User login
T-VEC plus pembrolizumab yields promising response rate in phase 2 sarcoma study
The combination of oncolytic immunotherapy and an immune checkpoint inhibitor had promising activity in a phase 2 study including patients with previously treated advanced sarcoma, investigators report.
Responses were seen in about one-third of the patients (30%) at 24 weeks after starting treatment with talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) and pembrolizumab, according to the investigators, led by Ciara M. Kelly, MBBChBAO, MD, of the department of sarcoma oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“To our knowledge, this is one of the highest ORRs [objective response rates] reported in an unselected sarcoma-specific study population evaluating the efficacy of combination immunotherapy,” Dr. Kelly and coauthors wrote in JAMA Oncology.
Two of the patients who responded to the combination had previously failed regimens that included an immune checkpoint inhibitor, suggesting T-VEC might be augmenting the efficacy of pembrolizumab, according to the authors.
Among responders, the mean number of prior treatments was one, while by contrast, most of the study cohort (60%) had three or more prior treatments. “This finding supports the rationale to enroll patients with sarcoma in immunotherapy trials earlier in their treatment course,” Dr. Kelly and colleagues wrote.
In studies of immunotherapy in Merkel cell carcinoma and other cancer types, higher response rates have been seen in patients who were naive to chemotherapy, as opposed to those who were refractory to it.
The present single-institution, phase 2 study by Dr. Kelly and colleagues included 20 adult patients with histologically confirmed locally advanced or metastatic sarcoma. The patients received a fixed dose of pembrolizumab administered intravenously, and had T-VEC injected into palpable lesions, on day 1 of 21-day cycles.
While the ORR was 30% at 24 weeks (7 of 35 patients), an additional patient had a response at 32 weeks, bringing the ORR to 35%, according to the report.
“Maximal response to therapy may take a prolonged period to achieve,” the investigators wrote, noting that the median time to response was 14.4 weeks.
Median duration of response was 56.1 weeks, suggesting the combination provided durable disease control, they added.
Safety was consistent with what was seen in a previous study of T-VEC and pembrolizumab in melanoma. In this sarcoma study, the incidence of grade 3 treatment-related adverse events was 20%, while in studies of conventional chemotherapy in this setting, the rate of those events has been “comparable but generally higher,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Kelly and colleagues wrote that a randomized clinical trial is the “ideal next step” in the development of the regimen, adding that an expansion of the present phase 2 study is in progress.
The study was funded by Amgen and Merck, with additional grant support from Cycle for Survival and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute. Dr. Kelly reported disclosures related to Merck, Amgen, Agios Pharmaceuticals, and Exicure. Her coauthors reported disclosures with Regeneron, Novartis, Takeda, and Nektar, among others.
SOURCE: Kelly CM et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 23. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6152.
The combination of oncolytic immunotherapy and an immune checkpoint inhibitor had promising activity in a phase 2 study including patients with previously treated advanced sarcoma, investigators report.
Responses were seen in about one-third of the patients (30%) at 24 weeks after starting treatment with talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) and pembrolizumab, according to the investigators, led by Ciara M. Kelly, MBBChBAO, MD, of the department of sarcoma oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“To our knowledge, this is one of the highest ORRs [objective response rates] reported in an unselected sarcoma-specific study population evaluating the efficacy of combination immunotherapy,” Dr. Kelly and coauthors wrote in JAMA Oncology.
Two of the patients who responded to the combination had previously failed regimens that included an immune checkpoint inhibitor, suggesting T-VEC might be augmenting the efficacy of pembrolizumab, according to the authors.
Among responders, the mean number of prior treatments was one, while by contrast, most of the study cohort (60%) had three or more prior treatments. “This finding supports the rationale to enroll patients with sarcoma in immunotherapy trials earlier in their treatment course,” Dr. Kelly and colleagues wrote.
In studies of immunotherapy in Merkel cell carcinoma and other cancer types, higher response rates have been seen in patients who were naive to chemotherapy, as opposed to those who were refractory to it.
The present single-institution, phase 2 study by Dr. Kelly and colleagues included 20 adult patients with histologically confirmed locally advanced or metastatic sarcoma. The patients received a fixed dose of pembrolizumab administered intravenously, and had T-VEC injected into palpable lesions, on day 1 of 21-day cycles.
While the ORR was 30% at 24 weeks (7 of 35 patients), an additional patient had a response at 32 weeks, bringing the ORR to 35%, according to the report.
“Maximal response to therapy may take a prolonged period to achieve,” the investigators wrote, noting that the median time to response was 14.4 weeks.
Median duration of response was 56.1 weeks, suggesting the combination provided durable disease control, they added.
Safety was consistent with what was seen in a previous study of T-VEC and pembrolizumab in melanoma. In this sarcoma study, the incidence of grade 3 treatment-related adverse events was 20%, while in studies of conventional chemotherapy in this setting, the rate of those events has been “comparable but generally higher,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Kelly and colleagues wrote that a randomized clinical trial is the “ideal next step” in the development of the regimen, adding that an expansion of the present phase 2 study is in progress.
The study was funded by Amgen and Merck, with additional grant support from Cycle for Survival and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute. Dr. Kelly reported disclosures related to Merck, Amgen, Agios Pharmaceuticals, and Exicure. Her coauthors reported disclosures with Regeneron, Novartis, Takeda, and Nektar, among others.
SOURCE: Kelly CM et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 23. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6152.
The combination of oncolytic immunotherapy and an immune checkpoint inhibitor had promising activity in a phase 2 study including patients with previously treated advanced sarcoma, investigators report.
Responses were seen in about one-third of the patients (30%) at 24 weeks after starting treatment with talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) and pembrolizumab, according to the investigators, led by Ciara M. Kelly, MBBChBAO, MD, of the department of sarcoma oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“To our knowledge, this is one of the highest ORRs [objective response rates] reported in an unselected sarcoma-specific study population evaluating the efficacy of combination immunotherapy,” Dr. Kelly and coauthors wrote in JAMA Oncology.
Two of the patients who responded to the combination had previously failed regimens that included an immune checkpoint inhibitor, suggesting T-VEC might be augmenting the efficacy of pembrolizumab, according to the authors.
Among responders, the mean number of prior treatments was one, while by contrast, most of the study cohort (60%) had three or more prior treatments. “This finding supports the rationale to enroll patients with sarcoma in immunotherapy trials earlier in their treatment course,” Dr. Kelly and colleagues wrote.
In studies of immunotherapy in Merkel cell carcinoma and other cancer types, higher response rates have been seen in patients who were naive to chemotherapy, as opposed to those who were refractory to it.
The present single-institution, phase 2 study by Dr. Kelly and colleagues included 20 adult patients with histologically confirmed locally advanced or metastatic sarcoma. The patients received a fixed dose of pembrolizumab administered intravenously, and had T-VEC injected into palpable lesions, on day 1 of 21-day cycles.
While the ORR was 30% at 24 weeks (7 of 35 patients), an additional patient had a response at 32 weeks, bringing the ORR to 35%, according to the report.
“Maximal response to therapy may take a prolonged period to achieve,” the investigators wrote, noting that the median time to response was 14.4 weeks.
Median duration of response was 56.1 weeks, suggesting the combination provided durable disease control, they added.
Safety was consistent with what was seen in a previous study of T-VEC and pembrolizumab in melanoma. In this sarcoma study, the incidence of grade 3 treatment-related adverse events was 20%, while in studies of conventional chemotherapy in this setting, the rate of those events has been “comparable but generally higher,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Kelly and colleagues wrote that a randomized clinical trial is the “ideal next step” in the development of the regimen, adding that an expansion of the present phase 2 study is in progress.
