User login
Nailing the Nail Biopsy: Surgical Instruments and Their Function in Nail Biopsy Procedures
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
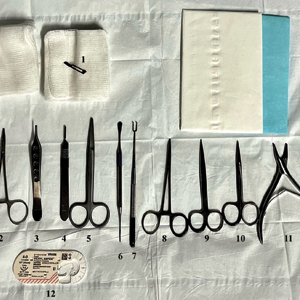
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.
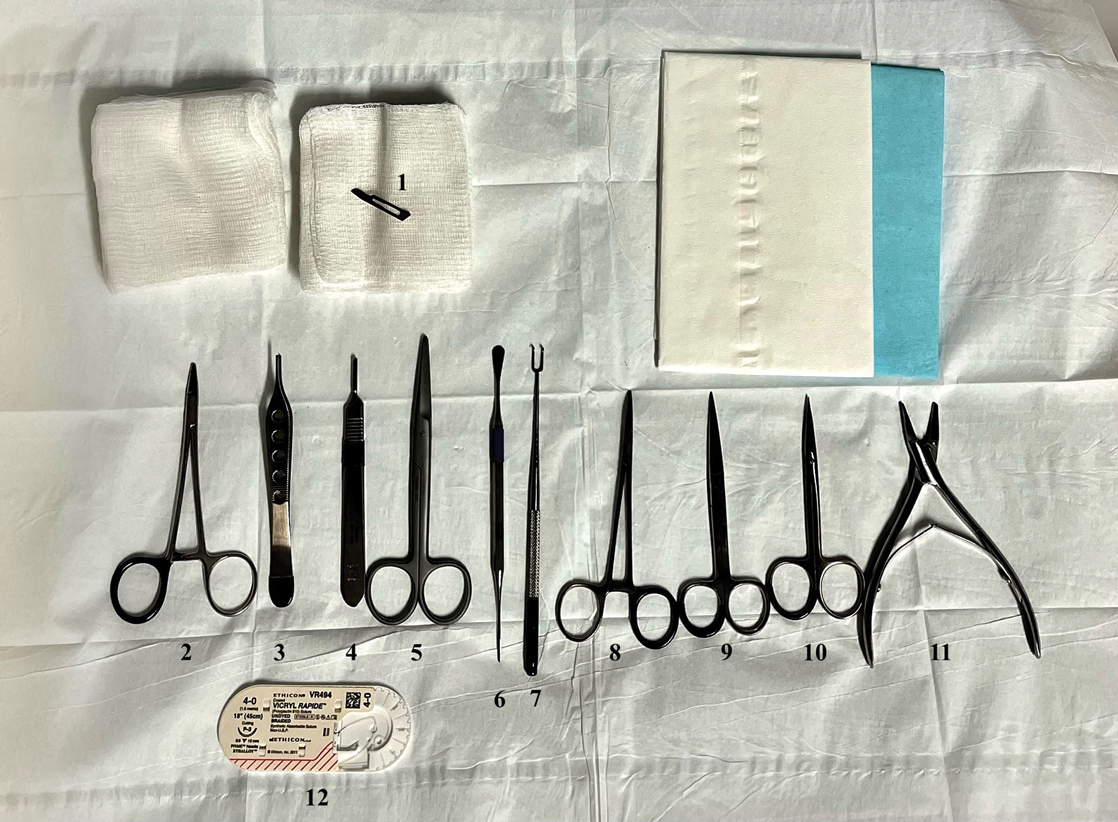
After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.

After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.

After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
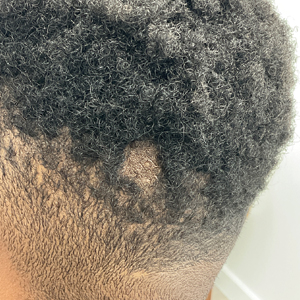
Hairless Scalp Lesion
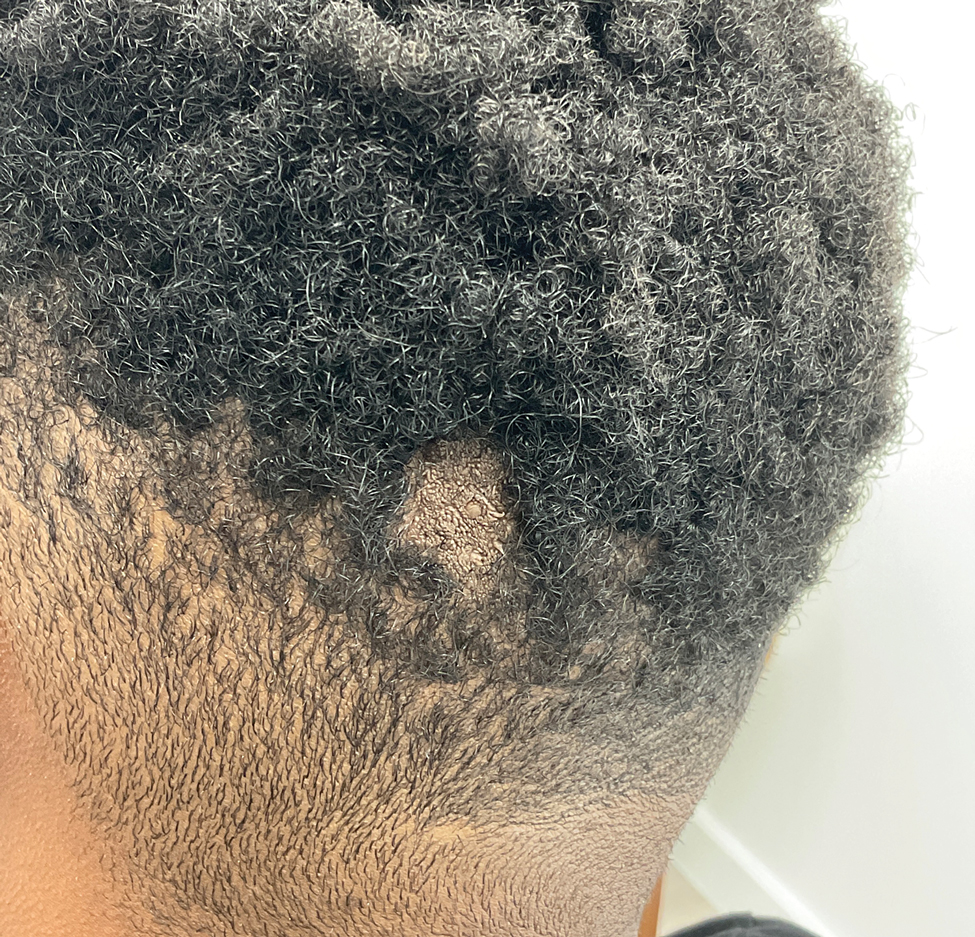
The Diagnosis: Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn
The diagnosis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn was made clinically based on the lesion’s appearance and presence since birth as well as the absence of systemic symptoms. Clinically, nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn typically manifests as a well-demarcated, yellow- brown plaque often located on the scalp, as was seen in our patient. The lack of pruritus and pain further supported the diagnosis in our patient. No biopsy was performed, as the presentation was considered classic for this condition. Our patient opted to forgo surgery and will be routinely monitored for any changes, as nevus sebaceus has a potential risk, albeit low, for malignant transformation later in life. No changes have been observed since the initial presentation, and regular follow-ups are planned to monitor for future developments.
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a hamartomatous lesion involving the pilosebaceous follicle and adjacent adnexal structures.1-3 It most commonly forms on the scalp (59.3%) and is accompanied by partial or total alopecia. 3,4 It is seen less often on the face, periauricular area, or neck1,4; thorax or limbs5; and oral or genital mucosae.6 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn affects approximately 0.3% of newborns,1 usually as a solitary lesion that can form an extensive plaque. The male-to-female occurrence ratio has been reported as equal to slightly more predominant in females; all races and ethnicities are affected.1,5
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn follows 3 stages of clinical development: infantile, adolescent, and adulthood. It manifests at birth or shortly afterward as a smooth hairless patch or plaque that is yellowish and can be hyperpigmented in Black patients.5 It may have an oval or linear configuration, typically is asymptomatic, and often arises along the Blaschko lines when it occurs as multiple lesions (a rare manifestation).1 During puberty, hormonal changes cause accelerated growth, sebaceous gland maturation, and epidermal hyperplasia. 7 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn often is not identified until this stage, when its classic wartlike appearance has fully developed.1
Patients with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn have a 10% to 20% risk for tumor development in adulthood.2,7 Trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum are the most frequently described neoplasms.8 Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant secondary neoplasm with an occurrence rate of 0.8%.6,9 However, basal cell carcinoma and trichoblastoma may share histopathologic features, which may lead to misdiagnosis and a higher reported incidence of basal cell carcinoma in adults than is accurate.2
Early prophylactic surgical removal of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn has been recommended; however, surgical management is controversial because the risk for a benign secondary neoplasm remains relatively high while the risk for malignancy is much lower.2,7 Surgical excision remains an acceptable option once the patient is mature enough to tolerate the procedure.1 However, patient education regarding watchful waiting vs a surgical approach— and the risks of each—is critical to ensure shared decision-making and a management plan tailored to the individual.
The differential diagnosis includes hypertrophic lichen planus, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type), epidermal nevus, and seborrheic keratosis. Hypertrophic lichen planus often occurs symmetrically on the dorsal feet and shins with thick, scaly, and extremely pruritic plaques. The lesions often persist for an average of 6 years and may lead to multiple keratoacanthomas or follicular base squamous cell carcinomas. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type) manifests with acute, disseminated, visceral, and cutaneous lesions before 2 years of age. These lesions appear as 1- to 2-mm, pink, seborrheic papules, pustules, or vesicles on the scalp, flexural neck, axilla, perineum, and trunk; they often are associated with petechiae, purpura, scale, crust, erosion, impetiginization, and tender fissures. Epidermal nevus occurs within the first year of life and is a hamartoma of the epidermis and papillary dermis. It manifests as papillomatous pigmented linear lines along the Blaschko lines. Seborrheic keratosis manifests as well-demarcated, waxy/verrucous, brown papules with a “stuck on” appearance on hair-bearing skin sparing the mucosae. They are common benign lesions associated with sun exposure and often manifest in the fourth decade of life.10
- Baigrie D, Troxell T, Cook C. Nevus sebaceus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482493/
- Terenzi V, Indrizzi E, Buonaccorsi S, et al. Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:1234-1239. doi:10.1097/01 .scs.0000221531.56529.cc
- Kelati A, Baybay H, Gallouj S, et al. Dermoscopic analysis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 13 cases. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3:83-91. doi:10.1159/000460258
- Ugras N, Ozgun G, Adim SB, et al. Nevus sebaceous at unusual location: a rare presentation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55:419-420. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.101768
- Serpas de Lopez RM, Hernandez-Perez E. Jadassohn’s sebaceous nevus. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1985;11:68-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725 .1985.tb02893.x
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2 pt 1):263-268. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90136-1
- Santibanez-Gallerani A, Marshall D, Duarte AM, et al. Should nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn in children be excised? a study of 757 cases, and literature review. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14:658-660. doi:10.1097/00001665-200309000-00010
- Chahboun F, Eljazouly M, Elomari M, et al. Trichoblastoma arising from the nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Cureus. 2021;13:E15325. doi:10.7759/cureus.15325
- Cazzato G, Cimmino A, Colagrande A, et al. The multiple faces of nodular trichoblastoma: review of the literature with case presentation. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:265-270. doi:10.3390 /dermatopathology8030032
- Dandekar MN, Gandhi RK. Neoplastic dermatology. In: Alikhan A, Hocker TLH (eds). Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2016: 321-366.
