User login
Self-reported falls can predict osteoporotic fracture risk
A single, simple question about a patient’s experience of falls in the previous year can help predict their risk of fractures, a study suggests.
In Osteoporosis International, researchers reported the outcomes of a cohort study using Manitoba clinical registry data from 24,943 men and women aged 40 years and older within the province who had undergone a fracture-probability assessment, and had data on self-reported falls for the previous year and fracture outcomes.
William D. Leslie, MD, of the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, and coauthors wrote that a frequent criticism of the FRAX fracture risk assessment tool was the fact that it didn’t include falls or fall risk in predicting fractures.
“Recent evidence derived from carefully conducted research cohort studies in men found that falls increase fracture risk independent of FRAX probability,” they wrote. “However, data are inconsistent with a paucity of evidence demonstrating usefulness of self-reported fall data as collected in routine clinical practice.”
0.8% experienced a hip fracture, and 4.9% experienced any incident fracture.
The analysis showed an increased risk of fracture with the increasing number of self-reported falls experienced in the previous year. The risk of major osteoporotic fracture was 49% higher among individuals who reported one fall, 74% in those who reported two falls and 2.6-fold higher for those who reported three or more falls in the previous year, compared with those who did not report any falls.
A similar pattern was seen for any incident fracture and hip fracture, with a 3.4-fold higher risk of hip fracture seen in those who reported three or more falls. The study also showed an increase in mortality risk with increasing number of falls.
“We documented that a simple question regarding self-reported falls in the previous year could be easily collected during routine clinical practice and that this information was strongly predictive of short-term fracture risk independent of multiple clinical risk factors including fracture probability using the FRAX tool with BMD [bone mineral density],” the authors wrote.
The analysis did not find an interaction with age or sex and the number of falls.
John A. Kanis, MD, reported grants from Amgen, Lily, and Radius Health. Three other coauthors reported nothing to declare for the context of this article, but reported research grants, speaking honoraria, consultancies from a variety of pharmaceutical companies and organizations. The remaining five coauthors declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Leslie WD et al. Osteoporos Int. 2019 Aug. 2. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05106-3.
Fragility fractures remain a major contributor to morbidity and even mortality of aging populations. Concerted efforts of clinicians, epidemiologists, and researchers have yielded an assortment of diagnostic strategies and prognostic algorithms in efforts to identify individuals at fracture risk. A variety of demographic (age, sex), biological (family history, specific disorders and medications), anatomical (bone mineral density, body mass index), and behavioral (smoking, alcohol consumption) parameters are recognized as predictors of fracture risk, and often are incorporated in predictive algorithms for fracture predisposition. FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment) is a widely used screening tool that is valid in offering fracture risk quantification across populations (Arch Osteoporos. 2016 Dec;11[1]:25; World Health Organization Assessment of Osteoporosis at the Primary Health Care Level).
Aging and accompanying neurocognitive deterioration, visual impairment, as well as iatrogenic factors are recognized to contribute to predisposition to falls in aging populations. A propensity for falls has long been regarded as a fracture risk (Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2008;6[4]:149-54). However, the evidence to support this logical assumption has been mixed with resulting exclusion of tendency to fall from commonly utilized fracture risk predictive models and tools. A predisposition to and frequency of falls is considered neither a risk modulator nor a mediator in the commonly utilized FRAX-based fracture risk assessments, and it is believed that fracture probability may be underestimated by FRAX in those predisposed to frequent falls (J Clin Densitom. 2011 Jul-Sep;14[3]:194–204).
The landscape of fracture risk assessment and quantification in the aforementioned backdrop has been refreshingly enhanced by a recent contribution by Leslie et al. wherein the authors provide real-life evidence relating self-reported falls to fracture risk. In a robust population sample nearing 25,000 women, increasing number of falls within the past year was associated with an increasing fracture risk, and this relationship persisted after adjusting for covariates that are recognized to predispose to fragility fractures, including age, body mass index, and bone mineral density. Women’s health providers are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the work of Leslie et al.; the authors’ message, that fall history be incorporated into risk quantification measures, is striking in its simplicity and profound in its preventative potential given that fall risk in and of itself may be mitigated in many through targeted interventions.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, MS, is professor and fellowship director of the division of reproductive endocrinology & infertility at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. She also is the director of the Yale reproductive endocrinology & infertility menopause program. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
Fragility fractures remain a major contributor to morbidity and even mortality of aging populations. Concerted efforts of clinicians, epidemiologists, and researchers have yielded an assortment of diagnostic strategies and prognostic algorithms in efforts to identify individuals at fracture risk. A variety of demographic (age, sex), biological (family history, specific disorders and medications), anatomical (bone mineral density, body mass index), and behavioral (smoking, alcohol consumption) parameters are recognized as predictors of fracture risk, and often are incorporated in predictive algorithms for fracture predisposition. FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment) is a widely used screening tool that is valid in offering fracture risk quantification across populations (Arch Osteoporos. 2016 Dec;11[1]:25; World Health Organization Assessment of Osteoporosis at the Primary Health Care Level).
Aging and accompanying neurocognitive deterioration, visual impairment, as well as iatrogenic factors are recognized to contribute to predisposition to falls in aging populations. A propensity for falls has long been regarded as a fracture risk (Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2008;6[4]:149-54). However, the evidence to support this logical assumption has been mixed with resulting exclusion of tendency to fall from commonly utilized fracture risk predictive models and tools. A predisposition to and frequency of falls is considered neither a risk modulator nor a mediator in the commonly utilized FRAX-based fracture risk assessments, and it is believed that fracture probability may be underestimated by FRAX in those predisposed to frequent falls (J Clin Densitom. 2011 Jul-Sep;14[3]:194–204).
The landscape of fracture risk assessment and quantification in the aforementioned backdrop has been refreshingly enhanced by a recent contribution by Leslie et al. wherein the authors provide real-life evidence relating self-reported falls to fracture risk. In a robust population sample nearing 25,000 women, increasing number of falls within the past year was associated with an increasing fracture risk, and this relationship persisted after adjusting for covariates that are recognized to predispose to fragility fractures, including age, body mass index, and bone mineral density. Women’s health providers are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the work of Leslie et al.; the authors’ message, that fall history be incorporated into risk quantification measures, is striking in its simplicity and profound in its preventative potential given that fall risk in and of itself may be mitigated in many through targeted interventions.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, MS, is professor and fellowship director of the division of reproductive endocrinology & infertility at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. She also is the director of the Yale reproductive endocrinology & infertility menopause program. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
Fragility fractures remain a major contributor to morbidity and even mortality of aging populations. Concerted efforts of clinicians, epidemiologists, and researchers have yielded an assortment of diagnostic strategies and prognostic algorithms in efforts to identify individuals at fracture risk. A variety of demographic (age, sex), biological (family history, specific disorders and medications), anatomical (bone mineral density, body mass index), and behavioral (smoking, alcohol consumption) parameters are recognized as predictors of fracture risk, and often are incorporated in predictive algorithms for fracture predisposition. FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment) is a widely used screening tool that is valid in offering fracture risk quantification across populations (Arch Osteoporos. 2016 Dec;11[1]:25; World Health Organization Assessment of Osteoporosis at the Primary Health Care Level).
Aging and accompanying neurocognitive deterioration, visual impairment, as well as iatrogenic factors are recognized to contribute to predisposition to falls in aging populations. A propensity for falls has long been regarded as a fracture risk (Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2008;6[4]:149-54). However, the evidence to support this logical assumption has been mixed with resulting exclusion of tendency to fall from commonly utilized fracture risk predictive models and tools. A predisposition to and frequency of falls is considered neither a risk modulator nor a mediator in the commonly utilized FRAX-based fracture risk assessments, and it is believed that fracture probability may be underestimated by FRAX in those predisposed to frequent falls (J Clin Densitom. 2011 Jul-Sep;14[3]:194–204).
The landscape of fracture risk assessment and quantification in the aforementioned backdrop has been refreshingly enhanced by a recent contribution by Leslie et al. wherein the authors provide real-life evidence relating self-reported falls to fracture risk. In a robust population sample nearing 25,000 women, increasing number of falls within the past year was associated with an increasing fracture risk, and this relationship persisted after adjusting for covariates that are recognized to predispose to fragility fractures, including age, body mass index, and bone mineral density. Women’s health providers are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the work of Leslie et al.; the authors’ message, that fall history be incorporated into risk quantification measures, is striking in its simplicity and profound in its preventative potential given that fall risk in and of itself may be mitigated in many through targeted interventions.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, MS, is professor and fellowship director of the division of reproductive endocrinology & infertility at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. She also is the director of the Yale reproductive endocrinology & infertility menopause program. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
A single, simple question about a patient’s experience of falls in the previous year can help predict their risk of fractures, a study suggests.
In Osteoporosis International, researchers reported the outcomes of a cohort study using Manitoba clinical registry data from 24,943 men and women aged 40 years and older within the province who had undergone a fracture-probability assessment, and had data on self-reported falls for the previous year and fracture outcomes.
William D. Leslie, MD, of the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, and coauthors wrote that a frequent criticism of the FRAX fracture risk assessment tool was the fact that it didn’t include falls or fall risk in predicting fractures.
“Recent evidence derived from carefully conducted research cohort studies in men found that falls increase fracture risk independent of FRAX probability,” they wrote. “However, data are inconsistent with a paucity of evidence demonstrating usefulness of self-reported fall data as collected in routine clinical practice.”
0.8% experienced a hip fracture, and 4.9% experienced any incident fracture.
The analysis showed an increased risk of fracture with the increasing number of self-reported falls experienced in the previous year. The risk of major osteoporotic fracture was 49% higher among individuals who reported one fall, 74% in those who reported two falls and 2.6-fold higher for those who reported three or more falls in the previous year, compared with those who did not report any falls.
A similar pattern was seen for any incident fracture and hip fracture, with a 3.4-fold higher risk of hip fracture seen in those who reported three or more falls. The study also showed an increase in mortality risk with increasing number of falls.
“We documented that a simple question regarding self-reported falls in the previous year could be easily collected during routine clinical practice and that this information was strongly predictive of short-term fracture risk independent of multiple clinical risk factors including fracture probability using the FRAX tool with BMD [bone mineral density],” the authors wrote.
The analysis did not find an interaction with age or sex and the number of falls.
John A. Kanis, MD, reported grants from Amgen, Lily, and Radius Health. Three other coauthors reported nothing to declare for the context of this article, but reported research grants, speaking honoraria, consultancies from a variety of pharmaceutical companies and organizations. The remaining five coauthors declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Leslie WD et al. Osteoporos Int. 2019 Aug. 2. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05106-3.
A single, simple question about a patient’s experience of falls in the previous year can help predict their risk of fractures, a study suggests.
In Osteoporosis International, researchers reported the outcomes of a cohort study using Manitoba clinical registry data from 24,943 men and women aged 40 years and older within the province who had undergone a fracture-probability assessment, and had data on self-reported falls for the previous year and fracture outcomes.
William D. Leslie, MD, of the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, and coauthors wrote that a frequent criticism of the FRAX fracture risk assessment tool was the fact that it didn’t include falls or fall risk in predicting fractures.
“Recent evidence derived from carefully conducted research cohort studies in men found that falls increase fracture risk independent of FRAX probability,” they wrote. “However, data are inconsistent with a paucity of evidence demonstrating usefulness of self-reported fall data as collected in routine clinical practice.”
0.8% experienced a hip fracture, and 4.9% experienced any incident fracture.
The analysis showed an increased risk of fracture with the increasing number of self-reported falls experienced in the previous year. The risk of major osteoporotic fracture was 49% higher among individuals who reported one fall, 74% in those who reported two falls and 2.6-fold higher for those who reported three or more falls in the previous year, compared with those who did not report any falls.
A similar pattern was seen for any incident fracture and hip fracture, with a 3.4-fold higher risk of hip fracture seen in those who reported three or more falls. The study also showed an increase in mortality risk with increasing number of falls.
“We documented that a simple question regarding self-reported falls in the previous year could be easily collected during routine clinical practice and that this information was strongly predictive of short-term fracture risk independent of multiple clinical risk factors including fracture probability using the FRAX tool with BMD [bone mineral density],” the authors wrote.
The analysis did not find an interaction with age or sex and the number of falls.
John A. Kanis, MD, reported grants from Amgen, Lily, and Radius Health. Three other coauthors reported nothing to declare for the context of this article, but reported research grants, speaking honoraria, consultancies from a variety of pharmaceutical companies and organizations. The remaining five coauthors declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Leslie WD et al. Osteoporos Int. 2019 Aug. 2. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05106-3.
FROM OSTEOPOROSIS INTERNATIONAL
Addressing suicidality among Indigenous women, girls
Historical trauma and current social factors contribute to depression, PTSD, anxiety disorders
The history of abuse and genocide has its precursors in antiquity. A brief sketch of this history will provide some insights into the impact of intergenerational trauma and a rationale for the crisis of missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls in the United States and Canada, or Turtle Island, as the Indigenous People call it.
Such a review also will provide a partial explanation of why the suicide rate among non-Hispanic Native American or Alaska Native women increased by 139%1 during 1999-2017 – a time when more Indigenous women were gaining access to law and medical school, as well as positions of authority in their tribes.
Church-, state-sanctioned transgressions
The psychological impact of our past history haunts us today. Papal bulletins – decrees from the pope – gave permission to Christian explorers to take land, wealth, and slaves from any nonbeliever. This permission was labeled the Doctrine of Discovery. It was incorporated into U.S. law in 1823, and by the Supreme Court case, Johnson v. M’intosh. It also provided rationale for the Indian Removal Act, which was passed on May 28, 1830, and signed into law by U.S. President Andrew Jackson. As a result of that law, Indigenous People were forced onto reservations, often removed from their traditional and sacred homelands. Many died during forced relocation.2
From the time of “discovery” by settlers until well into the 19th century, the U.S. governmental intent was genocide. It was manifest by the outright murder of Indigenous People, displacement from land, and the disruption of families when children were taken, put into boarding schools, and were forbidden to speak their language. Indigenous medicine people were killed or jailed for practicing their traditional ceremonies. Indigenous nations had their laws, languages, and agricultural practices denied them. Even today, they must practice U.S. law, adapt colonizing forms of land ownership, and engage in the economic practices of the dominant culture. The economic system currently in place rewards rape of the land and creates a trickle-up economy that keeps rewarding the rich at the expense of the poor. The economic system even gives corporations legal status as individuals, and, in some cases, is allowed to supersede the rights of Indigenous nations.
