User login
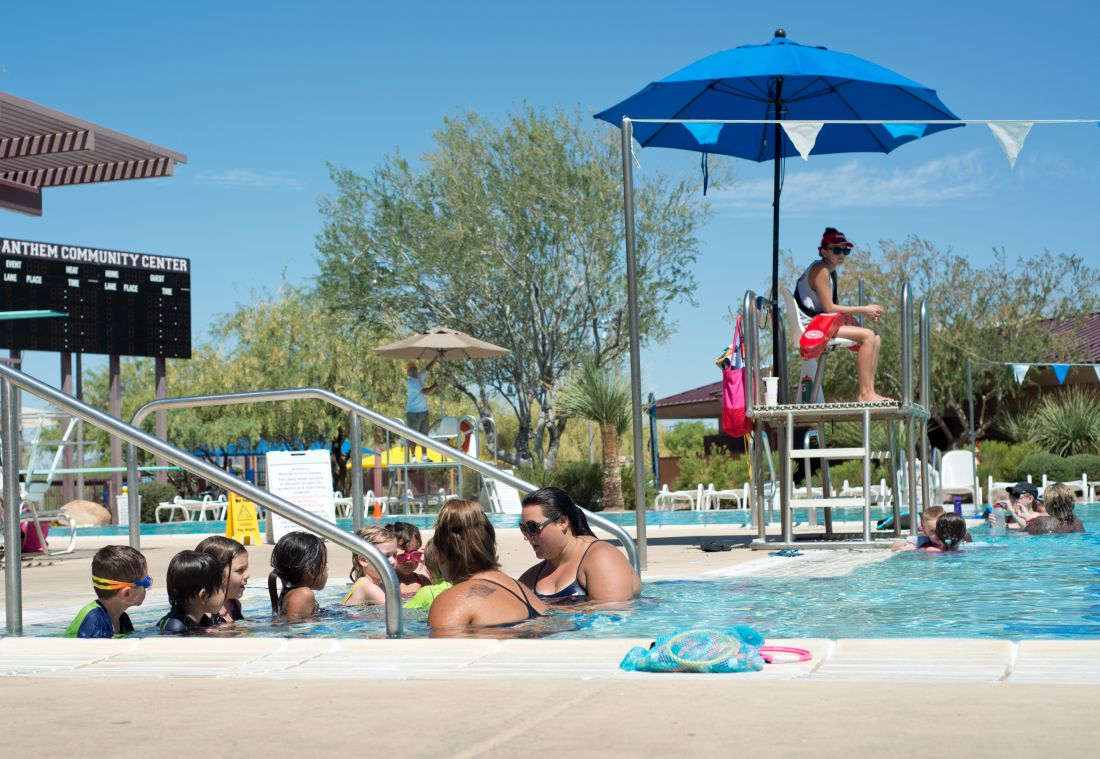
The pool is closed!
At a recent Recreation Commission meeting here in Brunswick, the first agenda item under new business was “Coffin Pond Pool Closing.” As I and my fellow commissioners listened, we were told that for the first time in the last 3 decades the town’s only public swimming area would not be opening. While in the past there have been delayed openings and temporary closings due to water conditions, this year the pool would not open, period. The cause of the pool’s closure was the Parks and Recreation Department’s failure to fill even a skeleton crew of lifeguards.
We learned that the situation here in Brunswick was not unique and most other communities around the state and even around the country were struggling to find lifeguards. The shortage of trained staff has been nationwide for several years, and many beaches and pools particularly in the Northeast and Middle Atlantic states were being forced to close or shorten hours of operation (“During the Pool Season Even Lifeguard Numbers are Taking a Dive,” by Leoneda Inge, July 28, 2015, NPR’s All Thing Considered).
You might think that here on the coast we would have ample places for children to swim, but in Brunswick our shore is rocky and often inaccessible. At the few sandy beaches, the water temperature is too cold for all but the hardy souls until late August. Lower-income families will be particularly affected by the loss of the pool.
When I was growing up, lifeguarding was a plum job that was highly coveted. While it did not pay as well as working construction, the perks of a pleasant atmosphere, the chance to swim every day, and the opportunity to work outside with children prompted me at age 16 to sell my lawn mower and bequeath my lucrative landscaping customers to a couple of preteens. Looking back, my 4 years of lifeguarding were probably a major influence when it came time to choose a specialty.
However, a perfect storm of socioeconomic factors has combined to create a climate in which being a lifeguard has lost its appeal as a summertime job. First, there is record low unemployment nationwide. Young people looking for work have their pick, and while wages still remain low, they can be choosy when it comes to hours and benefits. Lifeguarding does require a skill set and several hoops of certification to be navigated. I don’t recall having to pay much of anything to become certified. But I understand that the process now costs hundreds of dollars of upfront investment with no guarantee of passing the test.
In May, the American Academy of Pediatrics published a policy paper titled “Prevention of Drowning” (Pediatrics. 2019 May 1. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0850) in which the authors offer the troubling statistics on the toll that water-related accidents take on the children of this country annually. They go on to provide a broad list of actions that parents, communities, and pediatricians can take to prevent drownings. Under the category of Community Interventions and Advocacy Opportunities, recommendation No. 4 is “Pediatricians should work with community partners to provide access to programs that develop water-competency swim skills for all children.”
Obviously, these programs can’t happen without an adequate supply of lifeguards.
Unfortunately, the AAP’s statement fails to acknowledge or directly address the lifeguard shortage that has been going on for several years. While an adequate supply of lifeguards is probably not as important as increasing parental attentiveness and mandating pool fences in the overall scheme of drowning prevention, it is an issue that demands action both by the academy and those of us practicing in communities both large and small.
For my part, I am going to work here in Brunswick to see that we can offer lifeguards pay that is more than competitive and then develop an in-house training program to ensure a continuing supply for the future. If we are committed to encouraging our patients to be active, swimming is one of the best activities we should promote and support.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
At a recent Recreation Commission meeting here in Brunswick, the first agenda item under new business was “Coffin Pond Pool Closing.” As I and my fellow commissioners listened, we were told that for the first time in the last 3 decades the town’s only public swimming area would not be opening. While in the past there have been delayed openings and temporary closings due to water conditions, this year the pool would not open, period. The cause of the pool’s closure was the Parks and Recreation Department’s failure to fill even a skeleton crew of lifeguards.
We learned that the situation here in Brunswick was not unique and most other communities around the state and even around the country were struggling to find lifeguards. The shortage of trained staff has been nationwide for several years, and many beaches and pools particularly in the Northeast and Middle Atlantic states were being forced to close or shorten hours of operation (“During the Pool Season Even Lifeguard Numbers are Taking a Dive,” by Leoneda Inge, July 28, 2015, NPR’s All Thing Considered).
You might think that here on the coast we would have ample places for children to swim, but in Brunswick our shore is rocky and often inaccessible. At the few sandy beaches, the water temperature is too cold for all but the hardy souls until late August. Lower-income families will be particularly affected by the loss of the pool.
When I was growing up, lifeguarding was a plum job that was highly coveted. While it did not pay as well as working construction, the perks of a pleasant atmosphere, the chance to swim every day, and the opportunity to work outside with children prompted me at age 16 to sell my lawn mower and bequeath my lucrative landscaping customers to a couple of preteens. Looking back, my 4 years of lifeguarding were probably a major influence when it came time to choose a specialty.
However, a perfect storm of socioeconomic factors has combined to create a climate in which being a lifeguard has lost its appeal as a summertime job. First, there is record low unemployment nationwide. Young people looking for work have their pick, and while wages still remain low, they can be choosy when it comes to hours and benefits. Lifeguarding does require a skill set and several hoops of certification to be navigated. I don’t recall having to pay much of anything to become certified. But I understand that the process now costs hundreds of dollars of upfront investment with no guarantee of passing the test.
In May, the American Academy of Pediatrics published a policy paper titled “Prevention of Drowning” (Pediatrics. 2019 May 1. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0850) in which the authors offer the troubling statistics on the toll that water-related accidents take on the children of this country annually. They go on to provide a broad list of actions that parents, communities, and pediatricians can take to prevent drownings. Under the category of Community Interventions and Advocacy Opportunities, recommendation No. 4 is “Pediatricians should work with community partners to provide access to programs that develop water-competency swim skills for all children.”
Obviously, these programs can’t happen without an adequate supply of lifeguards.
Unfortunately, the AAP’s statement fails to acknowledge or directly address the lifeguard shortage that has been going on for several years. While an adequate supply of lifeguards is probably not as important as increasing parental attentiveness and mandating pool fences in the overall scheme of drowning prevention, it is an issue that demands action both by the academy and those of us practicing in communities both large and small.
For my part, I am going to work here in Brunswick to see that we can offer lifeguards pay that is more than competitive and then develop an in-house training program to ensure a continuing supply for the future. If we are committed to encouraging our patients to be active, swimming is one of the best activities we should promote and support.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
At a recent Recreation Commission meeting here in Brunswick, the first agenda item under new business was “Coffin Pond Pool Closing.” As I and my fellow commissioners listened, we were told that for the first time in the last 3 decades the town’s only public swimming area would not be opening. While in the past there have been delayed openings and temporary closings due to water conditions, this year the pool would not open, period. The cause of the pool’s closure was the Parks and Recreation Department’s failure to fill even a skeleton crew of lifeguards.
We learned that the situation here in Brunswick was not unique and most other communities around the state and even around the country were struggling to find lifeguards. The shortage of trained staff has been nationwide for several years, and many beaches and pools particularly in the Northeast and Middle Atlantic states were being forced to close or shorten hours of operation (“During the Pool Season Even Lifeguard Numbers are Taking a Dive,” by Leoneda Inge, July 28, 2015, NPR’s All Thing Considered).
You might think that here on the coast we would have ample places for children to swim, but in Brunswick our shore is rocky and often inaccessible. At the few sandy beaches, the water temperature is too cold for all but the hardy souls until late August. Lower-income families will be particularly affected by the loss of the pool.
When I was growing up, lifeguarding was a plum job that was highly coveted. While it did not pay as well as working construction, the perks of a pleasant atmosphere, the chance to swim every day, and the opportunity to work outside with children prompted me at age 16 to sell my lawn mower and bequeath my lucrative landscaping customers to a couple of preteens. Looking back, my 4 years of lifeguarding were probably a major influence when it came time to choose a specialty.
