User login
Pregnant women at greater risk for severe COVID-19, CDC says
Pregnant women may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness, according to a new report published online June 26 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among reproductive-aged women (15-44 years) infected with SARS-CoV-2, Pregnant women were 5.4 times more likely to be hospitalized, 1.5 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU, and 1.7 times more likely to need mechanical ventilation, after adjustment for age, underlying conditions, and race/ethnicity.
Furthermore, Hispanic and non-Hispanic black pregnant women appear to be disproportionately impacted by the infection.
Sascha Ellington, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Response Pregnancy and Infant Linked Outcomes Team, and colleagues said that preventing COVID-19 infection in pregnant women should be a priority and any potential barriers to compliance with preventive measures need to be removed.
“During pregnancy, women experience immunologic and physiologic changes that could increase their risk for more severe illness from respiratory infections,” they wrote.
As of June 7, a total of 8,207 cases of COVID-19 in pregnant women were reported to the CDC, approximately 9% of COVID-19 cases among reproductive-aged women with known pregnancy status. The authors compared outcomes in these pregnant patients with those in 83,205 nonpregnant women with COVID-19. There was a substantially greater proportion of hospital admissions among pregnant patients (2,587; 31.5%) compared with nonpregnant patients (4,840; 5.8%) with COVID-19.
The authors cautioned that there were no data to differentiate between hospitalizations for COVID-19–related problems as opposed to those arising from pregnancy, including delivery.
For other severity measures, ICU admissions were reported for 1.5% of pregnant women compared with 0.9% for their nonpregnant counterparts, whereas mechanical ventilation was required for 0.5% compared with 0.3%, respectively. Mortality was identical, affecting 0.2% in both groups, with 16 deaths in pregnant patients with COVID-19 and 208 in nonpregnant patients.
Age had an impact as well, with hospitalization more frequent among those aged 35-44 years than among those aged 15-24, regardless of pregnancy status. When stratified by race/ethnicity, ICU admission was most frequently reported among pregnant women who were of non-Hispanic Asian lineage: 3.5% compared with 1.5% in all pregnant women.
Among pregnant women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection reporting race/ethnicity, 46% were Hispanic, 22% were black, and 23% were white, whereas among women who gave birth in 2019, 24% were Hispanic, 15% were black, and 51% were white. “Although data on race/ethnicity were missing for 20% of pregnant women in this study, these findings suggest that pregnant women who are Hispanic and black might be disproportionately affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy,” the authors wrote.
They noted that in a recent meta-analysis of influenza, pregnancy was similarly associated with a sevenfold risk for hospitalization, but a lower risk for ICU admission and no increased risk for death. A recent study suggested that COVID-19 severity during pregnancy may be lower than in other respiratory infections such as H1N1.
ACOG responds
In a response to the CDC findings, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) advises calm, noting that the risk of needing the severity-associated interventions in the CDC report remains low and pregnant COVID-19 patients do not appear to have a greater risk for mortality.
Nevertheless, ACOG is reviewing all its COVID-19–related clinical and patient materials and “will make any necessary revisions to recommendations.”
In the meantime, the college advises clinicians to alert patients to the potential increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness during pregnancy. They should also stress to pregnant women and their families the need for precautions to prevent infection, paying particular attention to measures to protect those with greater occupational exposure to the virus.
ACOG also criticized the exclusion of pregnant and lactating women from clinical trials of potential coronavirus vaccines, noting that the new CDC findings underscore the importance of prioritizing pregnant patients to receive coronavirus vaccination when it becomes available.
“ACOG again urges the federal government to use its resources to ensure the safe inclusion of pregnant and lactating patients, including patients of color, in trials for vaccines and therapeutics to ensure that all populations are included in the search for ways to prevent and treat COVID-19,” the statement reads.
The CDC authors said that their report also highlights the need for more complete data to fully understand the risk for severe illness in pregnant women. To address these gaps, the CDC is collaborating with health departments in COVID-19 pregnancy surveillance for the reporting of outcomes in pregnant women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A version of article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness, according to a new report published online June 26 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among reproductive-aged women (15-44 years) infected with SARS-CoV-2, Pregnant women were 5.4 times more likely to be hospitalized, 1.5 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU, and 1.7 times more likely to need mechanical ventilation, after adjustment for age, underlying conditions, and race/ethnicity.
Furthermore, Hispanic and non-Hispanic black pregnant women appear to be disproportionately impacted by the infection.
Sascha Ellington, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Response Pregnancy and Infant Linked Outcomes Team, and colleagues said that preventing COVID-19 infection in pregnant women should be a priority and any potential barriers to compliance with preventive measures need to be removed.
“During pregnancy, women experience immunologic and physiologic changes that could increase their risk for more severe illness from respiratory infections,” they wrote.
As of June 7, a total of 8,207 cases of COVID-19 in pregnant women were reported to the CDC, approximately 9% of COVID-19 cases among reproductive-aged women with known pregnancy status. The authors compared outcomes in these pregnant patients with those in 83,205 nonpregnant women with COVID-19. There was a substantially greater proportion of hospital admissions among pregnant patients (2,587; 31.5%) compared with nonpregnant patients (4,840; 5.8%) with COVID-19.
The authors cautioned that there were no data to differentiate between hospitalizations for COVID-19–related problems as opposed to those arising from pregnancy, including delivery.
For other severity measures, ICU admissions were reported for 1.5% of pregnant women compared with 0.9% for their nonpregnant counterparts, whereas mechanical ventilation was required for 0.5% compared with 0.3%, respectively. Mortality was identical, affecting 0.2% in both groups, with 16 deaths in pregnant patients with COVID-19 and 208 in nonpregnant patients.
Age had an impact as well, with hospitalization more frequent among those aged 35-44 years than among those aged 15-24, regardless of pregnancy status. When stratified by race/ethnicity, ICU admission was most frequently reported among pregnant women who were of non-Hispanic Asian lineage: 3.5% compared with 1.5% in all pregnant women.
Among pregnant women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection reporting race/ethnicity, 46% were Hispanic, 22% were black, and 23% were white, whereas among women who gave birth in 2019, 24% were Hispanic, 15% were black, and 51% were white. “Although data on race/ethnicity were missing for 20% of pregnant women in this study, these findings suggest that pregnant women who are Hispanic and black might be disproportionately affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy,” the authors wrote.
They noted that in a recent meta-analysis of influenza, pregnancy was similarly associated with a sevenfold risk for hospitalization, but a lower risk for ICU admission and no increased risk for death. A recent study suggested that COVID-19 severity during pregnancy may be lower than in other respiratory infections such as H1N1.
ACOG responds
In a response to the CDC findings, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) advises calm, noting that the risk of needing the severity-associated interventions in the CDC report remains low and pregnant COVID-19 patients do not appear to have a greater risk for mortality.
Nevertheless, ACOG is reviewing all its COVID-19–related clinical and patient materials and “will make any necessary revisions to recommendations.”
In the meantime, the college advises clinicians to alert patients to the potential increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness during pregnancy. They should also stress to pregnant women and their families the need for precautions to prevent infection, paying particular attention to measures to protect those with greater occupational exposure to the virus.
ACOG also criticized the exclusion of pregnant and lactating women from clinical trials of potential coronavirus vaccines, noting that the new CDC findings underscore the importance of prioritizing pregnant patients to receive coronavirus vaccination when it becomes available.
“ACOG again urges the federal government to use its resources to ensure the safe inclusion of pregnant and lactating patients, including patients of color, in trials for vaccines and therapeutics to ensure that all populations are included in the search for ways to prevent and treat COVID-19,” the statement reads.
The CDC authors said that their report also highlights the need for more complete data to fully understand the risk for severe illness in pregnant women. To address these gaps, the CDC is collaborating with health departments in COVID-19 pregnancy surveillance for the reporting of outcomes in pregnant women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A version of article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness, according to a new report published online June 26 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among reproductive-aged women (15-44 years) infected with SARS-CoV-2, Pregnant women were 5.4 times more likely to be hospitalized, 1.5 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU, and 1.7 times more likely to need mechanical ventilation, after adjustment for age, underlying conditions, and race/ethnicity.
Furthermore, Hispanic and non-Hispanic black pregnant women appear to be disproportionately impacted by the infection.
Sascha Ellington, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Response Pregnancy and Infant Linked Outcomes Team, and colleagues said that preventing COVID-19 infection in pregnant women should be a priority and any potential barriers to compliance with preventive measures need to be removed.
“During pregnancy, women experience immunologic and physiologic changes that could increase their risk for more severe illness from respiratory infections,” they wrote.
As of June 7, a total of 8,207 cases of COVID-19 in pregnant women were reported to the CDC, approximately 9% of COVID-19 cases among reproductive-aged women with known pregnancy status. The authors compared outcomes in these pregnant patients with those in 83,205 nonpregnant women with COVID-19. There was a substantially greater proportion of hospital admissions among pregnant patients (2,587; 31.5%) compared with nonpregnant patients (4,840; 5.8%) with COVID-19.
The authors cautioned that there were no data to differentiate between hospitalizations for COVID-19–related problems as opposed to those arising from pregnancy, including delivery.
For other severity measures, ICU admissions were reported for 1.5% of pregnant women compared with 0.9% for their nonpregnant counterparts, whereas mechanical ventilation was required for 0.5% compared with 0.3%, respectively. Mortality was identical, affecting 0.2% in both groups, with 16 deaths in pregnant patients with COVID-19 and 208 in nonpregnant patients.
Age had an impact as well, with hospitalization more frequent among those aged 35-44 years than among those aged 15-24, regardless of pregnancy status. When stratified by race/ethnicity, ICU admission was most frequently reported among pregnant women who were of non-Hispanic Asian lineage: 3.5% compared with 1.5% in all pregnant women.
Among pregnant women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection reporting race/ethnicity, 46% were Hispanic, 22% were black, and 23% were white, whereas among women who gave birth in 2019, 24% were Hispanic, 15% were black, and 51% were white. “Although data on race/ethnicity were missing for 20% of pregnant women in this study, these findings suggest that pregnant women who are Hispanic and black might be disproportionately affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy,” the authors wrote.
They noted that in a recent meta-analysis of influenza, pregnancy was similarly associated with a sevenfold risk for hospitalization, but a lower risk for ICU admission and no increased risk for death. A recent study suggested that COVID-19 severity during pregnancy may be lower than in other respiratory infections such as H1N1.
ACOG responds
In a response to the CDC findings, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) advises calm, noting that the risk of needing the severity-associated interventions in the CDC report remains low and pregnant COVID-19 patients do not appear to have a greater risk for mortality.
Nevertheless, ACOG is reviewing all its COVID-19–related clinical and patient materials and “will make any necessary revisions to recommendations.”
In the meantime, the college advises clinicians to alert patients to the potential increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness during pregnancy. They should also stress to pregnant women and their families the need for precautions to prevent infection, paying particular attention to measures to protect those with greater occupational exposure to the virus.
ACOG also criticized the exclusion of pregnant and lactating women from clinical trials of potential coronavirus vaccines, noting that the new CDC findings underscore the importance of prioritizing pregnant patients to receive coronavirus vaccination when it becomes available.
“ACOG again urges the federal government to use its resources to ensure the safe inclusion of pregnant and lactating patients, including patients of color, in trials for vaccines and therapeutics to ensure that all populations are included in the search for ways to prevent and treat COVID-19,” the statement reads.
The CDC authors said that their report also highlights the need for more complete data to fully understand the risk for severe illness in pregnant women. To address these gaps, the CDC is collaborating with health departments in COVID-19 pregnancy surveillance for the reporting of outcomes in pregnant women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A version of article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: ‘dramatic’ surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in NYC
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs) that placed a huge burden on first responders, a new analysis shows.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
New York City has the largest and busiest EMS system in the United States, serving a population of more than 8.4 million people and responding to more than 1.5 million calls every year.
To gauge the impact of COVID-19 on first responders, Dr. Prezant and colleagues analyzed data for adults with OHCA who received EMS resuscitation from March 1, when the first case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in the city, through April 25, when EMS call volume had receded to pre-COVID-19 levels.
Compared with the same period in 2019, the COVID-19 period had an excess of 2,653 patients with OHCA who underwent EMS resuscitation attempts (3,989 in 2020 vs. 1,336 in 2019, P < .001), an incidence rate triple that of 2019 (47.5 vs. 15.9 per 100,000).
On the worst day – Monday, April 6 – OHCAs peaked at 305 cases, an increase of nearly 10-fold compared with the same day in 2019.
Despite the surge in cases, the median response time of available EMS units to OHCAs increased by about 1 minute over 2019, a nonsignificant difference. Although the average time varied, median response time during the COVID-19 period was less than 3 minutes.
A more vulnerable group
Compared with 2019, patients suffering OHCA during the pandemic period were older (mean age 72 vs. 68 years), less likely to be white (20% white vs. 33%) and more likely to have hypertension (54% vs. 46%), diabetes (36% vs. 26%), physical limitations (57% vs. 48%) and cardiac rhythms that don’t respond to defibrillator shocks (92% vs. 81%).
Compared with 2019, the COVID-19 period had substantial reductions in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (18% vs. 35%; P < .001) and sustained ROSC (11% vs. 25%; P < .001). The case fatality rate was 90% in the COVID-19 period vs. 75% a year earlier.
“The tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is not just the number of patients infected, but the large increase in OHCAs and deaths,” Dr. Prezant and colleagues said.
Identifying patients with the greatest risk for OHCA and death during the COVID-19 pandemic “should allow for early, targeted interventions in the outpatient setting that could lead to reductions in out-of-hospital deaths,” they noted.
“Vulnerable patient populations need outreach, telephonic medicine, televideo medicine, home visits, not just temperature monitoring but home O2 saturation monitoring,” Dr. Prezant said in an interview. “Barriers need to be removed, not just for this pandemic but for the future – no matter what the trigger is.”
Unsung heroes
In an Editor’s Note in JAMA Cardiology, Robert O. Bonow, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues said the American people owe a debt of gratitude to first responders for their “heroic work” triaging, resuscitating, and transporting thousands of people affected by COVID-19.
“Although the typically bustling NYC streets remained eerily deserted, the characteristic cacophony of sounds of the ‘City that Never Sleeps’ was replaced by sirens wailing all hours of the night,” they wrote.
First responders to OHCAs in the COVID-19 era place themselves at extremely high risk, in some cases without optimal personal protective equipment, they pointed out. “Sadly,” many first responders have fallen ill to COVID-19 infection, they added.
As of June 1, 29 EMS workers and volunteers across the United States had died of COVID-19.
They are James Villecco, Gregory Hodge, Tony Thomas, Mike Field, John Redd, Idris Bey, Richard Seaberry, and Sal Mancuso of New York; Israel Tolentino, Reuven Maroth, Liana Sá, Kevin Leiva, Frank Molinari, Robert Weber, Robert Tarrant, Solomon Donald, Scott Geiger, John Farrarella, John Careccia, Bill Nauta, and David Pinto of New Jersey; Kevin Bundy, Robert Zerman, and Jeremy Emerich of Pennsylvania; Paul Cary of Colorado; Paul Novicki of Michigan; David Martin of Mississippi; Billy Birmingham of Missouri; and John “JP” Granger of South Carolina.
“We offer their families, friends, and colleagues our sincerest condolences and honor their memory with our highest respect and gratitude,” Dr. Bonow and colleagues wrote.
This study was supported by the City of New York and the Fire Department of the City of New York. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs) that placed a huge burden on first responders, a new analysis shows.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
New York City has the largest and busiest EMS system in the United States, serving a population of more than 8.4 million people and responding to more than 1.5 million calls every year.
To gauge the impact of COVID-19 on first responders, Dr. Prezant and colleagues analyzed data for adults with OHCA who received EMS resuscitation from March 1, when the first case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in the city, through April 25, when EMS call volume had receded to pre-COVID-19 levels.