The Diagnosis: Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn
The diagnosis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn was made clinically based on the lesion’s appearance and presence since birth as well as the absence of systemic symptoms. Clinically, nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn typically manifests as a well-demarcated, yellow- brown plaque often located on the scalp, as was seen in our patient. The lack of pruritus and pain further supported the diagnosis in our patient. No biopsy was performed, as the presentation was considered classic for this condition. Our patient opted to forgo surgery and will be routinely monitored for any changes, as nevus sebaceus has a potential risk, albeit low, for malignant transformation later in life. No changes have been observed since the initial presentation, and regular follow-ups are planned to monitor for future developments.
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a hamartomatous lesion involving the pilosebaceous follicle and adjacent adnexal structures.1-3 It most commonly forms on the scalp (59.3%) and is accompanied by partial or total alopecia. 3,4 It is seen less often on the face, periauricular area, or neck1,4; thorax or limbs5; and oral or genital mucosae.6 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn affects approximately 0.3% of newborns,1 usually as a solitary lesion that can form an extensive plaque. The male-to-female occurrence ratio has been reported as equal to slightly more predominant in females; all races and ethnicities are affected.1,5
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn follows 3 stages of clinical development: infantile, adolescent, and adulthood. It manifests at birth or shortly afterward as a smooth hairless patch or plaque that is yellowish and can be hyperpigmented in Black patients.5 It may have an oval or linear configuration, typically is asymptomatic, and often arises along the Blaschko lines when it occurs as multiple lesions (a rare manifestation).1 During puberty, hormonal changes cause accelerated growth, sebaceous gland maturation, and epidermal hyperplasia. 7 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn often is not identified until this stage, when its classic wartlike appearance has fully developed.1
Patients with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn have a 10% to 20% risk for tumor development in adulthood.2,7 Trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum are the most frequently described neoplasms.8 Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant secondary neoplasm with an occurrence rate of 0.8%.6,9 However, basal cell carcinoma and trichoblastoma may share histopathologic features, which may lead to misdiagnosis and a higher reported incidence of basal cell carcinoma in adults than is accurate.2
Early prophylactic surgical removal of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn has been recommended; however, surgical management is controversial because the risk for a benign secondary neoplasm remains relatively high while the risk for malignancy is much lower.2,7 Surgical excision remains an acceptable option once the patient is mature enough to tolerate the procedure.1 However, patient education regarding watchful waiting vs a surgical approach— and the risks of each—is critical to ensure shared decision-making and a management plan tailored to the individual.
The differential diagnosis includes hypertrophic lichen planus, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type), epidermal nevus, and seborrheic keratosis. Hypertrophic lichen planus often occurs symmetrically on the dorsal feet and shins with thick, scaly, and extremely pruritic plaques. The lesions often persist for an average of 6 years and may lead to multiple keratoacanthomas or follicular base squamous cell carcinomas. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type) manifests with acute, disseminated, visceral, and cutaneous lesions before 2 years of age. These lesions appear as 1- to 2-mm, pink, seborrheic papules, pustules, or vesicles on the scalp, flexural neck, axilla, perineum, and trunk; they often are associated with petechiae, purpura, scale, crust, erosion, impetiginization, and tender fissures. Epidermal nevus occurs within the first year of life and is a hamartoma of the epidermis and papillary dermis. It manifests as papillomatous pigmented linear lines along the Blaschko lines. Seborrheic keratosis manifests as well-demarcated, waxy/verrucous, brown papules with a “stuck on” appearance on hair-bearing skin sparing the mucosae. They are common benign lesions associated with sun exposure and often manifest in the fourth decade of life.10
The Diagnosis: Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn
The diagnosis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn was made clinically based on the lesion’s appearance and presence since birth as well as the absence of systemic symptoms. Clinically, nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn typically manifests as a well-demarcated, yellow- brown plaque often located on the scalp, as was seen in our patient. The lack of pruritus and pain further supported the diagnosis in our patient. No biopsy was performed, as the presentation was considered classic for this condition. Our patient opted to forgo surgery and will be routinely monitored for any changes, as nevus sebaceus has a potential risk, albeit low, for malignant transformation later in life. No changes have been observed since the initial presentation, and regular follow-ups are planned to monitor for future developments.
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a hamartomatous lesion involving the pilosebaceous follicle and adjacent adnexal structures.1-3 It most commonly forms on the scalp (59.3%) and is accompanied by partial or total alopecia. 3,4 It is seen less often on the face, periauricular area, or neck1,4; thorax or limbs5; and oral or genital mucosae.6 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn affects approximately 0.3% of newborns,1 usually as a solitary lesion that can form an extensive plaque. The male-to-female occurrence ratio has been reported as equal to slightly more predominant in females; all races and ethnicities are affected.1,5
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn follows 3 stages of clinical development: infantile, adolescent, and adulthood. It manifests at birth or shortly afterward as a smooth hairless patch or plaque that is yellowish and can be hyperpigmented in Black patients.5 It may have an oval or linear configuration, typically is asymptomatic, and often arises along the Blaschko lines when it occurs as multiple lesions (a rare manifestation).1 During puberty, hormonal changes cause accelerated growth, sebaceous gland maturation, and epidermal hyperplasia. 7 Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn often is not identified until this stage, when its classic wartlike appearance has fully developed.1
Patients with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn have a 10% to 20% risk for tumor development in adulthood.2,7 Trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum are the most frequently described neoplasms.8 Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant secondary neoplasm with an occurrence rate of 0.8%.6,9 However, basal cell carcinoma and trichoblastoma may share histopathologic features, which may lead to misdiagnosis and a higher reported incidence of basal cell carcinoma in adults than is accurate.2
Early prophylactic surgical removal of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn has been recommended; however, surgical management is controversial because the risk for a benign secondary neoplasm remains relatively high while the risk for malignancy is much lower.2,7 Surgical excision remains an acceptable option once the patient is mature enough to tolerate the procedure.1 However, patient education regarding watchful waiting vs a surgical approach— and the risks of each—is critical to ensure shared decision-making and a management plan tailored to the individual.
The differential diagnosis includes hypertrophic lichen planus, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type), epidermal nevus, and seborrheic keratosis. Hypertrophic lichen planus often occurs symmetrically on the dorsal feet and shins with thick, scaly, and extremely pruritic plaques. The lesions often persist for an average of 6 years and may lead to multiple keratoacanthomas or follicular base squamous cell carcinomas. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease type) manifests with acute, disseminated, visceral, and cutaneous lesions before 2 years of age. These lesions appear as 1- to 2-mm, pink, seborrheic papules, pustules, or vesicles on the scalp, flexural neck, axilla, perineum, and trunk; they often are associated with petechiae, purpura, scale, crust, erosion, impetiginization, and tender fissures. Epidermal nevus occurs within the first year of life and is a hamartoma of the epidermis and papillary dermis. It manifests as papillomatous pigmented linear lines along the Blaschko lines. Seborrheic keratosis manifests as well-demarcated, waxy/verrucous, brown papules with a “stuck on” appearance on hair-bearing skin sparing the mucosae. They are common benign lesions associated with sun exposure and often manifest in the fourth decade of life.10
- Baigrie D, Troxell T, Cook C. Nevus sebaceus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482493/
- Terenzi V, Indrizzi E, Buonaccorsi S, et al. Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:1234-1239. doi:10.1097/01 .scs.0000221531.56529.cc
- Kelati A, Baybay H, Gallouj S, et al. Dermoscopic analysis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 13 cases. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3:83-91. doi:10.1159/000460258
- Ugras N, Ozgun G, Adim SB, et al. Nevus sebaceous at unusual location: a rare presentation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55:419-420. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.101768
- Serpas de Lopez RM, Hernandez-Perez E. Jadassohn’s sebaceous nevus. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1985;11:68-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725 .1985.tb02893.x
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2 pt 1):263-268. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90136-1
- Santibanez-Gallerani A, Marshall D, Duarte AM, et al. Should nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn in children be excised? a study of 757 cases, and literature review. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14:658-660. doi:10.1097/00001665-200309000-00010
- Chahboun F, Eljazouly M, Elomari M, et al. Trichoblastoma arising from the nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Cureus. 2021;13:E15325. doi:10.7759/cureus.15325
- Cazzato G, Cimmino A, Colagrande A, et al. The multiple faces of nodular trichoblastoma: review of the literature with case presentation. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:265-270. doi:10.3390 /dermatopathology8030032
- Dandekar MN, Gandhi RK. Neoplastic dermatology. In: Alikhan A, Hocker TLH (eds). Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2016: 321-366.
- Baigrie D, Troxell T, Cook C. Nevus sebaceus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482493/
- Terenzi V, Indrizzi E, Buonaccorsi S, et al. Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:1234-1239. doi:10.1097/01 .scs.0000221531.56529.cc
- Kelati A, Baybay H, Gallouj S, et al. Dermoscopic analysis of nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 13 cases. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3:83-91. doi:10.1159/000460258
- Ugras N, Ozgun G, Adim SB, et al. Nevus sebaceous at unusual location: a rare presentation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2012;55:419-420. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.101768
- Serpas de Lopez RM, Hernandez-Perez E. Jadassohn’s sebaceous nevus. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1985;11:68-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725 .1985.tb02893.x
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2 pt 1):263-268. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90136-1
- Santibanez-Gallerani A, Marshall D, Duarte AM, et al. Should nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn in children be excised? a study of 757 cases, and literature review. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14:658-660. doi:10.1097/00001665-200309000-00010
- Chahboun F, Eljazouly M, Elomari M, et al. Trichoblastoma arising from the nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn. Cureus. 2021;13:E15325. doi:10.7759/cureus.15325
- Cazzato G, Cimmino A, Colagrande A, et al. The multiple faces of nodular trichoblastoma: review of the literature with case presentation. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:265-270. doi:10.3390 /dermatopathology8030032
- Dandekar MN, Gandhi RK. Neoplastic dermatology. In: Alikhan A, Hocker TLH (eds). Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2016: 321-366.
A 23-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with hair loss on the scalp of several years’ duration. The patient reported persistent pigmented bumps on the back of the scalp. He denied any pruritus or pain and had no systemic symptoms or comorbidities. Physical examination revealed a 1×1.5-cm, yellow-brown, hairless plaque on the left parietal scalp.
