User login
Multiple myeloma treatment produces a similar survival benefit in very elderly patients
More than a third of patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma (MM) are over the age of 80, and yet most treatment successes have been reported in younger patients. However, patients over the age of 80 years received similar benefits as younger patients from MM treatment, according to a study reported online in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
Researchers identified 2,155 patients diagnosed with MM at age 80 years or older in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER)–Medicare database from 2007 to 2013. A cohort of 2,933 similar patients diagnosed with myeloma at age 70-79 was used for comparison.
The researcher found that the number of patients receiving treatment for myeloma within 6 months of diagnosis was significantly lower in the 80 years and older group, compared with the 70-79 years group. Only 51% of patients in the 80 years and older cohort received systemic treatment within 6 months following diagnosis, compared with 71% of patients in the 70-79 years cohort received systemic treatment in the same timeframe (P < .001)
The analysis showed that treatment was associated with an overall 26% decrease in hazard for death, independent of age, race, gender, poverty, comorbidities, and proxy measures of performance status. There was no statistically significant difference in treatment benefit based on age cohort (P = .610).
The median overall survival for patients diagnosed at age 80 years or older was 13.4 months, with those patients receiving systemic treatment having a median overall survival of 21.4 months, compared with 6.4 months for those not receiving treatment. In comparison, patients between ages 70 and 79 years had a median overall survival of 30.1 months with treatment.
The population over 80, when myeloma incidence peaks, is projected to triple over the next few decades, according to the researchers. “Antimyeloma treatment in the era of novel therapies seems to have a similar improvement on survival for the oldest-old, those beyond 80 years, as other patients. With growing knowledge of and experience with novel agents in older patients with myeloma, treatment rates have increased, which have in turn improved survival,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. One author reported research funding from Janssen. The other authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fiala MA et al. J Geriatric Oncol. 2020 Mar 10. doi.org/10.1016/j.jgo.2020.03.005.
More than a third of patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma (MM) are over the age of 80, and yet most treatment successes have been reported in younger patients. However, patients over the age of 80 years received similar benefits as younger patients from MM treatment, according to a study reported online in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
Researchers identified 2,155 patients diagnosed with MM at age 80 years or older in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER)–Medicare database from 2007 to 2013. A cohort of 2,933 similar patients diagnosed with myeloma at age 70-79 was used for comparison.
The researcher found that the number of patients receiving treatment for myeloma within 6 months of diagnosis was significantly lower in the 80 years and older group, compared with the 70-79 years group. Only 51% of patients in the 80 years and older cohort received systemic treatment within 6 months following diagnosis, compared with 71% of patients in the 70-79 years cohort received systemic treatment in the same timeframe (P < .001)
The analysis showed that treatment was associated with an overall 26% decrease in hazard for death, independent of age, race, gender, poverty, comorbidities, and proxy measures of performance status. There was no statistically significant difference in treatment benefit based on age cohort (P = .610).
The median overall survival for patients diagnosed at age 80 years or older was 13.4 months, with those patients receiving systemic treatment having a median overall survival of 21.4 months, compared with 6.4 months for those not receiving treatment. In comparison, patients between ages 70 and 79 years had a median overall survival of 30.1 months with treatment.
The population over 80, when myeloma incidence peaks, is projected to triple over the next few decades, according to the researchers. “Antimyeloma treatment in the era of novel therapies seems to have a similar improvement on survival for the oldest-old, those beyond 80 years, as other patients. With growing knowledge of and experience with novel agents in older patients with myeloma, treatment rates have increased, which have in turn improved survival,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. One author reported research funding from Janssen. The other authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fiala MA et al. J Geriatric Oncol. 2020 Mar 10. doi.org/10.1016/j.jgo.2020.03.005.
More than a third of patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma (MM) are over the age of 80, and yet most treatment successes have been reported in younger patients. However, patients over the age of 80 years received similar benefits as younger patients from MM treatment, according to a study reported online in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
Researchers identified 2,155 patients diagnosed with MM at age 80 years or older in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER)–Medicare database from 2007 to 2013. A cohort of 2,933 similar patients diagnosed with myeloma at age 70-79 was used for comparison.
The researcher found that the number of patients receiving treatment for myeloma within 6 months of diagnosis was significantly lower in the 80 years and older group, compared with the 70-79 years group. Only 51% of patients in the 80 years and older cohort received systemic treatment within 6 months following diagnosis, compared with 71% of patients in the 70-79 years cohort received systemic treatment in the same timeframe (P < .001)
The analysis showed that treatment was associated with an overall 26% decrease in hazard for death, independent of age, race, gender, poverty, comorbidities, and proxy measures of performance status. There was no statistically significant difference in treatment benefit based on age cohort (P = .610).
The median overall survival for patients diagnosed at age 80 years or older was 13.4 months, with those patients receiving systemic treatment having a median overall survival of 21.4 months, compared with 6.4 months for those not receiving treatment. In comparison, patients between ages 70 and 79 years had a median overall survival of 30.1 months with treatment.
The population over 80, when myeloma incidence peaks, is projected to triple over the next few decades, according to the researchers. “Antimyeloma treatment in the era of novel therapies seems to have a similar improvement on survival for the oldest-old, those beyond 80 years, as other patients. With growing knowledge of and experience with novel agents in older patients with myeloma, treatment rates have increased, which have in turn improved survival,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. One author reported research funding from Janssen. The other authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fiala MA et al. J Geriatric Oncol. 2020 Mar 10. doi.org/10.1016/j.jgo.2020.03.005.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC ONCOLOGY
Lessons from Seattle: Prepping a critical care system for COVID-19
What can the nation’s critical care systems do to prepare for the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Mark Tonelli, MD, is professor of medicine and section head of the University of Washington Medical Center’s division of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. In an audio interview, Dr. Tonelli outlines exactly how the University of Washington and the region’s other health systems are readying their critical care departments for the demands of the COVID-19 pandemic. And he offers advice from the front lines for health systems nationwide as they prep their own critical care systems.
To listen to the interview, click the play button below.
What can the nation’s critical care systems do to prepare for the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Mark Tonelli, MD, is professor of medicine and section head of the University of Washington Medical Center’s division of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. In an audio interview, Dr. Tonelli outlines exactly how the University of Washington and the region’s other health systems are readying their critical care departments for the demands of the COVID-19 pandemic. And he offers advice from the front lines for health systems nationwide as they prep their own critical care systems.
To listen to the interview, click the play button below.
What can the nation’s critical care systems do to prepare for the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Mark Tonelli, MD, is professor of medicine and section head of the University of Washington Medical Center’s division of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. In an audio interview, Dr. Tonelli outlines exactly how the University of Washington and the region’s other health systems are readying their critical care departments for the demands of the COVID-19 pandemic. And he offers advice from the front lines for health systems nationwide as they prep their own critical care systems.
To listen to the interview, click the play button below.
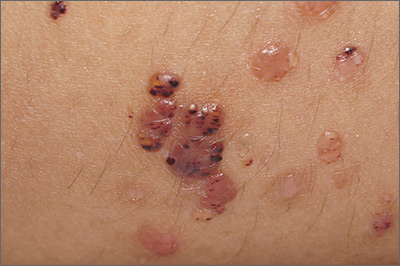
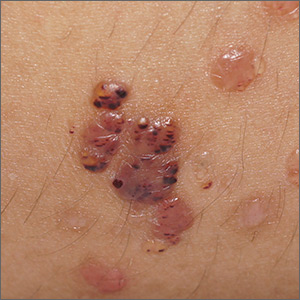
Vesicles on the thigh
On very close inspection, the physician noted translucent chambers within each vesicle, and within each chamber there was a horizontal line (parallel to the floor) separating serum-colored fluid from dark blood. This unique appearance prompted the physician to diagnose lymphangioma circumscriptum in this patient.
Lymphangioma circumscriptum is a rare type of microcytic lymphatic malformation most commonly found on the shoulders, limbs, axilla, and tongue that may enlarge during puberty. The clustered vesicles are firm. Vesicles can be red, brown, or straw colored in appearance and are focal to widespread; rarely, they may bleed or become infected. Their appearance has been compared to frog spawn.
Lymphangioma circumscriptum is benign and requires no treatment. Any suspected infection could be treated with antibiotics. If removal is desired for cosmesis or functional treatment, areas may be treated with dermabrasion, sclerotherapy, laser ablation, or excision if feasible. Lymphangioma circumscriptum tends to recur in time and appropriate anticipatory guidance is key.
This patient was treated with sclerotherapy using hypertonic saline that was injected monthly for 3 months. The physician injected a 30-g needle into the broadest ectatic chambers after each area was anesthetized with lidocaine. The patient tolerated the injections well, and the treated areas resolved as slightly hypopigmented macules. No recurrence was noted at posttreatment follow-up 1 year later.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444.
On very close inspection, the physician noted translucent chambers within each vesicle, and within each chamber there was a horizontal line (parallel to the floor) separating serum-colored fluid from dark blood. This unique appearance prompted the physician to diagnose lymphangioma circumscriptum in this patient.
Lymphangioma circumscriptum is a rare type of microcytic lymphatic malformation most commonly found on the shoulders, limbs, axilla, and tongue that may enlarge during puberty. The clustered vesicles are firm. Vesicles can be red, brown, or straw colored in appearance and are focal to widespread; rarely, they may bleed or become infected. Their appearance has been compared to frog spawn.
Lymphangioma circumscriptum is benign and requires no treatment. Any suspected infection could be treated with antibiotics. If removal is desired for cosmesis or functional treatment, areas may be treated with dermabrasion, sclerotherapy, laser ablation, or excision if feasible. Lymphangioma circumscriptum tends to recur in time and appropriate anticipatory guidance is key.
This patient was treated with sclerotherapy using hypertonic saline that was injected monthly for 3 months. The physician injected a 30-g needle into the broadest ectatic chambers after each area was anesthetized with lidocaine. The patient tolerated the injections well, and the treated areas resolved as slightly hypopigmented macules. No recurrence was noted at posttreatment follow-up 1 year later.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
On very close inspection, the physician noted translucent chambers within each vesicle, and within each chamber there was a horizontal line (parallel to the floor) separating serum-colored fluid from dark blood. This unique appearance prompted the physician to diagnose lymphangioma circumscriptum in this patient.
Lymphangioma circumscriptum is a rare type of microcytic lymphatic malformation most commonly found on the shoulders, limbs, axilla, and tongue that may enlarge during puberty. The clustered vesicles are firm. Vesicles can be red, brown, or straw colored in appearance and are focal to widespread; rarely, they may bleed or become infected. Their appearance has been compared to frog spawn.
Lymphangioma circumscriptum is benign and requires no treatment. Any suspected infection could be treated with antibiotics. If removal is desired for cosmesis or functional treatment, areas may be treated with dermabrasion, sclerotherapy, laser ablation, or excision if feasible. Lymphangioma circumscriptum tends to recur in time and appropriate anticipatory guidance is key.
This patient was treated with sclerotherapy using hypertonic saline that was injected monthly for 3 months. The physician injected a 30-g needle into the broadest ectatic chambers after each area was anesthetized with lidocaine. The patient tolerated the injections well, and the treated areas resolved as slightly hypopigmented macules. No recurrence was noted at posttreatment follow-up 1 year later.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444.
Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444.
Psychiatrists deemed ‘essential’ in time of COVID-19
New American Psychiatric Association poll shows depth of anxiety
The coronavirus pandemic weighs heavily on psychiatric patients with conditions such as anxiety, depression and PTSD. Meanwhile, a national poll released March 25 by the American Psychiatric Association shows that almost half of all Americans are anxious about contracting COVID-19 and 40% are anxious about becoming seriously ill or dying from the virus. In light of stressors on patients and nonpatients alike, mental health professionals have a key role in helping to alleviate suffering tied to the public health crisis, according to psychiatrists from across the country.
“There’s so much we can do to help people put order on this chaos,” said Shaili Jain, MD, section chief of outpatient mental health with the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System, in an interview. “We are essential workers in this time.”
Dr. Jain, who specializes in treating PTSD, said those patients are especially vulnerable to the stress and disruptions spawned by the pandemic. “When you go to the grocery store and there’s no food, that can be triggering for people who survived situations with a feeling of calamity or panic,” she said. “People are reporting worsening of nightmares and spontaneous panic attacks after having been stable with symptoms for many months. These are the kinds of stories that are starting to filter through.”
To make things even more difficult, she said, shelter-in-place orders are preventing patients from taking advantage of healthy coping strategies, such as working out at the gym or going to support groups. “We have an invaluable role to play in trying to prevent long-term consequences by going into problem-solving modes with patients.” Dr. Jain offered several tips that might help patients who are suffering:
- Use technology to stay in touch with support communities and boost self-care. “How can you be flexible with FaceTime, Skype, or phone even if you might not be able to have that face-to-face time? What are you doing to double down on your efforts at self-care – listening to music, reading, daily meditation, or walks? Double down on what you can do to prevent anxiety and stress levels from building up.”
- Take breaks from the news, which can contribute to hypervigilance and disrupted sleep. “I’m seeing that people are going down these rabbit holes of having the news or social media on 24/7,” Dr. Jain said. “You have to stay informed. But you need to pick trusted news sources and have chunks of time that are free of coronavirus coverage.” Understand that life is going to be difficult for a while. “We’re doing a lot of reassurance and education,” she said, “helping people to know and accept that the next few days, weeks, and months are going to be stressful.”
Dr. Jain cautioned colleagues, however, that “there will be a tsunami” of mental illness when the coronavirus crisis lifts. She is especially concerned about patient populations that are socioeconomically disadvantaged already and how their lives with be affected by lost wages, unemployment, and business failures. “Medical professionals will see the consequences of this in the days and weeks and months after the pandemic has settled,” she predicted.
The APA poll shows that, early in the crisis, more than 60% of people are anxious about family and loved ones contracting COVID-19.
Maintaining ‘reflective space’ essential
At the Austen Riggs Center, a psychiatric residential treatment facility in Stockbridge, Mass., staff and patients are adjusting to new rules that aim to prevent transmission of the novel coronavirus. “Social distancing requirements are having a huge impact,” said Eric M. Plakun, MD, medical director and CEO of Austen Riggs, in an interview. “You can’t have groups in the same way; you can’t have families come in for a family meeting; you can’t have quite the same the freedom to come and go. A lot of management issues are being addressed, but it is crucial also to maintain the ‘reflective space’ essential to do the kind of clinical work we do.” One approach, he said, is virtual meetings with colleagues that address on-the-job management issues, but also leave a space for how staff members are feeling.
“It’s easy to get into crisis-response mode,” he said, “where you’re always managing but never leave a space to talk about vulnerability, helplessness, and fear.”
As the facility’s staff adjusts by embracing teleconference technology and adapting group meetings to the 6-feet-apart rule,
Dr. Plakun said he said, noting that patients have approached staff members to say they want to collaborate about changes. “That’s a credible offer we intend to accept.”
Still, communicating with patients as a whole about the coronavirus can be difficult. As Dr. Plakun noted, it’s now impossible to bring 75 people together into one room for a meeting. “If you have four to five smaller meetings, how do you maintain some congruence in the information that’s presented?”
Dr. Plakun suggested that colleagues find time to engage in the familiar, such as face-to-face clinical work. “That’s been the most reassuring and rewarding part of my day since it feels almost like normal,” he said.
Stocking up on medications
Jessica “Jessi” Gold, MD, MS, an assistant professor at Washington University in St. Louis, often treats college students. Asian students started to worry early in the pandemic, she said in an interview.
“At the beginning, there were a lot of concerns about the public’s view: ‘Did this come from China? Is it China’s fault?’ A lot of our students felt that if they coughed, and they were a white person, they’d be OK. But if they were Asian, everyone would wonder why they were in class and not at home. That got worse over time: the fear about – and anxiety from – stoking racism.”
