User login
COVID-19 may cause subacute thyroiditis
Coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) may lead to subacute thyroiditis in some patients, which is suspected to have viral or postviral origin, especially with upper respiratory tract infections, according to a case study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Alessandro Brancatella, a PhD student at the University Hospital Pisa (Italy), and colleagues described the case of an 18-year-old woman who was tested Feb. 21 for SARS-CoV-2 infection after her father was hospitalized because of COVID-19. Her results were positive for the virus, and not long after, she developed mild symptoms. By March 13 and again on March 14, test swabs for SARS-CoV-2 were both negative.
On March 17, she presented with fever, fatigue, palpitations, and neck pain that radiated to her jaw. Testing and physical examination pointed to subacute thyroiditis, and she was soon diagnosed and treated with prednisone. Her neck pain and fever disappeared within 2 days, and the remaining symptoms went away within a week.
The authors noted that the woman’s thyroid had been evaluated before she tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, and at that time, thyroid disease was ruled out. They also pointed out that, although the exact etiology for subacute thyroiditis is unknown, “it is common opinion that the disease is due to a viral infection or to a post-viral inflammatory reaction in genetically predisposed subjects.” They cited examples of viruses with suspected causal associations, including mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, and HIV, and they suggested that, based on the timing of the woman’s subacute thyroiditis and the normal results of her thyroid evaluation before developing COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 be added to that list.
“To our knowledge, this is the first case of [subacute thyroiditis] related to SARS-CoV-2,” they concluded. “We therefore believe that physicians should be alerted about the possibility of this additional clinical manifestation related to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
One author reported funding from the University of Pisa.
SOURCE: Brancatella A et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May 21. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa276.
Coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) may lead to subacute thyroiditis in some patients, which is suspected to have viral or postviral origin, especially with upper respiratory tract infections, according to a case study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Alessandro Brancatella, a PhD student at the University Hospital Pisa (Italy), and colleagues described the case of an 18-year-old woman who was tested Feb. 21 for SARS-CoV-2 infection after her father was hospitalized because of COVID-19. Her results were positive for the virus, and not long after, she developed mild symptoms. By March 13 and again on March 14, test swabs for SARS-CoV-2 were both negative.
On March 17, she presented with fever, fatigue, palpitations, and neck pain that radiated to her jaw. Testing and physical examination pointed to subacute thyroiditis, and she was soon diagnosed and treated with prednisone. Her neck pain and fever disappeared within 2 days, and the remaining symptoms went away within a week.
The authors noted that the woman’s thyroid had been evaluated before she tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, and at that time, thyroid disease was ruled out. They also pointed out that, although the exact etiology for subacute thyroiditis is unknown, “it is common opinion that the disease is due to a viral infection or to a post-viral inflammatory reaction in genetically predisposed subjects.” They cited examples of viruses with suspected causal associations, including mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, and HIV, and they suggested that, based on the timing of the woman’s subacute thyroiditis and the normal results of her thyroid evaluation before developing COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 be added to that list.
“To our knowledge, this is the first case of [subacute thyroiditis] related to SARS-CoV-2,” they concluded. “We therefore believe that physicians should be alerted about the possibility of this additional clinical manifestation related to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
One author reported funding from the University of Pisa.
SOURCE: Brancatella A et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May 21. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa276.
Coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) may lead to subacute thyroiditis in some patients, which is suspected to have viral or postviral origin, especially with upper respiratory tract infections, according to a case study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Alessandro Brancatella, a PhD student at the University Hospital Pisa (Italy), and colleagues described the case of an 18-year-old woman who was tested Feb. 21 for SARS-CoV-2 infection after her father was hospitalized because of COVID-19. Her results were positive for the virus, and not long after, she developed mild symptoms. By March 13 and again on March 14, test swabs for SARS-CoV-2 were both negative.
On March 17, she presented with fever, fatigue, palpitations, and neck pain that radiated to her jaw. Testing and physical examination pointed to subacute thyroiditis, and she was soon diagnosed and treated with prednisone. Her neck pain and fever disappeared within 2 days, and the remaining symptoms went away within a week.
The authors noted that the woman’s thyroid had been evaluated before she tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, and at that time, thyroid disease was ruled out. They also pointed out that, although the exact etiology for subacute thyroiditis is unknown, “it is common opinion that the disease is due to a viral infection or to a post-viral inflammatory reaction in genetically predisposed subjects.” They cited examples of viruses with suspected causal associations, including mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, and HIV, and they suggested that, based on the timing of the woman’s subacute thyroiditis and the normal results of her thyroid evaluation before developing COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 be added to that list.
“To our knowledge, this is the first case of [subacute thyroiditis] related to SARS-CoV-2,” they concluded. “We therefore believe that physicians should be alerted about the possibility of this additional clinical manifestation related to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
One author reported funding from the University of Pisa.
SOURCE: Brancatella A et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May 21. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa276.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM
Before pandemic, gastroenterologist earnings were holding steady
COVID-19 has changed many things in the medical landscape as practices have closed, many physicians are transitioning to telemedicine, and emergency departments struggle to provide safe environments for their employees.
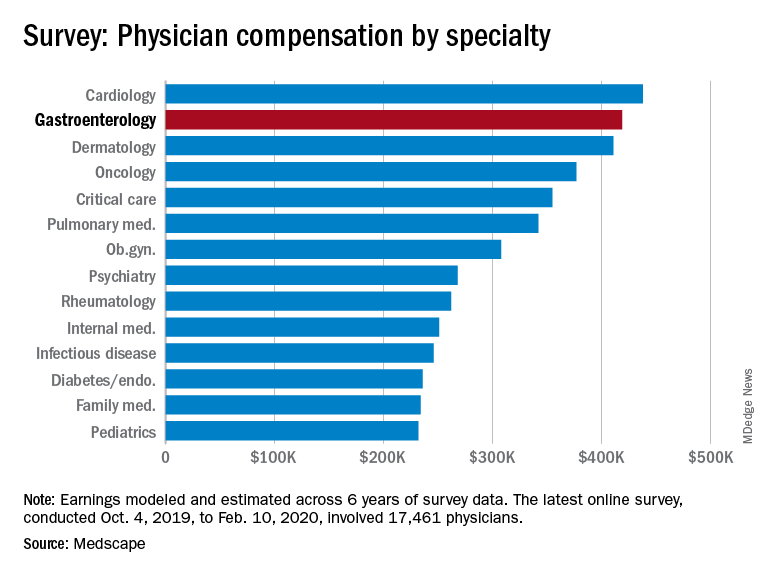
Medscape’s latest physician survey, conducted from Oct. 4, 2019, to Feb. 10, 2020, illustrates what gastroenterology looked like just before the coronavirus arrived.
While the average gastroenterologist salary did rise from 2019, the increase was minimal, going from $417,000 in 2019 to $419,000 in 2020, a 0.48% increase. In comparison, average income for all specialists was $346,000 in this year’s survey, up by 1.5% from the $341,000 earned in 2019, Medscape reported.
Prospects for next year, however, are grim. “We found out that we have a 10% salary decrease effective May 2 to Dec. 25. Our bonus will be based on clinical productivity, and since our numbers are down, that is likely to go away,” a pediatric emergency physician told Medscape.
Many gastroenterologists felt unfairly compensated in 2020, with only 52% reporting that they were satisfied with their salary. This was on the lower end of the 29 specialties included in the survey, which ranged from nephrology at 44% to oncology, emergency medicine, and radiology at 67%.
There was a notable disparity in the number of hours men spent seeing patients in comparison with women – while female GIs worked 38.3 hours a week, male GIs worked 42.5 hours. The average specialist saw patients 38 hours a week. This disparity in hours also translated into a notably higher salary for men: $430,000 versus $375,000. The number of hours gastroenterologists spent on paperwork and administration was roughly middle of the pack at 14.3 hours a week.
In the end, 80% of gastroenterologists said that they would choose to practice medicine again, compared with 77% for all physicians, and 91% said that they would choose gastroenterology again.