Diabetes Drug Improved Symptoms in Small Study of Women With Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Imaging Tool Helps Identify Features of Nail Disorders
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The single-center, observational cross-sectional pilot study evaluated patients aged ≥ 7 years with newly diagnosed nail disorders between January 2022 and May 2023.
- A total of 128 patients (average age, 46.1 years; range, 8-84 years) with nail psoriasis, onychomycosis, idiopathic/traumatic onycholysis, brittle nail syndrome, nail lichen planus, retronychia, and other nail conditions and those with no nail findings (controls) were enrolled.
- Researchers performed nailfold capillaroscopy imaging and compared capillary features between patients with nail conditions and the controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with nail psoriasis had decreased capillary density and length (P < .001), more crossed and tortuous capillaries (P < .02), and increased abnormal capillary morphology (P = .03) compared with controls. Specific abnormalities, such as branching and meandering capillaries, were more common among those with nail psoriasis (both 26.5%).
- Patients with fingernail and toenail onychomycosis had a higher frequency of abnormal capillary morphology (P < .02), particularly meandering capillaries (75.0% for fingernails and 76.9% for toenails). However, other abnormalities were less frequently observed.
- Patients with nail lichen planus (P < .01), onychopapilloma (P = .01), and retronychia (P = .03) showed significantly shorter capillaries than controls. Retronychia was also associated with increased disorganized polymorphic capillaries (P = .02).
- Patients with brittle nail syndrome and eczema showed no significant differences compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings highlight nailfold capillaroscopy as a potentially quick, cost-effective, and noninvasive imaging modality as an adjunct for diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with onychodystrophies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan K. Hwang, MD, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, and was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included a small sample size for certain nail conditions and the single-center design, which limited generalizability. Additionally, the uneven surface, scaling, onycholysis, and thickening of toenails made some capillaroscopy images difficult to capture and interpret.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. One author reported serving as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Ortho-Dermatologics, BelleTorus, and Moberg Pharma.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The single-center, observational cross-sectional pilot study evaluated patients aged ≥ 7 years with newly diagnosed nail disorders between January 2022 and May 2023.
- A total of 128 patients (average age, 46.1 years; range, 8-84 years) with nail psoriasis, onychomycosis, idiopathic/traumatic onycholysis, brittle nail syndrome, nail lichen planus, retronychia, and other nail conditions and those with no nail findings (controls) were enrolled.
- Researchers performed nailfold capillaroscopy imaging and compared capillary features between patients with nail conditions and the controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with nail psoriasis had decreased capillary density and length (P < .001), more crossed and tortuous capillaries (P < .02), and increased abnormal capillary morphology (P = .03) compared with controls. Specific abnormalities, such as branching and meandering capillaries, were more common among those with nail psoriasis (both 26.5%).
- Patients with fingernail and toenail onychomycosis had a higher frequency of abnormal capillary morphology (P < .02), particularly meandering capillaries (75.0% for fingernails and 76.9% for toenails). However, other abnormalities were less frequently observed.
- Patients with nail lichen planus (P < .01), onychopapilloma (P = .01), and retronychia (P = .03) showed significantly shorter capillaries than controls. Retronychia was also associated with increased disorganized polymorphic capillaries (P = .02).
- Patients with brittle nail syndrome and eczema showed no significant differences compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings highlight nailfold capillaroscopy as a potentially quick, cost-effective, and noninvasive imaging modality as an adjunct for diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with onychodystrophies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan K. Hwang, MD, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, and was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included a small sample size for certain nail conditions and the single-center design, which limited generalizability. Additionally, the uneven surface, scaling, onycholysis, and thickening of toenails made some capillaroscopy images difficult to capture and interpret.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. One author reported serving as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Ortho-Dermatologics, BelleTorus, and Moberg Pharma.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The single-center, observational cross-sectional pilot study evaluated patients aged ≥ 7 years with newly diagnosed nail disorders between January 2022 and May 2023.
- A total of 128 patients (average age, 46.1 years; range, 8-84 years) with nail psoriasis, onychomycosis, idiopathic/traumatic onycholysis, brittle nail syndrome, nail lichen planus, retronychia, and other nail conditions and those with no nail findings (controls) were enrolled.
- Researchers performed nailfold capillaroscopy imaging and compared capillary features between patients with nail conditions and the controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with nail psoriasis had decreased capillary density and length (P < .001), more crossed and tortuous capillaries (P < .02), and increased abnormal capillary morphology (P = .03) compared with controls. Specific abnormalities, such as branching and meandering capillaries, were more common among those with nail psoriasis (both 26.5%).
- Patients with fingernail and toenail onychomycosis had a higher frequency of abnormal capillary morphology (P < .02), particularly meandering capillaries (75.0% for fingernails and 76.9% for toenails). However, other abnormalities were less frequently observed.
- Patients with nail lichen planus (P < .01), onychopapilloma (P = .01), and retronychia (P = .03) showed significantly shorter capillaries than controls. Retronychia was also associated with increased disorganized polymorphic capillaries (P = .02).
- Patients with brittle nail syndrome and eczema showed no significant differences compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings highlight nailfold capillaroscopy as a potentially quick, cost-effective, and noninvasive imaging modality as an adjunct for diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with onychodystrophies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan K. Hwang, MD, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, and was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included a small sample size for certain nail conditions and the single-center design, which limited generalizability. Additionally, the uneven surface, scaling, onycholysis, and thickening of toenails made some capillaroscopy images difficult to capture and interpret.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. One author reported serving as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Ortho-Dermatologics, BelleTorus, and Moberg Pharma.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Connected to Sunscreen Usage?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has become increasingly common since it was first described in 1994.1 A positive correlation between FFA and the use of sunscreens was reported in an observational study.2 The geographic distribution of this association has spanned the United Kingdom (UK), Europe, and Asia, though data from the United States are lacking. Various international studies have demonstrated an association between FFA and sunscreen use, further exemplifying this stark contrast.
In the United Kingdom (UK), Aldoori et al2 found that women who used sunscreen at least twice weekly had 2 times the likelihood of developing FFA compared with women who did not use sunscreen regularly. Kidambi et al3 found similar results in UK men with FFA who had higher rates of primary sunscreen use and higher rates of at least twice-weekly use of facial moisturizer with unspecified sunscreen content.
These associations between FFA and sunscreen use are not unique to the UK. A study conducted in Spain identified a statistical association between FFA and use of facial sunscreen in women (odds ratio, 1.6 [95% CI, 1.06-2.41]) and men (odds ratio, 1.84 [95% CI, 1.04-3.23]).4 In Thailand, FFA was nearly twice as likely to be present in patients with regular sunscreen use compared to controls who did not apply sunscreen regularly.5 Interestingly, a Brazilian study showed no connection between sunscreen use and FFA. Instead, FFA was associated with hair straightening with formalin or use of facial soap orfacial moisturizer.6 An international systematic review of 1248 patients with FFA and 1459 controls determined that sunscreen users were 2.21 times more likely to develop FFA than their counterparts who did not use sunscreen regularly.7
Quite glaring is the lack of data from the United States, which could be used to compare FFA and sunscreen associations to other nations. It is possible that certain regions of the world such as the United States may not have an increased risk for FFA in sunscreen users due to other environmental factors, differing sunscreen application practices, or differing chemical ingredients. At the same time, many other countries cannot afford or lack access to sunscreens or facial moisturizers, which is an additional variable that may complicate this association. These populations need to be studied to determine whether they are as susceptible to FFA as those who use sunscreen regularly around the world.
Another underlying factor supporting this association is the inherent need for sunscreen use. For instance, research has shown that patients with FFA had higher rates of actinic skin damage, which could explain increased sunscreen use.8
To make more clear and distinct claims, further studies are needed in regions that are known to use sunscreen extensively (eg, United States) to compare with their European, Asian, and South American counterparts. Moreover, it also is important to study regions where sunscreen access is limited and whether there is FFA development in these populations.
Given the potential association between sunscreen use and FFA, dermatologists can take a cautious approach tailored to the patient by recommending noncomedogenic mineral sunscreens with zinc or titanium oxide, which are less irritating than chemical sunscreens. Avoidance of sunscreen application to the hairline and use of additional sun-protection methods such as broad-brimmed hats also should be emphasized.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens: a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767.
- Kidambi AD, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with leave-on facial cosmetics and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2020;175:61-67.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case-control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Leecharoen W, Thanomkitti K, Thuangtong R, et al. Use of facial care products and frontal fibrosing alopecia: coincidence or true association? J Dermatol. 2021;48:1557-1563.
- Müller Ramos P, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:712-718. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.07
- Kam O, Na S, Guo W, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and personal care product use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2313-2331. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02604-7
- Porriño-Bustamante ML, Montero-Vílchez T, Pinedo-Moraleda FJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and sunscreen use: a cross-sectionalstudy of actinic damage. Acta Derm Venereol. Published online August 11, 2022. doi:10.2340/actadv.v102.306
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has become increasingly common since it was first described in 1994.1 A positive correlation between FFA and the use of sunscreens was reported in an observational study.2 The geographic distribution of this association has spanned the United Kingdom (UK), Europe, and Asia, though data from the United States are lacking. Various international studies have demonstrated an association between FFA and sunscreen use, further exemplifying this stark contrast.
In the United Kingdom (UK), Aldoori et al2 found that women who used sunscreen at least twice weekly had 2 times the likelihood of developing FFA compared with women who did not use sunscreen regularly. Kidambi et al3 found similar results in UK men with FFA who had higher rates of primary sunscreen use and higher rates of at least twice-weekly use of facial moisturizer with unspecified sunscreen content.
These associations between FFA and sunscreen use are not unique to the UK. A study conducted in Spain identified a statistical association between FFA and use of facial sunscreen in women (odds ratio, 1.6 [95% CI, 1.06-2.41]) and men (odds ratio, 1.84 [95% CI, 1.04-3.23]).4 In Thailand, FFA was nearly twice as likely to be present in patients with regular sunscreen use compared to controls who did not apply sunscreen regularly.5 Interestingly, a Brazilian study showed no connection between sunscreen use and FFA. Instead, FFA was associated with hair straightening with formalin or use of facial soap orfacial moisturizer.6 An international systematic review of 1248 patients with FFA and 1459 controls determined that sunscreen users were 2.21 times more likely to develop FFA than their counterparts who did not use sunscreen regularly.7
Quite glaring is the lack of data from the United States, which could be used to compare FFA and sunscreen associations to other nations. It is possible that certain regions of the world such as the United States may not have an increased risk for FFA in sunscreen users due to other environmental factors, differing sunscreen application practices, or differing chemical ingredients. At the same time, many other countries cannot afford or lack access to sunscreens or facial moisturizers, which is an additional variable that may complicate this association. These populations need to be studied to determine whether they are as susceptible to FFA as those who use sunscreen regularly around the world.
Another underlying factor supporting this association is the inherent need for sunscreen use. For instance, research has shown that patients with FFA had higher rates of actinic skin damage, which could explain increased sunscreen use.8
To make more clear and distinct claims, further studies are needed in regions that are known to use sunscreen extensively (eg, United States) to compare with their European, Asian, and South American counterparts. Moreover, it also is important to study regions where sunscreen access is limited and whether there is FFA development in these populations.