Today, the federal government still can appropriate land for minerals, pipelines,3 and even put indigenous land and water sovereignty at risk of contamination and pollution by mines established upstream.4 Most of those practices are repugnant to Indigenous nations. The Doctrine of Discovery established prior to 1492 is still alive and well on Turtle Island.
It is this background that denies the rights of Mother Earth, and this backdrop that, in turn, generalizes the denial of the rights of Indigenous women. There are women today, who, against their will and knowledge, have been sterilized.5 There are cases in which women have been raped and beaten, and their perpetrators were never been brought to justice.6 There are jurisdictional issues in the federal law that keep non-native perpetrators from being punished for their actions on tribal sovereign land.
This history and those current practices affect Indigenous families. Historical trauma produces epigenetic changes7 that create more anxiety and depression. Families in which one or both parents were taken away have a harder time providing a loving, safe, addiction-free environment for their children. Children often have high scores on measurements of adverse childhood experiences and suffer PTSD. As psychiatrists, we have treated PTSD from residential and boarding school survivors, families with family members who were victims of being missing or murdered, and survivors of sexual abuse – both in the United States and Canada. According to the final Canadian report of the inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls, the murder rate for Indigenous women was 12 times that of non-Indigenous women.8
We assert that this combination of historical trauma and current social factors contributes to depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders that currently feed the rise in attempted and completed suicide. Less-than-optimal educational opportunities and unemployment, often above 10% on reservations,9 along with food insecurity, accentuate the settings in which women and girls live.
Women achieving despite challenges
Yet, Indigenous women are making great strides within their cultures and communities. For example, Indigenous women are leading language revitalization, and within their culture, are healers and carriers of knowledge. Many Indigenous women are doctors, lawyers, dentists, teachers, poets, authors, and artists.10 Voters in last year’s midterms elected two Native American women to the U.S. Congress. Often, however, those achievements within the Western culture come at a cost, and some might have difficulty balancing those roles with their traditional cultures.
Current societal pressures feed the rise of suicide. Santa Fe, N.M., is known for its affluence and reputation as a tricultural city of Anglos, Hispanics, and Native Americans, and yet, a recent health impact assessment survey of urban Indigenous families stated that food insecurity was the leading concern for those families. Unemployment on the Navajo Nation is above 50%.11 The Indian Health Service (IHS) in the United States, which provides the majority of mental services to the Indigenous population, has identified mental health issues as the No. 1 health problem. However, only 7% of the IHS budget is allocated for mental health and substance abuse services. This represents an underfudging of services to American Indian and Alaska Native communities. In fact, there were only two psychiatrists per 100,000 people served by the IHS, which is one-seventh the number of psychiatrists available to the general population in the United States.12
Best practices for psychiatrists working with Indigenous women demands that we know the history, know how that history is still being manifest in subtle ways, and understand how such antiquated papal bulletins as the Doctrine of Discovery still operate to justify the taking and misuse of indigenous land. We must realize that the dominant economic systems, laws, and policing strategies are imposed on cultures that are sophisticated in their own right. This will then allow compassionate care with a level of understanding.
13
We can advocate at all levels, considering that the role of the federal government, the state, corporations, tribes, families, and provision of quality care to individuals can continue the positive collective advancement of women, and reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with suicide attempts.
We need to be sensitive to our patients and their risks of suicide. Treat suicidal ideation as the serious threat that it is. Address the depression, anxiety, PTSD, historical trauma, substance abuse, emotional dysregulation, and loss of relationship in persons with attachment disorders as serious and valid life events than can lead to serious consequences – including completed suicide.
Indigenous women are resilient, and the approach should be to also balance knowledge of those potential barriers with validating the feminine, and supporting the traditional roles of women and men that value women and children, and revere the matriarchs. Encouraging and supporting Indigenous resurgence of cultural practices and values is significant for positive outcomes for healing and wellness. Doing so can carry a greater meaning within Indigenous and First Nations society.
References
1. Curtin SC and H Hedegaard. Suicide rates for females and males by race and ethnicity: United States, 1999 and 2017. NCHS Health E-Stat. 2019.
2. Anderson GC. Ethnic cleansing and the Indian: The crime that should haunt America. Norman, Okla.: University of Oklahoma Press, 2014.
3. Rausch N. “Standing Rock, Morton County work to mend relationships post-DAPL protests.” Billingsgazette.com. Aug 10, 2019.
4. Roy A. “5 ways the government keeps Native Americans in poverty.” Forbes.com. Mar 13, 2014.
5. Blakemore E. “The little-known history of forced sterilization of Native American women.” JSTOR.org. Aug 25, 2016.
6. Bleir G and A Zoledziowski. “Murdered and missing Native American women challenge police and courts.” Publicintegrity.org. Aug 27, 2018.
7. Brockie TN et al. A framework to examine the role of epigenetics in health disparities among Native Americans. Nurs Res Prac. 2013;2013:410395.
8. “Reclaiming power and place: The final report of the national inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls.” Vancouver: Privy Office. Jun 3, 2019.
9. Hagan S. “Where U.S. unemployment is still sky-high: Indian reservations.” Bloomberg.com. Apr 5, 2018.
10. Morin B. “Meet 10 Indigenous women who are making the world a better place.” Indian Country Today. Jul 1, 2019.
11. Fact sheet. Discovernavajo.com.
12. Sarche M and P Spicer. Poverty and health disparities for American Indian and Alaska Native children: Current knowledge and future prospects. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2008 Jul 25;1136:126-36.
13. Lewis-Fernández R et al. Culture and psychiatric evaluation: Operationalizing cultural formulation for DSM-5. Psychiatry. 2014 Summer;77(2):130-54.
Dr. Roessel is a Navajo board-certified psychiatrist practicing in Santa Fe, N.M., working with the local Indigenous population. She has special expertise in cultural psychiatry; her childhood was spent growing up in the Navajo nation with her grandfather, who was a Navajo medicine man. Her psychiatric practice focuses on integrating Indigenous knowledge and principles. Dr. Roessel is a distinguished fellow of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Neidhardt is a board-certified psychiatrist who lives in Santa Fe and has an integrative, holistic psychiatric practice that also specializes in trauma-focused therapy. He has provided care for Indigenous People in the Southwest United States and in Canada, and has worked with Navajo medicine people to develop training for mental health professionals with his wife, Dr. Mary Hasbah Roessel. Dr. Reinhardt is a life fellow of the APA.
Historical trauma and current social factors contribute to depression, PTSD, anxiety disorders
Historical trauma and current social factors contribute to depression, PTSD, anxiety disorders
The history of abuse and genocide has its precursors in antiquity. A brief sketch of this history will provide some insights into the impact of intergenerational trauma and a rationale for the crisis of missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls in the United States and Canada, or Turtle Island, as the Indigenous People call it.
Such a review also will provide a partial explanation of why the suicide rate among non-Hispanic Native American or Alaska Native women increased by 139%1 during 1999-2017 – a time when more Indigenous women were gaining access to law and medical school, as well as positions of authority in their tribes.
Church-, state-sanctioned transgressions
The psychological impact of our past history haunts us today. Papal bulletins – decrees from the pope – gave permission to Christian explorers to take land, wealth, and slaves from any nonbeliever. This permission was labeled the Doctrine of Discovery. It was incorporated into U.S. law in 1823, and by the Supreme Court case, Johnson v. M’intosh. It also provided rationale for the Indian Removal Act, which was passed on May 28, 1830, and signed into law by U.S. President Andrew Jackson. As a result of that law, Indigenous People were forced onto reservations, often removed from their traditional and sacred homelands. Many died during forced relocation.2
From the time of “discovery” by settlers until well into the 19th century, the U.S. governmental intent was genocide. It was manifest by the outright murder of Indigenous People, displacement from land, and the disruption of families when children were taken, put into boarding schools, and were forbidden to speak their language. Indigenous medicine people were killed or jailed for practicing their traditional ceremonies. Indigenous nations had their laws, languages, and agricultural practices denied them. Even today, they must practice U.S. law, adapt colonizing forms of land ownership, and engage in the economic practices of the dominant culture. The economic system currently in place rewards rape of the land and creates a trickle-up economy that keeps rewarding the rich at the expense of the poor. The economic system even gives corporations legal status as individuals, and, in some cases, is allowed to supersede the rights of Indigenous nations.
Today, the federal government still can appropriate land for minerals, pipelines,3 and even put indigenous land and water sovereignty at risk of contamination and pollution by mines established upstream.4 Most of those practices are repugnant to Indigenous nations. The Doctrine of Discovery established prior to 1492 is still alive and well on Turtle Island.
It is this background that denies the rights of Mother Earth, and this backdrop that, in turn, generalizes the denial of the rights of Indigenous women. There are women today, who, against their will and knowledge, have been sterilized.5 There are cases in which women have been raped and beaten, and their perpetrators were never been brought to justice.6 There are jurisdictional issues in the federal law that keep non-native perpetrators from being punished for their actions on tribal sovereign land.
This history and those current practices affect Indigenous families. Historical trauma produces epigenetic changes7 that create more anxiety and depression. Families in which one or both parents were taken away have a harder time providing a loving, safe, addiction-free environment for their children. Children often have high scores on measurements of adverse childhood experiences and suffer PTSD. As psychiatrists, we have treated PTSD from residential and boarding school survivors, families with family members who were victims of being missing or murdered, and survivors of sexual abuse – both in the United States and Canada. According to the final Canadian report of the inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls, the murder rate for Indigenous women was 12 times that of non-Indigenous women.8
We assert that this combination of historical trauma and current social factors contributes to depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders that currently feed the rise in attempted and completed suicide. Less-than-optimal educational opportunities and unemployment, often above 10% on reservations,9 along with food insecurity, accentuate the settings in which women and girls live.
Women achieving despite challenges
Yet, Indigenous women are making great strides within their cultures and communities. For example, Indigenous women are leading language revitalization, and within their culture, are healers and carriers of knowledge. Many Indigenous women are doctors, lawyers, dentists, teachers, poets, authors, and artists.10 Voters in last year’s midterms elected two Native American women to the U.S. Congress. Often, however, those achievements within the Western culture come at a cost, and some might have difficulty balancing those roles with their traditional cultures.
Current societal pressures feed the rise of suicide. Santa Fe, N.M., is known for its affluence and reputation as a tricultural city of Anglos, Hispanics, and Native Americans, and yet, a recent health impact assessment survey of urban Indigenous families stated that food insecurity was the leading concern for those families. Unemployment on the Navajo Nation is above 50%.11 The Indian Health Service (IHS) in the United States, which provides the majority of mental services to the Indigenous population, has identified mental health issues as the No. 1 health problem. However, only 7% of the IHS budget is allocated for mental health and substance abuse services. This represents an underfudging of services to American Indian and Alaska Native communities. In fact, there were only two psychiatrists per 100,000 people served by the IHS, which is one-seventh the number of psychiatrists available to the general population in the United States.12
Best practices for psychiatrists working with Indigenous women demands that we know the history, know how that history is still being manifest in subtle ways, and understand how such antiquated papal bulletins as the Doctrine of Discovery still operate to justify the taking and misuse of indigenous land. We must realize that the dominant economic systems, laws, and policing strategies are imposed on cultures that are sophisticated in their own right. This will then allow compassionate care with a level of understanding.
13
We can advocate at all levels, considering that the role of the federal government, the state, corporations, tribes, families, and provision of quality care to individuals can continue the positive collective advancement of women, and reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with suicide attempts.
We need to be sensitive to our patients and their risks of suicide. Treat suicidal ideation as the serious threat that it is. Address the depression, anxiety, PTSD, historical trauma, substance abuse, emotional dysregulation, and loss of relationship in persons with attachment disorders as serious and valid life events than can lead to serious consequences – including completed suicide.
Indigenous women are resilient, and the approach should be to also balance knowledge of those potential barriers with validating the feminine, and supporting the traditional roles of women and men that value women and children, and revere the matriarchs. Encouraging and supporting Indigenous resurgence of cultural practices and values is significant for positive outcomes for healing and wellness. Doing so can carry a greater meaning within Indigenous and First Nations society.
References
1. Curtin SC and H Hedegaard. Suicide rates for females and males by race and ethnicity: United States, 1999 and 2017. NCHS Health E-Stat. 2019.
2. Anderson GC. Ethnic cleansing and the Indian: The crime that should haunt America. Norman, Okla.: University of Oklahoma Press, 2014.
3. Rausch N. “Standing Rock, Morton County work to mend relationships post-DAPL protests.” Billingsgazette.com. Aug 10, 2019.
4. Roy A. “5 ways the government keeps Native Americans in poverty.” Forbes.com. Mar 13, 2014.
5. Blakemore E. “The little-known history of forced sterilization of Native American women.” JSTOR.org. Aug 25, 2016.
6. Bleir G and A Zoledziowski. “Murdered and missing Native American women challenge police and courts.” Publicintegrity.org. Aug 27, 2018.
7. Brockie TN et al. A framework to examine the role of epigenetics in health disparities among Native Americans. Nurs Res Prac. 2013;2013:410395.
8. “Reclaiming power and place: The final report of the national inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls.” Vancouver: Privy Office. Jun 3, 2019.
9. Hagan S. “Where U.S. unemployment is still sky-high: Indian reservations.” Bloomberg.com. Apr 5, 2018.
10. Morin B. “Meet 10 Indigenous women who are making the world a better place.” Indian Country Today. Jul 1, 2019.
11. Fact sheet. Discovernavajo.com.
12. Sarche M and P Spicer. Poverty and health disparities for American Indian and Alaska Native children: Current knowledge and future prospects. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2008 Jul 25;1136:126-36.
13. Lewis-Fernández R et al. Culture and psychiatric evaluation: Operationalizing cultural formulation for DSM-5. Psychiatry. 2014 Summer;77(2):130-54.
Dr. Roessel is a Navajo board-certified psychiatrist practicing in Santa Fe, N.M., working with the local Indigenous population. She has special expertise in cultural psychiatry; her childhood was spent growing up in the Navajo nation with her grandfather, who was a Navajo medicine man. Her psychiatric practice focuses on integrating Indigenous knowledge and principles. Dr. Roessel is a distinguished fellow of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Neidhardt is a board-certified psychiatrist who lives in Santa Fe and has an integrative, holistic psychiatric practice that also specializes in trauma-focused therapy. He has provided care for Indigenous People in the Southwest United States and in Canada, and has worked with Navajo medicine people to develop training for mental health professionals with his wife, Dr. Mary Hasbah Roessel. Dr. Reinhardt is a life fellow of the APA.