Later, as classes began to be canceled, Dr. Gold started to see the psychological effects of disruption and uncertainty about the future. “This can lead people to feel like what they knew before is just not there anymore. This can obviously cause anxiety but also has the potential to cause depression.” Patients also might slip into overuse of alcohol and drugs, or they might engage in other kinds of harmful behavior. Eating disorders, for example, “are ways to have control when other things aren’t in control,” she said.
Dr. Gold pointed to research into the mental health after effects of quarantines, such as those imposed during the SARS outbreak. A review of 24 studies published this year found that most “reported negative psychological effects, including post-traumatic stress symptoms, confusion, and anger. Stressors included longer quarantine duration, infection fears, frustration, boredom, inadequate supplies, inadequate information, financial loss, and stigma. Some researchers have suggested long-lasting effects” (Lancet. 2020;395:912-20).
Dr. Gold is urging patients to recall the warning signs that alerted them to psychological downturns in the past: “Try to remember what those warning signs are and pay attention to whether you see them.” And, Dr. Gold said, she asks patients to think about what has helped them get better.
In some cases, she said, patients are already preparing themselves for experiencing mental distress by stocking up on medications. “Some people have a bottle of 10-20 pills that they only use in emergencies and keep as a kind of security blanket,” she said, and she’s seen some of them ask for refills. It seems they’ve either taken the pills recently or want to stash them just in case. This makes sense, since their anxiety is higher, she said.
Dr. Gold cautioned that psychiatrists need to be careful to not overextend themselves when they’re not treating patients. “It is easy to be therapist to friends, family, and colleagues,” she said, “but we need to take care of ourselves, too.”
Dr. Jain is author of “The Unspeakable Mind: Stories of Trauma and Healing From the Frontlines of PTSD Science” (New York: Harper, 2019). She has no other disclosures. Dr. Plakun and Dr. Gold reported no relevant disclosures.
New American Psychiatric Association poll shows depth of anxiety
New American Psychiatric Association poll shows depth of anxiety
The coronavirus pandemic weighs heavily on psychiatric patients with conditions such as anxiety, depression and PTSD. Meanwhile, a national poll released March 25 by the American Psychiatric Association shows that almost half of all Americans are anxious about contracting COVID-19 and 40% are anxious about becoming seriously ill or dying from the virus. In light of stressors on patients and nonpatients alike, mental health professionals have a key role in helping to alleviate suffering tied to the public health crisis, according to psychiatrists from across the country.
“There’s so much we can do to help people put order on this chaos,” said Shaili Jain, MD, section chief of outpatient mental health with the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System, in an interview. “We are essential workers in this time.”
Dr. Jain, who specializes in treating PTSD, said those patients are especially vulnerable to the stress and disruptions spawned by the pandemic. “When you go to the grocery store and there’s no food, that can be triggering for people who survived situations with a feeling of calamity or panic,” she said. “People are reporting worsening of nightmares and spontaneous panic attacks after having been stable with symptoms for many months. These are the kinds of stories that are starting to filter through.”
To make things even more difficult, she said, shelter-in-place orders are preventing patients from taking advantage of healthy coping strategies, such as working out at the gym or going to support groups. “We have an invaluable role to play in trying to prevent long-term consequences by going into problem-solving modes with patients.” Dr. Jain offered several tips that might help patients who are suffering:
- Use technology to stay in touch with support communities and boost self-care. “How can you be flexible with FaceTime, Skype, or phone even if you might not be able to have that face-to-face time? What are you doing to double down on your efforts at self-care – listening to music, reading, daily meditation, or walks? Double down on what you can do to prevent anxiety and stress levels from building up.”
- Take breaks from the news, which can contribute to hypervigilance and disrupted sleep. “I’m seeing that people are going down these rabbit holes of having the news or social media on 24/7,” Dr. Jain said. “You have to stay informed. But you need to pick trusted news sources and have chunks of time that are free of coronavirus coverage.” Understand that life is going to be difficult for a while. “We’re doing a lot of reassurance and education,” she said, “helping people to know and accept that the next few days, weeks, and months are going to be stressful.”
Dr. Jain cautioned colleagues, however, that “there will be a tsunami” of mental illness when the coronavirus crisis lifts. She is especially concerned about patient populations that are socioeconomically disadvantaged already and how their lives with be affected by lost wages, unemployment, and business failures. “Medical professionals will see the consequences of this in the days and weeks and months after the pandemic has settled,” she predicted.
The APA poll shows that, early in the crisis, more than 60% of people are anxious about family and loved ones contracting COVID-19.
Maintaining ‘reflective space’ essential
At the Austen Riggs Center, a psychiatric residential treatment facility in Stockbridge, Mass., staff and patients are adjusting to new rules that aim to prevent transmission of the novel coronavirus. “Social distancing requirements are having a huge impact,” said Eric M. Plakun, MD, medical director and CEO of Austen Riggs, in an interview. “You can’t have groups in the same way; you can’t have families come in for a family meeting; you can’t have quite the same the freedom to come and go. A lot of management issues are being addressed, but it is crucial also to maintain the ‘reflective space’ essential to do the kind of clinical work we do.” One approach, he said, is virtual meetings with colleagues that address on-the-job management issues, but also leave a space for how staff members are feeling.
“It’s easy to get into crisis-response mode,” he said, “where you’re always managing but never leave a space to talk about vulnerability, helplessness, and fear.”
As the facility’s staff adjusts by embracing teleconference technology and adapting group meetings to the 6-feet-apart rule,
Dr. Plakun said he said, noting that patients have approached staff members to say they want to collaborate about changes. “That’s a credible offer we intend to accept.”
Still, communicating with patients as a whole about the coronavirus can be difficult. As Dr. Plakun noted, it’s now impossible to bring 75 people together into one room for a meeting. “If you have four to five smaller meetings, how do you maintain some congruence in the information that’s presented?”
Dr. Plakun suggested that colleagues find time to engage in the familiar, such as face-to-face clinical work. “That’s been the most reassuring and rewarding part of my day since it feels almost like normal,” he said.
Stocking up on medications
Jessica “Jessi” Gold, MD, MS, an assistant professor at Washington University in St. Louis, often treats college students. Asian students started to worry early in the pandemic, she said in an interview.
“At the beginning, there were a lot of concerns about the public’s view: ‘Did this come from China? Is it China’s fault?’ A lot of our students felt that if they coughed, and they were a white person, they’d be OK. But if they were Asian, everyone would wonder why they were in class and not at home. That got worse over time: the fear about – and anxiety from – stoking racism.”
Later, as classes began to be canceled, Dr. Gold started to see the psychological effects of disruption and uncertainty about the future. “This can lead people to feel like what they knew before is just not there anymore. This can obviously cause anxiety but also has the potential to cause depression.” Patients also might slip into overuse of alcohol and drugs, or they might engage in other kinds of harmful behavior. Eating disorders, for example, “are ways to have control when other things aren’t in control,” she said.
Dr. Gold pointed to research into the mental health after effects of quarantines, such as those imposed during the SARS outbreak. A review of 24 studies published this year found that most “reported negative psychological effects, including post-traumatic stress symptoms, confusion, and anger. Stressors included longer quarantine duration, infection fears, frustration, boredom, inadequate supplies, inadequate information, financial loss, and stigma. Some researchers have suggested long-lasting effects” (Lancet. 2020;395:912-20).
Dr. Gold is urging patients to recall the warning signs that alerted them to psychological downturns in the past: “Try to remember what those warning signs are and pay attention to whether you see them.” And, Dr. Gold said, she asks patients to think about what has helped them get better.
In some cases, she said, patients are already preparing themselves for experiencing mental distress by stocking up on medications. “Some people have a bottle of 10-20 pills that they only use in emergencies and keep as a kind of security blanket,” she said, and she’s seen some of them ask for refills. It seems they’ve either taken the pills recently or want to stash them just in case. This makes sense, since their anxiety is higher, she said.
Dr. Gold cautioned that psychiatrists need to be careful to not overextend themselves when they’re not treating patients. “It is easy to be therapist to friends, family, and colleagues,” she said, “but we need to take care of ourselves, too.”
Dr. Jain is author of “The Unspeakable Mind: Stories of Trauma and Healing From the Frontlines of PTSD Science” (New York: Harper, 2019). She has no other disclosures. Dr. Plakun and Dr. Gold reported no relevant disclosures.
The coronavirus pandemic weighs heavily on psychiatric patients with conditions such as anxiety, depression and PTSD. Meanwhile, a national poll released March 25 by the American Psychiatric Association shows that almost half of all Americans are anxious about contracting COVID-19 and 40% are anxious about becoming seriously ill or dying from the virus. In light of stressors on patients and nonpatients alike, mental health professionals have a key role in helping to alleviate suffering tied to the public health crisis, according to psychiatrists from across the country.
“There’s so much we can do to help people put order on this chaos,” said Shaili Jain, MD, section chief of outpatient mental health with the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System, in an interview. “We are essential workers in this time.”
Dr. Jain, who specializes in treating PTSD, said those patients are especially vulnerable to the stress and disruptions spawned by the pandemic. “When you go to the grocery store and there’s no food, that can be triggering for people who survived situations with a feeling of calamity or panic,” she said. “People are reporting worsening of nightmares and spontaneous panic attacks after having been stable with symptoms for many months. These are the kinds of stories that are starting to filter through.”
To make things even more difficult, she said, shelter-in-place orders are preventing patients from taking advantage of healthy coping strategies, such as working out at the gym or going to support groups. “We have an invaluable role to play in trying to prevent long-term consequences by going into problem-solving modes with patients.” Dr. Jain offered several tips that might help patients who are suffering:
- Use technology to stay in touch with support communities and boost self-care. “How can you be flexible with FaceTime, Skype, or phone even if you might not be able to have that face-to-face time? What are you doing to double down on your efforts at self-care – listening to music, reading, daily meditation, or walks? Double down on what you can do to prevent anxiety and stress levels from building up.”
- Take breaks from the news, which can contribute to hypervigilance and disrupted sleep. “I’m seeing that people are going down these rabbit holes of having the news or social media on 24/7,” Dr. Jain said. “You have to stay informed. But you need to pick trusted news sources and have chunks of time that are free of coronavirus coverage.” Understand that life is going to be difficult for a while. “We’re doing a lot of reassurance and education,” she said, “helping people to know and accept that the next few days, weeks, and months are going to be stressful.”
Dr. Jain cautioned colleagues, however, that “there will be a tsunami” of mental illness when the coronavirus crisis lifts. She is especially concerned about patient populations that are socioeconomically disadvantaged already and how their lives with be affected by lost wages, unemployment, and business failures. “Medical professionals will see the consequences of this in the days and weeks and months after the pandemic has settled,” she predicted.
The APA poll shows that, early in the crisis, more than 60% of people are anxious about family and loved ones contracting COVID-19.
Maintaining ‘reflective space’ essential
At the Austen Riggs Center, a psychiatric residential treatment facility in Stockbridge, Mass., staff and patients are adjusting to new rules that aim to prevent transmission of the novel coronavirus. “Social distancing requirements are having a huge impact,” said Eric M. Plakun, MD, medical director and CEO of Austen Riggs, in an interview. “You can’t have groups in the same way; you can’t have families come in for a family meeting; you can’t have quite the same the freedom to come and go. A lot of management issues are being addressed, but it is crucial also to maintain the ‘reflective space’ essential to do the kind of clinical work we do.” One approach, he said, is virtual meetings with colleagues that address on-the-job management issues, but also leave a space for how staff members are feeling.
“It’s easy to get into crisis-response mode,” he said, “where you’re always managing but never leave a space to talk about vulnerability, helplessness, and fear.”
As the facility’s staff adjusts by embracing teleconference technology and adapting group meetings to the 6-feet-apart rule,
Dr. Plakun said he said, noting that patients have approached staff members to say they want to collaborate about changes. “That’s a credible offer we intend to accept.”
Still, communicating with patients as a whole about the coronavirus can be difficult. As Dr. Plakun noted, it’s now impossible to bring 75 people together into one room for a meeting. “If you have four to five smaller meetings, how do you maintain some congruence in the information that’s presented?”
Dr. Plakun suggested that colleagues find time to engage in the familiar, such as face-to-face clinical work. “That’s been the most reassuring and rewarding part of my day since it feels almost like normal,” he said.
Stocking up on medications
Jessica “Jessi” Gold, MD, MS, an assistant professor at Washington University in St. Louis, often treats college students. Asian students started to worry early in the pandemic, she said in an interview.
“At the beginning, there were a lot of concerns about the public’s view: ‘Did this come from China? Is it China’s fault?’ A lot of our students felt that if they coughed, and they were a white person, they’d be OK. But if they were Asian, everyone would wonder why they were in class and not at home. That got worse over time: the fear about – and anxiety from – stoking racism.”
Later, as classes began to be canceled, Dr. Gold started to see the psychological effects of disruption and uncertainty about the future. “This can lead people to feel like what they knew before is just not there anymore. This can obviously cause anxiety but also has the potential to cause depression.” Patients also might slip into overuse of alcohol and drugs, or they might engage in other kinds of harmful behavior. Eating disorders, for example, “are ways to have control when other things aren’t in control,” she said.
Dr. Gold pointed to research into the mental health after effects of quarantines, such as those imposed during the SARS outbreak. A review of 24 studies published this year found that most “reported negative psychological effects, including post-traumatic stress symptoms, confusion, and anger. Stressors included longer quarantine duration, infection fears, frustration, boredom, inadequate supplies, inadequate information, financial loss, and stigma. Some researchers have suggested long-lasting effects” (Lancet. 2020;395:912-20).
Dr. Gold is urging patients to recall the warning signs that alerted them to psychological downturns in the past: “Try to remember what those warning signs are and pay attention to whether you see them.” And, Dr. Gold said, she asks patients to think about what has helped them get better.
In some cases, she said, patients are already preparing themselves for experiencing mental distress by stocking up on medications. “Some people have a bottle of 10-20 pills that they only use in emergencies and keep as a kind of security blanket,” she said, and she’s seen some of them ask for refills. It seems they’ve either taken the pills recently or want to stash them just in case. This makes sense, since their anxiety is higher, she said.
Dr. Gold cautioned that psychiatrists need to be careful to not overextend themselves when they’re not treating patients. “It is easy to be therapist to friends, family, and colleagues,” she said, “but we need to take care of ourselves, too.”
Dr. Jain is author of “The Unspeakable Mind: Stories of Trauma and Healing From the Frontlines of PTSD Science” (New York: Harper, 2019). She has no other disclosures. Dr. Plakun and Dr. Gold reported no relevant disclosures.
Hospitals muzzle doctors and nurses on PPE, COVID-19 cases
Over the past month, an orthopedic surgeon has watched as the crowd of sick patients at his hospital has grown, while the supply of personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff has diminished. As he prepares for another day of staffing testing tents and places his one and only mask across his face, he also receives a daily reminder from hospital management: Don’t talk about it.
The surgeon, who works in a COVID-19 hot spot in the Northeast, spoke on the condition of anonymity for fear of employer retribution.
“It’s very clear; no one is allowed to speak for the institution or of the institution,” he said in an interview. “We get a daily warning about being very prudent about posts on personal accounts. They’ve talked about this with respect to various issues: case numbers, case severity, testing availability, [and] PPEs.”
The warnings mean staff at the hospital suffer in silence, unable to share the troubling situation with the public or request assistance with supplies.
“I have one mask. We’re expected to reuse them, unless you were exposed or worked with a known COVID victim,” the surgeon said. “However, with the numbers in our region rapidly increasing, you can’t assume that people don’t have it or that you don’t have particles on your mask, even if you’re not in a known quarantine zone within the institution.”
