User login
Disseminated Invasive Candidiasis in an Immunocompetent Host
Candida albicans (C albicans) is a normal commensal in the human gastrointestinal (GI) tract. In addition to localized infections in healthy human beings, dissemination with fatal outcome can occur in immunocompromised individuals.1
Invasive candidiasis (IC) due to C albicans is the most common nosocomial mycosis in the world and has 2 forms, candidemia and deep-seated tissue candidiasis, which can lead to multisystem organ failure.2 The deep-seated form may originate from nonhematogenous routes, such as introduction through a peritoneal catheter or ascending infection from cystitis.2 In addition, about 50% of primary candidemia cases lead to secondary deep-seated candidiasis; however, only about 40% of these cases show positive blood cultures. Since the window of opportunity for a positive culture is narrow, active candidemia may be missed.3,4
Once developed, the prognosis for IC is grim: Mortality is 40% regardless of therapy.2 IC typically occurs in immunocompromised hosts; IC in immunocompetent persons has rarely been reported.5,6 It is challenging to diagnose IC in the immunocompetent patients as 50% to 70% of the general population is naturally colonized by this organism, and when found, it is assumed to be mostly innocuous. Neutrophil-driven cell-mediated immunity associated with IL-1 and IL-17 response prevent fungal growth and dissemination, protecting the immunocompetent host.7
We report on a patient who showed no neutropenia or leukocytopenia but developed disseminated candidiasis. This report is one of the rare cases of full-blown disseminated candidiasis with lesions related to C albicans found in almost all of the important organs.
Case Presentation
A 67-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, daily heavy alcohol consumption, and a 50-pack-year history of smoking developed gangrene of the left fifth toe. He underwent vascular surgery consultation with an aortogram/left lower extremity angiography that showed occlusion of the left external iliac artery as well as the left common femoral artery. It was decided to improve inflow in the common iliac artery by placing a bare metal stent and subsequent balloon dilatation before a right to left femoral to femoral artery bypass. The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged home.
Two days later, the patient was admitted to a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) complexity level 1a hospital with weakness and worsening pain in the left lower extremities. Examination revealed chronic ischemic changes in the feet bilaterally and evidence of dry gangrene in the left fifth toe requiring femoral bypass surgery. But poor nutritional status and cardiac status prevented pursuing a permanent solution.
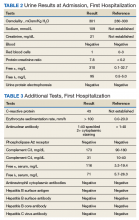
Following completion of a stress echocardiogram, the patient developed shock with systolic blood pressure of 60 mm Hg, and atrial fibrillation (AF) with rapid ventricular rate (RVR). He was initially treated with IV fluid supplementation, vasopressor therapy, synchronized cardioversion, and IV amiodarone/anticoagulation therapy, due to his persistent AF with RVR. The patient was transferred to a tertiary care center for persistent hypothermia and received treatment with warm saline. After initial recovery with warm saline resuscitation, he had a prolonged, complicated hospital course in which he developed progressive respiratory failure requiring intubation and critical care support. He developed a right internal jugular deep venous thrombosis, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, lower GI bleeding requiring emergent embolization by interventional radiology, inferior vena cava filter placement, renal failure requiring dialysis, small bowel obstruction secondary to right lower quadrant phlegmon and perforation requiring small bowel resection and end ileostomy. His antibiotic regimen included therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam.
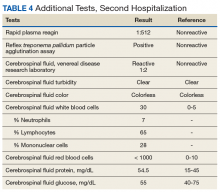
He eventually recovered and was extubated and subsequently transferred back to the VA hospital where cefepime was initiated because of suspicion of a urinary tract infection and septicemia (urine cultures eventually grew C albicans). Over the subsequent 3 days, the patient’s renal output and hyperkalemia worsened, he also developed increased anion gap metabolic acidosis and was intubated again and placed on full mechanical ventilatory support. His blood cultures were negative, and sputum cultures revealed normal respiratory flora and 1+ C albicans. Infectious diseases consultation recommended an abdominal ultrasound, which revealed nonspecific findings. The antibiotic regimen was changed to daptomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam. A follow-up chest X-ray revealed a developing right lower lobe pneumonia and hilar prominence suggestive of lymphadenopathy. The patient’s clinical condition deteriorated, and he subsequently developed cardiac arrest; resuscitation was not successful and he expired.
Outcome and Follow-up
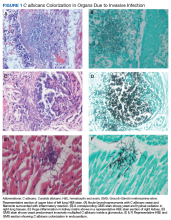
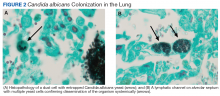
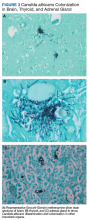
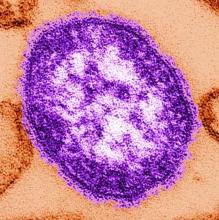
An autopsy disclosed the cause of death to be bilateral candida pneumonia, part of a disseminated (invasive) candidiasis, in a patient rendered vulnerable to such infection by peripheral vascular disease and renal insufficiency. Purulent inflammation was noted at the site of disarticulation of the left foot and confluent consolidation of the lower lobes of both lungs as well as focal consolidation of the middle lobe of the right lung. Examination of histologic sections, with staining both by routine method (hematoxylin and eosin) and the Grocott-Gömöri methenamine silver method for fungus, disclosed fungal forms (yeast and filamentous) in most tissues, including the lungs (Figure 1 A and B) and kidneys (Figure 1 C and D). The pulmonary sections in addition to massive inflammation showed macrophages with engulfed yeast (Figure 2 A) and a lymphatic channel, stuffed with yeast in an alveolar septum (Figure 2 B). These findings confirmed the antemortem presence of the fungus and the body’s response to it. Inflammation was noted around glomeruli overgrown by candida (Figure 1 C and D); fungi also were seen in capsular regions (not depicted). C albicans was present in the myocardium (Figure 1 E and F), brain, thyroid, and adrenal glands (Figure 3); the only organ without C albicans was the liver, either because invasion was truly absent here or because sampling had not managed to retrieve it.
Paraffin-embedded blocks of lung tissue, sent to the University of Washington Molecular Diagnosis Microbiology Laboratory for broad-range polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification, were positive for C albicans after extraction of gDNA and conduction of PCR using internal transcribed spacer 1 and 2 specific primers.
Discussion
IC is rare among immunocompetent individuals, but C albicans can evolve into a fatal disseminated infection. We report an atypical case of IC, with profound pulmonary infection in a patient who died 1 month after hospitalization for lower extremity pain.
Cell-mediated immunity involving neutrophils and macrophages plays a major role in protection against candidiasis, while cytokines and chemokines involve regulating balanced immunity.1,2 A series of recent studies show that alcohol impairs neutrophil-mediated killing and phagocytic-mediated uptake of a pathogen in this process.8,9 As the patient chronically misused alcohol, his immune system may have experienced a subclinical immunosuppression, which would have become clinically relevant once C albicans was introduced systemically. Recent studies of bacterial pathogenesis and alcoholism strongly support this hypothesis.10,11
Most patients with the unusual diagnosis of candida pneumonia have had a background of malignancy or immunosuppressive factors (eg, administration of corticosteroids).12 In a series of 20 cases, 14 had sputum cultures positive for the organism, 6 had positive urine cultures, and 6 had positive blood cultures. Chest radiographs usually showed confluent bronchopneumonia. Five patients were diagnosed antemortem and treated with amphotericin B, but none survived.13 In the literature a positive blood culture or demonstration of yeast within pulmonary histiocytes has been considered proof of the pathogenicity of the fungus, as opposed to noninvasive colonization of the airways, a common occurrence in patients receiving mechanical ventilation.2
As previously discussed, blood cultures are often negative with invasive candidiasis, as the window of opportunity is short and may be missed. As shown in murine models, it is easy to miss a narrow window of candidemia, leading to false-negative blood cultures in clinical practice.14,15 Mouse model studies also have found that the window of candidemia is very short in disseminated candidiasis as a lethal IV dose of C albicans disappeared from blood within 48 hours of postinoculation.15 The biomarker of serum procalcitonin is a great diagnostic resource for the elimination of a likely bacterial sepsis, and conversely, the early suspicion of a fungemia, as serum procalcitonin would typically be elevated in a bacterial but not a fungal septicemia.16 The average cost per test is only about $30, and we recommend testing for serum procalcitonin as well as monitoring of serum lactate levels in cases of nonresponding septicemia.
The C albicans in this case may have been introduced hematogenously from the amputation site or through an ascending cystitis, or possibly have been derived from commensal flora in the GI tract. The iron supplementation provided to the patient may have promoted the growth and virulence of the candida; studies have shown that the kidneys assimilate increased levels of iron during disseminated candidiasis thus providing a more favorable site for colonization.17The presence of C albicans in a single collection of sputum or urine does not ordinarily indicate infection in an immunocompetent individual. Estimation of serum procalcitonin, a biomarker for bacterial infection and sepsis, might be useful if negative, for turning attention to a nonbacterial (such as, candida) source as the causative agent.18
Conclusion
C albicans can rarely cause disseminated disease in nonimmunocompromised critically ill patients. Low serum procalcitonin levels in a septic patient might indicate nonbacterial cause such as candidiasis. Even with disseminated candidiasis, blood cultures may remain negative.
1. Navarathna DH, Stein EV, Lessey-Morillon EC, Nayak D, Martin-Manso G, Roberts DD. CD47 promotes protective innate and adaptive immunity in a mouse model of disseminated candidiasis. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0128220.
2. Kullberg BJ, Arendrup MC. Invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(15):1445-1456.
3. Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Diagnosing invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56(5):e01909-e01917.
4. Ericson EL, Klingspor L, Ullberg M, Ozenci V. Clinical comparison of the Bactec Mycosis IC/F, BacT/Alert FA, and BacT/Alert FN blood culture vials for the detection of candidemia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;73(2):153-156.
5. Baum GL. The significance of Candida albicans in human sputum. N Engl J Med. 1960;263:70-73.
6. el-Ebiary M, Torres A, Fàbregas N, et al. Significance of the isolation of Candida species from respiratory samples in critically ill, non-neutropenic patients. An immediate postmortem histologic study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(2, pt 1):583-590.
7. Altmeier S, Toska A, Sparber F, Teijeira A, Halin C, LeibundGut-Landmann S. IL-1 coordinates the neutrophil response to C. albicans in the oral mucosa. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(9):e1005882.
8. Karavitis J, Kovacs EJ. Macrophage phagocytosis: effects of environmental pollutants, alcohol, cigarette smoke, and other external factors. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90(6):1065-1078.
9. Chiu C-H, Wang Y-C, Yeh K-M, Lin J-C, Siu LK, Chang F-Y. Influence of ethanol concentration in the phagocytic function of neutrophils against Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in an experimental model. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018;51(1):64-69.
10. Khocht A, Schleifer S, Janal M, Keller S. Neutrophil function and periodontitis in alcohol-dependent males without medical disorders. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2013;15(3):68-74.
11. Gandhi JA, Ekhar VV, Asplund MB, et al. Alcohol enhances Acinetobacter baumannii-associated pneumonia and systemic dissemination by impairing neutrophil antimicrobial activity in a murine model of infection. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95707.
12. Mohsenifar Z, Chopra SK, Johnson BL, Simmons DH. Candida pneumonia: experience with 20 patients. West J Med. 1979;131(3):196-200.
13. Jones JM. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990;3(1):32-45.
14. Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Finding the “missing 50%” of invasive candidiasis: how nonculture diagnostics will improve understanding of disease spectrum and transform patient care. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(9):1284-1292.
15. Kappe R, Mu¨ ller J. Rapid clearance of Candida albicans mannan antigens by liver and spleen in contrast to prolonged circulation of Cryptococcus neoformans antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1991;29(8):1665-1669.
16. Balk RA, Kadri SS, Cao Z, Robinson SB, Lipkin C, Bozzette SA. Effect of procalcitonin testing on health-care utilization and costs in critically ill patients in the United States. Chest. 2017;151(1):23-33.
17. Potrykus J, Stead D, Maccallum DM, et al. Fungal iron availability during deep seated candidiasis is defined by a complex interplay involving systemic and local events. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(10):e1003676.
18. Soni NJ, Samson DJ, Galaydick JL, Vats V, Pitrak DL, Aronson N. Procalcitonin-Guided Antibiotic Therapy. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2012.
Candida albicans (C albicans) is a normal commensal in the human gastrointestinal (GI) tract. In addition to localized infections in healthy human beings, dissemination with fatal outcome can occur in immunocompromised individuals.1
Invasive candidiasis (IC) due to C albicans is the most common nosocomial mycosis in the world and has 2 forms, candidemia and deep-seated tissue candidiasis, which can lead to multisystem organ failure.2 The deep-seated form may originate from nonhematogenous routes, such as introduction through a peritoneal catheter or ascending infection from cystitis.2 In addition, about 50% of primary candidemia cases lead to secondary deep-seated candidiasis; however, only about 40% of these cases show positive blood cultures. Since the window of opportunity for a positive culture is narrow, active candidemia may be missed.3,4
Once developed, the prognosis for IC is grim: Mortality is 40% regardless of therapy.2 IC typically occurs in immunocompromised hosts; IC in immunocompetent persons has rarely been reported.5,6 It is challenging to diagnose IC in the immunocompetent patients as 50% to 70% of the general population is naturally colonized by this organism, and when found, it is assumed to be mostly innocuous. Neutrophil-driven cell-mediated immunity associated with IL-1 and IL-17 response prevent fungal growth and dissemination, protecting the immunocompetent host.7
We report on a patient who showed no neutropenia or leukocytopenia but developed disseminated candidiasis. This report is one of the rare cases of full-blown disseminated candidiasis with lesions related to C albicans found in almost all of the important organs.
Case Presentation
A 67-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, daily heavy alcohol consumption, and a 50-pack-year history of smoking developed gangrene of the left fifth toe. He underwent vascular surgery consultation with an aortogram/left lower extremity angiography that showed occlusion of the left external iliac artery as well as the left common femoral artery. It was decided to improve inflow in the common iliac artery by placing a bare metal stent and subsequent balloon dilatation before a right to left femoral to femoral artery bypass. The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged home.
Two days later, the patient was admitted to a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) complexity level 1a hospital with weakness and worsening pain in the left lower extremities. Examination revealed chronic ischemic changes in the feet bilaterally and evidence of dry gangrene in the left fifth toe requiring femoral bypass surgery. But poor nutritional status and cardiac status prevented pursuing a permanent solution.
Following completion of a stress echocardiogram, the patient developed shock with systolic blood pressure of 60 mm Hg, and atrial fibrillation (AF) with rapid ventricular rate (RVR). He was initially treated with IV fluid supplementation, vasopressor therapy, synchronized cardioversion, and IV amiodarone/anticoagulation therapy, due to his persistent AF with RVR. The patient was transferred to a tertiary care center for persistent hypothermia and received treatment with warm saline. After initial recovery with warm saline resuscitation, he had a prolonged, complicated hospital course in which he developed progressive respiratory failure requiring intubation and critical care support. He developed a right internal jugular deep venous thrombosis, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, lower GI bleeding requiring emergent embolization by interventional radiology, inferior vena cava filter placement, renal failure requiring dialysis, small bowel obstruction secondary to right lower quadrant phlegmon and perforation requiring small bowel resection and end ileostomy. His antibiotic regimen included therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam.
He eventually recovered and was extubated and subsequently transferred back to the VA hospital where cefepime was initiated because of suspicion of a urinary tract infection and septicemia (urine cultures eventually grew C albicans). Over the subsequent 3 days, the patient’s renal output and hyperkalemia worsened, he also developed increased anion gap metabolic acidosis and was intubated again and placed on full mechanical ventilatory support. His blood cultures were negative, and sputum cultures revealed normal respiratory flora and 1+ C albicans. Infectious diseases consultation recommended an abdominal ultrasound, which revealed nonspecific findings. The antibiotic regimen was changed to daptomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam. A follow-up chest X-ray revealed a developing right lower lobe pneumonia and hilar prominence suggestive of lymphadenopathy. The patient’s clinical condition deteriorated, and he subsequently developed cardiac arrest; resuscitation was not successful and he expired.
Outcome and Follow-up
An autopsy disclosed the cause of death to be bilateral candida pneumonia, part of a disseminated (invasive) candidiasis, in a patient rendered vulnerable to such infection by peripheral vascular disease and renal insufficiency. Purulent inflammation was noted at the site of disarticulation of the left foot and confluent consolidation of the lower lobes of both lungs as well as focal consolidation of the middle lobe of the right lung. Examination of histologic sections, with staining both by routine method (hematoxylin and eosin) and the Grocott-Gömöri methenamine silver method for fungus, disclosed fungal forms (yeast and filamentous) in most tissues, including the lungs (Figure 1 A and B) and kidneys (Figure 1 C and D). The pulmonary sections in addition to massive inflammation showed macrophages with engulfed yeast (Figure 2 A) and a lymphatic channel, stuffed with yeast in an alveolar septum (Figure 2 B). These findings confirmed the antemortem presence of the fungus and the body’s response to it. Inflammation was noted around glomeruli overgrown by candida (Figure 1 C and D); fungi also were seen in capsular regions (not depicted). C albicans was present in the myocardium (Figure 1 E and F), brain, thyroid, and adrenal glands (Figure 3); the only organ without C albicans was the liver, either because invasion was truly absent here or because sampling had not managed to retrieve it.
Paraffin-embedded blocks of lung tissue, sent to the University of Washington Molecular Diagnosis Microbiology Laboratory for broad-range polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification, were positive for C albicans after extraction of gDNA and conduction of PCR using internal transcribed spacer 1 and 2 specific primers.
Discussion
IC is rare among immunocompetent individuals, but C albicans can evolve into a fatal disseminated infection. We report an atypical case of IC, with profound pulmonary infection in a patient who died 1 month after hospitalization for lower extremity pain.
Cell-mediated immunity involving neutrophils and macrophages plays a major role in protection against candidiasis, while cytokines and chemokines involve regulating balanced immunity.1,2 A series of recent studies show that alcohol impairs neutrophil-mediated killing and phagocytic-mediated uptake of a pathogen in this process.8,9 As the patient chronically misused alcohol, his immune system may have experienced a subclinical immunosuppression, which would have become clinically relevant once C albicans was introduced systemically. Recent studies of bacterial pathogenesis and alcoholism strongly support this hypothesis.10,11
Most patients with the unusual diagnosis of candida pneumonia have had a background of malignancy or immunosuppressive factors (eg, administration of corticosteroids).12 In a series of 20 cases, 14 had sputum cultures positive for the organism, 6 had positive urine cultures, and 6 had positive blood cultures. Chest radiographs usually showed confluent bronchopneumonia. Five patients were diagnosed antemortem and treated with amphotericin B, but none survived.13 In the literature a positive blood culture or demonstration of yeast within pulmonary histiocytes has been considered proof of the pathogenicity of the fungus, as opposed to noninvasive colonization of the airways, a common occurrence in patients receiving mechanical ventilation.2
As previously discussed, blood cultures are often negative with invasive candidiasis, as the window of opportunity is short and may be missed. As shown in murine models, it is easy to miss a narrow window of candidemia, leading to false-negative blood cultures in clinical practice.14,15 Mouse model studies also have found that the window of candidemia is very short in disseminated candidiasis as a lethal IV dose of C albicans disappeared from blood within 48 hours of postinoculation.15 The biomarker of serum procalcitonin is a great diagnostic resource for the elimination of a likely bacterial sepsis, and conversely, the early suspicion of a fungemia, as serum procalcitonin would typically be elevated in a bacterial but not a fungal septicemia.16 The average cost per test is only about $30, and we recommend testing for serum procalcitonin as well as monitoring of serum lactate levels in cases of nonresponding septicemia.
The C albicans in this case may have been introduced hematogenously from the amputation site or through an ascending cystitis, or possibly have been derived from commensal flora in the GI tract. The iron supplementation provided to the patient may have promoted the growth and virulence of the candida; studies have shown that the kidneys assimilate increased levels of iron during disseminated candidiasis thus providing a more favorable site for colonization.17The presence of C albicans in a single collection of sputum or urine does not ordinarily indicate infection in an immunocompetent individual. Estimation of serum procalcitonin, a biomarker for bacterial infection and sepsis, might be useful if negative, for turning attention to a nonbacterial (such as, candida) source as the causative agent.18
Conclusion
C albicans can rarely cause disseminated disease in nonimmunocompromised critically ill patients. Low serum procalcitonin levels in a septic patient might indicate nonbacterial cause such as candidiasis. Even with disseminated candidiasis, blood cultures may remain negative.
Candida albicans (C albicans) is a normal commensal in the human gastrointestinal (GI) tract. In addition to localized infections in healthy human beings, dissemination with fatal outcome can occur in immunocompromised individuals.1
Invasive candidiasis (IC) due to C albicans is the most common nosocomial mycosis in the world and has 2 forms, candidemia and deep-seated tissue candidiasis, which can lead to multisystem organ failure.2 The deep-seated form may originate from nonhematogenous routes, such as introduction through a peritoneal catheter or ascending infection from cystitis.2 In addition, about 50% of primary candidemia cases lead to secondary deep-seated candidiasis; however, only about 40% of these cases show positive blood cultures. Since the window of opportunity for a positive culture is narrow, active candidemia may be missed.3,4
Once developed, the prognosis for IC is grim: Mortality is 40% regardless of therapy.2 IC typically occurs in immunocompromised hosts; IC in immunocompetent persons has rarely been reported.5,6 It is challenging to diagnose IC in the immunocompetent patients as 50% to 70% of the general population is naturally colonized by this organism, and when found, it is assumed to be mostly innocuous. Neutrophil-driven cell-mediated immunity associated with IL-1 and IL-17 response prevent fungal growth and dissemination, protecting the immunocompetent host.7
We report on a patient who showed no neutropenia or leukocytopenia but developed disseminated candidiasis. This report is one of the rare cases of full-blown disseminated candidiasis with lesions related to C albicans found in almost all of the important organs.
Case Presentation
A 67-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, daily heavy alcohol consumption, and a 50-pack-year history of smoking developed gangrene of the left fifth toe. He underwent vascular surgery consultation with an aortogram/left lower extremity angiography that showed occlusion of the left external iliac artery as well as the left common femoral artery. It was decided to improve inflow in the common iliac artery by placing a bare metal stent and subsequent balloon dilatation before a right to left femoral to femoral artery bypass. The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged home.
Two days later, the patient was admitted to a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) complexity level 1a hospital with weakness and worsening pain in the left lower extremities. Examination revealed chronic ischemic changes in the feet bilaterally and evidence of dry gangrene in the left fifth toe requiring femoral bypass surgery. But poor nutritional status and cardiac status prevented pursuing a permanent solution.
Following completion of a stress echocardiogram, the patient developed shock with systolic blood pressure of 60 mm Hg, and atrial fibrillation (AF) with rapid ventricular rate (RVR). He was initially treated with IV fluid supplementation, vasopressor therapy, synchronized cardioversion, and IV amiodarone/anticoagulation therapy, due to his persistent AF with RVR. The patient was transferred to a tertiary care center for persistent hypothermia and received treatment with warm saline. After initial recovery with warm saline resuscitation, he had a prolonged, complicated hospital course in which he developed progressive respiratory failure requiring intubation and critical care support. He developed a right internal jugular deep venous thrombosis, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, lower GI bleeding requiring emergent embolization by interventional radiology, inferior vena cava filter placement, renal failure requiring dialysis, small bowel obstruction secondary to right lower quadrant phlegmon and perforation requiring small bowel resection and end ileostomy. His antibiotic regimen included therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam.
He eventually recovered and was extubated and subsequently transferred back to the VA hospital where cefepime was initiated because of suspicion of a urinary tract infection and septicemia (urine cultures eventually grew C albicans). Over the subsequent 3 days, the patient’s renal output and hyperkalemia worsened, he also developed increased anion gap metabolic acidosis and was intubated again and placed on full mechanical ventilatory support. His blood cultures were negative, and sputum cultures revealed normal respiratory flora and 1+ C albicans. Infectious diseases consultation recommended an abdominal ultrasound, which revealed nonspecific findings. The antibiotic regimen was changed to daptomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam. A follow-up chest X-ray revealed a developing right lower lobe pneumonia and hilar prominence suggestive of lymphadenopathy. The patient’s clinical condition deteriorated, and he subsequently developed cardiac arrest; resuscitation was not successful and he expired.
Outcome and Follow-up
An autopsy disclosed the cause of death to be bilateral candida pneumonia, part of a disseminated (invasive) candidiasis, in a patient rendered vulnerable to such infection by peripheral vascular disease and renal insufficiency. Purulent inflammation was noted at the site of disarticulation of the left foot and confluent consolidation of the lower lobes of both lungs as well as focal consolidation of the middle lobe of the right lung. Examination of histologic sections, with staining both by routine method (hematoxylin and eosin) and the Grocott-Gömöri methenamine silver method for fungus, disclosed fungal forms (yeast and filamentous) in most tissues, including the lungs (Figure 1 A and B) and kidneys (Figure 1 C and D). The pulmonary sections in addition to massive inflammation showed macrophages with engulfed yeast (Figure 2 A) and a lymphatic channel, stuffed with yeast in an alveolar septum (Figure 2 B). These findings confirmed the antemortem presence of the fungus and the body’s response to it. Inflammation was noted around glomeruli overgrown by candida (Figure 1 C and D); fungi also were seen in capsular regions (not depicted). C albicans was present in the myocardium (Figure 1 E and F), brain, thyroid, and adrenal glands (Figure 3); the only organ without C albicans was the liver, either because invasion was truly absent here or because sampling had not managed to retrieve it.
Paraffin-embedded blocks of lung tissue, sent to the University of Washington Molecular Diagnosis Microbiology Laboratory for broad-range polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification, were positive for C albicans after extraction of gDNA and conduction of PCR using internal transcribed spacer 1 and 2 specific primers.
Discussion
IC is rare among immunocompetent individuals, but C albicans can evolve into a fatal disseminated infection. We report an atypical case of IC, with profound pulmonary infection in a patient who died 1 month after hospitalization for lower extremity pain.
Cell-mediated immunity involving neutrophils and macrophages plays a major role in protection against candidiasis, while cytokines and chemokines involve regulating balanced immunity.1,2 A series of recent studies show that alcohol impairs neutrophil-mediated killing and phagocytic-mediated uptake of a pathogen in this process.8,9 As the patient chronically misused alcohol, his immune system may have experienced a subclinical immunosuppression, which would have become clinically relevant once C albicans was introduced systemically. Recent studies of bacterial pathogenesis and alcoholism strongly support this hypothesis.10,11
Most patients with the unusual diagnosis of candida pneumonia have had a background of malignancy or immunosuppressive factors (eg, administration of corticosteroids).12 In a series of 20 cases, 14 had sputum cultures positive for the organism, 6 had positive urine cultures, and 6 had positive blood cultures. Chest radiographs usually showed confluent bronchopneumonia. Five patients were diagnosed antemortem and treated with amphotericin B, but none survived.13 In the literature a positive blood culture or demonstration of yeast within pulmonary histiocytes has been considered proof of the pathogenicity of the fungus, as opposed to noninvasive colonization of the airways, a common occurrence in patients receiving mechanical ventilation.2
As previously discussed, blood cultures are often negative with invasive candidiasis, as the window of opportunity is short and may be missed. As shown in murine models, it is easy to miss a narrow window of candidemia, leading to false-negative blood cultures in clinical practice.14,15 Mouse model studies also have found that the window of candidemia is very short in disseminated candidiasis as a lethal IV dose of C albicans disappeared from blood within 48 hours of postinoculation.15 The biomarker of serum procalcitonin is a great diagnostic resource for the elimination of a likely bacterial sepsis, and conversely, the early suspicion of a fungemia, as serum procalcitonin would typically be elevated in a bacterial but not a fungal septicemia.16 The average cost per test is only about $30, and we recommend testing for serum procalcitonin as well as monitoring of serum lactate levels in cases of nonresponding septicemia.
The C albicans in this case may have been introduced hematogenously from the amputation site or through an ascending cystitis, or possibly have been derived from commensal flora in the GI tract. The iron supplementation provided to the patient may have promoted the growth and virulence of the candida; studies have shown that the kidneys assimilate increased levels of iron during disseminated candidiasis thus providing a more favorable site for colonization.17The presence of C albicans in a single collection of sputum or urine does not ordinarily indicate infection in an immunocompetent individual. Estimation of serum procalcitonin, a biomarker for bacterial infection and sepsis, might be useful if negative, for turning attention to a nonbacterial (such as, candida) source as the causative agent.18
Conclusion
C albicans can rarely cause disseminated disease in nonimmunocompromised critically ill patients. Low serum procalcitonin levels in a septic patient might indicate nonbacterial cause such as candidiasis. Even with disseminated candidiasis, blood cultures may remain negative.
1. Navarathna DH, Stein EV, Lessey-Morillon EC, Nayak D, Martin-Manso G, Roberts DD. CD47 promotes protective innate and adaptive immunity in a mouse model of disseminated candidiasis. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0128220.
2. Kullberg BJ, Arendrup MC. Invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(15):1445-1456.
3. Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Diagnosing invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56(5):e01909-e01917.
4. Ericson EL, Klingspor L, Ullberg M, Ozenci V. Clinical comparison of the Bactec Mycosis IC/F, BacT/Alert FA, and BacT/Alert FN blood culture vials for the detection of candidemia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;73(2):153-156.
5. Baum GL. The significance of Candida albicans in human sputum. N Engl J Med. 1960;263:70-73.
6. el-Ebiary M, Torres A, Fàbregas N, et al. Significance of the isolation of Candida species from respiratory samples in critically ill, non-neutropenic patients. An immediate postmortem histologic study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(2, pt 1):583-590.
7. Altmeier S, Toska A, Sparber F, Teijeira A, Halin C, LeibundGut-Landmann S. IL-1 coordinates the neutrophil response to C. albicans in the oral mucosa. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(9):e1005882.
8. Karavitis J, Kovacs EJ. Macrophage phagocytosis: effects of environmental pollutants, alcohol, cigarette smoke, and other external factors. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90(6):1065-1078.
9. Chiu C-H, Wang Y-C, Yeh K-M, Lin J-C, Siu LK, Chang F-Y. Influence of ethanol concentration in the phagocytic function of neutrophils against Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in an experimental model. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018;51(1):64-69.
10. Khocht A, Schleifer S, Janal M, Keller S. Neutrophil function and periodontitis in alcohol-dependent males without medical disorders. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2013;15(3):68-74.
11. Gandhi JA, Ekhar VV, Asplund MB, et al. Alcohol enhances Acinetobacter baumannii-associated pneumonia and systemic dissemination by impairing neutrophil antimicrobial activity in a murine model of infection. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95707.
12. Mohsenifar Z, Chopra SK, Johnson BL, Simmons DH. Candida pneumonia: experience with 20 patients. West J Med. 1979;131(3):196-200.
13. Jones JM. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990;3(1):32-45.
14. Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Finding the “missing 50%” of invasive candidiasis: how nonculture diagnostics will improve understanding of disease spectrum and transform patient care. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(9):1284-1292.
15. Kappe R, Mu¨ ller J. Rapid clearance of Candida albicans mannan antigens by liver and spleen in contrast to prolonged circulation of Cryptococcus neoformans antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1991;29(8):1665-1669.
16. Balk RA, Kadri SS, Cao Z, Robinson SB, Lipkin C, Bozzette SA. Effect of procalcitonin testing on health-care utilization and costs in critically ill patients in the United States. Chest. 2017;151(1):23-33.
17. Potrykus J, Stead D, Maccallum DM, et al. Fungal iron availability during deep seated candidiasis is defined by a complex interplay involving systemic and local events. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(10):e1003676.
18. Soni NJ, Samson DJ, Galaydick JL, Vats V, Pitrak DL, Aronson N. Procalcitonin-Guided Antibiotic Therapy. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2012.
1. Navarathna DH, Stein EV, Lessey-Morillon EC, Nayak D, Martin-Manso G, Roberts DD. CD47 promotes protective innate and adaptive immunity in a mouse model of disseminated candidiasis. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0128220.
2. Kullberg BJ, Arendrup MC. Invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(15):1445-1456.
3. Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Diagnosing invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56(5):e01909-e01917.
4. Ericson EL, Klingspor L, Ullberg M, Ozenci V. Clinical comparison of the Bactec Mycosis IC/F, BacT/Alert FA, and BacT/Alert FN blood culture vials for the detection of candidemia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;73(2):153-156.
5. Baum GL. The significance of Candida albicans in human sputum. N Engl J Med. 1960;263:70-73.
6. el-Ebiary M, Torres A, Fàbregas N, et al. Significance of the isolation of Candida species from respiratory samples in critically ill, non-neutropenic patients. An immediate postmortem histologic study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(2, pt 1):583-590.
7. Altmeier S, Toska A, Sparber F, Teijeira A, Halin C, LeibundGut-Landmann S. IL-1 coordinates the neutrophil response to C. albicans in the oral mucosa. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(9):e1005882.
8. Karavitis J, Kovacs EJ. Macrophage phagocytosis: effects of environmental pollutants, alcohol, cigarette smoke, and other external factors. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90(6):1065-1078.
9. Chiu C-H, Wang Y-C, Yeh K-M, Lin J-C, Siu LK, Chang F-Y. Influence of ethanol concentration in the phagocytic function of neutrophils against Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in an experimental model. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018;51(1):64-69.
10. Khocht A, Schleifer S, Janal M, Keller S. Neutrophil function and periodontitis in alcohol-dependent males without medical disorders. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2013;15(3):68-74.
11. Gandhi JA, Ekhar VV, Asplund MB, et al. Alcohol enhances Acinetobacter baumannii-associated pneumonia and systemic dissemination by impairing neutrophil antimicrobial activity in a murine model of infection. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95707.
12. Mohsenifar Z, Chopra SK, Johnson BL, Simmons DH. Candida pneumonia: experience with 20 patients. West J Med. 1979;131(3):196-200.
13. Jones JM. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990;3(1):32-45.
14. Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Finding the “missing 50%” of invasive candidiasis: how nonculture diagnostics will improve understanding of disease spectrum and transform patient care. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(9):1284-1292.
15. Kappe R, Mu¨ ller J. Rapid clearance of Candida albicans mannan antigens by liver and spleen in contrast to prolonged circulation of Cryptococcus neoformans antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1991;29(8):1665-1669.
16. Balk RA, Kadri SS, Cao Z, Robinson SB, Lipkin C, Bozzette SA. Effect of procalcitonin testing on health-care utilization and costs in critically ill patients in the United States. Chest. 2017;151(1):23-33.
17. Potrykus J, Stead D, Maccallum DM, et al. Fungal iron availability during deep seated candidiasis is defined by a complex interplay involving systemic and local events. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(10):e1003676.
18. Soni NJ, Samson DJ, Galaydick JL, Vats V, Pitrak DL, Aronson N. Procalcitonin-Guided Antibiotic Therapy. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2012.
Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis
Impressive progress has been made in recent years in the management and treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) and its comorbidities; however, there is a major need for state-of-the-art, evidence-based, multidisciplinary education for AD management. To address this need, the first Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Conference was held in April 2019 in Chicago, Illinois, featuring cutting-edge research presented by globally recognized experts in dermatology, allergy and immunology, sleep medicine, ophthalmology, and nursing care. The following is a recap of the latest topics in AD research presented at the conference.
Diagnosis and Assessment of AD: Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH
Although diagnosis of AD typically is straightforward in children, it can be challenging in adults, even for expert clinicians. These challenges stem from the different lesional distribution and morphology of AD in adults vs children.1,2 Additionally, the conditions included in the differential diagnosis of AD (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis) are far more common in adults than in children. Formal diagnostic criteria can be useful to improve the diagnosis of AD in clinical practice.3 It is important to note that flexural lesions and early disease onset are diagnostic criteria in AD; nevertheless, neither are essential nor sufficient on their own to make the diagnosis.
Patch Testing: Jacob P. Thyssen, MD, PhD, DmSci, and Noreen Heer Nicol, PhD, RN, FNP, NEA-BC
Patch testing can be used in AD patients to rule out contact dermatitis as an alternative or comorbid diagnosis.4-6 Because contact dermatitis can mimic AD, patch testing is recommended for all patients with adolescent and adult-onset AD.5 Additionally, refractory cases of AD across all ages, especially prior to initiation of systemic therapy, warrant patch testing. The unique challenges of patch testing in AD patients were reviewed.
Patient Panel
Atopic dermatitis can be a considerable disease burden on both patients and society in general. At the 2019 RAD Conference, a panel of patients bravely shared their AD journeys. Their eye-opening stories highlighted opportunities for improving real-world assessment and management of AD. Some key takeaways included the importance of adequately assessing the symptom burden of AD and not merely relying on visual inspection of the skin. The need for long-term treatment approaches beyond quick fixes with steroids also was discussed.
Pathogenesis of AD: Mark Boguniewicz, MD
There have been many advances in our understanding of the complex pathogenesis of AD,7-11 which is characterized by an altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Filaggrin deficiency in the skin has structural and biophysical consequences. A subset of patients with AD has filaggrin loss-of-function genetic polymorphisms inherited in an autosomal-semidominant pattern; however, many other genetic polymorphisms have been identified that affect different components of the skin architecture and immune system. Many cytokine pathways have been found to be upregulated in AD lesions, including IL-13, IL-4, IL-31, and IL-5 in acute and chronic lesions, and IFN-γ and other helper T cell (TH1) cytokines in chronic lesions. IL-4 and IL-13 (TH2 cytokines) have been shown to decrease epidermal expression of filaggrin and lead to lipid abnormalities in the skin of patients with AD. Even normal-appearing, nonlesional skin has substantial immune activation and barrier abnormalities in patients with moderate to severe AD. Activation of different immune pathways may contribute to the heterogeneous clinical presentation of AD. There also is an increasingly recognized role of superantigen-producing Staphylococcus aureus and decreased microbial diversity in AD.
Therapies for AD
The advances in our understanding of AD pathophysiology have led to the development of 2 recently approved therapeutic agents.7-10 Crisaborole ointment 2% is a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2016 for treatment of mild to moderate AD. Treatment with crisaborole ointment 2% demonstrated improvement in lesion severity, itch, and quality of life in children and adults with AD. Dupilumab, an injectable biologic therapy that inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2017 for adults and in 2019 for adolescents aged 12 to 17 years with moderate to severe AD. The expert panel of speakers at the 2019 RAD Conference discussed many practical clinical pearls regarding patient education, optimization of both short- and long-term efficacy, and prevention and management of treatment-related adverse events. The discussion included evidence-based guidelines for bathing practices and topical therapy in AD, as well as practical pearls for patient and provider education in AD, reviewed by Dr. Nicol. Evidence-based guidelines for use of phototherapy and systemic and biologic therapy for AD also were highlighted by Dr. Silverberg.
After decades of limited therapeutic options, there is a large therapeutic pipeline of topical, oral, and biologic agents in development for the treatment AD.7-9 Dr. Boguniewicz reviewed the state-of-the-art treatments that are the furthest advanced in development. Many of these agents may be approved within the next couple of years and look promising in terms of their potential to improve the care of patients with AD.
Comorbidities of AD
The impact of AD is not just skin deep. Atopic dermatitis is associated with myriad comorbid health conditions.12-16 Dr. Boguniewicz reviewed the relationship between AD and atopic comorbidities, including asthma, hay fever, and food allergies, which are common across all AD patients. In addition, a subset of children with AD demonstrated the atopic march, in which AD first appears early in life followed by the development of other atopic comorbidities in later childhood or adulthood. In particular, children with filaggrin null mutations were found to be at increased risk of early-onset, severe, persistent AD with asthma and allergic sensitization.17 More recently, eosinophilic esophagitis was demonstrated to be a late-onset comorbidity of the atopic march.18 The allergy guidelines for which patients are appropriate candidates for food and/or aeroallergen testing were discussed,19 and it was emphasized that patients with AD should not routinely receive this testing.
Atopic dermatitis is associated with many other comorbidities, including sleep disturbances. Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD, provided a brilliant review of circadian regulation of physiology and the immune system. Sleep is one of the most important determinants of patients’ health and well-being. Atopic dermatitis is associated with disturbances of sleep and circadian rhythms. Sleep disturbances are gaining recognition as an important end point to assess for improvement in clinical practice and trials.
Patients with AD have long been recognized to have increased ophthalmic comorbidities, including allergic conjunctivitis, atopic keratoconjunctivitis, and cataracts. More recently, conjunctivitis has emerged as an important adverse event with dupilumab treatment.20 Jeanine Baqai, MD, reviewed the various ophthalmic comorbidities and shared numerous clinical signs of ophthalmic comorbidities that dermatologists can assess with the naked eye (no slit-lamp examination needed). Pearls to manage dupilumab-related conjunctivitis shared by Dr. Baqai and the speaker panel included elimination of eye rubbing, cold compresses, avoidance of exacerbating factors, artificial tears, and timely referral to an ophthalmologist. Medications discussed were mast cell stabilizers, antihistamines, and corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors.
Final Thoughts
There has been an explosion of new research that has increased our understanding of all aspects of AD, and the standard of care is truly being revolutionized. Clinicians should stay tuned to a wealth of new evidence-based recommendations coming down the pike.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis: characteristics and management [published online May 28, 2019]. Am J Clin Dermatol. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00453-7.
- Silverberg JI. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7:28-33.
- Hanifin J, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh). 1980;92(suppl):44-47.
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78.
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302.
- Rastogi S, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to personal care products and topical medications in adults with atopic dermatitis [published online July 25, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:1028-1033.e6.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. New and emerging therapies for paediatric atopic dermatitis. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2019;3:343-353.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. New therapies for atopic dermatitis: additional treatment classes [published online December 14, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S76-S83.
- Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis treatment: current state of the art and emerging therapies. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2017;38:243-249.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. Monoclonal antibodies for atopic dermatitis: progress and potential. BioDrugs. 2017;31:409-422.
- Silverberg NB, Silverberg JI. Inside out or outside in: does atopic dermatitis disrupt barrier function or does disruption of barrier function trigger atopic dermatitis? Cutis. 2015;96:359-361.
- Silverberg JI. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;123:144-151.
- Brunner PM, Silverberg JI, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Increasing comorbidities suggest that atopic dermatitis is a systemic disorder. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:18-25.
- Silverberg J, Garg N, Silverberg NB. New developments in comorbidities of atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2014;93:222-224.
- Silverberg JI. Selected comorbidities of atopic dermatitis: atopy, neuropsychiatric, and musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:360-366.
- Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, et al. Association of atopic dermatitis with allergic, autoimmune, and cardiovascular comorbidities in US adults. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:604-612.e603.
- Henderson J, Northstone K, Lee SP, et al. The burden of disease associated with filaggrin mutations: a population-based, longitudinal birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:872-877.e879.
- Hill DA, Grundmeier RW, Ramos M, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis is a late manifestation of the allergic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;6:1528-1533.
- Boyce JA, Assa’ad A, Burks AW, et al; NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel. Guidelines for th
e diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:1105-1118. - Akinlade B, Guttman-Yassky E, de Bruin-Weller M, et al. Conjunctivitis in dupilumab clinical trials [published online March 9, 2019]. Br J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/bjd.17869.
Impressive progress has been made in recent years in the management and treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) and its comorbidities; however, there is a major need for state-of-the-art, evidence-based, multidisciplinary education for AD management. To address this need, the first Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Conference was held in April 2019 in Chicago, Illinois, featuring cutting-edge research presented by globally recognized experts in dermatology, allergy and immunology, sleep medicine, ophthalmology, and nursing care. The following is a recap of the latest topics in AD research presented at the conference.
Diagnosis and Assessment of AD: Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH
Although diagnosis of AD typically is straightforward in children, it can be challenging in adults, even for expert clinicians. These challenges stem from the different lesional distribution and morphology of AD in adults vs children.1,2 Additionally, the conditions included in the differential diagnosis of AD (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis) are far more common in adults than in children. Formal diagnostic criteria can be useful to improve the diagnosis of AD in clinical practice.3 It is important to note that flexural lesions and early disease onset are diagnostic criteria in AD; nevertheless, neither are essential nor sufficient on their own to make the diagnosis.
Patch Testing: Jacob P. Thyssen, MD, PhD, DmSci, and Noreen Heer Nicol, PhD, RN, FNP, NEA-BC
Patch testing can be used in AD patients to rule out contact dermatitis as an alternative or comorbid diagnosis.4-6 Because contact dermatitis can mimic AD, patch testing is recommended for all patients with adolescent and adult-onset AD.5 Additionally, refractory cases of AD across all ages, especially prior to initiation of systemic therapy, warrant patch testing. The unique challenges of patch testing in AD patients were reviewed.
Patient Panel
Atopic dermatitis can be a considerable disease burden on both patients and society in general. At the 2019 RAD Conference, a panel of patients bravely shared their AD journeys. Their eye-opening stories highlighted opportunities for improving real-world assessment and management of AD. Some key takeaways included the importance of adequately assessing the symptom burden of AD and not merely relying on visual inspection of the skin. The need for long-term treatment approaches beyond quick fixes with steroids also was discussed.
Pathogenesis of AD: Mark Boguniewicz, MD
There have been many advances in our understanding of the complex pathogenesis of AD,7-11 which is characterized by an altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Filaggrin deficiency in the skin has structural and biophysical consequences. A subset of patients with AD has filaggrin loss-of-function genetic polymorphisms inherited in an autosomal-semidominant pattern; however, many other genetic polymorphisms have been identified that affect different components of the skin architecture and immune system. Many cytokine pathways have been found to be upregulated in AD lesions, including IL-13, IL-4, IL-31, and IL-5 in acute and chronic lesions, and IFN-γ and other helper T cell (TH1) cytokines in chronic lesions. IL-4 and IL-13 (TH2 cytokines) have been shown to decrease epidermal expression of filaggrin and lead to lipid abnormalities in the skin of patients with AD. Even normal-appearing, nonlesional skin has substantial immune activation and barrier abnormalities in patients with moderate to severe AD. Activation of different immune pathways may contribute to the heterogeneous clinical presentation of AD. There also is an increasingly recognized role of superantigen-producing Staphylococcus aureus and decreased microbial diversity in AD.
Therapies for AD
The advances in our understanding of AD pathophysiology have led to the development of 2 recently approved therapeutic agents.7-10 Crisaborole ointment 2% is a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2016 for treatment of mild to moderate AD. Treatment with crisaborole ointment 2% demonstrated improvement in lesion severity, itch, and quality of life in children and adults with AD. Dupilumab, an injectable biologic therapy that inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2017 for adults and in 2019 for adolescents aged 12 to 17 years with moderate to severe AD. The expert panel of speakers at the 2019 RAD Conference discussed many practical clinical pearls regarding patient education, optimization of both short- and long-term efficacy, and prevention and management of treatment-related adverse events. The discussion included evidence-based guidelines for bathing practices and topical therapy in AD, as well as practical pearls for patient and provider education in AD, reviewed by Dr. Nicol. Evidence-based guidelines for use of phototherapy and systemic and biologic therapy for AD also were highlighted by Dr. Silverberg.
After decades of limited therapeutic options, there is a large therapeutic pipeline of topical, oral, and biologic agents in development for the treatment AD.7-9 Dr. Boguniewicz reviewed the state-of-the-art treatments that are the furthest advanced in development. Many of these agents may be approved within the next couple of years and look promising in terms of their potential to improve the care of patients with AD.
Comorbidities of AD
The impact of AD is not just skin deep. Atopic dermatitis is associated with myriad comorbid health conditions.12-16 Dr. Boguniewicz reviewed the relationship between AD and atopic comorbidities, including asthma, hay fever, and food allergies, which are common across all AD patients. In addition, a subset of children with AD demonstrated the atopic march, in which AD first appears early in life followed by the development of other atopic comorbidities in later childhood or adulthood. In particular, children with filaggrin null mutations were found to be at increased risk of early-onset, severe, persistent AD with asthma and allergic sensitization.17 More recently, eosinophilic esophagitis was demonstrated to be a late-onset comorbidity of the atopic march.18 The allergy guidelines for which patients are appropriate candidates for food and/or aeroallergen testing were discussed,19 and it was emphasized that patients with AD should not routinely receive this testing.
Atopic dermatitis is associated with many other comorbidities, including sleep disturbances. Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD, provided a brilliant review of circadian regulation of physiology and the immune system. Sleep is one of the most important determinants of patients’ health and well-being. Atopic dermatitis is associated with disturbances of sleep and circadian rhythms. Sleep disturbances are gaining recognition as an important end point to assess for improvement in clinical practice and trials.
Patients with AD have long been recognized to have increased ophthalmic comorbidities, including allergic conjunctivitis, atopic keratoconjunctivitis, and cataracts. More recently, conjunctivitis has emerged as an important adverse event with dupilumab treatment.20 Jeanine Baqai, MD, reviewed the various ophthalmic comorbidities and shared numerous clinical signs of ophthalmic comorbidities that dermatologists can assess with the naked eye (no slit-lamp examination needed). Pearls to manage dupilumab-related conjunctivitis shared by Dr. Baqai and the speaker panel included elimination of eye rubbing, cold compresses, avoidance of exacerbating factors, artificial tears, and timely referral to an ophthalmologist. Medications discussed were mast cell stabilizers, antihistamines, and corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors.
Final Thoughts
There has been an explosion of new research that has increased our understanding of all aspects of AD, and the standard of care is truly being revolutionized. Clinicians should stay tuned to a wealth of new evidence-based recommendations coming down the pike.
Impressive progress has been made in recent years in the management and treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) and its comorbidities; however, there is a major need for state-of-the-art, evidence-based, multidisciplinary education for AD management. To address this need, the first Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Conference was held in April 2019 in Chicago, Illinois, featuring cutting-edge research presented by globally recognized experts in dermatology, allergy and immunology, sleep medicine, ophthalmology, and nursing care. The following is a recap of the latest topics in AD research presented at the conference.
Diagnosis and Assessment of AD: Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH
Although diagnosis of AD typically is straightforward in children, it can be challenging in adults, even for expert clinicians. These challenges stem from the different lesional distribution and morphology of AD in adults vs children.1,2 Additionally, the conditions included in the differential diagnosis of AD (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis) are far more common in adults than in children. Formal diagnostic criteria can be useful to improve the diagnosis of AD in clinical practice.3 It is important to note that flexural lesions and early disease onset are diagnostic criteria in AD; nevertheless, neither are essential nor sufficient on their own to make the diagnosis.
Patch Testing: Jacob P. Thyssen, MD, PhD, DmSci, and Noreen Heer Nicol, PhD, RN, FNP, NEA-BC
Patch testing can be used in AD patients to rule out contact dermatitis as an alternative or comorbid diagnosis.4-6 Because contact dermatitis can mimic AD, patch testing is recommended for all patients with adolescent and adult-onset AD.5 Additionally, refractory cases of AD across all ages, especially prior to initiation of systemic therapy, warrant patch testing. The unique challenges of patch testing in AD patients were reviewed.
Patient Panel
Atopic dermatitis can be a considerable disease burden on both patients and society in general. At the 2019 RAD Conference, a panel of patients bravely shared their AD journeys. Their eye-opening stories highlighted opportunities for improving real-world assessment and management of AD. Some key takeaways included the importance of adequately assessing the symptom burden of AD and not merely relying on visual inspection of the skin. The need for long-term treatment approaches beyond quick fixes with steroids also was discussed.
Pathogenesis of AD: Mark Boguniewicz, MD
There have been many advances in our understanding of the complex pathogenesis of AD,7-11 which is characterized by an altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Filaggrin deficiency in the skin has structural and biophysical consequences. A subset of patients with AD has filaggrin loss-of-function genetic polymorphisms inherited in an autosomal-semidominant pattern; however, many other genetic polymorphisms have been identified that affect different components of the skin architecture and immune system. Many cytokine pathways have been found to be upregulated in AD lesions, including IL-13, IL-4, IL-31, and IL-5 in acute and chronic lesions, and IFN-γ and other helper T cell (TH1) cytokines in chronic lesions. IL-4 and IL-13 (TH2 cytokines) have been shown to decrease epidermal expression of filaggrin and lead to lipid abnormalities in the skin of patients with AD. Even normal-appearing, nonlesional skin has substantial immune activation and barrier abnormalities in patients with moderate to severe AD. Activation of different immune pathways may contribute to the heterogeneous clinical presentation of AD. There also is an increasingly recognized role of superantigen-producing Staphylococcus aureus and decreased microbial diversity in AD.
Therapies for AD
The advances in our understanding of AD pathophysiology have led to the development of 2 recently approved therapeutic agents.7-10 Crisaborole ointment 2% is a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2016 for treatment of mild to moderate AD. Treatment with crisaborole ointment 2% demonstrated improvement in lesion severity, itch, and quality of life in children and adults with AD. Dupilumab, an injectable biologic therapy that inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2017 for adults and in 2019 for adolescents aged 12 to 17 years with moderate to severe AD. The expert panel of speakers at the 2019 RAD Conference discussed many practical clinical pearls regarding patient education, optimization of both short- and long-term efficacy, and prevention and management of treatment-related adverse events. The discussion included evidence-based guidelines for bathing practices and topical therapy in AD, as well as practical pearls for patient and provider education in AD, reviewed by Dr. Nicol. Evidence-based guidelines for use of phototherapy and systemic and biologic therapy for AD also were highlighted by Dr. Silverberg.
After decades of limited therapeutic options, there is a large therapeutic pipeline of topical, oral, and biologic agents in development for the treatment AD.7-9 Dr. Boguniewicz reviewed the state-of-the-art treatments that are the furthest advanced in development. Many of these agents may be approved within the next couple of years and look promising in terms of their potential to improve the care of patients with AD.
Comorbidities of AD
The impact of AD is not just skin deep. Atopic dermatitis is associated with myriad comorbid health conditions.12-16 Dr. Boguniewicz reviewed the relationship between AD and atopic comorbidities, including asthma, hay fever, and food allergies, which are common across all AD patients. In addition, a subset of children with AD demonstrated the atopic march, in which AD first appears early in life followed by the development of other atopic comorbidities in later childhood or adulthood. In particular, children with filaggrin null mutations were found to be at increased risk of early-onset, severe, persistent AD with asthma and allergic sensitization.17 More recently, eosinophilic esophagitis was demonstrated to be a late-onset comorbidity of the atopic march.18 The allergy guidelines for which patients are appropriate candidates for food and/or aeroallergen testing were discussed,19 and it was emphasized that patients with AD should not routinely receive this testing.
Atopic dermatitis is associated with many other comorbidities, including sleep disturbances. Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD, provided a brilliant review of circadian regulation of physiology and the immune system. Sleep is one of the most important determinants of patients’ health and well-being. Atopic dermatitis is associated with disturbances of sleep and circadian rhythms. Sleep disturbances are gaining recognition as an important end point to assess for improvement in clinical practice and trials.
Patients with AD have long been recognized to have increased ophthalmic comorbidities, including allergic conjunctivitis, atopic keratoconjunctivitis, and cataracts. More recently, conjunctivitis has emerged as an important adverse event with dupilumab treatment.20 Jeanine Baqai, MD, reviewed the various ophthalmic comorbidities and shared numerous clinical signs of ophthalmic comorbidities that dermatologists can assess with the naked eye (no slit-lamp examination needed). Pearls to manage dupilumab-related conjunctivitis shared by Dr. Baqai and the speaker panel included elimination of eye rubbing, cold compresses, avoidance of exacerbating factors, artificial tears, and timely referral to an ophthalmologist. Medications discussed were mast cell stabilizers, antihistamines, and corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors.
Final Thoughts
There has been an explosion of new research that has increased our understanding of all aspects of AD, and the standard of care is truly being revolutionized. Clinicians should stay tuned to a wealth of new evidence-based recommendations coming down the pike.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis: characteristics and management [published online May 28, 2019]. Am J Clin Dermatol. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00453-7.
- Silverberg JI. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7:28-33.
- Hanifin J, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh). 1980;92(suppl):44-47.
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78.
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302.
- Rastogi S, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to personal care products and topical medications in adults with atopic dermatitis [published online July 25, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:1028-1033.e6.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. New and emerging therapies for paediatric atopic dermatitis. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2019;3:343-353.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. New therapies for atopic dermatitis: additional treatment classes [published online December 14, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S76-S83.
- Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis treatment: current state of the art and emerging therapies. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2017;38:243-249.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. Monoclonal antibodies for atopic dermatitis: progress and potential. BioDrugs. 2017;31:409-422.
- Silverberg NB, Silverberg JI. Inside out or outside in: does atopic dermatitis disrupt barrier function or does disruption of barrier function trigger atopic dermatitis? Cutis. 2015;96:359-361.
- Silverberg JI. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;123:144-151.
- Brunner PM, Silverberg JI, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Increasing comorbidities suggest that atopic dermatitis is a systemic disorder. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:18-25.
- Silverberg J, Garg N, Silverberg NB. New developments in comorbidities of atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2014;93:222-224.
- Silverberg JI. Selected comorbidities of atopic dermatitis: atopy, neuropsychiatric, and musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:360-366.
- Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, et al. Association of atopic dermatitis with allergic, autoimmune, and cardiovascular comorbidities in US adults. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:604-612.e603.
- Henderson J, Northstone K, Lee SP, et al. The burden of disease associated with filaggrin mutations: a population-based, longitudinal birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:872-877.e879.
- Hill DA, Grundmeier RW, Ramos M, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis is a late manifestation of the allergic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;6:1528-1533.
- Boyce JA, Assa’ad A, Burks AW, et al; NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel. Guidelines for th
e diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:1105-1118. - Akinlade B, Guttman-Yassky E, de Bruin-Weller M, et al. Conjunctivitis in dupilumab clinical trials [published online March 9, 2019]. Br J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/bjd.17869.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis: characteristics and management [published online May 28, 2019]. Am J Clin Dermatol. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00453-7.
- Silverberg JI. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7:28-33.
- Hanifin J, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh). 1980;92(suppl):44-47.
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78.
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302.
- Rastogi S, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to personal care products and topical medications in adults with atopic dermatitis [published online July 25, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:1028-1033.e6.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. New and emerging therapies for paediatric atopic dermatitis. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2019;3:343-353.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. New therapies for atopic dermatitis: additional treatment classes [published online December 14, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(3 suppl 1):S76-S83.
- Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis treatment: current state of the art and emerging therapies. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2017;38:243-249.
- Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. Monoclonal antibodies for atopic dermatitis: progress and potential. BioDrugs. 2017;31:409-422.
- Silverberg NB, Silverberg JI. Inside out or outside in: does atopic dermatitis disrupt barrier function or does disruption of barrier function trigger atopic dermatitis? Cutis. 2015;96:359-361.
- Silverberg JI. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;123:144-151.
- Brunner PM, Silverberg JI, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Increasing comorbidities suggest that atopic dermatitis is a systemic disorder. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:18-25.
- Silverberg J, Garg N, Silverberg NB. New developments in comorbidities of atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2014;93:222-224.
- Silverberg JI. Selected comorbidities of atopic dermatitis: atopy, neuropsychiatric, and musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:360-366.
- Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, et al. Association of atopic dermatitis with allergic, autoimmune, and cardiovascular comorbidities in US adults. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:604-612.e603.
- Henderson J, Northstone K, Lee SP, et al. The burden of disease associated with filaggrin mutations: a population-based, longitudinal birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:872-877.e879.
- Hill DA, Grundmeier RW, Ramos M, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis is a late manifestation of the allergic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;6:1528-1533.
- Boyce JA, Assa’ad A, Burks AW, et al; NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel. Guidelines for th
e diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:1105-1118. - Akinlade B, Guttman-Yassky E, de Bruin-Weller M, et al. Conjunctivitis in dupilumab clinical trials [published online March 9, 2019]. Br J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/bjd.17869.
Addressing the Shortage of Physician Assistants in Medicine Clerkship Sites
The Federal Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 37% job growth for physician assistants (PAs) from 2016 to 2026, much greater than the average for all other occupations as well as for other medical professions.1 This growth has been accompanied by increased enrollment in medical (doctor of medicine [MD], doctor of osteopathic medicine) and nurse practitioner (NP) schools.2 Clinical teaching sites serve a crucial function in the training of all clinical disciplines. These sites provide hands-on and experiential learning in medical settings, necessary components for learners practicing to become clinicians. Significant PA program expansion has led to increased demand for clinical training, creating competition for sites and a shortage of willing and well-trained preceptors.3
This challenge has been recognized by PA program directors. In the Joint Report of the 2013 Multi-Discipline Clerkship/Clinical Training Site Survey, PA program directors expressed concern about the adequacy of clinical opportunities for students, increased difficulty developing new core sites, and preserving existing core sites. In addition, they noted that a shortage of clinical sites was one of the greatest barriers to the PA programs’ sustained growth and success.4
Program directors also indicated difficulty securing clinical training sites in internal medicine (IM) and high rates of attrition of medicine clinical preceptors for their students.5 The reasons are multifold: increasing clinical demands, time, teaching competence, lack of experience, academic affiliation, lack of reimbursement, or compensation. Moreover, there is a declining number of PAs who work in primary care compared with specialty and subspecialty care, limiting the availability of clinical training preceptors in medicine and primary care.6-8 According to the American Academy of PAs (AAPA) census and salary survey data, the percentage of PAs working in the primary care specialties (ie, family medicine, IM, and general pediatrics) has decreased from > 47% in 1995 to 24% in 2017.9 As such, there is a need to broaden the educational landscape to provide more high-quality training sites in IM.
The postacute health care setting may address this training need. It offers a unique clinical opportunity to expose learners to a broad range of disease complexity and clinical acuity, as the percentage of patients discharged from hospitals to postacute care (PAC) has increased and care shifts from the hospital to the PAC setting.10,11 The longer PAC length of stay also enables learners to follow patients longitudinally over several weeks and experience interprofessional team-based care. In addition, the PAC setting offers learners the ability to acquire the necessary skills for smooth and effective transitions of care. This setting has been extensively used for trainees of nursing, pharmacy, physical therapy (PT) and occupational therapy (OT), speech-language pathology, psychology, and social work (SW), but few programs have used the PAC setting as clerkship sites for IM rotations for PA students. To address this need for IM sites, the VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS), in conjunction with the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program, developed a novel medicine clinical clerkship site for physician assistants in the PAC unit of the community living center (CLC) at VABHS. This report describes the program structure, curriculum, and participant evaluation results.
Clinical Clerkship Program
VABHS CLC is a 110-bed facility comprising 3 units: a 65-bed PAC unit, a 15-bed closed hospice/palliative care unit, and a 30-bed long-term care unit. The service is staffed continuously with physicians, PAs, and NPs. A majority of patients are admitted from the acute care hospital of VABHS (West Roxbury campus) and other regional VA facilities. The CLC offers dynamic services, including phlebotomy, general radiology, IV diuretics and antibiotics, wound care, and subacute PT, OT, and speech-language pathology rehabilitation. The CLC serves as a venue for transitioning patients from acute inpatient care to home. The patient population is often elderly, with multiple active comorbidities and variable medical literacy, adherence, and follow-up.
The CLC provides a diverse interprofessional learning environment, offering core IM rotations for first-year psychiatry residents, oral and maxillofacial surgery residents, and PA students. The CLC also has expanded as a clinical site both for transitions-in-care IM resident curricula and electives as well as a geriatrics fellowship. In addition, the site offers rotations for NPs, nursing, pharmacy, physical and occupational therapies, speech-language pathology, psychology, and SW.
The Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program was founded in 2015 as a master’s degree program completed over 28 months. The first 12 months are didactic, and the following 16 months are clinical training with 14 months of rotations (2 IM, family medicine, pediatrics, emergency medicine, general surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, neurology, and 5 elective rotations), and 2 months for a thesis. The program has about 30 students per year and 4 clerkship sites for IM.
Program Description
The VABHS medicine clerkship hosts 1 to 2 PA students for 4-week blocks in the PAC unit of the CLC. Each student rotates on both PA and MD teams. Students follow 3 to 4 patients and participate fully in their care from admission to discharge; they prepare daily presentations and participate in medical management, family meetings, chart documentation, and care coordination with the interprofessional team. Students are provided a physical examination checklist and feedback form, and they are expected to track findings and record feedback and goals with their supervising preceptor weekly. They also make formal case presentations and participate in monthly medicine didactic rounds available to all VABHS IM students and trainees via videoconference.
In addition, beginning in July 2017, all PA students in the CLC began to participate in a 4-week Interprofessional Curriculum in Transitional Care. The curriculum includes 14 didactic lectures taught by 16 interprofessional faculty, including medicine, geriatric, and palliative care physicians; PAs; social workers; physical and occupational therapists; pharmacists; and a geriatric psychologist. The didactics include topics on the interprofessional team, the care continuum, teams and teamwork, interdisciplinary coordination of care, components of effective transitions in care, medication reconciliation, approaching difficult conversations, advance care planning, and quality improvement. The goal of the curriculum is to provide learners the knowledge, skills, and dispositions necessary for high-quality transitional care and interprofessional practice as well as specific training for effective and safe transfers of care between clinical settings. Although PA students are the main participants in this curriculum, all other learners in the PAC unit are also invited to attend the lectures.
The unique attributes of this training site include direct interaction with supervising PAs and physicians, rather than experiencing the traditional teaching hierarchy (with interns, residents, fellows); observation of the natural progression of disease of both acute care and primary care issues due to the longer length of stay (2 to 6 weeks, where the typical student will see the same patient 7 to 10 times during their rotation); exposure to a host of medically complex patients offering a multitude of clinical scenarios and abnormal physical exam findings; exposure to a hospice/palliative care ward and end-of-life care; and interaction within an interprofessional training environment of nursing, pharmacy, PT, OT, speech-language pathology, psychology, and SW trainees.
Program Evaluation
At the end of rotations continuously through the year, PA students electronically complete a site evaluation from the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program. The evaluation consists of 14 questions: 6 about site quality and 8 about instruction quality. The questions are answered on a 5-point Likert scale. Also included are 2 open-ended response questions that ask what they liked about the rotation and what they felt could be improved. Results are anonymous, de-identified and blinded both to the program as well as the clerkship site. Results are aggregated and provided to program sites annually. Responses are converted to a dichotomous variable, where any good or excellent response (4 or 5) is considered positive and any neutral or below (3, 2, 1) is considered a nonpositive response.
Results
The clerkship site has been operational since June 22, 2015. There have been 59 students who participated in the rotation. A different scale in these evaluations was used between June 22, 2015, and September 13, 2015. Therefore, 7 responses were excluded from the analysis, leaving 52 usable evaluations. The responses were analyzed both in total (for the CLC as well as other IM rotation sites) and by individual clerkship year to look for any trends over time: September 14, 2015, through April 24, 2016; April 25, 2016, through April 28, 2017; and May 1, 2017, through March 1, 2018 (Table).
Site evaluations showed high satisfaction regarding the quality of the physical environment as well as the learning environment. Students endorsed the PAC unit having resources and physical space for them, such as a desk and computer, opportunity for participation in patient care, and parking (100%; n = 52). Site evaluations revealed high satisfaction with the quality of teaching and faculty encouragement and support of their learning (100%; n = 52). The evaluations revealed that bedside teaching was strong (94%; n = 49). The students reported high satisfaction with the volume of patients provided (92%; n = 48) as well as the diversity of diagnoses (92%; n = 48).
There were fewer positive responses in the first 2 years of the rotation with regard to formal lectures (50% and 67%; 7/14 and 16/24, respectively). In the third year of the rotation, students had a much higher satisfaction rate (93%; 13/14). This increased satisfaction was associated with the development and incorporation of the Interprofessional Curriculum in Transitional Care in 2017.
Discussion
Access to high-quality PA student clerkship sites has become a pressing issue in recent years because of increased competition for sites and a shortage of willing and well-trained preceptors. There has been marked growth in schools and enrollment across all medical professions. The Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the PA (ARC-PA) reported that the total number of accredited entry-level PA programs in 2018 was 246, with 58 new accredited programs projected by 2022.12 The Joint Report of the 2013 Multi-Discipline Clerkship/Clinical Training Site Survey reported a 66% increase in first-year enrollment in PA programs from 2002 to 2012.5 Programs must implement alternative strategies to attract clinical sites (eg, academic appointments, increased clinical resources to training sites) or face continued challenges with recruiting training sites for their students. Postacute care may be a natural extension to expand the footprint for clinical sites for these programs, augmenting acute inpatient and outpatient rotations. This implementation would increase the pool of clinical training sites and preceptors.
The experience with this novel training site, based on PA student feedback and evaluations, has been positive, and the postacute setting can provide students with high-quality IM clinical experiences. Students report adequate patient volume and diversity. In addition, evaluations are comparable with that of other IM site rotations the students experience. Qualitative feedback has emphasized the value of following patients over longer periods; eg, weeks vs days (as in acute care) enabling students to build relationships with patients as well as observe a richer clinical spectrum of disease over a less compressed period. “Patients have complex issues, so from a medical standpoint it challenges you to think of new ways to manage their care,” commented a representative student. “It is really beneficial that you can follow them over time.”
Furthermore, in response to student feedback on didactics, an interprofessional curriculum was developed to add formal structure as well as to create a curriculum in care transitions. This curriculum provided a unique opportunity for PA students to receive formal instruction on areas of particular relevance for transitional care (eg, care continuum, end of life issues, and care transitions). The curriculum also allows the interprofessional faculty a unique and enjoyable opportunity for interprofessional collaboration.
The 1 month PAC rotation is augmented with inpatient IM and outpatient family medicine rotations, consequently giving exposure to the full continuum of care. The PAC setting provides learners multifaceted benefits: the opportunity to strengthen and develop the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary for IM; increased understanding of other professions by observing and interacting as a team caring for a patient over a longer period as opposed to the acute care setting; the ability to perform effective, efficient, and safe transfer between clinical settings; and broad exposure to transitional care. As a result, the PAC rotation enhances but does not replace the necessary and essential rotations of inpatient and outpatient medicine.
