User login
Lorcaserin withdrawn from U.S. market due to cancer risk
The Food and Drug Administration asked Eisai to voluntary withdraw the weight-loss drug lorcaserin (Belviq and Belviq XR) on Feb. 13 after a post-marketing trial with more than 12,000 subjects revealed an increased occurrence of cancer.
In a Drug Safety Communication, the agency said “health care professionals should stop prescribing and dispensing lorcaserin to patients. Contact patients currently taking lorcaserin, inform them of the increased occurrence of cancer seen in the clinical trial, and ask them to stop taking the medicine. Discuss alternative weight-loss medicines or strategies with your patients.”
Eisai is complying with the withdrawal request.
The decision is based on the agency’s review of the 5-year trial, which was designed to evaluate cardiac risk with the drug and ended in June 2018. In total, 7.7% of patients randomized to 10 mg lorcaserin twice daily were diagnosed with 520 primary cancers, compared with 7.1% of placebo subjects diagnosed with 470 cancers, over a median follow-up of 3 years and 3 months. There was one additional cancer observed for every 470 patients treated for 1 year.
“There was no apparent difference in the incidence of cancer over the initial months of treatment, but the imbalance increased with longer duration on lorcaserin,” FDA said. Pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancers were among those diagnosed.
In short, “we believe that the risks of lorcaserin outweigh its benefits based on our completed review of” the data, the agency said. The FDA is not recommending special cancer screenings for patients who have taken lorcaserin.
The action follows an FDA alert in January about a possible elevated cancer risk based on its preliminary analysis of the study.
Patients were also advised Feb. 13 to stop taking the drug and talk to their providers about alternative weight-loss medications and weight-management programs.
They were also told to dispose of the pills at a drug take-back location if available, but if not, to mix them with an “unappealing substance” such as dirt, cat litter, or used coffee grounds; seal them in plastic bag; and put them in the trash.
The Food and Drug Administration asked Eisai to voluntary withdraw the weight-loss drug lorcaserin (Belviq and Belviq XR) on Feb. 13 after a post-marketing trial with more than 12,000 subjects revealed an increased occurrence of cancer.
In a Drug Safety Communication, the agency said “health care professionals should stop prescribing and dispensing lorcaserin to patients. Contact patients currently taking lorcaserin, inform them of the increased occurrence of cancer seen in the clinical trial, and ask them to stop taking the medicine. Discuss alternative weight-loss medicines or strategies with your patients.”
Eisai is complying with the withdrawal request.
The decision is based on the agency’s review of the 5-year trial, which was designed to evaluate cardiac risk with the drug and ended in June 2018. In total, 7.7% of patients randomized to 10 mg lorcaserin twice daily were diagnosed with 520 primary cancers, compared with 7.1% of placebo subjects diagnosed with 470 cancers, over a median follow-up of 3 years and 3 months. There was one additional cancer observed for every 470 patients treated for 1 year.
“There was no apparent difference in the incidence of cancer over the initial months of treatment, but the imbalance increased with longer duration on lorcaserin,” FDA said. Pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancers were among those diagnosed.
In short, “we believe that the risks of lorcaserin outweigh its benefits based on our completed review of” the data, the agency said. The FDA is not recommending special cancer screenings for patients who have taken lorcaserin.
The action follows an FDA alert in January about a possible elevated cancer risk based on its preliminary analysis of the study.
Patients were also advised Feb. 13 to stop taking the drug and talk to their providers about alternative weight-loss medications and weight-management programs.
They were also told to dispose of the pills at a drug take-back location if available, but if not, to mix them with an “unappealing substance” such as dirt, cat litter, or used coffee grounds; seal them in plastic bag; and put them in the trash.
The Food and Drug Administration asked Eisai to voluntary withdraw the weight-loss drug lorcaserin (Belviq and Belviq XR) on Feb. 13 after a post-marketing trial with more than 12,000 subjects revealed an increased occurrence of cancer.
In a Drug Safety Communication, the agency said “health care professionals should stop prescribing and dispensing lorcaserin to patients. Contact patients currently taking lorcaserin, inform them of the increased occurrence of cancer seen in the clinical trial, and ask them to stop taking the medicine. Discuss alternative weight-loss medicines or strategies with your patients.”
Eisai is complying with the withdrawal request.
The decision is based on the agency’s review of the 5-year trial, which was designed to evaluate cardiac risk with the drug and ended in June 2018. In total, 7.7% of patients randomized to 10 mg lorcaserin twice daily were diagnosed with 520 primary cancers, compared with 7.1% of placebo subjects diagnosed with 470 cancers, over a median follow-up of 3 years and 3 months. There was one additional cancer observed for every 470 patients treated for 1 year.
“There was no apparent difference in the incidence of cancer over the initial months of treatment, but the imbalance increased with longer duration on lorcaserin,” FDA said. Pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancers were among those diagnosed.
In short, “we believe that the risks of lorcaserin outweigh its benefits based on our completed review of” the data, the agency said. The FDA is not recommending special cancer screenings for patients who have taken lorcaserin.
The action follows an FDA alert in January about a possible elevated cancer risk based on its preliminary analysis of the study.
Patients were also advised Feb. 13 to stop taking the drug and talk to their providers about alternative weight-loss medications and weight-management programs.
They were also told to dispose of the pills at a drug take-back location if available, but if not, to mix them with an “unappealing substance” such as dirt, cat litter, or used coffee grounds; seal them in plastic bag; and put them in the trash.
Fast-track surgery for hip fracture does not reduce mortality
An accelerated path to surgery after hip fracture did not improve mortality or major complications, according to a new international randomized trial. However, a fast track to surgery hastened mobilization, weight-bearing, and hospital discharge, and reduced the risk of urinary tract infection and delirium.
The HIP ATTACK (Hip Fracture Accelerated Surgical Treatment and Care Track) study enrolled 2,970 patients (median age, 79 years; 69% women) during March 2014-May 2019. The study excluded patients younger than 45 years, as well as those who were on nonreversible anticoagulation and who had high-energy or more complex hip fractures. In all, 1,487 patients were randomly assigned to the accelerated-surgery group, which received early medical evaluation with a goal of heading to surgery within 6 hours of a hip fracture diagnosis. The goal was achieved, with patients in the intervention arm receiving care at a median 6 hours after diagnosis. Patients in the 69 participating hospitals in 17 countries who were assigned to standard of care received surgery at a median 24 hours after diagnosis (P less than .001).
“Observational data, clinical experience, and biological rationale suggest that the longer a patient is immobile and lying in a bed, the higher the risk of poor outcomes,” wrote principal investigators Philip J. Devereaux, MD, PhD, and Mohit Bhandari, MD, PhD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and their colleagues on the HIP ATTACK writing committee.
The study was the first large, randomized trial that directly compared accelerated surgery with standard of care, noted the authors. Previous observational studies had shown worse outcomes for those usual-care patients who waited longer for surgery.
In HIP ATTACK, there was no difference in the primary outcome measures of 90-day mortality and major complications for patients receiving surgery within 6 hours after hip fracture diagnosis, compared with those who received surgery within 24 hours. The coprimary outcome measures included serious complications, such as MI, stroke, venous thromboembolism, sepsis, pneumonia, and life-threatening or major bleeding.
In practice, the researchers found that patients in the accelerated-surgery group received medical clearance in a median time of 2 hours after a diagnosis of hip fracture, whereas the standard of care group was cleared in 4 hours.
At 90 days, 9% of patients in the accelerated-surgery group and 10% of those in the usual-care group had died, a nonsignificant difference between the two groups. In both groups, 22% of patients experienced a major complication. A post hoc analysis that looked for any site-clustering effects did not detect different outcomes, the investigators wrote.
Delirium occurred in 132 patients (9%) of the accelerated-surgery group and in 175 patients (12%) in the usual-care group (odds ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-0.92). Infection without sepsis and urinary tract infection were both less common in the accelerated-surgery group (hazard ratio, 0.80 and 0.78, respectively).
The authors noted that the potential benefits of a speedy course to surgery, including reduced immobility and less pain, could be negated if physicians had less time to optimize medical care for older patients with multiple comorbidities and who make up a significant proportion of those who sustain low-energy hip fractures. However, medical complications, such as MI and new-onset atrial fibrillation, were not seen more frequently in the accelerated-surgery group.
In an editorial accompanying the study, Alejandro Lizaur-Utrilla, MD, and Fernando Lopez-Prats, MD, of the Universidad Miguel Hernández, Alicante, Spain, observed that the 6-hour window for hip fracture surgery may be difficult to achieve given clinical practicalities and that, in some cases, the 6-hour window might be unavoidable if severe comorbidities and overall poor health make early surgery inadvisable.
They also expressed concern that, despite the lack of harm shown in the patients who underwent accelerated surgery, the surgery “might negatively affect patients’ outcomes by preventing or limiting the opportunity for optimization of patients’ medical conditions before surgery.” They called for further study to delineate how fitness for surgery affects outcomes in accelerated surgery and to further examine whether the better outcomes are associated with improved cost-effectiveness.
Multiple HIP ATTACK coinvestigators reported relationships with pharmaceutical and medical device companies, including companies that manufacture hip prosthesis and orthopedic surgical devices and implants. The study was sponsored by the Canadian Population Health Research Institute, the Ontario Strategy for Patient Oriented Research Support Unit, the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, the Hamilton Health Sciences Foundation, Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation, Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research and Care, Smith & Nephew (to recruit patients in Spain), and Indiegogo Crowdfunding.
SOURCE: Borges F et al. Lancet. 2020 Feb. 9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30058-1.
An accelerated path to surgery after hip fracture did not improve mortality or major complications, according to a new international randomized trial. However, a fast track to surgery hastened mobilization, weight-bearing, and hospital discharge, and reduced the risk of urinary tract infection and delirium.
The HIP ATTACK (Hip Fracture Accelerated Surgical Treatment and Care Track) study enrolled 2,970 patients (median age, 79 years; 69% women) during March 2014-May 2019. The study excluded patients younger than 45 years, as well as those who were on nonreversible anticoagulation and who had high-energy or more complex hip fractures. In all, 1,487 patients were randomly assigned to the accelerated-surgery group, which received early medical evaluation with a goal of heading to surgery within 6 hours of a hip fracture diagnosis. The goal was achieved, with patients in the intervention arm receiving care at a median 6 hours after diagnosis. Patients in the 69 participating hospitals in 17 countries who were assigned to standard of care received surgery at a median 24 hours after diagnosis (P less than .001).
“Observational data, clinical experience, and biological rationale suggest that the longer a patient is immobile and lying in a bed, the higher the risk of poor outcomes,” wrote principal investigators Philip J. Devereaux, MD, PhD, and Mohit Bhandari, MD, PhD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and their colleagues on the HIP ATTACK writing committee.
The study was the first large, randomized trial that directly compared accelerated surgery with standard of care, noted the authors. Previous observational studies had shown worse outcomes for those usual-care patients who waited longer for surgery.
In HIP ATTACK, there was no difference in the primary outcome measures of 90-day mortality and major complications for patients receiving surgery within 6 hours after hip fracture diagnosis, compared with those who received surgery within 24 hours. The coprimary outcome measures included serious complications, such as MI, stroke, venous thromboembolism, sepsis, pneumonia, and life-threatening or major bleeding.
In practice, the researchers found that patients in the accelerated-surgery group received medical clearance in a median time of 2 hours after a diagnosis of hip fracture, whereas the standard of care group was cleared in 4 hours.
At 90 days, 9% of patients in the accelerated-surgery group and 10% of those in the usual-care group had died, a nonsignificant difference between the two groups. In both groups, 22% of patients experienced a major complication. A post hoc analysis that looked for any site-clustering effects did not detect different outcomes, the investigators wrote.
Delirium occurred in 132 patients (9%) of the accelerated-surgery group and in 175 patients (12%) in the usual-care group (odds ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-0.92). Infection without sepsis and urinary tract infection were both less common in the accelerated-surgery group (hazard ratio, 0.80 and 0.78, respectively).
The authors noted that the potential benefits of a speedy course to surgery, including reduced immobility and less pain, could be negated if physicians had less time to optimize medical care for older patients with multiple comorbidities and who make up a significant proportion of those who sustain low-energy hip fractures. However, medical complications, such as MI and new-onset atrial fibrillation, were not seen more frequently in the accelerated-surgery group.
In an editorial accompanying the study, Alejandro Lizaur-Utrilla, MD, and Fernando Lopez-Prats, MD, of the Universidad Miguel Hernández, Alicante, Spain, observed that the 6-hour window for hip fracture surgery may be difficult to achieve given clinical practicalities and that, in some cases, the 6-hour window might be unavoidable if severe comorbidities and overall poor health make early surgery inadvisable.
They also expressed concern that, despite the lack of harm shown in the patients who underwent accelerated surgery, the surgery “might negatively affect patients’ outcomes by preventing or limiting the opportunity for optimization of patients’ medical conditions before surgery.” They called for further study to delineate how fitness for surgery affects outcomes in accelerated surgery and to further examine whether the better outcomes are associated with improved cost-effectiveness.
Multiple HIP ATTACK coinvestigators reported relationships with pharmaceutical and medical device companies, including companies that manufacture hip prosthesis and orthopedic surgical devices and implants. The study was sponsored by the Canadian Population Health Research Institute, the Ontario Strategy for Patient Oriented Research Support Unit, the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, the Hamilton Health Sciences Foundation, Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation, Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research and Care, Smith & Nephew (to recruit patients in Spain), and Indiegogo Crowdfunding.
SOURCE: Borges F et al. Lancet. 2020 Feb. 9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30058-1.