The study was funded by Amgen and Merck, with additional grant support from Cycle for Survival and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute. Dr. Kelly reported disclosures related to Merck, Amgen, Agios Pharmaceuticals, and Exicure. Her coauthors reported disclosures with Regeneron, Novartis, Takeda, and Nektar, among others.
SOURCE: Kelly CM et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 23. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6152.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
GI societies meet with ABIM
Recently, the leadership of AGA, AASLD, ACG, and ASGE met with Richard Battaglia, MD, the chief medical officer of ABIM, about the status of ABIM’s efforts to move toward a longitudinal testing model, which ABIM describes as “a self-paced pathway for physicians to acquire and demonstrate ongoing knowledge.”
ABIM anticipates that the new option will be available beginning in 2022, in as many specialties as possible. In the meantime, all current MOC program policies remain in effect and ABIM directs diplomates to use the current options to maintain certification.
While we would like to see ABIM waive testing requirements while it works with GI to create a new longitudinal model, ABIM has declined to do so. Notwithstanding this fact, the GI societies are committed to advocating for the needs of gastroenterology while working with ABIM to ensure the new model is relevant to gastroenterology and hepatology.
Recently, the leadership of AGA, AASLD, ACG, and ASGE met with Richard Battaglia, MD, the chief medical officer of ABIM, about the status of ABIM’s efforts to move toward a longitudinal testing model, which ABIM describes as “a self-paced pathway for physicians to acquire and demonstrate ongoing knowledge.”
ABIM anticipates that the new option will be available beginning in 2022, in as many specialties as possible. In the meantime, all current MOC program policies remain in effect and ABIM directs diplomates to use the current options to maintain certification.
While we would like to see ABIM waive testing requirements while it works with GI to create a new longitudinal model, ABIM has declined to do so. Notwithstanding this fact, the GI societies are committed to advocating for the needs of gastroenterology while working with ABIM to ensure the new model is relevant to gastroenterology and hepatology.
Recently, the leadership of AGA, AASLD, ACG, and ASGE met with Richard Battaglia, MD, the chief medical officer of ABIM, about the status of ABIM’s efforts to move toward a longitudinal testing model, which ABIM describes as “a self-paced pathway for physicians to acquire and demonstrate ongoing knowledge.”
ABIM anticipates that the new option will be available beginning in 2022, in as many specialties as possible. In the meantime, all current MOC program policies remain in effect and ABIM directs diplomates to use the current options to maintain certification.
While we would like to see ABIM waive testing requirements while it works with GI to create a new longitudinal model, ABIM has declined to do so. Notwithstanding this fact, the GI societies are committed to advocating for the needs of gastroenterology while working with ABIM to ensure the new model is relevant to gastroenterology and hepatology.
Watch your step (therapy) — understanding ‘fail first’
Sometimes known as “fail first,” step therapy is a tool used by insurance companies that requires patients to fail medications before agreeing to cover a health care provider’s initial treatment recommendation.
Largely affecting patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), step therapy focuses on the use of insurer-preferred treatments rather than effective, patient-centric therapies. In addition to causing many patient hardships and health problems, this protocol allows insurance companies to come between the provider-patient relationship and dictate a patient’s course of treatment.
To help clinicians navigate this challenging landscape, AGA is pleased to offer a new step therapy webpage, gastro.org/step-therapy, that details the step therapy protocol and opportunities to advocate for patient protections.
Additional education modules — including videos, podcasts and other resources — are also available for several states that have implemented safe step therapy laws, including Illinois, New York, and Texas.
Visit the Navigating State Step Therapy Laws program page to learn more:
- What is the step therapy protocol?
- How does step therapy impact a health care provider’s ability to provide patient care?
- Which states have implemented step therapy laws?
- How do state step therapy laws provide physician rights and patient protection?
- Tips to share with your patients.
- What are AGA’s advocacy efforts — and how can I help?
Education modules for additional states will be available in early 2020.
AGA’s Navigating State Step Therapy Laws program is funded by an unrestricted educational grant from Takeda and Pfizer.
ginews@gastro.org
Sometimes known as “fail first,” step therapy is a tool used by insurance companies that requires patients to fail medications before agreeing to cover a health care provider’s initial treatment recommendation.
Largely affecting patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), step therapy focuses on the use of insurer-preferred treatments rather than effective, patient-centric therapies. In addition to causing many patient hardships and health problems, this protocol allows insurance companies to come between the provider-patient relationship and dictate a patient’s course of treatment.
To help clinicians navigate this challenging landscape, AGA is pleased to offer a new step therapy webpage, gastro.org/step-therapy, that details the step therapy protocol and opportunities to advocate for patient protections.
Additional education modules — including videos, podcasts and other resources — are also available for several states that have implemented safe step therapy laws, including Illinois, New York, and Texas.
Visit the Navigating State Step Therapy Laws program page to learn more:
- What is the step therapy protocol?
- How does step therapy impact a health care provider’s ability to provide patient care?
- Which states have implemented step therapy laws?
- How do state step therapy laws provide physician rights and patient protection?
- Tips to share with your patients.
- What are AGA’s advocacy efforts — and how can I help?
Education modules for additional states will be available in early 2020.
AGA’s Navigating State Step Therapy Laws program is funded by an unrestricted educational grant from Takeda and Pfizer.
ginews@gastro.org
Sometimes known as “fail first,” step therapy is a tool used by insurance companies that requires patients to fail medications before agreeing to cover a health care provider’s initial treatment recommendation.
Largely affecting patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), step therapy focuses on the use of insurer-preferred treatments rather than effective, patient-centric therapies. In addition to causing many patient hardships and health problems, this protocol allows insurance companies to come between the provider-patient relationship and dictate a patient’s course of treatment.
To help clinicians navigate this challenging landscape, AGA is pleased to offer a new step therapy webpage, gastro.org/step-therapy, that details the step therapy protocol and opportunities to advocate for patient protections.
Additional education modules — including videos, podcasts and other resources — are also available for several states that have implemented safe step therapy laws, including Illinois, New York, and Texas.
Visit the Navigating State Step Therapy Laws program page to learn more:
- What is the step therapy protocol?
- How does step therapy impact a health care provider’s ability to provide patient care?
- Which states have implemented step therapy laws?
- How do state step therapy laws provide physician rights and patient protection?
- Tips to share with your patients.
- What are AGA’s advocacy efforts — and how can I help?
Education modules for additional states will be available in early 2020.
AGA’s Navigating State Step Therapy Laws program is funded by an unrestricted educational grant from Takeda and Pfizer.