The history of abuse and genocide has its precursors in antiquity. A brief sketch of this history will provide some insights into the impact of intergenerational trauma and a rationale for the crisis of missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls in the United States and Canada, or Turtle Island, as the Indigenous People call it.
Such a review also will provide a partial explanation of why the suicide rate among non-Hispanic Native American or Alaska Native women increased by 139%1 during 1999-2017 – a time when more Indigenous women were gaining access to law and medical school, as well as positions of authority in their tribes.
Church-, state-sanctioned transgressions
The psychological impact of our past history haunts us today. Papal bulletins – decrees from the pope – gave permission to Christian explorers to take land, wealth, and slaves from any nonbeliever. This permission was labeled the Doctrine of Discovery. It was incorporated into U.S. law in 1823, and by the Supreme Court case, Johnson v. M’intosh. It also provided rationale for the Indian Removal Act, which was passed on May 28, 1830, and signed into law by U.S. President Andrew Jackson. As a result of that law, Indigenous People were forced onto reservations, often removed from their traditional and sacred homelands. Many died during forced relocation.2
From the time of “discovery” by settlers until well into the 19th century, the U.S. governmental intent was genocide. It was manifest by the outright murder of Indigenous People, displacement from land, and the disruption of families when children were taken, put into boarding schools, and were forbidden to speak their language. Indigenous medicine people were killed or jailed for practicing their traditional ceremonies. Indigenous nations had their laws, languages, and agricultural practices denied them. Even today, they must practice U.S. law, adapt colonizing forms of land ownership, and engage in the economic practices of the dominant culture. The economic system currently in place rewards rape of the land and creates a trickle-up economy that keeps rewarding the rich at the expense of the poor. The economic system even gives corporations legal status as individuals, and, in some cases, is allowed to supersede the rights of Indigenous nations.
Today, the federal government still can appropriate land for minerals, pipelines,3 and even put indigenous land and water sovereignty at risk of contamination and pollution by mines established upstream.4 Most of those practices are repugnant to Indigenous nations. The Doctrine of Discovery established prior to 1492 is still alive and well on Turtle Island.
It is this background that denies the rights of Mother Earth, and this backdrop that, in turn, generalizes the denial of the rights of Indigenous women. There are women today, who, against their will and knowledge, have been sterilized.5 There are cases in which women have been raped and beaten, and their perpetrators were never been brought to justice.6 There are jurisdictional issues in the federal law that keep non-native perpetrators from being punished for their actions on tribal sovereign land.
This history and those current practices affect Indigenous families. Historical trauma produces epigenetic changes7 that create more anxiety and depression. Families in which one or both parents were taken away have a harder time providing a loving, safe, addiction-free environment for their children. Children often have high scores on measurements of adverse childhood experiences and suffer PTSD. As psychiatrists, we have treated PTSD from residential and boarding school survivors, families with family members who were victims of being missing or murdered, and survivors of sexual abuse – both in the United States and Canada. According to the final Canadian report of the inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls, the murder rate for Indigenous women was 12 times that of non-Indigenous women.8
We assert that this combination of historical trauma and current social factors contributes to depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders that currently feed the rise in attempted and completed suicide. Less-than-optimal educational opportunities and unemployment, often above 10% on reservations,9 along with food insecurity, accentuate the settings in which women and girls live.
Women achieving despite challenges
Yet, Indigenous women are making great strides within their cultures and communities. For example, Indigenous women are leading language revitalization, and within their culture, are healers and carriers of knowledge. Many Indigenous women are doctors, lawyers, dentists, teachers, poets, authors, and artists.10 Voters in last year’s midterms elected two Native American women to the U.S. Congress. Often, however, those achievements within the Western culture come at a cost, and some might have difficulty balancing those roles with their traditional cultures.
Current societal pressures feed the rise of suicide. Santa Fe, N.M., is known for its affluence and reputation as a tricultural city of Anglos, Hispanics, and Native Americans, and yet, a recent health impact assessment survey of urban Indigenous families stated that food insecurity was the leading concern for those families. Unemployment on the Navajo Nation is above 50%.11 The Indian Health Service (IHS) in the United States, which provides the majority of mental services to the Indigenous population, has identified mental health issues as the No. 1 health problem. However, only 7% of the IHS budget is allocated for mental health and substance abuse services. This represents an underfudging of services to American Indian and Alaska Native communities. In fact, there were only two psychiatrists per 100,000 people served by the IHS, which is one-seventh the number of psychiatrists available to the general population in the United States.12
Best practices for psychiatrists working with Indigenous women demands that we know the history, know how that history is still being manifest in subtle ways, and understand how such antiquated papal bulletins as the Doctrine of Discovery still operate to justify the taking and misuse of indigenous land. We must realize that the dominant economic systems, laws, and policing strategies are imposed on cultures that are sophisticated in their own right. This will then allow compassionate care with a level of understanding.
13
We can advocate at all levels, considering that the role of the federal government, the state, corporations, tribes, families, and provision of quality care to individuals can continue the positive collective advancement of women, and reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with suicide attempts.
We need to be sensitive to our patients and their risks of suicide. Treat suicidal ideation as the serious threat that it is. Address the depression, anxiety, PTSD, historical trauma, substance abuse, emotional dysregulation, and loss of relationship in persons with attachment disorders as serious and valid life events than can lead to serious consequences – including completed suicide.
Indigenous women are resilient, and the approach should be to also balance knowledge of those potential barriers with validating the feminine, and supporting the traditional roles of women and men that value women and children, and revere the matriarchs. Encouraging and supporting Indigenous resurgence of cultural practices and values is significant for positive outcomes for healing and wellness. Doing so can carry a greater meaning within Indigenous and First Nations society.
References
1. Curtin SC and H Hedegaard. Suicide rates for females and males by race and ethnicity: United States, 1999 and 2017. NCHS Health E-Stat. 2019.
2. Anderson GC. Ethnic cleansing and the Indian: The crime that should haunt America. Norman, Okla.: University of Oklahoma Press, 2014.
3. Rausch N. “Standing Rock, Morton County work to mend relationships post-DAPL protests.” Billingsgazette.com. Aug 10, 2019.
4. Roy A. “5 ways the government keeps Native Americans in poverty.” Forbes.com. Mar 13, 2014.
5. Blakemore E. “The little-known history of forced sterilization of Native American women.” JSTOR.org. Aug 25, 2016.
6. Bleir G and A Zoledziowski. “Murdered and missing Native American women challenge police and courts.” Publicintegrity.org. Aug 27, 2018.
7. Brockie TN et al. A framework to examine the role of epigenetics in health disparities among Native Americans. Nurs Res Prac. 2013;2013:410395.
8. “Reclaiming power and place: The final report of the national inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls.” Vancouver: Privy Office. Jun 3, 2019.
9. Hagan S. “Where U.S. unemployment is still sky-high: Indian reservations.” Bloomberg.com. Apr 5, 2018.
10. Morin B. “Meet 10 Indigenous women who are making the world a better place.” Indian Country Today. Jul 1, 2019.
11. Fact sheet. Discovernavajo.com.
12. Sarche M and P Spicer. Poverty and health disparities for American Indian and Alaska Native children: Current knowledge and future prospects. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2008 Jul 25;1136:126-36.
13. Lewis-Fernández R et al. Culture and psychiatric evaluation: Operationalizing cultural formulation for DSM-5. Psychiatry. 2014 Summer;77(2):130-54.
Dr. Roessel is a Navajo board-certified psychiatrist practicing in Santa Fe, N.M., working with the local Indigenous population. She has special expertise in cultural psychiatry; her childhood was spent growing up in the Navajo nation with her grandfather, who was a Navajo medicine man. Her psychiatric practice focuses on integrating Indigenous knowledge and principles. Dr. Roessel is a distinguished fellow of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Neidhardt is a board-certified psychiatrist who lives in Santa Fe and has an integrative, holistic psychiatric practice that also specializes in trauma-focused therapy. He has provided care for Indigenous People in the Southwest United States and in Canada, and has worked with Navajo medicine people to develop training for mental health professionals with his wife, Dr. Mary Hasbah Roessel. Dr. Reinhardt is a life fellow of the APA.
Planned Parenthood withdraws from Title X
Planned Parenthood will no longer participate in the federal Title X family planning program in response to a Trump administration rule that prohibits physicians from counseling patients about abortion and referring patients for the procedure.
In an Aug. 19 announcement, Alexis McGill Johnson, Planned Parenthood Federation of America president and CEO, said the Title X changes, which amount to “an unethical and dangerous gag rule,” has forced the organization out of Title X after being part of the program for 50 years. Planned Parenthood health centers are the largest Title X provider, serving 40% of patients who receive care through the program.
“We believe that the Trump administration is doing this as an attack on reproductive health care and to keep providers like Planned Parenthood from serving our patients,” Ms. McGill said in a statement. “Health care shouldn’t come down to how much you earn, where you live, or who you are. Congress must act now. It’s time for the U.S. Senate to act to pass a spending bill that will reverse the harmful rule and restore access to birth control, STD testing, and other critical services to people with low incomes.”
In an Aug. 19 statement, Mia Palmieri Heck, director of external affairs for the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services said every current Title X grantee has the choice to accept their grant and comply with the changes, or reject their funding by refusing to comply.
“The new Title X regulations were final at the time the current grant awards were announced,” Ms. Heck said a statement. “Some grantees are now blaming the government for their own actions – having chosen to accept the grant while failing to comply with the regulations that accompany it – and they are abandoning their obligations to serve their patients under the program. HHS is grateful for the many grantees who continue to serve their patients under the Title X program, and we will work to ensure all patients continue to be served.”
The announcement by Planned Parenthood comes about a month after HHS gave family planning clinics more time to comply with the new rule if they are making good faith efforts to comply with the new rules. The changes to the Title X program make health clinics ineligible for funding if they offer, promote, or support abortion as a method of family planning.
So far, more than 20 states and several abortion rights organizations, including Planned Parenthood, have sued over the rules in four separate states. District judges in Oregon, Washington, and California temporarily blocked the rules from taking effect. In a June 20 decision, the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that the federal government may go forward with its plan to restrict Title X funding from clinics that provide abortion counseling or referrals. The decision overturned the lower court injunctions.
Clare Coleman, president and CEO for the National Family Planning & Reproductive Health Association, said she expects further withdrawals from the Title X program to follow Planned Parenthood’s departure.
“The administration’s Title X rule is forcing the program’s 90 grantees and nearly 4,000 service sites to make gut-wrenching choices,” Ms. Coleman said in a statement. “They can stay in the program, despite the rule’s harms and compromises to Title X’s quality of care, for the sake of continuing to offer some Title X care for low-income individuals [or] they can leave the program and forego funding in order to avoid the rule’s limits on pregnancy counseling and other essential care, contrary to HHS’s own professional standards.”
HHS has previously said that the Title X changes ensure that grants and contracts awarded under the program fully comply with the statutory program integrity requirements, “thereby fulfilling the purpose of Title X, so that more women and men can receive services that help them consider and achieve both their short-term and long-term family planning needs.” The agency recently posted guidance on its website on myths vs. facts about the changes.
Ms. Johnson meanwhile, said Planned Parenthood clinics will remain open to serve patients, and that the organization will continue to fight the Title X changes in court.
agallegos@mdedge.com
Planned Parenthood will no longer participate in the federal Title X family planning program in response to a Trump administration rule that prohibits physicians from counseling patients about abortion and referring patients for the procedure.
In an Aug. 19 announcement, Alexis McGill Johnson, Planned Parenthood Federation of America president and CEO, said the Title X changes, which amount to “an unethical and dangerous gag rule,” has forced the organization out of Title X after being part of the program for 50 years. Planned Parenthood health centers are the largest Title X provider, serving 40% of patients who receive care through the program.
“We believe that the Trump administration is doing this as an attack on reproductive health care and to keep providers like Planned Parenthood from serving our patients,” Ms. McGill said in a statement. “Health care shouldn’t come down to how much you earn, where you live, or who you are. Congress must act now. It’s time for the U.S. Senate to act to pass a spending bill that will reverse the harmful rule and restore access to birth control, STD testing, and other critical services to people with low incomes.”
In an Aug. 19 statement, Mia Palmieri Heck, director of external affairs for the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services said every current Title X grantee has the choice to accept their grant and comply with the changes, or reject their funding by refusing to comply.
“The new Title X regulations were final at the time the current grant awards were announced,” Ms. Heck said a statement. “Some grantees are now blaming the government for their own actions – having chosen to accept the grant while failing to comply with the regulations that accompany it – and they are abandoning their obligations to serve their patients under the program. HHS is grateful for the many grantees who continue to serve their patients under the Title X program, and we will work to ensure all patients continue to be served.”
The announcement by Planned Parenthood comes about a month after HHS gave family planning clinics more time to comply with the new rule if they are making good faith efforts to comply with the new rules. The changes to the Title X program make health clinics ineligible for funding if they offer, promote, or support abortion as a method of family planning.
So far, more than 20 states and several abortion rights organizations, including Planned Parenthood, have sued over the rules in four separate states. District judges in Oregon, Washington, and California temporarily blocked the rules from taking effect. In a June 20 decision, the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that the federal government may go forward with its plan to restrict Title X funding from clinics that provide abortion counseling or referrals. The decision overturned the lower court injunctions.
Clare Coleman, president and CEO for the National Family Planning & Reproductive Health Association, said she expects further withdrawals from the Title X program to follow Planned Parenthood’s departure.
“The administration’s Title X rule is forcing the program’s 90 grantees and nearly 4,000 service sites to make gut-wrenching choices,” Ms. Coleman said in a statement. “They can stay in the program, despite the rule’s harms and compromises to Title X’s quality of care, for the sake of continuing to offer some Title X care for low-income individuals [or] they can leave the program and forego funding in order to avoid the rule’s limits on pregnancy counseling and other essential care, contrary to HHS’s own professional standards.”
HHS has previously said that the Title X changes ensure that grants and contracts awarded under the program fully comply with the statutory program integrity requirements, “thereby fulfilling the purpose of Title X, so that more women and men can receive services that help them consider and achieve both their short-term and long-term family planning needs.” The agency recently posted guidance on its website on myths vs. facts about the changes.
Ms. Johnson meanwhile, said Planned Parenthood clinics will remain open to serve patients, and that the organization will continue to fight the Title X changes in court.
agallegos@mdedge.com
Planned Parenthood will no longer participate in the federal Title X family planning program in response to a Trump administration rule that prohibits physicians from counseling patients about abortion and referring patients for the procedure.