However, a perfect storm of socioeconomic factors has combined to create a climate in which being a lifeguard has lost its appeal as a summertime job. First, there is record low unemployment nationwide. Young people looking for work have their pick, and while wages still remain low, they can be choosy when it comes to hours and benefits. Lifeguarding does require a skill set and several hoops of certification to be navigated. I don’t recall having to pay much of anything to become certified. But I understand that the process now costs hundreds of dollars of upfront investment with no guarantee of passing the test.
In May, the American Academy of Pediatrics published a policy paper titled “Prevention of Drowning” (Pediatrics. 2019 May 1. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0850) in which the authors offer the troubling statistics on the toll that water-related accidents take on the children of this country annually. They go on to provide a broad list of actions that parents, communities, and pediatricians can take to prevent drownings. Under the category of Community Interventions and Advocacy Opportunities, recommendation No. 4 is “Pediatricians should work with community partners to provide access to programs that develop water-competency swim skills for all children.”
Obviously, these programs can’t happen without an adequate supply of lifeguards.
Unfortunately, the AAP’s statement fails to acknowledge or directly address the lifeguard shortage that has been going on for several years. While an adequate supply of lifeguards is probably not as important as increasing parental attentiveness and mandating pool fences in the overall scheme of drowning prevention, it is an issue that demands action both by the academy and those of us practicing in communities both large and small.
For my part, I am going to work here in Brunswick to see that we can offer lifeguards pay that is more than competitive and then develop an in-house training program to ensure a continuing supply for the future. If we are committed to encouraging our patients to be active, swimming is one of the best activities we should promote and support.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
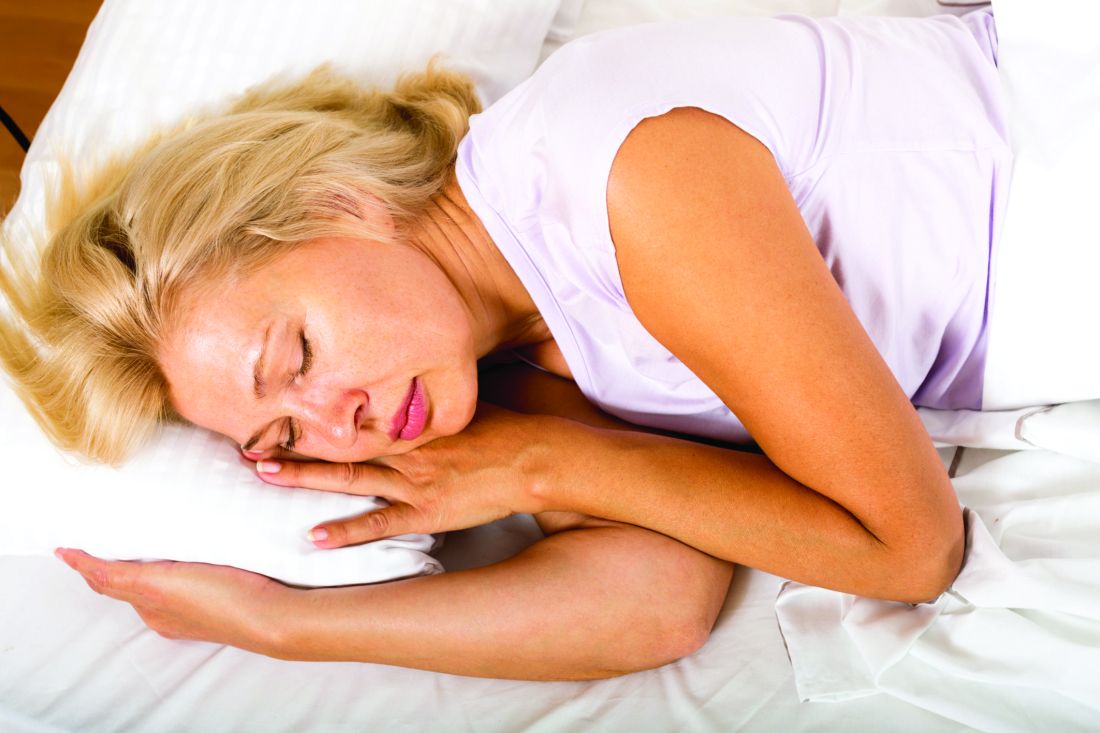
Transdermal estradiol may modulate the relationship between sleep, cognition
LOS ANGELES – Estrogen therapy may have scored another goal in its comeback game, as a 7-year prospective study shows that a transdermal formulation preserves some measures of cognitive function and brain architecture in postmenopausal women.
In addition to performing better on subjective tests of memory, women using the estrogen patch experienced less cortical atrophy and were less likely to show amyloid on brain imaging. The observations were moderately associated with the improved sleep these women reported, Burcu Zeydan, MD, said at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
“By 7 years, among the cognitive domains studied ... [less brain and cognitive change] correlated with lower global sleep score, meaning better sleep quality in the estradiol group,” said Dr. Zeydan, assistant professor of radiology at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “We previously found that preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex over 7 years was associated with lower cortical beta-amyloid deposition on PET only in the estradiol group, pointing out the potential role of estrogen receptors in modulating this relationship.”
Dysregulated sleep is more common among women than men, particularly as menopause approaches and estrogen levels fluctuate, then decline, Dr. Zeydan said.
Dr. Zeydan reported the sleep substudy of KEEPS (the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multisite trial that compared oral conjugated equine estrogen with transdermal estradiol. A control group received oral placebo and a placebo patch.*
Brain architecture was similar between the placebo and transdermal groups, but it was actually worse in some measures in the oral-estrogen group, compared with the placebo group. Women taking oral estrogen had more white matter hyperintensities, greater ventricle enlargement, and more cortical thinning. Those differences resolved after they stopped taking the oral formulation, bringing them into line with the transdermal and placebo groups.
The investigation also found that the transdermal group showed lower cerebral amyloid binding on PET scans relative to both placebo and oral estrogen.
“The relative preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortical volume in the [transdermal estradiol] group over 7 years indicates that hormone therapy may have long-term effects on the brain,” the team concluded. They noted that the original KEEPS study didn’t find any cognitive correlation with these changes.
The subanalysis looked at 69 women of the KEEPS cohort who had been followed for the full 7 years (4 years on treatment and 3 years off treatment). They were randomized to oral placebo and a placebo patch,* oral conjugated equine estrogen (0.45 mg/day), or transdermal estradiol (50 mcg/day). Participants in the active treatment groups received oral micronized progesterone 12 days each month. All had complete data on cognitive testing and brain imaging. Sleep quality was measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Dr. Zeydan compared cognition and brain architecture findings in relation to the sleep score; lower scores mean better sleep.
The women were aged 42-58 years at baseline, and within 36 months from menopause. They had no history of menopausal hormone therapy or cardiovascular disease.
The investigators were particularly interested in how estrogen might have modulated the disturbed sleep patterns that often accompany perimenopause and early menopause, and whether the observed brain and cognitive changes tracked with sleep quality.
“During this time, 40% to 60% of women report problems sleeping, and estrogen decline seems to play an important role in sleep disturbances during this phase,” Dr. Zeydan said. “Although poor sleep quality is common in recently menopausal women, sleep quality improves with hormone therapy, as was previously demonstrated in KEEPS hormone therapy trial in recently menopausal women.”
By year 7, the cohort’s mean age was 61 years. The majority had at least some college education. The percentage who carried an apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 allele varied by group, with 15% positivity in the oral group, 48% in the transdermal group, and 16% in the placebo group.
Cognitive function was estimated with a global cognitive measure and four cognitive domain scores: verbal learning and memory, auditory attention and working memory, visual attention and executive function, and mental flexibility.
Higher attention and executive function scores were moderately correlated with a lower sleep score in the transdermal group (r = –0.54, a significant difference compared with the oral formulation). Lower sleep scores also showed a moderate correlation with preserved cortical volume of the dorsolateral prefrontal region (r = –0.47, also significantly different from the oral group).
Lower brain amyloid also positively correlated with better sleep. The correlation between sleep and global amyloid burden in the transdermal group was also moderate (r = 0.45), while the correlation in the oral group was significantly weaker (r = 0.18).
“We can say that sleep quality and transdermal estradiol during early postmenopausal years somehow interact to influence beta-amyloid deposition, preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex volume, and attention and executive function,” Dr. Zeydan said.
Dr. Zeydan had no financial disclosures.
*Correction, 8/7/2019: An earlier version of this story did not make clear that participants in the control group received oral placebo and a placebo patch.
LOS ANGELES – Estrogen therapy may have scored another goal in its comeback game, as a 7-year prospective study shows that a transdermal formulation preserves some measures of cognitive function and brain architecture in postmenopausal women.
In addition to performing better on subjective tests of memory, women using the estrogen patch experienced less cortical atrophy and were less likely to show amyloid on brain imaging. The observations were moderately associated with the improved sleep these women reported, Burcu Zeydan, MD, said at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
“By 7 years, among the cognitive domains studied ... [less brain and cognitive change] correlated with lower global sleep score, meaning better sleep quality in the estradiol group,” said Dr. Zeydan, assistant professor of radiology at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “We previously found that preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex over 7 years was associated with lower cortical beta-amyloid deposition on PET only in the estradiol group, pointing out the potential role of estrogen receptors in modulating this relationship.”
Dysregulated sleep is more common among women than men, particularly as menopause approaches and estrogen levels fluctuate, then decline, Dr. Zeydan said.
Dr. Zeydan reported the sleep substudy of KEEPS (the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multisite trial that compared oral conjugated equine estrogen with transdermal estradiol. A control group received oral placebo and a placebo patch.*
Brain architecture was similar between the placebo and transdermal groups, but it was actually worse in some measures in the oral-estrogen group, compared with the placebo group. Women taking oral estrogen had more white matter hyperintensities, greater ventricle enlargement, and more cortical thinning. Those differences resolved after they stopped taking the oral formulation, bringing them into line with the transdermal and placebo groups.
The investigation also found that the transdermal group showed lower cerebral amyloid binding on PET scans relative to both placebo and oral estrogen.
“The relative preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortical volume in the [transdermal estradiol] group over 7 years indicates that hormone therapy may have long-term effects on the brain,” the team concluded. They noted that the original KEEPS study didn’t find any cognitive correlation with these changes.