The respondents were Medscape members who had been invited to participate. The sample size was 17,461 physicians, and compensation was modeled and estimated based on a range of variables across 6 years of survey data. The sampling error was ±0.74%.
COVID-19 has changed many things in the medical landscape as practices have closed, many physicians are transitioning to telemedicine, and emergency departments struggle to provide safe environments for their employees.

Medscape’s latest physician survey, conducted from Oct. 4, 2019, to Feb. 10, 2020, illustrates what gastroenterology looked like just before the coronavirus arrived.
While the average gastroenterologist salary did rise from 2019, the increase was minimal, going from $417,000 in 2019 to $419,000 in 2020, a 0.48% increase. In comparison, average income for all specialists was $346,000 in this year’s survey, up by 1.5% from the $341,000 earned in 2019, Medscape reported.
Prospects for next year, however, are grim. “We found out that we have a 10% salary decrease effective May 2 to Dec. 25. Our bonus will be based on clinical productivity, and since our numbers are down, that is likely to go away,” a pediatric emergency physician told Medscape.
Many gastroenterologists felt unfairly compensated in 2020, with only 52% reporting that they were satisfied with their salary. This was on the lower end of the 29 specialties included in the survey, which ranged from nephrology at 44% to oncology, emergency medicine, and radiology at 67%.
There was a notable disparity in the number of hours men spent seeing patients in comparison with women – while female GIs worked 38.3 hours a week, male GIs worked 42.5 hours. The average specialist saw patients 38 hours a week. This disparity in hours also translated into a notably higher salary for men: $430,000 versus $375,000. The number of hours gastroenterologists spent on paperwork and administration was roughly middle of the pack at 14.3 hours a week.
In the end, 80% of gastroenterologists said that they would choose to practice medicine again, compared with 77% for all physicians, and 91% said that they would choose gastroenterology again.
The respondents were Medscape members who had been invited to participate. The sample size was 17,461 physicians, and compensation was modeled and estimated based on a range of variables across 6 years of survey data. The sampling error was ±0.74%.
COVID-19 has changed many things in the medical landscape as practices have closed, many physicians are transitioning to telemedicine, and emergency departments struggle to provide safe environments for their employees.

Medscape’s latest physician survey, conducted from Oct. 4, 2019, to Feb. 10, 2020, illustrates what gastroenterology looked like just before the coronavirus arrived.
While the average gastroenterologist salary did rise from 2019, the increase was minimal, going from $417,000 in 2019 to $419,000 in 2020, a 0.48% increase. In comparison, average income for all specialists was $346,000 in this year’s survey, up by 1.5% from the $341,000 earned in 2019, Medscape reported.
Prospects for next year, however, are grim. “We found out that we have a 10% salary decrease effective May 2 to Dec. 25. Our bonus will be based on clinical productivity, and since our numbers are down, that is likely to go away,” a pediatric emergency physician told Medscape.
Many gastroenterologists felt unfairly compensated in 2020, with only 52% reporting that they were satisfied with their salary. This was on the lower end of the 29 specialties included in the survey, which ranged from nephrology at 44% to oncology, emergency medicine, and radiology at 67%.
There was a notable disparity in the number of hours men spent seeing patients in comparison with women – while female GIs worked 38.3 hours a week, male GIs worked 42.5 hours. The average specialist saw patients 38 hours a week. This disparity in hours also translated into a notably higher salary for men: $430,000 versus $375,000. The number of hours gastroenterologists spent on paperwork and administration was roughly middle of the pack at 14.3 hours a week.
In the end, 80% of gastroenterologists said that they would choose to practice medicine again, compared with 77% for all physicians, and 91% said that they would choose gastroenterology again.
The respondents were Medscape members who had been invited to participate. The sample size was 17,461 physicians, and compensation was modeled and estimated based on a range of variables across 6 years of survey data. The sampling error was ±0.74%.
Annual U.S. death toll from drugs, alcohol, suicide tops 150,000
Despite decreases in overall opioid overdose deaths in 2018, deaths involving synthetic opioids, cocaine, and other psychostimulants increased sharply in the United States, and alcohol and suicide deaths also rose, new data show.
A report released May 21 by the Trust for America’s Health (TFAH) and the Well Being Trust shows that 151,964 Americans died from alcohol, drugs, and suicide. Experts warn that these “deaths of despair” may well increase in the wake of COVID-19.
A study released earlier in May estimated that an additional 75,000 Americans could die by suicide, drugs, or alcohol abuse because of the pandemic (Petterson S et al. “Projected Deaths of Despair From COVID-19,” Well Being Trust. May 8, 2020. WellBeingTrust.org).
“These data are a clarion call to action,” TFAH President and CEO John Auerbach said in a news release.
“We know what works to address deaths of despair but progress has been uneven and death rates continue to climb, with communities of color experiencing higher rates of increases in drug-induced and alcohol deaths,” he said.
“And there’s another immediate concern: The COVID-19 crisis has increased the health burdens and economic pressures on many communities of color,” said Mr. Auerbach.
According to the report, the 2018 national rate for alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths combined was only slightly lower than that reported in 2017 (46.4 vs 46.6 per 100,000).
Among the key findings in the report:
- 37,329 Americans died from alcohol-induced causes in 2018; the rate was up 4% over 2017.
- Alcohol-induced deaths were highest among American Indians (30.0 per 100,000) and adults aged 55 to 74 (27.6 per 100,000). For all population groups, rates of alcohol-related deaths were higher in 2018 than in 2017 except for people aged 17 years and younger, for whom the rate held steady.
- Despite a 4% decline in all drug-induced deaths and a 2% drop in all opioid-related deaths, 2018 saw sharp increases in deaths involving synthetic opioids (up 10%), cocaine (up 5%), and other psychostimulants, such as methamphetamine, ecstasy, amphetamine, and prescription stimulants (up 22%).
- Suicide claimed the lives of 48,344 Americans in 2018. The suicide rate in 2018 was 2% higher than in 2017 and 25% higher than in 2008.
- Suicide rates increased across all demographics except for adults aged 18-54 years, among whom the rate remained stable. Suicide death rates were highest in males (23.4 per 100,000), rural residents (19.7 per 100,000), whites (16.8 per 100,000), and American Indian/Alaska Natives (14.1 per 100,000).
- Between 2017 and 2018, 27 states had higher rates (above 0.04%) of alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths; 23 states and the District of Columbia had lower rates of deaths from those causes.
- States with the highest alcohol, drug, and suicide death rates in 2018 were West Virginia (84.9 per 100,000), New Mexico (82.8 per 100,000), New Hampshire (68.2 per 100,000), and Alaska (67.8 per 100,000).
- States with the lowest rates in 2018 were Texas (31.7 per 100,000), Mississippi (31.7 per 100,000), and Hawaii (34.6 per 100,000).
“Quite simply, too many Americans are dying from preventable causes. The profound racial health disparities seen in these data show that many ethnic minority groups are being left behind in our response efforts,” Benjamin F. Miller, PsyD, Well Being Trust chief strategy officer, said in the release.
“The nation needs a comprehensive framework for excellence in mental health and well-being, one that intentionally provides solutions for American Indians, blacks, Asians and Latinos. said Dr. Miller.
Policy recommendations outlined in the report include investing in prevention; reducing risk factors and promoting resilience in children, families, and communities; engaging all sectors of society to address mental health and substance use disorders; limiting access to lethal means of suicide; and promoting safe storage of medications and firearms.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite decreases in overall opioid overdose deaths in 2018, deaths involving synthetic opioids, cocaine, and other psychostimulants increased sharply in the United States, and alcohol and suicide deaths also rose, new data show.
A report released May 21 by the Trust for America’s Health (TFAH) and the Well Being Trust shows that 151,964 Americans died from alcohol, drugs, and suicide. Experts warn that these “deaths of despair” may well increase in the wake of COVID-19.
A study released earlier in May estimated that an additional 75,000 Americans could die by suicide, drugs, or alcohol abuse because of the pandemic (Petterson S et al. “Projected Deaths of Despair From COVID-19,” Well Being Trust. May 8, 2020. WellBeingTrust.org).
“These data are a clarion call to action,” TFAH President and CEO John Auerbach said in a news release.