An accelerated path to surgery after hip fracture did not improve mortality or major complications, according to a new international randomized trial. However, a fast track to surgery hastened mobilization, weight-bearing, and hospital discharge, and reduced the risk of urinary tract infection and delirium.
The HIP ATTACK (Hip Fracture Accelerated Surgical Treatment and Care Track) study enrolled 2,970 patients (median age, 79 years; 69% women) during March 2014-May 2019. The study excluded patients younger than 45 years, as well as those who were on nonreversible anticoagulation and who had high-energy or more complex hip fractures. In all, 1,487 patients were randomly assigned to the accelerated-surgery group, which received early medical evaluation with a goal of heading to surgery within 6 hours of a hip fracture diagnosis. The goal was achieved, with patients in the intervention arm receiving care at a median 6 hours after diagnosis. Patients in the 69 participating hospitals in 17 countries who were assigned to standard of care received surgery at a median 24 hours after diagnosis (P less than .001).
“Observational data, clinical experience, and biological rationale suggest that the longer a patient is immobile and lying in a bed, the higher the risk of poor outcomes,” wrote principal investigators Philip J. Devereaux, MD, PhD, and Mohit Bhandari, MD, PhD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and their colleagues on the HIP ATTACK writing committee.
The study was the first large, randomized trial that directly compared accelerated surgery with standard of care, noted the authors. Previous observational studies had shown worse outcomes for those usual-care patients who waited longer for surgery.
In HIP ATTACK, there was no difference in the primary outcome measures of 90-day mortality and major complications for patients receiving surgery within 6 hours after hip fracture diagnosis, compared with those who received surgery within 24 hours. The coprimary outcome measures included serious complications, such as MI, stroke, venous thromboembolism, sepsis, pneumonia, and life-threatening or major bleeding.
In practice, the researchers found that patients in the accelerated-surgery group received medical clearance in a median time of 2 hours after a diagnosis of hip fracture, whereas the standard of care group was cleared in 4 hours.
At 90 days, 9% of patients in the accelerated-surgery group and 10% of those in the usual-care group had died, a nonsignificant difference between the two groups. In both groups, 22% of patients experienced a major complication. A post hoc analysis that looked for any site-clustering effects did not detect different outcomes, the investigators wrote.
Delirium occurred in 132 patients (9%) of the accelerated-surgery group and in 175 patients (12%) in the usual-care group (odds ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-0.92). Infection without sepsis and urinary tract infection were both less common in the accelerated-surgery group (hazard ratio, 0.80 and 0.78, respectively).
The authors noted that the potential benefits of a speedy course to surgery, including reduced immobility and less pain, could be negated if physicians had less time to optimize medical care for older patients with multiple comorbidities and who make up a significant proportion of those who sustain low-energy hip fractures. However, medical complications, such as MI and new-onset atrial fibrillation, were not seen more frequently in the accelerated-surgery group.
In an editorial accompanying the study, Alejandro Lizaur-Utrilla, MD, and Fernando Lopez-Prats, MD, of the Universidad Miguel Hernández, Alicante, Spain, observed that the 6-hour window for hip fracture surgery may be difficult to achieve given clinical practicalities and that, in some cases, the 6-hour window might be unavoidable if severe comorbidities and overall poor health make early surgery inadvisable.
They also expressed concern that, despite the lack of harm shown in the patients who underwent accelerated surgery, the surgery “might negatively affect patients’ outcomes by preventing or limiting the opportunity for optimization of patients’ medical conditions before surgery.” They called for further study to delineate how fitness for surgery affects outcomes in accelerated surgery and to further examine whether the better outcomes are associated with improved cost-effectiveness.
Multiple HIP ATTACK coinvestigators reported relationships with pharmaceutical and medical device companies, including companies that manufacture hip prosthesis and orthopedic surgical devices and implants. The study was sponsored by the Canadian Population Health Research Institute, the Ontario Strategy for Patient Oriented Research Support Unit, the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, the Hamilton Health Sciences Foundation, Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation, Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research and Care, Smith & Nephew (to recruit patients in Spain), and Indiegogo Crowdfunding.
SOURCE: Borges F et al. Lancet. 2020 Feb. 9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30058-1.
Shortened CAPOX regimen appears effective in stage II colorectal cancer
For patients with high-risk stage II resected colorectal cancer (CRC), 3 months of adjuvant therapy with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (CAPOX) may be significantly safer and nearly as effective as a 6-month course, based on results of the phase 3 TOSCA trial.
In contrast, a shortened duration of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) may negatively impact 5-year recurrence-free survival, reported Fausto Petrelli, MD, of ASST Bergamo Ovest in Treviglio, Italy, and colleagues.
An earlier analysis from the Italian Three or Six Colon Adjuvant (TOSCA) trial showed that 6 months of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy was superior to a 3-month regimen among patients with stage III CRC, the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology.
To determine if this finding carried over to patients with less advanced disease, the investigators recruited 1,254 patients with high-risk stage II resected CRC who were treated at 130 centers in Italy. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive a 6-month or 3-month regimen of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy (either FOLFOX or CAPOX). The primary outcome was a test for noninferiority between the two durations, with the null hypothesis rejected by a hazard ratio of at least 1.2.
Almost two-thirds (61.9%) of patients received FOLFOX, while the remainder (38.1%) received CAPOX. Across all of these patients, 6 months of therapy was associated with a 5-year recurrence-free survival rate of 88.2%, compared with 82.2% for the 3-month course. This translates to a hazard ratio of 1.41, which is insufficient to reject noninferiority (P = .86) and suggests a longer duration of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy is significantly more effective.
However, when the CAPOX and FOLFOX subgroups were considered independently, distinct efficacy trends emerged. The difference in the 5-year recurrence-free survival rate between 6 months and 3 months of CAPOX was only slightly in favor of the longer course (0.76%). There was a much greater survival rate difference of 8.56% that favored the 6-month course of FOLFOX.
The investigators noted that 6 months of adjuvant therapy was associated with significantly more adverse events than a 3-month course, particularly for grade 3/4 neuropathy (8.4% vs. 1.3%; P less than .001). Taken together, the findings suggest the shortened CAPOX regimen may be a viable option.
“[E]ither 3 months of CAPOX or 6 months of FOLFOX treatment can be used whenever an oxaliplatin doublet is indicated for use in patients with stage II CRC,” the investigators wrote. At the same time, they suggested the subgroup findings be interpreted with caution, as the study was not powered for these analyses.
“[T]he utility of oxaliplatin in stage II CRC remains unclear, and the choice between 6 months of fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy and 3 or 6 months of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy must be made on an individual basis,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the Italian Group for the Study of Digestive Tract Cancers (GISCAD) Foundation and Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco. The investigators disclosed relationships with Servier, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
SOURCE: Petrelli F et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6486.
For patients with high-risk stage II resected colorectal cancer (CRC), 3 months of adjuvant therapy with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (CAPOX) may be significantly safer and nearly as effective as a 6-month course, based on results of the phase 3 TOSCA trial.
In contrast, a shortened duration of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) may negatively impact 5-year recurrence-free survival, reported Fausto Petrelli, MD, of ASST Bergamo Ovest in Treviglio, Italy, and colleagues.
An earlier analysis from the Italian Three or Six Colon Adjuvant (TOSCA) trial showed that 6 months of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy was superior to a 3-month regimen among patients with stage III CRC, the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology.
To determine if this finding carried over to patients with less advanced disease, the investigators recruited 1,254 patients with high-risk stage II resected CRC who were treated at 130 centers in Italy. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive a 6-month or 3-month regimen of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy (either FOLFOX or CAPOX). The primary outcome was a test for noninferiority between the two durations, with the null hypothesis rejected by a hazard ratio of at least 1.2.
Almost two-thirds (61.9%) of patients received FOLFOX, while the remainder (38.1%) received CAPOX. Across all of these patients, 6 months of therapy was associated with a 5-year recurrence-free survival rate of 88.2%, compared with 82.2% for the 3-month course. This translates to a hazard ratio of 1.41, which is insufficient to reject noninferiority (P = .86) and suggests a longer duration of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy is significantly more effective.
However, when the CAPOX and FOLFOX subgroups were considered independently, distinct efficacy trends emerged. The difference in the 5-year recurrence-free survival rate between 6 months and 3 months of CAPOX was only slightly in favor of the longer course (0.76%). There was a much greater survival rate difference of 8.56% that favored the 6-month course of FOLFOX.
The investigators noted that 6 months of adjuvant therapy was associated with significantly more adverse events than a 3-month course, particularly for grade 3/4 neuropathy (8.4% vs. 1.3%; P less than .001). Taken together, the findings suggest the shortened CAPOX regimen may be a viable option.
“[E]ither 3 months of CAPOX or 6 months of FOLFOX treatment can be used whenever an oxaliplatin doublet is indicated for use in patients with stage II CRC,” the investigators wrote. At the same time, they suggested the subgroup findings be interpreted with caution, as the study was not powered for these analyses.
“[T]he utility of oxaliplatin in stage II CRC remains unclear, and the choice between 6 months of fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy and 3 or 6 months of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy must be made on an individual basis,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the Italian Group for the Study of Digestive Tract Cancers (GISCAD) Foundation and Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco. The investigators disclosed relationships with Servier, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
SOURCE: Petrelli F et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6486.
For patients with high-risk stage II resected colorectal cancer (CRC), 3 months of adjuvant therapy with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (CAPOX) may be significantly safer and nearly as effective as a 6-month course, based on results of the phase 3 TOSCA trial.
In contrast, a shortened duration of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) may negatively impact 5-year recurrence-free survival, reported Fausto Petrelli, MD, of ASST Bergamo Ovest in Treviglio, Italy, and colleagues.
An earlier analysis from the Italian Three or Six Colon Adjuvant (TOSCA) trial showed that 6 months of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy was superior to a 3-month regimen among patients with stage III CRC, the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology.
To determine if this finding carried over to patients with less advanced disease, the investigators recruited 1,254 patients with high-risk stage II resected CRC who were treated at 130 centers in Italy. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive a 6-month or 3-month regimen of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy (either FOLFOX or CAPOX). The primary outcome was a test for noninferiority between the two durations, with the null hypothesis rejected by a hazard ratio of at least 1.2.
Almost two-thirds (61.9%) of patients received FOLFOX, while the remainder (38.1%) received CAPOX. Across all of these patients, 6 months of therapy was associated with a 5-year recurrence-free survival rate of 88.2%, compared with 82.2% for the 3-month course. This translates to a hazard ratio of 1.41, which is insufficient to reject noninferiority (P = .86) and suggests a longer duration of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy is significantly more effective.
However, when the CAPOX and FOLFOX subgroups were considered independently, distinct efficacy trends emerged. The difference in the 5-year recurrence-free survival rate between 6 months and 3 months of CAPOX was only slightly in favor of the longer course (0.76%). There was a much greater survival rate difference of 8.56% that favored the 6-month course of FOLFOX.
The investigators noted that 6 months of adjuvant therapy was associated with significantly more adverse events than a 3-month course, particularly for grade 3/4 neuropathy (8.4% vs. 1.3%; P less than .001). Taken together, the findings suggest the shortened CAPOX regimen may be a viable option.
“[E]ither 3 months of CAPOX or 6 months of FOLFOX treatment can be used whenever an oxaliplatin doublet is indicated for use in patients with stage II CRC,” the investigators wrote. At the same time, they suggested the subgroup findings be interpreted with caution, as the study was not powered for these analyses.
“[T]he utility of oxaliplatin in stage II CRC remains unclear, and the choice between 6 months of fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy and 3 or 6 months of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy must be made on an individual basis,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the Italian Group for the Study of Digestive Tract Cancers (GISCAD) Foundation and Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco. The investigators disclosed relationships with Servier, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
SOURCE: Petrelli F et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6486.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Marijuana, drug use a mystery in IBD
AUSTIN, TEX. – As more states legalize recreational and medical marijuana and cannabinoid products, and as evidence shows that up to 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease may be users, their gastroenterologists and other medical providers may be failing to even ask if they’re using, let alone talk to them about how it could impact their disease, according to a study of a hospital population in Washington, where recreational marijuana is legal.
The single-center, chart-review study at George Washington University found that providers noted they inquired about marijuana/CBD use in fewer than half of encounters with IBD patients – 47.8% to be precise – and that 4.9% of charts actually noted patients were users, according to a poster at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“This study acknowledges the growth of recreational and medical marijuana use as well as CBD products,” said poster presenter Scott Baumgartner, PA, a fourth-year medical student. “Understanding that because there’s increased legalization of both medical and recreational marijuana, our patients may be using them at increased rates. But are we asking them?”
According to the Drug Policy Alliance, recreational marijuana is legal in 11 states as well as Washington, which legalized recreational pot in 2014, and medical marijuana is legal in 33 states. The prevalence of cannabis use in patients with IBD has been reported at 15%-40% (Gastroenterol Hepatol [NY]. 2016;12:668-79).
The study consisted of a retrospective review of 381 charts of patients with IBD. Of the 19 charts that noted marijuana/CBD use, only 2 noted a prescription for medical purposes, although 4 noted IBD symptoms as the reason for use. Three charts noted recreational use and 12 gave no reason.
Mr. Baumgartner noted that it’s important gastroenterologists and other providers ask about marijuana/CBD use in their patients because of the inconclusive evidence about how it affects the disease (Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2696-8). “If you’re using marijuana for an IBD such as Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis because you think it’s relieving your symptoms, does it actually work in your long-term course?” he asked. “Does it relieve some symptoms but make other disease manifestations worse. We need more research in that area.”