The subanalysis looked at 69 women of the KEEPS cohort who had been followed for the full 7 years (4 years on treatment and 3 years off treatment). They were randomized to oral placebo and a placebo patch,* oral conjugated equine estrogen (0.45 mg/day), or transdermal estradiol (50 mcg/day). Participants in the active treatment groups received oral micronized progesterone 12 days each month. All had complete data on cognitive testing and brain imaging. Sleep quality was measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Dr. Zeydan compared cognition and brain architecture findings in relation to the sleep score; lower scores mean better sleep.
The women were aged 42-58 years at baseline, and within 36 months from menopause. They had no history of menopausal hormone therapy or cardiovascular disease.
The investigators were particularly interested in how estrogen might have modulated the disturbed sleep patterns that often accompany perimenopause and early menopause, and whether the observed brain and cognitive changes tracked with sleep quality.
“During this time, 40% to 60% of women report problems sleeping, and estrogen decline seems to play an important role in sleep disturbances during this phase,” Dr. Zeydan said. “Although poor sleep quality is common in recently menopausal women, sleep quality improves with hormone therapy, as was previously demonstrated in KEEPS hormone therapy trial in recently menopausal women.”
By year 7, the cohort’s mean age was 61 years. The majority had at least some college education. The percentage who carried an apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 allele varied by group, with 15% positivity in the oral group, 48% in the transdermal group, and 16% in the placebo group.
Cognitive function was estimated with a global cognitive measure and four cognitive domain scores: verbal learning and memory, auditory attention and working memory, visual attention and executive function, and mental flexibility.
Higher attention and executive function scores were moderately correlated with a lower sleep score in the transdermal group (r = –0.54, a significant difference compared with the oral formulation). Lower sleep scores also showed a moderate correlation with preserved cortical volume of the dorsolateral prefrontal region (r = –0.47, also significantly different from the oral group).
Lower brain amyloid also positively correlated with better sleep. The correlation between sleep and global amyloid burden in the transdermal group was also moderate (r = 0.45), while the correlation in the oral group was significantly weaker (r = 0.18).
“We can say that sleep quality and transdermal estradiol during early postmenopausal years somehow interact to influence beta-amyloid deposition, preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex volume, and attention and executive function,” Dr. Zeydan said.
Dr. Zeydan had no financial disclosures.
*Correction, 8/7/2019: An earlier version of this story did not make clear that participants in the control group received oral placebo and a placebo patch.
LOS ANGELES – Estrogen therapy may have scored another goal in its comeback game, as a 7-year prospective study shows that a transdermal formulation preserves some measures of cognitive function and brain architecture in postmenopausal women.
In addition to performing better on subjective tests of memory, women using the estrogen patch experienced less cortical atrophy and were less likely to show amyloid on brain imaging. The observations were moderately associated with the improved sleep these women reported, Burcu Zeydan, MD, said at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
“By 7 years, among the cognitive domains studied ... [less brain and cognitive change] correlated with lower global sleep score, meaning better sleep quality in the estradiol group,” said Dr. Zeydan, assistant professor of radiology at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “We previously found that preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex over 7 years was associated with lower cortical beta-amyloid deposition on PET only in the estradiol group, pointing out the potential role of estrogen receptors in modulating this relationship.”
Dysregulated sleep is more common among women than men, particularly as menopause approaches and estrogen levels fluctuate, then decline, Dr. Zeydan said.
Dr. Zeydan reported the sleep substudy of KEEPS (the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multisite trial that compared oral conjugated equine estrogen with transdermal estradiol. A control group received oral placebo and a placebo patch.*
Brain architecture was similar between the placebo and transdermal groups, but it was actually worse in some measures in the oral-estrogen group, compared with the placebo group. Women taking oral estrogen had more white matter hyperintensities, greater ventricle enlargement, and more cortical thinning. Those differences resolved after they stopped taking the oral formulation, bringing them into line with the transdermal and placebo groups.
The investigation also found that the transdermal group showed lower cerebral amyloid binding on PET scans relative to both placebo and oral estrogen.
“The relative preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortical volume in the [transdermal estradiol] group over 7 years indicates that hormone therapy may have long-term effects on the brain,” the team concluded. They noted that the original KEEPS study didn’t find any cognitive correlation with these changes.
The subanalysis looked at 69 women of the KEEPS cohort who had been followed for the full 7 years (4 years on treatment and 3 years off treatment). They were randomized to oral placebo and a placebo patch,* oral conjugated equine estrogen (0.45 mg/day), or transdermal estradiol (50 mcg/day). Participants in the active treatment groups received oral micronized progesterone 12 days each month. All had complete data on cognitive testing and brain imaging. Sleep quality was measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Dr. Zeydan compared cognition and brain architecture findings in relation to the sleep score; lower scores mean better sleep.
The women were aged 42-58 years at baseline, and within 36 months from menopause. They had no history of menopausal hormone therapy or cardiovascular disease.
The investigators were particularly interested in how estrogen might have modulated the disturbed sleep patterns that often accompany perimenopause and early menopause, and whether the observed brain and cognitive changes tracked with sleep quality.
“During this time, 40% to 60% of women report problems sleeping, and estrogen decline seems to play an important role in sleep disturbances during this phase,” Dr. Zeydan said. “Although poor sleep quality is common in recently menopausal women, sleep quality improves with hormone therapy, as was previously demonstrated in KEEPS hormone therapy trial in recently menopausal women.”
By year 7, the cohort’s mean age was 61 years. The majority had at least some college education. The percentage who carried an apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 allele varied by group, with 15% positivity in the oral group, 48% in the transdermal group, and 16% in the placebo group.
Cognitive function was estimated with a global cognitive measure and four cognitive domain scores: verbal learning and memory, auditory attention and working memory, visual attention and executive function, and mental flexibility.
Higher attention and executive function scores were moderately correlated with a lower sleep score in the transdermal group (r = –0.54, a significant difference compared with the oral formulation). Lower sleep scores also showed a moderate correlation with preserved cortical volume of the dorsolateral prefrontal region (r = –0.47, also significantly different from the oral group).
Lower brain amyloid also positively correlated with better sleep. The correlation between sleep and global amyloid burden in the transdermal group was also moderate (r = 0.45), while the correlation in the oral group was significantly weaker (r = 0.18).
“We can say that sleep quality and transdermal estradiol during early postmenopausal years somehow interact to influence beta-amyloid deposition, preservation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex volume, and attention and executive function,” Dr. Zeydan said.
Dr. Zeydan had no financial disclosures.
*Correction, 8/7/2019: An earlier version of this story did not make clear that participants in the control group received oral placebo and a placebo patch.
REPORTING FROM AAIC 2019
New oral polio vaccine is noninferior to currently licensed vaccine
according to Khalequ Zaman, MBBS, PhD, of the International Center for Diarrheal Disease Research in Dhaka, Bangladesh, and associates.
In the first part of the observer-blind, randomized, controlled study, 40 patients aged 5-6 years received either the new vaccine (BBio bOPV) or the licensed vaccine (SII bOPV). In the second part, 1,080 patients aged 6-8 weeks received either BBio bOPV or SII bOPV at age 6, 10, and 14 weeks. Blood samples were taken to assess neutralizing antibody responses against poliovirus types 1 and 3, and safety also was assessed.
In the first part of the study, 12 adverse events were reported, none of which were serious and none of which were related to the vaccines. All participants demonstrated seroprotective titers against both poliovirus types 1 month after vaccination.
In the second part, more than 96% of infants demonstrated seroprotection and seroconversion against both poliovirus types. Geometric mean titers were equivalent in both groups. A total of 387 participants had at least one adverse event, and 18 serious adverse events were reported. None of these were related to the vaccines.
“The BBio bOPV has been proven safe and immunogenic in the target infant population in Bangladesh. As the use of bOPV is expected to be continued until at least 2022, availability of new bOPV bulk manufacturer will be helpful in securing adequate supplies of bOPV for global demand in the polio endgame strategy,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by Bilthoven Biologicals. Four coauthors are employed by Bilthoven, manufacturer of the study vaccine; two others are employed by the Serum Institute of India, which provided the control vaccine.
SOURCE: Zaman K et al. Vaccine. 2019 Jun 22. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.06.048.
according to Khalequ Zaman, MBBS, PhD, of the International Center for Diarrheal Disease Research in Dhaka, Bangladesh, and associates.
In the first part of the observer-blind, randomized, controlled study, 40 patients aged 5-6 years received either the new vaccine (BBio bOPV) or the licensed vaccine (SII bOPV). In the second part, 1,080 patients aged 6-8 weeks received either BBio bOPV or SII bOPV at age 6, 10, and 14 weeks. Blood samples were taken to assess neutralizing antibody responses against poliovirus types 1 and 3, and safety also was assessed.
In the first part of the study, 12 adverse events were reported, none of which were serious and none of which were related to the vaccines. All participants demonstrated seroprotective titers against both poliovirus types 1 month after vaccination.
In the second part, more than 96% of infants demonstrated seroprotection and seroconversion against both poliovirus types. Geometric mean titers were equivalent in both groups. A total of 387 participants had at least one adverse event, and 18 serious adverse events were reported. None of these were related to the vaccines.
“The BBio bOPV has been proven safe and immunogenic in the target infant population in Bangladesh. As the use of bOPV is expected to be continued until at least 2022, availability of new bOPV bulk manufacturer will be helpful in securing adequate supplies of bOPV for global demand in the polio endgame strategy,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by Bilthoven Biologicals. Four coauthors are employed by Bilthoven, manufacturer of the study vaccine; two others are employed by the Serum Institute of India, which provided the control vaccine.
SOURCE: Zaman K et al. Vaccine. 2019 Jun 22. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.06.048.
according to Khalequ Zaman, MBBS, PhD, of the International Center for Diarrheal Disease Research in Dhaka, Bangladesh, and associates.
In the first part of the observer-blind, randomized, controlled study, 40 patients aged 5-6 years received either the new vaccine (BBio bOPV) or the licensed vaccine (SII bOPV). In the second part, 1,080 patients aged 6-8 weeks received either BBio bOPV or SII bOPV at age 6, 10, and 14 weeks. Blood samples were taken to assess neutralizing antibody responses against poliovirus types 1 and 3, and safety also was assessed.
In the first part of the study, 12 adverse events were reported, none of which were serious and none of which were related to the vaccines. All participants demonstrated seroprotective titers against both poliovirus types 1 month after vaccination.