“We know what works to address deaths of despair but progress has been uneven and death rates continue to climb, with communities of color experiencing higher rates of increases in drug-induced and alcohol deaths,” he said.
“And there’s another immediate concern: The COVID-19 crisis has increased the health burdens and economic pressures on many communities of color,” said Mr. Auerbach.
According to the report, the 2018 national rate for alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths combined was only slightly lower than that reported in 2017 (46.4 vs 46.6 per 100,000).
Among the key findings in the report:
- 37,329 Americans died from alcohol-induced causes in 2018; the rate was up 4% over 2017.
- Alcohol-induced deaths were highest among American Indians (30.0 per 100,000) and adults aged 55 to 74 (27.6 per 100,000). For all population groups, rates of alcohol-related deaths were higher in 2018 than in 2017 except for people aged 17 years and younger, for whom the rate held steady.
- Despite a 4% decline in all drug-induced deaths and a 2% drop in all opioid-related deaths, 2018 saw sharp increases in deaths involving synthetic opioids (up 10%), cocaine (up 5%), and other psychostimulants, such as methamphetamine, ecstasy, amphetamine, and prescription stimulants (up 22%).
- Suicide claimed the lives of 48,344 Americans in 2018. The suicide rate in 2018 was 2% higher than in 2017 and 25% higher than in 2008.
- Suicide rates increased across all demographics except for adults aged 18-54 years, among whom the rate remained stable. Suicide death rates were highest in males (23.4 per 100,000), rural residents (19.7 per 100,000), whites (16.8 per 100,000), and American Indian/Alaska Natives (14.1 per 100,000).
- Between 2017 and 2018, 27 states had higher rates (above 0.04%) of alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths; 23 states and the District of Columbia had lower rates of deaths from those causes.
- States with the highest alcohol, drug, and suicide death rates in 2018 were West Virginia (84.9 per 100,000), New Mexico (82.8 per 100,000), New Hampshire (68.2 per 100,000), and Alaska (67.8 per 100,000).
- States with the lowest rates in 2018 were Texas (31.7 per 100,000), Mississippi (31.7 per 100,000), and Hawaii (34.6 per 100,000).
“Quite simply, too many Americans are dying from preventable causes. The profound racial health disparities seen in these data show that many ethnic minority groups are being left behind in our response efforts,” Benjamin F. Miller, PsyD, Well Being Trust chief strategy officer, said in the release.
“The nation needs a comprehensive framework for excellence in mental health and well-being, one that intentionally provides solutions for American Indians, blacks, Asians and Latinos. said Dr. Miller.
Policy recommendations outlined in the report include investing in prevention; reducing risk factors and promoting resilience in children, families, and communities; engaging all sectors of society to address mental health and substance use disorders; limiting access to lethal means of suicide; and promoting safe storage of medications and firearms.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite decreases in overall opioid overdose deaths in 2018, deaths involving synthetic opioids, cocaine, and other psychostimulants increased sharply in the United States, and alcohol and suicide deaths also rose, new data show.
A report released May 21 by the Trust for America’s Health (TFAH) and the Well Being Trust shows that 151,964 Americans died from alcohol, drugs, and suicide. Experts warn that these “deaths of despair” may well increase in the wake of COVID-19.
A study released earlier in May estimated that an additional 75,000 Americans could die by suicide, drugs, or alcohol abuse because of the pandemic (Petterson S et al. “Projected Deaths of Despair From COVID-19,” Well Being Trust. May 8, 2020. WellBeingTrust.org).
“These data are a clarion call to action,” TFAH President and CEO John Auerbach said in a news release.
“We know what works to address deaths of despair but progress has been uneven and death rates continue to climb, with communities of color experiencing higher rates of increases in drug-induced and alcohol deaths,” he said.
“And there’s another immediate concern: The COVID-19 crisis has increased the health burdens and economic pressures on many communities of color,” said Mr. Auerbach.
According to the report, the 2018 national rate for alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths combined was only slightly lower than that reported in 2017 (46.4 vs 46.6 per 100,000).
Among the key findings in the report:
- 37,329 Americans died from alcohol-induced causes in 2018; the rate was up 4% over 2017.
- Alcohol-induced deaths were highest among American Indians (30.0 per 100,000) and adults aged 55 to 74 (27.6 per 100,000). For all population groups, rates of alcohol-related deaths were higher in 2018 than in 2017 except for people aged 17 years and younger, for whom the rate held steady.
- Despite a 4% decline in all drug-induced deaths and a 2% drop in all opioid-related deaths, 2018 saw sharp increases in deaths involving synthetic opioids (up 10%), cocaine (up 5%), and other psychostimulants, such as methamphetamine, ecstasy, amphetamine, and prescription stimulants (up 22%).
- Suicide claimed the lives of 48,344 Americans in 2018. The suicide rate in 2018 was 2% higher than in 2017 and 25% higher than in 2008.
- Suicide rates increased across all demographics except for adults aged 18-54 years, among whom the rate remained stable. Suicide death rates were highest in males (23.4 per 100,000), rural residents (19.7 per 100,000), whites (16.8 per 100,000), and American Indian/Alaska Natives (14.1 per 100,000).
- Between 2017 and 2018, 27 states had higher rates (above 0.04%) of alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths; 23 states and the District of Columbia had lower rates of deaths from those causes.
- States with the highest alcohol, drug, and suicide death rates in 2018 were West Virginia (84.9 per 100,000), New Mexico (82.8 per 100,000), New Hampshire (68.2 per 100,000), and Alaska (67.8 per 100,000).
- States with the lowest rates in 2018 were Texas (31.7 per 100,000), Mississippi (31.7 per 100,000), and Hawaii (34.6 per 100,000).
“Quite simply, too many Americans are dying from preventable causes. The profound racial health disparities seen in these data show that many ethnic minority groups are being left behind in our response efforts,” Benjamin F. Miller, PsyD, Well Being Trust chief strategy officer, said in the release.
“The nation needs a comprehensive framework for excellence in mental health and well-being, one that intentionally provides solutions for American Indians, blacks, Asians and Latinos. said Dr. Miller.
Policy recommendations outlined in the report include investing in prevention; reducing risk factors and promoting resilience in children, families, and communities; engaging all sectors of society to address mental health and substance use disorders; limiting access to lethal means of suicide; and promoting safe storage of medications and firearms.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel penclomedine shows promise for some AYAs with CNS cancers
according to phase 1/2 clinical trial findings.
The trial included 15 patients, aged 15-39 years, with measurable cancer involving the CNS who were treated with the agent 4-Demethyl-4-cholesteryloxycarbonylpenclomedine (DM-CHOC-PEN).
Two of these patients were “in their 59th month of survival and doing well” as of April, when the data were presented at the AACR virtual meeting I.
One of the patients with long-term survival benefit had non–small cell lung cancer, and one had astrocytoma, Lee Roy Morgan, MD, PhD, chief executive officer of Dekk-Tec Inc., New Orleans, reported during a poster presentation.
Patients with glioblastoma, however, “did not do well,” said Dr. Morgan, an adjunct professor at Tulane University in New Orleans. He noted that none of the five glioblastoma patients experienced a long-term response.
Safety
Study subjects were treated with the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of DM-CHOC-PEN as identified in an earlier study. Patients with liver involvement received 75 mg/m2, and those without liver involvement received up to 98.7 mg/m2. Dosing was by 3-hour intravenous administration once every 21 days as lab tests and subject status allowed.
DM-CHOC-PEN was generally well tolerated. One patient experienced grade 2 vasogenic edema, and another experienced seizures. Both were secondary to tumor swelling, and both resolved with tumor regression.
No grade 3 toxicities occurred at the MTD, and “no renal, hematological, hepatic, or pulmonary toxicities were noted using the MTD in this trial,” Dr. Morgan said.
Mechanism
DM-CHOC-PEN is a polychlorinated pyridine with a cholesteryl carbonate attachment that induces lipophilicity, which potentiates the drug’s penetration of the blood-brain barrier and its entry into the brain and brain cancers, Dr. Morgan explained.