Given the potential association between sunscreen use and FFA, dermatologists can take a cautious approach tailored to the patient by recommending noncomedogenic mineral sunscreens with zinc or titanium oxide, which are less irritating than chemical sunscreens. Avoidance of sunscreen application to the hairline and use of additional sun-protection methods such as broad-brimmed hats also should be emphasized.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has become increasingly common since it was first described in 1994.1 A positive correlation between FFA and the use of sunscreens was reported in an observational study.2 The geographic distribution of this association has spanned the United Kingdom (UK), Europe, and Asia, though data from the United States are lacking. Various international studies have demonstrated an association between FFA and sunscreen use, further exemplifying this stark contrast.
In the United Kingdom (UK), Aldoori et al2 found that women who used sunscreen at least twice weekly had 2 times the likelihood of developing FFA compared with women who did not use sunscreen regularly. Kidambi et al3 found similar results in UK men with FFA who had higher rates of primary sunscreen use and higher rates of at least twice-weekly use of facial moisturizer with unspecified sunscreen content.
These associations between FFA and sunscreen use are not unique to the UK. A study conducted in Spain identified a statistical association between FFA and use of facial sunscreen in women (odds ratio, 1.6 [95% CI, 1.06-2.41]) and men (odds ratio, 1.84 [95% CI, 1.04-3.23]).4 In Thailand, FFA was nearly twice as likely to be present in patients with regular sunscreen use compared to controls who did not apply sunscreen regularly.5 Interestingly, a Brazilian study showed no connection between sunscreen use and FFA. Instead, FFA was associated with hair straightening with formalin or use of facial soap orfacial moisturizer.6 An international systematic review of 1248 patients with FFA and 1459 controls determined that sunscreen users were 2.21 times more likely to develop FFA than their counterparts who did not use sunscreen regularly.7
Quite glaring is the lack of data from the United States, which could be used to compare FFA and sunscreen associations to other nations. It is possible that certain regions of the world such as the United States may not have an increased risk for FFA in sunscreen users due to other environmental factors, differing sunscreen application practices, or differing chemical ingredients. At the same time, many other countries cannot afford or lack access to sunscreens or facial moisturizers, which is an additional variable that may complicate this association. These populations need to be studied to determine whether they are as susceptible to FFA as those who use sunscreen regularly around the world.
Another underlying factor supporting this association is the inherent need for sunscreen use. For instance, research has shown that patients with FFA had higher rates of actinic skin damage, which could explain increased sunscreen use.8
To make more clear and distinct claims, further studies are needed in regions that are known to use sunscreen extensively (eg, United States) to compare with their European, Asian, and South American counterparts. Moreover, it also is important to study regions where sunscreen access is limited and whether there is FFA development in these populations.
Given the potential association between sunscreen use and FFA, dermatologists can take a cautious approach tailored to the patient by recommending noncomedogenic mineral sunscreens with zinc or titanium oxide, which are less irritating than chemical sunscreens. Avoidance of sunscreen application to the hairline and use of additional sun-protection methods such as broad-brimmed hats also should be emphasized.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens: a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767.
- Kidambi AD, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with leave-on facial cosmetics and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2020;175:61-67.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case-control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Leecharoen W, Thanomkitti K, Thuangtong R, et al. Use of facial care products and frontal fibrosing alopecia: coincidence or true association? J Dermatol. 2021;48:1557-1563.
- Müller Ramos P, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:712-718. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.07
- Kam O, Na S, Guo W, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and personal care product use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2313-2331. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02604-7
- Porriño-Bustamante ML, Montero-Vílchez T, Pinedo-Moraleda FJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and sunscreen use: a cross-sectionalstudy of actinic damage. Acta Derm Venereol. Published online August 11, 2022. doi:10.2340/actadv.v102.306
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens: a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767.
- Kidambi AD, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with leave-on facial cosmetics and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2020;175:61-67.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case-control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Leecharoen W, Thanomkitti K, Thuangtong R, et al. Use of facial care products and frontal fibrosing alopecia: coincidence or true association? J Dermatol. 2021;48:1557-1563.
- Müller Ramos P, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:712-718. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.07
- Kam O, Na S, Guo W, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and personal care product use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2313-2331. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02604-7
- Porriño-Bustamante ML, Montero-Vílchez T, Pinedo-Moraleda FJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and sunscreen use: a cross-sectionalstudy of actinic damage. Acta Derm Venereol. Published online August 11, 2022. doi:10.2340/actadv.v102.306
Metformin Led to Improvements in Women with Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia
TOPLINE:
, in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 upregulated genes, which included upregulated of 23 hair keratin-associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were downregulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. In addition, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 upregulated genes, which included upregulated of 23 hair keratin-associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were downregulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. In addition, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 upregulated genes, which included upregulated of 23 hair keratin-associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were downregulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. In addition, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Storybooks Can Help Children Deal with Skin Conditions
TORONTO —
So far, “the study demonstrates that these books have value to patients and families,” one of the study authors, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“There are tools to help kids cope with their skin conditions, but we’re underutilizing them,” she added. “And part of the reason we’re underutilizing storybooks is that we just don’t know what’s out there.” For the study, the researchers received funding to purchase 18 “creative and thoughtful” storybooks related to pediatric skin conditions, reviewed by at least two pediatric dermatologists before being selected, which are just a sample of related books that are available.
The study results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Children with visible skin conditions, which can include port-wine stains, capillary malformations, and congenital moles, may be subjected to teasing or bullying at school, and the conditions can also affect their quality of life.
Beauty and the Birthmark
The books include one titled “Beauty with a Birthmark” and another, “My Hair Went on Vacation.” An illustrated book, “Just Ask: Be Different, Be Brave, Be You,” by US Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor, offers tips on how to answer common questions about someone’s appearance.
Dr. Havele said that Justice Sotomayor’s book “empowers kids, their siblings, their classmates ... to ask questions, and it teaches patients not to be afraid of those questions, and to really lean into educating their peers, and their family members.”
“Kids are really just curious,” she added. “They’ll make comments like: ‘Hey, what’s that spot on your face?’ Or, they’ll ask about vitiligo because they’ve never seen somebody with it before.”
To evaluate the psychosocial impact of these types of books for children with visible skin conditions, Dr. Havele and colleagues designed a study that includes patients aged 2-12 years dealing with issues related to self-esteem, acceptance, coping, or bullying. Parents are provided with a relevant storybook to read at home with their child in a “safe and comfortable space” and “at their own pace and their own time,” said Dr. Havele.
Inside the book is a QR code to access the validated Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). Families complete the survey at baseline and provide feedback after reading the book. Researchers collect information about demographics, age, gender, and skin conditions, which included atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hemangioma, and port-wine stain.
The response rate so far is 34%, and close to 80 parents have completed the survey with their child, Dr. Havele said.
At baseline, many of the children were either moderately or severely affected in terms of their quality of life (45% scored ≥ 6 on the CDLQI).
After reading the book, about 80% of parents reported it had a positive impact, and about 20% said it had a somewhat positive impact on their child’s self-image or confidence. Almost 80% agreed, and the remainder somewhat agreed it encouraged their child to embrace differences.
Most respondents also said the book helped the parent and child cope with the child’s condition. “So really, it was overall a positive response,” said Dr. Havele. “We are able to demonstrate that these books have value in a more scientific or objective way.”
This may not be surprising. Dr. Havele referred to more formal bibliotherapy (book therapy), which has been studied in other pediatric populations, including patients with cancer and those who have experienced trauma.
Awesome Space
Pediatric dermatologists are perfectly positioned to play a role in improving the lives of their patients with skin issues. “We see the impact of visible skin disease on children all the time,” said Dr. Havele. “The dermatology visit is an awesome space and opportunity to introduce these books to families and potentially help them talk about the skin condition with their child.”
In addition to prescribing therapies, “we’re also with these kids through an emotional journey, and I think giving them tools for that emotional journey is very helpful,” she added.
Such books would have been a great help to Dr. Havele herself. Growing up, she had severe atopic dermatitis covering much of her body. “Having such a resource would have helped me better cope with my reality of being different than everyone else.”
She hopes a database will be established to house these resources so other providers can refer patients to the list of books. Other books include “The Itchy-saurus: The Dino with an itch that can’t be scratched,” “Hair in My Brush,” and “I am Unique!”
Dr. Havele had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TORONTO —
So far, “the study demonstrates that these books have value to patients and families,” one of the study authors, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“There are tools to help kids cope with their skin conditions, but we’re underutilizing them,” she added. “And part of the reason we’re underutilizing storybooks is that we just don’t know what’s out there.” For the study, the researchers received funding to purchase 18 “creative and thoughtful” storybooks related to pediatric skin conditions, reviewed by at least two pediatric dermatologists before being selected, which are just a sample of related books that are available.
The study results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Children with visible skin conditions, which can include port-wine stains, capillary malformations, and congenital moles, may be subjected to teasing or bullying at school, and the conditions can also affect their quality of life.
Beauty and the Birthmark
The books include one titled “Beauty with a Birthmark” and another, “My Hair Went on Vacation.” An illustrated book, “Just Ask: Be Different, Be Brave, Be You,” by US Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor, offers tips on how to answer common questions about someone’s appearance.
Dr. Havele said that Justice Sotomayor’s book “empowers kids, their siblings, their classmates ... to ask questions, and it teaches patients not to be afraid of those questions, and to really lean into educating their peers, and their family members.”
“Kids are really just curious,” she added. “They’ll make comments like: ‘Hey, what’s that spot on your face?’ Or, they’ll ask about vitiligo because they’ve never seen somebody with it before.”
To evaluate the psychosocial impact of these types of books for children with visible skin conditions, Dr. Havele and colleagues designed a study that includes patients aged 2-12 years dealing with issues related to self-esteem, acceptance, coping, or bullying. Parents are provided with a relevant storybook to read at home with their child in a “safe and comfortable space” and “at their own pace and their own time,” said Dr. Havele.
Inside the book is a QR code to access the validated Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). Families complete the survey at baseline and provide feedback after reading the book. Researchers collect information about demographics, age, gender, and skin conditions, which included atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hemangioma, and port-wine stain.
The response rate so far is 34%, and close to 80 parents have completed the survey with their child, Dr. Havele said.
At baseline, many of the children were either moderately or severely affected in terms of their quality of life (45% scored ≥ 6 on the CDLQI).
After reading the book, about 80% of parents reported it had a positive impact, and about 20% said it had a somewhat positive impact on their child’s self-image or confidence. Almost 80% agreed, and the remainder somewhat agreed it encouraged their child to embrace differences.
Most respondents also said the book helped the parent and child cope with the child’s condition. “So really, it was overall a positive response,” said Dr. Havele. “We are able to demonstrate that these books have value in a more scientific or objective way.”