The takeaway of the study: “We need to do a better job of asking whether or not patients are using recreational drugs,” Mr. Baumgartner said. “And if they are using recreational drugs, what recreational drugs they are using, because it could have a big impact on the outcome of their disease.”
The next steps for this research, Mr. Baumgartner said, is to focus on the specific questions providers are asking about their patients’ marijuana and recreational drug use and how they’re documenting those responses. “Once we see that, we could consider looking at a cohort of patients who are using and see if they are reporting symptom relief, or if we are seeing disease remission, or not,” Mr. Baumgartner said.
Mr. Baumgartner has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Baumgartner S et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020. 2020 Jan 23. Poster 011.
AUSTIN, TEX. – As more states legalize recreational and medical marijuana and cannabinoid products, and as evidence shows that up to 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease may be users, their gastroenterologists and other medical providers may be failing to even ask if they’re using, let alone talk to them about how it could impact their disease, according to a study of a hospital population in Washington, where recreational marijuana is legal.
The single-center, chart-review study at George Washington University found that providers noted they inquired about marijuana/CBD use in fewer than half of encounters with IBD patients – 47.8% to be precise – and that 4.9% of charts actually noted patients were users, according to a poster at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“This study acknowledges the growth of recreational and medical marijuana use as well as CBD products,” said poster presenter Scott Baumgartner, PA, a fourth-year medical student. “Understanding that because there’s increased legalization of both medical and recreational marijuana, our patients may be using them at increased rates. But are we asking them?”
According to the Drug Policy Alliance, recreational marijuana is legal in 11 states as well as Washington, which legalized recreational pot in 2014, and medical marijuana is legal in 33 states. The prevalence of cannabis use in patients with IBD has been reported at 15%-40% (Gastroenterol Hepatol [NY]. 2016;12:668-79).
The study consisted of a retrospective review of 381 charts of patients with IBD. Of the 19 charts that noted marijuana/CBD use, only 2 noted a prescription for medical purposes, although 4 noted IBD symptoms as the reason for use. Three charts noted recreational use and 12 gave no reason.
Mr. Baumgartner noted that it’s important gastroenterologists and other providers ask about marijuana/CBD use in their patients because of the inconclusive evidence about how it affects the disease (Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2696-8). “If you’re using marijuana for an IBD such as Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis because you think it’s relieving your symptoms, does it actually work in your long-term course?” he asked. “Does it relieve some symptoms but make other disease manifestations worse. We need more research in that area.”
The takeaway of the study: “We need to do a better job of asking whether or not patients are using recreational drugs,” Mr. Baumgartner said. “And if they are using recreational drugs, what recreational drugs they are using, because it could have a big impact on the outcome of their disease.”
The next steps for this research, Mr. Baumgartner said, is to focus on the specific questions providers are asking about their patients’ marijuana and recreational drug use and how they’re documenting those responses. “Once we see that, we could consider looking at a cohort of patients who are using and see if they are reporting symptom relief, or if we are seeing disease remission, or not,” Mr. Baumgartner said.
Mr. Baumgartner has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Baumgartner S et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020. 2020 Jan 23. Poster 011.
AUSTIN, TEX. – As more states legalize recreational and medical marijuana and cannabinoid products, and as evidence shows that up to 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease may be users, their gastroenterologists and other medical providers may be failing to even ask if they’re using, let alone talk to them about how it could impact their disease, according to a study of a hospital population in Washington, where recreational marijuana is legal.
The single-center, chart-review study at George Washington University found that providers noted they inquired about marijuana/CBD use in fewer than half of encounters with IBD patients – 47.8% to be precise – and that 4.9% of charts actually noted patients were users, according to a poster at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“This study acknowledges the growth of recreational and medical marijuana use as well as CBD products,” said poster presenter Scott Baumgartner, PA, a fourth-year medical student. “Understanding that because there’s increased legalization of both medical and recreational marijuana, our patients may be using them at increased rates. But are we asking them?”
According to the Drug Policy Alliance, recreational marijuana is legal in 11 states as well as Washington, which legalized recreational pot in 2014, and medical marijuana is legal in 33 states. The prevalence of cannabis use in patients with IBD has been reported at 15%-40% (Gastroenterol Hepatol [NY]. 2016;12:668-79).
The study consisted of a retrospective review of 381 charts of patients with IBD. Of the 19 charts that noted marijuana/CBD use, only 2 noted a prescription for medical purposes, although 4 noted IBD symptoms as the reason for use. Three charts noted recreational use and 12 gave no reason.
Mr. Baumgartner noted that it’s important gastroenterologists and other providers ask about marijuana/CBD use in their patients because of the inconclusive evidence about how it affects the disease (Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2696-8). “If you’re using marijuana for an IBD such as Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis because you think it’s relieving your symptoms, does it actually work in your long-term course?” he asked. “Does it relieve some symptoms but make other disease manifestations worse. We need more research in that area.”
The takeaway of the study: “We need to do a better job of asking whether or not patients are using recreational drugs,” Mr. Baumgartner said. “And if they are using recreational drugs, what recreational drugs they are using, because it could have a big impact on the outcome of their disease.”
The next steps for this research, Mr. Baumgartner said, is to focus on the specific questions providers are asking about their patients’ marijuana and recreational drug use and how they’re documenting those responses. “Once we see that, we could consider looking at a cohort of patients who are using and see if they are reporting symptom relief, or if we are seeing disease remission, or not,” Mr. Baumgartner said.
Mr. Baumgartner has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Baumgartner S et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020. 2020 Jan 23. Poster 011.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
Antiepileptic drugs may not independently impair cognition
according to research published online ahead of print Feb. 3 in Neurology. Optimizing AED therapy to reduce or prevent seizures is thus unlikely to affect cognition, according to the investigators.
Patients who take AEDs commonly report cognitive problems, but investigations into the cognitive effects of AEDs have yielded inconsistent results. “We were also interested in this association, as we often treat complex patients taking multiple or high-dose AEDs, and our patients often report cognitive dysfunction,” said Emma Foster, MBBS, an epilepsy fellow at Alfred Health and the Royal Melbourne Hospital in Victoria, Australia. “We were particularly interested to examine how much AEDs affect cognition relative to other factors. We commonly see patients in our tertiary epilepsy care unit who have had severe epilepsy for a long time or who have psychiatric disorders, and these factors may also contribute to cognitive dysfunction.”
Researchers analyzed patients admitted for video EEG monitoring
For their study, Dr. Foster and colleagues prospectively enrolled patients admitted to the Royal Melbourne Hospital’s video EEG monitoring unit between January 2009 and December 2016. Patients were included in the study if they were age 18 years or older, had been admitted for diagnostic or surgical evaluation, and had complete data for the relevant variables. Patients were prescribed AED monotherapy or polytherapy.
The researchers based epilepsy diagnoses on the 2014 International League Against Epilepsy criteria. Diagnoses of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) were based on a consensus of epileptologists at weekly multidisciplinary clinical meetings, which was supported by evaluation of all available data. Some patients received a diagnosis of comorbid epilepsy and PNES. If data were insufficient to support a diagnosis of epilepsy or PNES, the admission was considered nondiagnostic.
All participants underwent neuropsychologic and neuropsychiatric screening. Researchers assessed patients’ objective, global cognitive function using the Neuropsychiatry Unit Cognitive Assessment Tool (NUCOG), a validated instrument. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Epilepsy inventory (QOLIE-89) to provide a measure of subjective cognitive function. They also responded to the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) to screen for mood disorders.
Dr. Foster and colleagues measured seizure frequency through patient self-report. Patients averaged their seizure frequency during the 12-month period before admission to the video EEG unit. They categorized it according to a 12-point system in which 0 denotes patients who are seizure-free and not taking AEDs and 12 denotes patients in status epilepticus. Patients with PNES used the same scale to report event frequency, although the system was not designed for this purpose.
Almost half of patients were prescribed polypharmacy
The researchers included 331 patients in their analysis. The population’s mean age was 39.3 years, and about 62% of patients were female. Approximately 47% of patients had epilepsy, 25.7% had PNES, 6.6% had comorbid epilepsy and PNES, and 20.5% had a nondiagnostic outcome. Among patients with epilepsy, most (54.5%) had temporal lobe epilepsy, followed by extratemporal focal epilepsy (32.1%) and generalized epilepsy (13.5%). The mean number of AEDs prescribed on admission was 1.6, and mean seizure or event frequency score was 7.2, which indicated 1-3 seizures per month. Mean HADS depression score was within the normal range (5.7), and mean HADS anxiety score was in the borderline range (8.2).
Approximately 45% of patients were prescribed AED polypharmacy on admission, 25.1% were prescribed AED monotherapy, and 29.9% were prescribed no AED. Levetiracetam, valproate, and carbamazepine were the most frequently prescribed AEDs. Most patients with epilepsy (73.1%) were on polypharmacy, compared with 17.6% of patients with PNES, 63.6% of patients with epilepsy and PNES, and 8.8% of nondiagnostic patients.
Older age and greater seizure frequency predicted impaired objective cognitive function. Comorbid epilepsy and PNES appeared to predict impaired objective cognitive function as well, but the data were inconclusive. No AED was a significant predictor of objective cognitive function. Higher depression and anxiety scores and greater seizure frequency predicted impaired subjective cognitive function. No AED predicted subjective cognitive function.
Future studies could address particular cognitive domains
Previous studies have suggested that treatment with topiramate predicts objective or subjective cognitive function, but Dr. Foster and colleagues did not observe this result. The current findings suggest that topiramate may have a less significant effect on cognition than the literature suggests, they wrote. In addition, more evidence is needed to fully understand the effects of clobazam, valproate, phenytoin, and gabapentin because the analysis was underpowered for these drugs.
Although NUCOG assesses global cognitive function reliably, its ability to measure particular cognitive subdomains is limited. “We aim to conduct future research investigating the complex associations between different cognitive functions, including processing speed, and specific AEDs in this heterogeneous population,” said Dr. Foster.
Despite the study’s large sample size, the researchers could not explore potential interactions between various predictor variables. “Epilepsy may interact with the aging process or with other medical conditions associated with aging, such as hypertension and diabetes, and this may increase the risk of cognitive decline,” said Dr. Foster. “Older age may also be associated with reduced capacity to metabolize drugs, increased sensitivity to the cognitive and neurological effects of drugs, less cognitive reserve, and increased likelihood of taking multiple medications, which, along with AEDs, may exert a cognitive effect.”
The current findings may reduce concerns about the effects of AEDs on cognitive function and encourage neurologists to pursue the proper dosing for optimal seizure control, wrote the authors. “However, it is possible that some individuals may be more susceptible than others to AED-related cognitive dysfunction,” said Dr. Foster. “We do not have a robust way to predict who these patients will be, and it is still good practice to make patients aware that some people experience adverse cognitive effects from AEDs. However, it needs to be emphasized that it is unlikely to be the sole reason for their cognitive impairment. Other issues, such as poor seizure control or unrecognized or undertreated mood disorders, are even more important factors for impaired cognition.”
Patients who report cognitive problems should be screened for mood disorders, Dr. Foster continued. “It would also be important to consider whether the patients’ cognitive complaints arise from subtle clinical or subclinical seizure activity and subsequent postictal periods. To investigate this [question] further, clinicians may arrange for prolonged EEG monitoring. This [monitoring] could be done in an ambulatory setting or during an inpatient admission.”
The study was conducted without external funding. Dr. Foster and other investigators reported research funding from professional associations and pharmaceutical companies that was unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Foster E et al. Neurology. 2020 Feb 3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009061.
according to research published online ahead of print Feb. 3 in Neurology. Optimizing AED therapy to reduce or prevent seizures is thus unlikely to affect cognition, according to the investigators.
Patients who take AEDs commonly report cognitive problems, but investigations into the cognitive effects of AEDs have yielded inconsistent results. “We were also interested in this association, as we often treat complex patients taking multiple or high-dose AEDs, and our patients often report cognitive dysfunction,” said Emma Foster, MBBS, an epilepsy fellow at Alfred Health and the Royal Melbourne Hospital in Victoria, Australia. “We were particularly interested to examine how much AEDs affect cognition relative to other factors. We commonly see patients in our tertiary epilepsy care unit who have had severe epilepsy for a long time or who have psychiatric disorders, and these factors may also contribute to cognitive dysfunction.”
Researchers analyzed patients admitted for video EEG monitoring
For their study, Dr. Foster and colleagues prospectively enrolled patients admitted to the Royal Melbourne Hospital’s video EEG monitoring unit between January 2009 and December 2016. Patients were included in the study if they were age 18 years or older, had been admitted for diagnostic or surgical evaluation, and had complete data for the relevant variables. Patients were prescribed AED monotherapy or polytherapy.
The researchers based epilepsy diagnoses on the 2014 International League Against Epilepsy criteria. Diagnoses of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) were based on a consensus of epileptologists at weekly multidisciplinary clinical meetings, which was supported by evaluation of all available data. Some patients received a diagnosis of comorbid epilepsy and PNES. If data were insufficient to support a diagnosis of epilepsy or PNES, the admission was considered nondiagnostic.
All participants underwent neuropsychologic and neuropsychiatric screening. Researchers assessed patients’ objective, global cognitive function using the Neuropsychiatry Unit Cognitive Assessment Tool (NUCOG), a validated instrument. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Epilepsy inventory (QOLIE-89) to provide a measure of subjective cognitive function. They also responded to the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) to screen for mood disorders.
