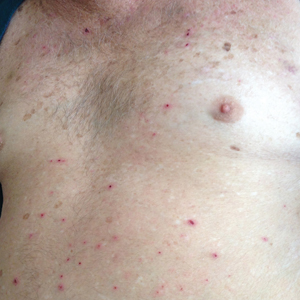
User login
Intervention for AVM still too high risk: The latest from ARUBA
Enrollment into the trial, which compared medical management alone with medical management with interventional therapy (neurosurgery, embolization, or stereotactic radiotherapy, alone or in combination), was stopped prematurely in 2013 after 33 months of follow-up because of a much higher rate of death and stroke in the intervention group.
Reaffirming the benefit of no intervention
Now the investigators are reporting extended follow-up to 50 months. The results were very similar to those at 33 months.
The current 50-month follow-up results show that 15 of 110 patients in the medical group had died or had a stroke (3.39 per 100 patient-years) versus 41 of 116 (12.32 per 100 patient-years) in the intervention group. The results reaffirm the strong benefit of not undergoing intervention (hazard ratio, 0.31; 95% confidence interval, 0.17-0.56).
These latest results were published in the July issue of the Lancet Neurology.
“With an AVM, the natural reflex is to try and fix it, but our trial shows that the tools we have to do that seem to be more damaging than just living with the AVM. If we try to take it out, the stroke risk is three to five times higher than just leaving it alone,” coauthor Christian Stapf, MD, a professor at the University of Montreal, said in an interview.
Dr. Stapf explained that an AVM is a congenital abnormality in the linking of the arteries to the veins. “There are an excess number of arteries and veins. They usually sit there silently, but they can trigger seizures, as they can tickle the neurons in the vicinity.”
It is estimated that one to two AVMs are found spontaneously in every 100,000 persons every year, but this is dependent on the availability of MRI, and many go undetected, he noted. In MRI studies in healthy volunteers, the rate was about one AVM in every 2,000 individuals.
Challenging standard practice
With AVMs, rupture and intracerebral hemorrhage occur at a rate of about 1%-2% per year. Until the ARUBA results were published, the standard practice was to intervene to embolize or excise the malformation, Dr. Stapf said.
“The standard treatment was intervention. The experiment was not to do it. We were challenging standard practice, and the trial was not popular with interventionalists,” he said.
The initial study, which was published in 2014, received much criticism from the interventionalist community. Among the criticisms were that the selection criteria for enrollment limited its generalizability, fewer patients than expected in the intervention arm were referred for microvascular surgery, and the follow-up was too short to allow a meaningful comparison.
“The study received criticism, but this was mainly from interventionalists, who were having their income threatened,” Dr. Stapf said. “This was very unhappy news for them, especially in the U.S., with the fee-for-service system.”
But he says these longer-term results, together with additional analyses and data from other cohorts, reinforce their initial conclusions.
The current report also shows a benefit in functional outcome in the medical group. “After 5 years, patients are twice as likely to have a neurological handicap, defined as a score of 2 or higher on the modified Rankin scale in the intervention group,” he noted. “We also found that more patients in the intervention group had deficits not related to stroke, such as an increase in seizures.”
Results of subgroup analysis were consistent in all patient groups.
The “study was designed for 400 patients, but we only recruited about half that number. But even so, the effect of intervention on stroke is so strong there is no subgroup where it looks favorable,” Dr. Stapf said. “This result was not heterogeneous. The same effect is seen regardless of age, gender, presence of symptoms, size of AVM, location, anatomy, drainage. No matter how you look, there is no benefit for intervention.”
He also referred to a Scottish population-based cohort study that showed a similar risk reduction from not intervening. “This was an unselected population of every unruptured AVM patient in Scotland, which found a 65% relative reduction in death/stroke over 12 years. We found a 69% reduction. The Scottish study did not select any particular types of patients but showed the same result as us,” he noted. “It is hard to argue against these findings.”
Regarding the claim of selection bias, Dr. Stapf acknowledged that the study excluded patients who were judged to be in need of intervention and those judged to be at very low risk and who would not be considered for an intervention.
“But when we compared our cohort to two other unselected cohorts, they look very similar, apart from the fact that very large AVMs were not entered in our study, as they were considered too difficult to treat,” he said. “If there is a selection bias at all, it actually trends towards the intervention group, as we excluded those at the highest treatment risk, but we still showed more benefit of not intervening.”
He also says the microvascular surgery rates were consistent with real-world practice, with about 25% of patients undergoing such surgery. “This is similar to the Scottish population study. Our trial also showed a similar result in patients treated with the various different interventions – they all showed a much higher risk than not intervening,” he added.
He says practice has changed since the trial was first reported. “There are far fewer interventions now for unruptured AVMs. Most interventionalists have accepted the results now, although there are some who continue to find reasons to criticize the trial and carry on with the procedures.”
He says his advice to patients who have an unruptured AVM is to forget about it. “There doesn’t seem to be a trigger for rupture,” he said. “It doesn’t seem to be dependent on blood pressure or physical activity, and we can’t tell if it’s just about to go by looking at it. They are very different from an aneurysm in that regard.
“When I explain to patients that they are at an increased stroke risk and tell them about the results of the ARUBA study, they say they would prefer to get that stroke later in life than earlier. These patents can live for 30 or 40 years without a stroke.
“But, yes, there remains a major unmet need. We need to find a way to protect these patients. In future, we might find a better way of intervening, but at this point in time, the treatment we have is more dangerous than doing nothing,” he said.
Longer follow-up needed
In an editorial that accompanies the current study, Peter M. Rothwell, MD, of the University of Oxford, England, also dismisses much of the criticism of the ARUBA study. On the issue of external validity, he said: “I do not think that this is really any greater an issue for ARUBA than for most other similar trials.”
But Dr. Rothwell does believe that follow-up for longer than 5 years is needed. “To really understand the benefit/risk balance, we would need a 20- or 30-year follow-up. These patients are often in their 20s, 30s, or 40s, so we really need to know their cumulative risk over decades,” he said in an interview.
Noting that the study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), Dr. Rothwell said funding should have been provided for much longer follow-up. “Patients who generously agreed to be randomly assigned in ARUBA and future similar patients have been let down by NINDS.
“We probably now won’t ever know the very–long-term impact, although the Scottish population study is following patients longer term,” he added.
“After this trial was first published, the guidelines recommended not to intervene. These latest results will not change that,” he said.
The ARUBA trial was funded internationally by the National Institutes of Health/NINDS. Dr. Stapf and Dr. Rothwell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Enrollment into the trial, which compared medical management alone with medical management with interventional therapy (neurosurgery, embolization, or stereotactic radiotherapy, alone or in combination), was stopped prematurely in 2013 after 33 months of follow-up because of a much higher rate of death and stroke in the intervention group.
Reaffirming the benefit of no intervention
Now the investigators are reporting extended follow-up to 50 months. The results were very similar to those at 33 months.
The current 50-month follow-up results show that 15 of 110 patients in the medical group had died or had a stroke (3.39 per 100 patient-years) versus 41 of 116 (12.32 per 100 patient-years) in the intervention group. The results reaffirm the strong benefit of not undergoing intervention (hazard ratio, 0.31; 95% confidence interval, 0.17-0.56).
These latest results were published in the July issue of the Lancet Neurology.
“With an AVM, the natural reflex is to try and fix it, but our trial shows that the tools we have to do that seem to be more damaging than just living with the AVM. If we try to take it out, the stroke risk is three to five times higher than just leaving it alone,” coauthor Christian Stapf, MD, a professor at the University of Montreal, said in an interview.
Dr. Stapf explained that an AVM is a congenital abnormality in the linking of the arteries to the veins. “There are an excess number of arteries and veins. They usually sit there silently, but they can trigger seizures, as they can tickle the neurons in the vicinity.”
It is estimated that one to two AVMs are found spontaneously in every 100,000 persons every year, but this is dependent on the availability of MRI, and many go undetected, he noted. In MRI studies in healthy volunteers, the rate was about one AVM in every 2,000 individuals.
Challenging standard practice
With AVMs, rupture and intracerebral hemorrhage occur at a rate of about 1%-2% per year. Until the ARUBA results were published, the standard practice was to intervene to embolize or excise the malformation, Dr. Stapf said.
“The standard treatment was intervention. The experiment was not to do it. We were challenging standard practice, and the trial was not popular with interventionalists,” he said.
The initial study, which was published in 2014, received much criticism from the interventionalist community. Among the criticisms were that the selection criteria for enrollment limited its generalizability, fewer patients than expected in the intervention arm were referred for microvascular surgery, and the follow-up was too short to allow a meaningful comparison.
“The study received criticism, but this was mainly from interventionalists, who were having their income threatened,” Dr. Stapf said. “This was very unhappy news for them, especially in the U.S., with the fee-for-service system.”
But he says these longer-term results, together with additional analyses and data from other cohorts, reinforce their initial conclusions.
The current report also shows a benefit in functional outcome in the medical group. “After 5 years, patients are twice as likely to have a neurological handicap, defined as a score of 2 or higher on the modified Rankin scale in the intervention group,” he noted. “We also found that more patients in the intervention group had deficits not related to stroke, such as an increase in seizures.”
Results of subgroup analysis were consistent in all patient groups.
The “study was designed for 400 patients, but we only recruited about half that number. But even so, the effect of intervention on stroke is so strong there is no subgroup where it looks favorable,” Dr. Stapf said. “This result was not heterogeneous. The same effect is seen regardless of age, gender, presence of symptoms, size of AVM, location, anatomy, drainage. No matter how you look, there is no benefit for intervention.”
He also referred to a Scottish population-based cohort study that showed a similar risk reduction from not intervening. “This was an unselected population of every unruptured AVM patient in Scotland, which found a 65% relative reduction in death/stroke over 12 years. We found a 69% reduction. The Scottish study did not select any particular types of patients but showed the same result as us,” he noted. “It is hard to argue against these findings.”
Regarding the claim of selection bias, Dr. Stapf acknowledged that the study excluded patients who were judged to be in need of intervention and those judged to be at very low risk and who would not be considered for an intervention.
“But when we compared our cohort to two other unselected cohorts, they look very similar, apart from the fact that very large AVMs were not entered in our study, as they were considered too difficult to treat,” he said. “If there is a selection bias at all, it actually trends towards the intervention group, as we excluded those at the highest treatment risk, but we still showed more benefit of not intervening.”
He also says the microvascular surgery rates were consistent with real-world practice, with about 25% of patients undergoing such surgery. “This is similar to the Scottish population study. Our trial also showed a similar result in patients treated with the various different interventions – they all showed a much higher risk than not intervening,” he added.
He says practice has changed since the trial was first reported. “There are far fewer interventions now for unruptured AVMs. Most interventionalists have accepted the results now, although there are some who continue to find reasons to criticize the trial and carry on with the procedures.”
He says his advice to patients who have an unruptured AVM is to forget about it. “There doesn’t seem to be a trigger for rupture,” he said. “It doesn’t seem to be dependent on blood pressure or physical activity, and we can’t tell if it’s just about to go by looking at it. They are very different from an aneurysm in that regard.
“When I explain to patients that they are at an increased stroke risk and tell them about the results of the ARUBA study, they say they would prefer to get that stroke later in life than earlier. These patents can live for 30 or 40 years without a stroke.
“But, yes, there remains a major unmet need. We need to find a way to protect these patients. In future, we might find a better way of intervening, but at this point in time, the treatment we have is more dangerous than doing nothing,” he said.
Longer follow-up needed
In an editorial that accompanies the current study, Peter M. Rothwell, MD, of the University of Oxford, England, also dismisses much of the criticism of the ARUBA study. On the issue of external validity, he said: “I do not think that this is really any greater an issue for ARUBA than for most other similar trials.”
But Dr. Rothwell does believe that follow-up for longer than 5 years is needed. “To really understand the benefit/risk balance, we would need a 20- or 30-year follow-up. These patients are often in their 20s, 30s, or 40s, so we really need to know their cumulative risk over decades,” he said in an interview.
Noting that the study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), Dr. Rothwell said funding should have been provided for much longer follow-up. “Patients who generously agreed to be randomly assigned in ARUBA and future similar patients have been let down by NINDS.
“We probably now won’t ever know the very–long-term impact, although the Scottish population study is following patients longer term,” he added.
“After this trial was first published, the guidelines recommended not to intervene. These latest results will not change that,” he said.
The ARUBA trial was funded internationally by the National Institutes of Health/NINDS. Dr. Stapf and Dr. Rothwell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Enrollment into the trial, which compared medical management alone with medical management with interventional therapy (neurosurgery, embolization, or stereotactic radiotherapy, alone or in combination), was stopped prematurely in 2013 after 33 months of follow-up because of a much higher rate of death and stroke in the intervention group.
Reaffirming the benefit of no intervention
Now the investigators are reporting extended follow-up to 50 months. The results were very similar to those at 33 months.
The current 50-month follow-up results show that 15 of 110 patients in the medical group had died or had a stroke (3.39 per 100 patient-years) versus 41 of 116 (12.32 per 100 patient-years) in the intervention group. The results reaffirm the strong benefit of not undergoing intervention (hazard ratio, 0.31; 95% confidence interval, 0.17-0.56).
These latest results were published in the July issue of the Lancet Neurology.
“With an AVM, the natural reflex is to try and fix it, but our trial shows that the tools we have to do that seem to be more damaging than just living with the AVM. If we try to take it out, the stroke risk is three to five times higher than just leaving it alone,” coauthor Christian Stapf, MD, a professor at the University of Montreal, said in an interview.
Dr. Stapf explained that an AVM is a congenital abnormality in the linking of the arteries to the veins. “There are an excess number of arteries and veins. They usually sit there silently, but they can trigger seizures, as they can tickle the neurons in the vicinity.”
It is estimated that one to two AVMs are found spontaneously in every 100,000 persons every year, but this is dependent on the availability of MRI, and many go undetected, he noted. In MRI studies in healthy volunteers, the rate was about one AVM in every 2,000 individuals.
Challenging standard practice
With AVMs, rupture and intracerebral hemorrhage occur at a rate of about 1%-2% per year. Until the ARUBA results were published, the standard practice was to intervene to embolize or excise the malformation, Dr. Stapf said.
“The standard treatment was intervention. The experiment was not to do it. We were challenging standard practice, and the trial was not popular with interventionalists,” he said.
The initial study, which was published in 2014, received much criticism from the interventionalist community. Among the criticisms were that the selection criteria for enrollment limited its generalizability, fewer patients than expected in the intervention arm were referred for microvascular surgery, and the follow-up was too short to allow a meaningful comparison.
“The study received criticism, but this was mainly from interventionalists, who were having their income threatened,” Dr. Stapf said. “This was very unhappy news for them, especially in the U.S., with the fee-for-service system.”
But he says these longer-term results, together with additional analyses and data from other cohorts, reinforce their initial conclusions.
The current report also shows a benefit in functional outcome in the medical group. “After 5 years, patients are twice as likely to have a neurological handicap, defined as a score of 2 or higher on the modified Rankin scale in the intervention group,” he noted. “We also found that more patients in the intervention group had deficits not related to stroke, such as an increase in seizures.”
Results of subgroup analysis were consistent in all patient groups.
The “study was designed for 400 patients, but we only recruited about half that number. But even so, the effect of intervention on stroke is so strong there is no subgroup where it looks favorable,” Dr. Stapf said. “This result was not heterogeneous. The same effect is seen regardless of age, gender, presence of symptoms, size of AVM, location, anatomy, drainage. No matter how you look, there is no benefit for intervention.”
He also referred to a Scottish population-based cohort study that showed a similar risk reduction from not intervening. “This was an unselected population of every unruptured AVM patient in Scotland, which found a 65% relative reduction in death/stroke over 12 years. We found a 69% reduction. The Scottish study did not select any particular types of patients but showed the same result as us,” he noted. “It is hard to argue against these findings.”
Regarding the claim of selection bias, Dr. Stapf acknowledged that the study excluded patients who were judged to be in need of intervention and those judged to be at very low risk and who would not be considered for an intervention.
“But when we compared our cohort to two other unselected cohorts, they look very similar, apart from the fact that very large AVMs were not entered in our study, as they were considered too difficult to treat,” he said. “If there is a selection bias at all, it actually trends towards the intervention group, as we excluded those at the highest treatment risk, but we still showed more benefit of not intervening.”
He also says the microvascular surgery rates were consistent with real-world practice, with about 25% of patients undergoing such surgery. “This is similar to the Scottish population study. Our trial also showed a similar result in patients treated with the various different interventions – they all showed a much higher risk than not intervening,” he added.