This may not be surprising. Dr. Havele referred to more formal bibliotherapy (book therapy), which has been studied in other pediatric populations, including patients with cancer and those who have experienced trauma.
Awesome Space
Pediatric dermatologists are perfectly positioned to play a role in improving the lives of their patients with skin issues. “We see the impact of visible skin disease on children all the time,” said Dr. Havele. “The dermatology visit is an awesome space and opportunity to introduce these books to families and potentially help them talk about the skin condition with their child.”
In addition to prescribing therapies, “we’re also with these kids through an emotional journey, and I think giving them tools for that emotional journey is very helpful,” she added.
Such books would have been a great help to Dr. Havele herself. Growing up, she had severe atopic dermatitis covering much of her body. “Having such a resource would have helped me better cope with my reality of being different than everyone else.”
She hopes a database will be established to house these resources so other providers can refer patients to the list of books. Other books include “The Itchy-saurus: The Dino with an itch that can’t be scratched,” “Hair in My Brush,” and “I am Unique!”
Dr. Havele had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TORONTO —
So far, “the study demonstrates that these books have value to patients and families,” one of the study authors, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“There are tools to help kids cope with their skin conditions, but we’re underutilizing them,” she added. “And part of the reason we’re underutilizing storybooks is that we just don’t know what’s out there.” For the study, the researchers received funding to purchase 18 “creative and thoughtful” storybooks related to pediatric skin conditions, reviewed by at least two pediatric dermatologists before being selected, which are just a sample of related books that are available.
The study results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Children with visible skin conditions, which can include port-wine stains, capillary malformations, and congenital moles, may be subjected to teasing or bullying at school, and the conditions can also affect their quality of life.
Beauty and the Birthmark
The books include one titled “Beauty with a Birthmark” and another, “My Hair Went on Vacation.” An illustrated book, “Just Ask: Be Different, Be Brave, Be You,” by US Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor, offers tips on how to answer common questions about someone’s appearance.
Dr. Havele said that Justice Sotomayor’s book “empowers kids, their siblings, their classmates ... to ask questions, and it teaches patients not to be afraid of those questions, and to really lean into educating their peers, and their family members.”
“Kids are really just curious,” she added. “They’ll make comments like: ‘Hey, what’s that spot on your face?’ Or, they’ll ask about vitiligo because they’ve never seen somebody with it before.”
To evaluate the psychosocial impact of these types of books for children with visible skin conditions, Dr. Havele and colleagues designed a study that includes patients aged 2-12 years dealing with issues related to self-esteem, acceptance, coping, or bullying. Parents are provided with a relevant storybook to read at home with their child in a “safe and comfortable space” and “at their own pace and their own time,” said Dr. Havele.
Inside the book is a QR code to access the validated Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). Families complete the survey at baseline and provide feedback after reading the book. Researchers collect information about demographics, age, gender, and skin conditions, which included atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hemangioma, and port-wine stain.
The response rate so far is 34%, and close to 80 parents have completed the survey with their child, Dr. Havele said.
At baseline, many of the children were either moderately or severely affected in terms of their quality of life (45% scored ≥ 6 on the CDLQI).
After reading the book, about 80% of parents reported it had a positive impact, and about 20% said it had a somewhat positive impact on their child’s self-image or confidence. Almost 80% agreed, and the remainder somewhat agreed it encouraged their child to embrace differences.
Most respondents also said the book helped the parent and child cope with the child’s condition. “So really, it was overall a positive response,” said Dr. Havele. “We are able to demonstrate that these books have value in a more scientific or objective way.”
This may not be surprising. Dr. Havele referred to more formal bibliotherapy (book therapy), which has been studied in other pediatric populations, including patients with cancer and those who have experienced trauma.
Awesome Space
Pediatric dermatologists are perfectly positioned to play a role in improving the lives of their patients with skin issues. “We see the impact of visible skin disease on children all the time,” said Dr. Havele. “The dermatology visit is an awesome space and opportunity to introduce these books to families and potentially help them talk about the skin condition with their child.”
In addition to prescribing therapies, “we’re also with these kids through an emotional journey, and I think giving them tools for that emotional journey is very helpful,” she added.
Such books would have been a great help to Dr. Havele herself. Growing up, she had severe atopic dermatitis covering much of her body. “Having such a resource would have helped me better cope with my reality of being different than everyone else.”
She hopes a database will be established to house these resources so other providers can refer patients to the list of books. Other books include “The Itchy-saurus: The Dino with an itch that can’t be scratched,” “Hair in My Brush,” and “I am Unique!”
Dr. Havele had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Optimizing Patient Care With Teledermatology: Improving Access, Efficiency, and Satisfaction
Telemedicine interest, which was relatively quiescent prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has surged in popularity in the past few years.1 It can now be utilized seamlessly in dermatology practices to deliver exceptional patient care while reducing costs and travel time and offering dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance. Teledermatology applications include synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid platforms.2 For synchronous teledermatology, patient visits are carried out in real time with audio and video technology.3 For asynchronous teledermatology—also known as the store-and-forward model—the dermatologist receives the patient’s history and photographs and then renders an assessment and treatment plan.2 Hybrid teledermatology uses real-time audio and video conferencing for history taking, assessment and treatment plan, and patient education, with photographs sent asynchronously.3 Telemedicine may not be initially intuitive or easy to integrate into clinical practice, but with time and effort, it will complement your dermatology practice, making it run more efficiently.
Patient Satisfaction With Teledermatology
Studies generally have shown very high patient satisfaction rates and shorter wait times with teledermatology vs in-person visits; for example, in a systematic review of 15 teledermatology studies including 7781 patients, more than 80% of participants reported high satisfaction with their telemedicine visit, with up to 92% reporting that they would choose to do a televisit again.4 In a retrospective analysis of 615 Zocdoc physicians, 65% of whom were dermatologists, mean wait times were 2.4 days for virtual appointments compared with 11.7 days for in-person appointments.5 Similarly, in a retrospective single-institution study, mean wait times for televisits were 14.3 days compared with 34.7 days for in-person referrals.6
Follow-Up Visits for Nail Disorders Via Teledermatology
Teledermatology may be particularly well suited for treating patients with nail disorders. In a prospective observational study, Onyeka et al7 accessed 813 images from 63 dermatology patients via teledermatology over a 6-month period to assess distance, focus, brightness, background, and image quality; of them, 83% were rated as high quality. Notably, images of nail disorders, skin growths, or pigmentation disorders were rated as having better image quality than images of inflammatory skin conditions (odds ratio [OR], 4.2-12.9 [P<.005]).7 In a retrospective study of 107 telemedicine visits for nail disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients with longitudinal melanonychia were recommended for in-person visits for physical examination and dermoscopy, as were patients with suspected onychomycosis, who required nail plate sampling for diagnostic confirmation; however, approximately half of visits did not require in-person follow-up, including those patients with confirmed onychomycosis.8 Onychomycosis patients could be examined for clinical improvement and counseled on medication compliance via telemedicine. Other patients who did not require in-person follow-ups were those with traumatic nail disorders such as subungual hematoma and retronychia as well as those with body‐focused repetitive behaviors, including habit-tic nail deformity, onychophagia, and onychotillomania.8
Patients undergoing nail biopsies to rule out malignancies or to diagnose inflammatory nail disorders also may be managed via telemedicine. Patients for whom nail biopsies are recommended often are anxious about the procedure, which may be due to portrayal of nail trauma in the media9 or lack of accurate information on nail biopsies online.10 Therefore, counseling via telemedicine about the details of the procedure in a patient-friendly way (eg, showing an animated video and narrating it11) can allay anxiety without the inconvenience, cost, and time missed from work associated with traveling to an in-person visit. In addition, postoperative counseling ideally is performed via telemedicine because complications following nail procedures are uncommon. In a retrospective study of 502 patients who underwent a nail biopsy at a single academic center, only 14 developed surgical site infections within 8 days on average (range, 5–13 days), with a higher infection risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (P<.0003).12
Advantages and Limitations
There are many benefits to incorporating telemedicine into dermatology practices, including reduced overhead costs, convenience and time saved for patients, and flexibility and improved work-life balance for dermatologists. In addition, because the number of in-person visits seen generally is fixed due to space constraints and work-hour restrictions, delegating follow-up visits to telemedicine can free up in-person slots for new patients and those needing procedures. However, there also are some inherent limitations to telemedicine: technology access, vision or hearing difficulties or low digital health literacy, or language barriers. In the prospective observational study by Onyeka et al7 analyzing 813 teledermatology images, patients aged 65 to 74 years sent in more clinically useful images (OR, 7.9) and images that were more often in focus (OR, 2.6) compared with patients older than 85 years.
Final Thoughts
Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice is a valuable tool for triaging patients with acute issues, improving patient care and health care access, making practices more efficient, and improving dermatologist flexibility and work-life balance. Further development of teledermatology to provide access to underserved populations prioritizing dermatologist reimbursement and progress on technologic innovations will make teledermatology even more useful in the coming years.
- He A, Ti Kim T, Nguyen KD. Utilization of teledermatology services for dermatological diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1059-1062.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Wang RH, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL, et al. Synchronous and asynchronous teledermatology: a narrative review of strengths and limitations. J Telemed Telecare. 2022;28:533-538.
- Miller J, Jones E. Shaping the future of teledermatology: a literature review of patient and provider satisfaction with synchronous teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1903-1909.
- Gu L, Xiang L, Lipner SR. Analysis of availability of online dermatology appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:517-520.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an eConsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;83:1633-1638.
- Onyeka S, Kim J, Eid E, et al. Quality of images submitted by older patients to a teledermatology platform. Abstract presented at the Society of Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting; May 15-18, 2024; Dallas, TX.
- Chang MJ, Stewart CR, Lipner SR. Retrospective study of nail telemedicine visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14630.
- Albucker SJ, Falotico JM, Lipner SR. A real nail biter: a cross-sectional study of 75 nail trauma scenes in international films and television series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2023;27:288-291.
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Hill RC, Ho B, Lipner SR. Assuaging patient anxiety about nail biopsies with an animated educational video. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online March 29, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.031.
- Axler E, Lu A, Darrell M, et al. Surgical site infections are uncommon following nail biopsies in a single-center case-control study of 502 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online May 15, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.017
Telemedicine interest, which was relatively quiescent prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has surged in popularity in the past few years.1 It can now be utilized seamlessly in dermatology practices to deliver exceptional patient care while reducing costs and travel time and offering dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance. Teledermatology applications include synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid platforms.2 For synchronous teledermatology, patient visits are carried out in real time with audio and video technology.3 For asynchronous teledermatology—also known as the store-and-forward model—the dermatologist receives the patient’s history and photographs and then renders an assessment and treatment plan.2 Hybrid teledermatology uses real-time audio and video conferencing for history taking, assessment and treatment plan, and patient education, with photographs sent asynchronously.3 Telemedicine may not be initially intuitive or easy to integrate into clinical practice, but with time and effort, it will complement your dermatology practice, making it run more efficiently.