Dr. Foster and colleagues measured seizure frequency through patient self-report. Patients averaged their seizure frequency during the 12-month period before admission to the video EEG unit. They categorized it according to a 12-point system in which 0 denotes patients who are seizure-free and not taking AEDs and 12 denotes patients in status epilepticus. Patients with PNES used the same scale to report event frequency, although the system was not designed for this purpose.
Almost half of patients were prescribed polypharmacy
The researchers included 331 patients in their analysis. The population’s mean age was 39.3 years, and about 62% of patients were female. Approximately 47% of patients had epilepsy, 25.7% had PNES, 6.6% had comorbid epilepsy and PNES, and 20.5% had a nondiagnostic outcome. Among patients with epilepsy, most (54.5%) had temporal lobe epilepsy, followed by extratemporal focal epilepsy (32.1%) and generalized epilepsy (13.5%). The mean number of AEDs prescribed on admission was 1.6, and mean seizure or event frequency score was 7.2, which indicated 1-3 seizures per month. Mean HADS depression score was within the normal range (5.7), and mean HADS anxiety score was in the borderline range (8.2).
Approximately 45% of patients were prescribed AED polypharmacy on admission, 25.1% were prescribed AED monotherapy, and 29.9% were prescribed no AED. Levetiracetam, valproate, and carbamazepine were the most frequently prescribed AEDs. Most patients with epilepsy (73.1%) were on polypharmacy, compared with 17.6% of patients with PNES, 63.6% of patients with epilepsy and PNES, and 8.8% of nondiagnostic patients.
Older age and greater seizure frequency predicted impaired objective cognitive function. Comorbid epilepsy and PNES appeared to predict impaired objective cognitive function as well, but the data were inconclusive. No AED was a significant predictor of objective cognitive function. Higher depression and anxiety scores and greater seizure frequency predicted impaired subjective cognitive function. No AED predicted subjective cognitive function.
Future studies could address particular cognitive domains
Previous studies have suggested that treatment with topiramate predicts objective or subjective cognitive function, but Dr. Foster and colleagues did not observe this result. The current findings suggest that topiramate may have a less significant effect on cognition than the literature suggests, they wrote. In addition, more evidence is needed to fully understand the effects of clobazam, valproate, phenytoin, and gabapentin because the analysis was underpowered for these drugs.
Although NUCOG assesses global cognitive function reliably, its ability to measure particular cognitive subdomains is limited. “We aim to conduct future research investigating the complex associations between different cognitive functions, including processing speed, and specific AEDs in this heterogeneous population,” said Dr. Foster.
Despite the study’s large sample size, the researchers could not explore potential interactions between various predictor variables. “Epilepsy may interact with the aging process or with other medical conditions associated with aging, such as hypertension and diabetes, and this may increase the risk of cognitive decline,” said Dr. Foster. “Older age may also be associated with reduced capacity to metabolize drugs, increased sensitivity to the cognitive and neurological effects of drugs, less cognitive reserve, and increased likelihood of taking multiple medications, which, along with AEDs, may exert a cognitive effect.”
The current findings may reduce concerns about the effects of AEDs on cognitive function and encourage neurologists to pursue the proper dosing for optimal seizure control, wrote the authors. “However, it is possible that some individuals may be more susceptible than others to AED-related cognitive dysfunction,” said Dr. Foster. “We do not have a robust way to predict who these patients will be, and it is still good practice to make patients aware that some people experience adverse cognitive effects from AEDs. However, it needs to be emphasized that it is unlikely to be the sole reason for their cognitive impairment. Other issues, such as poor seizure control or unrecognized or undertreated mood disorders, are even more important factors for impaired cognition.”
Patients who report cognitive problems should be screened for mood disorders, Dr. Foster continued. “It would also be important to consider whether the patients’ cognitive complaints arise from subtle clinical or subclinical seizure activity and subsequent postictal periods. To investigate this [question] further, clinicians may arrange for prolonged EEG monitoring. This [monitoring] could be done in an ambulatory setting or during an inpatient admission.”
The study was conducted without external funding. Dr. Foster and other investigators reported research funding from professional associations and pharmaceutical companies that was unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Foster E et al. Neurology. 2020 Feb 3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009061.
according to research published online ahead of print Feb. 3 in Neurology. Optimizing AED therapy to reduce or prevent seizures is thus unlikely to affect cognition, according to the investigators.
Patients who take AEDs commonly report cognitive problems, but investigations into the cognitive effects of AEDs have yielded inconsistent results. “We were also interested in this association, as we often treat complex patients taking multiple or high-dose AEDs, and our patients often report cognitive dysfunction,” said Emma Foster, MBBS, an epilepsy fellow at Alfred Health and the Royal Melbourne Hospital in Victoria, Australia. “We were particularly interested to examine how much AEDs affect cognition relative to other factors. We commonly see patients in our tertiary epilepsy care unit who have had severe epilepsy for a long time or who have psychiatric disorders, and these factors may also contribute to cognitive dysfunction.”
Researchers analyzed patients admitted for video EEG monitoring
For their study, Dr. Foster and colleagues prospectively enrolled patients admitted to the Royal Melbourne Hospital’s video EEG monitoring unit between January 2009 and December 2016. Patients were included in the study if they were age 18 years or older, had been admitted for diagnostic or surgical evaluation, and had complete data for the relevant variables. Patients were prescribed AED monotherapy or polytherapy.
The researchers based epilepsy diagnoses on the 2014 International League Against Epilepsy criteria. Diagnoses of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) were based on a consensus of epileptologists at weekly multidisciplinary clinical meetings, which was supported by evaluation of all available data. Some patients received a diagnosis of comorbid epilepsy and PNES. If data were insufficient to support a diagnosis of epilepsy or PNES, the admission was considered nondiagnostic.
All participants underwent neuropsychologic and neuropsychiatric screening. Researchers assessed patients’ objective, global cognitive function using the Neuropsychiatry Unit Cognitive Assessment Tool (NUCOG), a validated instrument. Patients responded to the Quality of Life in Epilepsy inventory (QOLIE-89) to provide a measure of subjective cognitive function. They also responded to the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) to screen for mood disorders.
Dr. Foster and colleagues measured seizure frequency through patient self-report. Patients averaged their seizure frequency during the 12-month period before admission to the video EEG unit. They categorized it according to a 12-point system in which 0 denotes patients who are seizure-free and not taking AEDs and 12 denotes patients in status epilepticus. Patients with PNES used the same scale to report event frequency, although the system was not designed for this purpose.
Almost half of patients were prescribed polypharmacy
The researchers included 331 patients in their analysis. The population’s mean age was 39.3 years, and about 62% of patients were female. Approximately 47% of patients had epilepsy, 25.7% had PNES, 6.6% had comorbid epilepsy and PNES, and 20.5% had a nondiagnostic outcome. Among patients with epilepsy, most (54.5%) had temporal lobe epilepsy, followed by extratemporal focal epilepsy (32.1%) and generalized epilepsy (13.5%). The mean number of AEDs prescribed on admission was 1.6, and mean seizure or event frequency score was 7.2, which indicated 1-3 seizures per month. Mean HADS depression score was within the normal range (5.7), and mean HADS anxiety score was in the borderline range (8.2).
Approximately 45% of patients were prescribed AED polypharmacy on admission, 25.1% were prescribed AED monotherapy, and 29.9% were prescribed no AED. Levetiracetam, valproate, and carbamazepine were the most frequently prescribed AEDs. Most patients with epilepsy (73.1%) were on polypharmacy, compared with 17.6% of patients with PNES, 63.6% of patients with epilepsy and PNES, and 8.8% of nondiagnostic patients.
Older age and greater seizure frequency predicted impaired objective cognitive function. Comorbid epilepsy and PNES appeared to predict impaired objective cognitive function as well, but the data were inconclusive. No AED was a significant predictor of objective cognitive function. Higher depression and anxiety scores and greater seizure frequency predicted impaired subjective cognitive function. No AED predicted subjective cognitive function.
Future studies could address particular cognitive domains
Previous studies have suggested that treatment with topiramate predicts objective or subjective cognitive function, but Dr. Foster and colleagues did not observe this result. The current findings suggest that topiramate may have a less significant effect on cognition than the literature suggests, they wrote. In addition, more evidence is needed to fully understand the effects of clobazam, valproate, phenytoin, and gabapentin because the analysis was underpowered for these drugs.
Although NUCOG assesses global cognitive function reliably, its ability to measure particular cognitive subdomains is limited. “We aim to conduct future research investigating the complex associations between different cognitive functions, including processing speed, and specific AEDs in this heterogeneous population,” said Dr. Foster.
Despite the study’s large sample size, the researchers could not explore potential interactions between various predictor variables. “Epilepsy may interact with the aging process or with other medical conditions associated with aging, such as hypertension and diabetes, and this may increase the risk of cognitive decline,” said Dr. Foster. “Older age may also be associated with reduced capacity to metabolize drugs, increased sensitivity to the cognitive and neurological effects of drugs, less cognitive reserve, and increased likelihood of taking multiple medications, which, along with AEDs, may exert a cognitive effect.”
The current findings may reduce concerns about the effects of AEDs on cognitive function and encourage neurologists to pursue the proper dosing for optimal seizure control, wrote the authors. “However, it is possible that some individuals may be more susceptible than others to AED-related cognitive dysfunction,” said Dr. Foster. “We do not have a robust way to predict who these patients will be, and it is still good practice to make patients aware that some people experience adverse cognitive effects from AEDs. However, it needs to be emphasized that it is unlikely to be the sole reason for their cognitive impairment. Other issues, such as poor seizure control or unrecognized or undertreated mood disorders, are even more important factors for impaired cognition.”
Patients who report cognitive problems should be screened for mood disorders, Dr. Foster continued. “It would also be important to consider whether the patients’ cognitive complaints arise from subtle clinical or subclinical seizure activity and subsequent postictal periods. To investigate this [question] further, clinicians may arrange for prolonged EEG monitoring. This [monitoring] could be done in an ambulatory setting or during an inpatient admission.”
The study was conducted without external funding. Dr. Foster and other investigators reported research funding from professional associations and pharmaceutical companies that was unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Foster E et al. Neurology. 2020 Feb 3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009061.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Burnout rate lower among psychiatrists than physicians overall
Psychiatrists do better compared with those in most specialties in finding happiness at work, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.
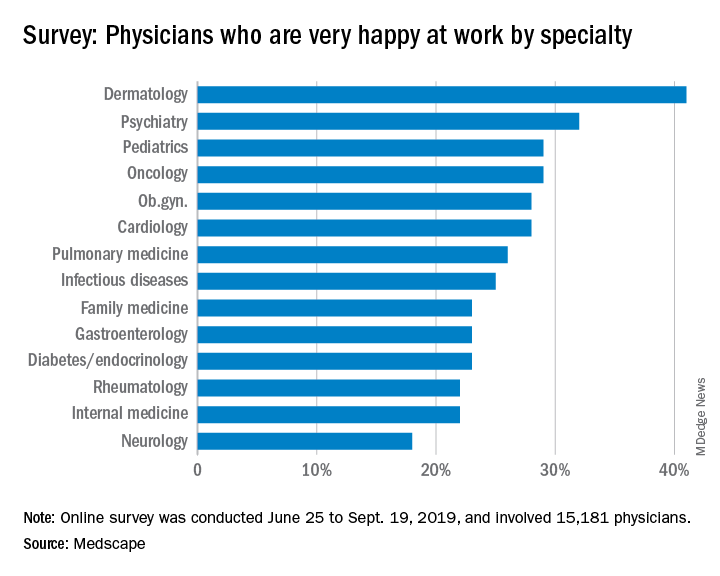
About 32% of psychiatrists reported being happy at work, according to the Medscape survey, though they lagged well behind dermatologists, who were the most satisfied with their work lives. In terms of happiness outside the office, psychiatrists were in the middle of the pack with 51% reporting that they were happy.
Somewhat fewer psychiatrists reported being burned out, compared with physicians overall, at 37% versus 41%. The biggest contributing factors to psychiatrist burnout were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (63%), increased time devoted to EHRs (34%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (32%).
Psychiatrists most commonly dealt with burnout by isolating themselves from others (57%), sleeping (43%), and talking with family/friends (42%). Just under half of psychiatrists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of all physicians, and 33% took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
and 1% reported that they had attempted suicide. About 45% said that they were currently seeking professional help, planning to seek help, or had used help in the past to deal with burnout or depression; 48% said that they were not planning to seek help and had not done so in the past.
In an interview, Carol A. Bernstein, MD, said it is challenging to find the meaning in these survey results.
“The challenge with surveys that measure burnout is that the drivers may be somewhat different in different specialties. I am less interested in looking at ‘who has it worse’ than I am at trying to address those systemic factors that are important for all physicians, regardless of specialty,” said Dr. Bernstein of Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
“The survey noted some of these factors: the increased burden of regulation and bureaucratic tasks, an EHR that was designed for billing and scheduling – not for taking care of patients – and challenges of professionalism in the workplace. These are issues that we must address for the benefit of all health care providers and patients.”
Dr. Bernstein, a past president of the American Psychiatric Association, is vice chair for faculty development and well-being at Montefiore/Albert Einstein. She is a professor in the departments of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and obstetrics/gynecology & women’s health.
The Medscape survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians.
Psychiatrists do better compared with those in most specialties in finding happiness at work, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.

About 32% of psychiatrists reported being happy at work, according to the Medscape survey, though they lagged well behind dermatologists, who were the most satisfied with their work lives. In terms of happiness outside the office, psychiatrists were in the middle of the pack with 51% reporting that they were happy.
Somewhat fewer psychiatrists reported being burned out, compared with physicians overall, at 37% versus 41%. The biggest contributing factors to psychiatrist burnout were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (63%), increased time devoted to EHRs (34%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (32%).