He says practice has changed since the trial was first reported. “There are far fewer interventions now for unruptured AVMs. Most interventionalists have accepted the results now, although there are some who continue to find reasons to criticize the trial and carry on with the procedures.”
He says his advice to patients who have an unruptured AVM is to forget about it. “There doesn’t seem to be a trigger for rupture,” he said. “It doesn’t seem to be dependent on blood pressure or physical activity, and we can’t tell if it’s just about to go by looking at it. They are very different from an aneurysm in that regard.
“When I explain to patients that they are at an increased stroke risk and tell them about the results of the ARUBA study, they say they would prefer to get that stroke later in life than earlier. These patents can live for 30 or 40 years without a stroke.
“But, yes, there remains a major unmet need. We need to find a way to protect these patients. In future, we might find a better way of intervening, but at this point in time, the treatment we have is more dangerous than doing nothing,” he said.
Longer follow-up needed
In an editorial that accompanies the current study, Peter M. Rothwell, MD, of the University of Oxford, England, also dismisses much of the criticism of the ARUBA study. On the issue of external validity, he said: “I do not think that this is really any greater an issue for ARUBA than for most other similar trials.”
But Dr. Rothwell does believe that follow-up for longer than 5 years is needed. “To really understand the benefit/risk balance, we would need a 20- or 30-year follow-up. These patients are often in their 20s, 30s, or 40s, so we really need to know their cumulative risk over decades,” he said in an interview.
Noting that the study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), Dr. Rothwell said funding should have been provided for much longer follow-up. “Patients who generously agreed to be randomly assigned in ARUBA and future similar patients have been let down by NINDS.
“We probably now won’t ever know the very–long-term impact, although the Scottish population study is following patients longer term,” he added.
“After this trial was first published, the guidelines recommended not to intervene. These latest results will not change that,” he said.
The ARUBA trial was funded internationally by the National Institutes of Health/NINDS. Dr. Stapf and Dr. Rothwell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM LANCET NEUROLOGY
The CGRP Receptor: What Neurologists Need to Know

Click here to read the content.
USA-334-84065

Click here to read the content.
USA-334-84065

Click here to read the content.
USA-334-84065
Two pandemics
This column is adapted from Dr. Eleryan’s speech at the George Washington University dermatology residency program’s virtual graduation ceremony on June 12.
I’ve been reflecting on my entire residency and the last 2 weeks have stood out the most. I have to admit that I’ve been angry, and so are numerous others who look like me. However, after conversations with a few important people in my life, I’ve realized that people care and are open to listening and changing if I give them the opportunity to see through my lens. I don’t want my legacy to be one of anger, but to be one of change, one of activism, one of heroism, and one of taking a stand in the midst of adversity.
So thank you to everyone who has played a part in my residency and is here to celebrate as I transition to the next step in my career.
But I must pause for a moment to say “I can’t breathe.” I can’t breathe because while I sit here in a place of honor for my accomplishments, I can’t forget that I’m standing in the gap for all of the black men and women who will never have the opportunity to experience a moment like this.
I can’t breathe because George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Tony McDade, Trayvon Martin, Philando Castile, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Tamir Rice, Mike Brown, Emmett Till, and so many others will never get to experience a celebratory occasion such as this because of their senseless executions as a likely result of racial bias.
As a black person in “the land of the free,” I have to live with the fact that my life may be taken for simply taking a stroll through a park, jogging through a neighborhood, driving down the street, walking back home from the store, or even sitting in my own home!
As a black physician, I must contend with the very notion that my privilege as a physician does not shield me from discrimination and bias. I recognize that my race walks into the room before I ever do. I know that many of my patients will question my abilities or my title – thinking I am the receptionist, food services worker, or even part of the janitorial staff – simply because of the color of my skin. And what’s even more disturbing is that some of my colleagues will confuse me with another black woman whom I look nothing like or challenge my intelligence and abilities and how I got my position.
All of this boils down to racism – pure and simple. Black people in this country don’t have the privilege of ignoring this truth. We know that this world is not colorblind; neither is anyone in it. We know that this is entrenched racism that for generations has created racial disparities in health care, education, housing, employment, and law enforcement. We weren’t born into a fragile or vulnerable state, yet we were born into a system of dis-enfranchisement, dis-investment, dis-crimination, dis-advantage, and dis-respect.
As physicians, we must recognize and acknowledge the lived experiences that walk through the door with our black patients. And we must understand that black patients walk around with the effects of trauma and toxic stress from just being black in America. That trauma and stress show up in very real ways that contribute to black people experiencing the brunt of chronic diseases and poorer health outcomes. There is no better example than the current COVID-19 pandemic. We are in the midst of a global pandemic from a virus that does not discriminate based on race, but black people are almost three times as likely to be hospitalized as are white people with COVID-19 . And why is that? Because of the “comorbidity” of racism that black people in this country live with. It is not a mere coincidence that the black population is overrepresented in essential jobs and black people are more likely to work in health care than are white people – all positions that increase the risk of infection and death from the virus. So, if we call COVID-19 a pandemic, racism most certainly has been a pandemic that this country has refused to acknowledge, treat, and vaccinate for centuries. We cannot ignore that both have tragically affected black people.
So as Pastor Reginald Sharpe Jr. in Chicago recently said, we’re dealing with two pandemics: One has no vaccination and one has no explanation; one can physiologically take your breath away because it affects the respiratory system, while the second can also take your breath away. Just ask Eric Garner and George Floyd.
As physicians, we must recognize that the mechanisms that tragically resulted in the deaths of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and so many other black men and women are the same mechanisms that are harming and killing black people in our health care system. It’s not acceptable for institutions that built themselves on black and brown bodies to offer condolences, but to continue to do nothing about the racism that still runs rampant within. It’s not acceptable to do nothing. It’s important to note: Racist systems do not perpetuate themselves – the individuals operating within them do.
Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “He who passively accepts evil is as much involved in it as he who helps to perpetuate it. He who accepts evil without protesting against it is really cooperating with it.” Being well-intentioned, good-hearted, sad, or disheartened is not enough. We won’t be able to tear down the systems and institutions that have been a breeding ground for racism until outrage is met by action, not just from black people and people of color, but also by the white majority.
As physicians it’s time for us to look at how our health care institution – an institution instrumental in the victimization of black people – is affecting the health and well-being of our black patients. (For example, increased maternal mortality among black women.)
Are they being seen and heard? Are they receiving culturally relevant and sensitive care? Are their needs and concerns receiving the same amount of time and attention as other patients? It’s time to understand that, for many black patients, the health care system is another place of injustice that has not proved itself to be trustworthy or inclusive of black culture.
As physicians, we must affirm that the lives and health of black and brown people matter to us, that we see the racism they experience, and that we will use our platform as physicians to eliminate racism not just in the hospitals but in the world our patients live in.
So while I didn’t choose the body that I was born into, I fully embrace it and the challenges that come with it. I’m not here to make people feel comfortable, I’m here to continue the work of my ancestors, accomplish the dreams that they fought and lost their lives for, and most importantly, I’m here to continue the fight against the systems that work to prevent other marginalized persons from getting to where I am and even further.
The author James Baldwin once wrote, “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” So, I urge you to be loudly antiracist in every space that you hold. I urge you to educate yourselves about racism and white supremacy and privilege and how it permeates our health care system. I urge you to stand beside black people rather than in front of them. Use your privilege to amplify underheard voices and to challenge the biases of your peers, friends, and family members. Use your platform as physicians to advocate for a more just and equitable health care system.
So let me repeat ... we as physicians have the responsibility to eliminate racial bias in the practice of medicine and recognize racism as a threat to the health and well-being of black people and other people of color.
How do we do this? We are beyond lengthy dialogue and “Black History Month” talks. Now is the time for action. Taking action includes the following:
1. Medical academic institutions committing to having a diverse and inclusive faculty. We know it is critical and vital to the recruitment, success, and matriculation of medical students and residents of color to see faculty, particularly senior level faculty in their specialty, who look like them and can serve as mentors. Every year, these institutions need to set a goal that they will take additional steps to have at least one-third of their faculty be black and another third persons of color. In addition, senior faculty positions – those setting curricula, selecting incoming students and residents – must include at least one-third from underrepresented backgrounds (black, Hispanic, Native American/Indigenous).
2. Hospital administration has to resemble the communities in which the hospital serves. Unfortunately, all too often, we know this is not the case, and as a result, decisions that affect the care of black and brown people are often to their detriment because they perpetuate the racism within the existing system. In order to dismantle racism in the hospital system, hospital administrations must consist of diverse individuals. Therefore, hospitals need to commit to hiring and promoting black and brown staff to ensure one-third of its senior leaderships consists of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
3. Improving the pipeline that matriculates black and brown students into medical school and residency programs. Lack of access to mentors within the medical field, lack of funding for travel to/from interviews, and lack of knowledge of the overall application process are a few barriers faced by students of color seeking to enter into the medical field. In addition to current scholarship opportunities, medical schools need to allocate funds to connect underrepresented minority students with a range of lived experiences (not just those from impoverished backgrounds but also those from middle class backgrounds who face difficulty gaining acceptance into medical school and residency programs), such as connecting them with mentors by opening opportunities for them to shadow professionals at a conference, travel to residency interviews with most, if not all, expenses covered up front, and have access to local programs that expose them to physicians in several specialties.
These are just a few examples of the active steps we can take to dismantle racism and reconcile the effects of it in the medical field. So if I may borrow from other movements, “Time’s Up” for silence regarding the existence of racism and white supremacy, and now it’s time to truly show that “We are all in this together.”
It is not just my duty but yours also – to ensure that we never have to hear another black man, woman, or child say “I can’t breathe” at the hands of injustice.
Dr. Eleryan (@skinclusionMD) is a social justice activist and was co-chief resident in dermatology (2019-2020) at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and is an Alpha Omega Alpha inductee (2020). She will be a micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles, in July 2020.
This column is adapted from Dr. Eleryan’s speech at the George Washington University dermatology residency program’s virtual graduation ceremony on June 12.
I’ve been reflecting on my entire residency and the last 2 weeks have stood out the most. I have to admit that I’ve been angry, and so are numerous others who look like me. However, after conversations with a few important people in my life, I’ve realized that people care and are open to listening and changing if I give them the opportunity to see through my lens. I don’t want my legacy to be one of anger, but to be one of change, one of activism, one of heroism, and one of taking a stand in the midst of adversity.
So thank you to everyone who has played a part in my residency and is here to celebrate as I transition to the next step in my career.
But I must pause for a moment to say “I can’t breathe.” I can’t breathe because while I sit here in a place of honor for my accomplishments, I can’t forget that I’m standing in the gap for all of the black men and women who will never have the opportunity to experience a moment like this.
I can’t breathe because George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Tony McDade, Trayvon Martin, Philando Castile, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Tamir Rice, Mike Brown, Emmett Till, and so many others will never get to experience a celebratory occasion such as this because of their senseless executions as a likely result of racial bias.
As a black person in “the land of the free,” I have to live with the fact that my life may be taken for simply taking a stroll through a park, jogging through a neighborhood, driving down the street, walking back home from the store, or even sitting in my own home!
As a black physician, I must contend with the very notion that my privilege as a physician does not shield me from discrimination and bias. I recognize that my race walks into the room before I ever do. I know that many of my patients will question my abilities or my title – thinking I am the receptionist, food services worker, or even part of the janitorial staff – simply because of the color of my skin. And what’s even more disturbing is that some of my colleagues will confuse me with another black woman whom I look nothing like or challenge my intelligence and abilities and how I got my position.
All of this boils down to racism – pure and simple. Black people in this country don’t have the privilege of ignoring this truth. We know that this world is not colorblind; neither is anyone in it. We know that this is entrenched racism that for generations has created racial disparities in health care, education, housing, employment, and law enforcement. We weren’t born into a fragile or vulnerable state, yet we were born into a system of dis-enfranchisement, dis-investment, dis-crimination, dis-advantage, and dis-respect.
As physicians, we must recognize and acknowledge the lived experiences that walk through the door with our black patients. And we must understand that black patients walk around with the effects of trauma and toxic stress from just being black in America. That trauma and stress show up in very real ways that contribute to black people experiencing the brunt of chronic diseases and poorer health outcomes. There is no better example than the current COVID-19 pandemic. We are in the midst of a global pandemic from a virus that does not discriminate based on race, but black people are almost three times as likely to be hospitalized as are white people with COVID-19 . And why is that? Because of the “comorbidity” of racism that black people in this country live with. It is not a mere coincidence that the black population is overrepresented in essential jobs and black people are more likely to work in health care than are white people – all positions that increase the risk of infection and death from the virus. So, if we call COVID-19 a pandemic, racism most certainly has been a pandemic that this country has refused to acknowledge, treat, and vaccinate for centuries. We cannot ignore that both have tragically affected black people.
So as Pastor Reginald Sharpe Jr. in Chicago recently said, we’re dealing with two pandemics: One has no vaccination and one has no explanation; one can physiologically take your breath away because it affects the respiratory system, while the second can also take your breath away. Just ask Eric Garner and George Floyd.
As physicians, we must recognize that the mechanisms that tragically resulted in the deaths of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and so many other black men and women are the same mechanisms that are harming and killing black people in our health care system. It’s not acceptable for institutions that built themselves on black and brown bodies to offer condolences, but to continue to do nothing about the racism that still runs rampant within. It’s not acceptable to do nothing. It’s important to note: Racist systems do not perpetuate themselves – the individuals operating within them do.
Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “He who passively accepts evil is as much involved in it as he who helps to perpetuate it. He who accepts evil without protesting against it is really cooperating with it.” Being well-intentioned, good-hearted, sad, or disheartened is not enough. We won’t be able to tear down the systems and institutions that have been a breeding ground for racism until outrage is met by action, not just from black people and people of color, but also by the white majority.
As physicians it’s time for us to look at how our health care institution – an institution instrumental in the victimization of black people – is affecting the health and well-being of our black patients. (For example, increased maternal mortality among black women.)
Are they being seen and heard? Are they receiving culturally relevant and sensitive care? Are their needs and concerns receiving the same amount of time and attention as other patients? It’s time to understand that, for many black patients, the health care system is another place of injustice that has not proved itself to be trustworthy or inclusive of black culture.
As physicians, we must affirm that the lives and health of black and brown people matter to us, that we see the racism they experience, and that we will use our platform as physicians to eliminate racism not just in the hospitals but in the world our patients live in.
So while I didn’t choose the body that I was born into, I fully embrace it and the challenges that come with it. I’m not here to make people feel comfortable, I’m here to continue the work of my ancestors, accomplish the dreams that they fought and lost their lives for, and most importantly, I’m here to continue the fight against the systems that work to prevent other marginalized persons from getting to where I am and even further.
The author James Baldwin once wrote, “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” So, I urge you to be loudly antiracist in every space that you hold. I urge you to educate yourselves about racism and white supremacy and privilege and how it permeates our health care system. I urge you to stand beside black people rather than in front of them. Use your privilege to amplify underheard voices and to challenge the biases of your peers, friends, and family members. Use your platform as physicians to advocate for a more just and equitable health care system.
So let me repeat ... we as physicians have the responsibility to eliminate racial bias in the practice of medicine and recognize racism as a threat to the health and well-being of black people and other people of color.
How do we do this? We are beyond lengthy dialogue and “Black History Month” talks. Now is the time for action. Taking action includes the following:
1. Medical academic institutions committing to having a diverse and inclusive faculty. We know it is critical and vital to the recruitment, success, and matriculation of medical students and residents of color to see faculty, particularly senior level faculty in their specialty, who look like them and can serve as mentors. Every year, these institutions need to set a goal that they will take additional steps to have at least one-third of their faculty be black and another third persons of color. In addition, senior faculty positions – those setting curricula, selecting incoming students and residents – must include at least one-third from underrepresented backgrounds (black, Hispanic, Native American/Indigenous).
2. Hospital administration has to resemble the communities in which the hospital serves. Unfortunately, all too often, we know this is not the case, and as a result, decisions that affect the care of black and brown people are often to their detriment because they perpetuate the racism within the existing system. In order to dismantle racism in the hospital system, hospital administrations must consist of diverse individuals. Therefore, hospitals need to commit to hiring and promoting black and brown staff to ensure one-third of its senior leaderships consists of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
3. Improving the pipeline that matriculates black and brown students into medical school and residency programs. Lack of access to mentors within the medical field, lack of funding for travel to/from interviews, and lack of knowledge of the overall application process are a few barriers faced by students of color seeking to enter into the medical field. In addition to current scholarship opportunities, medical schools need to allocate funds to connect underrepresented minority students with a range of lived experiences (not just those from impoverished backgrounds but also those from middle class backgrounds who face difficulty gaining acceptance into medical school and residency programs), such as connecting them with mentors by opening opportunities for them to shadow professionals at a conference, travel to residency interviews with most, if not all, expenses covered up front, and have access to local programs that expose them to physicians in several specialties.