Patient Satisfaction With Teledermatology
Studies generally have shown very high patient satisfaction rates and shorter wait times with teledermatology vs in-person visits; for example, in a systematic review of 15 teledermatology studies including 7781 patients, more than 80% of participants reported high satisfaction with their telemedicine visit, with up to 92% reporting that they would choose to do a televisit again.4 In a retrospective analysis of 615 Zocdoc physicians, 65% of whom were dermatologists, mean wait times were 2.4 days for virtual appointments compared with 11.7 days for in-person appointments.5 Similarly, in a retrospective single-institution study, mean wait times for televisits were 14.3 days compared with 34.7 days for in-person referrals.6
Follow-Up Visits for Nail Disorders Via Teledermatology
Teledermatology may be particularly well suited for treating patients with nail disorders. In a prospective observational study, Onyeka et al7 accessed 813 images from 63 dermatology patients via teledermatology over a 6-month period to assess distance, focus, brightness, background, and image quality; of them, 83% were rated as high quality. Notably, images of nail disorders, skin growths, or pigmentation disorders were rated as having better image quality than images of inflammatory skin conditions (odds ratio [OR], 4.2-12.9 [P<.005]).7 In a retrospective study of 107 telemedicine visits for nail disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients with longitudinal melanonychia were recommended for in-person visits for physical examination and dermoscopy, as were patients with suspected onychomycosis, who required nail plate sampling for diagnostic confirmation; however, approximately half of visits did not require in-person follow-up, including those patients with confirmed onychomycosis.8 Onychomycosis patients could be examined for clinical improvement and counseled on medication compliance via telemedicine. Other patients who did not require in-person follow-ups were those with traumatic nail disorders such as subungual hematoma and retronychia as well as those with body‐focused repetitive behaviors, including habit-tic nail deformity, onychophagia, and onychotillomania.8
Patients undergoing nail biopsies to rule out malignancies or to diagnose inflammatory nail disorders also may be managed via telemedicine. Patients for whom nail biopsies are recommended often are anxious about the procedure, which may be due to portrayal of nail trauma in the media9 or lack of accurate information on nail biopsies online.10 Therefore, counseling via telemedicine about the details of the procedure in a patient-friendly way (eg, showing an animated video and narrating it11) can allay anxiety without the inconvenience, cost, and time missed from work associated with traveling to an in-person visit. In addition, postoperative counseling ideally is performed via telemedicine because complications following nail procedures are uncommon. In a retrospective study of 502 patients who underwent a nail biopsy at a single academic center, only 14 developed surgical site infections within 8 days on average (range, 5–13 days), with a higher infection risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (P<.0003).12
Advantages and Limitations
There are many benefits to incorporating telemedicine into dermatology practices, including reduced overhead costs, convenience and time saved for patients, and flexibility and improved work-life balance for dermatologists. In addition, because the number of in-person visits seen generally is fixed due to space constraints and work-hour restrictions, delegating follow-up visits to telemedicine can free up in-person slots for new patients and those needing procedures. However, there also are some inherent limitations to telemedicine: technology access, vision or hearing difficulties or low digital health literacy, or language barriers. In the prospective observational study by Onyeka et al7 analyzing 813 teledermatology images, patients aged 65 to 74 years sent in more clinically useful images (OR, 7.9) and images that were more often in focus (OR, 2.6) compared with patients older than 85 years.
Final Thoughts
Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice is a valuable tool for triaging patients with acute issues, improving patient care and health care access, making practices more efficient, and improving dermatologist flexibility and work-life balance. Further development of teledermatology to provide access to underserved populations prioritizing dermatologist reimbursement and progress on technologic innovations will make teledermatology even more useful in the coming years.
Telemedicine interest, which was relatively quiescent prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has surged in popularity in the past few years.1 It can now be utilized seamlessly in dermatology practices to deliver exceptional patient care while reducing costs and travel time and offering dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance. Teledermatology applications include synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid platforms.2 For synchronous teledermatology, patient visits are carried out in real time with audio and video technology.3 For asynchronous teledermatology—also known as the store-and-forward model—the dermatologist receives the patient’s history and photographs and then renders an assessment and treatment plan.2 Hybrid teledermatology uses real-time audio and video conferencing for history taking, assessment and treatment plan, and patient education, with photographs sent asynchronously.3 Telemedicine may not be initially intuitive or easy to integrate into clinical practice, but with time and effort, it will complement your dermatology practice, making it run more efficiently.
Patient Satisfaction With Teledermatology
Studies generally have shown very high patient satisfaction rates and shorter wait times with teledermatology vs in-person visits; for example, in a systematic review of 15 teledermatology studies including 7781 patients, more than 80% of participants reported high satisfaction with their telemedicine visit, with up to 92% reporting that they would choose to do a televisit again.4 In a retrospective analysis of 615 Zocdoc physicians, 65% of whom were dermatologists, mean wait times were 2.4 days for virtual appointments compared with 11.7 days for in-person appointments.5 Similarly, in a retrospective single-institution study, mean wait times for televisits were 14.3 days compared with 34.7 days for in-person referrals.6
Follow-Up Visits for Nail Disorders Via Teledermatology
Teledermatology may be particularly well suited for treating patients with nail disorders. In a prospective observational study, Onyeka et al7 accessed 813 images from 63 dermatology patients via teledermatology over a 6-month period to assess distance, focus, brightness, background, and image quality; of them, 83% were rated as high quality. Notably, images of nail disorders, skin growths, or pigmentation disorders were rated as having better image quality than images of inflammatory skin conditions (odds ratio [OR], 4.2-12.9 [P<.005]).7 In a retrospective study of 107 telemedicine visits for nail disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients with longitudinal melanonychia were recommended for in-person visits for physical examination and dermoscopy, as were patients with suspected onychomycosis, who required nail plate sampling for diagnostic confirmation; however, approximately half of visits did not require in-person follow-up, including those patients with confirmed onychomycosis.8 Onychomycosis patients could be examined for clinical improvement and counseled on medication compliance via telemedicine. Other patients who did not require in-person follow-ups were those with traumatic nail disorders such as subungual hematoma and retronychia as well as those with body‐focused repetitive behaviors, including habit-tic nail deformity, onychophagia, and onychotillomania.8
Patients undergoing nail biopsies to rule out malignancies or to diagnose inflammatory nail disorders also may be managed via telemedicine. Patients for whom nail biopsies are recommended often are anxious about the procedure, which may be due to portrayal of nail trauma in the media9 or lack of accurate information on nail biopsies online.10 Therefore, counseling via telemedicine about the details of the procedure in a patient-friendly way (eg, showing an animated video and narrating it11) can allay anxiety without the inconvenience, cost, and time missed from work associated with traveling to an in-person visit. In addition, postoperative counseling ideally is performed via telemedicine because complications following nail procedures are uncommon. In a retrospective study of 502 patients who underwent a nail biopsy at a single academic center, only 14 developed surgical site infections within 8 days on average (range, 5–13 days), with a higher infection risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (P<.0003).12
Advantages and Limitations
There are many benefits to incorporating telemedicine into dermatology practices, including reduced overhead costs, convenience and time saved for patients, and flexibility and improved work-life balance for dermatologists. In addition, because the number of in-person visits seen generally is fixed due to space constraints and work-hour restrictions, delegating follow-up visits to telemedicine can free up in-person slots for new patients and those needing procedures. However, there also are some inherent limitations to telemedicine: technology access, vision or hearing difficulties or low digital health literacy, or language barriers. In the prospective observational study by Onyeka et al7 analyzing 813 teledermatology images, patients aged 65 to 74 years sent in more clinically useful images (OR, 7.9) and images that were more often in focus (OR, 2.6) compared with patients older than 85 years.
Final Thoughts
Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice is a valuable tool for triaging patients with acute issues, improving patient care and health care access, making practices more efficient, and improving dermatologist flexibility and work-life balance. Further development of teledermatology to provide access to underserved populations prioritizing dermatologist reimbursement and progress on technologic innovations will make teledermatology even more useful in the coming years.
- He A, Ti Kim T, Nguyen KD. Utilization of teledermatology services for dermatological diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1059-1062.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Wang RH, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL, et al. Synchronous and asynchronous teledermatology: a narrative review of strengths and limitations. J Telemed Telecare. 2022;28:533-538.
- Miller J, Jones E. Shaping the future of teledermatology: a literature review of patient and provider satisfaction with synchronous teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1903-1909.
- Gu L, Xiang L, Lipner SR. Analysis of availability of online dermatology appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:517-520.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an eConsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;83:1633-1638.
- Onyeka S, Kim J, Eid E, et al. Quality of images submitted by older patients to a teledermatology platform. Abstract presented at the Society of Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting; May 15-18, 2024; Dallas, TX.
- Chang MJ, Stewart CR, Lipner SR. Retrospective study of nail telemedicine visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14630.
- Albucker SJ, Falotico JM, Lipner SR. A real nail biter: a cross-sectional study of 75 nail trauma scenes in international films and television series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2023;27:288-291.
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Hill RC, Ho B, Lipner SR. Assuaging patient anxiety about nail biopsies with an animated educational video. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online March 29, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.031.
- Axler E, Lu A, Darrell M, et al. Surgical site infections are uncommon following nail biopsies in a single-center case-control study of 502 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online May 15, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.017
- He A, Ti Kim T, Nguyen KD. Utilization of teledermatology services for dermatological diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1059-1062.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Wang RH, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL, et al. Synchronous and asynchronous teledermatology: a narrative review of strengths and limitations. J Telemed Telecare. 2022;28:533-538.
- Miller J, Jones E. Shaping the future of teledermatology: a literature review of patient and provider satisfaction with synchronous teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1903-1909.
- Gu L, Xiang L, Lipner SR. Analysis of availability of online dermatology appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:517-520.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an eConsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;83:1633-1638.
- Onyeka S, Kim J, Eid E, et al. Quality of images submitted by older patients to a teledermatology platform. Abstract presented at the Society of Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting; May 15-18, 2024; Dallas, TX.
- Chang MJ, Stewart CR, Lipner SR. Retrospective study of nail telemedicine visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14630.
- Albucker SJ, Falotico JM, Lipner SR. A real nail biter: a cross-sectional study of 75 nail trauma scenes in international films and television series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2023;27:288-291.
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Hill RC, Ho B, Lipner SR. Assuaging patient anxiety about nail biopsies with an animated educational video. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online March 29, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.031.
- Axler E, Lu A, Darrell M, et al. Surgical site infections are uncommon following nail biopsies in a single-center case-control study of 502 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online May 15, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.017
Practice Points
- Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice can improve patient access, reduce costs, and offer dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance.
- Patient satisfaction with telemedicine is exceedingly high, and teledermatology may be particularly well suited for caring for patients with nail disorders.
