User login
2019-2020 flu season starts off full throttle
For the week ending Nov. 23, there were five states, along with Puerto Rico, at the highest level of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1-10 scale of flu activity. That’s more than any year since 2012, including the pandemic season of 2017-2018, according to CDC data, and may suggest either an early peak or the beginning of a particularly bad winter.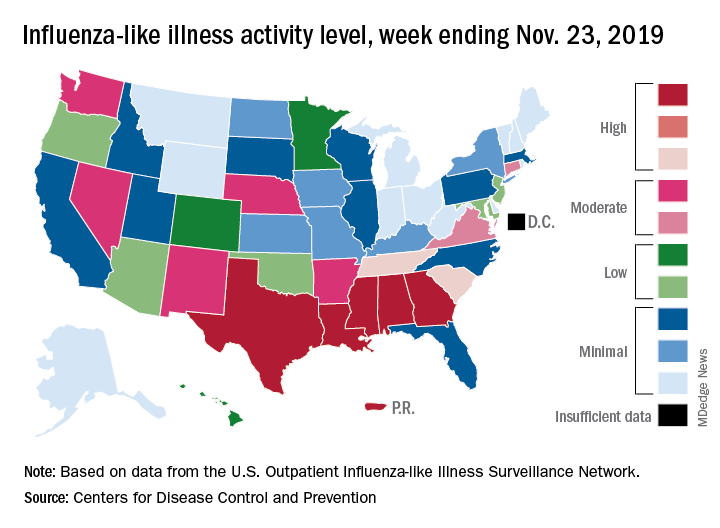
“Nationally, ILI [influenza-like illness] activity has been at or above baseline for 3 weeks; however, the amount of influenza activity across the country varies with the south and parts of the west seeing elevated activity while other parts of the country are still seeing low activity,” the CDC’s influenza division said in its weekly FluView report.
The five highest-activity states – Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas – are all at level 10, and they join two others – South Carolina and Tennessee, which are at level 8 – in the “high” range from 8-10 on the ILI activity scale; Puerto Rico also is at level 10. ILI is defined as “fever (temperature of 100° F [37.8° C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza,” the CDC said.
The activity scale is based on the percentage of outpatient visits for ILI in each state, which is reported to the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) each week. The national rate for the week ending Nov. 23 was 2.9%, which is above the new-for-this-season baseline rate of 2.4%. For the three previous flu seasons, the national baseline was 2.2%, having been raised from its previous level of 2.1% in 2015-2016, CDC data show.
The peak month of flu activity occurs most often in February – 15 times from 1982-1983 to 2017-2018 – but there were seven peaks in December and six each in January and March over that time period, along with one peak each in October and November, the CDC said. The October peak occurred during the H1N1 pandemic year of 2009, when the national outpatient ILI rate climbed to just over 7.7%.
For the week ending Nov. 23, there were five states, along with Puerto Rico, at the highest level of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1-10 scale of flu activity. That’s more than any year since 2012, including the pandemic season of 2017-2018, according to CDC data, and may suggest either an early peak or the beginning of a particularly bad winter.
“Nationally, ILI [influenza-like illness] activity has been at or above baseline for 3 weeks; however, the amount of influenza activity across the country varies with the south and parts of the west seeing elevated activity while other parts of the country are still seeing low activity,” the CDC’s influenza division said in its weekly FluView report.
The five highest-activity states – Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas – are all at level 10, and they join two others – South Carolina and Tennessee, which are at level 8 – in the “high” range from 8-10 on the ILI activity scale; Puerto Rico also is at level 10. ILI is defined as “fever (temperature of 100° F [37.8° C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza,” the CDC said.
The activity scale is based on the percentage of outpatient visits for ILI in each state, which is reported to the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) each week. The national rate for the week ending Nov. 23 was 2.9%, which is above the new-for-this-season baseline rate of 2.4%. For the three previous flu seasons, the national baseline was 2.2%, having been raised from its previous level of 2.1% in 2015-2016, CDC data show.
The peak month of flu activity occurs most often in February – 15 times from 1982-1983 to 2017-2018 – but there were seven peaks in December and six each in January and March over that time period, along with one peak each in October and November, the CDC said. The October peak occurred during the H1N1 pandemic year of 2009, when the national outpatient ILI rate climbed to just over 7.7%.
For the week ending Nov. 23, there were five states, along with Puerto Rico, at the highest level of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1-10 scale of flu activity. That’s more than any year since 2012, including the pandemic season of 2017-2018, according to CDC data, and may suggest either an early peak or the beginning of a particularly bad winter.
“Nationally, ILI [influenza-like illness] activity has been at or above baseline for 3 weeks; however, the amount of influenza activity across the country varies with the south and parts of the west seeing elevated activity while other parts of the country are still seeing low activity,” the CDC’s influenza division said in its weekly FluView report.
The five highest-activity states – Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas – are all at level 10, and they join two others – South Carolina and Tennessee, which are at level 8 – in the “high” range from 8-10 on the ILI activity scale; Puerto Rico also is at level 10. ILI is defined as “fever (temperature of 100° F [37.8° C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza,” the CDC said.
The activity scale is based on the percentage of outpatient visits for ILI in each state, which is reported to the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) each week. The national rate for the week ending Nov. 23 was 2.9%, which is above the new-for-this-season baseline rate of 2.4%. For the three previous flu seasons, the national baseline was 2.2%, having been raised from its previous level of 2.1% in 2015-2016, CDC data show.
The peak month of flu activity occurs most often in February – 15 times from 1982-1983 to 2017-2018 – but there were seven peaks in December and six each in January and March over that time period, along with one peak each in October and November, the CDC said. The October peak occurred during the H1N1 pandemic year of 2009, when the national outpatient ILI rate climbed to just over 7.7%.
Endoscopy-related occupational injuries run rampant in gastroenterology
SAN ANTONIO – Swati Pawa, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Moreover, most respondents said they received zero training in ergonomic strategies for endoscopy-related injury (ERI) prevention during their fellowship training. And there’s been none since. Eighty-one percent of respondents indicated they would welcome such training, added Dr. Pawa, a gastroenterologist at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
The survey results expose a glaring unmet need in clinical practice, she said: “There have been no published guidelines from any of the major professional GI societies to date addressing how to prevent endoscopy-related injuries.”
The 38-item survey was created by the ACG Women in GI Committee and sponsored by the ACG governing board.
Among the key findings was the identification of sex differences in the types of ERIs reported, which suggests different contributory mechanisms. For example, female gastroenterologists were more likely than were their male colleagues to have experienced ERIs involving the upper back, by a margin of 49% to 36%. Upper extremity pain was more common among the women, too, with 63% reporting hand or finger pain, compared with 53% of men. Twenty-four percent of women reported carpal tunnel syndrome and an equal percentage developed tendonitis, compared with 18% and 17% of men, respectively.
Seventy-one percent of women attributed their ERI to torquing with their right hand, as did 63% of men. Women also more frequently cited having to deal with a nonadjustable bed or monitor as contributing to injury. In contrast, roughly twice as many men as women attributed their ERI to wearing a lead apron or use of the elevator on the duodenoscope.
Equally common causes of ERIs in men and women included standing in awkward positions while supporting an endoscope, standing for a long time, and adjusting tip angulation with the left hand.
Male and female gastroenterologists differed in their practice patterns. The men had been performing endoscopy for a mean of 23 years, compared with 13 years for the women. Fifty-six percent of the men were in private practice, compared with 35% of the women. In contrast, 43% of the women worked in academic settings versus 28% of the men. Thirty percent of the male gastroenterologists characterized themselves as interventional specialists, a rate more than twice that in women, who more commonly specialized in inflammatory bowel disease.
The survey was sent to nearly 16,000 ACG members. It generated a 14% response rate. Roughly two-thirds of responses were provided by male gastroenterologists.
Dr. Pawa and her coinvestigators are now drilling down through the survey data in an effort to identify an appropriate endoscopy workload limit that’s associated with reduced ERI risk.
One audience member commented, “The incidence of ERI in your survey is much higher than most of us would expect.” He speculated that response bias might be at work, with gastroenterologists who have personally experienced an ERI being perhaps more highly motivated to be among the 14% who completed the 38-question survey. Dr. Pawa replied that the survey figures are in line with other, smaller studies.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.
Visit https://www.ddwnews.org/
SAN ANTONIO – Swati Pawa, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Moreover, most respondents said they received zero training in ergonomic strategies for endoscopy-related injury (ERI) prevention during their fellowship training. And there’s been none since. Eighty-one percent of respondents indicated they would welcome such training, added Dr. Pawa, a gastroenterologist at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
The survey results expose a glaring unmet need in clinical practice, she said: “There have been no published guidelines from any of the major professional GI societies to date addressing how to prevent endoscopy-related injuries.”
The 38-item survey was created by the ACG Women in GI Committee and sponsored by the ACG governing board.
Among the key findings was the identification of sex differences in the types of ERIs reported, which suggests different contributory mechanisms. For example, female gastroenterologists were more likely than were their male colleagues to have experienced ERIs involving the upper back, by a margin of 49% to 36%. Upper extremity pain was more common among the women, too, with 63% reporting hand or finger pain, compared with 53% of men. Twenty-four percent of women reported carpal tunnel syndrome and an equal percentage developed tendonitis, compared with 18% and 17% of men, respectively.