In an Aug. 19 announcement, Alexis McGill Johnson, Planned Parenthood Federation of America president and CEO, said the Title X changes, which amount to “an unethical and dangerous gag rule,” has forced the organization out of Title X after being part of the program for 50 years. Planned Parenthood health centers are the largest Title X provider, serving 40% of patients who receive care through the program.
“We believe that the Trump administration is doing this as an attack on reproductive health care and to keep providers like Planned Parenthood from serving our patients,” Ms. McGill said in a statement. “Health care shouldn’t come down to how much you earn, where you live, or who you are. Congress must act now. It’s time for the U.S. Senate to act to pass a spending bill that will reverse the harmful rule and restore access to birth control, STD testing, and other critical services to people with low incomes.”
In an Aug. 19 statement, Mia Palmieri Heck, director of external affairs for the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services said every current Title X grantee has the choice to accept their grant and comply with the changes, or reject their funding by refusing to comply.
“The new Title X regulations were final at the time the current grant awards were announced,” Ms. Heck said a statement. “Some grantees are now blaming the government for their own actions – having chosen to accept the grant while failing to comply with the regulations that accompany it – and they are abandoning their obligations to serve their patients under the program. HHS is grateful for the many grantees who continue to serve their patients under the Title X program, and we will work to ensure all patients continue to be served.”
The announcement by Planned Parenthood comes about a month after HHS gave family planning clinics more time to comply with the new rule if they are making good faith efforts to comply with the new rules. The changes to the Title X program make health clinics ineligible for funding if they offer, promote, or support abortion as a method of family planning.
So far, more than 20 states and several abortion rights organizations, including Planned Parenthood, have sued over the rules in four separate states. District judges in Oregon, Washington, and California temporarily blocked the rules from taking effect. In a June 20 decision, the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that the federal government may go forward with its plan to restrict Title X funding from clinics that provide abortion counseling or referrals. The decision overturned the lower court injunctions.
Clare Coleman, president and CEO for the National Family Planning & Reproductive Health Association, said she expects further withdrawals from the Title X program to follow Planned Parenthood’s departure.
“The administration’s Title X rule is forcing the program’s 90 grantees and nearly 4,000 service sites to make gut-wrenching choices,” Ms. Coleman said in a statement. “They can stay in the program, despite the rule’s harms and compromises to Title X’s quality of care, for the sake of continuing to offer some Title X care for low-income individuals [or] they can leave the program and forego funding in order to avoid the rule’s limits on pregnancy counseling and other essential care, contrary to HHS’s own professional standards.”
HHS has previously said that the Title X changes ensure that grants and contracts awarded under the program fully comply with the statutory program integrity requirements, “thereby fulfilling the purpose of Title X, so that more women and men can receive services that help them consider and achieve both their short-term and long-term family planning needs.” The agency recently posted guidance on its website on myths vs. facts about the changes.
Ms. Johnson meanwhile, said Planned Parenthood clinics will remain open to serve patients, and that the organization will continue to fight the Title X changes in court.
agallegos@mdedge.com
New measles outbreak reported in western N.Y.
A new measles outbreak in western New York has affected five people within a Mennonite community, according to the New York State Department of Health.
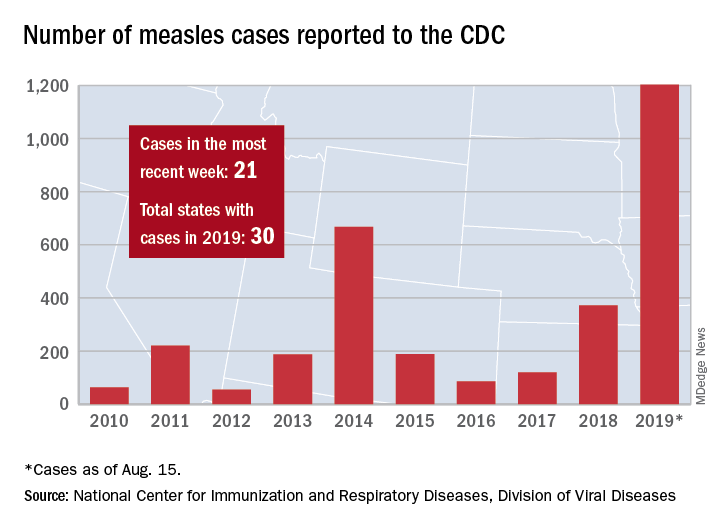
The five cases in Wyoming County, located east of Buffalo, were reported Aug. 8 and no further cases have been confirmed as of Aug. 16, the county health department said on its website.
Those five cases, along with six new cases in Rockland County, N.Y., and 10 more around the country, brought the total for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest reporting week to 21 and the total for the year to 1,203, the CDC said Aug. 19.
Along with Wyoming County and Rockland County (296 cases since Sept. 2018), the CDC currently is tracking outbreaks in New York City (653 cases since Sept. 2018), Washington state (85 cases in 2019; 13 in the current outbreak), California (65 cases in 2019; 5 in the current outbreak), and Texas (21 cases in 2019; 6 in the current outbreak).
“More than 75% of the cases this year are linked to outbreaks in New York and New York City,” the CDC said on its website, while also noting that “124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 64 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.”
A new measles outbreak in western New York has affected five people within a Mennonite community, according to the New York State Department of Health.

The five cases in Wyoming County, located east of Buffalo, were reported Aug. 8 and no further cases have been confirmed as of Aug. 16, the county health department said on its website.
Those five cases, along with six new cases in Rockland County, N.Y., and 10 more around the country, brought the total for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest reporting week to 21 and the total for the year to 1,203, the CDC said Aug. 19.
Along with Wyoming County and Rockland County (296 cases since Sept. 2018), the CDC currently is tracking outbreaks in New York City (653 cases since Sept. 2018), Washington state (85 cases in 2019; 13 in the current outbreak), California (65 cases in 2019; 5 in the current outbreak), and Texas (21 cases in 2019; 6 in the current outbreak).
“More than 75% of the cases this year are linked to outbreaks in New York and New York City,” the CDC said on its website, while also noting that “124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 64 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.”
A new measles outbreak in western New York has affected five people within a Mennonite community, according to the New York State Department of Health.

The five cases in Wyoming County, located east of Buffalo, were reported Aug. 8 and no further cases have been confirmed as of Aug. 16, the county health department said on its website.
Those five cases, along with six new cases in Rockland County, N.Y., and 10 more around the country, brought the total for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest reporting week to 21 and the total for the year to 1,203, the CDC said Aug. 19.
Along with Wyoming County and Rockland County (296 cases since Sept. 2018), the CDC currently is tracking outbreaks in New York City (653 cases since Sept. 2018), Washington state (85 cases in 2019; 13 in the current outbreak), California (65 cases in 2019; 5 in the current outbreak), and Texas (21 cases in 2019; 6 in the current outbreak).
“More than 75% of the cases this year are linked to outbreaks in New York and New York City,” the CDC said on its website, while also noting that “124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 64 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.”
ACP unveils clinical guideline disclosure strategy
The American College of Physicians recently described its methods for developing clinical guidelines and guidance statements, in a paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Any person involved in the development of an ACP clinical guideline or guidance statement must disclose all financial and intellectual interests related to health care from the previous 3 years,” Amir Qaseem, MD, and Timothy J. Wilt, MD, wrote.
“The goals of our process are to mitigate any actual bias during the development of ACP’s clinical recommendations and to ensure creditability and public trust in our clinical policies by reducing the potential for perceived bias,” noted Robert M. McLean, MD, president of the ACP, in a statement.
This paper’s publication comes on the heels of authors of a Cancer paper having reported that nearly 25% of the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s guideline authors who were not exempt from reporting conflicts of interest failed to disclose receiving industry payments.
The ACP committee’s guiding principle for collection of disclosures of interest and management of conflicts of interests “is to prioritize the interests of the patient over any competing or professional interests via an evidence-based assessment of the benefits, harms, and costs of an intervention,” wrote the authors on behalf of the CGC.
The CGC created a tiered system to classify potential conflicts as low level, moderate level, or high level based on three tenets: transparency (all disclosures are freely accessible so readers can assess them for themselves), proportionality (not all conflicts of interest have equal risk), and consistency (policies should be impartially applied across all variables).
Examples of low-level conflicts of interest (COIs) include high-level COIs that have become inactive and intellectual interests tangentially related to the topic under discussion. Moderate-level COIs are usually intellectual interests clinically relevant to the guideline topic; these interests might prompt an individual to seek professional or financial advantages through association with guideline development.
High-level COIs are active relationships with high-risk entities, defined by the CGC as “an entity that has a direct financial stake in the clinical conclusions of a guideline or guidance statement.”
While the time frame for reporting health-related interests is 3 years, disclosure is an ongoing process when clinical guidelines are in development because interests change over time, the authors said. Prospective guidelines committee members complete disclosure of interest forms before working on CGC projects, and they update these forms before each in-person CGC meeting.
“The CGC’s policy does not mandate disclosure of interests related primarily to personal matters or relationships outside the household,” such as political, religious, or ideological views, they noted.
The CGC maintains a DOI-COI Review and Management Panel to reviews conflicts, and all ACP guidelines include a list of relevant conflicts for committee members.
The authors of this paper disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Qaseem A and TJ Wilt. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 20. doi: 10.7326/M18-3279 .
This article was updated 8/22/19.
The American College of Physicians recently described its methods for developing clinical guidelines and guidance statements, in a paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Any person involved in the development of an ACP clinical guideline or guidance statement must disclose all financial and intellectual interests related to health care from the previous 3 years,” Amir Qaseem, MD, and Timothy J. Wilt, MD, wrote.
“The goals of our process are to mitigate any actual bias during the development of ACP’s clinical recommendations and to ensure creditability and public trust in our clinical policies by reducing the potential for perceived bias,” noted Robert M. McLean, MD, president of the ACP, in a statement.
This paper’s publication comes on the heels of authors of a Cancer paper having reported that nearly 25% of the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s guideline authors who were not exempt from reporting conflicts of interest failed to disclose receiving industry payments.
The ACP committee’s guiding principle for collection of disclosures of interest and management of conflicts of interests “is to prioritize the interests of the patient over any competing or professional interests via an evidence-based assessment of the benefits, harms, and costs of an intervention,” wrote the authors on behalf of the CGC.
The CGC created a tiered system to classify potential conflicts as low level, moderate level, or high level based on three tenets: transparency (all disclosures are freely accessible so readers can assess them for themselves), proportionality (not all conflicts of interest have equal risk), and consistency (policies should be impartially applied across all variables).
Examples of low-level conflicts of interest (COIs) include high-level COIs that have become inactive and intellectual interests tangentially related to the topic under discussion. Moderate-level COIs are usually intellectual interests clinically relevant to the guideline topic; these interests might prompt an individual to seek professional or financial advantages through association with guideline development.
High-level COIs are active relationships with high-risk entities, defined by the CGC as “an entity that has a direct financial stake in the clinical conclusions of a guideline or guidance statement.”
While the time frame for reporting health-related interests is 3 years, disclosure is an ongoing process when clinical guidelines are in development because interests change over time, the authors said. Prospective guidelines committee members complete disclosure of interest forms before working on CGC projects, and they update these forms before each in-person CGC meeting.
“The CGC’s policy does not mandate disclosure of interests related primarily to personal matters or relationships outside the household,” such as political, religious, or ideological views, they noted.
The CGC maintains a DOI-COI Review and Management Panel to reviews conflicts, and all ACP guidelines include a list of relevant conflicts for committee members.
The authors of this paper disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Qaseem A and TJ Wilt. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 20. doi: 10.7326/M18-3279 .
This article was updated 8/22/19.
The American College of Physicians recently described its methods for developing clinical guidelines and guidance statements, in a paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Any person involved in the development of an ACP clinical guideline or guidance statement must disclose all financial and intellectual interests related to health care from the previous 3 years,” Amir Qaseem, MD, and Timothy J. Wilt, MD, wrote.
“The goals of our process are to mitigate any actual bias during the development of ACP’s clinical recommendations and to ensure creditability and public trust in our clinical policies by reducing the potential for perceived bias,” noted Robert M. McLean, MD, president of the ACP, in a statement.
This paper’s publication comes on the heels of authors of a Cancer paper having reported that nearly 25% of the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s guideline authors who were not exempt from reporting conflicts of interest failed to disclose receiving industry payments.
The ACP committee’s guiding principle for collection of disclosures of interest and management of conflicts of interests “is to prioritize the interests of the patient over any competing or professional interests via an evidence-based assessment of the benefits, harms, and costs of an intervention,” wrote the authors on behalf of the CGC.
The CGC created a tiered system to classify potential conflicts as low level, moderate level, or high level based on three tenets: transparency (all disclosures are freely accessible so readers can assess them for themselves), proportionality (not all conflicts of interest have equal risk), and consistency (policies should be impartially applied across all variables).
Examples of low-level conflicts of interest (COIs) include high-level COIs that have become inactive and intellectual interests tangentially related to the topic under discussion. Moderate-level COIs are usually intellectual interests clinically relevant to the guideline topic; these interests might prompt an individual to seek professional or financial advantages through association with guideline development.
High-level COIs are active relationships with high-risk entities, defined by the CGC as “an entity that has a direct financial stake in the clinical conclusions of a guideline or guidance statement.”
While the time frame for reporting health-related interests is 3 years, disclosure is an ongoing process when clinical guidelines are in development because interests change over time, the authors said. Prospective guidelines committee members complete disclosure of interest forms before working on CGC projects, and they update these forms before each in-person CGC meeting.
“The CGC’s policy does not mandate disclosure of interests related primarily to personal matters or relationships outside the household,” such as political, religious, or ideological views, they noted.
The CGC maintains a DOI-COI Review and Management Panel to reviews conflicts, and all ACP guidelines include a list of relevant conflicts for committee members.
The authors of this paper disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Qaseem A and TJ Wilt. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 20. doi: 10.7326/M18-3279 .
This article was updated 8/22/19.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Statins hamper hepatocellular carcinoma in viral hepatitis patients
Lipophilic statin therapy significantly reduced the incidence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with viral hepatitis, based on data from 16,668 patients.
The mortality rates for hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States and Europe have been on the rise for decades, and the risk may persist in severe cases despite the use of hepatitis B virus suppression or hepatitis C virus eradication, wrote Tracey G. Simon, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that statins might reduce HCC risk in viral hepatitis patients, but evidence supporting one type of statin over another for HCC prevention is limited, they said.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from a national registry of hepatitis patients in Sweden to assess the effect of lipophilic or hydrophilic statin use on HCC incidence and mortality.