These are just a few examples of the active steps we can take to dismantle racism and reconcile the effects of it in the medical field. So if I may borrow from other movements, “Time’s Up” for silence regarding the existence of racism and white supremacy, and now it’s time to truly show that “We are all in this together.”
It is not just my duty but yours also – to ensure that we never have to hear another black man, woman, or child say “I can’t breathe” at the hands of injustice.
Dr. Eleryan (@skinclusionMD) is a social justice activist and was co-chief resident in dermatology (2019-2020) at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and is an Alpha Omega Alpha inductee (2020). She will be a micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles, in July 2020.
This column is adapted from Dr. Eleryan’s speech at the George Washington University dermatology residency program’s virtual graduation ceremony on June 12.
I’ve been reflecting on my entire residency and the last 2 weeks have stood out the most. I have to admit that I’ve been angry, and so are numerous others who look like me. However, after conversations with a few important people in my life, I’ve realized that people care and are open to listening and changing if I give them the opportunity to see through my lens. I don’t want my legacy to be one of anger, but to be one of change, one of activism, one of heroism, and one of taking a stand in the midst of adversity.
So thank you to everyone who has played a part in my residency and is here to celebrate as I transition to the next step in my career.
But I must pause for a moment to say “I can’t breathe.” I can’t breathe because while I sit here in a place of honor for my accomplishments, I can’t forget that I’m standing in the gap for all of the black men and women who will never have the opportunity to experience a moment like this.
I can’t breathe because George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Tony McDade, Trayvon Martin, Philando Castile, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Tamir Rice, Mike Brown, Emmett Till, and so many others will never get to experience a celebratory occasion such as this because of their senseless executions as a likely result of racial bias.
As a black person in “the land of the free,” I have to live with the fact that my life may be taken for simply taking a stroll through a park, jogging through a neighborhood, driving down the street, walking back home from the store, or even sitting in my own home!
As a black physician, I must contend with the very notion that my privilege as a physician does not shield me from discrimination and bias. I recognize that my race walks into the room before I ever do. I know that many of my patients will question my abilities or my title – thinking I am the receptionist, food services worker, or even part of the janitorial staff – simply because of the color of my skin. And what’s even more disturbing is that some of my colleagues will confuse me with another black woman whom I look nothing like or challenge my intelligence and abilities and how I got my position.
All of this boils down to racism – pure and simple. Black people in this country don’t have the privilege of ignoring this truth. We know that this world is not colorblind; neither is anyone in it. We know that this is entrenched racism that for generations has created racial disparities in health care, education, housing, employment, and law enforcement. We weren’t born into a fragile or vulnerable state, yet we were born into a system of dis-enfranchisement, dis-investment, dis-crimination, dis-advantage, and dis-respect.
As physicians, we must recognize and acknowledge the lived experiences that walk through the door with our black patients. And we must understand that black patients walk around with the effects of trauma and toxic stress from just being black in America. That trauma and stress show up in very real ways that contribute to black people experiencing the brunt of chronic diseases and poorer health outcomes. There is no better example than the current COVID-19 pandemic. We are in the midst of a global pandemic from a virus that does not discriminate based on race, but black people are almost three times as likely to be hospitalized as are white people with COVID-19 . And why is that? Because of the “comorbidity” of racism that black people in this country live with. It is not a mere coincidence that the black population is overrepresented in essential jobs and black people are more likely to work in health care than are white people – all positions that increase the risk of infection and death from the virus. So, if we call COVID-19 a pandemic, racism most certainly has been a pandemic that this country has refused to acknowledge, treat, and vaccinate for centuries. We cannot ignore that both have tragically affected black people.
So as Pastor Reginald Sharpe Jr. in Chicago recently said, we’re dealing with two pandemics: One has no vaccination and one has no explanation; one can physiologically take your breath away because it affects the respiratory system, while the second can also take your breath away. Just ask Eric Garner and George Floyd.
As physicians, we must recognize that the mechanisms that tragically resulted in the deaths of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and so many other black men and women are the same mechanisms that are harming and killing black people in our health care system. It’s not acceptable for institutions that built themselves on black and brown bodies to offer condolences, but to continue to do nothing about the racism that still runs rampant within. It’s not acceptable to do nothing. It’s important to note: Racist systems do not perpetuate themselves – the individuals operating within them do.
Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “He who passively accepts evil is as much involved in it as he who helps to perpetuate it. He who accepts evil without protesting against it is really cooperating with it.” Being well-intentioned, good-hearted, sad, or disheartened is not enough. We won’t be able to tear down the systems and institutions that have been a breeding ground for racism until outrage is met by action, not just from black people and people of color, but also by the white majority.
As physicians it’s time for us to look at how our health care institution – an institution instrumental in the victimization of black people – is affecting the health and well-being of our black patients. (For example, increased maternal mortality among black women.)
Are they being seen and heard? Are they receiving culturally relevant and sensitive care? Are their needs and concerns receiving the same amount of time and attention as other patients? It’s time to understand that, for many black patients, the health care system is another place of injustice that has not proved itself to be trustworthy or inclusive of black culture.
As physicians, we must affirm that the lives and health of black and brown people matter to us, that we see the racism they experience, and that we will use our platform as physicians to eliminate racism not just in the hospitals but in the world our patients live in.
So while I didn’t choose the body that I was born into, I fully embrace it and the challenges that come with it. I’m not here to make people feel comfortable, I’m here to continue the work of my ancestors, accomplish the dreams that they fought and lost their lives for, and most importantly, I’m here to continue the fight against the systems that work to prevent other marginalized persons from getting to where I am and even further.
The author James Baldwin once wrote, “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” So, I urge you to be loudly antiracist in every space that you hold. I urge you to educate yourselves about racism and white supremacy and privilege and how it permeates our health care system. I urge you to stand beside black people rather than in front of them. Use your privilege to amplify underheard voices and to challenge the biases of your peers, friends, and family members. Use your platform as physicians to advocate for a more just and equitable health care system.
So let me repeat ... we as physicians have the responsibility to eliminate racial bias in the practice of medicine and recognize racism as a threat to the health and well-being of black people and other people of color.
How do we do this? We are beyond lengthy dialogue and “Black History Month” talks. Now is the time for action. Taking action includes the following:
1. Medical academic institutions committing to having a diverse and inclusive faculty. We know it is critical and vital to the recruitment, success, and matriculation of medical students and residents of color to see faculty, particularly senior level faculty in their specialty, who look like them and can serve as mentors. Every year, these institutions need to set a goal that they will take additional steps to have at least one-third of their faculty be black and another third persons of color. In addition, senior faculty positions – those setting curricula, selecting incoming students and residents – must include at least one-third from underrepresented backgrounds (black, Hispanic, Native American/Indigenous).
2. Hospital administration has to resemble the communities in which the hospital serves. Unfortunately, all too often, we know this is not the case, and as a result, decisions that affect the care of black and brown people are often to their detriment because they perpetuate the racism within the existing system. In order to dismantle racism in the hospital system, hospital administrations must consist of diverse individuals. Therefore, hospitals need to commit to hiring and promoting black and brown staff to ensure one-third of its senior leaderships consists of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
3. Improving the pipeline that matriculates black and brown students into medical school and residency programs. Lack of access to mentors within the medical field, lack of funding for travel to/from interviews, and lack of knowledge of the overall application process are a few barriers faced by students of color seeking to enter into the medical field. In addition to current scholarship opportunities, medical schools need to allocate funds to connect underrepresented minority students with a range of lived experiences (not just those from impoverished backgrounds but also those from middle class backgrounds who face difficulty gaining acceptance into medical school and residency programs), such as connecting them with mentors by opening opportunities for them to shadow professionals at a conference, travel to residency interviews with most, if not all, expenses covered up front, and have access to local programs that expose them to physicians in several specialties.
These are just a few examples of the active steps we can take to dismantle racism and reconcile the effects of it in the medical field. So if I may borrow from other movements, “Time’s Up” for silence regarding the existence of racism and white supremacy, and now it’s time to truly show that “We are all in this together.”
It is not just my duty but yours also – to ensure that we never have to hear another black man, woman, or child say “I can’t breathe” at the hands of injustice.
Dr. Eleryan (@skinclusionMD) is a social justice activist and was co-chief resident in dermatology (2019-2020) at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and is an Alpha Omega Alpha inductee (2020). She will be a micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles, in July 2020.
Skin patterns of COVID-19 vary widely
according to Christine Ko, MD.
“Things are very fluid,” Dr. Ko, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said during the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “New studies are coming out daily. Due to the need for rapid dissemination, a lot of the studies are case reports, but there are some nice case series. Another caveat for the literature is that a lot of these cases were not necessarily confirmed with testing for SARS-CoV-2, but some were.”
Dr. Ko framed her remarks largely on a case collection survey of images and clinical data from 375 patients in Spain with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 that was published online April 29, 2020, in the British Journal of Dermatology (doi: 10.1111/bjd.19163). Cutaneous manifestations included early vesicular eruptions mainly on the trunk or limbs (9%), maculopapular (47%) to urticarial lesions (19%) mainly on the trunk, and acral areas of erythema sometimes with vesicles or erosion (perniosis-like) (19%) that seemed to be a later manifestation of COVID-19. Retiform purpura or necrosis (6%) was most concerning in terms of skin disease, with an associated with a mortality of 10%.
On histology, the early vesicular eruptions are typically marked by dyskeratotic keratinocytes, Dr. Ko said, while urticarial lesions are characterized by a mixed dermal infiltrate; maculopapular lesions were a broad category. “There are some case reports that show spongiotic dermatitis or parakeratosis with a lymphocytic infiltrate,” she said. “A caveat to keep in mind is that, although these patients may definitely have COVID-19 and be confirmed to have it by testing, hypersensitivity reactions may be due to the multiple medications they’re on.”
Patients can develop a spectrum of lesions that are suggestive of vascular damage or occlusion, Dr. Ko continued. Livedoid lesions may remain static and not eventuate into necrosis or purpura but will self-resolve. Purpuric lesions and acral gangrene have been described, and these lesions correspond to vascular occlusion on biopsy.
A later manifestation are the so-called “COVID toes” with a superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate, as published June 1, 2020, in JAAD Case Reports: (doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.04.011).
“There are patients in the literature that have slightly different pathology, with lymphocytic inflammation as well as occlusion of vessels,” Dr. Ko said. A paper published June 20, 2020, in the British Journal of Dermatology used immunohistochemical staining against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and biopsies of “COVID toes” had positive staining of endothelial cells, supporting the notion that “COVID toes” are a direct manifestation of viral infection (doi: 10.1111/bjd.19327).
“There’s a lot that we still don’t know, and some patterns are going to be outliers,” Dr. Ko concluded. “[As for] determining which skin manifestations are directly from coronavirus infection within the skin, more study is needed and likely time will tell.” She reported having no financial disclosures relevant to her talk.
according to Christine Ko, MD.
“Things are very fluid,” Dr. Ko, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said during the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “New studies are coming out daily. Due to the need for rapid dissemination, a lot of the studies are case reports, but there are some nice case series. Another caveat for the literature is that a lot of these cases were not necessarily confirmed with testing for SARS-CoV-2, but some were.”
Dr. Ko framed her remarks largely on a case collection survey of images and clinical data from 375 patients in Spain with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 that was published online April 29, 2020, in the British Journal of Dermatology (doi: 10.1111/bjd.19163). Cutaneous manifestations included early vesicular eruptions mainly on the trunk or limbs (9%), maculopapular (47%) to urticarial lesions (19%) mainly on the trunk, and acral areas of erythema sometimes with vesicles or erosion (perniosis-like) (19%) that seemed to be a later manifestation of COVID-19. Retiform purpura or necrosis (6%) was most concerning in terms of skin disease, with an associated with a mortality of 10%.
On histology, the early vesicular eruptions are typically marked by dyskeratotic keratinocytes, Dr. Ko said, while urticarial lesions are characterized by a mixed dermal infiltrate; maculopapular lesions were a broad category. “There are some case reports that show spongiotic dermatitis or parakeratosis with a lymphocytic infiltrate,” she said. “A caveat to keep in mind is that, although these patients may definitely have COVID-19 and be confirmed to have it by testing, hypersensitivity reactions may be due to the multiple medications they’re on.”
Patients can develop a spectrum of lesions that are suggestive of vascular damage or occlusion, Dr. Ko continued. Livedoid lesions may remain static and not eventuate into necrosis or purpura but will self-resolve. Purpuric lesions and acral gangrene have been described, and these lesions correspond to vascular occlusion on biopsy.
A later manifestation are the so-called “COVID toes” with a superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate, as published June 1, 2020, in JAAD Case Reports: (doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.04.011).
“There are patients in the literature that have slightly different pathology, with lymphocytic inflammation as well as occlusion of vessels,” Dr. Ko said. A paper published June 20, 2020, in the British Journal of Dermatology used immunohistochemical staining against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and biopsies of “COVID toes” had positive staining of endothelial cells, supporting the notion that “COVID toes” are a direct manifestation of viral infection (doi: 10.1111/bjd.19327).
“There’s a lot that we still don’t know, and some patterns are going to be outliers,” Dr. Ko concluded. “[As for] determining which skin manifestations are directly from coronavirus infection within the skin, more study is needed and likely time will tell.” She reported having no financial disclosures relevant to her talk.
according to Christine Ko, MD.
“Things are very fluid,” Dr. Ko, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said during the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “New studies are coming out daily. Due to the need for rapid dissemination, a lot of the studies are case reports, but there are some nice case series. Another caveat for the literature is that a lot of these cases were not necessarily confirmed with testing for SARS-CoV-2, but some were.”
Dr. Ko framed her remarks largely on a case collection survey of images and clinical data from 375 patients in Spain with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 that was published online April 29, 2020, in the British Journal of Dermatology (doi: 10.1111/bjd.19163). Cutaneous manifestations included early vesicular eruptions mainly on the trunk or limbs (9%), maculopapular (47%) to urticarial lesions (19%) mainly on the trunk, and acral areas of erythema sometimes with vesicles or erosion (perniosis-like) (19%) that seemed to be a later manifestation of COVID-19. Retiform purpura or necrosis (6%) was most concerning in terms of skin disease, with an associated with a mortality of 10%.
On histology, the early vesicular eruptions are typically marked by dyskeratotic keratinocytes, Dr. Ko said, while urticarial lesions are characterized by a mixed dermal infiltrate; maculopapular lesions were a broad category. “There are some case reports that show spongiotic dermatitis or parakeratosis with a lymphocytic infiltrate,” she said. “A caveat to keep in mind is that, although these patients may definitely have COVID-19 and be confirmed to have it by testing, hypersensitivity reactions may be due to the multiple medications they’re on.”
Patients can develop a spectrum of lesions that are suggestive of vascular damage or occlusion, Dr. Ko continued. Livedoid lesions may remain static and not eventuate into necrosis or purpura but will self-resolve. Purpuric lesions and acral gangrene have been described, and these lesions correspond to vascular occlusion on biopsy.
A later manifestation are the so-called “COVID toes” with a superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate, as published June 1, 2020, in JAAD Case Reports: (doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.04.011).
“There are patients in the literature that have slightly different pathology, with lymphocytic inflammation as well as occlusion of vessels,” Dr. Ko said. A paper published June 20, 2020, in the British Journal of Dermatology used immunohistochemical staining against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and biopsies of “COVID toes” had positive staining of endothelial cells, supporting the notion that “COVID toes” are a direct manifestation of viral infection (doi: 10.1111/bjd.19327).
“There’s a lot that we still don’t know, and some patterns are going to be outliers,” Dr. Ko concluded. “[As for] determining which skin manifestations are directly from coronavirus infection within the skin, more study is needed and likely time will tell.” She reported having no financial disclosures relevant to her talk.
FROM AAD 20
Novel rapid acoustic pulse device shows promise for treating cellulite
After a single treatment, it provided a roughly 1.16 point reduction in the five-point Cellulite Severity Scale at 12 weeks, which corresponds to a roughly 32.5% reduction in cellulite.