Seventy-one percent of women attributed their ERI to torquing with their right hand, as did 63% of men. Women also more frequently cited having to deal with a nonadjustable bed or monitor as contributing to injury. In contrast, roughly twice as many men as women attributed their ERI to wearing a lead apron or use of the elevator on the duodenoscope.
Equally common causes of ERIs in men and women included standing in awkward positions while supporting an endoscope, standing for a long time, and adjusting tip angulation with the left hand.
Male and female gastroenterologists differed in their practice patterns. The men had been performing endoscopy for a mean of 23 years, compared with 13 years for the women. Fifty-six percent of the men were in private practice, compared with 35% of the women. In contrast, 43% of the women worked in academic settings versus 28% of the men. Thirty percent of the male gastroenterologists characterized themselves as interventional specialists, a rate more than twice that in women, who more commonly specialized in inflammatory bowel disease.
The survey was sent to nearly 16,000 ACG members. It generated a 14% response rate. Roughly two-thirds of responses were provided by male gastroenterologists.
Dr. Pawa and her coinvestigators are now drilling down through the survey data in an effort to identify an appropriate endoscopy workload limit that’s associated with reduced ERI risk.
One audience member commented, “The incidence of ERI in your survey is much higher than most of us would expect.” He speculated that response bias might be at work, with gastroenterologists who have personally experienced an ERI being perhaps more highly motivated to be among the 14% who completed the 38-question survey. Dr. Pawa replied that the survey figures are in line with other, smaller studies.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.
Visit https://www.ddwnews.org/
SAN ANTONIO – Swati Pawa, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Moreover, most respondents said they received zero training in ergonomic strategies for endoscopy-related injury (ERI) prevention during their fellowship training. And there’s been none since. Eighty-one percent of respondents indicated they would welcome such training, added Dr. Pawa, a gastroenterologist at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
The survey results expose a glaring unmet need in clinical practice, she said: “There have been no published guidelines from any of the major professional GI societies to date addressing how to prevent endoscopy-related injuries.”
The 38-item survey was created by the ACG Women in GI Committee and sponsored by the ACG governing board.
Among the key findings was the identification of sex differences in the types of ERIs reported, which suggests different contributory mechanisms. For example, female gastroenterologists were more likely than were their male colleagues to have experienced ERIs involving the upper back, by a margin of 49% to 36%. Upper extremity pain was more common among the women, too, with 63% reporting hand or finger pain, compared with 53% of men. Twenty-four percent of women reported carpal tunnel syndrome and an equal percentage developed tendonitis, compared with 18% and 17% of men, respectively.
Seventy-one percent of women attributed their ERI to torquing with their right hand, as did 63% of men. Women also more frequently cited having to deal with a nonadjustable bed or monitor as contributing to injury. In contrast, roughly twice as many men as women attributed their ERI to wearing a lead apron or use of the elevator on the duodenoscope.
Equally common causes of ERIs in men and women included standing in awkward positions while supporting an endoscope, standing for a long time, and adjusting tip angulation with the left hand.
Male and female gastroenterologists differed in their practice patterns. The men had been performing endoscopy for a mean of 23 years, compared with 13 years for the women. Fifty-six percent of the men were in private practice, compared with 35% of the women. In contrast, 43% of the women worked in academic settings versus 28% of the men. Thirty percent of the male gastroenterologists characterized themselves as interventional specialists, a rate more than twice that in women, who more commonly specialized in inflammatory bowel disease.
The survey was sent to nearly 16,000 ACG members. It generated a 14% response rate. Roughly two-thirds of responses were provided by male gastroenterologists.
Dr. Pawa and her coinvestigators are now drilling down through the survey data in an effort to identify an appropriate endoscopy workload limit that’s associated with reduced ERI risk.
One audience member commented, “The incidence of ERI in your survey is much higher than most of us would expect.” He speculated that response bias might be at work, with gastroenterologists who have personally experienced an ERI being perhaps more highly motivated to be among the 14% who completed the 38-question survey. Dr. Pawa replied that the survey figures are in line with other, smaller studies.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.
Visit https://www.ddwnews.org/
REPORTING FROM ACG 2019
Use of PEP prophylaxis techniques may diverge from the evidence
(PEP), according to research published online in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. In addition, methods for PEP prophylaxis in clinical practice are not implemented to the extent that the current evidence warrants.
“Future studies should not only further clarify the optimal PEP prophylaxis strategy, but should also focus on strategies to improve the implementation of evidence-based PEP prophylaxis techniques,” wrote Patrick Avila, MD, MPH, gastroenterologist at the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
A survey of American endoscopists
Approximately 4% of patients who undergo biliopancreatic endoscopy develop PEP, which has a mortality rate of 3%. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) recommends prophylactic pancreatic duct stent placement and rectal NSAIDs to reduce the incidence and severity of PEP in patients at high risk. The ASGE further suggests that rectal indomethacin may decrease the risk and severity of PEP in patients at average risk.
The European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) recommends rectal indomethacin for all patients undergoing ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Several surveys of European endoscopists, however, indicate that relatively few respondents have adopted the recommended prophylactic techniques. The literature does not contain information about practice patterns among American endoscopists, and Dr. Avila and colleagues decided to investigate this question.
The researchers developed a 16-question online survey to assess current practice patterns with regard to PEP prophylaxis. They defined ERCPs that entailed a high risk for PEP as any that involved pancreatic or precut sphincterotomy, traumatic biliary sphincterotomy, balloon dilation of the biliary sphincter, injection of the pancreatic duct, extensive pancreatic duct instrumentation, difficult cannulation, suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, previous PEP, or a female patient. Dr. Avila and colleagues distributed the survey to 233 advanced endoscopists involved in advanced endoscopy fellowship training programs.
Respondents had years of experience
Sixty-two endoscopists (26.7%) completed the survey. Respondents’ mean age was 47 years, and most respondents (74.6%) had been performing ERCP for more than 5 years. Almost all respondents (95%) worked at a tertiary referral center, and all worked with fellows.
All respondents reported having used pancreatic duct stent placement to prevent PEP. Most responders (72%) used pancreatic duct stent placement only in patients at high risk of PEP, and 64% reported using pancreatic duct stent placement in 25% or less of the ERCPs that they had performed. Four respondents (6.8%) used pancreatic duct stent placement for PEP in more than half of ERCPs. Among endoscopists who rarely use pancreatic duct stent placement for PEP, the major reasons cited included concern about increased risk of PEP with failed pancreatic duct insertion, the belief that stents do not provide additional benefit beyond pharmacologic prophylaxis, and difficulties in following up patients to ensure stent passage.
About 98% of respondents reported using rectal NSAIDs for PEP. Thirty-four respondents (59.7%) used this treatment only for patients at high risk, and 23 respondents (40.1%) used it for patients at average risk. Among respondents who used rectal NSAIDs to prevent PEP, 67.8% used the treatment in half or more of ERCPs. The NSAID of choice was indomethacin for all respondents. One respondent reported never using rectal NSAIDs for PEP because of doubts about its efficacy, in addition to cost and availability.
In addition, 49 respondents (83.0%) reported using rapid intravenous fluids to prevent PEP. None reported using octreotide or antibiotics to prevent PEP.
Results may reflect recall bias
The survey reveals “a significant divergence from the scientific evidence in how PEP techniques are used in routine clinical practice,” wrote Dr. Avila and colleagues. Several studies, including a randomized controlled trial, support the use of rectal NSAIDs as prophylaxis as patients at average risk of PEP, but less than half of respondents reported using it. The ASGE guidelines state that this treatment is “reasonable,” but do not advocate for it. “If appropriate, adopting a stronger stance in our practice guidelines may lead to further widespread use of rectal NSAIDs in this group of patients,” wrote Dr. Avila and colleagues.
Pancreatic duct stent placement is a difficult procedure to perform. The success rate in one British study was 51%, and a study of expert pancreaticobiliary endoscopists found a failure rate of 7%. It therefore may not be surprising that pancreatic duct stent placement was used less often than rectal NSAIDs among respondents, according to the authors.
Dr. Avila and colleagues acknowledged that the survey’s low response rate could have introduced nonresponse bias into the findings. They also stated that the study may have been affected by selection and recall biases. The results thus may not be generalizable to other practice settings, they concluded.
The authors did not report any study funding or disclosures.
SOURCE: Avila P et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Nov 16. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.11.013.
AGA offers resources to help your patients understand ECRP and scope safety. Learn more at https://www.gastro.org/
(PEP), according to research published online in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. In addition, methods for PEP prophylaxis in clinical practice are not implemented to the extent that the current evidence warrants.
“Future studies should not only further clarify the optimal PEP prophylaxis strategy, but should also focus on strategies to improve the implementation of evidence-based PEP prophylaxis techniques,” wrote Patrick Avila, MD, MPH, gastroenterologist at the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
A survey of American endoscopists
Approximately 4% of patients who undergo biliopancreatic endoscopy develop PEP, which has a mortality rate of 3%. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) recommends prophylactic pancreatic duct stent placement and rectal NSAIDs to reduce the incidence and severity of PEP in patients at high risk. The ASGE further suggests that rectal indomethacin may decrease the risk and severity of PEP in patients at average risk.
The European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) recommends rectal indomethacin for all patients undergoing ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Several surveys of European endoscopists, however, indicate that relatively few respondents have adopted the recommended prophylactic techniques. The literature does not contain information about practice patterns among American endoscopists, and Dr. Avila and colleagues decided to investigate this question.