They found a significant reduction in 10-year HCC risk for lipophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (8.1% vs. 3.3%. However, the difference was not significant for hydrophilic statin users vs. nonusers (8.0% vs. 6.8%). The effect of lipophilic statin use was dose dependent; the largest effect on reduction in HCC risk occurred with 600 or more lipophilic statin cumulative daily doses in users, compared with nonusers (8.4% vs. 2.5%).
The study population included 6,554 lipophilic statin users and 1,780 hydrophilic statin users, matched with 8,334 nonusers. Patient demographics were similar between both types of statin user and nonuser groups.
In addition, 10-year mortality was significantly lower for lipophilic statin users compared with nonusers (15.2% vs. 7.3%) and also for hydrophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (16.0% vs. 11.5%).
In a small number of patients with liver disease (462), liver-specific mortality was significantly reduced in lipophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 vs. 0.98).
“Of note, our findings were robust across several sensitivity analyses and were similar in all predefined subgroups, including among men and women and persons with and without cirrhosis or antiviral therapy use,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential confounding from variables such as smoking, hepatitis B viral DNA, hepatitis C virus eradication, stage of fibrosis, and HCC screening, as well as a lack of laboratory data to assess cholesterol levels’ impact on statin use, the researchers said. In addition, the study did not compare lipophilic and hydrophilic statins.
However, the results suggest potential distinct benefits of lipophilic statins to reduce HCC risk and support the need for further research, the researchers concluded.
Dr. Simon had no financial conflicts to disclose, but disclosed support from a North American Training Grant from the American College of Gastroenterology. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and Merck Sharp & Dohme. The study was supported in part by the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Boston Nutrition Obesity Research Center, the National Institutes of Health, Nyckelfonden, Region Orebro (Sweden) County, and the Karolinska Institutet.
SOURCE: Simon TG et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.7326/M18-2753.
Lipophilic statin therapy significantly reduced the incidence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with viral hepatitis, based on data from 16,668 patients.
The mortality rates for hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States and Europe have been on the rise for decades, and the risk may persist in severe cases despite the use of hepatitis B virus suppression or hepatitis C virus eradication, wrote Tracey G. Simon, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that statins might reduce HCC risk in viral hepatitis patients, but evidence supporting one type of statin over another for HCC prevention is limited, they said.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from a national registry of hepatitis patients in Sweden to assess the effect of lipophilic or hydrophilic statin use on HCC incidence and mortality.
They found a significant reduction in 10-year HCC risk for lipophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (8.1% vs. 3.3%. However, the difference was not significant for hydrophilic statin users vs. nonusers (8.0% vs. 6.8%). The effect of lipophilic statin use was dose dependent; the largest effect on reduction in HCC risk occurred with 600 or more lipophilic statin cumulative daily doses in users, compared with nonusers (8.4% vs. 2.5%).
The study population included 6,554 lipophilic statin users and 1,780 hydrophilic statin users, matched with 8,334 nonusers. Patient demographics were similar between both types of statin user and nonuser groups.
In addition, 10-year mortality was significantly lower for lipophilic statin users compared with nonusers (15.2% vs. 7.3%) and also for hydrophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (16.0% vs. 11.5%).
In a small number of patients with liver disease (462), liver-specific mortality was significantly reduced in lipophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 vs. 0.98).
“Of note, our findings were robust across several sensitivity analyses and were similar in all predefined subgroups, including among men and women and persons with and without cirrhosis or antiviral therapy use,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential confounding from variables such as smoking, hepatitis B viral DNA, hepatitis C virus eradication, stage of fibrosis, and HCC screening, as well as a lack of laboratory data to assess cholesterol levels’ impact on statin use, the researchers said. In addition, the study did not compare lipophilic and hydrophilic statins.
However, the results suggest potential distinct benefits of lipophilic statins to reduce HCC risk and support the need for further research, the researchers concluded.
Dr. Simon had no financial conflicts to disclose, but disclosed support from a North American Training Grant from the American College of Gastroenterology. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and Merck Sharp & Dohme. The study was supported in part by the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Boston Nutrition Obesity Research Center, the National Institutes of Health, Nyckelfonden, Region Orebro (Sweden) County, and the Karolinska Institutet.
SOURCE: Simon TG et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.7326/M18-2753.
Lipophilic statin therapy significantly reduced the incidence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with viral hepatitis, based on data from 16,668 patients.
The mortality rates for hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States and Europe have been on the rise for decades, and the risk may persist in severe cases despite the use of hepatitis B virus suppression or hepatitis C virus eradication, wrote Tracey G. Simon, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that statins might reduce HCC risk in viral hepatitis patients, but evidence supporting one type of statin over another for HCC prevention is limited, they said.
In a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from a national registry of hepatitis patients in Sweden to assess the effect of lipophilic or hydrophilic statin use on HCC incidence and mortality.
They found a significant reduction in 10-year HCC risk for lipophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (8.1% vs. 3.3%. However, the difference was not significant for hydrophilic statin users vs. nonusers (8.0% vs. 6.8%). The effect of lipophilic statin use was dose dependent; the largest effect on reduction in HCC risk occurred with 600 or more lipophilic statin cumulative daily doses in users, compared with nonusers (8.4% vs. 2.5%).
The study population included 6,554 lipophilic statin users and 1,780 hydrophilic statin users, matched with 8,334 nonusers. Patient demographics were similar between both types of statin user and nonuser groups.
In addition, 10-year mortality was significantly lower for lipophilic statin users compared with nonusers (15.2% vs. 7.3%) and also for hydrophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (16.0% vs. 11.5%).
In a small number of patients with liver disease (462), liver-specific mortality was significantly reduced in lipophilic statin users, compared with nonusers (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 vs. 0.98).
“Of note, our findings were robust across several sensitivity analyses and were similar in all predefined subgroups, including among men and women and persons with and without cirrhosis or antiviral therapy use,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential confounding from variables such as smoking, hepatitis B viral DNA, hepatitis C virus eradication, stage of fibrosis, and HCC screening, as well as a lack of laboratory data to assess cholesterol levels’ impact on statin use, the researchers said. In addition, the study did not compare lipophilic and hydrophilic statins.
However, the results suggest potential distinct benefits of lipophilic statins to reduce HCC risk and support the need for further research, the researchers concluded.
Dr. Simon had no financial conflicts to disclose, but disclosed support from a North American Training Grant from the American College of Gastroenterology. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and Merck Sharp & Dohme. The study was supported in part by the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Boston Nutrition Obesity Research Center, the National Institutes of Health, Nyckelfonden, Region Orebro (Sweden) County, and the Karolinska Institutet.
SOURCE: Simon TG et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.7326/M18-2753.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Use of lipophilic statins significantly reduced incidence and mortality of hepatocellular cancer in adults with viral hepatitis.
Major finding: The 10-year risk of HCC was 8.1% among patients taking lipophilic statins, compared with 3.3% among those not on statins.
Study details: The data come from a population-based cohort study of 16,668 adult with viral hepatitis from a national registry in Sweden.
Disclosures: Dr. Simon had no financial conflicts to disclose, but disclosed support from a North American Training Grant from the American College of Gastroenterology. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, and MSD.
Source: Simon TG et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.7326/M18-2753.
Digital health and big data: New tools for making the most of real-world evidence
LAKE BUENA VISTA, FLA. – Digital health technology is vastly expanding the real-world data pool for clinical and comparative effectiveness research, according to Jeffrey Curtis, MD.
The trick is to harness the power of that data to improve patient care and outcomes, and that can be achieved in part through linkage of data sources and through point-of-care access, Dr. Curtis, professor of medicine in the division of clinical immunology and rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB), said at the annual meeting of the Florida Society of Rheumatology.
“We want to take care of patients, but probably what you and I also want is to have real-world evidence ... evidence relevant for people [we] take care of on a day-to-day basis – not people in highly selected phase 3 or even phase 4 trials,” he said.
Real-world data, which gained particular cachet through the 21st Century Cures Act permitting the Food and Drug Administration to consider real-world evidence as part of the regulatory process and in post-marketing surveillance, includes information from electronic health records (EHRs), health plan claims, traditional registries, and mobile health and technology, explained Dr. Curtis, who also is codirector of the UAB Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics Unit.
“And you and I want it because patients are different, and in medicine we only have about 20% of patients where there is direct evidence about what we should do,” he added. “Give me the trial that describes the 75-year-old African American smoker with diabetes and how well he does on biologic du jour; there’s no trial like that, and yet you and I need to make those kinds of decisions in light of patients’ comorbidities and other features.”
Generating real-world evidence, however, requires new approaches and new tools, he said, explaining that efficiency is key for applying the data in busy practices, as is compatibility with delivering an intervention and with randomization.
Imagine using the EHR at the point of care to look up what happened to “the last 10 patients like this” based on how they were treated by you or your colleagues, he said.
“That would be useful information to have. In fact, the day is not so far in the future where you could, perhaps, randomize within your EHR if you had a clinically important question that really needed an answer and a protocol attached,” he added.
Real-world data collection
Pragmatic trials offer one approach to garnering real-world data by addressing a simple question – usually with a hard outcome – using very few inclusion and exclusion criteria, Dr. Curtis said, describing the recently completed VERVE Zoster Vaccine trial.
He and his colleagues randomized 617 patients from 33 sites to look at the safety of the live-virus Zostavax herpes zoster vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis patients over age 50 years on any anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy. Half of the patients received saline, the other half received the vaccine, and no cases of varicella zoster occurred in either group.
“So, to the extent that half of 617 people with zero cases was reassuring, we now have some evidence where heretofore there was none,” he said, noting that those results will be presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting. “But the focus of this talk is not on vaccination, it’s really on how we do real-world effectiveness or safety studies in a way that doesn’t slow us way down and doesn’t require some big research operation.”
One way is through efficient recruitment, and depending on how complicated the study is, qualified patients may be easily identifiable through the EHR. In fact, numerous tools are available to codify and search both structured and unstructured data, Dr. Curtis said, noting that he and his colleagues used the web-based i2b2 Query Tool for the VERVE study.
The study sites that did the best with recruiting had the ability to search their own EHRs for patients who met the inclusion criteria, and those patients were then invited to participate. A short video was created to educate those who were interested, and a “knowledge review” quiz was administered afterward to ensure informed consent, which was provided via digital signature.
Health plan and other “big data” can also be very useful for answering certain questions. One example is how soon biologics should be stopped before elective orthopedic surgery? Dr. Curtis and colleagues looked at this using claims data for nearly 4,300 patients undergoing elective hip or knee arthroplasty and found no evidence that administering infliximab within 4 weeks of surgery increased serious infection risk within 30 days or prosthetic joint infection within 1 year.
“Where else are you going to go run a prospective study of 4,300 elective hips and knees,” he said, stressing that it wouldn’t be easy.
Other sources that can help generate real-world effectiveness data include traditional or single-center registries and EHR-based registries.
“The EHR registries are, I think, the newest that many are part of in our field,” he said, noting that “a number of groups are aggregating that,” including the ACR RISE registry and some physician groups, for example.
“What we’re really after is to have a clinically integrated network and a learning health care environment,” he explained, adding that the goal is to develop care pathways.
The approach represents a shift from evidence-based practice to practice-based evidence, he noted.
“When you and I practice, we’re generating that evidence and now we just need to harness that data to get smarter to take care of patients,” he said, adding that the lack of randomization for much of these data isn’t necessarily a problem.
“Do you have to randomize? I would argue that you don’t necessarily have to randomize if the source of variability in how we treat patients is very related to patients’ characteristics,” he said.
If the evidence for a specific approach is weak, or a decision is based on physician preference, physician practice, or insurance company considerations instead of patient characteristics, randomization may not be necessary, he explained.
In fact, insurance company requirements often create “natural experiments” that can be used to help identify better practices. For example, if one only covers adalimumab for first-line TNF inhibition, and another has a “different fail-first policy and that’s not first line and everybody gets some other TNF inhibitor, then I can probably compare those quite reasonably,” he said.
“That’s a great setting where you might not need randomization.”
Of note, “having more data sometimes trumps smarter algorithms,” but that means finding and linking more data that “exist in the wild,” Dr. Curtis said.
Linking data sources
When he and his colleagues wanted to assess the cost of not achieving RA remission, no single data source provided all of the information they needed. They used both CORRONA registry data and health claims data to look at various outcome measures across disease activity categories and with adjustment for comorbidity clusters. They previously reported on the feasibility and validity of the approach.
“We’re currently doing another project where one of the local Blue Cross plans said ‘I’m interested to support you to see how efficient you are; we will donate or loan you our claims data [and] let you link it to your practice so you can actually tell us ... cost conditional on [a patient’s] disease activity,’ ” he said.
Another example involves a recent study looking at biomarker-based cardiovascular disease risk prediction in RA using data from nearly 31,000 Medicare patients linked with multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) test results, with which they “basically built and validated a risk prediction model,” he said.
The point is that such data linkage provided tools for use at the point of care that can predict CVD risk using “some simple things that you and I have in our EHR,” he said. “But you couldn’t do this if you had to assemble a prospective cohort of tens of thousands of arthritis patients and then wait years for follow-up.”
Patient-reported outcomes collected at the point of care and by patients at home between visits, such as digital data collected via wearable technology, can provide additional information to help improve patient care and management.
“My interest is not to think about [these data sources] in isolation, but really to think about how we bring these together,” he said. “I’m interested in maximizing value for both patients and clinicians, and not having to pick only one of these data sources, but really to harness several of them if that’s what we need to take better care of patients and to answer important questions.”
Doing so is increasingly important given the workforce shortage in rheumatology, he noted.
“The point is that we’re going to need to be a whole lot more efficient as a field because there are going to be fewer of us even at a time when more of us are needed,” he said.
It’s a topic in which the ACR has shown a lot of interest, he said, noting that he cochaired a preconference course on mobile health technologies at the 2018 ACR annual meeting and is involved with a similar course on “big data” ahead of the 2019 meeting.
The thought of making use of the various digital health and “big data” sources can be overwhelming, but the key is to start with the question that needs an answer or the problem that needs to be solved.
“Don’t start with the data,” he explained. “Start with [asking] ... ‘What am I trying to do?’ ”
Dr. Curtis reported funding from the National Institute on Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. He has also consulted for or received research grants from Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CORRONA, Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Novartis, Roche, Pfizer, and Sanofi/Regeneron.
LAKE BUENA VISTA, FLA. – Digital health technology is vastly expanding the real-world data pool for clinical and comparative effectiveness research, according to Jeffrey Curtis, MD.