As the COVID-19 health crisis rages on, online platforms have become a common place for health professionals to lament short supplies, share concerns, tell stories, and plead for help. But at the same time, other physicians, nurses, and health care workers are being muzzled by hospital administrators and threatened with discipline for speaking out about coronavirus caseloads and dwindling supplies. Some worry the gag orders are muddying the picture of how hospitals are faring in the pandemic, while placing the safety of frontline workers at risk.
The silencing of physicians by hospitals about PPE shortages and other COVID-19 issues has become widespread, said Nisha Mehta, MD, a physician advocate and community leader who writes about PPE on social media. Physicians are being warned not to speak or post publicly about their COVID-19 experiences, including PPE shortages, case specifics, and the percentage of full hospital beds, Dr. Mehta said in an interview. In some cases, physicians who have posted have been forced to take down the posts or have faced retribution for speaking out, she said.
“There’s definitely a big fear among physicians, particularly employed physicians, in terms of what the consequences may be for telling their stories,” Dr. Mehta said. “I find that counterproductive. I understand not inducing panic, but these are real stories that are important for people to understand so they do stay home and increase the systemic pressure to get sufficient PPE, so that we can preserve our health care workforce for a problem that is going to get worse before it gets better.”
Meanwhile, an Indiana hospitalist who took to social media to ask for masks for hospitals in his area says he was immediately reprimanded by his management after the posts came to light. The hospitalist posted on a social media platform to request donations of N95 masks after hearing members of the public had purchased such masks. He hoped his plea would aid preparation for the pandemic at local hospitals, explained the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Shortly afterward, administrators from his hospital contacted the online forum’s moderator and the posts were removed, he said. During a subsequent conversation, administrators warned the doctor not to make such posts about PPE because it made the hospital appear incompetent.
“I was told, ‘we can handle this, we don’t need the public’s help,’” the physician said. “I was hurt and upset. I was trying to help protect my peers.”
After landing on the management’s radar, the hospitalist said he was reprimanded a second time about posts on a separate personal social media account. The second time, the private posts to friends and family were related to COVID-19 and PPE, but did not include any protected health information, he said. However, administrators did not like the content of the posts, and he was told management was monitoring his activity on social media, he said.
“The larger message is that patients are money,” the hospitalist said. “The corporate side of medicine rules out over the medicine side. Image and making sure there is a consistent cash flow trumps all else.”
Another frontline physician who works at a large New York hospital, said staff have been cautioned not to talk with the media and to be careful what they post on social media regarding COVID-19. The general rule is that only information approved by administrators can be shared, said the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“[The health system] is very protective of their public image,” he said. “In the past, people that have posted things that they don’t like get spoken to quickly and/or fired depending on what was written. I could only imagine that would be the situation regarding COVID-19. They are very strict.”
The frontline physician, who has close contact with COVID-19 patients, said he has access to N95 masks at the moment, but when he requested higher-level protective gear, hospital management refused the request and denied that such supplies were needed.
“Safety of frontline workers appears to not be taken seriously,” he said of his hospital. “Everyone is stressed, but at the end of the day, the administration is sitting there, while the rest of us are putting ourselves at risk.”
We reached out to one hospital for comment, but messages were not returned. Other hospitals were not contacted because physicians feared they would face retribution. We also contacted the American Hospital Association but they did not immediately respond.
In Chicago, an email by a nurse to her coworkers about the safety of masks has resulted in a lawsuit after the nurse says she was fired for sharing her concerns with staff. The nurse, Lauri Mazurkiewicz, sent an email to staffers at Northwestern Memorial Hospital stating the surgical masks provided by the hospital were less effective against airborne particles than were N95 masks, according to a lawsuit filed March 23 in Cook County Circuit Court. Ms. Mazurkiewicz was terminated the next day in retaliation for her email, the lawsuit alleges.
Ms. Mazurkiewicz could not be reached for comment by press time.
Christopher King, a spokesman for Northwestern Medicine, said the hospital is reviewing the lawsuit.
“As Northwestern Medicine continues to respond to this unprecedented health care pandemic, the health and well-being of our patients, our staff and our employees is our highest priority,” he said in a statement. “We take these matters seriously and we are currently reviewing the complaint. At this time, we will not be commenting further.”
John Mandrola, MD, a Louisville, Ky.–based cardiologist who has written about the recent muzzling of frontline physicians with respect to the coronavirus, said he is not surprised that some hospitals are preventing physicians from sharing their experiences.
“Before C19, in many hospital systems, there was a culture of fear amongst employed clinicians,” he said. “Employed clinicians see other employed physicians being terminated for speaking frankly about problems. It takes scant few of these cases to create a culture of silence.”
Dr. Mandrola, who is a regular Medscape contributor, said that a number of doctors have reached out to him privately about PPE scarcity and shared that they were explicitly warned by administrators not to talk about the shortfalls. Leadership at Dr. Mandrola’s hospital has not issued the same warnings, he said.
“From the hat of total transparency, I think the public is not getting a full view of the impending potential problems that are going to come by doctors not speaking publicly,” he said. “On the other hand, hospital leadership is doing the best they can. It’s not the hospitals’ fault. Hospital administrators can’t manufacture masks.”
From a public health standpoint, Dr. Mehta said that not allowing health professionals to speak publicly about the situations at their hospitals is “irresponsible.” The public deserves to know what is happening, she said, and the health care workforce needs to prepare for what is to come.
“It’s so important that we hear from our colleagues,” she said. “It’s important to hear those accounts so we can prepare for what we’re about to face. Data is crucial. The more you learn from each other, the better shot we have at successfully treating cases and ultimately beating this.”
With the critical shortage of PPE at his hospital and the inability to speak out about the problem, the orthopedic surgeon foresees the dilemma continuing to worsen.
“It’s not only the lives of front-line health care workers that are at risk, but it’s those that they’re going to spread it to and those that are going to be coming to the hospital requiring our care,” he said. “If we don’t have a fully functioning health care force, our capacity is going to be diminished that much further.”
Over the past month, an orthopedic surgeon has watched as the crowd of sick patients at his hospital has grown, while the supply of personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff has diminished. As he prepares for another day of staffing testing tents and places his one and only mask across his face, he also receives a daily reminder from hospital management: Don’t talk about it.
The surgeon, who works in a COVID-19 hot spot in the Northeast, spoke on the condition of anonymity for fear of employer retribution.
“It’s very clear; no one is allowed to speak for the institution or of the institution,” he said in an interview. “We get a daily warning about being very prudent about posts on personal accounts. They’ve talked about this with respect to various issues: case numbers, case severity, testing availability, [and] PPEs.”
The warnings mean staff at the hospital suffer in silence, unable to share the troubling situation with the public or request assistance with supplies.
“I have one mask. We’re expected to reuse them, unless you were exposed or worked with a known COVID victim,” the surgeon said. “However, with the numbers in our region rapidly increasing, you can’t assume that people don’t have it or that you don’t have particles on your mask, even if you’re not in a known quarantine zone within the institution.”
As the COVID-19 health crisis rages on, online platforms have become a common place for health professionals to lament short supplies, share concerns, tell stories, and plead for help. But at the same time, other physicians, nurses, and health care workers are being muzzled by hospital administrators and threatened with discipline for speaking out about coronavirus caseloads and dwindling supplies. Some worry the gag orders are muddying the picture of how hospitals are faring in the pandemic, while placing the safety of frontline workers at risk.
The silencing of physicians by hospitals about PPE shortages and other COVID-19 issues has become widespread, said Nisha Mehta, MD, a physician advocate and community leader who writes about PPE on social media. Physicians are being warned not to speak or post publicly about their COVID-19 experiences, including PPE shortages, case specifics, and the percentage of full hospital beds, Dr. Mehta said in an interview. In some cases, physicians who have posted have been forced to take down the posts or have faced retribution for speaking out, she said.
“There’s definitely a big fear among physicians, particularly employed physicians, in terms of what the consequences may be for telling their stories,” Dr. Mehta said. “I find that counterproductive. I understand not inducing panic, but these are real stories that are important for people to understand so they do stay home and increase the systemic pressure to get sufficient PPE, so that we can preserve our health care workforce for a problem that is going to get worse before it gets better.”
Meanwhile, an Indiana hospitalist who took to social media to ask for masks for hospitals in his area says he was immediately reprimanded by his management after the posts came to light. The hospitalist posted on a social media platform to request donations of N95 masks after hearing members of the public had purchased such masks. He hoped his plea would aid preparation for the pandemic at local hospitals, explained the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Shortly afterward, administrators from his hospital contacted the online forum’s moderator and the posts were removed, he said. During a subsequent conversation, administrators warned the doctor not to make such posts about PPE because it made the hospital appear incompetent.
“I was told, ‘we can handle this, we don’t need the public’s help,’” the physician said. “I was hurt and upset. I was trying to help protect my peers.”
After landing on the management’s radar, the hospitalist said he was reprimanded a second time about posts on a separate personal social media account. The second time, the private posts to friends and family were related to COVID-19 and PPE, but did not include any protected health information, he said. However, administrators did not like the content of the posts, and he was told management was monitoring his activity on social media, he said.
“The larger message is that patients are money,” the hospitalist said. “The corporate side of medicine rules out over the medicine side. Image and making sure there is a consistent cash flow trumps all else.”
Another frontline physician who works at a large New York hospital, said staff have been cautioned not to talk with the media and to be careful what they post on social media regarding COVID-19. The general rule is that only information approved by administrators can be shared, said the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“[The health system] is very protective of their public image,” he said. “In the past, people that have posted things that they don’t like get spoken to quickly and/or fired depending on what was written. I could only imagine that would be the situation regarding COVID-19. They are very strict.”
The frontline physician, who has close contact with COVID-19 patients, said he has access to N95 masks at the moment, but when he requested higher-level protective gear, hospital management refused the request and denied that such supplies were needed.
“Safety of frontline workers appears to not be taken seriously,” he said of his hospital. “Everyone is stressed, but at the end of the day, the administration is sitting there, while the rest of us are putting ourselves at risk.”
We reached out to one hospital for comment, but messages were not returned. Other hospitals were not contacted because physicians feared they would face retribution. We also contacted the American Hospital Association but they did not immediately respond.
In Chicago, an email by a nurse to her coworkers about the safety of masks has resulted in a lawsuit after the nurse says she was fired for sharing her concerns with staff. The nurse, Lauri Mazurkiewicz, sent an email to staffers at Northwestern Memorial Hospital stating the surgical masks provided by the hospital were less effective against airborne particles than were N95 masks, according to a lawsuit filed March 23 in Cook County Circuit Court. Ms. Mazurkiewicz was terminated the next day in retaliation for her email, the lawsuit alleges.
Ms. Mazurkiewicz could not be reached for comment by press time.
Christopher King, a spokesman for Northwestern Medicine, said the hospital is reviewing the lawsuit.
“As Northwestern Medicine continues to respond to this unprecedented health care pandemic, the health and well-being of our patients, our staff and our employees is our highest priority,” he said in a statement. “We take these matters seriously and we are currently reviewing the complaint. At this time, we will not be commenting further.”
John Mandrola, MD, a Louisville, Ky.–based cardiologist who has written about the recent muzzling of frontline physicians with respect to the coronavirus, said he is not surprised that some hospitals are preventing physicians from sharing their experiences.
“Before C19, in many hospital systems, there was a culture of fear amongst employed clinicians,” he said. “Employed clinicians see other employed physicians being terminated for speaking frankly about problems. It takes scant few of these cases to create a culture of silence.”
Dr. Mandrola, who is a regular Medscape contributor, said that a number of doctors have reached out to him privately about PPE scarcity and shared that they were explicitly warned by administrators not to talk about the shortfalls. Leadership at Dr. Mandrola’s hospital has not issued the same warnings, he said.
“From the hat of total transparency, I think the public is not getting a full view of the impending potential problems that are going to come by doctors not speaking publicly,” he said. “On the other hand, hospital leadership is doing the best they can. It’s not the hospitals’ fault. Hospital administrators can’t manufacture masks.”
From a public health standpoint, Dr. Mehta said that not allowing health professionals to speak publicly about the situations at their hospitals is “irresponsible.” The public deserves to know what is happening, she said, and the health care workforce needs to prepare for what is to come.
“It’s so important that we hear from our colleagues,” she said. “It’s important to hear those accounts so we can prepare for what we’re about to face. Data is crucial. The more you learn from each other, the better shot we have at successfully treating cases and ultimately beating this.”
With the critical shortage of PPE at his hospital and the inability to speak out about the problem, the orthopedic surgeon foresees the dilemma continuing to worsen.
“It’s not only the lives of front-line health care workers that are at risk, but it’s those that they’re going to spread it to and those that are going to be coming to the hospital requiring our care,” he said. “If we don’t have a fully functioning health care force, our capacity is going to be diminished that much further.”
Over the past month, an orthopedic surgeon has watched as the crowd of sick patients at his hospital has grown, while the supply of personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff has diminished. As he prepares for another day of staffing testing tents and places his one and only mask across his face, he also receives a daily reminder from hospital management: Don’t talk about it.
The surgeon, who works in a COVID-19 hot spot in the Northeast, spoke on the condition of anonymity for fear of employer retribution.
“It’s very clear; no one is allowed to speak for the institution or of the institution,” he said in an interview. “We get a daily warning about being very prudent about posts on personal accounts. They’ve talked about this with respect to various issues: case numbers, case severity, testing availability, [and] PPEs.”
The warnings mean staff at the hospital suffer in silence, unable to share the troubling situation with the public or request assistance with supplies.
“I have one mask. We’re expected to reuse them, unless you were exposed or worked with a known COVID victim,” the surgeon said. “However, with the numbers in our region rapidly increasing, you can’t assume that people don’t have it or that you don’t have particles on your mask, even if you’re not in a known quarantine zone within the institution.”
As the COVID-19 health crisis rages on, online platforms have become a common place for health professionals to lament short supplies, share concerns, tell stories, and plead for help. But at the same time, other physicians, nurses, and health care workers are being muzzled by hospital administrators and threatened with discipline for speaking out about coronavirus caseloads and dwindling supplies. Some worry the gag orders are muddying the picture of how hospitals are faring in the pandemic, while placing the safety of frontline workers at risk.
The silencing of physicians by hospitals about PPE shortages and other COVID-19 issues has become widespread, said Nisha Mehta, MD, a physician advocate and community leader who writes about PPE on social media. Physicians are being warned not to speak or post publicly about their COVID-19 experiences, including PPE shortages, case specifics, and the percentage of full hospital beds, Dr. Mehta said in an interview. In some cases, physicians who have posted have been forced to take down the posts or have faced retribution for speaking out, she said.
“There’s definitely a big fear among physicians, particularly employed physicians, in terms of what the consequences may be for telling their stories,” Dr. Mehta said. “I find that counterproductive. I understand not inducing panic, but these are real stories that are important for people to understand so they do stay home and increase the systemic pressure to get sufficient PPE, so that we can preserve our health care workforce for a problem that is going to get worse before it gets better.”
Meanwhile, an Indiana hospitalist who took to social media to ask for masks for hospitals in his area says he was immediately reprimanded by his management after the posts came to light. The hospitalist posted on a social media platform to request donations of N95 masks after hearing members of the public had purchased such masks. He hoped his plea would aid preparation for the pandemic at local hospitals, explained the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Shortly afterward, administrators from his hospital contacted the online forum’s moderator and the posts were removed, he said. During a subsequent conversation, administrators warned the doctor not to make such posts about PPE because it made the hospital appear incompetent.
“I was told, ‘we can handle this, we don’t need the public’s help,’” the physician said. “I was hurt and upset. I was trying to help protect my peers.”
