly, a high-fat diet and palmitic acid disrupt the intestinal integrity of the gut and increase the risk for psoriasis and obesity by triggering chronic inflammation of bacterial fragments that pass into the blood. Finally, the decrease in the amount of adiponectin and the increase in the amount of leptin in patients with obesity may cause psoriasis by increasing proinflammatory cytokines, which are similar to those involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.17 Additionally, psoriatic inflammation can cause insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, leading to obesity.18 The relationship between psoriasis and obesity cannot be solely explained by metabolic pathways. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle all are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to obesity.5 Our study revealed no significant difference in smoking or alcohol consumption between the normal weight and overweight/obesity groups. Based on our data, we determined that smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect obesity in our patients with psoriasis.
Observational and epidemiologic studies have shown that patients with psoriasis experience increased rates of depression, anxiety, and stress.19 In studies of pathogenesis, a connection between depression and psoriatic inflammation has been established.20 It is known that inflammatory cytokines similar to those in psoriasis are involved in the development of obesity.18 In addition, depression and anxiety can lead to binge eating, unhealthy food choices, and a more sedentary lifestyle.5 All of these variables may contribute to the associations between depression and anxiety with psoriasis and obesity. Zafiriou et al21 conducted a study to investigate the relationship between psoriasis, obesity, and depression through inflammatory pathways with a focus on the importance of IL-17. Data showing that IL-17–producing Th17-cell subgroups play a considerable role in the development of obesity and depression prompted the authors to suggest that psoriasis, obesity, and anxiety/depression may be interconnected manifestations of immune dysregulation, potentially linked to IL-17 and its associated cells.21 Mrowietz et al22 also suggested that metabolic inflammation may contribute to obesity and depression in patients with psoriasis and highlighted the importance of several cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-23. Our study revealed no significant differences in depression scores between BMI groups. Another meta-analysis reported conflicting findings on the incidence of depression in obese patients with psoriasis.23 Some of the studies had a small number of participants. Compared to depression, anxiety has received less attention in studies of patients with obesity with psoriasis. However, these studies have shown a positive correlation between anxiety scores and BMI in patients with psoriasis.24,25 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, overweight patients and those with obesitywho have psoriasis had significantly (P<.01) greater anxiety and stress scores than did normal weight patients with psoriasis.
Obesity should be assessed in patients with psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that takes into account genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.26 Eating disorders are considered to be one of the factors contributing to obesity. Numerous studies in the literature have demonstrated a greater incidence of EDs in patients with obesity vs those without obesity.5,6,27 Obesity and EDs have a bidirectional relationship: individuals with obesity are at risk for EDs due to body dissatisfaction, dieting habits, and depressive states. Conversely, poor eating behaviors in individuals with a normal weight can lead to obesity.28
There are few studies in the literature exploring the relationship between psoriasis and EDs. Crosta et al29 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis had impaired results on ED screening tests and that these scores deteriorated further as BMI increased. Moreover, Altunay et al30 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome had higher scores on the ED screening test. In this study, patients with higher scores also exhibited high levels of anxiety.30 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity had significantly (P<.01) greater EAT-26 scores than those in the normal weight group. Patients with high EAT-26 scores also exhibited elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress scores. Our study as well as other studies in the literature indicate that additional research is needed to determine the associations between EDs and obesity in psoriasis.
Conclusion
Managing obesity is crucial for patients with psoriasis. This study showed that EAT-26 scores were higher in patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity than in those who were normal weight. Participants with high EAT-26 scores (≥20 points) were more likely to be female and have higher anxiety and stress scores. In addition, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI as well as depression, anxiety, and stress scores. Eating disorders may contribute to the development of obesity in patients with psoriasis. Although our study was limited by a small sample size, the results suggest that there is a need for large-scale multicenter studies to investigate the relationship between psoriasis and EDs.
- Kalkan G. Comorbidities in psoriasis: the recognition of psoriasis as a systemic disease and current management. Turkderm-Turk Arch Dermatol Venereol. 2017;51:71-77.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Mirghani H, Altemani AT, Altemani ST, et al. The cross talk between psoriasis, obesity, and dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2023;15:e49253.
- Roehring M, Mashep MR, White MA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and behavioral correlates in obese patients with binge disorders. Obesity. 2009;17:481-486.
- da Luz FQ, Hay P, Touyz S, et al. Obesity with comorbid eating disorders: associated health risks and treatment approaches. Nutrients. 2018;10:829.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Ergüney Okumus¸ FE, Sertel Berk HÖ. The psychometric properties of the Eating Attitudes Test short form (EAT-26) in a college sample. Stud Psychol. 2020;40:57-78.
- Stoleru G, Leopold A, Auerbach A, et al. Female gender, dissatisfaction with weight, and number of IBD related surgeries as independent risk factors for eating disorders among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:438.
- Öztürkcan S, Ermertcan AT, Eser E, et al. Cross validation of the Turkish version of dermatology life quality index. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1300-1307.
- Demir GT, Ciciog˘lu HI˙. Attitude scale for healthy nutrition (ASHN): validity and reliability study. Gaziantep Univ J Sport Sci. 2019;4:256-274.
- Yılmaz O, Boz H, Arslan A. The validity and reliability of depression stress and anxiety scale (DASS 21) Turkish short form. Res Financial Econ Soc Stud. 2017;2:78-91.
- Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50:117-128.
- Strumia R, Manzata E, Gualandi M. Is there a role for dermatologists in eating disorders? Expert Rev Dermatol. 2017; 2:109-112.
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Disease concomitance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:982-986.
- Naldi L, Addis A, Chimenti S, et al. Impact of body mass index and obesity on clinical response to systemic treatment for psoriasis. evidence from the Psocare project. Dermatology. 2008;217:365-373.
- Barros G, Duran P, Vera I, et al. Exploring the links between obesity and psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7499.
- Hao Y, Zhu YJ, Zou S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: mechanisms and future directions. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711060.
- Jing D, Xiao H, Shen M, et al. Association of psoriasis with anxiety and depression: a case–control study in Chinese patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:771645.
- Sahi FM, Masood A, Danawar NA, et al. Association between psoriasis and depression: a traditional review. Cureus. 2020;12:E9708.
- Zafiriou E, Daponte AI, Siokas V, et al. Depression and obesity in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: is IL-17–mediated immune dysregulation the connecting link? Front Immunol. 2021;12:699848.
- Mrowietz U, Sümbül M, Gerdes S. Depression, a major comorbidity of psoriatic disease, is caused by metabolic inflammation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1731-1738.
- Pavlova NT, Kioskli K, Smith C, et al. Psychosocial aspects of obesity in adults with psoriasis: a systematic review. Skin Health Dis. 2021;1:E33.
- Innamorati M, Quinto RM, Imperatori C, et al. Health-related quality of life and its association with alexithymia and difficulties in emotion regulation in patients with psoriasis. Compr Psychiatry. 2016;70:200-208.
- Tabolli S, Naldi L, Pagliarello C, et al. Evaluation of the impact of writing exercises interventions on quality of life in patients with psoriasis undergoing systemic treatments. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1254‐1264.
- Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, et al. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull. 2017;123:159‐173.
- Balantekin KN, Grammer AC, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, et al. Overweight and obesity are associated with increased eating disorder correlates and general psychopathology in university women with eating disorders. Eat Behav. 2021;41:101482.
- Jebeile H, Lister NB, Baur LA, et al. Eating disorder risk in adolescents with obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22:E13173.
- Crosta ML, Caldarola G, Fraietta S, et al. Psychopathology and eating disorders in patients with psoriasis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014;149:355-361.
- Altunay I, Demirci GT, Ates B, et al. Do eating disorders accompany metabolic syndrome in psoriasis patients? results of a preliminary study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2011;4:139-143.
- Kalkan G. Comorbidities in psoriasis: the recognition of psoriasis as a systemic disease and current management. Turkderm-Turk Arch Dermatol Venereol. 2017;51:71-77.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Mirghani H, Altemani AT, Altemani ST, et al. The cross talk between psoriasis, obesity, and dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2023;15:e49253.
- Roehring M, Mashep MR, White MA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and behavioral correlates in obese patients with binge disorders. Obesity. 2009;17:481-486.
- da Luz FQ, Hay P, Touyz S, et al. Obesity with comorbid eating disorders: associated health risks and treatment approaches. Nutrients. 2018;10:829.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Ergüney Okumus¸ FE, Sertel Berk HÖ. The psychometric properties of the Eating Attitudes Test short form (EAT-26) in a college sample. Stud Psychol. 2020;40:57-78.
- Stoleru G, Leopold A, Auerbach A, et al. Female gender, dissatisfaction with weight, and number of IBD related surgeries as independent risk factors for eating disorders among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:438.
- Öztürkcan S, Ermertcan AT, Eser E, et al. Cross validation of the Turkish version of dermatology life quality index. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1300-1307.
- Demir GT, Ciciog˘lu HI˙. Attitude scale for healthy nutrition (ASHN): validity and reliability study. Gaziantep Univ J Sport Sci. 2019;4:256-274.
- Yılmaz O, Boz H, Arslan A. The validity and reliability of depression stress and anxiety scale (DASS 21) Turkish short form. Res Financial Econ Soc Stud. 2017;2:78-91.
- Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50:117-128.
- Strumia R, Manzata E, Gualandi M. Is there a role for dermatologists in eating disorders? Expert Rev Dermatol. 2017; 2:109-112.
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Disease concomitance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:982-986.
- Naldi L, Addis A, Chimenti S, et al. Impact of body mass index and obesity on clinical response to systemic treatment for psoriasis. evidence from the Psocare project. Dermatology. 2008;217:365-373.
- Barros G, Duran P, Vera I, et al. Exploring the links between obesity and psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7499.
- Hao Y, Zhu YJ, Zou S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: mechanisms and future directions. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711060.
- Jing D, Xiao H, Shen M, et al. Association of psoriasis with anxiety and depression: a case–control study in Chinese patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:771645.
- Sahi FM, Masood A, Danawar NA, et al. Association between psoriasis and depression: a traditional review. Cureus. 2020;12:E9708.
- Zafiriou E, Daponte AI, Siokas V, et al. Depression and obesity in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: is IL-17–mediated immune dysregulation the connecting link? Front Immunol. 2021;12:699848.
- Mrowietz U, Sümbül M, Gerdes S. Depression, a major comorbidity of psoriatic disease, is caused by metabolic inflammation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1731-1738.
- Pavlova NT, Kioskli K, Smith C, et al. Psychosocial aspects of obesity in adults with psoriasis: a systematic review. Skin Health Dis. 2021;1:E33.
- Innamorati M, Quinto RM, Imperatori C, et al. Health-related quality of life and its association with alexithymia and difficulties in emotion regulation in patients with psoriasis. Compr Psychiatry. 2016;70:200-208.
- Tabolli S, Naldi L, Pagliarello C, et al. Evaluation of the impact of writing exercises interventions on quality of life in patients with psoriasis undergoing systemic treatments. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1254‐1264.
- Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, et al. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull. 2017;123:159‐173.
- Balantekin KN, Grammer AC, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, et al. Overweight and obesity are associated with increased eating disorder correlates and general psychopathology in university women with eating disorders. Eat Behav. 2021;41:101482.
- Jebeile H, Lister NB, Baur LA, et al. Eating disorder risk in adolescents with obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22:E13173.
- Crosta ML, Caldarola G, Fraietta S, et al. Psychopathology and eating disorders in patients with psoriasis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014;149:355-361.
- Altunay I, Demirci GT, Ates B, et al. Do eating disorders accompany metabolic syndrome in psoriasis patients? results of a preliminary study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2011;4:139-143.
Practice Points
- Eating disorders are considered a contributing factor in obesity.
- Obesity is prevalent in patients with psoriasis, and current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate psoriasis or worsen existing disease.
- Obesity should be considered as contributory to the development of psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that accounts for genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.
Scurvy: A Diagnosis Still Relevant Today
“Petechial rash often prompts further investigation into hematological, dermatological, or vasculitis causes. However, if the above investigations are negative and skin biopsy has not revealed a cause, there is a Renaissance-era diagnosis that is often overlooked but is easily investigated and treated,” wrote Andrew Dermawan, MD, and colleagues from Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Nedlands, Australia, in BMJ Case Reports. The diagnosis they highlight is scurvy, a disease that has faded from common medical concern but is reemerging, partly because of the rise in bariatric surgery.
Diagnosing Scurvy in the 2020s
In their article, Dermawan and colleagues present the case of a 50-year-old man with a bilateral petechial rash on his lower limbs, without any history of trauma. The patient, who exhibited no infectious symptoms, also had gross hematuria, microcytic anemia, mild neutropenia, and lymphopenia. Tests for autoimmune and hematological diseases were negative, as were abdominal and leg CT scans, ruling out abdominal hemorrhage and vasculitis. Additionally, a skin biopsy showed no causative findings.
The doctors noted that the patient had undergone sleeve gastrectomy, prompting them to inquire about his diet. They discovered that, because of financial difficulties, his diet primarily consisted of processed foods with little to no fruits or vegetables, and he had stopped taking supplements recommended by his gastroenterologist. Further tests revealed a vitamin D deficiency and a severe deficiency in vitamin C. With the diagnosis of scurvy confirmed, the doctors treated the patient with 1000 mg of ascorbic acid daily, along with cholecalciferol, folic acid, and a multivitamin complex, leading to a complete resolution of his symptoms.
Risk Factors Then and Now
It can cause mucosal and gastric hemorrhages, and if left untreated, it can lead to fatal bleeding.
Historically known as “sailors’ disease,” scurvy plagued men on long voyages who lacked access to fresh fruits or vegetables and thus did not get enough vitamin C. In 1747, James Lind, a British physician in the Royal Navy, demonstrated that the consumption of oranges and lemons could combat scurvy.
Today’s risk factors for scurvy include malnutrition, gastrointestinal disorders (eg, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases), alcohol and tobacco use, eating disorders, psychiatric illnesses, dialysis, and the use of medications that reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid (such as corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors).
Scurvy remains more common among individuals with unfavorable socioeconomic conditions. The authors of the study emphasize how the rising cost of living — specifically in Australia but applicable elsewhere — is changing eating habits, leading to a high consumption of low-cost, nutritionally poor foods.
Poverty has always been a risk factor for scurvy, but today there may be an additional cause: bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these procedures are at a risk for deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and if their diet is inadequate, they may also experience a vitamin C deficiency. Awareness of this can facilitate the timely diagnosis of scurvy in these patients.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“Petechial rash often prompts further investigation into hematological, dermatological, or vasculitis causes. However, if the above investigations are negative and skin biopsy has not revealed a cause, there is a Renaissance-era diagnosis that is often overlooked but is easily investigated and treated,” wrote Andrew Dermawan, MD, and colleagues from Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Nedlands, Australia, in BMJ Case Reports. The diagnosis they highlight is scurvy, a disease that has faded from common medical concern but is reemerging, partly because of the rise in bariatric surgery.
Diagnosing Scurvy in the 2020s
In their article, Dermawan and colleagues present the case of a 50-year-old man with a bilateral petechial rash on his lower limbs, without any history of trauma. The patient, who exhibited no infectious symptoms, also had gross hematuria, microcytic anemia, mild neutropenia, and lymphopenia. Tests for autoimmune and hematological diseases were negative, as were abdominal and leg CT scans, ruling out abdominal hemorrhage and vasculitis. Additionally, a skin biopsy showed no causative findings.
The doctors noted that the patient had undergone sleeve gastrectomy, prompting them to inquire about his diet. They discovered that, because of financial difficulties, his diet primarily consisted of processed foods with little to no fruits or vegetables, and he had stopped taking supplements recommended by his gastroenterologist. Further tests revealed a vitamin D deficiency and a severe deficiency in vitamin C. With the diagnosis of scurvy confirmed, the doctors treated the patient with 1000 mg of ascorbic acid daily, along with cholecalciferol, folic acid, and a multivitamin complex, leading to a complete resolution of his symptoms.
Risk Factors Then and Now
It can cause mucosal and gastric hemorrhages, and if left untreated, it can lead to fatal bleeding.
Historically known as “sailors’ disease,” scurvy plagued men on long voyages who lacked access to fresh fruits or vegetables and thus did not get enough vitamin C. In 1747, James Lind, a British physician in the Royal Navy, demonstrated that the consumption of oranges and lemons could combat scurvy.
Today’s risk factors for scurvy include malnutrition, gastrointestinal disorders (eg, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases), alcohol and tobacco use, eating disorders, psychiatric illnesses, dialysis, and the use of medications that reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid (such as corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors).
Scurvy remains more common among individuals with unfavorable socioeconomic conditions. The authors of the study emphasize how the rising cost of living — specifically in Australia but applicable elsewhere — is changing eating habits, leading to a high consumption of low-cost, nutritionally poor foods.
Poverty has always been a risk factor for scurvy, but today there may be an additional cause: bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these procedures are at a risk for deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and if their diet is inadequate, they may also experience a vitamin C deficiency. Awareness of this can facilitate the timely diagnosis of scurvy in these patients.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“Petechial rash often prompts further investigation into hematological, dermatological, or vasculitis causes. However, if the above investigations are negative and skin biopsy has not revealed a cause, there is a Renaissance-era diagnosis that is often overlooked but is easily investigated and treated,” wrote Andrew Dermawan, MD, and colleagues from Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Nedlands, Australia, in BMJ Case Reports. The diagnosis they highlight is scurvy, a disease that has faded from common medical concern but is reemerging, partly because of the rise in bariatric surgery.
Diagnosing Scurvy in the 2020s
In their article, Dermawan and colleagues present the case of a 50-year-old man with a bilateral petechial rash on his lower limbs, without any history of trauma. The patient, who exhibited no infectious symptoms, also had gross hematuria, microcytic anemia, mild neutropenia, and lymphopenia. Tests for autoimmune and hematological diseases were negative, as were abdominal and leg CT scans, ruling out abdominal hemorrhage and vasculitis. Additionally, a skin biopsy showed no causative findings.