Moreover, this rotation provides unique and core IM training for PA students. Our site focuses on interprofessional collaboration, emphasizing the importance of team-based care, an essential concept in modern day medicine. Formal exposure to other care specialties, such as PT and OT, SW, and mental health, is essential for students to appreciate clinical medicine and a patient’s physical and mental experience over the course of a disease and clinical state. In addition, the physical exam checklist ensures that students are exposed to the full spectrum of IM examination findings during their rotation. Finally, weekly feedback forms require students to ask and receive concrete feedback from their supervising providers.
Limitations
The generalizability of this model requires careful consideration. VABHS is a tertiary care integrated health care system, enabling students to learn from patients moving through multiple care transitions in a single health care system. In addition, other settings may not have the staffing or clinical volume to sustain such a model. All PAC clinical faculty teach voluntarily, and local leadership has set expectations for all clinicians to participate in teaching of trainees and PA students. Evaluations also note less diversity in the patient population, a challenge that some VA facilities face. This issue could be addressed by ensuring that students also have IM rotations at other inpatient medical facilities. A more balanced experience, where students reap the positive benefits of PAC but do not lose exposure to a diverse patient pool, could result. Furthermore, some of the perceived positive impacts also may be related to professional and personal attributes of the teaching clinicians rather than to the PAC setting.
Conclusion
PAC settings can be effective training sites for medicine clerkships for PA students and can provide high-quality training in IM as PA programs continue to expand. This setting offers students exposure to interprofessional, team-based care and the opportunity to care for patients with a broad range of disease complexity. Learning is further enhanced by the ability to follow patients longitudinally over their disease course as well as to work directly with teaching faculty and other interprofessional health care professionals. Evaluations of this novel clerkship experience have shown high levels of student satisfaction in knowledge growth, clinical skills, bedside teaching, and mentorship.
Acknowledgments
We thank Juman Hijab for her critical role in establishing and maintaining the clerkship. We thank Steven Simon, Matt Russell, and Thomas Parrino for their leadership and guidance in establishing and maintaining the clerkship. We thank the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program Director Mary Warner for her support and guidance in creating and supporting the clerkship. In addition, we thank the interprofessional education faculty for their dedicated involvement in teaching, including Stephanie Saunders, Lindsay Lefers, Jessica Rawlins, Lindsay Brennan, Angela Viani, Eric Charette, Nicole O’Neil, Susan Nathan, Jordana Meyerson, Shivani Jindal, Wei Shen, Amy Hanson, Gilda Cain, and Kate Hinrichs.
1. US Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational outlook handbook: physician assistants. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physician-assistants.htm. Updated June 18, 2019. Accessed August 13, 2019.
2. Association of American Medical Colleges. 2019 update: the complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2017 to 2032. https://aamc-black.global.ssl.fastly.net/production/media/filer_public/31/13/3113ee5c-a038-4c16-89af-294a69826650/2019_update_-_the_complexities_of_physician_supply_and_demand_-_projections_from_2017-2032.pdf. Published April 2019. Accessed August 15, 2019.
3. Glicken AD, Miller AA. Physician assistants: from pipeline to practice. Acad Med. 2013;88(12):1883-1889.
4. Erikson C, Hamann R, Levitan T, Pankow S, Stanley J, Whatley M. Recruiting and maintaining US clinical training sites: joint report of the 2013 multi-discipline clerkship/clinical training site survey. https://paeaonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Recruiting-and-Maintaining-U.S.-Clinical-Training-Sites.pdf. Accessed August 13, 2019.
5. Physician Assistant Education Association. By the numbers: 30th annual report on physician assistant educational programs. 2015. http://paeaonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/2015-by-the-numbers-program-report-30.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed August 15, 2019.
6. Morgan P, Himmerick KA, Leach B, Dieter P, Everett C. Scarcity of primary care positions may divert physician assistants into specialty practice. Med Care Res Rev. 2017;74(1):109-122.
7. Coplan B, Cawley J, Stoehr J. Physician assistants in primary care: trends and characteristics. Ann Fam Med. 2013;11(1):75-79.
8. Morgan P, Leach B, Himmerick K, Everett C. Job openings for PAs by specialty. JAAPA. 2018;31(1):45-47.
9. American Academy of Physician Assistants. 2017 AAPA Salary Report. Alexandria, VA; 2017.
10. Barnett ML, Grabowski DC, Mehrotra A. Home-to-home time—measuring what matters to patients and payers. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):4-6.
11. Werner RM, Konetzka RT. Trends in post-acute care use among Medicare beneficiaries: 2000 to 2015. JAMA. 2018;319(15):1616-1617.
12. Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant. http://www.arc-pa.org/accreditation/accredited-programs. Accessed May 10, 2019.
The Federal Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 37% job growth for physician assistants (PAs) from 2016 to 2026, much greater than the average for all other occupations as well as for other medical professions.1 This growth has been accompanied by increased enrollment in medical (doctor of medicine [MD], doctor of osteopathic medicine) and nurse practitioner (NP) schools.2 Clinical teaching sites serve a crucial function in the training of all clinical disciplines. These sites provide hands-on and experiential learning in medical settings, necessary components for learners practicing to become clinicians. Significant PA program expansion has led to increased demand for clinical training, creating competition for sites and a shortage of willing and well-trained preceptors.3
This challenge has been recognized by PA program directors. In the Joint Report of the 2013 Multi-Discipline Clerkship/Clinical Training Site Survey, PA program directors expressed concern about the adequacy of clinical opportunities for students, increased difficulty developing new core sites, and preserving existing core sites. In addition, they noted that a shortage of clinical sites was one of the greatest barriers to the PA programs’ sustained growth and success.4
Program directors also indicated difficulty securing clinical training sites in internal medicine (IM) and high rates of attrition of medicine clinical preceptors for their students.5 The reasons are multifold: increasing clinical demands, time, teaching competence, lack of experience, academic affiliation, lack of reimbursement, or compensation. Moreover, there is a declining number of PAs who work in primary care compared with specialty and subspecialty care, limiting the availability of clinical training preceptors in medicine and primary care.6-8 According to the American Academy of PAs (AAPA) census and salary survey data, the percentage of PAs working in the primary care specialties (ie, family medicine, IM, and general pediatrics) has decreased from > 47% in 1995 to 24% in 2017.9 As such, there is a need to broaden the educational landscape to provide more high-quality training sites in IM.
The postacute health care setting may address this training need. It offers a unique clinical opportunity to expose learners to a broad range of disease complexity and clinical acuity, as the percentage of patients discharged from hospitals to postacute care (PAC) has increased and care shifts from the hospital to the PAC setting.10,11 The longer PAC length of stay also enables learners to follow patients longitudinally over several weeks and experience interprofessional team-based care. In addition, the PAC setting offers learners the ability to acquire the necessary skills for smooth and effective transitions of care. This setting has been extensively used for trainees of nursing, pharmacy, physical therapy (PT) and occupational therapy (OT), speech-language pathology, psychology, and social work (SW), but few programs have used the PAC setting as clerkship sites for IM rotations for PA students. To address this need for IM sites, the VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS), in conjunction with the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program, developed a novel medicine clinical clerkship site for physician assistants in the PAC unit of the community living center (CLC) at VABHS. This report describes the program structure, curriculum, and participant evaluation results.
Clinical Clerkship Program
VABHS CLC is a 110-bed facility comprising 3 units: a 65-bed PAC unit, a 15-bed closed hospice/palliative care unit, and a 30-bed long-term care unit. The service is staffed continuously with physicians, PAs, and NPs. A majority of patients are admitted from the acute care hospital of VABHS (West Roxbury campus) and other regional VA facilities. The CLC offers dynamic services, including phlebotomy, general radiology, IV diuretics and antibiotics, wound care, and subacute PT, OT, and speech-language pathology rehabilitation. The CLC serves as a venue for transitioning patients from acute inpatient care to home. The patient population is often elderly, with multiple active comorbidities and variable medical literacy, adherence, and follow-up.
The CLC provides a diverse interprofessional learning environment, offering core IM rotations for first-year psychiatry residents, oral and maxillofacial surgery residents, and PA students. The CLC also has expanded as a clinical site both for transitions-in-care IM resident curricula and electives as well as a geriatrics fellowship. In addition, the site offers rotations for NPs, nursing, pharmacy, physical and occupational therapies, speech-language pathology, psychology, and SW.
The Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program was founded in 2015 as a master’s degree program completed over 28 months. The first 12 months are didactic, and the following 16 months are clinical training with 14 months of rotations (2 IM, family medicine, pediatrics, emergency medicine, general surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, neurology, and 5 elective rotations), and 2 months for a thesis. The program has about 30 students per year and 4 clerkship sites for IM.
Program Description
The VABHS medicine clerkship hosts 1 to 2 PA students for 4-week blocks in the PAC unit of the CLC. Each student rotates on both PA and MD teams. Students follow 3 to 4 patients and participate fully in their care from admission to discharge; they prepare daily presentations and participate in medical management, family meetings, chart documentation, and care coordination with the interprofessional team. Students are provided a physical examination checklist and feedback form, and they are expected to track findings and record feedback and goals with their supervising preceptor weekly. They also make formal case presentations and participate in monthly medicine didactic rounds available to all VABHS IM students and trainees via videoconference.
In addition, beginning in July 2017, all PA students in the CLC began to participate in a 4-week Interprofessional Curriculum in Transitional Care. The curriculum includes 14 didactic lectures taught by 16 interprofessional faculty, including medicine, geriatric, and palliative care physicians; PAs; social workers; physical and occupational therapists; pharmacists; and a geriatric psychologist. The didactics include topics on the interprofessional team, the care continuum, teams and teamwork, interdisciplinary coordination of care, components of effective transitions in care, medication reconciliation, approaching difficult conversations, advance care planning, and quality improvement. The goal of the curriculum is to provide learners the knowledge, skills, and dispositions necessary for high-quality transitional care and interprofessional practice as well as specific training for effective and safe transfers of care between clinical settings. Although PA students are the main participants in this curriculum, all other learners in the PAC unit are also invited to attend the lectures.
The unique attributes of this training site include direct interaction with supervising PAs and physicians, rather than experiencing the traditional teaching hierarchy (with interns, residents, fellows); observation of the natural progression of disease of both acute care and primary care issues due to the longer length of stay (2 to 6 weeks, where the typical student will see the same patient 7 to 10 times during their rotation); exposure to a host of medically complex patients offering a multitude of clinical scenarios and abnormal physical exam findings; exposure to a hospice/palliative care ward and end-of-life care; and interaction within an interprofessional training environment of nursing, pharmacy, PT, OT, speech-language pathology, psychology, and SW trainees.
Program Evaluation
At the end of rotations continuously through the year, PA students electronically complete a site evaluation from the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program. The evaluation consists of 14 questions: 6 about site quality and 8 about instruction quality. The questions are answered on a 5-point Likert scale. Also included are 2 open-ended response questions that ask what they liked about the rotation and what they felt could be improved. Results are anonymous, de-identified and blinded both to the program as well as the clerkship site. Results are aggregated and provided to program sites annually. Responses are converted to a dichotomous variable, where any good or excellent response (4 or 5) is considered positive and any neutral or below (3, 2, 1) is considered a nonpositive response.
Results
The clerkship site has been operational since June 22, 2015. There have been 59 students who participated in the rotation. A different scale in these evaluations was used between June 22, 2015, and September 13, 2015. Therefore, 7 responses were excluded from the analysis, leaving 52 usable evaluations. The responses were analyzed both in total (for the CLC as well as other IM rotation sites) and by individual clerkship year to look for any trends over time: September 14, 2015, through April 24, 2016; April 25, 2016, through April 28, 2017; and May 1, 2017, through March 1, 2018 (Table).
Site evaluations showed high satisfaction regarding the quality of the physical environment as well as the learning environment. Students endorsed the PAC unit having resources and physical space for them, such as a desk and computer, opportunity for participation in patient care, and parking (100%; n = 52). Site evaluations revealed high satisfaction with the quality of teaching and faculty encouragement and support of their learning (100%; n = 52). The evaluations revealed that bedside teaching was strong (94%; n = 49). The students reported high satisfaction with the volume of patients provided (92%; n = 48) as well as the diversity of diagnoses (92%; n = 48).
There were fewer positive responses in the first 2 years of the rotation with regard to formal lectures (50% and 67%; 7/14 and 16/24, respectively). In the third year of the rotation, students had a much higher satisfaction rate (93%; 13/14). This increased satisfaction was associated with the development and incorporation of the Interprofessional Curriculum in Transitional Care in 2017.
Discussion
Access to high-quality PA student clerkship sites has become a pressing issue in recent years because of increased competition for sites and a shortage of willing and well-trained preceptors. There has been marked growth in schools and enrollment across all medical professions. The Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the PA (ARC-PA) reported that the total number of accredited entry-level PA programs in 2018 was 246, with 58 new accredited programs projected by 2022.12 The Joint Report of the 2013 Multi-Discipline Clerkship/Clinical Training Site Survey reported a 66% increase in first-year enrollment in PA programs from 2002 to 2012.5 Programs must implement alternative strategies to attract clinical sites (eg, academic appointments, increased clinical resources to training sites) or face continued challenges with recruiting training sites for their students. Postacute care may be a natural extension to expand the footprint for clinical sites for these programs, augmenting acute inpatient and outpatient rotations. This implementation would increase the pool of clinical training sites and preceptors.
The experience with this novel training site, based on PA student feedback and evaluations, has been positive, and the postacute setting can provide students with high-quality IM clinical experiences. Students report adequate patient volume and diversity. In addition, evaluations are comparable with that of other IM site rotations the students experience. Qualitative feedback has emphasized the value of following patients over longer periods; eg, weeks vs days (as in acute care) enabling students to build relationships with patients as well as observe a richer clinical spectrum of disease over a less compressed period. “Patients have complex issues, so from a medical standpoint it challenges you to think of new ways to manage their care,” commented a representative student. “It is really beneficial that you can follow them over time.”
Furthermore, in response to student feedback on didactics, an interprofessional curriculum was developed to add formal structure as well as to create a curriculum in care transitions. This curriculum provided a unique opportunity for PA students to receive formal instruction on areas of particular relevance for transitional care (eg, care continuum, end of life issues, and care transitions). The curriculum also allows the interprofessional faculty a unique and enjoyable opportunity for interprofessional collaboration.
The 1 month PAC rotation is augmented with inpatient IM and outpatient family medicine rotations, consequently giving exposure to the full continuum of care. The PAC setting provides learners multifaceted benefits: the opportunity to strengthen and develop the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary for IM; increased understanding of other professions by observing and interacting as a team caring for a patient over a longer period as opposed to the acute care setting; the ability to perform effective, efficient, and safe transfer between clinical settings; and broad exposure to transitional care. As a result, the PAC rotation enhances but does not replace the necessary and essential rotations of inpatient and outpatient medicine.
Moreover, this rotation provides unique and core IM training for PA students. Our site focuses on interprofessional collaboration, emphasizing the importance of team-based care, an essential concept in modern day medicine. Formal exposure to other care specialties, such as PT and OT, SW, and mental health, is essential for students to appreciate clinical medicine and a patient’s physical and mental experience over the course of a disease and clinical state. In addition, the physical exam checklist ensures that students are exposed to the full spectrum of IM examination findings during their rotation. Finally, weekly feedback forms require students to ask and receive concrete feedback from their supervising providers.
Limitations
The generalizability of this model requires careful consideration. VABHS is a tertiary care integrated health care system, enabling students to learn from patients moving through multiple care transitions in a single health care system. In addition, other settings may not have the staffing or clinical volume to sustain such a model. All PAC clinical faculty teach voluntarily, and local leadership has set expectations for all clinicians to participate in teaching of trainees and PA students. Evaluations also note less diversity in the patient population, a challenge that some VA facilities face. This issue could be addressed by ensuring that students also have IM rotations at other inpatient medical facilities. A more balanced experience, where students reap the positive benefits of PAC but do not lose exposure to a diverse patient pool, could result. Furthermore, some of the perceived positive impacts also may be related to professional and personal attributes of the teaching clinicians rather than to the PAC setting.
Conclusion
PAC settings can be effective training sites for medicine clerkships for PA students and can provide high-quality training in IM as PA programs continue to expand. This setting offers students exposure to interprofessional, team-based care and the opportunity to care for patients with a broad range of disease complexity. Learning is further enhanced by the ability to follow patients longitudinally over their disease course as well as to work directly with teaching faculty and other interprofessional health care professionals. Evaluations of this novel clerkship experience have shown high levels of student satisfaction in knowledge growth, clinical skills, bedside teaching, and mentorship.
Acknowledgments
We thank Juman Hijab for her critical role in establishing and maintaining the clerkship. We thank Steven Simon, Matt Russell, and Thomas Parrino for their leadership and guidance in establishing and maintaining the clerkship. We thank the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program Director Mary Warner for her support and guidance in creating and supporting the clerkship. In addition, we thank the interprofessional education faculty for their dedicated involvement in teaching, including Stephanie Saunders, Lindsay Lefers, Jessica Rawlins, Lindsay Brennan, Angela Viani, Eric Charette, Nicole O’Neil, Susan Nathan, Jordana Meyerson, Shivani Jindal, Wei Shen, Amy Hanson, Gilda Cain, and Kate Hinrichs.
The Federal Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 37% job growth for physician assistants (PAs) from 2016 to 2026, much greater than the average for all other occupations as well as for other medical professions.1 This growth has been accompanied by increased enrollment in medical (doctor of medicine [MD], doctor of osteopathic medicine) and nurse practitioner (NP) schools.2 Clinical teaching sites serve a crucial function in the training of all clinical disciplines. These sites provide hands-on and experiential learning in medical settings, necessary components for learners practicing to become clinicians. Significant PA program expansion has led to increased demand for clinical training, creating competition for sites and a shortage of willing and well-trained preceptors.3
This challenge has been recognized by PA program directors. In the Joint Report of the 2013 Multi-Discipline Clerkship/Clinical Training Site Survey, PA program directors expressed concern about the adequacy of clinical opportunities for students, increased difficulty developing new core sites, and preserving existing core sites. In addition, they noted that a shortage of clinical sites was one of the greatest barriers to the PA programs’ sustained growth and success.4
Program directors also indicated difficulty securing clinical training sites in internal medicine (IM) and high rates of attrition of medicine clinical preceptors for their students.5 The reasons are multifold: increasing clinical demands, time, teaching competence, lack of experience, academic affiliation, lack of reimbursement, or compensation. Moreover, there is a declining number of PAs who work in primary care compared with specialty and subspecialty care, limiting the availability of clinical training preceptors in medicine and primary care.6-8 According to the American Academy of PAs (AAPA) census and salary survey data, the percentage of PAs working in the primary care specialties (ie, family medicine, IM, and general pediatrics) has decreased from > 47% in 1995 to 24% in 2017.9 As such, there is a need to broaden the educational landscape to provide more high-quality training sites in IM.
The postacute health care setting may address this training need. It offers a unique clinical opportunity to expose learners to a broad range of disease complexity and clinical acuity, as the percentage of patients discharged from hospitals to postacute care (PAC) has increased and care shifts from the hospital to the PAC setting.10,11 The longer PAC length of stay also enables learners to follow patients longitudinally over several weeks and experience interprofessional team-based care. In addition, the PAC setting offers learners the ability to acquire the necessary skills for smooth and effective transitions of care. This setting has been extensively used for trainees of nursing, pharmacy, physical therapy (PT) and occupational therapy (OT), speech-language pathology, psychology, and social work (SW), but few programs have used the PAC setting as clerkship sites for IM rotations for PA students. To address this need for IM sites, the VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS), in conjunction with the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program, developed a novel medicine clinical clerkship site for physician assistants in the PAC unit of the community living center (CLC) at VABHS. This report describes the program structure, curriculum, and participant evaluation results.
Clinical Clerkship Program
VABHS CLC is a 110-bed facility comprising 3 units: a 65-bed PAC unit, a 15-bed closed hospice/palliative care unit, and a 30-bed long-term care unit. The service is staffed continuously with physicians, PAs, and NPs. A majority of patients are admitted from the acute care hospital of VABHS (West Roxbury campus) and other regional VA facilities. The CLC offers dynamic services, including phlebotomy, general radiology, IV diuretics and antibiotics, wound care, and subacute PT, OT, and speech-language pathology rehabilitation. The CLC serves as a venue for transitioning patients from acute inpatient care to home. The patient population is often elderly, with multiple active comorbidities and variable medical literacy, adherence, and follow-up.
The CLC provides a diverse interprofessional learning environment, offering core IM rotations for first-year psychiatry residents, oral and maxillofacial surgery residents, and PA students. The CLC also has expanded as a clinical site both for transitions-in-care IM resident curricula and electives as well as a geriatrics fellowship. In addition, the site offers rotations for NPs, nursing, pharmacy, physical and occupational therapies, speech-language pathology, psychology, and SW.
The Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program was founded in 2015 as a master’s degree program completed over 28 months. The first 12 months are didactic, and the following 16 months are clinical training with 14 months of rotations (2 IM, family medicine, pediatrics, emergency medicine, general surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, neurology, and 5 elective rotations), and 2 months for a thesis. The program has about 30 students per year and 4 clerkship sites for IM.
Program Description
The VABHS medicine clerkship hosts 1 to 2 PA students for 4-week blocks in the PAC unit of the CLC. Each student rotates on both PA and MD teams. Students follow 3 to 4 patients and participate fully in their care from admission to discharge; they prepare daily presentations and participate in medical management, family meetings, chart documentation, and care coordination with the interprofessional team. Students are provided a physical examination checklist and feedback form, and they are expected to track findings and record feedback and goals with their supervising preceptor weekly. They also make formal case presentations and participate in monthly medicine didactic rounds available to all VABHS IM students and trainees via videoconference.
In addition, beginning in July 2017, all PA students in the CLC began to participate in a 4-week Interprofessional Curriculum in Transitional Care. The curriculum includes 14 didactic lectures taught by 16 interprofessional faculty, including medicine, geriatric, and palliative care physicians; PAs; social workers; physical and occupational therapists; pharmacists; and a geriatric psychologist. The didactics include topics on the interprofessional team, the care continuum, teams and teamwork, interdisciplinary coordination of care, components of effective transitions in care, medication reconciliation, approaching difficult conversations, advance care planning, and quality improvement. The goal of the curriculum is to provide learners the knowledge, skills, and dispositions necessary for high-quality transitional care and interprofessional practice as well as specific training for effective and safe transfers of care between clinical settings. Although PA students are the main participants in this curriculum, all other learners in the PAC unit are also invited to attend the lectures.
The unique attributes of this training site include direct interaction with supervising PAs and physicians, rather than experiencing the traditional teaching hierarchy (with interns, residents, fellows); observation of the natural progression of disease of both acute care and primary care issues due to the longer length of stay (2 to 6 weeks, where the typical student will see the same patient 7 to 10 times during their rotation); exposure to a host of medically complex patients offering a multitude of clinical scenarios and abnormal physical exam findings; exposure to a hospice/palliative care ward and end-of-life care; and interaction within an interprofessional training environment of nursing, pharmacy, PT, OT, speech-language pathology, psychology, and SW trainees.
Program Evaluation
At the end of rotations continuously through the year, PA students electronically complete a site evaluation from the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program. The evaluation consists of 14 questions: 6 about site quality and 8 about instruction quality. The questions are answered on a 5-point Likert scale. Also included are 2 open-ended response questions that ask what they liked about the rotation and what they felt could be improved. Results are anonymous, de-identified and blinded both to the program as well as the clerkship site. Results are aggregated and provided to program sites annually. Responses are converted to a dichotomous variable, where any good or excellent response (4 or 5) is considered positive and any neutral or below (3, 2, 1) is considered a nonpositive response.
Results
The clerkship site has been operational since June 22, 2015. There have been 59 students who participated in the rotation. A different scale in these evaluations was used between June 22, 2015, and September 13, 2015. Therefore, 7 responses were excluded from the analysis, leaving 52 usable evaluations. The responses were analyzed both in total (for the CLC as well as other IM rotation sites) and by individual clerkship year to look for any trends over time: September 14, 2015, through April 24, 2016; April 25, 2016, through April 28, 2017; and May 1, 2017, through March 1, 2018 (Table).
Site evaluations showed high satisfaction regarding the quality of the physical environment as well as the learning environment. Students endorsed the PAC unit having resources and physical space for them, such as a desk and computer, opportunity for participation in patient care, and parking (100%; n = 52). Site evaluations revealed high satisfaction with the quality of teaching and faculty encouragement and support of their learning (100%; n = 52). The evaluations revealed that bedside teaching was strong (94%; n = 49). The students reported high satisfaction with the volume of patients provided (92%; n = 48) as well as the diversity of diagnoses (92%; n = 48).
There were fewer positive responses in the first 2 years of the rotation with regard to formal lectures (50% and 67%; 7/14 and 16/24, respectively). In the third year of the rotation, students had a much higher satisfaction rate (93%; 13/14). This increased satisfaction was associated with the development and incorporation of the Interprofessional Curriculum in Transitional Care in 2017.
Discussion
Access to high-quality PA student clerkship sites has become a pressing issue in recent years because of increased competition for sites and a shortage of willing and well-trained preceptors. There has been marked growth in schools and enrollment across all medical professions. The Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the PA (ARC-PA) reported that the total number of accredited entry-level PA programs in 2018 was 246, with 58 new accredited programs projected by 2022.12 The Joint Report of the 2013 Multi-Discipline Clerkship/Clinical Training Site Survey reported a 66% increase in first-year enrollment in PA programs from 2002 to 2012.5 Programs must implement alternative strategies to attract clinical sites (eg, academic appointments, increased clinical resources to training sites) or face continued challenges with recruiting training sites for their students. Postacute care may be a natural extension to expand the footprint for clinical sites for these programs, augmenting acute inpatient and outpatient rotations. This implementation would increase the pool of clinical training sites and preceptors.
The experience with this novel training site, based on PA student feedback and evaluations, has been positive, and the postacute setting can provide students with high-quality IM clinical experiences. Students report adequate patient volume and diversity. In addition, evaluations are comparable with that of other IM site rotations the students experience. Qualitative feedback has emphasized the value of following patients over longer periods; eg, weeks vs days (as in acute care) enabling students to build relationships with patients as well as observe a richer clinical spectrum of disease over a less compressed period. “Patients have complex issues, so from a medical standpoint it challenges you to think of new ways to manage their care,” commented a representative student. “It is really beneficial that you can follow them over time.”
Furthermore, in response to student feedback on didactics, an interprofessional curriculum was developed to add formal structure as well as to create a curriculum in care transitions. This curriculum provided a unique opportunity for PA students to receive formal instruction on areas of particular relevance for transitional care (eg, care continuum, end of life issues, and care transitions). The curriculum also allows the interprofessional faculty a unique and enjoyable opportunity for interprofessional collaboration.
The 1 month PAC rotation is augmented with inpatient IM and outpatient family medicine rotations, consequently giving exposure to the full continuum of care. The PAC setting provides learners multifaceted benefits: the opportunity to strengthen and develop the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary for IM; increased understanding of other professions by observing and interacting as a team caring for a patient over a longer period as opposed to the acute care setting; the ability to perform effective, efficient, and safe transfer between clinical settings; and broad exposure to transitional care. As a result, the PAC rotation enhances but does not replace the necessary and essential rotations of inpatient and outpatient medicine.
Moreover, this rotation provides unique and core IM training for PA students. Our site focuses on interprofessional collaboration, emphasizing the importance of team-based care, an essential concept in modern day medicine. Formal exposure to other care specialties, such as PT and OT, SW, and mental health, is essential for students to appreciate clinical medicine and a patient’s physical and mental experience over the course of a disease and clinical state. In addition, the physical exam checklist ensures that students are exposed to the full spectrum of IM examination findings during their rotation. Finally, weekly feedback forms require students to ask and receive concrete feedback from their supervising providers.
Limitations
The generalizability of this model requires careful consideration. VABHS is a tertiary care integrated health care system, enabling students to learn from patients moving through multiple care transitions in a single health care system. In addition, other settings may not have the staffing or clinical volume to sustain such a model. All PAC clinical faculty teach voluntarily, and local leadership has set expectations for all clinicians to participate in teaching of trainees and PA students. Evaluations also note less diversity in the patient population, a challenge that some VA facilities face. This issue could be addressed by ensuring that students also have IM rotations at other inpatient medical facilities. A more balanced experience, where students reap the positive benefits of PAC but do not lose exposure to a diverse patient pool, could result. Furthermore, some of the perceived positive impacts also may be related to professional and personal attributes of the teaching clinicians rather than to the PAC setting.
Conclusion
PAC settings can be effective training sites for medicine clerkships for PA students and can provide high-quality training in IM as PA programs continue to expand. This setting offers students exposure to interprofessional, team-based care and the opportunity to care for patients with a broad range of disease complexity. Learning is further enhanced by the ability to follow patients longitudinally over their disease course as well as to work directly with teaching faculty and other interprofessional health care professionals. Evaluations of this novel clerkship experience have shown high levels of student satisfaction in knowledge growth, clinical skills, bedside teaching, and mentorship.
Acknowledgments
We thank Juman Hijab for her critical role in establishing and maintaining the clerkship. We thank Steven Simon, Matt Russell, and Thomas Parrino for their leadership and guidance in establishing and maintaining the clerkship. We thank the Boston University School of Medicine Physician Assistant Program Director Mary Warner for her support and guidance in creating and supporting the clerkship. In addition, we thank the interprofessional education faculty for their dedicated involvement in teaching, including Stephanie Saunders, Lindsay Lefers, Jessica Rawlins, Lindsay Brennan, Angela Viani, Eric Charette, Nicole O’Neil, Susan Nathan, Jordana Meyerson, Shivani Jindal, Wei Shen, Amy Hanson, Gilda Cain, and Kate Hinrichs.
1. US Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational outlook handbook: physician assistants. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physician-assistants.htm. Updated June 18, 2019. Accessed August 13, 2019.
2. Association of American Medical Colleges. 2019 update: the complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2017 to 2032. https://aamc-black.global.ssl.fastly.net/production/media/filer_public/31/13/3113ee5c-a038-4c16-89af-294a69826650/2019_update_-_the_complexities_of_physician_supply_and_demand_-_projections_from_2017-2032.pdf. Published April 2019. Accessed August 15, 2019.
3. Glicken AD, Miller AA. Physician assistants: from pipeline to practice. Acad Med. 2013;88(12):1883-1889.
4. Erikson C, Hamann R, Levitan T, Pankow S, Stanley J, Whatley M. Recruiting and maintaining US clinical training sites: joint report of the 2013 multi-discipline clerkship/clinical training site survey. https://paeaonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Recruiting-and-Maintaining-U.S.-Clinical-Training-Sites.pdf. Accessed August 13, 2019.
5. Physician Assistant Education Association. By the numbers: 30th annual report on physician assistant educational programs. 2015. http://paeaonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/2015-by-the-numbers-program-report-30.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed August 15, 2019.
6. Morgan P, Himmerick KA, Leach B, Dieter P, Everett C. Scarcity of primary care positions may divert physician assistants into specialty practice. Med Care Res Rev. 2017;74(1):109-122.
7. Coplan B, Cawley J, Stoehr J. Physician assistants in primary care: trends and characteristics. Ann Fam Med. 2013;11(1):75-79.
8. Morgan P, Leach B, Himmerick K, Everett C. Job openings for PAs by specialty. JAAPA. 2018;31(1):45-47.
9. American Academy of Physician Assistants. 2017 AAPA Salary Report. Alexandria, VA; 2017.
10. Barnett ML, Grabowski DC, Mehrotra A. Home-to-home time—measuring what matters to patients and payers. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):4-6.
11. Werner RM, Konetzka RT. Trends in post-acute care use among Medicare beneficiaries: 2000 to 2015. JAMA. 2018;319(15):1616-1617.
12. Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant. http://www.arc-pa.org/accreditation/accredited-programs. Accessed May 10, 2019.
1. US Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational outlook handbook: physician assistants. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physician-assistants.htm. Updated June 18, 2019. Accessed August 13, 2019.
2. Association of American Medical Colleges. 2019 update: the complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2017 to 2032. https://aamc-black.global.ssl.fastly.net/production/media/filer_public/31/13/3113ee5c-a038-4c16-89af-294a69826650/2019_update_-_the_complexities_of_physician_supply_and_demand_-_projections_from_2017-2032.pdf. Published April 2019. Accessed August 15, 2019.
3. Glicken AD, Miller AA. Physician assistants: from pipeline to practice. Acad Med. 2013;88(12):1883-1889.
4. Erikson C, Hamann R, Levitan T, Pankow S, Stanley J, Whatley M. Recruiting and maintaining US clinical training sites: joint report of the 2013 multi-discipline clerkship/clinical training site survey. https://paeaonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Recruiting-and-Maintaining-U.S.-Clinical-Training-Sites.pdf. Accessed August 13, 2019.
5. Physician Assistant Education Association. By the numbers: 30th annual report on physician assistant educational programs. 2015. http://paeaonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/2015-by-the-numbers-program-report-30.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed August 15, 2019.
6. Morgan P, Himmerick KA, Leach B, Dieter P, Everett C. Scarcity of primary care positions may divert physician assistants into specialty practice. Med Care Res Rev. 2017;74(1):109-122.
7. Coplan B, Cawley J, Stoehr J. Physician assistants in primary care: trends and characteristics. Ann Fam Med. 2013;11(1):75-79.
8. Morgan P, Leach B, Himmerick K, Everett C. Job openings for PAs by specialty. JAAPA. 2018;31(1):45-47.
9. American Academy of Physician Assistants. 2017 AAPA Salary Report. Alexandria, VA; 2017.
10. Barnett ML, Grabowski DC, Mehrotra A. Home-to-home time—measuring what matters to patients and payers. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):4-6.
11. Werner RM, Konetzka RT. Trends in post-acute care use among Medicare beneficiaries: 2000 to 2015. JAMA. 2018;319(15):1616-1617.
12. Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant. http://www.arc-pa.org/accreditation/accredited-programs. Accessed May 10, 2019.
A Veteran Presenting With Leg Swelling, Dyspnea, and Proteinuria
*This article has been corrected to include a missing author.
Case Presentation. A 63-year-old male with well-controlled HIV (CD4 count 757, undetectable viral load), epilepsy, and hypertension presented to the VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS) emergency department with 1 week of bilateral leg swelling and exertional shortness of breath. He reported having no fever, cough, chest pain, pain with inspiration and orthopnea. There was no personal or family history of pulmonary embolism. He reported weight gain but was unable to quantify how much. He also reported flare up of chronic knee pain, without swelling for which he had taken up to 4 tablets of naproxen daily for several weeks. His physical examination was notable for a heart rate of 105 beats per minute and bilateral pitting edema to his knees. Laboratory testing revealed a creatinine level of 2.5 mg/dL, which was increased from a baseline of 1.0 mg/dL (Table 1), and a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 7.8 mg/mg (Table 2). A renal ultrasound showed normal-sized kidneys without hydronephrosis or obstructing renal calculi. The patient was admitted for further workup of his dyspnea and acute kidney injury.
► Jonathan Li, MD, Chief Medical Resident, VABHS and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC). Dr. William, based on the degree of proteinuria and edema, a diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome was made. How is nephrotic syndrome defined, and how is it distinguished from glomerulonephritis?