“In cellulite, we know that the septa within the fat – those fibrous bands that pull down the skin and tether – lead to the traditional look of cellulite dimples and ridges,” lead study author Elizabeth Tanzi, MD, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. A rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) device being developed by Soliton emits rapid acoustic pulses and shock waves at 50 Hz that are transmitted through the skin. The pulses “rupture and shear the fibrotic septa, which causes release of the septa and smoothing of the skin dimples,” explained Dr. Tanzi, director of Capital Laser & Skin Care in Chevy Chase, Md.
She added that the repetition rate of the RAP device makes it stand out from other technologies currently on the market for cellulite treatment. “The repetition rate and very short rise times provide microscopic mechanical destruction to the targeted cellular level structures and the vacuoles,” Dr. Tanzi said. “The high peak pressure and fast repetition rate exploit the viscoelastic nature of the tissue. It’s the rapid rate at which the energy is being delivered, as well as the very short times that energy is being delivered, that makes the technology an entirely different device-tissue interaction.”
The physical effects observed occur in the extracellular matrix and in the destruction of fibrous septa. “That’s the acoustic subcision,” she continued. “But also, there’s no cavitation and there are nonthermal physical effects. There is some investigational research going into what biologic effects those shock waves have on the rest of the tissue, looking into neocollagenesis, potential angiogenesis, potential lymphangiogenesis, as well as inflammation inhibition.”
In a prospective pivotal clinical trial conducted at four sites, Dr. Tanzi and her colleagues evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the RAP device in 62 female patients who were treated with a single, rapid acoustic pulse treatment comprised of 1-2 minutes on each identified dimple or large ridge of cellulite. This amounted to a 19- to 33-minute treatment session for each patient. No anesthesia was required, and photographs were taken on all sites with QuantifiCare medical imaging software.
“It’s completely noninvasive and it’s truly an incisionless treatment,” Dr. Tanzi said of the procedure. “The skin’s never punctured. There’s physician oversight, but it is highly delegatable, and there is no recovery time for the patient.”
Following treatment, adverse effects and tolerability were reported, and safety and efficacy were assessed at 12 weeks. Efficacy was determined by photographic assessment by three blinded independent physicians who used a validated, simplified version of the Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS), a 0-5 scale based on the number of cellulite depressions, as well as the average depth of those depressions.
The mean age of patients was 43 years, 92% were white, and their mean body mass index was 24.5 kg/m2. The average time of treatment was 28 minutes. Based on the CSS scores, the researchers found that 87% of the study subjects had some improvement of their cellulite after a single RAP treatment. “If you break the data down further, half of patients had at least a 30% reduction of their CSS, and almost one-quarter had a 50% improvement of their CSS,” Dr. Tanzi said. “Overall, we saw a reduction of a 1.16 level on that six-point scale, which translates roughly into 32.5% reduction of the look of their cellulite from the baseline score.”
In addition, 84% of the time, the blinded assessors were able to correctly identify pre- and posttreatment unlabeled photos that they were presented at the 3-month mark. Those same blinded assessors graded about 86% of the treated cellulite areas as appearing either improved, much improved, or very much improved on the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS).
“We found a very favorable side-effect profile, although 95% of patients had some redness to their skin,” Dr. Tanzi added. “They had some erythema and folliculitis, but it was transient and very mild. In addition, 98% of patients said that the procedure was tolerable.”
As for pain, on a 0-10 scale, with 10 being the worst, subjects rated their pain level at 2.4 during the treatment and 0.3 immediately afterward. On subject satisfaction surveys, 92% of the patient said that they “agree” or “strongly agree” that their cellulite appeared improved.
“Patients with moderate cellulite seem to respond [to this treatment], too,” Dr. Tanzi said. “I don’t think there’s a ceiling or a floor to which we have to pigeonhole patients into potentially treating with this device. I think the key is [targeting] cellulite and not necessarily skin laxity.”
She emphasized that much remains to be known about the RAP device for treating cellulite. “What happens if we do multiple treatments to the tissue?” she asked. “Also, we need to further investigate what’s happening in the tissue, because not only does it seem like we’re getting a cleaving of the fibrous septa, but what is happening to the fibroblasts? What’s really happening in the tissue on a molecular level when those rapid acoustic pulses are going through the skin? There’s a lot of unanswered questions, but this is exciting technology.”
According to a news release from Soliton, the company is further reviewing and analyzing these results for inclusion in a marketing application to the Food and Drug Administration.
Soliton sponsored the trial. Dr. Tanzi disclosed that she is either a consultant for or is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan/Coolsculpting, Beiersdorf, Cutera, Merz/Ulthera, Pulse Biosciences, Sciton, Soliton, Solta, and Syneron/Candela.
After a single treatment, it provided a roughly 1.16 point reduction in the five-point Cellulite Severity Scale at 12 weeks, which corresponds to a roughly 32.5% reduction in cellulite.
“In cellulite, we know that the septa within the fat – those fibrous bands that pull down the skin and tether – lead to the traditional look of cellulite dimples and ridges,” lead study author Elizabeth Tanzi, MD, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. A rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) device being developed by Soliton emits rapid acoustic pulses and shock waves at 50 Hz that are transmitted through the skin. The pulses “rupture and shear the fibrotic septa, which causes release of the septa and smoothing of the skin dimples,” explained Dr. Tanzi, director of Capital Laser & Skin Care in Chevy Chase, Md.
She added that the repetition rate of the RAP device makes it stand out from other technologies currently on the market for cellulite treatment. “The repetition rate and very short rise times provide microscopic mechanical destruction to the targeted cellular level structures and the vacuoles,” Dr. Tanzi said. “The high peak pressure and fast repetition rate exploit the viscoelastic nature of the tissue. It’s the rapid rate at which the energy is being delivered, as well as the very short times that energy is being delivered, that makes the technology an entirely different device-tissue interaction.”
The physical effects observed occur in the extracellular matrix and in the destruction of fibrous septa. “That’s the acoustic subcision,” she continued. “But also, there’s no cavitation and there are nonthermal physical effects. There is some investigational research going into what biologic effects those shock waves have on the rest of the tissue, looking into neocollagenesis, potential angiogenesis, potential lymphangiogenesis, as well as inflammation inhibition.”
In a prospective pivotal clinical trial conducted at four sites, Dr. Tanzi and her colleagues evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the RAP device in 62 female patients who were treated with a single, rapid acoustic pulse treatment comprised of 1-2 minutes on each identified dimple or large ridge of cellulite. This amounted to a 19- to 33-minute treatment session for each patient. No anesthesia was required, and photographs were taken on all sites with QuantifiCare medical imaging software.
“It’s completely noninvasive and it’s truly an incisionless treatment,” Dr. Tanzi said of the procedure. “The skin’s never punctured. There’s physician oversight, but it is highly delegatable, and there is no recovery time for the patient.”
Following treatment, adverse effects and tolerability were reported, and safety and efficacy were assessed at 12 weeks. Efficacy was determined by photographic assessment by three blinded independent physicians who used a validated, simplified version of the Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS), a 0-5 scale based on the number of cellulite depressions, as well as the average depth of those depressions.
The mean age of patients was 43 years, 92% were white, and their mean body mass index was 24.5 kg/m2. The average time of treatment was 28 minutes. Based on the CSS scores, the researchers found that 87% of the study subjects had some improvement of their cellulite after a single RAP treatment. “If you break the data down further, half of patients had at least a 30% reduction of their CSS, and almost one-quarter had a 50% improvement of their CSS,” Dr. Tanzi said. “Overall, we saw a reduction of a 1.16 level on that six-point scale, which translates roughly into 32.5% reduction of the look of their cellulite from the baseline score.”
In addition, 84% of the time, the blinded assessors were able to correctly identify pre- and posttreatment unlabeled photos that they were presented at the 3-month mark. Those same blinded assessors graded about 86% of the treated cellulite areas as appearing either improved, much improved, or very much improved on the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS).
“We found a very favorable side-effect profile, although 95% of patients had some redness to their skin,” Dr. Tanzi added. “They had some erythema and folliculitis, but it was transient and very mild. In addition, 98% of patients said that the procedure was tolerable.”
As for pain, on a 0-10 scale, with 10 being the worst, subjects rated their pain level at 2.4 during the treatment and 0.3 immediately afterward. On subject satisfaction surveys, 92% of the patient said that they “agree” or “strongly agree” that their cellulite appeared improved.
“Patients with moderate cellulite seem to respond [to this treatment], too,” Dr. Tanzi said. “I don’t think there’s a ceiling or a floor to which we have to pigeonhole patients into potentially treating with this device. I think the key is [targeting] cellulite and not necessarily skin laxity.”
She emphasized that much remains to be known about the RAP device for treating cellulite. “What happens if we do multiple treatments to the tissue?” she asked. “Also, we need to further investigate what’s happening in the tissue, because not only does it seem like we’re getting a cleaving of the fibrous septa, but what is happening to the fibroblasts? What’s really happening in the tissue on a molecular level when those rapid acoustic pulses are going through the skin? There’s a lot of unanswered questions, but this is exciting technology.”
According to a news release from Soliton, the company is further reviewing and analyzing these results for inclusion in a marketing application to the Food and Drug Administration.
Soliton sponsored the trial. Dr. Tanzi disclosed that she is either a consultant for or is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan/Coolsculpting, Beiersdorf, Cutera, Merz/Ulthera, Pulse Biosciences, Sciton, Soliton, Solta, and Syneron/Candela.
After a single treatment, it provided a roughly 1.16 point reduction in the five-point Cellulite Severity Scale at 12 weeks, which corresponds to a roughly 32.5% reduction in cellulite.
“In cellulite, we know that the septa within the fat – those fibrous bands that pull down the skin and tether – lead to the traditional look of cellulite dimples and ridges,” lead study author Elizabeth Tanzi, MD, said during a late-breaking abstract session at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. A rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) device being developed by Soliton emits rapid acoustic pulses and shock waves at 50 Hz that are transmitted through the skin. The pulses “rupture and shear the fibrotic septa, which causes release of the septa and smoothing of the skin dimples,” explained Dr. Tanzi, director of Capital Laser & Skin Care in Chevy Chase, Md.
She added that the repetition rate of the RAP device makes it stand out from other technologies currently on the market for cellulite treatment. “The repetition rate and very short rise times provide microscopic mechanical destruction to the targeted cellular level structures and the vacuoles,” Dr. Tanzi said. “The high peak pressure and fast repetition rate exploit the viscoelastic nature of the tissue. It’s the rapid rate at which the energy is being delivered, as well as the very short times that energy is being delivered, that makes the technology an entirely different device-tissue interaction.”
The physical effects observed occur in the extracellular matrix and in the destruction of fibrous septa. “That’s the acoustic subcision,” she continued. “But also, there’s no cavitation and there are nonthermal physical effects. There is some investigational research going into what biologic effects those shock waves have on the rest of the tissue, looking into neocollagenesis, potential angiogenesis, potential lymphangiogenesis, as well as inflammation inhibition.”
In a prospective pivotal clinical trial conducted at four sites, Dr. Tanzi and her colleagues evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the RAP device in 62 female patients who were treated with a single, rapid acoustic pulse treatment comprised of 1-2 minutes on each identified dimple or large ridge of cellulite. This amounted to a 19- to 33-minute treatment session for each patient. No anesthesia was required, and photographs were taken on all sites with QuantifiCare medical imaging software.
“It’s completely noninvasive and it’s truly an incisionless treatment,” Dr. Tanzi said of the procedure. “The skin’s never punctured. There’s physician oversight, but it is highly delegatable, and there is no recovery time for the patient.”
Following treatment, adverse effects and tolerability were reported, and safety and efficacy were assessed at 12 weeks. Efficacy was determined by photographic assessment by three blinded independent physicians who used a validated, simplified version of the Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS), a 0-5 scale based on the number of cellulite depressions, as well as the average depth of those depressions.
The mean age of patients was 43 years, 92% were white, and their mean body mass index was 24.5 kg/m2. The average time of treatment was 28 minutes. Based on the CSS scores, the researchers found that 87% of the study subjects had some improvement of their cellulite after a single RAP treatment. “If you break the data down further, half of patients had at least a 30% reduction of their CSS, and almost one-quarter had a 50% improvement of their CSS,” Dr. Tanzi said. “Overall, we saw a reduction of a 1.16 level on that six-point scale, which translates roughly into 32.5% reduction of the look of their cellulite from the baseline score.”
In addition, 84% of the time, the blinded assessors were able to correctly identify pre- and posttreatment unlabeled photos that they were presented at the 3-month mark. Those same blinded assessors graded about 86% of the treated cellulite areas as appearing either improved, much improved, or very much improved on the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS).
“We found a very favorable side-effect profile, although 95% of patients had some redness to their skin,” Dr. Tanzi added. “They had some erythema and folliculitis, but it was transient and very mild. In addition, 98% of patients said that the procedure was tolerable.”
As for pain, on a 0-10 scale, with 10 being the worst, subjects rated their pain level at 2.4 during the treatment and 0.3 immediately afterward. On subject satisfaction surveys, 92% of the patient said that they “agree” or “strongly agree” that their cellulite appeared improved.
“Patients with moderate cellulite seem to respond [to this treatment], too,” Dr. Tanzi said. “I don’t think there’s a ceiling or a floor to which we have to pigeonhole patients into potentially treating with this device. I think the key is [targeting] cellulite and not necessarily skin laxity.”
She emphasized that much remains to be known about the RAP device for treating cellulite. “What happens if we do multiple treatments to the tissue?” she asked. “Also, we need to further investigate what’s happening in the tissue, because not only does it seem like we’re getting a cleaving of the fibrous septa, but what is happening to the fibroblasts? What’s really happening in the tissue on a molecular level when those rapid acoustic pulses are going through the skin? There’s a lot of unanswered questions, but this is exciting technology.”
According to a news release from Soliton, the company is further reviewing and analyzing these results for inclusion in a marketing application to the Food and Drug Administration.
Soliton sponsored the trial. Dr. Tanzi disclosed that she is either a consultant for or is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan/Coolsculpting, Beiersdorf, Cutera, Merz/Ulthera, Pulse Biosciences, Sciton, Soliton, Solta, and Syneron/Candela.
FROM AAD 20
Daily Recap: Transgender patients turn to DIY treatments; ACIP plans priority vaccine groups
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Ignored by doctors, transgender patients turn to DIY treatments
Without access to quality medical care, trans people around the world are seeking hormones from friends or through illegal online markets, even when the cost exceeds what it would through insurance. Although rare, others are resorting to self-surgery by cutting off their own penis and testicles or breasts.
Even with a doctor’s oversight, the health risks of transgender hormone therapy remain unclear, but without formal medical care, the do-it-yourself transition may be downright dangerous. To minimize these risks, some experts suggest health care reforms such as making it easier for primary care physicians to assess trans patients and prescribe hormones or creating specialized clinics where doctors prescribe hormones on demand.
Treating gender dysphoria should be just like treating a patient for any other condition. “It wouldn't be acceptable for someone to come into a primary care provider’s office with diabetes” and for the doctor to say “‘I can't actually treat you. Please leave,’” Zil Goldstein, associate medical director for transgender and gender non-binary health at the Callen-Lorde Community Health Center in New York City. Primary care providers need to see transgender care, she adds, “as a regular part of their practice.” Read more.
ACIP plans priority groups in advance of COVID-19 vaccine
Early plans for prioritizing vaccination when a COVID-19 vaccine becomes available include placing critical health care workers in the first tier, according to Sarah Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
A COVID-19 vaccine work group is developing strategies and identifying priority groups for vaccination to help inform discussions about the use of COVID-19 vaccines, Dr. Mbaeyi said at a virtual meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
Based on current information, the work group has proposed that vaccine priority be given to health care personnel, essential workers, adults aged 65 years and older, long-term care facility residents, and persons with high-risk medical conditions.
Among these groups “a subset of critical health care and other workers should receive initial doses,” Dr. Mbaeyi said. Read more.
‘Nietzsche was wrong’: Past stressors do not create psychological resilience.
The famous quote from the German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, “That which does not kill us makes us stronger,” may not be true after all – at least when it comes to mental health.
Results of a new study show that individuals who have a history of a stressful life events are more likely to develop PTSD and/or major depressive disorder (MDD) following a major natural disaster than their counterparts who do not have such a history.
The investigation of more than a thousand Chilean residents – all of whom experienced one of the most powerful earthquakes in the country’s history – showed that the odds of developing postdisaster PTSD or MDD increased according to the number of predisaster stressors participants had experienced.