Psychiatrists most commonly dealt with burnout by isolating themselves from others (57%), sleeping (43%), and talking with family/friends (42%). Just under half of psychiatrists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of all physicians, and 33% took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
and 1% reported that they had attempted suicide. About 45% said that they were currently seeking professional help, planning to seek help, or had used help in the past to deal with burnout or depression; 48% said that they were not planning to seek help and had not done so in the past.
In an interview, Carol A. Bernstein, MD, said it is challenging to find the meaning in these survey results.
“The challenge with surveys that measure burnout is that the drivers may be somewhat different in different specialties. I am less interested in looking at ‘who has it worse’ than I am at trying to address those systemic factors that are important for all physicians, regardless of specialty,” said Dr. Bernstein of Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
“The survey noted some of these factors: the increased burden of regulation and bureaucratic tasks, an EHR that was designed for billing and scheduling – not for taking care of patients – and challenges of professionalism in the workplace. These are issues that we must address for the benefit of all health care providers and patients.”
Dr. Bernstein, a past president of the American Psychiatric Association, is vice chair for faculty development and well-being at Montefiore/Albert Einstein. She is a professor in the departments of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and obstetrics/gynecology & women’s health.
The Medscape survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians.
Psychiatrists do better compared with those in most specialties in finding happiness at work, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.

About 32% of psychiatrists reported being happy at work, according to the Medscape survey, though they lagged well behind dermatologists, who were the most satisfied with their work lives. In terms of happiness outside the office, psychiatrists were in the middle of the pack with 51% reporting that they were happy.
Somewhat fewer psychiatrists reported being burned out, compared with physicians overall, at 37% versus 41%. The biggest contributing factors to psychiatrist burnout were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (63%), increased time devoted to EHRs (34%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (32%).
Psychiatrists most commonly dealt with burnout by isolating themselves from others (57%), sleeping (43%), and talking with family/friends (42%). Just under half of psychiatrists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of all physicians, and 33% took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
and 1% reported that they had attempted suicide. About 45% said that they were currently seeking professional help, planning to seek help, or had used help in the past to deal with burnout or depression; 48% said that they were not planning to seek help and had not done so in the past.
In an interview, Carol A. Bernstein, MD, said it is challenging to find the meaning in these survey results.
“The challenge with surveys that measure burnout is that the drivers may be somewhat different in different specialties. I am less interested in looking at ‘who has it worse’ than I am at trying to address those systemic factors that are important for all physicians, regardless of specialty,” said Dr. Bernstein of Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
“The survey noted some of these factors: the increased burden of regulation and bureaucratic tasks, an EHR that was designed for billing and scheduling – not for taking care of patients – and challenges of professionalism in the workplace. These are issues that we must address for the benefit of all health care providers and patients.”
Dr. Bernstein, a past president of the American Psychiatric Association, is vice chair for faculty development and well-being at Montefiore/Albert Einstein. She is a professor in the departments of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and obstetrics/gynecology & women’s health.
The Medscape survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians.
Two new Novel Coronavirus cases confirmed among quarantined U.S. patients
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced two new patients now have the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), bringing the case total in the United States to 15.
The 14th case was discovered in California among a group of people under federal quarantine after returning from the Hubei Province in China. That patient was on a U.S. State Department–chartered flight that arrived in the United States on Feb. 7.
The 15th case was discovered in Texas among a group of people who also are under federal quarantine. That patient arrived on a State Department–chartered flight that arrived on Feb. 7. It is the first person in Texas that has tested positive for 2019-nCoV.
CDC said in a statement announcing the Texas case that there “will likely be additional cases in the coming days and weeks, including among other people recently returned from Wuhan.” Officials noted that more than 600 people who have returned as part of State Department–chartered flights are currently under that 14-day quarantine.
The agency is preparing for more widespread cases of 2019-nCoV.
Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said that containment has been the early focus for the agency.
“The goal of the measures we have taken to date are to slow the introduction and impact of this disease in the United States, but at some point, we are likely to see community spread in the U.S.,” Dr. Messonnier said during a Feb. 12 teleconference with reporters. She added that the federal response will change over time as the virus spreads.
Dr. Messonnier noted that public health officials are planning for the increased demands that a wider outbreak of 2019-nCov would place on the health care delivery system, including ensuring an adequate supply of medical equipment.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced two new patients now have the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), bringing the case total in the United States to 15.
The 14th case was discovered in California among a group of people under federal quarantine after returning from the Hubei Province in China. That patient was on a U.S. State Department–chartered flight that arrived in the United States on Feb. 7.
The 15th case was discovered in Texas among a group of people who also are under federal quarantine. That patient arrived on a State Department–chartered flight that arrived on Feb. 7. It is the first person in Texas that has tested positive for 2019-nCoV.
CDC said in a statement announcing the Texas case that there “will likely be additional cases in the coming days and weeks, including among other people recently returned from Wuhan.” Officials noted that more than 600 people who have returned as part of State Department–chartered flights are currently under that 14-day quarantine.
The agency is preparing for more widespread cases of 2019-nCoV.
Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said that containment has been the early focus for the agency.
“The goal of the measures we have taken to date are to slow the introduction and impact of this disease in the United States, but at some point, we are likely to see community spread in the U.S.,” Dr. Messonnier said during a Feb. 12 teleconference with reporters. She added that the federal response will change over time as the virus spreads.
Dr. Messonnier noted that public health officials are planning for the increased demands that a wider outbreak of 2019-nCov would place on the health care delivery system, including ensuring an adequate supply of medical equipment.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced two new patients now have the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), bringing the case total in the United States to 15.
The 14th case was discovered in California among a group of people under federal quarantine after returning from the Hubei Province in China. That patient was on a U.S. State Department–chartered flight that arrived in the United States on Feb. 7.
The 15th case was discovered in Texas among a group of people who also are under federal quarantine. That patient arrived on a State Department–chartered flight that arrived on Feb. 7. It is the first person in Texas that has tested positive for 2019-nCoV.
CDC said in a statement announcing the Texas case that there “will likely be additional cases in the coming days and weeks, including among other people recently returned from Wuhan.” Officials noted that more than 600 people who have returned as part of State Department–chartered flights are currently under that 14-day quarantine.
The agency is preparing for more widespread cases of 2019-nCoV.
Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said that containment has been the early focus for the agency.
“The goal of the measures we have taken to date are to slow the introduction and impact of this disease in the United States, but at some point, we are likely to see community spread in the U.S.,” Dr. Messonnier said during a Feb. 12 teleconference with reporters. She added that the federal response will change over time as the virus spreads.
Dr. Messonnier noted that public health officials are planning for the increased demands that a wider outbreak of 2019-nCov would place on the health care delivery system, including ensuring an adequate supply of medical equipment.
IFN-activated monocytes show early promise for ovarian cancer
ORLANDO –
The best response observed in the open-label, dose-escalation study was a partial response in 2 of 11 evaluable patients, with about a 30% reduction in target lesion size in both patients. An additional six patients had stable disease, and three had progressive disease.
Christopher Browning Cole, MD, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., reported these results at the ASCO-SITC Clinical Immuno-Oncology Symposium.
The primary objective of this study was to determine safety and identify the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). The study enrolled 18 patients with metastatic or unresectable ovarian cancer that was platinum resistant or refractory. They had a median age of 61 years and had received a median of five prior therapies.
The patients were enrolled in four dose cohorts in which they were treated every 28 days with intraperitoneal peginterferon alfa-2b (Sylatron) at doses of 25-250 mcg and interferon gamma-1b (Actimmune) at doses of 5-50 mcg, with or without autologous monocytes (75-750 x 106 cells).
In all, 15 patients were assigned to dose levels that included monocytes (dose levels 2, 3, and 4). Two of these patients were unable to tolerate apheresis and were reallocated, after two to four cycles of therapy, to “dose level 3-b,” which included 250 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 50 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and no monocytes, Dr. Cole said.
Results
Based on overall safety and tolerability, the highest dose (250 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 50 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and 750 x 106 autologous monocytes) was the MTD. Six patients received this dose.
One of the partial responders received one cycle of the MTD, and the other received eight cycles of the lowest dose (25 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 5 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and no monocytes).
The median number of cycles patients received was 3.2, but “several patients stayed on treatment much longer than that,” Dr. Cole said. Two patients are still on study, one of whom has received 10 cycles to date.
Toxicities were “largely expected” based on prior studies, and included fatigue, nausea, and abdominal pain, Dr. Cole said. He added that monocyte collection by apheresis was “tolerated pretty well” by all but the two patients reallocated to dose level 3-b, and no grade 4 or 5 toxicities occurred.
There was one grade 3 peritoneal infection associated with a catheter used for monocyte administration. After a switch to port access for administration, no other such complications occurred, Dr. Cole noted.
Rationale and next steps
“There were three sets of studies that really provided the basis for [this trial],” Dr. Cole said, explaining that the first involves the “long-standing observation that ovarian cancer is really a peritoneal disease.”
“This has led to a lot of interest in directing therapies directly to the tumor in the peritoneum ... and many of these trials have shown some really impressive results in terms of [overall survival] advantage in long-term follow up,” he added.
The second set includes pioneering studies using interferons, which are capable of activating innate immune cells, intraperitoneally to treat ovarian cancer. Interferon-gamma and interferon-alfa showed particular promise.
The third set of studies, including extensive preclinical data, shows that autologous monocytes can be activated by interferon-gamma and interferon-alfa to become tumoricidal, Dr. Cole said.
The findings of the current study support further assessment of this approach, he said, adding that exploratory analyses are ongoing to measure plasma cytokines at baseline and after therapy, specifically looking for cytokines secreted by activated monocytes.
In addition to interferon-gamma, several cytokines were present at detectable levels in the blood, including interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha, Dr. Cole noted.
He and colleagues seek to understand changes in immune cell populations induced by the therapy. They have developed a comprehensive set of panels to look at ligands and markers reflective of immune system activation, and “markers which might be targets for future therapies, potentially allowing us to develop some rational combinations, such as [programmed death-1, programmed death-ligand 1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4],” he added.
“What we’d like to do next is enroll an expansion cohort at the MTD to learn more about efficacy and immunomodulatory effects of this regimen, particularly ... what’s happening with the immune system in the tumor microenvironment, so we’re going to perform tumor biopsies before and after therapy to learn a little more about that,” Dr. Cole said. “What we ultimately envision this regimen becoming is a platform to combine intraperitoneal cellular immune therapies in the innate immune system with other immunotherapies, such as systemic therapy targeting the adaptive immune system.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Cole reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Cole C et al. ASCO-SITC: Abstract 1.
ORLANDO –
The best response observed in the open-label, dose-escalation study was a partial response in 2 of 11 evaluable patients, with about a 30% reduction in target lesion size in both patients. An additional six patients had stable disease, and three had progressive disease.
Christopher Browning Cole, MD, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., reported these results at the ASCO-SITC Clinical Immuno-Oncology Symposium.
The primary objective of this study was to determine safety and identify the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). The study enrolled 18 patients with metastatic or unresectable ovarian cancer that was platinum resistant or refractory. They had a median age of 61 years and had received a median of five prior therapies.
The patients were enrolled in four dose cohorts in which they were treated every 28 days with intraperitoneal peginterferon alfa-2b (Sylatron) at doses of 25-250 mcg and interferon gamma-1b (Actimmune) at doses of 5-50 mcg, with or without autologous monocytes (75-750 x 106 cells).
In all, 15 patients were assigned to dose levels that included monocytes (dose levels 2, 3, and 4). Two of these patients were unable to tolerate apheresis and were reallocated, after two to four cycles of therapy, to “dose level 3-b,” which included 250 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 50 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and no monocytes, Dr. Cole said.
Results
Based on overall safety and tolerability, the highest dose (250 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 50 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and 750 x 106 autologous monocytes) was the MTD. Six patients received this dose.
One of the partial responders received one cycle of the MTD, and the other received eight cycles of the lowest dose (25 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 5 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and no monocytes).
The median number of cycles patients received was 3.2, but “several patients stayed on treatment much longer than that,” Dr. Cole said. Two patients are still on study, one of whom has received 10 cycles to date.
Toxicities were “largely expected” based on prior studies, and included fatigue, nausea, and abdominal pain, Dr. Cole said. He added that monocyte collection by apheresis was “tolerated pretty well” by all but the two patients reallocated to dose level 3-b, and no grade 4 or 5 toxicities occurred.
There was one grade 3 peritoneal infection associated with a catheter used for monocyte administration. After a switch to port access for administration, no other such complications occurred, Dr. Cole noted.
Rationale and next steps
“There were three sets of studies that really provided the basis for [this trial],” Dr. Cole said, explaining that the first involves the “long-standing observation that ovarian cancer is really a peritoneal disease.”
“This has led to a lot of interest in directing therapies directly to the tumor in the peritoneum ... and many of these trials have shown some really impressive results in terms of [overall survival] advantage in long-term follow up,” he added.
The second set includes pioneering studies using interferons, which are capable of activating innate immune cells, intraperitoneally to treat ovarian cancer. Interferon-gamma and interferon-alfa showed particular promise.
The third set of studies, including extensive preclinical data, shows that autologous monocytes can be activated by interferon-gamma and interferon-alfa to become tumoricidal, Dr. Cole said.
The findings of the current study support further assessment of this approach, he said, adding that exploratory analyses are ongoing to measure plasma cytokines at baseline and after therapy, specifically looking for cytokines secreted by activated monocytes.