In the second part, more than 96% of infants demonstrated seroprotection and seroconversion against both poliovirus types. Geometric mean titers were equivalent in both groups. A total of 387 participants had at least one adverse event, and 18 serious adverse events were reported. None of these were related to the vaccines.
“The BBio bOPV has been proven safe and immunogenic in the target infant population in Bangladesh. As the use of bOPV is expected to be continued until at least 2022, availability of new bOPV bulk manufacturer will be helpful in securing adequate supplies of bOPV for global demand in the polio endgame strategy,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by Bilthoven Biologicals. Four coauthors are employed by Bilthoven, manufacturer of the study vaccine; two others are employed by the Serum Institute of India, which provided the control vaccine.
SOURCE: Zaman K et al. Vaccine. 2019 Jun 22. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.06.048.
FROM VACCINE
Flavopiridol elicits poor response in mantle cell lymphoma, DLBCL
Flavopiridol – also known as alvocidib – showed minimal clinical response in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and other B-cell lymphomas, according to results from a single-center, phase 1/2 trial.
“Promising preclinical data in cell lines derived from MCL and activated DLBCL led to a series of clinical trials of flavopiridol in various hematological malignancies,” wrote Milos D. Miljković, MD, and colleagues in the lymphoid malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. The findings were published in a letter to the editor in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The study included 28 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL, DLBCL, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who received a hybrid dosing regimen of the novel CDK inhibitor. Flavopiridol was administered as a 30-minute bolus, followed by a 4-hour infusion.
The researchers used an intrapatient dose escalation between the first and successive cycles, in addition to a three-plus-three interpatient escalation, to lessen the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
The primary outcomes were the clinical response rate, maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and toxicity profile of the hybrid dosing regimen.
Of 26 evaluable patients, one patient with DLBCL maintained a partial response for 84 days (overall response rate, 3.8%). One patient with MCL had a 50% decrease in the size of target lesions at 2 months, but this was not sustained at 4 months. In total, nine patients had stable disease for a disease control rate of 38.4%.
“[Flavopiridol] had minimal efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma, casting doubt on the utility of CDK inhibition in this disease,” the researchers wrote.
With respect to safety, there were eight dose-limiting toxicities reported in three patients. These included grade 3 TLS, elevated transaminase levels, hypoalbuminemia, hyperkalemia, non-neutropenic infection, and grade 4 metabolic acidosis and gastrointestinal perforation.
The most common treatment-related toxicities were hematologic, including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and lymphopenia.
Dr. Miljković and colleagues noted that CDK inhibitor therapy may elicit better responses when used in combination with other agents.
“Ongoing trials of more specific CDK inhibitors in combination with other agents will help elucidate their role in lymphoma treatment,” they wrote.
The trial is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the study authors are employees of the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Miljkovic MD et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1627540.
Flavopiridol – also known as alvocidib – showed minimal clinical response in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and other B-cell lymphomas, according to results from a single-center, phase 1/2 trial.
“Promising preclinical data in cell lines derived from MCL and activated DLBCL led to a series of clinical trials of flavopiridol in various hematological malignancies,” wrote Milos D. Miljković, MD, and colleagues in the lymphoid malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. The findings were published in a letter to the editor in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The study included 28 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL, DLBCL, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who received a hybrid dosing regimen of the novel CDK inhibitor. Flavopiridol was administered as a 30-minute bolus, followed by a 4-hour infusion.
The researchers used an intrapatient dose escalation between the first and successive cycles, in addition to a three-plus-three interpatient escalation, to lessen the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
The primary outcomes were the clinical response rate, maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and toxicity profile of the hybrid dosing regimen.
Of 26 evaluable patients, one patient with DLBCL maintained a partial response for 84 days (overall response rate, 3.8%). One patient with MCL had a 50% decrease in the size of target lesions at 2 months, but this was not sustained at 4 months. In total, nine patients had stable disease for a disease control rate of 38.4%.
“[Flavopiridol] had minimal efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma, casting doubt on the utility of CDK inhibition in this disease,” the researchers wrote.
With respect to safety, there were eight dose-limiting toxicities reported in three patients. These included grade 3 TLS, elevated transaminase levels, hypoalbuminemia, hyperkalemia, non-neutropenic infection, and grade 4 metabolic acidosis and gastrointestinal perforation.
The most common treatment-related toxicities were hematologic, including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and lymphopenia.
Dr. Miljković and colleagues noted that CDK inhibitor therapy may elicit better responses when used in combination with other agents.
“Ongoing trials of more specific CDK inhibitors in combination with other agents will help elucidate their role in lymphoma treatment,” they wrote.
The trial is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the study authors are employees of the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Miljkovic MD et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1627540.
Flavopiridol – also known as alvocidib – showed minimal clinical response in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and other B-cell lymphomas, according to results from a single-center, phase 1/2 trial.
“Promising preclinical data in cell lines derived from MCL and activated DLBCL led to a series of clinical trials of flavopiridol in various hematological malignancies,” wrote Milos D. Miljković, MD, and colleagues in the lymphoid malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. The findings were published in a letter to the editor in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The study included 28 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL, DLBCL, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who received a hybrid dosing regimen of the novel CDK inhibitor. Flavopiridol was administered as a 30-minute bolus, followed by a 4-hour infusion.
The researchers used an intrapatient dose escalation between the first and successive cycles, in addition to a three-plus-three interpatient escalation, to lessen the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
The primary outcomes were the clinical response rate, maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and toxicity profile of the hybrid dosing regimen.
Of 26 evaluable patients, one patient with DLBCL maintained a partial response for 84 days (overall response rate, 3.8%). One patient with MCL had a 50% decrease in the size of target lesions at 2 months, but this was not sustained at 4 months. In total, nine patients had stable disease for a disease control rate of 38.4%.
“[Flavopiridol] had minimal efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma, casting doubt on the utility of CDK inhibition in this disease,” the researchers wrote.
With respect to safety, there were eight dose-limiting toxicities reported in three patients. These included grade 3 TLS, elevated transaminase levels, hypoalbuminemia, hyperkalemia, non-neutropenic infection, and grade 4 metabolic acidosis and gastrointestinal perforation.
The most common treatment-related toxicities were hematologic, including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and lymphopenia.
Dr. Miljković and colleagues noted that CDK inhibitor therapy may elicit better responses when used in combination with other agents.
“Ongoing trials of more specific CDK inhibitors in combination with other agents will help elucidate their role in lymphoma treatment,” they wrote.
The trial is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the study authors are employees of the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Miljkovic MD et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1627540.
FROM LEUKEMIA & LYMPHOMA
A 3-year-old is brought to the clinic for evaluation of a localized, scaling inflamed lesion on the left leg
Nummular dermatitis, or nummular eczema, is an inflammatory skin condition that is considered to be a distinctive form of idiopathic eczema, while the term also is used to describe lesional morphology associated with other conditions.
The term nummular derives from the Latin word for “coin,” as lesions are commonly annular plaques. Lesions of nummular dermatitis can be single or multiple. The typical distribution involves the extremities and, although less common, it can affect the trunk as well.
Nummular dermatitis may be associated with atopic dermatitis, or it can be an isolated condition.1 While the pathogenesis is uncertain, instigating factors include xerotic skin, insect bites, or scratches or scrapes.1Staphylococcus infection or colonization, contact allergies to metals such as nickel and less commonly mercury, sensitivity to formaldehyde or medicines such as neomycin, and sensitization to an environmental aeroallergen (such as Candida albicans, dust mites) are considered risk factors.2
The diagnosis of nummular dermatitis is clinical. Laboratory testing and/or biopsy generally are not necessary, although a bacterial culture can be considered in patients with exudative and/or crusted lesions to rule out impetigo as a primary process of secondary infection. In some cases, patch testing for allergic contact dermatitis may be useful.
The differential diagnosis of nummular dermatitis includes tinea corporis (ringworm), atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, impetigo, and psoriasis. Tinea corporis usually presents as annular lesions with a distinct peripheral scaling, rather than the diffuse induration of nummular dermatitis. Potassium hydroxide preparation or fungal culture can identify tinea species. Nummular dermatitis may be seen in patients with atopic dermatitis, who should have typical history, morphology, and course consistent with standard diagnostic criteria. Allergic contact dermatitis can present with regional, localized eczematous plaques in areas exposed to contact allergens. Patterns of lesions in areas of contact and worsening with repeat exposures can be clues to this diagnosis. Impetigo can present with honey-colored crusted lesions and/or superficial erosions, or purulent pyoderma. Lesions can be single or multiple and generally appear less inflammatory than nummular dermatitis. Psoriasis lesions may be annular, are more common on extensor surfaces, and usually have more prominent overlying pinkish, silvery white or micaceous scale.
Management of nummular dermatitis requires strong anti-inflammatory medications, usually mid-potency or higher topical corticosteroids, along with moisturizers and limiting exposure to skin irritants. “Wet wraps,” with application of topical corticosteroids to wet skin with occlusive wet dressings can enhance response. Transition from higher strength topical corticosteroids to lower strength agents used intermittently can help achieve remission or cure. Management practices include less frequent bathing with lukewarm water, using hypoallergenic cleansers and detergents, and applying moisturizers frequently. If plaques do recur, they tend to do so in the same location and in some patients resolution may result in hyper or hypopigmentation. Refractory disease may be managed with intralesional steroid injections, or systemic medications such as methotrexate.3
Dr. Tracy is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Tracy nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012 Sep-Oct;29(5):580-3.
2. American Academy of Dermatology. Nummular Dermatitis Overview
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Sep;35(5):611-5.
Nummular dermatitis, or nummular eczema, is an inflammatory skin condition that is considered to be a distinctive form of idiopathic eczema, while the term also is used to describe lesional morphology associated with other conditions.
The term nummular derives from the Latin word for “coin,” as lesions are commonly annular plaques. Lesions of nummular dermatitis can be single or multiple. The typical distribution involves the extremities and, although less common, it can affect the trunk as well.
Nummular dermatitis may be associated with atopic dermatitis, or it can be an isolated condition.1 While the pathogenesis is uncertain, instigating factors include xerotic skin, insect bites, or scratches or scrapes.1Staphylococcus infection or colonization, contact allergies to metals such as nickel and less commonly mercury, sensitivity to formaldehyde or medicines such as neomycin, and sensitization to an environmental aeroallergen (such as Candida albicans, dust mites) are considered risk factors.2
The diagnosis of nummular dermatitis is clinical. Laboratory testing and/or biopsy generally are not necessary, although a bacterial culture can be considered in patients with exudative and/or crusted lesions to rule out impetigo as a primary process of secondary infection. In some cases, patch testing for allergic contact dermatitis may be useful.
