User login
Cautionary tale spurs ‘world’s first’ COVID-19 psychiatric ward
There was no hand sanitizer on the hospital’s psychiatric ward for fear patients would drink it; they slept together on futons in communal rooms and the windows were sealed shut to prevent suicide attempts — all conditions that created the perfect environment for the rapid spread of a potentially deadly virus.
This scenario may sound like a something out of a horror film, but as reported last month by the UK newspaper The Independent, it was the reality in the psychiatric ward of South Korea’s Daenam Hospital after COVID-19 struck. Eventually health officials put the ward on lockdown, but it wasn’t long before all but two of the unit’s 103 patients were positive for the virus.
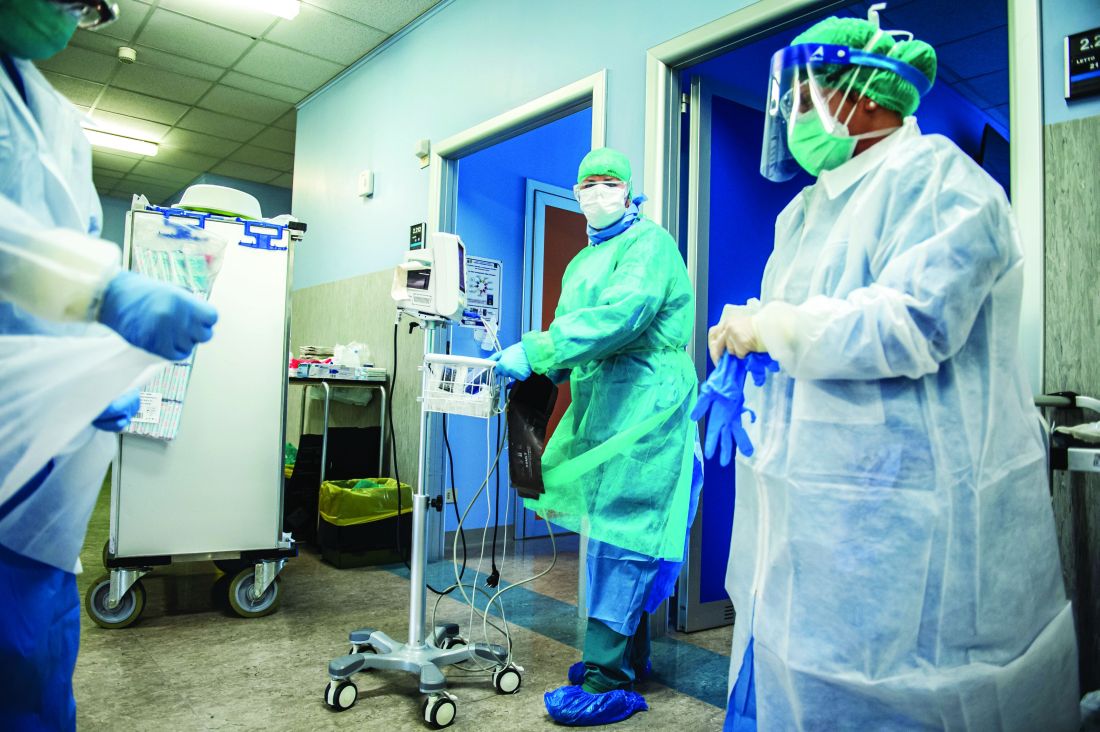
To avoid a similar catastrophe, staff at an Israeli hospital have created what they describe as the “world’s first” dedicated COVID-19 unit for psychiatric inpatients.
Clinicians at Israel’s national hospital, Sheba Medical Center Tel HaShomer in Tel Aviv, believe the 16-bed unit, which officially opened on March 26, will stop psychiatric inpatients with the virus — who may have trouble with social distancing — from spreading it to others on the ward.
“Psychiatric patients are going to get sick from coronavirus just like anybody else,” Mark Weiser, MD, head of the psychiatric division at the institution told Medscape Medical News. “But we’re concerned that, on a psychiatric ward, a patient who is COVID-19 positive can also be psychotic, manic, cognitively impaired, or have poor judgment … making it difficult for that patient to keep social distancing, and very quickly you’ll have an entire ward of patients infected.
“So the basic public health issue is how to prevent a single psychiatric patient who is hospitalized and COVID-19-positive from making everybody else sick,” he added.
Unique Challenges, Rapid Response
Adapting an existing psychiatric ward to one exclusively used by inpatients with COVID-19 required significant planning, coordination, and modifications to ensure the well-being of patients and staff.
A dedicated entrance for the exclusive use of infected psychiatric inpatients was also created.
In addition, two-way television cameras in patients’ rooms were installed to facilitate a constant flow of communication and enable therapeutic sessions and family visits. All of these modifications were completed in under a week.
“Under normal circumstances, we have cameras in the public areas of our wards, but in order to respect people’s privacy, we do not have cameras in their rooms.
“In this specific ward, on the other hand, we did put cameras in the rooms, so if a patient needs to be watched more closely, it could be done remotely without exposing staff to the virus. We have a person who’s watching the screens at all times, just to see what’s going on and see what patients are doing,” said Weiser.
Protective personal equipment (PPE) and clothing for staff was tailored to the unique challenges posed by the ward’s patient population.
“Of course, you need to wear clothes that are protective against the virus,” said Weiser. “But sometimes our patients can get agitated or even violent, so you’ve got protect against that as well.”
With this in mind, all personnel working on the ward must put on an extra layer of PPE as well as a tear-proof robe. The institution has also implemented a strict protocol that dictates the order in which PPE is donned and doffed.
“It’s got to be done in a very careful and very specific way,” said Weiser. “We have all of it organized with a poster that explains what should be taken off or put on, and in what order.”
For institutions considering setting up a similar unit, Weiser said close proximity to an active care hospital with the capacity to provide urgent care is key.
“We’re psychiatrists; we’re not great at treating acute respiratory problems. So patients with significant respiratory problems need a place to get appropriate care quickly,” he said.
In setting up the unit, there were still a few obstacles, Weiser noted. For instance, despite the many protective and safety measures undertaken by the institution, some of the hospital staff were concerned about their risk of contracting the virus.
To address these concerns, the hospital’s leadership brought in infectious disease experts to educate hospital personnel about the virus and transmission risk.
“They told our staff that given all the precautions we had taken, there was very little risk anyone else could become infected,” Weiser said.
Despite the many challenges, Weiser said he and his colleagues are thrilled with the dedicated ward and the positive reception it has received.
“My colleagues and the directors of psychiatric hospitals all around the country are very happy with this because now they’re not hospitalizing infected patients. They’re very happy for us to take care of this,” he said.
“No Easy Solutions”
Commenting on the initiative for Medscape Medical News, John M. Oldham, MD, chief of staff at Baylor College of Medicine’s Menninger Clinic in Houston, Texas, raised some questions.
“Is it really going to be the treatment unit or a quarantine unit? Because if you don’t have a comparable level of established, effective treatment for these patients, then you’re simply herding them off to a different place where they’re going to suffer both illnesses,” he cautioned.
Nevertheless, Oldham recognized that the issue of how to treat psychiatric patients who test positive for COVID-19 is complex.
“We’re still wrestling with that question here at Menninger. We have created an enclosed section of the inpatient area reserved for this possibility.
“If we have a patient who tests positive, we will immediately put that patient in one of these rooms in the quarantine section. Then we will use protective equipment for our staff to go and provide care for the patient,” he said.
However, he acknowledged that a psychiatric hospital is in no position to treat patients who develop severe illness from COVID-19.
“We’re certainly worried about it,” he said, “because how many inpatient general medical units are going to want to take a significantly symptomatic COVID-19 patient who was in the hospital for being acutely suicidal? There are no easy solutions.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There was no hand sanitizer on the hospital’s psychiatric ward for fear patients would drink it; they slept together on futons in communal rooms and the windows were sealed shut to prevent suicide attempts — all conditions that created the perfect environment for the rapid spread of a potentially deadly virus.
This scenario may sound like a something out of a horror film, but as reported last month by the UK newspaper The Independent, it was the reality in the psychiatric ward of South Korea’s Daenam Hospital after COVID-19 struck. Eventually health officials put the ward on lockdown, but it wasn’t long before all but two of the unit’s 103 patients were positive for the virus.
To avoid a similar catastrophe, staff at an Israeli hospital have created what they describe as the “world’s first” dedicated COVID-19 unit for psychiatric inpatients.
Clinicians at Israel’s national hospital, Sheba Medical Center Tel HaShomer in Tel Aviv, believe the 16-bed unit, which officially opened on March 26, will stop psychiatric inpatients with the virus — who may have trouble with social distancing — from spreading it to others on the ward.
“Psychiatric patients are going to get sick from coronavirus just like anybody else,” Mark Weiser, MD, head of the psychiatric division at the institution told Medscape Medical News. “But we’re concerned that, on a psychiatric ward, a patient who is COVID-19 positive can also be psychotic, manic, cognitively impaired, or have poor judgment … making it difficult for that patient to keep social distancing, and very quickly you’ll have an entire ward of patients infected.
“So the basic public health issue is how to prevent a single psychiatric patient who is hospitalized and COVID-19-positive from making everybody else sick,” he added.
Unique Challenges, Rapid Response
Adapting an existing psychiatric ward to one exclusively used by inpatients with COVID-19 required significant planning, coordination, and modifications to ensure the well-being of patients and staff.
A dedicated entrance for the exclusive use of infected psychiatric inpatients was also created.
In addition, two-way television cameras in patients’ rooms were installed to facilitate a constant flow of communication and enable therapeutic sessions and family visits. All of these modifications were completed in under a week.
“Under normal circumstances, we have cameras in the public areas of our wards, but in order to respect people’s privacy, we do not have cameras in their rooms.
“In this specific ward, on the other hand, we did put cameras in the rooms, so if a patient needs to be watched more closely, it could be done remotely without exposing staff to the virus. We have a person who’s watching the screens at all times, just to see what’s going on and see what patients are doing,” said Weiser.
Protective personal equipment (PPE) and clothing for staff was tailored to the unique challenges posed by the ward’s patient population.
“Of course, you need to wear clothes that are protective against the virus,” said Weiser. “But sometimes our patients can get agitated or even violent, so you’ve got protect against that as well.”
With this in mind, all personnel working on the ward must put on an extra layer of PPE as well as a tear-proof robe. The institution has also implemented a strict protocol that dictates the order in which PPE is donned and doffed.
“It’s got to be done in a very careful and very specific way,” said Weiser. “We have all of it organized with a poster that explains what should be taken off or put on, and in what order.”
For institutions considering setting up a similar unit, Weiser said close proximity to an active care hospital with the capacity to provide urgent care is key.
“We’re psychiatrists; we’re not great at treating acute respiratory problems. So patients with significant respiratory problems need a place to get appropriate care quickly,” he said.
In setting up the unit, there were still a few obstacles, Weiser noted. For instance, despite the many protective and safety measures undertaken by the institution, some of the hospital staff were concerned about their risk of contracting the virus.
To address these concerns, the hospital’s leadership brought in infectious disease experts to educate hospital personnel about the virus and transmission risk.
“They told our staff that given all the precautions we had taken, there was very little risk anyone else could become infected,” Weiser said.
Despite the many challenges, Weiser said he and his colleagues are thrilled with the dedicated ward and the positive reception it has received.
“My colleagues and the directors of psychiatric hospitals all around the country are very happy with this because now they’re not hospitalizing infected patients. They’re very happy for us to take care of this,” he said.
“No Easy Solutions”
Commenting on the initiative for Medscape Medical News, John M. Oldham, MD, chief of staff at Baylor College of Medicine’s Menninger Clinic in Houston, Texas, raised some questions.
“Is it really going to be the treatment unit or a quarantine unit? Because if you don’t have a comparable level of established, effective treatment for these patients, then you’re simply herding them off to a different place where they’re going to suffer both illnesses,” he cautioned.