The researchers developed a 16-question online survey to assess current practice patterns with regard to PEP prophylaxis. They defined ERCPs that entailed a high risk for PEP as any that involved pancreatic or precut sphincterotomy, traumatic biliary sphincterotomy, balloon dilation of the biliary sphincter, injection of the pancreatic duct, extensive pancreatic duct instrumentation, difficult cannulation, suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, previous PEP, or a female patient. Dr. Avila and colleagues distributed the survey to 233 advanced endoscopists involved in advanced endoscopy fellowship training programs.
Respondents had years of experience
Sixty-two endoscopists (26.7%) completed the survey. Respondents’ mean age was 47 years, and most respondents (74.6%) had been performing ERCP for more than 5 years. Almost all respondents (95%) worked at a tertiary referral center, and all worked with fellows.
All respondents reported having used pancreatic duct stent placement to prevent PEP. Most responders (72%) used pancreatic duct stent placement only in patients at high risk of PEP, and 64% reported using pancreatic duct stent placement in 25% or less of the ERCPs that they had performed. Four respondents (6.8%) used pancreatic duct stent placement for PEP in more than half of ERCPs. Among endoscopists who rarely use pancreatic duct stent placement for PEP, the major reasons cited included concern about increased risk of PEP with failed pancreatic duct insertion, the belief that stents do not provide additional benefit beyond pharmacologic prophylaxis, and difficulties in following up patients to ensure stent passage.
About 98% of respondents reported using rectal NSAIDs for PEP. Thirty-four respondents (59.7%) used this treatment only for patients at high risk, and 23 respondents (40.1%) used it for patients at average risk. Among respondents who used rectal NSAIDs to prevent PEP, 67.8% used the treatment in half or more of ERCPs. The NSAID of choice was indomethacin for all respondents. One respondent reported never using rectal NSAIDs for PEP because of doubts about its efficacy, in addition to cost and availability.
In addition, 49 respondents (83.0%) reported using rapid intravenous fluids to prevent PEP. None reported using octreotide or antibiotics to prevent PEP.
Results may reflect recall bias
The survey reveals “a significant divergence from the scientific evidence in how PEP techniques are used in routine clinical practice,” wrote Dr. Avila and colleagues. Several studies, including a randomized controlled trial, support the use of rectal NSAIDs as prophylaxis as patients at average risk of PEP, but less than half of respondents reported using it. The ASGE guidelines state that this treatment is “reasonable,” but do not advocate for it. “If appropriate, adopting a stronger stance in our practice guidelines may lead to further widespread use of rectal NSAIDs in this group of patients,” wrote Dr. Avila and colleagues.
Pancreatic duct stent placement is a difficult procedure to perform. The success rate in one British study was 51%, and a study of expert pancreaticobiliary endoscopists found a failure rate of 7%. It therefore may not be surprising that pancreatic duct stent placement was used less often than rectal NSAIDs among respondents, according to the authors.
Dr. Avila and colleagues acknowledged that the survey’s low response rate could have introduced nonresponse bias into the findings. They also stated that the study may have been affected by selection and recall biases. The results thus may not be generalizable to other practice settings, they concluded.
The authors did not report any study funding or disclosures.
SOURCE: Avila P et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Nov 16. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.11.013.
AGA offers resources to help your patients understand ECRP and scope safety. Learn more at https://www.gastro.org/
(PEP), according to research published online in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. In addition, methods for PEP prophylaxis in clinical practice are not implemented to the extent that the current evidence warrants.
“Future studies should not only further clarify the optimal PEP prophylaxis strategy, but should also focus on strategies to improve the implementation of evidence-based PEP prophylaxis techniques,” wrote Patrick Avila, MD, MPH, gastroenterologist at the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
A survey of American endoscopists
Approximately 4% of patients who undergo biliopancreatic endoscopy develop PEP, which has a mortality rate of 3%. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) recommends prophylactic pancreatic duct stent placement and rectal NSAIDs to reduce the incidence and severity of PEP in patients at high risk. The ASGE further suggests that rectal indomethacin may decrease the risk and severity of PEP in patients at average risk.
The European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) recommends rectal indomethacin for all patients undergoing ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Several surveys of European endoscopists, however, indicate that relatively few respondents have adopted the recommended prophylactic techniques. The literature does not contain information about practice patterns among American endoscopists, and Dr. Avila and colleagues decided to investigate this question.
The researchers developed a 16-question online survey to assess current practice patterns with regard to PEP prophylaxis. They defined ERCPs that entailed a high risk for PEP as any that involved pancreatic or precut sphincterotomy, traumatic biliary sphincterotomy, balloon dilation of the biliary sphincter, injection of the pancreatic duct, extensive pancreatic duct instrumentation, difficult cannulation, suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, previous PEP, or a female patient. Dr. Avila and colleagues distributed the survey to 233 advanced endoscopists involved in advanced endoscopy fellowship training programs.
Respondents had years of experience
Sixty-two endoscopists (26.7%) completed the survey. Respondents’ mean age was 47 years, and most respondents (74.6%) had been performing ERCP for more than 5 years. Almost all respondents (95%) worked at a tertiary referral center, and all worked with fellows.
All respondents reported having used pancreatic duct stent placement to prevent PEP. Most responders (72%) used pancreatic duct stent placement only in patients at high risk of PEP, and 64% reported using pancreatic duct stent placement in 25% or less of the ERCPs that they had performed. Four respondents (6.8%) used pancreatic duct stent placement for PEP in more than half of ERCPs. Among endoscopists who rarely use pancreatic duct stent placement for PEP, the major reasons cited included concern about increased risk of PEP with failed pancreatic duct insertion, the belief that stents do not provide additional benefit beyond pharmacologic prophylaxis, and difficulties in following up patients to ensure stent passage.
About 98% of respondents reported using rectal NSAIDs for PEP. Thirty-four respondents (59.7%) used this treatment only for patients at high risk, and 23 respondents (40.1%) used it for patients at average risk. Among respondents who used rectal NSAIDs to prevent PEP, 67.8% used the treatment in half or more of ERCPs. The NSAID of choice was indomethacin for all respondents. One respondent reported never using rectal NSAIDs for PEP because of doubts about its efficacy, in addition to cost and availability.
In addition, 49 respondents (83.0%) reported using rapid intravenous fluids to prevent PEP. None reported using octreotide or antibiotics to prevent PEP.
Results may reflect recall bias
The survey reveals “a significant divergence from the scientific evidence in how PEP techniques are used in routine clinical practice,” wrote Dr. Avila and colleagues. Several studies, including a randomized controlled trial, support the use of rectal NSAIDs as prophylaxis as patients at average risk of PEP, but less than half of respondents reported using it. The ASGE guidelines state that this treatment is “reasonable,” but do not advocate for it. “If appropriate, adopting a stronger stance in our practice guidelines may lead to further widespread use of rectal NSAIDs in this group of patients,” wrote Dr. Avila and colleagues.
Pancreatic duct stent placement is a difficult procedure to perform. The success rate in one British study was 51%, and a study of expert pancreaticobiliary endoscopists found a failure rate of 7%. It therefore may not be surprising that pancreatic duct stent placement was used less often than rectal NSAIDs among respondents, according to the authors.
Dr. Avila and colleagues acknowledged that the survey’s low response rate could have introduced nonresponse bias into the findings. They also stated that the study may have been affected by selection and recall biases. The results thus may not be generalizable to other practice settings, they concluded.
The authors did not report any study funding or disclosures.
SOURCE: Avila P et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Nov 16. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.11.013.
AGA offers resources to help your patients understand ECRP and scope safety. Learn more at https://www.gastro.org/
FROM GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
Dupilumab could be treatment option for chronic keloids
A new study has found that keloid formation may be driven by Th2 pathogenesis and, as such, Th2-targeting dupilumab may be useful in treating chronic keloids.
“This preliminary report demonstrates a novel use of dupilumab for chronic keloids, showing major reductions in skin fibrosis and keloidal scarring,” wrote Aisleen Diaz, from the department of dermatology and laboratory of inflammatory skin diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and coauthors. The study was published as a letter to the editor in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The authors described a 53-year-old black male patient with severe atopic dermatitis and two keloids who, after 7 months of treatment with dupilumab for AD, had significant improvements in AD – as well as shrinkage of the larger keloid and “complete disappearance” of the smaller keloid.
As a follow-up, the researchers used real-time polymerase chain reaction testing to monitor Th2 gene expression in lesional and nonlesional keloid skin from three black patients (mean age, 47.3 years) with severe keloids and no AD. Five healthy black controls (mean age, 39.8 years) were also included for comparison. In addition, 6-mm whole-skin biopsy specimens were obtained from all patients.
Interleukin-4 receptors, directly targeted by dupilumab, were highly up-regulated in keloid lesions, compared with controls (P less than .1). The Th2 cytokine IL-13 was significantly increased in lesional and nonlesional keloids, compared with controls (P less than .05), and the TH2 cytokine CCL18 was also highly increased in keloids, chiefly in nonlesional skin (P less than .05).
With regard to genes involved in cartilage and bone development that have been recognized as highly expressed in keloids – such as cadherin 11 and fibrillin 2 – all were increased in keloid lesions, compared with both controls and to nonlesional skin (P less than .05), the researchers reported.