ginews@gastro.org
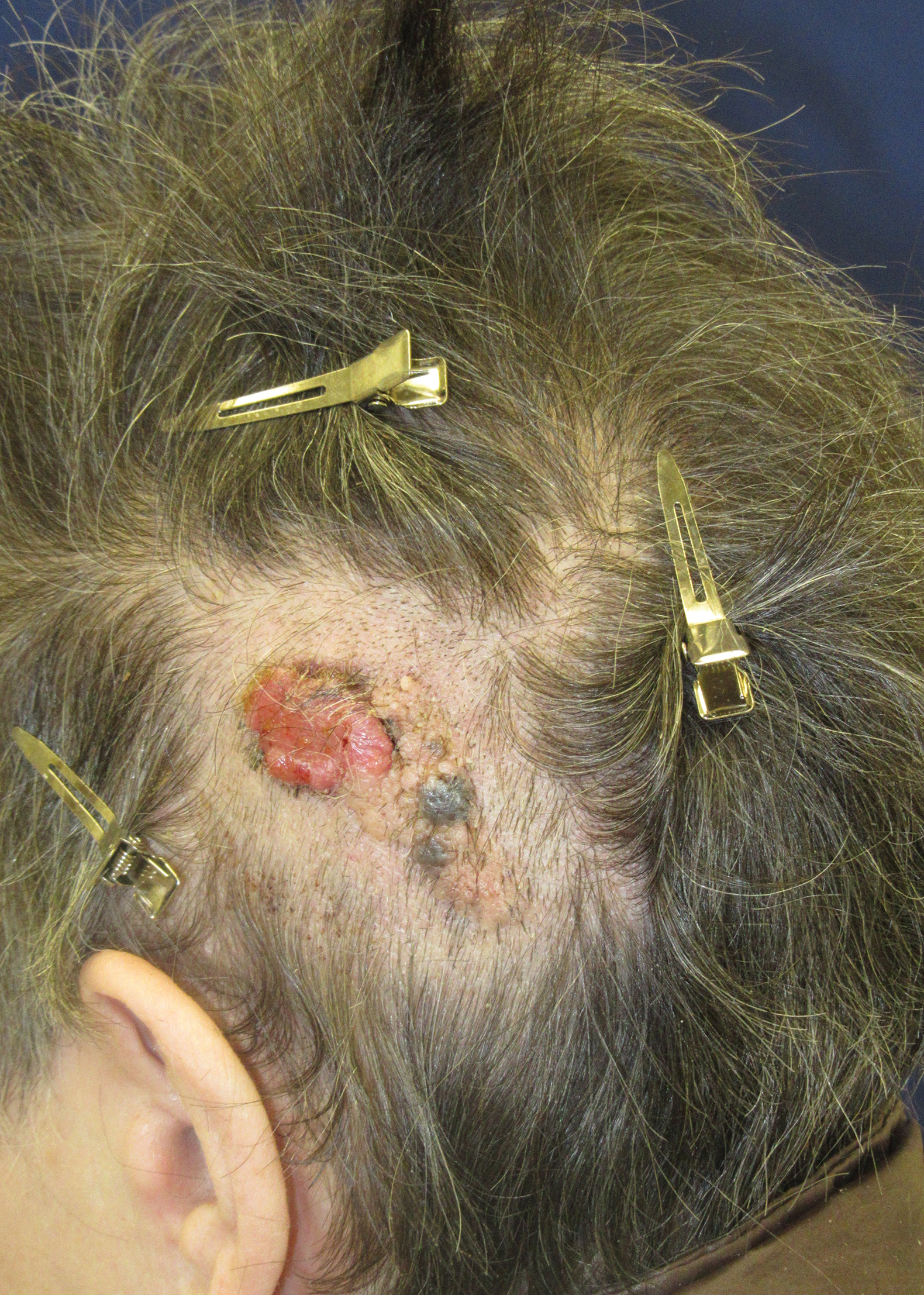
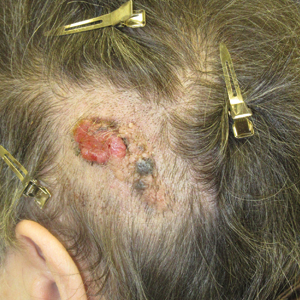
Friable Scalp Nodule
The Diagnosis: Adnexal Neoplasm Arising in a Nevus Sebaceus
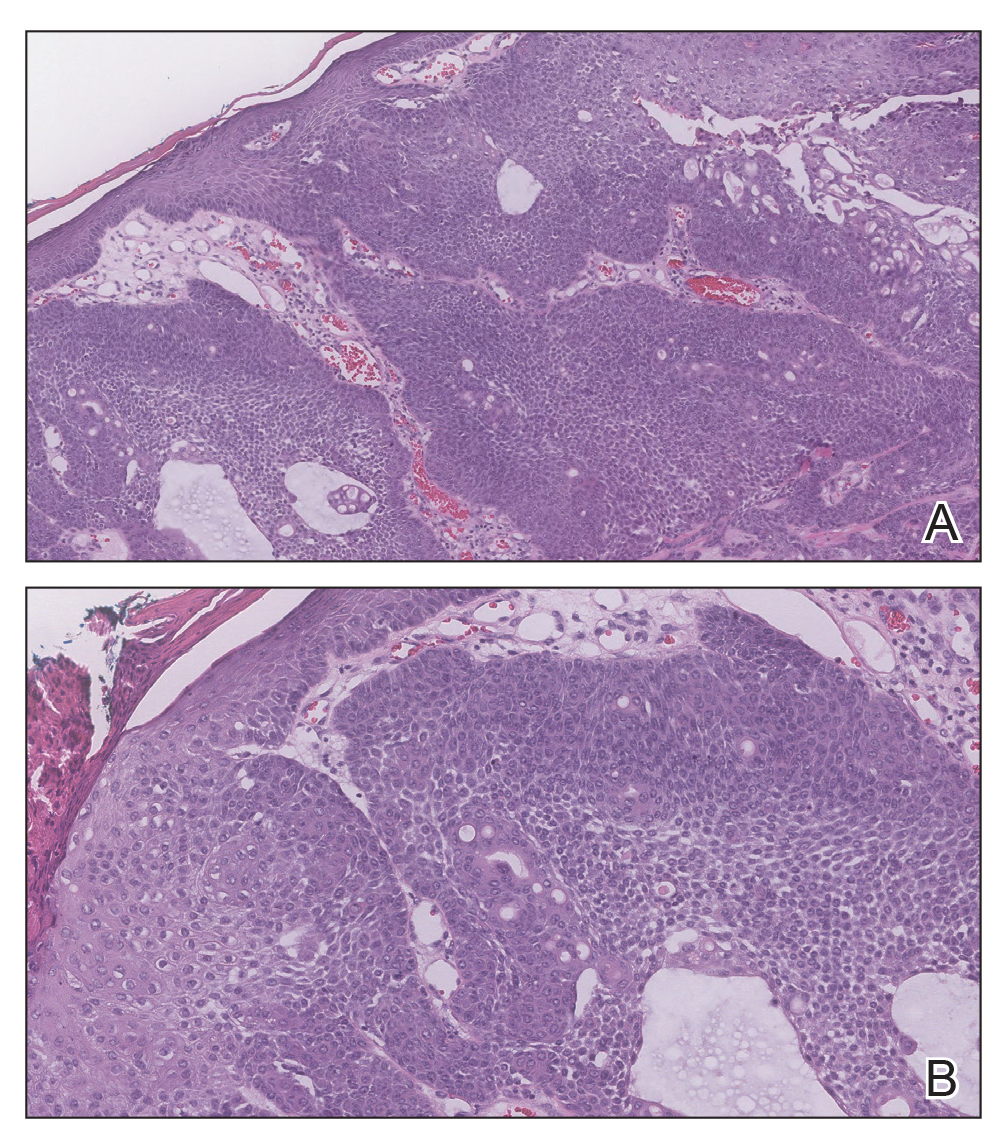
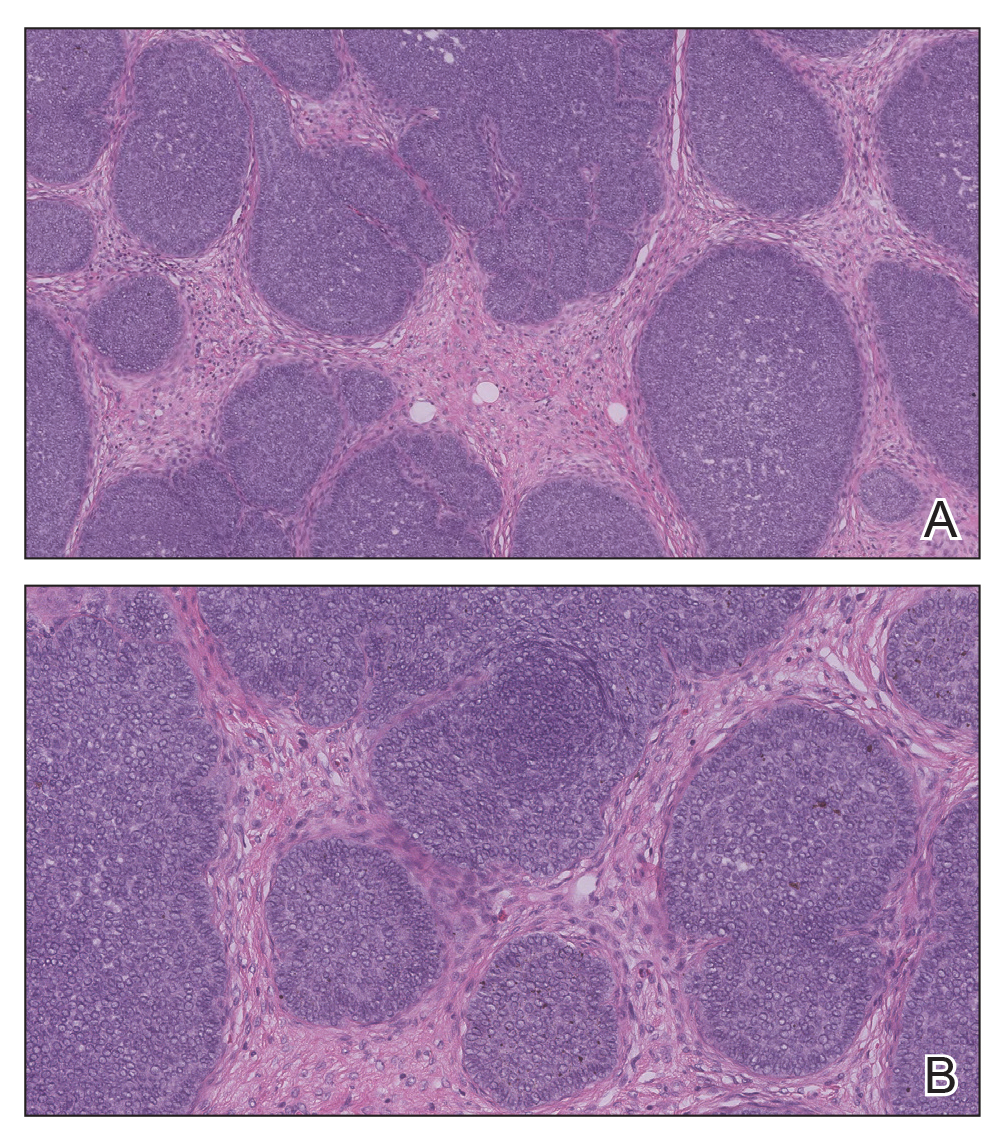
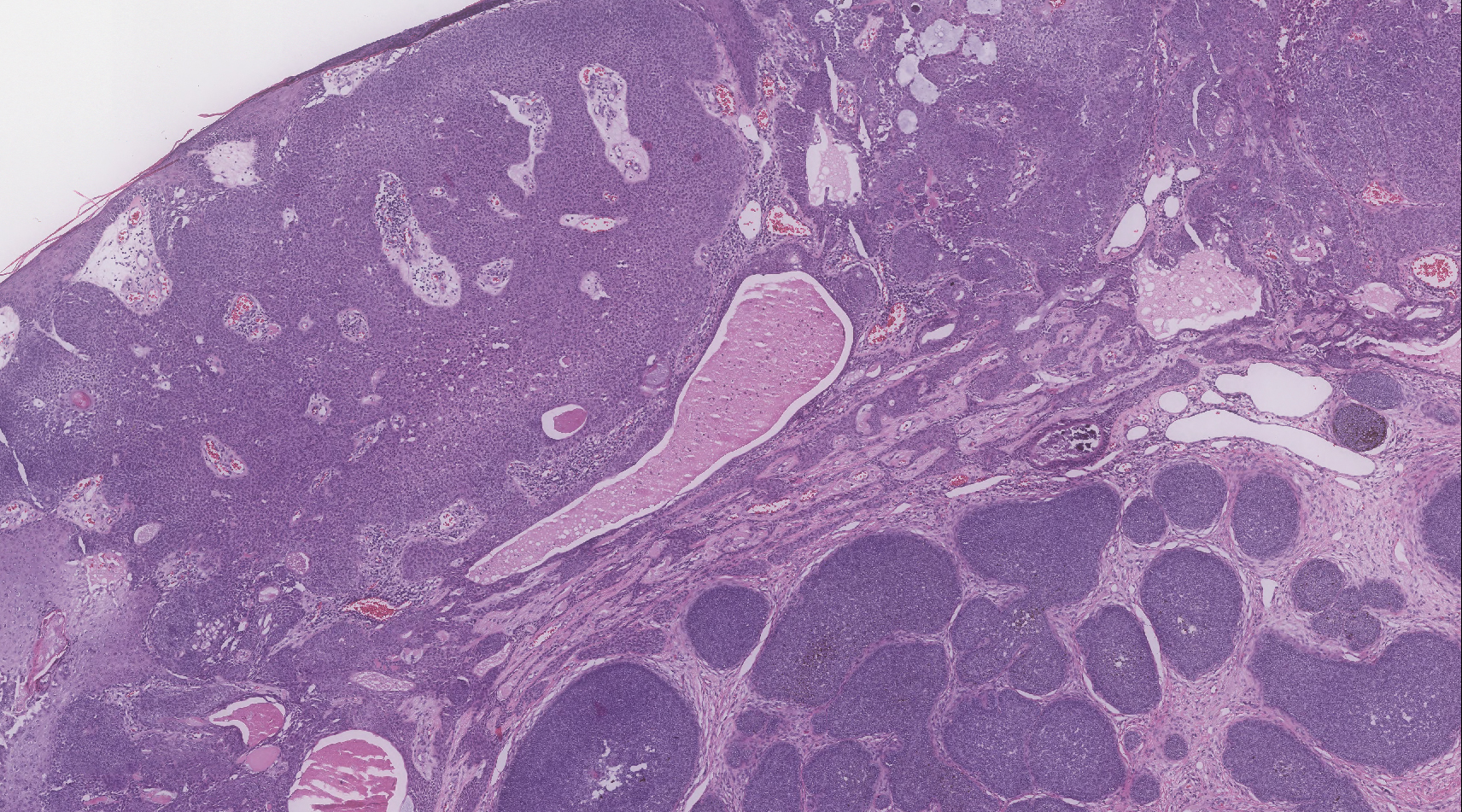
Biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of basaloid-appearing cells with focal ductal differentiation and ulceration consistent with poroma (Figure 1). Due to the superficial nature of the biopsy, the pathologist recommended excision to ensure complete removal and to rule out a well-differentiated porocarcinoma. Excision of the lesion showed large basaloid aggregates with a hypercellular stroma and a surrounding papillomatous epidermis with well-developed sebaceous lobules consistent with a trichoblastoma and a nevus sebaceus, respectively (Figure 2). There also was evidence of poroma; however, there were no findings concerning for porocarcinoma, which could lead to metastasis (Figure 3).
Nevus sebaceus is a benign, hamartomatous, congenital growth that occurs in approximately 1% of patients presenting to dermatology offices. It usually presents as a single asymptomatic plaque on the scalp (62.5%) or face (24.5%) that changes in morphology over its lifetime.1,2 In children, a nevus manifests as a yellowish, smooth, waxy skin lesion. As the sebaceous glands become more developed during adolescence, the lesion takes on more of a verrucous appearance and also can darken.