Nevertheless, Oldham recognized that the issue of how to treat psychiatric patients who test positive for COVID-19 is complex.
“We’re still wrestling with that question here at Menninger. We have created an enclosed section of the inpatient area reserved for this possibility.
“If we have a patient who tests positive, we will immediately put that patient in one of these rooms in the quarantine section. Then we will use protective equipment for our staff to go and provide care for the patient,” he said.
However, he acknowledged that a psychiatric hospital is in no position to treat patients who develop severe illness from COVID-19.
“We’re certainly worried about it,” he said, “because how many inpatient general medical units are going to want to take a significantly symptomatic COVID-19 patient who was in the hospital for being acutely suicidal? There are no easy solutions.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There was no hand sanitizer on the hospital’s psychiatric ward for fear patients would drink it; they slept together on futons in communal rooms and the windows were sealed shut to prevent suicide attempts — all conditions that created the perfect environment for the rapid spread of a potentially deadly virus.
This scenario may sound like a something out of a horror film, but as reported last month by the UK newspaper The Independent, it was the reality in the psychiatric ward of South Korea’s Daenam Hospital after COVID-19 struck. Eventually health officials put the ward on lockdown, but it wasn’t long before all but two of the unit’s 103 patients were positive for the virus.
To avoid a similar catastrophe, staff at an Israeli hospital have created what they describe as the “world’s first” dedicated COVID-19 unit for psychiatric inpatients.
Clinicians at Israel’s national hospital, Sheba Medical Center Tel HaShomer in Tel Aviv, believe the 16-bed unit, which officially opened on March 26, will stop psychiatric inpatients with the virus — who may have trouble with social distancing — from spreading it to others on the ward.
“Psychiatric patients are going to get sick from coronavirus just like anybody else,” Mark Weiser, MD, head of the psychiatric division at the institution told Medscape Medical News. “But we’re concerned that, on a psychiatric ward, a patient who is COVID-19 positive can also be psychotic, manic, cognitively impaired, or have poor judgment … making it difficult for that patient to keep social distancing, and very quickly you’ll have an entire ward of patients infected.
“So the basic public health issue is how to prevent a single psychiatric patient who is hospitalized and COVID-19-positive from making everybody else sick,” he added.
Unique Challenges, Rapid Response
Adapting an existing psychiatric ward to one exclusively used by inpatients with COVID-19 required significant planning, coordination, and modifications to ensure the well-being of patients and staff.
A dedicated entrance for the exclusive use of infected psychiatric inpatients was also created.
In addition, two-way television cameras in patients’ rooms were installed to facilitate a constant flow of communication and enable therapeutic sessions and family visits. All of these modifications were completed in under a week.
“Under normal circumstances, we have cameras in the public areas of our wards, but in order to respect people’s privacy, we do not have cameras in their rooms.
“In this specific ward, on the other hand, we did put cameras in the rooms, so if a patient needs to be watched more closely, it could be done remotely without exposing staff to the virus. We have a person who’s watching the screens at all times, just to see what’s going on and see what patients are doing,” said Weiser.
Protective personal equipment (PPE) and clothing for staff was tailored to the unique challenges posed by the ward’s patient population.
“Of course, you need to wear clothes that are protective against the virus,” said Weiser. “But sometimes our patients can get agitated or even violent, so you’ve got protect against that as well.”
With this in mind, all personnel working on the ward must put on an extra layer of PPE as well as a tear-proof robe. The institution has also implemented a strict protocol that dictates the order in which PPE is donned and doffed.
“It’s got to be done in a very careful and very specific way,” said Weiser. “We have all of it organized with a poster that explains what should be taken off or put on, and in what order.”
For institutions considering setting up a similar unit, Weiser said close proximity to an active care hospital with the capacity to provide urgent care is key.
“We’re psychiatrists; we’re not great at treating acute respiratory problems. So patients with significant respiratory problems need a place to get appropriate care quickly,” he said.
In setting up the unit, there were still a few obstacles, Weiser noted. For instance, despite the many protective and safety measures undertaken by the institution, some of the hospital staff were concerned about their risk of contracting the virus.
To address these concerns, the hospital’s leadership brought in infectious disease experts to educate hospital personnel about the virus and transmission risk.
“They told our staff that given all the precautions we had taken, there was very little risk anyone else could become infected,” Weiser said.
Despite the many challenges, Weiser said he and his colleagues are thrilled with the dedicated ward and the positive reception it has received.
“My colleagues and the directors of psychiatric hospitals all around the country are very happy with this because now they’re not hospitalizing infected patients. They’re very happy for us to take care of this,” he said.
“No Easy Solutions”
Commenting on the initiative for Medscape Medical News, John M. Oldham, MD, chief of staff at Baylor College of Medicine’s Menninger Clinic in Houston, Texas, raised some questions.
“Is it really going to be the treatment unit or a quarantine unit? Because if you don’t have a comparable level of established, effective treatment for these patients, then you’re simply herding them off to a different place where they’re going to suffer both illnesses,” he cautioned.
Nevertheless, Oldham recognized that the issue of how to treat psychiatric patients who test positive for COVID-19 is complex.
“We’re still wrestling with that question here at Menninger. We have created an enclosed section of the inpatient area reserved for this possibility.
“If we have a patient who tests positive, we will immediately put that patient in one of these rooms in the quarantine section. Then we will use protective equipment for our staff to go and provide care for the patient,” he said.
However, he acknowledged that a psychiatric hospital is in no position to treat patients who develop severe illness from COVID-19.
“We’re certainly worried about it,” he said, “because how many inpatient general medical units are going to want to take a significantly symptomatic COVID-19 patient who was in the hospital for being acutely suicidal? There are no easy solutions.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: How intensive care cardiology can inform the response
Because of their place at the interface between critical care and cardiovascular medicine, critical care cardiologists are in a good position to come up with novel approaches to adapting critical care systems to the current crisis. Health care and clinical resources have been severely strained in some places, and increasing evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 can cause injury to most organ systems. More than a quarter of hospitalized patients have cardiac injury, which can be a key reason for clinical deterioration.
An international group of critical care cardiologists led by Jason Katz, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., offered suggestions for scalable models for critical care delivery in the context of COVID-19 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Critical care cardiology developed in response to changes in patient populations and their clinical needs. Respiratory insufficiency, heart failure, structural heart disease, and multisystem organ dysfunction became more common than patients with complicated acute MI, leading cardiologists in critical care cardiology to become more proficient in general critical care medicine, and to become leaders in forming collaborative multidisciplinary teams. The authors argued that COVID-19 is precipitating a similar need to adapt to the changing needs of patients.
“This pandemic should serve as a clarion call to our health care systems that we should continue to develop a nimble workforce that can adapt to change quickly during a crisis. We believe critical care cardiologists are well positioned to help serve society in this capacity,” the authors wrote.
Surge staging
They proposed four surge stages based in part on an American College of Chest Physicians–endorsed model (Chest 2014 Oct;146:e61S-74S), which regards a 25% capacity surge as minor. At the other end of the spectrum, a 200% surge is defined as a “disaster.” In minor surges (less than 25% increase), the traditional cardiac ICU (CICU) model can continue to be applied. During moderate (25%-100% increases) or major (100%-200%) surges, the critical care cardiologist should collaborate or consult within multiple health care teams. Physicians not trained in critical care can assist with care of intubated and critically ill patients under the supervision of a critical care cardiologist or under the supervision of a partnership between a non–cardiac critical care medicine provider and a cardiologist. The number of patients cared for by each team should increase in step with the size of the surge.
In disaster situations (more than 200% surge), there should be adaptive and dynamic staffing reorganization. The report included an illustration of a range of steps that can be taken, including alterations to staffing, regional care systems, resource management, and triage practices. Scoring systems such as Sequential Organ Failure Assessment may be useful for triaging, but the authors also suggest employment of validated cardiac disease–specific scores, because traditional ICU measures don’t always apply well to CICU populations.
At the hospital level, deferrals should be made for elective cardiac procedures that require CICU or postanesthesia care unit recovery periods. Semielective procedures should be considered after risk-benefit considerations when delays could lead to morbidity or mortality. Even some traditional emergency procedures may need to be reevaluated in the COVID-19 context: For example, some low-risk ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) patients don’t require ICU care but are manageable in cardiac intermediate care beds instead. Historical triage practices should be reexamined to predict which STEMI patients will require ICU care.
Resource allocation
The CICU work flow will be affected as some of its beds are opened up to COVID-19 patients. Standard philosophies of concentrating intense resources will have to give way to a utilitarian approach that evaluates operations based on efficiency, equity, and justice. Physician-patient contact should be minimized using technological links when possible, and rounds might be reorganized to first examine patients without COVID-19, in order to minimize between-patient spread.
Military medicine, which is used to ramping up operations during times of crisis, has potential lessons for the current pandemic. In the face of mass casualties, military physicians often turn to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization triage system, which separates patients into four categories: immediate, requiring lifesaving intervention; delayed, requiring intervention within hours to days; minimal, where the patient is injured but ambulatory; and expectant patients who are deceased or too injured to save. Impersonal though this system may be, it may be required in the most severe scenarios when resources are scarce or absent.
The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Katz J et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.02.01.
Because of their place at the interface between critical care and cardiovascular medicine, critical care cardiologists are in a good position to come up with novel approaches to adapting critical care systems to the current crisis. Health care and clinical resources have been severely strained in some places, and increasing evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 can cause injury to most organ systems. More than a quarter of hospitalized patients have cardiac injury, which can be a key reason for clinical deterioration.
An international group of critical care cardiologists led by Jason Katz, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., offered suggestions for scalable models for critical care delivery in the context of COVID-19 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Critical care cardiology developed in response to changes in patient populations and their clinical needs. Respiratory insufficiency, heart failure, structural heart disease, and multisystem organ dysfunction became more common than patients with complicated acute MI, leading cardiologists in critical care cardiology to become more proficient in general critical care medicine, and to become leaders in forming collaborative multidisciplinary teams. The authors argued that COVID-19 is precipitating a similar need to adapt to the changing needs of patients.
“This pandemic should serve as a clarion call to our health care systems that we should continue to develop a nimble workforce that can adapt to change quickly during a crisis. We believe critical care cardiologists are well positioned to help serve society in this capacity,” the authors wrote.
Surge staging
They proposed four surge stages based in part on an American College of Chest Physicians–endorsed model (Chest 2014 Oct;146:e61S-74S), which regards a 25% capacity surge as minor. At the other end of the spectrum, a 200% surge is defined as a “disaster.” In minor surges (less than 25% increase), the traditional cardiac ICU (CICU) model can continue to be applied. During moderate (25%-100% increases) or major (100%-200%) surges, the critical care cardiologist should collaborate or consult within multiple health care teams. Physicians not trained in critical care can assist with care of intubated and critically ill patients under the supervision of a critical care cardiologist or under the supervision of a partnership between a non–cardiac critical care medicine provider and a cardiologist. The number of patients cared for by each team should increase in step with the size of the surge.
In disaster situations (more than 200% surge), there should be adaptive and dynamic staffing reorganization. The report included an illustration of a range of steps that can be taken, including alterations to staffing, regional care systems, resource management, and triage practices. Scoring systems such as Sequential Organ Failure Assessment may be useful for triaging, but the authors also suggest employment of validated cardiac disease–specific scores, because traditional ICU measures don’t always apply well to CICU populations.
At the hospital level, deferrals should be made for elective cardiac procedures that require CICU or postanesthesia care unit recovery periods. Semielective procedures should be considered after risk-benefit considerations when delays could lead to morbidity or mortality. Even some traditional emergency procedures may need to be reevaluated in the COVID-19 context: For example, some low-risk ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) patients don’t require ICU care but are manageable in cardiac intermediate care beds instead. Historical triage practices should be reexamined to predict which STEMI patients will require ICU care.