“Dupilumab and other Th2-targeting agents may provide treatment options for patients with severe keloids, warranting further studies,” they commented, adding that the patient they described was the first report of a keloid improving with dupilumab, which “blocks type 2 driven inflammation via IL-4/IL-13 signaling.”
Four authors, including Ms. Diaz, had no disclosures. Two authors reported numerous disclosures, including receiving grants, research funds, and personal and consulting fees, from various pharmaceutical companies, including dupilumab manufacturers Regeneron and/or Sanofi.
SOURCE: Diaz A et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Nov 20. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16097.
A new study has found that keloid formation may be driven by Th2 pathogenesis and, as such, Th2-targeting dupilumab may be useful in treating chronic keloids.
“This preliminary report demonstrates a novel use of dupilumab for chronic keloids, showing major reductions in skin fibrosis and keloidal scarring,” wrote Aisleen Diaz, from the department of dermatology and laboratory of inflammatory skin diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and coauthors. The study was published as a letter to the editor in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The authors described a 53-year-old black male patient with severe atopic dermatitis and two keloids who, after 7 months of treatment with dupilumab for AD, had significant improvements in AD – as well as shrinkage of the larger keloid and “complete disappearance” of the smaller keloid.
As a follow-up, the researchers used real-time polymerase chain reaction testing to monitor Th2 gene expression in lesional and nonlesional keloid skin from three black patients (mean age, 47.3 years) with severe keloids and no AD. Five healthy black controls (mean age, 39.8 years) were also included for comparison. In addition, 6-mm whole-skin biopsy specimens were obtained from all patients.
Interleukin-4 receptors, directly targeted by dupilumab, were highly up-regulated in keloid lesions, compared with controls (P less than .1). The Th2 cytokine IL-13 was significantly increased in lesional and nonlesional keloids, compared with controls (P less than .05), and the TH2 cytokine CCL18 was also highly increased in keloids, chiefly in nonlesional skin (P less than .05).
With regard to genes involved in cartilage and bone development that have been recognized as highly expressed in keloids – such as cadherin 11 and fibrillin 2 – all were increased in keloid lesions, compared with both controls and to nonlesional skin (P less than .05), the researchers reported.
“Dupilumab and other Th2-targeting agents may provide treatment options for patients with severe keloids, warranting further studies,” they commented, adding that the patient they described was the first report of a keloid improving with dupilumab, which “blocks type 2 driven inflammation via IL-4/IL-13 signaling.”
Four authors, including Ms. Diaz, had no disclosures. Two authors reported numerous disclosures, including receiving grants, research funds, and personal and consulting fees, from various pharmaceutical companies, including dupilumab manufacturers Regeneron and/or Sanofi.
SOURCE: Diaz A et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Nov 20. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16097.
A new study has found that keloid formation may be driven by Th2 pathogenesis and, as such, Th2-targeting dupilumab may be useful in treating chronic keloids.
“This preliminary report demonstrates a novel use of dupilumab for chronic keloids, showing major reductions in skin fibrosis and keloidal scarring,” wrote Aisleen Diaz, from the department of dermatology and laboratory of inflammatory skin diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and coauthors. The study was published as a letter to the editor in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The authors described a 53-year-old black male patient with severe atopic dermatitis and two keloids who, after 7 months of treatment with dupilumab for AD, had significant improvements in AD – as well as shrinkage of the larger keloid and “complete disappearance” of the smaller keloid.
As a follow-up, the researchers used real-time polymerase chain reaction testing to monitor Th2 gene expression in lesional and nonlesional keloid skin from three black patients (mean age, 47.3 years) with severe keloids and no AD. Five healthy black controls (mean age, 39.8 years) were also included for comparison. In addition, 6-mm whole-skin biopsy specimens were obtained from all patients.
Interleukin-4 receptors, directly targeted by dupilumab, were highly up-regulated in keloid lesions, compared with controls (P less than .1). The Th2 cytokine IL-13 was significantly increased in lesional and nonlesional keloids, compared with controls (P less than .05), and the TH2 cytokine CCL18 was also highly increased in keloids, chiefly in nonlesional skin (P less than .05).
With regard to genes involved in cartilage and bone development that have been recognized as highly expressed in keloids – such as cadherin 11 and fibrillin 2 – all were increased in keloid lesions, compared with both controls and to nonlesional skin (P less than .05), the researchers reported.
“Dupilumab and other Th2-targeting agents may provide treatment options for patients with severe keloids, warranting further studies,” they commented, adding that the patient they described was the first report of a keloid improving with dupilumab, which “blocks type 2 driven inflammation via IL-4/IL-13 signaling.”
Four authors, including Ms. Diaz, had no disclosures. Two authors reported numerous disclosures, including receiving grants, research funds, and personal and consulting fees, from various pharmaceutical companies, including dupilumab manufacturers Regeneron and/or Sanofi.
SOURCE: Diaz A et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Nov 20. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16097.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY
Simple prevention strategies can lessen postoperative delirium after orthopedic surgery
A new study has found that and a prevention program can help improve staff education and outcomes.
“In an aging society, it is very important to develop and implement a strategy for POD prevention to ensure that aging patients are treated as safely and effectively as possible,” wrote Jung-Yeon Choi of Seoul (South Korea) National University Bundang Hospital and coauthors. The study was published in BMC Geriatrics.
To determine how to better identify and treat high-risk patients for POD after orthopedic surgery, the researchers led a retrospective cohort study that included an intervention group of participants who were aged at least 65 years (n = 275) and a control group from a year prior (n = 274). Patients in the intervention group had their risk of delirium assessed and categorized using a simple screening tool, and those deemed at risk were entered into a multicomponent delirium prevention program.
Of the 275 patients in the intervention group, 144 required screening for delirium. Ninety-nine were classified as low risk, 29 were classified as high risk, and 16 missed the screening. Fifty-three additional patients were classified as high risk because they were aged 80 years or older. During the study, 17 participants experienced POD, 16 of whom were classified as high risk. In regard to estimating POD risk, the sensitivity and specificity of the delirium screening tool were 94.1% and 72.7%, respectively. Incidence rates of POD were 10.2% in the control group and 6.2% in the intervention group.
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including its design as a retrospective review of medical records rather than a prospective randomized controlled trial. In addition, because it was conducted in just one teaching hospital, they deemed it “not possible to determine the generalizability and long-term effect of our findings.”
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Choi JY et al. BMC Geriatr. 2019 Oct 26. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1303-z.
A new study has found that and a prevention program can help improve staff education and outcomes.
“In an aging society, it is very important to develop and implement a strategy for POD prevention to ensure that aging patients are treated as safely and effectively as possible,” wrote Jung-Yeon Choi of Seoul (South Korea) National University Bundang Hospital and coauthors. The study was published in BMC Geriatrics.
To determine how to better identify and treat high-risk patients for POD after orthopedic surgery, the researchers led a retrospective cohort study that included an intervention group of participants who were aged at least 65 years (n = 275) and a control group from a year prior (n = 274). Patients in the intervention group had their risk of delirium assessed and categorized using a simple screening tool, and those deemed at risk were entered into a multicomponent delirium prevention program.
Of the 275 patients in the intervention group, 144 required screening for delirium. Ninety-nine were classified as low risk, 29 were classified as high risk, and 16 missed the screening. Fifty-three additional patients were classified as high risk because they were aged 80 years or older. During the study, 17 participants experienced POD, 16 of whom were classified as high risk. In regard to estimating POD risk, the sensitivity and specificity of the delirium screening tool were 94.1% and 72.7%, respectively. Incidence rates of POD were 10.2% in the control group and 6.2% in the intervention group.
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including its design as a retrospective review of medical records rather than a prospective randomized controlled trial. In addition, because it was conducted in just one teaching hospital, they deemed it “not possible to determine the generalizability and long-term effect of our findings.”
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Choi JY et al. BMC Geriatr. 2019 Oct 26. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1303-z.
A new study has found that and a prevention program can help improve staff education and outcomes.
“In an aging society, it is very important to develop and implement a strategy for POD prevention to ensure that aging patients are treated as safely and effectively as possible,” wrote Jung-Yeon Choi of Seoul (South Korea) National University Bundang Hospital and coauthors. The study was published in BMC Geriatrics.
To determine how to better identify and treat high-risk patients for POD after orthopedic surgery, the researchers led a retrospective cohort study that included an intervention group of participants who were aged at least 65 years (n = 275) and a control group from a year prior (n = 274). Patients in the intervention group had their risk of delirium assessed and categorized using a simple screening tool, and those deemed at risk were entered into a multicomponent delirium prevention program.
Of the 275 patients in the intervention group, 144 required screening for delirium. Ninety-nine were classified as low risk, 29 were classified as high risk, and 16 missed the screening. Fifty-three additional patients were classified as high risk because they were aged 80 years or older. During the study, 17 participants experienced POD, 16 of whom were classified as high risk. In regard to estimating POD risk, the sensitivity and specificity of the delirium screening tool were 94.1% and 72.7%, respectively. Incidence rates of POD were 10.2% in the control group and 6.2% in the intervention group.
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including its design as a retrospective review of medical records rather than a prospective randomized controlled trial. In addition, because it was conducted in just one teaching hospital, they deemed it “not possible to determine the generalizability and long-term effect of our findings.”
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Choi JY et al. BMC Geriatr. 2019 Oct 26. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1303-z.