He added that DM-CHOC-PEN is a bis-alkylator that binds to DNA’s cytosine/guanine nucleotides. The agent does not require hepatic activation, it crosses the blood-brain barrier intact, and accumulates in CNS tumors but not normal CNS tissue, he said.
Further, it “is not a substrate for [p-glycoprotein] transport; thus, it doesn’t easily get out of the brain,” Dr. Morgan said. He noted that DM-CHOC-PEN can be used with other agents, such as temozolomide and bis-chloroethylnitrosourea, because of the difference in mechanisms of action.
This study was supported by Louisiana state grants, the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Small Business Innovation Research program. Dr. Morgan reported having no disclosures, but he is chief executive officer of Dekk-Tec Inc., which is developing DM-CHOC-PEN.
SOURCE: Morgan L et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT181.
according to phase 1/2 clinical trial findings.
The trial included 15 patients, aged 15-39 years, with measurable cancer involving the CNS who were treated with the agent 4-Demethyl-4-cholesteryloxycarbonylpenclomedine (DM-CHOC-PEN).
Two of these patients were “in their 59th month of survival and doing well” as of April, when the data were presented at the AACR virtual meeting I.
One of the patients with long-term survival benefit had non–small cell lung cancer, and one had astrocytoma, Lee Roy Morgan, MD, PhD, chief executive officer of Dekk-Tec Inc., New Orleans, reported during a poster presentation.
Patients with glioblastoma, however, “did not do well,” said Dr. Morgan, an adjunct professor at Tulane University in New Orleans. He noted that none of the five glioblastoma patients experienced a long-term response.
Safety
Study subjects were treated with the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of DM-CHOC-PEN as identified in an earlier study. Patients with liver involvement received 75 mg/m2, and those without liver involvement received up to 98.7 mg/m2. Dosing was by 3-hour intravenous administration once every 21 days as lab tests and subject status allowed.
DM-CHOC-PEN was generally well tolerated. One patient experienced grade 2 vasogenic edema, and another experienced seizures. Both were secondary to tumor swelling, and both resolved with tumor regression.
No grade 3 toxicities occurred at the MTD, and “no renal, hematological, hepatic, or pulmonary toxicities were noted using the MTD in this trial,” Dr. Morgan said.
Mechanism
DM-CHOC-PEN is a polychlorinated pyridine with a cholesteryl carbonate attachment that induces lipophilicity, which potentiates the drug’s penetration of the blood-brain barrier and its entry into the brain and brain cancers, Dr. Morgan explained.
He added that DM-CHOC-PEN is a bis-alkylator that binds to DNA’s cytosine/guanine nucleotides. The agent does not require hepatic activation, it crosses the blood-brain barrier intact, and accumulates in CNS tumors but not normal CNS tissue, he said.
Further, it “is not a substrate for [p-glycoprotein] transport; thus, it doesn’t easily get out of the brain,” Dr. Morgan said. He noted that DM-CHOC-PEN can be used with other agents, such as temozolomide and bis-chloroethylnitrosourea, because of the difference in mechanisms of action.
This study was supported by Louisiana state grants, the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Small Business Innovation Research program. Dr. Morgan reported having no disclosures, but he is chief executive officer of Dekk-Tec Inc., which is developing DM-CHOC-PEN.
SOURCE: Morgan L et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT181.
according to phase 1/2 clinical trial findings.
The trial included 15 patients, aged 15-39 years, with measurable cancer involving the CNS who were treated with the agent 4-Demethyl-4-cholesteryloxycarbonylpenclomedine (DM-CHOC-PEN).
Two of these patients were “in their 59th month of survival and doing well” as of April, when the data were presented at the AACR virtual meeting I.
One of the patients with long-term survival benefit had non–small cell lung cancer, and one had astrocytoma, Lee Roy Morgan, MD, PhD, chief executive officer of Dekk-Tec Inc., New Orleans, reported during a poster presentation.
Patients with glioblastoma, however, “did not do well,” said Dr. Morgan, an adjunct professor at Tulane University in New Orleans. He noted that none of the five glioblastoma patients experienced a long-term response.
Safety
Study subjects were treated with the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of DM-CHOC-PEN as identified in an earlier study. Patients with liver involvement received 75 mg/m2, and those without liver involvement received up to 98.7 mg/m2. Dosing was by 3-hour intravenous administration once every 21 days as lab tests and subject status allowed.
DM-CHOC-PEN was generally well tolerated. One patient experienced grade 2 vasogenic edema, and another experienced seizures. Both were secondary to tumor swelling, and both resolved with tumor regression.
No grade 3 toxicities occurred at the MTD, and “no renal, hematological, hepatic, or pulmonary toxicities were noted using the MTD in this trial,” Dr. Morgan said.
Mechanism
DM-CHOC-PEN is a polychlorinated pyridine with a cholesteryl carbonate attachment that induces lipophilicity, which potentiates the drug’s penetration of the blood-brain barrier and its entry into the brain and brain cancers, Dr. Morgan explained.
He added that DM-CHOC-PEN is a bis-alkylator that binds to DNA’s cytosine/guanine nucleotides. The agent does not require hepatic activation, it crosses the blood-brain barrier intact, and accumulates in CNS tumors but not normal CNS tissue, he said.
Further, it “is not a substrate for [p-glycoprotein] transport; thus, it doesn’t easily get out of the brain,” Dr. Morgan said. He noted that DM-CHOC-PEN can be used with other agents, such as temozolomide and bis-chloroethylnitrosourea, because of the difference in mechanisms of action.
This study was supported by Louisiana state grants, the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Small Business Innovation Research program. Dr. Morgan reported having no disclosures, but he is chief executive officer of Dekk-Tec Inc., which is developing DM-CHOC-PEN.
SOURCE: Morgan L et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT181.
FROM AACR 2020
COVID-19 vaccine won’t be a slam dunk
A successful vaccine for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection will probably need to incorporate T-cell epitopes to induce a long-term memory T-cell immune response to the virus, Mehrdad Matloubian, MD, PhD, predicted at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
Vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies may not be sufficient to reliably provide sustained protection against infection. In mouse studies, T-cell immunity has protected against reinfection with the novel coronaviruses. And in some but not all studies of patients infected with the SARS virus, which shares 80% genetic overlap with the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, neutralizing antibodies have waned over time.
“In one study, 20 of 26 patients with SARS had lost their antibody response by 6 years post infection. And they had no B-cell immunity against the SARS antigens. The good news is they did have T-cell memory against SARS virus, and people with more severe disease tended to have more T-cell memory against SARS. All of this has really important implications for vaccine development,” observed Dr. Matloubian, a rheumatologist at the University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Matloubian is among those who are convinced that the ongoing massive global accelerated effort to develop a safe and effective vaccine affords the best opportunity to gain the upper hand in the COVID-19 pandemic. A large array of vaccines are in development.
A key safety concern to watch for in the coming months is whether a vaccine candidate is able to sidestep the issue of antibody-dependent enhancement, whereby prior infection with a non-SARS coronavirus, such as those that cause the common cold, might result in creation of rogue subneutralizing coronavirus antibodies in response to vaccination. There is concern that these nonneutralizing antibodies could facilitate entry of the virus into monocytes and other cells lacking the ACE2 receptor, its usual portal of entry. This in turn could trigger expanded viral replication, a hyperinflammatory response, and viral spread to sites beyond the lung, such as the heart or kidneys.
Little optimism about antivirals’ impact
Dr. Matloubian predicted that antiviral medications, including the much-ballyhooed remdesivir, are unlikely to be a game changer in the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s because most patients who become symptomatic don’t do so until at least 2 days post infection. By that point, their viral load has already peaked and is waning and the B- and T-cell immune responses are starting to gear up.
“Timing seems to be everything when it comes to treatment with antivirals,” he observed. “The virus titer is usually declining by the time people present with severe COVID-19, suggesting that at this time antiviral therapy might be of little use to change the course of the disease, especially if it’s mainly immune-mediated by then. Even with influenza virus, there’s a really short window where Tamiflu [oseltamivir] is effective. It’s going to be the same case for antivirals used for treatment of COVID-19.”