Compared with the same period in 2019, the COVID-19 period had an excess of 2,653 patients with OHCA who underwent EMS resuscitation attempts (3,989 in 2020 vs. 1,336 in 2019, P < .001), an incidence rate triple that of 2019 (47.5 vs. 15.9 per 100,000).
On the worst day – Monday, April 6 – OHCAs peaked at 305 cases, an increase of nearly 10-fold compared with the same day in 2019.
Despite the surge in cases, the median response time of available EMS units to OHCAs increased by about 1 minute over 2019, a nonsignificant difference. Although the average time varied, median response time during the COVID-19 period was less than 3 minutes.
A more vulnerable group
Compared with 2019, patients suffering OHCA during the pandemic period were older (mean age 72 vs. 68 years), less likely to be white (20% white vs. 33%) and more likely to have hypertension (54% vs. 46%), diabetes (36% vs. 26%), physical limitations (57% vs. 48%) and cardiac rhythms that don’t respond to defibrillator shocks (92% vs. 81%).
Compared with 2019, the COVID-19 period had substantial reductions in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (18% vs. 35%; P < .001) and sustained ROSC (11% vs. 25%; P < .001). The case fatality rate was 90% in the COVID-19 period vs. 75% a year earlier.
“The tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is not just the number of patients infected, but the large increase in OHCAs and deaths,” Dr. Prezant and colleagues said.
Identifying patients with the greatest risk for OHCA and death during the COVID-19 pandemic “should allow for early, targeted interventions in the outpatient setting that could lead to reductions in out-of-hospital deaths,” they noted.
“Vulnerable patient populations need outreach, telephonic medicine, televideo medicine, home visits, not just temperature monitoring but home O2 saturation monitoring,” Dr. Prezant said in an interview. “Barriers need to be removed, not just for this pandemic but for the future – no matter what the trigger is.”
Unsung heroes
In an Editor’s Note in JAMA Cardiology, Robert O. Bonow, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues said the American people owe a debt of gratitude to first responders for their “heroic work” triaging, resuscitating, and transporting thousands of people affected by COVID-19.
“Although the typically bustling NYC streets remained eerily deserted, the characteristic cacophony of sounds of the ‘City that Never Sleeps’ was replaced by sirens wailing all hours of the night,” they wrote.
First responders to OHCAs in the COVID-19 era place themselves at extremely high risk, in some cases without optimal personal protective equipment, they pointed out. “Sadly,” many first responders have fallen ill to COVID-19 infection, they added.
As of June 1, 29 EMS workers and volunteers across the United States had died of COVID-19.
They are James Villecco, Gregory Hodge, Tony Thomas, Mike Field, John Redd, Idris Bey, Richard Seaberry, and Sal Mancuso of New York; Israel Tolentino, Reuven Maroth, Liana Sá, Kevin Leiva, Frank Molinari, Robert Weber, Robert Tarrant, Solomon Donald, Scott Geiger, John Farrarella, John Careccia, Bill Nauta, and David Pinto of New Jersey; Kevin Bundy, Robert Zerman, and Jeremy Emerich of Pennsylvania; Paul Cary of Colorado; Paul Novicki of Michigan; David Martin of Mississippi; Billy Birmingham of Missouri; and John “JP” Granger of South Carolina.
“We offer their families, friends, and colleagues our sincerest condolences and honor their memory with our highest respect and gratitude,” Dr. Bonow and colleagues wrote.
This study was supported by the City of New York and the Fire Department of the City of New York. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs) that placed a huge burden on first responders, a new analysis shows.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
New York City has the largest and busiest EMS system in the United States, serving a population of more than 8.4 million people and responding to more than 1.5 million calls every year.
To gauge the impact of COVID-19 on first responders, Dr. Prezant and colleagues analyzed data for adults with OHCA who received EMS resuscitation from March 1, when the first case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in the city, through April 25, when EMS call volume had receded to pre-COVID-19 levels.
Compared with the same period in 2019, the COVID-19 period had an excess of 2,653 patients with OHCA who underwent EMS resuscitation attempts (3,989 in 2020 vs. 1,336 in 2019, P < .001), an incidence rate triple that of 2019 (47.5 vs. 15.9 per 100,000).
On the worst day – Monday, April 6 – OHCAs peaked at 305 cases, an increase of nearly 10-fold compared with the same day in 2019.
Despite the surge in cases, the median response time of available EMS units to OHCAs increased by about 1 minute over 2019, a nonsignificant difference. Although the average time varied, median response time during the COVID-19 period was less than 3 minutes.
A more vulnerable group
Compared with 2019, patients suffering OHCA during the pandemic period were older (mean age 72 vs. 68 years), less likely to be white (20% white vs. 33%) and more likely to have hypertension (54% vs. 46%), diabetes (36% vs. 26%), physical limitations (57% vs. 48%) and cardiac rhythms that don’t respond to defibrillator shocks (92% vs. 81%).
Compared with 2019, the COVID-19 period had substantial reductions in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (18% vs. 35%; P < .001) and sustained ROSC (11% vs. 25%; P < .001). The case fatality rate was 90% in the COVID-19 period vs. 75% a year earlier.
“The tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is not just the number of patients infected, but the large increase in OHCAs and deaths,” Dr. Prezant and colleagues said.
Identifying patients with the greatest risk for OHCA and death during the COVID-19 pandemic “should allow for early, targeted interventions in the outpatient setting that could lead to reductions in out-of-hospital deaths,” they noted.
“Vulnerable patient populations need outreach, telephonic medicine, televideo medicine, home visits, not just temperature monitoring but home O2 saturation monitoring,” Dr. Prezant said in an interview. “Barriers need to be removed, not just for this pandemic but for the future – no matter what the trigger is.”
Unsung heroes
In an Editor’s Note in JAMA Cardiology, Robert O. Bonow, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues said the American people owe a debt of gratitude to first responders for their “heroic work” triaging, resuscitating, and transporting thousands of people affected by COVID-19.
“Although the typically bustling NYC streets remained eerily deserted, the characteristic cacophony of sounds of the ‘City that Never Sleeps’ was replaced by sirens wailing all hours of the night,” they wrote.
First responders to OHCAs in the COVID-19 era place themselves at extremely high risk, in some cases without optimal personal protective equipment, they pointed out. “Sadly,” many first responders have fallen ill to COVID-19 infection, they added.
As of June 1, 29 EMS workers and volunteers across the United States had died of COVID-19.
They are James Villecco, Gregory Hodge, Tony Thomas, Mike Field, John Redd, Idris Bey, Richard Seaberry, and Sal Mancuso of New York; Israel Tolentino, Reuven Maroth, Liana Sá, Kevin Leiva, Frank Molinari, Robert Weber, Robert Tarrant, Solomon Donald, Scott Geiger, John Farrarella, John Careccia, Bill Nauta, and David Pinto of New Jersey; Kevin Bundy, Robert Zerman, and Jeremy Emerich of Pennsylvania; Paul Cary of Colorado; Paul Novicki of Michigan; David Martin of Mississippi; Billy Birmingham of Missouri; and John “JP” Granger of South Carolina.
“We offer their families, friends, and colleagues our sincerest condolences and honor their memory with our highest respect and gratitude,” Dr. Bonow and colleagues wrote.
This study was supported by the City of New York and the Fire Department of the City of New York. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Tumor markers are ‘valuable’ for relapse detection in rare CNS tumors
according to a pooled analysis of cooperative group trials.
The findings suggest a role for the routine use of tumor markers for surveillance in CNS-NGGCT patients, said Adriana Fonseca, MD, a pediatric neuro-oncology fellow at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
She presented these findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
This pooled analysis represents the largest prospective cohort to date of relapsed intracranial germ cell tumors, Dr. Fonseca said. The analysis included 483 patients enrolled in five prospective CNS-NGGCT trials between 1989 and 2016. There were 106 patients who relapsed after the end of therapy; the relapsed patients had a median age of 13 years (range, 1-30 years) at diagnosis and 82% were male.
Tumor marker utility
There were 86 patients with tumor marker assessments at diagnosis, and 83 had tumor marker elevations in serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), or both.
The three patients without tumor marker elevations at diagnosis had mixed GCT, choriocarcinoma, and yolk sac tumor, which are usually associated with tumor marker elevation, so this will be investigated further, Dr. Fonseca said.
The sensitivity of tumor markers at diagnosis was 94% for serum, 83% for CSF, and 97% for either serum or CSF.
The median time to relapse was 15.5 months. Relapses were local in 45 patients (44%), distant in 32 (33%), and combined in 22 (21%). Three intracranial relapses were located outside of the radiation field and were classified as distant.
Only two patients presented with isolated tumor marker elevations as the sole evidence of relapse, and the elevations usually preceded the presence of macroscopic disease, Dr. Fonseca said.
At the time of relapse, 88% of patients (n = 73) had tumor marker elevations. The sensitivity of tumor markers was 82% in serum, 85% in CSF, and 88% in either.
To better understand if tumor markers can be used for surveillance, the researchers analyzed data from patients who had either serum or CSF tumor marker levels available at both diagnosis and relapse.
Of the 74 evaluable patients who had elevated tumor markers at diagnosis, 68 had elevated tumor markers at relapse as well. This means 92% of relapsed patients were detectable by tumor markers, Dr. Fonseca said.
“Only six patients had tumor marker–negative relapses, and interestingly, one patient who was tumor marker negative at diagnosis relapsed with tumor markers positive,” she added.
Rationale and next steps
CNS-NGGCTs are rare and heterogeneous tumors that respond best when treated using multimodal approaches, including surgical resection, chemotherapy, and radiation, according to Dr. Fonseca. The 5-year event-free and overall survival rates range from 72%-84% and 82%-93% respectively.
“GCTs are unique as they express tumor markers, such as AFP and beta-HCG, which we know are sensitive and specific and used for diagnostic and monitoring purposes,” Dr. Fonseca said.
Current surveillance strategies use a combination of brain and spine MRI and serum tumor markers with declining frequency over time.
“CSF tumor markers are not performed during follow-up, and they are usually obtained only at the time of relapse,” Dr. Fonseca said. “But what is the best surveillance strategy? We have to remember that some of our patients require sedation to undergo MRI, and recurrent sedations in children have been recently associated with potential detrimental neurocognitive effects.”
Similarly, the administration of gadolinium used for MRI has been associated with an increased risk of renal fibrosis and negative neurological outcomes.
“Additionally, nonspecific areas of enhancement are commonly encountered and can lead to unnecessary further investigations,” Dr. Fonseca said, adding that this can contribute to patients’ and parents’ anxiety and to increased overall health care costs and resource utilization.
Recent Children’s Oncology Group data showed that 98% of patients with extracranial germ cell tumors who relapsed were detectable by tumor markers alone, and this led to a change in surveillance guidelines for those patients. This raised the question as to whether a similar approach could be used in CNS-NCCGTs, Dr. Fonseca explained.
“We hypothesized that tumor markers alone may be sufficient for relapse detection in children and adolescents treated for CNS-NGGCT, and hence, the frequency and associated risk with serial MRIs could be safely avoided,” she said.
Though this study was limited by missing data in some cases, the inclusion of trials from different eras, and the use of different detection techniques across trials, the findings confirm the sensitivity of tumor markers in this setting.
“Tumor markers represent a valuable surveillance strategy with the potential to reduce MRI frequency in these patients,” Dr. Fonseca said. “Additionally, the higher proportion of tumor marker–negative relapses, compared to extracranial GCTs, suggests a different biological behavior. Further studies to investigate the biology of the primary versus relapsed samples in GCTs are currently needed.”
Dr. Fonseca and colleagues are “currently undertaking some correlative outcomes analyses to try to understand if the elevation or nonelevation to tumor markers is correlated with survival. We also would like to elucidate the optimal MRI frequency required for surveillance,” she said.
Dr. Fonseca reported having no disclosures, and the researchers disclosed no funding for the study.
sworcester@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Fonseca A et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 2503.
according to a pooled analysis of cooperative group trials.
The findings suggest a role for the routine use of tumor markers for surveillance in CNS-NGGCT patients, said Adriana Fonseca, MD, a pediatric neuro-oncology fellow at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
She presented these findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
This pooled analysis represents the largest prospective cohort to date of relapsed intracranial germ cell tumors, Dr. Fonseca said. The analysis included 483 patients enrolled in five prospective CNS-NGGCT trials between 1989 and 2016. There were 106 patients who relapsed after the end of therapy; the relapsed patients had a median age of 13 years (range, 1-30 years) at diagnosis and 82% were male.
Tumor marker utility
There were 86 patients with tumor marker assessments at diagnosis, and 83 had tumor marker elevations in serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), or both.
The three patients without tumor marker elevations at diagnosis had mixed GCT, choriocarcinoma, and yolk sac tumor, which are usually associated with tumor marker elevation, so this will be investigated further, Dr. Fonseca said.
The sensitivity of tumor markers at diagnosis was 94% for serum, 83% for CSF, and 97% for either serum or CSF.
The median time to relapse was 15.5 months. Relapses were local in 45 patients (44%), distant in 32 (33%), and combined in 22 (21%). Three intracranial relapses were located outside of the radiation field and were classified as distant.
Only two patients presented with isolated tumor marker elevations as the sole evidence of relapse, and the elevations usually preceded the presence of macroscopic disease, Dr. Fonseca said.
At the time of relapse, 88% of patients (n = 73) had tumor marker elevations. The sensitivity of tumor markers was 82% in serum, 85% in CSF, and 88% in either.
To better understand if tumor markers can be used for surveillance, the researchers analyzed data from patients who had either serum or CSF tumor marker levels available at both diagnosis and relapse.
Of the 74 evaluable patients who had elevated tumor markers at diagnosis, 68 had elevated tumor markers at relapse as well. This means 92% of relapsed patients were detectable by tumor markers, Dr. Fonseca said.
“Only six patients had tumor marker–negative relapses, and interestingly, one patient who was tumor marker negative at diagnosis relapsed with tumor markers positive,” she added.
Rationale and next steps
CNS-NGGCTs are rare and heterogeneous tumors that respond best when treated using multimodal approaches, including surgical resection, chemotherapy, and radiation, according to Dr. Fonseca. The 5-year event-free and overall survival rates range from 72%-84% and 82%-93% respectively.
“GCTs are unique as they express tumor markers, such as AFP and beta-HCG, which we know are sensitive and specific and used for diagnostic and monitoring purposes,” Dr. Fonseca said.
Current surveillance strategies use a combination of brain and spine MRI and serum tumor markers with declining frequency over time.
“CSF tumor markers are not performed during follow-up, and they are usually obtained only at the time of relapse,” Dr. Fonseca said. “But what is the best surveillance strategy? We have to remember that some of our patients require sedation to undergo MRI, and recurrent sedations in children have been recently associated with potential detrimental neurocognitive effects.”
Similarly, the administration of gadolinium used for MRI has been associated with an increased risk of renal fibrosis and negative neurological outcomes.
“Additionally, nonspecific areas of enhancement are commonly encountered and can lead to unnecessary further investigations,” Dr. Fonseca said, adding that this can contribute to patients’ and parents’ anxiety and to increased overall health care costs and resource utilization.
Recent Children’s Oncology Group data showed that 98% of patients with extracranial germ cell tumors who relapsed were detectable by tumor markers alone, and this led to a change in surveillance guidelines for those patients. This raised the question as to whether a similar approach could be used in CNS-NCCGTs, Dr. Fonseca explained.
“We hypothesized that tumor markers alone may be sufficient for relapse detection in children and adolescents treated for CNS-NGGCT, and hence, the frequency and associated risk with serial MRIs could be safely avoided,” she said.
Though this study was limited by missing data in some cases, the inclusion of trials from different eras, and the use of different detection techniques across trials, the findings confirm the sensitivity of tumor markers in this setting.
“Tumor markers represent a valuable surveillance strategy with the potential to reduce MRI frequency in these patients,” Dr. Fonseca said. “Additionally, the higher proportion of tumor marker–negative relapses, compared to extracranial GCTs, suggests a different biological behavior. Further studies to investigate the biology of the primary versus relapsed samples in GCTs are currently needed.”