Resource allocation
The CICU work flow will be affected as some of its beds are opened up to COVID-19 patients. Standard philosophies of concentrating intense resources will have to give way to a utilitarian approach that evaluates operations based on efficiency, equity, and justice. Physician-patient contact should be minimized using technological links when possible, and rounds might be reorganized to first examine patients without COVID-19, in order to minimize between-patient spread.
Military medicine, which is used to ramping up operations during times of crisis, has potential lessons for the current pandemic. In the face of mass casualties, military physicians often turn to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization triage system, which separates patients into four categories: immediate, requiring lifesaving intervention; delayed, requiring intervention within hours to days; minimal, where the patient is injured but ambulatory; and expectant patients who are deceased or too injured to save. Impersonal though this system may be, it may be required in the most severe scenarios when resources are scarce or absent.
The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Katz J et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.02.01.
Because of their place at the interface between critical care and cardiovascular medicine, critical care cardiologists are in a good position to come up with novel approaches to adapting critical care systems to the current crisis. Health care and clinical resources have been severely strained in some places, and increasing evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 can cause injury to most organ systems. More than a quarter of hospitalized patients have cardiac injury, which can be a key reason for clinical deterioration.
An international group of critical care cardiologists led by Jason Katz, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., offered suggestions for scalable models for critical care delivery in the context of COVID-19 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Critical care cardiology developed in response to changes in patient populations and their clinical needs. Respiratory insufficiency, heart failure, structural heart disease, and multisystem organ dysfunction became more common than patients with complicated acute MI, leading cardiologists in critical care cardiology to become more proficient in general critical care medicine, and to become leaders in forming collaborative multidisciplinary teams. The authors argued that COVID-19 is precipitating a similar need to adapt to the changing needs of patients.
“This pandemic should serve as a clarion call to our health care systems that we should continue to develop a nimble workforce that can adapt to change quickly during a crisis. We believe critical care cardiologists are well positioned to help serve society in this capacity,” the authors wrote.
Surge staging
They proposed four surge stages based in part on an American College of Chest Physicians–endorsed model (Chest 2014 Oct;146:e61S-74S), which regards a 25% capacity surge as minor. At the other end of the spectrum, a 200% surge is defined as a “disaster.” In minor surges (less than 25% increase), the traditional cardiac ICU (CICU) model can continue to be applied. During moderate (25%-100% increases) or major (100%-200%) surges, the critical care cardiologist should collaborate or consult within multiple health care teams. Physicians not trained in critical care can assist with care of intubated and critically ill patients under the supervision of a critical care cardiologist or under the supervision of a partnership between a non–cardiac critical care medicine provider and a cardiologist. The number of patients cared for by each team should increase in step with the size of the surge.
In disaster situations (more than 200% surge), there should be adaptive and dynamic staffing reorganization. The report included an illustration of a range of steps that can be taken, including alterations to staffing, regional care systems, resource management, and triage practices. Scoring systems such as Sequential Organ Failure Assessment may be useful for triaging, but the authors also suggest employment of validated cardiac disease–specific scores, because traditional ICU measures don’t always apply well to CICU populations.
At the hospital level, deferrals should be made for elective cardiac procedures that require CICU or postanesthesia care unit recovery periods. Semielective procedures should be considered after risk-benefit considerations when delays could lead to morbidity or mortality. Even some traditional emergency procedures may need to be reevaluated in the COVID-19 context: For example, some low-risk ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) patients don’t require ICU care but are manageable in cardiac intermediate care beds instead. Historical triage practices should be reexamined to predict which STEMI patients will require ICU care.
Resource allocation
The CICU work flow will be affected as some of its beds are opened up to COVID-19 patients. Standard philosophies of concentrating intense resources will have to give way to a utilitarian approach that evaluates operations based on efficiency, equity, and justice. Physician-patient contact should be minimized using technological links when possible, and rounds might be reorganized to first examine patients without COVID-19, in order to minimize between-patient spread.
Military medicine, which is used to ramping up operations during times of crisis, has potential lessons for the current pandemic. In the face of mass casualties, military physicians often turn to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization triage system, which separates patients into four categories: immediate, requiring lifesaving intervention; delayed, requiring intervention within hours to days; minimal, where the patient is injured but ambulatory; and expectant patients who are deceased or too injured to save. Impersonal though this system may be, it may be required in the most severe scenarios when resources are scarce or absent.
The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Katz J et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.02.01.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists may pose a risk during stroke

“It turns out that these drugs make the blood vessels of the brain dysfunctional, such that the collateral channels that bring in blood to the region that is having the stroke are impaired,” explains the study’s lead author, Cenk Ayata, MD, associate professor of neurology and radiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
In an interview, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, talks with Dr. Ayata about his study findings, and about CGRP receptor antagonists’ potential effects if a patient has an ischemic event.
This article was updated 4/21/20.

“It turns out that these drugs make the blood vessels of the brain dysfunctional, such that the collateral channels that bring in blood to the region that is having the stroke are impaired,” explains the study’s lead author, Cenk Ayata, MD, associate professor of neurology and radiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
In an interview, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, talks with Dr. Ayata about his study findings, and about CGRP receptor antagonists’ potential effects if a patient has an ischemic event.
This article was updated 4/21/20.

“It turns out that these drugs make the blood vessels of the brain dysfunctional, such that the collateral channels that bring in blood to the region that is having the stroke are impaired,” explains the study’s lead author, Cenk Ayata, MD, associate professor of neurology and radiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
In an interview, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, talks with Dr. Ayata about his study findings, and about CGRP receptor antagonists’ potential effects if a patient has an ischemic event.
This article was updated 4/21/20.
Lesion Has Been Giving Him an Earful
ANSWER
The correct answer is gouty tophus (choice “b”).
DISCUSSION
Gout is a defect of purine metabolism, usually caused by underexcretion of uric acid. Diet and heredity also play parts in gout’s development. Gouty tophi usually develop after years of hyperuricemia. As uric acid builds up in the bloodstream over time, it can then begin to be deposited into joints—most commonly the first metatarsal-phalangeal—as well as cartilage or even bones.
On further questioning, the patient recalled having been told on several occasions that his serum uric acid was elevated. In retrospect, his arthritis was most likely gouty in nature.
In terms of the differential, BCC (choice “a”) is common on helical rims, but it would not have contained the type of material found in this patient’s lesion. Also, it would not have waxed and waned as this lesion had done.
Epidermal cysts (choice “c”) can certainly come and go in prominence, but they are filled with a cheesy, pasty material—not the dry crystalline substance found in this lesion. Moreover, most epidermal cysts will have a small comedonal punctum over the center of the lesion. Dystrophic calcification (choice “d”) can mimic gouty tophi, but it is usually rough, firm, and fixed. It certainly would not be coming and going as it pleases.
TREATMENT
Surgical excision of the tophus was offered, but the patient was content with knowing the correct diagnosis. His PCP had previously explained therapeutic options—such as medication and dietary changes—that could address the overall problem. The patient elected to pursue treatment with his PCP.
ANSWER
The correct answer is gouty tophus (choice “b”).
DISCUSSION
Gout is a defect of purine metabolism, usually caused by underexcretion of uric acid. Diet and heredity also play parts in gout’s development. Gouty tophi usually develop after years of hyperuricemia. As uric acid builds up in the bloodstream over time, it can then begin to be deposited into joints—most commonly the first metatarsal-phalangeal—as well as cartilage or even bones.
On further questioning, the patient recalled having been told on several occasions that his serum uric acid was elevated. In retrospect, his arthritis was most likely gouty in nature.
In terms of the differential, BCC (choice “a”) is common on helical rims, but it would not have contained the type of material found in this patient’s lesion. Also, it would not have waxed and waned as this lesion had done.
Epidermal cysts (choice “c”) can certainly come and go in prominence, but they are filled with a cheesy, pasty material—not the dry crystalline substance found in this lesion. Moreover, most epidermal cysts will have a small comedonal punctum over the center of the lesion. Dystrophic calcification (choice “d”) can mimic gouty tophi, but it is usually rough, firm, and fixed. It certainly would not be coming and going as it pleases.
TREATMENT
Surgical excision of the tophus was offered, but the patient was content with knowing the correct diagnosis. His PCP had previously explained therapeutic options—such as medication and dietary changes—that could address the overall problem. The patient elected to pursue treatment with his PCP.
ANSWER
The correct answer is gouty tophus (choice “b”).
DISCUSSION
Gout is a defect of purine metabolism, usually caused by underexcretion of uric acid. Diet and heredity also play parts in gout’s development. Gouty tophi usually develop after years of hyperuricemia. As uric acid builds up in the bloodstream over time, it can then begin to be deposited into joints—most commonly the first metatarsal-phalangeal—as well as cartilage or even bones.
On further questioning, the patient recalled having been told on several occasions that his serum uric acid was elevated. In retrospect, his arthritis was most likely gouty in nature.
In terms of the differential, BCC (choice “a”) is common on helical rims, but it would not have contained the type of material found in this patient’s lesion. Also, it would not have waxed and waned as this lesion had done.
Epidermal cysts (choice “c”) can certainly come and go in prominence, but they are filled with a cheesy, pasty material—not the dry crystalline substance found in this lesion. Moreover, most epidermal cysts will have a small comedonal punctum over the center of the lesion. Dystrophic calcification (choice “d”) can mimic gouty tophi, but it is usually rough, firm, and fixed. It certainly would not be coming and going as it pleases.
TREATMENT
Surgical excision of the tophus was offered, but the patient was content with knowing the correct diagnosis. His PCP had previously explained therapeutic options—such as medication and dietary changes—that could address the overall problem. The patient elected to pursue treatment with his PCP.
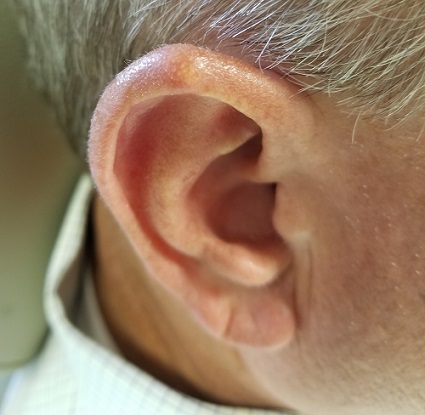
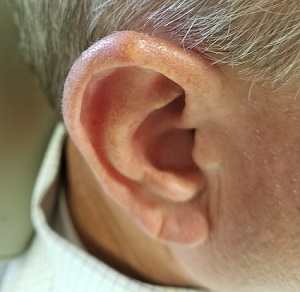
Over the years, the lesion on this 49-year-old man’s right ear has waxed and waned in prominence. Although it never causes pain, its unrelenting existence coupled with a history of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) on his face has caused him to worry. He has had no other lesions and is in otherwise good health, except for occasional bouts of arthritis, for which he takes ibuprofen, with good results.
While his family had suggested that the lesion could be a cyst, his primary care provider (PCP) disagreed and referred him to dermatology.
A 5-mm firm papule is located at the right helical crest. The lesion is skin-colored, with no redness, and nontender on palpation, although it is moderately firm and mobile. No punctum is noted.
The surrounding skin has no signs of sun damage, although the patient is quite fair. As a young man, he had far too much sun exposure, burning easily and tanning only with difficulty.
After consultation with the patient, the decision is made to incise the lesion using a #11 blade to examine its contents. The incision reveals a dry crystalline substance, which is easily cleared with brief curettage. This effectively leads to a flattening of the lesion.
HFpEF: Gender difference in sacubitril/valsartan response remains mystery
The explanation for the impressive clinical benefits of sacubitril/valsartan in women with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the PARAGON-HF trial – but not in the men – remains elusive, Jonathan W. Cunningham, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’ve all been trying to unravel the explanation for the differential effects between men and women in the primary trial. I don’t know that this NT-proBNP substudy gives a clear answer because we did see similar reduction in NT-proBNP in the men and women,” said Dr. Cunningham of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“Unfortunately, I think we’re still looking for the underlying physiological explanation for that very interesting interaction,” he added.