FROM BMC GERIATRICS
Supporting quality improvement strategies
Keys to improve PDSA cycle fidelity
As many hospitalists know, a frequently deployed approach to quality improvement (QI) is the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle method. But it comes with challenges, according to a recent paper in BMJ Quality & Safety.
“There is little evidence on the fidelity of PDSA cycles used by frontline teams, nor how to support and improve the method’s use,” according to the authors. They used document analysis and interviews to review 421 PDSA cycles, tracking fidelity over three annual rounds of projects.
The researchers found that modest, statistically significant improvements in PDSA fidelity occurred, but overall fidelity was low.
“Challenges to achieving greater fidelity reflected problems with understanding the PDSA methodology, intention to use and application in practice,” the authors reported. “These problems were exacerbated by assumptions made in the original QI training and support strategies: that PDSA was easy to understand, that teams would be motivated and willing to use PDSA, and that PDSA is easy to apply.”
The study describes several strategies to help improve PDSA cycle fidelity: different project selection process, redesign of training, increased hands-on support, and investment in training quality improvement support staff. “The findings suggest achieving high PDSA fidelity requires a gradual and negotiated process to explore different perspectives and encourage new ways of working,” the authors concluded.
Reference
1. McNicholas C et al. Evolving quality improvement support strategies to improve Plan-Do-Study–Act cycle fidelity: A retrospective mixed-methods study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019 Mar 18. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2017-007605.
Keys to improve PDSA cycle fidelity
Keys to improve PDSA cycle fidelity
As many hospitalists know, a frequently deployed approach to quality improvement (QI) is the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle method. But it comes with challenges, according to a recent paper in BMJ Quality & Safety.
“There is little evidence on the fidelity of PDSA cycles used by frontline teams, nor how to support and improve the method’s use,” according to the authors. They used document analysis and interviews to review 421 PDSA cycles, tracking fidelity over three annual rounds of projects.
The researchers found that modest, statistically significant improvements in PDSA fidelity occurred, but overall fidelity was low.
“Challenges to achieving greater fidelity reflected problems with understanding the PDSA methodology, intention to use and application in practice,” the authors reported. “These problems were exacerbated by assumptions made in the original QI training and support strategies: that PDSA was easy to understand, that teams would be motivated and willing to use PDSA, and that PDSA is easy to apply.”
The study describes several strategies to help improve PDSA cycle fidelity: different project selection process, redesign of training, increased hands-on support, and investment in training quality improvement support staff. “The findings suggest achieving high PDSA fidelity requires a gradual and negotiated process to explore different perspectives and encourage new ways of working,” the authors concluded.
Reference
1. McNicholas C et al. Evolving quality improvement support strategies to improve Plan-Do-Study–Act cycle fidelity: A retrospective mixed-methods study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019 Mar 18. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2017-007605.
As many hospitalists know, a frequently deployed approach to quality improvement (QI) is the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle method. But it comes with challenges, according to a recent paper in BMJ Quality & Safety.
“There is little evidence on the fidelity of PDSA cycles used by frontline teams, nor how to support and improve the method’s use,” according to the authors. They used document analysis and interviews to review 421 PDSA cycles, tracking fidelity over three annual rounds of projects.
The researchers found that modest, statistically significant improvements in PDSA fidelity occurred, but overall fidelity was low.
“Challenges to achieving greater fidelity reflected problems with understanding the PDSA methodology, intention to use and application in practice,” the authors reported. “These problems were exacerbated by assumptions made in the original QI training and support strategies: that PDSA was easy to understand, that teams would be motivated and willing to use PDSA, and that PDSA is easy to apply.”
The study describes several strategies to help improve PDSA cycle fidelity: different project selection process, redesign of training, increased hands-on support, and investment in training quality improvement support staff. “The findings suggest achieving high PDSA fidelity requires a gradual and negotiated process to explore different perspectives and encourage new ways of working,” the authors concluded.
Reference
1. McNicholas C et al. Evolving quality improvement support strategies to improve Plan-Do-Study–Act cycle fidelity: A retrospective mixed-methods study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019 Mar 18. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2017-007605.
Sequential CRT, immunotherapy nets high PFS in node-positive cervical cancer
Sequential chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and immunotherapy is safe, well tolerated, and efficacious among patients with locally advanced cervical cancer being treated with curative intent, a multicenter phase 1 trial suggests.
Less than 10% of patients treated with this sequence experienced a grade 3 toxicity. Meanwhile, more than 80% were alive and free of disease progression at 1 year.
“Despite standard CRT, most women with lymph node–positive cervical cancer experience disease recurrence,” note the investigators, led by Jyoti S. Mayadev, MD, associate professor in the department of radiation medicine and applied sciences, University of California, San Diego, in La Jolla. “Our study is potentially transformative in the standard treatment schema of locally advanced cervical cancer, with the prospect for immuno-oncology to add durable survival in patients with node-positive disease, a current unmet oncologic need.”
The investigators enrolled in the trial 32 women from Gynecology Oncology Cooperative Group member institutions who had stage IB2 to IVA cervical cancer with positive pelvic and/or para-aortic lymph nodes. Treatment consisted of six weekly doses of cisplatin, 40 mg/m2, concurrent with extended-field, 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, followed by the immune checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy) every 21 days for four cycles.
Results reported in JAMA Oncology showed that all 32 patients completed CRT and 21 patients went on to receive ipilimumab. Among the latter, 86% completed all four planned cycles and the rest completed two cycles.
In the group receiving sequential CRT and ipilimumab, 9.5% experienced grade 3 toxicity (lipase increase in one case and dermatitis in another case). Both toxicities were self-limited.
With a 14.8-month median follow-up, the patients treated with CRT-ipilimumab had a 12-month overall survival rate of 90%, and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 81% (median durations were not reached). Neither human papillomavirus genotype nor HLA subtype was associated with these outcomes.
Translational analyses showed that patients experienced an increase in peripheral blood T cells expressing programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) after CRT that was then sustained with ipilimumab therapy. “[T]he use of an immune checkpoint inhibitor could stimulate the antitumor activity of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells and augment radiation-induced neoantigen load,” the investigators proposed.
“To our knowledge, this phase 1 study is the first to show tolerability with a signal of efficacy of an immune check-point inhibitor ... as a part of the definitive treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer,” they concluded. “Our findings show promise for the use of immunotherapy in the definitive setting of locally advanced, node-positive cervical cancer; patients with this cancer historically have a poor prognosis with standard therapy alone.”
Dr. Mayadev disclosed receiving a grant from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study, personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants from NRG Oncology, and personal fees and nonfinancial support from the Gynecology Oncology Group Foundation outside the submitted work; receiving compensation for serving on the advisory board of Varian Medical Systems in 2018; and being a speaker for Samsung Medical Systems in 2017. The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute and by institutional funds.
SOURCE: Mayadev JS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3857.
Sequential chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and immunotherapy is safe, well tolerated, and efficacious among patients with locally advanced cervical cancer being treated with curative intent, a multicenter phase 1 trial suggests.
Less than 10% of patients treated with this sequence experienced a grade 3 toxicity. Meanwhile, more than 80% were alive and free of disease progression at 1 year.
“Despite standard CRT, most women with lymph node–positive cervical cancer experience disease recurrence,” note the investigators, led by Jyoti S. Mayadev, MD, associate professor in the department of radiation medicine and applied sciences, University of California, San Diego, in La Jolla. “Our study is potentially transformative in the standard treatment schema of locally advanced cervical cancer, with the prospect for immuno-oncology to add durable survival in patients with node-positive disease, a current unmet oncologic need.”
The investigators enrolled in the trial 32 women from Gynecology Oncology Cooperative Group member institutions who had stage IB2 to IVA cervical cancer with positive pelvic and/or para-aortic lymph nodes. Treatment consisted of six weekly doses of cisplatin, 40 mg/m2, concurrent with extended-field, 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, followed by the immune checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy) every 21 days for four cycles.
Results reported in JAMA Oncology showed that all 32 patients completed CRT and 21 patients went on to receive ipilimumab. Among the latter, 86% completed all four planned cycles and the rest completed two cycles.
In the group receiving sequential CRT and ipilimumab, 9.5% experienced grade 3 toxicity (lipase increase in one case and dermatitis in another case). Both toxicities were self-limited.
With a 14.8-month median follow-up, the patients treated with CRT-ipilimumab had a 12-month overall survival rate of 90%, and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 81% (median durations were not reached). Neither human papillomavirus genotype nor HLA subtype was associated with these outcomes.
Translational analyses showed that patients experienced an increase in peripheral blood T cells expressing programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) after CRT that was then sustained with ipilimumab therapy. “[T]he use of an immune checkpoint inhibitor could stimulate the antitumor activity of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells and augment radiation-induced neoantigen load,” the investigators proposed.
“To our knowledge, this phase 1 study is the first to show tolerability with a signal of efficacy of an immune check-point inhibitor ... as a part of the definitive treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer,” they concluded. “Our findings show promise for the use of immunotherapy in the definitive setting of locally advanced, node-positive cervical cancer; patients with this cancer historically have a poor prognosis with standard therapy alone.”
Dr. Mayadev disclosed receiving a grant from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study, personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants from NRG Oncology, and personal fees and nonfinancial support from the Gynecology Oncology Group Foundation outside the submitted work; receiving compensation for serving on the advisory board of Varian Medical Systems in 2018; and being a speaker for Samsung Medical Systems in 2017. The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute and by institutional funds.