Although nevus sebaceus is benign, it may give rise to both benign and malignant neoplasms. In a 2014 study of 707 cases of nevus sebaceus, 21.4% developed secondary neoplasms, 88% of which were benign.2 The origins of these neoplasms can be epithelial, sebaceous, apocrine, and/or follicular. The 3 most common secondary neoplasms found in nevus sebaceus are trichoblastoma (34.7%), syringocystadenoma papilliferum (24.7%), and apocrine/eccrine adenoma (10%), all of which are benign.2 Trichoblastomas represent a type of hair follicle tumor. Malignant lesions manifest in approximately 2.5% of cases, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) being the most common (5.3% of all neoplasms), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (2.7% of all neoplasms).2 Differentiating BCC from trichoblastoma can be difficult, but histologically BCCs usually have tumor stromal clefting while trichoblastomas do not.3 The incidence of secondary tumors in nevus sebaceus displays a strong correlation with age; thus, the highest proportion of neoplasms occur in adults.
Treatment of nevus sebaceus depends on the patient's age. In children, because of the low probability of secondary neoplasms, observation in lieu of surgical excision is a common approach. In adults, the approach typically is surgical excision or close follow-up, as there is a concern for secondary neoplasm and the potential for malignant degeneration.
A nevus sebaceus leading to 2 or more tumors within the same lesion is rare (seen in only 4.2% of lesions). The most common combination is trichoblastoma with syringocystadenoma papilliferum (0.6% of all cases).2 Poromas represent sweat gland tumors that usually appear on the soles (65%) or palms (10%).4 It is uncommon for these neoplasms to manifest on the scalp or within a nevus sebaceus. Three independent studies (N=596; N=707; N=450) did not report any occurrences of eccrine poroma.1,2,5 Eccrine poroma in conjunction with nodular trichoblastoma arising in a nevus sebaceus is unusual, and definitive excision should be strongly considered because of the possibility to develop a porocarcinoma.6
Atypical fibroxanthoma presents on sun-exposed areas as an exophytic nodule or plaque that frequently ulcerates. Pathology of this tumor shows a spindled cell proliferation that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1. Basal cell carcinoma presents as a pearly papule or nodule displaying basaloid-appearing aggregates with tumor stromal clefting and can stain with Ber-EP4. Cylindromas typically present on the scalp as large rubbery-appearing plaques and nodules. Cylindromas usually present as a solitary tumor, but in the familial form there can be clusters of multiple nodules. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma frequently appears as a bleeding nodule on the scalp in patients with known renal cell cancer or as the initial presentation.
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(pt 1):263-268.
- Idriss MH, Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:332-337.
- Wang E, Lee JS, Kazakov DV. A rare combination of sebaceoma with carcinomatous change (sebaceous carcinoma), trichoblastoma, and poroma arising from a nevus sebaceus. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:676-682.
- Bae MI, Cho TH, Shin MK, et al. An unusual clinical presentation of eccrine poroma occurring on the auricle. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:523.
- Hsu MC, Liau JY, Hong JL, et al. Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan. J Dermatol. 2016;43:175-180.
- Takhan II, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:413-415.
The Diagnosis: Adnexal Neoplasm Arising in a Nevus Sebaceus
Biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of basaloid-appearing cells with focal ductal differentiation and ulceration consistent with poroma (Figure 1). Due to the superficial nature of the biopsy, the pathologist recommended excision to ensure complete removal and to rule out a well-differentiated porocarcinoma. Excision of the lesion showed large basaloid aggregates with a hypercellular stroma and a surrounding papillomatous epidermis with well-developed sebaceous lobules consistent with a trichoblastoma and a nevus sebaceus, respectively (Figure 2). There also was evidence of poroma; however, there were no findings concerning for porocarcinoma, which could lead to metastasis (Figure 3).
Nevus sebaceus is a benign, hamartomatous, congenital growth that occurs in approximately 1% of patients presenting to dermatology offices. It usually presents as a single asymptomatic plaque on the scalp (62.5%) or face (24.5%) that changes in morphology over its lifetime.1,2 In children, a nevus manifests as a yellowish, smooth, waxy skin lesion. As the sebaceous glands become more developed during adolescence, the lesion takes on more of a verrucous appearance and also can darken.
Although nevus sebaceus is benign, it may give rise to both benign and malignant neoplasms. In a 2014 study of 707 cases of nevus sebaceus, 21.4% developed secondary neoplasms, 88% of which were benign.2 The origins of these neoplasms can be epithelial, sebaceous, apocrine, and/or follicular. The 3 most common secondary neoplasms found in nevus sebaceus are trichoblastoma (34.7%), syringocystadenoma papilliferum (24.7%), and apocrine/eccrine adenoma (10%), all of which are benign.2 Trichoblastomas represent a type of hair follicle tumor. Malignant lesions manifest in approximately 2.5% of cases, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) being the most common (5.3% of all neoplasms), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (2.7% of all neoplasms).2 Differentiating BCC from trichoblastoma can be difficult, but histologically BCCs usually have tumor stromal clefting while trichoblastomas do not.3 The incidence of secondary tumors in nevus sebaceus displays a strong correlation with age; thus, the highest proportion of neoplasms occur in adults.
Treatment of nevus sebaceus depends on the patient's age. In children, because of the low probability of secondary neoplasms, observation in lieu of surgical excision is a common approach. In adults, the approach typically is surgical excision or close follow-up, as there is a concern for secondary neoplasm and the potential for malignant degeneration.
A nevus sebaceus leading to 2 or more tumors within the same lesion is rare (seen in only 4.2% of lesions). The most common combination is trichoblastoma with syringocystadenoma papilliferum (0.6% of all cases).2 Poromas represent sweat gland tumors that usually appear on the soles (65%) or palms (10%).4 It is uncommon for these neoplasms to manifest on the scalp or within a nevus sebaceus. Three independent studies (N=596; N=707; N=450) did not report any occurrences of eccrine poroma.1,2,5 Eccrine poroma in conjunction with nodular trichoblastoma arising in a nevus sebaceus is unusual, and definitive excision should be strongly considered because of the possibility to develop a porocarcinoma.6
Atypical fibroxanthoma presents on sun-exposed areas as an exophytic nodule or plaque that frequently ulcerates. Pathology of this tumor shows a spindled cell proliferation that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1. Basal cell carcinoma presents as a pearly papule or nodule displaying basaloid-appearing aggregates with tumor stromal clefting and can stain with Ber-EP4. Cylindromas typically present on the scalp as large rubbery-appearing plaques and nodules. Cylindromas usually present as a solitary tumor, but in the familial form there can be clusters of multiple nodules. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma frequently appears as a bleeding nodule on the scalp in patients with known renal cell cancer or as the initial presentation.
The Diagnosis: Adnexal Neoplasm Arising in a Nevus Sebaceus
Biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of basaloid-appearing cells with focal ductal differentiation and ulceration consistent with poroma (Figure 1). Due to the superficial nature of the biopsy, the pathologist recommended excision to ensure complete removal and to rule out a well-differentiated porocarcinoma. Excision of the lesion showed large basaloid aggregates with a hypercellular stroma and a surrounding papillomatous epidermis with well-developed sebaceous lobules consistent with a trichoblastoma and a nevus sebaceus, respectively (Figure 2). There also was evidence of poroma; however, there were no findings concerning for porocarcinoma, which could lead to metastasis (Figure 3).
Nevus sebaceus is a benign, hamartomatous, congenital growth that occurs in approximately 1% of patients presenting to dermatology offices. It usually presents as a single asymptomatic plaque on the scalp (62.5%) or face (24.5%) that changes in morphology over its lifetime.1,2 In children, a nevus manifests as a yellowish, smooth, waxy skin lesion. As the sebaceous glands become more developed during adolescence, the lesion takes on more of a verrucous appearance and also can darken.