The doctors noted that the patient had undergone sleeve gastrectomy, prompting them to inquire about his diet. They discovered that, because of financial difficulties, his diet primarily consisted of processed foods with little to no fruits or vegetables, and he had stopped taking supplements recommended by his gastroenterologist. Further tests revealed a vitamin D deficiency and a severe deficiency in vitamin C. With the diagnosis of scurvy confirmed, the doctors treated the patient with 1000 mg of ascorbic acid daily, along with cholecalciferol, folic acid, and a multivitamin complex, leading to a complete resolution of his symptoms.
Risk Factors Then and Now
It can cause mucosal and gastric hemorrhages, and if left untreated, it can lead to fatal bleeding.
Historically known as “sailors’ disease,” scurvy plagued men on long voyages who lacked access to fresh fruits or vegetables and thus did not get enough vitamin C. In 1747, James Lind, a British physician in the Royal Navy, demonstrated that the consumption of oranges and lemons could combat scurvy.
Today’s risk factors for scurvy include malnutrition, gastrointestinal disorders (eg, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases), alcohol and tobacco use, eating disorders, psychiatric illnesses, dialysis, and the use of medications that reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid (such as corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors).
Scurvy remains more common among individuals with unfavorable socioeconomic conditions. The authors of the study emphasize how the rising cost of living — specifically in Australia but applicable elsewhere — is changing eating habits, leading to a high consumption of low-cost, nutritionally poor foods.
Poverty has always been a risk factor for scurvy, but today there may be an additional cause: bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these procedures are at a risk for deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and if their diet is inadequate, they may also experience a vitamin C deficiency. Awareness of this can facilitate the timely diagnosis of scurvy in these patients.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Lead to Worse Outcomes in Celiac Disease
PHILADELPHIA — , according to a study presented at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The association may be related to the similar pathophysiology between ARB-associated enteropathy and celiac disease, though additional research is needed.
“Based on our findings, people should take caution when prescribing angiotensin receptor blockers to people with celiac disease,” said lead author Isabel Hujoel, MD, clinical assistant professor of gastroenterology and clinic director of the Celiac Disease Center at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“When we see someone with nonresponsive celiac disease, meaning persistent symptoms despite a gluten-free diet, I do think we should review their medication list, and if they’re on an ARB, we should consider a trial off those medications to see if they respond,” she said. “A primary care provider may choose other hypertensives as well.”
Hujoel and co-author Margaux Hujoel, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; Broad Institute, Cambridge; and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us, a large publicly available US longitudinal dataset.
The researchers conducted a survival analysis of time-to-first event after celiac disease diagnosis, allowing patients to have a time-dependent covariate of ARB use. They looked at outcomes such as iron deficiency, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vitamin deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, low hemoglobin, and weight loss.
The analysis included 1849 patients with celiac disease, including 1460 women and 389 men, with a median age of nearly 50 years at diagnosis. While the vast majority of patients (nearly 1600) didn’t take an ARB, 120 started one before celiac disease diagnosis and 142 started one after diagnosis.
Overall, taking an ARB was associated with increased hazard ratios [HRs] for low hemoglobin, iron deficiency, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There weren’t increased risks for weight loss, malabsorption, or vitamin deficiencies.
When excluding those who had an ARB prescription before diagnosis, the HRs remained significantly higher for low hemoglobin (HR, 1.98) and iron deficiency (HR, 1.72) for those who started an ARB after diagnosis.
“The use of angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with worse outcomes in the setting of celiac disease, specifically persistent symptoms and possibly poor small bowel healing as evidenced by malabsorption,” Hujoel said.
Future studies could look specifically at losartan, which was the most common ARB prescribed in this analysis, she said. Other studies could also analyze different patient outcomes, whether patients were on a gluten-free diet, medication adherence, and recurrence or persistence of symptoms rather than initial occurrence. The associations between ARB use and celiac disease could shift among patients who are in remission, for instance.
“ARBs are some of the most widely used medications, so studies like these can help people to understand that they may have symptoms but not know it’s related to their medication. Public awareness of this fact is key,” said Patricia Jones, MD, a hepatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami. Jones co-moderated the plenary session on small intestine, functional, and liver research.
“There are many types of antihypertensives, so while ARBs are used often, other options are available if people have symptoms, especially if they have worsening symptoms with celiac disease,” she said. “It’s important to make changes in your practice.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Isabel Hujoel and Patricia Jones reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — , according to a study presented at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The association may be related to the similar pathophysiology between ARB-associated enteropathy and celiac disease, though additional research is needed.
“Based on our findings, people should take caution when prescribing angiotensin receptor blockers to people with celiac disease,” said lead author Isabel Hujoel, MD, clinical assistant professor of gastroenterology and clinic director of the Celiac Disease Center at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“When we see someone with nonresponsive celiac disease, meaning persistent symptoms despite a gluten-free diet, I do think we should review their medication list, and if they’re on an ARB, we should consider a trial off those medications to see if they respond,” she said. “A primary care provider may choose other hypertensives as well.”
Hujoel and co-author Margaux Hujoel, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; Broad Institute, Cambridge; and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us, a large publicly available US longitudinal dataset.
The researchers conducted a survival analysis of time-to-first event after celiac disease diagnosis, allowing patients to have a time-dependent covariate of ARB use. They looked at outcomes such as iron deficiency, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vitamin deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, low hemoglobin, and weight loss.
The analysis included 1849 patients with celiac disease, including 1460 women and 389 men, with a median age of nearly 50 years at diagnosis. While the vast majority of patients (nearly 1600) didn’t take an ARB, 120 started one before celiac disease diagnosis and 142 started one after diagnosis.
Overall, taking an ARB was associated with increased hazard ratios [HRs] for low hemoglobin, iron deficiency, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There weren’t increased risks for weight loss, malabsorption, or vitamin deficiencies.
When excluding those who had an ARB prescription before diagnosis, the HRs remained significantly higher for low hemoglobin (HR, 1.98) and iron deficiency (HR, 1.72) for those who started an ARB after diagnosis.
“The use of angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with worse outcomes in the setting of celiac disease, specifically persistent symptoms and possibly poor small bowel healing as evidenced by malabsorption,” Hujoel said.
Future studies could look specifically at losartan, which was the most common ARB prescribed in this analysis, she said. Other studies could also analyze different patient outcomes, whether patients were on a gluten-free diet, medication adherence, and recurrence or persistence of symptoms rather than initial occurrence. The associations between ARB use and celiac disease could shift among patients who are in remission, for instance.
“ARBs are some of the most widely used medications, so studies like these can help people to understand that they may have symptoms but not know it’s related to their medication. Public awareness of this fact is key,” said Patricia Jones, MD, a hepatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami. Jones co-moderated the plenary session on small intestine, functional, and liver research.
“There are many types of antihypertensives, so while ARBs are used often, other options are available if people have symptoms, especially if they have worsening symptoms with celiac disease,” she said. “It’s important to make changes in your practice.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Isabel Hujoel and Patricia Jones reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — , according to a study presented at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
The association may be related to the similar pathophysiology between ARB-associated enteropathy and celiac disease, though additional research is needed.
“Based on our findings, people should take caution when prescribing angiotensin receptor blockers to people with celiac disease,” said lead author Isabel Hujoel, MD, clinical assistant professor of gastroenterology and clinic director of the Celiac Disease Center at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“When we see someone with nonresponsive celiac disease, meaning persistent symptoms despite a gluten-free diet, I do think we should review their medication list, and if they’re on an ARB, we should consider a trial off those medications to see if they respond,” she said. “A primary care provider may choose other hypertensives as well.”
Hujoel and co-author Margaux Hujoel, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; Broad Institute, Cambridge; and Harvard Medical School, Boston, analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us, a large publicly available US longitudinal dataset.
The researchers conducted a survival analysis of time-to-first event after celiac disease diagnosis, allowing patients to have a time-dependent covariate of ARB use. They looked at outcomes such as iron deficiency, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vitamin deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, low hemoglobin, and weight loss.
The analysis included 1849 patients with celiac disease, including 1460 women and 389 men, with a median age of nearly 50 years at diagnosis. While the vast majority of patients (nearly 1600) didn’t take an ARB, 120 started one before celiac disease diagnosis and 142 started one after diagnosis.
Overall, taking an ARB was associated with increased hazard ratios [HRs] for low hemoglobin, iron deficiency, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. There weren’t increased risks for weight loss, malabsorption, or vitamin deficiencies.
When excluding those who had an ARB prescription before diagnosis, the HRs remained significantly higher for low hemoglobin (HR, 1.98) and iron deficiency (HR, 1.72) for those who started an ARB after diagnosis.
“The use of angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with worse outcomes in the setting of celiac disease, specifically persistent symptoms and possibly poor small bowel healing as evidenced by malabsorption,” Hujoel said.
Future studies could look specifically at losartan, which was the most common ARB prescribed in this analysis, she said. Other studies could also analyze different patient outcomes, whether patients were on a gluten-free diet, medication adherence, and recurrence or persistence of symptoms rather than initial occurrence. The associations between ARB use and celiac disease could shift among patients who are in remission, for instance.
“ARBs are some of the most widely used medications, so studies like these can help people to understand that they may have symptoms but not know it’s related to their medication. Public awareness of this fact is key,” said Patricia Jones, MD, a hepatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami. Jones co-moderated the plenary session on small intestine, functional, and liver research.