► Jeffrey William, MD, Nephrologist, BIDMC, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. The pathophysiology of nephrotic disease and glomerulonephritis are quite distinct, resulting in symptoms and systemic manifestations that only slightly overlap. Glomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation of the endothelial cells of the trilayered glomerular capillary, with a resulting active urine sediment with red blood cells, white blood cells, and casts. Nephrotic syndrome mostly affects the visceral epithelial cells of the glomerular capillary, commonly referred to as podocytes, and hence, the urine sediment in nephrotic disease is often inactive. Patients with nephrotic syndrome have nephrotic-range proteinuria (excretion of > 3.5 g per 24 h or a spot urine protein-creatinine ratio > 3.5 g in the steady state) and both hypoalbuminemia (< 3 g/dL) and peripheral edema. Lipiduria and hyperlipidemia are common findings in nephrotic syndrome but are not required for a clinical diagnosis.1 In contrast, glomerulonephritis is defined by a constellation of findings that include renal insufficiency (often indicated by an elevation in blood urea nitrogen and creatinine), hypertension, hematuria, and subnephrotic range proteinuria. In practice, patients may fulfill criteria of both nephrotic and nephritic syndromes, but the preponderance of clinical evidence often points one way or the other. In this case, nephrotic syndrome was diagnosed based on the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 7.8 mg/mg, hypoalbuminemia, and edema.
► Dr. Li. What would be your first-line workup for evaluation of the etiology of this patient’s nephrotic syndrome?
► Dr. William. Rather than memorizing a list of etiologies of nephrotic syndrome, it is essential to consider the pathophysiology of heavy proteinuria. Though the glomerular filtration barrier is extremely complex and defects in any component can cause proteinuria, disruption of the podocyte is often involved. Common disease processes that chiefly target the podocyte include minimal change disease, primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and membranous nephropathy, all by differing mechanisms. Minimal change disease and idiopathic/primary FSGS are increasingly thought to be at differing points on a spectrum of the same disease.2 Secondary FSGS, on the other hand, is a progressive disease, commonly resulting from longstanding hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity in adults. Membranous nephropathy can also be either primary or secondary. Primary membranous nephropathy is chiefly caused by a circulating IgG4 antibody to the podocyte membrane antigen PLA2R (M-type phospholipase A2 receptor), whereas secondary membranous nephropathy can be caused by a variety of systemic etiologies, including autoimmune disease (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus), certain malignancies, chronic infections (eg, hepatitis B and C), and many medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).3-5 Paraprotein deposition diseases can also cause glomerular damage leading to nephrotic-range proteinuria.
Given these potential diagnoses, a careful history should be taken to assess exposures and recent medication use. Urine sediment evaluation is essential in the evaluation of nephrotic syndrome to determine if there is an underlying nephritic process. Select serologies may be sent to look for autoimmune disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and common viral exposures like hepatitis B or C. Serum and urine protein electrophoreses would be appropriate initial tests of suspected paraprotein-related diseases. Other serologies, such as antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies or antiglomerular basement membrane antibodies, would not necessarily be indicated here given the lack of hematuria and presence of nephrotic-range proteinuria.
► Dr. Li. The initial evaluation was notable for an erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 120 (mm/h) and a weakly positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer of 1:40. The remainder of his initial workup did not reveal an etiology for his nephrotic syndrome (Table 3).
Dr. William, is there a role for starting urgent empiric steroids in nephrotic syndrome while workup is ongoing? If so, do the severity of proteinuria and/or symptoms play a role or is this determination based on something else?
► Dr. William. Edema is a primary symptom of nephrotic syndrome and can often be managed with diuretics alone. If a clear medication-mediated cause is suspected, discontinuation of this agent may result in spontaneous improvement without steroid treatment. However,in cases where an etiology is unclear and there are serious thrombotic complications requiring anticoagulation, and a renal biopsy is deemed to be too risky, then empiric steroid therapy may be necessary. Children with new-onset nephrotic syndrome are presumed to have minimal change disease, given its prevalence in this patient population, and are often given empiric steroids without obtaining a renal biopsy. However, in the adult population, a renal biopsy can typically be performed quickly and safely, with pathology results interpreted within days. In this patient, since a diagnosis was unclear and there was no contraindication to renal biopsy, a biopsy should be obtained before consideration of steroids.
► Dr. Li. Steroids were deferred in anticipation of renal biopsy, which showed stage I membranous nephropathy, suggestive of membranous lupus nephritis Class V. The deposits were strongly reactive for immunoglobuline G (IgG), IgA, and complement 1q (C1q), showed co-dominant staining for IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3, and were weakly positive for the PLA2 receptor. Focal intimal arteritis in a small interlobular vessel was seen.
Dr. William, the pathology returned suggestive of lupus nephritis. Does the overall clinical picture fit with lupus nephritis?
► Dr. William. Given the history and a rather low ANA, the diagnosis of lupus nephritis seems unlikely. The lack of IgG4 and PLA2R staining in the biopsy suggests that this membranous pattern on the biopsy is likely to be secondary to a systemic etiology, but further investigation should be pursued.
► Dr. Li. The patient was discharged after the biopsy with a planned outpatient nephrology follow-up to discuss results and treatment. He was prescribed an oral diuretic, and his symptoms improved. Several days after discharge, he developed blurry vision and was evaluated in the Ophthalmology clinic. On fundoscopy, he was found to have acute papillitis, a form of optic neuritis. As part of initial evaluation of infectious etiologies of papillitis, ophthalmology recommended testing for syphilis.
Dr. Strymish, when we are considering secondary syphilis, what is the recommended approach to diagnostic testing?
► Judith Strymish, MD, Infectious Diseases, BIDMC, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. The diagnosis of syphilis is usually made through serologic testing of blood specimens. Methods that detect the spirochete directly like dark-field smears are not readily available. Serologic tests include treponemal tests (eg, Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay [TPPA]) and nontreponemal tests (eg, rapid plasma reagin [RPR]). One needs a confirmatory test because either test is associated with false positives. Either test can be done first. Most laboratories, including those at VABHS are now performing treponemal tests first as these have become more cost-effective.6 The TPPA treponemal test was found to have a lower false negative rate in primary syphilis compared with that of nontreponemal tests.7 Nontreponemal tests can be followed for response to therapy. If a patient has a history of treated syphilis, a nontreponemal test should be sent, since the treponemal test will remain positive for life.
If there is clinical concern for neurosyphilis, cerebrospinal fluid fluorescent (CSF) treponemal antibody needs to be sampled and sent for the nontreponemal venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test. The VDRL is highly specific for neurosyphilis but not as sensitive. Cerebrospinal fluid fluorescent treponemal antibody (CSF FTA) may also be sent; it is very sensitive but not very specific for neurosyphilis.
► Dr. Li. An RPR returned positive at 1:512 (was negative 14 months prior on a routine screening test), with positive reflex TPPA (Table 4). A diagnosis of secondary syphilis was made. Dr. Strymish, at this point, what additional testing and treatment is necessary?
► Dr. Strymish. With papillitis and a very high RPR, we need to assume that he has ophthalmic syphilis. This can occur in any stage of syphilis, but his eye findings and high RPR are consistent with secondary syphilis. Ophthalmic syphilis has been on the upswing, even more than is expected with recent increases in syphilis cases.8 Ophthalmic syphilis is considered a form of neurosyphilis. A lumbar puncture and treatment for neurosyphilis is recommended.9,10
► Dr. Li. A lumbar puncture was performed, and his CSF was VDRL positive. This confirmed a diagnosis of neurosyphilis (Table 4). The patient was treated for neurosyphilis with IV penicillin. The patient shared that he had episodes of unprotected oral sexual activity within the past year and approximately 1 year ago, he came in close contact (but no sexual activity) with a person who had a rash consistent with syphilis.Dr. William, syphilis would be a potential unifying diagnosis of his renal and ophthalmologic manifestations. Is syphilis known to cause membranous nephropathy?
► Dr. William. Though it is uncommon, the nephrotic syndrome is a well-described complication of secondary syphilis.11,12 Syphilis has been shown to cause nephrotic syndrome in a variety of ways. Case reports abound linking syphilis to minimal change disease and other glomerular diseases.13,14 A case report from 1993 shows a membranous pattern of glomerular disease similar to this case.15 As a form of secondary membranous nephropathy, the immunofluorescence pattern can demonstrate staining similar to the “full house” seen in lupus nephritis (IgA, IgM, and C1q, in addition to IgG and C3).16 This explains the initial interpretation of this patient’s biopsy, as lupus nephritis would be a much more common etiology of secondary membranous nephropathy than is acute syphilis with this immunofluorescence pattern. However, the data in this case are highly suggestive of a causal relationship between secondary syphilis and membranous nephropathy.
► Dr. Li. Dr. Strymish, how should this patient be screened for syphilis reinfection, and at what intervals would you recommend?
► Dr. Strymish. He will need follow-up testing to make sure that his syphilis is effectively treated. If CSF pleocytosis was present initially, a CSF examination should be repeated every 6 months until the cell count is normal. He will also need follow-up for normalization of his RPR. Persons with HIV infection and primary or secondary syphilis should be evaluated clinically and serologically for treatment failure at 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 months after therapy according to US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines.9
His treponemal test for syphilis will likely stay positive for life. His RPR should decrease significantly with effective treatment. It makes sense to screen with RPR alone as long as he continues to have risk factors for acquiring syphilis. Routine syphilis testing is recommended for pregnant women, sexually active men who have sex with men, sexually active persons with HIV, and persons taking PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) for HIV prevention. He should be screened at least yearly for syphilis.
► Dr. Li. Over the next several months, the patient’s creatinine normalized and his proteinuria resolved. His vision recovered, and he has had no further ophthalmologic complications.
Dr. William, what is his long-term renal prognosis? Do you expect that his acute episode of membranous nephropathy will have permanent effects on his renal function?
► Dr. William. His rapid response to therapy for neurosyphilis provides evidence for this etiology of his renal dysfunction and glomerulonephritis. His long-term prognosis is quite good if the syphilis is the only reason for him to have renal disease. The renal damage is often reversible in these cases. However, given his prior extensive NSAID exposure and history of hypertension, he may be at higher risk for chronic kidney disease than an otherwise healthy patient, especially after an episode of acute kidney injury. Therefore, his renal function should continue to be monitored as an outpatient.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank this veteran for sharing his story and allowing us to learn from this unusual case for the benefit of our future patients.
1. Rennke H, Denker BM. Renal Pathophysiology: The Essentials. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014.
2. Maas RJ, Deegens JK, Smeets B, Moeller MJ, Wetzels JF. Minimal change disease and idiopathic FSGS: manifestations of the same disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(12):768-776.
3. Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):11-21.
4. Rennke HG. Secondary membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1995;47(2):643-656.
5. Nawaz FA, Larsen CP, Troxell ML. Membranous nephropathy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(5):1012-1017.
6. Pillay A. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Syphilis Summit—Diagnostics and laboratory issues. Sex Transm Dis. 2018;45(9S)(suppl 1):S13-S16.
7. Levett PN, Fonseca K, Tsang RS, et al. Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network laboratory guidelines for the use of serological tests (excluding point-of-care tests) for the diagnosis of syphilis in Canada. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2015;26(suppl A):6A-12A.
8. Oliver SE, Aubin M, Atwell L, et al. Ocular syphilis—eight jurisdictions, United States, 2014-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(43):1185-1188.
9. Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recommendations and Reports 2015;64(RR3):1-137. [Erratum in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(33):924.]
10. US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical advisory: ocular syphilis in the United States. https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/clinicaladvisoryos2015.htm. Updated March 24, 2016. Accessed August 12, 2019.
11. Braunstein GD, Lewis EJ, Galvanek EG, Hamilton A, Bell WR. The nephrotic syndrome associated with secondary syphilis: an immune deposit disease. Am J Med. 1970;48:643-648.1.
12. Handoko ML, Duijvestein M, Scheepstra CG, de Fijter CW. Syphilis: a reversible cause of nephrotic syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:pii:bcr2012008279
13. Krane NK, Espenan P, Walker PD, Bergman SM, Wallin JD. Renal disease and syphilis: a report of nephrotic syndrome with minimal change disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987;9(2):176-179.
14. Bhorade MS, Carag HB, Lee HJ, Potter EV, Dunea G. Nephropathy of secondary syphilis: a clinical and pathological spectrum. JAMA. 1971;216(7):1159-1166.
15. Hunte W, al-Ghraoui F, Cohen RJ. Secondary syphilis and the nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;3(7):1351-1355.
16. Gamble CN, Reardan JB. Immunopathogenesis of syphilitic glomerulonephritis. Elution of antitreponemal antibody from glomerular immune-complex deposits. N Engl J Med. 1975;292(9):449-454.
*This article has been corrected to include a missing author.
Case Presentation. A 63-year-old male with well-controlled HIV (CD4 count 757, undetectable viral load), epilepsy, and hypertension presented to the VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS) emergency department with 1 week of bilateral leg swelling and exertional shortness of breath. He reported having no fever, cough, chest pain, pain with inspiration and orthopnea. There was no personal or family history of pulmonary embolism. He reported weight gain but was unable to quantify how much. He also reported flare up of chronic knee pain, without swelling for which he had taken up to 4 tablets of naproxen daily for several weeks. His physical examination was notable for a heart rate of 105 beats per minute and bilateral pitting edema to his knees. Laboratory testing revealed a creatinine level of 2.5 mg/dL, which was increased from a baseline of 1.0 mg/dL (Table 1), and a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 7.8 mg/mg (Table 2). A renal ultrasound showed normal-sized kidneys without hydronephrosis or obstructing renal calculi. The patient was admitted for further workup of his dyspnea and acute kidney injury.
► Jonathan Li, MD, Chief Medical Resident, VABHS and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC). Dr. William, based on the degree of proteinuria and edema, a diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome was made. How is nephrotic syndrome defined, and how is it distinguished from glomerulonephritis?
► Jeffrey William, MD, Nephrologist, BIDMC, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. The pathophysiology of nephrotic disease and glomerulonephritis are quite distinct, resulting in symptoms and systemic manifestations that only slightly overlap. Glomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation of the endothelial cells of the trilayered glomerular capillary, with a resulting active urine sediment with red blood cells, white blood cells, and casts. Nephrotic syndrome mostly affects the visceral epithelial cells of the glomerular capillary, commonly referred to as podocytes, and hence, the urine sediment in nephrotic disease is often inactive. Patients with nephrotic syndrome have nephrotic-range proteinuria (excretion of > 3.5 g per 24 h or a spot urine protein-creatinine ratio > 3.5 g in the steady state) and both hypoalbuminemia (< 3 g/dL) and peripheral edema. Lipiduria and hyperlipidemia are common findings in nephrotic syndrome but are not required for a clinical diagnosis.1 In contrast, glomerulonephritis is defined by a constellation of findings that include renal insufficiency (often indicated by an elevation in blood urea nitrogen and creatinine), hypertension, hematuria, and subnephrotic range proteinuria. In practice, patients may fulfill criteria of both nephrotic and nephritic syndromes, but the preponderance of clinical evidence often points one way or the other. In this case, nephrotic syndrome was diagnosed based on the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 7.8 mg/mg, hypoalbuminemia, and edema.
► Dr. Li. What would be your first-line workup for evaluation of the etiology of this patient’s nephrotic syndrome?
► Dr. William. Rather than memorizing a list of etiologies of nephrotic syndrome, it is essential to consider the pathophysiology of heavy proteinuria. Though the glomerular filtration barrier is extremely complex and defects in any component can cause proteinuria, disruption of the podocyte is often involved. Common disease processes that chiefly target the podocyte include minimal change disease, primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and membranous nephropathy, all by differing mechanisms. Minimal change disease and idiopathic/primary FSGS are increasingly thought to be at differing points on a spectrum of the same disease.2 Secondary FSGS, on the other hand, is a progressive disease, commonly resulting from longstanding hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity in adults. Membranous nephropathy can also be either primary or secondary. Primary membranous nephropathy is chiefly caused by a circulating IgG4 antibody to the podocyte membrane antigen PLA2R (M-type phospholipase A2 receptor), whereas secondary membranous nephropathy can be caused by a variety of systemic etiologies, including autoimmune disease (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus), certain malignancies, chronic infections (eg, hepatitis B and C), and many medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).3-5 Paraprotein deposition diseases can also cause glomerular damage leading to nephrotic-range proteinuria.
Given these potential diagnoses, a careful history should be taken to assess exposures and recent medication use. Urine sediment evaluation is essential in the evaluation of nephrotic syndrome to determine if there is an underlying nephritic process. Select serologies may be sent to look for autoimmune disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and common viral exposures like hepatitis B or C. Serum and urine protein electrophoreses would be appropriate initial tests of suspected paraprotein-related diseases. Other serologies, such as antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies or antiglomerular basement membrane antibodies, would not necessarily be indicated here given the lack of hematuria and presence of nephrotic-range proteinuria.
► Dr. Li. The initial evaluation was notable for an erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 120 (mm/h) and a weakly positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer of 1:40. The remainder of his initial workup did not reveal an etiology for his nephrotic syndrome (Table 3).
Dr. William, is there a role for starting urgent empiric steroids in nephrotic syndrome while workup is ongoing? If so, do the severity of proteinuria and/or symptoms play a role or is this determination based on something else?
► Dr. William. Edema is a primary symptom of nephrotic syndrome and can often be managed with diuretics alone. If a clear medication-mediated cause is suspected, discontinuation of this agent may result in spontaneous improvement without steroid treatment. However,in cases where an etiology is unclear and there are serious thrombotic complications requiring anticoagulation, and a renal biopsy is deemed to be too risky, then empiric steroid therapy may be necessary. Children with new-onset nephrotic syndrome are presumed to have minimal change disease, given its prevalence in this patient population, and are often given empiric steroids without obtaining a renal biopsy. However, in the adult population, a renal biopsy can typically be performed quickly and safely, with pathology results interpreted within days. In this patient, since a diagnosis was unclear and there was no contraindication to renal biopsy, a biopsy should be obtained before consideration of steroids.
► Dr. Li. Steroids were deferred in anticipation of renal biopsy, which showed stage I membranous nephropathy, suggestive of membranous lupus nephritis Class V. The deposits were strongly reactive for immunoglobuline G (IgG), IgA, and complement 1q (C1q), showed co-dominant staining for IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3, and were weakly positive for the PLA2 receptor. Focal intimal arteritis in a small interlobular vessel was seen.
Dr. William, the pathology returned suggestive of lupus nephritis. Does the overall clinical picture fit with lupus nephritis?
► Dr. William. Given the history and a rather low ANA, the diagnosis of lupus nephritis seems unlikely. The lack of IgG4 and PLA2R staining in the biopsy suggests that this membranous pattern on the biopsy is likely to be secondary to a systemic etiology, but further investigation should be pursued.
► Dr. Li. The patient was discharged after the biopsy with a planned outpatient nephrology follow-up to discuss results and treatment. He was prescribed an oral diuretic, and his symptoms improved. Several days after discharge, he developed blurry vision and was evaluated in the Ophthalmology clinic. On fundoscopy, he was found to have acute papillitis, a form of optic neuritis. As part of initial evaluation of infectious etiologies of papillitis, ophthalmology recommended testing for syphilis.
Dr. Strymish, when we are considering secondary syphilis, what is the recommended approach to diagnostic testing?
► Judith Strymish, MD, Infectious Diseases, BIDMC, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. The diagnosis of syphilis is usually made through serologic testing of blood specimens. Methods that detect the spirochete directly like dark-field smears are not readily available. Serologic tests include treponemal tests (eg, Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay [TPPA]) and nontreponemal tests (eg, rapid plasma reagin [RPR]). One needs a confirmatory test because either test is associated with false positives. Either test can be done first. Most laboratories, including those at VABHS are now performing treponemal tests first as these have become more cost-effective.6 The TPPA treponemal test was found to have a lower false negative rate in primary syphilis compared with that of nontreponemal tests.7 Nontreponemal tests can be followed for response to therapy. If a patient has a history of treated syphilis, a nontreponemal test should be sent, since the treponemal test will remain positive for life.
If there is clinical concern for neurosyphilis, cerebrospinal fluid fluorescent (CSF) treponemal antibody needs to be sampled and sent for the nontreponemal venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test. The VDRL is highly specific for neurosyphilis but not as sensitive. Cerebrospinal fluid fluorescent treponemal antibody (CSF FTA) may also be sent; it is very sensitive but not very specific for neurosyphilis.
► Dr. Li. An RPR returned positive at 1:512 (was negative 14 months prior on a routine screening test), with positive reflex TPPA (Table 4). A diagnosis of secondary syphilis was made. Dr. Strymish, at this point, what additional testing and treatment is necessary?
► Dr. Strymish. With papillitis and a very high RPR, we need to assume that he has ophthalmic syphilis. This can occur in any stage of syphilis, but his eye findings and high RPR are consistent with secondary syphilis. Ophthalmic syphilis has been on the upswing, even more than is expected with recent increases in syphilis cases.8 Ophthalmic syphilis is considered a form of neurosyphilis. A lumbar puncture and treatment for neurosyphilis is recommended.9,10
► Dr. Li. A lumbar puncture was performed, and his CSF was VDRL positive. This confirmed a diagnosis of neurosyphilis (Table 4). The patient was treated for neurosyphilis with IV penicillin. The patient shared that he had episodes of unprotected oral sexual activity within the past year and approximately 1 year ago, he came in close contact (but no sexual activity) with a person who had a rash consistent with syphilis.Dr. William, syphilis would be a potential unifying diagnosis of his renal and ophthalmologic manifestations. Is syphilis known to cause membranous nephropathy?
► Dr. William. Though it is uncommon, the nephrotic syndrome is a well-described complication of secondary syphilis.11,12 Syphilis has been shown to cause nephrotic syndrome in a variety of ways. Case reports abound linking syphilis to minimal change disease and other glomerular diseases.13,14 A case report from 1993 shows a membranous pattern of glomerular disease similar to this case.15 As a form of secondary membranous nephropathy, the immunofluorescence pattern can demonstrate staining similar to the “full house” seen in lupus nephritis (IgA, IgM, and C1q, in addition to IgG and C3).16 This explains the initial interpretation of this patient’s biopsy, as lupus nephritis would be a much more common etiology of secondary membranous nephropathy than is acute syphilis with this immunofluorescence pattern. However, the data in this case are highly suggestive of a causal relationship between secondary syphilis and membranous nephropathy.
► Dr. Li. Dr. Strymish, how should this patient be screened for syphilis reinfection, and at what intervals would you recommend?
► Dr. Strymish. He will need follow-up testing to make sure that his syphilis is effectively treated. If CSF pleocytosis was present initially, a CSF examination should be repeated every 6 months until the cell count is normal. He will also need follow-up for normalization of his RPR. Persons with HIV infection and primary or secondary syphilis should be evaluated clinically and serologically for treatment failure at 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 months after therapy according to US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines.9
His treponemal test for syphilis will likely stay positive for life. His RPR should decrease significantly with effective treatment. It makes sense to screen with RPR alone as long as he continues to have risk factors for acquiring syphilis. Routine syphilis testing is recommended for pregnant women, sexually active men who have sex with men, sexually active persons with HIV, and persons taking PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) for HIV prevention. He should be screened at least yearly for syphilis.
► Dr. Li. Over the next several months, the patient’s creatinine normalized and his proteinuria resolved. His vision recovered, and he has had no further ophthalmologic complications.
Dr. William, what is his long-term renal prognosis? Do you expect that his acute episode of membranous nephropathy will have permanent effects on his renal function?
► Dr. William. His rapid response to therapy for neurosyphilis provides evidence for this etiology of his renal dysfunction and glomerulonephritis. His long-term prognosis is quite good if the syphilis is the only reason for him to have renal disease. The renal damage is often reversible in these cases. However, given his prior extensive NSAID exposure and history of hypertension, he may be at higher risk for chronic kidney disease than an otherwise healthy patient, especially after an episode of acute kidney injury. Therefore, his renal function should continue to be monitored as an outpatient.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank this veteran for sharing his story and allowing us to learn from this unusual case for the benefit of our future patients.
*This article has been corrected to include a missing author.
Case Presentation. A 63-year-old male with well-controlled HIV (CD4 count 757, undetectable viral load), epilepsy, and hypertension presented to the VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS) emergency department with 1 week of bilateral leg swelling and exertional shortness of breath. He reported having no fever, cough, chest pain, pain with inspiration and orthopnea. There was no personal or family history of pulmonary embolism. He reported weight gain but was unable to quantify how much. He also reported flare up of chronic knee pain, without swelling for which he had taken up to 4 tablets of naproxen daily for several weeks. His physical examination was notable for a heart rate of 105 beats per minute and bilateral pitting edema to his knees. Laboratory testing revealed a creatinine level of 2.5 mg/dL, which was increased from a baseline of 1.0 mg/dL (Table 1), and a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 7.8 mg/mg (Table 2). A renal ultrasound showed normal-sized kidneys without hydronephrosis or obstructing renal calculi. The patient was admitted for further workup of his dyspnea and acute kidney injury.
► Jonathan Li, MD, Chief Medical Resident, VABHS and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC). Dr. William, based on the degree of proteinuria and edema, a diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome was made. How is nephrotic syndrome defined, and how is it distinguished from glomerulonephritis?
► Jeffrey William, MD, Nephrologist, BIDMC, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. The pathophysiology of nephrotic disease and glomerulonephritis are quite distinct, resulting in symptoms and systemic manifestations that only slightly overlap. Glomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation of the endothelial cells of the trilayered glomerular capillary, with a resulting active urine sediment with red blood cells, white blood cells, and casts. Nephrotic syndrome mostly affects the visceral epithelial cells of the glomerular capillary, commonly referred to as podocytes, and hence, the urine sediment in nephrotic disease is often inactive. Patients with nephrotic syndrome have nephrotic-range proteinuria (excretion of > 3.5 g per 24 h or a spot urine protein-creatinine ratio > 3.5 g in the steady state) and both hypoalbuminemia (< 3 g/dL) and peripheral edema. Lipiduria and hyperlipidemia are common findings in nephrotic syndrome but are not required for a clinical diagnosis.1 In contrast, glomerulonephritis is defined by a constellation of findings that include renal insufficiency (often indicated by an elevation in blood urea nitrogen and creatinine), hypertension, hematuria, and subnephrotic range proteinuria. In practice, patients may fulfill criteria of both nephrotic and nephritic syndromes, but the preponderance of clinical evidence often points one way or the other. In this case, nephrotic syndrome was diagnosed based on the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio of 7.8 mg/mg, hypoalbuminemia, and edema.
► Dr. Li. What would be your first-line workup for evaluation of the etiology of this patient’s nephrotic syndrome?
► Dr. William. Rather than memorizing a list of etiologies of nephrotic syndrome, it is essential to consider the pathophysiology of heavy proteinuria. Though the glomerular filtration barrier is extremely complex and defects in any component can cause proteinuria, disruption of the podocyte is often involved. Common disease processes that chiefly target the podocyte include minimal change disease, primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and membranous nephropathy, all by differing mechanisms. Minimal change disease and idiopathic/primary FSGS are increasingly thought to be at differing points on a spectrum of the same disease.2 Secondary FSGS, on the other hand, is a progressive disease, commonly resulting from longstanding hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity in adults. Membranous nephropathy can also be either primary or secondary. Primary membranous nephropathy is chiefly caused by a circulating IgG4 antibody to the podocyte membrane antigen PLA2R (M-type phospholipase A2 receptor), whereas secondary membranous nephropathy can be caused by a variety of systemic etiologies, including autoimmune disease (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus), certain malignancies, chronic infections (eg, hepatitis B and C), and many medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).3-5 Paraprotein deposition diseases can also cause glomerular damage leading to nephrotic-range proteinuria.
Given these potential diagnoses, a careful history should be taken to assess exposures and recent medication use. Urine sediment evaluation is essential in the evaluation of nephrotic syndrome to determine if there is an underlying nephritic process. Select serologies may be sent to look for autoimmune disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and common viral exposures like hepatitis B or C. Serum and urine protein electrophoreses would be appropriate initial tests of suspected paraprotein-related diseases. Other serologies, such as antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies or antiglomerular basement membrane antibodies, would not necessarily be indicated here given the lack of hematuria and presence of nephrotic-range proteinuria.
► Dr. Li. The initial evaluation was notable for an erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 120 (mm/h) and a weakly positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer of 1:40. The remainder of his initial workup did not reveal an etiology for his nephrotic syndrome (Table 3).
Dr. William, is there a role for starting urgent empiric steroids in nephrotic syndrome while workup is ongoing? If so, do the severity of proteinuria and/or symptoms play a role or is this determination based on something else?
► Dr. William. Edema is a primary symptom of nephrotic syndrome and can often be managed with diuretics alone. If a clear medication-mediated cause is suspected, discontinuation of this agent may result in spontaneous improvement without steroid treatment. However,in cases where an etiology is unclear and there are serious thrombotic complications requiring anticoagulation, and a renal biopsy is deemed to be too risky, then empiric steroid therapy may be necessary. Children with new-onset nephrotic syndrome are presumed to have minimal change disease, given its prevalence in this patient population, and are often given empiric steroids without obtaining a renal biopsy. However, in the adult population, a renal biopsy can typically be performed quickly and safely, with pathology results interpreted within days. In this patient, since a diagnosis was unclear and there was no contraindication to renal biopsy, a biopsy should be obtained before consideration of steroids.
► Dr. Li. Steroids were deferred in anticipation of renal biopsy, which showed stage I membranous nephropathy, suggestive of membranous lupus nephritis Class V. The deposits were strongly reactive for immunoglobuline G (IgG), IgA, and complement 1q (C1q), showed co-dominant staining for IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3, and were weakly positive for the PLA2 receptor. Focal intimal arteritis in a small interlobular vessel was seen.
Dr. William, the pathology returned suggestive of lupus nephritis. Does the overall clinical picture fit with lupus nephritis?
► Dr. William. Given the history and a rather low ANA, the diagnosis of lupus nephritis seems unlikely. The lack of IgG4 and PLA2R staining in the biopsy suggests that this membranous pattern on the biopsy is likely to be secondary to a systemic etiology, but further investigation should be pursued.
► Dr. Li. The patient was discharged after the biopsy with a planned outpatient nephrology follow-up to discuss results and treatment. He was prescribed an oral diuretic, and his symptoms improved. Several days after discharge, he developed blurry vision and was evaluated in the Ophthalmology clinic. On fundoscopy, he was found to have acute papillitis, a form of optic neuritis. As part of initial evaluation of infectious etiologies of papillitis, ophthalmology recommended testing for syphilis.
Dr. Strymish, when we are considering secondary syphilis, what is the recommended approach to diagnostic testing?
► Judith Strymish, MD, Infectious Diseases, BIDMC, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. The diagnosis of syphilis is usually made through serologic testing of blood specimens. Methods that detect the spirochete directly like dark-field smears are not readily available. Serologic tests include treponemal tests (eg, Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay [TPPA]) and nontreponemal tests (eg, rapid plasma reagin [RPR]). One needs a confirmatory test because either test is associated with false positives. Either test can be done first. Most laboratories, including those at VABHS are now performing treponemal tests first as these have become more cost-effective.6 The TPPA treponemal test was found to have a lower false negative rate in primary syphilis compared with that of nontreponemal tests.7 Nontreponemal tests can be followed for response to therapy. If a patient has a history of treated syphilis, a nontreponemal test should be sent, since the treponemal test will remain positive for life.
If there is clinical concern for neurosyphilis, cerebrospinal fluid fluorescent (CSF) treponemal antibody needs to be sampled and sent for the nontreponemal venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test. The VDRL is highly specific for neurosyphilis but not as sensitive. Cerebrospinal fluid fluorescent treponemal antibody (CSF FTA) may also be sent; it is very sensitive but not very specific for neurosyphilis.
► Dr. Li. An RPR returned positive at 1:512 (was negative 14 months prior on a routine screening test), with positive reflex TPPA (Table 4). A diagnosis of secondary syphilis was made. Dr. Strymish, at this point, what additional testing and treatment is necessary?
► Dr. Strymish. With papillitis and a very high RPR, we need to assume that he has ophthalmic syphilis. This can occur in any stage of syphilis, but his eye findings and high RPR are consistent with secondary syphilis. Ophthalmic syphilis has been on the upswing, even more than is expected with recent increases in syphilis cases.8 Ophthalmic syphilis is considered a form of neurosyphilis. A lumbar puncture and treatment for neurosyphilis is recommended.9,10
► Dr. Li. A lumbar puncture was performed, and his CSF was VDRL positive. This confirmed a diagnosis of neurosyphilis (Table 4). The patient was treated for neurosyphilis with IV penicillin. The patient shared that he had episodes of unprotected oral sexual activity within the past year and approximately 1 year ago, he came in close contact (but no sexual activity) with a person who had a rash consistent with syphilis.Dr. William, syphilis would be a potential unifying diagnosis of his renal and ophthalmologic manifestations. Is syphilis known to cause membranous nephropathy?
► Dr. William. Though it is uncommon, the nephrotic syndrome is a well-described complication of secondary syphilis.11,12 Syphilis has been shown to cause nephrotic syndrome in a variety of ways. Case reports abound linking syphilis to minimal change disease and other glomerular diseases.13,14 A case report from 1993 shows a membranous pattern of glomerular disease similar to this case.15 As a form of secondary membranous nephropathy, the immunofluorescence pattern can demonstrate staining similar to the “full house” seen in lupus nephritis (IgA, IgM, and C1q, in addition to IgG and C3).16 This explains the initial interpretation of this patient’s biopsy, as lupus nephritis would be a much more common etiology of secondary membranous nephropathy than is acute syphilis with this immunofluorescence pattern. However, the data in this case are highly suggestive of a causal relationship between secondary syphilis and membranous nephropathy.
► Dr. Li. Dr. Strymish, how should this patient be screened for syphilis reinfection, and at what intervals would you recommend?
► Dr. Strymish. He will need follow-up testing to make sure that his syphilis is effectively treated. If CSF pleocytosis was present initially, a CSF examination should be repeated every 6 months until the cell count is normal. He will also need follow-up for normalization of his RPR. Persons with HIV infection and primary or secondary syphilis should be evaluated clinically and serologically for treatment failure at 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 months after therapy according to US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines.9
His treponemal test for syphilis will likely stay positive for life. His RPR should decrease significantly with effective treatment. It makes sense to screen with RPR alone as long as he continues to have risk factors for acquiring syphilis. Routine syphilis testing is recommended for pregnant women, sexually active men who have sex with men, sexually active persons with HIV, and persons taking PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) for HIV prevention. He should be screened at least yearly for syphilis.
► Dr. Li. Over the next several months, the patient’s creatinine normalized and his proteinuria resolved. His vision recovered, and he has had no further ophthalmologic complications.
Dr. William, what is his long-term renal prognosis? Do you expect that his acute episode of membranous nephropathy will have permanent effects on his renal function?