After landing on the management’s radar, the hospitalist said he was reprimanded a second time about posts on a separate personal social media account. The second time, the private posts to friends and family were related to COVID-19 and PPE, but did not include any protected health information, he said. However, administrators did not like the content of the posts, and he was told management was monitoring his activity on social media, he said.
“The larger message is that patients are money,” the hospitalist said. “The corporate side of medicine rules out over the medicine side. Image and making sure there is a consistent cash flow trumps all else.”
Another frontline physician who works at a large New York hospital, said staff have been cautioned not to talk with the media and to be careful what they post on social media regarding COVID-19. The general rule is that only information approved by administrators can be shared, said the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“[The health system] is very protective of their public image,” he said. “In the past, people that have posted things that they don’t like get spoken to quickly and/or fired depending on what was written. I could only imagine that would be the situation regarding COVID-19. They are very strict.”
The frontline physician, who has close contact with COVID-19 patients, said he has access to N95 masks at the moment, but when he requested higher-level protective gear, hospital management refused the request and denied that such supplies were needed.
“Safety of frontline workers appears to not be taken seriously,” he said of his hospital. “Everyone is stressed, but at the end of the day, the administration is sitting there, while the rest of us are putting ourselves at risk.”
We reached out to one hospital for comment, but messages were not returned. Other hospitals were not contacted because physicians feared they would face retribution. We also contacted the American Hospital Association but they did not immediately respond.
In Chicago, an email by a nurse to her coworkers about the safety of masks has resulted in a lawsuit after the nurse says she was fired for sharing her concerns with staff. The nurse, Lauri Mazurkiewicz, sent an email to staffers at Northwestern Memorial Hospital stating the surgical masks provided by the hospital were less effective against airborne particles than were N95 masks, according to a lawsuit filed March 23 in Cook County Circuit Court. Ms. Mazurkiewicz was terminated the next day in retaliation for her email, the lawsuit alleges.
Ms. Mazurkiewicz could not be reached for comment by press time.
Christopher King, a spokesman for Northwestern Medicine, said the hospital is reviewing the lawsuit.
“As Northwestern Medicine continues to respond to this unprecedented health care pandemic, the health and well-being of our patients, our staff and our employees is our highest priority,” he said in a statement. “We take these matters seriously and we are currently reviewing the complaint. At this time, we will not be commenting further.”
John Mandrola, MD, a Louisville, Ky.–based cardiologist who has written about the recent muzzling of frontline physicians with respect to the coronavirus, said he is not surprised that some hospitals are preventing physicians from sharing their experiences.
“Before C19, in many hospital systems, there was a culture of fear amongst employed clinicians,” he said. “Employed clinicians see other employed physicians being terminated for speaking frankly about problems. It takes scant few of these cases to create a culture of silence.”
Dr. Mandrola, who is a regular Medscape contributor, said that a number of doctors have reached out to him privately about PPE scarcity and shared that they were explicitly warned by administrators not to talk about the shortfalls. Leadership at Dr. Mandrola’s hospital has not issued the same warnings, he said.
“From the hat of total transparency, I think the public is not getting a full view of the impending potential problems that are going to come by doctors not speaking publicly,” he said. “On the other hand, hospital leadership is doing the best they can. It’s not the hospitals’ fault. Hospital administrators can’t manufacture masks.”
From a public health standpoint, Dr. Mehta said that not allowing health professionals to speak publicly about the situations at their hospitals is “irresponsible.” The public deserves to know what is happening, she said, and the health care workforce needs to prepare for what is to come.
“It’s so important that we hear from our colleagues,” she said. “It’s important to hear those accounts so we can prepare for what we’re about to face. Data is crucial. The more you learn from each other, the better shot we have at successfully treating cases and ultimately beating this.”
With the critical shortage of PPE at his hospital and the inability to speak out about the problem, the orthopedic surgeon foresees the dilemma continuing to worsen.
“It’s not only the lives of front-line health care workers that are at risk, but it’s those that they’re going to spread it to and those that are going to be coming to the hospital requiring our care,” he said. “If we don’t have a fully functioning health care force, our capacity is going to be diminished that much further.”
Hospitals muzzle doctors and nurses on PPE, COVID-19 cases
Over the past month, an orthopedic surgeon has watched as the crowd of sick patients at his hospital has grown, while the supply of personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff has diminished. As he prepares for another day of staffing testing tents and places his one and only mask across his face, he also receives a daily reminder from hospital management: Don’t talk about it.
“It’s very clear; no one is allowed to speak for the institution or of the institution,” he said in an interview. “We get a daily warning about being very prudent about posts on personal accounts. They’ve talked about this with respect to various issues: case numbers, case severity, testing availability, [and] PPEs.”
The warnings mean staff at the hospital suffer in silence, unable to share the troubling situation with the public or request assistance with supplies.
“I have one mask. We’re expected to reuse them, unless you were exposed or worked with a known COVID victim,” the surgeon said. “However, with the numbers in our region rapidly increasing, you can’t assume that people don’t have it or that you don’t have particles on your mask, even if you’re not in a known quarantine zone within the institution.”
As the COVID-19 health crisis rages on, online platforms have become a common place for health professionals to lament short supplies, share concerns, tell stories, and plead for help. But at the same time, other physicians, nurses, and health care workers are being muzzled by hospital administrators and threatened with discipline for speaking out about coronavirus caseloads and dwindling supplies. Some worry the gag orders are muddying the picture of how hospitals are faring in the pandemic, while placing the safety of frontline workers at risk.
The silencing of physicians by hospitals about PPE shortages and other COVID-19 issues has become widespread, said Nisha Mehta, MD, a physician advocate and community leader who writes about PPE on social media. Physicians are being warned not to speak or post publicly about their COVID-19 experiences, including PPE shortages, case specifics, and the percentage of full hospital beds, Dr. Mehta said in an interview. In some cases, physicians who have posted have been forced to take down the posts or have faced retribution for speaking out, she said.
“There’s definitely a big fear among physicians, particularly employed physicians, in terms of what the consequences may be for telling their stories,” Dr. Mehta said. “I find that counterproductive. I understand not inducing panic, but these are real stories that are important for people to understand so they do stay home and increase the systemic pressure to get sufficient PPE, so that we can preserve our health care workforce for a problem that is going to get worse before it gets better.”
Meanwhile, an Indiana hospitalist who took to social media to ask for masks for hospitals in his area says he was immediately reprimanded by his management after the posts came to light. The hospitalist posted on a social media platform to request donations of N95 masks after hearing members of the public had purchased such masks. He hoped his plea would aid preparation for the pandemic at local hospitals, explained the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Shortly afterward, administrators from his hospital contacted the online forum’s moderator and the posts were removed, he said. During a subsequent conversation, administrators warned the doctor not to make such posts about PPE because it made the hospital appear incompetent.
“I was told, ‘we can handle this, we don’t need the public’s help,’” the physician said. “I was hurt and upset. I was trying to help protect my peers.”
After landing on the management’s radar, the hospitalist said he was reprimanded a second time about posts on a separate personal social media account. The second time, the private posts to friends and family were related to COVID-19 and PPE, but did not include any protected health information, he said. However, administrators did not like the content of the posts, and he was told management was monitoring his activity on social media, he said.
“The larger message is that patients are money,” the hospitalist said. “The corporate side of medicine rules out over the medicine side. Image and making sure there is a consistent cash flow trumps all else.”
Another frontline physician who works at a large New York hospital, said staff have been cautioned not to talk with the media and to be careful what they post on social media regarding COVID-19. The general rule is that only information approved by administrators can be shared, said the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“[The health system] is very protective of their public image,” he said. “In the past, people that have posted things that they don’t like get spoken to quickly and/or fired depending on what was written. I could only imagine that would be the situation regarding COVID-19. They are very strict.”
The frontline physician, who has close contact with COVID-19 patients, said he has access to N95 masks at the moment, but when he requested higher-level protective gear, hospital management refused the request and denied that such supplies were needed.
“Safety of frontline workers appears to not be taken seriously,” he said of his hospital. “Everyone is stressed, but at the end of the day, the administration is sitting there, while the rest of us are putting ourselves at risk.”
We reached out to one hospital for comment, but messages were not returned. Other hospitals were not contacted because physicians feared they would face retribution. We also contacted the American Hospital Association but they did not immediately respond.
In Chicago, an email by a nurse to her coworkers about the safety of masks has resulted in a lawsuit after the nurse says she was fired for sharing her concerns with staff. The nurse, Lauri Mazurkiewicz, sent an email to staffers at Northwestern Memorial Hospital stating the surgical masks provided by the hospital were less effective against airborne particles than were N95 masks, according to a lawsuit filed March 23 in Cook County Circuit Court. Ms. Mazurkiewicz was terminated the next day in retaliation for her email, the lawsuit alleges.
Ms. Mazurkiewicz could not be reached for comment by press time.
Christopher King, a spokesman for Northwestern Medicine, said the hospital is reviewing the lawsuit.
“As Northwestern Medicine continues to respond to this unprecedented health care pandemic, the health and well-being of our patients, our staff and our employees is our highest priority,” he said in a statement. “We take these matters seriously and we are currently reviewing the complaint. At this time, we will not be commenting further.”
John Mandrola, MD, a Louisville, Ky.–based cardiologist who has written about the recent muzzling of frontline physicians with respect to the coronavirus, said he is not surprised that some hospitals are preventing physicians from sharing their experiences.
“Before C19, in many hospital systems, there was a culture of fear amongst employed clinicians,” he said. “Employed clinicians see other employed physicians being terminated for speaking frankly about problems. It takes scant few of these cases to create a culture of silence.”
Dr. Mandrola, who is a regular Medscape contributor, said that a number of doctors have reached out to him privately about PPE scarcity and shared that they were explicitly warned by administrators not to talk about the shortfalls. Leadership at Dr. Mandrola’s hospital has not issued the same warnings, he said.
“From the hat of total transparency, I think the public is not getting a full view of the impending potential problems that are going to come by doctors not speaking publicly,” he said. “On the other hand, hospital leadership is doing the best they can. It’s not the hospitals’ fault. Hospital administrators can’t manufacture masks.”
From a public health standpoint, Dr. Mehta said that not allowing health professionals to speak publicly about the situations at their hospitals is “irresponsible.” The public deserves to know what is happening, she said, and the health care workforce needs to prepare for what is to come.
“It’s so important that we hear from our colleagues,” she said. “It’s important to hear those accounts so we can prepare for what we’re about to face. Data is crucial. The more you learn from each other, the better shot we have at successfully treating cases and ultimately beating this.”
With the critical shortage of PPE at his hospital and the inability to speak out about the problem, the orthopedic surgeon foresees the dilemma continuing to worsen.
“It’s not only the lives of front-line health care workers that are at risk, but it’s those that they’re going to spread it to and those that are going to be coming to the hospital requiring our care,” he said. “If we don’t have a fully functioning health care force, our capacity is going to be diminished that much further.”
The American Gastroenterological Association, along with 44 other medical specialty societies representing more than 800,000 physicians, signed onto the Council of Medical Specialty Societies letter stating that all frontline health care professionals must have access to PPEs and be able to speak publicly about the lack of PPEs without retribution while pushing for adequate supply and distribution. Review the statement at https://cmss.org/cmss-statement-ppe.
agallegos@mdedge.com
Over the past month, an orthopedic surgeon has watched as the crowd of sick patients at his hospital has grown, while the supply of personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff has diminished. As he prepares for another day of staffing testing tents and places his one and only mask across his face, he also receives a daily reminder from hospital management: Don’t talk about it.
“It’s very clear; no one is allowed to speak for the institution or of the institution,” he said in an interview. “We get a daily warning about being very prudent about posts on personal accounts. They’ve talked about this with respect to various issues: case numbers, case severity, testing availability, [and] PPEs.”
The warnings mean staff at the hospital suffer in silence, unable to share the troubling situation with the public or request assistance with supplies.
“I have one mask. We’re expected to reuse them, unless you were exposed or worked with a known COVID victim,” the surgeon said. “However, with the numbers in our region rapidly increasing, you can’t assume that people don’t have it or that you don’t have particles on your mask, even if you’re not in a known quarantine zone within the institution.”
As the COVID-19 health crisis rages on, online platforms have become a common place for health professionals to lament short supplies, share concerns, tell stories, and plead for help. But at the same time, other physicians, nurses, and health care workers are being muzzled by hospital administrators and threatened with discipline for speaking out about coronavirus caseloads and dwindling supplies. Some worry the gag orders are muddying the picture of how hospitals are faring in the pandemic, while placing the safety of frontline workers at risk.
The silencing of physicians by hospitals about PPE shortages and other COVID-19 issues has become widespread, said Nisha Mehta, MD, a physician advocate and community leader who writes about PPE on social media. Physicians are being warned not to speak or post publicly about their COVID-19 experiences, including PPE shortages, case specifics, and the percentage of full hospital beds, Dr. Mehta said in an interview. In some cases, physicians who have posted have been forced to take down the posts or have faced retribution for speaking out, she said.
“There’s definitely a big fear among physicians, particularly employed physicians, in terms of what the consequences may be for telling their stories,” Dr. Mehta said. “I find that counterproductive. I understand not inducing panic, but these are real stories that are important for people to understand so they do stay home and increase the systemic pressure to get sufficient PPE, so that we can preserve our health care workforce for a problem that is going to get worse before it gets better.”
Meanwhile, an Indiana hospitalist who took to social media to ask for masks for hospitals in his area says he was immediately reprimanded by his management after the posts came to light. The hospitalist posted on a social media platform to request donations of N95 masks after hearing members of the public had purchased such masks. He hoped his plea would aid preparation for the pandemic at local hospitals, explained the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Shortly afterward, administrators from his hospital contacted the online forum’s moderator and the posts were removed, he said. During a subsequent conversation, administrators warned the doctor not to make such posts about PPE because it made the hospital appear incompetent.
“I was told, ‘we can handle this, we don’t need the public’s help,’” the physician said. “I was hurt and upset. I was trying to help protect my peers.”
After landing on the management’s radar, the hospitalist said he was reprimanded a second time about posts on a separate personal social media account. The second time, the private posts to friends and family were related to COVID-19 and PPE, but did not include any protected health information, he said. However, administrators did not like the content of the posts, and he was told management was monitoring his activity on social media, he said.
“The larger message is that patients are money,” the hospitalist said. “The corporate side of medicine rules out over the medicine side. Image and making sure there is a consistent cash flow trumps all else.”
Another frontline physician who works at a large New York hospital, said staff have been cautioned not to talk with the media and to be careful what they post on social media regarding COVID-19. The general rule is that only information approved by administrators can be shared, said the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“[The health system] is very protective of their public image,” he said. “In the past, people that have posted things that they don’t like get spoken to quickly and/or fired depending on what was written. I could only imagine that would be the situation regarding COVID-19. They are very strict.”
The frontline physician, who has close contact with COVID-19 patients, said he has access to N95 masks at the moment, but when he requested higher-level protective gear, hospital management refused the request and denied that such supplies were needed.
“Safety of frontline workers appears to not be taken seriously,” he said of his hospital. “Everyone is stressed, but at the end of the day, the administration is sitting there, while the rest of us are putting ourselves at risk.”
We reached out to one hospital for comment, but messages were not returned. Other hospitals were not contacted because physicians feared they would face retribution. We also contacted the American Hospital Association but they did not immediately respond.
In Chicago, an email by a nurse to her coworkers about the safety of masks has resulted in a lawsuit after the nurse says she was fired for sharing her concerns with staff. The nurse, Lauri Mazurkiewicz, sent an email to staffers at Northwestern Memorial Hospital stating the surgical masks provided by the hospital were less effective against airborne particles than were N95 masks, according to a lawsuit filed March 23 in Cook County Circuit Court. Ms. Mazurkiewicz was terminated the next day in retaliation for her email, the lawsuit alleges.