SOURCE: Mayadev JS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3857.
Sequential chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and immunotherapy is safe, well tolerated, and efficacious among patients with locally advanced cervical cancer being treated with curative intent, a multicenter phase 1 trial suggests.
Less than 10% of patients treated with this sequence experienced a grade 3 toxicity. Meanwhile, more than 80% were alive and free of disease progression at 1 year.
“Despite standard CRT, most women with lymph node–positive cervical cancer experience disease recurrence,” note the investigators, led by Jyoti S. Mayadev, MD, associate professor in the department of radiation medicine and applied sciences, University of California, San Diego, in La Jolla. “Our study is potentially transformative in the standard treatment schema of locally advanced cervical cancer, with the prospect for immuno-oncology to add durable survival in patients with node-positive disease, a current unmet oncologic need.”
The investigators enrolled in the trial 32 women from Gynecology Oncology Cooperative Group member institutions who had stage IB2 to IVA cervical cancer with positive pelvic and/or para-aortic lymph nodes. Treatment consisted of six weekly doses of cisplatin, 40 mg/m2, concurrent with extended-field, 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, followed by the immune checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy) every 21 days for four cycles.
Results reported in JAMA Oncology showed that all 32 patients completed CRT and 21 patients went on to receive ipilimumab. Among the latter, 86% completed all four planned cycles and the rest completed two cycles.
In the group receiving sequential CRT and ipilimumab, 9.5% experienced grade 3 toxicity (lipase increase in one case and dermatitis in another case). Both toxicities were self-limited.
With a 14.8-month median follow-up, the patients treated with CRT-ipilimumab had a 12-month overall survival rate of 90%, and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 81% (median durations were not reached). Neither human papillomavirus genotype nor HLA subtype was associated with these outcomes.
Translational analyses showed that patients experienced an increase in peripheral blood T cells expressing programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) after CRT that was then sustained with ipilimumab therapy. “[T]he use of an immune checkpoint inhibitor could stimulate the antitumor activity of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells and augment radiation-induced neoantigen load,” the investigators proposed.
“To our knowledge, this phase 1 study is the first to show tolerability with a signal of efficacy of an immune check-point inhibitor ... as a part of the definitive treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer,” they concluded. “Our findings show promise for the use of immunotherapy in the definitive setting of locally advanced, node-positive cervical cancer; patients with this cancer historically have a poor prognosis with standard therapy alone.”
Dr. Mayadev disclosed receiving a grant from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study, personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants from NRG Oncology, and personal fees and nonfinancial support from the Gynecology Oncology Group Foundation outside the submitted work; receiving compensation for serving on the advisory board of Varian Medical Systems in 2018; and being a speaker for Samsung Medical Systems in 2017. The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute and by institutional funds.
SOURCE: Mayadev JS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Nov 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3857.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Large state disparities seen for lung cancer screening
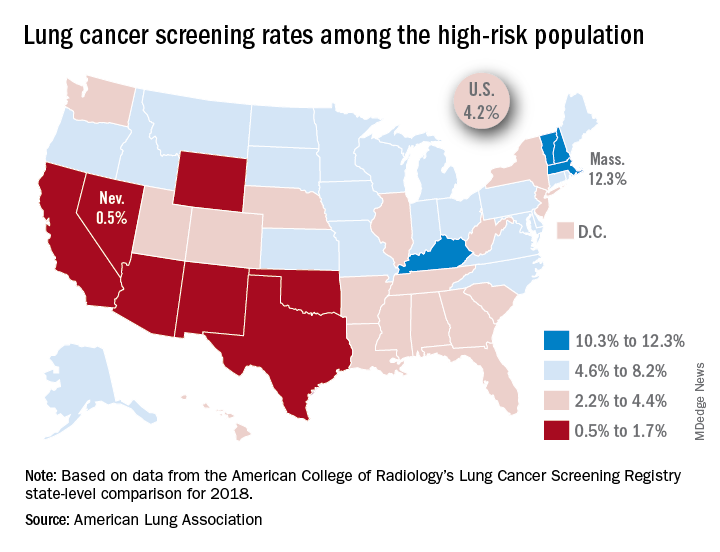
That disparity might suggest that Massachusetts has an exceptionally high rate, but it’s only 12.3%. And that means Nevada’s rate is very low, which it is: Only 0.5% of those at high risk are getting screened with annual low-dose CT scans, the ALA said in its 2019 State of Lung Cancer report.
“[The low rate of screening] may be because of a lack of access or low awareness and knowledge among patients and providers. As rates vary tremendously between states, it is clear that more can be done to increase screening rates,” the ALA stated.
Nationally, the screening rate is 4.2% among those at high risk for lung cancer, but “if everyone currently eligible were screened, close to 48,000 lives could be saved,” the ALA noted in its report.
Six states other than Nevada are below the 2% mark: Arizona, California, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Wyoming. Besides Massachusetts, the three other states above 10% are Kentucky, New Hampshire, and Vermont, according to data from the American College of Radiology’s Lung Cancer Screening Registry state-level comparison for 2018.
For individuals at high risk for lung cancer – those aged 55-80 years who have at least a 30 pack-year history and either still smoke or have quit within 15 years – “screening with annual low-dose CT scans can reduce the lung cancer death rate by up to 20% by detecting tumors at early stages when the cancer is more likely to be curable,” the ALA wrote.

That disparity might suggest that Massachusetts has an exceptionally high rate, but it’s only 12.3%. And that means Nevada’s rate is very low, which it is: Only 0.5% of those at high risk are getting screened with annual low-dose CT scans, the ALA said in its 2019 State of Lung Cancer report.
“[The low rate of screening] may be because of a lack of access or low awareness and knowledge among patients and providers. As rates vary tremendously between states, it is clear that more can be done to increase screening rates,” the ALA stated.
Nationally, the screening rate is 4.2% among those at high risk for lung cancer, but “if everyone currently eligible were screened, close to 48,000 lives could be saved,” the ALA noted in its report.
Six states other than Nevada are below the 2% mark: Arizona, California, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Wyoming. Besides Massachusetts, the three other states above 10% are Kentucky, New Hampshire, and Vermont, according to data from the American College of Radiology’s Lung Cancer Screening Registry state-level comparison for 2018.
For individuals at high risk for lung cancer – those aged 55-80 years who have at least a 30 pack-year history and either still smoke or have quit within 15 years – “screening with annual low-dose CT scans can reduce the lung cancer death rate by up to 20% by detecting tumors at early stages when the cancer is more likely to be curable,” the ALA wrote.

That disparity might suggest that Massachusetts has an exceptionally high rate, but it’s only 12.3%. And that means Nevada’s rate is very low, which it is: Only 0.5% of those at high risk are getting screened with annual low-dose CT scans, the ALA said in its 2019 State of Lung Cancer report.
“[The low rate of screening] may be because of a lack of access or low awareness and knowledge among patients and providers. As rates vary tremendously between states, it is clear that more can be done to increase screening rates,” the ALA stated.
Nationally, the screening rate is 4.2% among those at high risk for lung cancer, but “if everyone currently eligible were screened, close to 48,000 lives could be saved,” the ALA noted in its report.
Six states other than Nevada are below the 2% mark: Arizona, California, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Wyoming. Besides Massachusetts, the three other states above 10% are Kentucky, New Hampshire, and Vermont, according to data from the American College of Radiology’s Lung Cancer Screening Registry state-level comparison for 2018.
For individuals at high risk for lung cancer – those aged 55-80 years who have at least a 30 pack-year history and either still smoke or have quit within 15 years – “screening with annual low-dose CT scans can reduce the lung cancer death rate by up to 20% by detecting tumors at early stages when the cancer is more likely to be curable,” the ALA wrote.
Disposable duodenoscope shows clinical potential
A single-use duodenoscope may reduce the risk of postendoscopic infections while maintaining a high level of user satisfaction, based on a recent multicenter case series study.
At six tertiary referral centers in the United States, seven expert endoscopists performed more than 70 procedures with disposable scopes, ultimately reporting a median satisfaction score of 9 out of 10, according to lead author Venkataraman Muthusamy, MD, of UCLA Health in Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Writing for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the investigators noted that duodenoscope-related infections represent a serious threat to public health, particularly when considered in the context of antibiotic resistance and the high number of endoscopic procedures performed annually.
“Solutions to the duodenoscope contamination problem remain elusive,” the investigators wrote. “Evidence-based interventions are important to guard against labor-intensive measures that are unfeasible, unaffordable, and potentially ineffective.”
According to the investigators, routine culture surveillance and field investigations following suspected duodenoscope-related infections may fail to detect culprit bacteria or shortcomings in equipment reprocessing; and even when performed correctly, standard reprocessing can be insufficient.
“Using current reprocessing techniques, improved compliance with reprocessing guidelines is not a definitive solution because reusable duodenoscope contamination may be present even after high-level disinfection or sterilization,” the investigators wrote, going on to cite Food and Drug Administration–reported contamination rates of 5.4% for high-concern organisms.
To determine if a single-use endoscope could overcome such risks, the investigators first conducted preclinical testing with animal laboratories and simulations, finding that a single-use duodenoscope was comparable with three reusable scope models. The present study, which included 73 patients with normal pancreaticobiliary anatomy, evaluated clinical feasibility, safety, and performance. The single-use duodenoscope was a first-generation device by Boston Scientific named EXALT Model D.