The trick is to harness the power of that data to improve patient care and outcomes, and that can be achieved in part through linkage of data sources and through point-of-care access, Dr. Curtis, professor of medicine in the division of clinical immunology and rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB), said at the annual meeting of the Florida Society of Rheumatology.
“We want to take care of patients, but probably what you and I also want is to have real-world evidence ... evidence relevant for people [we] take care of on a day-to-day basis – not people in highly selected phase 3 or even phase 4 trials,” he said.
Real-world data, which gained particular cachet through the 21st Century Cures Act permitting the Food and Drug Administration to consider real-world evidence as part of the regulatory process and in post-marketing surveillance, includes information from electronic health records (EHRs), health plan claims, traditional registries, and mobile health and technology, explained Dr. Curtis, who also is codirector of the UAB Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics Unit.
“And you and I want it because patients are different, and in medicine we only have about 20% of patients where there is direct evidence about what we should do,” he added. “Give me the trial that describes the 75-year-old African American smoker with diabetes and how well he does on biologic du jour; there’s no trial like that, and yet you and I need to make those kinds of decisions in light of patients’ comorbidities and other features.”
Generating real-world evidence, however, requires new approaches and new tools, he said, explaining that efficiency is key for applying the data in busy practices, as is compatibility with delivering an intervention and with randomization.
Imagine using the EHR at the point of care to look up what happened to “the last 10 patients like this” based on how they were treated by you or your colleagues, he said.
“That would be useful information to have. In fact, the day is not so far in the future where you could, perhaps, randomize within your EHR if you had a clinically important question that really needed an answer and a protocol attached,” he added.
Real-world data collection
Pragmatic trials offer one approach to garnering real-world data by addressing a simple question – usually with a hard outcome – using very few inclusion and exclusion criteria, Dr. Curtis said, describing the recently completed VERVE Zoster Vaccine trial.
He and his colleagues randomized 617 patients from 33 sites to look at the safety of the live-virus Zostavax herpes zoster vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis patients over age 50 years on any anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy. Half of the patients received saline, the other half received the vaccine, and no cases of varicella zoster occurred in either group.
“So, to the extent that half of 617 people with zero cases was reassuring, we now have some evidence where heretofore there was none,” he said, noting that those results will be presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting. “But the focus of this talk is not on vaccination, it’s really on how we do real-world effectiveness or safety studies in a way that doesn’t slow us way down and doesn’t require some big research operation.”
One way is through efficient recruitment, and depending on how complicated the study is, qualified patients may be easily identifiable through the EHR. In fact, numerous tools are available to codify and search both structured and unstructured data, Dr. Curtis said, noting that he and his colleagues used the web-based i2b2 Query Tool for the VERVE study.
The study sites that did the best with recruiting had the ability to search their own EHRs for patients who met the inclusion criteria, and those patients were then invited to participate. A short video was created to educate those who were interested, and a “knowledge review” quiz was administered afterward to ensure informed consent, which was provided via digital signature.
Health plan and other “big data” can also be very useful for answering certain questions. One example is how soon biologics should be stopped before elective orthopedic surgery? Dr. Curtis and colleagues looked at this using claims data for nearly 4,300 patients undergoing elective hip or knee arthroplasty and found no evidence that administering infliximab within 4 weeks of surgery increased serious infection risk within 30 days or prosthetic joint infection within 1 year.
“Where else are you going to go run a prospective study of 4,300 elective hips and knees,” he said, stressing that it wouldn’t be easy.
Other sources that can help generate real-world effectiveness data include traditional or single-center registries and EHR-based registries.
“The EHR registries are, I think, the newest that many are part of in our field,” he said, noting that “a number of groups are aggregating that,” including the ACR RISE registry and some physician groups, for example.
“What we’re really after is to have a clinically integrated network and a learning health care environment,” he explained, adding that the goal is to develop care pathways.
The approach represents a shift from evidence-based practice to practice-based evidence, he noted.
“When you and I practice, we’re generating that evidence and now we just need to harness that data to get smarter to take care of patients,” he said, adding that the lack of randomization for much of these data isn’t necessarily a problem.
“Do you have to randomize? I would argue that you don’t necessarily have to randomize if the source of variability in how we treat patients is very related to patients’ characteristics,” he said.
If the evidence for a specific approach is weak, or a decision is based on physician preference, physician practice, or insurance company considerations instead of patient characteristics, randomization may not be necessary, he explained.
In fact, insurance company requirements often create “natural experiments” that can be used to help identify better practices. For example, if one only covers adalimumab for first-line TNF inhibition, and another has a “different fail-first policy and that’s not first line and everybody gets some other TNF inhibitor, then I can probably compare those quite reasonably,” he said.
“That’s a great setting where you might not need randomization.”
Of note, “having more data sometimes trumps smarter algorithms,” but that means finding and linking more data that “exist in the wild,” Dr. Curtis said.
Linking data sources
When he and his colleagues wanted to assess the cost of not achieving RA remission, no single data source provided all of the information they needed. They used both CORRONA registry data and health claims data to look at various outcome measures across disease activity categories and with adjustment for comorbidity clusters. They previously reported on the feasibility and validity of the approach.
“We’re currently doing another project where one of the local Blue Cross plans said ‘I’m interested to support you to see how efficient you are; we will donate or loan you our claims data [and] let you link it to your practice so you can actually tell us ... cost conditional on [a patient’s] disease activity,’ ” he said.
Another example involves a recent study looking at biomarker-based cardiovascular disease risk prediction in RA using data from nearly 31,000 Medicare patients linked with multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) test results, with which they “basically built and validated a risk prediction model,” he said.
The point is that such data linkage provided tools for use at the point of care that can predict CVD risk using “some simple things that you and I have in our EHR,” he said. “But you couldn’t do this if you had to assemble a prospective cohort of tens of thousands of arthritis patients and then wait years for follow-up.”
Patient-reported outcomes collected at the point of care and by patients at home between visits, such as digital data collected via wearable technology, can provide additional information to help improve patient care and management.
“My interest is not to think about [these data sources] in isolation, but really to think about how we bring these together,” he said. “I’m interested in maximizing value for both patients and clinicians, and not having to pick only one of these data sources, but really to harness several of them if that’s what we need to take better care of patients and to answer important questions.”
Doing so is increasingly important given the workforce shortage in rheumatology, he noted.
“The point is that we’re going to need to be a whole lot more efficient as a field because there are going to be fewer of us even at a time when more of us are needed,” he said.
It’s a topic in which the ACR has shown a lot of interest, he said, noting that he cochaired a preconference course on mobile health technologies at the 2018 ACR annual meeting and is involved with a similar course on “big data” ahead of the 2019 meeting.
The thought of making use of the various digital health and “big data” sources can be overwhelming, but the key is to start with the question that needs an answer or the problem that needs to be solved.
“Don’t start with the data,” he explained. “Start with [asking] ... ‘What am I trying to do?’ ”
Dr. Curtis reported funding from the National Institute on Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. He has also consulted for or received research grants from Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CORRONA, Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Novartis, Roche, Pfizer, and Sanofi/Regeneron.
LAKE BUENA VISTA, FLA. – Digital health technology is vastly expanding the real-world data pool for clinical and comparative effectiveness research, according to Jeffrey Curtis, MD.
The trick is to harness the power of that data to improve patient care and outcomes, and that can be achieved in part through linkage of data sources and through point-of-care access, Dr. Curtis, professor of medicine in the division of clinical immunology and rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB), said at the annual meeting of the Florida Society of Rheumatology.
“We want to take care of patients, but probably what you and I also want is to have real-world evidence ... evidence relevant for people [we] take care of on a day-to-day basis – not people in highly selected phase 3 or even phase 4 trials,” he said.
Real-world data, which gained particular cachet through the 21st Century Cures Act permitting the Food and Drug Administration to consider real-world evidence as part of the regulatory process and in post-marketing surveillance, includes information from electronic health records (EHRs), health plan claims, traditional registries, and mobile health and technology, explained Dr. Curtis, who also is codirector of the UAB Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics Unit.
“And you and I want it because patients are different, and in medicine we only have about 20% of patients where there is direct evidence about what we should do,” he added. “Give me the trial that describes the 75-year-old African American smoker with diabetes and how well he does on biologic du jour; there’s no trial like that, and yet you and I need to make those kinds of decisions in light of patients’ comorbidities and other features.”
Generating real-world evidence, however, requires new approaches and new tools, he said, explaining that efficiency is key for applying the data in busy practices, as is compatibility with delivering an intervention and with randomization.
Imagine using the EHR at the point of care to look up what happened to “the last 10 patients like this” based on how they were treated by you or your colleagues, he said.
“That would be useful information to have. In fact, the day is not so far in the future where you could, perhaps, randomize within your EHR if you had a clinically important question that really needed an answer and a protocol attached,” he added.
Real-world data collection
Pragmatic trials offer one approach to garnering real-world data by addressing a simple question – usually with a hard outcome – using very few inclusion and exclusion criteria, Dr. Curtis said, describing the recently completed VERVE Zoster Vaccine trial.
He and his colleagues randomized 617 patients from 33 sites to look at the safety of the live-virus Zostavax herpes zoster vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis patients over age 50 years on any anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy. Half of the patients received saline, the other half received the vaccine, and no cases of varicella zoster occurred in either group.
“So, to the extent that half of 617 people with zero cases was reassuring, we now have some evidence where heretofore there was none,” he said, noting that those results will be presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting. “But the focus of this talk is not on vaccination, it’s really on how we do real-world effectiveness or safety studies in a way that doesn’t slow us way down and doesn’t require some big research operation.”
One way is through efficient recruitment, and depending on how complicated the study is, qualified patients may be easily identifiable through the EHR. In fact, numerous tools are available to codify and search both structured and unstructured data, Dr. Curtis said, noting that he and his colleagues used the web-based i2b2 Query Tool for the VERVE study.
The study sites that did the best with recruiting had the ability to search their own EHRs for patients who met the inclusion criteria, and those patients were then invited to participate. A short video was created to educate those who were interested, and a “knowledge review” quiz was administered afterward to ensure informed consent, which was provided via digital signature.
Health plan and other “big data” can also be very useful for answering certain questions. One example is how soon biologics should be stopped before elective orthopedic surgery? Dr. Curtis and colleagues looked at this using claims data for nearly 4,300 patients undergoing elective hip or knee arthroplasty and found no evidence that administering infliximab within 4 weeks of surgery increased serious infection risk within 30 days or prosthetic joint infection within 1 year.
“Where else are you going to go run a prospective study of 4,300 elective hips and knees,” he said, stressing that it wouldn’t be easy.
Other sources that can help generate real-world effectiveness data include traditional or single-center registries and EHR-based registries.
“The EHR registries are, I think, the newest that many are part of in our field,” he said, noting that “a number of groups are aggregating that,” including the ACR RISE registry and some physician groups, for example.
“What we’re really after is to have a clinically integrated network and a learning health care environment,” he explained, adding that the goal is to develop care pathways.
The approach represents a shift from evidence-based practice to practice-based evidence, he noted.
“When you and I practice, we’re generating that evidence and now we just need to harness that data to get smarter to take care of patients,” he said, adding that the lack of randomization for much of these data isn’t necessarily a problem.
“Do you have to randomize? I would argue that you don’t necessarily have to randomize if the source of variability in how we treat patients is very related to patients’ characteristics,” he said.
If the evidence for a specific approach is weak, or a decision is based on physician preference, physician practice, or insurance company considerations instead of patient characteristics, randomization may not be necessary, he explained.
In fact, insurance company requirements often create “natural experiments” that can be used to help identify better practices. For example, if one only covers adalimumab for first-line TNF inhibition, and another has a “different fail-first policy and that’s not first line and everybody gets some other TNF inhibitor, then I can probably compare those quite reasonably,” he said.
“That’s a great setting where you might not need randomization.”
Of note, “having more data sometimes trumps smarter algorithms,” but that means finding and linking more data that “exist in the wild,” Dr. Curtis said.
Linking data sources
When he and his colleagues wanted to assess the cost of not achieving RA remission, no single data source provided all of the information they needed. They used both CORRONA registry data and health claims data to look at various outcome measures across disease activity categories and with adjustment for comorbidity clusters. They previously reported on the feasibility and validity of the approach.
“We’re currently doing another project where one of the local Blue Cross plans said ‘I’m interested to support you to see how efficient you are; we will donate or loan you our claims data [and] let you link it to your practice so you can actually tell us ... cost conditional on [a patient’s] disease activity,’ ” he said.
Another example involves a recent study looking at biomarker-based cardiovascular disease risk prediction in RA using data from nearly 31,000 Medicare patients linked with multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) test results, with which they “basically built and validated a risk prediction model,” he said.
The point is that such data linkage provided tools for use at the point of care that can predict CVD risk using “some simple things that you and I have in our EHR,” he said. “But you couldn’t do this if you had to assemble a prospective cohort of tens of thousands of arthritis patients and then wait years for follow-up.”
Patient-reported outcomes collected at the point of care and by patients at home between visits, such as digital data collected via wearable technology, can provide additional information to help improve patient care and management.
“My interest is not to think about [these data sources] in isolation, but really to think about how we bring these together,” he said. “I’m interested in maximizing value for both patients and clinicians, and not having to pick only one of these data sources, but really to harness several of them if that’s what we need to take better care of patients and to answer important questions.”
Doing so is increasingly important given the workforce shortage in rheumatology, he noted.
“The point is that we’re going to need to be a whole lot more efficient as a field because there are going to be fewer of us even at a time when more of us are needed,” he said.
It’s a topic in which the ACR has shown a lot of interest, he said, noting that he cochaired a preconference course on mobile health technologies at the 2018 ACR annual meeting and is involved with a similar course on “big data” ahead of the 2019 meeting.
The thought of making use of the various digital health and “big data” sources can be overwhelming, but the key is to start with the question that needs an answer or the problem that needs to be solved.
“Don’t start with the data,” he explained. “Start with [asking] ... ‘What am I trying to do?’ ”
Dr. Curtis reported funding from the National Institute on Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. He has also consulted for or received research grants from Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CORRONA, Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Novartis, Roche, Pfizer, and Sanofi/Regeneron.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM FSR 2019
Post-TAVR anticoagulation alone fails to cut stroke risk in AFib
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk.
By contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked to a reduced risk of stroke in those AFib-TAVR patients, regardless of whether an oral anticoagulant was on board, according to results of a substudy of the randomized PARTNER II (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valve II) trial and its associated registries.