The PARAGON-HF trial included 4,796 patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) who were randomized double-blind to sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) or valsartan on top of background guideline-directed medical therapy and followed for a median of 34 months (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381[17]:1609-20). The sacubitril/valsartan group’s 13% relative risk reduction in the primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and total heart failure hospitalizations fell tantalizingly short of statistical significance (P = 0.058).
In women, however, who comprised more than half of the study population, the benefit of sacubitril/valsartan was larger: a 27% relative risk reduction compared to valsartan alone. That’s a statistically significant difference in a prespecified subgroup analysis, but according to the rules of clinical trials and statistics it must be considered hypothesis-generating and nondefinitive, since the overall trial was negative. Men randomized to sacubitril/valsartan had a modest 3% increased risk of the primary endpoint compared to men on valsartan.
Because of the enormous unmet need for effective therapy for HFpEF, and the fact that HFpEF is more common in women than men, the search is on for an explanation that would account for the striking gender difference in outcome in PARAGON-HF. At ACC 2020, Dr. Cunningham presented a secondary analysis of the trial focusing on the relationships between baseline and on-treatment N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels and clinical outcomes.
Among the key findings was that the higher the baseline NT-proBNP, the greater the likelihood of the primary endpoint. Also, sacubitril/valsartan reduced NT-proBNP to a similar extent in men and women: For example, by 20% compared to valsartan in men and by 18% in women when measured 16 weeks after randomization. And reduction in NT-proBNP was associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations; indeed, 60% of participants in PARAGON-HF experienced a decrease in NT-proBNP, and they had a 23% lower event rate compared to patients whose NT-proBNP increased during the course of the study.
Another intriguing finding in the parent PARAGON-HF trial was that HFpEF patients with an LVEF of 45%-57% had a 22% lower rate of the primary endpoint than those with an LVEF of 58% or more. But as with the gender difference in clinical outcomes in response to sacubitril/valsartan, the difference in outcomes based on ejection fraction was not mediated by the drug’s impact on NT-proBNP, since sacubitril/valsartan reduced NT-proBNP to a similar degree in HFpEF patients with an LVEF above or below 57%.
The difference in outcomes by ejection fraction wasn’t entirely surprising, because those low-normal–range ejection fractions where sacubitril/valsartan had a favorable impact approach those characteristic of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and guidelines give sacubitril/valsartan a class I recommendation in patients with HFrEF on the strength of the medication’s demonstrated reduction in morbidity and mortality in the PARADIGM-HF trial.
Discussant Lee R. Goldberg, MD, predicted this analysis will have an impact on the design of future clinical trials in HFpEF, which up until now have required certain minimum NT-proBNP levels for participation.
“Maybe this is why so many of our trials in HFpEF have been unsuccessful. It’s a very heterogeneous population and perhaps NT-proBNP cutoffs are leading to a lot of mischief or heterogeneity that causes us some difficulty,” said Dr. Goldberg, professor of medicine and chief of the section of advanced heart failure and cardiac transplantation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Cunningham reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study. The PARAGON-HF trial was funded by Novartis.
Simultaneously with Dr. Cunningham’s presentation at ACC 2020, the study results were published online (JACC Heart Fail. 2020 Mar 26; doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.03.002.
SOURCE: Cunningham JW. ACC 2020, Abstract 412-08.
The explanation for the impressive clinical benefits of sacubitril/valsartan in women with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the PARAGON-HF trial – but not in the men – remains elusive, Jonathan W. Cunningham, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’ve all been trying to unravel the explanation for the differential effects between men and women in the primary trial. I don’t know that this NT-proBNP substudy gives a clear answer because we did see similar reduction in NT-proBNP in the men and women,” said Dr. Cunningham of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“Unfortunately, I think we’re still looking for the underlying physiological explanation for that very interesting interaction,” he added.
The PARAGON-HF trial included 4,796 patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) who were randomized double-blind to sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) or valsartan on top of background guideline-directed medical therapy and followed for a median of 34 months (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381[17]:1609-20). The sacubitril/valsartan group’s 13% relative risk reduction in the primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and total heart failure hospitalizations fell tantalizingly short of statistical significance (P = 0.058).
In women, however, who comprised more than half of the study population, the benefit of sacubitril/valsartan was larger: a 27% relative risk reduction compared to valsartan alone. That’s a statistically significant difference in a prespecified subgroup analysis, but according to the rules of clinical trials and statistics it must be considered hypothesis-generating and nondefinitive, since the overall trial was negative. Men randomized to sacubitril/valsartan had a modest 3% increased risk of the primary endpoint compared to men on valsartan.
Because of the enormous unmet need for effective therapy for HFpEF, and the fact that HFpEF is more common in women than men, the search is on for an explanation that would account for the striking gender difference in outcome in PARAGON-HF. At ACC 2020, Dr. Cunningham presented a secondary analysis of the trial focusing on the relationships between baseline and on-treatment N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels and clinical outcomes.
Among the key findings was that the higher the baseline NT-proBNP, the greater the likelihood of the primary endpoint. Also, sacubitril/valsartan reduced NT-proBNP to a similar extent in men and women: For example, by 20% compared to valsartan in men and by 18% in women when measured 16 weeks after randomization. And reduction in NT-proBNP was associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations; indeed, 60% of participants in PARAGON-HF experienced a decrease in NT-proBNP, and they had a 23% lower event rate compared to patients whose NT-proBNP increased during the course of the study.
Another intriguing finding in the parent PARAGON-HF trial was that HFpEF patients with an LVEF of 45%-57% had a 22% lower rate of the primary endpoint than those with an LVEF of 58% or more. But as with the gender difference in clinical outcomes in response to sacubitril/valsartan, the difference in outcomes based on ejection fraction was not mediated by the drug’s impact on NT-proBNP, since sacubitril/valsartan reduced NT-proBNP to a similar degree in HFpEF patients with an LVEF above or below 57%.
The difference in outcomes by ejection fraction wasn’t entirely surprising, because those low-normal–range ejection fractions where sacubitril/valsartan had a favorable impact approach those characteristic of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and guidelines give sacubitril/valsartan a class I recommendation in patients with HFrEF on the strength of the medication’s demonstrated reduction in morbidity and mortality in the PARADIGM-HF trial.
Discussant Lee R. Goldberg, MD, predicted this analysis will have an impact on the design of future clinical trials in HFpEF, which up until now have required certain minimum NT-proBNP levels for participation.
“Maybe this is why so many of our trials in HFpEF have been unsuccessful. It’s a very heterogeneous population and perhaps NT-proBNP cutoffs are leading to a lot of mischief or heterogeneity that causes us some difficulty,” said Dr. Goldberg, professor of medicine and chief of the section of advanced heart failure and cardiac transplantation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Cunningham reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study. The PARAGON-HF trial was funded by Novartis.
Simultaneously with Dr. Cunningham’s presentation at ACC 2020, the study results were published online (JACC Heart Fail. 2020 Mar 26; doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.03.002.
SOURCE: Cunningham JW. ACC 2020, Abstract 412-08.
The explanation for the impressive clinical benefits of sacubitril/valsartan in women with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the PARAGON-HF trial – but not in the men – remains elusive, Jonathan W. Cunningham, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’ve all been trying to unravel the explanation for the differential effects between men and women in the primary trial. I don’t know that this NT-proBNP substudy gives a clear answer because we did see similar reduction in NT-proBNP in the men and women,” said Dr. Cunningham of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“Unfortunately, I think we’re still looking for the underlying physiological explanation for that very interesting interaction,” he added.
The PARAGON-HF trial included 4,796 patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) who were randomized double-blind to sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) or valsartan on top of background guideline-directed medical therapy and followed for a median of 34 months (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381[17]:1609-20). The sacubitril/valsartan group’s 13% relative risk reduction in the primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and total heart failure hospitalizations fell tantalizingly short of statistical significance (P = 0.058).
In women, however, who comprised more than half of the study population, the benefit of sacubitril/valsartan was larger: a 27% relative risk reduction compared to valsartan alone. That’s a statistically significant difference in a prespecified subgroup analysis, but according to the rules of clinical trials and statistics it must be considered hypothesis-generating and nondefinitive, since the overall trial was negative. Men randomized to sacubitril/valsartan had a modest 3% increased risk of the primary endpoint compared to men on valsartan.
Because of the enormous unmet need for effective therapy for HFpEF, and the fact that HFpEF is more common in women than men, the search is on for an explanation that would account for the striking gender difference in outcome in PARAGON-HF. At ACC 2020, Dr. Cunningham presented a secondary analysis of the trial focusing on the relationships between baseline and on-treatment N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels and clinical outcomes.
Among the key findings was that the higher the baseline NT-proBNP, the greater the likelihood of the primary endpoint. Also, sacubitril/valsartan reduced NT-proBNP to a similar extent in men and women: For example, by 20% compared to valsartan in men and by 18% in women when measured 16 weeks after randomization. And reduction in NT-proBNP was associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations; indeed, 60% of participants in PARAGON-HF experienced a decrease in NT-proBNP, and they had a 23% lower event rate compared to patients whose NT-proBNP increased during the course of the study.
Another intriguing finding in the parent PARAGON-HF trial was that HFpEF patients with an LVEF of 45%-57% had a 22% lower rate of the primary endpoint than those with an LVEF of 58% or more. But as with the gender difference in clinical outcomes in response to sacubitril/valsartan, the difference in outcomes based on ejection fraction was not mediated by the drug’s impact on NT-proBNP, since sacubitril/valsartan reduced NT-proBNP to a similar degree in HFpEF patients with an LVEF above or below 57%.
The difference in outcomes by ejection fraction wasn’t entirely surprising, because those low-normal–range ejection fractions where sacubitril/valsartan had a favorable impact approach those characteristic of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and guidelines give sacubitril/valsartan a class I recommendation in patients with HFrEF on the strength of the medication’s demonstrated reduction in morbidity and mortality in the PARADIGM-HF trial.
Discussant Lee R. Goldberg, MD, predicted this analysis will have an impact on the design of future clinical trials in HFpEF, which up until now have required certain minimum NT-proBNP levels for participation.
“Maybe this is why so many of our trials in HFpEF have been unsuccessful. It’s a very heterogeneous population and perhaps NT-proBNP cutoffs are leading to a lot of mischief or heterogeneity that causes us some difficulty,” said Dr. Goldberg, professor of medicine and chief of the section of advanced heart failure and cardiac transplantation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Cunningham reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study. The PARAGON-HF trial was funded by Novartis.
Simultaneously with Dr. Cunningham’s presentation at ACC 2020, the study results were published online (JACC Heart Fail. 2020 Mar 26; doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.03.002.
SOURCE: Cunningham JW. ACC 2020, Abstract 412-08.
FROM ACC 2020
COVID-19 crisis: We must care for ourselves as we care for others
“I do not shrink from this responsibility – I welcome it.” – John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said: “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers – family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses – who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call – and take care of ourselves – in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So too must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in three domains: physical, mental, and social.
With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
To take care of our mental health, we need to have the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
From a social standpoint, we must be proactive about preventing emotional isolation. Technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, coworkers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant and someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946 after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms – to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
A version of this commentary originally appeared in the Journal of Family Practice (J Fam Pract. 2020 April;69[3]:119,153).
Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Aaron Sutton is a behavioral health consultant and faculty member in the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
References
1. Brockell G. “During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely.” The Washington Post. 2020 Mar 12.
2. Frankl VE. “Man’s Search for Meaning.” Boston: Beacon Press, 2006.
“I do not shrink from this responsibility – I welcome it.” – John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said: “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers – family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses – who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call – and take care of ourselves – in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So too must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in three domains: physical, mental, and social.