“There are many types of antihypertensives, so while ARBs are used often, other options are available if people have symptoms, especially if they have worsening symptoms with celiac disease,” she said. “It’s important to make changes in your practice.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Isabel Hujoel and Patricia Jones reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024
Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab: CLL’s New Power Duo?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 432 patients with previously untreated CLL and coexisting conditions were enrolled in the study.
- Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either 12 cycles of venetoclax with 6 cycles of obinutuzumab or 12 cycles of chlorambucil with 6 cycles of obinutuzumab.
- The primary endpoint was PFS, with secondary endpoints including TTNT, overall survival (OS), and adverse events.
- Minimal residual disease was assessed in peripheral blood and bone marrow at the end of treatment and at several follow-up points.
- The study was conducted across multiple centers and was registered with clinical trial identifiers NCT02242942 and EudraCT 2014-001810-24.
TAKEAWAY:
- The 6-year PFS rate was significantly higher in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group (53%) than in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (21.7%) (P < .0001).
- The TTNT rate was 65.2% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group vs 37.1% in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (P < .0001).
- The OS rate at 6 years was 78.7% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group and 69.2% in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (P = .052).
- Patients in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group reported better quality of life and less fatigue than those in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients treated with the venetoclax-obinutuzumab combination showed a statistically significant sustained prolongation of PFS, compared with patients treated with chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (76.2 vs 36.4 months). Overall, the PFS rate was 53% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group vs 21.7% after chlorambucil-obinutuzumab,” the study’s authors wrote.
In a related article, Silvia Deaglio, University of Turin in Italy, noted: “A second important observation of the study is that in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab arm, patients who relapsed more frequently presented with unmutated IGHV genes, deletion of 17p, or TP53 mutations.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Othman Al-Sawaf, Sandra Robrecht, and Can Zhang, University of Cologne in Germany. It was published online on October 31 in Blood.
LIMITATIONS:
This study’s limitations included the relatively small sample size and the short duration of follow-up for some endpoints. Additionally, the study population was limited to older adult patients with coexisting conditions, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to a broader CLL population.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and AbbVie. Al-Sawaf disclosed receiving grants from BeiGene, AbbVie, Janssen, and Roche. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 432 patients with previously untreated CLL and coexisting conditions were enrolled in the study.
- Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either 12 cycles of venetoclax with 6 cycles of obinutuzumab or 12 cycles of chlorambucil with 6 cycles of obinutuzumab.
- The primary endpoint was PFS, with secondary endpoints including TTNT, overall survival (OS), and adverse events.
- Minimal residual disease was assessed in peripheral blood and bone marrow at the end of treatment and at several follow-up points.
- The study was conducted across multiple centers and was registered with clinical trial identifiers NCT02242942 and EudraCT 2014-001810-24.
TAKEAWAY:
- The 6-year PFS rate was significantly higher in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group (53%) than in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (21.7%) (P < .0001).
- The TTNT rate was 65.2% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group vs 37.1% in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (P < .0001).
- The OS rate at 6 years was 78.7% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group and 69.2% in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (P = .052).
- Patients in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group reported better quality of life and less fatigue than those in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients treated with the venetoclax-obinutuzumab combination showed a statistically significant sustained prolongation of PFS, compared with patients treated with chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (76.2 vs 36.4 months). Overall, the PFS rate was 53% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group vs 21.7% after chlorambucil-obinutuzumab,” the study’s authors wrote.
In a related article, Silvia Deaglio, University of Turin in Italy, noted: “A second important observation of the study is that in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab arm, patients who relapsed more frequently presented with unmutated IGHV genes, deletion of 17p, or TP53 mutations.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Othman Al-Sawaf, Sandra Robrecht, and Can Zhang, University of Cologne in Germany. It was published online on October 31 in Blood.
LIMITATIONS:
This study’s limitations included the relatively small sample size and the short duration of follow-up for some endpoints. Additionally, the study population was limited to older adult patients with coexisting conditions, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to a broader CLL population.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and AbbVie. Al-Sawaf disclosed receiving grants from BeiGene, AbbVie, Janssen, and Roche. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 432 patients with previously untreated CLL and coexisting conditions were enrolled in the study.
- Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either 12 cycles of venetoclax with 6 cycles of obinutuzumab or 12 cycles of chlorambucil with 6 cycles of obinutuzumab.
- The primary endpoint was PFS, with secondary endpoints including TTNT, overall survival (OS), and adverse events.
- Minimal residual disease was assessed in peripheral blood and bone marrow at the end of treatment and at several follow-up points.
- The study was conducted across multiple centers and was registered with clinical trial identifiers NCT02242942 and EudraCT 2014-001810-24.
TAKEAWAY:
- The 6-year PFS rate was significantly higher in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group (53%) than in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (21.7%) (P < .0001).
- The TTNT rate was 65.2% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group vs 37.1% in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (P < .0001).
- The OS rate at 6 years was 78.7% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group and 69.2% in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group (P = .052).
- Patients in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group reported better quality of life and less fatigue than those in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients treated with the venetoclax-obinutuzumab combination showed a statistically significant sustained prolongation of PFS, compared with patients treated with chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (76.2 vs 36.4 months). Overall, the PFS rate was 53% in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab group vs 21.7% after chlorambucil-obinutuzumab,” the study’s authors wrote.
In a related article, Silvia Deaglio, University of Turin in Italy, noted: “A second important observation of the study is that in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab arm, patients who relapsed more frequently presented with unmutated IGHV genes, deletion of 17p, or TP53 mutations.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Othman Al-Sawaf, Sandra Robrecht, and Can Zhang, University of Cologne in Germany. It was published online on October 31 in Blood.
LIMITATIONS:
This study’s limitations included the relatively small sample size and the short duration of follow-up for some endpoints. Additionally, the study population was limited to older adult patients with coexisting conditions, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to a broader CLL population.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and AbbVie. Al-Sawaf disclosed receiving grants from BeiGene, AbbVie, Janssen, and Roche. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Plasma Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty Acids Inversely Associated With Cancer
TOPLINE:
Higher plasma levels of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are associated with a lower incidence of cancer. However, omega-3 fatty acids are linked to an increased risk for prostate cancer, specifically.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers looked for associations of plasma omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) with the incidence of cancer overall and 19 site-specific cancers in the large population-based prospective UK Biobank cohort.
- They included 253,138 participants aged 37-73 years who were followed for an average of 12.9 years, with 29,838 diagnosed with cancer.
- Plasma levels of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids were measured using nuclear magnetic resonance and expressed as percentages of total fatty acids.
- Participants with cancer diagnoses at baseline, those who withdrew from the study, and those with missing data on plasma PUFAs were excluded.
- The study adjusted for multiple covariates, including age, sex, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, lifestyle behaviors, and family history of diseases.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher plasma levels of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids were associated with a 2% and 1% reduction in overall cancer risk per SD increase, respectively (P = .001 and P = .03).
- Omega-6 fatty acids were inversely associated with 14 site-specific cancers, whereas omega-3 fatty acids were inversely associated with five site-specific cancers.
- Prostate cancer was positively associated with omega-3 fatty acids, with a 3% increased risk per SD increase (P = .049).
- A higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio was associated with an increased risk for overall cancer, and three site-specific cancers showed positive associations with the ratio. “Each standard deviation increase, corresponding to a 13.13 increase in the omega ratio, was associated with a 2% increase in the risk of rectum cancer,” for example, the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, our findings provide support for possible small net protective roles of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs in the development of new cancer incidence. Our study also suggests that the usage of circulating blood biomarkers captures different aspects of dietary intake, reduces measurement errors, and thus enhances statistical power. The differential effects of omega-6% and omega-3% in age and sex subgroups warrant future investigation,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yuchen Zhang of the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia. It was published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s potential for selective bias persists due to the participant sample skewing heavily toward European ancestry and White ethnicity. The number of events was small for some specific cancer sites, which may have limited the statistical power. The study focused on total omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs, with only two individual fatty acids measured. Future studies are needed to examine the roles of other individual PUFAs and specific genetic variants.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher plasma levels of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are associated with a lower incidence of cancer. However, omega-3 fatty acids are linked to an increased risk for prostate cancer, specifically.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers looked for associations of plasma omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) with the incidence of cancer overall and 19 site-specific cancers in the large population-based prospective UK Biobank cohort.
- They included 253,138 participants aged 37-73 years who were followed for an average of 12.9 years, with 29,838 diagnosed with cancer.
- Plasma levels of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids were measured using nuclear magnetic resonance and expressed as percentages of total fatty acids.
- Participants with cancer diagnoses at baseline, those who withdrew from the study, and those with missing data on plasma PUFAs were excluded.
- The study adjusted for multiple covariates, including age, sex, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, lifestyle behaviors, and family history of diseases.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher plasma levels of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids were associated with a 2% and 1% reduction in overall cancer risk per SD increase, respectively (P = .001 and P = .03).
- Omega-6 fatty acids were inversely associated with 14 site-specific cancers, whereas omega-3 fatty acids were inversely associated with five site-specific cancers.
- Prostate cancer was positively associated with omega-3 fatty acids, with a 3% increased risk per SD increase (P = .049).