“Anticoagulant therapy was associated with a reduced risk of stroke and the composite of death or stroke when used concomitantly with uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy following TAVR,” concluded authors of the analysis, led by Ioanna Kosmidou, MD, PhD, of Columbia University in New York.
Taken together, these findings suggest OAC alone is “not sufficient” to prevent cerebrovascular events after TAVR in patients with AFib, Dr. Kosmidou and colleagues reported in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The analysis of the PARTNER II substudy included a total of 1,621 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR who had a history of AFib and an absolute indication for anticoagulation as evidenced by a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
Despite the absolute indication for anticoagulation, more than 40% of these patients were not prescribed an OAC upon discharge, investigators wrote, though the rate of nonprescribing decreased over the 5-year enrollment period of 2011-2015.
OAC therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk in this cohort, investigators said. After 2 years, the rate of stroke was 6.6% for AFib-TAVR patients on anticoagulant therapy, and 5.6% for those who were not on anticoagulant therapy, a nonsignificant difference at P = 0.53, according to the reported data.
By contrast, uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy reduced both risk of stroke and risk of the composite endpoint of stroke and death at 2 years “irrespective of concomitant anticoagulation,” Dr. Kosmidou and coinvestigators wrote in the report.
The stroke rates were 5.4% for antiplatelet therapy plus OAC, versus 11.1% for those receiving neither antithrombotic treatment (P = 0.03), while the rates of stroke or death were 29.7% and 40.1%, respectively (P = 0.01), according to investigators.
After adjustment, stroke risk was not significantly reduced for OAC when compared with no OAC or antiplatelet therapy (HR, 0.61; P = .16), whereas stroke risk was indeed reduced for antiplatelet therapy alone (HR, 0.32; P = .002) and antiplatelet therapy with oral anticoagulation (HR, 0.44; P = .018).
The PARTNER II study was funded by Edwards Lifesciences. Senior author Martin B. Leon, MD, and several other study coauthors reported disclosures related to Edwards Lifesciences, in addition to Abbott Vascular, Cordis, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and other companies. Dr. Kosmidou reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Kosmidou I et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1580-9.
Results of this PARTNER II substudy investigation by Kosmidou and colleagues are timely and thought provoking because they imply that some current recommendations may be insufficient for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Specifically, the results showed no difference in risk of stroke or the composite of death and stroke at 2 years in oral anticoagulant (OAC) and non-OAC patient groups, whereas by contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked with reduced stroke risk versus no antithrombotic therapy, whether or not the patients received OAC.
The substudy reinforces the understanding that TAVR itself is a determinant of stroke because of mechanisms that go beyond thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage and are essentially platelet mediated.
How to manage antithrombotic therapy in patients with AFib who undergo TAVR remains a residual field of ambiguity.
However, observational studies cannot be conclusive, they said, so results of relevant prospective, randomized trials are eagerly awaited.
For example, the effects of novel oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists will be evaluated in the ENVISAGE-TAVI study, as well as the ATLANTIS trial, which will additionally include non-OAC patients.
The relative benefits of OAC alone versus OAC plus antiplatelet therapy will be evaluated in the AVATAR study, which will include AFib-TAVR patients randomized to OAC versus OAC plus aspirin, while the POPular-TAVI and CLOE trials will also include cohorts that help provide a more eloquent answer regarding the benefit-risk ratio of combining antiplatelet therapy and OAC in these patients.
Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, and Antonio Greco, MD, of the University of Catania (Italy) made these comments in an accompanying editorial (JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.07.004). Dr. Capodanno reported disclosures related to Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Sanofi. Dr. Greco reported having no relevant disclosures.
Results of this PARTNER II substudy investigation by Kosmidou and colleagues are timely and thought provoking because they imply that some current recommendations may be insufficient for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Specifically, the results showed no difference in risk of stroke or the composite of death and stroke at 2 years in oral anticoagulant (OAC) and non-OAC patient groups, whereas by contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked with reduced stroke risk versus no antithrombotic therapy, whether or not the patients received OAC.
The substudy reinforces the understanding that TAVR itself is a determinant of stroke because of mechanisms that go beyond thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage and are essentially platelet mediated.
How to manage antithrombotic therapy in patients with AFib who undergo TAVR remains a residual field of ambiguity.
However, observational studies cannot be conclusive, they said, so results of relevant prospective, randomized trials are eagerly awaited.
For example, the effects of novel oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists will be evaluated in the ENVISAGE-TAVI study, as well as the ATLANTIS trial, which will additionally include non-OAC patients.
The relative benefits of OAC alone versus OAC plus antiplatelet therapy will be evaluated in the AVATAR study, which will include AFib-TAVR patients randomized to OAC versus OAC plus aspirin, while the POPular-TAVI and CLOE trials will also include cohorts that help provide a more eloquent answer regarding the benefit-risk ratio of combining antiplatelet therapy and OAC in these patients.
Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, and Antonio Greco, MD, of the University of Catania (Italy) made these comments in an accompanying editorial (JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.07.004). Dr. Capodanno reported disclosures related to Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Sanofi. Dr. Greco reported having no relevant disclosures.
Results of this PARTNER II substudy investigation by Kosmidou and colleagues are timely and thought provoking because they imply that some current recommendations may be insufficient for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Specifically, the results showed no difference in risk of stroke or the composite of death and stroke at 2 years in oral anticoagulant (OAC) and non-OAC patient groups, whereas by contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked with reduced stroke risk versus no antithrombotic therapy, whether or not the patients received OAC.
The substudy reinforces the understanding that TAVR itself is a determinant of stroke because of mechanisms that go beyond thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage and are essentially platelet mediated.
How to manage antithrombotic therapy in patients with AFib who undergo TAVR remains a residual field of ambiguity.
However, observational studies cannot be conclusive, they said, so results of relevant prospective, randomized trials are eagerly awaited.
For example, the effects of novel oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists will be evaluated in the ENVISAGE-TAVI study, as well as the ATLANTIS trial, which will additionally include non-OAC patients.
The relative benefits of OAC alone versus OAC plus antiplatelet therapy will be evaluated in the AVATAR study, which will include AFib-TAVR patients randomized to OAC versus OAC plus aspirin, while the POPular-TAVI and CLOE trials will also include cohorts that help provide a more eloquent answer regarding the benefit-risk ratio of combining antiplatelet therapy and OAC in these patients.
Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, and Antonio Greco, MD, of the University of Catania (Italy) made these comments in an accompanying editorial (JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.07.004). Dr. Capodanno reported disclosures related to Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Sanofi. Dr. Greco reported having no relevant disclosures.
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk.
By contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked to a reduced risk of stroke in those AFib-TAVR patients, regardless of whether an oral anticoagulant was on board, according to results of a substudy of the randomized PARTNER II (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valve II) trial and its associated registries.
“Anticoagulant therapy was associated with a reduced risk of stroke and the composite of death or stroke when used concomitantly with uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy following TAVR,” concluded authors of the analysis, led by Ioanna Kosmidou, MD, PhD, of Columbia University in New York.
Taken together, these findings suggest OAC alone is “not sufficient” to prevent cerebrovascular events after TAVR in patients with AFib, Dr. Kosmidou and colleagues reported in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The analysis of the PARTNER II substudy included a total of 1,621 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR who had a history of AFib and an absolute indication for anticoagulation as evidenced by a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
Despite the absolute indication for anticoagulation, more than 40% of these patients were not prescribed an OAC upon discharge, investigators wrote, though the rate of nonprescribing decreased over the 5-year enrollment period of 2011-2015.
OAC therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk in this cohort, investigators said. After 2 years, the rate of stroke was 6.6% for AFib-TAVR patients on anticoagulant therapy, and 5.6% for those who were not on anticoagulant therapy, a nonsignificant difference at P = 0.53, according to the reported data.
By contrast, uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy reduced both risk of stroke and risk of the composite endpoint of stroke and death at 2 years “irrespective of concomitant anticoagulation,” Dr. Kosmidou and coinvestigators wrote in the report.
The stroke rates were 5.4% for antiplatelet therapy plus OAC, versus 11.1% for those receiving neither antithrombotic treatment (P = 0.03), while the rates of stroke or death were 29.7% and 40.1%, respectively (P = 0.01), according to investigators.
After adjustment, stroke risk was not significantly reduced for OAC when compared with no OAC or antiplatelet therapy (HR, 0.61; P = .16), whereas stroke risk was indeed reduced for antiplatelet therapy alone (HR, 0.32; P = .002) and antiplatelet therapy with oral anticoagulation (HR, 0.44; P = .018).
The PARTNER II study was funded by Edwards Lifesciences. Senior author Martin B. Leon, MD, and several other study coauthors reported disclosures related to Edwards Lifesciences, in addition to Abbott Vascular, Cordis, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and other companies. Dr. Kosmidou reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Kosmidou I et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1580-9.
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk.
By contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked to a reduced risk of stroke in those AFib-TAVR patients, regardless of whether an oral anticoagulant was on board, according to results of a substudy of the randomized PARTNER II (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valve II) trial and its associated registries.
“Anticoagulant therapy was associated with a reduced risk of stroke and the composite of death or stroke when used concomitantly with uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy following TAVR,” concluded authors of the analysis, led by Ioanna Kosmidou, MD, PhD, of Columbia University in New York.
Taken together, these findings suggest OAC alone is “not sufficient” to prevent cerebrovascular events after TAVR in patients with AFib, Dr. Kosmidou and colleagues reported in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The analysis of the PARTNER II substudy included a total of 1,621 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR who had a history of AFib and an absolute indication for anticoagulation as evidenced by a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
Despite the absolute indication for anticoagulation, more than 40% of these patients were not prescribed an OAC upon discharge, investigators wrote, though the rate of nonprescribing decreased over the 5-year enrollment period of 2011-2015.
OAC therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk in this cohort, investigators said. After 2 years, the rate of stroke was 6.6% for AFib-TAVR patients on anticoagulant therapy, and 5.6% for those who were not on anticoagulant therapy, a nonsignificant difference at P = 0.53, according to the reported data.
By contrast, uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy reduced both risk of stroke and risk of the composite endpoint of stroke and death at 2 years “irrespective of concomitant anticoagulation,” Dr. Kosmidou and coinvestigators wrote in the report.
The stroke rates were 5.4% for antiplatelet therapy plus OAC, versus 11.1% for those receiving neither antithrombotic treatment (P = 0.03), while the rates of stroke or death were 29.7% and 40.1%, respectively (P = 0.01), according to investigators.
After adjustment, stroke risk was not significantly reduced for OAC when compared with no OAC or antiplatelet therapy (HR, 0.61; P = .16), whereas stroke risk was indeed reduced for antiplatelet therapy alone (HR, 0.32; P = .002) and antiplatelet therapy with oral anticoagulation (HR, 0.44; P = .018).
The PARTNER II study was funded by Edwards Lifesciences. Senior author Martin B. Leon, MD, and several other study coauthors reported disclosures related to Edwards Lifesciences, in addition to Abbott Vascular, Cordis, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and other companies. Dr. Kosmidou reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Kosmidou I et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1580-9.
FROM JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS
FDA approves baroreflex activation for advanced HF
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Barostim Neo System, an electronic carotid sinus baroreceptor stimulator, for advanced heart failure patients who have a regular heart rhythm, an ejection fraction of 35% or less, and who are not candidates for cardiac resynchronization.
A tiny, unilateral electrode delivers a pulse that decreases sympathetic but increases parasympathetic tone. The effect is that blood vessels relax and production of stress hormones drops. The device is powered by a small generator implanted under the collarbone.
Approval was based on BeAT-HF, a randomized trial with 408 patients on guideline-directed medical therapy with left ventricular ejection fractions at or below 35% and New York Heart Association class III disease.
At 6 months, 125 patients implanted with the device had improved about 14 points more than controls on a quality of life scale, walked about 60 meters farther in 6 minutes, and were more likely to have improved a functional class or two. The benefits corresponded with a drop in the N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide.
Possible complications include infection, low blood pressure, nerve damage, arterial damage, heart failure exacerbation, stroke, and death. Contraindications include certain nervous system disorders, uncontrolled and symptomatic bradycardia, and atherosclerosis or ulcerative carotid plaques near the implant zone, the FDA said.
The system, from CRVx in Minneapolis, received priority review as a breakthrough device. The agency is requiring a phase 4 investigation of its potential to reduce hospitalizations and prolong life.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Barostim Neo System, an electronic carotid sinus baroreceptor stimulator, for advanced heart failure patients who have a regular heart rhythm, an ejection fraction of 35% or less, and who are not candidates for cardiac resynchronization.
A tiny, unilateral electrode delivers a pulse that decreases sympathetic but increases parasympathetic tone. The effect is that blood vessels relax and production of stress hormones drops. The device is powered by a small generator implanted under the collarbone.
Approval was based on BeAT-HF, a randomized trial with 408 patients on guideline-directed medical therapy with left ventricular ejection fractions at or below 35% and New York Heart Association class III disease.
At 6 months, 125 patients implanted with the device had improved about 14 points more than controls on a quality of life scale, walked about 60 meters farther in 6 minutes, and were more likely to have improved a functional class or two. The benefits corresponded with a drop in the N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide.
Possible complications include infection, low blood pressure, nerve damage, arterial damage, heart failure exacerbation, stroke, and death. Contraindications include certain nervous system disorders, uncontrolled and symptomatic bradycardia, and atherosclerosis or ulcerative carotid plaques near the implant zone, the FDA said.
The system, from CRVx in Minneapolis, received priority review as a breakthrough device. The agency is requiring a phase 4 investigation of its potential to reduce hospitalizations and prolong life.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Barostim Neo System, an electronic carotid sinus baroreceptor stimulator, for advanced heart failure patients who have a regular heart rhythm, an ejection fraction of 35% or less, and who are not candidates for cardiac resynchronization.
A tiny, unilateral electrode delivers a pulse that decreases sympathetic but increases parasympathetic tone. The effect is that blood vessels relax and production of stress hormones drops. The device is powered by a small generator implanted under the collarbone.
Approval was based on BeAT-HF, a randomized trial with 408 patients on guideline-directed medical therapy with left ventricular ejection fractions at or below 35% and New York Heart Association class III disease.
At 6 months, 125 patients implanted with the device had improved about 14 points more than controls on a quality of life scale, walked about 60 meters farther in 6 minutes, and were more likely to have improved a functional class or two. The benefits corresponded with a drop in the N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide.
Possible complications include infection, low blood pressure, nerve damage, arterial damage, heart failure exacerbation, stroke, and death. Contraindications include certain nervous system disorders, uncontrolled and symptomatic bradycardia, and atherosclerosis or ulcerative carotid plaques near the implant zone, the FDA said.