With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
To take care of our mental health, we need to have the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
From a social standpoint, we must be proactive about preventing emotional isolation. Technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, coworkers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant and someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946 after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms – to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
A version of this commentary originally appeared in the Journal of Family Practice (J Fam Pract. 2020 April;69[3]:119,153).
Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Aaron Sutton is a behavioral health consultant and faculty member in the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
References
1. Brockell G. “During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely.” The Washington Post. 2020 Mar 12.
2. Frankl VE. “Man’s Search for Meaning.” Boston: Beacon Press, 2006.
“I do not shrink from this responsibility – I welcome it.” – John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said: “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers – family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses – who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call – and take care of ourselves – in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So too must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in three domains: physical, mental, and social.
With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
To take care of our mental health, we need to have the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
From a social standpoint, we must be proactive about preventing emotional isolation. Technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, coworkers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant and someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946 after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms – to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
A version of this commentary originally appeared in the Journal of Family Practice (J Fam Pract. 2020 April;69[3]:119,153).
Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Aaron Sutton is a behavioral health consultant and faculty member in the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
References
1. Brockell G. “During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely.” The Washington Post. 2020 Mar 12.
2. Frankl VE. “Man’s Search for Meaning.” Boston: Beacon Press, 2006.
Obesity link to severe COVID-19, especially in patients aged under 60
It is becoming increasingly clear that obesity is one of the biggest risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease, particularly among younger patients.
Newly published data from New York show that, among those aged under 60 years, obesity was twice as likely to result in hospitalization for COVID-19 and also significantly increased the likelihood that a person would end up in intensive care.
“Obesity [in people younger than 60] appears to be a previously unrecognized risk factor for hospital admission and need for critical care. This has important and practical implications when nearly 40% of adults in the U.S. are obese with a body mass index [BMI] of [at least] 30,” wrote Jennifer Lighter, MD, of New York University Langone Health, and colleagues in their research letter published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Similar findings in a preprint publication, yet to be peer reviewed, from another New York hospital show that, with the exception of older age, obesity (BMI greater than 40 kg/m2) had the strongest association with hospitalization for COVID-19, increasing the risk more than 500%.
Meanwhile, a new French study shows a high frequency of obesity among patients admitted to one ICU for COVID-19; furthermore, disease severity increased with increasing BMI. One of the authors said in an interview that many of the presenting patients were younger, with their only risk factor being obesity.
“Patients with obesity should avoid any COVID-19 contamination by enforcing all prevention measures during the current pandemic,” wrote the authors, led by Arthur Simonnet, MD, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Lille (France).
They also stressed that COVID-19 patients “with severe obesity should be monitored more closely.”
Those with obesity are young and become very sick, very quickly
François Pattou, MD, PhD, coauthor of the French article published in Obesity said in an interview that, when patients with COVID-19 began to arrive at their ICU in Lille, there were young patients who did not have any other comorbidities.
“They were just obese,” he observed, adding that they seemed “to have a very specific disease, something different” from that seen before, with patients becoming very sick, very quickly.
In their study, they examined 124 consecutive patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 between Feb. 25 and April 5, 2020, and compared them with a historical control group of 306 patients admitted to the ICU at the same hospital for non–COVID-19-related severe acute respiratory disease in 2019.
By April 6, 60 patients with COVID-19 had been discharged from intensive care, 18 had died, and 46 remained in the unit. The majority (73%) were male, and their median age was 60 years. Obesity and severe obesity were significantly more prevalent among the patients with COVID-19, at 47.6% and 28.2% versus 25.2% and 10.8% among historical controls (P < .001 for trend).
A key finding was that those with a BMI greater than 35 had a more than 600% increased risk of requiring mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 7.36; P = .021), compared with those with a BMI less than 25, even after adjusting for age, diabetes, and hypertension.
Obesity in under 60s at least doubles risk of admission in U.S.
The studies out of New York, one of which was stratified by age, paint a similar picture.
Dr. Lighter and colleagues found that, of the 3,615 individuals who tested positive for COVID-19 in their series, 775 (21%) had a BMI of 30-34 and 595 (16%) had a BMI of at least 35. Obesity wasn’t a predictor of admission to hospital or the ICU in those over the age of 60 years, but in those younger than 60 years, it was.
Those under age 60 with a BMI of 30-34 were twice as likely to be admitted to hospital (hazard ratio, 2.0; P < .0001) and critical care (HR, 1.8; P = .006), compared with those under age 60 with a BMI less than 30. Likewise, those under age 60 with a BMI of at least 35 were 2.2 (P < .0001) and 3.6 (P < .0001) times more likely to be admitted to acute and critical care.
“Unfortunately, obesity in people [less than] 60 years is a newly identified epidemiologic risk factor which may contribute to increased morbidity rates [with COVID-19] experienced in the U.S.,” they concluded.
And in the other U.S. study, Christopher M. Petrilli, MD, of New York University, and colleagues looked at 4,103 patients with COVID-19 treated between March 1 and April 2, 2020, and followed to April 7.
Just under half of patients (48.7%) were hospitalized, of whom 22.3% required mechanical ventilation and 14.6% died or were discharged to hospice. The research was published on medRxiv, showing that, apart from age, the strongest predictors of hospitalization were BMI greater than 40 (OR, 6.2) and heart failure (OR, 4.3).
“It is notable that the chronic condition with the strongest association with critical illness was obesity, with a substantially higher odds ratio than any cardiovascular or pulmonary disease,” they noted.
Inflammation is a possible culprit
Dr. Pattou believes that the culprit behind the increased risk of disease severity seen with obesity in COVID-19 is inflammation, mediated by fibrin deposits in the circulation, which his colleagues have seen on autopsy, and which “block oxygen passage through the blood.”
This may help explain why mechanical ventilation can be less successful in these patients. “The answer is to get rid of this inflammation,” Dr. Pattou observed.
Dr. Petrilli and colleagues also observed that obesity “is well-recognized to be a proinflammatory condition.”
And their findings showed “the importance of inflammatory markers in distinguishing future critical from noncritical illness,” they said, noting that, among these markers, early elevations in C-reactive protein and D-dimer “had the strongest association with mechanical ventilation or mortality.”
Livio Luzi, MD, of IRCCS MultiMedica, Milan, Italy, has previously written on the relationship between influenza and obesity, and discussed in an interview the potential lessons for the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Obesity is characterized by an impairment of immune response and by a low-grade chronic inflammation. Furthermore, obese subjects have an altered dynamic of pulmonary ventilation, with reduced diaphragmatic excursion,” Dr. Luzi said. These factors, alongside others, “may help to explain” the current results, and stress the importance of close monitoring of those with obesity and COVID-19.
No relevant financial relationships were declared.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It is becoming increasingly clear that obesity is one of the biggest risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease, particularly among younger patients.
Newly published data from New York show that, among those aged under 60 years, obesity was twice as likely to result in hospitalization for COVID-19 and also significantly increased the likelihood that a person would end up in intensive care.
“Obesity [in people younger than 60] appears to be a previously unrecognized risk factor for hospital admission and need for critical care. This has important and practical implications when nearly 40% of adults in the U.S. are obese with a body mass index [BMI] of [at least] 30,” wrote Jennifer Lighter, MD, of New York University Langone Health, and colleagues in their research letter published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Similar findings in a preprint publication, yet to be peer reviewed, from another New York hospital show that, with the exception of older age, obesity (BMI greater than 40 kg/m2) had the strongest association with hospitalization for COVID-19, increasing the risk more than 500%.
Meanwhile, a new French study shows a high frequency of obesity among patients admitted to one ICU for COVID-19; furthermore, disease severity increased with increasing BMI. One of the authors said in an interview that many of the presenting patients were younger, with their only risk factor being obesity.
“Patients with obesity should avoid any COVID-19 contamination by enforcing all prevention measures during the current pandemic,” wrote the authors, led by Arthur Simonnet, MD, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Lille (France).
They also stressed that COVID-19 patients “with severe obesity should be monitored more closely.”
Those with obesity are young and become very sick, very quickly
François Pattou, MD, PhD, coauthor of the French article published in Obesity said in an interview that, when patients with COVID-19 began to arrive at their ICU in Lille, there were young patients who did not have any other comorbidities.
“They were just obese,” he observed, adding that they seemed “to have a very specific disease, something different” from that seen before, with patients becoming very sick, very quickly.
In their study, they examined 124 consecutive patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 between Feb. 25 and April 5, 2020, and compared them with a historical control group of 306 patients admitted to the ICU at the same hospital for non–COVID-19-related severe acute respiratory disease in 2019.
By April 6, 60 patients with COVID-19 had been discharged from intensive care, 18 had died, and 46 remained in the unit. The majority (73%) were male, and their median age was 60 years. Obesity and severe obesity were significantly more prevalent among the patients with COVID-19, at 47.6% and 28.2% versus 25.2% and 10.8% among historical controls (P < .001 for trend).
A key finding was that those with a BMI greater than 35 had a more than 600% increased risk of requiring mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 7.36; P = .021), compared with those with a BMI less than 25, even after adjusting for age, diabetes, and hypertension.
Obesity in under 60s at least doubles risk of admission in U.S.
The studies out of New York, one of which was stratified by age, paint a similar picture.
Dr. Lighter and colleagues found that, of the 3,615 individuals who tested positive for COVID-19 in their series, 775 (21%) had a BMI of 30-34 and 595 (16%) had a BMI of at least 35. Obesity wasn’t a predictor of admission to hospital or the ICU in those over the age of 60 years, but in those younger than 60 years, it was.
Those under age 60 with a BMI of 30-34 were twice as likely to be admitted to hospital (hazard ratio, 2.0; P < .0001) and critical care (HR, 1.8; P = .006), compared with those under age 60 with a BMI less than 30. Likewise, those under age 60 with a BMI of at least 35 were 2.2 (P < .0001) and 3.6 (P < .0001) times more likely to be admitted to acute and critical care.
“Unfortunately, obesity in people [less than] 60 years is a newly identified epidemiologic risk factor which may contribute to increased morbidity rates [with COVID-19] experienced in the U.S.,” they concluded.
And in the other U.S. study, Christopher M. Petrilli, MD, of New York University, and colleagues looked at 4,103 patients with COVID-19 treated between March 1 and April 2, 2020, and followed to April 7.
Just under half of patients (48.7%) were hospitalized, of whom 22.3% required mechanical ventilation and 14.6% died or were discharged to hospice. The research was published on medRxiv, showing that, apart from age, the strongest predictors of hospitalization were BMI greater than 40 (OR, 6.2) and heart failure (OR, 4.3).
“It is notable that the chronic condition with the strongest association with critical illness was obesity, with a substantially higher odds ratio than any cardiovascular or pulmonary disease,” they noted.
Inflammation is a possible culprit
Dr. Pattou believes that the culprit behind the increased risk of disease severity seen with obesity in COVID-19 is inflammation, mediated by fibrin deposits in the circulation, which his colleagues have seen on autopsy, and which “block oxygen passage through the blood.”
This may help explain why mechanical ventilation can be less successful in these patients. “The answer is to get rid of this inflammation,” Dr. Pattou observed.
Dr. Petrilli and colleagues also observed that obesity “is well-recognized to be a proinflammatory condition.”
And their findings showed “the importance of inflammatory markers in distinguishing future critical from noncritical illness,” they said, noting that, among these markers, early elevations in C-reactive protein and D-dimer “had the strongest association with mechanical ventilation or mortality.”
Livio Luzi, MD, of IRCCS MultiMedica, Milan, Italy, has previously written on the relationship between influenza and obesity, and discussed in an interview the potential lessons for the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Obesity is characterized by an impairment of immune response and by a low-grade chronic inflammation. Furthermore, obese subjects have an altered dynamic of pulmonary ventilation, with reduced diaphragmatic excursion,” Dr. Luzi said. These factors, alongside others, “may help to explain” the current results, and stress the importance of close monitoring of those with obesity and COVID-19.