Ms. Mazurkiewicz could not be reached for comment by press time.
Christopher King, a spokesman for Northwestern Medicine, said the hospital is reviewing the lawsuit.
“As Northwestern Medicine continues to respond to this unprecedented health care pandemic, the health and well-being of our patients, our staff and our employees is our highest priority,” he said in a statement. “We take these matters seriously and we are currently reviewing the complaint. At this time, we will not be commenting further.”
John Mandrola, MD, a Louisville, Ky.–based cardiologist who has written about the recent muzzling of frontline physicians with respect to the coronavirus, said he is not surprised that some hospitals are preventing physicians from sharing their experiences.
“Before C19, in many hospital systems, there was a culture of fear amongst employed clinicians,” he said. “Employed clinicians see other employed physicians being terminated for speaking frankly about problems. It takes scant few of these cases to create a culture of silence.”
Dr. Mandrola, who is a regular Medscape contributor, said that a number of doctors have reached out to him privately about PPE scarcity and shared that they were explicitly warned by administrators not to talk about the shortfalls. Leadership at Dr. Mandrola’s hospital has not issued the same warnings, he said.
“From the hat of total transparency, I think the public is not getting a full view of the impending potential problems that are going to come by doctors not speaking publicly,” he said. “On the other hand, hospital leadership is doing the best they can. It’s not the hospitals’ fault. Hospital administrators can’t manufacture masks.”
From a public health standpoint, Dr. Mehta said that not allowing health professionals to speak publicly about the situations at their hospitals is “irresponsible.” The public deserves to know what is happening, she said, and the health care workforce needs to prepare for what is to come.
“It’s so important that we hear from our colleagues,” she said. “It’s important to hear those accounts so we can prepare for what we’re about to face. Data is crucial. The more you learn from each other, the better shot we have at successfully treating cases and ultimately beating this.”
With the critical shortage of PPE at his hospital and the inability to speak out about the problem, the orthopedic surgeon foresees the dilemma continuing to worsen.
“It’s not only the lives of front-line health care workers that are at risk, but it’s those that they’re going to spread it to and those that are going to be coming to the hospital requiring our care,” he said. “If we don’t have a fully functioning health care force, our capacity is going to be diminished that much further.”
The American Gastroenterological Association, along with 44 other medical specialty societies representing more than 800,000 physicians, signed onto the Council of Medical Specialty Societies letter stating that all frontline health care professionals must have access to PPEs and be able to speak publicly about the lack of PPEs without retribution while pushing for adequate supply and distribution. Review the statement at https://cmss.org/cmss-statement-ppe.
agallegos@mdedge.com
Over the past month, an orthopedic surgeon has watched as the crowd of sick patients at his hospital has grown, while the supply of personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff has diminished. As he prepares for another day of staffing testing tents and places his one and only mask across his face, he also receives a daily reminder from hospital management: Don’t talk about it.
“It’s very clear; no one is allowed to speak for the institution or of the institution,” he said in an interview. “We get a daily warning about being very prudent about posts on personal accounts. They’ve talked about this with respect to various issues: case numbers, case severity, testing availability, [and] PPEs.”
The warnings mean staff at the hospital suffer in silence, unable to share the troubling situation with the public or request assistance with supplies.
“I have one mask. We’re expected to reuse them, unless you were exposed or worked with a known COVID victim,” the surgeon said. “However, with the numbers in our region rapidly increasing, you can’t assume that people don’t have it or that you don’t have particles on your mask, even if you’re not in a known quarantine zone within the institution.”
As the COVID-19 health crisis rages on, online platforms have become a common place for health professionals to lament short supplies, share concerns, tell stories, and plead for help. But at the same time, other physicians, nurses, and health care workers are being muzzled by hospital administrators and threatened with discipline for speaking out about coronavirus caseloads and dwindling supplies. Some worry the gag orders are muddying the picture of how hospitals are faring in the pandemic, while placing the safety of frontline workers at risk.
The silencing of physicians by hospitals about PPE shortages and other COVID-19 issues has become widespread, said Nisha Mehta, MD, a physician advocate and community leader who writes about PPE on social media. Physicians are being warned not to speak or post publicly about their COVID-19 experiences, including PPE shortages, case specifics, and the percentage of full hospital beds, Dr. Mehta said in an interview. In some cases, physicians who have posted have been forced to take down the posts or have faced retribution for speaking out, she said.
“There’s definitely a big fear among physicians, particularly employed physicians, in terms of what the consequences may be for telling their stories,” Dr. Mehta said. “I find that counterproductive. I understand not inducing panic, but these are real stories that are important for people to understand so they do stay home and increase the systemic pressure to get sufficient PPE, so that we can preserve our health care workforce for a problem that is going to get worse before it gets better.”
Meanwhile, an Indiana hospitalist who took to social media to ask for masks for hospitals in his area says he was immediately reprimanded by his management after the posts came to light. The hospitalist posted on a social media platform to request donations of N95 masks after hearing members of the public had purchased such masks. He hoped his plea would aid preparation for the pandemic at local hospitals, explained the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Shortly afterward, administrators from his hospital contacted the online forum’s moderator and the posts were removed, he said. During a subsequent conversation, administrators warned the doctor not to make such posts about PPE because it made the hospital appear incompetent.
“I was told, ‘we can handle this, we don’t need the public’s help,’” the physician said. “I was hurt and upset. I was trying to help protect my peers.”
After landing on the management’s radar, the hospitalist said he was reprimanded a second time about posts on a separate personal social media account. The second time, the private posts to friends and family were related to COVID-19 and PPE, but did not include any protected health information, he said. However, administrators did not like the content of the posts, and he was told management was monitoring his activity on social media, he said.
“The larger message is that patients are money,” the hospitalist said. “The corporate side of medicine rules out over the medicine side. Image and making sure there is a consistent cash flow trumps all else.”
Another frontline physician who works at a large New York hospital, said staff have been cautioned not to talk with the media and to be careful what they post on social media regarding COVID-19. The general rule is that only information approved by administrators can be shared, said the physician, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“[The health system] is very protective of their public image,” he said. “In the past, people that have posted things that they don’t like get spoken to quickly and/or fired depending on what was written. I could only imagine that would be the situation regarding COVID-19. They are very strict.”
The frontline physician, who has close contact with COVID-19 patients, said he has access to N95 masks at the moment, but when he requested higher-level protective gear, hospital management refused the request and denied that such supplies were needed.
“Safety of frontline workers appears to not be taken seriously,” he said of his hospital. “Everyone is stressed, but at the end of the day, the administration is sitting there, while the rest of us are putting ourselves at risk.”
We reached out to one hospital for comment, but messages were not returned. Other hospitals were not contacted because physicians feared they would face retribution. We also contacted the American Hospital Association but they did not immediately respond.
In Chicago, an email by a nurse to her coworkers about the safety of masks has resulted in a lawsuit after the nurse says she was fired for sharing her concerns with staff. The nurse, Lauri Mazurkiewicz, sent an email to staffers at Northwestern Memorial Hospital stating the surgical masks provided by the hospital were less effective against airborne particles than were N95 masks, according to a lawsuit filed March 23 in Cook County Circuit Court. Ms. Mazurkiewicz was terminated the next day in retaliation for her email, the lawsuit alleges.
Ms. Mazurkiewicz could not be reached for comment by press time.
Christopher King, a spokesman for Northwestern Medicine, said the hospital is reviewing the lawsuit.
“As Northwestern Medicine continues to respond to this unprecedented health care pandemic, the health and well-being of our patients, our staff and our employees is our highest priority,” he said in a statement. “We take these matters seriously and we are currently reviewing the complaint. At this time, we will not be commenting further.”
John Mandrola, MD, a Louisville, Ky.–based cardiologist who has written about the recent muzzling of frontline physicians with respect to the coronavirus, said he is not surprised that some hospitals are preventing physicians from sharing their experiences.
“Before C19, in many hospital systems, there was a culture of fear amongst employed clinicians,” he said. “Employed clinicians see other employed physicians being terminated for speaking frankly about problems. It takes scant few of these cases to create a culture of silence.”
Dr. Mandrola, who is a regular Medscape contributor, said that a number of doctors have reached out to him privately about PPE scarcity and shared that they were explicitly warned by administrators not to talk about the shortfalls. Leadership at Dr. Mandrola’s hospital has not issued the same warnings, he said.
“From the hat of total transparency, I think the public is not getting a full view of the impending potential problems that are going to come by doctors not speaking publicly,” he said. “On the other hand, hospital leadership is doing the best they can. It’s not the hospitals’ fault. Hospital administrators can’t manufacture masks.”
From a public health standpoint, Dr. Mehta said that not allowing health professionals to speak publicly about the situations at their hospitals is “irresponsible.” The public deserves to know what is happening, she said, and the health care workforce needs to prepare for what is to come.
“It’s so important that we hear from our colleagues,” she said. “It’s important to hear those accounts so we can prepare for what we’re about to face. Data is crucial. The more you learn from each other, the better shot we have at successfully treating cases and ultimately beating this.”
With the critical shortage of PPE at his hospital and the inability to speak out about the problem, the orthopedic surgeon foresees the dilemma continuing to worsen.
“It’s not only the lives of front-line health care workers that are at risk, but it’s those that they’re going to spread it to and those that are going to be coming to the hospital requiring our care,” he said. “If we don’t have a fully functioning health care force, our capacity is going to be diminished that much further.”
The American Gastroenterological Association, along with 44 other medical specialty societies representing more than 800,000 physicians, signed onto the Council of Medical Specialty Societies letter stating that all frontline health care professionals must have access to PPEs and be able to speak publicly about the lack of PPEs without retribution while pushing for adequate supply and distribution. Review the statement at https://cmss.org/cmss-statement-ppe.
agallegos@mdedge.com
Maternal methadone opioid maintenance therapy may be tied to smaller postnatal head circumference
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – compared with opioid maintenance therapy with buprenorphine, according to a study presented at the Pregnancy Meeting.
Antenatal ultrasound measurements do not differ by treatment, however, the researchers said. A separate study suggests that serial ultrasound examinations of fetal brain and biometry measurements may not be helpful in patients who receive these medications for opioid use disorder.
To examine the effects of methadone and buprenorphine opioid maintenance therapy on prenatal and postnatal growth parameters, Jay Davis, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine fellow at Stony Brook University in New York, and coinvestigators conducted a retrospective cohort study using medical records from an academic center during 2007-2017. They included women with singleton pregnancies receiving opioid maintenance therapy with methadone or buprenorphine. They compared head circumference percentile, abdominal circumference percentile, head circumference/abdominal circumference ratio, and postnatal head circumference percentile between the two groups. The investigators analyzed the data using the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test, chi-square test, and logistic regression.
The researchers studied 282 cases, including 120 patients who received buprenorphine and 162 who received methadone. Patients who received buprenorphine delivered at a later average gestational age (39 weeks vs. 37.8 weeks) and had newborns with greater average birth weights (3,206 g vs. 2,877 g). Compared with patients who received methadone, patients who received buprenorphine were significantly more likely to have a larger postnatal head circumference percentile (39 vs. 30), Dr. Davis and colleagues reported. This difference remained significant after controlling for race, prescriber, gestational age at delivery, and birth weight.
In a separate study presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Jose M. Perez Yordan, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and colleagues examined effects of medications for opioid use disorder on fetal brain and body measurements.
They found that maternal medications for opioid use disorder do not have a clinically significant effect on fetal brain and body measurements, compared with controls. “No consistent pattern of decreased fetal growth was identified, since the body measurement affected did not persist with serial ultrasounds,” they said. “Serial ultrasound examinations do not appear to be helpful in patients” who take medications of opioid use disorder, with or without alcohol coexposure, unless other risk factors are present.
To evaluate the effects of medications of opioid use disorder and alcohol coexposure on fetal brain and biometric measurements at the second- and third-trimester ultrasound measurements, the investigators are conducting a prospective study known as ENRICH-1. The study includes healthy controls, patients taking medications of opioid use disorder (that is, buprenorphine or methadone), and patients taking medications of opioid use disorder with alcohol coexposure.
Ultrasound measurements from the second and third trimesters evaluated biparietal diameter, femur length, frontal lobe width and length, front-thalamic distance, and caval-calvarial distance. Univariate and multivariate analyses assessed differences in measurements adjusting for gestational age and other factors.
The present analysis included data from 171 participants, including 56 healthy controls, 75 patients taking medications of opioid use disorder, and 40 patients taking medications of opioid use disorder with alcohol coexposure. There was no consistent pattern of decreased fetal growth. Affected measurements did not persist over time.
The study presented by Dr. Perez Yordan was supported by a National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism grant. The remaining investigators in both studies had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perez Yordan JM et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S110, Abstract 149; Davis J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S430, Abstract 678.
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – compared with opioid maintenance therapy with buprenorphine, according to a study presented at the Pregnancy Meeting.
Antenatal ultrasound measurements do not differ by treatment, however, the researchers said. A separate study suggests that serial ultrasound examinations of fetal brain and biometry measurements may not be helpful in patients who receive these medications for opioid use disorder.
To examine the effects of methadone and buprenorphine opioid maintenance therapy on prenatal and postnatal growth parameters, Jay Davis, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine fellow at Stony Brook University in New York, and coinvestigators conducted a retrospective cohort study using medical records from an academic center during 2007-2017. They included women with singleton pregnancies receiving opioid maintenance therapy with methadone or buprenorphine. They compared head circumference percentile, abdominal circumference percentile, head circumference/abdominal circumference ratio, and postnatal head circumference percentile between the two groups. The investigators analyzed the data using the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test, chi-square test, and logistic regression.
The researchers studied 282 cases, including 120 patients who received buprenorphine and 162 who received methadone. Patients who received buprenorphine delivered at a later average gestational age (39 weeks vs. 37.8 weeks) and had newborns with greater average birth weights (3,206 g vs. 2,877 g). Compared with patients who received methadone, patients who received buprenorphine were significantly more likely to have a larger postnatal head circumference percentile (39 vs. 30), Dr. Davis and colleagues reported. This difference remained significant after controlling for race, prescriber, gestational age at delivery, and birth weight.
In a separate study presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Jose M. Perez Yordan, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and colleagues examined effects of medications for opioid use disorder on fetal brain and body measurements.
They found that maternal medications for opioid use disorder do not have a clinically significant effect on fetal brain and body measurements, compared with controls. “No consistent pattern of decreased fetal growth was identified, since the body measurement affected did not persist with serial ultrasounds,” they said. “Serial ultrasound examinations do not appear to be helpful in patients” who take medications of opioid use disorder, with or without alcohol coexposure, unless other risk factors are present.
To evaluate the effects of medications of opioid use disorder and alcohol coexposure on fetal brain and biometric measurements at the second- and third-trimester ultrasound measurements, the investigators are conducting a prospective study known as ENRICH-1. The study includes healthy controls, patients taking medications of opioid use disorder (that is, buprenorphine or methadone), and patients taking medications of opioid use disorder with alcohol coexposure.
Ultrasound measurements from the second and third trimesters evaluated biparietal diameter, femur length, frontal lobe width and length, front-thalamic distance, and caval-calvarial distance. Univariate and multivariate analyses assessed differences in measurements adjusting for gestational age and other factors.
The present analysis included data from 171 participants, including 56 healthy controls, 75 patients taking medications of opioid use disorder, and 40 patients taking medications of opioid use disorder with alcohol coexposure. There was no consistent pattern of decreased fetal growth. Affected measurements did not persist over time.