► Dr. William. His rapid response to therapy for neurosyphilis provides evidence for this etiology of his renal dysfunction and glomerulonephritis. His long-term prognosis is quite good if the syphilis is the only reason for him to have renal disease. The renal damage is often reversible in these cases. However, given his prior extensive NSAID exposure and history of hypertension, he may be at higher risk for chronic kidney disease than an otherwise healthy patient, especially after an episode of acute kidney injury. Therefore, his renal function should continue to be monitored as an outpatient.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank this veteran for sharing his story and allowing us to learn from this unusual case for the benefit of our future patients.
1. Rennke H, Denker BM. Renal Pathophysiology: The Essentials. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014.
2. Maas RJ, Deegens JK, Smeets B, Moeller MJ, Wetzels JF. Minimal change disease and idiopathic FSGS: manifestations of the same disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(12):768-776.
3. Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):11-21.
4. Rennke HG. Secondary membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1995;47(2):643-656.
5. Nawaz FA, Larsen CP, Troxell ML. Membranous nephropathy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(5):1012-1017.
6. Pillay A. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Syphilis Summit—Diagnostics and laboratory issues. Sex Transm Dis. 2018;45(9S)(suppl 1):S13-S16.
7. Levett PN, Fonseca K, Tsang RS, et al. Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network laboratory guidelines for the use of serological tests (excluding point-of-care tests) for the diagnosis of syphilis in Canada. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2015;26(suppl A):6A-12A.
8. Oliver SE, Aubin M, Atwell L, et al. Ocular syphilis—eight jurisdictions, United States, 2014-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(43):1185-1188.
9. Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recommendations and Reports 2015;64(RR3):1-137. [Erratum in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(33):924.]
10. US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical advisory: ocular syphilis in the United States. https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/clinicaladvisoryos2015.htm. Updated March 24, 2016. Accessed August 12, 2019.
11. Braunstein GD, Lewis EJ, Galvanek EG, Hamilton A, Bell WR. The nephrotic syndrome associated with secondary syphilis: an immune deposit disease. Am J Med. 1970;48:643-648.1.
12. Handoko ML, Duijvestein M, Scheepstra CG, de Fijter CW. Syphilis: a reversible cause of nephrotic syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:pii:bcr2012008279
13. Krane NK, Espenan P, Walker PD, Bergman SM, Wallin JD. Renal disease and syphilis: a report of nephrotic syndrome with minimal change disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987;9(2):176-179.
14. Bhorade MS, Carag HB, Lee HJ, Potter EV, Dunea G. Nephropathy of secondary syphilis: a clinical and pathological spectrum. JAMA. 1971;216(7):1159-1166.
15. Hunte W, al-Ghraoui F, Cohen RJ. Secondary syphilis and the nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;3(7):1351-1355.
16. Gamble CN, Reardan JB. Immunopathogenesis of syphilitic glomerulonephritis. Elution of antitreponemal antibody from glomerular immune-complex deposits. N Engl J Med. 1975;292(9):449-454.
1. Rennke H, Denker BM. Renal Pathophysiology: The Essentials. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014.
2. Maas RJ, Deegens JK, Smeets B, Moeller MJ, Wetzels JF. Minimal change disease and idiopathic FSGS: manifestations of the same disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(12):768-776.
3. Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):11-21.
4. Rennke HG. Secondary membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1995;47(2):643-656.
5. Nawaz FA, Larsen CP, Troxell ML. Membranous nephropathy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(5):1012-1017.
6. Pillay A. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Syphilis Summit—Diagnostics and laboratory issues. Sex Transm Dis. 2018;45(9S)(suppl 1):S13-S16.
7. Levett PN, Fonseca K, Tsang RS, et al. Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network laboratory guidelines for the use of serological tests (excluding point-of-care tests) for the diagnosis of syphilis in Canada. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2015;26(suppl A):6A-12A.
8. Oliver SE, Aubin M, Atwell L, et al. Ocular syphilis—eight jurisdictions, United States, 2014-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(43):1185-1188.
9. Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recommendations and Reports 2015;64(RR3):1-137. [Erratum in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(33):924.]
10. US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical advisory: ocular syphilis in the United States. https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/clinicaladvisoryos2015.htm. Updated March 24, 2016. Accessed August 12, 2019.
11. Braunstein GD, Lewis EJ, Galvanek EG, Hamilton A, Bell WR. The nephrotic syndrome associated with secondary syphilis: an immune deposit disease. Am J Med. 1970;48:643-648.1.
12. Handoko ML, Duijvestein M, Scheepstra CG, de Fijter CW. Syphilis: a reversible cause of nephrotic syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:pii:bcr2012008279
13. Krane NK, Espenan P, Walker PD, Bergman SM, Wallin JD. Renal disease and syphilis: a report of nephrotic syndrome with minimal change disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987;9(2):176-179.
14. Bhorade MS, Carag HB, Lee HJ, Potter EV, Dunea G. Nephropathy of secondary syphilis: a clinical and pathological spectrum. JAMA. 1971;216(7):1159-1166.
15. Hunte W, al-Ghraoui F, Cohen RJ. Secondary syphilis and the nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;3(7):1351-1355.
16. Gamble CN, Reardan JB. Immunopathogenesis of syphilitic glomerulonephritis. Elution of antitreponemal antibody from glomerular immune-complex deposits. N Engl J Med. 1975;292(9):449-454.
Multispecialty Opioid Risk Reduction Program Targeting Chronic Pain and Addiction Management in Veterans
Chronic pain significantly affects 100 million Americans.1,2 Pain accounts for $560 to $635 billion in annual financial costs to society, including health care costs and loss of productivity (ie, days missed from work, hours of work lost, and lower wages).2,3 Although pain prevalence exceeds other chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, cancer, and heart disease, it lacks a sufficient body of evidence-based research and guidelines on the underlying mechanisms, valid methods of assessment, and comparative effectiveness of treatments to effectively implement into clinical practice.2,4 Prevention and treatment of pain are often delayed, inaccessible, or inadequate.2 Primary care providers (PCPs) are most often sought for pain management and treat about 52% of chronic pain patients.2,3,5 Veterans are especially vulnerable to chronic pain and are at risk for inadequate treatment.2
Background
There is an epidemic of drug abuse and mortality from opioid prescription medication.6 In the US, rates of overdose deaths from prescription opioids were 6.1 per 100,000 for men and 4.2 per 100,000 for women in 2017. Opioids were involved in 47,600 overdose deaths in 2017, accounting for 67.8% of all drug overdose deaths.7
A large number of patients on long-term opioids have preexisting substance use disorders and/or psychiatric disease, further complicating chronic pain management.8-10 Prescription opioid use has been the precursor for about 80% of people who are now heroin addicts.11 Iatrogenic addiction from prescription medications isn’t easily captured by standard addiction criteria. Consequently, in patients who are on opioid therapy for prolonged periods, separating complex opioid dependence from addiction is difficult.12 Improved addiction screening and risk mitigation strategies are needed along with aggressive treatment monitoring to curb the opioid epidemic.
Opioid Management in Primary Care
The majority of opioid medications are prescribed by PCPs, which is magnified in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system due to the high prevalence of service-related injuries.3,13 The VA is at the forefront of addressing the complexities of opioid addiction through several initiatives.14 The ability to offer the frequent visits needed to safely manage patients prescribed opioids and the integration of mental health and addiction treatment are often lacking in non-VA primary care clinics. Therefore, a key to solving the opioid crisis is developing these capabilities so they can be delivered within the primary care setting. There is substantial evidence in support of nonopioid alternatives to chronic pain management, including other pharmacologic approaches, exercise, physical therapy, acupuncture, weight loss, smoking cessation, chiropractic care, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other integrative health modalities.
A 2009 VA directive mandated the development of a comprehensive, integrated, systemwide approach to pain management.15 The VA Stepped-Care Biopsychosocial Model for Pain Management is dependent on timely access to secondary consultation from pain medicine, behavioral health, physical medicine, and other specialty consultation.15
History of VHA SCAN-ECHO Model
The Specialty Care Access Network–Extension for Community Health Outcomes (SCAN-ECHO) is a Veterans Health Administration (VHA) adaptation of a program that originated at the University of Mexico.16,17 The SCAN-ECHO model uses a multisite videoconferencing network to provide specialty care consultations to PCPs and patient aligned care teams (PACTs). During the 60- to 90-minute weekly sessions, case presentations are analyzed in real time so that over time, the PCPs gain knowledge, competency, and confidence in learning how to handle complex chronic conditions.
Since its implementation, the SCAN-ECHO program has been adopted across the VHA in a variety of specialties. One program, the SCAN-ECHO for Pain Management (SCAN-ECHO-PM) was implemented in 7 VHA networks in 31 states, spanning 47 medical centers and 148 community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs).18 The SCAN-ECHO-PM program successfully conducted 257 multidisciplinary pain consultations between 2011 and 2013, resulting in increased initiation of nonopioid medications.18
The aim of this article is to describe the implementation of a multicomponent primary care-based pain clinic with a fully integrated mental health service and addiction service at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System (NF/SGVHS). A practiced-based intervention of the biopsychosocial model with robust patient engagement has guided the development of the NF/SGVHS pain clinic (Figure 1).4,19
Pain CLinic
NF/SGVHS comprises the Malcom Randall and Lake City VA medical centers (VAMCs) hospitals, 3 satellite outpatient clinics, and 8 CBOCs. Spanning 33 counties in North Florida and 19 counties in South Georgia, the NF/SGVHS serves more than 140,000 patients. In 2010, the Malcom Randall VAMC established a multidisciplinary primary care pain clinic to manage veterans at high-risk for noncancer chronic pain and addiction. The noncancer pain policy was revised after garnering support from stakeholders who treat chronic pain, including the chiefs of psychiatry, rehabilitation medicine, neurosurgery, psychology, interventional pain, pharmacy, nursing, addiction medicine, and primary care. The clinic is staffed by primary care physicians trained in internal medicine and family medicine and is structured with 1-hour first visits, and 30-minute follow-up visits to allow enough time for comprehensive evaluation while meeting the needs for close follow-up support.
All physicians in the clinic have buprenorphine prescribing credentials to aid in the management of opioid addiction, as some patients feel more comfortable receiving addiction treatment in a primary care setting. The multimodal care model consists of several services that include addiction psychiatrists, interventional pain specialists, pain psychologists, and pain pharmacologists who coordinate the care to the veterans. The addiction psychiatrists offer a full range of services with inpatient residential and outpatient programs. Through recurring meetings with primary care pain clinic staff, the addiction psychiatrists are available to discuss use of buprenorphine and arrange follow-up for patients with complex pain addiction. There is ongoing collaboration to develop the best care plan that meets the patient’s needs for chronic pain, addiction, and/or mental health issues. The interventional pain service has 3 fellowship-trained pain care providers who deliver comprehensive evaluation, pharmacologic recommendations, and a full range of interventional and complementary therapies with an emphasis on objective functional improvement. Pain care providers offer alternatives to patients who are being weaned from opioids and support the multidisciplinary patient engagement model.
The pain psychology program, established in 2011, delivers CBT to 5 onsite locations and 5 telehealth locations. The service includes an advanced CBT program and a couples CBT program. The pharmacy pain fellowship program provides staff for an outpatient e-consult pain management service and an inpatient pharmacy consult service. Harnessing pain specialty pharmacists, the pharmacy service addresses pharmacokinetic issues, urine drug screen (UDS) results, opioid tapering and discharge planning for pain, addiction and mental health needs. The NF/SGVHS Primary Care Pain Clinic was established to support PCPs who did not feel comfortable managing chronic pain patients. These patients were typically on high-dose opioid therapy (> 100-mg morphine equivalent daily doses [MEDDs]); patients with a history of opioid addiction; patients with an addiction to opioids combined with benzodiazepines; and patients with comorbid medical issues (eg, sleep apnea), which complicated their management. The process of addressing opioid safety in these complex pain patients can be labor intensive and generally cannot be accomplished in a brief visit in a primary care setting where many other medical problems often need to be addressed.
Most patients on high-dose opioids are fearful of any changes in their medications. The difficult conversation regarding opioid safety is a lengthy one and frequently will occur over multiple visits. In addition, safely tapering opioids requires frequent follow-up to provide psychological support and to address withdrawal and mental health issues that may arise. As opioids are tapered, the clinic reinforces improved pain care through a multimodal biopsychosocial model. All veterans receiving pain care outside the VA are monitored annually to assure they are receiving evidence-based pain care as defined by the biopsychosocial model.
Education
Since 2011, the NF/SGVHS SCAN-ECHO pain and addiction educational forum has created > 50 hours of approved annual continuing medical education (CME) on pain management and addiction for PCPs. Initially, the 1-hour weekly educational audioconferences presented a pain management case along with related topics and involved specialists from interventional pain, physical therapy, psychiatry, nursing, neurology, and psychology departments. In 2013, in conjunction with the VA SCAN-ECHO program of Hunter Holmes McGuire VAMC in Richmond, Virginia, and Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, the audioconference was expanded to 2 days each week with additional topics on addiction management. Residency and fellowship rotations were developed that specifically targeted fellows from psychiatry, pharmacology, and interventional pain departments.
Currently, an 8-session pain school is delivered onsite and at 7 telehealth locations. The school is a collaborative effort involving interventional pain, psychology, pharmacy, nutrition, and the primary care pain clinic staff. As the cornerstone of the program, the pain school stresses the biopsychosocial patient engagement model.
Program Evaluation
The VA is equipped with multiple telehealth service networks that allow for the delivery of programs, such as the pain school, a pain psychology program, and a yoga program, onsite or offsite. The VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) manages electronic health records, allowing for rapid chart review and e-consults. The NF/SGVHS Pain Management Program provides about 1500 e-consults yearly. The CPRS includes templates with pain metrics to help PCPs deliver pain care more efficiently and evaluate performance measures. This system also allows for the capture of data to track improvements in the care of the veterans served.
From 2012 to 2017, more than 5000 NF/SGVHS patients were weaned from opioids. Overall, there was an 87% reduction in patients receiving opioids ( ≥ 100-mg MEDDs) within the NF/SGVHS, which is significantly more than the 49% seen nationally across the VHA (Figure 2). Percent reduction was calculated by taking the difference in number of patients receiving opioids in 2012 and 2017, dividing by the number of patients receiving opioids in 2012 and multiplying by 100. The largest proportion of opioid dose reductions for NF/SGVHS and VHA patients, respectively, were seen in 300-mg to 399-mg MEDDs (95% vs 67%, respectively); followed by ≥ 400-mg MEDDs (94% vs 71%, respectively); 200-mg to 299-mg MEDDs (91% vs 58%, respectively); and 100-mg to 199-mg MEDDs (84% vs 40%, respectively). When examining NF/SGVHS trends over time, there has been a consistent decline in patients prescribed opioids (18 223 in 2012 compared with 12 877 in 2017) with similar trends in benzodiazepine-opioid combination therapy (2694 in 2012 compared with 833 in 2017) (Figure 3).
Similar declines are seen when patients are stratified by the MEDD (Figure 4). From 2012 to 2017, 92% of the patients were successfully tapered off doses ≥ 400-mg MEDD (2012, n = 72; 2017, n = 6), and tapered off 300-mg to 399-mg MEDD (2012, n = 107; 2017, n = 5); 95% were tapered off 200-mg to 299-mg MEDD (2012, n = 262; 2017, n = 22); and 86% were tapered off 100-mg to 199-mg MEDD (2012, n = 876; 2017; n = 127).
Conclusion
Successful integration of primary care with mental health and addiction services is paramount to aggressively taper patients with chronic pain from opioids. There is evidence that drug dependence and chronic pain should be treated like other chronic illness.20 Both chronic pain and addiction can be treated with a multidimensional self-management approach. In view of the high incidence of mental health and addiction associated with opioid use, it makes sense that an integrated, 1-stop pain and addiction clinic that understands and addresses both issues is more likely to improve patient outcomes.
Acknowledgments
This material is the result of work supported by the resources and facilities at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System, Geriatric Research Education Clinical Center in Gainesville, Florida.
1. Dueñas M, Ojeda B, Salazar A, Mico JA, Failde I. A review of chronic pain impact on patients, their social environment and the health care system. J Pain Res. 2016;9:457-467.
2. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine; 2011.
3. Breuer B, Cruciani R, Portenoy RK. Pain management by primary care physicians, pain physicians, chiropractors, and acupuncturists: a national survey. South Med J. 2010;103(8):738-747.
4. Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol. 2014;69(2):119-130.
5. Meghani SH, Polomano RC, Tait RC, Vallerand AH, Anderson KO, Gallagher RM. Advancing a national agenda to eliminate disparities in pain care: directions for health policy, education, practice, and research. Pain Med. 2012;13(1):5-28.
6. McHugh RK, Nielsen S, Weiss RD. Prescription drug abuse: from epidemiology to public policy. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;48(1):1-7.
7. Scholl L, Seth P, Kariisa M, Wilson N, Baldwin G. Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths-United States, 2013-2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(5152):1419-1427.
8. Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8.
9. Højsted J, Sjøgren P. Addiction to opioids in chronic pain patients: a literature review. Eur J Pain. 2007;11(5):490-518.
10. Seal KH, Shi Y, Cohen G, et al. Association of mental health disorders with prescription opioids and high-risk opioid use in US veterans of Iraq and Afghanistan. JAMA. 2012;307(9):940-947.
11. Kolodny A, Courtwright DT, Hwang CS, et al. The prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:559-574.
12. Ballantyne JC, Sullivan MD, Kolodny A. Opioid dependence vs addiction: a distinction without a difference? Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(17):1342-1343.
13. Levy B, Paulozzi L, Mack KA, Jones CM. Trends in opioid analgesic-prescribing rates by specialty, U.S., 2007-2012. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49(3):409-413.
14. Gellad WF, Good CB, Shulkin DJ. Addressing the opioid epidemic in the United States: lessons from the Department of Veterans Affairs. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(5):611-612.
15. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veteran Health Administration Directive 2009-053, Pain Management. https://www.va.gov/painmanagement/docs/vha09paindirective.pdf. Published October 28, 2009. Accessed August 19, 2019.
16. Arora S, Geppert CM, Kalishman S, et al. Academic health center management of chronic diseases through knowledge networks: Project ECHO. Acad Med. 2007;82(2):154-160.
17. Kirsh S, Su GL, Sales A, Jain R. Access to outpatient specialty care: solutions from an integrated health care system. Am J Med Qual. 2015;30(1):88-90.
18. Frank JW, Carey EP, Fagan KM, et al. Evaluation of a telementoring intervention for pain management in the Veterans Health Administration. Pain Med. 2015;16(6):1090-1100.
19. Fillingim RB. Individual differences in pain: understanding the mosaic that makes pain personal. Pain. 2017;158 (suppl 1):S11-S18.
20. McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O’Brien CP, Kleber HD. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA. 2000;284(13):1689-1695.
Chronic pain significantly affects 100 million Americans.1,2 Pain accounts for $560 to $635 billion in annual financial costs to society, including health care costs and loss of productivity (ie, days missed from work, hours of work lost, and lower wages).2,3 Although pain prevalence exceeds other chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, cancer, and heart disease, it lacks a sufficient body of evidence-based research and guidelines on the underlying mechanisms, valid methods of assessment, and comparative effectiveness of treatments to effectively implement into clinical practice.2,4 Prevention and treatment of pain are often delayed, inaccessible, or inadequate.2 Primary care providers (PCPs) are most often sought for pain management and treat about 52% of chronic pain patients.2,3,5 Veterans are especially vulnerable to chronic pain and are at risk for inadequate treatment.2
Background
There is an epidemic of drug abuse and mortality from opioid prescription medication.6 In the US, rates of overdose deaths from prescription opioids were 6.1 per 100,000 for men and 4.2 per 100,000 for women in 2017. Opioids were involved in 47,600 overdose deaths in 2017, accounting for 67.8% of all drug overdose deaths.7
A large number of patients on long-term opioids have preexisting substance use disorders and/or psychiatric disease, further complicating chronic pain management.8-10 Prescription opioid use has been the precursor for about 80% of people who are now heroin addicts.11 Iatrogenic addiction from prescription medications isn’t easily captured by standard addiction criteria. Consequently, in patients who are on opioid therapy for prolonged periods, separating complex opioid dependence from addiction is difficult.12 Improved addiction screening and risk mitigation strategies are needed along with aggressive treatment monitoring to curb the opioid epidemic.
Opioid Management in Primary Care
The majority of opioid medications are prescribed by PCPs, which is magnified in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system due to the high prevalence of service-related injuries.3,13 The VA is at the forefront of addressing the complexities of opioid addiction through several initiatives.14 The ability to offer the frequent visits needed to safely manage patients prescribed opioids and the integration of mental health and addiction treatment are often lacking in non-VA primary care clinics. Therefore, a key to solving the opioid crisis is developing these capabilities so they can be delivered within the primary care setting. There is substantial evidence in support of nonopioid alternatives to chronic pain management, including other pharmacologic approaches, exercise, physical therapy, acupuncture, weight loss, smoking cessation, chiropractic care, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other integrative health modalities.
A 2009 VA directive mandated the development of a comprehensive, integrated, systemwide approach to pain management.15 The VA Stepped-Care Biopsychosocial Model for Pain Management is dependent on timely access to secondary consultation from pain medicine, behavioral health, physical medicine, and other specialty consultation.15
History of VHA SCAN-ECHO Model
The Specialty Care Access Network–Extension for Community Health Outcomes (SCAN-ECHO) is a Veterans Health Administration (VHA) adaptation of a program that originated at the University of Mexico.16,17 The SCAN-ECHO model uses a multisite videoconferencing network to provide specialty care consultations to PCPs and patient aligned care teams (PACTs). During the 60- to 90-minute weekly sessions, case presentations are analyzed in real time so that over time, the PCPs gain knowledge, competency, and confidence in learning how to handle complex chronic conditions.
Since its implementation, the SCAN-ECHO program has been adopted across the VHA in a variety of specialties. One program, the SCAN-ECHO for Pain Management (SCAN-ECHO-PM) was implemented in 7 VHA networks in 31 states, spanning 47 medical centers and 148 community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs).18 The SCAN-ECHO-PM program successfully conducted 257 multidisciplinary pain consultations between 2011 and 2013, resulting in increased initiation of nonopioid medications.18
The aim of this article is to describe the implementation of a multicomponent primary care-based pain clinic with a fully integrated mental health service and addiction service at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System (NF/SGVHS). A practiced-based intervention of the biopsychosocial model with robust patient engagement has guided the development of the NF/SGVHS pain clinic (Figure 1).4,19
Pain CLinic
NF/SGVHS comprises the Malcom Randall and Lake City VA medical centers (VAMCs) hospitals, 3 satellite outpatient clinics, and 8 CBOCs. Spanning 33 counties in North Florida and 19 counties in South Georgia, the NF/SGVHS serves more than 140,000 patients. In 2010, the Malcom Randall VAMC established a multidisciplinary primary care pain clinic to manage veterans at high-risk for noncancer chronic pain and addiction. The noncancer pain policy was revised after garnering support from stakeholders who treat chronic pain, including the chiefs of psychiatry, rehabilitation medicine, neurosurgery, psychology, interventional pain, pharmacy, nursing, addiction medicine, and primary care. The clinic is staffed by primary care physicians trained in internal medicine and family medicine and is structured with 1-hour first visits, and 30-minute follow-up visits to allow enough time for comprehensive evaluation while meeting the needs for close follow-up support.
All physicians in the clinic have buprenorphine prescribing credentials to aid in the management of opioid addiction, as some patients feel more comfortable receiving addiction treatment in a primary care setting. The multimodal care model consists of several services that include addiction psychiatrists, interventional pain specialists, pain psychologists, and pain pharmacologists who coordinate the care to the veterans. The addiction psychiatrists offer a full range of services with inpatient residential and outpatient programs. Through recurring meetings with primary care pain clinic staff, the addiction psychiatrists are available to discuss use of buprenorphine and arrange follow-up for patients with complex pain addiction. There is ongoing collaboration to develop the best care plan that meets the patient’s needs for chronic pain, addiction, and/or mental health issues. The interventional pain service has 3 fellowship-trained pain care providers who deliver comprehensive evaluation, pharmacologic recommendations, and a full range of interventional and complementary therapies with an emphasis on objective functional improvement. Pain care providers offer alternatives to patients who are being weaned from opioids and support the multidisciplinary patient engagement model.
The pain psychology program, established in 2011, delivers CBT to 5 onsite locations and 5 telehealth locations. The service includes an advanced CBT program and a couples CBT program. The pharmacy pain fellowship program provides staff for an outpatient e-consult pain management service and an inpatient pharmacy consult service. Harnessing pain specialty pharmacists, the pharmacy service addresses pharmacokinetic issues, urine drug screen (UDS) results, opioid tapering and discharge planning for pain, addiction and mental health needs. The NF/SGVHS Primary Care Pain Clinic was established to support PCPs who did not feel comfortable managing chronic pain patients. These patients were typically on high-dose opioid therapy (> 100-mg morphine equivalent daily doses [MEDDs]); patients with a history of opioid addiction; patients with an addiction to opioids combined with benzodiazepines; and patients with comorbid medical issues (eg, sleep apnea), which complicated their management. The process of addressing opioid safety in these complex pain patients can be labor intensive and generally cannot be accomplished in a brief visit in a primary care setting where many other medical problems often need to be addressed.
Most patients on high-dose opioids are fearful of any changes in their medications. The difficult conversation regarding opioid safety is a lengthy one and frequently will occur over multiple visits. In addition, safely tapering opioids requires frequent follow-up to provide psychological support and to address withdrawal and mental health issues that may arise. As opioids are tapered, the clinic reinforces improved pain care through a multimodal biopsychosocial model. All veterans receiving pain care outside the VA are monitored annually to assure they are receiving evidence-based pain care as defined by the biopsychosocial model.
Education
Since 2011, the NF/SGVHS SCAN-ECHO pain and addiction educational forum has created > 50 hours of approved annual continuing medical education (CME) on pain management and addiction for PCPs. Initially, the 1-hour weekly educational audioconferences presented a pain management case along with related topics and involved specialists from interventional pain, physical therapy, psychiatry, nursing, neurology, and psychology departments. In 2013, in conjunction with the VA SCAN-ECHO program of Hunter Holmes McGuire VAMC in Richmond, Virginia, and Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, the audioconference was expanded to 2 days each week with additional topics on addiction management. Residency and fellowship rotations were developed that specifically targeted fellows from psychiatry, pharmacology, and interventional pain departments.
Currently, an 8-session pain school is delivered onsite and at 7 telehealth locations. The school is a collaborative effort involving interventional pain, psychology, pharmacy, nutrition, and the primary care pain clinic staff. As the cornerstone of the program, the pain school stresses the biopsychosocial patient engagement model.
Program Evaluation
The VA is equipped with multiple telehealth service networks that allow for the delivery of programs, such as the pain school, a pain psychology program, and a yoga program, onsite or offsite. The VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) manages electronic health records, allowing for rapid chart review and e-consults. The NF/SGVHS Pain Management Program provides about 1500 e-consults yearly. The CPRS includes templates with pain metrics to help PCPs deliver pain care more efficiently and evaluate performance measures. This system also allows for the capture of data to track improvements in the care of the veterans served.
From 2012 to 2017, more than 5000 NF/SGVHS patients were weaned from opioids. Overall, there was an 87% reduction in patients receiving opioids ( ≥ 100-mg MEDDs) within the NF/SGVHS, which is significantly more than the 49% seen nationally across the VHA (Figure 2). Percent reduction was calculated by taking the difference in number of patients receiving opioids in 2012 and 2017, dividing by the number of patients receiving opioids in 2012 and multiplying by 100. The largest proportion of opioid dose reductions for NF/SGVHS and VHA patients, respectively, were seen in 300-mg to 399-mg MEDDs (95% vs 67%, respectively); followed by ≥ 400-mg MEDDs (94% vs 71%, respectively); 200-mg to 299-mg MEDDs (91% vs 58%, respectively); and 100-mg to 199-mg MEDDs (84% vs 40%, respectively). When examining NF/SGVHS trends over time, there has been a consistent decline in patients prescribed opioids (18 223 in 2012 compared with 12 877 in 2017) with similar trends in benzodiazepine-opioid combination therapy (2694 in 2012 compared with 833 in 2017) (Figure 3).
Similar declines are seen when patients are stratified by the MEDD (Figure 4). From 2012 to 2017, 92% of the patients were successfully tapered off doses ≥ 400-mg MEDD (2012, n = 72; 2017, n = 6), and tapered off 300-mg to 399-mg MEDD (2012, n = 107; 2017, n = 5); 95% were tapered off 200-mg to 299-mg MEDD (2012, n = 262; 2017, n = 22); and 86% were tapered off 100-mg to 199-mg MEDD (2012, n = 876; 2017; n = 127).
Conclusion
Successful integration of primary care with mental health and addiction services is paramount to aggressively taper patients with chronic pain from opioids. There is evidence that drug dependence and chronic pain should be treated like other chronic illness.20 Both chronic pain and addiction can be treated with a multidimensional self-management approach. In view of the high incidence of mental health and addiction associated with opioid use, it makes sense that an integrated, 1-stop pain and addiction clinic that understands and addresses both issues is more likely to improve patient outcomes.
Acknowledgments
This material is the result of work supported by the resources and facilities at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System, Geriatric Research Education Clinical Center in Gainesville, Florida.
Chronic pain significantly affects 100 million Americans.1,2 Pain accounts for $560 to $635 billion in annual financial costs to society, including health care costs and loss of productivity (ie, days missed from work, hours of work lost, and lower wages).2,3 Although pain prevalence exceeds other chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, cancer, and heart disease, it lacks a sufficient body of evidence-based research and guidelines on the underlying mechanisms, valid methods of assessment, and comparative effectiveness of treatments to effectively implement into clinical practice.2,4 Prevention and treatment of pain are often delayed, inaccessible, or inadequate.2 Primary care providers (PCPs) are most often sought for pain management and treat about 52% of chronic pain patients.2,3,5 Veterans are especially vulnerable to chronic pain and are at risk for inadequate treatment.2
Background
There is an epidemic of drug abuse and mortality from opioid prescription medication.6 In the US, rates of overdose deaths from prescription opioids were 6.1 per 100,000 for men and 4.2 per 100,000 for women in 2017. Opioids were involved in 47,600 overdose deaths in 2017, accounting for 67.8% of all drug overdose deaths.7
A large number of patients on long-term opioids have preexisting substance use disorders and/or psychiatric disease, further complicating chronic pain management.8-10 Prescription opioid use has been the precursor for about 80% of people who are now heroin addicts.11 Iatrogenic addiction from prescription medications isn’t easily captured by standard addiction criteria. Consequently, in patients who are on opioid therapy for prolonged periods, separating complex opioid dependence from addiction is difficult.12 Improved addiction screening and risk mitigation strategies are needed along with aggressive treatment monitoring to curb the opioid epidemic.
Opioid Management in Primary Care
The majority of opioid medications are prescribed by PCPs, which is magnified in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system due to the high prevalence of service-related injuries.3,13 The VA is at the forefront of addressing the complexities of opioid addiction through several initiatives.14 The ability to offer the frequent visits needed to safely manage patients prescribed opioids and the integration of mental health and addiction treatment are often lacking in non-VA primary care clinics. Therefore, a key to solving the opioid crisis is developing these capabilities so they can be delivered within the primary care setting. There is substantial evidence in support of nonopioid alternatives to chronic pain management, including other pharmacologic approaches, exercise, physical therapy, acupuncture, weight loss, smoking cessation, chiropractic care, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other integrative health modalities.
A 2009 VA directive mandated the development of a comprehensive, integrated, systemwide approach to pain management.15 The VA Stepped-Care Biopsychosocial Model for Pain Management is dependent on timely access to secondary consultation from pain medicine, behavioral health, physical medicine, and other specialty consultation.15
History of VHA SCAN-ECHO Model
The Specialty Care Access Network–Extension for Community Health Outcomes (SCAN-ECHO) is a Veterans Health Administration (VHA) adaptation of a program that originated at the University of Mexico.16,17 The SCAN-ECHO model uses a multisite videoconferencing network to provide specialty care consultations to PCPs and patient aligned care teams (PACTs). During the 60- to 90-minute weekly sessions, case presentations are analyzed in real time so that over time, the PCPs gain knowledge, competency, and confidence in learning how to handle complex chronic conditions.
Since its implementation, the SCAN-ECHO program has been adopted across the VHA in a variety of specialties. One program, the SCAN-ECHO for Pain Management (SCAN-ECHO-PM) was implemented in 7 VHA networks in 31 states, spanning 47 medical centers and 148 community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs).18 The SCAN-ECHO-PM program successfully conducted 257 multidisciplinary pain consultations between 2011 and 2013, resulting in increased initiation of nonopioid medications.18
The aim of this article is to describe the implementation of a multicomponent primary care-based pain clinic with a fully integrated mental health service and addiction service at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System (NF/SGVHS). A practiced-based intervention of the biopsychosocial model with robust patient engagement has guided the development of the NF/SGVHS pain clinic (Figure 1).4,19
Pain CLinic
NF/SGVHS comprises the Malcom Randall and Lake City VA medical centers (VAMCs) hospitals, 3 satellite outpatient clinics, and 8 CBOCs. Spanning 33 counties in North Florida and 19 counties in South Georgia, the NF/SGVHS serves more than 140,000 patients. In 2010, the Malcom Randall VAMC established a multidisciplinary primary care pain clinic to manage veterans at high-risk for noncancer chronic pain and addiction. The noncancer pain policy was revised after garnering support from stakeholders who treat chronic pain, including the chiefs of psychiatry, rehabilitation medicine, neurosurgery, psychology, interventional pain, pharmacy, nursing, addiction medicine, and primary care. The clinic is staffed by primary care physicians trained in internal medicine and family medicine and is structured with 1-hour first visits, and 30-minute follow-up visits to allow enough time for comprehensive evaluation while meeting the needs for close follow-up support.
All physicians in the clinic have buprenorphine prescribing credentials to aid in the management of opioid addiction, as some patients feel more comfortable receiving addiction treatment in a primary care setting. The multimodal care model consists of several services that include addiction psychiatrists, interventional pain specialists, pain psychologists, and pain pharmacologists who coordinate the care to the veterans. The addiction psychiatrists offer a full range of services with inpatient residential and outpatient programs. Through recurring meetings with primary care pain clinic staff, the addiction psychiatrists are available to discuss use of buprenorphine and arrange follow-up for patients with complex pain addiction. There is ongoing collaboration to develop the best care plan that meets the patient’s needs for chronic pain, addiction, and/or mental health issues. The interventional pain service has 3 fellowship-trained pain care providers who deliver comprehensive evaluation, pharmacologic recommendations, and a full range of interventional and complementary therapies with an emphasis on objective functional improvement. Pain care providers offer alternatives to patients who are being weaned from opioids and support the multidisciplinary patient engagement model.