He noted that in a placebo-controlled, randomized trial of remdesivir in 236 Chinese patients with severe COVID-19, intravenous remdesivir wasn’t associated with a significantly shorter time to clinical improvement, although there was a trend in that direction in the subgroup with symptom duration of 10 days or less at initiation of treatment.
A National Institutes of Health press release announcing that remdesivir had a positive impact on duration of hospitalization in a separate randomized trial drew enormous attention from a public desperate for good news. However, the full study has yet to be published, and it’s unclear when during the disease course the antiviral agent was started.
“We need a blockbuster antiviral that’s oral, highly effective, and doesn’t have any side effects to be used in prophylaxis of health care workers and for people who are exposed by family members being infected. And so far there is no such thing, even on the horizon,” according to the rheumatologist.
Fellow panelist Jinoos Yazdany, MD, concurred.
“As we talk to experts around the country, it seems like there isn’t very much optimism about such a blockbuster drug. Most people are actually putting their hope in a vaccine,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
Another research priority is identification of biomarkers in blood or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid to identify early on the subgroup of infected patients who are likely to crash and develop severe disease. That would permit a targeted approach to inhibition of the inflammatory pathways contributing to development of acute respiratory distress syndrome before this full-blown cytokine storm-like syndrome can occur. There is great interest in trying to achieve this by repurposing many biologic agents widely used by rheumatologists, including the interleukin-1 blocker anakinra (Kineret) and the IL-6 blocker tocilizumab (Actemra).
Dr. Matloubian reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his presentation.
A successful vaccine for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection will probably need to incorporate T-cell epitopes to induce a long-term memory T-cell immune response to the virus, Mehrdad Matloubian, MD, PhD, predicted at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
Vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies may not be sufficient to reliably provide sustained protection against infection. In mouse studies, T-cell immunity has protected against reinfection with the novel coronaviruses. And in some but not all studies of patients infected with the SARS virus, which shares 80% genetic overlap with the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, neutralizing antibodies have waned over time.
“In one study, 20 of 26 patients with SARS had lost their antibody response by 6 years post infection. And they had no B-cell immunity against the SARS antigens. The good news is they did have T-cell memory against SARS virus, and people with more severe disease tended to have more T-cell memory against SARS. All of this has really important implications for vaccine development,” observed Dr. Matloubian, a rheumatologist at the University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Matloubian is among those who are convinced that the ongoing massive global accelerated effort to develop a safe and effective vaccine affords the best opportunity to gain the upper hand in the COVID-19 pandemic. A large array of vaccines are in development.
A key safety concern to watch for in the coming months is whether a vaccine candidate is able to sidestep the issue of antibody-dependent enhancement, whereby prior infection with a non-SARS coronavirus, such as those that cause the common cold, might result in creation of rogue subneutralizing coronavirus antibodies in response to vaccination. There is concern that these nonneutralizing antibodies could facilitate entry of the virus into monocytes and other cells lacking the ACE2 receptor, its usual portal of entry. This in turn could trigger expanded viral replication, a hyperinflammatory response, and viral spread to sites beyond the lung, such as the heart or kidneys.
Little optimism about antivirals’ impact
Dr. Matloubian predicted that antiviral medications, including the much-ballyhooed remdesivir, are unlikely to be a game changer in the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s because most patients who become symptomatic don’t do so until at least 2 days post infection. By that point, their viral load has already peaked and is waning and the B- and T-cell immune responses are starting to gear up.
“Timing seems to be everything when it comes to treatment with antivirals,” he observed. “The virus titer is usually declining by the time people present with severe COVID-19, suggesting that at this time antiviral therapy might be of little use to change the course of the disease, especially if it’s mainly immune-mediated by then. Even with influenza virus, there’s a really short window where Tamiflu [oseltamivir] is effective. It’s going to be the same case for antivirals used for treatment of COVID-19.”
He noted that in a placebo-controlled, randomized trial of remdesivir in 236 Chinese patients with severe COVID-19, intravenous remdesivir wasn’t associated with a significantly shorter time to clinical improvement, although there was a trend in that direction in the subgroup with symptom duration of 10 days or less at initiation of treatment.
A National Institutes of Health press release announcing that remdesivir had a positive impact on duration of hospitalization in a separate randomized trial drew enormous attention from a public desperate for good news. However, the full study has yet to be published, and it’s unclear when during the disease course the antiviral agent was started.
“We need a blockbuster antiviral that’s oral, highly effective, and doesn’t have any side effects to be used in prophylaxis of health care workers and for people who are exposed by family members being infected. And so far there is no such thing, even on the horizon,” according to the rheumatologist.
Fellow panelist Jinoos Yazdany, MD, concurred.
“As we talk to experts around the country, it seems like there isn’t very much optimism about such a blockbuster drug. Most people are actually putting their hope in a vaccine,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
Another research priority is identification of biomarkers in blood or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid to identify early on the subgroup of infected patients who are likely to crash and develop severe disease. That would permit a targeted approach to inhibition of the inflammatory pathways contributing to development of acute respiratory distress syndrome before this full-blown cytokine storm-like syndrome can occur. There is great interest in trying to achieve this by repurposing many biologic agents widely used by rheumatologists, including the interleukin-1 blocker anakinra (Kineret) and the IL-6 blocker tocilizumab (Actemra).
Dr. Matloubian reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his presentation.
A successful vaccine for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection will probably need to incorporate T-cell epitopes to induce a long-term memory T-cell immune response to the virus, Mehrdad Matloubian, MD, PhD, predicted at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
Vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies may not be sufficient to reliably provide sustained protection against infection. In mouse studies, T-cell immunity has protected against reinfection with the novel coronaviruses. And in some but not all studies of patients infected with the SARS virus, which shares 80% genetic overlap with the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, neutralizing antibodies have waned over time.
“In one study, 20 of 26 patients with SARS had lost their antibody response by 6 years post infection. And they had no B-cell immunity against the SARS antigens. The good news is they did have T-cell memory against SARS virus, and people with more severe disease tended to have more T-cell memory against SARS. All of this has really important implications for vaccine development,” observed Dr. Matloubian, a rheumatologist at the University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Matloubian is among those who are convinced that the ongoing massive global accelerated effort to develop a safe and effective vaccine affords the best opportunity to gain the upper hand in the COVID-19 pandemic. A large array of vaccines are in development.
A key safety concern to watch for in the coming months is whether a vaccine candidate is able to sidestep the issue of antibody-dependent enhancement, whereby prior infection with a non-SARS coronavirus, such as those that cause the common cold, might result in creation of rogue subneutralizing coronavirus antibodies in response to vaccination. There is concern that these nonneutralizing antibodies could facilitate entry of the virus into monocytes and other cells lacking the ACE2 receptor, its usual portal of entry. This in turn could trigger expanded viral replication, a hyperinflammatory response, and viral spread to sites beyond the lung, such as the heart or kidneys.
Little optimism about antivirals’ impact
Dr. Matloubian predicted that antiviral medications, including the much-ballyhooed remdesivir, are unlikely to be a game changer in the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s because most patients who become symptomatic don’t do so until at least 2 days post infection. By that point, their viral load has already peaked and is waning and the B- and T-cell immune responses are starting to gear up.
“Timing seems to be everything when it comes to treatment with antivirals,” he observed. “The virus titer is usually declining by the time people present with severe COVID-19, suggesting that at this time antiviral therapy might be of little use to change the course of the disease, especially if it’s mainly immune-mediated by then. Even with influenza virus, there’s a really short window where Tamiflu [oseltamivir] is effective. It’s going to be the same case for antivirals used for treatment of COVID-19.”
He noted that in a placebo-controlled, randomized trial of remdesivir in 236 Chinese patients with severe COVID-19, intravenous remdesivir wasn’t associated with a significantly shorter time to clinical improvement, although there was a trend in that direction in the subgroup with symptom duration of 10 days or less at initiation of treatment.
A National Institutes of Health press release announcing that remdesivir had a positive impact on duration of hospitalization in a separate randomized trial drew enormous attention from a public desperate for good news. However, the full study has yet to be published, and it’s unclear when during the disease course the antiviral agent was started.