The study presented by Dr. Perez Yordan was supported by a National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism grant. The remaining investigators in both studies had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perez Yordan JM et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S110, Abstract 149; Davis J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S430, Abstract 678.
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – compared with opioid maintenance therapy with buprenorphine, according to a study presented at the Pregnancy Meeting.
Antenatal ultrasound measurements do not differ by treatment, however, the researchers said. A separate study suggests that serial ultrasound examinations of fetal brain and biometry measurements may not be helpful in patients who receive these medications for opioid use disorder.
To examine the effects of methadone and buprenorphine opioid maintenance therapy on prenatal and postnatal growth parameters, Jay Davis, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine fellow at Stony Brook University in New York, and coinvestigators conducted a retrospective cohort study using medical records from an academic center during 2007-2017. They included women with singleton pregnancies receiving opioid maintenance therapy with methadone or buprenorphine. They compared head circumference percentile, abdominal circumference percentile, head circumference/abdominal circumference ratio, and postnatal head circumference percentile between the two groups. The investigators analyzed the data using the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test, chi-square test, and logistic regression.
The researchers studied 282 cases, including 120 patients who received buprenorphine and 162 who received methadone. Patients who received buprenorphine delivered at a later average gestational age (39 weeks vs. 37.8 weeks) and had newborns with greater average birth weights (3,206 g vs. 2,877 g). Compared with patients who received methadone, patients who received buprenorphine were significantly more likely to have a larger postnatal head circumference percentile (39 vs. 30), Dr. Davis and colleagues reported. This difference remained significant after controlling for race, prescriber, gestational age at delivery, and birth weight.
In a separate study presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Jose M. Perez Yordan, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and colleagues examined effects of medications for opioid use disorder on fetal brain and body measurements.
They found that maternal medications for opioid use disorder do not have a clinically significant effect on fetal brain and body measurements, compared with controls. “No consistent pattern of decreased fetal growth was identified, since the body measurement affected did not persist with serial ultrasounds,” they said. “Serial ultrasound examinations do not appear to be helpful in patients” who take medications of opioid use disorder, with or without alcohol coexposure, unless other risk factors are present.
To evaluate the effects of medications of opioid use disorder and alcohol coexposure on fetal brain and biometric measurements at the second- and third-trimester ultrasound measurements, the investigators are conducting a prospective study known as ENRICH-1. The study includes healthy controls, patients taking medications of opioid use disorder (that is, buprenorphine or methadone), and patients taking medications of opioid use disorder with alcohol coexposure.
Ultrasound measurements from the second and third trimesters evaluated biparietal diameter, femur length, frontal lobe width and length, front-thalamic distance, and caval-calvarial distance. Univariate and multivariate analyses assessed differences in measurements adjusting for gestational age and other factors.
The present analysis included data from 171 participants, including 56 healthy controls, 75 patients taking medications of opioid use disorder, and 40 patients taking medications of opioid use disorder with alcohol coexposure. There was no consistent pattern of decreased fetal growth. Affected measurements did not persist over time.
The study presented by Dr. Perez Yordan was supported by a National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism grant. The remaining investigators in both studies had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perez Yordan JM et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S110, Abstract 149; Davis J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S430, Abstract 678.
REPORTING FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
Step 1 scoring moves to pass/fail: Hospitalists’ role and unintended consequences
The National Board of Medical Examiners recently announced a change in the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score reporting from a 3-digit score to a pass/fail score beginning in 2022.1 Endorsed by a broad coalition of organizations involved in undergraduate (UME) and graduate medical education (GME), this change is intended as a first step toward systemic improvements in the UME-GME transition to residency by promoting holistic reviews of applicants. Additionally, it is meant to tackle widespread concerns about medical student distress brought about by the residency selection process. For example, switching to pass/fail preclinical curricula has resulted in an improvement in medical student well-being at many medical schools.2 It is the hope that a mirrored change in Step 1 may similarly improve mental health and encourage a growth mindset towards learning.
On the other hand, many residency programs rely on USMLE scores for screening potential candidates, especially as application inflation has burdened programs with thousands of applications.3 The change to a pass/fail Step 1 score will likely shift emphasis and stress to the Step 2 CK Exam, essentially negating the intended effect. Furthermore, for schools still reporting NBME Subject (shelf) Exam scores and Clerkship grades, there will likely be a greater emphasis placed on these metrics as well. The need for objective assessment methods are seen by many as so critical that some GME leaders have advocated for instituting entrance exams or requiring a Standardized Letter of Evaluation as a prerequisite to residency application. Finally, medical students jockeying for competitive residency positions may also feel pressured to distinguish themselves by boosting other aspects of their portfolio by taking a research year or applying for away electives, which risks marginalizing students of lesser means or with family responsibilities.
Ultimately, the change to a pass/fail Step 1 exam will likely do little to address the expanding gulf between the UME and GME communities. Residency program directors are searching for students with qualities of a good physician, such as interpersonal skills, “teamsmanship,” compassion, and professionalism, but reliable, objective, and standardized assessment tools are not available. Currently our best tools are clinical evaluations which are subject to grade inflation and implicit racial and gender biases. Furthermore, other components of a residency application, such as letters of recommendation, Chair’s letters, and the Medical Student Performance Evaluation (Dean’s letter), are regarded to be less informative as schools move toward no student rankings, pass/fail grading schemes, and nonstandardized summative adjectives to describe medical students overall medical school performance.
Finally, medical student distress in the residency application process may stem from the perpetuation of elitism that extends from medical school to fellowship training and academic hospital medicine. Rankings of medical schools, residencies, fellowships, and hospitals serve to create a hierarchical system. Competitive residency applicants see admittance into the best training programs as opening doors to opportunities, while not getting into these programs is seen as closing doors to career paths and opportunities.
With this change in Step 1 score reporting, where do we as hospitalists fit in? Hospitalists are at the forefront of educating and evaluating medical students in academic medical centers, and we are often asked to write letters of recommendation and serve as mentors. If done well, these activities can have a positive impact on medical student applications to residency by alleviating some of the stresses and mitigating the downsides to the new Step 1 scoring system. Writing impactful letters and thoughtful evaluations are all skills that should be incorporated in hospitalist faculty development programs. Moreover, in order to serve as better advocates for our students, it is important that academic hospitalists understand the evolving landscape of the residency application process and are mindful of the stresses that medical students face. Changing Step 1 scoring to pass/fail will likely have unintended consequences for our medical students, and we as hospitalists must be ready to improve our knowledge and skills in order to continue to support and advocate for our medical students.
Dr. Esquivel is a hospitalist and assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York; Dr. Chang is associate professor and interprofessional education thread director (MD curriculum) at Washington University, St. Louis; Dr. Ricotta is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School; Dr. Rendon is a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque; Dr. Kwan is a hospitalist at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System and associate professor at the University of California, San Diego. He is the chair of SHM’s Physicians in Training committee.
References
1. United States Medical Licensing Examination (2020 Feb). Change to pass/fail score reporting for Step 1.
2. Slavin SJ and Chibnall JT. Finding the why, changing the how: Improving the mental health of medical students, residents, and physicians. Academic Medicine. 2016;91(9):1194‐6.
3. Pereira AG, Chelminski PR, et al. Application inflation for internal medicine applicants in the Match: Drivers, consequences, and potential solutions. Am J Med. 2016 Aug;129(8): 885-91.
The National Board of Medical Examiners recently announced a change in the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score reporting from a 3-digit score to a pass/fail score beginning in 2022.1 Endorsed by a broad coalition of organizations involved in undergraduate (UME) and graduate medical education (GME), this change is intended as a first step toward systemic improvements in the UME-GME transition to residency by promoting holistic reviews of applicants. Additionally, it is meant to tackle widespread concerns about medical student distress brought about by the residency selection process. For example, switching to pass/fail preclinical curricula has resulted in an improvement in medical student well-being at many medical schools.2 It is the hope that a mirrored change in Step 1 may similarly improve mental health and encourage a growth mindset towards learning.
On the other hand, many residency programs rely on USMLE scores for screening potential candidates, especially as application inflation has burdened programs with thousands of applications.3 The change to a pass/fail Step 1 score will likely shift emphasis and stress to the Step 2 CK Exam, essentially negating the intended effect. Furthermore, for schools still reporting NBME Subject (shelf) Exam scores and Clerkship grades, there will likely be a greater emphasis placed on these metrics as well. The need for objective assessment methods are seen by many as so critical that some GME leaders have advocated for instituting entrance exams or requiring a Standardized Letter of Evaluation as a prerequisite to residency application. Finally, medical students jockeying for competitive residency positions may also feel pressured to distinguish themselves by boosting other aspects of their portfolio by taking a research year or applying for away electives, which risks marginalizing students of lesser means or with family responsibilities.
Ultimately, the change to a pass/fail Step 1 exam will likely do little to address the expanding gulf between the UME and GME communities. Residency program directors are searching for students with qualities of a good physician, such as interpersonal skills, “teamsmanship,” compassion, and professionalism, but reliable, objective, and standardized assessment tools are not available. Currently our best tools are clinical evaluations which are subject to grade inflation and implicit racial and gender biases. Furthermore, other components of a residency application, such as letters of recommendation, Chair’s letters, and the Medical Student Performance Evaluation (Dean’s letter), are regarded to be less informative as schools move toward no student rankings, pass/fail grading schemes, and nonstandardized summative adjectives to describe medical students overall medical school performance.
Finally, medical student distress in the residency application process may stem from the perpetuation of elitism that extends from medical school to fellowship training and academic hospital medicine. Rankings of medical schools, residencies, fellowships, and hospitals serve to create a hierarchical system. Competitive residency applicants see admittance into the best training programs as opening doors to opportunities, while not getting into these programs is seen as closing doors to career paths and opportunities.
With this change in Step 1 score reporting, where do we as hospitalists fit in? Hospitalists are at the forefront of educating and evaluating medical students in academic medical centers, and we are often asked to write letters of recommendation and serve as mentors. If done well, these activities can have a positive impact on medical student applications to residency by alleviating some of the stresses and mitigating the downsides to the new Step 1 scoring system. Writing impactful letters and thoughtful evaluations are all skills that should be incorporated in hospitalist faculty development programs. Moreover, in order to serve as better advocates for our students, it is important that academic hospitalists understand the evolving landscape of the residency application process and are mindful of the stresses that medical students face. Changing Step 1 scoring to pass/fail will likely have unintended consequences for our medical students, and we as hospitalists must be ready to improve our knowledge and skills in order to continue to support and advocate for our medical students.
Dr. Esquivel is a hospitalist and assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York; Dr. Chang is associate professor and interprofessional education thread director (MD curriculum) at Washington University, St. Louis; Dr. Ricotta is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School; Dr. Rendon is a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque; Dr. Kwan is a hospitalist at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System and associate professor at the University of California, San Diego. He is the chair of SHM’s Physicians in Training committee.
References
1. United States Medical Licensing Examination (2020 Feb). Change to pass/fail score reporting for Step 1.
2. Slavin SJ and Chibnall JT. Finding the why, changing the how: Improving the mental health of medical students, residents, and physicians. Academic Medicine. 2016;91(9):1194‐6.
3. Pereira AG, Chelminski PR, et al. Application inflation for internal medicine applicants in the Match: Drivers, consequences, and potential solutions. Am J Med. 2016 Aug;129(8): 885-91.
The National Board of Medical Examiners recently announced a change in the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score reporting from a 3-digit score to a pass/fail score beginning in 2022.1 Endorsed by a broad coalition of organizations involved in undergraduate (UME) and graduate medical education (GME), this change is intended as a first step toward systemic improvements in the UME-GME transition to residency by promoting holistic reviews of applicants. Additionally, it is meant to tackle widespread concerns about medical student distress brought about by the residency selection process. For example, switching to pass/fail preclinical curricula has resulted in an improvement in medical student well-being at many medical schools.2 It is the hope that a mirrored change in Step 1 may similarly improve mental health and encourage a growth mindset towards learning.
On the other hand, many residency programs rely on USMLE scores for screening potential candidates, especially as application inflation has burdened programs with thousands of applications.3 The change to a pass/fail Step 1 score will likely shift emphasis and stress to the Step 2 CK Exam, essentially negating the intended effect. Furthermore, for schools still reporting NBME Subject (shelf) Exam scores and Clerkship grades, there will likely be a greater emphasis placed on these metrics as well. The need for objective assessment methods are seen by many as so critical that some GME leaders have advocated for instituting entrance exams or requiring a Standardized Letter of Evaluation as a prerequisite to residency application. Finally, medical students jockeying for competitive residency positions may also feel pressured to distinguish themselves by boosting other aspects of their portfolio by taking a research year or applying for away electives, which risks marginalizing students of lesser means or with family responsibilities.
Ultimately, the change to a pass/fail Step 1 exam will likely do little to address the expanding gulf between the UME and GME communities. Residency program directors are searching for students with qualities of a good physician, such as interpersonal skills, “teamsmanship,” compassion, and professionalism, but reliable, objective, and standardized assessment tools are not available. Currently our best tools are clinical evaluations which are subject to grade inflation and implicit racial and gender biases. Furthermore, other components of a residency application, such as letters of recommendation, Chair’s letters, and the Medical Student Performance Evaluation (Dean’s letter), are regarded to be less informative as schools move toward no student rankings, pass/fail grading schemes, and nonstandardized summative adjectives to describe medical students overall medical school performance.
Finally, medical student distress in the residency application process may stem from the perpetuation of elitism that extends from medical school to fellowship training and academic hospital medicine. Rankings of medical schools, residencies, fellowships, and hospitals serve to create a hierarchical system. Competitive residency applicants see admittance into the best training programs as opening doors to opportunities, while not getting into these programs is seen as closing doors to career paths and opportunities.
With this change in Step 1 score reporting, where do we as hospitalists fit in? Hospitalists are at the forefront of educating and evaluating medical students in academic medical centers, and we are often asked to write letters of recommendation and serve as mentors. If done well, these activities can have a positive impact on medical student applications to residency by alleviating some of the stresses and mitigating the downsides to the new Step 1 scoring system. Writing impactful letters and thoughtful evaluations are all skills that should be incorporated in hospitalist faculty development programs. Moreover, in order to serve as better advocates for our students, it is important that academic hospitalists understand the evolving landscape of the residency application process and are mindful of the stresses that medical students face. Changing Step 1 scoring to pass/fail will likely have unintended consequences for our medical students, and we as hospitalists must be ready to improve our knowledge and skills in order to continue to support and advocate for our medical students.
Dr. Esquivel is a hospitalist and assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York; Dr. Chang is associate professor and interprofessional education thread director (MD curriculum) at Washington University, St. Louis; Dr. Ricotta is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School; Dr. Rendon is a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque; Dr. Kwan is a hospitalist at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System and associate professor at the University of California, San Diego. He is the chair of SHM’s Physicians in Training committee.
References
1. United States Medical Licensing Examination (2020 Feb). Change to pass/fail score reporting for Step 1.
2. Slavin SJ and Chibnall JT. Finding the why, changing the how: Improving the mental health of medical students, residents, and physicians. Academic Medicine. 2016;91(9):1194‐6.
3. Pereira AG, Chelminski PR, et al. Application inflation for internal medicine applicants in the Match: Drivers, consequences, and potential solutions. Am J Med. 2016 Aug;129(8): 885-91.
COVID-19 shifts telehealth to the center of cardiology
during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During a recent telehealth webinar, Ami Bhatt, MD, director of the adult congenital heart disease program, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said they’ve gone from seeing 400 patients a day in their clinic to fewer than 40 and are trying to push that number even lower and use virtual care as much as possible.
“The reason is we are having to send home physicians who are exposed and it’s cutting into our workforce very quickly. So the more people you could have at home doing work virtually is important because you’re going to need to call them in [during] the next couple of weeks,” she said. “And our PPE [personal protective equipment] is running low. So if we can afford to not have someone come in the office and not wear a mask because they had a cough, that’s a mask that can be used by someone performing CPR in an ICU.”