Although nevus sebaceus is benign, it may give rise to both benign and malignant neoplasms. In a 2014 study of 707 cases of nevus sebaceus, 21.4% developed secondary neoplasms, 88% of which were benign.2 The origins of these neoplasms can be epithelial, sebaceous, apocrine, and/or follicular. The 3 most common secondary neoplasms found in nevus sebaceus are trichoblastoma (34.7%), syringocystadenoma papilliferum (24.7%), and apocrine/eccrine adenoma (10%), all of which are benign.2 Trichoblastomas represent a type of hair follicle tumor. Malignant lesions manifest in approximately 2.5% of cases, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) being the most common (5.3% of all neoplasms), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (2.7% of all neoplasms).2 Differentiating BCC from trichoblastoma can be difficult, but histologically BCCs usually have tumor stromal clefting while trichoblastomas do not.3 The incidence of secondary tumors in nevus sebaceus displays a strong correlation with age; thus, the highest proportion of neoplasms occur in adults.
Treatment of nevus sebaceus depends on the patient's age. In children, because of the low probability of secondary neoplasms, observation in lieu of surgical excision is a common approach. In adults, the approach typically is surgical excision or close follow-up, as there is a concern for secondary neoplasm and the potential for malignant degeneration.
A nevus sebaceus leading to 2 or more tumors within the same lesion is rare (seen in only 4.2% of lesions). The most common combination is trichoblastoma with syringocystadenoma papilliferum (0.6% of all cases).2 Poromas represent sweat gland tumors that usually appear on the soles (65%) or palms (10%).4 It is uncommon for these neoplasms to manifest on the scalp or within a nevus sebaceus. Three independent studies (N=596; N=707; N=450) did not report any occurrences of eccrine poroma.1,2,5 Eccrine poroma in conjunction with nodular trichoblastoma arising in a nevus sebaceus is unusual, and definitive excision should be strongly considered because of the possibility to develop a porocarcinoma.6
Atypical fibroxanthoma presents on sun-exposed areas as an exophytic nodule or plaque that frequently ulcerates. Pathology of this tumor shows a spindled cell proliferation that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1. Basal cell carcinoma presents as a pearly papule or nodule displaying basaloid-appearing aggregates with tumor stromal clefting and can stain with Ber-EP4. Cylindromas typically present on the scalp as large rubbery-appearing plaques and nodules. Cylindromas usually present as a solitary tumor, but in the familial form there can be clusters of multiple nodules. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma frequently appears as a bleeding nodule on the scalp in patients with known renal cell cancer or as the initial presentation.
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(pt 1):263-268.
- Idriss MH, Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:332-337.
- Wang E, Lee JS, Kazakov DV. A rare combination of sebaceoma with carcinomatous change (sebaceous carcinoma), trichoblastoma, and poroma arising from a nevus sebaceus. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:676-682.
- Bae MI, Cho TH, Shin MK, et al. An unusual clinical presentation of eccrine poroma occurring on the auricle. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:523.
- Hsu MC, Liau JY, Hong JL, et al. Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan. J Dermatol. 2016;43:175-180.
- Takhan II, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:413-415.
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(pt 1):263-268.
- Idriss MH, Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:332-337.
- Wang E, Lee JS, Kazakov DV. A rare combination of sebaceoma with carcinomatous change (sebaceous carcinoma), trichoblastoma, and poroma arising from a nevus sebaceus. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:676-682.
- Bae MI, Cho TH, Shin MK, et al. An unusual clinical presentation of eccrine poroma occurring on the auricle. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:523.
- Hsu MC, Liau JY, Hong JL, et al. Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan. J Dermatol. 2016;43:175-180.
- Takhan II, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:413-415.
A 75-year-old woman presented with an enlarging plaque on the scalp of 5 years' duration. Physical examination revealed a 5.6.2 ×2.9-cm, tan-colored, verrucous plaque with an overlying pink friable nodule on the left occipital scalp. The lesion was not painful or pruritic, and the patient did not have any constitutional symptoms such as fever, night sweats, or weight loss. The patient denied prior tanning bed use and reported intermittent sun exposure over her lifetime. She denied any prior surgical intervention. There was no family history of similar lesions.
Highlights from AGA’s FDA engagement
AGA members and staff worked closely with representatives across the FDA on a number of key issues impacting gastroenterologists including duodenoscope reprocessing, fecal microbiota transplantation and new drug approvals for GI indications.
Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). The issue of duodenoscope reprocessing regained national attention when a safety communication issued by CDRH was covered by the New York Times.
The safety communication had noted that about one in 20 samples collected from reprocessed duodenoscopes tested positive for high-concern organisms such as E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
AGA partnered with ACG, ASGE and SGNA to develop a letter to the editor and provided insights to AGA members in subsequent communications. CDRH issued another safety communication in August recommending a transition to disposable-component duodenoscopes and convened a public advisory committee meeting in November where AGA gave public testimony including several overarching principles for the evolution of clinical practice focusing on patient safety and outcomes. AGA has been at the forefront of this issue since risk of infection transmission during ERCP first came to light in 2015, and we will continue to work closely with FDA and industry to ensure solutions, like the recently approved disposable scopes and parts, meet the needs of our members.
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Though it is not an approved therapy for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI), FDA permits the use of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) for CDI unresponsive to standard antibiotic therapies under a temporary “enforcement policy” that has been in place since 2013. In response to concerns from the physician community that patient access to FMT may be discontinued once manufactured microbiota-based products come to market, AGA reengaged CBER in dialogue about the future of FMT through a meeting with CBER Director Peter Marks and eight senior CBER officials. In response to a June safety alert reporting a patient death from FMT using donor stool that was not screened for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli, AGA requested clarification from CBER on new donor screening requirements announced for those who hold investigational new drug permits for FMT. Most recently, AGA was the only professional society to give public testimony at a November public hearing on the use of FMT to treat CDI. AGA will continue to engage CBER as the agency works to finalize its policy on FMT.
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). AGA organized two joint scientific sessions at Digestive Disease Week® 2019 with representatives from CDER’s Division of Gastrointestinal and Inborn Errors Products: the inaugural FDA Town Hall and a session on controversies around measuring drug toxicity. The FDA Town Hall, which will continue at DDW 2020, featured four FDA speakers providing the data and rationale behind recent GI drug approvals. The session titled, “Controversies Around Measuring Drug Toxicity” gave FDA and gastroenterologists’ perspectives on 5-HT3 antagonists (e.g., alosetron) and 5-HT4 agonists (e.g., prucalopride), as well as proton pump inhibitors. These sessions aimed to promote an interchange of ideas among regulators, clinicians and pharmaceutical manufacturers to advance the development and use of new therapies for GI disorders.
AGA members and staff worked closely with representatives across the FDA on a number of key issues impacting gastroenterologists including duodenoscope reprocessing, fecal microbiota transplantation and new drug approvals for GI indications.
Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). The issue of duodenoscope reprocessing regained national attention when a safety communication issued by CDRH was covered by the New York Times.
The safety communication had noted that about one in 20 samples collected from reprocessed duodenoscopes tested positive for high-concern organisms such as E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
AGA partnered with ACG, ASGE and SGNA to develop a letter to the editor and provided insights to AGA members in subsequent communications. CDRH issued another safety communication in August recommending a transition to disposable-component duodenoscopes and convened a public advisory committee meeting in November where AGA gave public testimony including several overarching principles for the evolution of clinical practice focusing on patient safety and outcomes. AGA has been at the forefront of this issue since risk of infection transmission during ERCP first came to light in 2015, and we will continue to work closely with FDA and industry to ensure solutions, like the recently approved disposable scopes and parts, meet the needs of our members.