Dr. Fonseca and colleagues are “currently undertaking some correlative outcomes analyses to try to understand if the elevation or nonelevation to tumor markers is correlated with survival. We also would like to elucidate the optimal MRI frequency required for surveillance,” she said.
Dr. Fonseca reported having no disclosures, and the researchers disclosed no funding for the study.
sworcester@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Fonseca A et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 2503.
according to a pooled analysis of cooperative group trials.
The findings suggest a role for the routine use of tumor markers for surveillance in CNS-NGGCT patients, said Adriana Fonseca, MD, a pediatric neuro-oncology fellow at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
She presented these findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
This pooled analysis represents the largest prospective cohort to date of relapsed intracranial germ cell tumors, Dr. Fonseca said. The analysis included 483 patients enrolled in five prospective CNS-NGGCT trials between 1989 and 2016. There were 106 patients who relapsed after the end of therapy; the relapsed patients had a median age of 13 years (range, 1-30 years) at diagnosis and 82% were male.
Tumor marker utility
There were 86 patients with tumor marker assessments at diagnosis, and 83 had tumor marker elevations in serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), or both.
The three patients without tumor marker elevations at diagnosis had mixed GCT, choriocarcinoma, and yolk sac tumor, which are usually associated with tumor marker elevation, so this will be investigated further, Dr. Fonseca said.
The sensitivity of tumor markers at diagnosis was 94% for serum, 83% for CSF, and 97% for either serum or CSF.
The median time to relapse was 15.5 months. Relapses were local in 45 patients (44%), distant in 32 (33%), and combined in 22 (21%). Three intracranial relapses were located outside of the radiation field and were classified as distant.
Only two patients presented with isolated tumor marker elevations as the sole evidence of relapse, and the elevations usually preceded the presence of macroscopic disease, Dr. Fonseca said.
At the time of relapse, 88% of patients (n = 73) had tumor marker elevations. The sensitivity of tumor markers was 82% in serum, 85% in CSF, and 88% in either.
To better understand if tumor markers can be used for surveillance, the researchers analyzed data from patients who had either serum or CSF tumor marker levels available at both diagnosis and relapse.
Of the 74 evaluable patients who had elevated tumor markers at diagnosis, 68 had elevated tumor markers at relapse as well. This means 92% of relapsed patients were detectable by tumor markers, Dr. Fonseca said.
“Only six patients had tumor marker–negative relapses, and interestingly, one patient who was tumor marker negative at diagnosis relapsed with tumor markers positive,” she added.
Rationale and next steps
CNS-NGGCTs are rare and heterogeneous tumors that respond best when treated using multimodal approaches, including surgical resection, chemotherapy, and radiation, according to Dr. Fonseca. The 5-year event-free and overall survival rates range from 72%-84% and 82%-93% respectively.
“GCTs are unique as they express tumor markers, such as AFP and beta-HCG, which we know are sensitive and specific and used for diagnostic and monitoring purposes,” Dr. Fonseca said.
Current surveillance strategies use a combination of brain and spine MRI and serum tumor markers with declining frequency over time.
“CSF tumor markers are not performed during follow-up, and they are usually obtained only at the time of relapse,” Dr. Fonseca said. “But what is the best surveillance strategy? We have to remember that some of our patients require sedation to undergo MRI, and recurrent sedations in children have been recently associated with potential detrimental neurocognitive effects.”
Similarly, the administration of gadolinium used for MRI has been associated with an increased risk of renal fibrosis and negative neurological outcomes.
“Additionally, nonspecific areas of enhancement are commonly encountered and can lead to unnecessary further investigations,” Dr. Fonseca said, adding that this can contribute to patients’ and parents’ anxiety and to increased overall health care costs and resource utilization.
Recent Children’s Oncology Group data showed that 98% of patients with extracranial germ cell tumors who relapsed were detectable by tumor markers alone, and this led to a change in surveillance guidelines for those patients. This raised the question as to whether a similar approach could be used in CNS-NCCGTs, Dr. Fonseca explained.
“We hypothesized that tumor markers alone may be sufficient for relapse detection in children and adolescents treated for CNS-NGGCT, and hence, the frequency and associated risk with serial MRIs could be safely avoided,” she said.
Though this study was limited by missing data in some cases, the inclusion of trials from different eras, and the use of different detection techniques across trials, the findings confirm the sensitivity of tumor markers in this setting.
“Tumor markers represent a valuable surveillance strategy with the potential to reduce MRI frequency in these patients,” Dr. Fonseca said. “Additionally, the higher proportion of tumor marker–negative relapses, compared to extracranial GCTs, suggests a different biological behavior. Further studies to investigate the biology of the primary versus relapsed samples in GCTs are currently needed.”
Dr. Fonseca and colleagues are “currently undertaking some correlative outcomes analyses to try to understand if the elevation or nonelevation to tumor markers is correlated with survival. We also would like to elucidate the optimal MRI frequency required for surveillance,” she said.
Dr. Fonseca reported having no disclosures, and the researchers disclosed no funding for the study.
sworcester@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Fonseca A et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 2503.
FROM ASCO 2020
Endoscopic full-thickness resection of colorectal lesions appears safe and effective
Endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR) of complex colorectal lesions appears safe and effective, based on prospective data from 20 Dutch hospitals.
Macroscopic complete en bloc resection was achieved in 83.9% of procedures with an adverse event rate of 9.3%, reported lead author Liselotte W. Zwager, a PhD candidate at the University of Amsterdam, and colleagues.
“With the advantage of enabling a transmural resection, eFTR offers an alternative to radical surgery in lesions considered incurable with current resection techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD),” the investigators wrote in Endoscopy.
But more data are needed for widespread adoption, they noted. “Several studies have reported encouraging results on the short-term safety and efficacy of eFTR for numerous indications. However, firm conclusions on clinical results will require analysis of large prospective series of patients in everyday clinical practice.”
The present study provided data from 362 patients who underwent 367 procedures at 5 academic and 15 nonacademic centers in the Netherlands.
Patients were eligible for eFTR if polyps were nonlifting or in difficult-to-reach locations, or if T1 colorectal cancer (CRC) was suspected. In addition, eFTR was performed for subepithelial tumors, and as secondary completion treatment after incomplete endoscopic resection of T1 CRC with a positive or nonassessable resection margin. Lesions greater than 30 mm were excluded because of device diameter constraints.
The primary outcome was macroscopic complete en bloc resection. Secondary outcomes included adverse events, full-thickness resection rate, and clinical success, the latter of which was defined by tumor-free resection margins (R0).
Out of 367 procedures, eFTR was most frequently conducted because of incomplete resection of T1 CRC (41%), followed by nonlifting or difficult-to-reach polyps (36%), suspected T1 CRC (19%), and least often, subepithelial tumors (4%).
Complete en bloc resection was achieved in 83.9% of procedures. Excluding 21 procedures in which eFTR was not performed because of inaccessibility of the lesion (n = 7) or immobility of tissue prohibiting retraction of the lesion into the cap (n = 14), R0 was achieved in 82.4% of cases. Among the same group, full-thickness resection rate was comparable, at 83.2%.
Adverse events occurred in 34 patients (9.3%), among whom 10 (2.7%) underwent emergency surgery for perforations or appendicitis.
“In conclusion,” the investigators wrote, “eFTR is an exciting, innovative resection technique that is clinically feasible and safe for complex colorectal lesions, with the potential to obviate the need for surgical resection. Further efficacy studies on eFTR as a primary and secondary treatment option for T1 CRC are needed, focusing on both the short- and long-term oncologic results.”
Peter V. Draganov, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, called the R0 resection rate “respectable,” and suggested that the study “reconfirms on a larger scale that eFTR with the full-thickness resection device is successful in the majority of cases.”
“The full-thickness resection device expands our armamentarium to remove difficult polyps and early CRC,” he said.
Still, Dr. Draganov, who has previously advised careful patient selection for eFTR, noted certain drawbacks of the technique. “The presented data highlight some of the limitations of the full-thickness resection device, including the relatively small size of the lesion [median diameter, 23 mm] that can be resected, and challenges related to accessing and capturing the lesion due to the limited visibility and maneuverability of the device.”
Ultimately, Dr. Draganov supported the investigators’ call for more data. “Before eFTR becomes a primary modality for management of T1 CRC, we do need follow-up data on long-term cancer-related outcomes,” he said.
The study was supported by Ovesco Endoscopy. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Cook, Ethicon, Olympus, and others.
SOURCE: Zwager LW et al. Endoscopy. 2020 Jun 4. doi: 10.1055/a-1176-1107.
Endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR) of complex colorectal lesions appears safe and effective, based on prospective data from 20 Dutch hospitals.
Macroscopic complete en bloc resection was achieved in 83.9% of procedures with an adverse event rate of 9.3%, reported lead author Liselotte W. Zwager, a PhD candidate at the University of Amsterdam, and colleagues.
“With the advantage of enabling a transmural resection, eFTR offers an alternative to radical surgery in lesions considered incurable with current resection techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD),” the investigators wrote in Endoscopy.
But more data are needed for widespread adoption, they noted. “Several studies have reported encouraging results on the short-term safety and efficacy of eFTR for numerous indications. However, firm conclusions on clinical results will require analysis of large prospective series of patients in everyday clinical practice.”
The present study provided data from 362 patients who underwent 367 procedures at 5 academic and 15 nonacademic centers in the Netherlands.
Patients were eligible for eFTR if polyps were nonlifting or in difficult-to-reach locations, or if T1 colorectal cancer (CRC) was suspected. In addition, eFTR was performed for subepithelial tumors, and as secondary completion treatment after incomplete endoscopic resection of T1 CRC with a positive or nonassessable resection margin. Lesions greater than 30 mm were excluded because of device diameter constraints.
The primary outcome was macroscopic complete en bloc resection. Secondary outcomes included adverse events, full-thickness resection rate, and clinical success, the latter of which was defined by tumor-free resection margins (R0).
Out of 367 procedures, eFTR was most frequently conducted because of incomplete resection of T1 CRC (41%), followed by nonlifting or difficult-to-reach polyps (36%), suspected T1 CRC (19%), and least often, subepithelial tumors (4%).
Complete en bloc resection was achieved in 83.9% of procedures. Excluding 21 procedures in which eFTR was not performed because of inaccessibility of the lesion (n = 7) or immobility of tissue prohibiting retraction of the lesion into the cap (n = 14), R0 was achieved in 82.4% of cases. Among the same group, full-thickness resection rate was comparable, at 83.2%.
Adverse events occurred in 34 patients (9.3%), among whom 10 (2.7%) underwent emergency surgery for perforations or appendicitis.
“In conclusion,” the investigators wrote, “eFTR is an exciting, innovative resection technique that is clinically feasible and safe for complex colorectal lesions, with the potential to obviate the need for surgical resection. Further efficacy studies on eFTR as a primary and secondary treatment option for T1 CRC are needed, focusing on both the short- and long-term oncologic results.”
Peter V. Draganov, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, called the R0 resection rate “respectable,” and suggested that the study “reconfirms on a larger scale that eFTR with the full-thickness resection device is successful in the majority of cases.”
“The full-thickness resection device expands our armamentarium to remove difficult polyps and early CRC,” he said.
Still, Dr. Draganov, who has previously advised careful patient selection for eFTR, noted certain drawbacks of the technique. “The presented data highlight some of the limitations of the full-thickness resection device, including the relatively small size of the lesion [median diameter, 23 mm] that can be resected, and challenges related to accessing and capturing the lesion due to the limited visibility and maneuverability of the device.”
Ultimately, Dr. Draganov supported the investigators’ call for more data. “Before eFTR becomes a primary modality for management of T1 CRC, we do need follow-up data on long-term cancer-related outcomes,” he said.
The study was supported by Ovesco Endoscopy. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Cook, Ethicon, Olympus, and others.
SOURCE: Zwager LW et al. Endoscopy. 2020 Jun 4. doi: 10.1055/a-1176-1107.
Endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR) of complex colorectal lesions appears safe and effective, based on prospective data from 20 Dutch hospitals.
Macroscopic complete en bloc resection was achieved in 83.9% of procedures with an adverse event rate of 9.3%, reported lead author Liselotte W. Zwager, a PhD candidate at the University of Amsterdam, and colleagues.
“With the advantage of enabling a transmural resection, eFTR offers an alternative to radical surgery in lesions considered incurable with current resection techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD),” the investigators wrote in Endoscopy.
But more data are needed for widespread adoption, they noted. “Several studies have reported encouraging results on the short-term safety and efficacy of eFTR for numerous indications. However, firm conclusions on clinical results will require analysis of large prospective series of patients in everyday clinical practice.”
The present study provided data from 362 patients who underwent 367 procedures at 5 academic and 15 nonacademic centers in the Netherlands.
Patients were eligible for eFTR if polyps were nonlifting or in difficult-to-reach locations, or if T1 colorectal cancer (CRC) was suspected. In addition, eFTR was performed for subepithelial tumors, and as secondary completion treatment after incomplete endoscopic resection of T1 CRC with a positive or nonassessable resection margin. Lesions greater than 30 mm were excluded because of device diameter constraints.
The primary outcome was macroscopic complete en bloc resection. Secondary outcomes included adverse events, full-thickness resection rate, and clinical success, the latter of which was defined by tumor-free resection margins (R0).
Out of 367 procedures, eFTR was most frequently conducted because of incomplete resection of T1 CRC (41%), followed by nonlifting or difficult-to-reach polyps (36%), suspected T1 CRC (19%), and least often, subepithelial tumors (4%).
Complete en bloc resection was achieved in 83.9% of procedures. Excluding 21 procedures in which eFTR was not performed because of inaccessibility of the lesion (n = 7) or immobility of tissue prohibiting retraction of the lesion into the cap (n = 14), R0 was achieved in 82.4% of cases. Among the same group, full-thickness resection rate was comparable, at 83.2%.
Adverse events occurred in 34 patients (9.3%), among whom 10 (2.7%) underwent emergency surgery for perforations or appendicitis.
“In conclusion,” the investigators wrote, “eFTR is an exciting, innovative resection technique that is clinically feasible and safe for complex colorectal lesions, with the potential to obviate the need for surgical resection. Further efficacy studies on eFTR as a primary and secondary treatment option for T1 CRC are needed, focusing on both the short- and long-term oncologic results.”
Peter V. Draganov, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, called the R0 resection rate “respectable,” and suggested that the study “reconfirms on a larger scale that eFTR with the full-thickness resection device is successful in the majority of cases.”
“The full-thickness resection device expands our armamentarium to remove difficult polyps and early CRC,” he said.
Still, Dr. Draganov, who has previously advised careful patient selection for eFTR, noted certain drawbacks of the technique. “The presented data highlight some of the limitations of the full-thickness resection device, including the relatively small size of the lesion [median diameter, 23 mm] that can be resected, and challenges related to accessing and capturing the lesion due to the limited visibility and maneuverability of the device.”
Ultimately, Dr. Draganov supported the investigators’ call for more data. “Before eFTR becomes a primary modality for management of T1 CRC, we do need follow-up data on long-term cancer-related outcomes,” he said.
The study was supported by Ovesco Endoscopy. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Cook, Ethicon, Olympus, and others.
SOURCE: Zwager LW et al. Endoscopy. 2020 Jun 4. doi: 10.1055/a-1176-1107.
FROM ENDOSCOPY
Dapagliflozin benefits low-EF heart failure regardless of diuretic dose: DAPA-HF
The DAPA-HF trial has already changed cardiology in opening up a new class of drugs to patients with heart failure (HF), whether or not they have diabetes. Now the trial is yielding clues as to how it benefits them. For now, it’s doing so by process of elimination.