No relevant financial relationships were declared.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It is becoming increasingly clear that obesity is one of the biggest risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease, particularly among younger patients.
Newly published data from New York show that, among those aged under 60 years, obesity was twice as likely to result in hospitalization for COVID-19 and also significantly increased the likelihood that a person would end up in intensive care.
“Obesity [in people younger than 60] appears to be a previously unrecognized risk factor for hospital admission and need for critical care. This has important and practical implications when nearly 40% of adults in the U.S. are obese with a body mass index [BMI] of [at least] 30,” wrote Jennifer Lighter, MD, of New York University Langone Health, and colleagues in their research letter published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Similar findings in a preprint publication, yet to be peer reviewed, from another New York hospital show that, with the exception of older age, obesity (BMI greater than 40 kg/m2) had the strongest association with hospitalization for COVID-19, increasing the risk more than 500%.
Meanwhile, a new French study shows a high frequency of obesity among patients admitted to one ICU for COVID-19; furthermore, disease severity increased with increasing BMI. One of the authors said in an interview that many of the presenting patients were younger, with their only risk factor being obesity.
“Patients with obesity should avoid any COVID-19 contamination by enforcing all prevention measures during the current pandemic,” wrote the authors, led by Arthur Simonnet, MD, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Lille (France).
They also stressed that COVID-19 patients “with severe obesity should be monitored more closely.”
Those with obesity are young and become very sick, very quickly
François Pattou, MD, PhD, coauthor of the French article published in Obesity said in an interview that, when patients with COVID-19 began to arrive at their ICU in Lille, there were young patients who did not have any other comorbidities.
“They were just obese,” he observed, adding that they seemed “to have a very specific disease, something different” from that seen before, with patients becoming very sick, very quickly.
In their study, they examined 124 consecutive patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 between Feb. 25 and April 5, 2020, and compared them with a historical control group of 306 patients admitted to the ICU at the same hospital for non–COVID-19-related severe acute respiratory disease in 2019.
By April 6, 60 patients with COVID-19 had been discharged from intensive care, 18 had died, and 46 remained in the unit. The majority (73%) were male, and their median age was 60 years. Obesity and severe obesity were significantly more prevalent among the patients with COVID-19, at 47.6% and 28.2% versus 25.2% and 10.8% among historical controls (P < .001 for trend).
A key finding was that those with a BMI greater than 35 had a more than 600% increased risk of requiring mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 7.36; P = .021), compared with those with a BMI less than 25, even after adjusting for age, diabetes, and hypertension.
Obesity in under 60s at least doubles risk of admission in U.S.
The studies out of New York, one of which was stratified by age, paint a similar picture.
Dr. Lighter and colleagues found that, of the 3,615 individuals who tested positive for COVID-19 in their series, 775 (21%) had a BMI of 30-34 and 595 (16%) had a BMI of at least 35. Obesity wasn’t a predictor of admission to hospital or the ICU in those over the age of 60 years, but in those younger than 60 years, it was.
Those under age 60 with a BMI of 30-34 were twice as likely to be admitted to hospital (hazard ratio, 2.0; P < .0001) and critical care (HR, 1.8; P = .006), compared with those under age 60 with a BMI less than 30. Likewise, those under age 60 with a BMI of at least 35 were 2.2 (P < .0001) and 3.6 (P < .0001) times more likely to be admitted to acute and critical care.
“Unfortunately, obesity in people [less than] 60 years is a newly identified epidemiologic risk factor which may contribute to increased morbidity rates [with COVID-19] experienced in the U.S.,” they concluded.
And in the other U.S. study, Christopher M. Petrilli, MD, of New York University, and colleagues looked at 4,103 patients with COVID-19 treated between March 1 and April 2, 2020, and followed to April 7.
Just under half of patients (48.7%) were hospitalized, of whom 22.3% required mechanical ventilation and 14.6% died or were discharged to hospice. The research was published on medRxiv, showing that, apart from age, the strongest predictors of hospitalization were BMI greater than 40 (OR, 6.2) and heart failure (OR, 4.3).
“It is notable that the chronic condition with the strongest association with critical illness was obesity, with a substantially higher odds ratio than any cardiovascular or pulmonary disease,” they noted.
Inflammation is a possible culprit
Dr. Pattou believes that the culprit behind the increased risk of disease severity seen with obesity in COVID-19 is inflammation, mediated by fibrin deposits in the circulation, which his colleagues have seen on autopsy, and which “block oxygen passage through the blood.”
This may help explain why mechanical ventilation can be less successful in these patients. “The answer is to get rid of this inflammation,” Dr. Pattou observed.
Dr. Petrilli and colleagues also observed that obesity “is well-recognized to be a proinflammatory condition.”
And their findings showed “the importance of inflammatory markers in distinguishing future critical from noncritical illness,” they said, noting that, among these markers, early elevations in C-reactive protein and D-dimer “had the strongest association with mechanical ventilation or mortality.”
Livio Luzi, MD, of IRCCS MultiMedica, Milan, Italy, has previously written on the relationship between influenza and obesity, and discussed in an interview the potential lessons for the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Obesity is characterized by an impairment of immune response and by a low-grade chronic inflammation. Furthermore, obese subjects have an altered dynamic of pulmonary ventilation, with reduced diaphragmatic excursion,” Dr. Luzi said. These factors, alongside others, “may help to explain” the current results, and stress the importance of close monitoring of those with obesity and COVID-19.
No relevant financial relationships were declared.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. prevalence of antinuclear antibodies has steadily risen, study finds
Between 1988 and 2012, the prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in the United States increased from 11% to 15.9%, especially among adolescents, males, and non-Hispanic whites.
The finding comes from a retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of serum samples from individuals who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey over three time periods: 1988-1991, 1999-2004, and 2011-2012.
“Autoimmune diseases are a diverse group of disorders characterized by damaging immune responses to self-antigens and, for the most part, are of unknown etiology,” authors led by Gregg E. Dinse, ScD, wrote in a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “They are thought to impact 3%-5% of the population, with rising rates noted several decades ago. Recent studies suggest continued increases for certain autoimmune diseases, but it is unclear whether these trends are due to changes in recognition and diagnosis, or are true temporal changes in incidence.”
Dr. Dinse, of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences in Research Triangle Park, N.C., and his colleagues evaluated sera samples of 14,211 survey participants aged 12 years and older at 1:80 dilution for antinuclear antibodies (ANA) using a standard indirect immunofluorescence assay (HEp-2 assay). The samples that received a grade of 3 or 4 on a 0-4 scale (compared with standard references, with values of 1-4 indicating positivity) underwent additional assessment by sequential ANA titers up to 1:1,280 dilution. To estimate changes in ANA prevalence over the time periods, they used logistic regression adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, and survey design variables.
The researchers observed an ANA prevalence of 11% in 1988-1991, 11.5% in 1999-2004, and 15.9% in 2011-2012. This corresponds to 22, 27, and 41 million affected individuals, respectively. Females were more likely than males to have ANA (odds ratios of 2.53, 2.97, and 1.94 in 1988-1991, 1999-2004, and 2011-2012, respectively; P less than .0001), as were older adults relative to adolescents (ORs of 3.63, 1.80, and 1.71; P less than .002). Among adolescents, the prevalence of ANA rose steeply, with odds ratios of 2.02 in 1999-2004 and 2.88 in 2011-2012 in the second and third time periods relative to the first (trend P less than .0001). The researchers also found that, compared with non-Hispanic whites, the odds of having ANA were higher for non-Hispanic blacks (OR, 1.75) and Mexican-Americans (OR, 1.87) in 1988-1991, but racial/ethnic differences diminished in 1999-2004 and 2011-2012.
After adjustment for covariates, the researchers found that the estimated odds ratios for the second and third time periods relative to the first were 1.02 and 1.47, respectively, reflecting an overall ANA time trend (P less than .0001). Increases in ANA prevalence among cohorts did not correlate with contemporaneous trends in body mass index, smoking, or alcohol consumption.
Dr. Dinse and his colleagues acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that associations were based on cross-sectional data rather than repeated measures, and that some variables were self-reported, including the limited questionnaire data on autoimmune diseases.
In an interview, David S. Pisetsky, MD, professor of medicine/rheumatology and immunology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., characterized the study findings as “hypothesis generating” and said that he would like to know if the researchers would find the same results if they used a different ANA assay. “There’s a lot of variability from ANA kit to ANA kit – much greater than what was thought,” said Dr. Pisetsky, who is an authority on the topic. “One thing that needs to be done is to find out what the frequency is with other tests. One should recognize that the actual frequency is going to vary by the assay used. In another test format, the frequency may have been lower; it could have been higher.”
He added that the precise reasons why the prevalence of ANAs are rising in the general population remains elusive. “We know the target antigens in people with autoantibody-associated rheumatic disease,” Dr. Pisetsky said. “But what we don’t know a lot of times is, what are the target antigens in the otherwise healthy population? There has only been one antibody system that people have felt is associated with the otherwise healthy population. Those are called anti-DFS-70 antibodies, but there is even uncertainty about those. If you know what the antigens recognized were, then I think you could begin to speculate more about what’s going on in the population that’s increasing the frequency [of ANAs].”
In an accompanying editorial, Richard J. Bucala, MD, chief of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that the origins of autoantibodies in different rheumatic diseases and the steps that lead to disease progression remain elusive. “Modern societies experience an ever increasing variety of exposures due to travel and population migration, an increase in both the internationalization of agriculture and the industrialization of food production, a higher environmental burden of synthetic chemicals, emerging pathogens, and the inexorable effects of climate change,” Dr. Bucala wrote. “The speed and intensity of these influences is arguably unprecedented in human history and clearly outpace the possibility of protective genetic mechanisms to evolve and adapt.” He went on to note that the study’s findings “give impetus to multidisciplinary efforts aimed at preventative strategies, identifying environmental hazards, defining high-risk individuals, and preventing disease development in susceptible populations.”
The study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Dinse G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 April 7. doi: 10.1002/ART.41214.
Between 1988 and 2012, the prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in the United States increased from 11% to 15.9%, especially among adolescents, males, and non-Hispanic whites.
The finding comes from a retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of serum samples from individuals who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey over three time periods: 1988-1991, 1999-2004, and 2011-2012.
“Autoimmune diseases are a diverse group of disorders characterized by damaging immune responses to self-antigens and, for the most part, are of unknown etiology,” authors led by Gregg E. Dinse, ScD, wrote in a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “They are thought to impact 3%-5% of the population, with rising rates noted several decades ago. Recent studies suggest continued increases for certain autoimmune diseases, but it is unclear whether these trends are due to changes in recognition and diagnosis, or are true temporal changes in incidence.”
Dr. Dinse, of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences in Research Triangle Park, N.C., and his colleagues evaluated sera samples of 14,211 survey participants aged 12 years and older at 1:80 dilution for antinuclear antibodies (ANA) using a standard indirect immunofluorescence assay (HEp-2 assay). The samples that received a grade of 3 or 4 on a 0-4 scale (compared with standard references, with values of 1-4 indicating positivity) underwent additional assessment by sequential ANA titers up to 1:1,280 dilution. To estimate changes in ANA prevalence over the time periods, they used logistic regression adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, and survey design variables.
The researchers observed an ANA prevalence of 11% in 1988-1991, 11.5% in 1999-2004, and 15.9% in 2011-2012. This corresponds to 22, 27, and 41 million affected individuals, respectively. Females were more likely than males to have ANA (odds ratios of 2.53, 2.97, and 1.94 in 1988-1991, 1999-2004, and 2011-2012, respectively; P less than .0001), as were older adults relative to adolescents (ORs of 3.63, 1.80, and 1.71; P less than .002). Among adolescents, the prevalence of ANA rose steeply, with odds ratios of 2.02 in 1999-2004 and 2.88 in 2011-2012 in the second and third time periods relative to the first (trend P less than .0001). The researchers also found that, compared with non-Hispanic whites, the odds of having ANA were higher for non-Hispanic blacks (OR, 1.75) and Mexican-Americans (OR, 1.87) in 1988-1991, but racial/ethnic differences diminished in 1999-2004 and 2011-2012.