In addition to interferon-gamma, several cytokines were present at detectable levels in the blood, including interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha, Dr. Cole noted.
He and colleagues seek to understand changes in immune cell populations induced by the therapy. They have developed a comprehensive set of panels to look at ligands and markers reflective of immune system activation, and “markers which might be targets for future therapies, potentially allowing us to develop some rational combinations, such as [programmed death-1, programmed death-ligand 1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4],” he added.
“What we’d like to do next is enroll an expansion cohort at the MTD to learn more about efficacy and immunomodulatory effects of this regimen, particularly ... what’s happening with the immune system in the tumor microenvironment, so we’re going to perform tumor biopsies before and after therapy to learn a little more about that,” Dr. Cole said. “What we ultimately envision this regimen becoming is a platform to combine intraperitoneal cellular immune therapies in the innate immune system with other immunotherapies, such as systemic therapy targeting the adaptive immune system.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Cole reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Cole C et al. ASCO-SITC: Abstract 1.
ORLANDO –
The best response observed in the open-label, dose-escalation study was a partial response in 2 of 11 evaluable patients, with about a 30% reduction in target lesion size in both patients. An additional six patients had stable disease, and three had progressive disease.
Christopher Browning Cole, MD, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., reported these results at the ASCO-SITC Clinical Immuno-Oncology Symposium.
The primary objective of this study was to determine safety and identify the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). The study enrolled 18 patients with metastatic or unresectable ovarian cancer that was platinum resistant or refractory. They had a median age of 61 years and had received a median of five prior therapies.
The patients were enrolled in four dose cohorts in which they were treated every 28 days with intraperitoneal peginterferon alfa-2b (Sylatron) at doses of 25-250 mcg and interferon gamma-1b (Actimmune) at doses of 5-50 mcg, with or without autologous monocytes (75-750 x 106 cells).
In all, 15 patients were assigned to dose levels that included monocytes (dose levels 2, 3, and 4). Two of these patients were unable to tolerate apheresis and were reallocated, after two to four cycles of therapy, to “dose level 3-b,” which included 250 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 50 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and no monocytes, Dr. Cole said.
Results
Based on overall safety and tolerability, the highest dose (250 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 50 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and 750 x 106 autologous monocytes) was the MTD. Six patients received this dose.
One of the partial responders received one cycle of the MTD, and the other received eight cycles of the lowest dose (25 mcg of peginterferon alfa-2b, 5 mcg of interferon gamma-1b, and no monocytes).
The median number of cycles patients received was 3.2, but “several patients stayed on treatment much longer than that,” Dr. Cole said. Two patients are still on study, one of whom has received 10 cycles to date.
Toxicities were “largely expected” based on prior studies, and included fatigue, nausea, and abdominal pain, Dr. Cole said. He added that monocyte collection by apheresis was “tolerated pretty well” by all but the two patients reallocated to dose level 3-b, and no grade 4 or 5 toxicities occurred.
There was one grade 3 peritoneal infection associated with a catheter used for monocyte administration. After a switch to port access for administration, no other such complications occurred, Dr. Cole noted.
Rationale and next steps
“There were three sets of studies that really provided the basis for [this trial],” Dr. Cole said, explaining that the first involves the “long-standing observation that ovarian cancer is really a peritoneal disease.”
“This has led to a lot of interest in directing therapies directly to the tumor in the peritoneum ... and many of these trials have shown some really impressive results in terms of [overall survival] advantage in long-term follow up,” he added.
The second set includes pioneering studies using interferons, which are capable of activating innate immune cells, intraperitoneally to treat ovarian cancer. Interferon-gamma and interferon-alfa showed particular promise.
The third set of studies, including extensive preclinical data, shows that autologous monocytes can be activated by interferon-gamma and interferon-alfa to become tumoricidal, Dr. Cole said.
The findings of the current study support further assessment of this approach, he said, adding that exploratory analyses are ongoing to measure plasma cytokines at baseline and after therapy, specifically looking for cytokines secreted by activated monocytes.
In addition to interferon-gamma, several cytokines were present at detectable levels in the blood, including interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha, Dr. Cole noted.
He and colleagues seek to understand changes in immune cell populations induced by the therapy. They have developed a comprehensive set of panels to look at ligands and markers reflective of immune system activation, and “markers which might be targets for future therapies, potentially allowing us to develop some rational combinations, such as [programmed death-1, programmed death-ligand 1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4],” he added.
“What we’d like to do next is enroll an expansion cohort at the MTD to learn more about efficacy and immunomodulatory effects of this regimen, particularly ... what’s happening with the immune system in the tumor microenvironment, so we’re going to perform tumor biopsies before and after therapy to learn a little more about that,” Dr. Cole said. “What we ultimately envision this regimen becoming is a platform to combine intraperitoneal cellular immune therapies in the innate immune system with other immunotherapies, such as systemic therapy targeting the adaptive immune system.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Cole reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Cole C et al. ASCO-SITC: Abstract 1.
REPORTING FROM THE CLINICAL IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY SYMPOSIUM
Pathways to new therapeutic agents for human coronaviruses
No specific treatment is currently available for human coronaviruses to date, but numerous antiviral agents are being identified through a variety of approaches, according to Thanigaimalai Pillaiyar, PhD, and colleagues in a review published in Drug Discovery Today.
Using the six previously discovered human coronaviruses – human CoV 229E (HCoV-229E), OC43 (HCoV-OC43), NL63 (HCoV-NL63), HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1); severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV; and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) CoV – the investigators examined progress in the use and development of therapeutic drugs, focusing on the potential roles of virus inhibitors.
“Research has mainly been focused on SARS- and MERS-CoV infections, because they were responsible for severe illness when compared with other CoVs,” Dr. Pillaiyar, of the department of pharmaceutical and medicinal chemistry at the University of Bonn (Germany), and colleagues wrote.
2019-nCov has been linked genomically as most closely related to SARS, and the Coronavirus Study Group of the International Committee on Virus Taxonomy, which has the responsibility for naming viruses, has designated the new virus SARS-CoV-2.
Examining extant drugs
The first approach to identifying possible antiviral agents reevaluates known, broadly acting antiviral drugs that have been used for other viral infections or other indications. The initial research into coronavirus therapeutics, in particular, has examined current antiviral therapeutics for their effectiveness against both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but with mixed results.
For example, in a search of potential antiviral agents against CoVs, researchers identified four drugs – chloroquine, chlorpromazine, loperamide, and lopinavir – by screening drug libraries approved by the Food and Drug Administration. They were all able to inhibit the replication of MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and HCoV-229E in the low-micromolar range, which suggested that they could be used for broad-spectrum antiviral activity, according to Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues.
Other research groups have also reported the discovery of antiviral drugs using this drug-repurposing approach, which included a number of broad-spectrum inhibitors of HCoVs (lycorine, emetine, monensin sodium, mycophenolate mofetil, mycophenolic acid, phenazopyridine, and pyrvinium pamoate) that showed strong inhibition of replication by four CoVs in vitro at low-micromolar concentrations and suppressed the replication of all CoVs in a dose-dependent manner. Findings from in vivo studies showed lycorine protected mice against lethal HCoV-OC43 infection.
Along with the aforementioned drugs, a number of others have also shown potential usefulness, but, as yet, none has been validated for use in humans.
Developing new antivirals
The second approach for anti-CoV drug discovery involves the development of new therapeutics based on the genomic and biophysical understanding of the individual CoV in order to interfere with the virus itself or to disrupt its direct metabolic requirements. This can take several approaches.
MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV PL protease inhibitors
Of particular interest are antiviral therapies that attack papain-like protease, which is an important target because it is a multifunctional protein involved in proteolytic deubiquitination and viral evasion of the innate immune response. One such potential therapeutic that takes advantage of this target is disulfiram, an FDA-approved drug for use in alcohol-aversion therapy. Disulfiram has been reported as an allosteric inhibitor of MERS-CoV papain-like protease. Numerous other drug categories are being examined, with promising results in targeting the papain-like protease enzymes of both SARS and MERS.
Replicase inhibitors
Helicase (nsP13) protein is a crucial component required for virus replication in host cells and could serve as a feasible target for anti-MERS and anti-SARS chemical therapies, the review authors wrote, citing as an example, the recent development of a small 1,2,4-triazole derivative that inhibited the viral NTPase/helicase of SARS- and MERS-CoVs and demonstrated high antiviral activity and low cytotoxicity.
Membrane-bound viral RNA synthesis inhibitors
Antiviral agents that target membrane-bound coronaviral RNA synthesis represent a novel and attractive approach, according to Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues. And recently, an inhibitor was developed that targets membrane-bound coronaviral RNA synthesis and “showed potent antiviral activity of MERS-CoV infection with remarkable efficacy.”
Host-based, anti-CoV treatment options
An alternate therapeutic tactic is to bolster host defenses or to modify host susceptibilities to prevent virus infection or replication. The innate interferon response of the host is crucial for the control of viral replication after infection, and the addition of exogenous recombinant interferon or use of drugs to stimulate the normal host interferon response are both potential therapeutic avenues. For example, nitazoxanide is a potent type I interferon inducer that has been used in humans for parasitic infections, and a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative was found to exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activities against RNA and DNA viruses, including some coronaviruses.
Numerous other host pathways are being investigated as potential areas to enhance defense against infection and replication, for example, using inhibitors to block nucleic acid synthesis has been shown to provide broad-spectrum activity against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
One particular example is remdesivir, a novel nucleotide analog antiviral drug, that was developed as a therapy for Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus infections. It was later shown to provide “reasonable antiviral activity against more distantly related viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus, Junin virus, Lassa fever virus, and MERS-CoV,” the authors wrote.
Also of interest regarding remdesivir’s potential broad-spectrum use is that it has shown potent in vitro “antiviral activity against Malaysian and Bangladesh genotypes of Nipah virus (an RNA virus, although not a coronavirus, that infects both humans and animals) and reduced replication of Malaysian Nipah virus in primary human lung microvascular endothelial cells by more than four orders of magnitude,” Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues added. Of particular note, all remdesivir-treated, Nipah virus–infected animals “survived the lethal challenge, indicating that remdesivir represents a promising antiviral treatment.”
In a press briefing earlier this month, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, reported that a randomized, controlled, phase 3 trial of the antiviral drug remdesivir is currently underway in China to establish whether the drug would be an effective and safe treatment for adults patients with mild or moderate 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) disease.
“Our increasing understanding of novel emerging coronaviruses will be accompanied by increasing opportunities for the reasonable design of therapeutics. Importantly, understanding this basic information about CoV protease targets will not only aid the public health against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV but also help in advance to target new coronaviruses that might emerge in the future,” the authors concluded.
Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues reported that they had no financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pillaiyar T et al. Drug Discov Today. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.01.015.
No specific treatment is currently available for human coronaviruses to date, but numerous antiviral agents are being identified through a variety of approaches, according to Thanigaimalai Pillaiyar, PhD, and colleagues in a review published in Drug Discovery Today.
Using the six previously discovered human coronaviruses – human CoV 229E (HCoV-229E), OC43 (HCoV-OC43), NL63 (HCoV-NL63), HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1); severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV; and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) CoV – the investigators examined progress in the use and development of therapeutic drugs, focusing on the potential roles of virus inhibitors.
“Research has mainly been focused on SARS- and MERS-CoV infections, because they were responsible for severe illness when compared with other CoVs,” Dr. Pillaiyar, of the department of pharmaceutical and medicinal chemistry at the University of Bonn (Germany), and colleagues wrote.
2019-nCov has been linked genomically as most closely related to SARS, and the Coronavirus Study Group of the International Committee on Virus Taxonomy, which has the responsibility for naming viruses, has designated the new virus SARS-CoV-2.
Examining extant drugs
The first approach to identifying possible antiviral agents reevaluates known, broadly acting antiviral drugs that have been used for other viral infections or other indications. The initial research into coronavirus therapeutics, in particular, has examined current antiviral therapeutics for their effectiveness against both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but with mixed results.
For example, in a search of potential antiviral agents against CoVs, researchers identified four drugs – chloroquine, chlorpromazine, loperamide, and lopinavir – by screening drug libraries approved by the Food and Drug Administration. They were all able to inhibit the replication of MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and HCoV-229E in the low-micromolar range, which suggested that they could be used for broad-spectrum antiviral activity, according to Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues.
Other research groups have also reported the discovery of antiviral drugs using this drug-repurposing approach, which included a number of broad-spectrum inhibitors of HCoVs (lycorine, emetine, monensin sodium, mycophenolate mofetil, mycophenolic acid, phenazopyridine, and pyrvinium pamoate) that showed strong inhibition of replication by four CoVs in vitro at low-micromolar concentrations and suppressed the replication of all CoVs in a dose-dependent manner. Findings from in vivo studies showed lycorine protected mice against lethal HCoV-OC43 infection.
Along with the aforementioned drugs, a number of others have also shown potential usefulness, but, as yet, none has been validated for use in humans.
Developing new antivirals
The second approach for anti-CoV drug discovery involves the development of new therapeutics based on the genomic and biophysical understanding of the individual CoV in order to interfere with the virus itself or to disrupt its direct metabolic requirements. This can take several approaches.
MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV PL protease inhibitors
Of particular interest are antiviral therapies that attack papain-like protease, which is an important target because it is a multifunctional protein involved in proteolytic deubiquitination and viral evasion of the innate immune response. One such potential therapeutic that takes advantage of this target is disulfiram, an FDA-approved drug for use in alcohol-aversion therapy. Disulfiram has been reported as an allosteric inhibitor of MERS-CoV papain-like protease. Numerous other drug categories are being examined, with promising results in targeting the papain-like protease enzymes of both SARS and MERS.