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Though it is not an approved therapy for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI), FDA permits the use of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) for CDI unresponsive to standard antibiotic therapies under a temporary “enforcement policy” that has been in place since 2013. In response to concerns from the physician community that patient access to FMT may be discontinued once manufactured microbiota-based products come to market, AGA reengaged CBER in dialogue about the future of FMT through a meeting with CBER Director Peter Marks and eight senior CBER officials. In response to a June safety alert reporting a patient death from FMT using donor stool that was not screened for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli, AGA requested clarification from CBER on new donor screening requirements announced for those who hold investigational new drug permits for FMT. Most recently, AGA was the only professional society to give public testimony at a November public hearing on the use of FMT to treat CDI. AGA will continue to engage CBER as the agency works to finalize its policy on FMT.
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). AGA organized two joint scientific sessions at Digestive Disease Week® 2019 with representatives from CDER’s Division of Gastrointestinal and Inborn Errors Products: the inaugural FDA Town Hall and a session on controversies around measuring drug toxicity. The FDA Town Hall, which will continue at DDW 2020, featured four FDA speakers providing the data and rationale behind recent GI drug approvals. The session titled, “Controversies Around Measuring Drug Toxicity” gave FDA and gastroenterologists’ perspectives on 5-HT3 antagonists (e.g., alosetron) and 5-HT4 agonists (e.g., prucalopride), as well as proton pump inhibitors. These sessions aimed to promote an interchange of ideas among regulators, clinicians and pharmaceutical manufacturers to advance the development and use of new therapies for GI disorders.
AGA members and staff worked closely with representatives across the FDA on a number of key issues impacting gastroenterologists including duodenoscope reprocessing, fecal microbiota transplantation and new drug approvals for GI indications.
Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). The issue of duodenoscope reprocessing regained national attention when a safety communication issued by CDRH was covered by the New York Times.
The safety communication had noted that about one in 20 samples collected from reprocessed duodenoscopes tested positive for high-concern organisms such as E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
AGA partnered with ACG, ASGE and SGNA to develop a letter to the editor and provided insights to AGA members in subsequent communications. CDRH issued another safety communication in August recommending a transition to disposable-component duodenoscopes and convened a public advisory committee meeting in November where AGA gave public testimony including several overarching principles for the evolution of clinical practice focusing on patient safety and outcomes. AGA has been at the forefront of this issue since risk of infection transmission during ERCP first came to light in 2015, and we will continue to work closely with FDA and industry to ensure solutions, like the recently approved disposable scopes and parts, meet the needs of our members.
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Though it is not an approved therapy for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI), FDA permits the use of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) for CDI unresponsive to standard antibiotic therapies under a temporary “enforcement policy” that has been in place since 2013. In response to concerns from the physician community that patient access to FMT may be discontinued once manufactured microbiota-based products come to market, AGA reengaged CBER in dialogue about the future of FMT through a meeting with CBER Director Peter Marks and eight senior CBER officials. In response to a June safety alert reporting a patient death from FMT using donor stool that was not screened for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli, AGA requested clarification from CBER on new donor screening requirements announced for those who hold investigational new drug permits for FMT. Most recently, AGA was the only professional society to give public testimony at a November public hearing on the use of FMT to treat CDI. AGA will continue to engage CBER as the agency works to finalize its policy on FMT.
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). AGA organized two joint scientific sessions at Digestive Disease Week® 2019 with representatives from CDER’s Division of Gastrointestinal and Inborn Errors Products: the inaugural FDA Town Hall and a session on controversies around measuring drug toxicity. The FDA Town Hall, which will continue at DDW 2020, featured four FDA speakers providing the data and rationale behind recent GI drug approvals. The session titled, “Controversies Around Measuring Drug Toxicity” gave FDA and gastroenterologists’ perspectives on 5-HT3 antagonists (e.g., alosetron) and 5-HT4 agonists (e.g., prucalopride), as well as proton pump inhibitors. These sessions aimed to promote an interchange of ideas among regulators, clinicians and pharmaceutical manufacturers to advance the development and use of new therapies for GI disorders.
Many children who present to headache clinics have joint hypermobility
Key clinical point: About one-quarter of pediatric patients with headache have joint hypermobility.
Major finding: Among children with headache and joint hypermobility, 80% had severe headache disability.
Study details: A prospective, single-center study of 76 children with headache.
Disclosures: The study was not supported by funding, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Citation: Sahjwani D et al. CNS 2019, Abstract 101.
Key clinical point: About one-quarter of pediatric patients with headache have joint hypermobility.
Major finding: Among children with headache and joint hypermobility, 80% had severe headache disability.
Study details: A prospective, single-center study of 76 children with headache.
Disclosures: The study was not supported by funding, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Citation: Sahjwani D et al. CNS 2019, Abstract 101.
Key clinical point: About one-quarter of pediatric patients with headache have joint hypermobility.
Major finding: Among children with headache and joint hypermobility, 80% had severe headache disability.
Study details: A prospective, single-center study of 76 children with headache.
Disclosures: The study was not supported by funding, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Citation: Sahjwani D et al. CNS 2019, Abstract 101.
Researchers seek to characterize pediatric new daily persistent headache
Key clinical point: New daily persistent headache may be relatively common among children presenting to headache clinics.
Major finding: Girls with new daily persistent headache report symptoms such as photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea significantly more frequently than boys do.
Study details: An observational study of 454 pediatric patients with new daily persistent headache.
Disclosures: The study was not supported by funding, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Citation: Pierce E et al. CNS 2019, Abstract 100.
Key clinical point: New daily persistent headache may be relatively common among children presenting to headache clinics.
Major finding: Girls with new daily persistent headache report symptoms such as photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea significantly more frequently than boys do.
Study details: An observational study of 454 pediatric patients with new daily persistent headache.
Disclosures: The study was not supported by funding, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Citation: Pierce E et al. CNS 2019, Abstract 100.
Key clinical point: New daily persistent headache may be relatively common among children presenting to headache clinics.
Major finding: Girls with new daily persistent headache report symptoms such as photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea significantly more frequently than boys do.
Study details: An observational study of 454 pediatric patients with new daily persistent headache.
Disclosures: The study was not supported by funding, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Citation: Pierce E et al. CNS 2019, Abstract 100.
Suicide rate higher than average for female clinicians
The suicide rate for women who provide health care is higher than that of all women of working age, while male health care practitioners are less likely to end their lives than working-age men as a whole, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
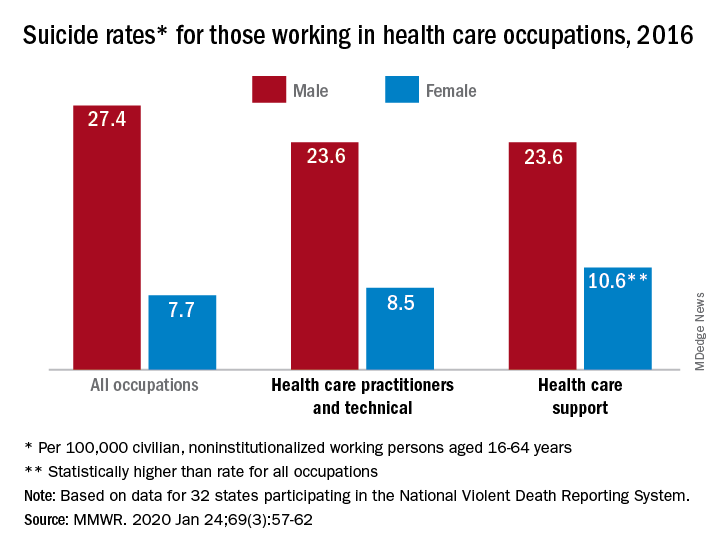
In 2016, the suicide rate for women classified as “healthcare practitioners and technical” – a category that includes physicians and surgeons, as well as chiropractors, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners – was 8.5 per 100,000 population, compared with 7.7 per 100,000 for all working women aged 16-64 years. That difference, however, was not statistically significant, Cora Peterson, PhD, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
For females classified as “healthcare support” – medical assistants and transcriptionists, phlebotomists, and pharmacy aides – the suicide rate of 10.6 per 100,000 was significantly higher than that of all working women, the investigators noted.