The differential diagnosis of nummular dermatitis includes tinea corporis (ringworm), atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, impetigo, and psoriasis. Tinea corporis usually presents as annular lesions with a distinct peripheral scaling, rather than the diffuse induration of nummular dermatitis. Potassium hydroxide preparation or fungal culture can identify tinea species. Nummular dermatitis may be seen in patients with atopic dermatitis, who should have typical history, morphology, and course consistent with standard diagnostic criteria. Allergic contact dermatitis can present with regional, localized eczematous plaques in areas exposed to contact allergens. Patterns of lesions in areas of contact and worsening with repeat exposures can be clues to this diagnosis. Impetigo can present with honey-colored crusted lesions and/or superficial erosions, or purulent pyoderma. Lesions can be single or multiple and generally appear less inflammatory than nummular dermatitis. Psoriasis lesions may be annular, are more common on extensor surfaces, and usually have more prominent overlying pinkish, silvery white or micaceous scale.
Management of nummular dermatitis requires strong anti-inflammatory medications, usually mid-potency or higher topical corticosteroids, along with moisturizers and limiting exposure to skin irritants. “Wet wraps,” with application of topical corticosteroids to wet skin with occlusive wet dressings can enhance response. Transition from higher strength topical corticosteroids to lower strength agents used intermittently can help achieve remission or cure. Management practices include less frequent bathing with lukewarm water, using hypoallergenic cleansers and detergents, and applying moisturizers frequently. If plaques do recur, they tend to do so in the same location and in some patients resolution may result in hyper or hypopigmentation. Refractory disease may be managed with intralesional steroid injections, or systemic medications such as methotrexate.3
Dr. Tracy is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Tracy nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012 Sep-Oct;29(5):580-3.
2. American Academy of Dermatology. Nummular Dermatitis Overview
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Sep;35(5):611-5.
Nummular dermatitis, or nummular eczema, is an inflammatory skin condition that is considered to be a distinctive form of idiopathic eczema, while the term also is used to describe lesional morphology associated with other conditions.
The term nummular derives from the Latin word for “coin,” as lesions are commonly annular plaques. Lesions of nummular dermatitis can be single or multiple. The typical distribution involves the extremities and, although less common, it can affect the trunk as well.
Nummular dermatitis may be associated with atopic dermatitis, or it can be an isolated condition.1 While the pathogenesis is uncertain, instigating factors include xerotic skin, insect bites, or scratches or scrapes.1Staphylococcus infection or colonization, contact allergies to metals such as nickel and less commonly mercury, sensitivity to formaldehyde or medicines such as neomycin, and sensitization to an environmental aeroallergen (such as Candida albicans, dust mites) are considered risk factors.2
The diagnosis of nummular dermatitis is clinical. Laboratory testing and/or biopsy generally are not necessary, although a bacterial culture can be considered in patients with exudative and/or crusted lesions to rule out impetigo as a primary process of secondary infection. In some cases, patch testing for allergic contact dermatitis may be useful.
The differential diagnosis of nummular dermatitis includes tinea corporis (ringworm), atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, impetigo, and psoriasis. Tinea corporis usually presents as annular lesions with a distinct peripheral scaling, rather than the diffuse induration of nummular dermatitis. Potassium hydroxide preparation or fungal culture can identify tinea species. Nummular dermatitis may be seen in patients with atopic dermatitis, who should have typical history, morphology, and course consistent with standard diagnostic criteria. Allergic contact dermatitis can present with regional, localized eczematous plaques in areas exposed to contact allergens. Patterns of lesions in areas of contact and worsening with repeat exposures can be clues to this diagnosis. Impetigo can present with honey-colored crusted lesions and/or superficial erosions, or purulent pyoderma. Lesions can be single or multiple and generally appear less inflammatory than nummular dermatitis. Psoriasis lesions may be annular, are more common on extensor surfaces, and usually have more prominent overlying pinkish, silvery white or micaceous scale.
Management of nummular dermatitis requires strong anti-inflammatory medications, usually mid-potency or higher topical corticosteroids, along with moisturizers and limiting exposure to skin irritants. “Wet wraps,” with application of topical corticosteroids to wet skin with occlusive wet dressings can enhance response. Transition from higher strength topical corticosteroids to lower strength agents used intermittently can help achieve remission or cure. Management practices include less frequent bathing with lukewarm water, using hypoallergenic cleansers and detergents, and applying moisturizers frequently. If plaques do recur, they tend to do so in the same location and in some patients resolution may result in hyper or hypopigmentation. Refractory disease may be managed with intralesional steroid injections, or systemic medications such as methotrexate.3
Dr. Tracy is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Tracy nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012 Sep-Oct;29(5):580-3.
2. American Academy of Dermatology. Nummular Dermatitis Overview
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Sep;35(5):611-5.
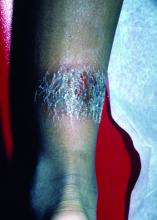
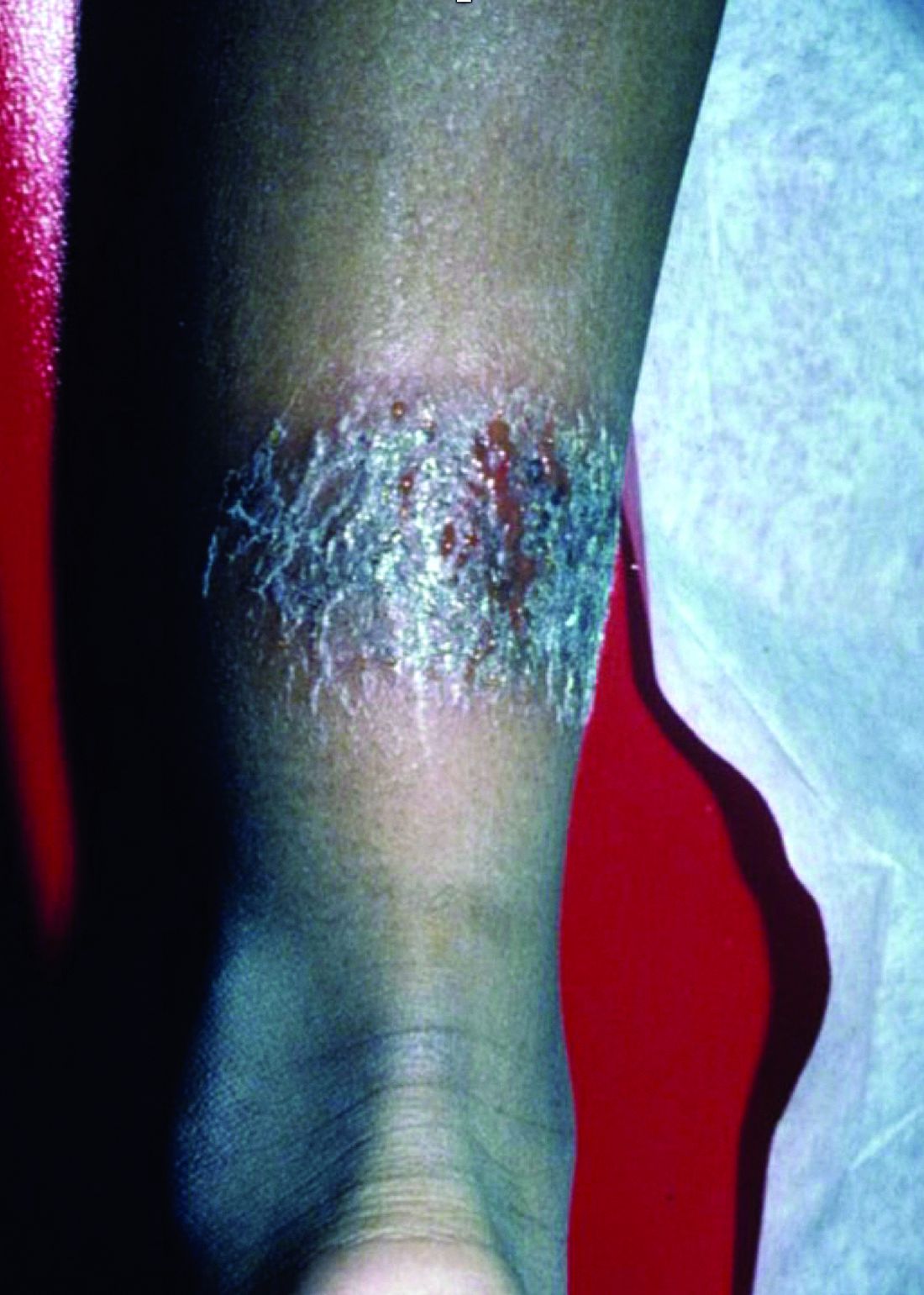
On physical exam, he is noted to have a localized eczematous plaque with erythema and edema. Also, he is noted to have diffuse, fine xerosis of the bilateral lower extremities. His skin is otherwise nonremarkable.
Smoking-cessation attempts changed little over 7-year span
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The median percentage of adult smokers who tried to quit cigarettes over the past year went from 64.9% in 2011 to 65.4% in 2017, CDC investigators reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, but the rate has gone down since 2014, when it reached 66.9%.
“The limited progress in increasing quit attempts … together with the variation in quit attempt prevalence among states, underscores the importance of enhanced efforts to motivate and help smokers to quit,” wrote Kimp Walton, MS, of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and associates.
State-specific trends in quit-attempt rates reflected the national situation. The prevalence of past-year cessation attempts went up significantly in four states (Kansas, Louisiana, Virginia, and West Virginia) from 2011 to 2017, went down significantly in two states (New York and Tennessee), and did not change significantly in the other 44 states and the District of Columbia, they wrote.
In 2017, cigarette smokers in Connecticut were the most likely to have tried to quit in the past year, with a rate of 71.6%. The only other places with rates greater than 70% were Delaware, D.C., New Jersey, and Texas. The lowest quit-attempt rate that year, 58.6%, belonged to Wisconsin, with Iowa and Missouri the only other states under 60%, the investigators reported based on data from annual Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System surveys.