Replicase inhibitors
Helicase (nsP13) protein is a crucial component required for virus replication in host cells and could serve as a feasible target for anti-MERS and anti-SARS chemical therapies, the review authors wrote, citing as an example, the recent development of a small 1,2,4-triazole derivative that inhibited the viral NTPase/helicase of SARS- and MERS-CoVs and demonstrated high antiviral activity and low cytotoxicity.
Membrane-bound viral RNA synthesis inhibitors
Antiviral agents that target membrane-bound coronaviral RNA synthesis represent a novel and attractive approach, according to Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues. And recently, an inhibitor was developed that targets membrane-bound coronaviral RNA synthesis and “showed potent antiviral activity of MERS-CoV infection with remarkable efficacy.”
Host-based, anti-CoV treatment options
An alternate therapeutic tactic is to bolster host defenses or to modify host susceptibilities to prevent virus infection or replication. The innate interferon response of the host is crucial for the control of viral replication after infection, and the addition of exogenous recombinant interferon or use of drugs to stimulate the normal host interferon response are both potential therapeutic avenues. For example, nitazoxanide is a potent type I interferon inducer that has been used in humans for parasitic infections, and a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative was found to exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activities against RNA and DNA viruses, including some coronaviruses.
Numerous other host pathways are being investigated as potential areas to enhance defense against infection and replication, for example, using inhibitors to block nucleic acid synthesis has been shown to provide broad-spectrum activity against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
One particular example is remdesivir, a novel nucleotide analog antiviral drug, that was developed as a therapy for Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus infections. It was later shown to provide “reasonable antiviral activity against more distantly related viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus, Junin virus, Lassa fever virus, and MERS-CoV,” the authors wrote.
Also of interest regarding remdesivir’s potential broad-spectrum use is that it has shown potent in vitro “antiviral activity against Malaysian and Bangladesh genotypes of Nipah virus (an RNA virus, although not a coronavirus, that infects both humans and animals) and reduced replication of Malaysian Nipah virus in primary human lung microvascular endothelial cells by more than four orders of magnitude,” Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues added. Of particular note, all remdesivir-treated, Nipah virus–infected animals “survived the lethal challenge, indicating that remdesivir represents a promising antiviral treatment.”
In a press briefing earlier this month, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, reported that a randomized, controlled, phase 3 trial of the antiviral drug remdesivir is currently underway in China to establish whether the drug would be an effective and safe treatment for adults patients with mild or moderate 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) disease.
“Our increasing understanding of novel emerging coronaviruses will be accompanied by increasing opportunities for the reasonable design of therapeutics. Importantly, understanding this basic information about CoV protease targets will not only aid the public health against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV but also help in advance to target new coronaviruses that might emerge in the future,” the authors concluded.
Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues reported that they had no financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pillaiyar T et al. Drug Discov Today. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.01.015.
No specific treatment is currently available for human coronaviruses to date, but numerous antiviral agents are being identified through a variety of approaches, according to Thanigaimalai Pillaiyar, PhD, and colleagues in a review published in Drug Discovery Today.
Using the six previously discovered human coronaviruses – human CoV 229E (HCoV-229E), OC43 (HCoV-OC43), NL63 (HCoV-NL63), HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1); severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV; and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) CoV – the investigators examined progress in the use and development of therapeutic drugs, focusing on the potential roles of virus inhibitors.
“Research has mainly been focused on SARS- and MERS-CoV infections, because they were responsible for severe illness when compared with other CoVs,” Dr. Pillaiyar, of the department of pharmaceutical and medicinal chemistry at the University of Bonn (Germany), and colleagues wrote.
2019-nCov has been linked genomically as most closely related to SARS, and the Coronavirus Study Group of the International Committee on Virus Taxonomy, which has the responsibility for naming viruses, has designated the new virus SARS-CoV-2.
Examining extant drugs
The first approach to identifying possible antiviral agents reevaluates known, broadly acting antiviral drugs that have been used for other viral infections or other indications. The initial research into coronavirus therapeutics, in particular, has examined current antiviral therapeutics for their effectiveness against both SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but with mixed results.
For example, in a search of potential antiviral agents against CoVs, researchers identified four drugs – chloroquine, chlorpromazine, loperamide, and lopinavir – by screening drug libraries approved by the Food and Drug Administration. They were all able to inhibit the replication of MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and HCoV-229E in the low-micromolar range, which suggested that they could be used for broad-spectrum antiviral activity, according to Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues.
Other research groups have also reported the discovery of antiviral drugs using this drug-repurposing approach, which included a number of broad-spectrum inhibitors of HCoVs (lycorine, emetine, monensin sodium, mycophenolate mofetil, mycophenolic acid, phenazopyridine, and pyrvinium pamoate) that showed strong inhibition of replication by four CoVs in vitro at low-micromolar concentrations and suppressed the replication of all CoVs in a dose-dependent manner. Findings from in vivo studies showed lycorine protected mice against lethal HCoV-OC43 infection.
Along with the aforementioned drugs, a number of others have also shown potential usefulness, but, as yet, none has been validated for use in humans.
Developing new antivirals
The second approach for anti-CoV drug discovery involves the development of new therapeutics based on the genomic and biophysical understanding of the individual CoV in order to interfere with the virus itself or to disrupt its direct metabolic requirements. This can take several approaches.
MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV PL protease inhibitors
Of particular interest are antiviral therapies that attack papain-like protease, which is an important target because it is a multifunctional protein involved in proteolytic deubiquitination and viral evasion of the innate immune response. One such potential therapeutic that takes advantage of this target is disulfiram, an FDA-approved drug for use in alcohol-aversion therapy. Disulfiram has been reported as an allosteric inhibitor of MERS-CoV papain-like protease. Numerous other drug categories are being examined, with promising results in targeting the papain-like protease enzymes of both SARS and MERS.
Replicase inhibitors
Helicase (nsP13) protein is a crucial component required for virus replication in host cells and could serve as a feasible target for anti-MERS and anti-SARS chemical therapies, the review authors wrote, citing as an example, the recent development of a small 1,2,4-triazole derivative that inhibited the viral NTPase/helicase of SARS- and MERS-CoVs and demonstrated high antiviral activity and low cytotoxicity.
Membrane-bound viral RNA synthesis inhibitors
Antiviral agents that target membrane-bound coronaviral RNA synthesis represent a novel and attractive approach, according to Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues. And recently, an inhibitor was developed that targets membrane-bound coronaviral RNA synthesis and “showed potent antiviral activity of MERS-CoV infection with remarkable efficacy.”
Host-based, anti-CoV treatment options
An alternate therapeutic tactic is to bolster host defenses or to modify host susceptibilities to prevent virus infection or replication. The innate interferon response of the host is crucial for the control of viral replication after infection, and the addition of exogenous recombinant interferon or use of drugs to stimulate the normal host interferon response are both potential therapeutic avenues. For example, nitazoxanide is a potent type I interferon inducer that has been used in humans for parasitic infections, and a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative was found to exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activities against RNA and DNA viruses, including some coronaviruses.
Numerous other host pathways are being investigated as potential areas to enhance defense against infection and replication, for example, using inhibitors to block nucleic acid synthesis has been shown to provide broad-spectrum activity against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
One particular example is remdesivir, a novel nucleotide analog antiviral drug, that was developed as a therapy for Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus infections. It was later shown to provide “reasonable antiviral activity against more distantly related viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus, Junin virus, Lassa fever virus, and MERS-CoV,” the authors wrote.
Also of interest regarding remdesivir’s potential broad-spectrum use is that it has shown potent in vitro “antiviral activity against Malaysian and Bangladesh genotypes of Nipah virus (an RNA virus, although not a coronavirus, that infects both humans and animals) and reduced replication of Malaysian Nipah virus in primary human lung microvascular endothelial cells by more than four orders of magnitude,” Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues added. Of particular note, all remdesivir-treated, Nipah virus–infected animals “survived the lethal challenge, indicating that remdesivir represents a promising antiviral treatment.”
In a press briefing earlier this month, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, reported that a randomized, controlled, phase 3 trial of the antiviral drug remdesivir is currently underway in China to establish whether the drug would be an effective and safe treatment for adults patients with mild or moderate 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) disease.
“Our increasing understanding of novel emerging coronaviruses will be accompanied by increasing opportunities for the reasonable design of therapeutics. Importantly, understanding this basic information about CoV protease targets will not only aid the public health against SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV but also help in advance to target new coronaviruses that might emerge in the future,” the authors concluded.
Dr. Pillaiyar and colleagues reported that they had no financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pillaiyar T et al. Drug Discov Today. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.01.015.
FROM DRUG DISCOVERY TODAY
An unusual ‘retirement’ option
Whether “retirement” is withdrawing from one’s occupation or from an active working life, it is of utmost importance to not let one’s mind degenerate. Some individuals move on to gathering new intellectual skills by attending new educational courses or meetings, some travel, some become semiprofessional golfers or fishermen, and some find other forms of personal extension. I now serve to develop cost-saving medical programs for county jails in the state of Texas while attempting to improve the overall quality of inmate care.
Initially I was a pediatrician in Houston with special training in allergy and immunology, but because of a medical problem I was forced to abandon my first love – primary pediatrics. My move to a small town at the age of 40 required me to reevaluate my professional life, and I opted to provide care only in my allergy and immunology specialty.
However, living in a small town is different from life in a metropolis, and it was not uncommon for doctors to be asked to assist the community. A number of years ago, our county judge asked if I would help evaluate why our county jail was spending so much money. After several attempts to refuse, I eventually did evaluate the program there, and was flabbergasted by how much money was being wasted. I made some rather simple suggestions as how to correct the problem, but when no primary care doctor stepped forward to implement the changes and run the jail medical program, I became its medical director. When we saved $120,000 the first year, even I was astounded.
While I continued to run my private practice, I did accept other small community’s offers to look into their county jails’ programs. I found that their problems in cost control and quality of health care mirrored those I found in the first jail, and they were easily solvable if the county judge and the local sheriff wanted solutions. I also found that politics makes strange bedfellows, as the saying goes, and often the obvious changes were met with obstruction in one form or another. Nonetheless, I found that I could serve these communities in addition to my individual patients. When it was time for retirement, I continued to have a real desire to make the towns around which I lived and my own community more livable. So
In most things, I found that the same business philosophy and personal medical approach I learned in my pediatrics training and as a private practitioner applied to the jail system. Let me mention some specifics. Using generic medicines was less expensive than using brand names. The diagnoses which patients claimed when they entered jail might or might not be correct, so reevaluating the diagnosis and treatment was appropriate as soon as possible. Hospital and ED visits should be limited to patients’ medically requiring them rather than using the ED as a screening tool.
But I did come to understand that medical care in the county jail is different from medical care outside an incarcerated facility in that sometimes the prisoners had their own reasons for seeking medical care. This was complicated by the fact that often there were critically ill patients presenting to county jails. So carefully established criteria and protocols were an absolute necessity to save lives.
Let me expand on the topic of seeking medical care by the inmate-patients. A relatively small number of these individuals required immediate emergency treatment, without which they could not do well: The diabetic who was not taking his insulin, the out-of-control paranoid schizophrenic who decided he was cured and therefore was unattended, the alcoholic or drug addict who would develop delirium tremens if medications were stopped abruptly. These people had to be identified as quickly as possible and correctly treated. Confounding the problem was the fact that many, and I repeat many, individuals try to use the medical route to manipulate their incarceration environment. I called this the B problem: beds, blankets, barter, buzz, better food, and be out of here. They might claim an illness existed, and often they might believe it did.
A related situation might exist when individuals would demand psychiatric and pain medications, often in large quantities, when they in fact had not taken them for some time in the outside world. Often these patients were addicts, and of course this could create an entire other relationship with the medical team. A third example would be the claim of hypoglycemia so that the prisoner would receive more frequent meals.
One might think that as a pediatrician I was ill prepared to treat adults, and in fact, there was much review of the general medical care needed when I began this program. However, the internists and family physicians in town were glad to assist me whenever I encountered a difficult patient. When hospitalizations were required, the inpatient always was covered by one of the internists on hospital staff. Quite frankly, the doctors seemed pleased to not be dealing with this group of individuals as much as they had in the past.
On a slightly different note, skills honed during my pediatric career were extremely valuable. Children, particularly young children, do not verbally communicate with their parents or their doctor particularly well, so pediatricians are well trained in the skill of observation. The patient who claims a guard hurt his shoulder so badly during an altercation that he cannot move it is found out when he easily whips his arms over his head when asked to remove his shirt. It is not uncommon for an individual to demand antidepressant medications from the medical staff, but when evaluated more thoroughly and for a longer period of time, the patient ends up laughing, even denying any suicidal ideation or any other sign of depression. One also deals with a lot of adolescent behavior from the inmates, such as the individuals who say that unless they don’t get their way (more food) they are not going to take their medications and thus get sicker. That’s Adolescent Medicine 101.
Some of the modalities I utilized in modifying the jail programs will be familiar to every practicing pediatrician. I educate; I teach; I train. Parents of my asthmatic patients had to know what medications to keep handy and when to use them. It is pretty easy to see how that relates to jail medicine. Many patients come into jail with inhalers and with a diagnosis of asthma. Some have the condition, and some do not. By training jail and medical staff how to observe breathing patterns and by performing pulse oximetry, we eliminated a large number of unnecessary ED visits, and we often made the diagnosis of hyperventilation syndrome rather than misdiagnosed asthma.