“We need a blockbuster antiviral that’s oral, highly effective, and doesn’t have any side effects to be used in prophylaxis of health care workers and for people who are exposed by family members being infected. And so far there is no such thing, even on the horizon,” according to the rheumatologist.
Fellow panelist Jinoos Yazdany, MD, concurred.
“As we talk to experts around the country, it seems like there isn’t very much optimism about such a blockbuster drug. Most people are actually putting their hope in a vaccine,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
Another research priority is identification of biomarkers in blood or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid to identify early on the subgroup of infected patients who are likely to crash and develop severe disease. That would permit a targeted approach to inhibition of the inflammatory pathways contributing to development of acute respiratory distress syndrome before this full-blown cytokine storm-like syndrome can occur. There is great interest in trying to achieve this by repurposing many biologic agents widely used by rheumatologists, including the interleukin-1 blocker anakinra (Kineret) and the IL-6 blocker tocilizumab (Actemra).
Dr. Matloubian reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his presentation.
FROM SOTA 2020
AHA offers advice on prehospital acute stroke triage amid COVID-19
A key goal is to ensure timely transfer of patients while minimizing the risk of infectious exposure for EMS personnel, coworkers, and other patients, the writing group says.
“Acute ischemic stroke is still a highly devastating disease and the Time Is Brain paradigm remains true during the COVID-19 pandemic as well,” said writing group chair Mayank Goyal, MD, of the University of Calgary (Alta.)
“We have highly effective and proven treatments available. As such, treatment delays due to additional screening requirements and personal protection equipment (PPE) should be kept at a minimum,” Dr. Goyal said.
“Practicing COVID-19 stroke work flows, through simulation training, can help to reduce treatment delays, minimize the risk of infectious exposure for patients and staff, and help alleviate stress,” he added.
A new layer of complexity
The guidance statement, Prehospital Triage of Acute Stroke Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic, was published online May 13 in the journal Stroke.
“The need to limit infectious spread during the COVID-19 pandemic has added a new layer of complexity to prehospital stroke triage and transfer,” the writing group noted. “Timely and enhanced” communication between EMS, hospitals, and local coordinating authorities are critical, especially ambulance-and facility-based telestroke networks, they wrote.
The main factors to guide the triage decision are the likelihood of a large vessel occlusion; the magnitude of additional delays because of interhospital transfer and work flow efficiency at the primary stroke center or acute stroke ready hospital; the need for advanced critical care resources; and the available bed, staff, and PPE resources at the hospitals.
The group said it “seems reasonable” to lower the threshold to bypass hospitals that can’t provide acute stroke treatment in favor of transporting to a hospital that is “stroke ready,” particularly in patients likely to require advanced care. They cautioned, however, that taking all acute stroke patients to a comprehensive stroke center could overwhelm these centers and lead to clustering of COVID-19 patients.
They said it is equally important to ensure “necessary transfers” of stroke patients who would benefit from endovascular therapy or neurocritical care and avoid unnecessary patient transfers. “Doing so will likely require local hospital boards and health care authorities to collaborate and establish local guidelines and protocols,” the writing group said.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is more important than ever to ensure that stroke patients are taken to the right hospital that can meet their urgent needs at the outset,” Dr. Goyal commented in an AHA news release.
The writing group emphasized that the principles put forth in the document are intended as suggestions rather than strict rules and will be adapted and updated to meet the evolving needs during the COVID-19 crisis and future pandemics.
“The process of improving stroke work flow and getting the correct patient to the correct hospital fast is dependent on training, protocols, simulation, technology, and – probably most importantly – teamwork. These principles are extremely important during the current pandemic but will be useful in improving stroke care afterwards as well,” Dr. Goyal said.
This research had no commercial funding. Members of the writing committee are on several AHA/ASA Council Science Subcommittees, including the Emergency Neurovascular Care, the Telestroke, and the Neurovascular Intervention committees. Goyal is a consultant for Medtronic, Stryker, Microvention, GE Healthcare, and Mentice. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A key goal is to ensure timely transfer of patients while minimizing the risk of infectious exposure for EMS personnel, coworkers, and other patients, the writing group says.
“Acute ischemic stroke is still a highly devastating disease and the Time Is Brain paradigm remains true during the COVID-19 pandemic as well,” said writing group chair Mayank Goyal, MD, of the University of Calgary (Alta.)
“We have highly effective and proven treatments available. As such, treatment delays due to additional screening requirements and personal protection equipment (PPE) should be kept at a minimum,” Dr. Goyal said.
“Practicing COVID-19 stroke work flows, through simulation training, can help to reduce treatment delays, minimize the risk of infectious exposure for patients and staff, and help alleviate stress,” he added.
A new layer of complexity
The guidance statement, Prehospital Triage of Acute Stroke Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic, was published online May 13 in the journal Stroke.
“The need to limit infectious spread during the COVID-19 pandemic has added a new layer of complexity to prehospital stroke triage and transfer,” the writing group noted. “Timely and enhanced” communication between EMS, hospitals, and local coordinating authorities are critical, especially ambulance-and facility-based telestroke networks, they wrote.
The main factors to guide the triage decision are the likelihood of a large vessel occlusion; the magnitude of additional delays because of interhospital transfer and work flow efficiency at the primary stroke center or acute stroke ready hospital; the need for advanced critical care resources; and the available bed, staff, and PPE resources at the hospitals.
The group said it “seems reasonable” to lower the threshold to bypass hospitals that can’t provide acute stroke treatment in favor of transporting to a hospital that is “stroke ready,” particularly in patients likely to require advanced care. They cautioned, however, that taking all acute stroke patients to a comprehensive stroke center could overwhelm these centers and lead to clustering of COVID-19 patients.
They said it is equally important to ensure “necessary transfers” of stroke patients who would benefit from endovascular therapy or neurocritical care and avoid unnecessary patient transfers. “Doing so will likely require local hospital boards and health care authorities to collaborate and establish local guidelines and protocols,” the writing group said.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is more important than ever to ensure that stroke patients are taken to the right hospital that can meet their urgent needs at the outset,” Dr. Goyal commented in an AHA news release.
The writing group emphasized that the principles put forth in the document are intended as suggestions rather than strict rules and will be adapted and updated to meet the evolving needs during the COVID-19 crisis and future pandemics.
“The process of improving stroke work flow and getting the correct patient to the correct hospital fast is dependent on training, protocols, simulation, technology, and – probably most importantly – teamwork. These principles are extremely important during the current pandemic but will be useful in improving stroke care afterwards as well,” Dr. Goyal said.
This research had no commercial funding. Members of the writing committee are on several AHA/ASA Council Science Subcommittees, including the Emergency Neurovascular Care, the Telestroke, and the Neurovascular Intervention committees. Goyal is a consultant for Medtronic, Stryker, Microvention, GE Healthcare, and Mentice. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A key goal is to ensure timely transfer of patients while minimizing the risk of infectious exposure for EMS personnel, coworkers, and other patients, the writing group says.
“Acute ischemic stroke is still a highly devastating disease and the Time Is Brain paradigm remains true during the COVID-19 pandemic as well,” said writing group chair Mayank Goyal, MD, of the University of Calgary (Alta.)
“We have highly effective and proven treatments available. As such, treatment delays due to additional screening requirements and personal protection equipment (PPE) should be kept at a minimum,” Dr. Goyal said.
“Practicing COVID-19 stroke work flows, through simulation training, can help to reduce treatment delays, minimize the risk of infectious exposure for patients and staff, and help alleviate stress,” he added.
A new layer of complexity
The guidance statement, Prehospital Triage of Acute Stroke Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic, was published online May 13 in the journal Stroke.
“The need to limit infectious spread during the COVID-19 pandemic has added a new layer of complexity to prehospital stroke triage and transfer,” the writing group noted. “Timely and enhanced” communication between EMS, hospitals, and local coordinating authorities are critical, especially ambulance-and facility-based telestroke networks, they wrote.