- A higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio was associated with an increased risk for overall cancer, and three site-specific cancers showed positive associations with the ratio. “Each standard deviation increase, corresponding to a 13.13 increase in the omega ratio, was associated with a 2% increase in the risk of rectum cancer,” for example, the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, our findings provide support for possible small net protective roles of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs in the development of new cancer incidence. Our study also suggests that the usage of circulating blood biomarkers captures different aspects of dietary intake, reduces measurement errors, and thus enhances statistical power. The differential effects of omega-6% and omega-3% in age and sex subgroups warrant future investigation,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yuchen Zhang of the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia. It was published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s potential for selective bias persists due to the participant sample skewing heavily toward European ancestry and White ethnicity. The number of events was small for some specific cancer sites, which may have limited the statistical power. The study focused on total omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs, with only two individual fatty acids measured. Future studies are needed to examine the roles of other individual PUFAs and specific genetic variants.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher plasma levels of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are associated with a lower incidence of cancer. However, omega-3 fatty acids are linked to an increased risk for prostate cancer, specifically.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers looked for associations of plasma omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) with the incidence of cancer overall and 19 site-specific cancers in the large population-based prospective UK Biobank cohort.
- They included 253,138 participants aged 37-73 years who were followed for an average of 12.9 years, with 29,838 diagnosed with cancer.
- Plasma levels of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids were measured using nuclear magnetic resonance and expressed as percentages of total fatty acids.
- Participants with cancer diagnoses at baseline, those who withdrew from the study, and those with missing data on plasma PUFAs were excluded.
- The study adjusted for multiple covariates, including age, sex, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, lifestyle behaviors, and family history of diseases.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher plasma levels of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids were associated with a 2% and 1% reduction in overall cancer risk per SD increase, respectively (P = .001 and P = .03).
- Omega-6 fatty acids were inversely associated with 14 site-specific cancers, whereas omega-3 fatty acids were inversely associated with five site-specific cancers.
- Prostate cancer was positively associated with omega-3 fatty acids, with a 3% increased risk per SD increase (P = .049).
- A higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio was associated with an increased risk for overall cancer, and three site-specific cancers showed positive associations with the ratio. “Each standard deviation increase, corresponding to a 13.13 increase in the omega ratio, was associated with a 2% increase in the risk of rectum cancer,” for example, the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, our findings provide support for possible small net protective roles of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs in the development of new cancer incidence. Our study also suggests that the usage of circulating blood biomarkers captures different aspects of dietary intake, reduces measurement errors, and thus enhances statistical power. The differential effects of omega-6% and omega-3% in age and sex subgroups warrant future investigation,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yuchen Zhang of the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia. It was published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s potential for selective bias persists due to the participant sample skewing heavily toward European ancestry and White ethnicity. The number of events was small for some specific cancer sites, which may have limited the statistical power. The study focused on total omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs, with only two individual fatty acids measured. Future studies are needed to examine the roles of other individual PUFAs and specific genetic variants.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Prostate Cancer Treatment Associated With More Complications
TOPLINE:
Radiotherapy increases the risk for bladder cancer and radiation-specific complications, according to the new cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cohort study to try to characterize long-term treatment-related adverse effects and complications in patients treated for prostate cancer, compared with a general population of older males.
- They used data from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial and the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial, linked with Medicare claims. A total of 29,196 participants were included in the study’s control group. Of 3946 patients diagnosed with prostate cancer, 655 were treated with prostatectomy, and 1056 were treated with radiotherapy.
- Participants were followed for a median of 10.2 years, with specific follow-up durations being 10.5 years and 8.5 years for the prostatectomy and radiotherapy groups, respectively.
- The study analyzed ten potential treatment-related complications using Medicare claims data, including urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and secondary cancers.
- Multivariable Cox regression was used to adjust for age, race, and year of time-at-risk initiation, with stratification by study and intervention arm.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 years, there was a 7.23 increase in hazard risk for urinary or sexual complications for patients who had prostatectomy, compared with controls (P < .001).
- Radiotherapy-treated patients had a nearly three times greater hazard risk for bladder cancer and a 100-fold increased hazard risk for radiation-specific complications, such as radiation cystitis and radiation proctitis (P < .001).
- The incidence of any treatment-related complication per 1000 person-years was 124.26 for prostatectomy, 62.15 for radiotherapy, and 23.61 for untreated participants.
- The authors stated that these findings highlight the importance of patient counseling before prostate cancer screening and treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“We found that, after accounting for baseline population rates, most patients with PCA undergoing treatment experience complications associated with worse quality of life and/or new health risks. The magnitude of these risks, compared with the relatively small benefit found by randomized clinical trials of PCA screening and treatment, should be explicitly reflected in national cancer screening and treatment guidelines and be integral to shared decision-making with patients before initiation of PSA screening, biopsy, or PCA treatment,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Joseph M. Unger, PhD, SWOG Statistics and Data Management Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Washington. It was published online on November 7, 2024, in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not account for multiple comparisons, which may affect the statistical significance of some findings. Claims data are subject to misclassification and may underreport complications that are not reported to a physician. The study did not differentiate among strategies of prostatectomy or radiotherapy, which may result in different patterns of complications. The cohort comprised men enrolled in large, randomized prevention trials, which may limit the generalizability of the incidence estimates. Confounding by unknown factors cannot be ruled out, affecting the attribution of risks to prostate cancer treatment alone.
DISCLOSURES:
Unger disclosed consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Loxo/Lilly outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from the US National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study. Another coauthor reported employment with Flatiron Health at the time of manuscript submission and review. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Radiotherapy increases the risk for bladder cancer and radiation-specific complications, according to the new cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cohort study to try to characterize long-term treatment-related adverse effects and complications in patients treated for prostate cancer, compared with a general population of older males.
- They used data from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial and the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial, linked with Medicare claims. A total of 29,196 participants were included in the study’s control group. Of 3946 patients diagnosed with prostate cancer, 655 were treated with prostatectomy, and 1056 were treated with radiotherapy.
- Participants were followed for a median of 10.2 years, with specific follow-up durations being 10.5 years and 8.5 years for the prostatectomy and radiotherapy groups, respectively.
- The study analyzed ten potential treatment-related complications using Medicare claims data, including urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and secondary cancers.
- Multivariable Cox regression was used to adjust for age, race, and year of time-at-risk initiation, with stratification by study and intervention arm.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 years, there was a 7.23 increase in hazard risk for urinary or sexual complications for patients who had prostatectomy, compared with controls (P < .001).
- Radiotherapy-treated patients had a nearly three times greater hazard risk for bladder cancer and a 100-fold increased hazard risk for radiation-specific complications, such as radiation cystitis and radiation proctitis (P < .001).
- The incidence of any treatment-related complication per 1000 person-years was 124.26 for prostatectomy, 62.15 for radiotherapy, and 23.61 for untreated participants.
- The authors stated that these findings highlight the importance of patient counseling before prostate cancer screening and treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“We found that, after accounting for baseline population rates, most patients with PCA undergoing treatment experience complications associated with worse quality of life and/or new health risks. The magnitude of these risks, compared with the relatively small benefit found by randomized clinical trials of PCA screening and treatment, should be explicitly reflected in national cancer screening and treatment guidelines and be integral to shared decision-making with patients before initiation of PSA screening, biopsy, or PCA treatment,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Joseph M. Unger, PhD, SWOG Statistics and Data Management Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Washington. It was published online on November 7, 2024, in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not account for multiple comparisons, which may affect the statistical significance of some findings. Claims data are subject to misclassification and may underreport complications that are not reported to a physician. The study did not differentiate among strategies of prostatectomy or radiotherapy, which may result in different patterns of complications. The cohort comprised men enrolled in large, randomized prevention trials, which may limit the generalizability of the incidence estimates. Confounding by unknown factors cannot be ruled out, affecting the attribution of risks to prostate cancer treatment alone.
DISCLOSURES:
Unger disclosed consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Loxo/Lilly outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from the US National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study. Another coauthor reported employment with Flatiron Health at the time of manuscript submission and review. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Radiotherapy increases the risk for bladder cancer and radiation-specific complications, according to the new cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cohort study to try to characterize long-term treatment-related adverse effects and complications in patients treated for prostate cancer, compared with a general population of older males.
- They used data from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial and the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial, linked with Medicare claims. A total of 29,196 participants were included in the study’s control group. Of 3946 patients diagnosed with prostate cancer, 655 were treated with prostatectomy, and 1056 were treated with radiotherapy.
- Participants were followed for a median of 10.2 years, with specific follow-up durations being 10.5 years and 8.5 years for the prostatectomy and radiotherapy groups, respectively.
- The study analyzed ten potential treatment-related complications using Medicare claims data, including urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and secondary cancers.
- Multivariable Cox regression was used to adjust for age, race, and year of time-at-risk initiation, with stratification by study and intervention arm.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 years, there was a 7.23 increase in hazard risk for urinary or sexual complications for patients who had prostatectomy, compared with controls (P < .001).
- Radiotherapy-treated patients had a nearly three times greater hazard risk for bladder cancer and a 100-fold increased hazard risk for radiation-specific complications, such as radiation cystitis and radiation proctitis (P < .001).