A new analysis suggests that dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) didn’t need help from loop diuretics to cut the risk for clinical events in patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a benefit seen across the spectrum of glycosylated hemoglobin levels and without compromising renal function, said DAPA-HF investigators. Also, use of dapagliflozin and its clinical effects were not associated with changes in loop diuretic dosage. Those findings and others suggest the drug helps in HFrEF at least partly by some other mechanism than its own diuretic effect, the researchers say.
Such insights will likely be important to case-by-case decisions on whether to use the drug, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor once reserved for patients with diabetes, given the recently broader landscape of HF treatment options.
As previously reported from DAPA-HF, with more than 4,700 patients, those who received dapagliflozin showed significant reductions in the primary end point, a composite of cardiovascular (CV) death, HF hospitalization, and urgent HF visit requiring IV therapy over about 18 months. The 45% of patients with and 55% without type 2 diabetes enjoyed about equal benefit in the placebo-controlled trial for that end point, as well as for all-cause mortality.
SGLT2 inhibitors work in diabetes by promoting urinary glucose excretion. That had led some to speculate that its benefit in HFrEF comes primarily from a diuretic effect; the current findings largely put that question to rest.
“Our findings show that treatment with dapagliflozin was effective regardless of diuretic use or diuretic dose. They also show that dapagliflozin did not lead to an increase in renal adverse events or discontinuation of therapy in patients treated with a diuretic,” trialist Alice M. Jackson, MB, ChB, said in an interview.
“In fact, renal adverse events were generally less common in patients treated with dapagliflozin, across the diuretic categories,” said Dr. Jackson, from the University of Glasgow.
Dr. Jackson presented the new analysis at a Late-Breaking Science Session during the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Discoveries virtual meeting. The HFA sessions were conducted virtually this year due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
At baseline, 84% of patients were on conventional diuretics. The post hoc analysis broke out all patients by loop-diuretic dosage level: none; less than 40 mg furosemide equivalents (FE); 40 mg FE; or more than 40 mg FE. Clinical outcomes were similar across the four groups.
Clinicians in the trial “were not given specific advice about adjusting diuretic doses, but were encouraged to assess volume status and make changes to medical therapy based on this, if necessary,” Dr. Jackson said. “This suggests that, for most patients, starting dapagliflozin will not necessitate a change in diuretic dose.”
With the caveat that the event rate was low in the relatively few patients not prescribed loop diuretics, she said, “the magnitude of the benefit from dapagliflozin appeared to be larger in patients not treated with a diuretic.”
There was no suggestion of a diuretic dose–response effect or statistical interaction between diuretic use and clinical outcomes on dapagliflozin, Dr. Jackson observed in the interview.
Of note in the analysis, hematocrit levels shot up soon after patients started active therapy, but they didn’t rise much in the placebo group. The sustained hematocrit elevation on dapagliflozin, seen at all diuretic dosage levels, persisted even after dosage reductions at 6 months, she said.
“Dapagliflozin is effective in HFrEF irrespective of background diuretic therapy; therefore, it is almost certainly not purely acting as a diuretic,” Andrew J. Coats, MD, DSc, MBA, said in an interview.
The findings also “lessen the concern that dapagliflozin’s beneficial effects are only seen only in patients without effective diuretic dosing,” said Dr. Coats, from University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
“Altogether, these data give further reassurance that dapagliflozin can safely be used in heart failure, and has a beneficial effect independent of the use of diuretic drugs,” invited discussant Wolfram Doehner, MD, PhD, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said after Dr. Jackson’s presentation of the analysis.
He made special mention of the sustained hematocrit elevation on dapagliflozin. “While this effect may likely relate to the mild reduction in plasma volume secondary to dapagliflozin therapy, it is noted that the increase in hematocrit was independent of any change of the diuretic dose,” Doehner said. “If additional mechanisms have a role for this observed increase in hematocrit, it may be of interest in further investigations.”
Dr. Jackson pointed to several observations that suggest the hematocrit finding isn’t explained by hemoconcentration from reduced plasma volume, at least not entirely.
For example, hematocrit levels rose “without any suggestion of a relationship between diuretic dose and degree of hematocrit elevation with dapagliflozin,” she said.
The elevations persisted even with diuretic dose reductions at 6 and 12 months, “which should have led to a decrease in hemoconcentration if it was caused by volume contraction.”
Also, she said, “among patients not taking a diuretic, volume depletion occurred less frequently in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group, but there was still a similar rise in hematocrit with dapagliflozin.”
Both Dr. Jackson and Dr. Coats said the sustained elevation in hematocrit on the drug is unlikely to pose a major hazard.
Dr. Coats said that, theoretically, “increased hematocrit could reduce peripheral vessel blood flow, making ischemia and thrombosis more likely. But the size of the effect is small and unlikely to be clinically important.”
A diuretic dose could not be determined for 128 of the trial’s 4,744 randomized patients with HFrEF, so the post hoc analysis was limited to the remaining 4,616. Of those, 746 were not on diuretics at baseline, 1,311 were on loop diuretics at less than 40 mg FE or on non-loop diuretics only, 1,365 were taking 40 mg FE, and 1,204 were on higher doses of loop diuretics.
The mean baseline dosage was 60 mg FE, which rose slightly throughout the trial. But the baseline dosage and the increases were both similar in the placebo and dapagliflozin groups. Dr. Jackson said 84% and 83% of patients on dapagliflozin and placebo, respectively, maintained their baseline dose at 6 months and about 77% in both groups at 12 months.
The overall trial’s significant primary endpoint reduction for dapagliflozin versus placebo applied similarly to patients not on a diuretics and to those on any dose of diuretic, with an interaction P value of .23 for the effect of diuretic use. The hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) were 0.57 (0.36-0.92) for patients not on diuretics, 0.78 (0.68-0.90) for patients on any diuretic dosage, and 0.74 (0.65-0.85) overall
Dr. Jackson said during her formal online presentation that patients on diuretics showed a “tendency toward slightly more volume depletion in those on dapagliflozin than in those on placebo, but the excess was small and not greater than approximately 3% in those taking 40 mg furosemide equivalent diuretic. And fortunately, this did not result in an increase in frequency in renal adverse events nor of discontinuation of study drug.”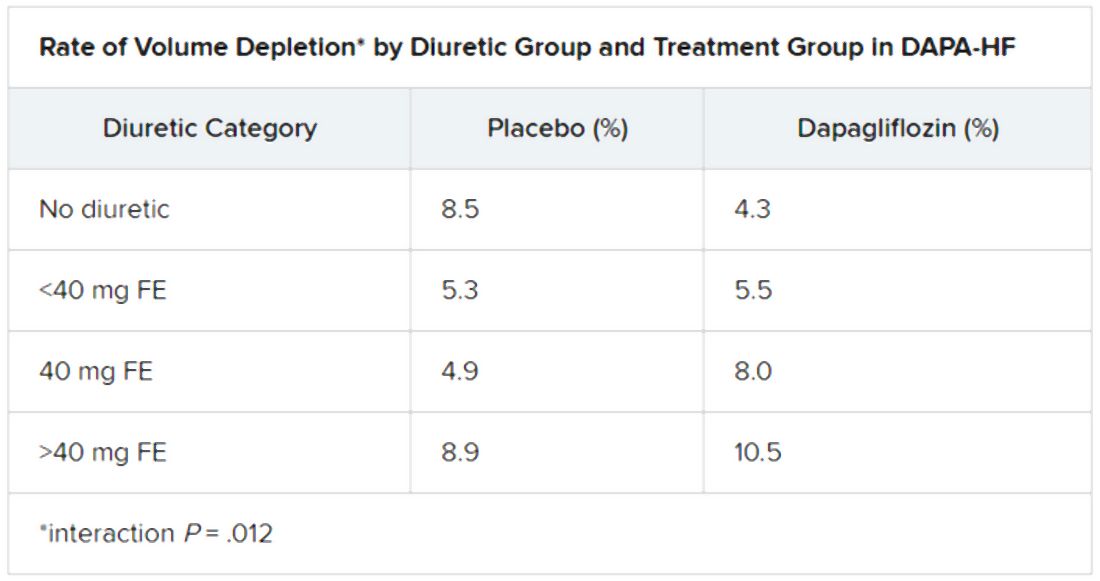
Renal adverse events were similarly prevalent in the two treatment groups, as were such events leading to treatment discontinuation. But serious renal events were less common in the dapagliflozin group (1.6% vs 2.7%; P = .009), as was investigator-reported serious acute kidney injury (1.0% vs 1.9%; P = .007).
“Overall, renal events were infrequent,” Dr. Jackson said, and “because of the small number of events, it is very difficult to draw conclusions about the impact of dapagliflozin on renal function according to diuretic-dose subgroups.”
Still, she said, worsening renal function was less common on dapagliflozin in three of the four groups by diuretic dosage; the exception was the less than 40 mg FE group, “but the absolute difference in this group was only two events.”
There seem to be dapagliflozin mechanisms “underneath the surface that need to be unraveled,” Dr. Doehner said as discussant, processes that are favorable for the treatment of HFrEF in which “diuretics play no big role.”
Dr. Jackson has no disclosures. Dr. Coats has disclosed receiving personal fees from Actimed, AstraZeneca, Faraday, WL Gore, Menarini, Novartis, Nutricia, Respicardia, Servier, Stealth Peptides, Verona, and Vifor. Dr. Doener has recently disclosed receiving grants and personal fees from Vifor, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sphingotec, ZS Pharma, Bayer, and Medtronic.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The DAPA-HF trial has already changed cardiology in opening up a new class of drugs to patients with heart failure (HF), whether or not they have diabetes. Now the trial is yielding clues as to how it benefits them. For now, it’s doing so by process of elimination.
A new analysis suggests that dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) didn’t need help from loop diuretics to cut the risk for clinical events in patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a benefit seen across the spectrum of glycosylated hemoglobin levels and without compromising renal function, said DAPA-HF investigators. Also, use of dapagliflozin and its clinical effects were not associated with changes in loop diuretic dosage. Those findings and others suggest the drug helps in HFrEF at least partly by some other mechanism than its own diuretic effect, the researchers say.
Such insights will likely be important to case-by-case decisions on whether to use the drug, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor once reserved for patients with diabetes, given the recently broader landscape of HF treatment options.
As previously reported from DAPA-HF, with more than 4,700 patients, those who received dapagliflozin showed significant reductions in the primary end point, a composite of cardiovascular (CV) death, HF hospitalization, and urgent HF visit requiring IV therapy over about 18 months. The 45% of patients with and 55% without type 2 diabetes enjoyed about equal benefit in the placebo-controlled trial for that end point, as well as for all-cause mortality.
SGLT2 inhibitors work in diabetes by promoting urinary glucose excretion. That had led some to speculate that its benefit in HFrEF comes primarily from a diuretic effect; the current findings largely put that question to rest.
“Our findings show that treatment with dapagliflozin was effective regardless of diuretic use or diuretic dose. They also show that dapagliflozin did not lead to an increase in renal adverse events or discontinuation of therapy in patients treated with a diuretic,” trialist Alice M. Jackson, MB, ChB, said in an interview.
“In fact, renal adverse events were generally less common in patients treated with dapagliflozin, across the diuretic categories,” said Dr. Jackson, from the University of Glasgow.
Dr. Jackson presented the new analysis at a Late-Breaking Science Session during the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Discoveries virtual meeting. The HFA sessions were conducted virtually this year due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
At baseline, 84% of patients were on conventional diuretics. The post hoc analysis broke out all patients by loop-diuretic dosage level: none; less than 40 mg furosemide equivalents (FE); 40 mg FE; or more than 40 mg FE. Clinical outcomes were similar across the four groups.
Clinicians in the trial “were not given specific advice about adjusting diuretic doses, but were encouraged to assess volume status and make changes to medical therapy based on this, if necessary,” Dr. Jackson said. “This suggests that, for most patients, starting dapagliflozin will not necessitate a change in diuretic dose.”
With the caveat that the event rate was low in the relatively few patients not prescribed loop diuretics, she said, “the magnitude of the benefit from dapagliflozin appeared to be larger in patients not treated with a diuretic.”
There was no suggestion of a diuretic dose–response effect or statistical interaction between diuretic use and clinical outcomes on dapagliflozin, Dr. Jackson observed in the interview.
Of note in the analysis, hematocrit levels shot up soon after patients started active therapy, but they didn’t rise much in the placebo group. The sustained hematocrit elevation on dapagliflozin, seen at all diuretic dosage levels, persisted even after dosage reductions at 6 months, she said.
“Dapagliflozin is effective in HFrEF irrespective of background diuretic therapy; therefore, it is almost certainly not purely acting as a diuretic,” Andrew J. Coats, MD, DSc, MBA, said in an interview.
The findings also “lessen the concern that dapagliflozin’s beneficial effects are only seen only in patients without effective diuretic dosing,” said Dr. Coats, from University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
“Altogether, these data give further reassurance that dapagliflozin can safely be used in heart failure, and has a beneficial effect independent of the use of diuretic drugs,” invited discussant Wolfram Doehner, MD, PhD, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said after Dr. Jackson’s presentation of the analysis.
He made special mention of the sustained hematocrit elevation on dapagliflozin. “While this effect may likely relate to the mild reduction in plasma volume secondary to dapagliflozin therapy, it is noted that the increase in hematocrit was independent of any change of the diuretic dose,” Doehner said. “If additional mechanisms have a role for this observed increase in hematocrit, it may be of interest in further investigations.”
Dr. Jackson pointed to several observations that suggest the hematocrit finding isn’t explained by hemoconcentration from reduced plasma volume, at least not entirely.
For example, hematocrit levels rose “without any suggestion of a relationship between diuretic dose and degree of hematocrit elevation with dapagliflozin,” she said.
The elevations persisted even with diuretic dose reductions at 6 and 12 months, “which should have led to a decrease in hemoconcentration if it was caused by volume contraction.”
Also, she said, “among patients not taking a diuretic, volume depletion occurred less frequently in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group, but there was still a similar rise in hematocrit with dapagliflozin.”
Both Dr. Jackson and Dr. Coats said the sustained elevation in hematocrit on the drug is unlikely to pose a major hazard.
Dr. Coats said that, theoretically, “increased hematocrit could reduce peripheral vessel blood flow, making ischemia and thrombosis more likely. But the size of the effect is small and unlikely to be clinically important.”
A diuretic dose could not be determined for 128 of the trial’s 4,744 randomized patients with HFrEF, so the post hoc analysis was limited to the remaining 4,616. Of those, 746 were not on diuretics at baseline, 1,311 were on loop diuretics at less than 40 mg FE or on non-loop diuretics only, 1,365 were taking 40 mg FE, and 1,204 were on higher doses of loop diuretics.
The mean baseline dosage was 60 mg FE, which rose slightly throughout the trial. But the baseline dosage and the increases were both similar in the placebo and dapagliflozin groups. Dr. Jackson said 84% and 83% of patients on dapagliflozin and placebo, respectively, maintained their baseline dose at 6 months and about 77% in both groups at 12 months.
The overall trial’s significant primary endpoint reduction for dapagliflozin versus placebo applied similarly to patients not on a diuretics and to those on any dose of diuretic, with an interaction P value of .23 for the effect of diuretic use. The hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) were 0.57 (0.36-0.92) for patients not on diuretics, 0.78 (0.68-0.90) for patients on any diuretic dosage, and 0.74 (0.65-0.85) overall
Dr. Jackson said during her formal online presentation that patients on diuretics showed a “tendency toward slightly more volume depletion in those on dapagliflozin than in those on placebo, but the excess was small and not greater than approximately 3% in those taking 40 mg furosemide equivalent diuretic. And fortunately, this did not result in an increase in frequency in renal adverse events nor of discontinuation of study drug.”
Renal adverse events were similarly prevalent in the two treatment groups, as were such events leading to treatment discontinuation. But serious renal events were less common in the dapagliflozin group (1.6% vs 2.7%; P = .009), as was investigator-reported serious acute kidney injury (1.0% vs 1.9%; P = .007).
“Overall, renal events were infrequent,” Dr. Jackson said, and “because of the small number of events, it is very difficult to draw conclusions about the impact of dapagliflozin on renal function according to diuretic-dose subgroups.”
Still, she said, worsening renal function was less common on dapagliflozin in three of the four groups by diuretic dosage; the exception was the less than 40 mg FE group, “but the absolute difference in this group was only two events.”
There seem to be dapagliflozin mechanisms “underneath the surface that need to be unraveled,” Dr. Doehner said as discussant, processes that are favorable for the treatment of HFrEF in which “diuretics play no big role.”
Dr. Jackson has no disclosures. Dr. Coats has disclosed receiving personal fees from Actimed, AstraZeneca, Faraday, WL Gore, Menarini, Novartis, Nutricia, Respicardia, Servier, Stealth Peptides, Verona, and Vifor. Dr. Doener has recently disclosed receiving grants and personal fees from Vifor, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sphingotec, ZS Pharma, Bayer, and Medtronic.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The DAPA-HF trial has already changed cardiology in opening up a new class of drugs to patients with heart failure (HF), whether or not they have diabetes. Now the trial is yielding clues as to how it benefits them. For now, it’s doing so by process of elimination.
A new analysis suggests that dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) didn’t need help from loop diuretics to cut the risk for clinical events in patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a benefit seen across the spectrum of glycosylated hemoglobin levels and without compromising renal function, said DAPA-HF investigators. Also, use of dapagliflozin and its clinical effects were not associated with changes in loop diuretic dosage. Those findings and others suggest the drug helps in HFrEF at least partly by some other mechanism than its own diuretic effect, the researchers say.
Such insights will likely be important to case-by-case decisions on whether to use the drug, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor once reserved for patients with diabetes, given the recently broader landscape of HF treatment options.
As previously reported from DAPA-HF, with more than 4,700 patients, those who received dapagliflozin showed significant reductions in the primary end point, a composite of cardiovascular (CV) death, HF hospitalization, and urgent HF visit requiring IV therapy over about 18 months. The 45% of patients with and 55% without type 2 diabetes enjoyed about equal benefit in the placebo-controlled trial for that end point, as well as for all-cause mortality.
SGLT2 inhibitors work in diabetes by promoting urinary glucose excretion. That had led some to speculate that its benefit in HFrEF comes primarily from a diuretic effect; the current findings largely put that question to rest.
“Our findings show that treatment with dapagliflozin was effective regardless of diuretic use or diuretic dose. They also show that dapagliflozin did not lead to an increase in renal adverse events or discontinuation of therapy in patients treated with a diuretic,” trialist Alice M. Jackson, MB, ChB, said in an interview.
“In fact, renal adverse events were generally less common in patients treated with dapagliflozin, across the diuretic categories,” said Dr. Jackson, from the University of Glasgow.
Dr. Jackson presented the new analysis at a Late-Breaking Science Session during the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Discoveries virtual meeting. The HFA sessions were conducted virtually this year due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
At baseline, 84% of patients were on conventional diuretics. The post hoc analysis broke out all patients by loop-diuretic dosage level: none; less than 40 mg furosemide equivalents (FE); 40 mg FE; or more than 40 mg FE. Clinical outcomes were similar across the four groups.
Clinicians in the trial “were not given specific advice about adjusting diuretic doses, but were encouraged to assess volume status and make changes to medical therapy based on this, if necessary,” Dr. Jackson said. “This suggests that, for most patients, starting dapagliflozin will not necessitate a change in diuretic dose.”
With the caveat that the event rate was low in the relatively few patients not prescribed loop diuretics, she said, “the magnitude of the benefit from dapagliflozin appeared to be larger in patients not treated with a diuretic.”
There was no suggestion of a diuretic dose–response effect or statistical interaction between diuretic use and clinical outcomes on dapagliflozin, Dr. Jackson observed in the interview.
Of note in the analysis, hematocrit levels shot up soon after patients started active therapy, but they didn’t rise much in the placebo group. The sustained hematocrit elevation on dapagliflozin, seen at all diuretic dosage levels, persisted even after dosage reductions at 6 months, she said.
“Dapagliflozin is effective in HFrEF irrespective of background diuretic therapy; therefore, it is almost certainly not purely acting as a diuretic,” Andrew J. Coats, MD, DSc, MBA, said in an interview.
The findings also “lessen the concern that dapagliflozin’s beneficial effects are only seen only in patients without effective diuretic dosing,” said Dr. Coats, from University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
“Altogether, these data give further reassurance that dapagliflozin can safely be used in heart failure, and has a beneficial effect independent of the use of diuretic drugs,” invited discussant Wolfram Doehner, MD, PhD, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said after Dr. Jackson’s presentation of the analysis.
He made special mention of the sustained hematocrit elevation on dapagliflozin. “While this effect may likely relate to the mild reduction in plasma volume secondary to dapagliflozin therapy, it is noted that the increase in hematocrit was independent of any change of the diuretic dose,” Doehner said. “If additional mechanisms have a role for this observed increase in hematocrit, it may be of interest in further investigations.”
Dr. Jackson pointed to several observations that suggest the hematocrit finding isn’t explained by hemoconcentration from reduced plasma volume, at least not entirely.
For example, hematocrit levels rose “without any suggestion of a relationship between diuretic dose and degree of hematocrit elevation with dapagliflozin,” she said.
The elevations persisted even with diuretic dose reductions at 6 and 12 months, “which should have led to a decrease in hemoconcentration if it was caused by volume contraction.”
Also, she said, “among patients not taking a diuretic, volume depletion occurred less frequently in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group, but there was still a similar rise in hematocrit with dapagliflozin.”
Both Dr. Jackson and Dr. Coats said the sustained elevation in hematocrit on the drug is unlikely to pose a major hazard.
Dr. Coats said that, theoretically, “increased hematocrit could reduce peripheral vessel blood flow, making ischemia and thrombosis more likely. But the size of the effect is small and unlikely to be clinically important.”
A diuretic dose could not be determined for 128 of the trial’s 4,744 randomized patients with HFrEF, so the post hoc analysis was limited to the remaining 4,616. Of those, 746 were not on diuretics at baseline, 1,311 were on loop diuretics at less than 40 mg FE or on non-loop diuretics only, 1,365 were taking 40 mg FE, and 1,204 were on higher doses of loop diuretics.
The mean baseline dosage was 60 mg FE, which rose slightly throughout the trial. But the baseline dosage and the increases were both similar in the placebo and dapagliflozin groups. Dr. Jackson said 84% and 83% of patients on dapagliflozin and placebo, respectively, maintained their baseline dose at 6 months and about 77% in both groups at 12 months.
The overall trial’s significant primary endpoint reduction for dapagliflozin versus placebo applied similarly to patients not on a diuretics and to those on any dose of diuretic, with an interaction P value of .23 for the effect of diuretic use. The hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) were 0.57 (0.36-0.92) for patients not on diuretics, 0.78 (0.68-0.90) for patients on any diuretic dosage, and 0.74 (0.65-0.85) overall
Dr. Jackson said during her formal online presentation that patients on diuretics showed a “tendency toward slightly more volume depletion in those on dapagliflozin than in those on placebo, but the excess was small and not greater than approximately 3% in those taking 40 mg furosemide equivalent diuretic. And fortunately, this did not result in an increase in frequency in renal adverse events nor of discontinuation of study drug.”
Renal adverse events were similarly prevalent in the two treatment groups, as were such events leading to treatment discontinuation. But serious renal events were less common in the dapagliflozin group (1.6% vs 2.7%; P = .009), as was investigator-reported serious acute kidney injury (1.0% vs 1.9%; P = .007).
“Overall, renal events were infrequent,” Dr. Jackson said, and “because of the small number of events, it is very difficult to draw conclusions about the impact of dapagliflozin on renal function according to diuretic-dose subgroups.”
Still, she said, worsening renal function was less common on dapagliflozin in three of the four groups by diuretic dosage; the exception was the less than 40 mg FE group, “but the absolute difference in this group was only two events.”
There seem to be dapagliflozin mechanisms “underneath the surface that need to be unraveled,” Dr. Doehner said as discussant, processes that are favorable for the treatment of HFrEF in which “diuretics play no big role.”
Dr. Jackson has no disclosures. Dr. Coats has disclosed receiving personal fees from Actimed, AstraZeneca, Faraday, WL Gore, Menarini, Novartis, Nutricia, Respicardia, Servier, Stealth Peptides, Verona, and Vifor. Dr. Doener has recently disclosed receiving grants and personal fees from Vifor, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sphingotec, ZS Pharma, Bayer, and Medtronic.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2020
VA readmissions program not linked to increased death
with no concurrent increase in 30-day mortality, a large cohort study suggests.
Unlike the Center for Medicare & Medicaid’s Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), whose primary objective is reducing payments to hospitals with excess readmissions, the VA’s efforts to reduce readmissions across their system did not include any financial penalties.
“The intervention focused on encouraging participation in transitions of care programs, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Hospital to Home Initiative and the creation of a heart failure provider network that included more than 900 heart failure providers throughout the VA system,” said the study’s lead author Justin T. Parizo, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University.
The only measuring sticks the VA used were the public reporting of 30-day readmission rates (starting in 2012) and inclusion of those rates into hospitals’ overall star ratings (starting in 2014).
“The readmissions reductions we saw were similar in magnitude to those seen in patients in CMS fee-for-service categories in the HRRP,” said Dr. Parizo. “And while we had no ability to evaluate causality here, our best guess from what we can see is that there’s been no impact of the readmissions program on mortality,” he added.
Their results were published online June 17 in JAMA Cardiology.
Dr. Parizo and colleagues conducted a cohort study of 304,374 heart failure hospital admissions in 164,566 patients from January 2007 to September 2017. Importantly, he stressed, the researchers were able to do sophisticated risk adjustment for illness trends, something that has been a sticking point in some of the HRRP studies to date.
“We leveraged the robust dataset that the VA provides to adjust for illness severity. Accounting for clinical factors, like blood pressure, weight, creatinine, BNP [B-type natriuretic peptide], and other markers of heart failure severity, but also for changes in coding,” said Dr. Parizo.
Stratification according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) showed similar results both in terms of 30-day readmission and 30-day mortality for those with LVEF of 40% or greater and those with LVEF less than 40%.
In an interview, Dr. Parizo noted that they actually saw a small but significant uptick in mortality in the 2011-2012 period (compared with 2007-2008) that remains unexplained. “By the 2015-2017 period, 30-day death had returned to baseline levels,” he said.
In contrast, the HRRP, which was rolled out in 2012, has also been shown to reduce readmissions but, in most studies, 30-day mortality had gone up.
“The VA has a very robust quality infrastructure and a robust mechanism for prioritizing certain quality-improvement goals and getting them accomplished that I think they are underrecognized for,” said Leora Horwitz, MD, MHS, the director of the Center for Healthcare Innovation and Delivery Science at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York.
In an interview, she also noted some concern with the uptick seen in the 2011-2012 period, noting that the increase might be the same signal seen with the HRRP intervention.
“This is around the same time period where other people were writing the HRRP papers that showed an increase in mortality, so that’s something to consider,” she said.
Dr. Horwitz coauthored a study published in 2017 indicating that, on a hospital level (compared with a patient level, the approach most other studies took), reductions in readmissions were only weakly correlated with 30-day mortality rates after discharge.
“So, if you think that a hospital that’s behaving badly and keeping people out of the hospital inappropriately to cut down their readmissions, you’d expect to see increased mortality in that hospital, and in our study there was no correlation whatsoever. So there is still debate as to what is behind the increase in mortality on a patient level with heart failure that we’ve seen in some studies,” she said.
Dr. Horwitz doubts an intervention such as the one undertaken in the VA system – even with its fairly soft-touch “name and shame” component – would work in the non-VA hospital world.
“Those who have been in favor of financial penalties have pointed to the fact that, in general, it’s hard to get health systems to respond without financial alignment, even if it’s not an overt financial incentive,” she said.
“The VA is a unique environment,” she noted. “They have a very strong top-down command control focus where people are kind of used to being told, ‘OK, here are the measures we have to address this year.’ It’s good to see that the system that has worked for them for other outcomes also worked for them for heart failure readmissions too.”
Dr. Parizo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Horwitz has worked under contract to Medicare to develop readmission measures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
with no concurrent increase in 30-day mortality, a large cohort study suggests.
Unlike the Center for Medicare & Medicaid’s Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), whose primary objective is reducing payments to hospitals with excess readmissions, the VA’s efforts to reduce readmissions across their system did not include any financial penalties.
“The intervention focused on encouraging participation in transitions of care programs, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Hospital to Home Initiative and the creation of a heart failure provider network that included more than 900 heart failure providers throughout the VA system,” said the study’s lead author Justin T. Parizo, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University.
The only measuring sticks the VA used were the public reporting of 30-day readmission rates (starting in 2012) and inclusion of those rates into hospitals’ overall star ratings (starting in 2014).
“The readmissions reductions we saw were similar in magnitude to those seen in patients in CMS fee-for-service categories in the HRRP,” said Dr. Parizo. “And while we had no ability to evaluate causality here, our best guess from what we can see is that there’s been no impact of the readmissions program on mortality,” he added.
Their results were published online June 17 in JAMA Cardiology.
Dr. Parizo and colleagues conducted a cohort study of 304,374 heart failure hospital admissions in 164,566 patients from January 2007 to September 2017. Importantly, he stressed, the researchers were able to do sophisticated risk adjustment for illness trends, something that has been a sticking point in some of the HRRP studies to date.
“We leveraged the robust dataset that the VA provides to adjust for illness severity. Accounting for clinical factors, like blood pressure, weight, creatinine, BNP [B-type natriuretic peptide], and other markers of heart failure severity, but also for changes in coding,” said Dr. Parizo.
Stratification according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) showed similar results both in terms of 30-day readmission and 30-day mortality for those with LVEF of 40% or greater and those with LVEF less than 40%.
In an interview, Dr. Parizo noted that they actually saw a small but significant uptick in mortality in the 2011-2012 period (compared with 2007-2008) that remains unexplained. “By the 2015-2017 period, 30-day death had returned to baseline levels,” he said.
In contrast, the HRRP, which was rolled out in 2012, has also been shown to reduce readmissions but, in most studies, 30-day mortality had gone up.
“The VA has a very robust quality infrastructure and a robust mechanism for prioritizing certain quality-improvement goals and getting them accomplished that I think they are underrecognized for,” said Leora Horwitz, MD, MHS, the director of the Center for Healthcare Innovation and Delivery Science at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York.
In an interview, she also noted some concern with the uptick seen in the 2011-2012 period, noting that the increase might be the same signal seen with the HRRP intervention.
“This is around the same time period where other people were writing the HRRP papers that showed an increase in mortality, so that’s something to consider,” she said.
Dr. Horwitz coauthored a study published in 2017 indicating that, on a hospital level (compared with a patient level, the approach most other studies took), reductions in readmissions were only weakly correlated with 30-day mortality rates after discharge.
“So, if you think that a hospital that’s behaving badly and keeping people out of the hospital inappropriately to cut down their readmissions, you’d expect to see increased mortality in that hospital, and in our study there was no correlation whatsoever. So there is still debate as to what is behind the increase in mortality on a patient level with heart failure that we’ve seen in some studies,” she said.
Dr. Horwitz doubts an intervention such as the one undertaken in the VA system – even with its fairly soft-touch “name and shame” component – would work in the non-VA hospital world.
“Those who have been in favor of financial penalties have pointed to the fact that, in general, it’s hard to get health systems to respond without financial alignment, even if it’s not an overt financial incentive,” she said.
“The VA is a unique environment,” she noted. “They have a very strong top-down command control focus where people are kind of used to being told, ‘OK, here are the measures we have to address this year.’ It’s good to see that the system that has worked for them for other outcomes also worked for them for heart failure readmissions too.”
Dr. Parizo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Horwitz has worked under contract to Medicare to develop readmission measures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
with no concurrent increase in 30-day mortality, a large cohort study suggests.
Unlike the Center for Medicare & Medicaid’s Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), whose primary objective is reducing payments to hospitals with excess readmissions, the VA’s efforts to reduce readmissions across their system did not include any financial penalties.
“The intervention focused on encouraging participation in transitions of care programs, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Hospital to Home Initiative and the creation of a heart failure provider network that included more than 900 heart failure providers throughout the VA system,” said the study’s lead author Justin T. Parizo, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University.
The only measuring sticks the VA used were the public reporting of 30-day readmission rates (starting in 2012) and inclusion of those rates into hospitals’ overall star ratings (starting in 2014).
“The readmissions reductions we saw were similar in magnitude to those seen in patients in CMS fee-for-service categories in the HRRP,” said Dr. Parizo. “And while we had no ability to evaluate causality here, our best guess from what we can see is that there’s been no impact of the readmissions program on mortality,” he added.
Their results were published online June 17 in JAMA Cardiology.
Dr. Parizo and colleagues conducted a cohort study of 304,374 heart failure hospital admissions in 164,566 patients from January 2007 to September 2017. Importantly, he stressed, the researchers were able to do sophisticated risk adjustment for illness trends, something that has been a sticking point in some of the HRRP studies to date.
“We leveraged the robust dataset that the VA provides to adjust for illness severity. Accounting for clinical factors, like blood pressure, weight, creatinine, BNP [B-type natriuretic peptide], and other markers of heart failure severity, but also for changes in coding,” said Dr. Parizo.
Stratification according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) showed similar results both in terms of 30-day readmission and 30-day mortality for those with LVEF of 40% or greater and those with LVEF less than 40%.
In an interview, Dr. Parizo noted that they actually saw a small but significant uptick in mortality in the 2011-2012 period (compared with 2007-2008) that remains unexplained. “By the 2015-2017 period, 30-day death had returned to baseline levels,” he said.
In contrast, the HRRP, which was rolled out in 2012, has also been shown to reduce readmissions but, in most studies, 30-day mortality had gone up.
“The VA has a very robust quality infrastructure and a robust mechanism for prioritizing certain quality-improvement goals and getting them accomplished that I think they are underrecognized for,” said Leora Horwitz, MD, MHS, the director of the Center for Healthcare Innovation and Delivery Science at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York.
In an interview, she also noted some concern with the uptick seen in the 2011-2012 period, noting that the increase might be the same signal seen with the HRRP intervention.
“This is around the same time period where other people were writing the HRRP papers that showed an increase in mortality, so that’s something to consider,” she said.
Dr. Horwitz coauthored a study published in 2017 indicating that, on a hospital level (compared with a patient level, the approach most other studies took), reductions in readmissions were only weakly correlated with 30-day mortality rates after discharge.
“So, if you think that a hospital that’s behaving badly and keeping people out of the hospital inappropriately to cut down their readmissions, you’d expect to see increased mortality in that hospital, and in our study there was no correlation whatsoever. So there is still debate as to what is behind the increase in mortality on a patient level with heart failure that we’ve seen in some studies,” she said.
Dr. Horwitz doubts an intervention such as the one undertaken in the VA system – even with its fairly soft-touch “name and shame” component – would work in the non-VA hospital world.
“Those who have been in favor of financial penalties have pointed to the fact that, in general, it’s hard to get health systems to respond without financial alignment, even if it’s not an overt financial incentive,” she said.
“The VA is a unique environment,” she noted. “They have a very strong top-down command control focus where people are kind of used to being told, ‘OK, here are the measures we have to address this year.’ It’s good to see that the system that has worked for them for other outcomes also worked for them for heart failure readmissions too.”
Dr. Parizo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Horwitz has worked under contract to Medicare to develop readmission measures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily Recap: COVID-19 care delays mean excess cancer deaths; flu vaccine recommendations
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
COVID-related care delays mean excess cancer deaths
There could be 10,000 excess deaths from breast and colorectal cancer over the next 10 years as a result of missed screenings, delays in diagnosis, and reductions in oncology care caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to predictions generated by a National Cancer Institute model.
The number of excess deaths per year would peak in the next year or two, likely sooner for colorectal cancer than for breast cancer.
In an editorial published June 19 in Science, NCI Director Norman “Ned” Sharpless, MD, highlighted the modeling. In an interview, he pointed out that this analysis is conservative because the researchers evaluated only two types of cancer. They chose breast and colorectal cancer because these are common cancers – accounting for about one-sixth of all cancers – with relatively high screening rates.
“We didn’t model other cancer types, but we have no reason to think that we’re not going to see the same thing with other types of malignancies,” he said. “That is a significant amount of excess mortality.” Read more.
Diabetes control in U.S. youth has worsened over time
Glycemic control among youth with diabetes is no better today than it was in 2002 and in some subgroups it’s worse, according to data reported at the virtual American Diabetes Association scientific sessions. This finding comes despite the increased availability of diabetes technology, newer therapies, and more aggressive recommended blood glucose targets.
A particularly striking data point was seen among youth who had type 2 diabetes for 10 years or more: average A1c skyrocketed from 7.9% in 2008-2013 to 10.1% in 2014-2019. The numbers were small, 25 patients in the earlier cohort and 149 patients in the later, yet the difference was still statistically significant.
“Our finding that current youth and young adults with diabetes are not demonstrating improved glycemic control, compared to earlier cohorts in the SEARCH study, was surprising given how the landscape of diabetes management has changed dramatically over the past decade,” Faisal S. Malik, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and Seattle Children’s Research Institute, said in an interview. Read more.
CDC advisors approve flu vaccine recommendations for 2020-2021
A pair of new vaccines for adults aged 65 years and older will be available for the 2020-2021 flu season – Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, which replaces the trivalent Fluzone high-dose and Fluad quadrivalent (Seqirus), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
At a virtual meeting on June 24, the committee voted unanimously to approve the vaccine recommendations for annual influenza immunization of all individuals aged 6 months and older. They also voted to accept some guidance and language changes to the recommendations. Read more.
How can we better engage black men as patients?
In a new commentary, Kevin M. Simon, MD, seeks to answer a key question: “How do psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians better engage men of color?” Dr. Simon, a psychiatrist at Boston Children’s Hospital, recommends creating a comfortable environment, allowing for storytelling, assuring confidentiality, being aware of nonverbal language, and being respectful.
“Those on the front lines providing mental health services should understand black men’s mental health from an ecological perspective. Beyond the emotional burden that mental illness imposes on the individual, there are more considerable interpersonal and societal implications for the state of black men’s mental health. As such, in our full capacity like other men, black men play an essential role within families, churches, neighborhoods, and organizations,” Dr. Simon wrote. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
COVID-related care delays mean excess cancer deaths
There could be 10,000 excess deaths from breast and colorectal cancer over the next 10 years as a result of missed screenings, delays in diagnosis, and reductions in oncology care caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to predictions generated by a National Cancer Institute model.
The number of excess deaths per year would peak in the next year or two, likely sooner for colorectal cancer than for breast cancer.
In an editorial published June 19 in Science, NCI Director Norman “Ned” Sharpless, MD, highlighted the modeling. In an interview, he pointed out that this analysis is conservative because the researchers evaluated only two types of cancer. They chose breast and colorectal cancer because these are common cancers – accounting for about one-sixth of all cancers – with relatively high screening rates.
“We didn’t model other cancer types, but we have no reason to think that we’re not going to see the same thing with other types of malignancies,” he said. “That is a significant amount of excess mortality.” Read more.
Diabetes control in U.S. youth has worsened over time
Glycemic control among youth with diabetes is no better today than it was in 2002 and in some subgroups it’s worse, according to data reported at the virtual American Diabetes Association scientific sessions. This finding comes despite the increased availability of diabetes technology, newer therapies, and more aggressive recommended blood glucose targets.
A particularly striking data point was seen among youth who had type 2 diabetes for 10 years or more: average A1c skyrocketed from 7.9% in 2008-2013 to 10.1% in 2014-2019. The numbers were small, 25 patients in the earlier cohort and 149 patients in the later, yet the difference was still statistically significant.
“Our finding that current youth and young adults with diabetes are not demonstrating improved glycemic control, compared to earlier cohorts in the SEARCH study, was surprising given how the landscape of diabetes management has changed dramatically over the past decade,” Faisal S. Malik, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and Seattle Children’s Research Institute, said in an interview. Read more.
CDC advisors approve flu vaccine recommendations for 2020-2021
A pair of new vaccines for adults aged 65 years and older will be available for the 2020-2021 flu season – Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, which replaces the trivalent Fluzone high-dose and Fluad quadrivalent (Seqirus), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
At a virtual meeting on June 24, the committee voted unanimously to approve the vaccine recommendations for annual influenza immunization of all individuals aged 6 months and older. They also voted to accept some guidance and language changes to the recommendations. Read more.
How can we better engage black men as patients?
In a new commentary, Kevin M. Simon, MD, seeks to answer a key question: “How do psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians better engage men of color?” Dr. Simon, a psychiatrist at Boston Children’s Hospital, recommends creating a comfortable environment, allowing for storytelling, assuring confidentiality, being aware of nonverbal language, and being respectful.
“Those on the front lines providing mental health services should understand black men’s mental health from an ecological perspective. Beyond the emotional burden that mental illness imposes on the individual, there are more considerable interpersonal and societal implications for the state of black men’s mental health. As such, in our full capacity like other men, black men play an essential role within families, churches, neighborhoods, and organizations,” Dr. Simon wrote. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
COVID-related care delays mean excess cancer deaths
There could be 10,000 excess deaths from breast and colorectal cancer over the next 10 years as a result of missed screenings, delays in diagnosis, and reductions in oncology care caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to predictions generated by a National Cancer Institute model.
The number of excess deaths per year would peak in the next year or two, likely sooner for colorectal cancer than for breast cancer.
In an editorial published June 19 in Science, NCI Director Norman “Ned” Sharpless, MD, highlighted the modeling. In an interview, he pointed out that this analysis is conservative because the researchers evaluated only two types of cancer. They chose breast and colorectal cancer because these are common cancers – accounting for about one-sixth of all cancers – with relatively high screening rates.
“We didn’t model other cancer types, but we have no reason to think that we’re not going to see the same thing with other types of malignancies,” he said. “That is a significant amount of excess mortality.” Read more.
Diabetes control in U.S. youth has worsened over time
Glycemic control among youth with diabetes is no better today than it was in 2002 and in some subgroups it’s worse, according to data reported at the virtual American Diabetes Association scientific sessions. This finding comes despite the increased availability of diabetes technology, newer therapies, and more aggressive recommended blood glucose targets.
A particularly striking data point was seen among youth who had type 2 diabetes for 10 years or more: average A1c skyrocketed from 7.9% in 2008-2013 to 10.1% in 2014-2019. The numbers were small, 25 patients in the earlier cohort and 149 patients in the later, yet the difference was still statistically significant.
“Our finding that current youth and young adults with diabetes are not demonstrating improved glycemic control, compared to earlier cohorts in the SEARCH study, was surprising given how the landscape of diabetes management has changed dramatically over the past decade,” Faisal S. Malik, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, and Seattle Children’s Research Institute, said in an interview. Read more.
CDC advisors approve flu vaccine recommendations for 2020-2021
A pair of new vaccines for adults aged 65 years and older will be available for the 2020-2021 flu season – Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, which replaces the trivalent Fluzone high-dose and Fluad quadrivalent (Seqirus), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
At a virtual meeting on June 24, the committee voted unanimously to approve the vaccine recommendations for annual influenza immunization of all individuals aged 6 months and older. They also voted to accept some guidance and language changes to the recommendations. Read more.
How can we better engage black men as patients?
In a new commentary, Kevin M. Simon, MD, seeks to answer a key question: “How do psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians better engage men of color?” Dr. Simon, a psychiatrist at Boston Children’s Hospital, recommends creating a comfortable environment, allowing for storytelling, assuring confidentiality, being aware of nonverbal language, and being respectful.
“Those on the front lines providing mental health services should understand black men’s mental health from an ecological perspective. Beyond the emotional burden that mental illness imposes on the individual, there are more considerable interpersonal and societal implications for the state of black men’s mental health. As such, in our full capacity like other men, black men play an essential role within families, churches, neighborhoods, and organizations,” Dr. Simon wrote. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Erythematous Plaques on a Tattoo
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination demonstrated acanthosis and coarse hypergranulosis with enlarged keratinocytes exhibiting blue cytoplasmic discoloration (Figure), which was suggestive of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).
Acquired EV is a rare dermatologic condition associated with specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types that presents with recalcitrant lesions most commonly in the setting of immunosuppression.1 The most common HPV types associated with EV are HPV-5 and -8, but associations with HPV-3, -9, -10, -12, -14, -15, -17, -19 to -25, -36 to -38, -47, and -50 also have been reported.1,2 Acquired EV has been identified in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients with organ transplantation, Hodgkin lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, and IgM deficiency, and in patients taking immunosuppressive medications such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.1,3 The diagnosis is clinicopathological with potential polymerase chain reaction studies to identify underlying HPV types.
Acquired EV presents as hypopigmented to red, tinea versicolor-like macules or as verrucous, flat-topped papules on the trunk, arms, and/or legs.4 Histopathology reveals viral epidermal cytopathic changes, blue cytoplasm, and coarse hypogranulosis.4
There is no standardized treatment regimen for acquired EV, and no single approach has proven to yield an efficacious clinical outcome. Topical treatment options include steroids, retinoids, immunomodulators, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, whereas retinoids or interferon alfa have been used as oral systemic therapy. Photodynamic therapy also has been shown to improve symptoms.3 Combination therapy such as interferon alfa with zidovudine or imiquimod with oral isotretinoin has shown better results than any single treatment.4 Due to the underlying HPV infection and its role in promotion of skin cancer development, lesions can characteristically undergo malignant transformations into Bowen disease but most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), with initial lesions preferentially affecting sun-exposed areas due to the synergistic effect of UV light with EV-HPV lesions. The EV-HPV strains 5, 8, and 41 carry the highest oncogenic potential.5 Little is known of the true incidence of oncogenicity for acquired EV. Regardless, consistent sun protection and lifelong clinical examinations are critical for prognosis.5
The differential diagnosis of EV presenting in a tattoo includes allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous sarcoidosis, pityriasis versicolor, and SCC. The pathology is critical to differentiate between these entities. The most frequently reported skin reactions to tattoo ink include inflammatory diseases (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous reaction) or infectious diseases (eg, bacterial, viral, fungal).6 Allergic contact dermatitis, typically red pigment, is a common tattoo reaction. The most common histologic feature, however, is spongiosis, which results from intercellular edema. It often is limited to the lower epidermis but may affect the upper layers if the reaction is severe.7 Cutaneous sarcoidosis is a great masquerader that can present in various ways; however, its salient features on pathology are noncaseating granuloma involving the basal cell layer and epithelioid granuloma consisting of Langerhans giant cells.8 Although pityriasis versicolor can present in young immunocompromised adults, histologically salient features are the presence of both spores and hyphae in the stratum corneum.9 Although immunosuppression is a known risk factor for SCC, it is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis with thickened and elongated rete ridges. Scattered atypical cells and frequent mitoses are present.10
- Schultz B, Nguyen CV, Jacobson-Dunlop E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in setting of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol Case Rep. 2018;4:805-807.
- DeVilliers EM, Fauquet C, Brocker TR, et al. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17-27.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Berk DR, Bruckner AL, Lu D. Epidermodysplasia verruciform-like lesions in an HIV patient. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:1.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Cappello M, et al. Skin diseases and tattoos: a five-year experience. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:644-648.
- Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:242-259.
- Ferringer T. Granulomatous and histiocytic diseases. In: Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko C, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. China: Elsevier; 2019:175-176.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1329-1346.
- Soyer HP, Rigel DS, McMeniman E. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1887-1884.
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination demonstrated acanthosis and coarse hypergranulosis with enlarged keratinocytes exhibiting blue cytoplasmic discoloration (Figure), which was suggestive of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).

Acquired EV is a rare dermatologic condition associated with specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types that presents with recalcitrant lesions most commonly in the setting of immunosuppression.1 The most common HPV types associated with EV are HPV-5 and -8, but associations with HPV-3, -9, -10, -12, -14, -15, -17, -19 to -25, -36 to -38, -47, and -50 also have been reported.1,2 Acquired EV has been identified in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients with organ transplantation, Hodgkin lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, and IgM deficiency, and in patients taking immunosuppressive medications such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.1,3 The diagnosis is clinicopathological with potential polymerase chain reaction studies to identify underlying HPV types.
Acquired EV presents as hypopigmented to red, tinea versicolor-like macules or as verrucous, flat-topped papules on the trunk, arms, and/or legs.4 Histopathology reveals viral epidermal cytopathic changes, blue cytoplasm, and coarse hypogranulosis.4
There is no standardized treatment regimen for acquired EV, and no single approach has proven to yield an efficacious clinical outcome. Topical treatment options include steroids, retinoids, immunomodulators, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, whereas retinoids or interferon alfa have been used as oral systemic therapy. Photodynamic therapy also has been shown to improve symptoms.3 Combination therapy such as interferon alfa with zidovudine or imiquimod with oral isotretinoin has shown better results than any single treatment.4 Due to the underlying HPV infection and its role in promotion of skin cancer development, lesions can characteristically undergo malignant transformations into Bowen disease but most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), with initial lesions preferentially affecting sun-exposed areas due to the synergistic effect of UV light with EV-HPV lesions. The EV-HPV strains 5, 8, and 41 carry the highest oncogenic potential.5 Little is known of the true incidence of oncogenicity for acquired EV. Regardless, consistent sun protection and lifelong clinical examinations are critical for prognosis.5
The differential diagnosis of EV presenting in a tattoo includes allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous sarcoidosis, pityriasis versicolor, and SCC. The pathology is critical to differentiate between these entities. The most frequently reported skin reactions to tattoo ink include inflammatory diseases (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous reaction) or infectious diseases (eg, bacterial, viral, fungal).6 Allergic contact dermatitis, typically red pigment, is a common tattoo reaction. The most common histologic feature, however, is spongiosis, which results from intercellular edema. It often is limited to the lower epidermis but may affect the upper layers if the reaction is severe.7 Cutaneous sarcoidosis is a great masquerader that can present in various ways; however, its salient features on pathology are noncaseating granuloma involving the basal cell layer and epithelioid granuloma consisting of Langerhans giant cells.8 Although pityriasis versicolor can present in young immunocompromised adults, histologically salient features are the presence of both spores and hyphae in the stratum corneum.9 Although immunosuppression is a known risk factor for SCC, it is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis with thickened and elongated rete ridges. Scattered atypical cells and frequent mitoses are present.10
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination demonstrated acanthosis and coarse hypergranulosis with enlarged keratinocytes exhibiting blue cytoplasmic discoloration (Figure), which was suggestive of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).

Acquired EV is a rare dermatologic condition associated with specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types that presents with recalcitrant lesions most commonly in the setting of immunosuppression.1 The most common HPV types associated with EV are HPV-5 and -8, but associations with HPV-3, -9, -10, -12, -14, -15, -17, -19 to -25, -36 to -38, -47, and -50 also have been reported.1,2 Acquired EV has been identified in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients with organ transplantation, Hodgkin lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, and IgM deficiency, and in patients taking immunosuppressive medications such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.1,3 The diagnosis is clinicopathological with potential polymerase chain reaction studies to identify underlying HPV types.
Acquired EV presents as hypopigmented to red, tinea versicolor-like macules or as verrucous, flat-topped papules on the trunk, arms, and/or legs.4 Histopathology reveals viral epidermal cytopathic changes, blue cytoplasm, and coarse hypogranulosis.4
There is no standardized treatment regimen for acquired EV, and no single approach has proven to yield an efficacious clinical outcome. Topical treatment options include steroids, retinoids, immunomodulators, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, whereas retinoids or interferon alfa have been used as oral systemic therapy. Photodynamic therapy also has been shown to improve symptoms.3 Combination therapy such as interferon alfa with zidovudine or imiquimod with oral isotretinoin has shown better results than any single treatment.4 Due to the underlying HPV infection and its role in promotion of skin cancer development, lesions can characteristically undergo malignant transformations into Bowen disease but most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), with initial lesions preferentially affecting sun-exposed areas due to the synergistic effect of UV light with EV-HPV lesions. The EV-HPV strains 5, 8, and 41 carry the highest oncogenic potential.5 Little is known of the true incidence of oncogenicity for acquired EV. Regardless, consistent sun protection and lifelong clinical examinations are critical for prognosis.5
The differential diagnosis of EV presenting in a tattoo includes allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous sarcoidosis, pityriasis versicolor, and SCC. The pathology is critical to differentiate between these entities. The most frequently reported skin reactions to tattoo ink include inflammatory diseases (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous reaction) or infectious diseases (eg, bacterial, viral, fungal).6 Allergic contact dermatitis, typically red pigment, is a common tattoo reaction. The most common histologic feature, however, is spongiosis, which results from intercellular edema. It often is limited to the lower epidermis but may affect the upper layers if the reaction is severe.7 Cutaneous sarcoidosis is a great masquerader that can present in various ways; however, its salient features on pathology are noncaseating granuloma involving the basal cell layer and epithelioid granuloma consisting of Langerhans giant cells.8 Although pityriasis versicolor can present in young immunocompromised adults, histologically salient features are the presence of both spores and hyphae in the stratum corneum.9 Although immunosuppression is a known risk factor for SCC, it is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis with thickened and elongated rete ridges. Scattered atypical cells and frequent mitoses are present.10
- Schultz B, Nguyen CV, Jacobson-Dunlop E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in setting of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol Case Rep. 2018;4:805-807.
- DeVilliers EM, Fauquet C, Brocker TR, et al. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17-27.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Berk DR, Bruckner AL, Lu D. Epidermodysplasia verruciform-like lesions in an HIV patient. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:1.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Cappello M, et al. Skin diseases and tattoos: a five-year experience. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:644-648.
- Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:242-259.
- Ferringer T. Granulomatous and histiocytic diseases. In: Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko C, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. China: Elsevier; 2019:175-176.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1329-1346.
- Soyer HP, Rigel DS, McMeniman E. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1887-1884.
- Schultz B, Nguyen CV, Jacobson-Dunlop E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in setting of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol Case Rep. 2018;4:805-807.
- DeVilliers EM, Fauquet C, Brocker TR, et al. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17-27.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Berk DR, Bruckner AL, Lu D. Epidermodysplasia verruciform-like lesions in an HIV patient. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:1.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Cappello M, et al. Skin diseases and tattoos: a five-year experience. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:644-648.
- Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:242-259.
- Ferringer T. Granulomatous and histiocytic diseases. In: Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko C, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. China: Elsevier; 2019:175-176.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1329-1346.
- Soyer HP, Rigel DS, McMeniman E. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1887-1884.
A 29-year-old man presented with increased redness, dryness, and pruritus at the periphery of a tattoo (arrows) on the upper back of 4 months' duration. He was diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus 8 months prior to presentation and had a history of cystic fibrosis, eczema, and genital molluscum contagiosum. Laboratory analysis 1 month prior revealed a CD4 count of 42 cells/mm3 (reference range, 500-1200 cells/mm3), and the viral load was 2388 copies/mL (reference range, 20-10,000,000 copies/mL). Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous, eczematous, linear plaques along the dark gray lines of the tattoo. A 1.1.2 ×0.7.2 ×0.1-cm shave biopsy specimen was obtained. After the biopsy, tretinoin cream 0.1% and betamethasone dipropionate ointment 0.05% were prescribed to be alternately applied on the tattoo lesions until resolution.
Suicide thoughts, attempts in adolescence correlate with mental health symptoms
About one in five adolescents has thought about suicide, about 10% have experienced serious suicidal ideation, and 7% have attempted suicide by age 20 years, according to a longitudinal study of Canadian adolescents published online in Pediatrics.
In multivariable analyses, depression and anxiety were independently associated with passive and serious suicidal ideation at some ages, but none of the externalizing problems were significantly associated with passive or serious suicidal ideation. However, “both depressive and conduct symptoms [were] independently associated with suicidal risk,” the researchers found. Most adolescents with suicidal ideation or suicide attempt met criteria for at least one mental health problem.
“These findings suggest that suicide risk should be systematically assessed in adolescents who present with mental health symptoms and not solely in adolescents with clinically diagnosed mental disorders,” said Massimiliano Orri, PhD, and colleagues. Dr. Orri is affiliated with the McGill Group for Suicide Studies, Douglas Mental Health University Institute, Montreal, and the University of Bordeaux (France).
To document the prevalence of passive or serious suicidal ideation and suicide attempt from ages 13-20 years and examine correlations with mental health symptoms, Dr. Orri and colleagues analyzed data from 1,618 participants in the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development. The population-based study follows individuals born in 1997 and 1998 in Quebec. Participants answered questions about suicidal ideation or suicide attempt in the past year at ages 13, 15, 17, or 20 years (“Did you ever think about suicide?” “Did you ever seriously think of attempting suicide?” and “How many times did you attempt suicide?”). The researchers assessed symptoms of mental health problems using self-report questionnaires.
Lifetime prevalence of suicide-related outcomes was higher for female participants than for male participants. The prevalence of passive suicidal ideation was 28% in females versus 15% in males. The prevalence of serious suicidal ideation was 12% in females versus 8% in males. The prevalence of suicide attempt was 9% in females versus 4% in males. “Sex differences in suicidal ideation and suicide attempt might be attributed to various factors, such as mental health (e.g., higher prevalence of depression in female participants) or social stigma (e.g., greater stigma around suicide in male than in female participants),” the authors wrote.
In the entire cohort, the prevalence of passive suicidal ideation increased from 12% at 13 years to 18% at 17 years. The prevalence of serious suicidal ideation increased from 3% at 13 years to 10% at 20 years. The prevalence of suicide attempt was approximately 4% at each age.
“Although having a major depressive episode is a well-known risk factor of suicidal ideation and suicide attempt, our study adds to the general body of knowledge by showing associations with suicide-related outcomes across the full spectrum of depressive symptoms,” Dr. Orri and colleagues wrote. “This suggests that youth who present with depressive symptoms (and not solely those who are clinically depressed) may be more likely to experience suicidal ideation or attempt suicide.”
The estimated rates of serious suicidal ideation and attempted suicide by age 20 years are consistent with previous U.S. and Canadian surveys. Sample attrition, the use of different questionnaires in early and late adolescence, and the lack of information about substance use and psychotic symptoms are among the study’s limitations.
Six of the authors were supported by grants from a variety of Canadian and European agencies and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. All of the authors said they had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Orri M et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jun 8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3823.
Interestingly, this study by Orri et al. found that there was not a peak in suicide attempts in mid-adolescence; instead, rates of attempts were stable throughout adolescence and serious suicidal ideation actually increased with age. This was an unexpected finding for me, and something I will be more mindful about in my clinical practice when seeing older teens and young adults. Additionally, all mental health problems – not just depression – evaluated in univariate analyses in the study were associated with suicidal thoughts and attempts. On multivariable analysis that accounted for the impact of the effect of comorbid mental health symptoms, depressive symptoms had the highest and most consistent correlation to suicidal thoughts, and conduct symptoms were associated with an increase in suicide attempts. The authors conclude that youth with mental health symptoms – not just those who meet diagnostic criteria – should be assessed for suicide risk.
In my subspecialty practice, we screen every new patient for suicide regardless of the reason for their visit and more often for those with mental health symptoms. I know this may seem onerous, but screening and counseling typically take under 5 minutes – and in many instances around 1-2 minutes. Having ready-to-go resources including mental health professionals to refer to, screening algorithms (such as protocols published in MedEdPORTAL or Family Practice Management), and suicide prevention resources for patients and family for those who screen positive can help expedite this process. I think these recommendations can be adapted with relative ease into any visit for a teen or young adult who is presenting with a mental health complaint.
Kelly A. Curran, MD, is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma in Oklahoma City. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. Dr. Curran said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Interestingly, this study by Orri et al. found that there was not a peak in suicide attempts in mid-adolescence; instead, rates of attempts were stable throughout adolescence and serious suicidal ideation actually increased with age. This was an unexpected finding for me, and something I will be more mindful about in my clinical practice when seeing older teens and young adults. Additionally, all mental health problems – not just depression – evaluated in univariate analyses in the study were associated with suicidal thoughts and attempts. On multivariable analysis that accounted for the impact of the effect of comorbid mental health symptoms, depressive symptoms had the highest and most consistent correlation to suicidal thoughts, and conduct symptoms were associated with an increase in suicide attempts. The authors conclude that youth with mental health symptoms – not just those who meet diagnostic criteria – should be assessed for suicide risk.
In my subspecialty practice, we screen every new patient for suicide regardless of the reason for their visit and more often for those with mental health symptoms. I know this may seem onerous, but screening and counseling typically take under 5 minutes – and in many instances around 1-2 minutes. Having ready-to-go resources including mental health professionals to refer to, screening algorithms (such as protocols published in MedEdPORTAL or Family Practice Management), and suicide prevention resources for patients and family for those who screen positive can help expedite this process. I think these recommendations can be adapted with relative ease into any visit for a teen or young adult who is presenting with a mental health complaint.
Kelly A. Curran, MD, is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma in Oklahoma City. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. Dr. Curran said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Interestingly, this study by Orri et al. found that there was not a peak in suicide attempts in mid-adolescence; instead, rates of attempts were stable throughout adolescence and serious suicidal ideation actually increased with age. This was an unexpected finding for me, and something I will be more mindful about in my clinical practice when seeing older teens and young adults. Additionally, all mental health problems – not just depression – evaluated in univariate analyses in the study were associated with suicidal thoughts and attempts. On multivariable analysis that accounted for the impact of the effect of comorbid mental health symptoms, depressive symptoms had the highest and most consistent correlation to suicidal thoughts, and conduct symptoms were associated with an increase in suicide attempts. The authors conclude that youth with mental health symptoms – not just those who meet diagnostic criteria – should be assessed for suicide risk.
In my subspecialty practice, we screen every new patient for suicide regardless of the reason for their visit and more often for those with mental health symptoms. I know this may seem onerous, but screening and counseling typically take under 5 minutes – and in many instances around 1-2 minutes. Having ready-to-go resources including mental health professionals to refer to, screening algorithms (such as protocols published in MedEdPORTAL or Family Practice Management), and suicide prevention resources for patients and family for those who screen positive can help expedite this process. I think these recommendations can be adapted with relative ease into any visit for a teen or young adult who is presenting with a mental health complaint.
Kelly A. Curran, MD, is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma in Oklahoma City. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. Dr. Curran said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
About one in five adolescents has thought about suicide, about 10% have experienced serious suicidal ideation, and 7% have attempted suicide by age 20 years, according to a longitudinal study of Canadian adolescents published online in Pediatrics.
In multivariable analyses, depression and anxiety were independently associated with passive and serious suicidal ideation at some ages, but none of the externalizing problems were significantly associated with passive or serious suicidal ideation. However, “both depressive and conduct symptoms [were] independently associated with suicidal risk,” the researchers found. Most adolescents with suicidal ideation or suicide attempt met criteria for at least one mental health problem.
“These findings suggest that suicide risk should be systematically assessed in adolescents who present with mental health symptoms and not solely in adolescents with clinically diagnosed mental disorders,” said Massimiliano Orri, PhD, and colleagues. Dr. Orri is affiliated with the McGill Group for Suicide Studies, Douglas Mental Health University Institute, Montreal, and the University of Bordeaux (France).