“At the clinical level, these findings help the clinician know which patients are more likely to need more intensive services,” said Stephen L. Buka, PhD. “And the more trauma and hardship they’ve experienced, the more attention they need and the less likely they’re going to be able to cope and manage on their own.” Read more.
High-impact training can build bone in older women
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are often advised to pursue low-impact, low-intensity exercise as a way to preserve joint health, but that approach might actually contribute to a decline in bone mineral density, researchers report.
Concerns about falls and fracture risk have led many clinicians to advise against higher-impact activities, like jumping, but that is exactly the type of activity that improves bone density and physical function, said Belinda Beck, PhD, professor at the Griffith University School of Allied Health Sciences in Southport, Australia. But new findings show that high-intensity resistance and impact training was a safe and effective way to improve bone mass.
“Once women hit 60, they’re somehow regarded as frail, but that becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy when we take this kinder, gentler approach to exercise,” said Vanessa Yingling, PhD. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Ignored by doctors, transgender patients turn to DIY treatments
Without access to quality medical care, trans people around the world are seeking hormones from friends or through illegal online markets, even when the cost exceeds what it would through insurance. Although rare, others are resorting to self-surgery by cutting off their own penis and testicles or breasts.
Even with a doctor’s oversight, the health risks of transgender hormone therapy remain unclear, but without formal medical care, the do-it-yourself transition may be downright dangerous. To minimize these risks, some experts suggest health care reforms such as making it easier for primary care physicians to assess trans patients and prescribe hormones or creating specialized clinics where doctors prescribe hormones on demand.
Treating gender dysphoria should be just like treating a patient for any other condition. “It wouldn't be acceptable for someone to come into a primary care provider’s office with diabetes” and for the doctor to say “‘I can't actually treat you. Please leave,’” Zil Goldstein, associate medical director for transgender and gender non-binary health at the Callen-Lorde Community Health Center in New York City. Primary care providers need to see transgender care, she adds, “as a regular part of their practice.” Read more.
ACIP plans priority groups in advance of COVID-19 vaccine
Early plans for prioritizing vaccination when a COVID-19 vaccine becomes available include placing critical health care workers in the first tier, according to Sarah Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
A COVID-19 vaccine work group is developing strategies and identifying priority groups for vaccination to help inform discussions about the use of COVID-19 vaccines, Dr. Mbaeyi said at a virtual meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
Based on current information, the work group has proposed that vaccine priority be given to health care personnel, essential workers, adults aged 65 years and older, long-term care facility residents, and persons with high-risk medical conditions.
Among these groups “a subset of critical health care and other workers should receive initial doses,” Dr. Mbaeyi said. Read more.
‘Nietzsche was wrong’: Past stressors do not create psychological resilience.
The famous quote from the German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, “That which does not kill us makes us stronger,” may not be true after all – at least when it comes to mental health.
Results of a new study show that individuals who have a history of a stressful life events are more likely to develop PTSD and/or major depressive disorder (MDD) following a major natural disaster than their counterparts who do not have such a history.
The investigation of more than a thousand Chilean residents – all of whom experienced one of the most powerful earthquakes in the country’s history – showed that the odds of developing postdisaster PTSD or MDD increased according to the number of predisaster stressors participants had experienced.
“At the clinical level, these findings help the clinician know which patients are more likely to need more intensive services,” said Stephen L. Buka, PhD. “And the more trauma and hardship they’ve experienced, the more attention they need and the less likely they’re going to be able to cope and manage on their own.” Read more.
High-impact training can build bone in older women
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are often advised to pursue low-impact, low-intensity exercise as a way to preserve joint health, but that approach might actually contribute to a decline in bone mineral density, researchers report.
Concerns about falls and fracture risk have led many clinicians to advise against higher-impact activities, like jumping, but that is exactly the type of activity that improves bone density and physical function, said Belinda Beck, PhD, professor at the Griffith University School of Allied Health Sciences in Southport, Australia. But new findings show that high-intensity resistance and impact training was a safe and effective way to improve bone mass.
“Once women hit 60, they’re somehow regarded as frail, but that becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy when we take this kinder, gentler approach to exercise,” said Vanessa Yingling, PhD. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Ignored by doctors, transgender patients turn to DIY treatments
Without access to quality medical care, trans people around the world are seeking hormones from friends or through illegal online markets, even when the cost exceeds what it would through insurance. Although rare, others are resorting to self-surgery by cutting off their own penis and testicles or breasts.
Even with a doctor’s oversight, the health risks of transgender hormone therapy remain unclear, but without formal medical care, the do-it-yourself transition may be downright dangerous. To minimize these risks, some experts suggest health care reforms such as making it easier for primary care physicians to assess trans patients and prescribe hormones or creating specialized clinics where doctors prescribe hormones on demand.
Treating gender dysphoria should be just like treating a patient for any other condition. “It wouldn't be acceptable for someone to come into a primary care provider’s office with diabetes” and for the doctor to say “‘I can't actually treat you. Please leave,’” Zil Goldstein, associate medical director for transgender and gender non-binary health at the Callen-Lorde Community Health Center in New York City. Primary care providers need to see transgender care, she adds, “as a regular part of their practice.” Read more.
ACIP plans priority groups in advance of COVID-19 vaccine
Early plans for prioritizing vaccination when a COVID-19 vaccine becomes available include placing critical health care workers in the first tier, according to Sarah Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
A COVID-19 vaccine work group is developing strategies and identifying priority groups for vaccination to help inform discussions about the use of COVID-19 vaccines, Dr. Mbaeyi said at a virtual meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
Based on current information, the work group has proposed that vaccine priority be given to health care personnel, essential workers, adults aged 65 years and older, long-term care facility residents, and persons with high-risk medical conditions.
Among these groups “a subset of critical health care and other workers should receive initial doses,” Dr. Mbaeyi said. Read more.
‘Nietzsche was wrong’: Past stressors do not create psychological resilience.
The famous quote from the German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, “That which does not kill us makes us stronger,” may not be true after all – at least when it comes to mental health.
Results of a new study show that individuals who have a history of a stressful life events are more likely to develop PTSD and/or major depressive disorder (MDD) following a major natural disaster than their counterparts who do not have such a history.
The investigation of more than a thousand Chilean residents – all of whom experienced one of the most powerful earthquakes in the country’s history – showed that the odds of developing postdisaster PTSD or MDD increased according to the number of predisaster stressors participants had experienced.
“At the clinical level, these findings help the clinician know which patients are more likely to need more intensive services,” said Stephen L. Buka, PhD. “And the more trauma and hardship they’ve experienced, the more attention they need and the less likely they’re going to be able to cope and manage on their own.” Read more.
High-impact training can build bone in older women
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are often advised to pursue low-impact, low-intensity exercise as a way to preserve joint health, but that approach might actually contribute to a decline in bone mineral density, researchers report.
Concerns about falls and fracture risk have led many clinicians to advise against higher-impact activities, like jumping, but that is exactly the type of activity that improves bone density and physical function, said Belinda Beck, PhD, professor at the Griffith University School of Allied Health Sciences in Southport, Australia. But new findings show that high-intensity resistance and impact training was a safe and effective way to improve bone mass.
“Once women hit 60, they’re somehow regarded as frail, but that becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy when we take this kinder, gentler approach to exercise,” said Vanessa Yingling, PhD. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Don't Let the Bedbugs Bite: An Unusual Presentation of Bedbug Infestation Resulting in Life-Threatening Anemia
To the Editor:
A 61-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the right leg, generalized pruritus, and chest pain. The patient described intermittent exertional pressure-like chest pain over the last few days but had no known prior cardiac history. He also noted worsening edema of the right leg with erythema. Three months prior he had been hospitalized for a similar presentation and was diagnosed with cellulitis of the right leg. The patient was treated with a course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and permethrin cream for presumed scabies and followed up with dermatology for the persistent generalized pruritic rash and cellulitis. At that time, he was diagnosed with stasis dermatitis with dermatitis neglecta and excoriations. He was educated on general hygiene and treated with triamcinolone, hydrophilic ointment, and pramoxine lotion for pruritus. He also was empirically treated again for scabies.
At the current presentation, preliminary investigation showed profound anemia with a hemoglobin level of 6.2 g/dL (baseline hemoglobin level 3 months prior, 13.1 g/dL). He was subsequently admitted to the general medicine ward for further investigation of severe symptomatic anemia. A medical history revealed moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux disease, xerosis, and fracture of the right ankle following open reduction internal fixation 6 years prior to admission. There was no history of blood loss, antiplatelet agents, or anticoagulants. He was on disability and lived in a single-room occupancy hotel. He did not report any high-risk sexual behaviors or abuse of alcohol or drugs. He actively smoked 1.5 packs of cigarettes per day for the last 30 years. He denied any allergies.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile, nontoxic, disheveled, and in no acute distress. He had anicteric sclera and pale conjunctiva. The right leg appeared more erythematous and edematous compared to the left leg but without warmth or tenderness to palpation. He had innumerable 4- to 5-mm, erythematous, excoriated papules on the skin (Figure). His bed sheets were noted to have multiple rusty-black specks thought to be related to the crusted lesions. Physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.
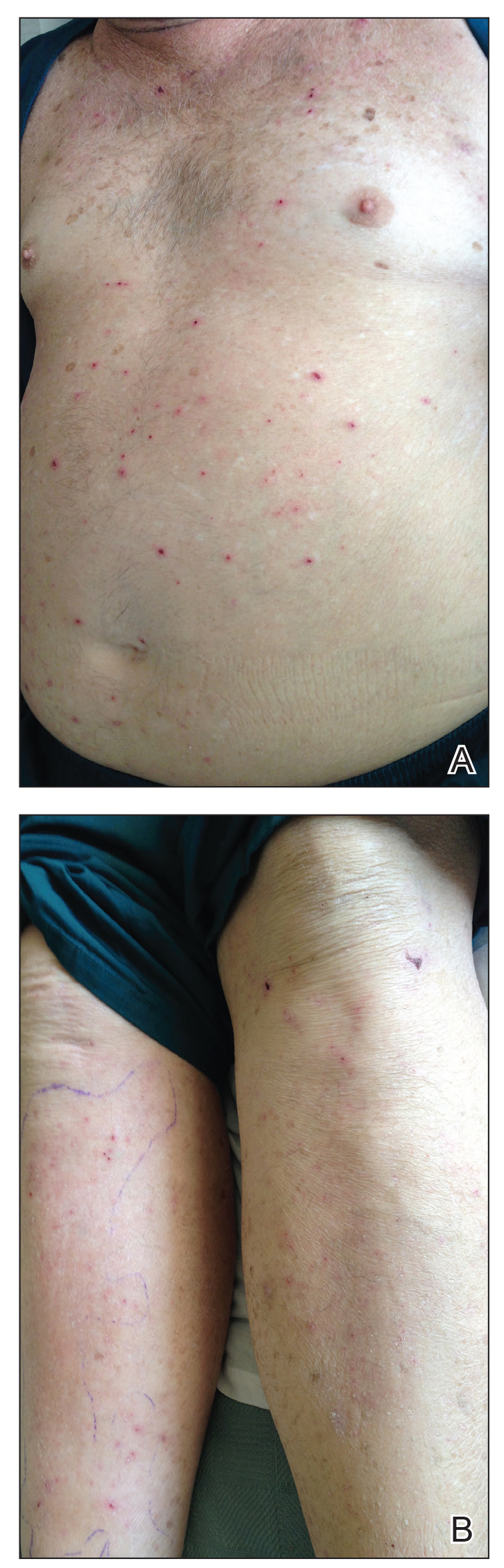
Laboratory workup revealed severe iron-deficiency anemia without any evidence of hemolysis, marrow suppression, infection, or immune compromise (Table). He had a vitamin B12 deficiency (197 pg/mL [reference range, 239-931 pg/mL]), but we felt it was very unlikely to be responsible for his profound, sudden-onset microcytic anemia. Further evaluation for occult bleeding revealed an unremarkable upper endoscopy with push enteroscopy and colonoscopy. An alternate etiology of the anemia could not be identified.
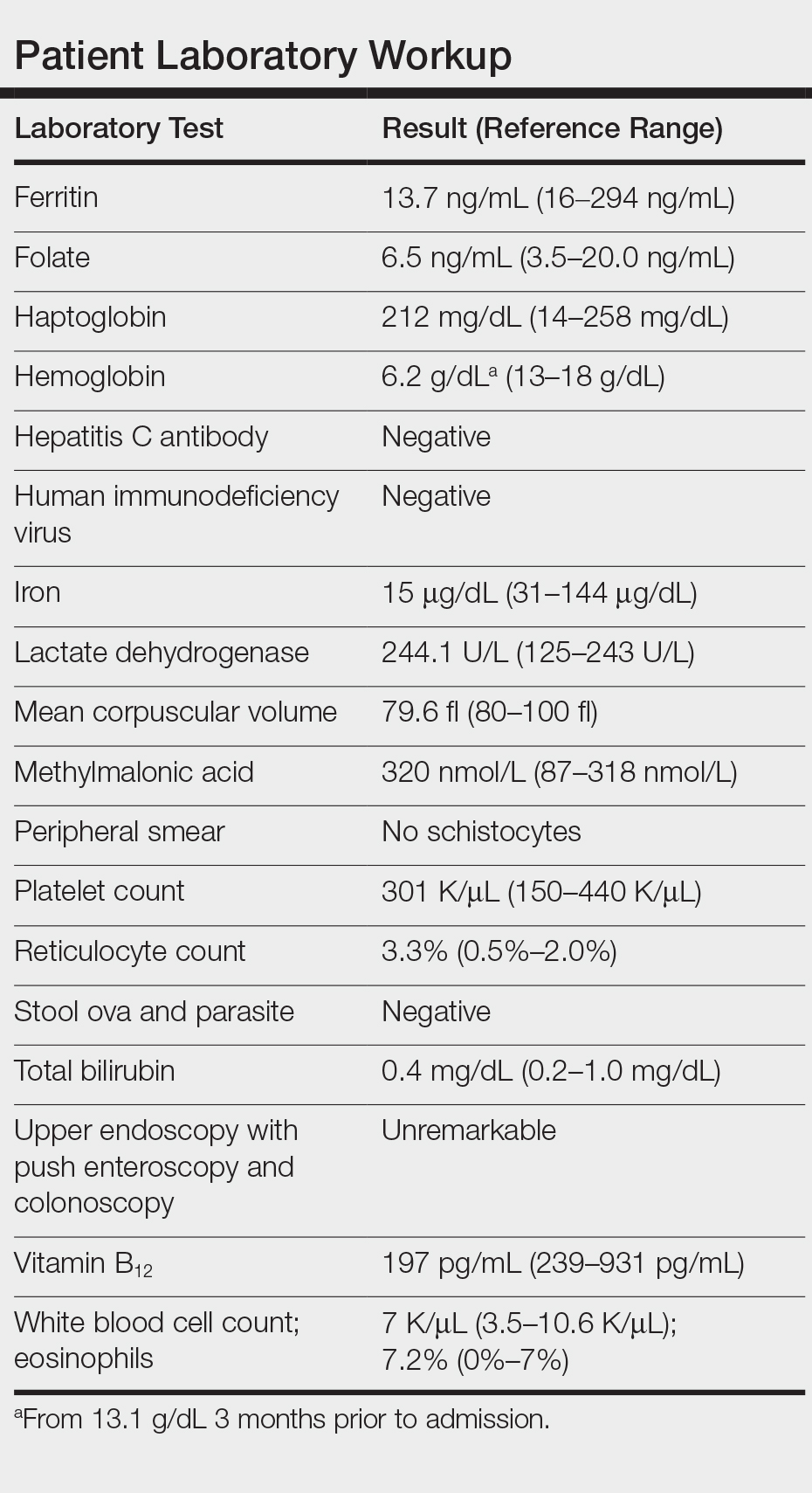
Subsequently, he reported multiple pruritic bug bites sustained at the hotel room where he resided and continued to note pruritus while hospitalized. Pest control inspected the hospital room and identified bedbugs, Cimex lectularius, among his belongings. Upon further review, his clothes and walker were found to be completely infested with these organisms in different stages of development. Treatment included blood transfusions, iron supplementation, and environmental control of the infested living space both in the hospital and at his residence, with subsequent resolution of symptoms and anemia. Two weeks following discharge, the patient no longer reported pruritus, and his hemoglobin level had returned to baseline.