The hospital also adopted a train-the-trainer method to bring its existing telehealth program to cardiology, said Dr. Bhatt, who coauthored the American College of Cardiology’s recent guidance on establishing telehealth in the cardiology clinic.
“We find that sending people tip sheets and PowerPoints in addition to everything that is happening ... is too much,” Dr. Bhatt observed. “So actually holding your friend’s hand and walking them through it once you’ve learned how to do it has been really great in terms of adoption. Otherwise, everyone would fall back on phone, which is OK for now, but we need to establish a long-term plan.”
During the same March 20 webinar, David Konur, CEO of the Cardiovascular Institute of the South, Houma, La., said they began doing telecardiology more than 5 years ago and now do about 30,000 “patient touches” a month with 24/7 access.
“This is certainly an unprecedented time,” he said. “COVID-19 is shining a very bright light on the barriers that exist in health care, as well as the friction that exists to accessing care for all of our patients.”
New mandates
A new Food and Drug Administration policy, temporarily relaxing prior guidance on certain connected remote monitoring devices such as ECGs and cardiac monitors, is part of a shifting landscape to reduce barriers to telehealth during the ongoing pandemic. The increased flexibility may increase access to important patient physiological data, while eliminating unnecessary patient contact and easing the burden on healthcare facilities and providers, the agency said in the new guidance, issued March 20.
As such, the FDA “does not intend to object to limited modifications to the indications, claims, functionality, or hardware or software of FDA-cleared noninvasive remote monitoring devices that are used to support patient monitoring.”
Modifications could include the addition of monitoring statements for patients with COVID-19 or coexisting conditions such as hypertension and heart failure; a change to the indications or claims related to home use of devices previously cleared for use only in health care settings; and changes to hardware or software to increase remote monitoring capability. The approved devices listed in the guidance are clinical electronic thermometers, ECGs, cardiac monitors, ECG software for over-the-counter use, pulse oximetry, noninvasive blood pressure monitors, respiratory rate/breathing frequency monitors, and electronic stethoscopes.
The FDA policy comes just days after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services expanded telehealth coverage to Medicare beneficiaries and the Office for Civil Rights at the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services said it would not penalize health care providers for using such non–HIPAA compliant third-party apps as Skype or Google Hangouts video. The HHS also signaled that physicians would be allowed to practice across state lines during the COVID-19 crisis.
“All these mandates have come in a time of desperation where we’re doing the best that we can to provide for patients and keep them safe,” Eugenia Gianos, MD, system director of cardiovascular prevention at Northwell Health and director of the Women’s Cardiovascular Center, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in an interview. “Realistically, the whole digital realm has a lot of promise for our patients.” She noted that telehealth programs are still being developed for the department, but that office visits have been purposely scaled back by more than 75% to protect patients as well as health care providers. “In times of need, the most promising technologies we have, have to come to the forefront,” Dr. Gianos said. “So using the data from the home – whether they have a blood pressure cuff or something that tracks their heart rate or their weight – when we don’t otherwise have data, is of great value.”
Andrew M. Freeman, MD, director of clinical cardiology and operations at National Jewish Hospital in Denver, said “in the current situation, telehealth is the most viable option because it keeps patients safe and physicians safe. So it wouldn’t surprise me if every institution in the country, if not worldwide, is very rapidly pursuing this kind of approach.”
Exactly how many programs or cardiologists were already using telehealth is impossible to say, although the ACC is planning to survey its members on their practices during the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted.
The situation is so fluid that ACC is already revising its March 13 telehealth guidance to reflect the recent policy changes. Another document is being prepared to provide physicians with a template for the telehealth space, said Dr. Freeman, who coauthored the telehealth guidance and also serves on the ACC’s Innovation Leadership Council.
The new FDA policy allowing greater flexibility on remote monitoring devices is somewhat “vaguely worded,” Dr. Freeman noted, but highlights the ability of existing technology to provide essential patient data from home. “I think as we add adjuncts to the things we’re used to in the normal face-to-face visit, it’s going to make the face-to-face visit less required,” he said.
Questions remain, however, on implementing telehealth for new patients and whether payers will follow HHS’s decision not to conduct audits to ensure a prior relationship existed. The potential for telehealth to reach across state lines also is being viewed cautiously until tested legally, Dr. Freeman observed.
“If there’s one blessing in this awful disease that we have received, is that it may really give the power to clinicians, hospital systems, and payers to make telehealth a true viable, sustainable solution for good care that’s readily available to folks,” he said.
Fast-tracked research
On March 24, the American Heart Association announced it is committing $2.5 million for fast-tracked research grants for projects than can turn around results within 9-12 months and focus on how this novel coronavirus affects heart and brain health.
Additional funding also will be made available to the AHA’s new Center for Health Technology & Innovation’s Strategically Focused Research Networks to develop rapid technology solutions to aid in dealing with the pandemic.
The rapid response grant is an “unprecedented but logical move for the organization in these extraordinary times,” AHA President Bob Harrington, MD, chair of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a statement. “We are committed to quickly bringing together and supporting some of the brightest minds in research science and clinical care who are shovel ready with the laboratories, tools, and data resources to immediately begin work on addressing this emergent issue.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Bhatt have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrington is on the editorial board for Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com
during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During a recent telehealth webinar, Ami Bhatt, MD, director of the adult congenital heart disease program, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said they’ve gone from seeing 400 patients a day in their clinic to fewer than 40 and are trying to push that number even lower and use virtual care as much as possible.
“The reason is we are having to send home physicians who are exposed and it’s cutting into our workforce very quickly. So the more people you could have at home doing work virtually is important because you’re going to need to call them in [during] the next couple of weeks,” she said. “And our PPE [personal protective equipment] is running low. So if we can afford to not have someone come in the office and not wear a mask because they had a cough, that’s a mask that can be used by someone performing CPR in an ICU.”
The hospital also adopted a train-the-trainer method to bring its existing telehealth program to cardiology, said Dr. Bhatt, who coauthored the American College of Cardiology’s recent guidance on establishing telehealth in the cardiology clinic.
“We find that sending people tip sheets and PowerPoints in addition to everything that is happening ... is too much,” Dr. Bhatt observed. “So actually holding your friend’s hand and walking them through it once you’ve learned how to do it has been really great in terms of adoption. Otherwise, everyone would fall back on phone, which is OK for now, but we need to establish a long-term plan.”
During the same March 20 webinar, David Konur, CEO of the Cardiovascular Institute of the South, Houma, La., said they began doing telecardiology more than 5 years ago and now do about 30,000 “patient touches” a month with 24/7 access.
“This is certainly an unprecedented time,” he said. “COVID-19 is shining a very bright light on the barriers that exist in health care, as well as the friction that exists to accessing care for all of our patients.”
New mandates
A new Food and Drug Administration policy, temporarily relaxing prior guidance on certain connected remote monitoring devices such as ECGs and cardiac monitors, is part of a shifting landscape to reduce barriers to telehealth during the ongoing pandemic. The increased flexibility may increase access to important patient physiological data, while eliminating unnecessary patient contact and easing the burden on healthcare facilities and providers, the agency said in the new guidance, issued March 20.
As such, the FDA “does not intend to object to limited modifications to the indications, claims, functionality, or hardware or software of FDA-cleared noninvasive remote monitoring devices that are used to support patient monitoring.”
Modifications could include the addition of monitoring statements for patients with COVID-19 or coexisting conditions such as hypertension and heart failure; a change to the indications or claims related to home use of devices previously cleared for use only in health care settings; and changes to hardware or software to increase remote monitoring capability. The approved devices listed in the guidance are clinical electronic thermometers, ECGs, cardiac monitors, ECG software for over-the-counter use, pulse oximetry, noninvasive blood pressure monitors, respiratory rate/breathing frequency monitors, and electronic stethoscopes.
The FDA policy comes just days after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services expanded telehealth coverage to Medicare beneficiaries and the Office for Civil Rights at the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services said it would not penalize health care providers for using such non–HIPAA compliant third-party apps as Skype or Google Hangouts video. The HHS also signaled that physicians would be allowed to practice across state lines during the COVID-19 crisis.
“All these mandates have come in a time of desperation where we’re doing the best that we can to provide for patients and keep them safe,” Eugenia Gianos, MD, system director of cardiovascular prevention at Northwell Health and director of the Women’s Cardiovascular Center, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in an interview. “Realistically, the whole digital realm has a lot of promise for our patients.” She noted that telehealth programs are still being developed for the department, but that office visits have been purposely scaled back by more than 75% to protect patients as well as health care providers. “In times of need, the most promising technologies we have, have to come to the forefront,” Dr. Gianos said. “So using the data from the home – whether they have a blood pressure cuff or something that tracks their heart rate or their weight – when we don’t otherwise have data, is of great value.”
Andrew M. Freeman, MD, director of clinical cardiology and operations at National Jewish Hospital in Denver, said “in the current situation, telehealth is the most viable option because it keeps patients safe and physicians safe. So it wouldn’t surprise me if every institution in the country, if not worldwide, is very rapidly pursuing this kind of approach.”
Exactly how many programs or cardiologists were already using telehealth is impossible to say, although the ACC is planning to survey its members on their practices during the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted.
The situation is so fluid that ACC is already revising its March 13 telehealth guidance to reflect the recent policy changes. Another document is being prepared to provide physicians with a template for the telehealth space, said Dr. Freeman, who coauthored the telehealth guidance and also serves on the ACC’s Innovation Leadership Council.
The new FDA policy allowing greater flexibility on remote monitoring devices is somewhat “vaguely worded,” Dr. Freeman noted, but highlights the ability of existing technology to provide essential patient data from home. “I think as we add adjuncts to the things we’re used to in the normal face-to-face visit, it’s going to make the face-to-face visit less required,” he said.
Questions remain, however, on implementing telehealth for new patients and whether payers will follow HHS’s decision not to conduct audits to ensure a prior relationship existed. The potential for telehealth to reach across state lines also is being viewed cautiously until tested legally, Dr. Freeman observed.
“If there’s one blessing in this awful disease that we have received, is that it may really give the power to clinicians, hospital systems, and payers to make telehealth a true viable, sustainable solution for good care that’s readily available to folks,” he said.
Fast-tracked research
On March 24, the American Heart Association announced it is committing $2.5 million for fast-tracked research grants for projects than can turn around results within 9-12 months and focus on how this novel coronavirus affects heart and brain health.
Additional funding also will be made available to the AHA’s new Center for Health Technology & Innovation’s Strategically Focused Research Networks to develop rapid technology solutions to aid in dealing with the pandemic.
The rapid response grant is an “unprecedented but logical move for the organization in these extraordinary times,” AHA President Bob Harrington, MD, chair of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a statement. “We are committed to quickly bringing together and supporting some of the brightest minds in research science and clinical care who are shovel ready with the laboratories, tools, and data resources to immediately begin work on addressing this emergent issue.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Bhatt have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrington is on the editorial board for Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com
during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During a recent telehealth webinar, Ami Bhatt, MD, director of the adult congenital heart disease program, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said they’ve gone from seeing 400 patients a day in their clinic to fewer than 40 and are trying to push that number even lower and use virtual care as much as possible.
“The reason is we are having to send home physicians who are exposed and it’s cutting into our workforce very quickly. So the more people you could have at home doing work virtually is important because you’re going to need to call them in [during] the next couple of weeks,” she said. “And our PPE [personal protective equipment] is running low. So if we can afford to not have someone come in the office and not wear a mask because they had a cough, that’s a mask that can be used by someone performing CPR in an ICU.”
The hospital also adopted a train-the-trainer method to bring its existing telehealth program to cardiology, said Dr. Bhatt, who coauthored the American College of Cardiology’s recent guidance on establishing telehealth in the cardiology clinic.
“We find that sending people tip sheets and PowerPoints in addition to everything that is happening ... is too much,” Dr. Bhatt observed. “So actually holding your friend’s hand and walking them through it once you’ve learned how to do it has been really great in terms of adoption. Otherwise, everyone would fall back on phone, which is OK for now, but we need to establish a long-term plan.”
During the same March 20 webinar, David Konur, CEO of the Cardiovascular Institute of the South, Houma, La., said they began doing telecardiology more than 5 years ago and now do about 30,000 “patient touches” a month with 24/7 access.
“This is certainly an unprecedented time,” he said. “COVID-19 is shining a very bright light on the barriers that exist in health care, as well as the friction that exists to accessing care for all of our patients.”
New mandates
A new Food and Drug Administration policy, temporarily relaxing prior guidance on certain connected remote monitoring devices such as ECGs and cardiac monitors, is part of a shifting landscape to reduce barriers to telehealth during the ongoing pandemic. The increased flexibility may increase access to important patient physiological data, while eliminating unnecessary patient contact and easing the burden on healthcare facilities and providers, the agency said in the new guidance, issued March 20.
As such, the FDA “does not intend to object to limited modifications to the indications, claims, functionality, or hardware or software of FDA-cleared noninvasive remote monitoring devices that are used to support patient monitoring.”
Modifications could include the addition of monitoring statements for patients with COVID-19 or coexisting conditions such as hypertension and heart failure; a change to the indications or claims related to home use of devices previously cleared for use only in health care settings; and changes to hardware or software to increase remote monitoring capability. The approved devices listed in the guidance are clinical electronic thermometers, ECGs, cardiac monitors, ECG software for over-the-counter use, pulse oximetry, noninvasive blood pressure monitors, respiratory rate/breathing frequency monitors, and electronic stethoscopes.
The FDA policy comes just days after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services expanded telehealth coverage to Medicare beneficiaries and the Office for Civil Rights at the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services said it would not penalize health care providers for using such non–HIPAA compliant third-party apps as Skype or Google Hangouts video. The HHS also signaled that physicians would be allowed to practice across state lines during the COVID-19 crisis.
“All these mandates have come in a time of desperation where we’re doing the best that we can to provide for patients and keep them safe,” Eugenia Gianos, MD, system director of cardiovascular prevention at Northwell Health and director of the Women’s Cardiovascular Center, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in an interview. “Realistically, the whole digital realm has a lot of promise for our patients.” She noted that telehealth programs are still being developed for the department, but that office visits have been purposely scaled back by more than 75% to protect patients as well as health care providers. “In times of need, the most promising technologies we have, have to come to the forefront,” Dr. Gianos said. “So using the data from the home – whether they have a blood pressure cuff or something that tracks their heart rate or their weight – when we don’t otherwise have data, is of great value.”
Andrew M. Freeman, MD, director of clinical cardiology and operations at National Jewish Hospital in Denver, said “in the current situation, telehealth is the most viable option because it keeps patients safe and physicians safe. So it wouldn’t surprise me if every institution in the country, if not worldwide, is very rapidly pursuing this kind of approach.”
Exactly how many programs or cardiologists were already using telehealth is impossible to say, although the ACC is planning to survey its members on their practices during the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted.
The situation is so fluid that ACC is already revising its March 13 telehealth guidance to reflect the recent policy changes. Another document is being prepared to provide physicians with a template for the telehealth space, said Dr. Freeman, who coauthored the telehealth guidance and also serves on the ACC’s Innovation Leadership Council.
The new FDA policy allowing greater flexibility on remote monitoring devices is somewhat “vaguely worded,” Dr. Freeman noted, but highlights the ability of existing technology to provide essential patient data from home. “I think as we add adjuncts to the things we’re used to in the normal face-to-face visit, it’s going to make the face-to-face visit less required,” he said.
Questions remain, however, on implementing telehealth for new patients and whether payers will follow HHS’s decision not to conduct audits to ensure a prior relationship existed. The potential for telehealth to reach across state lines also is being viewed cautiously until tested legally, Dr. Freeman observed.