Customized Dermal Curette: An Alternative and Effective Shaving Tool in Nail Surgery
Practice Gap
Longitudinal melanonychia (LM) is characterized by the presence of a dark brown, longitudinal, pigmented band on the nail unit, often caused by melanocytic activation or melanocytic hyperplasia in the nail matrix. Distinguishing between benign and early malignant LM is crucial due to their similar clinical presentations.1 Hence, surgical excision of the pigmented nail matrix followed by histopathologic examination is a common procedure aimed at managing LM and reducing the risk for delayed diagnosis of subungual melanoma.
Tangential matrix excision combined with the nail window technique has emerged as a common and favored surgical strategy for managing LM.2 This method is highly valued for its ability to minimize the risk for severe permanent nail dystrophy and effectively reduce postsurgical pigmentation recurrence.
The procedure begins with the creation of a matrix window along the lateral edge of the pigmented band followed by 1 lateral incision carefully made on each side of the nail fold. This meticulous approach allows for the complete exposure of the pigmented lesion. Subsequently, the nail fold is separated from the dorsal surface of the nail plate to facilitate access to the pigmented nail matrix. Finally, the target pigmented area is excised using a scalpel.
Despite the recognized efficacy of this procedure, challenges do arise, particularly when the width of the pigmented matrix lesion is narrow. Holding the scalpel horizontally to ensure precise excision can prove to be demanding, leading to difficulty achieving complete lesion removal and obtaining the desired cosmetic outcomes. As such, there is a clear need to explore alternative tools that can effectively address these challenges while ensuring optimal surgical outcomes for patients with LM. We propose the use of the customized dermal curette.
The Technique
An improved curette tool is a practical solution for complete removal of the pigmented nail matrix. This enhanced instrument is crafted from a sterile disposable dermal curette with its top flattened using a needle holder(Figure 1). Termed the customized dermal curette, this device is a simple yet accurate tool for the precise excision of pigmented lesions within the nail matrix. Importantly, it offers versatility by accommodating different widths of pigmented lesions through the availability of various sizes of dermal curettes (Figure 2).
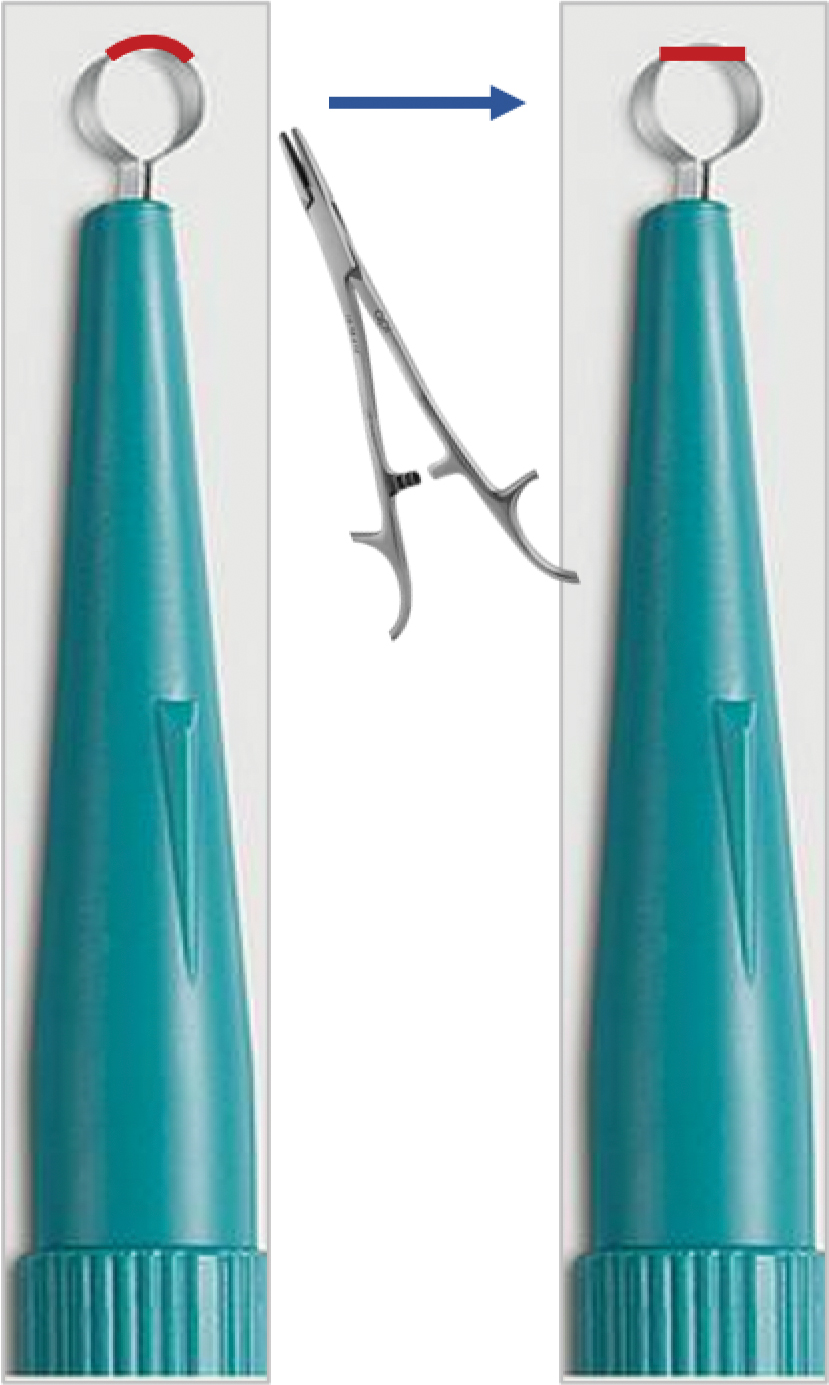

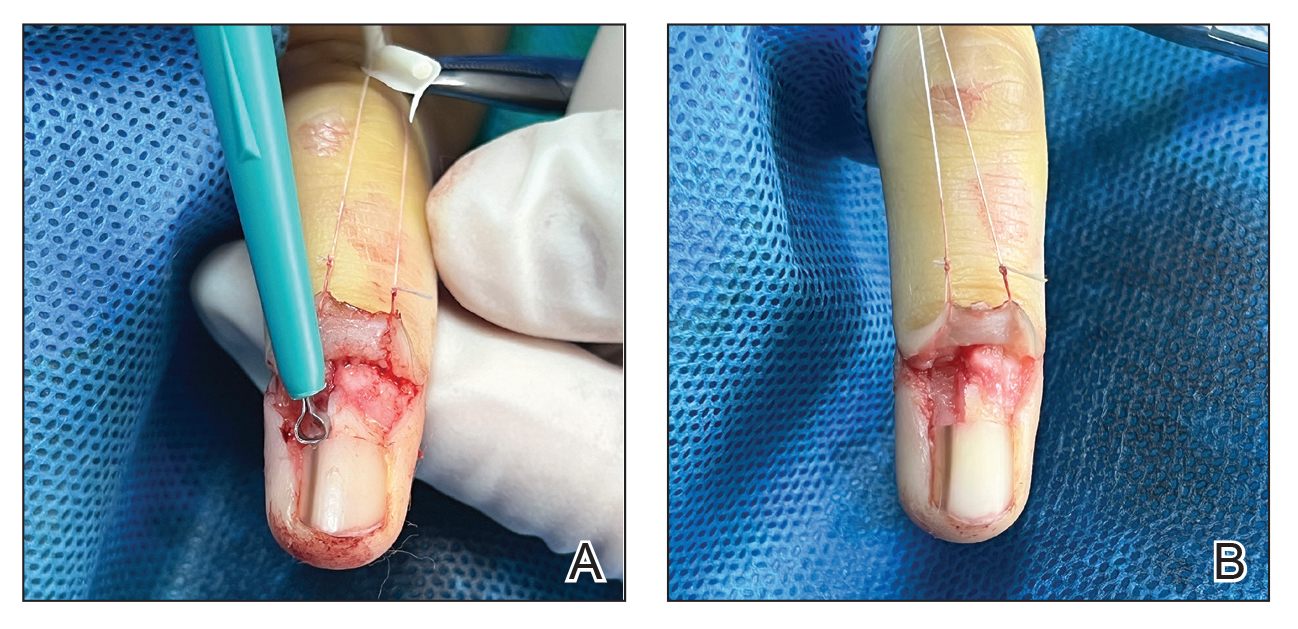
Histopathologically, we have found that the scalpel technique may lead to variable tissue removal, resulting in differences in tissue thickness, fragility, and completeness (Figure 3A). Conversely, the customized dermal curette consistently provides more accurate tissue excision, resulting in uniform tissue thickness and integrity (Figure 3B).
Practice Implications
Compared to the traditional scalpel, this modified tool offers distinct advantages. Specifically, the customized dermal curette provides enhanced maneuverability and control during the procedure, thereby improving the overall efficacy of the excision process. It also offers a more accurate approach to completely remove pigmented bands, which reduces the risk for postoperative recurrence. The simplicity, affordability, and ease of operation associated with customized dermal curettes holds promise as an effective alternative for tissue shaving, especially in cases involving narrow pigmented matrix lesions, thereby addressing a notable practice gap and enhancing patient care.
- Tan WC, Wang DY, Seghers AC, et al. Should we biopsy melanonychia striata in Asian children? a retrospective observational study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:864-868. doi:10.1111/pde.13934
- Zhou Y, Chen W, Liu ZR, et al. Modified shave surgery combined with nail window technique for the treatment of longitudinal melanonychia: evaluation of the method on a series of 67 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:717-722. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.03.065
Practice Gap
Longitudinal melanonychia (LM) is characterized by the presence of a dark brown, longitudinal, pigmented band on the nail unit, often caused by melanocytic activation or melanocytic hyperplasia in the nail matrix. Distinguishing between benign and early malignant LM is crucial due to their similar clinical presentations.1 Hence, surgical excision of the pigmented nail matrix followed by histopathologic examination is a common procedure aimed at managing LM and reducing the risk for delayed diagnosis of subungual melanoma.
Tangential matrix excision combined with the nail window technique has emerged as a common and favored surgical strategy for managing LM.2 This method is highly valued for its ability to minimize the risk for severe permanent nail dystrophy and effectively reduce postsurgical pigmentation recurrence.
The procedure begins with the creation of a matrix window along the lateral edge of the pigmented band followed by 1 lateral incision carefully made on each side of the nail fold. This meticulous approach allows for the complete exposure of the pigmented lesion. Subsequently, the nail fold is separated from the dorsal surface of the nail plate to facilitate access to the pigmented nail matrix. Finally, the target pigmented area is excised using a scalpel.
Despite the recognized efficacy of this procedure, challenges do arise, particularly when the width of the pigmented matrix lesion is narrow. Holding the scalpel horizontally to ensure precise excision can prove to be demanding, leading to difficulty achieving complete lesion removal and obtaining the desired cosmetic outcomes. As such, there is a clear need to explore alternative tools that can effectively address these challenges while ensuring optimal surgical outcomes for patients with LM. We propose the use of the customized dermal curette.