“Because most smokers make multiple quit attempts before succeeding, as many as 30 on average, tobacco dependence is viewed as a chronic, relapsing condition that requires repeated intervention. Smokers should be encouraged to keep trying to quit until they succeed, and health care providers should be encouraged to keep supporting smokers until they quit,” investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Walton K et al. MMWR. 2019 Jul 19;68(28):621-6.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The median percentage of adult smokers who tried to quit cigarettes over the past year went from 64.9% in 2011 to 65.4% in 2017, CDC investigators reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, but the rate has gone down since 2014, when it reached 66.9%.
“The limited progress in increasing quit attempts … together with the variation in quit attempt prevalence among states, underscores the importance of enhanced efforts to motivate and help smokers to quit,” wrote Kimp Walton, MS, of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and associates.
State-specific trends in quit-attempt rates reflected the national situation. The prevalence of past-year cessation attempts went up significantly in four states (Kansas, Louisiana, Virginia, and West Virginia) from 2011 to 2017, went down significantly in two states (New York and Tennessee), and did not change significantly in the other 44 states and the District of Columbia, they wrote.
In 2017, cigarette smokers in Connecticut were the most likely to have tried to quit in the past year, with a rate of 71.6%. The only other places with rates greater than 70% were Delaware, D.C., New Jersey, and Texas. The lowest quit-attempt rate that year, 58.6%, belonged to Wisconsin, with Iowa and Missouri the only other states under 60%, the investigators reported based on data from annual Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System surveys.
“Because most smokers make multiple quit attempts before succeeding, as many as 30 on average, tobacco dependence is viewed as a chronic, relapsing condition that requires repeated intervention. Smokers should be encouraged to keep trying to quit until they succeed, and health care providers should be encouraged to keep supporting smokers until they quit,” investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Walton K et al. MMWR. 2019 Jul 19;68(28):621-6.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The median percentage of adult smokers who tried to quit cigarettes over the past year went from 64.9% in 2011 to 65.4% in 2017, CDC investigators reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, but the rate has gone down since 2014, when it reached 66.9%.
“The limited progress in increasing quit attempts … together with the variation in quit attempt prevalence among states, underscores the importance of enhanced efforts to motivate and help smokers to quit,” wrote Kimp Walton, MS, of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and associates.
State-specific trends in quit-attempt rates reflected the national situation. The prevalence of past-year cessation attempts went up significantly in four states (Kansas, Louisiana, Virginia, and West Virginia) from 2011 to 2017, went down significantly in two states (New York and Tennessee), and did not change significantly in the other 44 states and the District of Columbia, they wrote.
In 2017, cigarette smokers in Connecticut were the most likely to have tried to quit in the past year, with a rate of 71.6%. The only other places with rates greater than 70% were Delaware, D.C., New Jersey, and Texas. The lowest quit-attempt rate that year, 58.6%, belonged to Wisconsin, with Iowa and Missouri the only other states under 60%, the investigators reported based on data from annual Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System surveys.
“Because most smokers make multiple quit attempts before succeeding, as many as 30 on average, tobacco dependence is viewed as a chronic, relapsing condition that requires repeated intervention. Smokers should be encouraged to keep trying to quit until they succeed, and health care providers should be encouraged to keep supporting smokers until they quit,” investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Walton K et al. MMWR. 2019 Jul 19;68(28):621-6.
FROM MMWR
Increased daily water intake benefits premenopausal women with recurrent UTIs
Background: Acute cystitis is a common condition in women and associated with morbidity. A commonly recommended preventative measure is increased oral hydration, but there is limited evidence to support this claim.
Study design: Open-label, randomized, controlled study.
Setting: Clinical research center based in Sofia, Bulgaria.
Synopsis: A 12-month trial done at a clinical research center including healthy women with recurrent cystitis who drank less than 1.5 L of fluid daily. One group was instructed to drink 1.5 L of water/day in addition to their normal fluid intake, and the other was advised not to drink any additional fluid. The mean number of cystitis episodes in the intervention group was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.5-1.8), compared with 3.2 (95% CI, 3.0-3.4) in the control group, which was a statistically significant difference of 1.5 (95% CI, 1.2-1.8; P less than .01).
Though antibiotic prophylaxis is more effective at reducing cystitis, increased daily water intake is a safe and inexpensive method to prevent cystitis without increasing exposure to antimicrobial therapy. This study did rely on information obtained from phone calls with patients. It is also an open-label study design in which patients were not blinded to their assigned group. This would be less of an issue if episodes of cystitis were confirmed with culture. Another limitation of this study is that it included only ambulatory patients and excluded patients with pyelonephritis, so it may be less applicable to our hospitalized patients.
Bottom line: This study shows a benefit in recurrent cystitis by increased water intake in premenopausal women.
Citation: Hooton TM et al. Effect of increased daily water intake in premenopausal women with recurrent urinary tract infections. JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Nov;178(11):1509-15.
Dr. Astik is medical director, clinical documentation, at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital, both in Chicago.
Background: Acute cystitis is a common condition in women and associated with morbidity. A commonly recommended preventative measure is increased oral hydration, but there is limited evidence to support this claim.
Study design: Open-label, randomized, controlled study.
Setting: Clinical research center based in Sofia, Bulgaria.
Synopsis: A 12-month trial done at a clinical research center including healthy women with recurrent cystitis who drank less than 1.5 L of fluid daily. One group was instructed to drink 1.5 L of water/day in addition to their normal fluid intake, and the other was advised not to drink any additional fluid. The mean number of cystitis episodes in the intervention group was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.5-1.8), compared with 3.2 (95% CI, 3.0-3.4) in the control group, which was a statistically significant difference of 1.5 (95% CI, 1.2-1.8; P less than .01).
Though antibiotic prophylaxis is more effective at reducing cystitis, increased daily water intake is a safe and inexpensive method to prevent cystitis without increasing exposure to antimicrobial therapy. This study did rely on information obtained from phone calls with patients. It is also an open-label study design in which patients were not blinded to their assigned group. This would be less of an issue if episodes of cystitis were confirmed with culture. Another limitation of this study is that it included only ambulatory patients and excluded patients with pyelonephritis, so it may be less applicable to our hospitalized patients.
Bottom line: This study shows a benefit in recurrent cystitis by increased water intake in premenopausal women.
Citation: Hooton TM et al. Effect of increased daily water intake in premenopausal women with recurrent urinary tract infections. JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Nov;178(11):1509-15.
Dr. Astik is medical director, clinical documentation, at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital, both in Chicago.
Background: Acute cystitis is a common condition in women and associated with morbidity. A commonly recommended preventative measure is increased oral hydration, but there is limited evidence to support this claim.
Study design: Open-label, randomized, controlled study.
Setting: Clinical research center based in Sofia, Bulgaria.
Synopsis: A 12-month trial done at a clinical research center including healthy women with recurrent cystitis who drank less than 1.5 L of fluid daily. One group was instructed to drink 1.5 L of water/day in addition to their normal fluid intake, and the other was advised not to drink any additional fluid. The mean number of cystitis episodes in the intervention group was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.5-1.8), compared with 3.2 (95% CI, 3.0-3.4) in the control group, which was a statistically significant difference of 1.5 (95% CI, 1.2-1.8; P less than .01).
Though antibiotic prophylaxis is more effective at reducing cystitis, increased daily water intake is a safe and inexpensive method to prevent cystitis without increasing exposure to antimicrobial therapy. This study did rely on information obtained from phone calls with patients. It is also an open-label study design in which patients were not blinded to their assigned group. This would be less of an issue if episodes of cystitis were confirmed with culture. Another limitation of this study is that it included only ambulatory patients and excluded patients with pyelonephritis, so it may be less applicable to our hospitalized patients.
Bottom line: This study shows a benefit in recurrent cystitis by increased water intake in premenopausal women.
Citation: Hooton TM et al. Effect of increased daily water intake in premenopausal women with recurrent urinary tract infections. JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Nov;178(11):1509-15.
Dr. Astik is medical director, clinical documentation, at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital, both in Chicago.
iPledge: Fetal exposure to isotretinoin continues
but pregnancy, abortions, and fetal defects associated with isotretinoin exposure are still occurring in women of reproductive age, according to a retrospective study published in JAMA Dermatology.
In 2006, the Food and Drug Administration implemented the iPledge program, with requirements that include women of childbearing age having a negative pregnancy test and evidence of using two forms of contraception monthly to use isotretinoin, a teratogen. “Although the number of pregnancy-related adverse events for patients taking isotretinoin has decreased since 2006, pregnancies, abortions, and fetal defects associated with isotretinoin exposure continue to be a problem,” Elizabeth Tkachenko, BS, from the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, and coauthors concluded. “Further research is required to determine the most efficacious system to reduce complications for patients and administrative requirements for physicians while at the same time maintaining access to this important drug.” (iPledge followed other Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy systems for isotretinoin.)
She and her colleagues performed a retrospective evaluation of pregnancy-related adverse events related to isotretinoin that had occurred between January 1997 and December 2017 using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), which receives reports from prescribers, consumers, and pharmaceutical manufacturers. While there could be many different classification terms for each individual, any number of adverse events reported by an individual was counted as one pregnancy. Ms. Tkachenko and colleagues classified abortions, pregnancies during contraception use, and pregnancy-related defects into separate subgroups for analysis.
From 1997 to 2017, there were 6,740 pregnancies among women (mean age, 24.6 years) during treatment with isotretinoin reported to FAERS, with 7 reports in 1997, and a peak of 768 pregnancies in 2006. Almost 70% (4,647) of the pregnancies were reported after iPledge was introduced. Between 2011 and 2017, there were 218-310 pregnancy reports each year.
Of the total number of pregnancy reports during the study period, 1,896 were abortions (28.1% of the total); 10.9% of the total number of pregnancy reports were spontaneous abortions (733). The number of abortions peaked in 2008, with 291 reports, of which 85% were therapeutic abortions. Also peaking in 2008 was the number of reports of pregnancies while taking a contraceptive (64). After 2008, pregnancies and abortions dropped.
Fetal defects peaked in 2000, with 34 cases reported, and dropped to four or fewer reports annually after 2008.
“Our findings demonstrate that reports of pregnancy among women taking isotretinoin are concentrated among those aged 20 to 29 years, peaked in 2006, and have been consistent since 2011,” the authors wrote.