Jail medicine is a large part of the cost of housing inmates. I did consultation work for a large urban jail, and we saved over $7 million in 1 year. In a medium-sized jail, the cost-savings after a 4-month consultation was over $300,000. This is a lot of money to me, and I suspect is to you, too. Just as in our general communities, we have enough resources to provide medical care and to provide a high level of care for all. However, we cannot waste money by providing inappropriate care or overtesting or overtreating. The medical care must be what treats the disease the patient actually has ... nothing more and nothing less!
If it sounds as if I am cynical about inmate patients, that is not true. However, I am realistic that no one wishes to be in jail. I realize that the medical route is just one that prisoners can and do use to modify their situation. I understand that the medical staff within a jail needs constant education and supervision at first, and with time they become more astute – just like a physician in this arena – at distinguishing the very serious from the mildly serious from malingering. In spite of this, we doctors also can be fooled. However, through constant vigilance and constant education we can get better.
Jail medicine is not for everyone in retirement. Heck, it is not for everyone ever. I found it interesting because it required me to match my diagnostic skills against the diseases and the psychodynamics of individuals who often – not always – made that diagnosis more difficult. Diagnosing illness and curing it – isn’t this why we all went into medicine?
Dr. Yoffe is a retired pediatrician specializing in allergy and immunology who resides in Brenham, Tex. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
This article was updated 2/13/2020.
Whether “retirement” is withdrawing from one’s occupation or from an active working life, it is of utmost importance to not let one’s mind degenerate. Some individuals move on to gathering new intellectual skills by attending new educational courses or meetings, some travel, some become semiprofessional golfers or fishermen, and some find other forms of personal extension. I now serve to develop cost-saving medical programs for county jails in the state of Texas while attempting to improve the overall quality of inmate care.
Initially I was a pediatrician in Houston with special training in allergy and immunology, but because of a medical problem I was forced to abandon my first love – primary pediatrics. My move to a small town at the age of 40 required me to reevaluate my professional life, and I opted to provide care only in my allergy and immunology specialty.
However, living in a small town is different from life in a metropolis, and it was not uncommon for doctors to be asked to assist the community. A number of years ago, our county judge asked if I would help evaluate why our county jail was spending so much money. After several attempts to refuse, I eventually did evaluate the program there, and was flabbergasted by how much money was being wasted. I made some rather simple suggestions as how to correct the problem, but when no primary care doctor stepped forward to implement the changes and run the jail medical program, I became its medical director. When we saved $120,000 the first year, even I was astounded.
While I continued to run my private practice, I did accept other small community’s offers to look into their county jails’ programs. I found that their problems in cost control and quality of health care mirrored those I found in the first jail, and they were easily solvable if the county judge and the local sheriff wanted solutions. I also found that politics makes strange bedfellows, as the saying goes, and often the obvious changes were met with obstruction in one form or another. Nonetheless, I found that I could serve these communities in addition to my individual patients. When it was time for retirement, I continued to have a real desire to make the towns around which I lived and my own community more livable. So
In most things, I found that the same business philosophy and personal medical approach I learned in my pediatrics training and as a private practitioner applied to the jail system. Let me mention some specifics. Using generic medicines was less expensive than using brand names. The diagnoses which patients claimed when they entered jail might or might not be correct, so reevaluating the diagnosis and treatment was appropriate as soon as possible. Hospital and ED visits should be limited to patients’ medically requiring them rather than using the ED as a screening tool.
But I did come to understand that medical care in the county jail is different from medical care outside an incarcerated facility in that sometimes the prisoners had their own reasons for seeking medical care. This was complicated by the fact that often there were critically ill patients presenting to county jails. So carefully established criteria and protocols were an absolute necessity to save lives.
Let me expand on the topic of seeking medical care by the inmate-patients. A relatively small number of these individuals required immediate emergency treatment, without which they could not do well: The diabetic who was not taking his insulin, the out-of-control paranoid schizophrenic who decided he was cured and therefore was unattended, the alcoholic or drug addict who would develop delirium tremens if medications were stopped abruptly. These people had to be identified as quickly as possible and correctly treated. Confounding the problem was the fact that many, and I repeat many, individuals try to use the medical route to manipulate their incarceration environment. I called this the B problem: beds, blankets, barter, buzz, better food, and be out of here. They might claim an illness existed, and often they might believe it did.
A related situation might exist when individuals would demand psychiatric and pain medications, often in large quantities, when they in fact had not taken them for some time in the outside world. Often these patients were addicts, and of course this could create an entire other relationship with the medical team. A third example would be the claim of hypoglycemia so that the prisoner would receive more frequent meals.
One might think that as a pediatrician I was ill prepared to treat adults, and in fact, there was much review of the general medical care needed when I began this program. However, the internists and family physicians in town were glad to assist me whenever I encountered a difficult patient. When hospitalizations were required, the inpatient always was covered by one of the internists on hospital staff. Quite frankly, the doctors seemed pleased to not be dealing with this group of individuals as much as they had in the past.
On a slightly different note, skills honed during my pediatric career were extremely valuable. Children, particularly young children, do not verbally communicate with their parents or their doctor particularly well, so pediatricians are well trained in the skill of observation. The patient who claims a guard hurt his shoulder so badly during an altercation that he cannot move it is found out when he easily whips his arms over his head when asked to remove his shirt. It is not uncommon for an individual to demand antidepressant medications from the medical staff, but when evaluated more thoroughly and for a longer period of time, the patient ends up laughing, even denying any suicidal ideation or any other sign of depression. One also deals with a lot of adolescent behavior from the inmates, such as the individuals who say that unless they don’t get their way (more food) they are not going to take their medications and thus get sicker. That’s Adolescent Medicine 101.
Some of the modalities I utilized in modifying the jail programs will be familiar to every practicing pediatrician. I educate; I teach; I train. Parents of my asthmatic patients had to know what medications to keep handy and when to use them. It is pretty easy to see how that relates to jail medicine. Many patients come into jail with inhalers and with a diagnosis of asthma. Some have the condition, and some do not. By training jail and medical staff how to observe breathing patterns and by performing pulse oximetry, we eliminated a large number of unnecessary ED visits, and we often made the diagnosis of hyperventilation syndrome rather than misdiagnosed asthma.
Jail medicine is a large part of the cost of housing inmates. I did consultation work for a large urban jail, and we saved over $7 million in 1 year. In a medium-sized jail, the cost-savings after a 4-month consultation was over $300,000. This is a lot of money to me, and I suspect is to you, too. Just as in our general communities, we have enough resources to provide medical care and to provide a high level of care for all. However, we cannot waste money by providing inappropriate care or overtesting or overtreating. The medical care must be what treats the disease the patient actually has ... nothing more and nothing less!
If it sounds as if I am cynical about inmate patients, that is not true. However, I am realistic that no one wishes to be in jail. I realize that the medical route is just one that prisoners can and do use to modify their situation. I understand that the medical staff within a jail needs constant education and supervision at first, and with time they become more astute – just like a physician in this arena – at distinguishing the very serious from the mildly serious from malingering. In spite of this, we doctors also can be fooled. However, through constant vigilance and constant education we can get better.
Jail medicine is not for everyone in retirement. Heck, it is not for everyone ever. I found it interesting because it required me to match my diagnostic skills against the diseases and the psychodynamics of individuals who often – not always – made that diagnosis more difficult. Diagnosing illness and curing it – isn’t this why we all went into medicine?
Dr. Yoffe is a retired pediatrician specializing in allergy and immunology who resides in Brenham, Tex. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
This article was updated 2/13/2020.
Whether “retirement” is withdrawing from one’s occupation or from an active working life, it is of utmost importance to not let one’s mind degenerate. Some individuals move on to gathering new intellectual skills by attending new educational courses or meetings, some travel, some become semiprofessional golfers or fishermen, and some find other forms of personal extension. I now serve to develop cost-saving medical programs for county jails in the state of Texas while attempting to improve the overall quality of inmate care.
Initially I was a pediatrician in Houston with special training in allergy and immunology, but because of a medical problem I was forced to abandon my first love – primary pediatrics. My move to a small town at the age of 40 required me to reevaluate my professional life, and I opted to provide care only in my allergy and immunology specialty.
However, living in a small town is different from life in a metropolis, and it was not uncommon for doctors to be asked to assist the community. A number of years ago, our county judge asked if I would help evaluate why our county jail was spending so much money. After several attempts to refuse, I eventually did evaluate the program there, and was flabbergasted by how much money was being wasted. I made some rather simple suggestions as how to correct the problem, but when no primary care doctor stepped forward to implement the changes and run the jail medical program, I became its medical director. When we saved $120,000 the first year, even I was astounded.
While I continued to run my private practice, I did accept other small community’s offers to look into their county jails’ programs. I found that their problems in cost control and quality of health care mirrored those I found in the first jail, and they were easily solvable if the county judge and the local sheriff wanted solutions. I also found that politics makes strange bedfellows, as the saying goes, and often the obvious changes were met with obstruction in one form or another. Nonetheless, I found that I could serve these communities in addition to my individual patients. When it was time for retirement, I continued to have a real desire to make the towns around which I lived and my own community more livable. So
In most things, I found that the same business philosophy and personal medical approach I learned in my pediatrics training and as a private practitioner applied to the jail system. Let me mention some specifics. Using generic medicines was less expensive than using brand names. The diagnoses which patients claimed when they entered jail might or might not be correct, so reevaluating the diagnosis and treatment was appropriate as soon as possible. Hospital and ED visits should be limited to patients’ medically requiring them rather than using the ED as a screening tool.
But I did come to understand that medical care in the county jail is different from medical care outside an incarcerated facility in that sometimes the prisoners had their own reasons for seeking medical care. This was complicated by the fact that often there were critically ill patients presenting to county jails. So carefully established criteria and protocols were an absolute necessity to save lives.
Let me expand on the topic of seeking medical care by the inmate-patients. A relatively small number of these individuals required immediate emergency treatment, without which they could not do well: The diabetic who was not taking his insulin, the out-of-control paranoid schizophrenic who decided he was cured and therefore was unattended, the alcoholic or drug addict who would develop delirium tremens if medications were stopped abruptly. These people had to be identified as quickly as possible and correctly treated. Confounding the problem was the fact that many, and I repeat many, individuals try to use the medical route to manipulate their incarceration environment. I called this the B problem: beds, blankets, barter, buzz, better food, and be out of here. They might claim an illness existed, and often they might believe it did.
A related situation might exist when individuals would demand psychiatric and pain medications, often in large quantities, when they in fact had not taken them for some time in the outside world. Often these patients were addicts, and of course this could create an entire other relationship with the medical team. A third example would be the claim of hypoglycemia so that the prisoner would receive more frequent meals.
One might think that as a pediatrician I was ill prepared to treat adults, and in fact, there was much review of the general medical care needed when I began this program. However, the internists and family physicians in town were glad to assist me whenever I encountered a difficult patient. When hospitalizations were required, the inpatient always was covered by one of the internists on hospital staff. Quite frankly, the doctors seemed pleased to not be dealing with this group of individuals as much as they had in the past.
On a slightly different note, skills honed during my pediatric career were extremely valuable. Children, particularly young children, do not verbally communicate with their parents or their doctor particularly well, so pediatricians are well trained in the skill of observation. The patient who claims a guard hurt his shoulder so badly during an altercation that he cannot move it is found out when he easily whips his arms over his head when asked to remove his shirt. It is not uncommon for an individual to demand antidepressant medications from the medical staff, but when evaluated more thoroughly and for a longer period of time, the patient ends up laughing, even denying any suicidal ideation or any other sign of depression. One also deals with a lot of adolescent behavior from the inmates, such as the individuals who say that unless they don’t get their way (more food) they are not going to take their medications and thus get sicker. That’s Adolescent Medicine 101.
Some of the modalities I utilized in modifying the jail programs will be familiar to every practicing pediatrician. I educate; I teach; I train. Parents of my asthmatic patients had to know what medications to keep handy and when to use them. It is pretty easy to see how that relates to jail medicine. Many patients come into jail with inhalers and with a diagnosis of asthma. Some have the condition, and some do not. By training jail and medical staff how to observe breathing patterns and by performing pulse oximetry, we eliminated a large number of unnecessary ED visits, and we often made the diagnosis of hyperventilation syndrome rather than misdiagnosed asthma.
Jail medicine is a large part of the cost of housing inmates. I did consultation work for a large urban jail, and we saved over $7 million in 1 year. In a medium-sized jail, the cost-savings after a 4-month consultation was over $300,000. This is a lot of money to me, and I suspect is to you, too. Just as in our general communities, we have enough resources to provide medical care and to provide a high level of care for all. However, we cannot waste money by providing inappropriate care or overtesting or overtreating. The medical care must be what treats the disease the patient actually has ... nothing more and nothing less!
If it sounds as if I am cynical about inmate patients, that is not true. However, I am realistic that no one wishes to be in jail. I realize that the medical route is just one that prisoners can and do use to modify their situation. I understand that the medical staff within a jail needs constant education and supervision at first, and with time they become more astute – just like a physician in this arena – at distinguishing the very serious from the mildly serious from malingering. In spite of this, we doctors also can be fooled. However, through constant vigilance and constant education we can get better.
Jail medicine is not for everyone in retirement. Heck, it is not for everyone ever. I found it interesting because it required me to match my diagnostic skills against the diseases and the psychodynamics of individuals who often – not always – made that diagnosis more difficult. Diagnosing illness and curing it – isn’t this why we all went into medicine?
Dr. Yoffe is a retired pediatrician specializing in allergy and immunology who resides in Brenham, Tex. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
This article was updated 2/13/2020.