Of the 73 patients, 13 underwent roll-in maneuvers and 60 underwent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The most common cause for ERCP was exchange or removal of biliary stent (55.0%), followed by evaluation of biliary defect or stricture (26.7%), then bile duct stone clearance (18.3%). The majority of ERCPs had an American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) procedural complexity grade of 2 (43.3%) or 3 (43.3%), while a minority were graded 1 (11.7%) or, most severe, 4 (1.7%).
Two ERCPs required crossover to a reusable duodenoscope for completion. In the first instance, crossover was needed because dilation of a biliary stricture was unsuccessful, with the endoscopist reporting difficulties maneuvering the disposable scope, possibly because of shaft stiffness. In the second case, crossover was elected because cannulation was unsuccessful with standard access techniques; however, cannulation also was not possible with the reusable scope, necessitating an alternative approach.
According to the investigators, safety signals were comparable with standard practice. No serious, scope-related adverse events were reported. Serious adverse events of any kind were relatively uncommon; three patients developed post-ERCP pancreatitis within 7 days of ERCP, one developed a postsphincterotomy bleed, and one had worsening of a preexisting infection that required hospitalization.
As described above, the endoscopists reported a median overall satisfaction score of 9 out of 10. Specifically, 17 out of 23 scored ERCP maneuvers (73.9%) received a median 5 out of 5 performance rating. Out of 1,289 total ratings, almost all (98.1%) received a performance rating of at least 3 out of 5. Low-scoring performance characteristics (receiving at least one “1” rating), included elevator function; aspects of positioning; visualization; image quality, brightness, or appearance; and ease and ability of passing ancillary devices through the channel of the single-use duodenoscope and into the papilla.
“The new device provides an alternative to reusable duodenoscopes that may harbor residual contamination despite appropriately implemented reprocessing,” the investigators concluded.
They also pointed out that switching to disposable scopes would not completely put an end to postendoscopic infections.
“The single-use duodenoscope is a timely and innovative option to improve exogenous infection control, and must be used with awareness of the continued risk of endogenous infection, with standard infection control precautions and continued diligence in the use of existing reusable devices,” they wrote.
The study was funded by Boston Scientific. The investigators reported additional relationships with Medtronic, Ethicon/Torax, CapsoVision, and others.
SOURCE: Muthusamy V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.052.
A single-use duodenoscope may reduce the risk of postendoscopic infections while maintaining a high level of user satisfaction, based on a recent multicenter case series study.
At six tertiary referral centers in the United States, seven expert endoscopists performed more than 70 procedures with disposable scopes, ultimately reporting a median satisfaction score of 9 out of 10, according to lead author Venkataraman Muthusamy, MD, of UCLA Health in Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Writing for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the investigators noted that duodenoscope-related infections represent a serious threat to public health, particularly when considered in the context of antibiotic resistance and the high number of endoscopic procedures performed annually.
“Solutions to the duodenoscope contamination problem remain elusive,” the investigators wrote. “Evidence-based interventions are important to guard against labor-intensive measures that are unfeasible, unaffordable, and potentially ineffective.”
According to the investigators, routine culture surveillance and field investigations following suspected duodenoscope-related infections may fail to detect culprit bacteria or shortcomings in equipment reprocessing; and even when performed correctly, standard reprocessing can be insufficient.
“Using current reprocessing techniques, improved compliance with reprocessing guidelines is not a definitive solution because reusable duodenoscope contamination may be present even after high-level disinfection or sterilization,” the investigators wrote, going on to cite Food and Drug Administration–reported contamination rates of 5.4% for high-concern organisms.
To determine if a single-use endoscope could overcome such risks, the investigators first conducted preclinical testing with animal laboratories and simulations, finding that a single-use duodenoscope was comparable with three reusable scope models. The present study, which included 73 patients with normal pancreaticobiliary anatomy, evaluated clinical feasibility, safety, and performance. The single-use duodenoscope was a first-generation device by Boston Scientific named EXALT Model D.
Of the 73 patients, 13 underwent roll-in maneuvers and 60 underwent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The most common cause for ERCP was exchange or removal of biliary stent (55.0%), followed by evaluation of biliary defect or stricture (26.7%), then bile duct stone clearance (18.3%). The majority of ERCPs had an American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) procedural complexity grade of 2 (43.3%) or 3 (43.3%), while a minority were graded 1 (11.7%) or, most severe, 4 (1.7%).
Two ERCPs required crossover to a reusable duodenoscope for completion. In the first instance, crossover was needed because dilation of a biliary stricture was unsuccessful, with the endoscopist reporting difficulties maneuvering the disposable scope, possibly because of shaft stiffness. In the second case, crossover was elected because cannulation was unsuccessful with standard access techniques; however, cannulation also was not possible with the reusable scope, necessitating an alternative approach.
According to the investigators, safety signals were comparable with standard practice. No serious, scope-related adverse events were reported. Serious adverse events of any kind were relatively uncommon; three patients developed post-ERCP pancreatitis within 7 days of ERCP, one developed a postsphincterotomy bleed, and one had worsening of a preexisting infection that required hospitalization.
As described above, the endoscopists reported a median overall satisfaction score of 9 out of 10. Specifically, 17 out of 23 scored ERCP maneuvers (73.9%) received a median 5 out of 5 performance rating. Out of 1,289 total ratings, almost all (98.1%) received a performance rating of at least 3 out of 5. Low-scoring performance characteristics (receiving at least one “1” rating), included elevator function; aspects of positioning; visualization; image quality, brightness, or appearance; and ease and ability of passing ancillary devices through the channel of the single-use duodenoscope and into the papilla.
“The new device provides an alternative to reusable duodenoscopes that may harbor residual contamination despite appropriately implemented reprocessing,” the investigators concluded.
They also pointed out that switching to disposable scopes would not completely put an end to postendoscopic infections.
“The single-use duodenoscope is a timely and innovative option to improve exogenous infection control, and must be used with awareness of the continued risk of endogenous infection, with standard infection control precautions and continued diligence in the use of existing reusable devices,” they wrote.
The study was funded by Boston Scientific. The investigators reported additional relationships with Medtronic, Ethicon/Torax, CapsoVision, and others.
SOURCE: Muthusamy V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.052.
A single-use duodenoscope may reduce the risk of postendoscopic infections while maintaining a high level of user satisfaction, based on a recent multicenter case series study.
At six tertiary referral centers in the United States, seven expert endoscopists performed more than 70 procedures with disposable scopes, ultimately reporting a median satisfaction score of 9 out of 10, according to lead author Venkataraman Muthusamy, MD, of UCLA Health in Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Writing for Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the investigators noted that duodenoscope-related infections represent a serious threat to public health, particularly when considered in the context of antibiotic resistance and the high number of endoscopic procedures performed annually.
“Solutions to the duodenoscope contamination problem remain elusive,” the investigators wrote. “Evidence-based interventions are important to guard against labor-intensive measures that are unfeasible, unaffordable, and potentially ineffective.”
According to the investigators, routine culture surveillance and field investigations following suspected duodenoscope-related infections may fail to detect culprit bacteria or shortcomings in equipment reprocessing; and even when performed correctly, standard reprocessing can be insufficient.
“Using current reprocessing techniques, improved compliance with reprocessing guidelines is not a definitive solution because reusable duodenoscope contamination may be present even after high-level disinfection or sterilization,” the investigators wrote, going on to cite Food and Drug Administration–reported contamination rates of 5.4% for high-concern organisms.
To determine if a single-use endoscope could overcome such risks, the investigators first conducted preclinical testing with animal laboratories and simulations, finding that a single-use duodenoscope was comparable with three reusable scope models. The present study, which included 73 patients with normal pancreaticobiliary anatomy, evaluated clinical feasibility, safety, and performance. The single-use duodenoscope was a first-generation device by Boston Scientific named EXALT Model D.
Of the 73 patients, 13 underwent roll-in maneuvers and 60 underwent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The most common cause for ERCP was exchange or removal of biliary stent (55.0%), followed by evaluation of biliary defect or stricture (26.7%), then bile duct stone clearance (18.3%). The majority of ERCPs had an American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) procedural complexity grade of 2 (43.3%) or 3 (43.3%), while a minority were graded 1 (11.7%) or, most severe, 4 (1.7%).
Two ERCPs required crossover to a reusable duodenoscope for completion. In the first instance, crossover was needed because dilation of a biliary stricture was unsuccessful, with the endoscopist reporting difficulties maneuvering the disposable scope, possibly because of shaft stiffness. In the second case, crossover was elected because cannulation was unsuccessful with standard access techniques; however, cannulation also was not possible with the reusable scope, necessitating an alternative approach.
According to the investigators, safety signals were comparable with standard practice. No serious, scope-related adverse events were reported. Serious adverse events of any kind were relatively uncommon; three patients developed post-ERCP pancreatitis within 7 days of ERCP, one developed a postsphincterotomy bleed, and one had worsening of a preexisting infection that required hospitalization.
As described above, the endoscopists reported a median overall satisfaction score of 9 out of 10. Specifically, 17 out of 23 scored ERCP maneuvers (73.9%) received a median 5 out of 5 performance rating. Out of 1,289 total ratings, almost all (98.1%) received a performance rating of at least 3 out of 5. Low-scoring performance characteristics (receiving at least one “1” rating), included elevator function; aspects of positioning; visualization; image quality, brightness, or appearance; and ease and ability of passing ancillary devices through the channel of the single-use duodenoscope and into the papilla.