The system, from CRVx in Minneapolis, received priority review as a breakthrough device. The agency is requiring a phase 4 investigation of its potential to reduce hospitalizations and prolong life.
Fluoride exposure during pregnancy tied to lower IQ score in children
with boys having a lower mean score than girls, according to a recent prospective, multicenter birth cohort study.
“These findings were observed at fluoride levels typically found in white North American women,” wrote Rivka Green, York University, Toronto, and colleagues. “This indicates the possible need to reduce fluoride intake during pregnancy.”
This study confirms findings in a 2017 study suggesting a relationship between maternal fluoride levels and children’s later cognitive scores.
Ms. Green and colleagues evaluated 512 mother-child pairs in the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) cohort from six Canadian cities. The children were born between 2008 and 2012, underwent neurodevelopmental testing between 3 and 4 years, and were assessed using the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, Third Edition. Full Scale IQ (FSIQ) test.
Of these, 400 mother-child pairs had data on fluoride intake, IQ, and complete covariate data; 141 of these mothers lived in areas with fluoridated tap water, while 228 mothers lived in areas without fluoridated tap water. Maternal urinary fluoride adjusted for specific gravity (MUFSG) was averaged across three trimesters of data, and the estimated fluoride level was obtained through self-reported exposure by women included in the study.
The researchers found mothers living in areas with fluoridated water had significantly higher MUFSG levels (0.69 mg/L), compared with women in areas without fluoridated water (0.40 mg/L; P equals .001). The median estimated fluoride intake was significantly higher among women living in areas with fluoridated water (0.93 mg per day) than in women who did not live in areas with fluoridated water (0.30 mg per day; P less than .001).
Overall, children scored a mean 107.16 (range, 52-143) on the IQ test, and girls had significantly higher mean IQ scores than did boys (109.56 vs. 104.61; P = .001). After adjusting for covariates of maternal age, race, parity, smoking, and alcohol status during pregnancy, child gender, gestational age, and birth weight, the researchers found a significant interaction between MUFSG and the child’s gender (P = .02), and a 1-mg/L MUFSG increase was associated with a decrease in 4.49 IQ points in boys (95% confidence interval, −8.38 to −0.60) but not girls. There also was an association between 1-mg higher daily intake of maternal fluoride intake and decreased IQ score in both boys and girls (−3.66; 95% CI, −7.16 to −0.15 ; P = .04).
Ms. Green and her colleagues acknowledged several limitations with the study, such as the short half-life of urinary fluoride and the potential inaccuracy of maternal urinary samples at predicting fetal exposure to fluoride, the self-reported nature of estimated fluoride consumption, lack of availability of maternal IQ data, and not including postnatal exposure and consumption of fluoride.
In a related editorial, David C. Bellinger, PhD, MSc, referred to a previous prospective study in Mexico City by Bashash et al. that found a maternal fluoride level of 0.9 mg/L was associated with a decrease in cognitive scores in children at 4 years and between 6 years and 12 years (Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125(9):097017. doi: 10.1289/EHP655), and noted the effect sizes seen in the Mexico City study were similar to those reported by Green et al. “If the effect sizes reported by Green et al. and others are valid, the total cognitive loss at the population level that might be associated with children’s prenatal exposure to fluoride could be substantial,” he said.
The study raises many questions, including whether there is a concentration where neurotoxicity risk is negligible, if gender plays a role (there was no gender risk difference in Bashash et al.), whether other developmental domains are affected apart from IQ, and if postnatal exposure carries a risk, Dr. Bellinger said. “The findings of Green et al. and others indicate that a dispassionate and tempered discussion of fluoride’s potential neurotoxicity is warranted, including consideration of what additional research is needed to reach more definitive conclusions about the implications, if any, for public health,” he said.
Dimitri A. Christakis, MD, MPH, editor of JAMA Pediatrics and director of the Center for Child Health, Behavior, and Development at Seattle Children’s Research Institute, said in an editor’s note that it was not an easy decision to publish the article because of the potential implications of the findings.
“The mission of the journal is to ensure that child health is optimized by bringing the best available evidence to the fore,” he said. “Publishing it serves as testament to the fact that JAMA Pediatrics is committed to disseminating the best science based entirely on the rigor of the methods and the soundness of the hypotheses tested, regardless of how contentious the results may be.”
However, “scientific inquiry is an iterative process,” Dr. Christakis said, and rarely does a single study provide “definitive evidence.
“We hope that purveyors and consumers of these findings are mindful of that as the implications of this study are debated in the public arena.”
This study was funded in a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Science, and the MIREC Study was funded by Chemicals Management Plan at Health Canada, the Ontario Ministry of the Environment, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. Dr. Bruce Lanphear reported being an unpaid expert witness for an upcoming case involving the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and water fluoridation. Dr. Richard Hornung reported receiving personal fees from York University. Dr. E. Angeles Martinez-Mier reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health. The other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Bellinger reported no relevant conflicts of interest with regard to his editorial.
SOURCEs: Green R et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1729; Bellinger. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/ jamapediatrics.2019.1728.
with boys having a lower mean score than girls, according to a recent prospective, multicenter birth cohort study.
“These findings were observed at fluoride levels typically found in white North American women,” wrote Rivka Green, York University, Toronto, and colleagues. “This indicates the possible need to reduce fluoride intake during pregnancy.”
This study confirms findings in a 2017 study suggesting a relationship between maternal fluoride levels and children’s later cognitive scores.
Ms. Green and colleagues evaluated 512 mother-child pairs in the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) cohort from six Canadian cities. The children were born between 2008 and 2012, underwent neurodevelopmental testing between 3 and 4 years, and were assessed using the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, Third Edition. Full Scale IQ (FSIQ) test.
Of these, 400 mother-child pairs had data on fluoride intake, IQ, and complete covariate data; 141 of these mothers lived in areas with fluoridated tap water, while 228 mothers lived in areas without fluoridated tap water. Maternal urinary fluoride adjusted for specific gravity (MUFSG) was averaged across three trimesters of data, and the estimated fluoride level was obtained through self-reported exposure by women included in the study.
The researchers found mothers living in areas with fluoridated water had significantly higher MUFSG levels (0.69 mg/L), compared with women in areas without fluoridated water (0.40 mg/L; P equals .001). The median estimated fluoride intake was significantly higher among women living in areas with fluoridated water (0.93 mg per day) than in women who did not live in areas with fluoridated water (0.30 mg per day; P less than .001).
Overall, children scored a mean 107.16 (range, 52-143) on the IQ test, and girls had significantly higher mean IQ scores than did boys (109.56 vs. 104.61; P = .001). After adjusting for covariates of maternal age, race, parity, smoking, and alcohol status during pregnancy, child gender, gestational age, and birth weight, the researchers found a significant interaction between MUFSG and the child’s gender (P = .02), and a 1-mg/L MUFSG increase was associated with a decrease in 4.49 IQ points in boys (95% confidence interval, −8.38 to −0.60) but not girls. There also was an association between 1-mg higher daily intake of maternal fluoride intake and decreased IQ score in both boys and girls (−3.66; 95% CI, −7.16 to −0.15 ; P = .04).
Ms. Green and her colleagues acknowledged several limitations with the study, such as the short half-life of urinary fluoride and the potential inaccuracy of maternal urinary samples at predicting fetal exposure to fluoride, the self-reported nature of estimated fluoride consumption, lack of availability of maternal IQ data, and not including postnatal exposure and consumption of fluoride.
In a related editorial, David C. Bellinger, PhD, MSc, referred to a previous prospective study in Mexico City by Bashash et al. that found a maternal fluoride level of 0.9 mg/L was associated with a decrease in cognitive scores in children at 4 years and between 6 years and 12 years (Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125(9):097017. doi: 10.1289/EHP655), and noted the effect sizes seen in the Mexico City study were similar to those reported by Green et al. “If the effect sizes reported by Green et al. and others are valid, the total cognitive loss at the population level that might be associated with children’s prenatal exposure to fluoride could be substantial,” he said.
The study raises many questions, including whether there is a concentration where neurotoxicity risk is negligible, if gender plays a role (there was no gender risk difference in Bashash et al.), whether other developmental domains are affected apart from IQ, and if postnatal exposure carries a risk, Dr. Bellinger said. “The findings of Green et al. and others indicate that a dispassionate and tempered discussion of fluoride’s potential neurotoxicity is warranted, including consideration of what additional research is needed to reach more definitive conclusions about the implications, if any, for public health,” he said.
Dimitri A. Christakis, MD, MPH, editor of JAMA Pediatrics and director of the Center for Child Health, Behavior, and Development at Seattle Children’s Research Institute, said in an editor’s note that it was not an easy decision to publish the article because of the potential implications of the findings.
“The mission of the journal is to ensure that child health is optimized by bringing the best available evidence to the fore,” he said. “Publishing it serves as testament to the fact that JAMA Pediatrics is committed to disseminating the best science based entirely on the rigor of the methods and the soundness of the hypotheses tested, regardless of how contentious the results may be.”
However, “scientific inquiry is an iterative process,” Dr. Christakis said, and rarely does a single study provide “definitive evidence.
“We hope that purveyors and consumers of these findings are mindful of that as the implications of this study are debated in the public arena.”
This study was funded in a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Science, and the MIREC Study was funded by Chemicals Management Plan at Health Canada, the Ontario Ministry of the Environment, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. Dr. Bruce Lanphear reported being an unpaid expert witness for an upcoming case involving the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and water fluoridation. Dr. Richard Hornung reported receiving personal fees from York University. Dr. E. Angeles Martinez-Mier reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health. The other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Bellinger reported no relevant conflicts of interest with regard to his editorial.
SOURCEs: Green R et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1729; Bellinger. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/ jamapediatrics.2019.1728.
with boys having a lower mean score than girls, according to a recent prospective, multicenter birth cohort study.
“These findings were observed at fluoride levels typically found in white North American women,” wrote Rivka Green, York University, Toronto, and colleagues. “This indicates the possible need to reduce fluoride intake during pregnancy.”
This study confirms findings in a 2017 study suggesting a relationship between maternal fluoride levels and children’s later cognitive scores.
Ms. Green and colleagues evaluated 512 mother-child pairs in the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) cohort from six Canadian cities. The children were born between 2008 and 2012, underwent neurodevelopmental testing between 3 and 4 years, and were assessed using the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, Third Edition. Full Scale IQ (FSIQ) test.
Of these, 400 mother-child pairs had data on fluoride intake, IQ, and complete covariate data; 141 of these mothers lived in areas with fluoridated tap water, while 228 mothers lived in areas without fluoridated tap water. Maternal urinary fluoride adjusted for specific gravity (MUFSG) was averaged across three trimesters of data, and the estimated fluoride level was obtained through self-reported exposure by women included in the study.
The researchers found mothers living in areas with fluoridated water had significantly higher MUFSG levels (0.69 mg/L), compared with women in areas without fluoridated water (0.40 mg/L; P equals .001). The median estimated fluoride intake was significantly higher among women living in areas with fluoridated water (0.93 mg per day) than in women who did not live in areas with fluoridated water (0.30 mg per day; P less than .001).
Overall, children scored a mean 107.16 (range, 52-143) on the IQ test, and girls had significantly higher mean IQ scores than did boys (109.56 vs. 104.61; P = .001). After adjusting for covariates of maternal age, race, parity, smoking, and alcohol status during pregnancy, child gender, gestational age, and birth weight, the researchers found a significant interaction between MUFSG and the child’s gender (P = .02), and a 1-mg/L MUFSG increase was associated with a decrease in 4.49 IQ points in boys (95% confidence interval, −8.38 to −0.60) but not girls. There also was an association between 1-mg higher daily intake of maternal fluoride intake and decreased IQ score in both boys and girls (−3.66; 95% CI, −7.16 to −0.15 ; P = .04).
Ms. Green and her colleagues acknowledged several limitations with the study, such as the short half-life of urinary fluoride and the potential inaccuracy of maternal urinary samples at predicting fetal exposure to fluoride, the self-reported nature of estimated fluoride consumption, lack of availability of maternal IQ data, and not including postnatal exposure and consumption of fluoride.
In a related editorial, David C. Bellinger, PhD, MSc, referred to a previous prospective study in Mexico City by Bashash et al. that found a maternal fluoride level of 0.9 mg/L was associated with a decrease in cognitive scores in children at 4 years and between 6 years and 12 years (Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125(9):097017. doi: 10.1289/EHP655), and noted the effect sizes seen in the Mexico City study were similar to those reported by Green et al. “If the effect sizes reported by Green et al. and others are valid, the total cognitive loss at the population level that might be associated with children’s prenatal exposure to fluoride could be substantial,” he said.
The study raises many questions, including whether there is a concentration where neurotoxicity risk is negligible, if gender plays a role (there was no gender risk difference in Bashash et al.), whether other developmental domains are affected apart from IQ, and if postnatal exposure carries a risk, Dr. Bellinger said. “The findings of Green et al. and others indicate that a dispassionate and tempered discussion of fluoride’s potential neurotoxicity is warranted, including consideration of what additional research is needed to reach more definitive conclusions about the implications, if any, for public health,” he said.
Dimitri A. Christakis, MD, MPH, editor of JAMA Pediatrics and director of the Center for Child Health, Behavior, and Development at Seattle Children’s Research Institute, said in an editor’s note that it was not an easy decision to publish the article because of the potential implications of the findings.
“The mission of the journal is to ensure that child health is optimized by bringing the best available evidence to the fore,” he said. “Publishing it serves as testament to the fact that JAMA Pediatrics is committed to disseminating the best science based entirely on the rigor of the methods and the soundness of the hypotheses tested, regardless of how contentious the results may be.”
However, “scientific inquiry is an iterative process,” Dr. Christakis said, and rarely does a single study provide “definitive evidence.
“We hope that purveyors and consumers of these findings are mindful of that as the implications of this study are debated in the public arena.”
This study was funded in a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Science, and the MIREC Study was funded by Chemicals Management Plan at Health Canada, the Ontario Ministry of the Environment, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. Dr. Bruce Lanphear reported being an unpaid expert witness for an upcoming case involving the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and water fluoridation. Dr. Richard Hornung reported receiving personal fees from York University. Dr. E. Angeles Martinez-Mier reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health. The other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Bellinger reported no relevant conflicts of interest with regard to his editorial.
SOURCEs: Green R et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1729; Bellinger. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/ jamapediatrics.2019.1728.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS











