User login
Almost 90% of COVID-19 admissions involve comorbidities
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
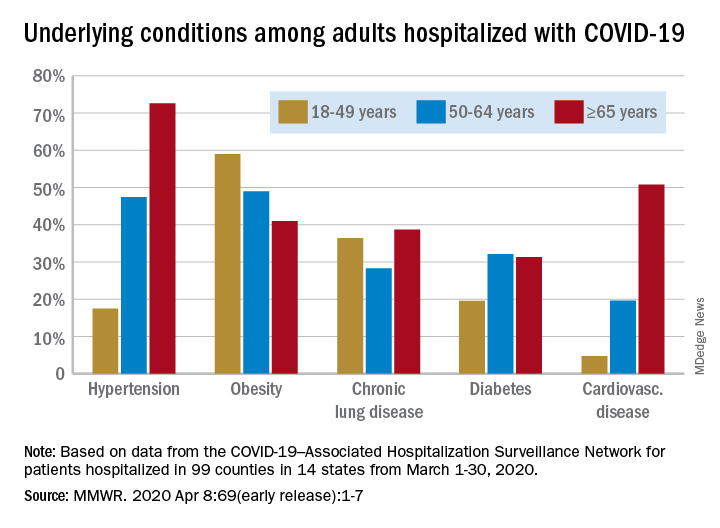
Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
FROM THE MMWR
The wide-ranging impact of hospital closures
Clinicians struggle to balance priorities
On June 26, 2019, American Academic Health System and Philadelphia Academic Health System announced that Hahnemann University Hospital, a 496-bed tertiary care center in North Philadelphia in operation for over 170 years, would close that September.
The emergency department closed 52 days after the announcement, leaving little time for physicians and staff to coordinate care for patients and secure new employment. The announcement was also made right at the beginning of the new academic year, which meant residents and fellows were forced to find new training programs. In total, 2,500 workers at Hahnemann, including more than 570 hospitalists and physicians training as residents and fellows, were displaced as the hospital closed – the largest such closing in U.S. history.
For most of its existence, Hahnemann was a teaching hospital. While trainees were all eventually placed in new programs thanks to efforts from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), some of the permanent staff at Hahnemann weren’t so lucky. A month after the announcement, Drexel University’s president told university employees that 40% of the staff who worked at Hahnemann would be cut as a result of the closing. Drexel, also based in Philadelphia, had long had an academic affiliation agreement for training Drexel’s medical school students as a primary academic partner. Overall, Drexel’s entire clinical staff at Hahnemann was let go, and Tower Health Medical Group is expected to hire about 60% of the former Hahnemann staff.
Kevin D’Mello, MD, FACP, FHM, a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at Drexel University, said residents during Hahnemann’s closure were essentially teaching themselves how to swim. “There were just no laws, no rules,” he said.
The vast majority of programs accepting applications from residents at Hahnemann were sympathetic and accommodating, he said, but a few programs applied “pressure tactics” to some of the residents offered a transfer position, despite graduate medical education rules in place to prevent such a situation from happening. “The resident says: ‘Oh, well, I’m waiting to hear from this other program,’ ” said Dr. D’Mello. “They’d say: ‘Okay, well, we’re giving you a position now. You have 12 hours to answer.’ ”
Decision makers at the hospital also were not very forthcoming with information to residents, fellows and program directors, according to a recent paper written by Thomas J. Nasca, MD, current president and CEO of ACGME, and colleagues in the journal Academic Medicine (Nasca T et al. Acad Med. 2019 Dec 17. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003133). When Dr. Nasca and colleagues went to investigate the situation at Hahnemann firsthand, “the team found that residents, fellows, and program directors alike considered their voices to have been ignored in decision making and deemed themselves ‘out of the loop’ of important information that would affect their career transitions.”
While the hospital closed in September 2019, the effects are still being felt. In Pennsylvania, the Medical Care Availability and Reduction of Error Act requires that hospitals and providers have malpractice insurance, including tail insurance for when a doctor’s insurance policy expires. American Academic announced it would not be paying tail insurance for claims made while physicians were at Hahnemann. This meant residents, fellows and physicians who worked at Hahnemann during the closure would be on the hook for paying their own malpractice insurance.
“On one hand, the risk is very low for the house staff. Lawsuits that come up later for house staff are generally dropped at some point,” said William W. Pinsky, MD, FAAP, FACC, president and CEO of the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG). “But who wants to take that risk going forward? It’s an issue that’s still not resolved.”
The American Medical Association, Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), the Philadelphia County Medical Society, and other medical societies have collectively put pressure on Hahnemann’s owners to pay for tail coverage. Beyond a Feb. 10, 2020 deadline, former Hahnemann physicians were still expected to cover their own tail insurance.
To further complicate matters, American Academic attempted to auction more than 570 residency slots at Hahnemann. The slots were sold to a consortium of six health systems in the area – Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals, Einstein Healthcare Network, Temple University Health System, Main Line Health, Cooper University Health Care, and Christiana Care Health System – for $55 million. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services opposed the sale, arguing that the slots are a contract that hospitals enter into with CMS, rather than an asset to be sold. An appeal is currently pending.
The case is being watched by former physicians at Hahnemann. “American Academic said, ‘If we don’t get this $55 million, we’re not going to be able to cover this tail insurance.’ They’re kind of linking the two things,” said Dr. D’Mello. “To me, it’s almost like putting pressure to allow the sale to happen.”
Urban hospital closures disrupt health system balance
When an urban hospital like Hahnemann University Hospital closes, there is a major disruption to patient care. Patients need to relocate to other nearby centers, and they may not always be able to follow their physician to the next health center.
If patients have comorbidities, are being tracked across multiple care points, or change physicians during a hospital closure, details can be missed and care can become more complicated for physicians who end up seeing the patient at a new center. For example, a patient receiving obstetrics care at a hospital that closes will have to reschedule their delivery at another health center, noted Dr. Pinsky.
“Where patients get lost is when there’s not a physician or an individual can keep track of all that, coordinate, and help to be sure that the patient follows through,” he said.
Patients at a closing hospital need to go somewhere else for care, and patient volume naturally increases at other nearby centers, potentially causing problems for systems without the resources to handle the spike in traffic.
“I’m a service director of quality improvement and patient safety for Drexel internal medicine. I know that those sort of jumps and volumes are what increases medical errors and potentially could create some adverse outcomes,” said Dr. D’Mello. “That’s something I’m particularly worried about.”
Physicians are also reconciling their own personal situations during a hospital closure, attempting to figure out their next step while at the same time helping patients figure out theirs. In the case of international medical graduates on J-1 or H1-B visas, who are dependent on hospital positions and training programs to remain in the United States, the situation can be even more dire.
During Hahnemann’s closure, Dr. Pinsky said that the ECFMG, which represents 11,000 individuals with J-1 visas across the country, reached out to the 55 individuals on J-1 visas at the hospital and offered them assistance, including working with the Department of State to ensure they aren’t in jeopardy of deportation before they secure another training program position.
The ECFMG, AMA, AAMC, and ACGME also offered funding to help J-1 visa holders who needed to relocate outside Philadelphia. “Many of them spent a lot of their money or all their money just coming over here,” said Dr. Pinsky. “This was a way to help defray some immediate costs that they might have.”
Education and research, of which hospitalists and residents play a large role, are likewise affected during a hospital closure, Dr. Pinsky said. “Education and research in the hospital is an important contributor to the community, health care and medical education nationally overall. When it’s not considered, there can be a significant asset that is lost in the process, which is hard to ever regain.
“The hospitalists have an integral role in medical education. In most hospitals where there is graduate medical education, particularly in internal medicine or pediatrics, and where there is a hospitalist program, it’s the hospitalists that do the majority of the in-hospital or inpatient training and education,” he added.
Rural hospital closures affect access to care
Since 2005, 163 rural hospitals have closed in the United States. When rural hospitals close, the situation for hospitalists and other physicians is different. In communities where a larger health system owns a hospital, such as when Vidant Health closed Pungo District Hospital in Belhaven, N.C., in 2014 before reopening a nonemergency clinic in the area in 2016, health care services for the community may have limited interruption.
However, if there isn’t a nearby system to join, many doctors will end up leaving the area. More than half of rural hospitals that close end up not providing any kind of supplementary health care service, according to the NC Rural Health Research Program.
“A lot of the hospitals that have closed have not been owned by a system,” said George H. Pink, PhD, deputy director of the NC Rural Health Research Program at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “They’ve been independent, freestanding, and that perhaps is one of the reasons why they’re closing, is because they haven’t been able to find a system that would buy them out and inject capital into the community.”
This can also have an effect on the number of health care providers in the area, Dr. Pink said. “Their ability to refer patients and treat patients locally may be affected. That’s why, in many towns where hospitals have closed, we see a drop in the number of providers, particularly primary care doctors who actually live in the community.”
Politicians and federal entities have proposed a number of solutions to help protect rural hospitals from closure. Sen. Charles Grassley (R-Iowa), Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), and Sen. Cory Gardener (R-Colo.) have sponsored bills in the Senate, while Rep. Sam Graves (R-Mo.) has introduced legislation in the House. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission has proposed two models of rural hospital care, and there are additional models proposed by the Kansas Hospital Association. A pilot program in Pennsylvania, the Pennsylvania Rural Health Model, is testing how a global budget by CMS for all inpatient and hospital-based outcomes might help rural hospitals.
“What we haven’t had a lot of action on is actually testing these models out and seeing whether they will work, and in what kinds of communities they will work,” Dr. Pink said.
Hospitalists as community advocates
Dr. D’Mello, who wrote an article for the Journal of Hospital Medicine on Hahnemann’s ownership by a private equity firm (doi: 10.12788/jhm.3378), said that the inherent nature of a for-profit entity trying to make a hospital profitable is a bad sign for a hospital and not necessarily what is in the best interest for an academic institution or for doctors who train there.
“I don’t know if I could blame the private equity firm completely, but in retrospect, the private equity firms stepping in was like the death knell of the hospital,” he said of Hahnemann’s closure.
“I think what the community needs to know – what the health care community, patient community, the hospitalist community need to know – is that there’s got to be more attention paid to these types of issues during mergers and acquisitions to prevent this from happening,” Dr. Pinsky said.
One larger issue was Hahnemann’s position as a safety net hospital, which partly played into American Academic’s lack of success in making the hospital as profitable as they wanted it to be, Dr. D’Mello noted. Hahnemann’s patient population consisted mostly of minority patients on Medicare, Medicaid, and charity care insurance, while recent studies have shown that hospitals are more likely to succeed when they have a larger proportion of patients with private insurance.
“Studies show that, to [make more] money from private insurance, you really have to have this huge footprint, because then you’ve got a better ability to negotiate with these private insurance companies,” Dr. D’Mello said. “Whether that’s actually good for health care is a different issue.”
Despite their own situations, it is not unusual for hospitalists and hospital physicians to step up during a hospital closure and advocate for their patients on behalf of the community, Dr. Pink said.
“When hospitals are in financial difficulty and there’s the risk of closure, typically, the medical staff are among the first to step up and warn the community: ‘We’re at risk of losing our service. We need some help,’ ” he said. “Generally speaking, the local physicians have been at the forefront of helping to keep access to hospital care available in some of these small communities – unfortunately, not always successfully.”
Dr. D’Mello, Dr. Pinsky, and Dr. Pink report no relevant conflicts of interest.
Clinicians struggle to balance priorities
Clinicians struggle to balance priorities
On June 26, 2019, American Academic Health System and Philadelphia Academic Health System announced that Hahnemann University Hospital, a 496-bed tertiary care center in North Philadelphia in operation for over 170 years, would close that September.
The emergency department closed 52 days after the announcement, leaving little time for physicians and staff to coordinate care for patients and secure new employment. The announcement was also made right at the beginning of the new academic year, which meant residents and fellows were forced to find new training programs. In total, 2,500 workers at Hahnemann, including more than 570 hospitalists and physicians training as residents and fellows, were displaced as the hospital closed – the largest such closing in U.S. history.
For most of its existence, Hahnemann was a teaching hospital. While trainees were all eventually placed in new programs thanks to efforts from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), some of the permanent staff at Hahnemann weren’t so lucky. A month after the announcement, Drexel University’s president told university employees that 40% of the staff who worked at Hahnemann would be cut as a result of the closing. Drexel, also based in Philadelphia, had long had an academic affiliation agreement for training Drexel’s medical school students as a primary academic partner. Overall, Drexel’s entire clinical staff at Hahnemann was let go, and Tower Health Medical Group is expected to hire about 60% of the former Hahnemann staff.
Kevin D’Mello, MD, FACP, FHM, a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at Drexel University, said residents during Hahnemann’s closure were essentially teaching themselves how to swim. “There were just no laws, no rules,” he said.
The vast majority of programs accepting applications from residents at Hahnemann were sympathetic and accommodating, he said, but a few programs applied “pressure tactics” to some of the residents offered a transfer position, despite graduate medical education rules in place to prevent such a situation from happening. “The resident says: ‘Oh, well, I’m waiting to hear from this other program,’ ” said Dr. D’Mello. “They’d say: ‘Okay, well, we’re giving you a position now. You have 12 hours to answer.’ ”
Decision makers at the hospital also were not very forthcoming with information to residents, fellows and program directors, according to a recent paper written by Thomas J. Nasca, MD, current president and CEO of ACGME, and colleagues in the journal Academic Medicine (Nasca T et al. Acad Med. 2019 Dec 17. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003133). When Dr. Nasca and colleagues went to investigate the situation at Hahnemann firsthand, “the team found that residents, fellows, and program directors alike considered their voices to have been ignored in decision making and deemed themselves ‘out of the loop’ of important information that would affect their career transitions.”
While the hospital closed in September 2019, the effects are still being felt. In Pennsylvania, the Medical Care Availability and Reduction of Error Act requires that hospitals and providers have malpractice insurance, including tail insurance for when a doctor’s insurance policy expires. American Academic announced it would not be paying tail insurance for claims made while physicians were at Hahnemann. This meant residents, fellows and physicians who worked at Hahnemann during the closure would be on the hook for paying their own malpractice insurance.
“On one hand, the risk is very low for the house staff. Lawsuits that come up later for house staff are generally dropped at some point,” said William W. Pinsky, MD, FAAP, FACC, president and CEO of the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG). “But who wants to take that risk going forward? It’s an issue that’s still not resolved.”
The American Medical Association, Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), the Philadelphia County Medical Society, and other medical societies have collectively put pressure on Hahnemann’s owners to pay for tail coverage. Beyond a Feb. 10, 2020 deadline, former Hahnemann physicians were still expected to cover their own tail insurance.
To further complicate matters, American Academic attempted to auction more than 570 residency slots at Hahnemann. The slots were sold to a consortium of six health systems in the area – Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals, Einstein Healthcare Network, Temple University Health System, Main Line Health, Cooper University Health Care, and Christiana Care Health System – for $55 million. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services opposed the sale, arguing that the slots are a contract that hospitals enter into with CMS, rather than an asset to be sold. An appeal is currently pending.
The case is being watched by former physicians at Hahnemann. “American Academic said, ‘If we don’t get this $55 million, we’re not going to be able to cover this tail insurance.’ They’re kind of linking the two things,” said Dr. D’Mello. “To me, it’s almost like putting pressure to allow the sale to happen.”
Urban hospital closures disrupt health system balance
When an urban hospital like Hahnemann University Hospital closes, there is a major disruption to patient care. Patients need to relocate to other nearby centers, and they may not always be able to follow their physician to the next health center.
If patients have comorbidities, are being tracked across multiple care points, or change physicians during a hospital closure, details can be missed and care can become more complicated for physicians who end up seeing the patient at a new center. For example, a patient receiving obstetrics care at a hospital that closes will have to reschedule their delivery at another health center, noted Dr. Pinsky.
“Where patients get lost is when there’s not a physician or an individual can keep track of all that, coordinate, and help to be sure that the patient follows through,” he said.
Patients at a closing hospital need to go somewhere else for care, and patient volume naturally increases at other nearby centers, potentially causing problems for systems without the resources to handle the spike in traffic.
“I’m a service director of quality improvement and patient safety for Drexel internal medicine. I know that those sort of jumps and volumes are what increases medical errors and potentially could create some adverse outcomes,” said Dr. D’Mello. “That’s something I’m particularly worried about.”
Physicians are also reconciling their own personal situations during a hospital closure, attempting to figure out their next step while at the same time helping patients figure out theirs. In the case of international medical graduates on J-1 or H1-B visas, who are dependent on hospital positions and training programs to remain in the United States, the situation can be even more dire.
During Hahnemann’s closure, Dr. Pinsky said that the ECFMG, which represents 11,000 individuals with J-1 visas across the country, reached out to the 55 individuals on J-1 visas at the hospital and offered them assistance, including working with the Department of State to ensure they aren’t in jeopardy of deportation before they secure another training program position.
The ECFMG, AMA, AAMC, and ACGME also offered funding to help J-1 visa holders who needed to relocate outside Philadelphia. “Many of them spent a lot of their money or all their money just coming over here,” said Dr. Pinsky. “This was a way to help defray some immediate costs that they might have.”
Education and research, of which hospitalists and residents play a large role, are likewise affected during a hospital closure, Dr. Pinsky said. “Education and research in the hospital is an important contributor to the community, health care and medical education nationally overall. When it’s not considered, there can be a significant asset that is lost in the process, which is hard to ever regain.
“The hospitalists have an integral role in medical education. In most hospitals where there is graduate medical education, particularly in internal medicine or pediatrics, and where there is a hospitalist program, it’s the hospitalists that do the majority of the in-hospital or inpatient training and education,” he added.
Rural hospital closures affect access to care
Since 2005, 163 rural hospitals have closed in the United States. When rural hospitals close, the situation for hospitalists and other physicians is different. In communities where a larger health system owns a hospital, such as when Vidant Health closed Pungo District Hospital in Belhaven, N.C., in 2014 before reopening a nonemergency clinic in the area in 2016, health care services for the community may have limited interruption.
However, if there isn’t a nearby system to join, many doctors will end up leaving the area. More than half of rural hospitals that close end up not providing any kind of supplementary health care service, according to the NC Rural Health Research Program.
“A lot of the hospitals that have closed have not been owned by a system,” said George H. Pink, PhD, deputy director of the NC Rural Health Research Program at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “They’ve been independent, freestanding, and that perhaps is one of the reasons why they’re closing, is because they haven’t been able to find a system that would buy them out and inject capital into the community.”
This can also have an effect on the number of health care providers in the area, Dr. Pink said. “Their ability to refer patients and treat patients locally may be affected. That’s why, in many towns where hospitals have closed, we see a drop in the number of providers, particularly primary care doctors who actually live in the community.”
Politicians and federal entities have proposed a number of solutions to help protect rural hospitals from closure. Sen. Charles Grassley (R-Iowa), Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), and Sen. Cory Gardener (R-Colo.) have sponsored bills in the Senate, while Rep. Sam Graves (R-Mo.) has introduced legislation in the House. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission has proposed two models of rural hospital care, and there are additional models proposed by the Kansas Hospital Association. A pilot program in Pennsylvania, the Pennsylvania Rural Health Model, is testing how a global budget by CMS for all inpatient and hospital-based outcomes might help rural hospitals.
“What we haven’t had a lot of action on is actually testing these models out and seeing whether they will work, and in what kinds of communities they will work,” Dr. Pink said.
Hospitalists as community advocates
Dr. D’Mello, who wrote an article for the Journal of Hospital Medicine on Hahnemann’s ownership by a private equity firm (doi: 10.12788/jhm.3378), said that the inherent nature of a for-profit entity trying to make a hospital profitable is a bad sign for a hospital and not necessarily what is in the best interest for an academic institution or for doctors who train there.
“I don’t know if I could blame the private equity firm completely, but in retrospect, the private equity firms stepping in was like the death knell of the hospital,” he said of Hahnemann’s closure.
“I think what the community needs to know – what the health care community, patient community, the hospitalist community need to know – is that there’s got to be more attention paid to these types of issues during mergers and acquisitions to prevent this from happening,” Dr. Pinsky said.
One larger issue was Hahnemann’s position as a safety net hospital, which partly played into American Academic’s lack of success in making the hospital as profitable as they wanted it to be, Dr. D’Mello noted. Hahnemann’s patient population consisted mostly of minority patients on Medicare, Medicaid, and charity care insurance, while recent studies have shown that hospitals are more likely to succeed when they have a larger proportion of patients with private insurance.
“Studies show that, to [make more] money from private insurance, you really have to have this huge footprint, because then you’ve got a better ability to negotiate with these private insurance companies,” Dr. D’Mello said. “Whether that’s actually good for health care is a different issue.”
Despite their own situations, it is not unusual for hospitalists and hospital physicians to step up during a hospital closure and advocate for their patients on behalf of the community, Dr. Pink said.
“When hospitals are in financial difficulty and there’s the risk of closure, typically, the medical staff are among the first to step up and warn the community: ‘We’re at risk of losing our service. We need some help,’ ” he said. “Generally speaking, the local physicians have been at the forefront of helping to keep access to hospital care available in some of these small communities – unfortunately, not always successfully.”
Dr. D’Mello, Dr. Pinsky, and Dr. Pink report no relevant conflicts of interest.
On June 26, 2019, American Academic Health System and Philadelphia Academic Health System announced that Hahnemann University Hospital, a 496-bed tertiary care center in North Philadelphia in operation for over 170 years, would close that September.
The emergency department closed 52 days after the announcement, leaving little time for physicians and staff to coordinate care for patients and secure new employment. The announcement was also made right at the beginning of the new academic year, which meant residents and fellows were forced to find new training programs. In total, 2,500 workers at Hahnemann, including more than 570 hospitalists and physicians training as residents and fellows, were displaced as the hospital closed – the largest such closing in U.S. history.
For most of its existence, Hahnemann was a teaching hospital. While trainees were all eventually placed in new programs thanks to efforts from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), some of the permanent staff at Hahnemann weren’t so lucky. A month after the announcement, Drexel University’s president told university employees that 40% of the staff who worked at Hahnemann would be cut as a result of the closing. Drexel, also based in Philadelphia, had long had an academic affiliation agreement for training Drexel’s medical school students as a primary academic partner. Overall, Drexel’s entire clinical staff at Hahnemann was let go, and Tower Health Medical Group is expected to hire about 60% of the former Hahnemann staff.
Kevin D’Mello, MD, FACP, FHM, a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at Drexel University, said residents during Hahnemann’s closure were essentially teaching themselves how to swim. “There were just no laws, no rules,” he said.
The vast majority of programs accepting applications from residents at Hahnemann were sympathetic and accommodating, he said, but a few programs applied “pressure tactics” to some of the residents offered a transfer position, despite graduate medical education rules in place to prevent such a situation from happening. “The resident says: ‘Oh, well, I’m waiting to hear from this other program,’ ” said Dr. D’Mello. “They’d say: ‘Okay, well, we’re giving you a position now. You have 12 hours to answer.’ ”
Decision makers at the hospital also were not very forthcoming with information to residents, fellows and program directors, according to a recent paper written by Thomas J. Nasca, MD, current president and CEO of ACGME, and colleagues in the journal Academic Medicine (Nasca T et al. Acad Med. 2019 Dec 17. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003133). When Dr. Nasca and colleagues went to investigate the situation at Hahnemann firsthand, “the team found that residents, fellows, and program directors alike considered their voices to have been ignored in decision making and deemed themselves ‘out of the loop’ of important information that would affect their career transitions.”
While the hospital closed in September 2019, the effects are still being felt. In Pennsylvania, the Medical Care Availability and Reduction of Error Act requires that hospitals and providers have malpractice insurance, including tail insurance for when a doctor’s insurance policy expires. American Academic announced it would not be paying tail insurance for claims made while physicians were at Hahnemann. This meant residents, fellows and physicians who worked at Hahnemann during the closure would be on the hook for paying their own malpractice insurance.
“On one hand, the risk is very low for the house staff. Lawsuits that come up later for house staff are generally dropped at some point,” said William W. Pinsky, MD, FAAP, FACC, president and CEO of the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG). “But who wants to take that risk going forward? It’s an issue that’s still not resolved.”
The American Medical Association, Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), the Philadelphia County Medical Society, and other medical societies have collectively put pressure on Hahnemann’s owners to pay for tail coverage. Beyond a Feb. 10, 2020 deadline, former Hahnemann physicians were still expected to cover their own tail insurance.
To further complicate matters, American Academic attempted to auction more than 570 residency slots at Hahnemann. The slots were sold to a consortium of six health systems in the area – Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals, Einstein Healthcare Network, Temple University Health System, Main Line Health, Cooper University Health Care, and Christiana Care Health System – for $55 million. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services opposed the sale, arguing that the slots are a contract that hospitals enter into with CMS, rather than an asset to be sold. An appeal is currently pending.
The case is being watched by former physicians at Hahnemann. “American Academic said, ‘If we don’t get this $55 million, we’re not going to be able to cover this tail insurance.’ They’re kind of linking the two things,” said Dr. D’Mello. “To me, it’s almost like putting pressure to allow the sale to happen.”
Urban hospital closures disrupt health system balance
When an urban hospital like Hahnemann University Hospital closes, there is a major disruption to patient care. Patients need to relocate to other nearby centers, and they may not always be able to follow their physician to the next health center.
If patients have comorbidities, are being tracked across multiple care points, or change physicians during a hospital closure, details can be missed and care can become more complicated for physicians who end up seeing the patient at a new center. For example, a patient receiving obstetrics care at a hospital that closes will have to reschedule their delivery at another health center, noted Dr. Pinsky.
“Where patients get lost is when there’s not a physician or an individual can keep track of all that, coordinate, and help to be sure that the patient follows through,” he said.
Patients at a closing hospital need to go somewhere else for care, and patient volume naturally increases at other nearby centers, potentially causing problems for systems without the resources to handle the spike in traffic.
“I’m a service director of quality improvement and patient safety for Drexel internal medicine. I know that those sort of jumps and volumes are what increases medical errors and potentially could create some adverse outcomes,” said Dr. D’Mello. “That’s something I’m particularly worried about.”
Physicians are also reconciling their own personal situations during a hospital closure, attempting to figure out their next step while at the same time helping patients figure out theirs. In the case of international medical graduates on J-1 or H1-B visas, who are dependent on hospital positions and training programs to remain in the United States, the situation can be even more dire.
During Hahnemann’s closure, Dr. Pinsky said that the ECFMG, which represents 11,000 individuals with J-1 visas across the country, reached out to the 55 individuals on J-1 visas at the hospital and offered them assistance, including working with the Department of State to ensure they aren’t in jeopardy of deportation before they secure another training program position.
The ECFMG, AMA, AAMC, and ACGME also offered funding to help J-1 visa holders who needed to relocate outside Philadelphia. “Many of them spent a lot of their money or all their money just coming over here,” said Dr. Pinsky. “This was a way to help defray some immediate costs that they might have.”
Education and research, of which hospitalists and residents play a large role, are likewise affected during a hospital closure, Dr. Pinsky said. “Education and research in the hospital is an important contributor to the community, health care and medical education nationally overall. When it’s not considered, there can be a significant asset that is lost in the process, which is hard to ever regain.
“The hospitalists have an integral role in medical education. In most hospitals where there is graduate medical education, particularly in internal medicine or pediatrics, and where there is a hospitalist program, it’s the hospitalists that do the majority of the in-hospital or inpatient training and education,” he added.
Rural hospital closures affect access to care
Since 2005, 163 rural hospitals have closed in the United States. When rural hospitals close, the situation for hospitalists and other physicians is different. In communities where a larger health system owns a hospital, such as when Vidant Health closed Pungo District Hospital in Belhaven, N.C., in 2014 before reopening a nonemergency clinic in the area in 2016, health care services for the community may have limited interruption.
However, if there isn’t a nearby system to join, many doctors will end up leaving the area. More than half of rural hospitals that close end up not providing any kind of supplementary health care service, according to the NC Rural Health Research Program.
“A lot of the hospitals that have closed have not been owned by a system,” said George H. Pink, PhD, deputy director of the NC Rural Health Research Program at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “They’ve been independent, freestanding, and that perhaps is one of the reasons why they’re closing, is because they haven’t been able to find a system that would buy them out and inject capital into the community.”
This can also have an effect on the number of health care providers in the area, Dr. Pink said. “Their ability to refer patients and treat patients locally may be affected. That’s why, in many towns where hospitals have closed, we see a drop in the number of providers, particularly primary care doctors who actually live in the community.”
Politicians and federal entities have proposed a number of solutions to help protect rural hospitals from closure. Sen. Charles Grassley (R-Iowa), Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), and Sen. Cory Gardener (R-Colo.) have sponsored bills in the Senate, while Rep. Sam Graves (R-Mo.) has introduced legislation in the House. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission has proposed two models of rural hospital care, and there are additional models proposed by the Kansas Hospital Association. A pilot program in Pennsylvania, the Pennsylvania Rural Health Model, is testing how a global budget by CMS for all inpatient and hospital-based outcomes might help rural hospitals.
“What we haven’t had a lot of action on is actually testing these models out and seeing whether they will work, and in what kinds of communities they will work,” Dr. Pink said.
Hospitalists as community advocates
Dr. D’Mello, who wrote an article for the Journal of Hospital Medicine on Hahnemann’s ownership by a private equity firm (doi: 10.12788/jhm.3378), said that the inherent nature of a for-profit entity trying to make a hospital profitable is a bad sign for a hospital and not necessarily what is in the best interest for an academic institution or for doctors who train there.
“I don’t know if I could blame the private equity firm completely, but in retrospect, the private equity firms stepping in was like the death knell of the hospital,” he said of Hahnemann’s closure.
“I think what the community needs to know – what the health care community, patient community, the hospitalist community need to know – is that there’s got to be more attention paid to these types of issues during mergers and acquisitions to prevent this from happening,” Dr. Pinsky said.
One larger issue was Hahnemann’s position as a safety net hospital, which partly played into American Academic’s lack of success in making the hospital as profitable as they wanted it to be, Dr. D’Mello noted. Hahnemann’s patient population consisted mostly of minority patients on Medicare, Medicaid, and charity care insurance, while recent studies have shown that hospitals are more likely to succeed when they have a larger proportion of patients with private insurance.
“Studies show that, to [make more] money from private insurance, you really have to have this huge footprint, because then you’ve got a better ability to negotiate with these private insurance companies,” Dr. D’Mello said. “Whether that’s actually good for health care is a different issue.”
Despite their own situations, it is not unusual for hospitalists and hospital physicians to step up during a hospital closure and advocate for their patients on behalf of the community, Dr. Pink said.
“When hospitals are in financial difficulty and there’s the risk of closure, typically, the medical staff are among the first to step up and warn the community: ‘We’re at risk of losing our service. We need some help,’ ” he said. “Generally speaking, the local physicians have been at the forefront of helping to keep access to hospital care available in some of these small communities – unfortunately, not always successfully.”
Dr. D’Mello, Dr. Pinsky, and Dr. Pink report no relevant conflicts of interest.
Higher baseline fitness may help maintain weight loss
Participants who had higher levels of fitness when beginning a behavioral weight-loss intervention kept off more weight over the course of an 18-month study, compared with those with lower levels of fitness at baseline.
Those with higher baseline fitness also were able to achieve higher levels of moderate to vigorous physical activity at the 18-month mark, Adnin Zaman, MD, said during a virtual news conference held by the Endocrine Society. The study had been slated for presentation during ENDO 2020, the society's annual meeting, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our study really comes from an observation that we often see significant variability in how much weight participants lose during a behavioral weight-loss intervention study, said Dr. Zaman, an endocrinology research fellow at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
She and her colleagues wanted to look at baseline cardiovascular fitness as an individual-specific factor that could affect how much weight people lost when participating in a behavioral intervention.
“Very little is known about how cardiovascular fitness affects [people’s] ability to lose weight [or] to adhere to high levels of physical activity, which is a very common recommendation during a program for both weight loss and weight-loss maintenance,” she added.
Dr. Zaman and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of data from an 18-month trial of behavioral interventions for weight loss. The trial randomized 170 participants 1:1 to receive either concurrent exercise and a dietary behavior modification intervention or sequential dietary and exercise interventions.
The 85 participants in the concurrent intervention arm received 18 months of combined dietary modifications (calorie-restricted diet and group-based behavioral support) and exercise (supervised for the first 6 months of the study, unsupervised for the final 12). Those participating in the sequential intervention arm received a diet-only intervention during the first 6 months of the study, after which supervised exercise was added to the dietary intervention for 6 months, followed by a final 6 months of unsupervised exercise.
Participants in both study arms worked up to 300 minutes a week of moderate to vigorous physical activity in the supervised exercise phase.
For the secondary analysis, Dr. Zaman and colleagues looked only at the 60 participants who received concurrent diet and exercise interventions and who completed the full 18-month study. The mean age in that group was 40 years, mean baseline body mass index (BMI) was 34.6 kg/m2, and 80% of participants in the group were women.
Cardiovascular fitness as measured by VO2max was assessed at baseline using a graded exercise test. Participants were designated as having either “very poor” or “poor or better” cardiovascular fitness (20 and 40 participants, respectively).
Participants in the original trial were inactive at baseline and had a BMI range of 27-42 kg/m2. Among the subset of participants studied by Dr. Zaman and colleagues, those who were in the poor or better fitness category actually weighed less at baseline and had a lower BMI, compared with those in the very poor group (33.7 vs. 36.2, respectively), she said. Mean VO2max for those with very poor fitness was 22.5 mL/kg per minute, compared with 25.6 mL/kg per minute for those with poor or better fitness.
“Despite those differences, it is interesting to note that, during the supervised exercise portion of the study ... everyone lost pretty much the same amount of weight in the first 6 months,” said Dr. Zaman. At the 6-month mark, those with very poor fitness had lost 9.2 kg (20.3 pounds), and those with poor or better fitness had lost 9.1 kg (20.1 pounds). However, weight regain was less likely in those with poor or better fitness, and those participants had a net loss of weight from baseline of 8.2 kg (18.1 pounds), compared with 4.4 kg (9.7 pounds) for those with very poor fitness.
Those with poor or better fitness were able to sustain a 33-minute bout of moderate to vigorous physical activity at baseline, whereas those with very poor fitness could achieve only about half of that. The difference in achievable physical activity between the two groups persisted throughout the study, with a peak at the 6-month mark, at about 60 minutes for the more fit participants and 38 minutes for those in the poor fitness group. By the end of the study, the less-fit participants achieved about 24 minutes of activity, whereas those who were more fit could sustain about 42 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity.
Physical activity levels were measured with a validated, wrist-worn device during a 1-week period at baseline and again at study months 6, 12, and 18.
Dr. Zaman noted that baseline weight may have confounded fitness categorization, because VO2max includes body weight in its calculations. A newer method of calculating cardiorespiratory fitness that scales VO2max to body weight may help minimize this potential confounder.
The investigators reported no outside sources of funding and reported that they had no financial conflicts of interest.
The research will be published in a special supplemental issue of the Journal of the Endocrine Society. In addition to a series of news conferences on March 30-31, the society will host ENDO Online 2020 during June 8-22, which will present programming for clinicians and researchers.
SOURCE: Zaman A et al. ENDO 2020, Abstract 575.
This article was updated on 4/17/2020.
Participants who had higher levels of fitness when beginning a behavioral weight-loss intervention kept off more weight over the course of an 18-month study, compared with those with lower levels of fitness at baseline.
Those with higher baseline fitness also were able to achieve higher levels of moderate to vigorous physical activity at the 18-month mark, Adnin Zaman, MD, said during a virtual news conference held by the Endocrine Society. The study had been slated for presentation during ENDO 2020, the society's annual meeting, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our study really comes from an observation that we often see significant variability in how much weight participants lose during a behavioral weight-loss intervention study, said Dr. Zaman, an endocrinology research fellow at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
She and her colleagues wanted to look at baseline cardiovascular fitness as an individual-specific factor that could affect how much weight people lost when participating in a behavioral intervention.
“Very little is known about how cardiovascular fitness affects [people’s] ability to lose weight [or] to adhere to high levels of physical activity, which is a very common recommendation during a program for both weight loss and weight-loss maintenance,” she added.
Dr. Zaman and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of data from an 18-month trial of behavioral interventions for weight loss. The trial randomized 170 participants 1:1 to receive either concurrent exercise and a dietary behavior modification intervention or sequential dietary and exercise interventions.
The 85 participants in the concurrent intervention arm received 18 months of combined dietary modifications (calorie-restricted diet and group-based behavioral support) and exercise (supervised for the first 6 months of the study, unsupervised for the final 12). Those participating in the sequential intervention arm received a diet-only intervention during the first 6 months of the study, after which supervised exercise was added to the dietary intervention for 6 months, followed by a final 6 months of unsupervised exercise.
Participants in both study arms worked up to 300 minutes a week of moderate to vigorous physical activity in the supervised exercise phase.
For the secondary analysis, Dr. Zaman and colleagues looked only at the 60 participants who received concurrent diet and exercise interventions and who completed the full 18-month study. The mean age in that group was 40 years, mean baseline body mass index (BMI) was 34.6 kg/m2, and 80% of participants in the group were women.
Cardiovascular fitness as measured by VO2max was assessed at baseline using a graded exercise test. Participants were designated as having either “very poor” or “poor or better” cardiovascular fitness (20 and 40 participants, respectively).
Participants in the original trial were inactive at baseline and had a BMI range of 27-42 kg/m2. Among the subset of participants studied by Dr. Zaman and colleagues, those who were in the poor or better fitness category actually weighed less at baseline and had a lower BMI, compared with those in the very poor group (33.7 vs. 36.2, respectively), she said. Mean VO2max for those with very poor fitness was 22.5 mL/kg per minute, compared with 25.6 mL/kg per minute for those with poor or better fitness.
“Despite those differences, it is interesting to note that, during the supervised exercise portion of the study ... everyone lost pretty much the same amount of weight in the first 6 months,” said Dr. Zaman. At the 6-month mark, those with very poor fitness had lost 9.2 kg (20.3 pounds), and those with poor or better fitness had lost 9.1 kg (20.1 pounds). However, weight regain was less likely in those with poor or better fitness, and those participants had a net loss of weight from baseline of 8.2 kg (18.1 pounds), compared with 4.4 kg (9.7 pounds) for those with very poor fitness.
Those with poor or better fitness were able to sustain a 33-minute bout of moderate to vigorous physical activity at baseline, whereas those with very poor fitness could achieve only about half of that. The difference in achievable physical activity between the two groups persisted throughout the study, with a peak at the 6-month mark, at about 60 minutes for the more fit participants and 38 minutes for those in the poor fitness group. By the end of the study, the less-fit participants achieved about 24 minutes of activity, whereas those who were more fit could sustain about 42 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity.
Physical activity levels were measured with a validated, wrist-worn device during a 1-week period at baseline and again at study months 6, 12, and 18.
Dr. Zaman noted that baseline weight may have confounded fitness categorization, because VO2max includes body weight in its calculations. A newer method of calculating cardiorespiratory fitness that scales VO2max to body weight may help minimize this potential confounder.
The investigators reported no outside sources of funding and reported that they had no financial conflicts of interest.
The research will be published in a special supplemental issue of the Journal of the Endocrine Society. In addition to a series of news conferences on March 30-31, the society will host ENDO Online 2020 during June 8-22, which will present programming for clinicians and researchers.
SOURCE: Zaman A et al. ENDO 2020, Abstract 575.
This article was updated on 4/17/2020.
Participants who had higher levels of fitness when beginning a behavioral weight-loss intervention kept off more weight over the course of an 18-month study, compared with those with lower levels of fitness at baseline.
Those with higher baseline fitness also were able to achieve higher levels of moderate to vigorous physical activity at the 18-month mark, Adnin Zaman, MD, said during a virtual news conference held by the Endocrine Society. The study had been slated for presentation during ENDO 2020, the society's annual meeting, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our study really comes from an observation that we often see significant variability in how much weight participants lose during a behavioral weight-loss intervention study, said Dr. Zaman, an endocrinology research fellow at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
She and her colleagues wanted to look at baseline cardiovascular fitness as an individual-specific factor that could affect how much weight people lost when participating in a behavioral intervention.
“Very little is known about how cardiovascular fitness affects [people’s] ability to lose weight [or] to adhere to high levels of physical activity, which is a very common recommendation during a program for both weight loss and weight-loss maintenance,” she added.
Dr. Zaman and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of data from an 18-month trial of behavioral interventions for weight loss. The trial randomized 170 participants 1:1 to receive either concurrent exercise and a dietary behavior modification intervention or sequential dietary and exercise interventions.
The 85 participants in the concurrent intervention arm received 18 months of combined dietary modifications (calorie-restricted diet and group-based behavioral support) and exercise (supervised for the first 6 months of the study, unsupervised for the final 12). Those participating in the sequential intervention arm received a diet-only intervention during the first 6 months of the study, after which supervised exercise was added to the dietary intervention for 6 months, followed by a final 6 months of unsupervised exercise.
Participants in both study arms worked up to 300 minutes a week of moderate to vigorous physical activity in the supervised exercise phase.
For the secondary analysis, Dr. Zaman and colleagues looked only at the 60 participants who received concurrent diet and exercise interventions and who completed the full 18-month study. The mean age in that group was 40 years, mean baseline body mass index (BMI) was 34.6 kg/m2, and 80% of participants in the group were women.
Cardiovascular fitness as measured by VO2max was assessed at baseline using a graded exercise test. Participants were designated as having either “very poor” or “poor or better” cardiovascular fitness (20 and 40 participants, respectively).
Participants in the original trial were inactive at baseline and had a BMI range of 27-42 kg/m2. Among the subset of participants studied by Dr. Zaman and colleagues, those who were in the poor or better fitness category actually weighed less at baseline and had a lower BMI, compared with those in the very poor group (33.7 vs. 36.2, respectively), she said. Mean VO2max for those with very poor fitness was 22.5 mL/kg per minute, compared with 25.6 mL/kg per minute for those with poor or better fitness.
“Despite those differences, it is interesting to note that, during the supervised exercise portion of the study ... everyone lost pretty much the same amount of weight in the first 6 months,” said Dr. Zaman. At the 6-month mark, those with very poor fitness had lost 9.2 kg (20.3 pounds), and those with poor or better fitness had lost 9.1 kg (20.1 pounds). However, weight regain was less likely in those with poor or better fitness, and those participants had a net loss of weight from baseline of 8.2 kg (18.1 pounds), compared with 4.4 kg (9.7 pounds) for those with very poor fitness.
Those with poor or better fitness were able to sustain a 33-minute bout of moderate to vigorous physical activity at baseline, whereas those with very poor fitness could achieve only about half of that. The difference in achievable physical activity between the two groups persisted throughout the study, with a peak at the 6-month mark, at about 60 minutes for the more fit participants and 38 minutes for those in the poor fitness group. By the end of the study, the less-fit participants achieved about 24 minutes of activity, whereas those who were more fit could sustain about 42 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity.
Physical activity levels were measured with a validated, wrist-worn device during a 1-week period at baseline and again at study months 6, 12, and 18.
Dr. Zaman noted that baseline weight may have confounded fitness categorization, because VO2max includes body weight in its calculations. A newer method of calculating cardiorespiratory fitness that scales VO2max to body weight may help minimize this potential confounder.
The investigators reported no outside sources of funding and reported that they had no financial conflicts of interest.
The research will be published in a special supplemental issue of the Journal of the Endocrine Society. In addition to a series of news conferences on March 30-31, the society will host ENDO Online 2020 during June 8-22, which will present programming for clinicians and researchers.
SOURCE: Zaman A et al. ENDO 2020, Abstract 575.
This article was updated on 4/17/2020.
FROM ENDO 2020
BPA analogs increase blood pressure in animal study
findings in a new study have shown.
Researchers tested exposures to BPA, as well as bisphenol-S (BPS) and bisphenol-F (BPF), which have been introduced in recent years as BPA alternatives and are now increasingly detectable in human and animal tissues. BPS and BPF are often found in products labeled as “BPA free.”
BPS and BPF have similar physiochemical properties to BPA, and there is concern over their effects.
But their physiological impact is not yet clear, according to Puliyur MohanKumar, DVM, PhD, of the University of Georgia Regenerative Bioscience Center, Athens. “We are exposed to BPA and related compounds on a regular basis, and the important thing is that BPA and related compounds easily cross the placental barrier,” Dr. MohanKumar said during a virtual news conference held by the Endocrine Society. The study had been slated for presentation during ENDO 2020, the society's annual meeting, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues exposed pregnant rats to BPA, BPS, or BPF. When the offspring reached adulthood, the researchers implanted them with radiotelemetry devices to track systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which they measured every 10 minutes over a 24-hour period. This was repeated once a week for 11 weeks.
“The female offspring had elevated systolic as well as diastolic blood pressure, and this was an increase of about 8 mm [Hg] higher than the control animals. That was pretty significant. Keeping these animals at such a prehypertensive state for such a long period of time is going to [lead to] lots of cardiovascular issues later on,” said Dr. MohanKumar.
Robert Sargis, MD, PhD, professor of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Illinois at Chicago, noted that, although animal studies don’t necessarily translate to similar outcomes in humans, the results are cause for concern.
“What’s particularly interesting, is that there is whole area of essential hypertension, where people develop hypertension and we don’t really know why. We just treat it,” he said in an interview. “But thinking about biological origins [of hypertension] is potentially interesting for a couple of reasons. These bisphenol compounds are really common. Most Americans are exposed to bisphenol A, and it’s been associated with other adverse metabolic effects, including alterations to body weight and glucose homeostasis.
“[These findings] feed into a whole series of studies that have begun to look at the BPA replacements and the fact that they may be, at best, as bad as BPA, and at worst, possibly slightly worse, depending on which outcomes you’re looking at,” Dr. Sargis added.
In the study, seven pregnant rats were orally exposed to saline, four pregnant rats to 5 mcg/kg BPA, four to 5 mcg/kg BPS, and five to 1 mcg/kg BPF during days 6-21 of pregnancy. The lower dose of BPF was used because a dose of 5 mcg/kg proved too toxic. When the offspring reached adulthood, the researchers implanted radiotelemetry devices in the offspring’s femoral artery.
Mean daytime systolic BP was highest in the BPA group (133.3 mg Hg; P < .05), followed by BPS (132.5 mm Hg; P < .05) and BPF (129.2 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 125.2 mm Hg in controls. Nighttime systolic BP was again highest in the BPA group (134.2 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPS (133.2 mm Hg; P < .05) and BPF (129.6 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 125.1 mm Hg in controls.
During the day, diastolic BP was highest in the BPS group (91.3 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPA (88.8 mm Hg; nonsignificant) and BPF (88.6 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 84.1 mm Hg in controls. At night, diastolic BP was highest in the BPS group (89.7 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPA (89.6 mm Hg; P < .01) and BPF (88.6 mm Hg; P < .01), compared with 83.3 mm Hg in controls.
During the day, mean arterial pressure was highest in the BPA group (110.5 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPS (108.9 mm Hg; P < .01) and BPF (105.2 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 102.6 mm Hg in controls. At night, mean arterial pressure was highest in BPS (108.6 mm Hg; P < .05), followed by BPA (107.5 mm Hg; nonsignificant) and BPF (105.7 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 101.8 mm Hg in controls.
“These results indicate that prenatal exposure to low levels of BPA analogs has a profound effect on hypertension” in the offspring of pregnant rats exposed to bisphenols, Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues wrote in the abstract.
He noted during his presentation that he and his colleagues plan to repeat the study in male offspring to determine if there are sex differences.
Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Sargis also reported no conflicts of interest.
The research will be published in a special supplemental issue of the Journal of the Endocrine Society. In addition to a series of news conferences on March 30-31, the society will host ENDO Online 2020 during June 8-22, which will present programming for clinicians and researchers.
SOURCE: MohanKumar P et al. ENDO 2020, Abstract 719.
This article was updated on 4/17/2020.
findings in a new study have shown.
Researchers tested exposures to BPA, as well as bisphenol-S (BPS) and bisphenol-F (BPF), which have been introduced in recent years as BPA alternatives and are now increasingly detectable in human and animal tissues. BPS and BPF are often found in products labeled as “BPA free.”
BPS and BPF have similar physiochemical properties to BPA, and there is concern over their effects.
But their physiological impact is not yet clear, according to Puliyur MohanKumar, DVM, PhD, of the University of Georgia Regenerative Bioscience Center, Athens. “We are exposed to BPA and related compounds on a regular basis, and the important thing is that BPA and related compounds easily cross the placental barrier,” Dr. MohanKumar said during a virtual news conference held by the Endocrine Society. The study had been slated for presentation during ENDO 2020, the society's annual meeting, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues exposed pregnant rats to BPA, BPS, or BPF. When the offspring reached adulthood, the researchers implanted them with radiotelemetry devices to track systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which they measured every 10 minutes over a 24-hour period. This was repeated once a week for 11 weeks.
“The female offspring had elevated systolic as well as diastolic blood pressure, and this was an increase of about 8 mm [Hg] higher than the control animals. That was pretty significant. Keeping these animals at such a prehypertensive state for such a long period of time is going to [lead to] lots of cardiovascular issues later on,” said Dr. MohanKumar.
Robert Sargis, MD, PhD, professor of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Illinois at Chicago, noted that, although animal studies don’t necessarily translate to similar outcomes in humans, the results are cause for concern.
“What’s particularly interesting, is that there is whole area of essential hypertension, where people develop hypertension and we don’t really know why. We just treat it,” he said in an interview. “But thinking about biological origins [of hypertension] is potentially interesting for a couple of reasons. These bisphenol compounds are really common. Most Americans are exposed to bisphenol A, and it’s been associated with other adverse metabolic effects, including alterations to body weight and glucose homeostasis.
“[These findings] feed into a whole series of studies that have begun to look at the BPA replacements and the fact that they may be, at best, as bad as BPA, and at worst, possibly slightly worse, depending on which outcomes you’re looking at,” Dr. Sargis added.
In the study, seven pregnant rats were orally exposed to saline, four pregnant rats to 5 mcg/kg BPA, four to 5 mcg/kg BPS, and five to 1 mcg/kg BPF during days 6-21 of pregnancy. The lower dose of BPF was used because a dose of 5 mcg/kg proved too toxic. When the offspring reached adulthood, the researchers implanted radiotelemetry devices in the offspring’s femoral artery.
Mean daytime systolic BP was highest in the BPA group (133.3 mg Hg; P < .05), followed by BPS (132.5 mm Hg; P < .05) and BPF (129.2 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 125.2 mm Hg in controls. Nighttime systolic BP was again highest in the BPA group (134.2 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPS (133.2 mm Hg; P < .05) and BPF (129.6 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 125.1 mm Hg in controls.
During the day, diastolic BP was highest in the BPS group (91.3 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPA (88.8 mm Hg; nonsignificant) and BPF (88.6 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 84.1 mm Hg in controls. At night, diastolic BP was highest in the BPS group (89.7 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPA (89.6 mm Hg; P < .01) and BPF (88.6 mm Hg; P < .01), compared with 83.3 mm Hg in controls.
During the day, mean arterial pressure was highest in the BPA group (110.5 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPS (108.9 mm Hg; P < .01) and BPF (105.2 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 102.6 mm Hg in controls. At night, mean arterial pressure was highest in BPS (108.6 mm Hg; P < .05), followed by BPA (107.5 mm Hg; nonsignificant) and BPF (105.7 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 101.8 mm Hg in controls.
“These results indicate that prenatal exposure to low levels of BPA analogs has a profound effect on hypertension” in the offspring of pregnant rats exposed to bisphenols, Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues wrote in the abstract.
He noted during his presentation that he and his colleagues plan to repeat the study in male offspring to determine if there are sex differences.
Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Sargis also reported no conflicts of interest.
The research will be published in a special supplemental issue of the Journal of the Endocrine Society. In addition to a series of news conferences on March 30-31, the society will host ENDO Online 2020 during June 8-22, which will present programming for clinicians and researchers.
SOURCE: MohanKumar P et al. ENDO 2020, Abstract 719.
This article was updated on 4/17/2020.
findings in a new study have shown.
Researchers tested exposures to BPA, as well as bisphenol-S (BPS) and bisphenol-F (BPF), which have been introduced in recent years as BPA alternatives and are now increasingly detectable in human and animal tissues. BPS and BPF are often found in products labeled as “BPA free.”
BPS and BPF have similar physiochemical properties to BPA, and there is concern over their effects.
But their physiological impact is not yet clear, according to Puliyur MohanKumar, DVM, PhD, of the University of Georgia Regenerative Bioscience Center, Athens. “We are exposed to BPA and related compounds on a regular basis, and the important thing is that BPA and related compounds easily cross the placental barrier,” Dr. MohanKumar said during a virtual news conference held by the Endocrine Society. The study had been slated for presentation during ENDO 2020, the society's annual meeting, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues exposed pregnant rats to BPA, BPS, or BPF. When the offspring reached adulthood, the researchers implanted them with radiotelemetry devices to track systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which they measured every 10 minutes over a 24-hour period. This was repeated once a week for 11 weeks.
“The female offspring had elevated systolic as well as diastolic blood pressure, and this was an increase of about 8 mm [Hg] higher than the control animals. That was pretty significant. Keeping these animals at such a prehypertensive state for such a long period of time is going to [lead to] lots of cardiovascular issues later on,” said Dr. MohanKumar.
Robert Sargis, MD, PhD, professor of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Illinois at Chicago, noted that, although animal studies don’t necessarily translate to similar outcomes in humans, the results are cause for concern.
“What’s particularly interesting, is that there is whole area of essential hypertension, where people develop hypertension and we don’t really know why. We just treat it,” he said in an interview. “But thinking about biological origins [of hypertension] is potentially interesting for a couple of reasons. These bisphenol compounds are really common. Most Americans are exposed to bisphenol A, and it’s been associated with other adverse metabolic effects, including alterations to body weight and glucose homeostasis.
“[These findings] feed into a whole series of studies that have begun to look at the BPA replacements and the fact that they may be, at best, as bad as BPA, and at worst, possibly slightly worse, depending on which outcomes you’re looking at,” Dr. Sargis added.
In the study, seven pregnant rats were orally exposed to saline, four pregnant rats to 5 mcg/kg BPA, four to 5 mcg/kg BPS, and five to 1 mcg/kg BPF during days 6-21 of pregnancy. The lower dose of BPF was used because a dose of 5 mcg/kg proved too toxic. When the offspring reached adulthood, the researchers implanted radiotelemetry devices in the offspring’s femoral artery.
Mean daytime systolic BP was highest in the BPA group (133.3 mg Hg; P < .05), followed by BPS (132.5 mm Hg; P < .05) and BPF (129.2 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 125.2 mm Hg in controls. Nighttime systolic BP was again highest in the BPA group (134.2 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPS (133.2 mm Hg; P < .05) and BPF (129.6 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 125.1 mm Hg in controls.
During the day, diastolic BP was highest in the BPS group (91.3 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPA (88.8 mm Hg; nonsignificant) and BPF (88.6 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 84.1 mm Hg in controls. At night, diastolic BP was highest in the BPS group (89.7 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPA (89.6 mm Hg; P < .01) and BPF (88.6 mm Hg; P < .01), compared with 83.3 mm Hg in controls.
During the day, mean arterial pressure was highest in the BPA group (110.5 mm Hg; P < .01), followed by BPS (108.9 mm Hg; P < .01) and BPF (105.2 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 102.6 mm Hg in controls. At night, mean arterial pressure was highest in BPS (108.6 mm Hg; P < .05), followed by BPA (107.5 mm Hg; nonsignificant) and BPF (105.7 mm Hg; nonsignificant), compared with 101.8 mm Hg in controls.
“These results indicate that prenatal exposure to low levels of BPA analogs has a profound effect on hypertension” in the offspring of pregnant rats exposed to bisphenols, Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues wrote in the abstract.
He noted during his presentation that he and his colleagues plan to repeat the study in male offspring to determine if there are sex differences.
Dr. MohanKumar and colleagues reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Sargis also reported no conflicts of interest.
The research will be published in a special supplemental issue of the Journal of the Endocrine Society. In addition to a series of news conferences on March 30-31, the society will host ENDO Online 2020 during June 8-22, which will present programming for clinicians and researchers.
SOURCE: MohanKumar P et al. ENDO 2020, Abstract 719.
This article was updated on 4/17/2020.
FROM ENDO 2020
Silicosis. Palliative care. Respiratory therapy. Sleep apnea. Immunotherapy.
Occupational and Environmental Health
Severe silicosis in engineered stone fabrication workers: An emerging epidemic
Silicosis is an irreversible fibrotic lung disease caused by inhalation of respirable forms of crystalline silica. Silica exposure is also associated with increased risk for mycobacterial infections, lung cancer, emphysema, autoimmune diseases, and kidney disease (Leung CC, et al. Lancet. 2012;379[9830]:2008; Bang KM, et al. MMWR. 2015;64[5]:117). Engineered stone is a manufactured quartz-based composite increasingly used for countertops in the United States where imports of engineered stone for this use have increased around 800% from 2010 to 2018. With this, reported silicosis cases among engineered stone fabrication workers have risen. Silica content in different stones varies from up to 45% in natural stones (granite) to >90% in engineered stone and quartz. The act of cutting, grinding, sanding, drilling, polishing, and installing this stone puts workers with direct and indirect contact with these tasks at risk for hazardous levels of inhaled silica exposure (OSHA et al. https://www.osha.gov/Publications/OSHA3768.pdf. 2015).
A growing number of cases associated with stone fabrication have been reported worldwide (Kramer MR, et al. Chest. 2012;142[2]:419; Kirby T. Lancet. 2019;393:861). The CDC recently published a report of 18 cases of accelerated silicosis over a two-year period among engineered stone fabrication workers. The majority of patients were aged <50 years, five patients had autoimmune disease, two patients had latent TB, and two died (Rose C, et al. MMWR. 2019;68[38]:813). Thus, the experience of engineered stone fabrication workers appears to parallel that of patient exposed to silica in other occupations.
Control measures (see resources below) for silica exposure, prevention, and medical surveillance have been updated since 2016 at the federal level prompting a recent revision of OSHA’s National Emphasis Program for respirable crystalline silica as of February 2020 (OSHA, https://www.osha.gov/news/newsreleases/trade/02052020, published February 5, 2020). Despite these measures, enforcement within the stone fabrication industry remains challenging. Small-scale operations with limited expertise in exposure control combined with high density of immigrant workers with limited health-care access and potential threat of retaliation have limited compliance with updated standards (Rose C, et al. MMWR. 2019;68[38]:813).
Silicosis is preventable, and efforts to minimize workplace exposure and enhance medical surveillance of stone fabrication workers should be prioritized.
Useful resources for silica workplace control measures:
https://www.cdph.ca.gov/silica-stonefabricators
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/silica/
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/enforcement/directives/CPL_03-00-023.pdf
Sujith Cherian MD, FCCP
Haala Rokadia MD, FCCP
Steering Committee Members
Palliative and end-of-life care
Building primary palliative care competencies in the CHEST community
The CHEST community cares for many patients with serious illnesses characterized by a high risk of mortality, burdensome symptoms or treatments, and caregiver distress, which negatively impact quality of life (QOL) (Kelly, et al. J Palliat Med. 2018;21[S2]:S7). Specialist palliative care (PC) clinicians work in partnership with other specialties to optimize QOL and alleviate suffering for seriously ill patients (i.e., advanced or chronic respiratory disease and/or critical illness).
Referral for specialist PC integration should be based on the complex needs of patients and not prognosis. PC can and should be delivered alongside disease-directed and life-prolonging therapies. Early PC referral in serious illness has been associated with improved QOL, better prognostic awareness, and, in some instances, increased survival. Additionally, reductions in medical costs at the end-of-life have been observed with early PC integration (Parikh, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369[24]:2347). However, patients with chronic or advanced respiratory diseases often receive PC late, if at all (Brown, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016;13[5]:684). This might be explained by significant shortages within the PC workforce, misconceptions that PC is only delivered at the end of life, and limited proficiency or comfort in primary PC delivery. Primary PC competencies have already been defined for pulmonary and critical care clinicians (Lanken, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:912). The Palliative and End-of-Life Care NetWork is focused on promoting awareness of specialty PC while providing education and resources to support primary PC competencies within the CHEST community. Look for NetWork-sponsored sessions at the annual meeting and follow conversations on social media using the hashtag #CHESTPalCare.
Dina Khateeb, DO
Fellow-in-Training Member
Respiratory care
I am a new respiratory therapist and a team member
It’s 11:00 pm and relatively quiet in the ICU. Then, that all too familiar sound, Code Blue. I rush to the room and assess the situation. As a new grad, this is one of the skills I am still developing; balancing my adrenaline with critical thinking in order to help manage the situation. Whether it is an unplanned extubation, acute respiratory failure, or cardiac arrest, as the respiratory therapist, I am there to bring an expertise to the assessment and management of airway and breathing. Once the crisis is resolved, my work is not done. I remain at the bedside to ensure ventilator management, explain to the family the respiratory interventions, and work with the medical team to implement the best plan of care.
As the bedside RT, I have unique perspective and training. My education prepared me with the knowledge base to work in this arena, but I still have so much to learn. And, as a new grad, one of the biggest lessons I have learned so far is to speak up. Whether it is during rounds, a code situation, or just conversations with the team. I owe it to my patients to advocate for their care and provide the expertise that I bring to the team. To the doctor or nurse, I hope you will give me that opportunity to help care for our patients; to learn; and even teach to improve that care.
Bethlehem Markos
Fellow-in-Training Member
Sleep medicine
What’s new in the sleep apnea treatment pipeline?
While weight loss in obese patients with sleep apnea is an effective treatment strategy, researchers honed in on a particular site of impact – the tongue fat (Wang SH, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2020;201[6]:718). After a weight loss program, they studied the changes in the tongue, pterygoid, lateral pharyngeal wall, and abdominal fat volumes using MRI. It turned out that reduced tongue fat volume was the primary mediator associated with AHI improvement. The authors suggested a reduction in tongue fat volume may be a potential OSA treatment strategy. Future studies will tell whether this is feasible and effective.
Recently, the FDA approved a new medication to treat residual daytime sleepiness in patients with sleep apnea – solriamfetol. Like other wake-promoting agents, it acts on the central nervous system and improves the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine. We look forward to head-to-head studies with current agents (modafinil or armodafinil).
Though not entirely new, two devices have been gaining popularity for sleep apnea treatment. Both are nerve stimulators: one designed for obstructive sleep apnea, is a hypoglossal nerve stimulator; the other, a treatment for central sleep apnea, is a phrenic nerve stimulator. They are slowly gaining popularity, though their invasive nature, patient selection criteria, and cost may limit their widespread adaption. More importantly, data on long-term outcomes and impact on hard endpoints such as mortality and reduction in cardiovascular morbidity are sparse.
Ritwick Agrawal, MD, MS, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Thoracic oncology
The long and winding treatment road of advanced lung cancer: Long-term outcomes with immunotherapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed the landscape in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment, extending progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Pembrolizumab is approved in advanced NSCLC with ≥50% PD-L1 expression based on KEYNOTE-024 trial.1 Recent updated analysis of KEYNOTE 024 trial2 showed that patients with advanced NSCLC treated with pembrolizumab had a median OS of 30.0 months compared with 14.2 months for those treated with chemotherapy. More recently, 5-year outcomes of KEYNOTE-001 trial3 showed that OS was 23.2% for treatment-naive patients and 15.5% for previously treated patients with no grade 4 or 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Nivolumab is approved for the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC with progression of disease after standard chemotherapy (regardless of PD-L1 expression) based on CHECKMATE 017/057 trials.4,5 OS at 5 years in recently presented pooled analysis of these trials was 13.4% in nivolumab arm compared to 2.6% in docetaxel arm with a PFS of 8% and 0% respectively.6,7 Median duration of response was 19.9 months vs 5.6 months. At 5 years, almost one-third of patients who responded to the nivolumab were without disease progression. Similarly, a recent 5-year analysis of patients with advanced NSCLC treated with nivolumab showed OS of 16%, identical for squamous and nonsquamous histology. 75% of 5-year survivors were without disease progression.8
Treatment with immunotherapy in advanced NSCLC has resulted in a dramatic change in outcomes with a small percent of patients able to achieve durable responses.
Hiren Mehta, MD, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
References
1. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1823.
2. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:537.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:2518.
4. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:123.
5. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:1627.6. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35:3924.
7. https://wclc2019.iaslc.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/WCLC2019-Abstract-Book_web-friendly.pdf
8. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1675.
Occupational and Environmental Health
Severe silicosis in engineered stone fabrication workers: An emerging epidemic
Silicosis is an irreversible fibrotic lung disease caused by inhalation of respirable forms of crystalline silica. Silica exposure is also associated with increased risk for mycobacterial infections, lung cancer, emphysema, autoimmune diseases, and kidney disease (Leung CC, et al. Lancet. 2012;379[9830]:2008; Bang KM, et al. MMWR. 2015;64[5]:117). Engineered stone is a manufactured quartz-based composite increasingly used for countertops in the United States where imports of engineered stone for this use have increased around 800% from 2010 to 2018. With this, reported silicosis cases among engineered stone fabrication workers have risen. Silica content in different stones varies from up to 45% in natural stones (granite) to >90% in engineered stone and quartz. The act of cutting, grinding, sanding, drilling, polishing, and installing this stone puts workers with direct and indirect contact with these tasks at risk for hazardous levels of inhaled silica exposure (OSHA et al. https://www.osha.gov/Publications/OSHA3768.pdf. 2015).
A growing number of cases associated with stone fabrication have been reported worldwide (Kramer MR, et al. Chest. 2012;142[2]:419; Kirby T. Lancet. 2019;393:861). The CDC recently published a report of 18 cases of accelerated silicosis over a two-year period among engineered stone fabrication workers. The majority of patients were aged <50 years, five patients had autoimmune disease, two patients had latent TB, and two died (Rose C, et al. MMWR. 2019;68[38]:813). Thus, the experience of engineered stone fabrication workers appears to parallel that of patient exposed to silica in other occupations.
Control measures (see resources below) for silica exposure, prevention, and medical surveillance have been updated since 2016 at the federal level prompting a recent revision of OSHA’s National Emphasis Program for respirable crystalline silica as of February 2020 (OSHA, https://www.osha.gov/news/newsreleases/trade/02052020, published February 5, 2020). Despite these measures, enforcement within the stone fabrication industry remains challenging. Small-scale operations with limited expertise in exposure control combined with high density of immigrant workers with limited health-care access and potential threat of retaliation have limited compliance with updated standards (Rose C, et al. MMWR. 2019;68[38]:813).
Silicosis is preventable, and efforts to minimize workplace exposure and enhance medical surveillance of stone fabrication workers should be prioritized.
Useful resources for silica workplace control measures:
https://www.cdph.ca.gov/silica-stonefabricators
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/silica/
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/enforcement/directives/CPL_03-00-023.pdf
Sujith Cherian MD, FCCP
Haala Rokadia MD, FCCP
Steering Committee Members
Palliative and end-of-life care
Building primary palliative care competencies in the CHEST community
The CHEST community cares for many patients with serious illnesses characterized by a high risk of mortality, burdensome symptoms or treatments, and caregiver distress, which negatively impact quality of life (QOL) (Kelly, et al. J Palliat Med. 2018;21[S2]:S7). Specialist palliative care (PC) clinicians work in partnership with other specialties to optimize QOL and alleviate suffering for seriously ill patients (i.e., advanced or chronic respiratory disease and/or critical illness).
Referral for specialist PC integration should be based on the complex needs of patients and not prognosis. PC can and should be delivered alongside disease-directed and life-prolonging therapies. Early PC referral in serious illness has been associated with improved QOL, better prognostic awareness, and, in some instances, increased survival. Additionally, reductions in medical costs at the end-of-life have been observed with early PC integration (Parikh, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369[24]:2347). However, patients with chronic or advanced respiratory diseases often receive PC late, if at all (Brown, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016;13[5]:684). This might be explained by significant shortages within the PC workforce, misconceptions that PC is only delivered at the end of life, and limited proficiency or comfort in primary PC delivery. Primary PC competencies have already been defined for pulmonary and critical care clinicians (Lanken, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:912). The Palliative and End-of-Life Care NetWork is focused on promoting awareness of specialty PC while providing education and resources to support primary PC competencies within the CHEST community. Look for NetWork-sponsored sessions at the annual meeting and follow conversations on social media using the hashtag #CHESTPalCare.
Dina Khateeb, DO
Fellow-in-Training Member
Respiratory care
I am a new respiratory therapist and a team member
It’s 11:00 pm and relatively quiet in the ICU. Then, that all too familiar sound, Code Blue. I rush to the room and assess the situation. As a new grad, this is one of the skills I am still developing; balancing my adrenaline with critical thinking in order to help manage the situation. Whether it is an unplanned extubation, acute respiratory failure, or cardiac arrest, as the respiratory therapist, I am there to bring an expertise to the assessment and management of airway and breathing. Once the crisis is resolved, my work is not done. I remain at the bedside to ensure ventilator management, explain to the family the respiratory interventions, and work with the medical team to implement the best plan of care.
As the bedside RT, I have unique perspective and training. My education prepared me with the knowledge base to work in this arena, but I still have so much to learn. And, as a new grad, one of the biggest lessons I have learned so far is to speak up. Whether it is during rounds, a code situation, or just conversations with the team. I owe it to my patients to advocate for their care and provide the expertise that I bring to the team. To the doctor or nurse, I hope you will give me that opportunity to help care for our patients; to learn; and even teach to improve that care.
Bethlehem Markos
Fellow-in-Training Member
Sleep medicine
What’s new in the sleep apnea treatment pipeline?
While weight loss in obese patients with sleep apnea is an effective treatment strategy, researchers honed in on a particular site of impact – the tongue fat (Wang SH, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2020;201[6]:718). After a weight loss program, they studied the changes in the tongue, pterygoid, lateral pharyngeal wall, and abdominal fat volumes using MRI. It turned out that reduced tongue fat volume was the primary mediator associated with AHI improvement. The authors suggested a reduction in tongue fat volume may be a potential OSA treatment strategy. Future studies will tell whether this is feasible and effective.
Recently, the FDA approved a new medication to treat residual daytime sleepiness in patients with sleep apnea – solriamfetol. Like other wake-promoting agents, it acts on the central nervous system and improves the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine. We look forward to head-to-head studies with current agents (modafinil or armodafinil).
Though not entirely new, two devices have been gaining popularity for sleep apnea treatment. Both are nerve stimulators: one designed for obstructive sleep apnea, is a hypoglossal nerve stimulator; the other, a treatment for central sleep apnea, is a phrenic nerve stimulator. They are slowly gaining popularity, though their invasive nature, patient selection criteria, and cost may limit their widespread adaption. More importantly, data on long-term outcomes and impact on hard endpoints such as mortality and reduction in cardiovascular morbidity are sparse.
Ritwick Agrawal, MD, MS, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Thoracic oncology
The long and winding treatment road of advanced lung cancer: Long-term outcomes with immunotherapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed the landscape in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment, extending progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Pembrolizumab is approved in advanced NSCLC with ≥50% PD-L1 expression based on KEYNOTE-024 trial.1 Recent updated analysis of KEYNOTE 024 trial2 showed that patients with advanced NSCLC treated with pembrolizumab had a median OS of 30.0 months compared with 14.2 months for those treated with chemotherapy. More recently, 5-year outcomes of KEYNOTE-001 trial3 showed that OS was 23.2% for treatment-naive patients and 15.5% for previously treated patients with no grade 4 or 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Nivolumab is approved for the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC with progression of disease after standard chemotherapy (regardless of PD-L1 expression) based on CHECKMATE 017/057 trials.4,5 OS at 5 years in recently presented pooled analysis of these trials was 13.4% in nivolumab arm compared to 2.6% in docetaxel arm with a PFS of 8% and 0% respectively.6,7 Median duration of response was 19.9 months vs 5.6 months. At 5 years, almost one-third of patients who responded to the nivolumab were without disease progression. Similarly, a recent 5-year analysis of patients with advanced NSCLC treated with nivolumab showed OS of 16%, identical for squamous and nonsquamous histology. 75% of 5-year survivors were without disease progression.8
Treatment with immunotherapy in advanced NSCLC has resulted in a dramatic change in outcomes with a small percent of patients able to achieve durable responses.
Hiren Mehta, MD, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
References
1. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1823.
2. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:537.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:2518.
4. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:123.
5. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:1627.6. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35:3924.
7. https://wclc2019.iaslc.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/WCLC2019-Abstract-Book_web-friendly.pdf
8. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1675.
Occupational and Environmental Health
Severe silicosis in engineered stone fabrication workers: An emerging epidemic
Silicosis is an irreversible fibrotic lung disease caused by inhalation of respirable forms of crystalline silica. Silica exposure is also associated with increased risk for mycobacterial infections, lung cancer, emphysema, autoimmune diseases, and kidney disease (Leung CC, et al. Lancet. 2012;379[9830]:2008; Bang KM, et al. MMWR. 2015;64[5]:117). Engineered stone is a manufactured quartz-based composite increasingly used for countertops in the United States where imports of engineered stone for this use have increased around 800% from 2010 to 2018. With this, reported silicosis cases among engineered stone fabrication workers have risen. Silica content in different stones varies from up to 45% in natural stones (granite) to >90% in engineered stone and quartz. The act of cutting, grinding, sanding, drilling, polishing, and installing this stone puts workers with direct and indirect contact with these tasks at risk for hazardous levels of inhaled silica exposure (OSHA et al. https://www.osha.gov/Publications/OSHA3768.pdf. 2015).
A growing number of cases associated with stone fabrication have been reported worldwide (Kramer MR, et al. Chest. 2012;142[2]:419; Kirby T. Lancet. 2019;393:861). The CDC recently published a report of 18 cases of accelerated silicosis over a two-year period among engineered stone fabrication workers. The majority of patients were aged <50 years, five patients had autoimmune disease, two patients had latent TB, and two died (Rose C, et al. MMWR. 2019;68[38]:813). Thus, the experience of engineered stone fabrication workers appears to parallel that of patient exposed to silica in other occupations.
Control measures (see resources below) for silica exposure, prevention, and medical surveillance have been updated since 2016 at the federal level prompting a recent revision of OSHA’s National Emphasis Program for respirable crystalline silica as of February 2020 (OSHA, https://www.osha.gov/news/newsreleases/trade/02052020, published February 5, 2020). Despite these measures, enforcement within the stone fabrication industry remains challenging. Small-scale operations with limited expertise in exposure control combined with high density of immigrant workers with limited health-care access and potential threat of retaliation have limited compliance with updated standards (Rose C, et al. MMWR. 2019;68[38]:813).
Silicosis is preventable, and efforts to minimize workplace exposure and enhance medical surveillance of stone fabrication workers should be prioritized.
Useful resources for silica workplace control measures:
https://www.cdph.ca.gov/silica-stonefabricators
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/silica/
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/enforcement/directives/CPL_03-00-023.pdf
Sujith Cherian MD, FCCP
Haala Rokadia MD, FCCP
Steering Committee Members
Palliative and end-of-life care
Building primary palliative care competencies in the CHEST community
The CHEST community cares for many patients with serious illnesses characterized by a high risk of mortality, burdensome symptoms or treatments, and caregiver distress, which negatively impact quality of life (QOL) (Kelly, et al. J Palliat Med. 2018;21[S2]:S7). Specialist palliative care (PC) clinicians work in partnership with other specialties to optimize QOL and alleviate suffering for seriously ill patients (i.e., advanced or chronic respiratory disease and/or critical illness).
Referral for specialist PC integration should be based on the complex needs of patients and not prognosis. PC can and should be delivered alongside disease-directed and life-prolonging therapies. Early PC referral in serious illness has been associated with improved QOL, better prognostic awareness, and, in some instances, increased survival. Additionally, reductions in medical costs at the end-of-life have been observed with early PC integration (Parikh, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369[24]:2347). However, patients with chronic or advanced respiratory diseases often receive PC late, if at all (Brown, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016;13[5]:684). This might be explained by significant shortages within the PC workforce, misconceptions that PC is only delivered at the end of life, and limited proficiency or comfort in primary PC delivery. Primary PC competencies have already been defined for pulmonary and critical care clinicians (Lanken, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:912). The Palliative and End-of-Life Care NetWork is focused on promoting awareness of specialty PC while providing education and resources to support primary PC competencies within the CHEST community. Look for NetWork-sponsored sessions at the annual meeting and follow conversations on social media using the hashtag #CHESTPalCare.
Dina Khateeb, DO
Fellow-in-Training Member
Respiratory care
I am a new respiratory therapist and a team member
It’s 11:00 pm and relatively quiet in the ICU. Then, that all too familiar sound, Code Blue. I rush to the room and assess the situation. As a new grad, this is one of the skills I am still developing; balancing my adrenaline with critical thinking in order to help manage the situation. Whether it is an unplanned extubation, acute respiratory failure, or cardiac arrest, as the respiratory therapist, I am there to bring an expertise to the assessment and management of airway and breathing. Once the crisis is resolved, my work is not done. I remain at the bedside to ensure ventilator management, explain to the family the respiratory interventions, and work with the medical team to implement the best plan of care.
As the bedside RT, I have unique perspective and training. My education prepared me with the knowledge base to work in this arena, but I still have so much to learn. And, as a new grad, one of the biggest lessons I have learned so far is to speak up. Whether it is during rounds, a code situation, or just conversations with the team. I owe it to my patients to advocate for their care and provide the expertise that I bring to the team. To the doctor or nurse, I hope you will give me that opportunity to help care for our patients; to learn; and even teach to improve that care.
Bethlehem Markos
Fellow-in-Training Member
Sleep medicine
What’s new in the sleep apnea treatment pipeline?
While weight loss in obese patients with sleep apnea is an effective treatment strategy, researchers honed in on a particular site of impact – the tongue fat (Wang SH, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2020;201[6]:718). After a weight loss program, they studied the changes in the tongue, pterygoid, lateral pharyngeal wall, and abdominal fat volumes using MRI. It turned out that reduced tongue fat volume was the primary mediator associated with AHI improvement. The authors suggested a reduction in tongue fat volume may be a potential OSA treatment strategy. Future studies will tell whether this is feasible and effective.
Recently, the FDA approved a new medication to treat residual daytime sleepiness in patients with sleep apnea – solriamfetol. Like other wake-promoting agents, it acts on the central nervous system and improves the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine. We look forward to head-to-head studies with current agents (modafinil or armodafinil).
Though not entirely new, two devices have been gaining popularity for sleep apnea treatment. Both are nerve stimulators: one designed for obstructive sleep apnea, is a hypoglossal nerve stimulator; the other, a treatment for central sleep apnea, is a phrenic nerve stimulator. They are slowly gaining popularity, though their invasive nature, patient selection criteria, and cost may limit their widespread adaption. More importantly, data on long-term outcomes and impact on hard endpoints such as mortality and reduction in cardiovascular morbidity are sparse.
Ritwick Agrawal, MD, MS, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Thoracic oncology
The long and winding treatment road of advanced lung cancer: Long-term outcomes with immunotherapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed the landscape in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment, extending progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Pembrolizumab is approved in advanced NSCLC with ≥50% PD-L1 expression based on KEYNOTE-024 trial.1 Recent updated analysis of KEYNOTE 024 trial2 showed that patients with advanced NSCLC treated with pembrolizumab had a median OS of 30.0 months compared with 14.2 months for those treated with chemotherapy. More recently, 5-year outcomes of KEYNOTE-001 trial3 showed that OS was 23.2% for treatment-naive patients and 15.5% for previously treated patients with no grade 4 or 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Nivolumab is approved for the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC with progression of disease after standard chemotherapy (regardless of PD-L1 expression) based on CHECKMATE 017/057 trials.4,5 OS at 5 years in recently presented pooled analysis of these trials was 13.4% in nivolumab arm compared to 2.6% in docetaxel arm with a PFS of 8% and 0% respectively.6,7 Median duration of response was 19.9 months vs 5.6 months. At 5 years, almost one-third of patients who responded to the nivolumab were without disease progression. Similarly, a recent 5-year analysis of patients with advanced NSCLC treated with nivolumab showed OS of 16%, identical for squamous and nonsquamous histology. 75% of 5-year survivors were without disease progression.8
Treatment with immunotherapy in advanced NSCLC has resulted in a dramatic change in outcomes with a small percent of patients able to achieve durable responses.
Hiren Mehta, MD, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
References
1. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1823.
2. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:537.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:2518.
4. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:123.
5. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:1627.6. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35:3924.
7. https://wclc2019.iaslc.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/WCLC2019-Abstract-Book_web-friendly.pdf
8. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1675.
Meet the FISH Bowl finalists
CHEST 2019 marked the inaugural FISH Bowl competition for attendees. Inspired by Shark Tank, our kinder, gentler, yet still competitive and cutting-edge FISH Bowl (Furthering Innovation and Science for Health) featured CHEST members disrupting our beliefs about how clinical care and education are performed. As health-care providers, they presented innovative ideas pertaining to education and clinical disease for pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. Six finalists were chosen from dozens of submissions, and three emerged winners. In this new Meet the FISH Bowl Finalists series, CHEST introduces you to many of them – including Education Category Finalist Dr. Cota.
Name: Donna Cota, DO
Institutional Affiliation: Baystate Medical Center, PGY5 Critical Care
Position: 2nd Year Fellow in PGY5 Critical Care
Title: Time to Vent: A Blended Learning Experience
Brief Summary of Submission: Time to Vent is a blended learning experience focused on ventilator management that incorporates modalities for all learning types. It includes a handout, audio/visual presentation, and practice case scenarios.
1. What inspired your innovation? I remembered that as a resident, I had a very difficult time understanding ventilators and worked hard to try to understand them on my own. When I started fellowship, I thought I understood ventilator management and then realized I was still wrong. I have focused my training on education, and I wanted to create a concise resource geared toward the fundamentals of ventilators for the benefit of educational levels.
2. Who do you think can benefit most from it, and why? Right now, I have focused the project on teaching residents of varying specialties, such as internal medicine and emergency medicine. They are still in training and rotate through ICUs, needing to understand ventilators for effective patient care and questions are present on their board examinations.
3. What do you see as challenges to your innovation gaining widespread acceptance? How can they be overcome? The biggest challenge is making the website able to be found on Google. This is a work in progress. However, right now, the link is sent via email to interested parties.
4. Why was it meaningful for you to emerge as a finalist in FISH Bowl 2019? It built confidence that my lifelong project is important and has merit to it. And, it ended up becoming a way for people to learn about the project and ask me for the link.
5. What future do you envision for your innovation beyond FISH Bowl 2019? I am still going to continue to improve the project with current endeavors to include a piece on waveforms and dyssynchrony of the ventilator. My ultimate goal is to create a free virtual ventilator simulator with practice cases.
CHEST 2019 marked the inaugural FISH Bowl competition for attendees. Inspired by Shark Tank, our kinder, gentler, yet still competitive and cutting-edge FISH Bowl (Furthering Innovation and Science for Health) featured CHEST members disrupting our beliefs about how clinical care and education are performed. As health-care providers, they presented innovative ideas pertaining to education and clinical disease for pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. Six finalists were chosen from dozens of submissions, and three emerged winners. In this new Meet the FISH Bowl Finalists series, CHEST introduces you to many of them – including Education Category Finalist Dr. Cota.
Name: Donna Cota, DO
Institutional Affiliation: Baystate Medical Center, PGY5 Critical Care
Position: 2nd Year Fellow in PGY5 Critical Care
Title: Time to Vent: A Blended Learning Experience
Brief Summary of Submission: Time to Vent is a blended learning experience focused on ventilator management that incorporates modalities for all learning types. It includes a handout, audio/visual presentation, and practice case scenarios.
1. What inspired your innovation? I remembered that as a resident, I had a very difficult time understanding ventilators and worked hard to try to understand them on my own. When I started fellowship, I thought I understood ventilator management and then realized I was still wrong. I have focused my training on education, and I wanted to create a concise resource geared toward the fundamentals of ventilators for the benefit of educational levels.
2. Who do you think can benefit most from it, and why? Right now, I have focused the project on teaching residents of varying specialties, such as internal medicine and emergency medicine. They are still in training and rotate through ICUs, needing to understand ventilators for effective patient care and questions are present on their board examinations.
3. What do you see as challenges to your innovation gaining widespread acceptance? How can they be overcome? The biggest challenge is making the website able to be found on Google. This is a work in progress. However, right now, the link is sent via email to interested parties.
4. Why was it meaningful for you to emerge as a finalist in FISH Bowl 2019? It built confidence that my lifelong project is important and has merit to it. And, it ended up becoming a way for people to learn about the project and ask me for the link.
5. What future do you envision for your innovation beyond FISH Bowl 2019? I am still going to continue to improve the project with current endeavors to include a piece on waveforms and dyssynchrony of the ventilator. My ultimate goal is to create a free virtual ventilator simulator with practice cases.
CHEST 2019 marked the inaugural FISH Bowl competition for attendees. Inspired by Shark Tank, our kinder, gentler, yet still competitive and cutting-edge FISH Bowl (Furthering Innovation and Science for Health) featured CHEST members disrupting our beliefs about how clinical care and education are performed. As health-care providers, they presented innovative ideas pertaining to education and clinical disease for pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. Six finalists were chosen from dozens of submissions, and three emerged winners. In this new Meet the FISH Bowl Finalists series, CHEST introduces you to many of them – including Education Category Finalist Dr. Cota.
Name: Donna Cota, DO
Institutional Affiliation: Baystate Medical Center, PGY5 Critical Care
Position: 2nd Year Fellow in PGY5 Critical Care
Title: Time to Vent: A Blended Learning Experience
Brief Summary of Submission: Time to Vent is a blended learning experience focused on ventilator management that incorporates modalities for all learning types. It includes a handout, audio/visual presentation, and practice case scenarios.
1. What inspired your innovation? I remembered that as a resident, I had a very difficult time understanding ventilators and worked hard to try to understand them on my own. When I started fellowship, I thought I understood ventilator management and then realized I was still wrong. I have focused my training on education, and I wanted to create a concise resource geared toward the fundamentals of ventilators for the benefit of educational levels.
2. Who do you think can benefit most from it, and why? Right now, I have focused the project on teaching residents of varying specialties, such as internal medicine and emergency medicine. They are still in training and rotate through ICUs, needing to understand ventilators for effective patient care and questions are present on their board examinations.
3. What do you see as challenges to your innovation gaining widespread acceptance? How can they be overcome? The biggest challenge is making the website able to be found on Google. This is a work in progress. However, right now, the link is sent via email to interested parties.
4. Why was it meaningful for you to emerge as a finalist in FISH Bowl 2019? It built confidence that my lifelong project is important and has merit to it. And, it ended up becoming a way for people to learn about the project and ask me for the link.
5. What future do you envision for your innovation beyond FISH Bowl 2019? I am still going to continue to improve the project with current endeavors to include a piece on waveforms and dyssynchrony of the ventilator. My ultimate goal is to create a free virtual ventilator simulator with practice cases.
The “Windy City” waits for you!
CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 will be here before you know it and we’re here to guide you through our Second City home, Chicago, Illinois. We’re so excited to be hosting CHEST 2020 in our backyard this year and want to help you experience everything that the city has to offer when you aren’t taking in the latest education in clinical chest medicine.
Whether you’re looking to embrace the culture, discover new shops, seeking entertainment, or just looking for a photo opportunity, we’ve got you covered. There’s something for everyone! Here are a few suggestions to keep you busy after your courses and sessions end.
Millennium Park Campus
Located in the heart of the city, Millennium Park is home to the Art Institute of Chicago, Cloud Gate (“The Bean”), Maggie Daley Park, Crown Fountain, Park Grill restaurant, and more. This is the perfect place to take a fall stroll this October.
Cloud Gate (the bean)
Undoubtedly, one of Chicago’s most popular attractions, this reflective sculpture opposite of Millennium Park is a must for the perfect selfie. Don’t forget to bring your selfie stick to optimize your angles!
Field Museum
One of the largest history museums in the world, this space is filled with an extensive collection of artifacts and scientific-specimens, along with educational programs. Whether you’re interested in browsing through photo archives, taking a public tour, or strolling through the library of over 275,000 books, it would be easy to spend a few hours here during your breaks. (Kids will love it too!)
Wrigley Field Tours
The World Series is set to start during the meeting, fingers crossed the Cubs will be making a return to Wrigley Field. Regardless, you can still attend an off-season tour allowing you to visit the Visitors’ clubhouse, Cubs’ dugout, field, American Airlines 1914 Club, Maker’s Mark Barrel Room, and The W Club at the home of the Chicago Cubs.
Starbucks Reserve Roastery
While you’re strolling on Michigan Avenue, be sure to stop by the world’s largest Starbucks. Enjoy a latte while you take a tour of the roastery or even experience a master tasting.
Take a river boat tour
Embrace the outdoors by taking a scenic cruise on the Chicago River during a boat tour. Choose from tours that highlight architecture, classic Chicago spots, a dinner cruise, and more.
Skydeck Chicago
Take a step out on the Ledge during your stay in Chicago. Test your limits on the 103rd floor of the Willis Tower by stepping onto a glass platform 1,353 feet in the air. Skydeck Chicago also features museum-quality exhibits and theater presentation, Reaching For The Sky.
Navy Pier
Stretching more than 3,000 feet along the shoreline of Lake Michigan, Navy Pier offers access to parks, gardens, shops, dining experiences, live entertainment, and more. If you’re looking for an engaging experience for kids, Navy Pier is also home to the Chicago Children’s Museum.
Frank Lloyd Wright Tours
Wrap up your time in Chicago with the Wright Along the Lake tour, a half-day guided bus tour featuring some of Wright’s most iconic sites in Chicago. Tours are also available for select sites including the Frederick C. Robie House and the Rookery Light Court.
The Magnificent Mile
One of the most iconic shopping centers in the world, The Magnificent Mile stretches across downtown Michigan Avenue and features historic landmarks, more than 460 retailers, and more than 275 restaurants.
Don’t forget to bring your jacket for outdoor activities! They don’t call Chicago the Windy City for nothing.
We look forward to exploring clinical chest medicine and the city of Chicago with you at CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 in October. See you there!
CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 will be here before you know it and we’re here to guide you through our Second City home, Chicago, Illinois. We’re so excited to be hosting CHEST 2020 in our backyard this year and want to help you experience everything that the city has to offer when you aren’t taking in the latest education in clinical chest medicine.
Whether you’re looking to embrace the culture, discover new shops, seeking entertainment, or just looking for a photo opportunity, we’ve got you covered. There’s something for everyone! Here are a few suggestions to keep you busy after your courses and sessions end.
Millennium Park Campus
Located in the heart of the city, Millennium Park is home to the Art Institute of Chicago, Cloud Gate (“The Bean”), Maggie Daley Park, Crown Fountain, Park Grill restaurant, and more. This is the perfect place to take a fall stroll this October.
Cloud Gate (the bean)
Undoubtedly, one of Chicago’s most popular attractions, this reflective sculpture opposite of Millennium Park is a must for the perfect selfie. Don’t forget to bring your selfie stick to optimize your angles!
Field Museum
One of the largest history museums in the world, this space is filled with an extensive collection of artifacts and scientific-specimens, along with educational programs. Whether you’re interested in browsing through photo archives, taking a public tour, or strolling through the library of over 275,000 books, it would be easy to spend a few hours here during your breaks. (Kids will love it too!)
Wrigley Field Tours
The World Series is set to start during the meeting, fingers crossed the Cubs will be making a return to Wrigley Field. Regardless, you can still attend an off-season tour allowing you to visit the Visitors’ clubhouse, Cubs’ dugout, field, American Airlines 1914 Club, Maker’s Mark Barrel Room, and The W Club at the home of the Chicago Cubs.
Starbucks Reserve Roastery
While you’re strolling on Michigan Avenue, be sure to stop by the world’s largest Starbucks. Enjoy a latte while you take a tour of the roastery or even experience a master tasting.
Take a river boat tour
Embrace the outdoors by taking a scenic cruise on the Chicago River during a boat tour. Choose from tours that highlight architecture, classic Chicago spots, a dinner cruise, and more.
Skydeck Chicago
Take a step out on the Ledge during your stay in Chicago. Test your limits on the 103rd floor of the Willis Tower by stepping onto a glass platform 1,353 feet in the air. Skydeck Chicago also features museum-quality exhibits and theater presentation, Reaching For The Sky.
Navy Pier
Stretching more than 3,000 feet along the shoreline of Lake Michigan, Navy Pier offers access to parks, gardens, shops, dining experiences, live entertainment, and more. If you’re looking for an engaging experience for kids, Navy Pier is also home to the Chicago Children’s Museum.
Frank Lloyd Wright Tours
Wrap up your time in Chicago with the Wright Along the Lake tour, a half-day guided bus tour featuring some of Wright’s most iconic sites in Chicago. Tours are also available for select sites including the Frederick C. Robie House and the Rookery Light Court.
The Magnificent Mile
One of the most iconic shopping centers in the world, The Magnificent Mile stretches across downtown Michigan Avenue and features historic landmarks, more than 460 retailers, and more than 275 restaurants.
Don’t forget to bring your jacket for outdoor activities! They don’t call Chicago the Windy City for nothing.
We look forward to exploring clinical chest medicine and the city of Chicago with you at CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 in October. See you there!
CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 will be here before you know it and we’re here to guide you through our Second City home, Chicago, Illinois. We’re so excited to be hosting CHEST 2020 in our backyard this year and want to help you experience everything that the city has to offer when you aren’t taking in the latest education in clinical chest medicine.
Whether you’re looking to embrace the culture, discover new shops, seeking entertainment, or just looking for a photo opportunity, we’ve got you covered. There’s something for everyone! Here are a few suggestions to keep you busy after your courses and sessions end.
Millennium Park Campus
Located in the heart of the city, Millennium Park is home to the Art Institute of Chicago, Cloud Gate (“The Bean”), Maggie Daley Park, Crown Fountain, Park Grill restaurant, and more. This is the perfect place to take a fall stroll this October.
Cloud Gate (the bean)
Undoubtedly, one of Chicago’s most popular attractions, this reflective sculpture opposite of Millennium Park is a must for the perfect selfie. Don’t forget to bring your selfie stick to optimize your angles!
Field Museum
One of the largest history museums in the world, this space is filled with an extensive collection of artifacts and scientific-specimens, along with educational programs. Whether you’re interested in browsing through photo archives, taking a public tour, or strolling through the library of over 275,000 books, it would be easy to spend a few hours here during your breaks. (Kids will love it too!)
Wrigley Field Tours
The World Series is set to start during the meeting, fingers crossed the Cubs will be making a return to Wrigley Field. Regardless, you can still attend an off-season tour allowing you to visit the Visitors’ clubhouse, Cubs’ dugout, field, American Airlines 1914 Club, Maker’s Mark Barrel Room, and The W Club at the home of the Chicago Cubs.
Starbucks Reserve Roastery
While you’re strolling on Michigan Avenue, be sure to stop by the world’s largest Starbucks. Enjoy a latte while you take a tour of the roastery or even experience a master tasting.
Take a river boat tour
Embrace the outdoors by taking a scenic cruise on the Chicago River during a boat tour. Choose from tours that highlight architecture, classic Chicago spots, a dinner cruise, and more.
Skydeck Chicago
Take a step out on the Ledge during your stay in Chicago. Test your limits on the 103rd floor of the Willis Tower by stepping onto a glass platform 1,353 feet in the air. Skydeck Chicago also features museum-quality exhibits and theater presentation, Reaching For The Sky.
Navy Pier
Stretching more than 3,000 feet along the shoreline of Lake Michigan, Navy Pier offers access to parks, gardens, shops, dining experiences, live entertainment, and more. If you’re looking for an engaging experience for kids, Navy Pier is also home to the Chicago Children’s Museum.
Frank Lloyd Wright Tours
Wrap up your time in Chicago with the Wright Along the Lake tour, a half-day guided bus tour featuring some of Wright’s most iconic sites in Chicago. Tours are also available for select sites including the Frederick C. Robie House and the Rookery Light Court.
The Magnificent Mile
One of the most iconic shopping centers in the world, The Magnificent Mile stretches across downtown Michigan Avenue and features historic landmarks, more than 460 retailers, and more than 275 restaurants.
Don’t forget to bring your jacket for outdoor activities! They don’t call Chicago the Windy City for nothing.
We look forward to exploring clinical chest medicine and the city of Chicago with you at CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 in October. See you there!
CHEST strengthens advocacy presence with official NAMDRC integration announcement
On Thursday, March 12, The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) and the National Association for Medical Direction of Respiratory Care (NAMDRC) announced publicly our official intent to come together as one association, integrating all NAMDRC activities and operations into CHEST.
This integration launch followed months of discussion between CHEST and NAMDRC leadership. Our respective Boards agreed that united efforts will amplify our individual involvement in patient advocacy and policy.
CHEST and NAMDRC have an intertwined purpose of delivering the highest standard of care for our patients. For this reason, our likeminded advocacy agendas can be even better fulfilled when we can leverage strengths from both associations.
CHEST and NAMDRC have shared an overlapping membership and collaborative history of empowering patients through the advancement of public policy and clinical education for decades. In additional to our individual efforts, our associations historically leveraged a combined advocacy presence in Washington D.C. to advance legislation against major tobacco corporations.
Coming together as a joint advocacy-focused organization, the initiation of CHEST’s Health Policy and Advocacy Committee, which will be comprised of an equal selection of CHEST and NAMDRC leadership, will drive CHEST’s advocacy agenda. The committee will work directly with policymakers, and target legislative and regulatory issues impacting pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine.
A committee of this kind, dedicated strictly to advocacy efforts, will be absolutely invaluable to our united organization. This group will be a true asset for membership to turn, to voice concerns within our practice, and to direct action on policies that matter to our patients.
Members of both organizations were notified of the integration by email on Wednesday, March 11. Along with email notification, NAMDRC members also received a voting ballot, as the dissolution of a nonprofit organization for Virginia-based organizations requires a vote of approval by membership within a 25-day waiting period.
NAMDRC’s long regarded monthly publication, Washington Watchline, will continue through CHEST, as will the NAMDRC Annual Meeting, slated for next March 18-20, 2021 in Sonoma, California, in conjunction with the CHEST Spring Leadership Meeting.
Concentrating our efforts under one organization allows us offer the best possible opportunities to our membership, patients, and far-reaching network. This is an exciting time for everyone involved, and we are looking forward to seeing all we can accomplish together.
On Thursday, March 12, The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) and the National Association for Medical Direction of Respiratory Care (NAMDRC) announced publicly our official intent to come together as one association, integrating all NAMDRC activities and operations into CHEST.
This integration launch followed months of discussion between CHEST and NAMDRC leadership. Our respective Boards agreed that united efforts will amplify our individual involvement in patient advocacy and policy.
CHEST and NAMDRC have an intertwined purpose of delivering the highest standard of care for our patients. For this reason, our likeminded advocacy agendas can be even better fulfilled when we can leverage strengths from both associations.
CHEST and NAMDRC have shared an overlapping membership and collaborative history of empowering patients through the advancement of public policy and clinical education for decades. In additional to our individual efforts, our associations historically leveraged a combined advocacy presence in Washington D.C. to advance legislation against major tobacco corporations.
Coming together as a joint advocacy-focused organization, the initiation of CHEST’s Health Policy and Advocacy Committee, which will be comprised of an equal selection of CHEST and NAMDRC leadership, will drive CHEST’s advocacy agenda. The committee will work directly with policymakers, and target legislative and regulatory issues impacting pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine.
A committee of this kind, dedicated strictly to advocacy efforts, will be absolutely invaluable to our united organization. This group will be a true asset for membership to turn, to voice concerns within our practice, and to direct action on policies that matter to our patients.
Members of both organizations were notified of the integration by email on Wednesday, March 11. Along with email notification, NAMDRC members also received a voting ballot, as the dissolution of a nonprofit organization for Virginia-based organizations requires a vote of approval by membership within a 25-day waiting period.
NAMDRC’s long regarded monthly publication, Washington Watchline, will continue through CHEST, as will the NAMDRC Annual Meeting, slated for next March 18-20, 2021 in Sonoma, California, in conjunction with the CHEST Spring Leadership Meeting.
Concentrating our efforts under one organization allows us offer the best possible opportunities to our membership, patients, and far-reaching network. This is an exciting time for everyone involved, and we are looking forward to seeing all we can accomplish together.
On Thursday, March 12, The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) and the National Association for Medical Direction of Respiratory Care (NAMDRC) announced publicly our official intent to come together as one association, integrating all NAMDRC activities and operations into CHEST.
This integration launch followed months of discussion between CHEST and NAMDRC leadership. Our respective Boards agreed that united efforts will amplify our individual involvement in patient advocacy and policy.
CHEST and NAMDRC have an intertwined purpose of delivering the highest standard of care for our patients. For this reason, our likeminded advocacy agendas can be even better fulfilled when we can leverage strengths from both associations.
CHEST and NAMDRC have shared an overlapping membership and collaborative history of empowering patients through the advancement of public policy and clinical education for decades. In additional to our individual efforts, our associations historically leveraged a combined advocacy presence in Washington D.C. to advance legislation against major tobacco corporations.
Coming together as a joint advocacy-focused organization, the initiation of CHEST’s Health Policy and Advocacy Committee, which will be comprised of an equal selection of CHEST and NAMDRC leadership, will drive CHEST’s advocacy agenda. The committee will work directly with policymakers, and target legislative and regulatory issues impacting pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine.
A committee of this kind, dedicated strictly to advocacy efforts, will be absolutely invaluable to our united organization. This group will be a true asset for membership to turn, to voice concerns within our practice, and to direct action on policies that matter to our patients.
Members of both organizations were notified of the integration by email on Wednesday, March 11. Along with email notification, NAMDRC members also received a voting ballot, as the dissolution of a nonprofit organization for Virginia-based organizations requires a vote of approval by membership within a 25-day waiting period.
NAMDRC’s long regarded monthly publication, Washington Watchline, will continue through CHEST, as will the NAMDRC Annual Meeting, slated for next March 18-20, 2021 in Sonoma, California, in conjunction with the CHEST Spring Leadership Meeting.
Concentrating our efforts under one organization allows us offer the best possible opportunities to our membership, patients, and far-reaching network. This is an exciting time for everyone involved, and we are looking forward to seeing all we can accomplish together.
This month in the journal CHEST®
Editor’s Picks
Characterization of severe asthma worldwide: data from the International Severe Asthma Registry (ISAR). By Dr. D. B. Price, et al.
Validation of the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) as an outcome measure in bronchiectasis. By Dr. J. D. Chalmers, et al.
Comparative effects of LAMA-LABA-ICS versus LAMA-LABA for COPD: Cohort study in real world clinical practice. By Dr. S. Suissa, et al.
Airway Management in Critical Illness: An Update. By Dr. J. Scott, et al.
Extremes of age decrease survival in adults after lung transplant. By Dr. M. Valapour, et al.
Editor’s Picks
Characterization of severe asthma worldwide: data from the International Severe Asthma Registry (ISAR). By Dr. D. B. Price, et al.
Validation of the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) as an outcome measure in bronchiectasis. By Dr. J. D. Chalmers, et al.
Comparative effects of LAMA-LABA-ICS versus LAMA-LABA for COPD: Cohort study in real world clinical practice. By Dr. S. Suissa, et al.
Airway Management in Critical Illness: An Update. By Dr. J. Scott, et al.
Extremes of age decrease survival in adults after lung transplant. By Dr. M. Valapour, et al.
Editor’s Picks
Characterization of severe asthma worldwide: data from the International Severe Asthma Registry (ISAR). By Dr. D. B. Price, et al.
Validation of the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) as an outcome measure in bronchiectasis. By Dr. J. D. Chalmers, et al.
Comparative effects of LAMA-LABA-ICS versus LAMA-LABA for COPD: Cohort study in real world clinical practice. By Dr. S. Suissa, et al.
Airway Management in Critical Illness: An Update. By Dr. J. Scott, et al.
Extremes of age decrease survival in adults after lung transplant. By Dr. M. Valapour, et al.
COVID 19: Psychiatric patients may be among the hardest hit
The COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) and the healthcare systems that serve them, one expert warns.
However, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Georgia, says there are strategies that can help minimize the risk of exposure and transmission of the virus in SMI patients.
In a viewpoint published online April 3 in JAMA Psychiatry, Druss, professor and chair in mental health, notes that “disasters disproportionately affect poor and vulnerable populations, and patients with serious mental illness may be among the hardest hit.”
In an interview with Medscape Medical News, Druss said patients with SMI have “a whole range of vulnerabilities” that put them at higher risk for COVID-19.
These include high rates of smoking, cardiovascular and lung disease, poverty, and homelessness. In fact, estimates show 25% of the US homeless population has a serious mental illness, said Druss.
“You have to keep an eye on these overlapping circles of vulnerable populations: those with disabilities in general and people with serious mental illness in particular; people who are poor; and people who have limited social networks,” he said.
Tailored Communication Vital
It’s important for patients with SMI to have up-to-date, accurate information about mitigating risk and knowing when to seek medical treatment for COVID-19, Druss noted.
Communication materials developed for the general population need to be tailored to address limited health literacy and challenges in implementing physical distancing recommendations, he said.
Patients with SMI also need support in maintaining healthy habits, including diet and physical activity, as well as self-management of chronic mental and physical health conditions, he added.
He noted that even in the face of current constraints on mental health care delivery, ensuring access to services is essential. The increased emphasis on caring for, and keeping in touch with, SMI patients through telepsychiatry is one effective way of addressing this issue, said Druss.
Since mental health clinicians are often the first responders for people with SMI, these professionals need training to recognize the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and learn basic strategies to mitigate the spread of disease, not only for their patients but also for themselves, he added.
“Any given provider is going to be responsible for many, many patients, so keeping physically and mentally healthy will be vital.”
In order to ease the strain of COVID-19 on community mental health centers and psychiatric hospitals, which are at high risk for outbreaks and have limited capacity to treat medical illness, these institutions need contingency plans to detect and contain outbreaks if they occur.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Druss writes.
Voice of Experience
Commenting on the article for Medscape Medical News, Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, distinguished advisor for the New York State Office of Mental Health and adjunct professor at the Columbia School of Public Health in New York City, commended Druss for highlighting the need for more mental health services during the pandemic.
However, although Druss “has made some very good general statements,” these don’t really apply “in the wake of a real catastrophic event, which is what we’re having here,” Sederer said.
Sederer led Project Liberty, a massive mental health disaster response effort established in the wake of the Sept. 11 attacks in New York. Druss seems to infer that the mental health workforce is capable of expanding, but “what we learned is that the mental health system in this country is vastly undersupplied,” said Sederer.
During a disaster, the system “actually contracts” because clinics close and workforces are reduced. In this environment, some patients with a serious mental illness let their treatment “erode,” Sederer said.
While Druss called for clinics to have protocols for identifying and referring patients at risk for COVID-19, Sederer pointed out that “all the clinics are closed.”
However, he did note that many mental health clinics and hospitals are continuing to reach out to their vulnerable patients during this crisis.
On the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, Sederer and colleagues published an article in Psychiatric Services that highlighted the “lessons learned” from the Project Liberty experience. One of the biggest lessons was the need for crisis counseling, which is “a recognized, proven intervention,” said Sederer.
Such an initiative involves trained outreach workers, identifying the untreated seriously mentally ill in the community, and “literally shepherding them to services,” he added.
In this current pandemic, it would be up to the federal government to mobilize such a crisis counseling initiative, Sederer explained.
Sederer noted that rapid relief groups like the Federal Emergency Management Agency do not cover mental health services. In order to be effective, disaster-related mental health services need to include funding for treatment, including focused therapies and medication.
Druss and Sederer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) and the healthcare systems that serve them, one expert warns.
However, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Georgia, says there are strategies that can help minimize the risk of exposure and transmission of the virus in SMI patients.
In a viewpoint published online April 3 in JAMA Psychiatry, Druss, professor and chair in mental health, notes that “disasters disproportionately affect poor and vulnerable populations, and patients with serious mental illness may be among the hardest hit.”
In an interview with Medscape Medical News, Druss said patients with SMI have “a whole range of vulnerabilities” that put them at higher risk for COVID-19.
These include high rates of smoking, cardiovascular and lung disease, poverty, and homelessness. In fact, estimates show 25% of the US homeless population has a serious mental illness, said Druss.
“You have to keep an eye on these overlapping circles of vulnerable populations: those with disabilities in general and people with serious mental illness in particular; people who are poor; and people who have limited social networks,” he said.
Tailored Communication Vital
It’s important for patients with SMI to have up-to-date, accurate information about mitigating risk and knowing when to seek medical treatment for COVID-19, Druss noted.
Communication materials developed for the general population need to be tailored to address limited health literacy and challenges in implementing physical distancing recommendations, he said.
Patients with SMI also need support in maintaining healthy habits, including diet and physical activity, as well as self-management of chronic mental and physical health conditions, he added.
He noted that even in the face of current constraints on mental health care delivery, ensuring access to services is essential. The increased emphasis on caring for, and keeping in touch with, SMI patients through telepsychiatry is one effective way of addressing this issue, said Druss.
Since mental health clinicians are often the first responders for people with SMI, these professionals need training to recognize the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and learn basic strategies to mitigate the spread of disease, not only for their patients but also for themselves, he added.
“Any given provider is going to be responsible for many, many patients, so keeping physically and mentally healthy will be vital.”
In order to ease the strain of COVID-19 on community mental health centers and psychiatric hospitals, which are at high risk for outbreaks and have limited capacity to treat medical illness, these institutions need contingency plans to detect and contain outbreaks if they occur.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Druss writes.
Voice of Experience
Commenting on the article for Medscape Medical News, Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, distinguished advisor for the New York State Office of Mental Health and adjunct professor at the Columbia School of Public Health in New York City, commended Druss for highlighting the need for more mental health services during the pandemic.
However, although Druss “has made some very good general statements,” these don’t really apply “in the wake of a real catastrophic event, which is what we’re having here,” Sederer said.
Sederer led Project Liberty, a massive mental health disaster response effort established in the wake of the Sept. 11 attacks in New York. Druss seems to infer that the mental health workforce is capable of expanding, but “what we learned is that the mental health system in this country is vastly undersupplied,” said Sederer.
During a disaster, the system “actually contracts” because clinics close and workforces are reduced. In this environment, some patients with a serious mental illness let their treatment “erode,” Sederer said.
While Druss called for clinics to have protocols for identifying and referring patients at risk for COVID-19, Sederer pointed out that “all the clinics are closed.”
However, he did note that many mental health clinics and hospitals are continuing to reach out to their vulnerable patients during this crisis.
On the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, Sederer and colleagues published an article in Psychiatric Services that highlighted the “lessons learned” from the Project Liberty experience. One of the biggest lessons was the need for crisis counseling, which is “a recognized, proven intervention,” said Sederer.
Such an initiative involves trained outreach workers, identifying the untreated seriously mentally ill in the community, and “literally shepherding them to services,” he added.
In this current pandemic, it would be up to the federal government to mobilize such a crisis counseling initiative, Sederer explained.
Sederer noted that rapid relief groups like the Federal Emergency Management Agency do not cover mental health services. In order to be effective, disaster-related mental health services need to include funding for treatment, including focused therapies and medication.
Druss and Sederer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) and the healthcare systems that serve them, one expert warns.
However, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Georgia, says there are strategies that can help minimize the risk of exposure and transmission of the virus in SMI patients.
In a viewpoint published online April 3 in JAMA Psychiatry, Druss, professor and chair in mental health, notes that “disasters disproportionately affect poor and vulnerable populations, and patients with serious mental illness may be among the hardest hit.”
In an interview with Medscape Medical News, Druss said patients with SMI have “a whole range of vulnerabilities” that put them at higher risk for COVID-19.
These include high rates of smoking, cardiovascular and lung disease, poverty, and homelessness. In fact, estimates show 25% of the US homeless population has a serious mental illness, said Druss.
“You have to keep an eye on these overlapping circles of vulnerable populations: those with disabilities in general and people with serious mental illness in particular; people who are poor; and people who have limited social networks,” he said.
Tailored Communication Vital
It’s important for patients with SMI to have up-to-date, accurate information about mitigating risk and knowing when to seek medical treatment for COVID-19, Druss noted.
Communication materials developed for the general population need to be tailored to address limited health literacy and challenges in implementing physical distancing recommendations, he said.
Patients with SMI also need support in maintaining healthy habits, including diet and physical activity, as well as self-management of chronic mental and physical health conditions, he added.
He noted that even in the face of current constraints on mental health care delivery, ensuring access to services is essential. The increased emphasis on caring for, and keeping in touch with, SMI patients through telepsychiatry is one effective way of addressing this issue, said Druss.
Since mental health clinicians are often the first responders for people with SMI, these professionals need training to recognize the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and learn basic strategies to mitigate the spread of disease, not only for their patients but also for themselves, he added.
“Any given provider is going to be responsible for many, many patients, so keeping physically and mentally healthy will be vital.”
In order to ease the strain of COVID-19 on community mental health centers and psychiatric hospitals, which are at high risk for outbreaks and have limited capacity to treat medical illness, these institutions need contingency plans to detect and contain outbreaks if they occur.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Druss writes.
Voice of Experience
Commenting on the article for Medscape Medical News, Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, distinguished advisor for the New York State Office of Mental Health and adjunct professor at the Columbia School of Public Health in New York City, commended Druss for highlighting the need for more mental health services during the pandemic.
However, although Druss “has made some very good general statements,” these don’t really apply “in the wake of a real catastrophic event, which is what we’re having here,” Sederer said.
Sederer led Project Liberty, a massive mental health disaster response effort established in the wake of the Sept. 11 attacks in New York. Druss seems to infer that the mental health workforce is capable of expanding, but “what we learned is that the mental health system in this country is vastly undersupplied,” said Sederer.
During a disaster, the system “actually contracts” because clinics close and workforces are reduced. In this environment, some patients with a serious mental illness let their treatment “erode,” Sederer said.
While Druss called for clinics to have protocols for identifying and referring patients at risk for COVID-19, Sederer pointed out that “all the clinics are closed.”
However, he did note that many mental health clinics and hospitals are continuing to reach out to their vulnerable patients during this crisis.
On the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, Sederer and colleagues published an article in Psychiatric Services that highlighted the “lessons learned” from the Project Liberty experience. One of the biggest lessons was the need for crisis counseling, which is “a recognized, proven intervention,” said Sederer.
Such an initiative involves trained outreach workers, identifying the untreated seriously mentally ill in the community, and “literally shepherding them to services,” he added.
In this current pandemic, it would be up to the federal government to mobilize such a crisis counseling initiative, Sederer explained.
Sederer noted that rapid relief groups like the Federal Emergency Management Agency do not cover mental health services. In order to be effective, disaster-related mental health services need to include funding for treatment, including focused therapies and medication.
Druss and Sederer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.