- The incidence of any treatment-related complication per 1000 person-years was 124.26 for prostatectomy, 62.15 for radiotherapy, and 23.61 for untreated participants.
- The authors stated that these findings highlight the importance of patient counseling before prostate cancer screening and treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“We found that, after accounting for baseline population rates, most patients with PCA undergoing treatment experience complications associated with worse quality of life and/or new health risks. The magnitude of these risks, compared with the relatively small benefit found by randomized clinical trials of PCA screening and treatment, should be explicitly reflected in national cancer screening and treatment guidelines and be integral to shared decision-making with patients before initiation of PSA screening, biopsy, or PCA treatment,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Joseph M. Unger, PhD, SWOG Statistics and Data Management Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Washington. It was published online on November 7, 2024, in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not account for multiple comparisons, which may affect the statistical significance of some findings. Claims data are subject to misclassification and may underreport complications that are not reported to a physician. The study did not differentiate among strategies of prostatectomy or radiotherapy, which may result in different patterns of complications. The cohort comprised men enrolled in large, randomized prevention trials, which may limit the generalizability of the incidence estimates. Confounding by unknown factors cannot be ruled out, affecting the attribution of risks to prostate cancer treatment alone.
DISCLOSURES:
Unger disclosed consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Loxo/Lilly outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from the US National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study. Another coauthor reported employment with Flatiron Health at the time of manuscript submission and review. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Common Crohn’s Immune Response to Gut Bacteria Suggests Therapeutic Target
Many patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) have a heightened immune response to flagellins expressed by commensal gut bacteria Lachnospiraceae, with seroreactivity appearing up to 5 years prior to development of Crohn’s complications, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that lead author Qing Zhao, MD, PhD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues reported.
Previously, Zhao and colleagues found that about 30% of patients with CD had elevated IgG responses to multiple Lachnospiraceae flagellins, and stronger reactivity was associated with higher flagellin-specific CD4+ T cells in circulation.
“In this study, we aimed to identify immunodominant B cell peptide epitopes shared among Lachnospiraceae bacterial flagellins in patients with CD and to correlate this immune reactivity with the clinical disease course,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
To this end, the investigators analyzed serum samples from adult CD patients, pediatric CD patients, and healthy infants without inflammatory bowel disease, with data derived from multiple sources. Adult patients with CD were part of a regional cohort recruited at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, while pediatric patients with CD came from the RISK Stratification Study, a multisite cohort study across the United States and Canada. Samples from healthy infants were collected from three diverse geographic locations: Uganda, Sweden, and the United States, providing a broad comparison of immune responses to Lachnospiraceae flagellin across populations.
Samples were analyzed via two main methods: a flagellin peptide microarray and a cytometric bead array. The microarray, comprising sequential Lachnospiraceae-derived peptides, enabled identification of IgG responses specific to individual bacterial peptides. The cytometric bead array allowed for multiplexed detection of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies to these peptides, quantifying immune reactivity and enabling correlation with clinical disease data.
This approach revealed that nearly half of patients with CD — both adults and children — had a strong IgG immune response targeting a specific bacterial peptide in the Lachnospiraceae flagellin hinge region. This response was linked to an increased risk of disease complications over time, suggesting the peptide’s potential as a biomarker for CD severity and progression, according to the investigators.
Of note, healthy infants also exhibited an elevated IgG response to the same bacterial peptide at around 1 year of age, but this response declined as they grew older, in contrast to its persistence in CD patients. This difference points to a possible failure in immune tolerance in CD, where the natural immune response to gut bacteria in infancy may become dysregulated, Zhao and colleagues explained.
“The flagellin cytometric bead array used in this study holds potential for a simplified yet robust diagnostic and prognostic assay for Crohn’s disease,” they concluded. “Given that reactivity to the dominant flagellin epitope is strongly associated with the development of disease complications, this technique may also assist in identifying patients with Crohn’s disease who would benefit from early therapy.”
Zhao and colleagues also called for future studies to characterize the role of flagellin hinge peptide–specific IgG antibodies in CD pathogenesis, and to explore the hinge peptide as a potential therapeutic target.The study was supported by a Synergy Award from the Kenneth Rainin Foundation, a Career Development Award from the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, and grants from the Department of Veterans Affairs, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One coauthor and the University of Alabama at Birmingham hold a patent on Lachnospiraceae A4 Fla2, licensed for clinical application by Prometheus Laboratories. Four study coauthors have filed a patent for the flagellin peptide cytometric bead array. One coauthor serves as the founder and chief scientific officer of ImmPrev Bio, a company developing an antigen-directed immunotherapy for Crohn’s disease.
Many patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) have a heightened immune response to flagellins expressed by commensal gut bacteria Lachnospiraceae, with seroreactivity appearing up to 5 years prior to development of Crohn’s complications, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that lead author Qing Zhao, MD, PhD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues reported.
Previously, Zhao and colleagues found that about 30% of patients with CD had elevated IgG responses to multiple Lachnospiraceae flagellins, and stronger reactivity was associated with higher flagellin-specific CD4+ T cells in circulation.
“In this study, we aimed to identify immunodominant B cell peptide epitopes shared among Lachnospiraceae bacterial flagellins in patients with CD and to correlate this immune reactivity with the clinical disease course,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
To this end, the investigators analyzed serum samples from adult CD patients, pediatric CD patients, and healthy infants without inflammatory bowel disease, with data derived from multiple sources. Adult patients with CD were part of a regional cohort recruited at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, while pediatric patients with CD came from the RISK Stratification Study, a multisite cohort study across the United States and Canada. Samples from healthy infants were collected from three diverse geographic locations: Uganda, Sweden, and the United States, providing a broad comparison of immune responses to Lachnospiraceae flagellin across populations.
Samples were analyzed via two main methods: a flagellin peptide microarray and a cytometric bead array. The microarray, comprising sequential Lachnospiraceae-derived peptides, enabled identification of IgG responses specific to individual bacterial peptides. The cytometric bead array allowed for multiplexed detection of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies to these peptides, quantifying immune reactivity and enabling correlation with clinical disease data.
This approach revealed that nearly half of patients with CD — both adults and children — had a strong IgG immune response targeting a specific bacterial peptide in the Lachnospiraceae flagellin hinge region. This response was linked to an increased risk of disease complications over time, suggesting the peptide’s potential as a biomarker for CD severity and progression, according to the investigators.
Of note, healthy infants also exhibited an elevated IgG response to the same bacterial peptide at around 1 year of age, but this response declined as they grew older, in contrast to its persistence in CD patients. This difference points to a possible failure in immune tolerance in CD, where the natural immune response to gut bacteria in infancy may become dysregulated, Zhao and colleagues explained.
“The flagellin cytometric bead array used in this study holds potential for a simplified yet robust diagnostic and prognostic assay for Crohn’s disease,” they concluded. “Given that reactivity to the dominant flagellin epitope is strongly associated with the development of disease complications, this technique may also assist in identifying patients with Crohn’s disease who would benefit from early therapy.”
Zhao and colleagues also called for future studies to characterize the role of flagellin hinge peptide–specific IgG antibodies in CD pathogenesis, and to explore the hinge peptide as a potential therapeutic target.The study was supported by a Synergy Award from the Kenneth Rainin Foundation, a Career Development Award from the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, and grants from the Department of Veterans Affairs, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One coauthor and the University of Alabama at Birmingham hold a patent on Lachnospiraceae A4 Fla2, licensed for clinical application by Prometheus Laboratories. Four study coauthors have filed a patent for the flagellin peptide cytometric bead array. One coauthor serves as the founder and chief scientific officer of ImmPrev Bio, a company developing an antigen-directed immunotherapy for Crohn’s disease.
Many patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) have a heightened immune response to flagellins expressed by commensal gut bacteria Lachnospiraceae, with seroreactivity appearing up to 5 years prior to development of Crohn’s complications, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that lead author Qing Zhao, MD, PhD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues reported.
Previously, Zhao and colleagues found that about 30% of patients with CD had elevated IgG responses to multiple Lachnospiraceae flagellins, and stronger reactivity was associated with higher flagellin-specific CD4+ T cells in circulation.
“In this study, we aimed to identify immunodominant B cell peptide epitopes shared among Lachnospiraceae bacterial flagellins in patients with CD and to correlate this immune reactivity with the clinical disease course,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
To this end, the investigators analyzed serum samples from adult CD patients, pediatric CD patients, and healthy infants without inflammatory bowel disease, with data derived from multiple sources. Adult patients with CD were part of a regional cohort recruited at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, while pediatric patients with CD came from the RISK Stratification Study, a multisite cohort study across the United States and Canada. Samples from healthy infants were collected from three diverse geographic locations: Uganda, Sweden, and the United States, providing a broad comparison of immune responses to Lachnospiraceae flagellin across populations.
Samples were analyzed via two main methods: a flagellin peptide microarray and a cytometric bead array. The microarray, comprising sequential Lachnospiraceae-derived peptides, enabled identification of IgG responses specific to individual bacterial peptides. The cytometric bead array allowed for multiplexed detection of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies to these peptides, quantifying immune reactivity and enabling correlation with clinical disease data.