“The new device provides an alternative to reusable duodenoscopes that may harbor residual contamination despite appropriately implemented reprocessing,” the investigators concluded.
They also pointed out that switching to disposable scopes would not completely put an end to postendoscopic infections.
“The single-use duodenoscope is a timely and innovative option to improve exogenous infection control, and must be used with awareness of the continued risk of endogenous infection, with standard infection control precautions and continued diligence in the use of existing reusable devices,” they wrote.
The study was funded by Boston Scientific. The investigators reported additional relationships with Medtronic, Ethicon/Torax, CapsoVision, and others.
SOURCE: Muthusamy V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.052.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Icosapent ethyl cost effective in REDUCE-IT analysis
PHILADELPHIA – The overall costs of icosapent ethyl were less than placebo, and the medication reduced cardiovascular events by 30% at a cost that fits well within acceptable quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) parameters, according to a cost-effectiveness analysis of the REDUCE-IT trial.
Days before the presentation of the analysis at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel unanimously recommended approval of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) for a new indication for reducing CV event risk. Icosapent ethyl, a highly purified form of the ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid derived from fish oil, received FDA approval in 2012 for treatment of triglyceride levels of at least 500 mg/dL.
“What we found here is that icosapent ethyl is a dominant strategy,” said William S. Weintraub, MD, director of outcomes research at MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute in Washington, in reporting preliminary cost-analysis findings from REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With Icosapent Ethyl – Intervention Trial). “It’s offering better outcomes at a lower cost.”
The dominant strategy was demonstrated by cost savings in 70% of simulations the cost-effectiveness analysis ran, Dr. Weintraub said.
“These are very impressive results,” said session moderator Seth S. Martin, MD, an internist and cardiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “We don’t often see dominant strategies for new drugs. This is very exciting.”
“Almost never,” Dr. Weintraub responded.
REDUCE-IT randomized 8,179 patients with a diagnosis of CVD or with diabetes and other risk factors who had been on statins and had triglycerides of 135-499 mg/dL to either 4 g of icosapent ethyl daily or placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22). Trial results showed the treatment group had an absolute risk reduction of 4.8% and a relative risk reduction of 25% of first CV events and a 30% relative risk reduction for total events, Dr. Weintraub said.
The analysis determined that the QALYs for icosapent ethyl versus those for placebo were 3.34 and 3.27, respectively, during the trial period and 11.61 and 11.35 over a lifetime. The mean costs for the two treatments were $27,576 and $28,205 during the trial period and $235,352 and $236,636 lifetime, respectively, Dr. Weintraub said.
An analysis of cost effectiveness showed that almost all of the estimates fell below the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $50,000 per QALY gained, Dr. Weintraub said. “In fact, some 70% plus are in what’s called quadrant two; that is, decreased cost and increased efficacy.”
The analysis also calculated the value of icosapent ethyl at three different WTP thresholds: up to $6 a day at a WTP of $50,000, up to $12 a day at $100,000, and up to $18 a day at $150,000. The analysis used the actual net pricing of $4.16 a day, Dr. Weintraub said. “That’s why we showed we have the dominant strategy,” he said.
Further cost-effectiveness analyses of the REDUCE-IT data will focus on subgroups, such as U.S. and non–U.S. patients and people with diabetes. He also emphasized the data he reported were preliminary. “We have a lot more work to do,” Dr. Weintraub said.
Dr. Weintraub reported having financial relationships with Amarin Pharma, which markets Vascepa, and AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Weintraub WS. AHA 2019, Session FS.AOS.F1.
PHILADELPHIA – The overall costs of icosapent ethyl were less than placebo, and the medication reduced cardiovascular events by 30% at a cost that fits well within acceptable quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) parameters, according to a cost-effectiveness analysis of the REDUCE-IT trial.
Days before the presentation of the analysis at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel unanimously recommended approval of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) for a new indication for reducing CV event risk. Icosapent ethyl, a highly purified form of the ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid derived from fish oil, received FDA approval in 2012 for treatment of triglyceride levels of at least 500 mg/dL.
“What we found here is that icosapent ethyl is a dominant strategy,” said William S. Weintraub, MD, director of outcomes research at MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute in Washington, in reporting preliminary cost-analysis findings from REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With Icosapent Ethyl – Intervention Trial). “It’s offering better outcomes at a lower cost.”
The dominant strategy was demonstrated by cost savings in 70% of simulations the cost-effectiveness analysis ran, Dr. Weintraub said.
“These are very impressive results,” said session moderator Seth S. Martin, MD, an internist and cardiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “We don’t often see dominant strategies for new drugs. This is very exciting.”
“Almost never,” Dr. Weintraub responded.
REDUCE-IT randomized 8,179 patients with a diagnosis of CVD or with diabetes and other risk factors who had been on statins and had triglycerides of 135-499 mg/dL to either 4 g of icosapent ethyl daily or placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22). Trial results showed the treatment group had an absolute risk reduction of 4.8% and a relative risk reduction of 25% of first CV events and a 30% relative risk reduction for total events, Dr. Weintraub said.
The analysis determined that the QALYs for icosapent ethyl versus those for placebo were 3.34 and 3.27, respectively, during the trial period and 11.61 and 11.35 over a lifetime. The mean costs for the two treatments were $27,576 and $28,205 during the trial period and $235,352 and $236,636 lifetime, respectively, Dr. Weintraub said.
An analysis of cost effectiveness showed that almost all of the estimates fell below the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $50,000 per QALY gained, Dr. Weintraub said. “In fact, some 70% plus are in what’s called quadrant two; that is, decreased cost and increased efficacy.”
The analysis also calculated the value of icosapent ethyl at three different WTP thresholds: up to $6 a day at a WTP of $50,000, up to $12 a day at $100,000, and up to $18 a day at $150,000. The analysis used the actual net pricing of $4.16 a day, Dr. Weintraub said. “That’s why we showed we have the dominant strategy,” he said.
Further cost-effectiveness analyses of the REDUCE-IT data will focus on subgroups, such as U.S. and non–U.S. patients and people with diabetes. He also emphasized the data he reported were preliminary. “We have a lot more work to do,” Dr. Weintraub said.
Dr. Weintraub reported having financial relationships with Amarin Pharma, which markets Vascepa, and AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Weintraub WS. AHA 2019, Session FS.AOS.F1.
PHILADELPHIA – The overall costs of icosapent ethyl were less than placebo, and the medication reduced cardiovascular events by 30% at a cost that fits well within acceptable quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) parameters, according to a cost-effectiveness analysis of the REDUCE-IT trial.
Days before the presentation of the analysis at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel unanimously recommended approval of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) for a new indication for reducing CV event risk. Icosapent ethyl, a highly purified form of the ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid derived from fish oil, received FDA approval in 2012 for treatment of triglyceride levels of at least 500 mg/dL.
“What we found here is that icosapent ethyl is a dominant strategy,” said William S. Weintraub, MD, director of outcomes research at MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute in Washington, in reporting preliminary cost-analysis findings from REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events With Icosapent Ethyl – Intervention Trial). “It’s offering better outcomes at a lower cost.”
The dominant strategy was demonstrated by cost savings in 70% of simulations the cost-effectiveness analysis ran, Dr. Weintraub said.
“These are very impressive results,” said session moderator Seth S. Martin, MD, an internist and cardiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “We don’t often see dominant strategies for new drugs. This is very exciting.”
“Almost never,” Dr. Weintraub responded.
REDUCE-IT randomized 8,179 patients with a diagnosis of CVD or with diabetes and other risk factors who had been on statins and had triglycerides of 135-499 mg/dL to either 4 g of icosapent ethyl daily or placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22). Trial results showed the treatment group had an absolute risk reduction of 4.8% and a relative risk reduction of 25% of first CV events and a 30% relative risk reduction for total events, Dr. Weintraub said.
The analysis determined that the QALYs for icosapent ethyl versus those for placebo were 3.34 and 3.27, respectively, during the trial period and 11.61 and 11.35 over a lifetime. The mean costs for the two treatments were $27,576 and $28,205 during the trial period and $235,352 and $236,636 lifetime, respectively, Dr. Weintraub said.
An analysis of cost effectiveness showed that almost all of the estimates fell below the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $50,000 per QALY gained, Dr. Weintraub said. “In fact, some 70% plus are in what’s called quadrant two; that is, decreased cost and increased efficacy.”
The analysis also calculated the value of icosapent ethyl at three different WTP thresholds: up to $6 a day at a WTP of $50,000, up to $12 a day at $100,000, and up to $18 a day at $150,000. The analysis used the actual net pricing of $4.16 a day, Dr. Weintraub said. “That’s why we showed we have the dominant strategy,” he said.
Further cost-effectiveness analyses of the REDUCE-IT data will focus on subgroups, such as U.S. and non–U.S. patients and people with diabetes. He also emphasized the data he reported were preliminary. “We have a lot more work to do,” Dr. Weintraub said.
Dr. Weintraub reported having financial relationships with Amarin Pharma, which markets Vascepa, and AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Weintraub WS. AHA 2019, Session FS.AOS.F1.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019