After adjustment for covariates, the researchers found that the estimated odds ratios for the second and third time periods relative to the first were 1.02 and 1.47, respectively, reflecting an overall ANA time trend (P less than .0001). Increases in ANA prevalence among cohorts did not correlate with contemporaneous trends in body mass index, smoking, or alcohol consumption.
Dr. Dinse and his colleagues acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that associations were based on cross-sectional data rather than repeated measures, and that some variables were self-reported, including the limited questionnaire data on autoimmune diseases.
In an interview, David S. Pisetsky, MD, professor of medicine/rheumatology and immunology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., characterized the study findings as “hypothesis generating” and said that he would like to know if the researchers would find the same results if they used a different ANA assay. “There’s a lot of variability from ANA kit to ANA kit – much greater than what was thought,” said Dr. Pisetsky, who is an authority on the topic. “One thing that needs to be done is to find out what the frequency is with other tests. One should recognize that the actual frequency is going to vary by the assay used. In another test format, the frequency may have been lower; it could have been higher.”
He added that the precise reasons why the prevalence of ANAs are rising in the general population remains elusive. “We know the target antigens in people with autoantibody-associated rheumatic disease,” Dr. Pisetsky said. “But what we don’t know a lot of times is, what are the target antigens in the otherwise healthy population? There has only been one antibody system that people have felt is associated with the otherwise healthy population. Those are called anti-DFS-70 antibodies, but there is even uncertainty about those. If you know what the antigens recognized were, then I think you could begin to speculate more about what’s going on in the population that’s increasing the frequency [of ANAs].”
In an accompanying editorial, Richard J. Bucala, MD, chief of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that the origins of autoantibodies in different rheumatic diseases and the steps that lead to disease progression remain elusive. “Modern societies experience an ever increasing variety of exposures due to travel and population migration, an increase in both the internationalization of agriculture and the industrialization of food production, a higher environmental burden of synthetic chemicals, emerging pathogens, and the inexorable effects of climate change,” Dr. Bucala wrote. “The speed and intensity of these influences is arguably unprecedented in human history and clearly outpace the possibility of protective genetic mechanisms to evolve and adapt.” He went on to note that the study’s findings “give impetus to multidisciplinary efforts aimed at preventative strategies, identifying environmental hazards, defining high-risk individuals, and preventing disease development in susceptible populations.”
The study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Dinse G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 April 7. doi: 10.1002/ART.41214.
Between 1988 and 2012, the prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in the United States increased from 11% to 15.9%, especially among adolescents, males, and non-Hispanic whites.
The finding comes from a retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of serum samples from individuals who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey over three time periods: 1988-1991, 1999-2004, and 2011-2012.
“Autoimmune diseases are a diverse group of disorders characterized by damaging immune responses to self-antigens and, for the most part, are of unknown etiology,” authors led by Gregg E. Dinse, ScD, wrote in a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “They are thought to impact 3%-5% of the population, with rising rates noted several decades ago. Recent studies suggest continued increases for certain autoimmune diseases, but it is unclear whether these trends are due to changes in recognition and diagnosis, or are true temporal changes in incidence.”
Dr. Dinse, of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences in Research Triangle Park, N.C., and his colleagues evaluated sera samples of 14,211 survey participants aged 12 years and older at 1:80 dilution for antinuclear antibodies (ANA) using a standard indirect immunofluorescence assay (HEp-2 assay). The samples that received a grade of 3 or 4 on a 0-4 scale (compared with standard references, with values of 1-4 indicating positivity) underwent additional assessment by sequential ANA titers up to 1:1,280 dilution. To estimate changes in ANA prevalence over the time periods, they used logistic regression adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, and survey design variables.
The researchers observed an ANA prevalence of 11% in 1988-1991, 11.5% in 1999-2004, and 15.9% in 2011-2012. This corresponds to 22, 27, and 41 million affected individuals, respectively. Females were more likely than males to have ANA (odds ratios of 2.53, 2.97, and 1.94 in 1988-1991, 1999-2004, and 2011-2012, respectively; P less than .0001), as were older adults relative to adolescents (ORs of 3.63, 1.80, and 1.71; P less than .002). Among adolescents, the prevalence of ANA rose steeply, with odds ratios of 2.02 in 1999-2004 and 2.88 in 2011-2012 in the second and third time periods relative to the first (trend P less than .0001). The researchers also found that, compared with non-Hispanic whites, the odds of having ANA were higher for non-Hispanic blacks (OR, 1.75) and Mexican-Americans (OR, 1.87) in 1988-1991, but racial/ethnic differences diminished in 1999-2004 and 2011-2012.
After adjustment for covariates, the researchers found that the estimated odds ratios for the second and third time periods relative to the first were 1.02 and 1.47, respectively, reflecting an overall ANA time trend (P less than .0001). Increases in ANA prevalence among cohorts did not correlate with contemporaneous trends in body mass index, smoking, or alcohol consumption.
Dr. Dinse and his colleagues acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that associations were based on cross-sectional data rather than repeated measures, and that some variables were self-reported, including the limited questionnaire data on autoimmune diseases.
In an interview, David S. Pisetsky, MD, professor of medicine/rheumatology and immunology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., characterized the study findings as “hypothesis generating” and said that he would like to know if the researchers would find the same results if they used a different ANA assay. “There’s a lot of variability from ANA kit to ANA kit – much greater than what was thought,” said Dr. Pisetsky, who is an authority on the topic. “One thing that needs to be done is to find out what the frequency is with other tests. One should recognize that the actual frequency is going to vary by the assay used. In another test format, the frequency may have been lower; it could have been higher.”
He added that the precise reasons why the prevalence of ANAs are rising in the general population remains elusive. “We know the target antigens in people with autoantibody-associated rheumatic disease,” Dr. Pisetsky said. “But what we don’t know a lot of times is, what are the target antigens in the otherwise healthy population? There has only been one antibody system that people have felt is associated with the otherwise healthy population. Those are called anti-DFS-70 antibodies, but there is even uncertainty about those. If you know what the antigens recognized were, then I think you could begin to speculate more about what’s going on in the population that’s increasing the frequency [of ANAs].”
In an accompanying editorial, Richard J. Bucala, MD, chief of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., noted that the origins of autoantibodies in different rheumatic diseases and the steps that lead to disease progression remain elusive. “Modern societies experience an ever increasing variety of exposures due to travel and population migration, an increase in both the internationalization of agriculture and the industrialization of food production, a higher environmental burden of synthetic chemicals, emerging pathogens, and the inexorable effects of climate change,” Dr. Bucala wrote. “The speed and intensity of these influences is arguably unprecedented in human history and clearly outpace the possibility of protective genetic mechanisms to evolve and adapt.” He went on to note that the study’s findings “give impetus to multidisciplinary efforts aimed at preventative strategies, identifying environmental hazards, defining high-risk individuals, and preventing disease development in susceptible populations.”
The study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Dinse G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 April 7. doi: 10.1002/ART.41214.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
The necessity of being together
COVID-19 has prompted many changes in pediatric health care. They say necessity is the mother of invention. Sometimes, necessity is the motivator for the long-past-due adoption of a previous invention, such as telemedicine for minor illnesses. And sometimes necessity reminds us about what is really important in a world of high technology.
Unlike our nearly overwhelmed internal medicine, ED, and family physician colleagues, many pediatricians are in a lull that threatens the financial viability of our practices. We are postponing annual well visits. We have fewer sick visits and hospitalizations since respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza also have been reduced by social distancing. Parents are avoiding the risk of contagion in the waiting room and not bringing their children in for minor complaints. There is more telemedicine – a welcome change in financing and practice whose time has come, but was being delayed by lack of insurance coverage.
Technology has allowed clinicians to respond to the pandemic in ways that would not have been possible a few years ago. Online tools, such as subscription email lists, webinars, and electronic medical news services, provide updates when the information changes weekly on the virus’s contagiousness, asymptomatic and presymptomatic transmission, prevalence, the effectiveness of masks, and experimental treatment options. These changes have been so fast that many journal articles based on data from China were obsolete and contradicted before they appeared in print.
However, technology only helped us to more effectively do what we needed to do in the first place – come together in a world of physical distancing and work toward common goals. In many hospitals, pediatric wards were emptied by reduced RSV admissions and postponed elective surgeries. These units have been converted to accept adult patients up to age 30 or 40 years. Our med-peds colleagues quickly created webinars and online resource packages on topics pediatric hospitalists might need to care for that population. There were refresher courses on ventilator management and reminders that community pediatric hospitalists, who in the winter might have one-third of their admissions with RSV, have more experience managing viral pneumonia than the internists.
Ward teams were created with a pediatric attending and an internal medicine resident. The resident’s familiarity with the names of blood pressure medicines complemented the attending’s years of clinical judgment and bedside manner. People are stepping out of their comfort zones but initial reports from the front lines are that, with each other’s support, we’ve got this.
Mistakes in telemedicine are being made, shared, and learned from. Emergency physicians are collecting anecdotes of situations when things were missed or treatment delayed. Surgeons report seeing increased numbers of cases in which the diagnosis of appendicitis was delayed, which isn’t surprising when a pediatrician cannot lay hands on the belly. Perhaps any case in which a parent calls a second or third time should be seen in the flesh.
Some newborn nurseries are discharging mother and baby at 24 hours after birth and rediscovering what was learned about that practice, which became common in the 1990s. It works well for the vast majority of babies, but we need to be ready to detect the occasional jaundiced baby or the one where breastfeeding isn’t going well. The gray-haired pediatricians can recall those nuances.
Another key role is to help everyone process the frequent deaths during a pandemic. First, there are the families we care for. Children are losing grandparents with little warning. Parents may be overwhelmed with grief while ill themselves. That makes children vulnerable.
Our medical system in 2 months has moved heaven and earth – and significantly harmed the medical care and financial future of our children – trying to assure that every 80-year-old has the right to die while attached to a ventilator, even though only a small fraction of them will survive to discharge. Meanwhile, on the wards, visitation policies have people deteriorating and dying alone. I find this paradigm distressing and antithetical to my training.
Medicine and nursing both have long histories in which the practitioner recognized that there was little they could do to prevent the death. Their role was to compassionately guide the family through it. For some people, this connection is the most precious of the arts of medicine and nursing. We need to reexamine our values. We need to get creative. We need to involve palliative care experts and clergy with the same urgency with which we have automakers making ventilators.
Second, there are our colleagues. Pediatric caregivers, particularly trainees, rarely encounter deaths and can benefit from debriefing sessions, even short ones. There is comfort in having a colleague review the situation and say: “There was nothing you could have done.” Or even: “That minor omission did not alter the outcome.” Even when everything was done properly, deaths cause moral suffering that needs processing and healing. Even if you don’t have magic words to give, just being present aids in the healing. We are all in this, together.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
COVID-19 has prompted many changes in pediatric health care. They say necessity is the mother of invention. Sometimes, necessity is the motivator for the long-past-due adoption of a previous invention, such as telemedicine for minor illnesses. And sometimes necessity reminds us about what is really important in a world of high technology.
Unlike our nearly overwhelmed internal medicine, ED, and family physician colleagues, many pediatricians are in a lull that threatens the financial viability of our practices. We are postponing annual well visits. We have fewer sick visits and hospitalizations since respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza also have been reduced by social distancing. Parents are avoiding the risk of contagion in the waiting room and not bringing their children in for minor complaints. There is more telemedicine – a welcome change in financing and practice whose time has come, but was being delayed by lack of insurance coverage.