The main factors to guide the triage decision are the likelihood of a large vessel occlusion; the magnitude of additional delays because of interhospital transfer and work flow efficiency at the primary stroke center or acute stroke ready hospital; the need for advanced critical care resources; and the available bed, staff, and PPE resources at the hospitals.
The group said it “seems reasonable” to lower the threshold to bypass hospitals that can’t provide acute stroke treatment in favor of transporting to a hospital that is “stroke ready,” particularly in patients likely to require advanced care. They cautioned, however, that taking all acute stroke patients to a comprehensive stroke center could overwhelm these centers and lead to clustering of COVID-19 patients.
They said it is equally important to ensure “necessary transfers” of stroke patients who would benefit from endovascular therapy or neurocritical care and avoid unnecessary patient transfers. “Doing so will likely require local hospital boards and health care authorities to collaborate and establish local guidelines and protocols,” the writing group said.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is more important than ever to ensure that stroke patients are taken to the right hospital that can meet their urgent needs at the outset,” Dr. Goyal commented in an AHA news release.
The writing group emphasized that the principles put forth in the document are intended as suggestions rather than strict rules and will be adapted and updated to meet the evolving needs during the COVID-19 crisis and future pandemics.
“The process of improving stroke work flow and getting the correct patient to the correct hospital fast is dependent on training, protocols, simulation, technology, and – probably most importantly – teamwork. These principles are extremely important during the current pandemic but will be useful in improving stroke care afterwards as well,” Dr. Goyal said.
This research had no commercial funding. Members of the writing committee are on several AHA/ASA Council Science Subcommittees, including the Emergency Neurovascular Care, the Telestroke, and the Neurovascular Intervention committees. Goyal is a consultant for Medtronic, Stryker, Microvention, GE Healthcare, and Mentice. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccination regimen effective in preventing pneumonia in MM patients
Patients with hematological malignancies are at high risk of invasive Staphylococcus pneumoniae. Multiple myeloma (MM) patients, in particular, have been found to have one of the highest incidences of invasive pneumococcal disease. However, researchers found that a full three-dose vaccination regimen by 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine was protective in MM patients when provided between treatment courses, according to a study reported in Vaccine.
The researchers performed a prospective study of 18 adult patients who were vaccinated with PCV13, compared with 18 control-matched patients from 2017 to 2020. The three-dose vaccination regimen was provided between treatment courses with novel target agents (bortezomib, lenalidomide, ixazomib) with a minimum of a 1-month interval. They used the incidence of pneumonias during the one-year observation period as the primary outcome.
Totally there were 12 cases (33.3%) of clinically and radiologically confirmed pneumonias in the entire study group (n = 36), with a distribution between the vaccinated and nonvaccinated groups of 3 (16.7%) and 9 (50%). respectively (P = .037).
The absolute risk reduction seen with vaccination was 33.3%, and the number needed to treat with PCV13 vaccination in MM patients receiving novel agents was 3.0; (95% confidence interval 1.61-22.1). In addition, there were no adverse effects seen from vaccination, according to the authors.
“Despite the expected decrease in immunological response to vaccination during the chemotherapy, we have shown the clinical effectiveness of a PCV13 vaccination schedule based on 3 doses given with a minimum 1 month interval between the courses of novel agents,” the investigators concluded.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Stoma I et al. Vaccine. 2020 May 14; doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.024.
Patients with hematological malignancies are at high risk of invasive Staphylococcus pneumoniae. Multiple myeloma (MM) patients, in particular, have been found to have one of the highest incidences of invasive pneumococcal disease. However, researchers found that a full three-dose vaccination regimen by 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine was protective in MM patients when provided between treatment courses, according to a study reported in Vaccine.
The researchers performed a prospective study of 18 adult patients who were vaccinated with PCV13, compared with 18 control-matched patients from 2017 to 2020. The three-dose vaccination regimen was provided between treatment courses with novel target agents (bortezomib, lenalidomide, ixazomib) with a minimum of a 1-month interval. They used the incidence of pneumonias during the one-year observation period as the primary outcome.
Totally there were 12 cases (33.3%) of clinically and radiologically confirmed pneumonias in the entire study group (n = 36), with a distribution between the vaccinated and nonvaccinated groups of 3 (16.7%) and 9 (50%). respectively (P = .037).
The absolute risk reduction seen with vaccination was 33.3%, and the number needed to treat with PCV13 vaccination in MM patients receiving novel agents was 3.0; (95% confidence interval 1.61-22.1). In addition, there were no adverse effects seen from vaccination, according to the authors.
“Despite the expected decrease in immunological response to vaccination during the chemotherapy, we have shown the clinical effectiveness of a PCV13 vaccination schedule based on 3 doses given with a minimum 1 month interval between the courses of novel agents,” the investigators concluded.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Stoma I et al. Vaccine. 2020 May 14; doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.024.
Patients with hematological malignancies are at high risk of invasive Staphylococcus pneumoniae. Multiple myeloma (MM) patients, in particular, have been found to have one of the highest incidences of invasive pneumococcal disease. However, researchers found that a full three-dose vaccination regimen by 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine was protective in MM patients when provided between treatment courses, according to a study reported in Vaccine.
The researchers performed a prospective study of 18 adult patients who were vaccinated with PCV13, compared with 18 control-matched patients from 2017 to 2020. The three-dose vaccination regimen was provided between treatment courses with novel target agents (bortezomib, lenalidomide, ixazomib) with a minimum of a 1-month interval. They used the incidence of pneumonias during the one-year observation period as the primary outcome.
Totally there were 12 cases (33.3%) of clinically and radiologically confirmed pneumonias in the entire study group (n = 36), with a distribution between the vaccinated and nonvaccinated groups of 3 (16.7%) and 9 (50%). respectively (P = .037).
The absolute risk reduction seen with vaccination was 33.3%, and the number needed to treat with PCV13 vaccination in MM patients receiving novel agents was 3.0; (95% confidence interval 1.61-22.1). In addition, there were no adverse effects seen from vaccination, according to the authors.
“Despite the expected decrease in immunological response to vaccination during the chemotherapy, we have shown the clinical effectiveness of a PCV13 vaccination schedule based on 3 doses given with a minimum 1 month interval between the courses of novel agents,” the investigators concluded.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Stoma I et al. Vaccine. 2020 May 14; doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.024.
FROM VACCINE
FDA approves olaparib for certain metastatic prostate cancers
The Food and Drug Administration approved olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca) for deleterious or suspected deleterious germline or somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
The drug is limited to use in men who have progressed following prior treatment with enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Olaparib becomes the second PARP inhibitor approved by the FDA for use in prostate cancer this week. Earlier, rucaparib (Rubraca, Clovis Oncology) was approved for use in patients with mCRPC that harbor deleterious BRCA mutations (germline and/or somatic).
Olaparib is also indicated for use in ovarian, breast, and pancreatic cancers.
The FDA also approved two companion diagnostic devices for treatment with olaparib: the FoundationOne CDx test (Foundation Medicine) for the selection of patients carrying HRR gene alterations and the BRACAnalysis CDx test (Myriad Genetic Laboratories) for the selection of patients carrying germline BRCA1/2 alterations.
The approval was based on results from the open-label, multicenter PROfound trial, which randomly assigned 387 patients to olaparib 300 mg twice daily and to investigator’s choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone acetate. All patients received a GnRH analogue or had prior bilateral orchiectomy.
The study involved two cohorts. Patients with mutations in either BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM were randomly assigned in cohort A (n = 245); patients with mutations among 12 other genes involved in the HRR pathway were randomly assigned in cohort B (n = 142); those with co-mutations were assigned to cohort A.
The major efficacy outcome of the trial was radiological progression-free survival (rPFS) (cohort A).
In cohort A, patients receiving olaparib had a median rPFS of 7.4 months vs 3.6 months among patients receiving investigator’s choice (hazard ratio [HR], 0.34; P < .0001). Median overall survival was 19.1 months vs 14.7 months (HR, 0.69; P = .0175) and the overall response rate was 33% vs 2% (P < .0001).
In cohort A+B, patients receiving olaparib had a median rPFS of 5.8 months vs 3.5 months among patients receiving investigator’s choice (HR, 0.49; P < .0001).