“If there’s one blessing in this awful disease that we have received, is that it may really give the power to clinicians, hospital systems, and payers to make telehealth a true viable, sustainable solution for good care that’s readily available to folks,” he said.
Fast-tracked research
On March 24, the American Heart Association announced it is committing $2.5 million for fast-tracked research grants for projects than can turn around results within 9-12 months and focus on how this novel coronavirus affects heart and brain health.
Additional funding also will be made available to the AHA’s new Center for Health Technology & Innovation’s Strategically Focused Research Networks to develop rapid technology solutions to aid in dealing with the pandemic.
The rapid response grant is an “unprecedented but logical move for the organization in these extraordinary times,” AHA President Bob Harrington, MD, chair of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in a statement. “We are committed to quickly bringing together and supporting some of the brightest minds in research science and clinical care who are shovel ready with the laboratories, tools, and data resources to immediately begin work on addressing this emergent issue.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Bhatt have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrington is on the editorial board for Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com
Is COVID-19 leading to a mental illness pandemic?
People living through this crisis are experiencing trauma
We are in the midst of an epidemic and possibly pandemic of anxiety and distress. The worry that folks have about themselves, families, finances, and work is overwhelming for millions.
I speak with people who report periods of racing thoughts jumping back in time and thinking of roads not taken. They also talk about their thoughts jumping forward with life plans of what they’ll do to change their lives in the future – if they survive COVID-19.
that is well-controlled with care (and even without care). Those people are suffering even more. Meanwhile, people with obsessive-compulsive disorder that had been under control appear to have worsened with the added stress.
Social distancing has disrupted our everyday routines. For many, there is no work, no spending time with people we care about, no going to movies or shows, no doing discretionary shopping, no going to school. Parents with children at home report frustration about balancing working from home with completing home-schooling packets. Physicians on the front lines of this unprecedented time report not having the proper protective equipment and worrying about the possibility of exposing their families to SARS-CoV-2.
We hear stories about the illness and even deaths of some young and middle-aged people with no underlying conditions, not to mention the loss of older adults. People are bursting into tears, and becoming easily frustrated and angry. Add in nightmares, ongoing anxiety states, insomnia, and decreased concentration.
We are seeing news reports of people stocking up on guns and ammunition and a case of one taking – and dying from – nonpharmaceutical grade chloroquine in an effort to prevent COVID-19.
I spoke with Juliana Tseng, PsyD, a clinical psychologist based in New York, and she said that the hype, half-truths, and false information from some outlets in the popular media are making things worse. Dr. Tseng added that the lack of coordination among local, state, and federal governments also is increasing fear and alienation.
As I see this period in time, my first thoughts are that we are witnessing a national epidemic of trauma. Specifically, what we have here is a clinical picture of PTSD.
PTSD is defined clearly as a traumatic disorder with a real or perceived fracture with life. Isolation (which we are creating as a way to “flatten the curve” or slow the spread of COVID-19), although that strategy is in our best personal and public health interests, is both painful and stressful. Frustration, flashbacks of past life experiences plus flashbacks of being ill are reported in people I’ve spoken with. Avoidance, even though it is planned in this instance, is part of the PTSD complex.
What can we as mental health professionals do to help alleviate this suffering?
First, of course, we must listen to the scientific experts and the data – and tell people to do the same. Most experts will say that COVID-19 is a mild or moderate illness for the vast majority of people. We also must encourage people to observe precautions outlined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, such as distancing from people, hand washing, and avoiding those who are ill. Explain to people that, currently, there is no vaccine to prevent COVID-19. Treatment is mainly supportive, and some medication trials are being explored. However, we can empower people by helping them to develop skills aimed at increasing the ability to relax and focus on more positive aspects of life to break the chain of the stress and tension of anxiety as well as control the PTSD.
For more than 40 years, I have helped people master relaxation techniques and guided imagery. When taught properly, people are able to use these techniques on their own.
To begin, I teach people how to relax, using a simple three-point method:
- Get comfortable in a nice chair, and slowly count from one to three. At the count of one, do one thing: “roll your eyes up to the top of your head.”
- At the count of two, do two things, “close your lids on your eyes and take a deep breath.”
- At three, exhale slowly, relax your eyes, and concentrate on a restful feeling of floating.
- Do this for about 30 seconds to a minute.
- Count backward, from three to two to one and open your eyes.
The person will notice how nice and restful they will feel.
After that exercise, get the person to move to the graduate level and go beyond just relaxation. In the following exercise, people can go into a relaxed state by imagining a movie screen. Tell the person to do two things:
1. Look at the imagined movie screen and project on it any pleasant scene you wish; this is your screen. You will feel yourself becoming more and more relaxed. The person can do this one, two, three or whatever times a day. The exercise can last 1 minute or 5.
2. Incorporate the 1, 2, 3 relaxation described earlier, allowing yourself to float into this restful state and go to your movie screen. Now, on the screen, imagine a thick line down the center, and on the left side, project your worries and anxieties and fears. The idea is to see but not experience them. Then shift to the ride side of the screen, and again, visualize any pleasant scene you wish. Again, do this for 1 minute or 5 minutes, whatever works.
You will notice that the pleasant scene on the right will overcome the anxiety scene on the left, in that pleasantness, in most instances, overcomes anxiety. For many, these techniques have proved very useful – whether the problem is anxiety or fear – or both. In my experience, these techniques are a good beginning for controlling PTSD and successfully treating it.
We are in the midst of what could be the biggest public health crisis that America has faced since the 1918 pandemic, also known as the Spanish flu. The lockdowns, quarantines, and the myriad of other disruptions can lead to alienation. In fact, it would be strange for us not to experience strong emotions under these extreme conditions. Life will get better! In the meantime, let’s encourage people to hope, pray, and use relaxation techniques and guided imagery approaches to help control anxiety, worry, stress, and issues related to PTSD. These approaches can give our minds and bodies periods of relaxation and recovery, and ultimately, they can calm our minds.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist and has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in and writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
People living through this crisis are experiencing trauma
People living through this crisis are experiencing trauma
We are in the midst of an epidemic and possibly pandemic of anxiety and distress. The worry that folks have about themselves, families, finances, and work is overwhelming for millions.
I speak with people who report periods of racing thoughts jumping back in time and thinking of roads not taken. They also talk about their thoughts jumping forward with life plans of what they’ll do to change their lives in the future – if they survive COVID-19.
that is well-controlled with care (and even without care). Those people are suffering even more. Meanwhile, people with obsessive-compulsive disorder that had been under control appear to have worsened with the added stress.
Social distancing has disrupted our everyday routines. For many, there is no work, no spending time with people we care about, no going to movies or shows, no doing discretionary shopping, no going to school. Parents with children at home report frustration about balancing working from home with completing home-schooling packets. Physicians on the front lines of this unprecedented time report not having the proper protective equipment and worrying about the possibility of exposing their families to SARS-CoV-2.
We hear stories about the illness and even deaths of some young and middle-aged people with no underlying conditions, not to mention the loss of older adults. People are bursting into tears, and becoming easily frustrated and angry. Add in nightmares, ongoing anxiety states, insomnia, and decreased concentration.
We are seeing news reports of people stocking up on guns and ammunition and a case of one taking – and dying from – nonpharmaceutical grade chloroquine in an effort to prevent COVID-19.
I spoke with Juliana Tseng, PsyD, a clinical psychologist based in New York, and she said that the hype, half-truths, and false information from some outlets in the popular media are making things worse. Dr. Tseng added that the lack of coordination among local, state, and federal governments also is increasing fear and alienation.
As I see this period in time, my first thoughts are that we are witnessing a national epidemic of trauma. Specifically, what we have here is a clinical picture of PTSD.
PTSD is defined clearly as a traumatic disorder with a real or perceived fracture with life. Isolation (which we are creating as a way to “flatten the curve” or slow the spread of COVID-19), although that strategy is in our best personal and public health interests, is both painful and stressful. Frustration, flashbacks of past life experiences plus flashbacks of being ill are reported in people I’ve spoken with. Avoidance, even though it is planned in this instance, is part of the PTSD complex.
What can we as mental health professionals do to help alleviate this suffering?
First, of course, we must listen to the scientific experts and the data – and tell people to do the same. Most experts will say that COVID-19 is a mild or moderate illness for the vast majority of people. We also must encourage people to observe precautions outlined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, such as distancing from people, hand washing, and avoiding those who are ill. Explain to people that, currently, there is no vaccine to prevent COVID-19. Treatment is mainly supportive, and some medication trials are being explored. However, we can empower people by helping them to develop skills aimed at increasing the ability to relax and focus on more positive aspects of life to break the chain of the stress and tension of anxiety as well as control the PTSD.
For more than 40 years, I have helped people master relaxation techniques and guided imagery. When taught properly, people are able to use these techniques on their own.
To begin, I teach people how to relax, using a simple three-point method:
- Get comfortable in a nice chair, and slowly count from one to three. At the count of one, do one thing: “roll your eyes up to the top of your head.”
- At the count of two, do two things, “close your lids on your eyes and take a deep breath.”
- At three, exhale slowly, relax your eyes, and concentrate on a restful feeling of floating.
- Do this for about 30 seconds to a minute.
- Count backward, from three to two to one and open your eyes.
The person will notice how nice and restful they will feel.
After that exercise, get the person to move to the graduate level and go beyond just relaxation. In the following exercise, people can go into a relaxed state by imagining a movie screen. Tell the person to do two things:
1. Look at the imagined movie screen and project on it any pleasant scene you wish; this is your screen. You will feel yourself becoming more and more relaxed. The person can do this one, two, three or whatever times a day. The exercise can last 1 minute or 5.
2. Incorporate the 1, 2, 3 relaxation described earlier, allowing yourself to float into this restful state and go to your movie screen. Now, on the screen, imagine a thick line down the center, and on the left side, project your worries and anxieties and fears. The idea is to see but not experience them. Then shift to the ride side of the screen, and again, visualize any pleasant scene you wish. Again, do this for 1 minute or 5 minutes, whatever works.
You will notice that the pleasant scene on the right will overcome the anxiety scene on the left, in that pleasantness, in most instances, overcomes anxiety. For many, these techniques have proved very useful – whether the problem is anxiety or fear – or both. In my experience, these techniques are a good beginning for controlling PTSD and successfully treating it.
We are in the midst of what could be the biggest public health crisis that America has faced since the 1918 pandemic, also known as the Spanish flu. The lockdowns, quarantines, and the myriad of other disruptions can lead to alienation. In fact, it would be strange for us not to experience strong emotions under these extreme conditions. Life will get better! In the meantime, let’s encourage people to hope, pray, and use relaxation techniques and guided imagery approaches to help control anxiety, worry, stress, and issues related to PTSD. These approaches can give our minds and bodies periods of relaxation and recovery, and ultimately, they can calm our minds.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist and has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in and writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
We are in the midst of an epidemic and possibly pandemic of anxiety and distress. The worry that folks have about themselves, families, finances, and work is overwhelming for millions.
I speak with people who report periods of racing thoughts jumping back in time and thinking of roads not taken. They also talk about their thoughts jumping forward with life plans of what they’ll do to change their lives in the future – if they survive COVID-19.
that is well-controlled with care (and even without care). Those people are suffering even more. Meanwhile, people with obsessive-compulsive disorder that had been under control appear to have worsened with the added stress.
Social distancing has disrupted our everyday routines. For many, there is no work, no spending time with people we care about, no going to movies or shows, no doing discretionary shopping, no going to school. Parents with children at home report frustration about balancing working from home with completing home-schooling packets. Physicians on the front lines of this unprecedented time report not having the proper protective equipment and worrying about the possibility of exposing their families to SARS-CoV-2.
We hear stories about the illness and even deaths of some young and middle-aged people with no underlying conditions, not to mention the loss of older adults. People are bursting into tears, and becoming easily frustrated and angry. Add in nightmares, ongoing anxiety states, insomnia, and decreased concentration.
We are seeing news reports of people stocking up on guns and ammunition and a case of one taking – and dying from – nonpharmaceutical grade chloroquine in an effort to prevent COVID-19.
I spoke with Juliana Tseng, PsyD, a clinical psychologist based in New York, and she said that the hype, half-truths, and false information from some outlets in the popular media are making things worse. Dr. Tseng added that the lack of coordination among local, state, and federal governments also is increasing fear and alienation.
As I see this period in time, my first thoughts are that we are witnessing a national epidemic of trauma. Specifically, what we have here is a clinical picture of PTSD.
PTSD is defined clearly as a traumatic disorder with a real or perceived fracture with life. Isolation (which we are creating as a way to “flatten the curve” or slow the spread of COVID-19), although that strategy is in our best personal and public health interests, is both painful and stressful. Frustration, flashbacks of past life experiences plus flashbacks of being ill are reported in people I’ve spoken with. Avoidance, even though it is planned in this instance, is part of the PTSD complex.
What can we as mental health professionals do to help alleviate this suffering?
First, of course, we must listen to the scientific experts and the data – and tell people to do the same. Most experts will say that COVID-19 is a mild or moderate illness for the vast majority of people. We also must encourage people to observe precautions outlined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, such as distancing from people, hand washing, and avoiding those who are ill. Explain to people that, currently, there is no vaccine to prevent COVID-19. Treatment is mainly supportive, and some medication trials are being explored. However, we can empower people by helping them to develop skills aimed at increasing the ability to relax and focus on more positive aspects of life to break the chain of the stress and tension of anxiety as well as control the PTSD.
For more than 40 years, I have helped people master relaxation techniques and guided imagery. When taught properly, people are able to use these techniques on their own.
To begin, I teach people how to relax, using a simple three-point method:
- Get comfortable in a nice chair, and slowly count from one to three. At the count of one, do one thing: “roll your eyes up to the top of your head.”
- At the count of two, do two things, “close your lids on your eyes and take a deep breath.”
- At three, exhale slowly, relax your eyes, and concentrate on a restful feeling of floating.
- Do this for about 30 seconds to a minute.
- Count backward, from three to two to one and open your eyes.
The person will notice how nice and restful they will feel.
After that exercise, get the person to move to the graduate level and go beyond just relaxation. In the following exercise, people can go into a relaxed state by imagining a movie screen. Tell the person to do two things:
1. Look at the imagined movie screen and project on it any pleasant scene you wish; this is your screen. You will feel yourself becoming more and more relaxed. The person can do this one, two, three or whatever times a day. The exercise can last 1 minute or 5.
2. Incorporate the 1, 2, 3 relaxation described earlier, allowing yourself to float into this restful state and go to your movie screen. Now, on the screen, imagine a thick line down the center, and on the left side, project your worries and anxieties and fears. The idea is to see but not experience them. Then shift to the ride side of the screen, and again, visualize any pleasant scene you wish. Again, do this for 1 minute or 5 minutes, whatever works.
You will notice that the pleasant scene on the right will overcome the anxiety scene on the left, in that pleasantness, in most instances, overcomes anxiety. For many, these techniques have proved very useful – whether the problem is anxiety or fear – or both. In my experience, these techniques are a good beginning for controlling PTSD and successfully treating it.
We are in the midst of what could be the biggest public health crisis that America has faced since the 1918 pandemic, also known as the Spanish flu. The lockdowns, quarantines, and the myriad of other disruptions can lead to alienation. In fact, it would be strange for us not to experience strong emotions under these extreme conditions. Life will get better! In the meantime, let’s encourage people to hope, pray, and use relaxation techniques and guided imagery approaches to help control anxiety, worry, stress, and issues related to PTSD. These approaches can give our minds and bodies periods of relaxation and recovery, and ultimately, they can calm our minds.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist and has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in and writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.