Over the last decade there has been an exponential resurgence in C lectularius infestations in developed countries attributed to increasing global travel, growing pesticide resistance, lack of public awareness, and inadequate pest control programs. This re-emergence has resulted in a public health problem. Although bedbugs are not known to transmit infectious diseases, severe infestation can result in notable dermatitis, iron-deficiency anemia from chronic blood loss, superinfection, allergic reactions including anaphylaxis in rare cases, and psychologic distress.
Iron-deficiency anemia caused by excessive bedbug biting in infants and children has been documented as early as the 1960s.1 Our knowledge of severe anemia due to bedbug infestation is limited to only 4 cases in the literature, according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms bedbugs anemia and cimex anemia.1-4 All cases reported bedbug infestations involving personal clothing, belongings, and/or living spaces. Patient concerns at presentation ranged from lethargy and fatigue with pruritic rash to chest pain and syncope with findings of severe microcytic or normocytic anemia (hemoglobin level, 5-8 g/dL). All cases were treated supportively with blood transfusion and iron supplementation, with hemoglobin recovery after several weeks. Environmental extermination also was required to prevent recurrence.1-4 Given that each bedbug blood meal is on average 7 mm3, one would have to incur a minimum of 143,000 bites to experience a blood loss of 1 L.3
The differential diagnosis for a patient with generalized pruritus should be broad and includes dermatologic conditions (eg, xerosis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, urticaria, dermatophytosis, lichen simplex chronicus, psoriasis, scabies, pediculosis corporis and pubis, other arthropod bites, bullous pemphigoid), systemic disorders (eg, renal disease, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, cholestasis, human immunodeficiency virus), malignancy, connective tissue disease, medication side effects, and psychogenic and neuropathic itch.
The diagnosis of C lectularius infestation is confirmed by finding the wingless, reddish brown, flat and ovular arthropod, with adult lengths of 4 to 7 mm, approximately the size of an apple seed.5-11 Bedbugs typically are active at night and feed for 3 to 10 minutes. After their feed or during the day, bedbugs will return to their nest in furniture, mattresses, beds, walls, and floors. Bedbug bites appear as small clusters or lines of pruritic erythematous papules with a central hemorrhagic puncta. Other cutaneous symptoms include isolated pruritus, papules, nodules, and bullous eruptions.7 Additional signs of bedbug infestation include black fecal stains in areas of inhabitation as well as actual bedbugs feeding during the day due to overcrowding.
Treatment of pruritic localized cutaneous reactions is supportive and includes antipruritic agents, topical steroids, topical anesthetics, antihistamines, or topical or systemic antibiotics for secondary infections.5-11 Systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis, are treated with epinephrine, antihistamines, and/or corticosteroids, while severe anemia is treated supportively with blood transfusions and iron supplementation.5-11 To prevent reoccurrence, environmental control in the form of nonchemical and chemical treatments is crucial in controlling bedbug infestations.5-11
This case highlights the relevance of a rare but notable morbidity associated with bedbug infestation and the adverse effects of bedbugs on public health. This patient's living situation in a single-room occupancy hotel, poor hygiene, and possible cognitive impairment from his multiple medical conditions may have increased his risk for extreme bedbug infestation. With a good history, physical examination, proper inspection of the patient's belongings, and provider awareness of this epidemic, the severity of this patient's anemia may have been circumvented on the prior hospital admission and follow-up office visit. Once such an infestation is confirmed, a multidisciplinary approach including social work assistance, health services, and pest control is needed to appropriately treat the patient and the environment. Methods in preventing and managing this growing public health problem include improving hygiene, avoiding secondhand goods, and increasing awareness in the identification and proper elimination of bedbugs.5-7
- Venkatachalam PS, Belavady B. Loss of haemoglobin iron due to excessive biting by bed bugs. a possible aetiological factor in the iron deficiency anaemia of infants and children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1962;56:218-221.
- Pritchard MJ, Hwang SW. Severe anemia from bedbugs. CMAJ. 2009;181:287-288.
- Paulke-Korinek M, Széll M, Laferl H, et al. Bed bugs can cause severe anaemia in adults. Parasitol Res. 2012;110:2577-2579.
- Sabou M, Imperiale DG, Andrés E, et al. Bed bugs reproductive life cycle in the clothes of a patient suffering from Alzheimer's disease results in iron deficiency anemia. Parasite. 2013;20:16.
- Studdiford JS, Conniff KM, Trayes KP, et al. Bedbug infestation. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:653-658.
- Goddard J, deShazo R. Bed bugs (Cimex lectularis) and clinical consequences of their bites. JAMA. 2009;301:1358-1366.
- Bernardeschi C, Le Cleach L, Delaunay P, et al. Bed bug infestation. BMJ. 2013;346:f138.
- Silvia Munoz-Price L, Safdar N, Beier JC, et al. Bed bugs inhealthcare settings. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012;33:1137-1142.
- Huntington MK. When bed bugs bite. J Fam Pract. 2012;61:384-388.
- Delaunay P, Blanc V, Del Giudice P, et al. Bedbugs and infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:200-212.
- Doggett SL, Dwyer DE, Penas PF, et al. Bed bugs: clinical relevance and control options. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:164-192.
To the Editor:
A 61-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the right leg, generalized pruritus, and chest pain. The patient described intermittent exertional pressure-like chest pain over the last few days but had no known prior cardiac history. He also noted worsening edema of the right leg with erythema. Three months prior he had been hospitalized for a similar presentation and was diagnosed with cellulitis of the right leg. The patient was treated with a course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and permethrin cream for presumed scabies and followed up with dermatology for the persistent generalized pruritic rash and cellulitis. At that time, he was diagnosed with stasis dermatitis with dermatitis neglecta and excoriations. He was educated on general hygiene and treated with triamcinolone, hydrophilic ointment, and pramoxine lotion for pruritus. He also was empirically treated again for scabies.
At the current presentation, preliminary investigation showed profound anemia with a hemoglobin level of 6.2 g/dL (baseline hemoglobin level 3 months prior, 13.1 g/dL). He was subsequently admitted to the general medicine ward for further investigation of severe symptomatic anemia. A medical history revealed moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux disease, xerosis, and fracture of the right ankle following open reduction internal fixation 6 years prior to admission. There was no history of blood loss, antiplatelet agents, or anticoagulants. He was on disability and lived in a single-room occupancy hotel. He did not report any high-risk sexual behaviors or abuse of alcohol or drugs. He actively smoked 1.5 packs of cigarettes per day for the last 30 years. He denied any allergies.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile, nontoxic, disheveled, and in no acute distress. He had anicteric sclera and pale conjunctiva. The right leg appeared more erythematous and edematous compared to the left leg but without warmth or tenderness to palpation. He had innumerable 4- to 5-mm, erythematous, excoriated papules on the skin (Figure). His bed sheets were noted to have multiple rusty-black specks thought to be related to the crusted lesions. Physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.

Laboratory workup revealed severe iron-deficiency anemia without any evidence of hemolysis, marrow suppression, infection, or immune compromise (Table). He had a vitamin B12 deficiency (197 pg/mL [reference range, 239-931 pg/mL]), but we felt it was very unlikely to be responsible for his profound, sudden-onset microcytic anemia. Further evaluation for occult bleeding revealed an unremarkable upper endoscopy with push enteroscopy and colonoscopy. An alternate etiology of the anemia could not be identified.

Subsequently, he reported multiple pruritic bug bites sustained at the hotel room where he resided and continued to note pruritus while hospitalized. Pest control inspected the hospital room and identified bedbugs, Cimex lectularius, among his belongings. Upon further review, his clothes and walker were found to be completely infested with these organisms in different stages of development. Treatment included blood transfusions, iron supplementation, and environmental control of the infested living space both in the hospital and at his residence, with subsequent resolution of symptoms and anemia. Two weeks following discharge, the patient no longer reported pruritus, and his hemoglobin level had returned to baseline.
Over the last decade there has been an exponential resurgence in C lectularius infestations in developed countries attributed to increasing global travel, growing pesticide resistance, lack of public awareness, and inadequate pest control programs. This re-emergence has resulted in a public health problem. Although bedbugs are not known to transmit infectious diseases, severe infestation can result in notable dermatitis, iron-deficiency anemia from chronic blood loss, superinfection, allergic reactions including anaphylaxis in rare cases, and psychologic distress.
Iron-deficiency anemia caused by excessive bedbug biting in infants and children has been documented as early as the 1960s.1 Our knowledge of severe anemia due to bedbug infestation is limited to only 4 cases in the literature, according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms bedbugs anemia and cimex anemia.1-4 All cases reported bedbug infestations involving personal clothing, belongings, and/or living spaces. Patient concerns at presentation ranged from lethargy and fatigue with pruritic rash to chest pain and syncope with findings of severe microcytic or normocytic anemia (hemoglobin level, 5-8 g/dL). All cases were treated supportively with blood transfusion and iron supplementation, with hemoglobin recovery after several weeks. Environmental extermination also was required to prevent recurrence.1-4 Given that each bedbug blood meal is on average 7 mm3, one would have to incur a minimum of 143,000 bites to experience a blood loss of 1 L.3
The differential diagnosis for a patient with generalized pruritus should be broad and includes dermatologic conditions (eg, xerosis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, urticaria, dermatophytosis, lichen simplex chronicus, psoriasis, scabies, pediculosis corporis and pubis, other arthropod bites, bullous pemphigoid), systemic disorders (eg, renal disease, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, cholestasis, human immunodeficiency virus), malignancy, connective tissue disease, medication side effects, and psychogenic and neuropathic itch.
The diagnosis of C lectularius infestation is confirmed by finding the wingless, reddish brown, flat and ovular arthropod, with adult lengths of 4 to 7 mm, approximately the size of an apple seed.5-11 Bedbugs typically are active at night and feed for 3 to 10 minutes. After their feed or during the day, bedbugs will return to their nest in furniture, mattresses, beds, walls, and floors. Bedbug bites appear as small clusters or lines of pruritic erythematous papules with a central hemorrhagic puncta. Other cutaneous symptoms include isolated pruritus, papules, nodules, and bullous eruptions.7 Additional signs of bedbug infestation include black fecal stains in areas of inhabitation as well as actual bedbugs feeding during the day due to overcrowding.
Treatment of pruritic localized cutaneous reactions is supportive and includes antipruritic agents, topical steroids, topical anesthetics, antihistamines, or topical or systemic antibiotics for secondary infections.5-11 Systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis, are treated with epinephrine, antihistamines, and/or corticosteroids, while severe anemia is treated supportively with blood transfusions and iron supplementation.5-11 To prevent reoccurrence, environmental control in the form of nonchemical and chemical treatments is crucial in controlling bedbug infestations.5-11
This case highlights the relevance of a rare but notable morbidity associated with bedbug infestation and the adverse effects of bedbugs on public health. This patient's living situation in a single-room occupancy hotel, poor hygiene, and possible cognitive impairment from his multiple medical conditions may have increased his risk for extreme bedbug infestation. With a good history, physical examination, proper inspection of the patient's belongings, and provider awareness of this epidemic, the severity of this patient's anemia may have been circumvented on the prior hospital admission and follow-up office visit. Once such an infestation is confirmed, a multidisciplinary approach including social work assistance, health services, and pest control is needed to appropriately treat the patient and the environment. Methods in preventing and managing this growing public health problem include improving hygiene, avoiding secondhand goods, and increasing awareness in the identification and proper elimination of bedbugs.5-7
To the Editor:
A 61-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the right leg, generalized pruritus, and chest pain. The patient described intermittent exertional pressure-like chest pain over the last few days but had no known prior cardiac history. He also noted worsening edema of the right leg with erythema. Three months prior he had been hospitalized for a similar presentation and was diagnosed with cellulitis of the right leg. The patient was treated with a course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and permethrin cream for presumed scabies and followed up with dermatology for the persistent generalized pruritic rash and cellulitis. At that time, he was diagnosed with stasis dermatitis with dermatitis neglecta and excoriations. He was educated on general hygiene and treated with triamcinolone, hydrophilic ointment, and pramoxine lotion for pruritus. He also was empirically treated again for scabies.
At the current presentation, preliminary investigation showed profound anemia with a hemoglobin level of 6.2 g/dL (baseline hemoglobin level 3 months prior, 13.1 g/dL). He was subsequently admitted to the general medicine ward for further investigation of severe symptomatic anemia. A medical history revealed moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux disease, xerosis, and fracture of the right ankle following open reduction internal fixation 6 years prior to admission. There was no history of blood loss, antiplatelet agents, or anticoagulants. He was on disability and lived in a single-room occupancy hotel. He did not report any high-risk sexual behaviors or abuse of alcohol or drugs. He actively smoked 1.5 packs of cigarettes per day for the last 30 years. He denied any allergies.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile, nontoxic, disheveled, and in no acute distress. He had anicteric sclera and pale conjunctiva. The right leg appeared more erythematous and edematous compared to the left leg but without warmth or tenderness to palpation. He had innumerable 4- to 5-mm, erythematous, excoriated papules on the skin (Figure). His bed sheets were noted to have multiple rusty-black specks thought to be related to the crusted lesions. Physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.

Laboratory workup revealed severe iron-deficiency anemia without any evidence of hemolysis, marrow suppression, infection, or immune compromise (Table). He had a vitamin B12 deficiency (197 pg/mL [reference range, 239-931 pg/mL]), but we felt it was very unlikely to be responsible for his profound, sudden-onset microcytic anemia. Further evaluation for occult bleeding revealed an unremarkable upper endoscopy with push enteroscopy and colonoscopy. An alternate etiology of the anemia could not be identified.

Subsequently, he reported multiple pruritic bug bites sustained at the hotel room where he resided and continued to note pruritus while hospitalized. Pest control inspected the hospital room and identified bedbugs, Cimex lectularius, among his belongings. Upon further review, his clothes and walker were found to be completely infested with these organisms in different stages of development. Treatment included blood transfusions, iron supplementation, and environmental control of the infested living space both in the hospital and at his residence, with subsequent resolution of symptoms and anemia. Two weeks following discharge, the patient no longer reported pruritus, and his hemoglobin level had returned to baseline.
Over the last decade there has been an exponential resurgence in C lectularius infestations in developed countries attributed to increasing global travel, growing pesticide resistance, lack of public awareness, and inadequate pest control programs. This re-emergence has resulted in a public health problem. Although bedbugs are not known to transmit infectious diseases, severe infestation can result in notable dermatitis, iron-deficiency anemia from chronic blood loss, superinfection, allergic reactions including anaphylaxis in rare cases, and psychologic distress.
Iron-deficiency anemia caused by excessive bedbug biting in infants and children has been documented as early as the 1960s.1 Our knowledge of severe anemia due to bedbug infestation is limited to only 4 cases in the literature, according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms bedbugs anemia and cimex anemia.1-4 All cases reported bedbug infestations involving personal clothing, belongings, and/or living spaces. Patient concerns at presentation ranged from lethargy and fatigue with pruritic rash to chest pain and syncope with findings of severe microcytic or normocytic anemia (hemoglobin level, 5-8 g/dL). All cases were treated supportively with blood transfusion and iron supplementation, with hemoglobin recovery after several weeks. Environmental extermination also was required to prevent recurrence.1-4 Given that each bedbug blood meal is on average 7 mm3, one would have to incur a minimum of 143,000 bites to experience a blood loss of 1 L.3
The differential diagnosis for a patient with generalized pruritus should be broad and includes dermatologic conditions (eg, xerosis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, urticaria, dermatophytosis, lichen simplex chronicus, psoriasis, scabies, pediculosis corporis and pubis, other arthropod bites, bullous pemphigoid), systemic disorders (eg, renal disease, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, cholestasis, human immunodeficiency virus), malignancy, connective tissue disease, medication side effects, and psychogenic and neuropathic itch.
The diagnosis of C lectularius infestation is confirmed by finding the wingless, reddish brown, flat and ovular arthropod, with adult lengths of 4 to 7 mm, approximately the size of an apple seed.5-11 Bedbugs typically are active at night and feed for 3 to 10 minutes. After their feed or during the day, bedbugs will return to their nest in furniture, mattresses, beds, walls, and floors. Bedbug bites appear as small clusters or lines of pruritic erythematous papules with a central hemorrhagic puncta. Other cutaneous symptoms include isolated pruritus, papules, nodules, and bullous eruptions.7 Additional signs of bedbug infestation include black fecal stains in areas of inhabitation as well as actual bedbugs feeding during the day due to overcrowding.