The study results were first presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology. At that time, study investigator Maha Hussain, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, said the rPFS result and other outcomes were a “remarkable achievement” in such heavily pretreated patients with prostate cancer.
Patients with prostate cancer should now undergo genetic testing of tumor tissue to identify the roughly 30% of patients who can benefit – as is already routinely being done for breast, ovarian, and lung cancer, said experts at ESMO.
The most common adverse reactions with olaparib (≥10% of patients) were anemia, nausea, fatigue (including asthenia), decreased appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, thrombocytopenia, cough, and dyspnea. Venous thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism, occurred in 7% of patients randomly assigned to olaparib, compared with 3.1% of those receiving investigator’s choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Olaparib carries the warning that myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia (MDS/AML) occurred in <1.5% of patients exposed to it as a monotherapy, and that the majority of events had a fatal outcome.
The recommended olaparib dose is 300 mg taken orally twice daily, with or without food.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration approved olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca) for deleterious or suspected deleterious germline or somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
The drug is limited to use in men who have progressed following prior treatment with enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Olaparib becomes the second PARP inhibitor approved by the FDA for use in prostate cancer this week. Earlier, rucaparib (Rubraca, Clovis Oncology) was approved for use in patients with mCRPC that harbor deleterious BRCA mutations (germline and/or somatic).
Olaparib is also indicated for use in ovarian, breast, and pancreatic cancers.
The FDA also approved two companion diagnostic devices for treatment with olaparib: the FoundationOne CDx test (Foundation Medicine) for the selection of patients carrying HRR gene alterations and the BRACAnalysis CDx test (Myriad Genetic Laboratories) for the selection of patients carrying germline BRCA1/2 alterations.
The approval was based on results from the open-label, multicenter PROfound trial, which randomly assigned 387 patients to olaparib 300 mg twice daily and to investigator’s choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone acetate. All patients received a GnRH analogue or had prior bilateral orchiectomy.
The study involved two cohorts. Patients with mutations in either BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM were randomly assigned in cohort A (n = 245); patients with mutations among 12 other genes involved in the HRR pathway were randomly assigned in cohort B (n = 142); those with co-mutations were assigned to cohort A.
The major efficacy outcome of the trial was radiological progression-free survival (rPFS) (cohort A).
In cohort A, patients receiving olaparib had a median rPFS of 7.4 months vs 3.6 months among patients receiving investigator’s choice (hazard ratio [HR], 0.34; P < .0001). Median overall survival was 19.1 months vs 14.7 months (HR, 0.69; P = .0175) and the overall response rate was 33% vs 2% (P < .0001).
In cohort A+B, patients receiving olaparib had a median rPFS of 5.8 months vs 3.5 months among patients receiving investigator’s choice (HR, 0.49; P < .0001).
The study results were first presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology. At that time, study investigator Maha Hussain, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, said the rPFS result and other outcomes were a “remarkable achievement” in such heavily pretreated patients with prostate cancer.
Patients with prostate cancer should now undergo genetic testing of tumor tissue to identify the roughly 30% of patients who can benefit – as is already routinely being done for breast, ovarian, and lung cancer, said experts at ESMO.
The most common adverse reactions with olaparib (≥10% of patients) were anemia, nausea, fatigue (including asthenia), decreased appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, thrombocytopenia, cough, and dyspnea. Venous thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism, occurred in 7% of patients randomly assigned to olaparib, compared with 3.1% of those receiving investigator’s choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Olaparib carries the warning that myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia (MDS/AML) occurred in <1.5% of patients exposed to it as a monotherapy, and that the majority of events had a fatal outcome.
The recommended olaparib dose is 300 mg taken orally twice daily, with or without food.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration approved olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca) for deleterious or suspected deleterious germline or somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
The drug is limited to use in men who have progressed following prior treatment with enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Olaparib becomes the second PARP inhibitor approved by the FDA for use in prostate cancer this week. Earlier, rucaparib (Rubraca, Clovis Oncology) was approved for use in patients with mCRPC that harbor deleterious BRCA mutations (germline and/or somatic).
Olaparib is also indicated for use in ovarian, breast, and pancreatic cancers.
The FDA also approved two companion diagnostic devices for treatment with olaparib: the FoundationOne CDx test (Foundation Medicine) for the selection of patients carrying HRR gene alterations and the BRACAnalysis CDx test (Myriad Genetic Laboratories) for the selection of patients carrying germline BRCA1/2 alterations.
The approval was based on results from the open-label, multicenter PROfound trial, which randomly assigned 387 patients to olaparib 300 mg twice daily and to investigator’s choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone acetate. All patients received a GnRH analogue or had prior bilateral orchiectomy.
The study involved two cohorts. Patients with mutations in either BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM were randomly assigned in cohort A (n = 245); patients with mutations among 12 other genes involved in the HRR pathway were randomly assigned in cohort B (n = 142); those with co-mutations were assigned to cohort A.
The major efficacy outcome of the trial was radiological progression-free survival (rPFS) (cohort A).
In cohort A, patients receiving olaparib had a median rPFS of 7.4 months vs 3.6 months among patients receiving investigator’s choice (hazard ratio [HR], 0.34; P < .0001). Median overall survival was 19.1 months vs 14.7 months (HR, 0.69; P = .0175) and the overall response rate was 33% vs 2% (P < .0001).
In cohort A+B, patients receiving olaparib had a median rPFS of 5.8 months vs 3.5 months among patients receiving investigator’s choice (HR, 0.49; P < .0001).
The study results were first presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology. At that time, study investigator Maha Hussain, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, said the rPFS result and other outcomes were a “remarkable achievement” in such heavily pretreated patients with prostate cancer.
Patients with prostate cancer should now undergo genetic testing of tumor tissue to identify the roughly 30% of patients who can benefit – as is already routinely being done for breast, ovarian, and lung cancer, said experts at ESMO.
The most common adverse reactions with olaparib (≥10% of patients) were anemia, nausea, fatigue (including asthenia), decreased appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, thrombocytopenia, cough, and dyspnea. Venous thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism, occurred in 7% of patients randomly assigned to olaparib, compared with 3.1% of those receiving investigator’s choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Olaparib carries the warning that myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia (MDS/AML) occurred in <1.5% of patients exposed to it as a monotherapy, and that the majority of events had a fatal outcome.
The recommended olaparib dose is 300 mg taken orally twice daily, with or without food.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Delirium first, depression, anxiety, insomnia later?
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists’ income and satisfaction are up
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.
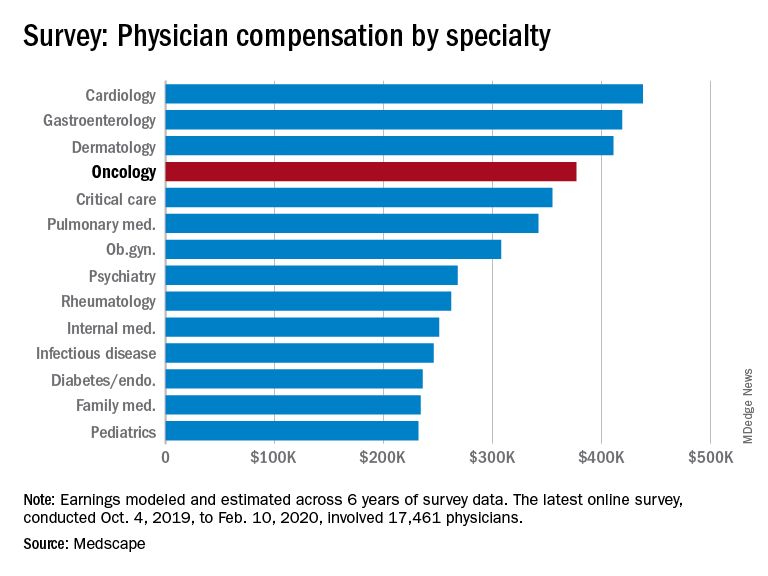
At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.

At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.

At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.