The pain psychology program, established in 2011, delivers CBT to 5 onsite locations and 5 telehealth locations. The service includes an advanced CBT program and a couples CBT program. The pharmacy pain fellowship program provides staff for an outpatient e-consult pain management service and an inpatient pharmacy consult service. Harnessing pain specialty pharmacists, the pharmacy service addresses pharmacokinetic issues, urine drug screen (UDS) results, opioid tapering and discharge planning for pain, addiction and mental health needs. The NF/SGVHS Primary Care Pain Clinic was established to support PCPs who did not feel comfortable managing chronic pain patients. These patients were typically on high-dose opioid therapy (> 100-mg morphine equivalent daily doses [MEDDs]); patients with a history of opioid addiction; patients with an addiction to opioids combined with benzodiazepines; and patients with comorbid medical issues (eg, sleep apnea), which complicated their management. The process of addressing opioid safety in these complex pain patients can be labor intensive and generally cannot be accomplished in a brief visit in a primary care setting where many other medical problems often need to be addressed.
Most patients on high-dose opioids are fearful of any changes in their medications. The difficult conversation regarding opioid safety is a lengthy one and frequently will occur over multiple visits. In addition, safely tapering opioids requires frequent follow-up to provide psychological support and to address withdrawal and mental health issues that may arise. As opioids are tapered, the clinic reinforces improved pain care through a multimodal biopsychosocial model. All veterans receiving pain care outside the VA are monitored annually to assure they are receiving evidence-based pain care as defined by the biopsychosocial model.
Education
Since 2011, the NF/SGVHS SCAN-ECHO pain and addiction educational forum has created > 50 hours of approved annual continuing medical education (CME) on pain management and addiction for PCPs. Initially, the 1-hour weekly educational audioconferences presented a pain management case along with related topics and involved specialists from interventional pain, physical therapy, psychiatry, nursing, neurology, and psychology departments. In 2013, in conjunction with the VA SCAN-ECHO program of Hunter Holmes McGuire VAMC in Richmond, Virginia, and Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, the audioconference was expanded to 2 days each week with additional topics on addiction management. Residency and fellowship rotations were developed that specifically targeted fellows from psychiatry, pharmacology, and interventional pain departments.
Currently, an 8-session pain school is delivered onsite and at 7 telehealth locations. The school is a collaborative effort involving interventional pain, psychology, pharmacy, nutrition, and the primary care pain clinic staff. As the cornerstone of the program, the pain school stresses the biopsychosocial patient engagement model.
Program Evaluation
The VA is equipped with multiple telehealth service networks that allow for the delivery of programs, such as the pain school, a pain psychology program, and a yoga program, onsite or offsite. The VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) manages electronic health records, allowing for rapid chart review and e-consults. The NF/SGVHS Pain Management Program provides about 1500 e-consults yearly. The CPRS includes templates with pain metrics to help PCPs deliver pain care more efficiently and evaluate performance measures. This system also allows for the capture of data to track improvements in the care of the veterans served.
From 2012 to 2017, more than 5000 NF/SGVHS patients were weaned from opioids. Overall, there was an 87% reduction in patients receiving opioids ( ≥ 100-mg MEDDs) within the NF/SGVHS, which is significantly more than the 49% seen nationally across the VHA (Figure 2). Percent reduction was calculated by taking the difference in number of patients receiving opioids in 2012 and 2017, dividing by the number of patients receiving opioids in 2012 and multiplying by 100. The largest proportion of opioid dose reductions for NF/SGVHS and VHA patients, respectively, were seen in 300-mg to 399-mg MEDDs (95% vs 67%, respectively); followed by ≥ 400-mg MEDDs (94% vs 71%, respectively); 200-mg to 299-mg MEDDs (91% vs 58%, respectively); and 100-mg to 199-mg MEDDs (84% vs 40%, respectively). When examining NF/SGVHS trends over time, there has been a consistent decline in patients prescribed opioids (18 223 in 2012 compared with 12 877 in 2017) with similar trends in benzodiazepine-opioid combination therapy (2694 in 2012 compared with 833 in 2017) (Figure 3).
Similar declines are seen when patients are stratified by the MEDD (Figure 4). From 2012 to 2017, 92% of the patients were successfully tapered off doses ≥ 400-mg MEDD (2012, n = 72; 2017, n = 6), and tapered off 300-mg to 399-mg MEDD (2012, n = 107; 2017, n = 5); 95% were tapered off 200-mg to 299-mg MEDD (2012, n = 262; 2017, n = 22); and 86% were tapered off 100-mg to 199-mg MEDD (2012, n = 876; 2017; n = 127).
Conclusion
Successful integration of primary care with mental health and addiction services is paramount to aggressively taper patients with chronic pain from opioids. There is evidence that drug dependence and chronic pain should be treated like other chronic illness.20 Both chronic pain and addiction can be treated with a multidimensional self-management approach. In view of the high incidence of mental health and addiction associated with opioid use, it makes sense that an integrated, 1-stop pain and addiction clinic that understands and addresses both issues is more likely to improve patient outcomes.
Acknowledgments
This material is the result of work supported by the resources and facilities at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System, Geriatric Research Education Clinical Center in Gainesville, Florida.
1. Dueñas M, Ojeda B, Salazar A, Mico JA, Failde I. A review of chronic pain impact on patients, their social environment and the health care system. J Pain Res. 2016;9:457-467.
2. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine; 2011.
3. Breuer B, Cruciani R, Portenoy RK. Pain management by primary care physicians, pain physicians, chiropractors, and acupuncturists: a national survey. South Med J. 2010;103(8):738-747.
4. Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol. 2014;69(2):119-130.
5. Meghani SH, Polomano RC, Tait RC, Vallerand AH, Anderson KO, Gallagher RM. Advancing a national agenda to eliminate disparities in pain care: directions for health policy, education, practice, and research. Pain Med. 2012;13(1):5-28.
6. McHugh RK, Nielsen S, Weiss RD. Prescription drug abuse: from epidemiology to public policy. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;48(1):1-7.
7. Scholl L, Seth P, Kariisa M, Wilson N, Baldwin G. Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths-United States, 2013-2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(5152):1419-1427.
8. Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8.
9. Højsted J, Sjøgren P. Addiction to opioids in chronic pain patients: a literature review. Eur J Pain. 2007;11(5):490-518.
10. Seal KH, Shi Y, Cohen G, et al. Association of mental health disorders with prescription opioids and high-risk opioid use in US veterans of Iraq and Afghanistan. JAMA. 2012;307(9):940-947.
11. Kolodny A, Courtwright DT, Hwang CS, et al. The prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:559-574.
12. Ballantyne JC, Sullivan MD, Kolodny A. Opioid dependence vs addiction: a distinction without a difference? Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(17):1342-1343.
13. Levy B, Paulozzi L, Mack KA, Jones CM. Trends in opioid analgesic-prescribing rates by specialty, U.S., 2007-2012. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49(3):409-413.
14. Gellad WF, Good CB, Shulkin DJ. Addressing the opioid epidemic in the United States: lessons from the Department of Veterans Affairs. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(5):611-612.
15. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veteran Health Administration Directive 2009-053, Pain Management. https://www.va.gov/painmanagement/docs/vha09paindirective.pdf. Published October 28, 2009. Accessed August 19, 2019.
16. Arora S, Geppert CM, Kalishman S, et al. Academic health center management of chronic diseases through knowledge networks: Project ECHO. Acad Med. 2007;82(2):154-160.
17. Kirsh S, Su GL, Sales A, Jain R. Access to outpatient specialty care: solutions from an integrated health care system. Am J Med Qual. 2015;30(1):88-90.
18. Frank JW, Carey EP, Fagan KM, et al. Evaluation of a telementoring intervention for pain management in the Veterans Health Administration. Pain Med. 2015;16(6):1090-1100.
19. Fillingim RB. Individual differences in pain: understanding the mosaic that makes pain personal. Pain. 2017;158 (suppl 1):S11-S18.
20. McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O’Brien CP, Kleber HD. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA. 2000;284(13):1689-1695.
1. Dueñas M, Ojeda B, Salazar A, Mico JA, Failde I. A review of chronic pain impact on patients, their social environment and the health care system. J Pain Res. 2016;9:457-467.
2. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine; 2011.
3. Breuer B, Cruciani R, Portenoy RK. Pain management by primary care physicians, pain physicians, chiropractors, and acupuncturists: a national survey. South Med J. 2010;103(8):738-747.
4. Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol. 2014;69(2):119-130.
5. Meghani SH, Polomano RC, Tait RC, Vallerand AH, Anderson KO, Gallagher RM. Advancing a national agenda to eliminate disparities in pain care: directions for health policy, education, practice, and research. Pain Med. 2012;13(1):5-28.
6. McHugh RK, Nielsen S, Weiss RD. Prescription drug abuse: from epidemiology to public policy. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;48(1):1-7.
7. Scholl L, Seth P, Kariisa M, Wilson N, Baldwin G. Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths-United States, 2013-2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(5152):1419-1427.
8. Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8.
9. Højsted J, Sjøgren P. Addiction to opioids in chronic pain patients: a literature review. Eur J Pain. 2007;11(5):490-518.
10. Seal KH, Shi Y, Cohen G, et al. Association of mental health disorders with prescription opioids and high-risk opioid use in US veterans of Iraq and Afghanistan. JAMA. 2012;307(9):940-947.
11. Kolodny A, Courtwright DT, Hwang CS, et al. The prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:559-574.
12. Ballantyne JC, Sullivan MD, Kolodny A. Opioid dependence vs addiction: a distinction without a difference? Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(17):1342-1343.
13. Levy B, Paulozzi L, Mack KA, Jones CM. Trends in opioid analgesic-prescribing rates by specialty, U.S., 2007-2012. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49(3):409-413.
14. Gellad WF, Good CB, Shulkin DJ. Addressing the opioid epidemic in the United States: lessons from the Department of Veterans Affairs. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(5):611-612.
15. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veteran Health Administration Directive 2009-053, Pain Management. https://www.va.gov/painmanagement/docs/vha09paindirective.pdf. Published October 28, 2009. Accessed August 19, 2019.
16. Arora S, Geppert CM, Kalishman S, et al. Academic health center management of chronic diseases through knowledge networks: Project ECHO. Acad Med. 2007;82(2):154-160.
17. Kirsh S, Su GL, Sales A, Jain R. Access to outpatient specialty care: solutions from an integrated health care system. Am J Med Qual. 2015;30(1):88-90.
18. Frank JW, Carey EP, Fagan KM, et al. Evaluation of a telementoring intervention for pain management in the Veterans Health Administration. Pain Med. 2015;16(6):1090-1100.
19. Fillingim RB. Individual differences in pain: understanding the mosaic that makes pain personal. Pain. 2017;158 (suppl 1):S11-S18.
20. McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O’Brien CP, Kleber HD. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA. 2000;284(13):1689-1695.
2019 Update on pelvic floor dysfunction
Fecal incontinence (FI), also known as accidental bowel leakage, is the involuntary loss of feces, which includes both liquid and solid stool as defined by the International Continence Society (ICS) and the International Urogynecological Association (IUGA).1,2 Fecal incontinence is common, occurring in 7% to 25% of community-dwelling women, and it increases with age.2-6 The condition is rarely addressed, with only 30% of women seeking care.6-8 This is due to patient embarrassment and the lack of a reliable screening tool. However, FI affects quality of life and mental health, and the associated economic burden likely will rise given the increased prevalence of FI among older women.2,4,7,9
Fecal incontinence occurs due to poor stool consistency, anal and pelvic muscle weakness, reduced rectal compliance, reduced or increased rectal sensation, or bowel inflammation or dysfunction. Many conditions can cause FI (TABLE 1).5,10,11 It is therefore important to elicit a full medical history with a focus on specific bowel symptoms, such as stool consistency type (TABLE 2),12 FI frequency, and duration of symptoms, as well as to perform a complete examination to identify any readily reversible or malignant causes. A colonoscopy is recommended for individuals who meet screening criteria or present with a change in bowel symptoms, such as diarrhea, bleeding, or obstruction.13,14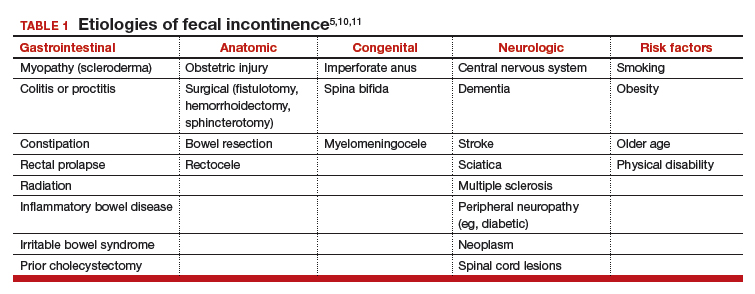

Fecal incontinence treatments include a range of approaches categorized from conservative, or first-line therapy, to fourth-line surgical managements (FIGURE 1).1,10,13,14 In this Update, we review the results of 3 well-designed trials that enrolled women with frequent nonneurogenic FI.
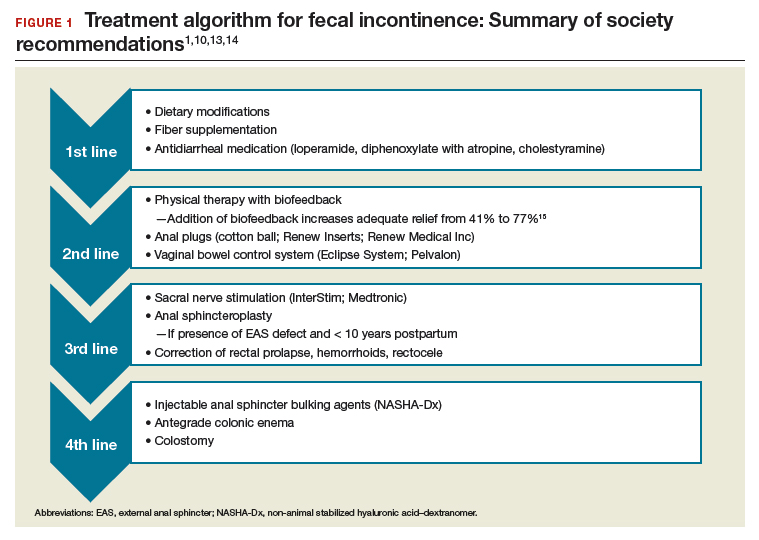
Common first- and second-line treatments produce equivalent improvements in FI symptoms at
6 months
Jelovsek JE, Markland AD, Whitehead WE, et al; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Controlling faecal incontinence in women by performing anal exercises with biofeedback or loperamide: a randomized clinical trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:698-710.
In a multicenter, randomized trial of first- and second-line treatments for FI, Jelovsek and colleagues evaluated the efficacy of oral placebo, loperamide, pelvic floor physical therapy (PFPT) with biofeedback using anorectal manometry, or combination therapy over a 24-week period.
Continue to: Four treatments compared...
Four treatments compared
Three hundred women with FI occurring monthly for 3 months were included in the trial. Women were excluded if they had a stool classification of type 1 or type 7 on the Bristol Stool Scale, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), history of rectovaginal fistula or cloacal defect, rectal prolapse, prior bowel diversion, fecal impaction, neurologic disorder leading to incontinence, use of loperamide or diphenoxylate within the last 30 days, childbirth within the last 3 months, need for antiretroviral drugs, hepatic impairment, or chronic abdominal pain without diarrhea.
Baseline characteristics and symptoms severity were similar among participants. The average age of the women was 63 years, with 79% white and 85% postmenopausal. Participants had a mean (SD) of 1.6 (1.8) leaks per day.
Participants were randomly assigned in a 0.5:1:1:1 fashion to receive oral placebo, loperamide, oral placebo with PFPT/biofeedback, or loperamide with PFPT/biofeedback. All participants received a standardized educational pamphlet that outlined dietary and behavioral recommendations.
Women assigned to PFPT/biofeedback received 6 sessions every other week. Loperamide was started at a dosage of 2 mg per day with the possibility of dose maintenance, escalation, reduction, or discontinuation.
Study outcomes. The primary outcome was a change from baseline to 24 weeks in the Vaizey FI symptom severity score, which assesses fecal frequency, urgency, and use of pads and medications. Secondary outcomes included assessment of a 7-day bowel diary and other quality-of-life measures. Data at 24 weeks were available for 89% of the women.
All treatment groups experienced improved FI symptoms
Based on changes in Vaizey scores after 24 weeks of treatment, women in all treatment groups had similar improvement in symptoms severity. However, those who received loperamide and PFPT/biofeedback had decreased pad changes per week and more accident-free days compared with women treated with placebo and biofeedback. Quality of life at 24 weeks was not statistically different between treatment groups as improvement was seen in all groups, including those who received oral placebo and patient education.
Adverse events. The proportion of gastrointestinal adverse effects was similar between treatment groups, ranging from 45% to 63%. Constipation was the most common adverse event overall and was more common in those taking loperamide, occurring in 51% of the loperamide plus PFPT/biofeedback group, 38% of those who received loperamide alone, 23% of the biofeedback with placebo group, and 12% of the placebo-alone group.
Strengths and limitations. Strengths of this study include its multisite, large sample size, low dropout rate, and sufficiently powered design to compare various combinations of first- and second-line therapies in women with a mean baseline FI of 1.6 leaks per day. Another strength is the robustness of the PFPT/biofeedback sessions that used anorectal manometry. This may, however, limit the study's external validity given that clinical use of this device is likely rare. Additionally, the population was comprised largely of postmenopausal and white women, which may make the findings less generalizable to other populations.
Women who suffer from frequent FI may require both loperamide and PFPT/biofeedback if they want to increase the likelihood of accident-free days and use of fewer pads. Should they note increased constipation or are not amenable to scheduled PFPT sessions, formalized education about dietary modifications, according to this study, will provide improvement in symptom severity.
Continue to: Novel vaginal bowel control system...
Novel vaginal bowel control system is effective, durable over 12 months for FI treatment
Richter HE, Dunivan G, Brown HW, et al. A 12-month clinical durability of effectiveness and safety evaluation of a vaginal bowel control system for the nonsurgical treatment of fecal incontinence. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2019;25:113-119.
Richter and colleagues characterized clinical success, effect on quality of life, and durability over 12 months of a novel vaginal bowel control device (Eclipse System; Pelvalon) for FI in a prospective cohort study. The device is a silicone-coated vaginal insert with a detachable pump and balloon that deflects the rectovaginal septum posteriorly, thus impeding the passage of stool in the rectum (FIGURE 2).
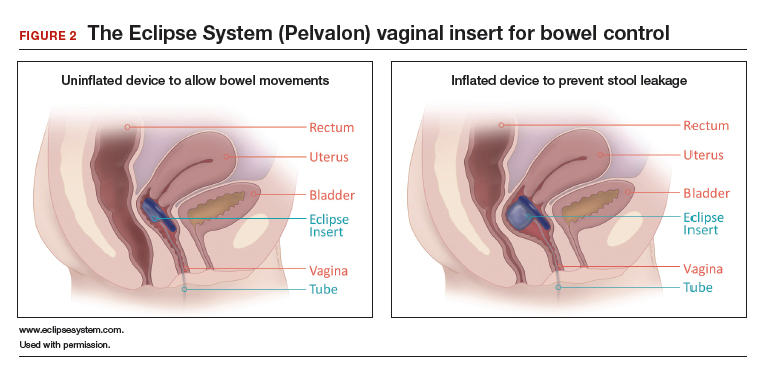
Study eligibility criteria and treatment protocol
Women were eligible for the study if they had 4 or more episodes of fecal soiling on a 2-week bowel diary and had FI for at least 6 months. Participants were excluded if they had prolapse outside the hymen, rectovaginal fistula, IBD, congenital anorectal malformation, urinary or colorectal infection, chronic pelvic or anorectal pain, pregnancy or planning pregnancy in the next 5 months, unmanaged chronic watery diarrhea, presence of an open wound or tear in the vagina, significant urogenital atrophy, or any psychiatric or neurologic disorder that would hinder the ability to participate.
Participants successfully fitted with the device (3 attempts were allowed) were entered into the study's run-in phase. Those who were successfully fitted and had a 50% or greater reduction in FI continued into the treatment phase with 12 months of follow-up.
Of the 137 women eligible for device fitting, 62% were successfully fitted. The 73 (86%) women who had a 50% or greater reduction in FI during the run-in period comprised the intent-to-treat study population. On average, these women were 61.3 years of age, with 70% white and 82% postmenopausal. At baseline, they had a mean of 14.1 episodes of FI over 2 weeks. (Prior to enrollment, 97.3% of women attempted self-management strategies, 17.8% to 23% failed conservative therapy, and 7.8% to 13.7% failed surgical therapy.) The follow-up rate at 12 months was 74%.
Study outcomes. The primary outcome was treatment success, defined as proportion of subjects with a 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes at 3 months; this outcome also was evaluated at 6 and 12 months. Secondary outcomes were the number of FI episodes and quality-of-life measures at 3, 6, and 12 months.
Treatment success, patient satisfaction high
In the treatment phase, women had sustained improvements in symptom severity and quality-of-life measures over 12 months. Treatment success was 73% at 3 months, 71% at 6 months, and 70% at 12 months. Complete continence was achieved in 46% of participants at 12 months, and major FI episodes (requiring immediate change of undergarments) decreased from 5.0 at baseline to 0.5 at 12 months. Quality-of-life measures were improved at 3 months, and improvement was sustained over 12 months. Satisfaction was 94% at 12 months.
Adverse events. No serious device-related adverse events occurred. Mild device-related adverse events were experienced by 45% of women during the fitting process and by 38% during treatment period. These included vaginal wall injury such as hyperemia and erosion; vaginal or pelvic discomfort; vaginal infection; constipation; and lower urinary tract issues such as urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. No adverse events led to treatment discontinuation.
Strengths and limitations. Strengths of this study include that it was conducted at multiple clinical sites, had a large sample size, and had a 1-year follow-up period in a population with daily FI. A limitation was that only women who had a 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes during the run-in period were followed for 12 months; however, this was 86% of the original cohort. The use of a comparative group using other devices, such as anal plugs, would have strengthened this study.
The Eclipse intravaginal bowel control device (approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2015) provided a sustained 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes in more than 70% of women wearing the device for 1 year, with high patient satisfaction. Thus, for women who fail conservative treatment methods for FI, clinicians should consider referring them to a urogynecologist or specialist who is knowledgeable in fitting this vaginal bowel control device.
Continue to: Sacroneuromodulation for FI…
Sacral neuromodulation for FI is effective long-term
Hull T, Giese C, Wexner SD, et al; for the SNS Study Group. Long-term durability of sacral nerve stimulation therapy for chronic fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:234-245.
In this multicenter, prospective cohort study, Hull and colleagues evaluated the 5-year efficacy of sacral neuromodulation (SNM), also known as sacral nerve stimulation, for treatment of FI. This study followed an earlier investigation by Wexner and colleagues, which reported that 83% of 120 patients treated with SNM had a 50% or greater improvement in FI episodes at 12 months.16
Details of the study
The investigators enrolled 133 participants (92% female) who had more than 2 episodes of FI per week for longer than 6 months (12 months after vaginal delivery). Participants were excluded if they had congenital anorectal malformations, prior rectal surgery within the past 12 months (or 24 months if due to cancer), defects greater than 120° of the external anal sphincter (EAS), IBD, unmanaged chronic watery diarrhea, stool consistency type 6 or type 7 on the Bristol Stool Scale, sequela of pelvic radiation, active anal abscess or fistula, pregnancy, or planned pregnancy.
Eligible participants underwent a 2-stage procedure with the InterStim bowel control device (Medtronic). If participants experienced a 50% or greater reduction in incontinence episodes with a wearable external SNM device in the test stimulation (stage 1), they received the chronic SNM implant device (stage 2).
Participants who underwent device implantation were followed at 1, 3, and 6 months and annually for 5 years or until they exited the study. Bowel diaries and quality of life assessments were completed at baseline and at follow-up.
The primary outcome was therapeutic success, defined as 50% or greater improvement in FI episodes per week.
A total of 120 participants (90%) underwent implantation of the chronic lead and neuromodulator, and 76 (63%) were followed for 5 years. Baseline characteristics available in the initial study of 133 participants showed that the mean age was 60.5 years; 25% had undergone a prior anal sphincteroplasty; and 16.5% and 10.5% had EAS or internal anal sphincter (IAS) defects, respectively, on endoanal ultrasonography.16
Therapeutic success was high at 5 years
At the 5-year follow-up, 89% (64/72) of participants met therapeutic success, with a reduction in weekly FI episodes from 9.1 at baseline to 1.7 at 5 years. The number of incontinence pads required decreased, and more participants wore no pads at 5 years. In the intention-to-treat analysis, carrying forward the baseline FI rate in participants who lacked follow-up data, the therapeutic success rate was 69%. Quality-of-life measures improved at 5 years, both statistically and by minimal clinical difference.
Adverse events. Sixty-eight percent of participants experienced device-related adverse events, including implant site pain, change in sensation of stimulation, change in efficacy, implant site infection, or neurostimulator battery depletion (neurostimulator use commonly expires after 3 to 5 years). Of these events, 80% were successfully treated with medications, reprogramming, or no intervention. The 5-year probability of device revision or replacement was 24.4%, and the 5-year probability of device explant was 19.0%.
Strengths and limitations. Overall, this study was a well-designed, multicenter trial with long-term follow-up that showed significant improvement in FI with the use of SNM. Its strengths include the enrollment of postmenopausal women who had current defects in EAS and/or IAS on endoanal ultrasonography and 25% who had a prior sphincteroplasty. The findings therefore are relevant to the gynecologic population in whom anal sphincteroplasty would not be recommended. The study also accounted for dropouts and reported the adjusted success rate of 69% at 5 years in that group.
The lack of a control arm to rule out the placebo effect is a limitation of this study, although randomized trials comparing the effect of SNM "on" versus "off" showed greater improvement with the device "on."17
Sacral neuromodulation is an excellent therapy for women with daily FI who have failed noninvasive options and desire to proceed to a more durable, long-lasting device therapy. Although adverse events may occur, they are mild and most often resolve with device reprogramming.
- Sultan AH, Monga A, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female anorectal dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017;36:10-34.
- Bharucha AE, Dunivan G, Goode PS, et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and classification of fecal incontinence: state of the science summary for the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) workshop. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:127-136.
- Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Locke GR, et al. Symptoms and quality of life in community women with fecal incontinence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1004-1008.
- Perry S, Shaw C, McGrother C, et al; Leicestershire MRC Incontinence Study Team. Prevalence of faecal incontinence in adults aged 40 years or more living in the community. Gut. 2002;50:480-484.
- Ditah I, Devaki P, Luma HN, et al. Prevalence, trends, and risk factors for fecal incontinence in United States adults, 2005-2010. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:636-643.e1-2.
- Brown HW, Wexner SD, Lukacz ES. Factors associated with care seeking among women with accidental bowel leakage. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2013;19:66-71.
- Norton NJ. The perspective of the patient. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(1 suppl 1):S175-S179.
- Guan W, Schmuhl NB, Brown HW. Response re: If we don't ask, they won't tell: screening for urinary and fecal incontinence by primary care providers. J Am Board Fam Med. 2019;32:119.3-120.
- Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, et al; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:512-517.
- Wald A, Bharucha AE, Cosman BC, et al. ACG clinical guideline: management of benign anorectal disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1141-1157.
- Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Schleck CD, et al. Bowel disturbances are the most important risk factors for late onset fecal incontinence: a population-based case-control study in women. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1559-1566.
- Lewis SJ, Heaton KW. Stool form scale as a useful guide to intestinal transit time. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:920-924.
- Paquette IM, Varma MG, Kaiser AM, et al. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons' clinical practice guideline for the treatment of fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015;58:623-636.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 210: Fecal incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e260-e273.
- Heymen S, Scarlett Y, Jones K, et al. Randomized controlled trial shows biofeedback to be superior to pelvic floor exercises for fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52:1730-1737.
- Wexner SD, Coller JA, Devroede G, et al. Sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence: results of a 120-patient prospective multicenter study. Ann Surg. 2010;251:441-449.
- Leroi AM, Parc Y, Lehur PA, et al. Efficacy of sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence: results of a multicenter double-blind crossover study. Ann Surg. 2005;242:662-669.
Fecal incontinence (FI), also known as accidental bowel leakage, is the involuntary loss of feces, which includes both liquid and solid stool as defined by the International Continence Society (ICS) and the International Urogynecological Association (IUGA).1,2 Fecal incontinence is common, occurring in 7% to 25% of community-dwelling women, and it increases with age.2-6 The condition is rarely addressed, with only 30% of women seeking care.6-8 This is due to patient embarrassment and the lack of a reliable screening tool. However, FI affects quality of life and mental health, and the associated economic burden likely will rise given the increased prevalence of FI among older women.2,4,7,9
Fecal incontinence occurs due to poor stool consistency, anal and pelvic muscle weakness, reduced rectal compliance, reduced or increased rectal sensation, or bowel inflammation or dysfunction. Many conditions can cause FI (TABLE 1).5,10,11 It is therefore important to elicit a full medical history with a focus on specific bowel symptoms, such as stool consistency type (TABLE 2),12 FI frequency, and duration of symptoms, as well as to perform a complete examination to identify any readily reversible or malignant causes. A colonoscopy is recommended for individuals who meet screening criteria or present with a change in bowel symptoms, such as diarrhea, bleeding, or obstruction.13,14

Fecal incontinence treatments include a range of approaches categorized from conservative, or first-line therapy, to fourth-line surgical managements (FIGURE 1).1,10,13,14 In this Update, we review the results of 3 well-designed trials that enrolled women with frequent nonneurogenic FI.

Common first- and second-line treatments produce equivalent improvements in FI symptoms at
6 months
Jelovsek JE, Markland AD, Whitehead WE, et al; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Controlling faecal incontinence in women by performing anal exercises with biofeedback or loperamide: a randomized clinical trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:698-710.
In a multicenter, randomized trial of first- and second-line treatments for FI, Jelovsek and colleagues evaluated the efficacy of oral placebo, loperamide, pelvic floor physical therapy (PFPT) with biofeedback using anorectal manometry, or combination therapy over a 24-week period.
Continue to: Four treatments compared...
Four treatments compared
Three hundred women with FI occurring monthly for 3 months were included in the trial. Women were excluded if they had a stool classification of type 1 or type 7 on the Bristol Stool Scale, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), history of rectovaginal fistula or cloacal defect, rectal prolapse, prior bowel diversion, fecal impaction, neurologic disorder leading to incontinence, use of loperamide or diphenoxylate within the last 30 days, childbirth within the last 3 months, need for antiretroviral drugs, hepatic impairment, or chronic abdominal pain without diarrhea.
Baseline characteristics and symptoms severity were similar among participants. The average age of the women was 63 years, with 79% white and 85% postmenopausal. Participants had a mean (SD) of 1.6 (1.8) leaks per day.
Participants were randomly assigned in a 0.5:1:1:1 fashion to receive oral placebo, loperamide, oral placebo with PFPT/biofeedback, or loperamide with PFPT/biofeedback. All participants received a standardized educational pamphlet that outlined dietary and behavioral recommendations.
Women assigned to PFPT/biofeedback received 6 sessions every other week. Loperamide was started at a dosage of 2 mg per day with the possibility of dose maintenance, escalation, reduction, or discontinuation.
Study outcomes. The primary outcome was a change from baseline to 24 weeks in the Vaizey FI symptom severity score, which assesses fecal frequency, urgency, and use of pads and medications. Secondary outcomes included assessment of a 7-day bowel diary and other quality-of-life measures. Data at 24 weeks were available for 89% of the women.
All treatment groups experienced improved FI symptoms
Based on changes in Vaizey scores after 24 weeks of treatment, women in all treatment groups had similar improvement in symptoms severity. However, those who received loperamide and PFPT/biofeedback had decreased pad changes per week and more accident-free days compared with women treated with placebo and biofeedback. Quality of life at 24 weeks was not statistically different between treatment groups as improvement was seen in all groups, including those who received oral placebo and patient education.
Adverse events. The proportion of gastrointestinal adverse effects was similar between treatment groups, ranging from 45% to 63%. Constipation was the most common adverse event overall and was more common in those taking loperamide, occurring in 51% of the loperamide plus PFPT/biofeedback group, 38% of those who received loperamide alone, 23% of the biofeedback with placebo group, and 12% of the placebo-alone group.
Strengths and limitations. Strengths of this study include its multisite, large sample size, low dropout rate, and sufficiently powered design to compare various combinations of first- and second-line therapies in women with a mean baseline FI of 1.6 leaks per day. Another strength is the robustness of the PFPT/biofeedback sessions that used anorectal manometry. This may, however, limit the study's external validity given that clinical use of this device is likely rare. Additionally, the population was comprised largely of postmenopausal and white women, which may make the findings less generalizable to other populations.
Women who suffer from frequent FI may require both loperamide and PFPT/biofeedback if they want to increase the likelihood of accident-free days and use of fewer pads. Should they note increased constipation or are not amenable to scheduled PFPT sessions, formalized education about dietary modifications, according to this study, will provide improvement in symptom severity.
Continue to: Novel vaginal bowel control system...
Novel vaginal bowel control system is effective, durable over 12 months for FI treatment
Richter HE, Dunivan G, Brown HW, et al. A 12-month clinical durability of effectiveness and safety evaluation of a vaginal bowel control system for the nonsurgical treatment of fecal incontinence. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2019;25:113-119.
Richter and colleagues characterized clinical success, effect on quality of life, and durability over 12 months of a novel vaginal bowel control device (Eclipse System; Pelvalon) for FI in a prospective cohort study. The device is a silicone-coated vaginal insert with a detachable pump and balloon that deflects the rectovaginal septum posteriorly, thus impeding the passage of stool in the rectum (FIGURE 2).

Study eligibility criteria and treatment protocol
Women were eligible for the study if they had 4 or more episodes of fecal soiling on a 2-week bowel diary and had FI for at least 6 months. Participants were excluded if they had prolapse outside the hymen, rectovaginal fistula, IBD, congenital anorectal malformation, urinary or colorectal infection, chronic pelvic or anorectal pain, pregnancy or planning pregnancy in the next 5 months, unmanaged chronic watery diarrhea, presence of an open wound or tear in the vagina, significant urogenital atrophy, or any psychiatric or neurologic disorder that would hinder the ability to participate.
Participants successfully fitted with the device (3 attempts were allowed) were entered into the study's run-in phase. Those who were successfully fitted and had a 50% or greater reduction in FI continued into the treatment phase with 12 months of follow-up.
Of the 137 women eligible for device fitting, 62% were successfully fitted. The 73 (86%) women who had a 50% or greater reduction in FI during the run-in period comprised the intent-to-treat study population. On average, these women were 61.3 years of age, with 70% white and 82% postmenopausal. At baseline, they had a mean of 14.1 episodes of FI over 2 weeks. (Prior to enrollment, 97.3% of women attempted self-management strategies, 17.8% to 23% failed conservative therapy, and 7.8% to 13.7% failed surgical therapy.) The follow-up rate at 12 months was 74%.
Study outcomes. The primary outcome was treatment success, defined as proportion of subjects with a 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes at 3 months; this outcome also was evaluated at 6 and 12 months. Secondary outcomes were the number of FI episodes and quality-of-life measures at 3, 6, and 12 months.
Treatment success, patient satisfaction high
In the treatment phase, women had sustained improvements in symptom severity and quality-of-life measures over 12 months. Treatment success was 73% at 3 months, 71% at 6 months, and 70% at 12 months. Complete continence was achieved in 46% of participants at 12 months, and major FI episodes (requiring immediate change of undergarments) decreased from 5.0 at baseline to 0.5 at 12 months. Quality-of-life measures were improved at 3 months, and improvement was sustained over 12 months. Satisfaction was 94% at 12 months.