This approach revealed that nearly half of patients with CD — both adults and children — had a strong IgG immune response targeting a specific bacterial peptide in the Lachnospiraceae flagellin hinge region. This response was linked to an increased risk of disease complications over time, suggesting the peptide’s potential as a biomarker for CD severity and progression, according to the investigators.
Of note, healthy infants also exhibited an elevated IgG response to the same bacterial peptide at around 1 year of age, but this response declined as they grew older, in contrast to its persistence in CD patients. This difference points to a possible failure in immune tolerance in CD, where the natural immune response to gut bacteria in infancy may become dysregulated, Zhao and colleagues explained.
“The flagellin cytometric bead array used in this study holds potential for a simplified yet robust diagnostic and prognostic assay for Crohn’s disease,” they concluded. “Given that reactivity to the dominant flagellin epitope is strongly associated with the development of disease complications, this technique may also assist in identifying patients with Crohn’s disease who would benefit from early therapy.”
Zhao and colleagues also called for future studies to characterize the role of flagellin hinge peptide–specific IgG antibodies in CD pathogenesis, and to explore the hinge peptide as a potential therapeutic target.The study was supported by a Synergy Award from the Kenneth Rainin Foundation, a Career Development Award from the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, and grants from the Department of Veterans Affairs, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One coauthor and the University of Alabama at Birmingham hold a patent on Lachnospiraceae A4 Fla2, licensed for clinical application by Prometheus Laboratories. Four study coauthors have filed a patent for the flagellin peptide cytometric bead array. One coauthor serves as the founder and chief scientific officer of ImmPrev Bio, a company developing an antigen-directed immunotherapy for Crohn’s disease.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Digital Danger: How Cyberattacks Put Patients at Risk
On September 27, 2024, UMC Health System in Lubbock, Texas, experienced an IT outage because of a cybersecurity incident that temporarily diverted patients to other healthcare facilities. So far, in 2024, there have been 386 cyberattacks on healthcare organizations. These high-impact ransomware attacks disrupt and delay patient care.
In recent years, many healthcare systems, including Scripps Health, Universal Health Services, Vastaamo, Sky Lakes, and the University of Vermont, have paid millions — even tens of millions — to recover data after a cyberattack or data breach. When healthcare systems come under cyber fire, the impact extends far past disrupting workflows and compromising data, patient safety can be also be compromised, vital information may be lost, and imaging and lab results can go missing or be held for ransom, making physicians’ job difficult or impossible.
In fact, cyberattacks on hospitals are far more common than you may realize. A new report issued by Ponemon and Proofpoint found that 92% of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyberattack in the past 12 months. Even more sobering is that about half of the organizations affected suffered disruptions in patient care.
Healthcare Systems = ‘Soft Targets’
Healthcare systems are a “soft target” for hackers for several reasons, pointed out Matthew Radolec, vice president, incident response and cloud operations at Varonis, a data security company. “One, they’re usually an amalgamation of many healthcare systems that are interconnected,” said Radolec. “A lot of hospitals are connected to other hospitals or connected to educational institutions, which means their computer vulnerabilities are shared ... and if they have an issue, it could very easily spread to your network.”
Another factor is the cost of securing data. “[With hospitals], they’ll say that a dollar spent on security is a dollar not spent on patient care,” said Radolec. “So the idea of investing in security is really tough from a budget standpoint…they’re choosing between a new MRI machine or better antivirus, backups, or data security.”
Because of the wealth of private data and healthcare information they maintain, hospitals are considered “high impact” for cybercriminals. Attackers know that if they get a foothold in a hospital, it’s more likely to pay — and pay quickly, Radolec told this news organization. Hospitals are also likely to have cyber insurance to help cover the cost of having their data stolen, encrypted, and ransomed.
The 2024 Microsoft Digital Defense Report also found that the bad actors are more sophisticated and better resourced and can challenge even the best cybersecurity. Improved defenses may not be good enough, and the sheer volume of attacks must be met with effective deterrence and government solutions that impose consequences for cybercriminals.
Vulnerable Users
Whether through a phishing email or text, password attack, or web attack, “the moment a ‘threat actor’ gets into your institution and gets credentials ... that’s the Nirvana state of a threat actor,” warned Ryan Witt, chair of the healthcare customer advisory board and vice president of Industry Solutions at Proofpoint, a cybersecurity platform. “They have those credentials and will go into deep reconnaissance mode. It often takes healthcare up to 6 months to even ascertain whether somebody’s actually in the network.” During that time, the hacker is learning how the institution works, what job functions matter, and how best to plan their attack.
“Attackers are getting in because they’re buying databases of usernames and passwords. And they’re trying them by the millions,” added Radolec. “For a sophisticated actor, all it takes is time and motivation. They have the skills. It’s just a matter of how persistent they want to be.”
Certain hospital staff are also more likely to be targeted by cyberhackers than others. “About 10% of a healthcare organization’s user base is much more vulnerable for all sorts of reasons — how they work, the value of their job title and job function, and therefore their access to systems,” said Witt.
High-profile staff are more likely to be targeted than those in lower-level positions; the so-called “CEO attack” is typical. However, staff in other hospital departments are also subject to cybercriminals, including hospice departments/hospice organizations and research arms of hospitals.
The Impact of Cyberattacks on Patients
Physicians and healthcare execs may have considered cybersecurity more of a compliance issue than a true threat to patients in the past. But this attitude is rapidly changing. “We are starting to see a very clear connection between a cyber event and how it can impact patient care and patient safety,” said Witt.
According to the Proofpoint report, cyber breaches can severely affect patient care. In 2024:
- 56% of respondents saw a delay in patient tests/procedures
- 53% experienced increased patient complications from medical procedures
- 52% noted a longer patient length of stay
- 44% saw an increase in patient transfers to other facilities
- 28% had an increase in mortality rate
What Hospitals and Physicians Can Do
Fortunately, hospitals can take measures to better protect their data and their patients. One strategy is segmenting networks to reduce the amount of data or systems one person or system can access. Educating staff about the dangers of phishing and spoofing emails also help protect organizations from ransomware attacks. Having staff avoid reusing passwords and updating logins and passwords frequently helps.
Most hospitals also need more robust security controls. Physicians and healthcare facilities must also embrace the cybersecurity controls found in other industries, said Witt. “Multifactor authentication is one of those things that can cause us frustration,” he said. “The controls can seem onerous, but they’re really valuable overall…and should become standard practice.”
Doctors can also prepare for a ransomware attack and protect patients by practicing some “old-school” medicine, like using paper systems and maintaining good patient notes — often, those notes are synced locally as well as offsite, so you’d be able to access them even during a data breach. “It’s smart to write prescriptions on pads sometimes,” said Radolec. “Don’t forget how to do those things because that will make you more resilient in the event of a ransomware attack.”
A Continuing Threat
Cyberattacks will continue. “When you look at the high likelihood [of success] and the soft target, you end up with ... a perfect storm,” said Radolec. “Hospitals have a lot of vulnerabilities. They have to keep operations going just to receive income, but also to deliver care to people.”
That means that the burden is on healthcare organizations — including physicians, nurses, staff, and C-level execs — to help keep the “security” in cybersecurity. “We are all part of the cybersecurity defense,” said Witt. Helping to maintain that defense has become a critical aspect of caring for patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On September 27, 2024, UMC Health System in Lubbock, Texas, experienced an IT outage because of a cybersecurity incident that temporarily diverted patients to other healthcare facilities. So far, in 2024, there have been 386 cyberattacks on healthcare organizations. These high-impact ransomware attacks disrupt and delay patient care.
In recent years, many healthcare systems, including Scripps Health, Universal Health Services, Vastaamo, Sky Lakes, and the University of Vermont, have paid millions — even tens of millions — to recover data after a cyberattack or data breach. When healthcare systems come under cyber fire, the impact extends far past disrupting workflows and compromising data, patient safety can be also be compromised, vital information may be lost, and imaging and lab results can go missing or be held for ransom, making physicians’ job difficult or impossible.
In fact, cyberattacks on hospitals are far more common than you may realize. A new report issued by Ponemon and Proofpoint found that 92% of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyberattack in the past 12 months. Even more sobering is that about half of the organizations affected suffered disruptions in patient care.
Healthcare Systems = ‘Soft Targets’
Healthcare systems are a “soft target” for hackers for several reasons, pointed out Matthew Radolec, vice president, incident response and cloud operations at Varonis, a data security company. “One, they’re usually an amalgamation of many healthcare systems that are interconnected,” said Radolec. “A lot of hospitals are connected to other hospitals or connected to educational institutions, which means their computer vulnerabilities are shared ... and if they have an issue, it could very easily spread to your network.”
Another factor is the cost of securing data. “[With hospitals], they’ll say that a dollar spent on security is a dollar not spent on patient care,” said Radolec. “So the idea of investing in security is really tough from a budget standpoint…they’re choosing between a new MRI machine or better antivirus, backups, or data security.”
Because of the wealth of private data and healthcare information they maintain, hospitals are considered “high impact” for cybercriminals. Attackers know that if they get a foothold in a hospital, it’s more likely to pay — and pay quickly, Radolec told this news organization. Hospitals are also likely to have cyber insurance to help cover the cost of having their data stolen, encrypted, and ransomed.