Treatment of pruritic localized cutaneous reactions is supportive and includes antipruritic agents, topical steroids, topical anesthetics, antihistamines, or topical or systemic antibiotics for secondary infections.5-11 Systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis, are treated with epinephrine, antihistamines, and/or corticosteroids, while severe anemia is treated supportively with blood transfusions and iron supplementation.5-11 To prevent reoccurrence, environmental control in the form of nonchemical and chemical treatments is crucial in controlling bedbug infestations.5-11
This case highlights the relevance of a rare but notable morbidity associated with bedbug infestation and the adverse effects of bedbugs on public health. This patient's living situation in a single-room occupancy hotel, poor hygiene, and possible cognitive impairment from his multiple medical conditions may have increased his risk for extreme bedbug infestation. With a good history, physical examination, proper inspection of the patient's belongings, and provider awareness of this epidemic, the severity of this patient's anemia may have been circumvented on the prior hospital admission and follow-up office visit. Once such an infestation is confirmed, a multidisciplinary approach including social work assistance, health services, and pest control is needed to appropriately treat the patient and the environment. Methods in preventing and managing this growing public health problem include improving hygiene, avoiding secondhand goods, and increasing awareness in the identification and proper elimination of bedbugs.5-7
- Venkatachalam PS, Belavady B. Loss of haemoglobin iron due to excessive biting by bed bugs. a possible aetiological factor in the iron deficiency anaemia of infants and children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1962;56:218-221.
- Pritchard MJ, Hwang SW. Severe anemia from bedbugs. CMAJ. 2009;181:287-288.
- Paulke-Korinek M, Széll M, Laferl H, et al. Bed bugs can cause severe anaemia in adults. Parasitol Res. 2012;110:2577-2579.
- Sabou M, Imperiale DG, Andrés E, et al. Bed bugs reproductive life cycle in the clothes of a patient suffering from Alzheimer's disease results in iron deficiency anemia. Parasite. 2013;20:16.
- Studdiford JS, Conniff KM, Trayes KP, et al. Bedbug infestation. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:653-658.
- Goddard J, deShazo R. Bed bugs (Cimex lectularis) and clinical consequences of their bites. JAMA. 2009;301:1358-1366.
- Bernardeschi C, Le Cleach L, Delaunay P, et al. Bed bug infestation. BMJ. 2013;346:f138.
- Silvia Munoz-Price L, Safdar N, Beier JC, et al. Bed bugs inhealthcare settings. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012;33:1137-1142.
- Huntington MK. When bed bugs bite. J Fam Pract. 2012;61:384-388.
- Delaunay P, Blanc V, Del Giudice P, et al. Bedbugs and infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:200-212.
- Doggett SL, Dwyer DE, Penas PF, et al. Bed bugs: clinical relevance and control options. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:164-192.
- Venkatachalam PS, Belavady B. Loss of haemoglobin iron due to excessive biting by bed bugs. a possible aetiological factor in the iron deficiency anaemia of infants and children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1962;56:218-221.
- Pritchard MJ, Hwang SW. Severe anemia from bedbugs. CMAJ. 2009;181:287-288.
- Paulke-Korinek M, Széll M, Laferl H, et al. Bed bugs can cause severe anaemia in adults. Parasitol Res. 2012;110:2577-2579.
- Sabou M, Imperiale DG, Andrés E, et al. Bed bugs reproductive life cycle in the clothes of a patient suffering from Alzheimer's disease results in iron deficiency anemia. Parasite. 2013;20:16.
- Studdiford JS, Conniff KM, Trayes KP, et al. Bedbug infestation. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:653-658.
- Goddard J, deShazo R. Bed bugs (Cimex lectularis) and clinical consequences of their bites. JAMA. 2009;301:1358-1366.
- Bernardeschi C, Le Cleach L, Delaunay P, et al. Bed bug infestation. BMJ. 2013;346:f138.
- Silvia Munoz-Price L, Safdar N, Beier JC, et al. Bed bugs inhealthcare settings. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012;33:1137-1142.
- Huntington MK. When bed bugs bite. J Fam Pract. 2012;61:384-388.
- Delaunay P, Blanc V, Del Giudice P, et al. Bedbugs and infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:200-212.
- Doggett SL, Dwyer DE, Penas PF, et al. Bed bugs: clinical relevance and control options. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:164-192.
Practice Points
- There has been a resurgence in bedbug (Cimex lectularius) infestations in developed countries.
- Although rare, anemia due to bedbug infestation should be considered in patients presenting with anemia and a widespread pruritic papular eruption.
- A thorough history and physical examination are essential to prevent a delay in diagnosis and avoid a costly and unnecessary workup.
- Successful treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach, which includes medical management, social services, and pest control.
Lipid-lowering drugs appear to decrease risk of colorectal cancer death across subgroups
Use of lipid-lowering medication was linked to a 56% lower risk of colorectal cancer death among individuals with no cancer at baseline who were enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. The reduction in mortality risk was evident regardless of sex, race, age, or how long patients had been on lipid-lowering drugs.
Michael T. Marrone, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues detailed these findings in a poster presented at the AACR virtual meeting II.
“Definitely for those individuals at average risk for colorectal cancer, if their primary care doctor recommends a lipid-lowering medication for cardiovascular disease prevention, they should follow their doctor’s advice,” Dr. Marrone said in an interview.
“We really can’t say that they should take this specifically for colon cancer prevention, but they should just follow the recommendation for cardiovascular disease prevention,” he added.
While previous studies have linked lipid-lowering drugs, and statins in particular, to a modestly reduced risk of developing colorectal cancer, the impact on risk by factors such as sex, race, and duration of use have not been well characterized, according to Dr. Marrone.
Another motivation for this study was to determine, in participants free of cancer at baseline, the risk of actually dying from this cancer. “That endpoint has not been well studied in the literature at all,” Dr. Marrone said.
To address those gaps, Dr. Marrone and colleagues analyzed data on 14,428 patients from the ARIC study who were cancer free at study visits between 1990 and 1992. Follow-up continued through the end of 2015 or until death, whichever came first.
A total of 384 incident colorectal cancer cases and 144 deaths were seen over 290,249 person-years at risk. The patients’ mean age was 57 years, 54.9% were women, and 27.9% were black. At scheduled follow-up visits from 1996 to 1998, 22% of patients were taking lipid-lowering drugs, mostly statins.
Compared with patients who never used lipid-lowering medications, patients who had ever used a lipid-lowering drug had a lower risk of colorectal cancer incidence (hazard ratio, 0.72). The incidence of colorectal cancer was lower among all lipid-lowering drug users, including men (HR, 0.69), women (HR, 0.76), black patients (HR, 0.60), and white patients (HR, 0.77).
Similarly, colorectal cancer–related death was lower among patients who had ever used a lipid-lowering drug (HR, 0.44). That association was apparent in men (HR, 0.58), women (HR, 0.33), black patients (HR, 0.63), and white patients (HR, 0.40).
In addition, the mortality risk was lower among lipid-lowering drug users regardless of duration of use or age at first use. The HR was 0.50 for patients taking lipid-lowering drugs for less than 15 years and 0.44 for patients taking the drugs for 15 years or more. HRs by age were 0.69 for patients aged 50-59 years, 0.45 for patients aged 60-69 years, and 0.57 for patients aged 70 and older.
While results of this particular study do help “move the needle forward” in terms of characterizing the relationship between lipid-lowering drugs and colorectal cancer risk, further studies are needed to better characterize the effects of long-term statin use, said Jennifer M. Weiss, MD, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Clinical studies of the impact of statins on colorectal neoplasias have produced inconsistent results, Dr. Weiss and coauthor Bryson W. Katona, MD, PhD, wrote in a review article on chemoprevention in colorectal cancer.
“I definitely think there have been some studies that showed a modestly reduced risk,” Dr. Weiss said in an interview. “Unfortunately, there are also are some studies that show an increased risk of adenomas, and then there’s some studies that show no significant change. So we just can’t unequivocally confirm that there’s a significant association between statin use and decreased risk of developing colorectal cancer or adenomas.”
This research was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Program of Cancer Registries; and the American Association for Cancer Research. Dr. Marrone disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Weiss was an investigator for the CPP FAP-310 trial (NCT01483144) and received no salary support for her participation in the trial.
SOURCE: Marrone MT et al. AACR 2020, Abstract 2357.
Use of lipid-lowering medication was linked to a 56% lower risk of colorectal cancer death among individuals with no cancer at baseline who were enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. The reduction in mortality risk was evident regardless of sex, race, age, or how long patients had been on lipid-lowering drugs.
Michael T. Marrone, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues detailed these findings in a poster presented at the AACR virtual meeting II.
“Definitely for those individuals at average risk for colorectal cancer, if their primary care doctor recommends a lipid-lowering medication for cardiovascular disease prevention, they should follow their doctor’s advice,” Dr. Marrone said in an interview.
“We really can’t say that they should take this specifically for colon cancer prevention, but they should just follow the recommendation for cardiovascular disease prevention,” he added.
While previous studies have linked lipid-lowering drugs, and statins in particular, to a modestly reduced risk of developing colorectal cancer, the impact on risk by factors such as sex, race, and duration of use have not been well characterized, according to Dr. Marrone.
Another motivation for this study was to determine, in participants free of cancer at baseline, the risk of actually dying from this cancer. “That endpoint has not been well studied in the literature at all,” Dr. Marrone said.
To address those gaps, Dr. Marrone and colleagues analyzed data on 14,428 patients from the ARIC study who were cancer free at study visits between 1990 and 1992. Follow-up continued through the end of 2015 or until death, whichever came first.
A total of 384 incident colorectal cancer cases and 144 deaths were seen over 290,249 person-years at risk. The patients’ mean age was 57 years, 54.9% were women, and 27.9% were black. At scheduled follow-up visits from 1996 to 1998, 22% of patients were taking lipid-lowering drugs, mostly statins.
Compared with patients who never used lipid-lowering medications, patients who had ever used a lipid-lowering drug had a lower risk of colorectal cancer incidence (hazard ratio, 0.72). The incidence of colorectal cancer was lower among all lipid-lowering drug users, including men (HR, 0.69), women (HR, 0.76), black patients (HR, 0.60), and white patients (HR, 0.77).
Similarly, colorectal cancer–related death was lower among patients who had ever used a lipid-lowering drug (HR, 0.44). That association was apparent in men (HR, 0.58), women (HR, 0.33), black patients (HR, 0.63), and white patients (HR, 0.40).
In addition, the mortality risk was lower among lipid-lowering drug users regardless of duration of use or age at first use. The HR was 0.50 for patients taking lipid-lowering drugs for less than 15 years and 0.44 for patients taking the drugs for 15 years or more. HRs by age were 0.69 for patients aged 50-59 years, 0.45 for patients aged 60-69 years, and 0.57 for patients aged 70 and older.
While results of this particular study do help “move the needle forward” in terms of characterizing the relationship between lipid-lowering drugs and colorectal cancer risk, further studies are needed to better characterize the effects of long-term statin use, said Jennifer M. Weiss, MD, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Clinical studies of the impact of statins on colorectal neoplasias have produced inconsistent results, Dr. Weiss and coauthor Bryson W. Katona, MD, PhD, wrote in a review article on chemoprevention in colorectal cancer.
“I definitely think there have been some studies that showed a modestly reduced risk,” Dr. Weiss said in an interview. “Unfortunately, there are also are some studies that show an increased risk of adenomas, and then there’s some studies that show no significant change. So we just can’t unequivocally confirm that there’s a significant association between statin use and decreased risk of developing colorectal cancer or adenomas.”
This research was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Program of Cancer Registries; and the American Association for Cancer Research. Dr. Marrone disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Weiss was an investigator for the CPP FAP-310 trial (NCT01483144) and received no salary support for her participation in the trial.
SOURCE: Marrone MT et al. AACR 2020, Abstract 2357.
Use of lipid-lowering medication was linked to a 56% lower risk of colorectal cancer death among individuals with no cancer at baseline who were enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. The reduction in mortality risk was evident regardless of sex, race, age, or how long patients had been on lipid-lowering drugs.
Michael T. Marrone, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues detailed these findings in a poster presented at the AACR virtual meeting II.
“Definitely for those individuals at average risk for colorectal cancer, if their primary care doctor recommends a lipid-lowering medication for cardiovascular disease prevention, they should follow their doctor’s advice,” Dr. Marrone said in an interview.
“We really can’t say that they should take this specifically for colon cancer prevention, but they should just follow the recommendation for cardiovascular disease prevention,” he added.
While previous studies have linked lipid-lowering drugs, and statins in particular, to a modestly reduced risk of developing colorectal cancer, the impact on risk by factors such as sex, race, and duration of use have not been well characterized, according to Dr. Marrone.
Another motivation for this study was to determine, in participants free of cancer at baseline, the risk of actually dying from this cancer. “That endpoint has not been well studied in the literature at all,” Dr. Marrone said.
To address those gaps, Dr. Marrone and colleagues analyzed data on 14,428 patients from the ARIC study who were cancer free at study visits between 1990 and 1992. Follow-up continued through the end of 2015 or until death, whichever came first.
A total of 384 incident colorectal cancer cases and 144 deaths were seen over 290,249 person-years at risk. The patients’ mean age was 57 years, 54.9% were women, and 27.9% were black. At scheduled follow-up visits from 1996 to 1998, 22% of patients were taking lipid-lowering drugs, mostly statins.
Compared with patients who never used lipid-lowering medications, patients who had ever used a lipid-lowering drug had a lower risk of colorectal cancer incidence (hazard ratio, 0.72). The incidence of colorectal cancer was lower among all lipid-lowering drug users, including men (HR, 0.69), women (HR, 0.76), black patients (HR, 0.60), and white patients (HR, 0.77).
Similarly, colorectal cancer–related death was lower among patients who had ever used a lipid-lowering drug (HR, 0.44). That association was apparent in men (HR, 0.58), women (HR, 0.33), black patients (HR, 0.63), and white patients (HR, 0.40).
In addition, the mortality risk was lower among lipid-lowering drug users regardless of duration of use or age at first use. The HR was 0.50 for patients taking lipid-lowering drugs for less than 15 years and 0.44 for patients taking the drugs for 15 years or more. HRs by age were 0.69 for patients aged 50-59 years, 0.45 for patients aged 60-69 years, and 0.57 for patients aged 70 and older.
While results of this particular study do help “move the needle forward” in terms of characterizing the relationship between lipid-lowering drugs and colorectal cancer risk, further studies are needed to better characterize the effects of long-term statin use, said Jennifer M. Weiss, MD, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Clinical studies of the impact of statins on colorectal neoplasias have produced inconsistent results, Dr. Weiss and coauthor Bryson W. Katona, MD, PhD, wrote in a review article on chemoprevention in colorectal cancer.
“I definitely think there have been some studies that showed a modestly reduced risk,” Dr. Weiss said in an interview. “Unfortunately, there are also are some studies that show an increased risk of adenomas, and then there’s some studies that show no significant change. So we just can’t unequivocally confirm that there’s a significant association between statin use and decreased risk of developing colorectal cancer or adenomas.”
This research was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Program of Cancer Registries; and the American Association for Cancer Research. Dr. Marrone disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Weiss was an investigator for the CPP FAP-310 trial (NCT01483144) and received no salary support for her participation in the trial.
SOURCE: Marrone MT et al. AACR 2020, Abstract 2357.
FROM AACR 2020
FDA approves first oral somatostatin analog for acromegaly
who previously responded to and tolerated octreotide or lanreotide injections.
“People living with acromegaly experience many challenges associated with injectable therapies and are in need of new treatment options,” Jill Sisco, president of Acromegaly Community, a patient support group, said in a Chiasma press release.
“The entire acromegaly community has long awaited oral therapeutic options and it is gratifying to see that the FDA has now approved the first oral somatostatin analog (SSA) therapy with the potential to make a significant impact in the lives of people with acromegaly and their caregivers,” she added.
Acromegaly, a rare, chronic disease usually caused by a benign pituitary tumor that leads to excess production of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) hormone, can be cured through the successful surgical removal of the pituitary tumor. However, management of the disease remains a lifelong challenge for many who must rely on chronic injections.
The new oral formulation of octreotide is the first and only oral somatostatin analog approved by the FDA.
The approval was based on the results of the 9-month, phase 3 pivotal CHIASMA OPTIMAL clinical trial, involving 56 adults with acromegaly controlled by injectable SSAs.
The patients, who were randomized 1:1 to octreotide capsules or placebo, were dose-titrated from 40 mg/day up to a maximum of 80 mg/day, equaling two capsules in the morning and two in the evening.
The study met its primary endpoint. Overall, 58% of patients taking octreotide maintained IGF-1 response compared with 19% of those on placebo at the end of 9 months (P = .008), according to the average of the last two IGF-1 levels that were 1 times or less the upper limit of normal, assessed at weeks 34 and 36.