Adverse events. No serious device-related adverse events occurred. Mild device-related adverse events were experienced by 45% of women during the fitting process and by 38% during treatment period. These included vaginal wall injury such as hyperemia and erosion; vaginal or pelvic discomfort; vaginal infection; constipation; and lower urinary tract issues such as urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. No adverse events led to treatment discontinuation.
Strengths and limitations. Strengths of this study include that it was conducted at multiple clinical sites, had a large sample size, and had a 1-year follow-up period in a population with daily FI. A limitation was that only women who had a 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes during the run-in period were followed for 12 months; however, this was 86% of the original cohort. The use of a comparative group using other devices, such as anal plugs, would have strengthened this study.
The Eclipse intravaginal bowel control device (approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2015) provided a sustained 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes in more than 70% of women wearing the device for 1 year, with high patient satisfaction. Thus, for women who fail conservative treatment methods for FI, clinicians should consider referring them to a urogynecologist or specialist who is knowledgeable in fitting this vaginal bowel control device.
Continue to: Sacroneuromodulation for FI…
Sacral neuromodulation for FI is effective long-term
Hull T, Giese C, Wexner SD, et al; for the SNS Study Group. Long-term durability of sacral nerve stimulation therapy for chronic fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:234-245.
In this multicenter, prospective cohort study, Hull and colleagues evaluated the 5-year efficacy of sacral neuromodulation (SNM), also known as sacral nerve stimulation, for treatment of FI. This study followed an earlier investigation by Wexner and colleagues, which reported that 83% of 120 patients treated with SNM had a 50% or greater improvement in FI episodes at 12 months.16
Details of the study
The investigators enrolled 133 participants (92% female) who had more than 2 episodes of FI per week for longer than 6 months (12 months after vaginal delivery). Participants were excluded if they had congenital anorectal malformations, prior rectal surgery within the past 12 months (or 24 months if due to cancer), defects greater than 120° of the external anal sphincter (EAS), IBD, unmanaged chronic watery diarrhea, stool consistency type 6 or type 7 on the Bristol Stool Scale, sequela of pelvic radiation, active anal abscess or fistula, pregnancy, or planned pregnancy.
Eligible participants underwent a 2-stage procedure with the InterStim bowel control device (Medtronic). If participants experienced a 50% or greater reduction in incontinence episodes with a wearable external SNM device in the test stimulation (stage 1), they received the chronic SNM implant device (stage 2).
Participants who underwent device implantation were followed at 1, 3, and 6 months and annually for 5 years or until they exited the study. Bowel diaries and quality of life assessments were completed at baseline and at follow-up.
The primary outcome was therapeutic success, defined as 50% or greater improvement in FI episodes per week.
A total of 120 participants (90%) underwent implantation of the chronic lead and neuromodulator, and 76 (63%) were followed for 5 years. Baseline characteristics available in the initial study of 133 participants showed that the mean age was 60.5 years; 25% had undergone a prior anal sphincteroplasty; and 16.5% and 10.5% had EAS or internal anal sphincter (IAS) defects, respectively, on endoanal ultrasonography.16
Therapeutic success was high at 5 years
At the 5-year follow-up, 89% (64/72) of participants met therapeutic success, with a reduction in weekly FI episodes from 9.1 at baseline to 1.7 at 5 years. The number of incontinence pads required decreased, and more participants wore no pads at 5 years. In the intention-to-treat analysis, carrying forward the baseline FI rate in participants who lacked follow-up data, the therapeutic success rate was 69%. Quality-of-life measures improved at 5 years, both statistically and by minimal clinical difference.
Adverse events. Sixty-eight percent of participants experienced device-related adverse events, including implant site pain, change in sensation of stimulation, change in efficacy, implant site infection, or neurostimulator battery depletion (neurostimulator use commonly expires after 3 to 5 years). Of these events, 80% were successfully treated with medications, reprogramming, or no intervention. The 5-year probability of device revision or replacement was 24.4%, and the 5-year probability of device explant was 19.0%.
Strengths and limitations. Overall, this study was a well-designed, multicenter trial with long-term follow-up that showed significant improvement in FI with the use of SNM. Its strengths include the enrollment of postmenopausal women who had current defects in EAS and/or IAS on endoanal ultrasonography and 25% who had a prior sphincteroplasty. The findings therefore are relevant to the gynecologic population in whom anal sphincteroplasty would not be recommended. The study also accounted for dropouts and reported the adjusted success rate of 69% at 5 years in that group.
The lack of a control arm to rule out the placebo effect is a limitation of this study, although randomized trials comparing the effect of SNM "on" versus "off" showed greater improvement with the device "on."17
Sacral neuromodulation is an excellent therapy for women with daily FI who have failed noninvasive options and desire to proceed to a more durable, long-lasting device therapy. Although adverse events may occur, they are mild and most often resolve with device reprogramming.
Fecal incontinence (FI), also known as accidental bowel leakage, is the involuntary loss of feces, which includes both liquid and solid stool as defined by the International Continence Society (ICS) and the International Urogynecological Association (IUGA).1,2 Fecal incontinence is common, occurring in 7% to 25% of community-dwelling women, and it increases with age.2-6 The condition is rarely addressed, with only 30% of women seeking care.6-8 This is due to patient embarrassment and the lack of a reliable screening tool. However, FI affects quality of life and mental health, and the associated economic burden likely will rise given the increased prevalence of FI among older women.2,4,7,9
Fecal incontinence occurs due to poor stool consistency, anal and pelvic muscle weakness, reduced rectal compliance, reduced or increased rectal sensation, or bowel inflammation or dysfunction. Many conditions can cause FI (TABLE 1).5,10,11 It is therefore important to elicit a full medical history with a focus on specific bowel symptoms, such as stool consistency type (TABLE 2),12 FI frequency, and duration of symptoms, as well as to perform a complete examination to identify any readily reversible or malignant causes. A colonoscopy is recommended for individuals who meet screening criteria or present with a change in bowel symptoms, such as diarrhea, bleeding, or obstruction.13,14

Fecal incontinence treatments include a range of approaches categorized from conservative, or first-line therapy, to fourth-line surgical managements (FIGURE 1).1,10,13,14 In this Update, we review the results of 3 well-designed trials that enrolled women with frequent nonneurogenic FI.

Common first- and second-line treatments produce equivalent improvements in FI symptoms at
6 months
Jelovsek JE, Markland AD, Whitehead WE, et al; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Controlling faecal incontinence in women by performing anal exercises with biofeedback or loperamide: a randomized clinical trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:698-710.
In a multicenter, randomized trial of first- and second-line treatments for FI, Jelovsek and colleagues evaluated the efficacy of oral placebo, loperamide, pelvic floor physical therapy (PFPT) with biofeedback using anorectal manometry, or combination therapy over a 24-week period.
Continue to: Four treatments compared...
Four treatments compared
Three hundred women with FI occurring monthly for 3 months were included in the trial. Women were excluded if they had a stool classification of type 1 or type 7 on the Bristol Stool Scale, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), history of rectovaginal fistula or cloacal defect, rectal prolapse, prior bowel diversion, fecal impaction, neurologic disorder leading to incontinence, use of loperamide or diphenoxylate within the last 30 days, childbirth within the last 3 months, need for antiretroviral drugs, hepatic impairment, or chronic abdominal pain without diarrhea.
Baseline characteristics and symptoms severity were similar among participants. The average age of the women was 63 years, with 79% white and 85% postmenopausal. Participants had a mean (SD) of 1.6 (1.8) leaks per day.
Participants were randomly assigned in a 0.5:1:1:1 fashion to receive oral placebo, loperamide, oral placebo with PFPT/biofeedback, or loperamide with PFPT/biofeedback. All participants received a standardized educational pamphlet that outlined dietary and behavioral recommendations.
Women assigned to PFPT/biofeedback received 6 sessions every other week. Loperamide was started at a dosage of 2 mg per day with the possibility of dose maintenance, escalation, reduction, or discontinuation.
Study outcomes. The primary outcome was a change from baseline to 24 weeks in the Vaizey FI symptom severity score, which assesses fecal frequency, urgency, and use of pads and medications. Secondary outcomes included assessment of a 7-day bowel diary and other quality-of-life measures. Data at 24 weeks were available for 89% of the women.
All treatment groups experienced improved FI symptoms
Based on changes in Vaizey scores after 24 weeks of treatment, women in all treatment groups had similar improvement in symptoms severity. However, those who received loperamide and PFPT/biofeedback had decreased pad changes per week and more accident-free days compared with women treated with placebo and biofeedback. Quality of life at 24 weeks was not statistically different between treatment groups as improvement was seen in all groups, including those who received oral placebo and patient education.
Adverse events. The proportion of gastrointestinal adverse effects was similar between treatment groups, ranging from 45% to 63%. Constipation was the most common adverse event overall and was more common in those taking loperamide, occurring in 51% of the loperamide plus PFPT/biofeedback group, 38% of those who received loperamide alone, 23% of the biofeedback with placebo group, and 12% of the placebo-alone group.
Strengths and limitations. Strengths of this study include its multisite, large sample size, low dropout rate, and sufficiently powered design to compare various combinations of first- and second-line therapies in women with a mean baseline FI of 1.6 leaks per day. Another strength is the robustness of the PFPT/biofeedback sessions that used anorectal manometry. This may, however, limit the study's external validity given that clinical use of this device is likely rare. Additionally, the population was comprised largely of postmenopausal and white women, which may make the findings less generalizable to other populations.
Women who suffer from frequent FI may require both loperamide and PFPT/biofeedback if they want to increase the likelihood of accident-free days and use of fewer pads. Should they note increased constipation or are not amenable to scheduled PFPT sessions, formalized education about dietary modifications, according to this study, will provide improvement in symptom severity.
Continue to: Novel vaginal bowel control system...
Novel vaginal bowel control system is effective, durable over 12 months for FI treatment
Richter HE, Dunivan G, Brown HW, et al. A 12-month clinical durability of effectiveness and safety evaluation of a vaginal bowel control system for the nonsurgical treatment of fecal incontinence. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2019;25:113-119.
Richter and colleagues characterized clinical success, effect on quality of life, and durability over 12 months of a novel vaginal bowel control device (Eclipse System; Pelvalon) for FI in a prospective cohort study. The device is a silicone-coated vaginal insert with a detachable pump and balloon that deflects the rectovaginal septum posteriorly, thus impeding the passage of stool in the rectum (FIGURE 2).

Study eligibility criteria and treatment protocol
Women were eligible for the study if they had 4 or more episodes of fecal soiling on a 2-week bowel diary and had FI for at least 6 months. Participants were excluded if they had prolapse outside the hymen, rectovaginal fistula, IBD, congenital anorectal malformation, urinary or colorectal infection, chronic pelvic or anorectal pain, pregnancy or planning pregnancy in the next 5 months, unmanaged chronic watery diarrhea, presence of an open wound or tear in the vagina, significant urogenital atrophy, or any psychiatric or neurologic disorder that would hinder the ability to participate.
Participants successfully fitted with the device (3 attempts were allowed) were entered into the study's run-in phase. Those who were successfully fitted and had a 50% or greater reduction in FI continued into the treatment phase with 12 months of follow-up.
Of the 137 women eligible for device fitting, 62% were successfully fitted. The 73 (86%) women who had a 50% or greater reduction in FI during the run-in period comprised the intent-to-treat study population. On average, these women were 61.3 years of age, with 70% white and 82% postmenopausal. At baseline, they had a mean of 14.1 episodes of FI over 2 weeks. (Prior to enrollment, 97.3% of women attempted self-management strategies, 17.8% to 23% failed conservative therapy, and 7.8% to 13.7% failed surgical therapy.) The follow-up rate at 12 months was 74%.
Study outcomes. The primary outcome was treatment success, defined as proportion of subjects with a 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes at 3 months; this outcome also was evaluated at 6 and 12 months. Secondary outcomes were the number of FI episodes and quality-of-life measures at 3, 6, and 12 months.
Treatment success, patient satisfaction high
In the treatment phase, women had sustained improvements in symptom severity and quality-of-life measures over 12 months. Treatment success was 73% at 3 months, 71% at 6 months, and 70% at 12 months. Complete continence was achieved in 46% of participants at 12 months, and major FI episodes (requiring immediate change of undergarments) decreased from 5.0 at baseline to 0.5 at 12 months. Quality-of-life measures were improved at 3 months, and improvement was sustained over 12 months. Satisfaction was 94% at 12 months.
Adverse events. No serious device-related adverse events occurred. Mild device-related adverse events were experienced by 45% of women during the fitting process and by 38% during treatment period. These included vaginal wall injury such as hyperemia and erosion; vaginal or pelvic discomfort; vaginal infection; constipation; and lower urinary tract issues such as urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. No adverse events led to treatment discontinuation.
Strengths and limitations. Strengths of this study include that it was conducted at multiple clinical sites, had a large sample size, and had a 1-year follow-up period in a population with daily FI. A limitation was that only women who had a 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes during the run-in period were followed for 12 months; however, this was 86% of the original cohort. The use of a comparative group using other devices, such as anal plugs, would have strengthened this study.
The Eclipse intravaginal bowel control device (approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2015) provided a sustained 50% or greater reduction in FI episodes in more than 70% of women wearing the device for 1 year, with high patient satisfaction. Thus, for women who fail conservative treatment methods for FI, clinicians should consider referring them to a urogynecologist or specialist who is knowledgeable in fitting this vaginal bowel control device.
Continue to: Sacroneuromodulation for FI…
Sacral neuromodulation for FI is effective long-term
Hull T, Giese C, Wexner SD, et al; for the SNS Study Group. Long-term durability of sacral nerve stimulation therapy for chronic fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:234-245.
In this multicenter, prospective cohort study, Hull and colleagues evaluated the 5-year efficacy of sacral neuromodulation (SNM), also known as sacral nerve stimulation, for treatment of FI. This study followed an earlier investigation by Wexner and colleagues, which reported that 83% of 120 patients treated with SNM had a 50% or greater improvement in FI episodes at 12 months.16
Details of the study
The investigators enrolled 133 participants (92% female) who had more than 2 episodes of FI per week for longer than 6 months (12 months after vaginal delivery). Participants were excluded if they had congenital anorectal malformations, prior rectal surgery within the past 12 months (or 24 months if due to cancer), defects greater than 120° of the external anal sphincter (EAS), IBD, unmanaged chronic watery diarrhea, stool consistency type 6 or type 7 on the Bristol Stool Scale, sequela of pelvic radiation, active anal abscess or fistula, pregnancy, or planned pregnancy.
Eligible participants underwent a 2-stage procedure with the InterStim bowel control device (Medtronic). If participants experienced a 50% or greater reduction in incontinence episodes with a wearable external SNM device in the test stimulation (stage 1), they received the chronic SNM implant device (stage 2).
Participants who underwent device implantation were followed at 1, 3, and 6 months and annually for 5 years or until they exited the study. Bowel diaries and quality of life assessments were completed at baseline and at follow-up.
The primary outcome was therapeutic success, defined as 50% or greater improvement in FI episodes per week.
A total of 120 participants (90%) underwent implantation of the chronic lead and neuromodulator, and 76 (63%) were followed for 5 years. Baseline characteristics available in the initial study of 133 participants showed that the mean age was 60.5 years; 25% had undergone a prior anal sphincteroplasty; and 16.5% and 10.5% had EAS or internal anal sphincter (IAS) defects, respectively, on endoanal ultrasonography.16
Therapeutic success was high at 5 years
At the 5-year follow-up, 89% (64/72) of participants met therapeutic success, with a reduction in weekly FI episodes from 9.1 at baseline to 1.7 at 5 years. The number of incontinence pads required decreased, and more participants wore no pads at 5 years. In the intention-to-treat analysis, carrying forward the baseline FI rate in participants who lacked follow-up data, the therapeutic success rate was 69%. Quality-of-life measures improved at 5 years, both statistically and by minimal clinical difference.
Adverse events. Sixty-eight percent of participants experienced device-related adverse events, including implant site pain, change in sensation of stimulation, change in efficacy, implant site infection, or neurostimulator battery depletion (neurostimulator use commonly expires after 3 to 5 years). Of these events, 80% were successfully treated with medications, reprogramming, or no intervention. The 5-year probability of device revision or replacement was 24.4%, and the 5-year probability of device explant was 19.0%.
Strengths and limitations. Overall, this study was a well-designed, multicenter trial with long-term follow-up that showed significant improvement in FI with the use of SNM. Its strengths include the enrollment of postmenopausal women who had current defects in EAS and/or IAS on endoanal ultrasonography and 25% who had a prior sphincteroplasty. The findings therefore are relevant to the gynecologic population in whom anal sphincteroplasty would not be recommended. The study also accounted for dropouts and reported the adjusted success rate of 69% at 5 years in that group.
The lack of a control arm to rule out the placebo effect is a limitation of this study, although randomized trials comparing the effect of SNM "on" versus "off" showed greater improvement with the device "on."17
Sacral neuromodulation is an excellent therapy for women with daily FI who have failed noninvasive options and desire to proceed to a more durable, long-lasting device therapy. Although adverse events may occur, they are mild and most often resolve with device reprogramming.
- Sultan AH, Monga A, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female anorectal dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017;36:10-34.
- Bharucha AE, Dunivan G, Goode PS, et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and classification of fecal incontinence: state of the science summary for the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) workshop. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:127-136.
- Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Locke GR, et al. Symptoms and quality of life in community women with fecal incontinence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1004-1008.
- Perry S, Shaw C, McGrother C, et al; Leicestershire MRC Incontinence Study Team. Prevalence of faecal incontinence in adults aged 40 years or more living in the community. Gut. 2002;50:480-484.
- Ditah I, Devaki P, Luma HN, et al. Prevalence, trends, and risk factors for fecal incontinence in United States adults, 2005-2010. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:636-643.e1-2.
- Brown HW, Wexner SD, Lukacz ES. Factors associated with care seeking among women with accidental bowel leakage. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2013;19:66-71.
- Norton NJ. The perspective of the patient. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(1 suppl 1):S175-S179.
- Guan W, Schmuhl NB, Brown HW. Response re: If we don't ask, they won't tell: screening for urinary and fecal incontinence by primary care providers. J Am Board Fam Med. 2019;32:119.3-120.
- Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, et al; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:512-517.
- Wald A, Bharucha AE, Cosman BC, et al. ACG clinical guideline: management of benign anorectal disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1141-1157.
- Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Schleck CD, et al. Bowel disturbances are the most important risk factors for late onset fecal incontinence: a population-based case-control study in women. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1559-1566.
- Lewis SJ, Heaton KW. Stool form scale as a useful guide to intestinal transit time. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:920-924.
- Paquette IM, Varma MG, Kaiser AM, et al. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons' clinical practice guideline for the treatment of fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015;58:623-636.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 210: Fecal incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e260-e273.
- Heymen S, Scarlett Y, Jones K, et al. Randomized controlled trial shows biofeedback to be superior to pelvic floor exercises for fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52:1730-1737.
- Wexner SD, Coller JA, Devroede G, et al. Sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence: results of a 120-patient prospective multicenter study. Ann Surg. 2010;251:441-449.
- Leroi AM, Parc Y, Lehur PA, et al. Efficacy of sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence: results of a multicenter double-blind crossover study. Ann Surg. 2005;242:662-669.
- Sultan AH, Monga A, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female anorectal dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017;36:10-34.
- Bharucha AE, Dunivan G, Goode PS, et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and classification of fecal incontinence: state of the science summary for the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) workshop. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:127-136.
- Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Locke GR, et al. Symptoms and quality of life in community women with fecal incontinence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1004-1008.
- Perry S, Shaw C, McGrother C, et al; Leicestershire MRC Incontinence Study Team. Prevalence of faecal incontinence in adults aged 40 years or more living in the community. Gut. 2002;50:480-484.
- Ditah I, Devaki P, Luma HN, et al. Prevalence, trends, and risk factors for fecal incontinence in United States adults, 2005-2010. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:636-643.e1-2.
- Brown HW, Wexner SD, Lukacz ES. Factors associated with care seeking among women with accidental bowel leakage. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2013;19:66-71.
- Norton NJ. The perspective of the patient. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(1 suppl 1):S175-S179.
- Guan W, Schmuhl NB, Brown HW. Response re: If we don't ask, they won't tell: screening for urinary and fecal incontinence by primary care providers. J Am Board Fam Med. 2019;32:119.3-120.
- Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, et al; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:512-517.
- Wald A, Bharucha AE, Cosman BC, et al. ACG clinical guideline: management of benign anorectal disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1141-1157.
- Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Schleck CD, et al. Bowel disturbances are the most important risk factors for late onset fecal incontinence: a population-based case-control study in women. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1559-1566.
- Lewis SJ, Heaton KW. Stool form scale as a useful guide to intestinal transit time. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:920-924.
- Paquette IM, Varma MG, Kaiser AM, et al. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons' clinical practice guideline for the treatment of fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015;58:623-636.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 210: Fecal incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e260-e273.
- Heymen S, Scarlett Y, Jones K, et al. Randomized controlled trial shows biofeedback to be superior to pelvic floor exercises for fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52:1730-1737.
- Wexner SD, Coller JA, Devroede G, et al. Sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence: results of a 120-patient prospective multicenter study. Ann Surg. 2010;251:441-449.
- Leroi AM, Parc Y, Lehur PA, et al. Efficacy of sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence: results of a multicenter double-blind crossover study. Ann Surg. 2005;242:662-669.
Reframing Clinician Distress: Moral Injury Not Burnout
*This version has been corrected. In the original version the first sentence incorrectly referred to moral injury instead of burnout.
For more than a decade, the term burnout has been used to describe clinician distress.1,2 Although some clinicians in federal health care systems may be protected from some of the drivers of burnout, other federal practitioners suffer from rule-driven health care practices and distant, top-down administration. The demand for health care is expanding, driven by the aging of the US population.3 Massive information technology investments, which promised efficiency for health care providers,4 have instead delivered a triple blow: They have diverted capital resources that might have been used to hire additional caregivers,5 diverted the time and attention of those already engaged in patient care,6 and done little to improve patient outcomes.7 Reimbursements are falling, and the only way for health systems to maintain their revenue is to increase the number of patients each clinician sees per day.8 As the resources of time and attention shrink, and as spending continues with no improvement in patient outcomes, clinician distress is on the rise.9 It will be important to understand exactly what the drivers of the problem are for federal clinicians so that solutions can be appropriately targeted. The first step in addressing the epidemic of physician distress is using the most accurate terminology to describe it.
Freudenberger defined burnout in 1975 as a constellation of symptoms—malaise, fatigue, frustration, cynicism, and inefficacy—that arise from “making excessive demands on energy, strength, or resources” in the workplace.10 The term was borrowed from other fields and applied to health care in the hopes of readily transferring the solutions that had worked in other industries to address a growing crisis among physicians. Unfortunately, the crisis in health care has proven resistant to solutions that have worked elsewhere, and many clinicians have resisted being characterized as burned out, citing a subtle, elusive disconnect between what they have experienced and what burnout encapsulates.
In July 2018, the conversation about clinician distress shifted with an article we wrote in STAT that described the moral injury of health care.11 The concept of moral injury was first described in service members who returned from the Vietnam War with symptoms that loosely fit a diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), but which did not respond to standard PTSD treatment and contained symptoms outside the PTSD constellation.12 On closer assessment, what these service members were experiencing had a different driver. Whereas those with PTSD experienced a real and imminent threat to their mortality and had come back deeply concerned for their individual, physical safety, those with this different presentation experienced repeated insults to their morality and had returned questioning whether they were still, at their core, moral beings. They had been forced, in some way, to act contrary to what their beliefs dictated was right by killing civilians on orders from their superiors, for example. This was a different category of psychological injury that required different treatment.
Moral injury occurs when we perpetrate, bear witness to, or fail to prevent an act that transgresses our deeply held moral beliefs. In the health care context, that deeply held moral belief is the oath each of us took when embarking on our paths as health care providers: Put the needs of patients first. That oath is the lynchpin of our working lives and our guiding principle when searching for the right course of action. But as clinicians, we are increasingly forced to consider the demands of other stakeholders—the electronic medical record (EMR), the insurers, the hospital, the health care system, even our own financial security—before the needs of our patients. Every time we are forced to make a decision that contravenes our patients’ best interests, we feel a sting of moral injustice. Over time, these repetitive insults amass into moral injury.
The difference between burnout and moral injury is important because using different terminology reframes the problem and the solutions. Burnout suggests that the problem resides within the individual, who is in some way deficient. It implies that the individual lacks the resources or resilience to withstand the work environment. Since the problem is in the individual, the solutions to burnout must be in the individual, too, and therefore, it is the individual’s responsibility to find and implement them. Many of the solutions to physician distress posited to date revolve around this conception; hence, the focus on yoga, mindfulness, wellness retreats, and meditation.13 While there is nothing inherently wrong with any of those practices, it is absurd to believe that yoga will solve the problems of treating a cancer patient with a declined preauthorization for chemotherapy, having no time to discuss a complex diagnosis, or relying on a computer system that places metrics ahead of communication. These problems are not the result of some failing on the part of the individual clinician.
Moral injury, on the other hand, describes the challenge of simultaneously knowing what care patients need but being unable to provide it due to constraints that are beyond our control. Moral injury is the consequence of the ever-present double binds in health care: Do we take care of our patient, the hospital, the insurer, the EMR, the health care system, or our productivity metrics first? There should be only 1 answer to that question, but the current business framework of medicine pressures us to serve all these masters at once. Moral injury locates the source of distress in a broken system, not a broken individual, and allows us to direct solutions at the causes of distress. And in the end, addressing the drivers of moral injury on a large scale may be the most effective preventive treatment for its cumulative effects among health care providers.
The long-term solutions to moral injury demand changes in the business framework of health care. The solutions reside not in promoting mindfulness or resilience among individual physicians, but in creating a health care environment that finally acknowledges the value of the time clinicians and patients spend together developing the trust, understanding, and compassion that accompany a true relationship. The long-term solutions to moral injury include a health care system that prioritizes healing over profit and that trusts its clinicians to always put their patients’ best interests first.
Treating moral injury will not be simple. It cannot happen quickly, and it will not happen without widespread clinician engagement. Change can begin when clinicians identify the double binds they face every day and convey those challenges to their administrators. If administrators and clinicians are willing to work together to resolve these double binds, health care will improve for everyone.
The following are our recommendations for how you can bring change both locally and on a broader scale.
Bring together the 2 sides of the health care house: administrators and clinicians. Invite administrators to join you on rounds, in clinic, or in the operating room. Ask them to follow you during a night of call or to spend an overnight shift with you in the emergency department. The majority of people, including health care administrators, have had only glancing encounters with the medical system. They see their primary care doctor, have regular screening procedures, and maybe get treated for a routine illness or injury. None of those encounters expose them to the depth of challenge in the system.
It takes exposure over a longer duration, or with greater intensity, to appreciate the tensions and double binds that patients and clinicians face regularly.14,15 Whether or not the administrators accept your invitation, you must also ask to see the challenges from their side. Block out an afternoon, a day, or a week to follow them and learn where they struggle in their work. Only when we understand the other party’s perspective can we truly begin to empathize and communicate meaningfully. That profound understanding is the place where commonality and compromises are found.
Make clinician satisfaction a financial priority. Although care team well-being is now part of the quadruple aim (patient experience, population health, reducing costs, and provider experience), organizations must be held accountable to ensure it is a priority. If we choose to link patient satisfaction with clinician compensation, why not link clinician satisfaction with executive compensation?
Make sure every physician leader has and uses the cell phone number of his or her legislators. Hospitals and big pharma have nearly bottomless lobbying budgets, which makes competing with them for lawmakers’ attention a formidable prospect. Despite this, physician leaders (ie, chief wellness officer, department chairperson, medical society president, etc) have a responsibility to communicate with legislators about the needs of patients (their constituents) and what role our legislators can play in fulfilling those needs. We must understand how policy, regulation, and legislation work, and we need to find seats at every table where the decisions that impact clinical care are made. The first step is opening lines of communication with those who have the power to enact large-scale change.
Reestablish a sense of community among clinicians. Too often clinicians are pitted against one another as resources shrink. Doctors compete with each other for referrals, advanced practitioners and nurses compete with doctors, and everyone feels overstressed. What we tend to forget is that we are all working toward the same goal: To give patients the best care possible. It’s time to view each other with the presumption of charity and to have each other’s backs. Uniting for support, camaraderie, mentorship, and activism is a necessary step in making change.
1 . West CP, Dyrbye LN, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Single item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are useful for assessing burnout in medical professionals. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(12):1318-1321.
2. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH. Executive leadership and physician well-being: nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92(1):129-146.
3. Institute of Medicine (US) National Cancer Policy Forum. Ensuring Quality Cancer Care through the Oncology Workforce: Sustaining Care in the 21st Century: Workshop Summary. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2009.
4. Menachemi N, Collum TH. Benefits and drawbacks of electronic health record systems. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2011;4:47-55.
5. Palabindala V, Pamarthy A, Jonnalagadda NR. Adoption of electronic health records and barriers. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2016;6(5):32643.
6. Zeng X. The impacts of electronic health record implementation on the health care workforce. N C Med J. 2016;77(2):112-114.
7. Squires D. U.S. health care from a global perspective: spending, use of services, prices, and health in 13 countries. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2015/oct/us-health-care-global-perspective. Published October 8, 2015. Accessed August 19, 2019.
8. Fifer R. Health care economics: the real source of reimbursement problems. https://www.asha.org/Articles/Health-Care-Economics-The-Real-Source-of-Reimbursement-Problems/. Published July 2016. Accessed August 19, 2019.
9. Jha AK, Iliff AR, Chaoui AA, Defossez S, Bombaugh MC, Miller YR. A crisis in health care: a call to action on physician burnout. http://www.massmed.org/News-and-Publications/MMS-News-Releases/Physician-Burnout-Report-2018/. Published March 28, 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
10. Freudenberger HJ. The staff burn-out syndrome in alternative institutions. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1975;12(1):73-82.
11. Dean W, Talbot S. Physicians aren’t “burning out.” They’re suffering from moral injury. STAT . July 26, 2018. https://www.statnews.com/2018/07/26/physicians-not-burning-out-they-are-suffering-moral-injury/. Accessed August 19, 2019.
12. Shay J. Moral injury. Psychoanal Psych. 2014;31(2):182-191.
13. Sinsky C, Shanafelt TD, Murphy ML, et al. Creating the organizational foundation for joy in medicine: organizational changes lead to physician satisfaction. https://edhub.ama-assn.org/steps-forward/module/2702510. Published September 7, 2017. Accessed August 19, 2019.
14. Golshan Ma. When a cancer surgeon becomes a cancer patient. https://elemental.medium.com/when-a-cancer-surgeon-becomes-a-cancer-patient-3b9d984066da. Published June 25, 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
15. Joseph S, Japa S. We were inspired to become primary care physicians. Now we’re reconsidering a field in crisis. STAT . June 20, 2019. https://www.statnews.com/2019/06/20/primary-care-field-crisis/. Accessed August 19, 2019.
*This version has been corrected. In the original version the first sentence incorrectly referred to moral injury instead of burnout.
For more than a decade, the term burnout has been used to describe clinician distress.1,2 Although some clinicians in federal health care systems may be protected from some of the drivers of burnout, other federal practitioners suffer from rule-driven health care practices and distant, top-down administration. The demand for health care is expanding, driven by the aging of the US population.3 Massive information technology investments, which promised efficiency for health care providers,4 have instead delivered a triple blow: They have diverted capital resources that might have been used to hire additional caregivers,5 diverted the time and attention of those already engaged in patient care,6 and done little to improve patient outcomes.7 Reimbursements are falling, and the only way for health systems to maintain their revenue is to increase the number of patients each clinician sees per day.8 As the resources of time and attention shrink, and as spending continues with no improvement in patient outcomes, clinician distress is on the rise.9 It will be important to understand exactly what the drivers of the problem are for federal clinicians so that solutions can be appropriately targeted. The first step in addressing the epidemic of physician distress is using the most accurate terminology to describe it.
Freudenberger defined burnout in 1975 as a constellation of symptoms—malaise, fatigue, frustration, cynicism, and inefficacy—that arise from “making excessive demands on energy, strength, or resources” in the workplace.10 The term was borrowed from other fields and applied to health care in the hopes of readily transferring the solutions that had worked in other industries to address a growing crisis among physicians. Unfortunately, the crisis in health care has proven resistant to solutions that have worked elsewhere, and many clinicians have resisted being characterized as burned out, citing a subtle, elusive disconnect between what they have experienced and what burnout encapsulates.
In July 2018, the conversation about clinician distress shifted with an article we wrote in STAT that described the moral injury of health care.11 The concept of moral injury was first described in service members who returned from the Vietnam War with symptoms that loosely fit a diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), but which did not respond to standard PTSD treatment and contained symptoms outside the PTSD constellation.12 On closer assessment, what these service members were experiencing had a different driver. Whereas those with PTSD experienced a real and imminent threat to their mortality and had come back deeply concerned for their individual, physical safety, those with this different presentation experienced repeated insults to their morality and had returned questioning whether they were still, at their core, moral beings. They had been forced, in some way, to act contrary to what their beliefs dictated was right by killing civilians on orders from their superiors, for example. This was a different category of psychological injury that required different treatment.
Moral injury occurs when we perpetrate, bear witness to, or fail to prevent an act that transgresses our deeply held moral beliefs. In the health care context, that deeply held moral belief is the oath each of us took when embarking on our paths as health care providers: Put the needs of patients first. That oath is the lynchpin of our working lives and our guiding principle when searching for the right course of action. But as clinicians, we are increasingly forced to consider the demands of other stakeholders—the electronic medical record (EMR), the insurers, the hospital, the health care system, even our own financial security—before the needs of our patients. Every time we are forced to make a decision that contravenes our patients’ best interests, we feel a sting of moral injustice. Over time, these repetitive insults amass into moral injury.
The difference between burnout and moral injury is important because using different terminology reframes the problem and the solutions. Burnout suggests that the problem resides within the individual, who is in some way deficient. It implies that the individual lacks the resources or resilience to withstand the work environment. Since the problem is in the individual, the solutions to burnout must be in the individual, too, and therefore, it is the individual’s responsibility to find and implement them. Many of the solutions to physician distress posited to date revolve around this conception; hence, the focus on yoga, mindfulness, wellness retreats, and meditation.13 While there is nothing inherently wrong with any of those practices, it is absurd to believe that yoga will solve the problems of treating a cancer patient with a declined preauthorization for chemotherapy, having no time to discuss a complex diagnosis, or relying on a computer system that places metrics ahead of communication. These problems are not the result of some failing on the part of the individual clinician.
Moral injury, on the other hand, describes the challenge of simultaneously knowing what care patients need but being unable to provide it due to constraints that are beyond our control. Moral injury is the consequence of the ever-present double binds in health care: Do we take care of our patient, the hospital, the insurer, the EMR, the health care system, or our productivity metrics first? There should be only 1 answer to that question, but the current business framework of medicine pressures us to serve all these masters at once. Moral injury locates the source of distress in a broken system, not a broken individual, and allows us to direct solutions at the causes of distress. And in the end, addressing the drivers of moral injury on a large scale may be the most effective preventive treatment for its cumulative effects among health care providers.