Technology has allowed clinicians to respond to the pandemic in ways that would not have been possible a few years ago. Online tools, such as subscription email lists, webinars, and electronic medical news services, provide updates when the information changes weekly on the virus’s contagiousness, asymptomatic and presymptomatic transmission, prevalence, the effectiveness of masks, and experimental treatment options. These changes have been so fast that many journal articles based on data from China were obsolete and contradicted before they appeared in print.
However, technology only helped us to more effectively do what we needed to do in the first place – come together in a world of physical distancing and work toward common goals. In many hospitals, pediatric wards were emptied by reduced RSV admissions and postponed elective surgeries. These units have been converted to accept adult patients up to age 30 or 40 years. Our med-peds colleagues quickly created webinars and online resource packages on topics pediatric hospitalists might need to care for that population. There were refresher courses on ventilator management and reminders that community pediatric hospitalists, who in the winter might have one-third of their admissions with RSV, have more experience managing viral pneumonia than the internists.
Ward teams were created with a pediatric attending and an internal medicine resident. The resident’s familiarity with the names of blood pressure medicines complemented the attending’s years of clinical judgment and bedside manner. People are stepping out of their comfort zones but initial reports from the front lines are that, with each other’s support, we’ve got this.
Mistakes in telemedicine are being made, shared, and learned from. Emergency physicians are collecting anecdotes of situations when things were missed or treatment delayed. Surgeons report seeing increased numbers of cases in which the diagnosis of appendicitis was delayed, which isn’t surprising when a pediatrician cannot lay hands on the belly. Perhaps any case in which a parent calls a second or third time should be seen in the flesh.
Some newborn nurseries are discharging mother and baby at 24 hours after birth and rediscovering what was learned about that practice, which became common in the 1990s. It works well for the vast majority of babies, but we need to be ready to detect the occasional jaundiced baby or the one where breastfeeding isn’t going well. The gray-haired pediatricians can recall those nuances.
Another key role is to help everyone process the frequent deaths during a pandemic. First, there are the families we care for. Children are losing grandparents with little warning. Parents may be overwhelmed with grief while ill themselves. That makes children vulnerable.
Our medical system in 2 months has moved heaven and earth – and significantly harmed the medical care and financial future of our children – trying to assure that every 80-year-old has the right to die while attached to a ventilator, even though only a small fraction of them will survive to discharge. Meanwhile, on the wards, visitation policies have people deteriorating and dying alone. I find this paradigm distressing and antithetical to my training.
Medicine and nursing both have long histories in which the practitioner recognized that there was little they could do to prevent the death. Their role was to compassionately guide the family through it. For some people, this connection is the most precious of the arts of medicine and nursing. We need to reexamine our values. We need to get creative. We need to involve palliative care experts and clergy with the same urgency with which we have automakers making ventilators.
Second, there are our colleagues. Pediatric caregivers, particularly trainees, rarely encounter deaths and can benefit from debriefing sessions, even short ones. There is comfort in having a colleague review the situation and say: “There was nothing you could have done.” Or even: “That minor omission did not alter the outcome.” Even when everything was done properly, deaths cause moral suffering that needs processing and healing. Even if you don’t have magic words to give, just being present aids in the healing. We are all in this, together.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
COVID-19 has prompted many changes in pediatric health care. They say necessity is the mother of invention. Sometimes, necessity is the motivator for the long-past-due adoption of a previous invention, such as telemedicine for minor illnesses. And sometimes necessity reminds us about what is really important in a world of high technology.
Unlike our nearly overwhelmed internal medicine, ED, and family physician colleagues, many pediatricians are in a lull that threatens the financial viability of our practices. We are postponing annual well visits. We have fewer sick visits and hospitalizations since respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza also have been reduced by social distancing. Parents are avoiding the risk of contagion in the waiting room and not bringing their children in for minor complaints. There is more telemedicine – a welcome change in financing and practice whose time has come, but was being delayed by lack of insurance coverage.
Technology has allowed clinicians to respond to the pandemic in ways that would not have been possible a few years ago. Online tools, such as subscription email lists, webinars, and electronic medical news services, provide updates when the information changes weekly on the virus’s contagiousness, asymptomatic and presymptomatic transmission, prevalence, the effectiveness of masks, and experimental treatment options. These changes have been so fast that many journal articles based on data from China were obsolete and contradicted before they appeared in print.
However, technology only helped us to more effectively do what we needed to do in the first place – come together in a world of physical distancing and work toward common goals. In many hospitals, pediatric wards were emptied by reduced RSV admissions and postponed elective surgeries. These units have been converted to accept adult patients up to age 30 or 40 years. Our med-peds colleagues quickly created webinars and online resource packages on topics pediatric hospitalists might need to care for that population. There were refresher courses on ventilator management and reminders that community pediatric hospitalists, who in the winter might have one-third of their admissions with RSV, have more experience managing viral pneumonia than the internists.
Ward teams were created with a pediatric attending and an internal medicine resident. The resident’s familiarity with the names of blood pressure medicines complemented the attending’s years of clinical judgment and bedside manner. People are stepping out of their comfort zones but initial reports from the front lines are that, with each other’s support, we’ve got this.
Mistakes in telemedicine are being made, shared, and learned from. Emergency physicians are collecting anecdotes of situations when things were missed or treatment delayed. Surgeons report seeing increased numbers of cases in which the diagnosis of appendicitis was delayed, which isn’t surprising when a pediatrician cannot lay hands on the belly. Perhaps any case in which a parent calls a second or third time should be seen in the flesh.
Some newborn nurseries are discharging mother and baby at 24 hours after birth and rediscovering what was learned about that practice, which became common in the 1990s. It works well for the vast majority of babies, but we need to be ready to detect the occasional jaundiced baby or the one where breastfeeding isn’t going well. The gray-haired pediatricians can recall those nuances.
Another key role is to help everyone process the frequent deaths during a pandemic. First, there are the families we care for. Children are losing grandparents with little warning. Parents may be overwhelmed with grief while ill themselves. That makes children vulnerable.
Our medical system in 2 months has moved heaven and earth – and significantly harmed the medical care and financial future of our children – trying to assure that every 80-year-old has the right to die while attached to a ventilator, even though only a small fraction of them will survive to discharge. Meanwhile, on the wards, visitation policies have people deteriorating and dying alone. I find this paradigm distressing and antithetical to my training.
Medicine and nursing both have long histories in which the practitioner recognized that there was little they could do to prevent the death. Their role was to compassionately guide the family through it. For some people, this connection is the most precious of the arts of medicine and nursing. We need to reexamine our values. We need to get creative. We need to involve palliative care experts and clergy with the same urgency with which we have automakers making ventilators.
Second, there are our colleagues. Pediatric caregivers, particularly trainees, rarely encounter deaths and can benefit from debriefing sessions, even short ones. There is comfort in having a colleague review the situation and say: “There was nothing you could have done.” Or even: “That minor omission did not alter the outcome.” Even when everything was done properly, deaths cause moral suffering that needs processing and healing. Even if you don’t have magic words to give, just being present aids in the healing. We are all in this, together.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
CLAM trial regimen shown safe, effective for r/r AML
A clofarabine-based treatment was found to be safe and effective in refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the phase 2 CLAM trial.
The CLAM protocol treatment was clofarabine, cytarabine, and mitoxantrone (intravenous infusion, days 1‐5), cytarabine (intravenous infusion starting 4 hours after clofarabine, days 1‐5), and mitoxantrone (intravenous infusion, days 3‐5).
Bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy were performed on day 28. A total of 52 patients (16 women), with an age range of 22-65 years and refractory/relapsed AML were treated.
The overall response rate after the first cycle of CLAM was 90.4% (complete remission, 69.2%; CR with incomplete hematologic recovery, 21.2%). In addition, the efficacy of CLAM was not apparently affected by high‐risk karyotypes and genetic mutations among the patients.
Patients with a response (marrow < 5% blasts) received a maximum of two cycles of CLAM consolidation, each at 50% dose reduction, given 6‐8 weeks apart. Responding patients with an HLA‐matched sibling or volunteer‐unrelated donor were offered allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Toxicity of CLAM was manageable and did not compromise subsequent allogeneic HSCT, the researchers added.
“In this era of molecular targeting, CLAM might still have a role to play,” according to the researchers. “It offers the advantage of a highly effective regimen that is readily available. It provides a median DOR of 5 months, which is meaningful for organization of HSCT. Delays associated with recruitment into clinical trials or sourcing of targeted drugs are obviated. Precious time is saved, so that patients can quickly be bridged to a potentially curative allogeneic HSCT.”
No disclosures or conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Gill H et al. Cancer Med. 2020 Mar 20. doi:10.1002/cam4.2865.
A clofarabine-based treatment was found to be safe and effective in refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the phase 2 CLAM trial.
The CLAM protocol treatment was clofarabine, cytarabine, and mitoxantrone (intravenous infusion, days 1‐5), cytarabine (intravenous infusion starting 4 hours after clofarabine, days 1‐5), and mitoxantrone (intravenous infusion, days 3‐5).
Bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy were performed on day 28. A total of 52 patients (16 women), with an age range of 22-65 years and refractory/relapsed AML were treated.
The overall response rate after the first cycle of CLAM was 90.4% (complete remission, 69.2%; CR with incomplete hematologic recovery, 21.2%). In addition, the efficacy of CLAM was not apparently affected by high‐risk karyotypes and genetic mutations among the patients.
Patients with a response (marrow < 5% blasts) received a maximum of two cycles of CLAM consolidation, each at 50% dose reduction, given 6‐8 weeks apart. Responding patients with an HLA‐matched sibling or volunteer‐unrelated donor were offered allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Toxicity of CLAM was manageable and did not compromise subsequent allogeneic HSCT, the researchers added.
“In this era of molecular targeting, CLAM might still have a role to play,” according to the researchers. “It offers the advantage of a highly effective regimen that is readily available. It provides a median DOR of 5 months, which is meaningful for organization of HSCT. Delays associated with recruitment into clinical trials or sourcing of targeted drugs are obviated. Precious time is saved, so that patients can quickly be bridged to a potentially curative allogeneic HSCT.”
No disclosures or conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Gill H et al. Cancer Med. 2020 Mar 20. doi:10.1002/cam4.2865.
A clofarabine-based treatment was found to be safe and effective in refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the phase 2 CLAM trial.
The CLAM protocol treatment was clofarabine, cytarabine, and mitoxantrone (intravenous infusion, days 1‐5), cytarabine (intravenous infusion starting 4 hours after clofarabine, days 1‐5), and mitoxantrone (intravenous infusion, days 3‐5).
Bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy were performed on day 28. A total of 52 patients (16 women), with an age range of 22-65 years and refractory/relapsed AML were treated.
The overall response rate after the first cycle of CLAM was 90.4% (complete remission, 69.2%; CR with incomplete hematologic recovery, 21.2%). In addition, the efficacy of CLAM was not apparently affected by high‐risk karyotypes and genetic mutations among the patients.
Patients with a response (marrow < 5% blasts) received a maximum of two cycles of CLAM consolidation, each at 50% dose reduction, given 6‐8 weeks apart. Responding patients with an HLA‐matched sibling or volunteer‐unrelated donor were offered allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Toxicity of CLAM was manageable and did not compromise subsequent allogeneic HSCT, the researchers added.
“In this era of molecular targeting, CLAM might still have a role to play,” according to the researchers. “It offers the advantage of a highly effective regimen that is readily available. It provides a median DOR of 5 months, which is meaningful for organization of HSCT. Delays associated with recruitment into clinical trials or sourcing of targeted drugs are obviated. Precious time is saved, so that patients can quickly be bridged to a potentially curative allogeneic HSCT.”
No disclosures or conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Gill H et al. Cancer Med. 2020 Mar 20. doi:10.1002/cam4.2865.
FROM CANCER MEDICINE