The Technique
An improved curette tool is a practical solution for complete removal of the pigmented nail matrix. This enhanced instrument is crafted from a sterile disposable dermal curette with its top flattened using a needle holder(Figure 1). Termed the customized dermal curette, this device is a simple yet accurate tool for the precise excision of pigmented lesions within the nail matrix. Importantly, it offers versatility by accommodating different widths of pigmented lesions through the availability of various sizes of dermal curettes (Figure 2).


Histopathologically, we have found that the scalpel technique may lead to variable tissue removal, resulting in differences in tissue thickness, fragility, and completeness (Figure 3A). Conversely, the customized dermal curette consistently provides more accurate tissue excision, resulting in uniform tissue thickness and integrity (Figure 3B).

Practice Implications
Compared to the traditional scalpel, this modified tool offers distinct advantages. Specifically, the customized dermal curette provides enhanced maneuverability and control during the procedure, thereby improving the overall efficacy of the excision process. It also offers a more accurate approach to completely remove pigmented bands, which reduces the risk for postoperative recurrence. The simplicity, affordability, and ease of operation associated with customized dermal curettes holds promise as an effective alternative for tissue shaving, especially in cases involving narrow pigmented matrix lesions, thereby addressing a notable practice gap and enhancing patient care.
Practice Gap
Longitudinal melanonychia (LM) is characterized by the presence of a dark brown, longitudinal, pigmented band on the nail unit, often caused by melanocytic activation or melanocytic hyperplasia in the nail matrix. Distinguishing between benign and early malignant LM is crucial due to their similar clinical presentations.1 Hence, surgical excision of the pigmented nail matrix followed by histopathologic examination is a common procedure aimed at managing LM and reducing the risk for delayed diagnosis of subungual melanoma.
Tangential matrix excision combined with the nail window technique has emerged as a common and favored surgical strategy for managing LM.2 This method is highly valued for its ability to minimize the risk for severe permanent nail dystrophy and effectively reduce postsurgical pigmentation recurrence.
The procedure begins with the creation of a matrix window along the lateral edge of the pigmented band followed by 1 lateral incision carefully made on each side of the nail fold. This meticulous approach allows for the complete exposure of the pigmented lesion. Subsequently, the nail fold is separated from the dorsal surface of the nail plate to facilitate access to the pigmented nail matrix. Finally, the target pigmented area is excised using a scalpel.
Despite the recognized efficacy of this procedure, challenges do arise, particularly when the width of the pigmented matrix lesion is narrow. Holding the scalpel horizontally to ensure precise excision can prove to be demanding, leading to difficulty achieving complete lesion removal and obtaining the desired cosmetic outcomes. As such, there is a clear need to explore alternative tools that can effectively address these challenges while ensuring optimal surgical outcomes for patients with LM. We propose the use of the customized dermal curette.
The Technique
An improved curette tool is a practical solution for complete removal of the pigmented nail matrix. This enhanced instrument is crafted from a sterile disposable dermal curette with its top flattened using a needle holder(Figure 1). Termed the customized dermal curette, this device is a simple yet accurate tool for the precise excision of pigmented lesions within the nail matrix. Importantly, it offers versatility by accommodating different widths of pigmented lesions through the availability of various sizes of dermal curettes (Figure 2).


Histopathologically, we have found that the scalpel technique may lead to variable tissue removal, resulting in differences in tissue thickness, fragility, and completeness (Figure 3A). Conversely, the customized dermal curette consistently provides more accurate tissue excision, resulting in uniform tissue thickness and integrity (Figure 3B).

Practice Implications
Compared to the traditional scalpel, this modified tool offers distinct advantages. Specifically, the customized dermal curette provides enhanced maneuverability and control during the procedure, thereby improving the overall efficacy of the excision process. It also offers a more accurate approach to completely remove pigmented bands, which reduces the risk for postoperative recurrence. The simplicity, affordability, and ease of operation associated with customized dermal curettes holds promise as an effective alternative for tissue shaving, especially in cases involving narrow pigmented matrix lesions, thereby addressing a notable practice gap and enhancing patient care.
- Tan WC, Wang DY, Seghers AC, et al. Should we biopsy melanonychia striata in Asian children? a retrospective observational study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:864-868. doi:10.1111/pde.13934
- Zhou Y, Chen W, Liu ZR, et al. Modified shave surgery combined with nail window technique for the treatment of longitudinal melanonychia: evaluation of the method on a series of 67 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:717-722. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.03.065
- Tan WC, Wang DY, Seghers AC, et al. Should we biopsy melanonychia striata in Asian children? a retrospective observational study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:864-868. doi:10.1111/pde.13934
- Zhou Y, Chen W, Liu ZR, et al. Modified shave surgery combined with nail window technique for the treatment of longitudinal melanonychia: evaluation of the method on a series of 67 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:717-722. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.03.065
Psychiatric, Autoimmune Comorbidities Increased in Patients with Alopecia Areata
TOPLINE:
and were at greater risk of developing those comorbidities after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated 63,384 patients with AA and 3,309,107 individuals without AA (aged 12-64 years) from the Merative MarketScan Research Databases.
- The matched cohorts included 16,512 patients with AA and 66,048 control individuals.
- Outcomes were the prevalence of psychiatric and autoimmune diseases at baseline and the incidence of new-onset psychiatric and autoimmune diseases during the year after diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, patients with AA showed a greater prevalence of any psychiatric disease (30.9% vs 26.8%; P < .001) and any immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (16.1% vs 8.9%; P < .0001) than those with controls.
- In matched cohorts, patients with AA also showed a higher incidence of any new-onset psychiatric diseases (10.2% vs 6.8%; P < .001) or immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (6.2% vs 1.5%; P <.001) within the first 12 months of AA diagnosis than those with controls.
- Among patients with AA, the risk of developing a psychiatric comorbidity was higher (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.3; 95% CI, 1.3-1.4). The highest risks were seen for adjustment disorder (aHR, 1.5), panic disorder (aHR, 1.4), and sexual dysfunction (aHR, 1.4).
- Compared with controls, patients with AA were also at an increased risk of developing immune-mediated or autoimmune comorbidities (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 2.5-2.8), with the highest for systemic lupus (aHR, 5.7), atopic dermatitis (aHR, 4.3), and vitiligo (aHR, 3.8).
IN PRACTICE:
“Routine monitoring of patients with AA, especially those at risk of developing comorbidities, may permit earlier and more effective intervention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston. It was published online on July 31, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Causality could not be inferred because of the retrospective nature of the study. Comorbidities were solely diagnosed on the basis of diagnostic codes, and researchers did not have access to characteristics such as lab values that could have indicated any underlying comorbidity before the AA diagnosis. This study also did not account for the varying levels of severity of the disease, which may have led to an underestimation of disease burden and the risk for comorbidities.
DISCLOSURES:
AbbVie provided funding for this study. Mostaghimi disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbvie and several other companies outside of this work. The other four authors were current or former employees of Abbvie and have or may have stock and/or stock options in AbbVie.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and were at greater risk of developing those comorbidities after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated 63,384 patients with AA and 3,309,107 individuals without AA (aged 12-64 years) from the Merative MarketScan Research Databases.
- The matched cohorts included 16,512 patients with AA and 66,048 control individuals.
- Outcomes were the prevalence of psychiatric and autoimmune diseases at baseline and the incidence of new-onset psychiatric and autoimmune diseases during the year after diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, patients with AA showed a greater prevalence of any psychiatric disease (30.9% vs 26.8%; P < .001) and any immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (16.1% vs 8.9%; P < .0001) than those with controls.
- In matched cohorts, patients with AA also showed a higher incidence of any new-onset psychiatric diseases (10.2% vs 6.8%; P < .001) or immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (6.2% vs 1.5%; P <.001) within the first 12 months of AA diagnosis than those with controls.
- Among patients with AA, the risk of developing a psychiatric comorbidity was higher (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.3; 95% CI, 1.3-1.4). The highest risks were seen for adjustment disorder (aHR, 1.5), panic disorder (aHR, 1.4), and sexual dysfunction (aHR, 1.4).
- Compared with controls, patients with AA were also at an increased risk of developing immune-mediated or autoimmune comorbidities (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 2.5-2.8), with the highest for systemic lupus (aHR, 5.7), atopic dermatitis (aHR, 4.3), and vitiligo (aHR, 3.8).
IN PRACTICE:
“Routine monitoring of patients with AA, especially those at risk of developing comorbidities, may permit earlier and more effective intervention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston. It was published online on July 31, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Causality could not be inferred because of the retrospective nature of the study. Comorbidities were solely diagnosed on the basis of diagnostic codes, and researchers did not have access to characteristics such as lab values that could have indicated any underlying comorbidity before the AA diagnosis. This study also did not account for the varying levels of severity of the disease, which may have led to an underestimation of disease burden and the risk for comorbidities.
DISCLOSURES:
AbbVie provided funding for this study. Mostaghimi disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbvie and several other companies outside of this work. The other four authors were current or former employees of Abbvie and have or may have stock and/or stock options in AbbVie.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and were at greater risk of developing those comorbidities after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated 63,384 patients with AA and 3,309,107 individuals without AA (aged 12-64 years) from the Merative MarketScan Research Databases.
- The matched cohorts included 16,512 patients with AA and 66,048 control individuals.
- Outcomes were the prevalence of psychiatric and autoimmune diseases at baseline and the incidence of new-onset psychiatric and autoimmune diseases during the year after diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, patients with AA showed a greater prevalence of any psychiatric disease (30.9% vs 26.8%; P < .001) and any immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (16.1% vs 8.9%; P < .0001) than those with controls.
- In matched cohorts, patients with AA also showed a higher incidence of any new-onset psychiatric diseases (10.2% vs 6.8%; P < .001) or immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (6.2% vs 1.5%; P <.001) within the first 12 months of AA diagnosis than those with controls.
- Among patients with AA, the risk of developing a psychiatric comorbidity was higher (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.3; 95% CI, 1.3-1.4). The highest risks were seen for adjustment disorder (aHR, 1.5), panic disorder (aHR, 1.4), and sexual dysfunction (aHR, 1.4).
- Compared with controls, patients with AA were also at an increased risk of developing immune-mediated or autoimmune comorbidities (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 2.5-2.8), with the highest for systemic lupus (aHR, 5.7), atopic dermatitis (aHR, 4.3), and vitiligo (aHR, 3.8).
IN PRACTICE:
“Routine monitoring of patients with AA, especially those at risk of developing comorbidities, may permit earlier and more effective intervention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston. It was published online on July 31, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Causality could not be inferred because of the retrospective nature of the study. Comorbidities were solely diagnosed on the basis of diagnostic codes, and researchers did not have access to characteristics such as lab values that could have indicated any underlying comorbidity before the AA diagnosis. This study also did not account for the varying levels of severity of the disease, which may have led to an underestimation of disease burden and the risk for comorbidities.
DISCLOSURES:
AbbVie provided funding for this study. Mostaghimi disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbvie and several other companies outside of this work. The other four authors were current or former employees of Abbvie and have or may have stock and/or stock options in AbbVie.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.