The long-term solutions to moral injury demand changes in the business framework of health care. The solutions reside not in promoting mindfulness or resilience among individual physicians, but in creating a health care environment that finally acknowledges the value of the time clinicians and patients spend together developing the trust, understanding, and compassion that accompany a true relationship. The long-term solutions to moral injury include a health care system that prioritizes healing over profit and that trusts its clinicians to always put their patients’ best interests first.
Treating moral injury will not be simple. It cannot happen quickly, and it will not happen without widespread clinician engagement. Change can begin when clinicians identify the double binds they face every day and convey those challenges to their administrators. If administrators and clinicians are willing to work together to resolve these double binds, health care will improve for everyone.
The following are our recommendations for how you can bring change both locally and on a broader scale.
Bring together the 2 sides of the health care house: administrators and clinicians. Invite administrators to join you on rounds, in clinic, or in the operating room. Ask them to follow you during a night of call or to spend an overnight shift with you in the emergency department. The majority of people, including health care administrators, have had only glancing encounters with the medical system. They see their primary care doctor, have regular screening procedures, and maybe get treated for a routine illness or injury. None of those encounters expose them to the depth of challenge in the system.
It takes exposure over a longer duration, or with greater intensity, to appreciate the tensions and double binds that patients and clinicians face regularly.14,15 Whether or not the administrators accept your invitation, you must also ask to see the challenges from their side. Block out an afternoon, a day, or a week to follow them and learn where they struggle in their work. Only when we understand the other party’s perspective can we truly begin to empathize and communicate meaningfully. That profound understanding is the place where commonality and compromises are found.
Make clinician satisfaction a financial priority. Although care team well-being is now part of the quadruple aim (patient experience, population health, reducing costs, and provider experience), organizations must be held accountable to ensure it is a priority. If we choose to link patient satisfaction with clinician compensation, why not link clinician satisfaction with executive compensation?
Make sure every physician leader has and uses the cell phone number of his or her legislators. Hospitals and big pharma have nearly bottomless lobbying budgets, which makes competing with them for lawmakers’ attention a formidable prospect. Despite this, physician leaders (ie, chief wellness officer, department chairperson, medical society president, etc) have a responsibility to communicate with legislators about the needs of patients (their constituents) and what role our legislators can play in fulfilling those needs. We must understand how policy, regulation, and legislation work, and we need to find seats at every table where the decisions that impact clinical care are made. The first step is opening lines of communication with those who have the power to enact large-scale change.
Reestablish a sense of community among clinicians. Too often clinicians are pitted against one another as resources shrink. Doctors compete with each other for referrals, advanced practitioners and nurses compete with doctors, and everyone feels overstressed. What we tend to forget is that we are all working toward the same goal: To give patients the best care possible. It’s time to view each other with the presumption of charity and to have each other’s backs. Uniting for support, camaraderie, mentorship, and activism is a necessary step in making change.
*This version has been corrected. In the original version the first sentence incorrectly referred to moral injury instead of burnout.
For more than a decade, the term burnout has been used to describe clinician distress.1,2 Although some clinicians in federal health care systems may be protected from some of the drivers of burnout, other federal practitioners suffer from rule-driven health care practices and distant, top-down administration. The demand for health care is expanding, driven by the aging of the US population.3 Massive information technology investments, which promised efficiency for health care providers,4 have instead delivered a triple blow: They have diverted capital resources that might have been used to hire additional caregivers,5 diverted the time and attention of those already engaged in patient care,6 and done little to improve patient outcomes.7 Reimbursements are falling, and the only way for health systems to maintain their revenue is to increase the number of patients each clinician sees per day.8 As the resources of time and attention shrink, and as spending continues with no improvement in patient outcomes, clinician distress is on the rise.9 It will be important to understand exactly what the drivers of the problem are for federal clinicians so that solutions can be appropriately targeted. The first step in addressing the epidemic of physician distress is using the most accurate terminology to describe it.
Freudenberger defined burnout in 1975 as a constellation of symptoms—malaise, fatigue, frustration, cynicism, and inefficacy—that arise from “making excessive demands on energy, strength, or resources” in the workplace.10 The term was borrowed from other fields and applied to health care in the hopes of readily transferring the solutions that had worked in other industries to address a growing crisis among physicians. Unfortunately, the crisis in health care has proven resistant to solutions that have worked elsewhere, and many clinicians have resisted being characterized as burned out, citing a subtle, elusive disconnect between what they have experienced and what burnout encapsulates.
In July 2018, the conversation about clinician distress shifted with an article we wrote in STAT that described the moral injury of health care.11 The concept of moral injury was first described in service members who returned from the Vietnam War with symptoms that loosely fit a diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), but which did not respond to standard PTSD treatment and contained symptoms outside the PTSD constellation.12 On closer assessment, what these service members were experiencing had a different driver. Whereas those with PTSD experienced a real and imminent threat to their mortality and had come back deeply concerned for their individual, physical safety, those with this different presentation experienced repeated insults to their morality and had returned questioning whether they were still, at their core, moral beings. They had been forced, in some way, to act contrary to what their beliefs dictated was right by killing civilians on orders from their superiors, for example. This was a different category of psychological injury that required different treatment.
Moral injury occurs when we perpetrate, bear witness to, or fail to prevent an act that transgresses our deeply held moral beliefs. In the health care context, that deeply held moral belief is the oath each of us took when embarking on our paths as health care providers: Put the needs of patients first. That oath is the lynchpin of our working lives and our guiding principle when searching for the right course of action. But as clinicians, we are increasingly forced to consider the demands of other stakeholders—the electronic medical record (EMR), the insurers, the hospital, the health care system, even our own financial security—before the needs of our patients. Every time we are forced to make a decision that contravenes our patients’ best interests, we feel a sting of moral injustice. Over time, these repetitive insults amass into moral injury.
The difference between burnout and moral injury is important because using different terminology reframes the problem and the solutions. Burnout suggests that the problem resides within the individual, who is in some way deficient. It implies that the individual lacks the resources or resilience to withstand the work environment. Since the problem is in the individual, the solutions to burnout must be in the individual, too, and therefore, it is the individual’s responsibility to find and implement them. Many of the solutions to physician distress posited to date revolve around this conception; hence, the focus on yoga, mindfulness, wellness retreats, and meditation.13 While there is nothing inherently wrong with any of those practices, it is absurd to believe that yoga will solve the problems of treating a cancer patient with a declined preauthorization for chemotherapy, having no time to discuss a complex diagnosis, or relying on a computer system that places metrics ahead of communication. These problems are not the result of some failing on the part of the individual clinician.
Moral injury, on the other hand, describes the challenge of simultaneously knowing what care patients need but being unable to provide it due to constraints that are beyond our control. Moral injury is the consequence of the ever-present double binds in health care: Do we take care of our patient, the hospital, the insurer, the EMR, the health care system, or our productivity metrics first? There should be only 1 answer to that question, but the current business framework of medicine pressures us to serve all these masters at once. Moral injury locates the source of distress in a broken system, not a broken individual, and allows us to direct solutions at the causes of distress. And in the end, addressing the drivers of moral injury on a large scale may be the most effective preventive treatment for its cumulative effects among health care providers.
The long-term solutions to moral injury demand changes in the business framework of health care. The solutions reside not in promoting mindfulness or resilience among individual physicians, but in creating a health care environment that finally acknowledges the value of the time clinicians and patients spend together developing the trust, understanding, and compassion that accompany a true relationship. The long-term solutions to moral injury include a health care system that prioritizes healing over profit and that trusts its clinicians to always put their patients’ best interests first.
Treating moral injury will not be simple. It cannot happen quickly, and it will not happen without widespread clinician engagement. Change can begin when clinicians identify the double binds they face every day and convey those challenges to their administrators. If administrators and clinicians are willing to work together to resolve these double binds, health care will improve for everyone.
The following are our recommendations for how you can bring change both locally and on a broader scale.
Bring together the 2 sides of the health care house: administrators and clinicians. Invite administrators to join you on rounds, in clinic, or in the operating room. Ask them to follow you during a night of call or to spend an overnight shift with you in the emergency department. The majority of people, including health care administrators, have had only glancing encounters with the medical system. They see their primary care doctor, have regular screening procedures, and maybe get treated for a routine illness or injury. None of those encounters expose them to the depth of challenge in the system.
It takes exposure over a longer duration, or with greater intensity, to appreciate the tensions and double binds that patients and clinicians face regularly.14,15 Whether or not the administrators accept your invitation, you must also ask to see the challenges from their side. Block out an afternoon, a day, or a week to follow them and learn where they struggle in their work. Only when we understand the other party’s perspective can we truly begin to empathize and communicate meaningfully. That profound understanding is the place where commonality and compromises are found.
Make clinician satisfaction a financial priority. Although care team well-being is now part of the quadruple aim (patient experience, population health, reducing costs, and provider experience), organizations must be held accountable to ensure it is a priority. If we choose to link patient satisfaction with clinician compensation, why not link clinician satisfaction with executive compensation?
Make sure every physician leader has and uses the cell phone number of his or her legislators. Hospitals and big pharma have nearly bottomless lobbying budgets, which makes competing with them for lawmakers’ attention a formidable prospect. Despite this, physician leaders (ie, chief wellness officer, department chairperson, medical society president, etc) have a responsibility to communicate with legislators about the needs of patients (their constituents) and what role our legislators can play in fulfilling those needs. We must understand how policy, regulation, and legislation work, and we need to find seats at every table where the decisions that impact clinical care are made. The first step is opening lines of communication with those who have the power to enact large-scale change.
Reestablish a sense of community among clinicians. Too often clinicians are pitted against one another as resources shrink. Doctors compete with each other for referrals, advanced practitioners and nurses compete with doctors, and everyone feels overstressed. What we tend to forget is that we are all working toward the same goal: To give patients the best care possible. It’s time to view each other with the presumption of charity and to have each other’s backs. Uniting for support, camaraderie, mentorship, and activism is a necessary step in making change.
1 . West CP, Dyrbye LN, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Single item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are useful for assessing burnout in medical professionals. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(12):1318-1321.
2. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH. Executive leadership and physician well-being: nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92(1):129-146.
3. Institute of Medicine (US) National Cancer Policy Forum. Ensuring Quality Cancer Care through the Oncology Workforce: Sustaining Care in the 21st Century: Workshop Summary. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2009.
4. Menachemi N, Collum TH. Benefits and drawbacks of electronic health record systems. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2011;4:47-55.
5. Palabindala V, Pamarthy A, Jonnalagadda NR. Adoption of electronic health records and barriers. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2016;6(5):32643.
6. Zeng X. The impacts of electronic health record implementation on the health care workforce. N C Med J. 2016;77(2):112-114.
7. Squires D. U.S. health care from a global perspective: spending, use of services, prices, and health in 13 countries. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2015/oct/us-health-care-global-perspective. Published October 8, 2015. Accessed August 19, 2019.
8. Fifer R. Health care economics: the real source of reimbursement problems. https://www.asha.org/Articles/Health-Care-Economics-The-Real-Source-of-Reimbursement-Problems/. Published July 2016. Accessed August 19, 2019.
9. Jha AK, Iliff AR, Chaoui AA, Defossez S, Bombaugh MC, Miller YR. A crisis in health care: a call to action on physician burnout. http://www.massmed.org/News-and-Publications/MMS-News-Releases/Physician-Burnout-Report-2018/. Published March 28, 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
10. Freudenberger HJ. The staff burn-out syndrome in alternative institutions. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1975;12(1):73-82.
11. Dean W, Talbot S. Physicians aren’t “burning out.” They’re suffering from moral injury. STAT . July 26, 2018. https://www.statnews.com/2018/07/26/physicians-not-burning-out-they-are-suffering-moral-injury/. Accessed August 19, 2019.
12. Shay J. Moral injury. Psychoanal Psych. 2014;31(2):182-191.
13. Sinsky C, Shanafelt TD, Murphy ML, et al. Creating the organizational foundation for joy in medicine: organizational changes lead to physician satisfaction. https://edhub.ama-assn.org/steps-forward/module/2702510. Published September 7, 2017. Accessed August 19, 2019.
14. Golshan Ma. When a cancer surgeon becomes a cancer patient. https://elemental.medium.com/when-a-cancer-surgeon-becomes-a-cancer-patient-3b9d984066da. Published June 25, 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
15. Joseph S, Japa S. We were inspired to become primary care physicians. Now we’re reconsidering a field in crisis. STAT . June 20, 2019. https://www.statnews.com/2019/06/20/primary-care-field-crisis/. Accessed August 19, 2019.
1 . West CP, Dyrbye LN, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Single item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are useful for assessing burnout in medical professionals. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(12):1318-1321.
2. Shanafelt TD, Noseworthy JH. Executive leadership and physician well-being: nine organizational strategies to promote engagement and reduce burnout. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92(1):129-146.
3. Institute of Medicine (US) National Cancer Policy Forum. Ensuring Quality Cancer Care through the Oncology Workforce: Sustaining Care in the 21st Century: Workshop Summary. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2009.
4. Menachemi N, Collum TH. Benefits and drawbacks of electronic health record systems. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2011;4:47-55.
5. Palabindala V, Pamarthy A, Jonnalagadda NR. Adoption of electronic health records and barriers. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2016;6(5):32643.
6. Zeng X. The impacts of electronic health record implementation on the health care workforce. N C Med J. 2016;77(2):112-114.
7. Squires D. U.S. health care from a global perspective: spending, use of services, prices, and health in 13 countries. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2015/oct/us-health-care-global-perspective. Published October 8, 2015. Accessed August 19, 2019.
8. Fifer R. Health care economics: the real source of reimbursement problems. https://www.asha.org/Articles/Health-Care-Economics-The-Real-Source-of-Reimbursement-Problems/. Published July 2016. Accessed August 19, 2019.
9. Jha AK, Iliff AR, Chaoui AA, Defossez S, Bombaugh MC, Miller YR. A crisis in health care: a call to action on physician burnout. http://www.massmed.org/News-and-Publications/MMS-News-Releases/Physician-Burnout-Report-2018/. Published March 28, 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
10. Freudenberger HJ. The staff burn-out syndrome in alternative institutions. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1975;12(1):73-82.
11. Dean W, Talbot S. Physicians aren’t “burning out.” They’re suffering from moral injury. STAT . July 26, 2018. https://www.statnews.com/2018/07/26/physicians-not-burning-out-they-are-suffering-moral-injury/. Accessed August 19, 2019.
12. Shay J. Moral injury. Psychoanal Psych. 2014;31(2):182-191.
13. Sinsky C, Shanafelt TD, Murphy ML, et al. Creating the organizational foundation for joy in medicine: organizational changes lead to physician satisfaction. https://edhub.ama-assn.org/steps-forward/module/2702510. Published September 7, 2017. Accessed August 19, 2019.
14. Golshan Ma. When a cancer surgeon becomes a cancer patient. https://elemental.medium.com/when-a-cancer-surgeon-becomes-a-cancer-patient-3b9d984066da. Published June 25, 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
15. Joseph S, Japa S. We were inspired to become primary care physicians. Now we’re reconsidering a field in crisis. STAT . June 20, 2019. https://www.statnews.com/2019/06/20/primary-care-field-crisis/. Accessed August 19, 2019.
Pyrotinib bests lapatinib in HER2+ metastatic breast cancer treatment
Among women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer enrolled in a phase 2 randomized trial, the pan-ErbB inhibitor pyrotinib plus capecitabine had manageable toxicity and a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) than lapatinib plus capecitabine, investigators reported.
The pyrotinib/capecitabine combination also led to significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) versus that of standard lapatinib/capecitabine treatment in these women, who had previously received treatment with taxanes, anthracyclines, and in some cases trastuzumab, the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“To our knowledge, this is the first trial to demonstrate that a novel epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2–targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor provides ORR and PFS benefits over lapatinib,” wrote Fei Ma, MD, of the National Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking, and colleagues.
In the phase 2 study, a total of 128 Chinese women with histologically confirmed relapsed or metastatic breast cancer were randomized to receive the pyrotinib- or lapatinib-containing regimens given in 21-day cycles.
Overall response rates, the primary end point, were 78% (51 of 65 patients) in the pyrotinib arm and 57.1% (36 of 63 patients) in the lapatinib arm (P = .01), Dr. Yu and colleagues reported.
Median PFS was 18.1 months versus 7.0 months in the pyrotinib and lapatinib arms, respectively (P less than .001). A “potential trend” toward improved overall survival was noted in the pyrotinib arm, though the data were premature and not statistically significant at the time of data analysis, according to the investigators.
Altogether, these efficacy results tracked with those of an earlier phase 1 investigation, and currently, a randomized phase 3 study is underway to confirm the findings, reported Dr. Yu and coauthors.
Hand-foot syndrome and diarrhea were the most common grade 3 adverse events seen with pyrotinib. The rate of grade 3 hand-foot syndrome wit pyrotinib was 24.6% versus 20.6% for the lapatinib group, and the rate of grade 3 diarrhea for the two groups was 15.4% and 4.8%, respectively.
Overall, grade 3 or 4 adverse events were seen in 61% of patients receiving pyrotinib, of which 3.1% were grade 4; they were seen in 47.6% of patients receiving lapatinib, of which 3.2% were grade 4.
Diarrhea of grade 3 severity occurred mainly in the first treatment cycle for both the pyrotinib and lapatinib groups, investigators said.
While the protocol for this randomized phase 2 study did not permit diarrhea prophylaxis, the use of prophylactic loperamide is being studied in a phase 3 study of pyrotinib plus trastuzumab and docetaxel in women with HER2-positive metastatic disease and no prior systemic therapy
Investigators said patients are told to interrupt capecitabine if they experience ongoing grade 3 diarrhea or grade 1 or 2 diarrhea with complications such as dehydration, nausea, vomiting, or fever. If the diarrhea persists after 3 days, pyrotinib should then be interrupted, they said.
Similar advice was given for hand-foot syndrome.
“To date, the only method proven to effectively manage hand-foot syndrome is interruption of treatment and, if necessary, dose reduction,” said the investigators, who recommended first interrupting capecitabine and later pyrotinib.
The study was sponsored by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine and supported by the CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine and the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology in China. The corresponding author of this study, Binghe Xu, MD, PHD, reported institutional research funding from Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine and other disclosures related to AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Roche, and Eisai. Two study coauthors reported employment with Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine.
SOURCE: Ma F et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Aug 20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00108.
Among women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer enrolled in a phase 2 randomized trial, the pan-ErbB inhibitor pyrotinib plus capecitabine had manageable toxicity and a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) than lapatinib plus capecitabine, investigators reported.
The pyrotinib/capecitabine combination also led to significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) versus that of standard lapatinib/capecitabine treatment in these women, who had previously received treatment with taxanes, anthracyclines, and in some cases trastuzumab, the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“To our knowledge, this is the first trial to demonstrate that a novel epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2–targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor provides ORR and PFS benefits over lapatinib,” wrote Fei Ma, MD, of the National Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking, and colleagues.
In the phase 2 study, a total of 128 Chinese women with histologically confirmed relapsed or metastatic breast cancer were randomized to receive the pyrotinib- or lapatinib-containing regimens given in 21-day cycles.
Overall response rates, the primary end point, were 78% (51 of 65 patients) in the pyrotinib arm and 57.1% (36 of 63 patients) in the lapatinib arm (P = .01), Dr. Yu and colleagues reported.
Median PFS was 18.1 months versus 7.0 months in the pyrotinib and lapatinib arms, respectively (P less than .001). A “potential trend” toward improved overall survival was noted in the pyrotinib arm, though the data were premature and not statistically significant at the time of data analysis, according to the investigators.
Altogether, these efficacy results tracked with those of an earlier phase 1 investigation, and currently, a randomized phase 3 study is underway to confirm the findings, reported Dr. Yu and coauthors.
Hand-foot syndrome and diarrhea were the most common grade 3 adverse events seen with pyrotinib. The rate of grade 3 hand-foot syndrome wit pyrotinib was 24.6% versus 20.6% for the lapatinib group, and the rate of grade 3 diarrhea for the two groups was 15.4% and 4.8%, respectively.
Overall, grade 3 or 4 adverse events were seen in 61% of patients receiving pyrotinib, of which 3.1% were grade 4; they were seen in 47.6% of patients receiving lapatinib, of which 3.2% were grade 4.
Diarrhea of grade 3 severity occurred mainly in the first treatment cycle for both the pyrotinib and lapatinib groups, investigators said.
While the protocol for this randomized phase 2 study did not permit diarrhea prophylaxis, the use of prophylactic loperamide is being studied in a phase 3 study of pyrotinib plus trastuzumab and docetaxel in women with HER2-positive metastatic disease and no prior systemic therapy
Investigators said patients are told to interrupt capecitabine if they experience ongoing grade 3 diarrhea or grade 1 or 2 diarrhea with complications such as dehydration, nausea, vomiting, or fever. If the diarrhea persists after 3 days, pyrotinib should then be interrupted, they said.
Similar advice was given for hand-foot syndrome.
“To date, the only method proven to effectively manage hand-foot syndrome is interruption of treatment and, if necessary, dose reduction,” said the investigators, who recommended first interrupting capecitabine and later pyrotinib.
The study was sponsored by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine and supported by the CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine and the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology in China. The corresponding author of this study, Binghe Xu, MD, PHD, reported institutional research funding from Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine and other disclosures related to AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Roche, and Eisai. Two study coauthors reported employment with Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine.
SOURCE: Ma F et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Aug 20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00108.
Among women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer enrolled in a phase 2 randomized trial, the pan-ErbB inhibitor pyrotinib plus capecitabine had manageable toxicity and a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) than lapatinib plus capecitabine, investigators reported.
The pyrotinib/capecitabine combination also led to significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) versus that of standard lapatinib/capecitabine treatment in these women, who had previously received treatment with taxanes, anthracyclines, and in some cases trastuzumab, the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“To our knowledge, this is the first trial to demonstrate that a novel epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2–targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor provides ORR and PFS benefits over lapatinib,” wrote Fei Ma, MD, of the National Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking, and colleagues.
In the phase 2 study, a total of 128 Chinese women with histologically confirmed relapsed or metastatic breast cancer were randomized to receive the pyrotinib- or lapatinib-containing regimens given in 21-day cycles.
Overall response rates, the primary end point, were 78% (51 of 65 patients) in the pyrotinib arm and 57.1% (36 of 63 patients) in the lapatinib arm (P = .01), Dr. Yu and colleagues reported.
Median PFS was 18.1 months versus 7.0 months in the pyrotinib and lapatinib arms, respectively (P less than .001). A “potential trend” toward improved overall survival was noted in the pyrotinib arm, though the data were premature and not statistically significant at the time of data analysis, according to the investigators.
Altogether, these efficacy results tracked with those of an earlier phase 1 investigation, and currently, a randomized phase 3 study is underway to confirm the findings, reported Dr. Yu and coauthors.
Hand-foot syndrome and diarrhea were the most common grade 3 adverse events seen with pyrotinib. The rate of grade 3 hand-foot syndrome wit pyrotinib was 24.6% versus 20.6% for the lapatinib group, and the rate of grade 3 diarrhea for the two groups was 15.4% and 4.8%, respectively.
Overall, grade 3 or 4 adverse events were seen in 61% of patients receiving pyrotinib, of which 3.1% were grade 4; they were seen in 47.6% of patients receiving lapatinib, of which 3.2% were grade 4.
Diarrhea of grade 3 severity occurred mainly in the first treatment cycle for both the pyrotinib and lapatinib groups, investigators said.
While the protocol for this randomized phase 2 study did not permit diarrhea prophylaxis, the use of prophylactic loperamide is being studied in a phase 3 study of pyrotinib plus trastuzumab and docetaxel in women with HER2-positive metastatic disease and no prior systemic therapy
Investigators said patients are told to interrupt capecitabine if they experience ongoing grade 3 diarrhea or grade 1 or 2 diarrhea with complications such as dehydration, nausea, vomiting, or fever. If the diarrhea persists after 3 days, pyrotinib should then be interrupted, they said.
Similar advice was given for hand-foot syndrome.
“To date, the only method proven to effectively manage hand-foot syndrome is interruption of treatment and, if necessary, dose reduction,” said the investigators, who recommended first interrupting capecitabine and later pyrotinib.
The study was sponsored by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine and supported by the CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine and the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology in China. The corresponding author of this study, Binghe Xu, MD, PHD, reported institutional research funding from Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine and other disclosures related to AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Roche, and Eisai. Two study coauthors reported employment with Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine.
SOURCE: Ma F et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Aug 20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00108.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Measles outbreak in New York City has ended
The measles outbreak in New York City, the largest in the nation this year, has officially ended, Mayor Bill de Blasio and city health officials announced Sept. 3.
“Ending the measles outbreak required extensive collaboration with community organizations and Jewish leaders. They helped encourage vaccinations and achieve record immunization levels in parts of Brooklyn,” Mayor de Blasio said in a written statement. “As we head back to school this week, we just remain vigilant. To keep our children and communities safe, I urge all New Yorkers to get vaccinated. It’s the best defense we have.”
A measles outbreak is considered to be over when 42 days, or two incubation periods, have elapsed since the last affected persons in the area were no longer infectious. “That time period has now passed for the people most recently infected with measles and reported,” the city health department said in the statement.
Since the outbreak began in October of last year, 654 individuals were diagnosed with measles in the five boroughs of New York, although 72% occurred in the Williamsburg neighborhood of Brooklyn. according to the health department. The majority of affected people were under 18 years of age (80%), and most were either unvaccinated (73%) or incompletely vaccinated (7%).
The end of the measles outbreak also brings an end to the public health emergency that was declared on April 9 for parts of Brooklyn, the statement noted.
“Vaccination coverage has increased significantly since the emergency order, which has been supported by community-led efforts. We are grateful to the New Yorkers who shared the truth about vaccines and protected the health of their friends and neighbors through this outbreak,” city health commissioner Dr. Oxiris Barbot said in the statement.
The measles outbreak in New York City, the largest in the nation this year, has officially ended, Mayor Bill de Blasio and city health officials announced Sept. 3.
“Ending the measles outbreak required extensive collaboration with community organizations and Jewish leaders. They helped encourage vaccinations and achieve record immunization levels in parts of Brooklyn,” Mayor de Blasio said in a written statement. “As we head back to school this week, we just remain vigilant. To keep our children and communities safe, I urge all New Yorkers to get vaccinated. It’s the best defense we have.”
A measles outbreak is considered to be over when 42 days, or two incubation periods, have elapsed since the last affected persons in the area were no longer infectious. “That time period has now passed for the people most recently infected with measles and reported,” the city health department said in the statement.
Since the outbreak began in October of last year, 654 individuals were diagnosed with measles in the five boroughs of New York, although 72% occurred in the Williamsburg neighborhood of Brooklyn. according to the health department. The majority of affected people were under 18 years of age (80%), and most were either unvaccinated (73%) or incompletely vaccinated (7%).
The end of the measles outbreak also brings an end to the public health emergency that was declared on April 9 for parts of Brooklyn, the statement noted.
“Vaccination coverage has increased significantly since the emergency order, which has been supported by community-led efforts. We are grateful to the New Yorkers who shared the truth about vaccines and protected the health of their friends and neighbors through this outbreak,” city health commissioner Dr. Oxiris Barbot said in the statement.
The measles outbreak in New York City, the largest in the nation this year, has officially ended, Mayor Bill de Blasio and city health officials announced Sept. 3.
“Ending the measles outbreak required extensive collaboration with community organizations and Jewish leaders. They helped encourage vaccinations and achieve record immunization levels in parts of Brooklyn,” Mayor de Blasio said in a written statement. “As we head back to school this week, we just remain vigilant. To keep our children and communities safe, I urge all New Yorkers to get vaccinated. It’s the best defense we have.”
A measles outbreak is considered to be over when 42 days, or two incubation periods, have elapsed since the last affected persons in the area were no longer infectious. “That time period has now passed for the people most recently infected with measles and reported,” the city health department said in the statement.
Since the outbreak began in October of last year, 654 individuals were diagnosed with measles in the five boroughs of New York, although 72% occurred in the Williamsburg neighborhood of Brooklyn. according to the health department. The majority of affected people were under 18 years of age (80%), and most were either unvaccinated (73%) or incompletely vaccinated (7%).
The end of the measles outbreak also brings an end to the public health emergency that was declared on April 9 for parts of Brooklyn, the statement noted.
“Vaccination coverage has increased significantly since the emergency order, which has been supported by community-led efforts. We are grateful to the New Yorkers who shared the truth about vaccines and protected the health of their friends and neighbors through this outbreak,” city health commissioner Dr. Oxiris Barbot said in the statement.
BPA substitutes bisphenol S and bisphenol F linked to obesity
Though exposure to the obesogen bisphenol A (BPA) is decreasing, a new study has linked substitute chemicals bisphenol S (BPS) and bisphenol F (BPF) to obesity as well.
“The potential health effects of BPS and other BPA replacement compounds should be monitored going forward, given that human exposure to these compounds is likely to continue to increase in the future,” wrote Melanie H. Jacobson, PhD, of New York University, and coauthors. Their report is in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
BPA is one of the best known synthetic chemical obesogens, the authors noted. “It enlarges adipocytes and enhances differentiation from mesenchymal cells to adipocytes, inhibits adiponectin function, and is a synthetic estrogen and thereby can have sex-specific effects on body mass,” they explained.
To determine if the BPA analogues, BPS and BPF, could also induce obesity, the researchers analyzed data from 1,831 children and adolescents gathered through the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 2013 to 2016. Concentrations of BPA, BPS, and BPF were measured in spot urine samples and they were detected in 97.5%, 87.8%, and 55.2% of samples, respectively.
Log-transformed BPS concentrations were associated with an increased prevalence of general obesity (odds ratio, 1.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.32), which was defined as being greater than or equal to the 95th percentile of standardized body mass index z scores. BPS concentrations were also associated with an increased prevalence of abdominal obesity (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02-1.27), as was BPF detection (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.01-1.64).
BPA and total bisphenols were not significantly associated with general or abdominal obesity.
“Though tissue and animal studies of the replacements are lacking, [BPS and BPF] have shown estrogenic activity. Further, BPS has been shown to promote preadipocyte differentiation, raising the possibility that these BPA replacements may induce the same obesogenic effects in humans,” the authors wrote.
They acknowledged that their results should be interpreted cautiously, because they were not able to determine if exposure to bisphenols influences weight gain or if obese children are merely more exposed to those compounds. In addition, because BPS and BPF are metabolized rapidly, spot urine samples cannot accurately reflect long-term exposure levels. Finally, because a good deal of food and beverage packaging contains bisphenols, “those who consume more of these products are more likely to have higher exposure levels,” they wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jacobson MH et al. J Endocr Soc. 2019 Jul 25. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00201.
Though exposure to the obesogen bisphenol A (BPA) is decreasing, a new study has linked substitute chemicals bisphenol S (BPS) and bisphenol F (BPF) to obesity as well.
“The potential health effects of BPS and other BPA replacement compounds should be monitored going forward, given that human exposure to these compounds is likely to continue to increase in the future,” wrote Melanie H. Jacobson, PhD, of New York University, and coauthors. Their report is in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
BPA is one of the best known synthetic chemical obesogens, the authors noted. “It enlarges adipocytes and enhances differentiation from mesenchymal cells to adipocytes, inhibits adiponectin function, and is a synthetic estrogen and thereby can have sex-specific effects on body mass,” they explained.
To determine if the BPA analogues, BPS and BPF, could also induce obesity, the researchers analyzed data from 1,831 children and adolescents gathered through the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 2013 to 2016. Concentrations of BPA, BPS, and BPF were measured in spot urine samples and they were detected in 97.5%, 87.8%, and 55.2% of samples, respectively.
Log-transformed BPS concentrations were associated with an increased prevalence of general obesity (odds ratio, 1.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.32), which was defined as being greater than or equal to the 95th percentile of standardized body mass index z scores. BPS concentrations were also associated with an increased prevalence of abdominal obesity (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02-1.27), as was BPF detection (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.01-1.64).
BPA and total bisphenols were not significantly associated with general or abdominal obesity.
“Though tissue and animal studies of the replacements are lacking, [BPS and BPF] have shown estrogenic activity. Further, BPS has been shown to promote preadipocyte differentiation, raising the possibility that these BPA replacements may induce the same obesogenic effects in humans,” the authors wrote.
They acknowledged that their results should be interpreted cautiously, because they were not able to determine if exposure to bisphenols influences weight gain or if obese children are merely more exposed to those compounds. In addition, because BPS and BPF are metabolized rapidly, spot urine samples cannot accurately reflect long-term exposure levels. Finally, because a good deal of food and beverage packaging contains bisphenols, “those who consume more of these products are more likely to have higher exposure levels,” they wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jacobson MH et al. J Endocr Soc. 2019 Jul 25. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00201.
Though exposure to the obesogen bisphenol A (BPA) is decreasing, a new study has linked substitute chemicals bisphenol S (BPS) and bisphenol F (BPF) to obesity as well.
“The potential health effects of BPS and other BPA replacement compounds should be monitored going forward, given that human exposure to these compounds is likely to continue to increase in the future,” wrote Melanie H. Jacobson, PhD, of New York University, and coauthors. Their report is in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
BPA is one of the best known synthetic chemical obesogens, the authors noted. “It enlarges adipocytes and enhances differentiation from mesenchymal cells to adipocytes, inhibits adiponectin function, and is a synthetic estrogen and thereby can have sex-specific effects on body mass,” they explained.
To determine if the BPA analogues, BPS and BPF, could also induce obesity, the researchers analyzed data from 1,831 children and adolescents gathered through the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 2013 to 2016. Concentrations of BPA, BPS, and BPF were measured in spot urine samples and they were detected in 97.5%, 87.8%, and 55.2% of samples, respectively.
Log-transformed BPS concentrations were associated with an increased prevalence of general obesity (odds ratio, 1.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.32), which was defined as being greater than or equal to the 95th percentile of standardized body mass index z scores. BPS concentrations were also associated with an increased prevalence of abdominal obesity (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02-1.27), as was BPF detection (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.01-1.64).
BPA and total bisphenols were not significantly associated with general or abdominal obesity.
“Though tissue and animal studies of the replacements are lacking, [BPS and BPF] have shown estrogenic activity. Further, BPS has been shown to promote preadipocyte differentiation, raising the possibility that these BPA replacements may induce the same obesogenic effects in humans,” the authors wrote.
They acknowledged that their results should be interpreted cautiously, because they were not able to determine if exposure to bisphenols influences weight gain or if obese children are merely more exposed to those compounds. In addition, because BPS and BPF are metabolized rapidly, spot urine samples cannot accurately reflect long-term exposure levels. Finally, because a good deal of food and beverage packaging contains bisphenols, “those who consume more of these products are more likely to have higher exposure levels,” they wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jacobson MH et al. J Endocr Soc. 2019 Jul 25. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00201.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE ENDOCRINE SOCIETY