The trial also met its secondary endpoints, which included the proportion of patients who maintain growth hormone response at week 36 compared with screening; time to loss of response; and proportion of patients requiring reversion to prior treatment.
Safety data were favorable. Adverse reactions to the drug, detailed in the prescribing information, include cholelithiasis and associated complications; hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia; thyroid function abnormalities; cardiac function abnormalities; decreased vitamin B12 levels, and abnormal Schilling’s test results.
Results from the clinical trial “are encouraging for patients with acromegaly,” the study’s principal investigator, Susan Samson, MD, PhD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in the Chiasma statement.
“Based on data from the CHIASMA OPTIMAL trial showing patients on therapy being able to maintain mean IGF-1 levels within the normal range at the end of treatment, I believe oral octreotide capsules hold meaningful promise for patients with this disease and will address a long-standing unmet treatment need,” she added.
Chiasma reports that it expects Mycapssa to be available in the fourth quarter of 2020, pending FDA approval of a planned manufacturing supplement to the approved new drug application.
The company further plans to provide patient support services including assistance with insurance providers and specialty pharmacies and support in incorporating treatment into patients’ daily routines.
Despite effective biochemical control of growth hormone, many patients with acromegaly continue to suffer symptoms, mainly because of comorbidities, so it is important that these are also adequately treated, a consensus group concluded earlier this year.
The CHIASMA OPTIMAL trial was funded by Chiasma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
who previously responded to and tolerated octreotide or lanreotide injections.
“People living with acromegaly experience many challenges associated with injectable therapies and are in need of new treatment options,” Jill Sisco, president of Acromegaly Community, a patient support group, said in a Chiasma press release.
“The entire acromegaly community has long awaited oral therapeutic options and it is gratifying to see that the FDA has now approved the first oral somatostatin analog (SSA) therapy with the potential to make a significant impact in the lives of people with acromegaly and their caregivers,” she added.
Acromegaly, a rare, chronic disease usually caused by a benign pituitary tumor that leads to excess production of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) hormone, can be cured through the successful surgical removal of the pituitary tumor. However, management of the disease remains a lifelong challenge for many who must rely on chronic injections.
The new oral formulation of octreotide is the first and only oral somatostatin analog approved by the FDA.
The approval was based on the results of the 9-month, phase 3 pivotal CHIASMA OPTIMAL clinical trial, involving 56 adults with acromegaly controlled by injectable SSAs.
The patients, who were randomized 1:1 to octreotide capsules or placebo, were dose-titrated from 40 mg/day up to a maximum of 80 mg/day, equaling two capsules in the morning and two in the evening.
The study met its primary endpoint. Overall, 58% of patients taking octreotide maintained IGF-1 response compared with 19% of those on placebo at the end of 9 months (P = .008), according to the average of the last two IGF-1 levels that were 1 times or less the upper limit of normal, assessed at weeks 34 and 36.
The trial also met its secondary endpoints, which included the proportion of patients who maintain growth hormone response at week 36 compared with screening; time to loss of response; and proportion of patients requiring reversion to prior treatment.
Safety data were favorable. Adverse reactions to the drug, detailed in the prescribing information, include cholelithiasis and associated complications; hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia; thyroid function abnormalities; cardiac function abnormalities; decreased vitamin B12 levels, and abnormal Schilling’s test results.
Results from the clinical trial “are encouraging for patients with acromegaly,” the study’s principal investigator, Susan Samson, MD, PhD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in the Chiasma statement.
“Based on data from the CHIASMA OPTIMAL trial showing patients on therapy being able to maintain mean IGF-1 levels within the normal range at the end of treatment, I believe oral octreotide capsules hold meaningful promise for patients with this disease and will address a long-standing unmet treatment need,” she added.
Chiasma reports that it expects Mycapssa to be available in the fourth quarter of 2020, pending FDA approval of a planned manufacturing supplement to the approved new drug application.
The company further plans to provide patient support services including assistance with insurance providers and specialty pharmacies and support in incorporating treatment into patients’ daily routines.
Despite effective biochemical control of growth hormone, many patients with acromegaly continue to suffer symptoms, mainly because of comorbidities, so it is important that these are also adequately treated, a consensus group concluded earlier this year.
The CHIASMA OPTIMAL trial was funded by Chiasma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
who previously responded to and tolerated octreotide or lanreotide injections.
“People living with acromegaly experience many challenges associated with injectable therapies and are in need of new treatment options,” Jill Sisco, president of Acromegaly Community, a patient support group, said in a Chiasma press release.
“The entire acromegaly community has long awaited oral therapeutic options and it is gratifying to see that the FDA has now approved the first oral somatostatin analog (SSA) therapy with the potential to make a significant impact in the lives of people with acromegaly and their caregivers,” she added.
Acromegaly, a rare, chronic disease usually caused by a benign pituitary tumor that leads to excess production of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) hormone, can be cured through the successful surgical removal of the pituitary tumor. However, management of the disease remains a lifelong challenge for many who must rely on chronic injections.
The new oral formulation of octreotide is the first and only oral somatostatin analog approved by the FDA.
The approval was based on the results of the 9-month, phase 3 pivotal CHIASMA OPTIMAL clinical trial, involving 56 adults with acromegaly controlled by injectable SSAs.
The patients, who were randomized 1:1 to octreotide capsules or placebo, were dose-titrated from 40 mg/day up to a maximum of 80 mg/day, equaling two capsules in the morning and two in the evening.
The study met its primary endpoint. Overall, 58% of patients taking octreotide maintained IGF-1 response compared with 19% of those on placebo at the end of 9 months (P = .008), according to the average of the last two IGF-1 levels that were 1 times or less the upper limit of normal, assessed at weeks 34 and 36.
The trial also met its secondary endpoints, which included the proportion of patients who maintain growth hormone response at week 36 compared with screening; time to loss of response; and proportion of patients requiring reversion to prior treatment.
Safety data were favorable. Adverse reactions to the drug, detailed in the prescribing information, include cholelithiasis and associated complications; hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia; thyroid function abnormalities; cardiac function abnormalities; decreased vitamin B12 levels, and abnormal Schilling’s test results.
Results from the clinical trial “are encouraging for patients with acromegaly,” the study’s principal investigator, Susan Samson, MD, PhD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in the Chiasma statement.
“Based on data from the CHIASMA OPTIMAL trial showing patients on therapy being able to maintain mean IGF-1 levels within the normal range at the end of treatment, I believe oral octreotide capsules hold meaningful promise for patients with this disease and will address a long-standing unmet treatment need,” she added.
Chiasma reports that it expects Mycapssa to be available in the fourth quarter of 2020, pending FDA approval of a planned manufacturing supplement to the approved new drug application.
The company further plans to provide patient support services including assistance with insurance providers and specialty pharmacies and support in incorporating treatment into patients’ daily routines.
Despite effective biochemical control of growth hormone, many patients with acromegaly continue to suffer symptoms, mainly because of comorbidities, so it is important that these are also adequately treated, a consensus group concluded earlier this year.
The CHIASMA OPTIMAL trial was funded by Chiasma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High-impact training can build bone in older women
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are often advised to pursue low-impact, low-intensity exercise as a way to preserve joint health, but that approach might actually contribute to a decline in bone mineral density, researchers report.
Concerns about falls and fracture risk have led many clinicians to advise against higher-impact activities, like jumping, but that is exactly the type of activity that improves bone density and physical function, said Belinda Beck, PhD, professor at the Griffith University School of Allied Health Sciences in Southport, Australia.
“There has always been a quandary in terms of pursuing research on this,” she said in an interview. “We know from animal studies that bone only responds to high-intensity activity, but we worry about advising that for people with low bone mass, so instead we give them medications.”
“But not everyone likes to go on meds, they’re not 100% effective, and they’re not free of side effects,” said Beck, who is also the owner and director of The Bone Clinic in Brisbane, Australia.
In 2014, to assess whether high-intensity resistance and impact training (HiRIT) was a safe and effective way to improve bone mass, Beck and her colleagues conducted the LIFTMOR study of 101 postmenopausal women. The researchers showed that bone mineral density in the lumbar spine and femoral neck regions and functional performance measures were significantly better in the 49 participants randomized to HiRIT for 8 months than in the 52 randomized to low-intensity training.
Three years after the completion of LIFTMOR, the researchers looked at bone mineral density in 23 women from the HiRIT group in their retrospective observational study, the results of which were presented at the virtual American College of Sports Medicine 2020 Annual Meeting.
Ongoing gains were significantly better for the seven participants who continued with HiRIT (at least 25% compliance) than for the 16 who did not when looking at both bone mineral density of the lumbar spine (8.63% vs. 2.18%; P = .042) and femoral neck (3.67% vs. 2.85%; P = 0.14).
However, the women who discontinued HiRIT after 8 months maintained the gains in bone mineral density that they had achieved 3 years earlier.
Functional outcomes in the women who continued HiRIT were better than those in the women who did not, but the differences were not significant.
“The takeaway here is that this type of exercise appears to be a highly effective therapy to reduce risk of osteoporotic fracture, since it improves bone mass,” Beck said.
Jump more, lose less bone density
Given the widespread reluctance to suggest HiRIT-type activity to those with low bone mass, this research is significant, said Vanessa Yingling, PhD, from the Department of Kinesiology at California State University, East Bay.
“Once women hit 60, they’re somehow regarded as frail, but that becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy when we take this kinder, gentler approach to exercise,” Yingling said in an interview. “Building bone density in older adults is important, but maintaining current bone density is just as crucial. Without high-impact activity, we are likely to see decelerating density at a faster rate.”
The other key to the recent research is the functional testing, Yingling added. In addition to bone density measures, high-intensity activity can improve mobility and muscle strength, as the study noted.
This type of activity can be done in shorter bursts, making these workouts more efficient, she explained. For example, a Tabata high-intensity interval training session usually takes about 10 minutes, warm-up and cool-down included.
“A HiRIT workout even once or twice a week would likely improve function, strength, and bone density maintenance,” Beck said. “The result of that would be better fall prevention and potentially less medication usage for BMD issues.”
Both men and women can benefit from a HiRIT workout, Beck and Yingling said. Initially, supervision by a knowledgeable trainer or physical therapist is ideal, they added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are often advised to pursue low-impact, low-intensity exercise as a way to preserve joint health, but that approach might actually contribute to a decline in bone mineral density, researchers report.
Concerns about falls and fracture risk have led many clinicians to advise against higher-impact activities, like jumping, but that is exactly the type of activity that improves bone density and physical function, said Belinda Beck, PhD, professor at the Griffith University School of Allied Health Sciences in Southport, Australia.
“There has always been a quandary in terms of pursuing research on this,” she said in an interview. “We know from animal studies that bone only responds to high-intensity activity, but we worry about advising that for people with low bone mass, so instead we give them medications.”
“But not everyone likes to go on meds, they’re not 100% effective, and they’re not free of side effects,” said Beck, who is also the owner and director of The Bone Clinic in Brisbane, Australia.
In 2014, to assess whether high-intensity resistance and impact training (HiRIT) was a safe and effective way to improve bone mass, Beck and her colleagues conducted the LIFTMOR study of 101 postmenopausal women. The researchers showed that bone mineral density in the lumbar spine and femoral neck regions and functional performance measures were significantly better in the 49 participants randomized to HiRIT for 8 months than in the 52 randomized to low-intensity training.
Three years after the completion of LIFTMOR, the researchers looked at bone mineral density in 23 women from the HiRIT group in their retrospective observational study, the results of which were presented at the virtual American College of Sports Medicine 2020 Annual Meeting.
Ongoing gains were significantly better for the seven participants who continued with HiRIT (at least 25% compliance) than for the 16 who did not when looking at both bone mineral density of the lumbar spine (8.63% vs. 2.18%; P = .042) and femoral neck (3.67% vs. 2.85%; P = 0.14).
However, the women who discontinued HiRIT after 8 months maintained the gains in bone mineral density that they had achieved 3 years earlier.
Functional outcomes in the women who continued HiRIT were better than those in the women who did not, but the differences were not significant.
“The takeaway here is that this type of exercise appears to be a highly effective therapy to reduce risk of osteoporotic fracture, since it improves bone mass,” Beck said.
Jump more, lose less bone density
Given the widespread reluctance to suggest HiRIT-type activity to those with low bone mass, this research is significant, said Vanessa Yingling, PhD, from the Department of Kinesiology at California State University, East Bay.
“Once women hit 60, they’re somehow regarded as frail, but that becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy when we take this kinder, gentler approach to exercise,” Yingling said in an interview. “Building bone density in older adults is important, but maintaining current bone density is just as crucial. Without high-impact activity, we are likely to see decelerating density at a faster rate.”
The other key to the recent research is the functional testing, Yingling added. In addition to bone density measures, high-intensity activity can improve mobility and muscle strength, as the study noted.
This type of activity can be done in shorter bursts, making these workouts more efficient, she explained. For example, a Tabata high-intensity interval training session usually takes about 10 minutes, warm-up and cool-down included.
“A HiRIT workout even once or twice a week would likely improve function, strength, and bone density maintenance,” Beck said. “The result of that would be better fall prevention and potentially less medication usage for BMD issues.”
Both men and women can benefit from a HiRIT workout, Beck and Yingling said. Initially, supervision by a knowledgeable trainer or physical therapist is ideal, they added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are often advised to pursue low-impact, low-intensity exercise as a way to preserve joint health, but that approach might actually contribute to a decline in bone mineral density, researchers report.
Concerns about falls and fracture risk have led many clinicians to advise against higher-impact activities, like jumping, but that is exactly the type of activity that improves bone density and physical function, said Belinda Beck, PhD, professor at the Griffith University School of Allied Health Sciences in Southport, Australia.
“There has always been a quandary in terms of pursuing research on this,” she said in an interview. “We know from animal studies that bone only responds to high-intensity activity, but we worry about advising that for people with low bone mass, so instead we give them medications.”
“But not everyone likes to go on meds, they’re not 100% effective, and they’re not free of side effects,” said Beck, who is also the owner and director of The Bone Clinic in Brisbane, Australia.
In 2014, to assess whether high-intensity resistance and impact training (HiRIT) was a safe and effective way to improve bone mass, Beck and her colleagues conducted the LIFTMOR study of 101 postmenopausal women. The researchers showed that bone mineral density in the lumbar spine and femoral neck regions and functional performance measures were significantly better in the 49 participants randomized to HiRIT for 8 months than in the 52 randomized to low-intensity training.
Three years after the completion of LIFTMOR, the researchers looked at bone mineral density in 23 women from the HiRIT group in their retrospective observational study, the results of which were presented at the virtual American College of Sports Medicine 2020 Annual Meeting.
Ongoing gains were significantly better for the seven participants who continued with HiRIT (at least 25% compliance) than for the 16 who did not when looking at both bone mineral density of the lumbar spine (8.63% vs. 2.18%; P = .042) and femoral neck (3.67% vs. 2.85%; P = 0.14).
However, the women who discontinued HiRIT after 8 months maintained the gains in bone mineral density that they had achieved 3 years earlier.
Functional outcomes in the women who continued HiRIT were better than those in the women who did not, but the differences were not significant.
“The takeaway here is that this type of exercise appears to be a highly effective therapy to reduce risk of osteoporotic fracture, since it improves bone mass,” Beck said.
Jump more, lose less bone density
Given the widespread reluctance to suggest HiRIT-type activity to those with low bone mass, this research is significant, said Vanessa Yingling, PhD, from the Department of Kinesiology at California State University, East Bay.
“Once women hit 60, they’re somehow regarded as frail, but that becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy when we take this kinder, gentler approach to exercise,” Yingling said in an interview. “Building bone density in older adults is important, but maintaining current bone density is just as crucial. Without high-impact activity, we are likely to see decelerating density at a faster rate.”
The other key to the recent research is the functional testing, Yingling added. In addition to bone density measures, high-intensity activity can improve mobility and muscle strength, as the study noted.
This type of activity can be done in shorter bursts, making these workouts more efficient, she explained. For example, a Tabata high-intensity interval training session usually takes about 10 minutes, warm-up and cool-down included.
“A HiRIT workout even once or twice a week would likely improve function, strength, and bone density maintenance,” Beck said. “The result of that would be better fall prevention and potentially less medication usage for BMD issues.”
Both men and women can benefit from a HiRIT workout, Beck and Yingling said. Initially, supervision by a knowledgeable trainer or physical therapist is ideal, they added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.