To document the prevalence of passive or serious suicidal ideation and suicide attempt from ages 13-20 years and examine correlations with mental health symptoms, Dr. Orri and colleagues analyzed data from 1,618 participants in the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development. The population-based study follows individuals born in 1997 and 1998 in Quebec. Participants answered questions about suicidal ideation or suicide attempt in the past year at ages 13, 15, 17, or 20 years (“Did you ever think about suicide?” “Did you ever seriously think of attempting suicide?” and “How many times did you attempt suicide?”). The researchers assessed symptoms of mental health problems using self-report questionnaires.
Lifetime prevalence of suicide-related outcomes was higher for female participants than for male participants. The prevalence of passive suicidal ideation was 28% in females versus 15% in males. The prevalence of serious suicidal ideation was 12% in females versus 8% in males. The prevalence of suicide attempt was 9% in females versus 4% in males. “Sex differences in suicidal ideation and suicide attempt might be attributed to various factors, such as mental health (e.g., higher prevalence of depression in female participants) or social stigma (e.g., greater stigma around suicide in male than in female participants),” the authors wrote.
In the entire cohort, the prevalence of passive suicidal ideation increased from 12% at 13 years to 18% at 17 years. The prevalence of serious suicidal ideation increased from 3% at 13 years to 10% at 20 years. The prevalence of suicide attempt was approximately 4% at each age.
“Although having a major depressive episode is a well-known risk factor of suicidal ideation and suicide attempt, our study adds to the general body of knowledge by showing associations with suicide-related outcomes across the full spectrum of depressive symptoms,” Dr. Orri and colleagues wrote. “This suggests that youth who present with depressive symptoms (and not solely those who are clinically depressed) may be more likely to experience suicidal ideation or attempt suicide.”
The estimated rates of serious suicidal ideation and attempted suicide by age 20 years are consistent with previous U.S. and Canadian surveys. Sample attrition, the use of different questionnaires in early and late adolescence, and the lack of information about substance use and psychotic symptoms are among the study’s limitations.
Six of the authors were supported by grants from a variety of Canadian and European agencies and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. All of the authors said they had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Orri M et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jun 8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3823.
About one in five adolescents has thought about suicide, about 10% have experienced serious suicidal ideation, and 7% have attempted suicide by age 20 years, according to a longitudinal study of Canadian adolescents published online in Pediatrics.
In multivariable analyses, depression and anxiety were independently associated with passive and serious suicidal ideation at some ages, but none of the externalizing problems were significantly associated with passive or serious suicidal ideation. However, “both depressive and conduct symptoms [were] independently associated with suicidal risk,” the researchers found. Most adolescents with suicidal ideation or suicide attempt met criteria for at least one mental health problem.
“These findings suggest that suicide risk should be systematically assessed in adolescents who present with mental health symptoms and not solely in adolescents with clinically diagnosed mental disorders,” said Massimiliano Orri, PhD, and colleagues. Dr. Orri is affiliated with the McGill Group for Suicide Studies, Douglas Mental Health University Institute, Montreal, and the University of Bordeaux (France).
To document the prevalence of passive or serious suicidal ideation and suicide attempt from ages 13-20 years and examine correlations with mental health symptoms, Dr. Orri and colleagues analyzed data from 1,618 participants in the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development. The population-based study follows individuals born in 1997 and 1998 in Quebec. Participants answered questions about suicidal ideation or suicide attempt in the past year at ages 13, 15, 17, or 20 years (“Did you ever think about suicide?” “Did you ever seriously think of attempting suicide?” and “How many times did you attempt suicide?”). The researchers assessed symptoms of mental health problems using self-report questionnaires.
Lifetime prevalence of suicide-related outcomes was higher for female participants than for male participants. The prevalence of passive suicidal ideation was 28% in females versus 15% in males. The prevalence of serious suicidal ideation was 12% in females versus 8% in males. The prevalence of suicide attempt was 9% in females versus 4% in males. “Sex differences in suicidal ideation and suicide attempt might be attributed to various factors, such as mental health (e.g., higher prevalence of depression in female participants) or social stigma (e.g., greater stigma around suicide in male than in female participants),” the authors wrote.
In the entire cohort, the prevalence of passive suicidal ideation increased from 12% at 13 years to 18% at 17 years. The prevalence of serious suicidal ideation increased from 3% at 13 years to 10% at 20 years. The prevalence of suicide attempt was approximately 4% at each age.
“Although having a major depressive episode is a well-known risk factor of suicidal ideation and suicide attempt, our study adds to the general body of knowledge by showing associations with suicide-related outcomes across the full spectrum of depressive symptoms,” Dr. Orri and colleagues wrote. “This suggests that youth who present with depressive symptoms (and not solely those who are clinically depressed) may be more likely to experience suicidal ideation or attempt suicide.”
The estimated rates of serious suicidal ideation and attempted suicide by age 20 years are consistent with previous U.S. and Canadian surveys. Sample attrition, the use of different questionnaires in early and late adolescence, and the lack of information about substance use and psychotic symptoms are among the study’s limitations.
Six of the authors were supported by grants from a variety of Canadian and European agencies and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. All of the authors said they had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Orri M et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jun 8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3823.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Personalized cancer vaccine may enhance checkpoint inhibitor activity
Combining a personalized cancer vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor induced neoantigen-specific immune responses in most patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1b study.
Only two clinical responses were seen in this early investigation of the vaccine, RO7198457, combined with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab. However, T-cell responses were observed in about three-quarters of the patients evaluated, according to study investigator Juanita Lopez, MB BChir, PhD.
Those immune responses, coupled with preliminary evidence of infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells into tumors, suggest the viability of this individualized anticancer strategy, according to Dr. Lopez, a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
“Failure of T-cell priming is a major cause of lack of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Lopez said in an interview. “We hoped that, by eliciting a tumor-specific T-cell response, we would be able to overcome this.”
Preclinical data suggested the combination of vaccine and immune checkpoint inhibitors improved outcomes, which prompted the current study, added Dr. Lopez, who presented results from this study at the American Association for Cancer Research virtual meeting II.
Dr. Lopez noted that mutated neoantigens are recognized as foreign and have been shown to induce stronger T-cell responses, compared with shared antigens, likely because of a lack of central tolerance.
“Most of these mutated neoantigens are not shared between the patients, and therefore, targeted neoantigen-specific therapy requires an individualized approach,” she explained.
RO7198457 is manufactured on a per-patient basis and includes as many as 20 tumor-specific neoepitopes.
Study details
Dr. Lopez presented results from dose-escalation and expansion cohorts of the study, which included 142 patients with advanced solid tumors. The patients had colorectal, skin, kidney, lung, urothelial, breast, gynecologic, and head and neck cancers.
Most patients had low or no PD-L1 expression, and nearly 40% had received prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Patients received nine doses of RO7198457 at 25-50 mcg during the 12-week induction stage. They then received RO7198457 every eight cycles until disease progression. Patients received atezolizumab at 1,200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle.
Induction of proinflammatory cytokines was observed at each dose tested, and ex vivo T-cell responses were noted in 46 of 63 patients evaluated, or 73%.
T-cell receptors specific to RO7198457 were present posttreatment in a patient with rectal cancer, providing some preliminary evidence suggesting infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells in the tumor, Dr. Lopez said.
There were two clinical responses. A patient with rectal cancer had a complete response, and a patient with triple-negative breast cancer had a partial response.
The combination of RO7198457 with atezolizumab was generally well tolerated, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached, Dr. Lopez said. Most adverse events were grade 1/2, and immune-mediated adverse events were rare.
Implications and next steps
This study furthers earlier observations from neoantigen vaccine studies by linking dosing of the vaccine to dosing with immune checkpoint inhibitor, rather than giving the vaccine in the period leading up to immune checkpoint inhibitor administration, according to former AACR President Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, both in Columbus.
That said, the implications for clinical practice remain unclear, according to Dr. Mardis.
“This combination did elicit an immune response that was highly specific for the neoantigen vaccine, but most patients did not receive a clinical benefit of disease response,” Dr. Mardis said in an interview. “This tells us the combination approach used was, overall, not quite right, and we need to continue to innovate in this area.”
The low clinical response rate in the study was likely caused in part by the fact that patients had very advanced disease and were heavily pretreated, according to Dr. Lopez
Randomized phase 2 studies of RO7198457 are now underway, Dr. Lopez said. One is a study of RO7198457 plus atezolizumab as adjuvant treatment for non–small cell lung cancer (NCT04267237). Another is testing RO7198457 in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for melanoma (NCT03815058).
The current study was funded by Genentech and BioNTech. Dr. Lopez reported disclosures related to Roche/Genentech, Basilea Pharmaceutica, and Genmab. Dr. Mardis reported disclosures related to Quiagen NV, PACT Pharma, Kiadis Pharma NV, and Interpreta.
SOURCE: Lopez J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT301.
Combining a personalized cancer vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor induced neoantigen-specific immune responses in most patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1b study.
Only two clinical responses were seen in this early investigation of the vaccine, RO7198457, combined with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab. However, T-cell responses were observed in about three-quarters of the patients evaluated, according to study investigator Juanita Lopez, MB BChir, PhD.
Those immune responses, coupled with preliminary evidence of infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells into tumors, suggest the viability of this individualized anticancer strategy, according to Dr. Lopez, a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
“Failure of T-cell priming is a major cause of lack of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Lopez said in an interview. “We hoped that, by eliciting a tumor-specific T-cell response, we would be able to overcome this.”
Preclinical data suggested the combination of vaccine and immune checkpoint inhibitors improved outcomes, which prompted the current study, added Dr. Lopez, who presented results from this study at the American Association for Cancer Research virtual meeting II.
Dr. Lopez noted that mutated neoantigens are recognized as foreign and have been shown to induce stronger T-cell responses, compared with shared antigens, likely because of a lack of central tolerance.
“Most of these mutated neoantigens are not shared between the patients, and therefore, targeted neoantigen-specific therapy requires an individualized approach,” she explained.
RO7198457 is manufactured on a per-patient basis and includes as many as 20 tumor-specific neoepitopes.
Study details
Dr. Lopez presented results from dose-escalation and expansion cohorts of the study, which included 142 patients with advanced solid tumors. The patients had colorectal, skin, kidney, lung, urothelial, breast, gynecologic, and head and neck cancers.
Most patients had low or no PD-L1 expression, and nearly 40% had received prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Patients received nine doses of RO7198457 at 25-50 mcg during the 12-week induction stage. They then received RO7198457 every eight cycles until disease progression. Patients received atezolizumab at 1,200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle.
Induction of proinflammatory cytokines was observed at each dose tested, and ex vivo T-cell responses were noted in 46 of 63 patients evaluated, or 73%.
T-cell receptors specific to RO7198457 were present posttreatment in a patient with rectal cancer, providing some preliminary evidence suggesting infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells in the tumor, Dr. Lopez said.
There were two clinical responses. A patient with rectal cancer had a complete response, and a patient with triple-negative breast cancer had a partial response.
The combination of RO7198457 with atezolizumab was generally well tolerated, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached, Dr. Lopez said. Most adverse events were grade 1/2, and immune-mediated adverse events were rare.
Implications and next steps
This study furthers earlier observations from neoantigen vaccine studies by linking dosing of the vaccine to dosing with immune checkpoint inhibitor, rather than giving the vaccine in the period leading up to immune checkpoint inhibitor administration, according to former AACR President Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, both in Columbus.
That said, the implications for clinical practice remain unclear, according to Dr. Mardis.
“This combination did elicit an immune response that was highly specific for the neoantigen vaccine, but most patients did not receive a clinical benefit of disease response,” Dr. Mardis said in an interview. “This tells us the combination approach used was, overall, not quite right, and we need to continue to innovate in this area.”
The low clinical response rate in the study was likely caused in part by the fact that patients had very advanced disease and were heavily pretreated, according to Dr. Lopez
Randomized phase 2 studies of RO7198457 are now underway, Dr. Lopez said. One is a study of RO7198457 plus atezolizumab as adjuvant treatment for non–small cell lung cancer (NCT04267237). Another is testing RO7198457 in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for melanoma (NCT03815058).
The current study was funded by Genentech and BioNTech. Dr. Lopez reported disclosures related to Roche/Genentech, Basilea Pharmaceutica, and Genmab. Dr. Mardis reported disclosures related to Quiagen NV, PACT Pharma, Kiadis Pharma NV, and Interpreta.
SOURCE: Lopez J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT301.
Combining a personalized cancer vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor induced neoantigen-specific immune responses in most patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1b study.
Only two clinical responses were seen in this early investigation of the vaccine, RO7198457, combined with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab. However, T-cell responses were observed in about three-quarters of the patients evaluated, according to study investigator Juanita Lopez, MB BChir, PhD.
Those immune responses, coupled with preliminary evidence of infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells into tumors, suggest the viability of this individualized anticancer strategy, according to Dr. Lopez, a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
“Failure of T-cell priming is a major cause of lack of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Lopez said in an interview. “We hoped that, by eliciting a tumor-specific T-cell response, we would be able to overcome this.”
Preclinical data suggested the combination of vaccine and immune checkpoint inhibitors improved outcomes, which prompted the current study, added Dr. Lopez, who presented results from this study at the American Association for Cancer Research virtual meeting II.
Dr. Lopez noted that mutated neoantigens are recognized as foreign and have been shown to induce stronger T-cell responses, compared with shared antigens, likely because of a lack of central tolerance.
“Most of these mutated neoantigens are not shared between the patients, and therefore, targeted neoantigen-specific therapy requires an individualized approach,” she explained.
RO7198457 is manufactured on a per-patient basis and includes as many as 20 tumor-specific neoepitopes.
Study details
Dr. Lopez presented results from dose-escalation and expansion cohorts of the study, which included 142 patients with advanced solid tumors. The patients had colorectal, skin, kidney, lung, urothelial, breast, gynecologic, and head and neck cancers.
Most patients had low or no PD-L1 expression, and nearly 40% had received prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Patients received nine doses of RO7198457 at 25-50 mcg during the 12-week induction stage. They then received RO7198457 every eight cycles until disease progression. Patients received atezolizumab at 1,200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle.
Induction of proinflammatory cytokines was observed at each dose tested, and ex vivo T-cell responses were noted in 46 of 63 patients evaluated, or 73%.
T-cell receptors specific to RO7198457 were present posttreatment in a patient with rectal cancer, providing some preliminary evidence suggesting infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells in the tumor, Dr. Lopez said.
There were two clinical responses. A patient with rectal cancer had a complete response, and a patient with triple-negative breast cancer had a partial response.
The combination of RO7198457 with atezolizumab was generally well tolerated, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached, Dr. Lopez said. Most adverse events were grade 1/2, and immune-mediated adverse events were rare.
Implications and next steps
This study furthers earlier observations from neoantigen vaccine studies by linking dosing of the vaccine to dosing with immune checkpoint inhibitor, rather than giving the vaccine in the period leading up to immune checkpoint inhibitor administration, according to former AACR President Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, both in Columbus.
That said, the implications for clinical practice remain unclear, according to Dr. Mardis.
“This combination did elicit an immune response that was highly specific for the neoantigen vaccine, but most patients did not receive a clinical benefit of disease response,” Dr. Mardis said in an interview. “This tells us the combination approach used was, overall, not quite right, and we need to continue to innovate in this area.”
The low clinical response rate in the study was likely caused in part by the fact that patients had very advanced disease and were heavily pretreated, according to Dr. Lopez
Randomized phase 2 studies of RO7198457 are now underway, Dr. Lopez said. One is a study of RO7198457 plus atezolizumab as adjuvant treatment for non–small cell lung cancer (NCT04267237). Another is testing RO7198457 in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for melanoma (NCT03815058).
The current study was funded by Genentech and BioNTech. Dr. Lopez reported disclosures related to Roche/Genentech, Basilea Pharmaceutica, and Genmab. Dr. Mardis reported disclosures related to Quiagen NV, PACT Pharma, Kiadis Pharma NV, and Interpreta.
SOURCE: Lopez J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT301.
FROM AACR 2020