Limitations of the study, they noted, include limitations of FAERS data and possible reporting fatigue among doctors and patients. The total number of isotretinoin courses prescribed to this patient population is also unknown, which affected their ability to determine the true rate of pregnancy-related adverse events, they noted.
The other authors for this study were from Harvard Medical School and the departments of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, as well as the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. One author reported support from an award by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health and salary support from a Pfizer Fellowship in Dermatology Patient Oriented Research grant to the trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tkachenko E et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1388.
The rate of fetal exposure to isotretinoin has generally decreased since the implementation of the iPledge program, but rates have plateaued since 2011, and it is unclear why the exposure rate does not continue to decrease, Arielle R. Nagler, MD, wrote in a related editorial.
As noted by Tkachenko et al., it is not possible to infer that iPledge resulted in declines in fetal exposure, abortions, and pregnancy-related complications. Use of long-acting reversible contraception, education about contraception use, and reporting fatigue could be factors in the decline, Dr. Nagler noted. “The inability to clearly demonstrate causality, combined with the unexplained delay and plateau in the number of fetal exposures to isotretinoin after the implementation of iPledge, makes it difficult to draw firm conclusions about the role of iPledge in this reported trend,” she said.
The decrease in fetal exposure could also potentially be explained by effects of iPledge on the availability of isotretinoin for women of childbearing age. Indeed, studies have shown a significant decrease in isotretinoin prescriptions in this patient population after iPledge was implemented.
Despite lack of data, there is still too much fetal exposure to isotretinoin, wrote Dr. Nagler, which calls into question the efficacy of the iPledge program. “We can all agree that 1 fetal exposure to isotretinoin should be too many, but without taking isotretinoin off the market, we will never achieve zero fetal exposures to isotretinoin. Still, we can – and should – expect more from a REMS [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy] program,” Dr. Nagler concluded.
Dr. Nagler is with the department of dermatology at New York University. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
The rate of fetal exposure to isotretinoin has generally decreased since the implementation of the iPledge program, but rates have plateaued since 2011, and it is unclear why the exposure rate does not continue to decrease, Arielle R. Nagler, MD, wrote in a related editorial.
As noted by Tkachenko et al., it is not possible to infer that iPledge resulted in declines in fetal exposure, abortions, and pregnancy-related complications. Use of long-acting reversible contraception, education about contraception use, and reporting fatigue could be factors in the decline, Dr. Nagler noted. “The inability to clearly demonstrate causality, combined with the unexplained delay and plateau in the number of fetal exposures to isotretinoin after the implementation of iPledge, makes it difficult to draw firm conclusions about the role of iPledge in this reported trend,” she said.
The decrease in fetal exposure could also potentially be explained by effects of iPledge on the availability of isotretinoin for women of childbearing age. Indeed, studies have shown a significant decrease in isotretinoin prescriptions in this patient population after iPledge was implemented.
Despite lack of data, there is still too much fetal exposure to isotretinoin, wrote Dr. Nagler, which calls into question the efficacy of the iPledge program. “We can all agree that 1 fetal exposure to isotretinoin should be too many, but without taking isotretinoin off the market, we will never achieve zero fetal exposures to isotretinoin. Still, we can – and should – expect more from a REMS [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy] program,” Dr. Nagler concluded.
Dr. Nagler is with the department of dermatology at New York University. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
The rate of fetal exposure to isotretinoin has generally decreased since the implementation of the iPledge program, but rates have plateaued since 2011, and it is unclear why the exposure rate does not continue to decrease, Arielle R. Nagler, MD, wrote in a related editorial.
As noted by Tkachenko et al., it is not possible to infer that iPledge resulted in declines in fetal exposure, abortions, and pregnancy-related complications. Use of long-acting reversible contraception, education about contraception use, and reporting fatigue could be factors in the decline, Dr. Nagler noted. “The inability to clearly demonstrate causality, combined with the unexplained delay and plateau in the number of fetal exposures to isotretinoin after the implementation of iPledge, makes it difficult to draw firm conclusions about the role of iPledge in this reported trend,” she said.
The decrease in fetal exposure could also potentially be explained by effects of iPledge on the availability of isotretinoin for women of childbearing age. Indeed, studies have shown a significant decrease in isotretinoin prescriptions in this patient population after iPledge was implemented.
Despite lack of data, there is still too much fetal exposure to isotretinoin, wrote Dr. Nagler, which calls into question the efficacy of the iPledge program. “We can all agree that 1 fetal exposure to isotretinoin should be too many, but without taking isotretinoin off the market, we will never achieve zero fetal exposures to isotretinoin. Still, we can – and should – expect more from a REMS [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy] program,” Dr. Nagler concluded.
Dr. Nagler is with the department of dermatology at New York University. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
but pregnancy, abortions, and fetal defects associated with isotretinoin exposure are still occurring in women of reproductive age, according to a retrospective study published in JAMA Dermatology.
In 2006, the Food and Drug Administration implemented the iPledge program, with requirements that include women of childbearing age having a negative pregnancy test and evidence of using two forms of contraception monthly to use isotretinoin, a teratogen. “Although the number of pregnancy-related adverse events for patients taking isotretinoin has decreased since 2006, pregnancies, abortions, and fetal defects associated with isotretinoin exposure continue to be a problem,” Elizabeth Tkachenko, BS, from the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, and coauthors concluded. “Further research is required to determine the most efficacious system to reduce complications for patients and administrative requirements for physicians while at the same time maintaining access to this important drug.” (iPledge followed other Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy systems for isotretinoin.)
She and her colleagues performed a retrospective evaluation of pregnancy-related adverse events related to isotretinoin that had occurred between January 1997 and December 2017 using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), which receives reports from prescribers, consumers, and pharmaceutical manufacturers. While there could be many different classification terms for each individual, any number of adverse events reported by an individual was counted as one pregnancy. Ms. Tkachenko and colleagues classified abortions, pregnancies during contraception use, and pregnancy-related defects into separate subgroups for analysis.
From 1997 to 2017, there were 6,740 pregnancies among women (mean age, 24.6 years) during treatment with isotretinoin reported to FAERS, with 7 reports in 1997, and a peak of 768 pregnancies in 2006. Almost 70% (4,647) of the pregnancies were reported after iPledge was introduced. Between 2011 and 2017, there were 218-310 pregnancy reports each year.
Of the total number of pregnancy reports during the study period, 1,896 were abortions (28.1% of the total); 10.9% of the total number of pregnancy reports were spontaneous abortions (733). The number of abortions peaked in 2008, with 291 reports, of which 85% were therapeutic abortions. Also peaking in 2008 was the number of reports of pregnancies while taking a contraceptive (64). After 2008, pregnancies and abortions dropped.
Fetal defects peaked in 2000, with 34 cases reported, and dropped to four or fewer reports annually after 2008.
“Our findings demonstrate that reports of pregnancy among women taking isotretinoin are concentrated among those aged 20 to 29 years, peaked in 2006, and have been consistent since 2011,” the authors wrote.
Limitations of the study, they noted, include limitations of FAERS data and possible reporting fatigue among doctors and patients. The total number of isotretinoin courses prescribed to this patient population is also unknown, which affected their ability to determine the true rate of pregnancy-related adverse events, they noted.
The other authors for this study were from Harvard Medical School and the departments of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, as well as the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. One author reported support from an award by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health and salary support from a Pfizer Fellowship in Dermatology Patient Oriented Research grant to the trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tkachenko E et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1388.
but pregnancy, abortions, and fetal defects associated with isotretinoin exposure are still occurring in women of reproductive age, according to a retrospective study published in JAMA Dermatology.
In 2006, the Food and Drug Administration implemented the iPledge program, with requirements that include women of childbearing age having a negative pregnancy test and evidence of using two forms of contraception monthly to use isotretinoin, a teratogen. “Although the number of pregnancy-related adverse events for patients taking isotretinoin has decreased since 2006, pregnancies, abortions, and fetal defects associated with isotretinoin exposure continue to be a problem,” Elizabeth Tkachenko, BS, from the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, and coauthors concluded. “Further research is required to determine the most efficacious system to reduce complications for patients and administrative requirements for physicians while at the same time maintaining access to this important drug.” (iPledge followed other Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy systems for isotretinoin.)
She and her colleagues performed a retrospective evaluation of pregnancy-related adverse events related to isotretinoin that had occurred between January 1997 and December 2017 using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), which receives reports from prescribers, consumers, and pharmaceutical manufacturers. While there could be many different classification terms for each individual, any number of adverse events reported by an individual was counted as one pregnancy. Ms. Tkachenko and colleagues classified abortions, pregnancies during contraception use, and pregnancy-related defects into separate subgroups for analysis.
From 1997 to 2017, there were 6,740 pregnancies among women (mean age, 24.6 years) during treatment with isotretinoin reported to FAERS, with 7 reports in 1997, and a peak of 768 pregnancies in 2006. Almost 70% (4,647) of the pregnancies were reported after iPledge was introduced. Between 2011 and 2017, there were 218-310 pregnancy reports each year.
Of the total number of pregnancy reports during the study period, 1,896 were abortions (28.1% of the total); 10.9% of the total number of pregnancy reports were spontaneous abortions (733). The number of abortions peaked in 2008, with 291 reports, of which 85% were therapeutic abortions. Also peaking in 2008 was the number of reports of pregnancies while taking a contraceptive (64). After 2008, pregnancies and abortions dropped.
Fetal defects peaked in 2000, with 34 cases reported, and dropped to four or fewer reports annually after 2008.
“Our findings demonstrate that reports of pregnancy among women taking isotretinoin are concentrated among those aged 20 to 29 years, peaked in 2006, and have been consistent since 2011,” the authors wrote.
Limitations of the study, they noted, include limitations of FAERS data and possible reporting fatigue among doctors and patients. The total number of isotretinoin courses prescribed to this patient population is also unknown, which affected their ability to determine the true rate of pregnancy-related adverse events, they noted.
The other authors for this study were from Harvard Medical School and the departments of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, as well as the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. One author reported support from an award by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health and salary support from a Pfizer Fellowship in Dermatology Patient Oriented Research grant to the trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tkachenko E et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1388.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
How to recognize pediatric leukemia cutis
Researchers have characterized the clinical presentation, progression, and prognosis of leukemia cutis in a pediatric population, according to findings from a retrospective case series.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest reported case series of pediatric leukemia cutis,” wrote Elena Corina Andriescu of the University of Texas, Houston, and colleagues. The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The study included 31 children with histologically confirmed leukemia cutis at one of two pediatric institutions. The researchers reviewed medical records to distinguish common features among patients.