The 2024 Microsoft Digital Defense Report also found that the bad actors are more sophisticated and better resourced and can challenge even the best cybersecurity. Improved defenses may not be good enough, and the sheer volume of attacks must be met with effective deterrence and government solutions that impose consequences for cybercriminals.
Vulnerable Users
Whether through a phishing email or text, password attack, or web attack, “the moment a ‘threat actor’ gets into your institution and gets credentials ... that’s the Nirvana state of a threat actor,” warned Ryan Witt, chair of the healthcare customer advisory board and vice president of Industry Solutions at Proofpoint, a cybersecurity platform. “They have those credentials and will go into deep reconnaissance mode. It often takes healthcare up to 6 months to even ascertain whether somebody’s actually in the network.” During that time, the hacker is learning how the institution works, what job functions matter, and how best to plan their attack.
“Attackers are getting in because they’re buying databases of usernames and passwords. And they’re trying them by the millions,” added Radolec. “For a sophisticated actor, all it takes is time and motivation. They have the skills. It’s just a matter of how persistent they want to be.”
Certain hospital staff are also more likely to be targeted by cyberhackers than others. “About 10% of a healthcare organization’s user base is much more vulnerable for all sorts of reasons — how they work, the value of their job title and job function, and therefore their access to systems,” said Witt.
High-profile staff are more likely to be targeted than those in lower-level positions; the so-called “CEO attack” is typical. However, staff in other hospital departments are also subject to cybercriminals, including hospice departments/hospice organizations and research arms of hospitals.
The Impact of Cyberattacks on Patients
Physicians and healthcare execs may have considered cybersecurity more of a compliance issue than a true threat to patients in the past. But this attitude is rapidly changing. “We are starting to see a very clear connection between a cyber event and how it can impact patient care and patient safety,” said Witt.
According to the Proofpoint report, cyber breaches can severely affect patient care. In 2024:
- 56% of respondents saw a delay in patient tests/procedures
- 53% experienced increased patient complications from medical procedures
- 52% noted a longer patient length of stay
- 44% saw an increase in patient transfers to other facilities
- 28% had an increase in mortality rate
What Hospitals and Physicians Can Do
Fortunately, hospitals can take measures to better protect their data and their patients. One strategy is segmenting networks to reduce the amount of data or systems one person or system can access. Educating staff about the dangers of phishing and spoofing emails also help protect organizations from ransomware attacks. Having staff avoid reusing passwords and updating logins and passwords frequently helps.
Most hospitals also need more robust security controls. Physicians and healthcare facilities must also embrace the cybersecurity controls found in other industries, said Witt. “Multifactor authentication is one of those things that can cause us frustration,” he said. “The controls can seem onerous, but they’re really valuable overall…and should become standard practice.”
Doctors can also prepare for a ransomware attack and protect patients by practicing some “old-school” medicine, like using paper systems and maintaining good patient notes — often, those notes are synced locally as well as offsite, so you’d be able to access them even during a data breach. “It’s smart to write prescriptions on pads sometimes,” said Radolec. “Don’t forget how to do those things because that will make you more resilient in the event of a ransomware attack.”
A Continuing Threat
Cyberattacks will continue. “When you look at the high likelihood [of success] and the soft target, you end up with ... a perfect storm,” said Radolec. “Hospitals have a lot of vulnerabilities. They have to keep operations going just to receive income, but also to deliver care to people.”
That means that the burden is on healthcare organizations — including physicians, nurses, staff, and C-level execs — to help keep the “security” in cybersecurity. “We are all part of the cybersecurity defense,” said Witt. Helping to maintain that defense has become a critical aspect of caring for patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On September 27, 2024, UMC Health System in Lubbock, Texas, experienced an IT outage because of a cybersecurity incident that temporarily diverted patients to other healthcare facilities. So far, in 2024, there have been 386 cyberattacks on healthcare organizations. These high-impact ransomware attacks disrupt and delay patient care.
In recent years, many healthcare systems, including Scripps Health, Universal Health Services, Vastaamo, Sky Lakes, and the University of Vermont, have paid millions — even tens of millions — to recover data after a cyberattack or data breach. When healthcare systems come under cyber fire, the impact extends far past disrupting workflows and compromising data, patient safety can be also be compromised, vital information may be lost, and imaging and lab results can go missing or be held for ransom, making physicians’ job difficult or impossible.
In fact, cyberattacks on hospitals are far more common than you may realize. A new report issued by Ponemon and Proofpoint found that 92% of healthcare organizations have experienced a cyberattack in the past 12 months. Even more sobering is that about half of the organizations affected suffered disruptions in patient care.
Healthcare Systems = ‘Soft Targets’
Healthcare systems are a “soft target” for hackers for several reasons, pointed out Matthew Radolec, vice president, incident response and cloud operations at Varonis, a data security company. “One, they’re usually an amalgamation of many healthcare systems that are interconnected,” said Radolec. “A lot of hospitals are connected to other hospitals or connected to educational institutions, which means their computer vulnerabilities are shared ... and if they have an issue, it could very easily spread to your network.”
Another factor is the cost of securing data. “[With hospitals], they’ll say that a dollar spent on security is a dollar not spent on patient care,” said Radolec. “So the idea of investing in security is really tough from a budget standpoint…they’re choosing between a new MRI machine or better antivirus, backups, or data security.”
Because of the wealth of private data and healthcare information they maintain, hospitals are considered “high impact” for cybercriminals. Attackers know that if they get a foothold in a hospital, it’s more likely to pay — and pay quickly, Radolec told this news organization. Hospitals are also likely to have cyber insurance to help cover the cost of having their data stolen, encrypted, and ransomed.
The 2024 Microsoft Digital Defense Report also found that the bad actors are more sophisticated and better resourced and can challenge even the best cybersecurity. Improved defenses may not be good enough, and the sheer volume of attacks must be met with effective deterrence and government solutions that impose consequences for cybercriminals.
Vulnerable Users
Whether through a phishing email or text, password attack, or web attack, “the moment a ‘threat actor’ gets into your institution and gets credentials ... that’s the Nirvana state of a threat actor,” warned Ryan Witt, chair of the healthcare customer advisory board and vice president of Industry Solutions at Proofpoint, a cybersecurity platform. “They have those credentials and will go into deep reconnaissance mode. It often takes healthcare up to 6 months to even ascertain whether somebody’s actually in the network.” During that time, the hacker is learning how the institution works, what job functions matter, and how best to plan their attack.
“Attackers are getting in because they’re buying databases of usernames and passwords. And they’re trying them by the millions,” added Radolec. “For a sophisticated actor, all it takes is time and motivation. They have the skills. It’s just a matter of how persistent they want to be.”
Certain hospital staff are also more likely to be targeted by cyberhackers than others. “About 10% of a healthcare organization’s user base is much more vulnerable for all sorts of reasons — how they work, the value of their job title and job function, and therefore their access to systems,” said Witt.
High-profile staff are more likely to be targeted than those in lower-level positions; the so-called “CEO attack” is typical. However, staff in other hospital departments are also subject to cybercriminals, including hospice departments/hospice organizations and research arms of hospitals.
The Impact of Cyberattacks on Patients
Physicians and healthcare execs may have considered cybersecurity more of a compliance issue than a true threat to patients in the past. But this attitude is rapidly changing. “We are starting to see a very clear connection between a cyber event and how it can impact patient care and patient safety,” said Witt.
According to the Proofpoint report, cyber breaches can severely affect patient care. In 2024:
- 56% of respondents saw a delay in patient tests/procedures
- 53% experienced increased patient complications from medical procedures
- 52% noted a longer patient length of stay
- 44% saw an increase in patient transfers to other facilities
- 28% had an increase in mortality rate
What Hospitals and Physicians Can Do
Fortunately, hospitals can take measures to better protect their data and their patients. One strategy is segmenting networks to reduce the amount of data or systems one person or system can access. Educating staff about the dangers of phishing and spoofing emails also help protect organizations from ransomware attacks. Having staff avoid reusing passwords and updating logins and passwords frequently helps.
Most hospitals also need more robust security controls. Physicians and healthcare facilities must also embrace the cybersecurity controls found in other industries, said Witt. “Multifactor authentication is one of those things that can cause us frustration,” he said. “The controls can seem onerous, but they’re really valuable overall…and should become standard practice.”
Doctors can also prepare for a ransomware attack and protect patients by practicing some “old-school” medicine, like using paper systems and maintaining good patient notes — often, those notes are synced locally as well as offsite, so you’d be able to access them even during a data breach. “It’s smart to write prescriptions on pads sometimes,” said Radolec. “Don’t forget how to do those things because that will make you more resilient in the event of a ransomware attack.”
A Continuing Threat
Cyberattacks will continue. “When you look at the high likelihood [of success] and the soft target, you end up with ... a perfect storm,” said Radolec. “Hospitals have a lot of vulnerabilities. They have to keep operations going just to receive income, but also to deliver care to people.”
That means that the burden is on healthcare organizations — including physicians, nurses, staff, and C-level execs — to help keep the “security” in cybersecurity. “We are all part of the cybersecurity defense,” said Witt. Helping to maintain that defense has become a critical aspect of caring for patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.