The suicide rate for males in each of the two occupation categories was 23.6 per 100,000 population in 2016, lower than the rate of 27.4 per 100,000 for males of all occupations, they said, based on data from 32 states that participated in the 2016 National Violent Death Reporting System.
For males, the highest suicide rates in occupations meeting criteria for sample size were “construction and extraction” (49.4 per 100,000); “installation, maintenance, and repair” (36.9); and “arts, design, entertainment, sports, and media” (32.0). Among females, the highest rates were seen in “construction and extraction” (25.5 per 100,000), “protective service” (14.0), and “transportation and material moving” (12.5), with healthcare support next, Dr. Peterson and associates reported.
“Although relative comparisons of suicide rates in this manner are useful for prevention purposes, Therefore, all industry sectors and occupational groups can contribute to reducing suicide incidence,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Peterson C et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):57-62.
The suicide rate for women who provide health care is higher than that of all women of working age, while male health care practitioners are less likely to end their lives than working-age men as a whole, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

In 2016, the suicide rate for women classified as “healthcare practitioners and technical” – a category that includes physicians and surgeons, as well as chiropractors, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners – was 8.5 per 100,000 population, compared with 7.7 per 100,000 for all working women aged 16-64 years. That difference, however, was not statistically significant, Cora Peterson, PhD, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
For females classified as “healthcare support” – medical assistants and transcriptionists, phlebotomists, and pharmacy aides – the suicide rate of 10.6 per 100,000 was significantly higher than that of all working women, the investigators noted.
The suicide rate for males in each of the two occupation categories was 23.6 per 100,000 population in 2016, lower than the rate of 27.4 per 100,000 for males of all occupations, they said, based on data from 32 states that participated in the 2016 National Violent Death Reporting System.
For males, the highest suicide rates in occupations meeting criteria for sample size were “construction and extraction” (49.4 per 100,000); “installation, maintenance, and repair” (36.9); and “arts, design, entertainment, sports, and media” (32.0). Among females, the highest rates were seen in “construction and extraction” (25.5 per 100,000), “protective service” (14.0), and “transportation and material moving” (12.5), with healthcare support next, Dr. Peterson and associates reported.
“Although relative comparisons of suicide rates in this manner are useful for prevention purposes, Therefore, all industry sectors and occupational groups can contribute to reducing suicide incidence,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Peterson C et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):57-62.
The suicide rate for women who provide health care is higher than that of all women of working age, while male health care practitioners are less likely to end their lives than working-age men as a whole, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

In 2016, the suicide rate for women classified as “healthcare practitioners and technical” – a category that includes physicians and surgeons, as well as chiropractors, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners – was 8.5 per 100,000 population, compared with 7.7 per 100,000 for all working women aged 16-64 years. That difference, however, was not statistically significant, Cora Peterson, PhD, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
For females classified as “healthcare support” – medical assistants and transcriptionists, phlebotomists, and pharmacy aides – the suicide rate of 10.6 per 100,000 was significantly higher than that of all working women, the investigators noted.
The suicide rate for males in each of the two occupation categories was 23.6 per 100,000 population in 2016, lower than the rate of 27.4 per 100,000 for males of all occupations, they said, based on data from 32 states that participated in the 2016 National Violent Death Reporting System.
For males, the highest suicide rates in occupations meeting criteria for sample size were “construction and extraction” (49.4 per 100,000); “installation, maintenance, and repair” (36.9); and “arts, design, entertainment, sports, and media” (32.0). Among females, the highest rates were seen in “construction and extraction” (25.5 per 100,000), “protective service” (14.0), and “transportation and material moving” (12.5), with healthcare support next, Dr. Peterson and associates reported.
“Although relative comparisons of suicide rates in this manner are useful for prevention purposes, Therefore, all industry sectors and occupational groups can contribute to reducing suicide incidence,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Peterson C et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):57-62.
FROM MMWR
Ubrogepant May Relieve Migraine Pain at 2 Hours
Key clinical point: Ubrogepant, an oral calcitonin gene–related peptide (CGRP)–receptor antagonist, may relieve patients’ migraine pain and their most bothersome associated symptom, such as photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea, at 2 hours after acute treatment.
Major finding: At 2 hours, pain freedom was reported by 101 of 464 participants in the ubrogepant 50-mg group (21.8%), 90 of 435 in the ubrogepant 25-mg group (20.7%), and 65 of 456 in the placebo group (14.3%).
Study details: ACHIEVE II was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-attack clinical trial that included more than 1,300 adults with migraine.
Disclosures: The trial was sponsored by Allergan, the company developing the drug. Several authors are Allergan employees. Dr. Lipton is a consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria from Allergan and other companies.
Citation: Lipton RB et al. JAMA. 2019;322(19):1887-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16711.
Key clinical point: Ubrogepant, an oral calcitonin gene–related peptide (CGRP)–receptor antagonist, may relieve patients’ migraine pain and their most bothersome associated symptom, such as photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea, at 2 hours after acute treatment.
Major finding: At 2 hours, pain freedom was reported by 101 of 464 participants in the ubrogepant 50-mg group (21.8%), 90 of 435 in the ubrogepant 25-mg group (20.7%), and 65 of 456 in the placebo group (14.3%).
Study details: ACHIEVE II was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-attack clinical trial that included more than 1,300 adults with migraine.
Disclosures: The trial was sponsored by Allergan, the company developing the drug. Several authors are Allergan employees. Dr. Lipton is a consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria from Allergan and other companies.
Citation: Lipton RB et al. JAMA. 2019;322(19):1887-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16711.
Key clinical point: Ubrogepant, an oral calcitonin gene–related peptide (CGRP)–receptor antagonist, may relieve patients’ migraine pain and their most bothersome associated symptom, such as photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea, at 2 hours after acute treatment.
Major finding: At 2 hours, pain freedom was reported by 101 of 464 participants in the ubrogepant 50-mg group (21.8%), 90 of 435 in the ubrogepant 25-mg group (20.7%), and 65 of 456 in the placebo group (14.3%).
Study details: ACHIEVE II was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-attack clinical trial that included more than 1,300 adults with migraine.
Disclosures: The trial was sponsored by Allergan, the company developing the drug. Several authors are Allergan employees. Dr. Lipton is a consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria from Allergan and other companies.
Citation: Lipton RB et al. JAMA. 2019;322(19):1887-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16711.
Headache may be a significant outcome of pediatric hemispherectomy
Key clinical point: Headache is a significant concern after pediatric hemispherectomy.
Major finding: Of 22 children who underwent hemispherectomy, 19 (86.4%) had headaches after the surgery.
Study details: A retrospective chart review and follow-up questionnaires that were administered to 22 children with hemispherectomy.
Citation: Pandit I et al. CNS 2019. Abstract 99.
Key clinical point: Headache is a significant concern after pediatric hemispherectomy.
Major finding: Of 22 children who underwent hemispherectomy, 19 (86.4%) had headaches after the surgery.
Study details: A retrospective chart review and follow-up questionnaires that were administered to 22 children with hemispherectomy.
Citation: Pandit I et al. CNS 2019. Abstract 99.
Key clinical point: Headache is a significant concern after pediatric hemispherectomy.
Major finding: Of 22 children who underwent hemispherectomy, 19 (86.4%) had headaches after the surgery.
Study details: A retrospective chart review and follow-up questionnaires that were administered to 22 children with hemispherectomy.
Citation: Pandit I et al. CNS 2019. Abstract 99.