Various clinical data, including disease subtype, related symptoms, management, and prognosis, were collected from January 1993 to March 2014. The children in the case series ranged in age up to 19 years with a median age at diagnosis of 26.8 months.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the magnitude and morphology of disease lesions differed among pediatric patients, with the most common sites being the lower extremities and head. The most common morphologies were nodules and papules. Additionally, the researchers found that lesions were often erythematous, violaceous, or both colors.
The majority of patients (65%) presented with concomitant systemic leukemia and leukemia cutis. The most common types of leukemia associated with the skin condition were acute myeloid leukemia (in 74% of cases) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (in 16% of cases). The researchers saw no significant differences in leukemia cutis morphology or distribution based on the leukemia diagnosis.
“Most cases of leukemia cutis arose during initial leukemia episodes, rather than with relapsed leukemia,” they added.
Because of an insufficiency of specific genetic data, investigators were unable to make prognostic inferences in the majority of participants.
Two key limitations of the study were the small sample size and retrospective design. As a result, the investigators were unable to prospectively classify skin findings in a systematic manner. Despite these limitations, the authors noted that these findings add to the present knowledge of leukemia cutis in pediatric patients.
“Importantly, the presence of [leukemia cutis] changed the management of systemic leukemia in one‐third of patients,” the researchers wrote. “The potential for major changes in treatment plans such as adding radiation therapy and deferring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation underscores the importance of diagnosing [leukemia cutis].”
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Andriescu EC et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/pde.13864.
Researchers have characterized the clinical presentation, progression, and prognosis of leukemia cutis in a pediatric population, according to findings from a retrospective case series.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest reported case series of pediatric leukemia cutis,” wrote Elena Corina Andriescu of the University of Texas, Houston, and colleagues. The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The study included 31 children with histologically confirmed leukemia cutis at one of two pediatric institutions. The researchers reviewed medical records to distinguish common features among patients.
Various clinical data, including disease subtype, related symptoms, management, and prognosis, were collected from January 1993 to March 2014. The children in the case series ranged in age up to 19 years with a median age at diagnosis of 26.8 months.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the magnitude and morphology of disease lesions differed among pediatric patients, with the most common sites being the lower extremities and head. The most common morphologies were nodules and papules. Additionally, the researchers found that lesions were often erythematous, violaceous, or both colors.
The majority of patients (65%) presented with concomitant systemic leukemia and leukemia cutis. The most common types of leukemia associated with the skin condition were acute myeloid leukemia (in 74% of cases) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (in 16% of cases). The researchers saw no significant differences in leukemia cutis morphology or distribution based on the leukemia diagnosis.
“Most cases of leukemia cutis arose during initial leukemia episodes, rather than with relapsed leukemia,” they added.
Because of an insufficiency of specific genetic data, investigators were unable to make prognostic inferences in the majority of participants.
Two key limitations of the study were the small sample size and retrospective design. As a result, the investigators were unable to prospectively classify skin findings in a systematic manner. Despite these limitations, the authors noted that these findings add to the present knowledge of leukemia cutis in pediatric patients.
“Importantly, the presence of [leukemia cutis] changed the management of systemic leukemia in one‐third of patients,” the researchers wrote. “The potential for major changes in treatment plans such as adding radiation therapy and deferring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation underscores the importance of diagnosing [leukemia cutis].”
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Andriescu EC et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/pde.13864.
Researchers have characterized the clinical presentation, progression, and prognosis of leukemia cutis in a pediatric population, according to findings from a retrospective case series.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest reported case series of pediatric leukemia cutis,” wrote Elena Corina Andriescu of the University of Texas, Houston, and colleagues. The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The study included 31 children with histologically confirmed leukemia cutis at one of two pediatric institutions. The researchers reviewed medical records to distinguish common features among patients.
Various clinical data, including disease subtype, related symptoms, management, and prognosis, were collected from January 1993 to March 2014. The children in the case series ranged in age up to 19 years with a median age at diagnosis of 26.8 months.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the magnitude and morphology of disease lesions differed among pediatric patients, with the most common sites being the lower extremities and head. The most common morphologies were nodules and papules. Additionally, the researchers found that lesions were often erythematous, violaceous, or both colors.
The majority of patients (65%) presented with concomitant systemic leukemia and leukemia cutis. The most common types of leukemia associated with the skin condition were acute myeloid leukemia (in 74% of cases) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (in 16% of cases). The researchers saw no significant differences in leukemia cutis morphology or distribution based on the leukemia diagnosis.
“Most cases of leukemia cutis arose during initial leukemia episodes, rather than with relapsed leukemia,” they added.
Because of an insufficiency of specific genetic data, investigators were unable to make prognostic inferences in the majority of participants.
Two key limitations of the study were the small sample size and retrospective design. As a result, the investigators were unable to prospectively classify skin findings in a systematic manner. Despite these limitations, the authors noted that these findings add to the present knowledge of leukemia cutis in pediatric patients.
“Importantly, the presence of [leukemia cutis] changed the management of systemic leukemia in one‐third of patients,” the researchers wrote. “The potential for major changes in treatment plans such as adding radiation therapy and deferring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation underscores the importance of diagnosing [leukemia cutis].”
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Andriescu EC et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/pde.13864.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Ovarian cancer diagnosed and treated earlier under ACA
CHICAGO – , according to a comparison of National Cancer Database surveys from 2006-2009 and 2011-2014.
During the post-Affordable Care Act (ACA) years of 2011-2014, compared with the pre-ACA years of 2004-2009, a treatment group of women aged 21-64 years with ovarian cancer was more likely to be diagnosed at an early stage, compared with a control group of women aged 65 years and older (difference-in-differences [DD]=1.7%), Anna Jo Smith, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Also, the ACA was associated with more women aged 21-64 receiving treatment within 30 days of diagnosis (DD = 1.6%), said Dr. Smith, a 4th-year resident at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Among women with public insurance, the ACA was associated with even greater improvement in early-stage diagnosis and treatment within 30 days in the treatment group vs. the controls (DD = 2.5% for each), she said, noting that the improvements were seen across race, income, and education groups.
The findings are based on pre-ACA surveys from 35,842 women aged 21-64 years and 28,895 women aged 65 years, and from post-ACA surveys from 37,145 women and 30,604 women in those age groups, respectively, and were adjusted for patient race, living in a rural area, area-level household income and education level, Charlson comorbidity score, distance traveled for care, Census region, and care at an academic center.
The 2010 ACA expanded access to insurance and care for many Americans, and the objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of that access on women with ovarian cancer, Dr. Smith explained.
“Under the 2010 Affordable Care Act, women with ovarian cancer were more likely to be diagnosed at an early stage and receive treatment within 30 days of diagnosis,” she said. “As stage and treatment are the major determinants of survival advantage, these gains under the ACA may have long-term impacts on the survival, health, and well-being of women with ovarian cancer.”
Dr. Smith reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Smith A et al., ASCO 2019. Abstract LBA5563.
CHICAGO – , according to a comparison of National Cancer Database surveys from 2006-2009 and 2011-2014.
During the post-Affordable Care Act (ACA) years of 2011-2014, compared with the pre-ACA years of 2004-2009, a treatment group of women aged 21-64 years with ovarian cancer was more likely to be diagnosed at an early stage, compared with a control group of women aged 65 years and older (difference-in-differences [DD]=1.7%), Anna Jo Smith, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Also, the ACA was associated with more women aged 21-64 receiving treatment within 30 days of diagnosis (DD = 1.6%), said Dr. Smith, a 4th-year resident at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Among women with public insurance, the ACA was associated with even greater improvement in early-stage diagnosis and treatment within 30 days in the treatment group vs. the controls (DD = 2.5% for each), she said, noting that the improvements were seen across race, income, and education groups.
The findings are based on pre-ACA surveys from 35,842 women aged 21-64 years and 28,895 women aged 65 years, and from post-ACA surveys from 37,145 women and 30,604 women in those age groups, respectively, and were adjusted for patient race, living in a rural area, area-level household income and education level, Charlson comorbidity score, distance traveled for care, Census region, and care at an academic center.
The 2010 ACA expanded access to insurance and care for many Americans, and the objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of that access on women with ovarian cancer, Dr. Smith explained.
“Under the 2010 Affordable Care Act, women with ovarian cancer were more likely to be diagnosed at an early stage and receive treatment within 30 days of diagnosis,” she said. “As stage and treatment are the major determinants of survival advantage, these gains under the ACA may have long-term impacts on the survival, health, and well-being of women with ovarian cancer.”
Dr. Smith reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Smith A et al., ASCO 2019. Abstract LBA5563.
CHICAGO – , according to a comparison of National Cancer Database surveys from 2006-2009 and 2011-2014.
During the post-Affordable Care Act (ACA) years of 2011-2014, compared with the pre-ACA years of 2004-2009, a treatment group of women aged 21-64 years with ovarian cancer was more likely to be diagnosed at an early stage, compared with a control group of women aged 65 years and older (difference-in-differences [DD]=1.7%), Anna Jo Smith, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Also, the ACA was associated with more women aged 21-64 receiving treatment within 30 days of diagnosis (DD = 1.6%), said Dr. Smith, a 4th-year resident at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Among women with public insurance, the ACA was associated with even greater improvement in early-stage diagnosis and treatment within 30 days in the treatment group vs. the controls (DD = 2.5% for each), she said, noting that the improvements were seen across race, income, and education groups.
The findings are based on pre-ACA surveys from 35,842 women aged 21-64 years and 28,895 women aged 65 years, and from post-ACA surveys from 37,145 women and 30,604 women in those age groups, respectively, and were adjusted for patient race, living in a rural area, area-level household income and education level, Charlson comorbidity score, distance traveled for care, Census region, and care at an academic center.
The 2010 ACA expanded access to insurance and care for many Americans, and the objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of that access on women with ovarian cancer, Dr. Smith explained.
“Under the 2010 Affordable Care Act, women with ovarian cancer were more likely to be diagnosed at an early stage and receive treatment within 30 days of diagnosis,” she said. “As stage and treatment are the major determinants of survival advantage, these gains under the ACA may have long-term impacts on the survival, health, and well-being of women with ovarian cancer.”
Dr. Smith reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Smith A et al., ASCO 2019. Abstract LBA5563.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019